Page 1

BITE
Battery Impedance Test Equipment
BITE®2 and BITE2P
Battery Impedance Test Equipment
n
Determines condition of lead-acid and
NiCd cells up to 7000 Ah
n
On-board Pass/Warning/Fail indications
n
Robust, repeatable instruments
n
On-line testing
n
Checks charger condition by measuring
BITE2P
BITE2
ac ripple current
n
Includes PowerDB LITE Software
®
2 and BITE2P
DESCRIPTION
The BITE2 and BITE2P Battery Impedance Test Equipment
determine the condition of lead-acid and nickel-cadmium cells
up to 7000 Ah. An advanced feature set has been developed
that includes Pass/Warning/Fail calculations based on a userentered baseline value, advanced printing functions and more.
The case of the BITE2P consists of both the transmitter and a
carrying case for all of the standard accessories and some of
the optional accessories, in an all-in-one unit. The BITE2 and
its accessories fit into a sturdy canvas case with a shoulder
strap.
The instruments work by applying a test signal across the
battery string while on-line, then calculates impedance based
on simultaneous measurements of current and resulting
voltage drop of each cell/jar. They also measure dc voltage
and interconnection (strap) resistance to help determine the
overall condition of the entire battery string’s electrical path
from terminal plate to terminal plate.
In addition, the BITE2 and BITE2P measure ac ripple current
which, if too high and over an extended period of time, can
damage the battery by heating it. (An increase of battery
temperature by 18ºF/10ºC will halve the life of lead-acid
batteries.) Battery manufacturers generally recommend a limit
of 5A of ac ripple current for every 100 Ah of battery capacity.
The first measurement that the instruments take is ac ripple
current which should be trended.
The BITE2 and BITE2P receiver stores the readings in its
internal memory. These measurements, along with other
maintenance data such as ambient and pilot cell temperatures
and ac ripple current, assist in determining the overall
condition of battery systems. Megger recommends that
impedance measurements with the
BITE2 or BITE2P be made part of a battery maintenance
program with readings taken and recorded semiannually for
flooded batteries and quarterly for VRLA.
Unlike load cycle testing that involves substantial downtime
and repeated discharges, using the instruments require no
battery discharge, nor do they stress the battery in any way
compared to other techniques. With a test time of less than 15
seconds for each cell and intercell connector, one person can
easily, quickly, and precisely measure internal cell impedance,
dc terminal voltage and intercell connection resistance
without taking the battery system off line and evaluate charger
condition also.
Naturally, everything you need to perform these tests is
included with the basic instruments. There is a full line of
optional accessories to enhance the capabilities of the BITE2
and BITE2P. Both have the ability to download to a PC for
data interpretation and to PowerDB, Megger’s battery database
management software. Additionally, the BITE2P has a built-in
printer to review the active test and also to leave a hard copy
record at the site
.
Receiver
The battery-operated receiver incorporates the potential leads,
clamp-on current sensor, and data storage capabilities. It stores
more than 2000 sets of data (cell impedance, cell voltage and
interconnecting strap resistance, date and time stamps) in up
to 300 tests. It also allows for printing the active test for easy
review and retest. Selective printing of any test and deleting
oldest tests are now included features to maintain in memory
the most critical tests.
At any time while performing a test, the operator can review
the current test results by using arrow keys and scrolling back
through the active test screen. The operator can also print the
active test using the BITE2P transmitter printer. If needed, the
operator can retest any of the cells and straps in the current
test. Stored data can also be downloaded via the RS-232
connector directly to a personal computer or the BITE2P
transmitter printer.
One additional feature of the receiver is that if you are called
away while in the middle of the test, simply shut down the
instrument and it will remember where you left off in the test.
The clamp-on current sensor is connected to the receiver
during testing and clamped around a convenient intertier or
intercell connection within the loop created by the transmitter’s
Page 2
BITE®2 and BITE2P
Circuit
Battery Impedance Test Equipment
current source leads and the battery string. If the intercell or
intertier connection consists of more cables than the diameter
of the clamp-on current sensor can encompass, the receiver
has a split-strap function.
There are optional RopeCTs
TM
available for large buss work.
With the optional bar-code wand, additional information such
as location ID, user ID, ambient and pilot cell temperatures
can be recorded and stored. There is space on the printout to
enter specific gravity readings.
Battery Analysis Report
Location ID:
User ID: _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Notes: _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Ambient Temp: Pilot Temp:
Ripple Current: .01A Test AC Current: 9.8 A
Multiplier: 1 B/W/F: 11.00 mW/20%/40%
Cell Sp.Gr. Zb mW P/W/F % RS mW Volts DC Time
001 12.09 P 09 0.412 13.52 11:13
002 12.22 P 11 0.407 13.34 11:14
003 14.02 W 27 0.405 13.59 11:14
004 14.54 W 32 0.403 13.48 11:15
005 12.60 P 14 0.042 13.27 11:16
006 12.09 P 09 0.405 13.38 11:17
Minimum Average Maximum
12.09 12.93 14.54
-10 0 10 20 30
001
002
003
004
005
006
Figure 1. Sample battery analysis report
05-SEP-2000
Cell Impedance Summary
Percent Deviation from Average
Transmitter
The transmitter provides the capacitively coupled ac test signal
to avoid transients on the dc buss and applies it to the cells
under test via the source leads. Both the BITE2 and BITE2P
transmitters have an LCD and built-in receiver charger, while
the BITE2P transmitter features a built-in printer.
Data, measured and stored in the receiver can be exported to
a PC. It can also be printed to the BITE2P transmitter printer
where it can be reviewed. Figure 1 shows a sample printout of
a full battery analysis report.
APPLICATIONS
A battery’s internal impedance increases with decreasing
capacity due to various conditions such as age, ambient
temperature, discharge history, etc. See Figure 2. Both the
BITE2 and BITE2P measure impedance values and dc voltage
for lead-acid and nickel-cadmium cells up to 7000 Ah capacity.
Impedance finds electrical path problems due to plate
sulphation, post-seal corrosion, dry-out, and poor intracell
and intercell connections. This information lets the operator
determine maintenance needs such as:
n
Cell replacement criteria based on impedance trends.
n
Jumpering out a cell or two.
n
Clean and/or retorque intercell connectors.
n
Shorten the maintenance interval, etc.
Typical installations that can be tested using the BITE2
and BITE2P include:
n
Electrical power generation plants.
n
Substations: utility, railroad, industrial
n
Telecommunications facilities: CO, Wireline, Wireless, MTSO
n
UPS systems
n
Railroad: Signals and Communications, substation
n
Aircraft power supplies
n
Marine, military
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
n
On-line testing requiring no downtime.
n
Enhanced printing and memory functions.
n
Calculates impedance automatically and stores results
for on-site review.
n
Requires no battery discharge.
n
Receiver can download stored data to PowerDB software for
quick, easy analysis.
n
Reduced test time: less than 3 seconds for each cell.
n
Measures impedance and dc voltage values for all lead-acid
and nickel-cadmium cells up to 7000 Ah.
n
Stores more than 2000 sets of readings in up to
300 tests.
n
Checks charger condition by measuring ac ripple current.
n
PowerDB LITE allows data to be stored and allows custom
reporting. (ideal for NERC & FERC requirements)
Test Procedure
The BITE2 and BITE2P work by applying a capacitively
coupled ac test signal across the battery string while online. The receiver and potential probe are placed at the cell
terminals to measure the signal and resulting voltage drop
for each cell/jar. During each measurement, impedance is
calculated following Ohm’s Law, displayed on the LCD and
stored. The instruments also measure, display and record
dc voltage and interconnection (strap) resistance to help
determine the overall condition of the entire battery string’s
electrical path from terminal plate to terminal plate. The also
measure ac ripple current, a charger parameter.
The BITE2 and BITE2P receiver stores the readings in its
internal memory. These measurements, along with other
maintenance data such as ambient and pilot cell temperatures
and ac ripple current, assist in determining the overall
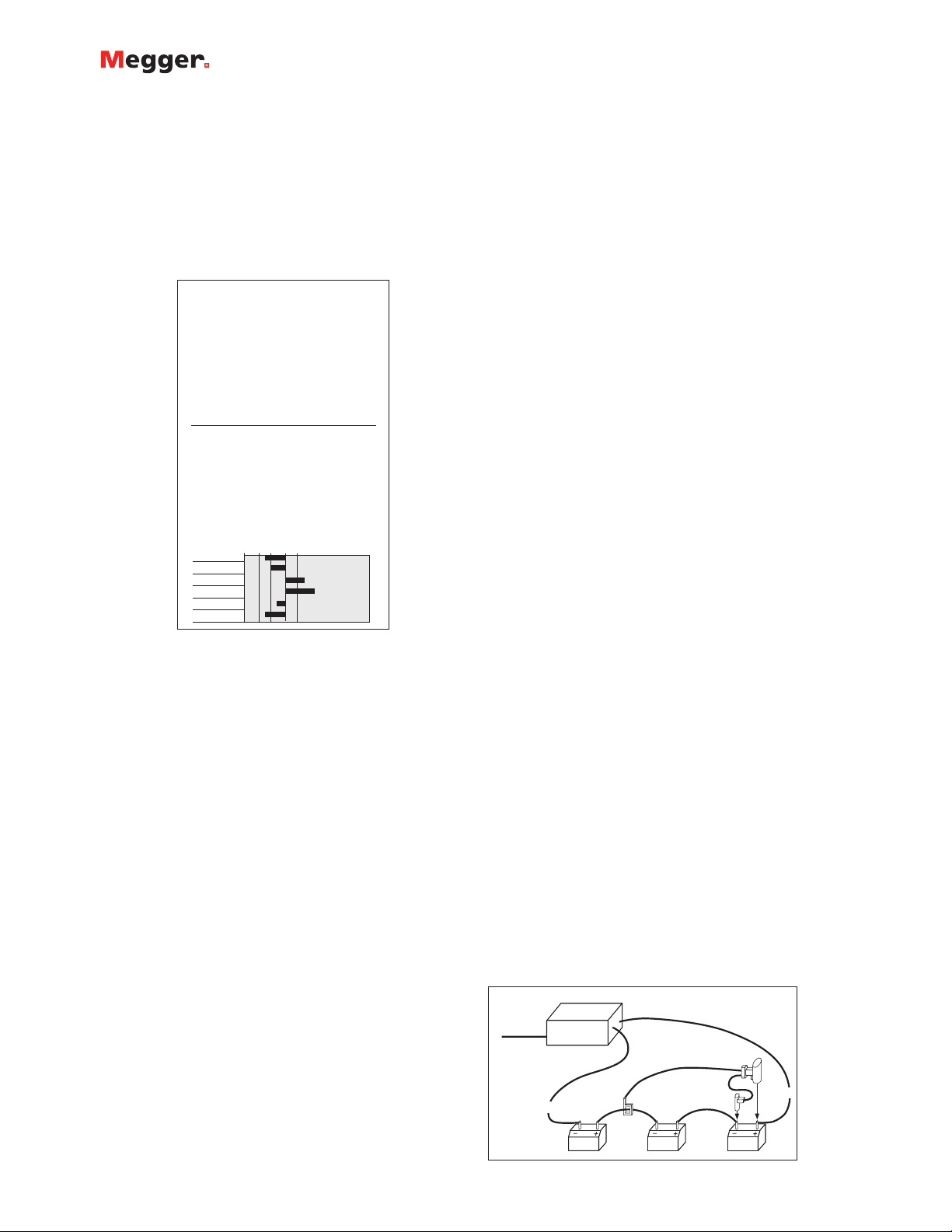
condition of battery systems. Figure 2 shows a typical test
setup.
STRAP
CURRENT SOURCE
LEAD
CELL
RED
TRANSMITTER
LINE
VOLTAGE
CURRENT SOURCE
LEAD
BLACK
Located
in Battery
Figure 2. A typical test setup
“CT”
Page 3

BITE®2 and BITE2P
Battery Impedance Test Equipment
Figure 3. Power DB reporting
Interpretation of Readings
Data produced by the BITE2 and BITE2P can be interpreted in
several modes: instantaneous, short-term and long-term time
frames. PowerDB makes data analysis fast & easy. See figure 3.
Instantaneous Interpretation
The operator can enter a baseline value from either the
impedance measurements obtained at commissioning. The
percent changes from baseline for warning and fail levels are
entered, but 20 percent and 40 percent are the default settings.
The LCD on the receiver will display the status of the cell for a
few seconds before proceeding to the
each cell/jar will be printed on the Battery Analysis Report.
next cell. The status of
Short-Term Interpretation
Impedance readings for individual cells can be used in the
short term to compare with the average impedance readings
for the entire battery string. Individual cell values with
deviations of more than ±15% for flooded lead-acid, ±35% for
VRLA, and 50% for NiCd cells from the battery string average
typically indicate a problem with that cell. Megger recommends
additional investigation of such cells including a verification of
intercell connections and a single cell load-cycle test.
Long-Term Interpretation
Impedance readings for the entire battery can be used
in the long term to determine replacement criteria.
Battery cell impedance values should be recorded
and compared to previous readings to determine the
position of the cell on the curve of impedance versus
cell life as shown in Figure 4. Based on experience,
a variation of ±20% from baseline for flooded leadacid, ±40% for VRLA and 50% for NiCd cells indicate
significant change in the electrical path to warrant
serious evaluation of the condition of the battery
system. Megger maintains a database of impedance
values by some manufacturers and battery size/type.
For comparison purposes, this information is available
upon request.
Figure 4. Impedance increases with battery age (and weakness)
Page 4

BITE®2 and BITE2P
Battery Impedance Test Equipment
SPECIFICATIONS
Application
The BITE2 and BITE2P test lead-acid and nickel-cadmium cells up
to 7000 Ah.
Maximum Total Voltage at Current Source Leads
275 V dc (larger battery systems can be sectioned to accommodate
this specification)
Transmitter
Supply Voltage
100 to 130 V, 50/60 Hz, 200 VA max
210 to 250 V, 50/60 Hz, 200 VA max
Source Output Current
10 A nominal, 50/60 Hz operation
Maximum Battery String Test Voltage
275 V dc at source lead terminals (section the battery if >275 Vdc)
Display
Digital LCD meter, 0 to 15 A
BITE2P Printer
Built-in thermal, with 4.25 in. (110 mm) printing width
Charger
Supply Voltage
100 to 130 V, 50/60 Hz, 14 VA
210 to 250 V, 50/60 Hz, 14 VA
Output
6.50 V dc @ 1.10 A dc charging (max)
9.60 V dc open circuit
Receiver
Accuracy
ac impedance 5% +1 LSD
dc voltage ±(0.5% of rdg +1 LSD)
Precision
Better than 0.5% one sigma
Voltage Range and Resolution
1 to 2.500 V dc, 1 mV resolution
2.5 to 25.00 V dc, 10 mV resolution
Impedance Range and Resolution
0 to 1.000 mΩ, 1µΩ resolution
1 to 10.00 mΩ, 10µΩ resolution
10 to 100.0 mΩ, 0.1mΩ resolution
Setting Time per Reading
3 seconds maximum
Display
LCD, 2 x 16 characters
Supply
4.8 V dc, 800 mAh, quick charge nickel-cadmium battery pack
Battery Pack Life, Full Charge
5 hours continuous
Maximum Cell/Jar Test Voltage
25 V dc between receiver and potential probe
Temperature
Operating: 32 to 105° F (0 to 40° C)
Storage: -5 to 130° F (-20 to 55° C)
Humidity: 20 to 90% RH, noncondensing
Clamp Range
Standard CT
2.0 in. (50 mm) maximum opening
Optional Miniature CT
0.5 in. (12 mm) maximum opening
Optional RopeCT
12 in. (300 mm) opening, approx.
Standards
Conforms to the EMC Directive 2004/108/EC and the
LVD Directive 2006/95/EC
Dimensions
Transmitter
BITE2: 6.5 H x 14 W x 10.6 D in. (16.5 H x 35.6 W x 27 D cm)
BITE2P: 7.5 H x 18.5 W x 14.6 D in. (19 H x 47 W x 37 D cm)
Receiver (irregular shape)
7.25 H x 11.25 W x 2 D in. (18 H x 29 W x 5 D cm)
Weight
Transmitter
BITE2: 17 lb (7.7 kg)
BITE2P: 18 lb (8.2 kg) alone, 32 lb (14.5 kg) packed
Receiver
1.6 lb (0.7 kg)
TM
Page 5

ORDERING INFORMATION
Item (Qty) Cat. No.
BITE2, 110/230 V ac, 50/60 Hz, CE-Marked 246002B
BITE2P, 110/230 V ac, 50/60 Hz, CE-Marked 246004
Included Accessories
Transmitter for BITE2 P30044-300
Transmitter for BITE2P P30044-100
Receiver P30620-3
Source Leads, 20 ft (6 m), fused 29386-2
Current sensor, 2 in. (50 mm) opening
with 5 ft (1.5 m) lead 33863
CT extension cable, 20 ft (6 m) 33864-2
Communication cable, 6 ft (1.8 m) 35340
Charger cable 35341
Thermal paper 26999
ac line cord, 8 ft (2.5 m) 17032-7
Item (Qty) Cat. No.
Manual for BITE2 and BITE2P AVTM246004
Accessory bag for BITE2 29996
Optional Accessories
Current sensor 0.5 in. (12 mm) opening
with 2.5 ft (0.8 m) lead 246034
Current sensor, RopeCT
Current sensor, RopeCT
TM
24 in. (60 cm) length 246050
TM
36 in. (90 cm) length 246051
CT extension cable, 20 ft (6 m) 246033
Current source leads, 10 ft (3 m), fused 246147
Current source leads, 30 ft (9.1 m), fused 246347
Current source leads, 40 ft (12.2 m), fused 246447
Bar code wand with preprinted code sheet 246201
Transit case for BITE2 35491
UK
Archcliffe Road, Dover
CT17 9EN England
T +44 (0) 1 304 502101
F +44 (0) 1 304 207342
UKsales@megger.com
UNITED STATES
4271 Bronze Way
Dallas, TX 75237-1019 USA
T 1 800 723 2861 (USA only)
T +1 214 333 3201
F +1 214 331 7399
USsales@megger.com
OTHER TECHNICAL SALES OFFICES
Valley Forge USA, College Station
USA, Sydney AUSTRALIA, Täby
SWEDEN, Ontario CANADA, Trappes
FRANCE, Oberursel GERMANY, Aargau
SWITZERLAND, Kingdom of BAHRAIN,
Mumbai INDIA, Johannesburg SOUTH
AFRICA, and Chonburi THAILAND
ISO STATEMENT
Registered to ISO 9001:2000 Cert. no. 10006.01
BITE2_2P_DS_en_V19
www.megger.com
Megger is a registered trademark
 Loading...
Loading...