Page 1

Resolute Onyx™
Zotarolimus-Eluting Coronary Stent System
Rapid Exchange and Over-the-Wire Delivery Systems
Instructions for Use
Caution: Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Symbol glossary ...................................................................................................................... 4
2 Resolute Onyx™ Zotarolimus-Eluting Coronary Stent System.......................................... 4
2.1 Device component description ........................................................................................ 6
2.2 Drug component description ........................................................................................... 7
2.2.1 Zotarolimus..................................................................................................................... 7
2.2.2 Polymer system description ........................................................................................... 8
2.2.3 Product matrix and zotarolimus content ......................................................................... 8
3 Indications .............................................................................................................................. 10
4 Contraindications .................................................................................................................. 10
5 Warnings ................................................................................................................................ 10
6 Precautions ............................................................................................................................ 10
6.1 Pre- and post-procedure antiplatelet regimen ............................................................. 11
6.1.1 Oral antiplatelet therapy ............................................................................................... 11
6.2 Use of multiple stents ..................................................................................................... 12
6.3 Use in conjunction with other procedures ................................................................... 13
6.4 Brachytherapy ................................................................................................................. 13
6.5 Use in special populations ............................................................................................. 13
6.5.1 Pregnancy .................................................................................................................... 13
6.5.2 Lactation ....................................................................................................................... 13
6.5.3 Gender ......................................................................................................................... 13
6.5.4 Ethnicity ........................................................................................................................ 13
6.5.5 Pediatric use ................................................................................................................ 13
6.5.6 Geriatric use ................................................................................................................. 14
6.5.7 Lesion/vessel characteristics ....................................................................................... 14
6.6 Drug interactions ............................................................................................................ 14
6.7 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) safety information .............................................. 14
6.8 Stent handling precautions ............................................................................................ 15
6.9 Stent placement precautions ......................................................................................... 15
6.10 Stent/system removal precautions ............................................................................... 16
6.11 Post-procedure ................................................................................................................ 16
7 Drug information ................................................................................................................... 17
7.1 Mechanisms of action .................................................................................................... 17
7.2 Metabolism ...................................................................................................................... 17
7.3 Pharmacokinetics of the Resolute OnyxTM stent ......................................................... 17
7.4 Pharmacokinetics following multi-dose intravenous administration of zotarolimus
.......................................................................................................................................... 18
7.5 Mutagenesis, carcinogenicity and reproductive toxicology ...................................... 19
7.5.1 Mutagenesis ................................................................................................................. 19
7.5.2 Carcinogenicity ............................................................................................................. 19
7.5.3 Reproductive toxicology ............................................................................................... 19
7.6 Pregnancy ........................................................................................................................ 19
7.7 Lactation .......................................................................................................................... 19
8 Overview of clinical trials ..................................................................................................... 20
i
Page 3

8.1
The RESOLUTE ONYX Clinical Program ...................................................................... 20
8.2 Supportive RESOLUTE and RESOLUTE INTEGRITY data: ........................................ 21
9 Clinical outcomes .................................................................................................................. 26
9.1 Clinical outcomes for RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study and
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study ..................................................................... 26
9.2 Potential adverse events ................................................................................................ 34
9.2.1 Potential adverse events related to zotarolimus .......................................................... 34
9.2.2 Potential adverse events related to BioLinx
9.2.3 Potential risks associated with percutaneous coronary diagnostic and treatment
procedures ................................................................................................................... 35
10 Clinical studies ...................................................................................................................... 35
10.1 Results of the RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study .............. 35
10.2 Results of the RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study ............................................ 40
10.3 Subjects with diabetes mellitus in the RESOLUTE pooled analysis ......................... 45
10.4 Subjects with diabetes mellitus in the RESOLUTE 38 mm length group .................. 48
10.5 Subjects receiving short-term DAPT ............................................................................ 49
10.5.1 Onyx ONE Clear Primary Analysis .............................................................................. 49
10.5.2 The Onyx ONE Global RCT ......................................................................................... 53
10.6 Subjects with chronic total occlusion .......................................................................... 53
10.7 Pooled results of the Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial Program (RESOLUTE FIM,
RESOLUTE US, RESOLUTE AC, RESOLUTE Int, RESOLUTE Japan) ....................... 58
TM*
polymer............................................... 34
11 Patient selection and treatment ........................................................................................... 65
12 Patient counseling information ............................................................................................ 65
13 How supplied ......................................................................................................................... 65
14 Directions for use .................................................................................................................. 65
14.1 Access to package holding sterile stent delivery system .......................................... 65
14.2 Inspection before use ..................................................................................................... 66
14.3 Materials required ........................................................................................................... 66
14.4 Preparation precaution ................................................................................................... 66
14.4.1 Guidewire lumen flush .................................................................................................. 66
14.4.2 Delivery system preparation......................................................................................... 66
14.5 Delivery procedure.......................................................................................................... 67
14.6 Deployment procedure ................................................................................................... 67
14.7 Removal procedure......................................................................................................... 68
14.8
14.9 Further dilatation of stented segment .......................................................................... 69
14.10 Instructions for simultaneous use of 2 devices in guide catheter (kissing balloon
15 Reuse precaution statement ................................................................................................ 70
In-vitro
technique) ........................................................................................................................ 69
information: ........................................................................................................ 68
ii
Page 4

The components of the Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system are
sterile.
© 2021. Medtronic. All rights reserved. Medtronic and Medtronic with logo are trademarks of
Medtronic, Inc. All other brands are trademarks of their respective owners.
3
Page 5

1 Symbol glossary
Explanation of symbols that may appear on package labeling
Refer to the device labeling to see which symbols apply to this product.
Standard title:
ISO 15223-1:2016 Cor 2017: Medical Devices — Symbols to be used with medical device
labels, labeling and information to be supplied
Symbol Reference Symbol title Explanatory text
ISO 15223-1,
Clause 5.4.3
ISO 15223-1,
Clause 5.2.8
Consult instructions for use
Do not use if package is
damaged
Indicates the need for the user to
consult the instructions for use.
Indicates a medical device that
should not be used if the package
has been damaged or opened.
Indicates a medical device that is
ISO 15223-1,
Clause 5.4.2
Do not reuse
intended for one use, or for use on
a single patient during a single
procedure.
Clause 5.1.5
ISO 15223-1,
Clause 5.1.1
ISO 15223-1,
ISO 15223-1,
Clause 5.1.6
ISO 15223-1,
Clause 5.2.3
ISO 15223-1,
Clause 5.1.4
ISO 15223-1,
Clause 5.1.3
Lot number
Manufacturer
Catalog number
Sterilized using ethylene
oxide
Use-by date
Date of manufacture
Indicates the manufacturer’s batch
code so that the batch or lot can
be identified.
Indicates the medical device
manufacturer.
Indicates the manufacturer's
catalogue number so that the
medical device can be identified.
Indicates a medical device that
has been sterilized using ethylene
oxide.
Indicates the date after which the
medical device is not to be used.
Indicates the date when the
medical device was manufactured.
2 Resolute Onyx™ Zotarolimus-Eluting Coronary Stent System
The Medtronic Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system (Resolute Onyx™
system) is a device/drug combination product that consists of the following device
components: the Resolute Onyx™ coronary stent and delivery system and a drug component
(a formulation of zotarolimus in a polymer coating). The characteristics of the Resolute
Onyx™ system are described in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1: Device component description and nominal dimensions
Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system
rapid exchange and over-the-wire delivery systems
Component
Stent design 1
(small vessel)
Available stent diameters (mm) 2.0, 2.25, 2.5 2.75, 3.0 3.5, 4.0 (RX only) – 4.5, 5.0
Stent design 2
(medium
vessel)
Stent design 3
(large vessel)
Stent design 4
(extra large vessel)
4
Page 6
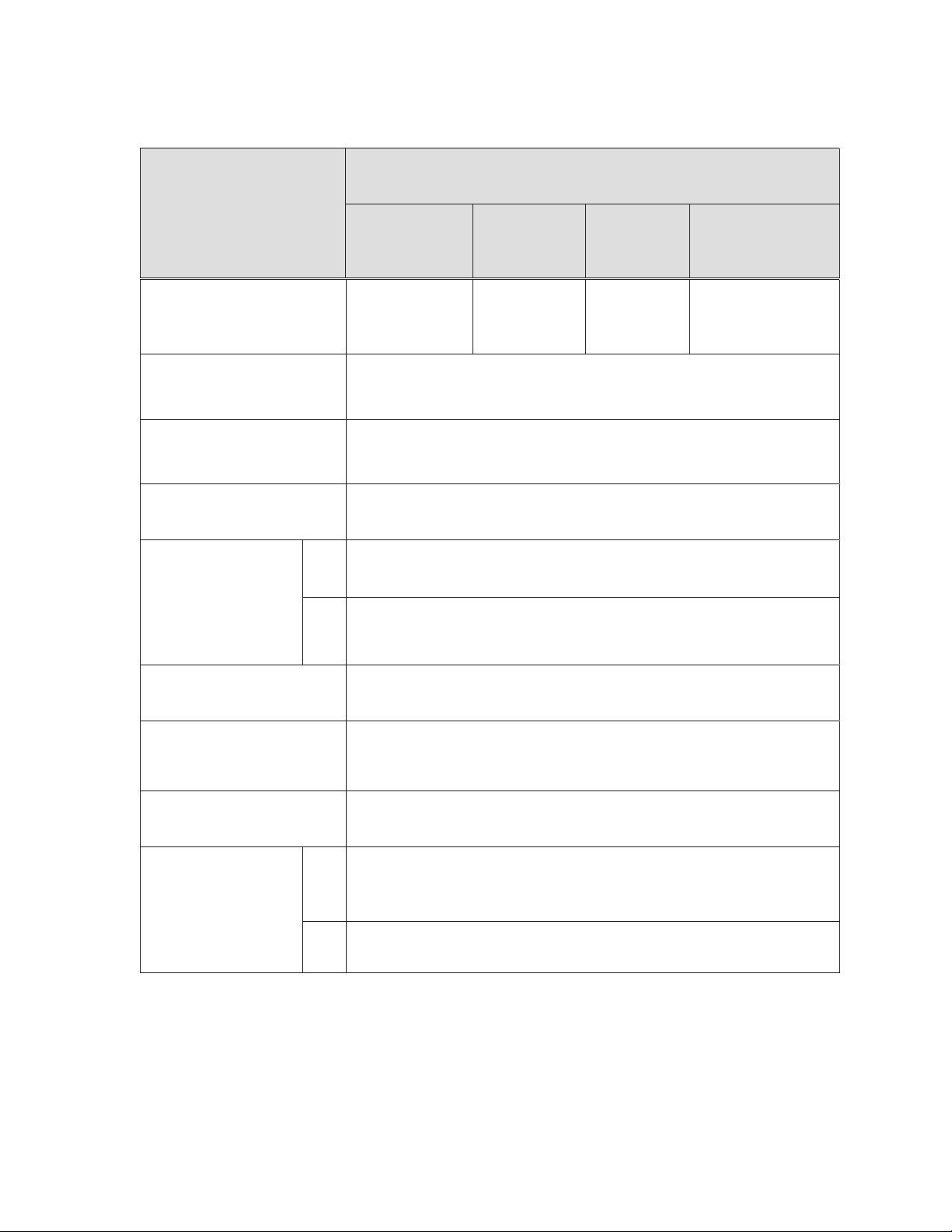
Table 2-1: Device component description and nominal dimensions
Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system
rapid exchange and over-the-wire delivery systems
Component
Available stent lengths (mm)
Stent material and geometry
Drug component
Delivery systems effective (working)
length
RX
Delivery system luer adapter
ports
OTW
Stent design 1
(small vessel)
8, 12, 15, 18, 22, 26,
30, 34*, 38*
*34, 38 mm lengths not
available in 2.0 mm
A continuous sinusoid pattern stent manufactured from a composite metal material, consisting
of a cobalt-based alloy shell conforming to ASTM F562 and a platinum-iridium alloy core
conforming to ASTM B684.
A coating of polymers loaded with zotarolimus in a formulation applied to the entire surface of
the stent at a dose of approximately 1.6 μg/mm2 which results in a maximum nominal drug
content of 317 μg on the stent with the largest surface area (4.0 x 38 mm).
140 cm
Single access port to the inflation lumen. A guidewire exit port is located approximately 25 cm
from the tip. Designed for guidewire less than or equal to 0.014 inch (0.36 mm).
Y-connector with side arm for access to balloon inflation/deflation lumen. Straight arm is
continuous with shaft inner lumen designed for guidewire less than or equal to 0.014 inch
(0.36 mm).
Stent design 2
(medium
vessel)
8, 12, 15, 18, 22,
26, 30, 34, 38
Stent design 3
(large vessel)
8, 12, 15, 18, 22,
26, 30, 34, 38
Stent design 4
(extra large vessel)
(RX only) – 12, 15, 18,
22, 26, 30
Stent delivery balloon
Balloon inflation pressure
Minimum guide catheter inner
diameter
Catheter shaft outer
diameter
Single-layer Pebax balloon, wrapped over an inner member tubing with 2 radiopaque marker
bands to locate the stent edges.
Nominal inflation pressure: 12 ATM (1216 kPa)
Rated burst pressure: 2.0-4.0 mm = 18 ATM (1824 kPa), RX only: 4.5-5.0 mm = 16 ATM
(1621kPa)
≥5 F (1.42 mm, 0.056 in)
Proximal shaft OD: 2.1 F (0.69 mm)
RX
Distal shaft OD 2.0 – 4.0 mm: 2.7 F (0.91 mm)
Distal shaft OD 4.5 and 5.0 mm: 3.2 F (1.07 mm)
Proximal shaft OD: 3.4 F (1.12 mm)
OTW
Distal shaft OD: 2.7 F (0.91 mm)
5
Page 7

2.1 Device component description
The Medtronic Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system (Resolute Onyx™
system) consists of a balloon-expandable, intracoronary, drug-eluting stent (DES)
premounted on a rapid exchange (RX) or an over-the-wire (OTW) stent delivery system. The
Resolute Onyx™ stent is manufactured from a composite material of cobalt alloy and
platinum-iridium alloy and is formed from a single wire bent into a continuous sinusoid pattern
and then laser fused back onto itself. The stents are available in multiple lengths and
diameters. The delivery system has 2 radiopaque markers to aid in the placement of the stent
during fluoroscopy and is compatible with 0.014 inch (0.36 mm) guidewires and 1.42 mm
(5 Fr / 0.056 in) minimum inner diameter guide catheters. The Resolute Onyx™ RX delivery
system (Figure 2-1) and the Resolute Onyx™ OTW delivery system (Figure 2-2) have an
effective length of 140 cm.
Diameter
(mm)
2.0
2.25
2.5
2.75
Figure 2-1: Resolute Onyx™ rapid exchange (RX) delivery system (with stent)
Illustration is not to scale
Figure 2-2: Resolute Onyx™ over-the-wire (OTW) delivery system (with stent)
Illustration is not to scale
The stent is crimped on various sizes of delivery catheter balloons, which range from 2.0 mm
to 5.0 mm. The Resolute Onyx™ available stent sizes are listed in Table 2-2.
Table 2-2: Resolute Onyx™ stent sizes
Stent length (mm)
8 12 15 18 22 26 30 34 38
9 9 9 9 9 9 9
9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
- -
6
Page 8
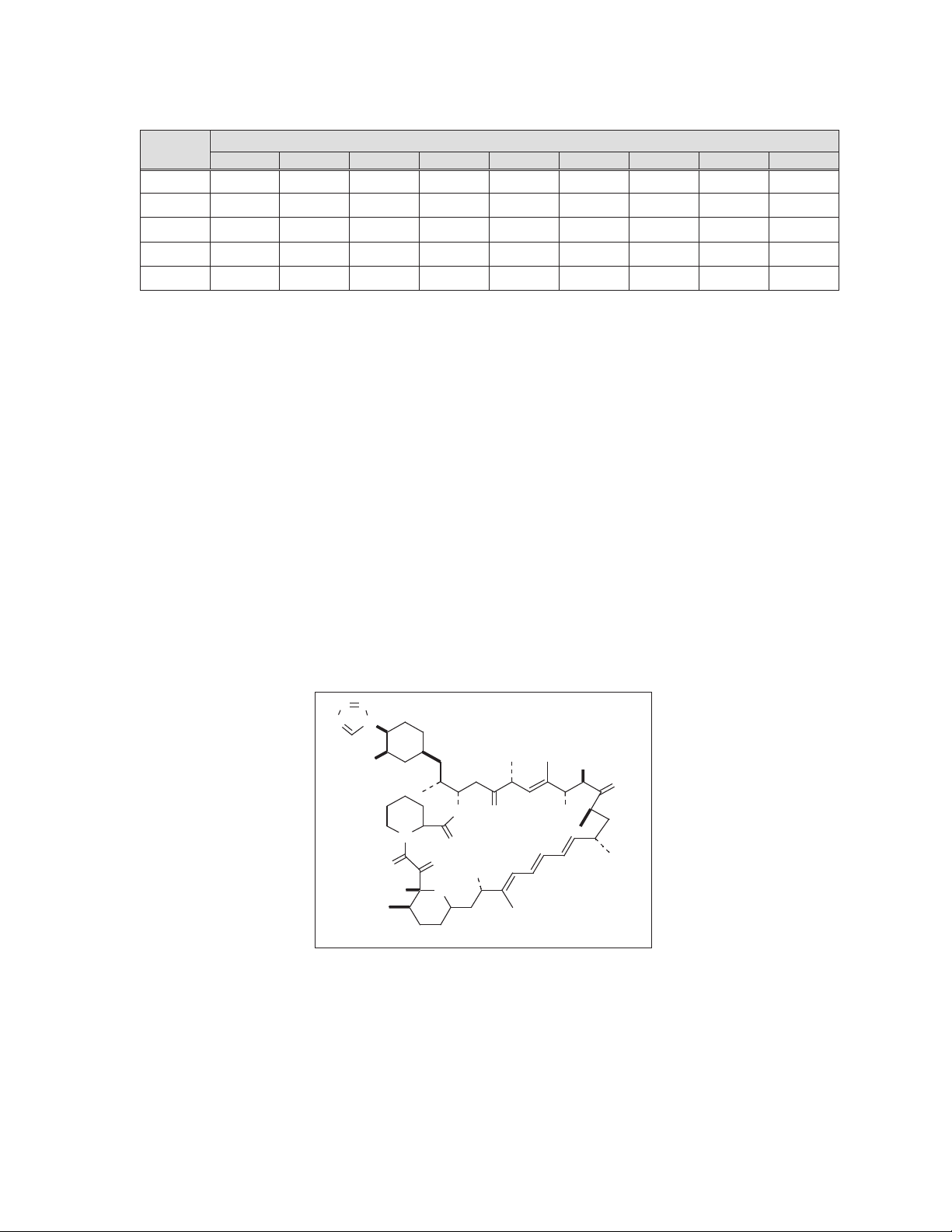
Table 2-2: Resolute Onyx™ stent sizes
Diameter
(mm)
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5 - 9* 9* 9* 9* 9* 9* - -
5.0 - 9* 9* 9* 9* 9* 9* - -
“-” Denotes stent length is not available
“*” Not available for OTW
8 12 15 18 22 26 30 34 38
9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
Stent length (mm)
2.2 Drug component description
The drug coating of the Resolute Onyx™ system consists of the drug zotarolimus (the active
®
ingredient) and the BioLinx
polymer system (the inactive ingredient).
2.2.1 Zotarolimus
The active pharmaceutical ingredient utilized in the Resolute Onyx™ system is zotarolimus. It
is a tetrazole-containing macrocyclic immunosuppressant.
The chemical name of zotarolimus is:
[3S-[3R*[S*(1R*,3S*,4R*)],6S*,7E,9S*,10S*,12S*,14R*,15E,17E,19E,21R*, 23R*,
26S*,27S*,34aR*]]-9,10,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,32,33,34,34a-hexadecahydro-9,27dihydroxy-3-[2-[3-methoxy-4-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)cyclohexyl]-1-methylethyl]-10,21-dimethoxy6,8,12,14,20,26-hexamethyl-23,27-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c] [1,4] oxaazacyclohentriacontine1,5,11,28,29(4H,6H,31H)-pentone.
The chemical structure of zotarolimus is shown in Figure 2-3:
NN
N
N
MeO
OO OH
N
O
O
O
MeO
OHO
OMe
O
Figure 2-3: Zotarolimus chemical structure
Zotarolimus has extremely low water solubility and is a lipophilic compound that is freely
soluble in propylene glycol, acetone, toluene, acetonitrile, ethanol, benzyl alcohol and DMSO.
The molecular formula of zotarolimus is C
52H79N5O12
and its molecular weight is 966.2.
Zotarolimus does not have any ionizable group(s) in the physiological pH range; therefore, its
solubility is expected to be unaltered in this range.
7
Page 9
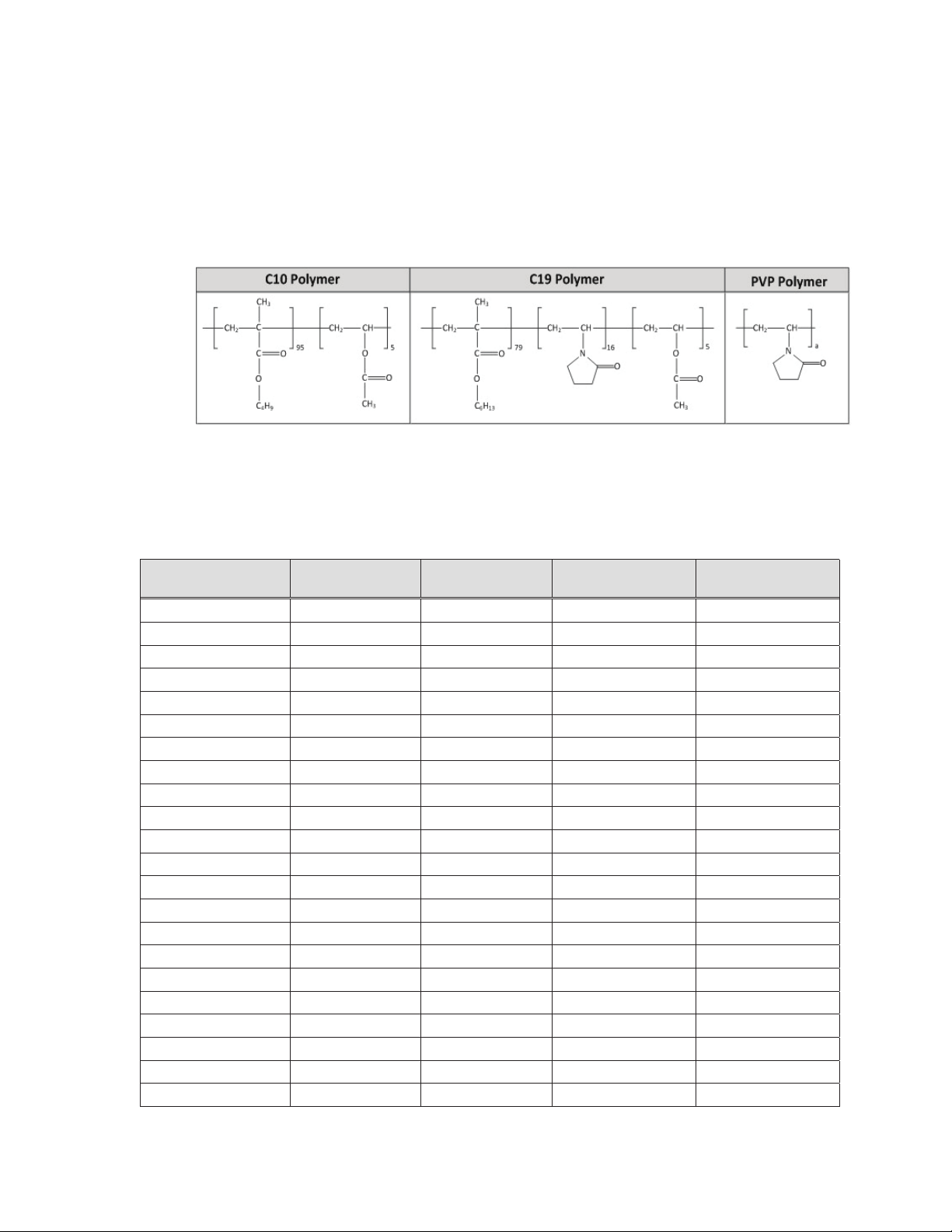
2.2.2 Polymer system description
The Resolute Onyx™ stent consists of a bare metal stent with a Parylene C primer coat and
a coating that consists of a blend of the drug zotarolimus and the BioLinx
TM
BioLinx
(polyvinyl pyrrolidone). The structural formula of the BioLinx
is a blend of the Medtronic proprietary components C10 and C19, and PVP
TM
polymer subunits are shown in
TM
polymer system.
Figure 2-4:
Figure 2-4: Chemical structure of the BioLinx
TM
polymer subunits
2.2.3 Product matrix and zotarolimus content
Table 2-3: Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system product matrix and
nominal zotarolimus doses
Product number
RX
RONYX20008UX RONYX20008W 2.0 8 51
RONYX22508UX RONYX22508W 2.25 8 51
RONYX25008UX RONYX25008W 2.5 8 51
RONYX27508UX RONYX27508W 2.75 8 67
RONYX30008UX RONYX30008W 3.0 8 67
RONYX35008UX RONYX35008W 3.5 8 77
RONYX40008UX RONYX40008W 4.0 8 77
RONYX20012UX RONYX20012W 2.0 12 70
RONYX22512UX RONYX22512W 2.25 12 70
RONYX25012UX RONYX25012W 2.5 12 70
RONYX27512UX RONYX27512W 2.75 12 94
RONYX30012UX RONYX30012W 3.0 12 94
RONYX35012UX RONYX35012W 3.5 12 108
RONYX40012UX RONYX40012W 4.0 12 108
RONYX45012UX - 4.5 12 132
RONYX50012UX - 5.0 12 132
RONYX20015UX RONYX20015W 2.0 15 85
RONYX22515UX RONYX22515W 2.25 15 85
RONYX25015UX RONYX25015W 2.5 15 85
RONYX27515UX RONYX27515W 2.75 15 117
RONYX30015UX RONYX30015W 3.0 15 117
RONYX35015UX RONYX35015W 3.5 15 132
Product number
OTW
Nominal expanded
stent ID (mm)
Nominal unexpanded
stent length (mm)
Nominal zotarolimus
content (μg)
8
Page 10

Table 2-3: Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system product matrix and
nominal zotarolimus doses
Product number
RX
RONYX40015UX RONYX40015W 4.0 15 132
RONYX45015UX - 4.5 15 158
RONYX50015UX - 5.0 15 158
RONYX20018UX RONYX20018W 2.0 18 104
RONYX22518UX RONYX22518W 2.25 18 104
RONYX25018UX RONYX25018W 2.5 18 104
RONYX27518UX RONYX27518W 2.75 18 140
RONYX30018UX RONYX30018W 3.0 18 140
RONYX35018UX RONYX35018W 3.5 18 156
RONYX40018UX RONYX40018W 4.0 18 156
RONYX45018UX - 4.5 18 188
RONYX50018UX - 5.0 18 188
RONYX20022UX RONYX20022W 2.0 22 127
RONYX22522UX RONYX22522W 2.25 22 127
RONYX25022UX RONYX25022W 2.5 22 127
RONYX27522UX RONYX27522W 2.75 22 171
RONYX30022UX RONYX30022W 3.0 22 171
RONYX35022UX RONYX35022W 3.5 22 186
RONYX40022UX RONYX40022W 4.0 22 186
RONYX45022UX - 4.5 22 227
RONYX50022UX - 5.0 22 227
RONYX20026UX RONYX20026W 2.0 26 146
RONYX22526UX RONYX22526W 2.25 26 146
RONYX25026UX RONYX25026W 2.5 26 146
RONYX27526UX RONYX27526W 2.75 26 198
RONYX30026UX RONYX30026W 3.0 26 198
RONYX35026UX RONYX35026W 3.5 26 221
RONYX40026UX RONYX40026W 4.0 26 221
RONYX45026UX - 4.5 26 265
RONYX50026UX - 5.0 26 265
RONYX20030UX RONYX20030W 2.0 30 168
RONYX22530UX RONYX22530W 2.25 30 168
RONYX25030UX RONYX25030W 2.5 30 168
RONYX27530UX RONYX27530W 2.75 30 225
RONYX30030UX RONYX30030W 3.0 30 225
RONYX35030UX RONYX35030W 3.5 30 252
RONYX40030UX RONYX40030W 4.0 30 252
RONYX45030UX - 4.5 30 304
RONYX50030UX - 5.0 30 304
RONYX22534UX RONYX22534W 2.25 34 187
Product number
OTW
Nominal expanded
stent ID (mm)
Nominal unexpanded
stent length (mm)
Nominal zotarolimus
content (μg)
9
Page 11
Table 2-3: Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system product matrix and
nominal zotarolimus doses
Product number
RX
RONYX25034UX RONYX25034W 2.5 34 187
RONYX27534UX RONYX27534W 2.75 34 257
RONYX30034UX RONYX30034W 3.0 34 257
RONYX35034UX RONYX35034W 3.5 34 282
RONYX40034UX RONYX40034W 4.0 34 282
RONYX22538UX RONYX22538W 2.25 38 206
RONYX25038UX RONYX25038W 2.5 38 206
RONYX27538UX RONYX27538W 2.75 38 284
RONYX30038UX RONYX30038W 3.0 38 284
RONYX35038UX RONYX35038W 3.5 38 317
RONYX40038UX RONYX40038W 4.0 38 317
Product number
OTW
Nominal expanded
stent ID (mm)
Nominal unexpanded
stent length (mm)
Nominal zotarolimus
content (μg)
3 Indications
The Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system is indicated for improving
coronary luminal diameters in patients, including those with diabetes mellitus or high bleeding
risk, with symptomatic ischemic heart disease due to de novo lesions of length 35 mm in native
coronary arteries with reference vessel diameters of 2.0 mm to 5.0 mm. In addition, the Resolute
Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system is indicated for treating de novo
chronic total
occlusions.
4 Contraindications
The Resolute Onyx™ system is contraindicated for use in:
• Patients with known hypersensitivity or allergies to aspirin, heparin, bivalirudin,
clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticagrelor, ticlopidine, drugs such as zotarolimus, tacrolimus,
sirolimus, everolimus, or similar drugs or any other analogue or derivative.
• Patients with a known hypersensitivity to the cobalt-based alloy (cobalt, nickel, chromium,
and molybdenum) or platinum-iridium alloy.
• Patients with a known hypersensitivity to the BioLinx® polymer or its individual
components (see details in Section 2.2.2 – Polymer system description).
Coronary artery stenting is contraindicated for use in:
• Patients in whom antiplatelet and/or anticoagulation therapy is contraindicated.
• Patients who are judged to have a lesion that prevents complete inflation of an
angioplasty balloon or proper placement of the stent or stent delivery system.
5 Warnings
• Ensure that the inner package has not been opened or damaged as this would indicate
that the sterile barrier has been breached.
• The use of this product carries the same risks associated with coronary artery stent
implantation procedures, which include subacute and late vessel thrombosis, vascular
complications, and bleeding events.
• This product should not be used in patients who are not likely to comply with the
recommended antiplatelet therapy.
6 Precautions
• Only physicians who have received adequate training should perform implantation of the
stent.
10
Page 12

• Subsequent stent restenosis or occlusion may require repeat catheter-based treatments
(including balloon dilatation) of the arterial segment containing the stent. The long-term
outcome following repeat catheter-based treatments of previously implanted stents is not
well characterized.
• The risks and benefits of stent implantation should be assessed for patients with a history
of severe reaction to contrast agents.
• Do not expose or wipe the product with organic solvents such as alcohol.
• The use of a DES outside of the labeled indications, including use in patients with more
tortuous anatomy, may have an increased risk of adverse events, including stent
thrombosis, stent embolization, myocardial infarction (MI), or death.
• Care should be taken to control the position of the guide catheter tip during stent delivery,
stent deployment, and balloon withdrawal. Before withdrawing the stent delivery system,
confirm complete balloon deflation using fluoroscopy to avoid arterial damage caused by
guiding catheter movement into the vessel.
• Stent thrombosis is a low-frequency event that is frequently associated with MI or death.
Data from the RESOLUTE clinical trials have been prospectively evaluated and
adjudicated using the definition developed by the Academic Research Consortium (ARC)
(see Section
for more information).
10.7 – Pooled results of the Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial Program
6.1 Pre- and post-procedure antiplatelet regimen
In the Medtronic RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm-4.0 mm) Clinical Study and RESOLUTE
ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study, the protocols specified administration of clopidogrel or
ticlopidine (or any approved P2Y12 platelet inhibitor), including dosages before the
procedure, and for a period of at least 6 months post-procedure. Aspirin was administered
before the procedure concomitantly with a P2Y12 platelet inhibitor and then continued postprocedure to reduce the risk of thrombosis.
• In the Medtronic RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm-4.0 mm) Clinical Study, 93.3%,
93.2%, 89.2%, and 52.2% of the subjects remained on dual antiplatelet therapy at 6
months, 8 months, 12 months, and 36 months, respectively.
• In the Medtronic RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study, 91.1%, 87.1%, and 51%
of the subjects remained on dual antiplatelet therapy at 6 months, 12 months, and 36
months, respectively.
6.1.1 Oral antiplatelet therapy
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) using a combination treatment of aspirin with a P2Y12
platelet inhibitor after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), reduces the risk of stent
thrombosis and ischemic cardiac events, but increases the risk of bleeding complications.
The optimal duration of DAPT (specifically a P2Y12 platelet inhibitor in addition to aspirin)
following DES implantation is unknown, and DES thrombosis may still occur despite
continued therapy. It is very important that the patient is compliant with the post-procedural
antiplatelet recommendations.
Per 2016 ACC/AHA guidelines,
after PCI. A P2Y12 platelet inhibitor should be given daily for at least 6 months in stable
1
a daily aspirin dose of 81 mg is recommended indefinitely
1 Levine GN, et al. 2016 ACC/AHA Guideline Focused Update on Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Patients With
Coronary Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on
Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016; doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2016.03.513. For full text, please refer to the
following website: http://content.onlinejacc.org/article.aspx?doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2016.03.513
11
Page 13

ischemic heart disease patients and for at least 12 months in patients with acute coronary
syndrome (ACS).
2
Consistent with the DAPT Study,
and the 2016 ACC/AHA guidelines, longer duration of
DAPT may be considered in patients at higher ischemic risk with lower bleeding risk.
The Academic Research Consortium (ARC) proposed a standardized definition for identifying
3
patients at high bleeding risk (HBR)
. Additionally, evidence from a dedicated study of
Resolute Onyx in HBR patients and those who are unable to tolerate long term DAPT after
4
PCI has been published
.
Based on the Onyx ONE Clear Analysis, Resolute Onyx is safe and effective in patients at
high risk of bleeding treated with one month of DAPT. The patients evaluated in the Onyx
ONE Clear Analysis met the pre-defined criteria for high bleeding risk and were those whom
in the opinion of their physician, the potential benefit of 1-Month DAPT outweighed the
potential risk. In addition to at least one HBR risk factor, enrollment included 48.6% ACS
patients (unstable angina 22.8%, Non-STEMI 21.7% and STEMI 4.2%). (see Section 10.5.1
- Onyx ONE Clear Primary Analysis).
Decisions about duration of DAPT are best made on an individual basis and should integrate
clinical judgment, assessment of the benefit/risk ratio, and patient preference.
Premature discontinuation or interruption of prescribed antiplatelet medication could result in
a higher risk of stent thrombosis, MI, or death. Before PCI, if premature discontinuation of
antiplatelet therapy is anticipated, physicians should carefully evaluate with the patient
whether a DES and its associated recommended DAPT regimen is the appropriate PCI
choice.
Following PCI, if elective noncardiac surgery requiring suspension of antiplatelet therapy is
considered, the risks and benefits of the procedure should be weighed against the possible
risk associated with interruption of antiplatelet therapy.
Patients who require premature DAPT discontinuation should be carefully monitored for
cardiac events. At the discretion of the patient’s treating physician(s), the antiplatelet therapy
should be restarted as soon as possible.
6.2 Use of multiple stents
The long-term effects of zotarolimus are currently unknown. The extent of the patient’s
exposure to the zotarolimus drug and the stent and polymer coating is directly related to the
number of stents and total stent length implanted.
When multiple stents are required, stent materials should be of similar composition. Placing
multiple stents of different materials in contact with each other may increase potential for
corrosion. To avoid the possibility of dissimilar metal corrosion, do not implant stents of
different materials in tandem where overlap or contact is possible.
Potential interactions of the Resolute Onyx™ stent with other drug-eluting or coated stents
have not been evaluated and should be avoided whenever possible.
When using two wires, care should be taken when introducing, torquing, and removing one or
both guidewires to avoid entanglement. In this situation, it is recommended that one
2 Mauri L, et al. Twelve or 30 Months of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Drug-Eluting Stents. N Engl J Med. 2014;
371:2155–66.
3 Urban P, Mehran R, Colleran R, et al. Defining High Bleeding Risk in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary
Intervention. Circulation 2019;140:240-6
4 Windecker S, Latib A, Kedhi E, et al. Polymer-based or Polymer-free Stents in Patients at High Bleeding Risk. The New
England Journal of Medicine 2020:10.1056/NEJMoa1910021.
12
Page 14

guidewire be completely withdrawn from the patient before removing any additional
equipment.
6.3 Use in conjunction with other procedures
The safety and effectiveness of using atherectomy devices with Resolute Onyx™
not been established.
6.4 Brachytherapy
The safety and effectiveness of the Resolute Onyx™ stent in target lesions treated with prior
brachytherapy, or the use of brachytherapy to treat in-stent restenosis of a Resolute Onyx™
stent, have not been established.
6.5 Use in special populations
Information on use of the Resolute Onyx™ stent in certain special patient populations is
derived from clinical studies of the Resolute stent system, which uses the same drug
(zotarolimus) – See Section 8 – Overview of clinical trials
6.5.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. There are no well-controlled studies in pregnant women or men
intending to father children. The Resolute Onyx™ stent should be used during pregnancy
only if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk to the embryo or fetus. Effective
contraception should be initiated before implanting a Resolute Onyx™ stent and for 1 year
after implantation.
See Section 7.6 – Pregnancy under Drug information.
stent have
6.5.2 Lactation
It is not known whether zotarolimus is excreted in human milk. The pharmacokinetic and
safety profiles of zotarolimus in infants are not known. Because many drugs are excreted in
human milk and because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants from
zotarolimus, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to implant a
Resolute Onyx™ stent, taking into account the importance of the stent to the mother.
See Section 7.7 – Lactation under Drug information.
6.5.3 Gender
TM
Clinical studies of the Resolute
stent did not suggest any significant differences in safety
and effectiveness for male and female patients.
6.5.4 Ethnicity
TM
Clinical studies of the Resolute
stent did not include sufficient numbers of patients to
assess for differences in safety and effectiveness due to ethnicity.
6.5.5 Pediatric use
The safety and effectiveness of the Resolute Onyx™ stent in patients below the age of 18
years have not been established.
13
Page 15

6.5.6 Geriatric use
The RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm-4.0 mm) Clinical Study,
mm Clinical Study, and the RESOLUTE clinical studies did not have an upper age limit.
Among the 1,242 patients treated with the Resolute stent in the RESOLUTE US Main Study,
which included 2.25 mm to 3.5 mm stents, 617 patients were age 65 or older and 88 patients
were age 80 or older. A post hoc analysis of patients treated with the Resolute stent showed
no significant differences in rates of cardiac death, target vessel MI, target lesion
revascularization, ARC definite or probable stent thrombosis, or target lesion failure at 12
months. The rate of all-cause death at 12 months was 0.3% in patients under age 65 vs.
1.8% in patients age 65 or older.
6.5.7 Lesion/vessel characteristics
The safety and effectiveness of the Resolute Onyx™ stent have not been established in the
cerebral, carotid, or peripheral vasculature or in the following coronary disease patient
populations:
• Patients with coronary artery reference vessel diameters < 2.0 mm or > 5.0 mm.
• Patients with evidence of an acute ST-elevation MI within 72 hours of intended stent
implantation.
• Patients with vessel thrombus at the lesion site.
• Patients with lesions located in a saphenous vein graft, in the left main coronary
artery, ostial lesions, or bifurcation lesions.
• Patients with diffuse disease or poor flow distal to identified lesions.
• Patients with 3 vessel disease.
6.6 Drug interactions
The effect of potential drug interactions on the safety or effectiveness of the Resolute Onyx™
stent has not been investigated. While no specific clinical data are available, drugs like
sirolimus that act through the same binding protein (FKBP12) may interfere with the efficacy
of zotarolimus. Zotarolimus is metabolized by CYP3A4, a human cytochrome P450 enzyme.
When administered concomitantly with 200 mg ketoconazole bid, a strong inhibitor of
CYP3A4, zotarolimus produces less than a 2-fold increase in AUC
Therefore, consideration should be given to the potential for drug interactions when deciding
to place a Resolute Onyx™ stent in a patient who is taking drugs that are known substrates
or inhibitors of the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4. Systemic exposure of zotarolimus
should also be taken into consideration if the patient is treated concomitantly with systemic
immunosuppressive therapy.
the RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0
with no effect on C
0-inf
max
.
Formal drug interaction studies have not been conducted with the Resolute Onyx™ stent.
6.7 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) safety information
Non-clinical testing has demonstrated that the Resolute Onyx™ stent is MR Conditional for
single and overlapping lengths up to 120 mm. A patient with this device can be safely
scanned in an MR system meeting the following conditions:
• Static magnetic field of 1.5 and 3 Tesla only
• Maximum spatial gradient magnetic field of 3000 gauss/cm (30 T/m) or less
• Maximum MR system reported, whole body averaged specific absorption rate (SAR) of
2.0 W/kg (Normal Operating Mode)
Under the scan conditions defined above, the Resolute Onyx™ stent is expected to produce
a maximum temperature rise of 4.3°C after 15 minutes of continuous scanning.
In non-clinical testing, the image artifact caused by the device extended approximately 10
mm from the Resolute Onyx™ stent when imaged with a spin echo pulse sequence and a 3
Tesla MRI system. The artifact does obscure the device lumen.
14
Page 16

6.8 Stent handling precautions
• For single use only. The Resolute Onyx™ system is provided sterile. Do not resterilize or
reuse this product. Note the use-by date on the product label. Do not use the product if
the package or product has been opened or damaged.
• Only the contents of the pouch should be considered sterile. The outside surface of the
pouch is not sterile.
• Do not remove the contents of the pouch until the device will be used immediately.
• Do not remove the stent from the delivery balloon; removal may damage the stent and
polymer coating and/or lead to stent embolization. The Resolute Onyx™ system is
intended to perform as a system. The stent is not designed to be crimped onto another
delivery device.
• Special care must be taken not to handle or in any way disrupt the stent on the balloon.
This is most important while removing the catheter from the packaging, placing it over the
guidewire, and advancing it through the rotating hemostatic valve and guide catheter hub.
• Do not try to straighten a kinked shaft or hypotube. Straightening a kinked metal shaft
may result in breakage of the shaft.
• Stent manipulation (for example, rolling the mounted stent with your fingers) may cause
coating damage, contamination, or dislodgement of the stent from the delivery system
balloon.
• The Resolute Onyx™ system must not be exposed to any direct handling or contact with
liquids before preparation and delivery as the coating may be susceptible to damage or
premature drug elution.
• Use only the appropriate balloon inflation media. Do not use air or any gaseous medium
to inflate the balloon as this may cause uneven expansion and difficulty in deployment of
the stent.
• The Resolute Onyx™ stent delivery systems should not be used in conjunction with any
other stents or for post-dilatation.
6.9 Stent placement precautions
• The vessel must be pre-dilated with an appropriately sized balloon. Refer to the pre-
dilatation balloon sizing described in Section 14.5 – Delivery procedure. Failure to do
so may increase the risk of placement difficulty and procedural complications.
• Do not prepare or pre-inflate the balloon before stent deployment other than as directed.
Use the balloon purging technique described in Section 14 –
• Guide catheters used must have lumen sizes that are suitable to accommodate the stent
delivery system (see Device component description in Table 2-1).
• After preparation of the stent delivery system, do not induce negative pressure on the
delivery catheter before placement of the stent across the lesion. This may cause
premature dislodgment of the stent from the balloon or delivery difficulties.
• Balloon pressures should be monitored during inflation. Do not exceed rated burst
pressure as indicated on the product label. Use of pressures higher than those specified
on the product label may result in a ruptured balloon with possible intimal damage and
dissection.
• In small or diffusely diseased vessels, the use of high balloon inflation pressures may
over-expand the vessel distal to the stent and could result in vessel dissection.
• Implanting a stent may lead to a dissection of the vessel distal and/or proximal to the
stented portion and may cause acute closure of the vessel requiring additional
intervention (for example, CABG, further dilatation, placement of additional stents, or
other intervention).
• Do not expand the stent if it is not properly positioned in the vessel (see Section
Precautions–Stent/system removal precautions).
• Placement of the stent has the potential to compromise side branch patency.
Directions for use.
6 -
15
Page 17

• Do not attempt to pull an unexpanded stent back through the guide catheter, as
dislodgement of the stent from the balloon may occur. Remove as a single unit per the
instructions in Section 6 - Precautions –Stent/system removal precautions.
• Under-expansion of the stent may result in stent movement. Care must be taken to
properly size the stent to ensure that the stent is in full contact with the arterial wall upon
deflation of the balloon.
• Stent retrieval methods (for example, use of additional wires, snares and/or forceps) may
result in additional trauma to the coronary vasculature and/or the vascular access site.
Complications may include bleeding, hematoma, or pseudoaneurysm.
• Ensure full coverage of the entire lesion/dissection site so that there are no gaps between
stents.
• Administration of appropriate anticoagulant, antiplatelet, and coronary vasodilator therapy
is critical to successful stent implantation.
6.10 Stent/system removal precautions
If removal of a stent system is required before deployment, ensure that the guide catheter is
coaxially positioned relative to the stent delivery system and cautiously withdraw the stent
delivery system into the guide catheter. Should unusual resistance be felt at any time when
withdrawing the stent towards the guide catheter, the stent delivery system and the guide
catheter should be removed as a single unit. This must be done under direct visualization
with fluoroscopy.
When removing the stent delivery system and guide catheter as a single unit:
• Do not retract the stent delivery system into the guide catheter. Maintain guidewire
placement across the lesion and carefully pull back the stent delivery system until the
proximal balloon marker of the stent delivery system is aligned with the distal tip of the
guide catheter.
• The system should be pulled back into the descending aorta toward the arterial sheath. As
the distal end of the guide catheter enters into the arterial sheath, the catheter will
straighten, allowing safe withdrawal of the stent delivery system into the guide catheter and
the subsequent removal of the stent delivery system and the guide catheter from the
arterial sheath.
Failure to follow these steps and/or applying excessive force to the stent delivery system can
potentially result in loss or damage to the stent and/or stent delivery system components
such as the balloon.
6.11 Post-procedure
• Care must be exercised when crossing a newly deployed stent with an intravascular
ultrasound (IVUS) catheter, an optical coherence tomography (OCT) catheter, a coronary
guidewire, or a balloon catheter to avoid disrupting the stent placement, apposition,
geometry, and coating.
• Post-dilatation: All efforts should be made to ensure that the stent is not under-dilated. If
the deployed stent is not fully apposed to the vessel wall, the stent may be expanded
further with a larger diameter balloon that is slightly shorter (about 2 mm) than the stent.
The post-dilatation can be done using a low-profile, high-pressure, non-compliant balloon
catheter. The balloon should not extend outside of the stented region. Do not use the
stent delivery balloon for post-dilatation.
• If patient requires MR imaging, refer to Section 6.7 – Magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI) safety information above.
• Antiplatelet therapy should be administered post-procedure (see Precautions – Section
6.1 - Pre- and post-procedure antiplatelet regimen). Patients who require early
discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy (for example, secondary to active bleeding), should
be monitored carefully for cardiac events. At the discretion of the patient's treating
physician, the antiplatelet therapy should be restarted as soon as possible.
16
Page 18

7 Drug information
7.1 Mechanisms of action
The suggested mechanism of action of zotarolimus is to bind to FKBP12, leading to the
formation of a trimeric complex with the protein kinase mTOR (mammalian target of
rapamycin), inhibiting its activity. Inhibition of mTOR results in the inhibition of protein
phosphorylation events associated with translation of mRNA and cell cycle control.
7.2 Metabolism
Zotarolimus undergoes oxidative metabolism in the liver to form the demethyl and
hydroxylated metabolites of the parent drug. Further metabolism can lead to the formation of
hydroxyl-demethyl and dihydroxyl-demethyl metabolites. Enzymes of the CYP3A family are
the major catalysts of oxidative metabolism of zotarolimus. Zotarolimus is a competitive
inhibitor of CYP3A-dependent activities, however the IC
fold higher than the systemic concentrations expected following implantation of a drug-eluting
stent. The anticipated zotarolimus blood levels in stented patients are expected to be less
than 0.004 μM, suggesting that clinically significant drug-drug interactions are unlikely.
7.3 Pharmacokinetics of the Resolute Onyx
The pharmacokinetics information for the Resolute Onyx™ stent system is derived from a
study conducted on the Resolute stent system. The Resolute Onyx™ stent system is similar
to the Resolute stent system with regards to the stent design, the stent coating technology
(dosing and drug to polymer ratio), and delivery system design and materials. Given these
similarities and supportive bench and animal study information, the pharmacokinetics
information from the RESOLUTE FIM PK Sub-study, as described below, is applicable to the
Resolute Onyx™ stent system.
TM
stent
values (3 μM and above) are many
50
The pharmacokinetics (PK) of zotarolimus delivered from the Resolute stent have been
determined in patients with coronary artery disease after stent implantation in the Medtronic
RESOLUTE FIM Clinical Trial. The dose of zotarolimus was calculated per stent unit surface
area and the key pharmacokinetic parameters determined from these patients are provided in
Table 7-1.
Table 7-1: Zotarolimus pharmacokinetics in the Medtronic RESOLUTE FIM clinical trial PK
Sub-study patients after implantation of Resolute zotarolimus-eluting coronary stents
Group I
PK
parameter Units
C
(ng/mL) 0.129 0.210 ± 0.062 0.300 ± 0.075 0.346 ± 0.133
max
T
(h) 1.00 0.9 ± 0.7 0.9 ± 0.5 0.8 ± 0.5
max
AUC
AUC
0-last
0-inf
$
(ng•h/mL)
(ng•h/mL)
(128 μg)
N = 1†
15.08 16.04 ± 4.74 35.89 ± 12.79 31.19 ± 17.69
41.89 39.09 ± 11.77 52.41 ± 12.57 80.12 ± 51.00
ȕ$ (1/h) 0.003 0.004 ± 0.001 0.004 ± 0.001 0.003 ± 0.002
‡,#
t
(h) 263.4 195.5 ± 74.4 167.4 ± 29.7 208.3 ± 144.4
½
CL/F$ (L/h) 3.06 5.23 ± 2.55 4.80 ± 1.11 5.14 ± 3.55
Vdȕ/F$ (L) 1161.2 1449.3 ± 221.6 1181.2 ± 336.4 1658.6 ± 494.8
Notes
Maximum observed blood concentration a Primary dose groups
C
max
T
Time to C
max
AUC
0-last
Area under the blood concentration-time curve
† No SD was reported when N = 1
max
(AUC) from time 0 to time of last measurable
concentration
AUC from time 0 to infinity (AUC
AUC
0-inf
). #
0-inf
Group IIa
(180 μg)
N = 11
Group IIIa
(240 μg)
N = 7
‡ Harmonic mean ± pseudo-standard deviation
Group IVa
(300 μg)
N = 3
17
Page 19
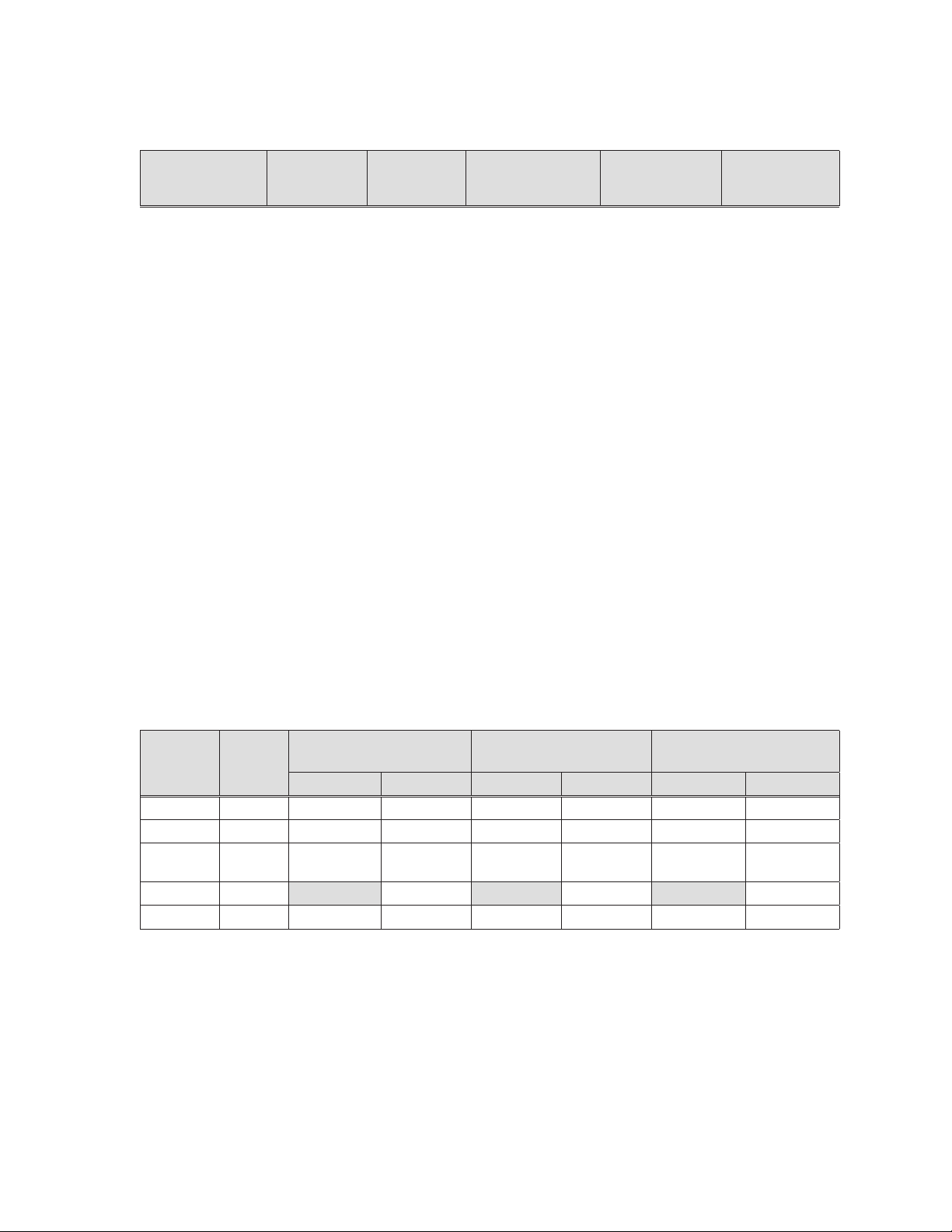
Table 7-1: Zotarolimus pharmacokinetics in the Medtronic RESOLUTE FIM clinical trial PK
Sub-study patients after implantation of Resolute zotarolimus-eluting coronary stents
Group I
PK
parameter Units
(128 μg)
N = 1†
t½ Harmonic mean half-life
CL/F Mean apparent clearance
Vd
/F Apparent volume of distribution $ Not a true sample
ȕ
Group IIa
(180 μg)
N = 11
Group IIIa
(240 μg)
N = 7
Group IVa
Not a true estimate of the elimination half-life as the drug
release from the stent was not complete during the
course of the pharmacokinetic sampling
(300 μg)
N = 3
The results in Table 7-1 show that the pharmacokinetics of zotarolimus were linear in the
primary dose-proportionality evaluation (including dose groups with N > 1), 180, 240, and 300
μg, following the implantation of the Resolute stents as illustrated by dose proportional
increases in maximum blood concentration (C
curve (AUC) from time 0 to time of last measurable concentration (AUC
time 0 to infinity(AUC
) for the primary dose groups ranged from 4.80 to 5.23 L/h and 167.4 to 208.3 h,
(t
1/2
). The mean apparent clearance (CL/F) and harmonic mean half-life
0-inf
respectively. The mean time to reach peak systemic concentration (T
), area under the blood concentration-time
max
) and AUC from
0-last
) ranged from 0.8 to
max
0.9 h after stent implantation.
The data demonstrate dose proportionality and linearity similar to that seen with increasing
zotarolimus doses from the Endeavor stent and intravenous administration. Based on
available zotarolimus pharmacokinetic data, systemic safety margins of 78-fold have been
established for the Resolute stent at 380 μg due to the extended elution of zotarolimus from
the BioLinx® polymer.
7.4 Pharmacokinetics following multi-dose intravenous administration of zotarolimus
Zotarolimus pharmacokinetic activity has been determined following intravenous
administration in healthy subjects. Table 7-2 provides a summary of the pharmacokinetic
analysis.
Table 7-2: Pharmacokinetic parameters (mean ± standard deviation) in patients following
multi-dose intravenous administration of zotarolimus
200 μg QD
PK
parameters Units
C
(ng/mL) 11.41± 1.38¥ 11.93 ± 1.25 21.99 ± 3.79 23.31± 3.15 37.72 ± 7.00 41.79 ± 6.68
max
T
(h) 1.05 ± 0.04¥ 1.03 ± 0.04 1.00 ± 0.14 1.05 ± 0.04 1.03 ± 0.04 1.03 ± 0.05
max
AUC
(ng•h/mL)
0-24
$
t
(h) 32.9 ± 6.8 37.6 ± 4.5 36.0 ± 4.7
1/2
CLb (L/h)
Notes
¥
N = 16;
$ Harmonic mean ± pseudo-standard deviation
b
Clearance data is calculated using compartmental methods.
34.19 ± 4.39¥ 47.70 ± 6.68 68.43 ± 15.41
4.2 ± 0.6 4.2 ± 0.6 4.0 ± 0.9 4.0 ± 0.9 4.6 ± 0.4 4.6 ± 0.4
N = 15
Day 1 Day 14 Day 1 Day 14 Day 1 Day 14
All other data presented in Table 7-2 is calculated using non-compartmental methods.
400 μg QD
N= 16
100.47 ±
18.02
123.48 ±
13.34
800 μg QD
N=16
174.43 ±
19.88
When administered intravenously for 14 consecutive days, zotarolimus showed dose
proportionality. Renal excretion is not a major route of elimination for zotarolimus as
approximately 0.1% of the dose was excreted as unchanged drug in the urine per day. In
multiple doses of 200, 400, and 800 μg, zotarolimus was generally well tolerated by the
18
Page 20

subjects. No clinically significant abnormalities in physical examinations, vital signs, or
laboratory measurements were observed during the study.
7.5 Mutagenesis, carcinogenicity and reproductive toxicology
7.5.1 Mutagenesis
Zotarolimus was not genotoxic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay, the human
peripheral lymphocyte chromosomal aberration assay, or the in vivo mouse micronucleus
assay.
7.5.2 Carcinogenicity
No long-term studies in animals have been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential
of zotarolimus. The carcinogenic potential of the Resolute stent is expected to be minimal
based on the types and quantities of materials present.
7.5.3 Reproductive toxicology
No effect on fertility or early embryonic development in female rats was observed following the
IV administration of zotarolimus at dosages up to 100 μg/kg/day (approximately 19 times the
cumulative blood exposure provided by Resolute stents coated with 300 μg zotarolimus).
For male rats, there was no effect on the fertility rate at IV dosages up to 30 μg/kg/day
(approximately 21 times the cumulative blood exposure provided by Resolute stents coated
with 300 μg zotarolimus). Reduced sperm counts and motility, and failure in sperm release
were observed in male rats following the IV administration of zotarolimus for 28 days at
dosages of >30 μg/kg/day. Testicular germ cell degeneration and histological lesions were
observed in rats following IV dosages of 30 μg/kg/day and above.
7.6 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: There are no well-controlled studies in pregnant women, lactating
women, or men intending to father children for this product.
Administration of zotarolimus to pregnant female rats in a developmental toxicity study at an
intravenous dosage of 60 μg/kg/day resulted in embryolethality. Fetal ossification delays were
also observed at this dosage, but no major fetal malformations or minor fetal anomalies were
observed in this study. A 60 μg/kg/day dose in rats results in approximately 47 times the
maximum blood level and about 11 times the cumulative blood exposure in patients receiving
Resolute Onyx™ stents coated with 300 μg zotarolimus total dose.
No embryo-fetal effects were observed in pregnant rabbits administered zotarolimus in a
developmental toxicity study at intravenous dosages up to 100 μg/kg/day. This dose in
rabbits results in approximately 215 times the maximum blood level and about 37 times the
cumulative blood exposure in patients receiving Resolute Onyx™ stents coated with 300 μg
zotarolimus total dose.
Effective contraception should be initiated before implanting a Resolute Onyx™ stent and
continued for one year post-stent implantation. The Resolute Onyx™ stent should be used in
pregnant women only if potential benefits justify potential risks.
7.7 Lactation
It is not known whether zotarolimus is excreted in human milk. The potential adverse
reactions in nursing infants from zotarolimus have not been determined. The pharmacokinetic
and safety profiles of zotarolimus in infants are not known. Because many drugs are excreted
in human milk and because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants from
zotarolimus, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to implant the
stent, taking into account the importance of the stent to the mother.
19
Page 21
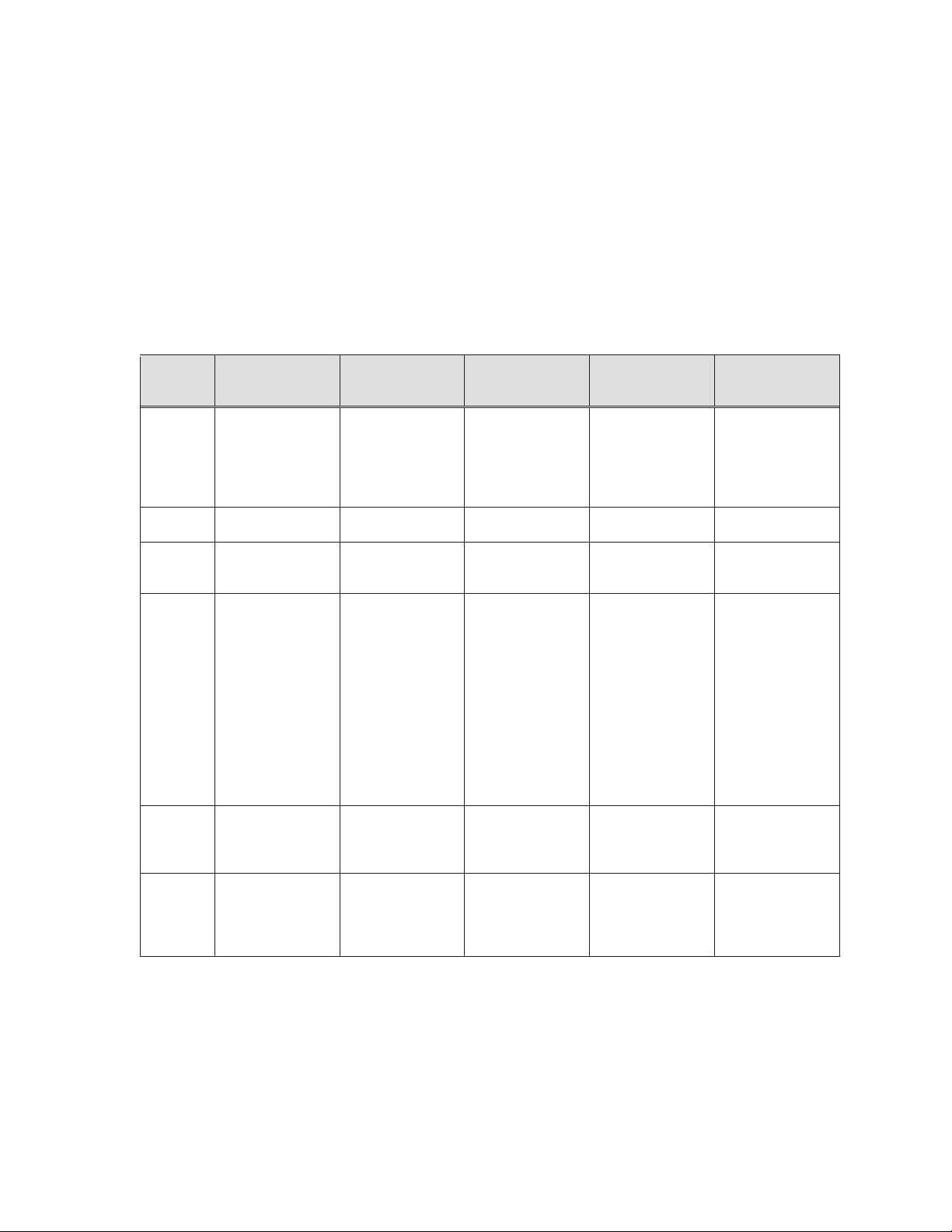
8 Overview of clinical trials
8.1 The RESOLUTE ONYX Clinical Program
The RESOLUTE ONYX Clinical Program currently includes the RESOLUTE ONYX Core
(2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study, conducted in the United States (US), the RESOLUTE
ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study conducted in the US and Japan, and the RESOLUTE ONYX
Post-Approval Study (PAS) – which consists of the Primary Cohort, the XLV Cohort, and the
Bifurcation Cohort.
Table 8-1 summarizes the clinical trial designs for the RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm –
4.0 mm) Clinical Study, the RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study, and the RESOLUTE
ONYX PAS.
Table 8-1: The RESOLUTE ONYX Clinical Program
Study type
Study site
location
Number of
subjects
enrolled
Lesion
criteria
Stent sizes
(Resolute
Onyx™)
Product
used
RESOLUTE ONYX™
Core (2.25 mm – 4.0
mm) Clinical Study
Prospective
Multi-center
Non-randomized
Historical controlled
trial
United States
75 101
Single or two de
novo lesions located
in separate target
vessels
Lesion(s) length ≤35
mm
Target vessel with
RVD between 2.25
to 4.2 mm
Stent diameter:
2.25 to 4.0 mm
Stent length:
8 to 38 mm
Resolute Onyx™ stent
on a rapid exchange
(RX) stent delivery
system
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0
mm Clinical Study
Prospective
Multi-center
Non-randomized
Compared to a
performance goal
United States and
Japan
Single or two de
novo lesions located
in separate target
vessels with at least
one of the target
lesions amenable to
treatment with a 2.0
mm study stent
Lesion(s) length ≤27
mm
Target vessel with
RVD between 2.0 to
2.25 mm
Stent diameter:
2.0 mm
Stent length:
8 to 30 mm
Resolute Onyx™ stent
on a rapid exchange
(RX) stent delivery
system
RESOLUTE ONYX™
Post-Approval Study
Primary Cohort
Prospective
Multi-center
Non-randomized
Compared to a
performance goal
United States and
Europe
416
Lesions located in
separate target
vessels with at least
one of the target
lesions amenable to
treatment with a 2.0
to 4.0 mm stent
Lesion(s) length ≤35
mm
Stent diameter:
2.0 to 4.0 mm
Stent length:
8 to 38 mm
Resolute Onyx™ stent
on a rapid exchange
(RX) or over-the-wire
(OTW) stent delivery
system
RESOLUTE ONYX™
Post-Approval Study
XLV Cohort
Prospective
Multi-center
Non-randomized
Descriptively
evaluate the TLF
rate
United States and
Europe
101
Lesions located in
separate target
vessels with at least
one of the target
lesions amenable to
treatment with a 4.5
or 5.0 mm stent
Lesion(s) length ≤35
mm
Stent diameter:
4.5 to 5.0 mm
Stent length:
12 to 30 mm
Resolute Onyx™ stent
on a rapid exchange
(RX) or over-the-wire
(OTW) stent delivery
system
RESOLUTE ONYX™
Post-Approval Study
Bifurcation Cohort
Prospective
Multi-center
Non-randomized
Compared to a
performance goal
United States and
Europe
205
Single de novo
bifurcated lesion
amenable to
treatment with a 2.0
to 5.0 mm stent with
provisional stenting
technique
Lesion(s) length ≤35
mm
Stent diameter:
2.0 to 5.0 mm
Stent length:
8 to 38 mm
Resolute Onyx™ stent
on a rapid exchange
(RX) or over-the-wire
(OTW) stent delivery
system
20
Page 22
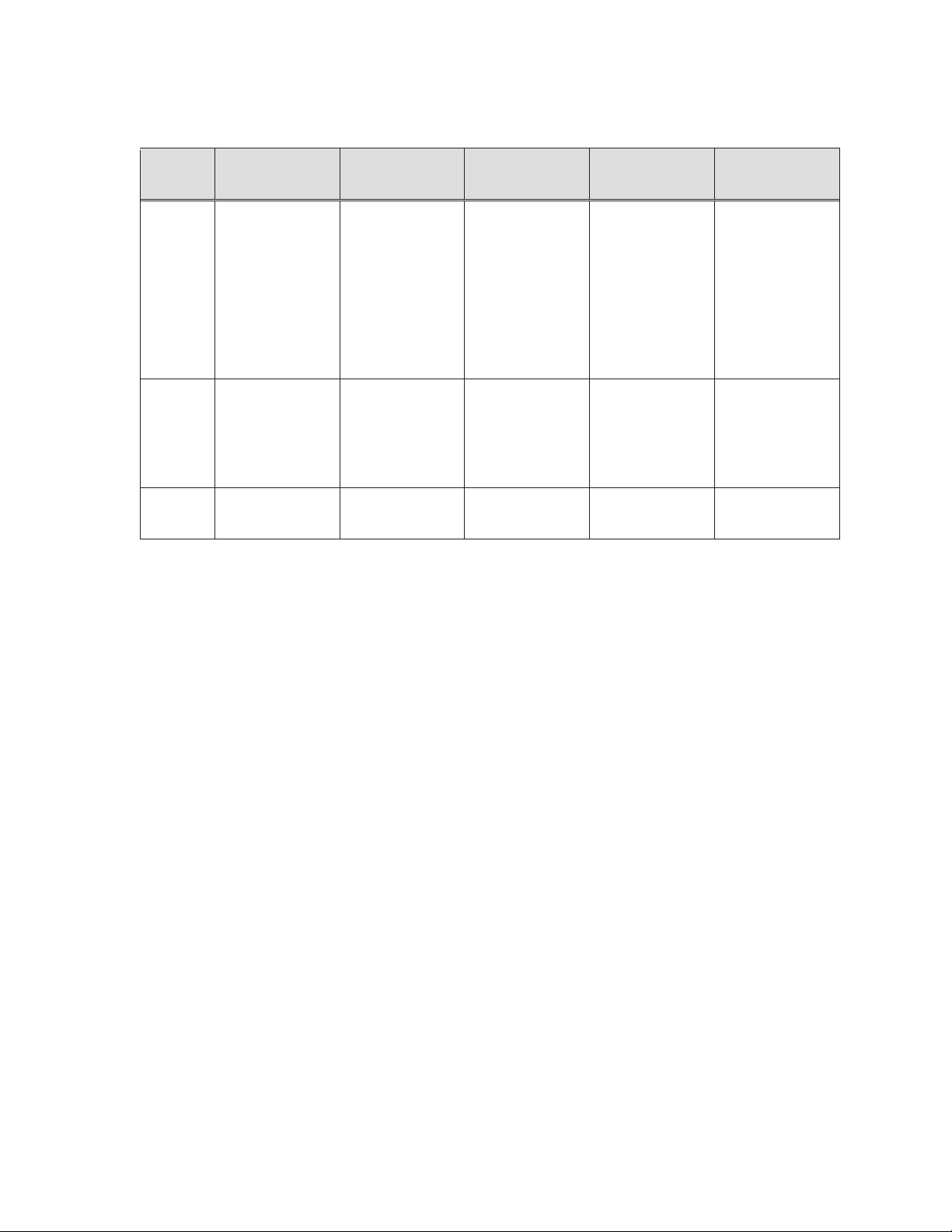
Table 8-1: The RESOLUTE ONYX Clinical Program
Postprocedure
antiplatelet
therapy
Follow-up
Status
RESOLUTE ONYX™
Core (2.25 mm – 4.0
mm) Clinical Study
Aspirin indefinitely and
market approved
thienopyridine
(clopidogrel, prasugrel,
ticagrelor, ticlopidine,
etc.) for a minimum of
6 months in all
subjects, and up to 12
months in subjects
who are not at high
risk of bleeding
30 days, 6 months, 1
to 3 years: clinical or
contact
8 months: clinical and
angiographic, IVUS
(subset)
8 months: clinical and
angiographic follow-up
is complete
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0
mm Clinical Study
Aspirin indefinitely and
market approved
thienopyridine
(clopidogrel, prasugrel,
ticagrelor, ticlopidine,
etc.) for a minimum of
6 months in all
subjects, and up to 12
months in subjects
who are not at high
risk of bleeding
30 days, 6 months, 1
to 3 years: clinical or
contact
13 months: clinical and
angiographic, IVUS
(subset)
13 months: clinical and
angiographic follow-up
is complete
RESOLUTE ONYX™
Post-Approval Study
Primary Cohort
Antiplatelet medication
should be
administered
according to hospital
routine and in line with
the applicable
guidelines on
percutaneous coronary
interventions and the
Instructions for Use of
the device.
30 days, 6 months, 1
year, 2 years, 3 years:
clinical or contact
12 months: clinical
follow-up is complete
RESOLUTE ONYX™
Post-Approval Study
Antiplatelet medication
should be
administered
according to hospital
routine and in line with
the applicable
guidelines on
percutaneous coronary
interventions and the
Instructions for Use of
the device.
30 days, 6 months, 1
year, 2 years, 3 years:
clinical or contact
Enrollment complete,
in follow-up
8.2 Supportive RESOLUTE and RESOLUTE INTEGRITY data:
The Resolute Onyx™ stent is an iterative design update to the Resolute Integrity
utilizing the same continuous sinusoid manufacturing technology with slight modifications
incorporated to provide a lower crossing profile and thus improved deliverability over
predicate products. Given the similarities between the Resolute stent system and the
Resolute Onyx™ stent system, and supportive bench and animal study information, the
findings from the RESOLUTE clinical studies are applicable to the Resolute Onyx™ stent
system.
XLV Cohort
RESOLUTE ONYX™
Post-Approval Study
Bifurcation Cohort
Antiplatelet medication
should be
administered
according to hospital
routine and in line with
the applicable
guidelines on
percutaneous coronary
interventions and the
Instructions for Use of
the device.
30 days, 6 months, 1
year, 2 years, 3 years:
clinical or contact
Enrollment complete,
in follow-up
TM
stent,
The principal safety and effectiveness information for the Resolute stent was derived from the
Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial Program, which consists of the following clinical trials – the
RESOLUTE United States Clinical Trial (R-US), the RESOLUTE All-Comers Clinical Trial (RAC), the RESOLUTE International Study (R-Int), the RESOLUTE First-in-Man (FIM) Clinical
Trial, and the RESOLUTE Japan Clinical Trial (R-J). These 5 studies have evaluated the
performance of the Resolute stent in improving coronary luminal diameters in patients,
including those with diabetes mellitus, with symptomatic ischemic heart disease due to de
novo lesions of length 35 mm in native coronary arteries with reference vessel diameters of
2.25 mm to 4.2 mm. Key elements of these studies are summarized below and in
Table 8-2.
The Resolute 38 mm Length Group was derived from subjects enrolled in the R-US and the
RESOLUTE Asia study (R-Asia) (for 38 mm Length Group data see Table 8-2). In addition,
the RESOLUTE INTEGRITY US Post Market Study, a prospective, multi-center evaluation of
the procedural and clinical outcomes of subjects who were treated with the Medtronic
TM
Resolute Integrity
safety and efficacy of the Resolute Integrity
zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system was designed to assess the
TM
stent for the treatment of de novo lesions in
native coronary arteries with a reference vessel diameter (RVD) of 2.25 mm to 4.2 mm in two
groups of patients, specifically those patients receiving stents mm in length, referred to
as the Primary Enrollment Group (PEG) and those patients who receive extended length
stents (34 mm or 38 mm) referred to as the Extended Length (XL) Sub-study.
Table 8-2 summarizes the clinical trial designs for the Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial
Program and RESOLUTE INTEGRITY US Post-Market Study.
21
Page 23

Sub-study)
RESOLUTE
INTEGRITY US (XL
Prospective
Multi-center
Non-randomized
Post approval
Study
(PEG)
RESOLUTE
RESOLUTE INTEGRITY US Post-Market
INTEGRITY US
Multi-center
Non-randomized
Prospective
38 mm Cohort
RESOLUTE Asia
Prospective
Multi-center
Non-randomized
Post approval
Table 8-2: RESOLUTE and RESOLUTE INTEGRITY clinical trials overview
Prospective
Multi-center
Non-randomized
RESOLUTE Japan
3
controlled trial
Single-arm
Historical
22
Prospective
Multi-center
Non-randomized
RESOLUTE FIM
2
Prospective
Multi-center
Non-randomized
RESOLUTE Int
1
Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial Program
Prospective
Multi-center
Randomized
Single-arm
Historical
Single-arm
Observational
Xience V®)
(1:1 Resolute vs.
controlled trial
PK Assessment
study
Real World subject
inferiority trial
Two-arm, non-
Total: 2349 Total: 139 Total: 100 Total: 109 Total:230 Total: 56
population
Total: 2292
(Resolute: 1140,
population
Real World subject
Xience V®: 1152)
subjects
Multi-center
Non-randomized
Study - 1242
subjects
controlled trial*
Historical
- 2.25–3.5 mm Main
Total: 1516
- 2.25 mm Cohort -
150 subjects
- 2.25–3.5 mm
Angio/IVUS sub-
study - 100
- 60 subjects
-114 subjects (38
mm Sub-study
total patient
population was
- 4.0 mm Sub-study
- 38 mm Sub-study
223 with 114 from
RESOLUTE US
and 109 from
RESOLUTE Asia)
RESOLUTE US* RESOLUTE AC
Study type Prospective
Number of
subjects
enrolled
Page 24

Sub-study)
RESOLUTE
INTEGRITY US (XL
Single target lesion
or two target
separate target
lesions located in
vessels
mm treated or
XL:
lesion length
Target lesion
Target vessel with
to 4.2 mm
RVD between 2.25
Stent diameter:
34-38 mm
3.0 – 4.0 mm
Stent length:
Resolute Integrity
stent on the rapid
exchange MicroTrac
delivery system
Aspirin indefinitely
and
clopidogrel/ticlopidine for months in all
subjects, up to 12
months if tolerated
Study
(PEG)
RESOLUTE
RESOLUTE INTEGRITY US Post-Market
INTEGRITY US
Single target lesion
or two target
separate target
lesions located in
vessels
mm
PEG:
Target lesion
Target vessel with
to 4.2 mm
RVD between 2.25
Stent diameter:
2.25 – 4.0 mm
8 – 30 mm
Stent length:
Resolute Integrity
stent on the rapid
exchange MicroTrac
delivery system
Aspirin indefinitely
and
clopidogrel/ticlopidine
subjects, up to 12
for months in all
months if tolerated
Table 8-2: RESOLUTE and RESOLUTE INTEGRITY clinical trials overview
38 mm Cohort
RESOLUTE Asia
Single or two de
Single or two de
RESOLUTE Japan
3
target vessels
coronary arteries
≤35 mm
Lesion(s) length
≤27 mm
Lesion(s) length
novo lesions
located in separate
novo lesions
located in separate
to 4.0 mm
RVD between 3.0
Target vessel with
RVD between 2.5
Target vessel with
received treatment
of up to two lesions second lesion RVD
(2.25 to 4.2 mm), if
the lesions were
located in separate
Patients may have
to 3.5 mm
target vessels.
Stent diameter:
Stent diameter:
3.0 – 4.0 mm Stent length: 38 mm
2.5 – 3.5 mm
Stent length:
Resolute stent on the
rapid exchange sprint
delivery system
Aspirin indefinitely
and
8 – 30 mm
Resolute stent on the
rapid exchange sprint
delivery system
Aspirin indefinitely
and
clopidogrel/ticlopidine for months in all
clopidogrel/ticlopidine
subjects, up to 12
subjects, up to 12
for months in all
months if tolerated
months if tolerated
23
lesion
14 to 27 mm
Lesion length from
Single de novo
RESOLUTE FIM
2
number of
lesion(s)/ vessel(s)
No limitation to
RESOLUTE Int
1
treated or lesion
Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial Program
number of
lesion(s)/ vessel(s)
No limitation to
treated or lesion
and 3.5 mm
RVD between 2.5
Target vessel with
length
length
to 4.0 mm
RVD between 2.25
Target vessel with
to 4.0 mm
RVD between 2.25
Target vessel with
Stent diameter:
Stent diameter:
Stent diameter:
8 – 30 mm
2.5 – 3.5 mm
Stent length:
2.25 – 4.0 mm
8 – 38 mm
Stent length:
2.25 – 4.0 mm
8 – 30 mm
Stent length:
Resolute stent on the
rapid exchange
Resolute stent on the
rapid exchange sprint
Resolute stent on the
rapid exchange sprint
AV100 delivery
delivery system
delivery system
system
Aspirin indefinitely
and
clopidogrel/ticlopidine months
clopidogrel/ticlopidine
clopidogrel/ticlopidine for months in all
subjects, up to 12
for months in all
subjects, up to 12
months if tolerated
months if tolerated
Aspirin indefinitely
and
Aspirin indefinitely
and
Single or two de
≤27 mm for the
Primary Enrollment
Group, ≤35 mm for
target vessels
novo lesions
located in separate
Lesion(s) length
the 38 mm Length
Group
to 4.2 mm
RVD between 2.25
Target vessel with
Stent diameter:
2.25 – 4.0 mm
Stent length:
8 – 30 mm for the
Group, 38 mm for the
Primary Enrollment
38 mm Length Group
Resolute stent on the
rapid exchange sprint
delivery system
Aspirin indefinitely
and
clopidogrel/ticlopidine for months in all
subjects, up to 12
months if tolerated
RESOLUTE US* RESOLUTE AC
Lesion
criteria
Stent sizes
(Resolute)
Product
used
Post-
procedure
antiplatelet therapy
Page 25

Sub-study)
RESOLUTE
INTEGRITY US (XL
30 days (contact); 6
months (contact); 12
months (clinic visit
with 12-lead ECG)
and 2 years:
(contact) 3 years
(contact)
36-month follow-up is
complete
Study
(PEG)
RESOLUTE
RESOLUTE INTEGRITY US Post-Market
INTEGRITY US
30 days (contact); 6
months (contact); 12
months (clinic visit
with 12-lead ECG)
and 2 years:
(contact)
38 mm Cohort
RESOLUTE Asia
30 days, 6, 9 (clinical
30 days and 12
RESOLUTE Japan
3
years
visit), 12, 18 months
then annually at 2 - 5
months: clinical
8 months:
angiographic/IVUS
6, 9 and 18 months
and 2-5 years:
telephone
24-month follow-up is
complete
60-month follow-up is
complete
60-month follow-up is
complete
24
30 days: clinical
4 (30 subject subset)
and 9 months (100
subject subset):
clinical and
angiographic/IVUS
6 months and 1-5
years: telephone
RESOLUTE FIM
2
telephone
30 days, 6 months, 1-
3 years: clinical or
RESOLUTE Int
1
60-month follow-up
36-month follow-up is
complete
complete
Table 8-2: RESOLUTE and RESOLUTE INTEGRITY clinical trials overview
Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial Program
30 days and 12
months: clinical
13 months (455
subject subset):
angiographic
6 months and 2-5
years: telephone
US) and 9 months
clinical visits
(preferred) or patient
contact 30 days (R-
Main Study: 30 days
and 9 months:
months, 2-5 years:
telephone
clinical; 6, 12 and 18
4.0 mm Sub-study: 8
months: clinical and
and 18 months, 2-5
angiographic; 6, 12
years: telephone
study: 8 months:
Angio/IVUS Sub-
2.25 mm - 3.5 mm
clinical and
months, 2-5 years:
telephone
38 mm Length Sub-
angiographic/
IVUS;6, 12 and 18
study: 30 days (R-
Asia), 6, 12, 18
RESOLUTE US* RESOLUTE AC
Follow-up 2.25 mm - 3.5 mm
60-month follow-up is
complete
at 2, 3, 4, 5 years
months then annually
complete.
551 subjects qualified
for 18-month follow-
up
Status 60-month follow-up is
Page 26

Sub-study)
RESOLUTE
INTEGRITY US (XL
Study
(PEG)
RESOLUTE
RESOLUTE INTEGRITY US Post-Market
INTEGRITY US
38 mm Cohort
RESOLUTE Asia
RESOLUTE Japan
3
25
RESOLUTE FIM
2
RESOLUTE Int
1
Table 8-2: RESOLUTE and RESOLUTE INTEGRITY clinical trials overview
Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial Program
RESOLUTE US* RESOLUTE AC
The term ‘AC’ refers to All-Comers. 2 The term ‘Int’ refers to International. 3 The term ‘FIM’ refers to First-In-Man.
* The RESOLUTE US trial is composed of 4 studies. The 2.5 mm - 3.5 mm subset of the Main Study, the 2.25 mm – 3.5 mm Angio/IVUS Sub-study, the 38 mm Length Sub-study, and the 4.0mm
Sub-study have historical control designs. The 2.25 mm Subset outcomes were compared to a performance goal.
1
Page 27

)
)
)
)
9 Clinical outcomes
9.1 Clinical outcomes for RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study and RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study
Table 9-1: Resolute Onyx™ clinical outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm
Clinical Study
(N=101 subjects N=104 lesions)
%(m/n)1
Safety and effectiveness measures
RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm - 4.0 mm)
Clinical Study
(N=75 subjects N=85 lesions) %(m/n)1
In-hospital
Target lesion failure (TLF
2
Target vessel failure (TVF)3
MACE4
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI)5
Death or TVMI
Death
Cardiac death
Non-cardiac death
TVMI (extended historical definition)6
Clinically-driven TLR7
Clinically-driven TVR8
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable9
4.0% (3/75)
4.0% (3/75)
4.0% (3/75)
2.7% (2/75)
2.7% (2/75)
0.0% (0/75)
0.0% (0/75)
0.0% (0/75)
2.7% (2/75)
1.3% (1/75)
1.3% (1/75)
1.3% (1/75)
30 days
MACE
4.0% (3/75)
Follow-up (12-months)
Target lesion failure (TLF
Target vessel failure (TVF
MACE4
2
3
9.3% (7/75) 5.0% (5/101)
14.7% (11/75) 5.0% (5/101)
13.3% (10/75) 5.0% (5/101)
2.0% (2/101)
2.0% (2/101)
2.0% (2/101)
2.0% (2/101)
2.0% (2/101)
0.0% (0/101)
0.0% (0/101)
0.0% (0/101)
2.0% (2/101)
0.0% (0/101)
0.0% (0/101)
0.0% (0/101)
2.0% (2/101)
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI)5 4.0% (3/75) 3.0% (3/101)
Death or TVMI 6.7% (5/75) 3.0% (3/101)
Death 2.7% (2/75) 0.0% (0/101)
Cardiac death 0.0% (0/75) 0.0% (0/101)
Non-cardiac death 2.7% (2/75) 0.0% (0/101)
TVMI (extended historical definition) 6 4.0% (3/75) 3.0% (3/101)
Clinically-driven TLR7 5.3% (4/75) 2.0% (2/101)
Clinically-driven TVR8 10.7% (8/75) 2.0% (2/101)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable9 1.3% (1/75) 0.0% (0/101)
Early thrombosis (30 days) 1.3% (1/75) 0.0% (0/100)
Late thrombosis (31-360 days) 0.0% (0/75) 0.0% (0/101)
Latest follow-up (36-months)
Target lesion failure (TLF
2
14.7% (11/75) 13.9% (14/101)
26
Page 28

)
Table 9-1: Resolute Onyx™ clinical outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm - 4.0 mm)
Safety and effectiveness measures
(N=75 subjects N=85 lesions) %(m/n)1
Target vessel failure (TVF
MACE4
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI)5 9.3% (7/75) 5.9% (6/101)
Death or TVMI 14.7% (11/75) 6.9% (7/101)
Death 8.0% (6/75) 3.0% (3/101)
Cardiac death 2.7% (2/75) 2.0% (2/101)
Non-cardiac death 5.3% (4/75) 1.0% (1/101)
TVMI (extended historical definition) 6 8.0% (6/75) 4.0% (4/101)
Clinically-driven TLR7 8.0% (6/75) 7.9% (8/101)
Clinically-driven TVR8 13.3% (10/75) 10.9% (11/101)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable9 1.3% (1/75) 0.0% (0/101)
Early thrombosis (30 days) 1.3% (1/75) 0.0% (0/101)
Late thrombosis (31-360 days) 0.0% (0/75) 0.0% (0/101)
Very late thrombosis (>360 days) 0.0% (0/75) 0.0% (0/101)
3
Clinical Study
18.7% (14/75) 14.9% (15/101)
21.3% (16/75) 14.9% (15/101)
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm
Clinical Study
(N=101 subjects N=104 lesions)
%(m/n)1
27
Page 29

e
Table 9-1: Resolute Onyx™ clinical outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm
Clinical Study
(N=101 subjects N=104 lesions)
%(m/n)1
Safety and effectiveness measures
Notes
1
N = The total number of subjects enrolled.
RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm - 4.0 mm)
Clinical Study
(N=75 subjects N=85 lesions) %(m/n)1
The numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
NA = Not applicable; variable and/or time point not calculated
In-hospital is defined as hospitalization less than or equal to the discharge date
12-month timeframe includes follow-up window (360 days ± 30 days).
36-month timeframe includes follow-up window (1080 days ± 30 days).
2
Target lesion failure (TLF) is defined as any cardiac death, clinically-driven target lesion revascularization by PCI or CABG or target vess
MI.
3
Target vessel failure (TVF) is defined as any cardiac death, clinically-driven target vessel revascularization by PCI or CABG or target
vessel MI.
4
Major adverse cardiac events (MACE) is defined as composite of death, MI (Q wave and non-Q wave), emergent bypass surgery, or
clinically-driven target lesion revascularization (repeat PTCA or CABG).
5
Cardiac death/TVMI is defined as cardiac death or myocardial infarction not clearly attributable to a non-target vessel.
6
TVMI is composed of both Q wave and non-Q wave MI which are not clearly attributable to a non-target vessel.
Q wave MI defined when any occurrence of chest pain or other acute symptoms consistent with myocardial ischemia and new
pathological Q waves in two or more contiguous ECG leads as determined by an ECG core laboratory or independent review of the
CEC, in the absence of timely cardiac enzyme data, or new pathologic Q waves in two or more contiguous ECG leads as determined by
an ECG core laboratory or independent review of the CEC and elevation of cardiac enzymes. In the absence of ECG data the CEC may
adjudicate Q wave MI based on the clinical scenario and appropriate cardiac enzyme data.
Non-Q Wave MI is defined as elevated CK 2X the upper laboratory normal with the presence of elevated CK-MB (any amount above
the institution’s upper limit of normal) in the absence of new pathological Q waves.
[Note: Periprocedural MIs (events <48 hours post-PCI) that did not fulfill the criteria for Q-wave MI are included in Non-Q Wave MI
category. Periprocedural MIs did not require clinical symptoms or ECG evidence of myocardial ischemia, and in the absence of CK
measurements, were based on an elevated CKMB > 3 X the upper laboratory normal, an elevated troponin > 3 X the upper laboratory
normal, or CEC adjudication of the clinical scenario.]
7
Target lesion revascularization (TLR) is defined as a clinically-driven repeat intervention of the target lesion by PCI or CABG
8
Target vessel revascularization (TVR) is defined as any clinically-driven repeat intervention of the target vessel by PCI or CABG.
9
Academic Research Consortium (ARC) stent thrombosis is defined as follows.
1. Definite ST is considered to have occurred after intracoronary stenting by either angiographic or pathologic confirmation of stent
thrombosis.
2. Probable ST is considered to have occurred after intracoronary stenting in the following cases: Any unexplained death within the
first 30 days following stent implantation. Irrespective of the time after the index procedure, any MI which is related to
documented acute ischemia in the territory of the implanted stent without angiographic confirmation of ST and in the absence of
any other obvious cause
See Section 10 - Clinical studies for a more complete description of the trial designs and results
.
The Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial Program has evaluated the performance of the Resolute stent in
subjects, including those with diabetes mellitus, with symptomatic ischemic heart disease in de novo
lesions of native coronary arteries. The RESOLUTE INTEGRITY US Post-Market Approval Study
assessed the safety and efficacy of the Resolute Integrity™ stent for the treatment of de novo lesions
in native coronary arteries. Clinical outcomes are shown in Table 9-2 below.
28
Page 30

Table 9-2: Clinical outcomes from post-procedure through latest available follow-up
38 mm Length
RESOLUTE
1
US
Resolute
(N = 1402)
RESOLUTE AC RESOLUTE Int
Resolute
(N = 1140)
Xience
V®
(N = 1152)
Resolute
(N = 2349)
In-hospital
TLF 1.3% (18/1402)
TVF
1.3% (18/1402)
MACE 1.3% (18/1402)
Total Death 0.0% (0/1402)
Cardiac
death
Non-cardiac
death
5
TVMI
0.0% (0/1402)
0.0% (0/1402)
1.1% (16/1402)
Q wave MI 0.1% (1/1402)
Non-Q wave
MI
Cardiac death
or TVMI
Clinically-driven
TVR
1.1% (15/1402)
1.1% (16/1402)
0.1% (2/1402)
TLR 0.1% (2/1402)
Non-TL TVR 0.0% (0/1402)
ARC Def/Prob
ST
0.0% (0/1402)
3.7%
(42/1140)
3.8%
(43/1140)
3.8%
(43/1140)
0.1%
(1/1140)
0.1%
(1/1140)
0.0%
(0/1140)
3.1%
(35/1140)
0.3%
(3/1140)
2.8%
(32/1140)
3.2%
(36/1140)
0.9%
(10/1140)
0.7%
(8/1140)
0.4%
(4/1140)
0.6%
(7/1140)
(52/1152)
(54/1152)
(56/1152)
(9/1152)
(7/1152)
(2/1152)
(42/1152)
(5/1152)
(37/1152)
(46/1152)
(10/1152)
(8/1152)
(2/1152)
(4/1152)
4.5%
4.7%
4.9%
0.8%
0.6%
0.2%
3.6%
0.4%
3.2%
4.0%
0.9%
0.7%
0.2%
0.3%
2.6% (61/2349) 4.3% (6/139) 2.0% (2/100) 3.6% (8/223) 1.7% (4/230) 1.8% (1/56)
2.6% (61/2349) 4.3% (6/139) 2.0% (2/100) 3.6% (8/223) 1.7% (4/230) 1.8% (1/56)
2.7% (63/2349) 4.3% (6/139) 2.0% (2/100) 3.6% (8/223) 1.7% (4/230) 1.8% (1/56)
0.3% (7/2349) 0.0% (0/139) 0.0% (0/100) 0.4% (1/223) 0.0% (0/230) 0.0% (0/56)
0.3% (6/2349) 0.0% (0/139) 0.0% (0/100) 0.4% (1/223) 0.0% (0/230) 0.0% (0/56)
0.0% (1/2349) 0.0% (0/139) 0.0% (0/100) 0.0% (0/223) 0.0% (0/230) 0.0% (0/56)
2.2% (51/2349) 4.3% (6/139) 2.0% (2/100) 3.1% (7/223) 1.7% (4/230) 1.8% (1/56)
0.3% (8/2349) 0.0% (0/139) 0.0% (0/100) 0.4% (1/223) 0.0% (0/230) 0.0% (0/56)
1.8% (43/2349) 4.3% (6/139) 2.0% (2/100) 2.7% (6/223) 1.7% (4/230) 1.8% (1/56)
2.4% (56/2349) 4.3% (6/139) 2.0% (2/100) 3.6% ((8/223) 1.7% (4/230) 1.8% (1/56)
0.4% 10/2349) 0.0% (0/139) 0.0% (0/100) 0.0% (0/223) 0.4% (1/230) 0.0% (0/56)
0.4% (10/2349) 0.0% (0/139) 0.0% (0/100) 0.0% (0/223) 0.4% (1/230) 0.0% (0/56)
0.0% (1/2349) 0.0% (0/139) 0.0% (0/100) 0.0% (0/223) 0.0% (0/230) 0.0% (0/56)
0.4% (9/2349) 0.0% (0/139) 0.0% (0/100) 0.4% (1/223) 0.0% (0/230) 1.8% (1/56)
30 days
MACE
1.4%
(20/1399)
4.4%
(50/1133)
5.2%
(60/1146)
3.3%
(78/2345)
12 months
TLF 4.7% (65/1390)
TVF 6.2% (86/1390)
MACE 5.5% (77/1390)
Total death 1.4% (19/1390)
Cardiac
death
Non-cardiac
death
0.7% (10/1390)
0.6% (9/1390)
8.1%
(92/1132)
8.9%
(101/1132)
8.6%
(97/1132)
1.6%
(18/1132)
1.3%
(15/1132)
0.3%
(3/1132)
8.5%
(97/1142)
9.7%
(111/1142)
9.8%
(112/1142)
2.7%
(31/1142)
1.7%
(19/1142)
1.1%
(12/1142)
7.1%
(165/2337)
7.7%
(180/2337)
8.3%
(193/2337)
2.4% (57/2337) 2.2% (3/139) 1.0% (1/100) 0.9% (2/222) 1.8% (4/226) 1.8% (1/56)
1.5% (34/2337) 0.7% (1/139) 0.0% (0/100) 0.9% (2/222) 1.3% (3/226) 1.8% (1/56)
1.0% (23/2337) 1.4% (2/139) 1.0% (1/100) 0.0% (0/222) 0.4% (1/226) 0.0% (0/56)
RESOLUTE
FIM
RESOLUTE
Japan
Sub-study
R-US N = 114
RESOLUTE INTEGRITY US
R-Asia N = 109
RESOLUTE
Resolute
(N = 139)
Resolute
(N = 100)
Resolute
(N = 223)
Resolute
Integrity (PEG)
(N=230)
INTEGRITY
US (XL
Sub-study)
(N=56)
4.3% (6/139) 3.0% (3/100)
4.5%
(10/223)
3.0% (7/230) 3.6% (2/56)
7.2% (10/139) 4.0% (4/100) 5.4% (12/222) 4.9% (11/226) 7.1% (4/56)
7.2% (10/139) 5.0% (5/100) 6.8% (15/222) 7.1% (16/226) 7.1% (4/56)
8.6% (12/139) 5.0% (5/100) 6.3% (14/222) 5.8% (13/226) 8.9% (5/56)
29
Page 31

Table 9-2: Clinical outcomes from post-procedure through latest available follow-up
TVMI 1.3% (18/1390)
Q wave MI
Non-Q wave
MI
Cardiac death
or TVMI
Clinically-driven
TVR
TLR 2.9% (40/1390)
Non-TL TVR 2.2% (30/1390)
ARC Def/Prob
ST
Latest followup
TLF
TVF
MACE
Total death
Cardiac
death
Non-cardiac
death
TVMI
Q wave MI
Non-Q wave
MI
Cardiac death
or TVMI
Clinically-driven
TVR
TLR 6.5% (86/1329)
RESOLUTE
1
US
Resolute
(N = 1402)
RESOLUTE AC RESOLUTE Int
Resolute
(N = 1140)
4.2%
(48/1132)
0.1% (2/1390)
1.2% (16/1390)
2.0% (28/1390)
4.6% (64/1390)
0.8%
(9/1132)
3.5%
(40/1132)
5.3%
(60/1132)
4.9%
(55/1132)
3.9%
(44/1132)
1.9%
(21/1132)
0.1% (2/1390)
1.6%
(18/1132)
60 months 60 months 36 months 60 months 60 months 60 months 24 months 36 months
12.3%
(164/1329)
17.5%
(233/1329)
18.0%
(239/1329)
9.6%
(127/1329)
4.1% (55/1329)
5.4% (72/1329)
3.2% (43/1329)
0.4% (5/1329)
2.9% (38/1329)
6.7% (89/1329)
12.5%
(166/1329)
17.0%
(191/1123)
20.0%
(225/1123)
21.9%
(246/1123)
11.0%
(123/1123)
6.5%
(73/1123)
4.5%
(50/1123)
5.7%
(64/1123)
1.3%
(15/1123)
4.6%
(52/1123)
11.5%
(129/1123)
11.4%
(128/1123)
7.8%
(88/1123)
Xience
V®
(N = 1152)
4.2%
(48/1142)
0.4%
(5/1142)
3.8%
(43/1142)
5.5%
(63/1142)
4.8%
(55/1142)
3.4%
(39/1142)
2.2%
(25/1142)
0.7%
(8/1142)
16.2%
(183/1133)
19.1%
(216/1133)
21.6%
(245/1133)
10.8%
(122/1133)
5.7%
(65/1133)
5.0%
(57/1133)
5.7%
(65/1133)
0.8%
(9/1133)
4.9%
(56/1133)
10.6%
(120/1133)
10.9%
(123/1133)
7.1%
(81/1133)
38 mm Length
RESOLUTE
FIM
RESOLUTE
Japan
Sub-study
R-US N = 114
RESOLUTE INTEGRITY US
R-Asia N = 109
RESOLUTE
Resolute
(N = 2349)
Resolute
(N = 139)
Resolute
(N = 100)
Resolute
(N = 223)
Resolute
Integrity (PEG)
(N=230)
INTEGRITY
US (XL
Sub-study)
(N=56)
3.0% (71/2337) 5.8% (8/139) 4.0% (4/100) 3.6% (8/222) 2.2% (5/226) 5.4% (3/56)
0.5% (12/2337) 0.0% (0/139) 0.0% (0/100) 0.9% (2/222) 0.0% (0/226) 1.8% (1/56)
2.5% (59/2337) 5.8% (8/139) 4.0% (4/100) 2.7% (6/222) 2.2% (5/226) 3.6% (2/56)
4.2% (99/2337) 6.5% (9/139) 4.0% (4/100) 4.5% (10/222) 3.5% (8/226) 7.1% (4/56)
4.2% (99/2337) 0.7% (1/139) 1.0% (1/100) 2.7% (6/222) 4.4% (10/226) 1.8% (1/56)
3.5% (81/2337) 0.7% (1/139) 0.0% (0/100) 1.4% (3/222) 2.2% (5/226) 1.8% (1/56)
1.2% (27/2337) 0.0% (0/139) 1.0% (1/100) 1.4% (3/222) 2.2% (5/226) 0.0% (0/56)
0.9% (20/2337) 0.0% (0/139) 0.0% (0/100)
11.4%
(261/2284)
12.9%
(294/2284)
14.4%
(329/2284)
6.1%
(139/2284)
11.0% (15/136) 6.1% (6/98)
13.2% (18/136) 10.2% (10/98)
16.2% (22/136) 14.3% (14/98)
6.6% (9/136) 7.1% (7/98)
3.6% (82/2284) 1.5% (2/136) 1.0% (1/98)
2.5% (57/2284) 5.1% (7/136) 6.1% (6/98)
0.9% (2/222)
13.8%
(30/217)
17.1%
(37/217)
17.5%
(38/217)
6.5% (14/217)
4.1% (9/217))
2.3% (5/217)
0.9% (2/226) 1.8% (1/56)
9.1% (20/219)
12.3% (27/219)
11.0% (24/219)
10.7%
(6/56)
12.5%
(7/56)
17.9%
(10/56)
2.7% (6/219) 3.6% (2/56)
1.8% (4/219) 1.8% (1/56)
0.9% (2/219) 1.8% (1/56)
3.9% (89/2284) 6.6% (9/136) 4.1% (4/98) 6.0% (13/217) 4.1% (9/219) 5.4% (3/56)
0.9% (20/2284) 0.0% (0/136) 0.0% (0/98) 0.9% (2/217) 0.9% (2/219) 1.8% (1/56)
3.0% (69/2284) 6.6% (9/136) 4.1% (4/98) 5.1% (11/217) 3.2% (7/219) 3.6% (2/56)
(161/2284)
(168/2284)
(130/2284)
7.0%
7.4%
5.7%
8.1% (11/136) 5.1% (5/98) 8.8% (19/217) 5.9% (13/219) 7.1% (4/56)
5.1% (7/136) 5.1% (5/98) 9.7% (21/217) 8.2% (18/219) 7.1% (4/56)
2.9% (4/136) 1.0% (1/98) 6.0% (13/217) 5.0% (11/219) 5.4% (3/56)
30
Page 32

Table 9-2: Clinical outcomes from post-procedure through latest available follow-up
38 mm Length
Non-TL TVR
ARC Def/Prob
ST
Notes
N = The total number of subjects enrolled.
The numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
The definitions of the outcomes are presented as table notes to Table 9-1.
In-hospital is defined as hospitalization less than or equal to the discharge date.
12-month timeframe includes follow-up window (360 days ± 30 days).
24-month timeframe includes follow-up window (720 days ±30 days).
36-month timeframe includes follow-up window (1080 days ± 30 days).
60-month timeframe includes follow-up window (1800 days ± 30 days).
1
Primary Enrollment Group consisted of 1402 subjects, including 1242 subjects in the 2.25 mm - 3.5 mm Main Study, 100 subjects in the 2.25 mm - 3.5 mm
Angio/IVUS Sub-study and 60 subjects in the 4.0 mm Sub-study. The Primary Enrollment Group does not include the 38 mm Length Sub-study.
RESOLUTE
1
US
Resolute
(N = 1402)
8.1%
(107/1329)
0.5% (7/1329)
RESOLUTE AC RESOLUTE Int
Resolute
(N = 1140)
6.1%
(68/1123)
2.4%
(27/1123)
Xience
V®
(N = 1152)
6.1%
(69/1133)
1.7%
(19/1133)
Resolute
(N = 2349)
2.6% (59/2284) 2.2% (3/136) 4.1% (4/98) 3.7% (8/217) 4.1% (9/219) 5.4% (3/56)
1.1% (26/2284) 0.0% (0/136) 0.0% (0/98) 1.4% (3/217) 1.8% (4/219) 1.8% (1/56)
RESOLUTE
FIM
Resolute
(N = 139)
RESOLUTE
Japan
Resolute
(N = 100)
Sub-study
R-US N = 114
R-Asia N = 109
Resolute
(N = 223)
RESOLUTE INTEGRITY US
RESOLUTE
Resolute
Integrity (PEG)
(N=230)
INTEGRITY
Sub-study)
TM
In the RESOLUTE All-Comers (R-AC) trial, a randomized trial comparing the Resolute
TM*
with the Xience V
EES for treatment of patients with coronary lesions who had minimal
ZES
exclusion criteria, there were similar safety and efficacy outcomes between the 2 stents.
Through 5 years of follow-up, the clinical effectiveness of the Resolute ZES was sustained in
the complex and non-complex cohorts as shown in Table 9-3, Table 9-4, and Table 9-5
below.
Table 9-3: R-AC Clinical outcomes (complex cohort)
Complex cohort
Composite safety and
effectiveness
Resolute
(N = 764)
12 months 60 months
Xience V®
(N = 756)
Resolute
(N = 764)
Xience V®
(N = 756)
US (XL
(N=56)
TLF 8.8% (67/760) 10.0% (75/750) 18.2% (137/751) 18.4% (137/745)
TVF 9.7% (74/760) 11.3% (85/750) 22.1% (166/751) 21.3% (159/745)
MACE 9.1% (69/760) 11.7% (88/750) 22.5% (169/751) 24.6% (183/745)
Effectiveness
Clinically-driven TVR 5.5% (42/760) 5.6% (42/750) 13.4% (101/751) 11.7% (87/745)
TLR 4.3% (33/760) 4.1% (31/750) 8.9% (67/751) 8.1% (60/745)
TLR, PCI 3.9% (30/760) 3.2% (24/750) 8.1% (61/751) 6.7% (50/745)
TLR, CABG 0.4% (3/760) 1.1% (8/750) 1.2% (9/751) 1.7% (13/745)
Safety
Total death 1.4% (11/760) 3.3% (25/750) 10.4% (78/751) 13.2% (98/745)
31
Page 33

Table 9-3: R-AC Clinical outcomes (complex cohort)
Complex cohort
Composite safety and
effectiveness
Cardiac death 1.3% (10/760) 2.1% (16/750) 6.4% (48/751) 7.4% (55/745)
Non-cardiac death 0.1% (1/760) 1.2% (9/750) 4.0% (30/751) 5.8% (43/745)
Cardiac death or TVMI 5.4% (41/760) 6.4% (48/750) 11.9% (89/751) 12.2% (91/745)
TVMI
Q wave MI 0.7% (5/760) 0.5% (4/750) 1.3% (10/751) 0.9% (7/745)
Non-Q wave MI 3.7% (28/760) 4.1% (31/750) 4.8% (36/751) 5.1% (38/745)
Stent thrombosis
ARC defined
Definite/probable 1.7% (13/759) 0.9% (7/749) 2.5% (19/751) 2.0% (15/745)
Definite 1.2% (9/759) 0.4% (3/749) 1.7% (13/751) 0.9% (7/745)
Probable 0.7% (5/759) 0.5% (4/749) 0.9% (7/751) 1.1% (8/745)
Notes
N = The total number of subjects enrolled.
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
Numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
The definitions of the outcomes are presented as table notes to Table 9-1.
12-month timeframe includes follow-up window (360 ± 30 days).
60-month timeframe includes follow-up window (1800 days ± 30 days).
Complex was defined as having one or more of the following patient or lesion characteristics: bifurcation, bypass graft, in stent
restenosis, AMI < 72 hr., LVEF < 30%, unprotected left main, >2 vessels stented, renal insufficiency or failure (serum creatinine >2.5
mg/dl), lesion length > 27 mm, > 1 lesion per vessel, lesion with thrombus or total occlusion (pre procedure TIMI = 0).
Resolute
(N = 764)
4.2% (32/760) 4.7% (35/750) 5.9% (44/751) 6.0% (45/745)
12 months 60 months
Xience V®
(N = 756)
Resolute
(N = 764)
Xience V®
(N = 756)
32
Page 34

Table 9-4: R-AC clinical outcomes (non-complex cohort)
Non-complex cohort
Composite safety and
effectiveness
TLF 6.7% (25/372) 5.6% (22/392) 14.5% (54/372) 11.9% (46/388)
TVF 7.3% (27/372) 6.6% (26/392) 15.9% (59/372) 14.7% (57/388)
MACE 7.5% (28/372) 6.1% (24/392) 20.7% (77/372) 16.0% (62/388)
Effectiveness
Clinically-driven TVR 3.5% (13/372) 3.3% (13/392) 7.3% (27/372) 9.3% (36/388)
TLR 3.0% (11/372) 2.0% (8/392) 5.6% (21/372) 5.4% (21/388)
TLR, PCI 2.2% (8/372) 1.8% (7/392) 4.3% (16/372) 4.6% (18/388)
TLR, CABG 0.8% (3/372) 0.3% (1/392) 1.9% (7/372) 0.8% (3/388)
Safety
Total death 1.9% (7/372) 1.5% (6/392) 12.1% (45/372) 6.2% (24/388)
Cardiac death 1.3% (5/372) 0.8% (3/392) 6.7% (25/372) 2.6% (10/388)
Non-cardiac death 0.5% (2/372) 0.8% (3/392) 5.4% (20/372) 3.6% (14/388)
Cardiac death or TVMI 5.1% (19/372) 3.8% (15/392) 10.8% (40/372) 7.5% (29/388)
TVMI
Q wave MI 1.1% (4/372) 0.3% (1/392) 1.3% (5/372) 0.5% (2/388)
Non-Q wave MI 3.2% (12/372) 3.1% (12/392) 4.3% (16/372) 4.6% (18/388)
Stent thrombosis
ARC defined
Definite/probable 1.3% (5/372) 0.3%(1/392) 2.2% (8/372) 1.0% (4/388)
Definite 1.1% (4/372) 0.0%(0/392) 1.3% (5/372) 0.5% (2/388)
Probable 0.3% (1/372) 0.3%(1/392) 0.8% (3/372) 0.5% (2/388)
Notes
N = The total number of subjects enrolled.
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
Numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
The definitions of the outcomes are presented as table notes to Table 9-1.
12-month timeframe includes follow-up window (360± 30 days).
60-month timeframe includes follow-up window (1800 days ± 30 days).
Complex was defined as having one or more of the following patient or lesion characteristics: bifurcation, bypass graft, in stent
restenosis, AMI < 72 hr., LVEF < 30%, unprotected left main, >2 vessels stented, renal insufficiency or failure (serum creatinine > 2.5
mg/dl), lesion length > 27 mm, > 1 lesion per vessel, lesion with thrombus or total occlusion (pre procedure TIMI = 0).
Resolute
(N = 376)
4.3% (16/372) 3.3% (13/392) 5.4% (20/372) 5.2% (20/388)
12 months
Xience V®
(N = 396)
Resolute
(N = 376)
60 months
Xience V®
(N = 396)
33
Page 35

Table 9-5: R-AC ARC defined definite/probable stent thrombosis through 60 months
(all subjects, and complex and non-complex subjects)
All Subjects Non-complex Complex
Cumulative stent thrombosis
through 1-Year
Cumulative stent thrombosis
through 5 -Years
Acute (0 - 1 day) 0.4% (5/1123) 0.2% (2/1133) 0.3% (1/372) 0.0% (0/388) 0.5% (4/751) 0.3% (2/745)
Subacute (2 - 30 days) 0.7% (8/1123) 0.4% (4/1133) 0.3% (1/372) 0.3% (1/388) 0.9% (7/751) 0.4% (3/745)
Late (31 – 360 days) 0.6% (7/1123) 0.2% (2/1133) 0.8% (3/372) 0.0% (0/388) 0.5% (4/751) 0.3% (2/745)
Very Late (361 – 1800 days) 0.8% (9/1123) 1.0% (11/1133) 0.8% (3/372) 0.8% (3/388) 0.8% (6/751) 1.1% (8/745)
Notes
N = The total number of subjects enrolled.
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
Numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
12-month timeframe includes follow-up window (360 ± 30 days)
60-month timeframe includes follow-up window (1800 days ± 30 days).
Complex was defined as having one or more of the following patient or lesion characteristics: bifurcation, bypass graft, in stent
restenosis, AMI < 72 hr., LVEF <30%, unprotected left main, >2 vessels stented, renal insufficiency or failure (serum creatinine > 2.5
mg/dl), lesion length > 27 mm, > 1 lesion per vessel, lesion with thrombus or total occlusion (pre procedure TIMI = 0).
Resolute
(N = 1140)
1.6% (18/1132) 0.7% (8/1142) 1.3% (5/372) 0.3% (1/392) 1.7% (13/760) 0.9% (7/750)
2.4% (27/1123) 1.7% (19/1133) 2.2% (8/372) 1.0% (4/388) 2.5% (19/751) 2.0% (15/745)
Xience V®
(N = 1152)
Resolute
(N = 376)
Xience V®
(N = 396)
Resolute
(N = 764)
Xience V®
(N = 756)
9.2 Potential adverse events
9.2.1 Potential adverse events related to zotarolimus
Patients’ exposure to zotarolimus is directly related to the total amount of stent length
implanted. The actual side effects/complications that may be associated with the use of
zotarolimus are not fully known.
The adverse events that have been associated with the intravenous injection of zotarolimus
in humans include but are not limited to:
• Anemia
• Diarrhea
• Dry skin
• Headache
• Hematuria
• Infection
• Injection site reaction
• Pain (abdominal, arthralgia, injection site)
• Rash
9.2.2 Potential adverse events related to BioLinx
Although the type of risks of the BioLinx
than those of other stent coatings, the potential for these risks are currently unknown as the
coating has limited previous use in humans. These risks may include but are not limited to
the following:
• Allergic reaction
• Focal inflammation at the site of stent implantation
• Restenosis of the stented artery
TM*
polymer
TM*
polymer coating are expected to be no different
34
Page 36

9.2.3 Potential risks associated with percutaneous coronary diagnostic and treatment procedures
Other risks associated with using this device are those associated with percutaneous
coronary diagnostic (including angiography and IVUS) and treatment procedures. These
risks (in alphabetical order) may include but are not limited to the following:
• Abrupt vessel closure
• Access site pain, hematoma, or hemorrhage
• Allergic reaction (to contrast, antiplatelet therapy, stent material, or drug and polymer
coating)
• Aneurysm, pseudoaneurysm, or arteriovenous fistula (AVF)
• Arrhythmias, including ventricular fibrillation
• Balloon rupture
• Bleeding
• Cardiac tamponade
• Coronary artery occlusion, perforation, rupture, or dissection
• Coronary artery spasm
• Death
• Embolism (air, tissue, device, or thrombus)
• Emergency surgery: peripheral vascular or coronary bypass
• Failure to deliver the stent
• Hemorrhage requiring transfusion
• Hypotension or hypertension
• Incomplete stent apposition
• Infection or fever
• Myocardial infarction (MI)
• Pericarditis
• Peripheral ischemia or peripheral nerve injury
• Renal failure
• Restenosis of the stented artery
• Shock or pulmonary edema
• Stable or unstable angina
• Stent deformation, collapse, or fracture
• Stent migration or embolization
• Stent misplacement
• Stroke or transient ischemic attack
• Thrombosis (acute, subacute, or late)
10 Clinical studies
10.1 Results of the RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study
Primary objective: The purpose of this study was to assess the safety and efficacy of the Resolute
Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system for the treatment of de novo lesions in native
coronary arteries with a reference vessel diameter of 2.25 mm to 4.2 mm.
Design: The Medtronic RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study is a single arm,
open label, multi-center trial that enrolled 75 subjects with ischemic heart disease attributable to
stenotic lesions of the native coronary arteries that are amenable to percutaneous treatment with
stenting. Subjects may have received treatment of one or two lesions with stent diameters 2.25 mm -
4.0 mm, one lesion per target vessel, for a maximum of two target vessels. Only one lesion may have
been treated in a single target vessel. All treatments with the study stents were to be performed
during a single index procedure. All enrolled subjects had an 8 month angiogram to assess late
lumen loss. The first 20 subjects were to also undergo an IVUS assessment at baseline and 8
months.
Primary endpoint: In-stent late lumen loss (LL) at 8-months post-procedure as measured by
quantitative coronary angiography (QCA).
35
Page 37

Follow-up was performed at 30 days, 6, and 8 months, and annually out to 3 years. Following the
index procedure, subjects were to be treated with aspirin indefinitely and clopidogrel/ticlopidine for a
minimum of 6 months and up to 12 months in those who were not at a high risk of bleeding.
Demographics: The mean age was 66 years with 73.3% (55/75) of subjects being males. Of the
subjects enrolled, 32.0% (24/75) had diabetes mellitus, 16.0% (12/75) were current smokers, 23.0%
(17/74) had prior MI, 40.0% (30/75) had prior PCI, 73.3% (55/75) had hypertension, and 85.3%
(64/75) reported hyperlipidemia. Baseline lesion characteristics include 49.3% (37/75) of subjects with
LAD lesions, a mean lesion length of 14.28 ± 6.68 mm, and 85.9% (73/85) ACC/AHA type B2/C
lesions. The mean RVD was 2.57 ± 0.48 mm and the percentage diameter stenosis was 62.98 ±
10.75%.
Results: The primary end point of in-stent late lumen loss (LL) at 8-months post-procedure as
measured by quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) demonstrated not only non-inferiority (p <
0.001), but also superiority (p = 0.027), when compared to the historical control in-stent late loss
value from the RESOLUTE US Angio/IVUS Sub-study.
The RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm to 4.0 mm) Clinical Study outcomes at 8-months are
consistent with the 9 month clinical outcomes of the RESOLUTE US 2.25-3.5 mm Angio/IVUS Substudy that evaluated a similar patient population (with mandated angiographic follow up at 8 months).
These analyses are based on the intent-to-treat population. The results are presented in the following
tables:
• Table 10-1: RESOLUTE ONYX™ - primary endpoint analysis
• Table 10-2: RESOLUTE ONYX™ - clinical and Angio / IVUS outcomes
• Table 10-3: RESOLUTE ONYX™ - ARC defined definite/probable stent thrombosis through 8
months
Table 10-1: RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study – primary endpoint
analysis (non-inferiority test with propensity score adjustment)
Historical
control
Resolute
(N=100
subjects
N=104
lesions)
Difference:
RESOLUTE
ONYX Core
- historical
control1
Upper
one-
sided
95% CI2
Non-
inferiority
margin
Non-
inferiority
P value
Superiority
P value3
Primary endpoint – In-
stent late lumen loss
at 8 months
RESOLUTE
ONYX Core
(N=75
subjects
N=85
lesions)
Primary analysis with available data:
– ITT set
– PP set
0.24 ± 0.05
(73)
0.24 ± 0.05
(66)
0.36 ± 0.05
(93)
0.35 ± 0.05
(89)
-0.14 -0.02 0.20 < 0.001 0.027
-0.15 -0.02 0.20 < 0.001 0.027
Secondary analysis with multiple imputation:
– ITT set 0.23 ± 0.05 0.36 ± 0.05 -0.15 -0.03 0.20 < 0.001
– PP set 0.22 ± 0.05 0.35 ± 0.05 -0.16 -0.03 0.20 < 0.001
1
The Resolute Onyx Core measure non-inferiority of 8-month in-stent late lumen loss compared to 8-month in-stent late lumen loss of
the historical control
All target lesions are included in the analysis. The treatment differences have been adjusted with propensity score quintile.
2
The CI is adjusted to propensity score, based on lesion-length, baseline RVD, age, sex, diabetes, history of MI, and worst Canadian
Cardiovascular Society Angina Class as the independent variables.
3
Superiority test was performed after non-inferiority was demonstrated.
0.023
0.023
36
Page 38

Table 10-2: RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study – clinical and Angio /
IVUS outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX
Safety measures (to 180 days)
Target lesion failure (TLF)
Target vessel failure (TVF)
MACE
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI)
Death or TVMI
Death
Cardiac death
Noncardiac death
TVMI (extended historical definition)
Clinically-driven TLR
Clinically-driven TVR
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable
Safety measures (to 240 days)
Target lesion failure (TLF)
Target vessel failure (TVF)
MACE
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI) 2.7% (2/75)
Death or TVMI 4.0% (3/75)
Death 1.3% (1/75)
Cardiac death 0.0% (0/75)
Non-cardiac death 1.3% (1/75)
TVMI (extended historical definition) 2.7% (2/75)
Clinically-driven TLR 4.0% (3/75)
Clinically-driven TVR 9.3% (7/75)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable 1.3% (1/75)
Early thrombosis (30 days) 1.3% (1/75)
Late thrombosis (31-240 days) 0.0% (0/75)
Safety measures (to 1080 days)
Target lesion failure (TLF)
Target vessel failure (TVF)
MACE
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI)
Death or TVMI
Death
(N=75 subjects N=85 lesions)
%(m/n)1
5.3% (4/75)
8.0% (6/75)
8.0% (6/75)
2.7% (2/75)
4.0% (3/75)
1.3% (1/75)
0.0% (0/75)
1.3% (1/75)
2.7% (2/75)
2.7% (2/75)
5.3% (4/75)
1.3% (1/75)
6.7% (5/75)
12.0% (9/75)
9.3% (7/75)
14.7% (11/75)
18.7% (14/75)
21.3% (16/75)
9.3% (7/75)
14.7% (11/75)
8.0% (6/75)
37
Page 39

Table 10-2: RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study – clinical and Angio /
IVUS outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX
Cardiac death
Non-cardiac death 5.3% (4/75)
TVMI (extended historical definition) 8.0% (6/75)
Clinically-driven TLR 8.0% (6/75)
Clinically-driven TVR 13.3% (10/75)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable 1.3% (1/75)
Early thrombosis (30 days) 1.3% (1/75)
Late thrombosis (31-240 days) 0.0% (0/75)
Very Late thrombosis (>360 days) 0.0% (0/75)
Angiography (8 months)
(N=75 subjects N=85 lesions)
%(m/n)1
2.7% (2/75)
Percent diameter stenosis (% DS)
In-stent
n 73
Mean±SD
Median (1Q, 3Q)
Min, max
In-segment
n
Mean±SD
Median (1Q, 3Q)
Min, max
Minimal lumen diameter (mm)
In-stent
n
Mean±SD
Median (1Q, 3Q)
Min, max
In-segment
n
Mean±SD
Median (1Q, 3Q)
Min, max
Late luminal loss (mm)
In-stent
15.56 ± 16.75
14.86 (5.26, 22.24)
-21.18, 82.89
73
25.84 ± 14.20
22.35 (17.71, 29.75)
4.99, 82.89
73
2.13 ± 0.55
2.14(1.80, 2.45)
0.45, 3.69
73
1.88 ± 0.49
1.89 (1.58, 2.19)
0.45, 3.10
38
Page 40

Table 10-2: RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study – clinical and Angio /
IVUS outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX
(N=75 subjects N=85 lesions)
%(m/n)1
n
Mean±SD
Median (1Q, 3Q)
Min, max
In-segment
n
Mean±SD
Median (1Q, 3Q)
Min, max
In-stent binary angiographic restenosis (BAR) rate
In-segment binary angiographic restenosis (BAR) rate
IVUS (8 months)
Incomplete stent apposition
Persistent 10.0% (2/20)
Late 0.0% (0/20)
Neointimal hyperplastic volume (mm3 )
n 17
Mean±SD (N) 9.88 ± 9.38
Median (Q1,Q3) 6.80 (2.20, 18.10)
Min, max 0.00, 27.20
Percent volume obstruction
n 17
Mean±SD (N) 6.88 ± 8.00
Median (Q1,Q3) 4.52 ( 1.48, 8.79)
Min, max 0.00, 31.38
Effectiveness measures
Lesion success2
Device success3
Procedure success4
73
0.24 ± 0.39
0.18 (0.03, 0.37)
-0.49, 2.06
73
0.16 ± 0.37
0.13 (-0.03, 0.29)
-0.65, 1.88
5.5% (4/73)
8.2% (6/73)
100.0% (85/85)
100.0% (85/85)
96.0% (72/75)
39
Page 41

Table 10-2: RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study – clinical and Angio /
IVUS outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX
1
Numerator (m) is the number of subjects with the specific classification, denominator (n) is the number of subjects in the study group
with known values, and percentage (%) was calculated as 100 × (m/n).
The definitions of the outcomes are presented as table notes to Table 9-1.
2
The attainment of <30% residual stenosis by QCA (or <20% by visual assessment) AND TIMI Flow 3 after the procedure, using any
percutaneous method.
3
The attainment of <30% residual stenosis by QCA (or <20% by visual assessment) AND TIMI Flow 3 after the procedure, using the
assigned device only.
4
The attainment of <30% residual stenosis by QCA (or <20% by visual assessment) AND TIMI Flow 3 after the procedure, using any
percutaneous method without the occurrence of MACE during the hospital stay.
8-month timeframe includes follow-up window (240 days ± 14 days).
Extended historical definition of MI is used for all the composite endpoints.
(N=75 subjects N=85 lesions)
%(m/n)1
Table 10-3: RESOLUTE ONYX Core (2.25 mm – 4.0 mm) Clinical Study – ARC defined
definite/probable stent thrombosis through 36 months
Stent thrombosis
Early thrombosis (30 days)
Late thrombosis (31-360 days)
Very late thrombosis (>360 days)
Notes
1
N = The total number of subjects enrolled.
Numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
36-month timeframe includes follow-up window (1080 days ± 30 days).
See Table 9-1 for the definition of the ARC defined stent thrombosis.
RESOLUTE ONYX™
(N=75 subjects N=85 lesions)
%(m/n)1
1.3% (1/75)
1.3% (1/75)
0.0% (0/75)
0.0% (0/75)
10.2 Results of the RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study
Primary objective: The purpose of this study is to assess the safety and efficacy of the Resolute
Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent system for the treatment of de novo lesions in native
coronary arteries that require the use of a 2.0 mm diameter stent.
Design: The Medtronic RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study is a single arm, open label, multicenter trial that enrolled 101 subjects in the US and Japan with ischemic heart disease attributable to
stenotic lesions of the native coronary arteries that are amenable to percutaneous treatment with
stenting. Subjects may have received treatment of one or two lesions with stent diameter 2.0 mm,
one lesion per target vessel, for a maximum of two target vessels. Only one lesion may have been
treated in a single target vessel. All treatments with the study stents were to be performed during a
single index procedure. The first 20 subjects were to undergo an angiogram assessment at 13
months.
Primary endpoint: Target lesion failure (TLF) at 12-months post-procedure, defined as cardiac
death, target vessel myocardial infarction (TVMI) (Q wave or non-Q wave) or target lesion
revascularization by percutaneous or surgical methods.
40
Page 42

Follow-up was performed at 30 days, 6, 12, and 13 months, and annually out to 3 years. Following
the index procedure, subjects were to be treated with aspirin indefinitely and clopidogrel/ticlopidine for
a minimum of 6 months and up to 12 months in those who were not at a high risk of bleeding.
Demographics: The mean age was 67.3 years with 70.3% (71/101) of subjects being males. Of the
subjects enrolled, 46.5% (47/101) had diabetes mellitus, 11.9% (12/101) were current smokers,
35.7% (35/98) had prior MI, 59.4% (60/101) had prior PCI, 82.2% (83/101) had hypertension, and
94.1% (95/101) reported hyperlipidemia. Baseline lesion characteristics include 36.6% (37/101) of
subjects with LAD lesions, a mean lesion length of 12.59 ± 6.27mm, and 65.4% (68/104) ACC/AHA
type B2/C lesions. The mean RVD was 1.91 ± 0.26 mm and the percentage diameter stenosis was
65.83 ± 10.89%.
Results: The rate of TLF in the ITT primary analysis set at 12 months was 5.0% (5/100), fulfilling the
pre-specified performance criterion (upper 1-sided 95% CI of 10.2%, compared with the performance
goal of 19%, p < 0.001). The primary endpoint was also analyzed by gender, resulting in a TLF rate of
7.0% (5/71) in male subjects and 0.0% (0/30) in female subjects.
These analyses are based on the intent-to-treat population. The results are presented in the following
tables:
• Table 10-4: RESOLUTE ONYX™ 2.0 mm - primary endpoint analysis
• Table 10-5: RESOLUTE ONYX™ 2.0 mm - clinical and angiographic outcomes
• Table 10-6: RESOLUTE ONYX™ 2.0 mm - ARC defined definite/probable stent thrombosis
through 12 months
• Table 10-7: RESOLUTE ONYX™ 2.0 mm – primary endpoint analysis by gender
Table 10-4: RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study – primary endpoint analysis
Resolute Onyx 2.0mm
Primary endpoint - TLF at 12-month
Primary analysis – with analysis lesion only 2
– ITT set 5.0% (5/100) 10.2% 19%
– PP set 2.2% (2/90) 6.8% 19%
Secondary analysis – with all lesions included 3
– ITT set 5.0% (5/100) 10.2% 19%
– PP set 2.2% (2/90) 6.8% 19%
1
The one-sided upper 95% CI is calculated by binomial (exact) distribution
2
The lesions with a Resolute Onyx 2.0 mm stent are included in the analysis. For 2 or more lesions with Resolute Onyx 2.0 mm stents
per subject, the lesion is randomly selected.
3
All target lesions are included in the analysis.
(N = 101 subjects)
One-side upper 95%
confidence interval1 Performance goal
Table 10-5: RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study – clinical and angiographic outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm
(N=101 subjects
N=104 lesions)
Safety and effectiveness measures
Safety measures (to 180 days)
Target lesion failure (TLF)2 4.0% (4/101)
Target vessel failure (TVF)3 4.0% (4/101)
MACE4 4.0% (4/101)
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI) 3.0% (3/101)
Death or TVMI 3.0% (3/101)
%(m/n)1
41
Page 43

Table 10-5: RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study – clinical and angiographic outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm
(N=101 subjects
N=104 lesions)
Safety and effectiveness measures
Death 0.0% (0/101)
Cardiac death 0.0% (0/101)
Non-cardiac death 0.0% (0/101)
TVMI (extended historical definition) 3.0% (3/101)
Clinically-driven TLR 1.0% (1/101)
Clinically-driven TVR 1.0% (1/101)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable 0.0% (0/101)
Safety measures (to 360 days)
Target lesion failure (TLF)2 5.0% (5/101)
Target vessel failure (TVF)3 5.0% (5/101)
MACE4 5.0% (5/101)
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI) 3.0% (3/101)
Death or TVMI 3.0% (3/101)
Death 0.0% (0/101)
Cardiac death 0.0% (0/101)
Non-cardiac death 0.0% (0/101)
TVMI (extended historical definition) 3.0% (3/101)
Clinically-driven TLR 2.0% (2/101)
Clinically-driven TVR 2.0% (2/101)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable 0.0% (0/101)
Early thrombosis (30 days) 0.0% (0/101)
Late thrombosis (31-360 days) 0.0% (0/101)
Safety measures (up to 1080 days)
Target lesion failure (TLF)2 13.9% (14/101)
Target vessel failure (TVF)3 14.9% (15/101)
MACE4 14.9% (15/101)
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI) 5.9% (6/101)
Death or TVMI 6.9% (7/101)
Death 3.0% (3/101)
Cardiac death 2.0% (2/101)
Non-cardiac death 1.0% (1/101)
TVMI (extended historical definition) 4.0% (4/101)
Clinically-driven TLR 7.9% (8/101)
Clinically-driven TVR 10.9% (11/101)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable 0.0% (0/101)
Early thrombosis (30 days) 0.0% (0/101)
Late thrombosis (31-360 days) 0.0% (0/101)
Very late thrombosis (>360 days) 0.0% (0/101)
Angiography (13 months)
%(m/n)1
42
Page 44

Table 10-5: RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study – clinical and angiographic outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm
(N=101 subjects
N=104 lesions)
Safety and effectiveness measures
Percent diameter stenosis (% DS)
In-stent
N 25
Mean±SD 22.49 ± 26.89
Median (Q1, Q3) 15.66 (9.57, 31.72)
Min, max -26.71, 100.00
In-segment
N 25
Mean±SD 37.92 ± 21.54
Median (Q1, Q3) 31.72 (23.54, 42.50)
Min, max 14.06, 100.00
Minimal lumen diameter (mm)
In-stent
N 25
Mean±SD 1.55 ± 0.52
Median (Q1, Q3) 1.63 (1.53, 1.81)
Min, max 0.00, 2.20
In-segment
N 25
Mean±SD 1.25 ± 0.46
Median (Q1, Q3) 1.44 (1.09, 1.52)
Min, max 0.00, 1.77
Late luminal loss (mm)
In-stent
N 25
Mean±SD 0.26 ± 0.48
Median (Q1, Q3) 0.06 (0.00, 0.33)
Min, max -0.42, 1.58
In-segment
N 25
Mean±SD 0.25 ± 0.41
Median (Q1, Q3) 0.21 (-0.08, 0.42)
Min, max -0.39, 1.30
In-stent binary angiographic restenosis (BAR) rate 12.0% (3/25)
In-segment binary angiographic restenosis (BAR) rate 20.0% (5/25)
Effectiveness measures
Lesion success5 99.0% (103/104)
Device success6 96.2% (100/104)
%(m/n)1
43
Page 45

Table 10-5: RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study – clinical and angiographic outcomes
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm
(N=101 subjects
N=104 lesions)
Safety and effectiveness measures
%(m/n)1
Procedure success7 97.0% (98/101)
1
Numerator (m) is the number of subjects with the specific classification, denominator (n) is the number of subjects in the study group
with known values, and percentage (%) was calculated as 100 × (m/n).
2
Cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction (Q wave and non-Q wave) or clinically-driven target lesion revascularization (TLR) by
percutaneous or surgical methods.
3
Cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction (Q wave and non-Q wave) or clinically-driven target vessel revascularization (TVR)
by percutaneous or surgical methods.
4
Defined as death, myocardial infarction (Q wave and non Q-wave), emergent coronary bypass surgery, or repeat target lesion
revascularization (clinically-driven/clinically-indicated) by percutaneous or surgical methods.
5
The attainment of <30% residual stenosis by QCA (or <20% by visual assessment) AND TIMI flow 3 after the procedure, using any
percutaneous method.
6
The attainment of <30% residual stenosis by QCA (or <20% by visual assessment) AND TIMI flow 3 after the procedure, using the
assigned device only.
7
The attainment of <30% residual stenosis by QCA (or <20% by visual assessment) AND TIMI flow 3 after the procedure, using any
percutaneous method without the occurrence of MACE during the hospital stay.
Extended historical definition of MI is used for all the composite endpoints.
Table 10-6: RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm Clinical Study – ARC defined definite/probable stent
thrombosis through 12 months
RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm
(N=101 subjects
N=104 lesions)
%(m/n)1
Stent thrombosis 0.0% (0/101)
Early thrombosis (30 days) 0.0% (0/101)
Late thrombosis (31-360 days) 0.0% (0/101)
Table 10-7: RESOLUTE ONYX 2.0 mm - primary endpoint analysis by gender
Male
Primary endpoint
(N = 71 subjects)
Target lesion failure to 12 months 7.0% (5/71) 0.0% (0/30)
Female
(N = 30 subjects)
44
Page 46

10.3 Subjects with diabetes mellitus in the RESOLUTE pooled analysis
Subjects with diabetes mellitus (DM) comprise an important patient subgroup that is at
5,6
increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality
. A Global Statistical Analysis Plan
(GSAP) was created with a pre-specified hypothesis to evaluate the safety and effectiveness
of the Resolute stent to treat stenotic lesions in diabetic subjects with coronary artery
disease. This section provides an overview of this plan and the results supporting the
indication of the Resolute stent to treat coronary artery disease in subjects with diabetes
mellitus.
Primary objective: To assess the safety and effectiveness of the Resolute zotarolimuseluting coronary stent system (Resolute stent) for the treatment of de novo lesions in native
coronary arteries in patients with DM with a reference vessel diameter (RVD) of 2.25 mm to
4.2 mm.
Population: The study population for the GSAP was selected by combining subjects with DM
from the Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial Program. The study population selected for this
analysis met pre-defined general and angiographic inclusion and exclusion criteria. Analysis
populations consisted of consecutively enrolled eligible diabetic subjects in the trials noted
below.
The following global RESOLUTE clinical trials contributed subjects to the diabetes mellitus
cohort:
• RESOLUTE FIM
• RESOLUTE All-Comers (AC)
• RESOLUTE International (Int)
• RESOLUTE United States (US), and
• RESOLUTE Japan
In total there were 878 subjects included in the RESOLUTE DM cohort. RESOLUTE US
provided the highest percentage of subjects at 54.9% (482/878) while RESOLUTE Int
contributed 27.6% (242/878), RESOLUTE AC 9.7% (85/878), RESOLUTE Japan 5.1%
(45/878), and RESOLUTE FIM 2.7% (24/878).
Subjects from the 38 mm Length sub-study are not included in this Resolute Pooled Analysis
of Subjects with Diabetes Mellitus. Additional information is provided in Section 10.4 for the
Resolute US 38 mm Length Group for subjects with Diabetes Mellitus.
Design: The Resolute stent performance for treatment of lesions in patients with DM was
compared with a performance goal (PG) derived from a meta-analysis of published studies of
coronary DES use in DM subjects and from data from the ENDEAVOR pooled studies.
Inclusion of study subjects in this analysis were required to have DM defined by either a
history of DM or use of medications to treat DM (i.e., oral hypoglycemics or insulin) at time of
enrollment. The Resolute stent DM subjects and those included in the meta-analysis were
also required to have clinical characteristics of an on-label population, consistent with the
enrollment criteria of the RESOLUTE US Clinical Trial. That is, subjects with the following
clinical or lesion characteristics were excluded: total lesion length per vessel >27mm, >2
lesions per vessel, unprotected left main lesions, bifurcation lesions, total occlusions, bypass
grafts, acute MI within 72 hours of the index procedure, thrombus-containing lesions, left
ventricular ejection fraction <30%, or renal impairment (serum creatinine >2.5 mg/dl).
5
American Heart Association. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics - 2008 Update. www.americanheart.org/statistics
[Online publication]. Accessed 12 November 2008, 2008.
6
Fang J, Alderman MH. Impact of the increasing burden of diabetes on acute myocardial infarction in New York City:
1990-2000. Diabetes. 2006;55(3):768-773.
45
Page 47

The Resolute DM TVF rate at 12-month follow-up was compared to a performance goal to
demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of the Resolute stent in diabetic subjects. The
objective of the primary endpoint analysis in the RESOLUTE DM cohort was to assess
whether the true primary endpoint rate of 12-month target vessel failure (TVF) for the
Resolute stent met the PG established as 14.5% (which is a 31% increase over the expected
rate of 11.08% for DES use in DM subjects derived from the meta-analysis). The hypothesis
for this analysis accounted for the differences in the protocols of the individual studies in the
published literature, the ENDEAVOR pooled studies, and the Global RESOLUTE Clinical
Trial Program. Specifically, in calculating the meta-analytic PG for DM subjects, adjustments
were made to the 12-month TVF rate based on protocol-required follow-up angiography and
protocol-required post-PCI cardiac biomarker measurements.
Demographics: The mean age of subjects was 65.2 years and 66.4% (583/878) were male.
28.5% (250/878) of the subjects were insulin-dependent diabetics. Of the subjects included in
this analysis, 24.9% (216/867) of the subjects had a prior MI and 28.9% (254/878) were
undergoing revascularization for unstable angina.
Primary endpoint: The primary endpoint was Target Vessel Failure (TVF) at 12 months
following the intervention. The TVF composite endpoint includes cardiac death, MI that
cannot be attributed to vessel(s) other than the target vessel, and clinically-driven target
vessel revascularization (TVR).
Results: The analysis met the primary endpoint’s performance goal of 14.5%, as the TVF
rate of the DM Cohort was 7.84% at 12 months with an upper bound of the 95% CI of 9.51%.
These analyses are based on the intent-to-treat population. The results are presented in the
following tables:
• Table 10-8: RESOLUTE diabetes mellitus cohort - primary endpoint analysis
• Table 10-9: RESOLUTE diabetes mellitus (DM) cohort: all DM subjects, insulin-
dependent DM subjects (IDDM), non-insulin dependent DM subjects (non-IDDM),
and non-DM subjects – principal safety and effectiveness
• Table 10-10: RESOLUTE diabetes mellitus cohort - ARC defined definite/probable
stent thrombosis events through 12 months
Table 10-8: RESOLUTE diabetes mellitus cohort - primary endpoint analysis
Primary endpoint
12-month TVF 7.84% (68/867) 9.51% 14.5% < 0.001
Notes
N is the total number of subjects.
Numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
The primary endpoint analysis utilized a randomly selected lesion from subjects who had treatment of dual lesions.
12-month timeframe includes follow-up window (360 days ± 30 days).
1
One-sided confidence interval using exact method.
2
One-sided p-value using exact test statistic to be compared at a 0.05 significance level.
RESOLUTE DM
(N = 878)
Upper bound of
95%CI
1
Performance goal P-value
2
46
Page 48

Table 10-9: RESOLUTE diabetes mellitus (DM) cohort: all DM subjects, insulin-dependent
DM subjects (IDDM), non-insulin dependent DM subjects (non-IDDM), and non-DM subjects
– principal safety and effectiveness through 12 months
Composite safety and effectiveness
TLF 6.6% (57/867) 10.6% (26/246) 5.0% (31/621) 4.9% (92/1867)
TVF 8.1% (70/867) 11.8% (29/246) 6.6% (41/621) 5.9% (110/1867)
MACE 7.5% (65/867) 11.8% (29/246) 5.8% (36/621) 5.7% (106/1867)
Effectiveness
Clinically-driven TVR
TLR 3.3% (29/867) 5.3% (13/246) 2.6% (16/621) 2.0% (38/1867)
TLR, CABG 0.2% (2/867) 0.8% (2/246) 0.0% (0/621) 0.3% (6/1867)
TLR, PCI 3.1% (27/867) 4.5% (11/246) 2.6% (16/621) 1.7% (32/1867)
Non-TL TVR 2.2% (19/867) 1.6% (4/246) 2.4% (15/621) 1.3% (24/1867)
Non-TL TVR, CABG 0.1% (1/867)
Non-TL TVR, PCI 2.1% (18/867)
Safety
Total death 2.8% (24/867) 4.1% (10/246) 2.3% (14/621) 1.0% (19/1867)
Cardiac death 2.0% (17/867) 2.8% (7/246) 1.6% (10/621) 0.4% (8/1867)
Non-cardiac death 0.8% (7/867) 1.2% (3/246) 0.6% (4/621) 0.6% (11/1867)
Cardiac death or TVMI 3.6% (31/867) 6.1% (15/246) 2.6% (16/621) 3.2% (59/1867)
TVMI 1.8% (16/867)
Q wave MI 0.3% (3/867)
Non-Q wave MI 1.5% (13/867) 3.3% (8/246) 0.8% (5/621) 2.5% (46/1867)
Stent thrombosis
ARC defined
Definite/probable 0.3% (3/867) 0.8% (2/246) 0.2% (1/621) 0.3% (6/1867)
Definite 0.2% (2/867) 0.4% (1/246) 0.2% (1/621) 0.2% (4/1867)
Probable 0.1% (1/867) 0.4% (1/246) 0.0% (0/621) 0.1% (2/1867)
Notes
N = The total number of subjects.
Numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
12-month timeframe includes follow-up window (360 days ± 30 days).
The definitions of the outcomes are presented as table notes to Table 9-1.
All DM subjects
(N = 878)
5.1% (44/867) 6.5% (16/246) 4.5% (28/621) 3.1% (57/1867)
IDDM
(N = 250)
0.0% (0/246) 0.2% (1/621)
1.6% (4/246) 2.3% (14/621)
4.1% (10/246) 1.0% (6/621)
0.8% (2/246) 0.2% (1/621)
Non IDDM
(N = 628)
Non DM
(N = 1903)
0.2% (4/1867)
1.1% (20/1867)
2.7% (51/1867)
0.3% (5/1867)
47
Page 49

Table 10-10: RESOLUTE diabetes mellitus cohort - ARC defined definite/probable stent
thrombosis events through 12 months
Resolute
Stent thrombosis 0.3% (3/867)
Acute (0 to 1 day) 0.1% (1/867)
Subacute (2 to 30 days) 0.1% (1/867)
Late (31 to 360 days)
Notes
N is the total number of subjects.
Numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
12-month time frame includes follow-up window (360 days ± 30 days).
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
(N = 878)
0.1% (1/867)
10.4 Subjects with diabetes mellitus in the RESOLUTE 38 mm length group
Additional information is provided in Table 10-11 for the RESOLUTE 38 mm length group in subjects
with diabetes mellitus.
Table 10-11: RESOLUTE 38 mm length group: all 38 mm subjects, insulin-dependent DM
subjects (IDDM), mon-insulin dependent DM subjects (non-IDDM), and non-DM subjects –
principal safety and effectiveness through 12 months
All diabetic 38 mm length
group subjects (N = 84
Composite safety and
effectiveness
TLF 6.0% (5/84) 4.3% (1/23) 6.6% (4/61) 5.1% (7/138)
TVF 7.1% (6/84) 4.3% (1/23) 8.2% (5/61) 6.5% (9/138)
MACE 8.3% (7/84) 4.3% (1/23) 9.8% (6/61) 5.1% (7/138)
Effectiveness
Clinically-driven TVR 3.6% (3/84) 0.0% (0/23) 4.9% (3/61) 2.2% (3/138)
TLR 2.4% (2/84) 0.0% (0/23) 3.3% (2/61) 0.7% (1/138)
Safety
Total death 1.2% (1/84) 0.0% (0/23) 1.6% (1/61) 0.7% (1/138)
Cardiac death 1.2% (1/84) 0.0% (0/23) 1.6% (1/61) 0.7% (1/138)
Non-cardiac death 0.0% (0/84) 0.0% (0/23) 0.0% (0/61) 0.0% (0/138)
Cardiac death or TVMI 3.6% (3/84) 4.3% (1/23) 3.3% (2/61) 5.1% (7/138)
TVMI 2.4% (2/84) 4.3% (1/23) 1.6% (1/61) 4.3% (6/138)
Stent thrombosis
ARC defined
Stent thrombosis (ARC
def/prob)
Early (30 days) 0.0% (0/84) 0.0% (0/23) 0.0% (0/61) 1.4% (2/138)
Late (>30 and 360 days) 0.0% (0/84) 0.0% (0/23) 0.0% (0/61) 0.0% (0/138)
patients)
0.0% (0/84) 0.0% (0/23) 0.0% (0/61) 1.4% (2/138)
38 mm length group
IDDM
(N = 23 patients)
38 mm length group –
non-IDDM
(N = 61 patients)
38 mm length group –
non-DM (N = 139
patients)
48
Page 50

10.5 Subjects receiving short-term DAPT
The Onyx ONE Clear Primary Analysis subject population was formed by pooling data from eligible
subjects enrolled into the Onyx ONE US & Japan Trial (a prospective, multi-center, single-arm trial,
which enrolled subjects in the United States and Japan) with data from eligible subjects treated with
Resolute Onyx only in the Onyx ONE Global RCT (a prospective, multi-center, randomized trial [See
Section 10.5.2]).
10.5.1 Onyx ONE Clear Primary Analysis
Primary Objective: To assess the safety and effectiveness of the Resolute Onyx stent with use of
one-month DAPT in subjects deemed at high risk for bleeding and/or medically unsuitable for more
than one-month DAPT treatment.
Population: Subjects with an indication for percutaneous coronary intervention deemed at high risk
for bleeding and/or candidates for one-month DAPT who are acceptable candidates to receive
treatment with the Resolute Onyx stent.
Design: The Onyx ONE US & Japan Trial is a prospective, multi-center, post-market single-arm
study which enrolled subjects undergoing attempted PCI. Subjects received DAPT through one
month, before transitioning to SAPT thereafter.
Eligible subjects enrolled in the Onyx ONE US & Japan Trial (N=751) combined with eligible subjects
from the Resolute Onyx arm of the Onyx ONE Global RCT (N=1018) (See Section 10.5.2) to form an
Onyx As Treated population (Onyx AT).
The one-month clear population excluded subjects who interrupted or discontinued DAPT (greater
than 3 cumulative days) within the first month of procedure (2.1%), those who experienced adverse
events that would prohibit them from discontinuing DAPT beyond one month (3.4%), who did not
intend to transition from DAPT to SAPT one month after procedure (6.2%), and who were lost to
follow-up (3.1%). Peri-procedural MIs did not exclude subjects from being considered as one-month
clear.
Assessment of the use of Resolute Onyx stents in HBR patients was based on analyses combining
outcomes from patients compared to a pre-specified performance goal (PG). The PG was based on a
clinically acceptable margin added to an expected composite event rate of cardiac death, and
myocardial infarction (CD/MI) rate at 12 months, adapted from historical short DAPT studies with
high-bleeding risk patient populations (LEADERS FREE
7
, ZEUS
8,9
, and SENIOR10). The expected
CD/MI rate between one month and one year was estimated to be 6.8%.
The PG for the composite event rate of CD/MI at one-year post-procedure in a one-month clear
population was 9.7% based on an estimated CD/MI rate of 6.8% and a one sided 0.025 significance
level.
Demographics: The mean age was 74.0 ± 9.5, 67.7% (1019/1506) were male, 72.4% (1091/1506)
reported dyslipidemia, 84.0% (1265/1506) had hypertension, 9.4% (141/1498) were current smokers,
39.4% (593/1506) were diabetic 13.7% (206/1506) reported as insulin dependent], 26.3% (396/1506)
had a prior MI, and 48.6% (701/1441) were classified as having acute coronary syndrome.
7
Urban P, Meredith IT, Abizaid A, et al. Polymer-free Drug-Coated Coronary Stents in Patients at
High Bleeding Risk. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2038-4.
8
Valgimigli M, Patialiakas A, Thury A, et al. Zotarolimus-eluting versus bare-metal stents in uncertain
drug-eluting stent candidates. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:805–15.
9
Ariotti S, Adamo M, Costa F, et al. Is Bare-Metal Stent Implantation Still Justifiable in High Bleeding
Risk Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention?: A Pre-Specified Analysis From
the ZEUS Trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2016;9:426-36.
10
Varenne O, Cook S, Sideris G, et al. Drug-eluting stents in elderly patients with coronary artery
disease (SENIOR): a randomised single-blind trial. Lancet. 2018 Jan 6;391(10115):41-50.
49
Page 51

The mean number of high bleeding risk criteria was 1.6±0.8. The most common HBR qualifying
features were age > 75 years, 59.0% (889/1506), long-term oral anticoagulation use, 41.0%
(617/1506), anemia (hemoglobin level <11 g/dL) or recent transfusion, 14.4% (217/1506) and chronic
kidney disease (creatinine clearance <40ml/min, 12.5% (188/1506).
Primary endpoint: The composite rate of cardiac death and myocardial infarction (CD/MI) at one
year for a one-month clear population [timeframe: one month to one year].
Results: The Onyx As Treated (Onyx AT) one-month clear population was defined as the primary
analysis population for the study. The CD/MI rate at one year for the Onyx ONE Clear cohort was
7.0% (104/1491) with the upper limit of 95% confidence interval of 8.4% which was lower than the
prespecified performance goal of 9.7%.
The Onyx ONE Clear Primary Analysis results are presented in Table 10-12 and Table 10-13.
Post hoc analyses by gender and ACS vs non-ACS presentation for the primary endpoint are
presented in Table 10-14 and Table 10-15. For gender, CD/MI rates at one year were 7.6%
(77/1010) in male subjects and 5.6% (27/481) in female subjects. Patients who presented with ACS
had a CD/MI rate at 1 year of 7.9% (55/694) compared with 6.0% (44/733) for patients who did not
present with ACS.
Table 10-12: Primary endpoint analysis – Onyx ONE Clear
Primary
Objective Met?
(Yes or No)
Primary Endpoint at 12 month1
Resolute Onyx
(N = 1506
Subjects)
Two-side 95%
Confidence
Interval2
Performance
Goal p-value
Primary Analysis
– Onyx ONE Clear 7.0% (104/1491) [5.7%, 8.4%] 9.7% <0.001 Yes
Best Case Analysis3
– Onyx ONE Clear 6.9% (104/1506) [5.7%, 8.3%] 9.7% <0.001 Yes
Worst Case Analysis4
– Onyx ONE Clear 7.9% (119/1506) [6.6%, 9.4%] 9.7% 0.009 Yes
1 The primary endpoint is a composite of cardiac death, myocardial infarction at one year post-procedure.
2 The two-sided 95% CI was calculated by binomial (exact) distribution carried out to assess statistical significance at the 0.025 level.
3 Best case analysis imputed all the missing 12-month primary endpoint status as no.
4 Worst case analysis imputed all the missing 12-month primary endpoint status as yes.
50
Page 52

Table 10-13: Principal safety and effectiveness results – Onyx ONE Clear
RESOLUTE ONYX
(N=1506 subjects
N=1960 lesions)
Safety and effectiveness measures
Safety measures (to 180 days)
Target lesion failure (TLF)2 4.1% (61/1500)
Target vessel failure (TVF)3 4.5% (67/1500)
MACE4 6.0% (90/1500)
Cardiac death, MI and definite/probable stent thrombosis 3.7% (56/1500)
Cardiac death or MI 3.7% (56/1500)
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI) 3.3% (50/1500)
Death or TVMI 4.9% (73/1500)
Death 2.5% (38/1500)
Cardiac death 1.0% (15/1500)
Non cardiac death 1.5% (23/1500)
TVMI (3rd UDMI) 2.5% (38/1500)
Clinically driven TLR 1.6% (24/1500)
Clinically driven TVR 2.2% (33/1500)
Stroke 0.7% (11/1500)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable 0.4% (6/1500)
Bleeding
All BARC 7.3% (110/1500)
BARC 3-5 2.3% (34/1500)
BARC 2-5 6.5% (97/1500)
Safety measures (to 365 days)
Target lesion failure (TLF)2 8.1% (121/1491)
Target vessel failure (TVF)3 8.8% (131/1491)
MACE4 11.7% (174/1491)
Cardiac death, MI and definite/probable stent thrombosis 7.0% (104/1491)
Cardiac death or MI 7.0% (104/1491)
Cardiac death or target vessel MI (TVMI) 6.5% (97/1491)
Death or TVMI 9.7% (144/1491)
Death 6.0% (89/1491)
Cardiac death 2.6% (39/1491)
Non cardiac death 3.4% (50/1491)
TVMI (3rd UDMI) 4.4% (65/1491)
Clinically driven TLR 3.4% (50/1491)
Clinically driven TVR 4.3% (64/1491)
%(m/n)1
51
Page 53

Table 10-13: Principal safety and effectiveness results – Onyx ONE Clear
RESOLUTE ONYX
(N=1506 subjects
N=1960 lesions)
Safety and effectiveness measures
%(m/n)1
Stroke 1.5% (22/1491)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable 0.7% (10/1491)
Bleeding
All BARC 13.1% (195/1491)
BARC 3-5 4.0% (60/1491)
BARC 2-5 11.7% (175/1491)
Effectiveness measures
Lesion success5 94.6% (1817/1920)
Device success6 93.3% (1790/1919)
Procedure success7 88.5% (1295/1463)
1
Numerator (m) is the number of Subjects with the specific classification, denominator (n) is the number of
Subjects in the study group with known values, and percentage (%) was calculated as 100 × (m/n)
2
Cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction (Q wave and non Q wave) or clinically-driven target lesion
revascularization (TLR) by percutaneous or surgical methods.
3
Cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction (Q wave and non Q wave) or clinically-driven target vessel
revascularization (TVR) by percutaneous or surgical methods.
4
Defined as death, myocardial infarction (Q wave and non Q-wave), emergent coronary bypass surgery, or
repeat target lesion
revascularization (clinically driven/clinically indicated) by percutaneous or surgical methods.
5
The attainment of <30% residual stenosis by QCA (or < 20% by visual assessment) AND TIMI flow 3 after the
procedure using any percutaneous method.
6
The attainment of <30% residual stenosis by QCA (or < 20% by visual assessment) AND TIMI flow 3 after the
procedure using the assigned device only.
7
The attainment of <30% residual stenosis by QCA (or < 20% by visual assessment) AND TIMI flow 3 after the
procedure using any percutaneous method without the occurrence of MACE during the hospital.
Third universal definition of MI is used for all the composite endpoints.
Table 10-14: Primary endpoint analysis by gender – Onyx ONE Clear
Primary endpoint Male subjects
Resolute Onyx
(N=1019 subjects)
% (m/n)
CD/MI at 12 months 7.6% (77/1010) 5.6% (27/481)
Female subjects
Resolute Onyx
(N=487 subjects)
% (m/n)
Table 10-15: Primary endpoint analysis ACS vs. non-ACS patients- Onyx ONE Clear
Non-ACS
(N=740 Subjects)
(N=958 Lesions)
Primary endpoint
%(m/n)1
CD/MI at 12 months 6.0% (44/733) 7.9% (55/694)
ACS
(N=701 Subjects)
(N=914 Lesions)
%(m/n)1
52
Page 54

10.5.2 The Onyx ONE Global RCT
Study design: The Onyx ONE Global RCT
11
was an international, randomized, single-blind trial, that
compared zotarolimus-eluting stents (Resolute Onyx) with polymer-free umirolimus–coated stents in
patients at high bleeding risk. After PCI, patients were treated with one-month of DAPT, followed by
SAPT. A total of 1996 HBR patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive Resolute Onyx
stents (1003 patients) or polymer-free drug-coated stents (993 patients).
Objective: The purpose of this clinical study was to evaluate the clinical safety of the Resolute Onyx
stent as compared to the polymer-free drug coated stents with use of 1 month DAPT in subjects
deemed at HBR and/or medically unsuitable for more than 1 month DAPT treatment. In the
LEADERS-FREE trial, the same polymer-free drug-coated stent showed superiority in safety and
effectiveness to a bare-metal stent in a similar HBR population treated with 1 month of DAPT.
Primary Endpoint: The composite rate of cardiac death, myocardial infarction and stent thrombosis
(definite/probable) at one year.
Results: At 1 year, the primary outcome was observed in 169 of 988 patients (17.1%) in the Resolute
Onyx stent group and in 164 of 969 (16.9%) in the polymer-free drug-coated stent group (risk
difference, 0.2 percentage points; upper boundary of the one-sided 97.5% confidence interval [CI],
3.5; noninferiority margin, 4.1; P = 0.01 for noninferiority). Among patients at HBR who received 1
month of DAPT after PCI, Resolute Onyx stents were noninferior to use of polymer-free drug-coated
stents with regard to safety and effectiveness composite outcomes.
10.6 Subjects with chronic total occlusion
The PERSPECTIVE Study – RESOLUTE CTO cohort
The PERSPECTIVE Study included a retrospective and a prospective study arm. Both arms of this
study enrolled approximately 250 patients at a single center experienced in CTO procedures. The
prospective arm essentially comprised a separate substudy designed to evaluate procedural and 1year clinical outcomes among consecutive patients undergoing attempted percutaneous Chronic
Total Occlusion (CTO) revascularization. The prospective arm of the PERSPECTIVE study included a
pre-specified subgroup analysis of patients treated with the Resolute family of drug-eluting stents (all
were Resolute Integrity).
Primary objective: To assess the safety and effectiveness of the Resolute zotarolimus-eluting
coronary stent system (Resolute ZES) for the treatment of chronic total occlusions.
Population: The population consisted of prospectively enrolled subjects undergoing attempted
percutaneous CTO revascularization and treated with the Resolute ZES.
Design: The PERSPECTIVE Study
(Prospective Arm/Prespecified Resolute ZES for CTO Analysis)
was a single-center, investigator-initiated, observational study which prospectively enrolled
approximately 250 subjects undergoing attempted CTO. Assessment of use of Resolute ZES stents
in CTO revascularization was based on prospectively enrolled CTO patients compared to a prespecified performance goal.
11
Windecker S, Latib A, Kedhi E, et al. Polymer-based or Polymer-free Stents in Patients at High
Bleeding Risk. New England Journal of Medicine 2020.
53
Page 55

An estimated MACE rate was derived based on a weighted average of the reported rates for drug-
12
eluting stents from the PRISON II
and EXPERT CTO13 studies. Due to difference in the definition of
myocardial infarction used in the PRISON II study, an adjustment for the MACE rate was made to
approximate the MACE rate if the ARC definition of myocardial infarction had been applied. The
weighted average produced an estimated MACE rate of 16.6% using the ARC definition of MI. The
performance goal (PG) for the pre-specified RESOLUTE CTO Cohort analysis was 25.2% based on
the estimated MACE rate of 16.6% and a one-sided 95% CI.
Demographics: In the RESOLUTE CTO Cohort of the PERSPECTIVE Study, the mean age was
63.4 ± 9.5, 79.8% (146/183) were male, 98.4% (180/183) reported dyslipidemia, 88.5% (162/183) had
hypertension, 18.0% (31/172) were current smokers, 35.5% (65/183) were diabetic including 12.6%
(23/182) reported as insulin-dependent, 33.3% (61/183) had a prior MI, and 80.9% (140/173) were
classified as having stable angina.
Primary endpoint: Major Adverse Cardiac Events (MACE) at one year; a composite of death,
myocardial infarction (MI) (ARC defined), and clinically-driven target lesion revascularization (TLR).
Results: The observed MACE rate at one year for the RESOLUTE CTO Cohort was 18.2% (33/181)
for the ITT population. The ITT population met the primary endpoint. The upper limit of the 95%
confidence interval was 23.6% which is lower than the pre-specified performance goal (25.2%). A
post hoc gender subgroup analysis of the primary endpoint resulted in MACE rates at one year of
18.8% (27/144) in male subjects and 16.2% (6/37) in female subjects.
The PERSPECTIVE Study results are presented in Table 10-16, Table 10-17, and Table 10-18:
Table 10-16: Primary endpoint analysis – MACE at 12 months (ITT)
One-side upper
RESOLUTE CTO cohort
Primary endpoint
MACE at 12 months
ITT 18.2% (33/181) 23.6% 25.2%
(N=183 Subjects)
95%
confidence interval
Table 10-17: Principal safety and effectiveness results
RESOLUTE CTO cohort
(N=183 subjects)
Safety and effectiveness measures
Safety measures (in-hospital)
TLF 15.3% (28/183)
TVF 15.3% (28/183)
MACE 15.3% (28/183)
Cardiac death or MI 15.3% (28/183)
Death or MI 15.3% (28/183)
Death 1.1% (2/183)
Cardiac death 1.1% (2/183)
12
Suttorp MJ, Laarman GJ, Rahel BM, et al. Primary Stenting of Totally Occluded Native Coronary Arteries II (PRISON II): a
randomized comparison of bare metal stent implantation with sirolimus-eluting stent implantation for the treatment of total coronary
occlusions. Circulation 2006; 114(9); 921 – 928.
13
Kandzari DE, Kini AS, Karmpaliotis D, et al. Safety and Effectiveness of Everolimus-Eluting Stents in Chronic Total Coronary
Occlusion Revascularization: Results From the EXPERT CTO Multicenter Trial (Evaluation of the XIENCE Coronary Stent,
Performance, and Technique in Chronic Total Occlusions). J Am Coll Cardiol Intv 2015; 8(6); 761 – 769.
%(m/n)
Performance
goal
54
Page 56

Table 10-17: Principal safety and effectiveness results
RESOLUTE CTO cohort
(N=183 subjects)
Safety and effectiveness measures
Non-cardiac death 0.0% (0/183)
MI 14.8% (27/183)
TLR 0.0% (0/183)
TVR 0.0% (0/183)
Safety measures (to 6 Months/183 days)
TLF 17.5% (32/183)
TVF 17.5% (32/183)
MACE 17.5% (32/183)
Cardiacdeath or MI 17.5% (32/183)
Death or MI 17.5% (32/183)
Death 2.7% (5/183)
Cardiac death 2.2% (4/183)
Non-cardiac death 0.5% (1/183)
MI 15.8% (29/183)
TLR 0.5% (1/183)
TVR 0.5% (1/183)
All stent thrombosis (ARC definite/probable/possible) 1.6% (3/183)
Stent thrombosis ARC definite/probable 0.6% (1/183)
Stent thrombosis ARC possible 1.1% (2/183)
Early stent thrombosis (0 to 30 days) 0.6% (1/183)
Definite 0.6% (1/183)
Probable 0.0% (0/183)
Possible 0.0% (0/183)
Late stent thrombosis (31 days to 6 months) 1.1% (2/183)
Definite 0.0% (0/183)
Probable 0.0% (0/183)
Possible 1.1% (2/183)
Safety measures (to 1 year/365 days)
TLF 18.2% (33/181)
TVF 18.2% (33/181)
MACE 18.2% (33/181)
Cardiac death or MI 17.7% (32/181)
Death or MI 17.7% (32/181)
Death 2.8% (5/181)
Cardiac death 2.2% (4/181)
Non-cardiac death 0.6% (1/181)
MI 16.0% (29/181)
TLR 1.1% (2/181)
TVR 1.1% (2/181)
All stent thrombosis (ARC definite/probable/possible) 1.7% (3/181)
Stent thrombosis ARC definite/probable 0.6% (1/181)
Stent thrombosis ARC possible 1.1% (2/181)
Early stent thrombosis (0 to 30 days) 0.6% (1/181)
Definite 0.6% (1/181)
Probable 0.0% (0/181)
Possible 0.0% (0/181)
%(m/n)
55
Page 57

Table 10-17: Principal safety and effectiveness results
RESOLUTE CTO cohort
(N=183 subjects)
Safety and effectiveness measures
Late stent thrombosis (31 days to 1 year) 1.1% (2/181)
Definite 0.0% (0/181)
Probable 0.0% (0/181)
Possible 1.1% (2/181)
Effectiveness measures
Clinical success
Technical success
1CTO procedural success as defined by achievement of <50% residual stenosis with 7,0, 2 antegrade flow
2
Successful guidewire crossing with placement in distal true lumen of CTO target lesion
1
2
%(m/n)
92.3% (169/183)
96.2% (175/182)
Table 10-18: RESOLUTE CTO cohort – primary endpoint analysis by gender
Male subjects
RESOLUTE CTO cohort
Primary endpoint
MACE at 12 months 18.8% (27/144) 16.2% (6/37)
(N=146 subjects)
% (m/n)
Female subjects
RESOLUTE CTO cohort
(N=37 subjects)
% (m/n)
Global RESOLUTE Clinical Program – RESOLUTE pooled CTO
Population: In order to provide additional support for the performance of the Resolute family of
stents in the treatment of CTOs, a retrospective, pooled analysis was performed which was
comprised of pooled CTO patients from the Global RESOLUTE Clinical Program.
The following Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trials contributed subjects to the CTO cohort:
• RESOLUTE International
The RESOLUTE International Study (R-Int) was a prospective, multi-center, nonrandomized, single-arm, observational study of the Resolute stent in a real world
subject population. A total 2349 subjects were enrolled into the study. Subjects were
followed for 3 years post-procedure. A total of 186 subjects from the R-Int study were
included in the RESOLUTE Pooled CTO analysis.
• RESOLUTE China Randomized Controlled Trial
The RESOLUTE China Randomized Controlled Trial (R-China RCT) was a
prospective, multi-center, randomized, open-label study designed to assess the noninferiority of the Resolute stent compared to the Taxus Liberte stent for in-stent late
lumen loss. A total of 198 subjects were treated with the Resolute stent. Subjects were
followed for 5 years post-procedure. A total of 15 subjects from the R-China RCT study
were included in the RESOLUTE Pooled CTO analysis.
• RESOLUTE China Registry
56
Page 58

The RESOLUTE China Registry (R-China Registry) was a prospective, multi-center,
non-randomized, single-arm, observational study of the Resolute stent in a real-world
patient population requiring stent implantation. A total of 1800 subjects were treated
with the Resolute stent. Subjects were followed for 5 years post-procedure. A total of
157 subjects from the R-China Registry were included in the RESOLUTE Pooled CTO
Analysis.
Design: The Resolute stent performance for the treatment of CTO lesions was analyzed from
data collected in the R-Int, R-China RCT, and R-China Registry studies. The results pooled
datasets from the 5-year data of R-China RCT, 4-year data of R-China Registry, and 3-year
data from R-Int. In total, 358 subjects were evaluable for this CTO subset.
Demographics: The average age in the RESOLUTE Pooled CTO subset (n=358) was 60.4 ±
11.3 years and 84.4% (302/358) were male. For this population, 37.7% (133/353) experienced
a prior MI, 65.1% (233/358) had hypertension, 50.3% (180/358) had hyperlipidemia and 26.5%
(95/358) had diabetes.
Global RESOLUTE Clinical Program results are presented in the following table:
Table 10-19: RESOLUTE pooled CTO analysis – safety and effectiveness results
RESOLUTE pooled CTO
(N=358 patients)
Safety and effectiveness endpoints
Effectiveness measures
Lesion success6 100.0% (526/526)
Device success7 94.1% (496/527)
Procedure success8 97.5% (348/357)
1 Year
TLF1 4.5% (16/352)
TVF2 4.8% (17/352)
MACE3 5.7% (20/352)
Composite endpoint4 12.2% (43/352)
Cardiac death or TVMI 3.1% (11/352)
Death or TVMI 4.0% (14/352)
Death 1.7% (6/352)
Cardiac death 0.9% (3/352)
Non-cardiac death 0.9% (3/352)
TVMI (extended historical definition) 2.3% (8/352)
Clinically-driven TLR 2.0% (7/352)
Clinically-driven TVR 2.3% (8/352)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable) 0.6% (2/352)
Early thrombosis(30 days) 0.3% (1/352)
Late thrombosis(>30 and 360 days) 0.3% (1/352)
Significant bleeding complications5 1.1% (4/352)
Stroke 0.9% (3/352)
3 Years
TLF1 8.9% (31/347)
TVF2 10.1% (35/347)
MACE3 10.1% (35/347)
Composite endpoint4 18.4% (64/347)
Cardiac death or TVMI 6.6% (23/347)
Death or TVMI 7.8% (27/347)
Death 5.5% (19/347)
Cardiac death 4.3% (15/347)
(N=527 lesions) %(m/n)9
57
Page 59

Table 10-19: RESOLUTE pooled CTO analysis – safety and effectiveness results
RESOLUTE pooled CTO
(N=358 patients)
Safety and effectiveness endpoints
Non-cardiac death 1.2% (4/347)
TVMI (extended historical definition) 3.2% (11/347)
Clinically-driven TLR 3.2% (11/347)
Clinically-driven TVR 4.3% (15/347)
Stent thrombosis (ARC) definite/probable) 1.2% (4/347)
Early thrombosis(30 days) 0.3% (1/347)
Late thrombosis(>30 and 360 days) 0.3% (1/347)
Very late thrombosis(>360 days) 0.9% (3/347)
Significant bleeding complications5 1.2% (4/347)
Stroke 1.7% (6/347)
1.Cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction (Q wave and non-Q wave), or clinically-driven target lesion revascularization (TLR) by
percutaneous or surgical methods.
2.Cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction, or clinically-driven target vessel revascularization.
3.Death, myocardial infarction, (Q wave and non-Q-wave), emergent coronary bypass surgery, or repeat target lesion revascularization (clinicallydriven/clinically-indicated) by percutaneous or surgical methods.
4.The combined clinical outcome of (all cause) mortality, myocardial infarction (Q-wave and non-Q wave), or (any) revascularization.
5.Bleeding complication is defined as a procedure related hemorrhagic event that requires a transfusion or surgical repair. These may include a
hematoma requiring treatment of retroperitoneal bleed.
Significant bleeding complication is defined as the bleeding complication that has at least one of the following scenarios:
Bleedings that led to an interruption of anti-platelet medication;
Bleedings that require transfusion;
Intracerebral bleedings; or
Bleedings that resulted in substantial hemodynamic compromise requiring treatment
6.The attainment of <50% residual stenosis of the target lesion using any percutaneous method.
7.The attainment of <50% residual stenosis of the target lesion using only the assigned device.
8.The attainment of <50% residual stenosis of the target lesion and no in-hospital MACE.
9.Numerator (m) is the number of patients (or lesions) with the specific classification, denominator (n) is the number of patients (or lesions) in the
study group with known values, and percentage () was calculated as 100 × (m/n)
Extended historical definition of MI is used for all the composite endpoints.
(N=527 lesions) %(m/n)9
10.7 Pooled results of the Global RESOLUTE Clinical Trial Program (RESOLUTE FIM, RESOLUTE US, RESOLUTE AC, RESOLUTE Int, RESOLUTE Japan)
In order to better estimate the incidence of low-frequency events or outcomes, a subject-level
pooled analysis was conducted. Table 10-20 below provides the total number of subjects
included in the analyses.
Table 10-20: Subjects included in the analyses by clinical study
RESOLUTE FIM 139 139
RESOLUTE All-Comers – Resolute 1140 376
RESOLUTE International 2349 763
All subjects On-label
58
Page 60

Table 10-20: Subjects included in the analyses by clinical study
RESOLUTE US 1402 1402
RESOLUTE Japan 100 100
Pooled Resolute Data set 5130 2780
Subjects from the 38 mm length sub-study were not included in the RESOLUTE pooled analysis presented here
All subjects On-label
The on-label subgroup includes all enrolled subjects except those that had a total occlusion,
target lesions involving a bifurcation lesion, target lesions involving a saphenous vein graft
lesion (SVG), an in-stent restenosis (ISR) target lesion, a subject having an acute myocardial
infarction (AMI) hrs), subjects with a demonstrated left-ventricular ejection fraction
(LVEF) less than 30%, target lesions located in an unprotected left main artery, subjects with
treated vessels, subjects with a serum creatinine of >2.5 mg/dl, a lesion length >27 mm, 2
or more lesions treated per vessel, and target lesions with the presence of a thrombus.
It is acknowledged that the results of retrospective pooled analyses have limitations. Definitive
proof of the presence or absence of any differences between sub-groups requires prospectively
powered assessments in clinical trials. The results are presented in the following tables:
• Table 10-21: RESOLUTE pooled analysis - principal safety and effectiveness
through 60 months
• Table 10-22: RESOLUTE pooled Analysis - ARC defined definite/probable stent
thrombosis through 60 months
• Table 10-23: RESOLUTE pooled analysis - subset outcomes through 12 months
• Table 10-24: RESOLUTE pooled analysis – subset outcomes through 12 months
• Table 10-25: RESOLUTE pooled analysis – subset outcomes through 12 months
Table 10-21: RESOLUTE pooled analysis - principal safety and effectiveness through 60
months
All subjects
(N = 5130)
Outcomes at 12 months
Composite safety and effectiveness
TLF
TVF
MACE
Effectiveness
Clinically-driven TVR
Clinically-driven TLR
Safety
Total death
Cardiac-death
Non-cardiac death
TVMI
Cardiac death or TVMI
6.6% (336/5098) 5.4% (150/2759)
7.5% (382/5098) 6.6% (181/2759)
7.5% (384/5098) 6.3% (174/2759)
4.3% (220/5098) 3.7% (103/2759)
3.3% (166/5098) 2.5% (69/2759)
1.9% (98/5098) 1.6% (44/2759)
1.2% (60/5098) 0.9% (26/2759)
0.7% (38/5098) 0.7% (18/2759)
2.9% (149/5098) 2.4% (66/2759)
3.9% (200/5098) 3.3% (90/2759)
On-label
(N = 2780)
59
Page 61

Table 10-21: RESOLUTE pooled analysis - principal safety and effectiveness through 60
months
All subjects
(N = 5130)
Stent thrombosis
ARC defined
Definite/probable
Definite
Probable
0.8% (40/5098) 0.3% (9/2759)
0.6% (29/5098) 0.2% (6/2759)
0.3% (13/5098) 0.1% (3/2759)
Outcomes at 36 months
Composite safety and effectiveness
TLF
TVF
MACE
10.8% (539/5012) 9.2% (249/2709)
13.0% (652/5012) 12.0% (324/2709)
13.5% (679/5012) 12.0% (325/2709)
Effectiveness
Clinically-driven TVR
Clinically-driven TLR
7.9% (397/5012) 7.5% (204/2709)
5.3% (267/5012) 4.4% (119/2709)
Safety
Total death
Cardiac death
Non-cardiac death
TVMI
Cardiac death or TVMI
Stent thrombosis
5.5% (275/5012) 5.0% (135/2709)
3.1% (156/5012) 2.6% (70/2709)
2.4% (119/5012) 2.4% (65/2709)
3.8% (188/5012) 3.1% (84/2709)
6.5% (324/5012) 5.4% (145/2709)
ARC defined
Definite/probable
Definite
Probable
Outcomes at 60 months*
Composite safety and effectiveness
TLF
TVF
MACE
Effectiveness
Clinically-driven TVR
TLR
Safety
Total death
Cardiac death
Non-cardiac death
1.1% (54/5012) 0.5% (13/2709)
0.7% (37/5012) 0.3% (7/2709)
0.4% (19/5012) 0.2% (6/2709)
14.0% (376/2688) 12.3% (239/1937)
18.1% (486/2688) 16.5% (320/1937)
19.4% (521/2688) 18.2% (352/1937)
11.4% (306/2688) 10.6% (205/1937)
6.7% (179/2688) 5.8% (112/1937)
9.9% (266/2688) 9.7% (188/1937)
4.9% (131/2688) 4.3% (83/1937)
5.0% (135/2688) 5.4% (105/1937)
On-label
(N = 2780)
60
Page 62

Table 10-21: RESOLUTE pooled analysis - principal safety and effectiveness through 60
months
All subjects
(N = 5130)
TVMI
Cardiac death or TVMI
Stent thrombosis ARC defined
Definite/probable
Definite
Probable
Notes
N = The total number of subjects enrolled.
Numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
12-month time frame includes follow-up window (360 days ± 30 days).
36-month timeframe includes follow-up window (1080 days ± 30 days).
60-month timeframe includes follow-up window (1800 days ± 30 days).
Note: R-Int. follow-up ends at 3 years and is not included in this analysis.
*
The definitions of the outcomes are presented as table notes to Table 9-1.
4.5% (120/2688) 3.9% (76/1937)
8.7% (234/2688) 7.5% (145/1937)
1.3% (34/2688) 0.8% (15/1937)
0.8% (22/2688) 0.5% (9/1937)
0.5% (13/2688) 0.3% (6/1937)
On-label
(N = 2780)
Table 10-22: RESOLUTE pooled analysis - ARC defined definite/probable stent thrombosis
through 60 months
Stent thrombosis
Early (0 to 30 days)
Late (31 to 360 days)
Very late (361 to 1440 days)*
N = The total number of subjects enrolled.
Numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
12-month time frame includes follow-up window (360 days ± 30 days).
60-month timeframe includes follow-up window (1800 days ± 30 days).
* Note: R-Int. follow-up ends at 3 years and is not included in this analysis.
All subjects*
(N = 2781)
1.3% (34/2688) 0.8% (15/1937)
0.5% (13/2688) 0.2% (3/1937)
0.3% (8/2688) 0.2% (4/1937)
0.5% (14/2688) 0.4% (8/1937)
On-label*
(N = 2017)
61
Page 63

mm
Lesion length
RVD
mm
B2/C lesions
Female
(N = 509)
(N = 1956)
(N = 3636)
(N = 1287)
1.8% (9/495)
Male
(N = 3843)
Age
yrs.
(N = 2547)
(N = 2466)
1.9% (48/2515) 1.0% (39/3780) 1.5% (19/1264) 1.0% (36/3577) 1.0% (20/1928)
Table 10-23: RESOLUTE pooled analysis - subset outcomes through 12 months
On-label single lesion
62
Composite safety and
effectiveness TLF 5.3% (128/2428) 7.0% (177/2515) 6.3% (239/3780) 7.4% (94/1264) 6.7% (239/3577) 7.3% (141/1928) 7.9% (39/495)
TVF 6.4% (155/2428) 8.0% (202/2515) 7.1% (270/3780) 8.6% (109/1264) 7.6% (272/3577) 8.5% (164/1928) 8.5% (42/495)
MACE 6.1% (147/2428) 8.4% (211/2515) 7.3% (277/3780) 8.0% (101/1264) 7.6% (271/3577) 8.1% (157/1928) 9.3% (46/495)
Effectiveness
Clinically-driven TVR 3.6% (88/2428) 4.3% (108/2515) 4.3% (162/3780) 4.4% (55/1264) 4.4% (157/3577) 5.0% (96/1928) 5.7% (28/495)
TLR 2.4% (58/2428) 3.1% (79/2515) 3.3% (124/3780) 3.1% (39/1264) 3.3% (118/3577) 3.7% (71/1928) 5.1% (25/495)
Safety
Total death 1.6% (39/2428) 3.1% (78/2515) 1.9% (70/3780) 2.1% (26/1264) 1.7% (62/3577) 1.7% (32/1928) 3.2% (16/495)
Cardiac death 0.9% (22/2428)
Non-cardiac death 0.7% (17/2428) 1.2% (30/2515) 0.8% (31/3780) 0.6% (7/1264) 0.7% (26/3577) 0.6% (12/1928) 1.4% (7/495)
TVMI 2.3% (57/2428) 2.9% (74/2515) 2.8% (105/3780) 3.6% (45/1264) 3.2% (115/3577) 3.5% (67/1928) 1.8% (9/495)
Cardiac death or TVMI 3.2% (77/2428) 4.5% (113/2515) 3.6% (137/3780) 4.9% (62/1264) 4.0% (144/3577) 4.4% (84/1928) 3.4% (17/495)
Stent thrombosis ARC defined
Definite/probable 0.3% (7/2428) 0.8% (19/2515) 0.8% (31/3780) 0.7% (9/1264) 0.9% (31/3577) 0.7% (14/1928) 1.0% (5/495)
Definite 0.2% (5/2428) 0.5% (12/2515) 0.6% (24/3780) 0.4% (5/1264) 0.7% (25/3577) 0.5% (10/1928) 0.6% (3/495)
Probable 0.1% (2/2428) 0.3% (8/2515) 0.2% (9/3780) 0.3% (4/1264) 0.2% (8/3577) 0.3% (6/1928) 0.4% (2/495)
Page 64

BMS in-stent restenosis
(N = 199)
12.1% (24/198)
11.1% (22/198)
9.1% (18/198)
8.1% (16/198)
3.0% (6/198)
2.0% (4/198)
1.0% (2/198)
4.0% (8/198)
3.0% (6/198)
2.5% (5/198)
1.5% (3/198)
1.0% (2/198)
Multi-vessel stenting
Saphenous vein graft
Overlapping stents
(N = 770)
(N = 64)
1.9% (14/756)
0.5% (4/756)
1.3% (10/756)
3.3% (25/756)
63
(N = 644)
(N = 1788)
Multiple stents
Table 10-24: RESOLUTE pooled analysis – subset outcomes through 12 months
Composite safety and effectiveness
TLF 7.8% (137/1758) 7.8% (49/632) 17.2% (11/64) 8.2% (62/756)
TVF 8.6% (152/1758) 8.7% (55/632) 17.2% (11/64) 8.9% (67/756)
MACE 8.8% (155/1758) 9.3% (59/632) 17.2% (11/64) 9.0% (68/756) 12.1% (24/198)
Effectiveness
Clinically-driven TVR 5.1% (89/1758) 5.4% (34/632) 10.9% (7/64) 5.0% (38/756)
TLR 4.1% (72/1758) 4.4% (28/632) 7.8% (5/64) 4.4% (33/756)
Safety
Total death 2.0% (36/1758) 3.0% (19/632) 3.1% (2/64)
Cardiac death 1.3% (22/1758) 1.4% (9/632) 3.1% (2/64)
Non-cardiac death 0.8% (14/1758) 1.6% (10/632) 0.0% (0/64)
TVMI 3.5% (62/1758) 3.3% (21/632) 7.8% (5/64)
Cardiac death or TVMI 4.5% (79/1758) 4.4% (28/632) 9.4% (6/64) 4.5% (34/756)
Stent thrombosis ARC defined
Definite/probable 1.1% (20/1758) 1.1% (7/632) 1.6% (1/64) 1.2% (9/756)
Definite 0.9% (15/1758) 0.6% (4/632) 0.0% (0/64) 0.7% (5/756)
Probable 0.4% (7/1758) 0.6% (4/632) 1.6% (1/64) 0.7% (5/756)
Page 65

AMI <72 hours
Renal
Unprotected
(N = 799)
2
(N = 135)
insufficiency
(N = 57)
left main
3.6% (2/56) 2.3% (3/133) 2.2% (17/788)
1.8% (1/56) 0.8% (1/133) 1.5% (12/788)
1.8% (1/56) 1.5% (2/133) 0.8% (6/788)
1
64
(N = 505)
Total occlusion
1.0% (5/497)
2.0% (10/497)
1.0% (5/497)
(N = 702)
Table 10-25: RESOLUTE pooled analysis – subset outcomes through 12 months
Bifurcation
Composite safety and
effectiveness
TLF 10.3% (71/690) 6.2% (31/497) 16.1% (9/56) 12.0% (16/133) 7.5% (59/788)
TVF 11.4% (79/690) 6.6% (33/497) 16.1% (9/56) 12.8% (17/133) 8.1% (64/788)
MACE 11.3% (78/690) 6.6% (33/497) 17.9% (10/56) 16.5% (22/133) 8.2% (65/788)
Effectiveness
Clinically-driven TVR 6.1% (42/690) 4.2% (21/497) 7.1% (4/56) 4.5% (6/133) 5.6% (44/788)
TLR 4.8% (33/690) 3.6% (18/497) 7.1% (4/56) 3.0% (4/133) 4.7% (37/788)
Safety
Total death 2.3% (16/690) 1.2% (6/497) 7.1% (4/56) 10.5% (14/133) 2.2% (17/788)
Cardiac death 1.6% (11/690) 1.0% (5/497) 5.4% (3/56) 6.8% (9/133) 1.5% (12/788)
Non-cardiac death 0.7% (5/690) 0.2% (1/497) 1.8% (1/56) 3.8% (5/133) 0.6% (5/788)
TVMI 5.9% (41/690) 2.4% (12/497) 7.1% (4/56) 5.3% (7/133) 2.4% (19/788)
Cardiac death or TVMI 7.1% (49/690) 3.4% (17/497) 10.7% (6/56) 9.8% (13/133) 3.8% (30/788)
Stent thrombosis ARC defined
Definite/probable 2.0% (14/690)
Definite 1.6% (11/690)
Probable 0.6% (4/690)
Numbers are % (count/number of eligible subjects).
Notes
N = The total number of subjects enrolled.
Total occlusion is defined as pre procedure TIMI = 0. 2Renal insufficiency is defined as serum creatinine >2.5 mg/dl.
The definitions of the outcomes are presented as table notes to Table 9-1.
Subjects are only counted once for each time period.
12-month time frame includes follow-up window (360 days ± 30 days).
1
Subjects from the 38 mm Length sub-study were not included in the RESOLUTE pooled analysis.
Page 66

11 Patient selection and treatment
See also Section 6.5 - Use in special populations. The risks and benefits described above
should be carefully considered for each patient before use of the Resolute Onyx™ system.
Factors to be utilized for patient selection should include an assessment of the risk of
prolonged anticoagulation. In accordance with the 2016 American College of Cardiology /
American Heart Association guidelines, administration of P2Y
recommended pre-procedure and for at least 6 months in stable ischemic heart disease
patients and for at least 12 months in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). In
patients at higher risk of bleeding, Resolute Onyx is safe and effective with one-month DAPT
based on results of the Onyx ONE Clear Primary Analysis as described in 6.1.1 Oral
antiplatelet therapy. Aspirin should be administered concomitantly with an approved
antiplatelet medication and then continued indefinitely.
12 Patient counseling information
Physicians should consider the following in counseling the patient about this product:
• Discuss the risks associated with stent placement
• Discuss the risks associated with a zotarolimus-eluting stent implant
• Discuss the risks and benefits tradeoff for the patient
• Discuss alteration to current lifestyle immediately following the procedure and over the long
term
• Discuss the risks of early discontinuation of the antiplatelet therapy
The following patient materials will be provided to physicians to educate their patients about
the options available for treating coronary artery disease and provide contact information to
the patient after their stent implant procedure:
platelet inhibitor is
12
• A Patient Guide which includes information on the Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting
coronary stent system, coronary artery disease, and the stent implantation procedure.
• A Stent Patient Implant Card that includes patient information, stent implant information
and MRI guidelines. All patients should be instructed to keep this card in their possession
at all times for procedure/stent identification.
13 How supplied
Sterile: This product is sterilized with ethylene oxide (EO) and is nonpyrogenic. Do not use
the product if the package is opened or damaged. Do not resterilize the product. If the
product or package is opened or damaged, return the product to Medtronic Returned Goods.
Contact your local Medtronic representative for return information.
Contents: The package contains one (1) Resolute Onyx™ zotarolimus-eluting coronary stent
mounted on either a rapid exchange (RX) or an over-the-wire (OTW) stent delivery system.
Storage: Store the product in the original container. Store at 25ºC (77ºF); excursions
permitted to 15 - 30ºC (59 - 86ºF). Use by the use-by date noted on the package.
Disposal instructions: After use, dispose of the product and packaging in accordance with
hospital, administrative and local government policy.
14 Directions for use
14.1 Access to package holding sterile stent delivery system
Remove the stent delivery system from the package. Special care must be taken not to
handle the stent or in any way disrupt its placement on the balloon. This is most important
during catheter removal from packaging, placement over guidewire, and advancement
through the rotating hemostatic valve and guiding catheter hub. Excessive manipulation, for
example, rolling the mounted stent, may cause dislodgement of the stent from the delivery
balloon.
65
Page 67

14.2 Inspection before use
Before opening the product, carefully inspect the stent delivery system package, and check
for damage to the sterile barrier. Do not use after the use-by date. If the sterile package is
intact, carefully remove the system from the package and inspect it for bends, kinks, and
other damage. Do not use the product if any damage to the packaging or system is noted.
A protective sheath covers the stent mounted on the balloon. After removal of the sheath,
visually inspect the stent to ensure that it has not been damaged or displaced from its original
position (between the proximal and distal marker bands) on the balloon.
14.3 Materials required
Quantity Material
N/A
2 to 3 20 cc syringe
1,000 u /500 cc Heparinized normal saline
1 Guidewire [ 0.014 in (0.36 mm) outer diameter]
1 Rotating hemostatic valve
N/A Contrast medium diluted 1:1 with heparinized normal saline
1 Inflation device
1 Stopcock (3-way minimum)
1 Torque device
N/A Appropriate anticoagulation and antiplatelet drugs
Guide catheter [≥ 5 Fr (1.42 mm, 0.056 in) inner diameter]
14.4 Preparation precaution
• Do not use product if the protective sheath is not present or the stent is damaged or
displaced.
• Avoid manipulation of the stent during flushing of the guidewire lumen, as this may disrupt
the placement of the stent on the balloon.
• Do not apply positive pressure to the balloon during the delivery system preparation.
14.4.1 Guidewire lumen flush
Flush the stent system guidewire lumen with heparinized normal saline until the fluid exits the
distal tip.
14.4.2 Delivery system preparation
Step Action
1. Prepare the guide catheter and guidewire according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2. Remove the stent delivery system from the package.
3. Remove the protective sheath covering from the stent/balloon. Removing the protective
sheath will also remove the stylette.
4. Inspect the stent to ensure that it has not been damaged or displaced from its original
position on the balloon. Verify that the stent is positioned between the proximal and distal
balloon markers. Verify that there is no visible damage to the stent or the balloon.
Note: Should there be movement of or damage to the stent, do not use.
5. Flush the stent delivery system guidewire lumen with heparinized normal saline in routine
manner.
6. Fill a 20 cc syringe with 5 cc of contrast/heparinized normal saline mixture (1:1).
7. Attach to delivery system and apply negative pressure for 20 to 30 seconds.
8. Slowly release pressure to allow negative pressure to draw the mixture into the balloon
lumen.
9. Detach the syringe and leave a meniscus of mixture on the hub of the balloon lumen.
10. Prepare the inflation device in standard manner and purge to remove all air from the
syringe and tubing.
66
Page 68

g
Step Action
11. Attach the inflation device to the catheter directly, ensuring no bubbles remain at the
connection.
12. Leave on ambient pressure (neutral position).
Note: Do not apply negative pressure on the inflation device after balloon preparation and
before delivering the stent.
14.5 Delivery procedure
Step Action
1. Prepare the vascular access site according to standard practice.
2. Pre-dilate the lesion with a PTCA catheter. Pre-dilatation must be performed using a
balloon with the following 3 characteristics:
• A diameter at least 0.5 mm smaller than the treatment stent.
• A length equal to or shorter than the lesion length to be dilated.
• A len
3. Maintain neutral pressure on the inflation device. Open the rotating hemostatic valve as
widely as possible.
Note: If resistance is encountered, do not force passage. Resistance may indicate a
problem and may result in damage to the stent if it is forced. Remove the system and
examine.
4. Ensure guide catheter stability before advancing the Resolute Onyx™ system into the
coronary artery. Carefully advance the Resolute Onyx™ system into the hub of the guide
catheter.
5. Advance the stent delivery system over the guidewire to the target lesion under direct
fluoroscopic visualization. Use the radiopaque balloon markers to position the stent
across the lesion; perform angiography to confirm the position of the stent. If the position
of the stent is not optimal, it should be carefully repositioned or removed (see
Precautions – 6 stent/system removal precautions). Expansion of the stent should not
be undertaken if the stent is not properly positioned in the target lesion segment of the
vessel.
6. Sufficiently tighten the rotating hemostatic valve. The stent is now ready to be deployed.
Note: Should unusual resistance be felt at any time during either lesion access or removal of the stent
delivery system before stent implantation, do not force passage. Maintain guidewire placement across the
lesion and remove the stent delivery system as a single unit. See Precautions – 6 Stent/system removal
precautions for specific stent delivery system removal instructions. In the event the stent is not deployed,
contact your local Medtronic representative for return information and avoid handling the stent with bare
hands.
th shorter than the stent to be implanted.
14.6 Deployment procedure
Step Action
1. Before stent expansion, utilize high-resolution fluoroscopy to verify that the stent has not
been damaged or shifted during positioning.
2. Maintain inflation pressure for 15 to 30 seconds for full expansion of the stent.
3. Do not exceed Rated Burst Pressure (RBP). The RBP is 18 atm for the 2.0 mm to
4.0 mm stent diameters and 16 atm for the 4.5 mm and 5.0 mm stent diameters. The
Resolute Onyx™ stents should not be expanded to a diameter beyond the
maximum diameter listed on the label. Do not dilate the 2.0, 2.25, and 2.5 mm
stents to greater than 3.5 mm. Do not dilate the 2.75 and 3.0 mm stents greater than
4.0. Do not dilate the 3.5 and 4.0 mm stents to greater than 5.0 mm. Do not dilate
the 4.5 mm and 5.0 mm stents to greater than 6.0 mm.
4. Fluoroscopic visualization during stent expansion should be used to properly judge the
optimum stent diameter as compared to the proximal and distal native coronary artery
67
Page 69

diameters (reference vessel diameters). Optimal stent expansion and proper apposition
requires that the stent be in full contact with the arterial wall.
14.7 Removal procedure
Step Action
1. Deflate the balloon by pulling negative pressure on the inflation device. Allow adequate
time, at least 30 seconds, for full balloon deflation. Longer stents may require more time
for deflation. Deflation of the balloon should be confirmed by absence of contrast within
the balloon.
2. Open the hemostatic valve to allow removal of the delivery system.
3. Maintain position of the guide catheter and guidewire. Very slowly, withdraw the balloon
from the stent, maintaining negative pressure, allowing movement of the myocardium to
gently dislodge the balloon from the stent.
4. After removal of the delivery system, tighten the hemostatic valve.
5. Repeat angiography and visually assess the vessel and the stent for proper expansion.
14.8
In-vitro
information:
Table 14-1: Inflation pressure recommendations
Pressure Stent nominal inner diameter (mm)
Nominal and
ATM kPa
7 atm 709 kPa 1.85 2.05 2.25 2.45 2.75 3.05 3.60 4.10 4.55
8 atm 811 kPa 1.90 2.10 2.30 2.55 2.80 3.15 3.70 4.20 4.65
9 atm 912 kPa 1.90 2.15 2.35 2.60 2.90 3.25 3.80 4.30 4.80
10 atm
11 atm
12 atm
13 atm
14 atm
15 atm
16 atm
17 atm
18 atm
19 atm
20 atm
21 atm
1013
kPa
1115
kPa
1216
kPa
1317
kPa
1419
kPa
1520
kPa
1621
kPa
1723
kPa
1824
kPa
1925
kPa
2027
kPa
2128
kPa
rated burst
pressure
1.95 2.20 2.45 2.65 2.95 3.35 3.85 4.40 4.90
2.00 2.25 2.50 2.70 3.00 3.40 3.95 4.45 4.95
Nominal
2.05 2.35 2.55 2.80 3.10 3.50 4.05 4.55 5.10
2.10 2.35 2.60 2.80 3.10 3.55 4.05 4.60 5.15
2.10 2.35 2.60 2.85 3.15 3.55 4.10 4.65 5.20
2.15 2.40 2.65 2.90 3.20 3.60 4.15 4.70 5.25
2.15 2.40 2.70 2.90 3.20 3.65 4.20 4.80 5.30
RBP
2.20 2.45 2.75 3.00 3.30 3.75 4.30
2.25 2.50 2.75 3.00 3.35 3.80 4.35
2.25 2.50 2.80 3.05 3.40 3.80 4.40
2.0 2.25 2.5 2.75 3.0 3.5 4.0
2.05 2.30 2.55 2.75 3.05 3.45 4.00 4.50 5.05
2.20 2.45 2.70 2.95 3.25 3.70 4.25 4.85 5.35
4.5
(RX
only)
5.0
(RX
only)
- -
- -
- -
68
Page 70

14.9 Further dilatation of stented segment
The stent delivery balloon may not be used for post-dilatation. Post-dilatation may be
performed at the physician’s discretion with appropriately sized (length and diameter)
balloons to ensure that the stent is in full contact with the vessel wall. To achieve this, a
balloon to artery ratio of 1.0 to 1.1:1.0 should be used to leave a residual diameter stenosis of
near 0% (with a recommended maximum of no greater than 10%). Whenever possible, avoid
the use of grossly oversized balloons (balloon: artery ratio > 1.2).
Precaution: Do not dilate the stent beyond the following limits:
Table 14-2: Nominal stent diameters and dilatation limits
Nominal stent diameter Dilatation limits
2.00 mm 3.50 mm
2.25 mm 3.50 mm
2.50 mm 3.50 mm
2.75 mm 4.00 mm
3.00 mm 4.00 mm
3.50 mm 5.00 mm
4.00 mm 5.00 mm
4.50 mm (RX Only) 6.00 mm
5.00 mm (RX Only) 6.00 mm
All efforts should be taken to ensure that the stent is not under-dilated. If the deployed stent
size is still inadequate with respect to vessel diameter, or if full contact with the vessel wall is
not achieved, a larger balloon may be used to expand the stent further. This further
expansion should be performed using a low profile, high pressure, and non-compliant balloon
catheter. If this is required, the stented segment should be recrossed carefully with a
prolapsed guidewire to avoid dislodging or displacing the stent. The balloon should be
centered within the stent and should not extend outside of the stented region. The Resolute
Onyx™ stents should not be expanded to a diameter beyond the maximum diameter
listed on the label. Do not dilate the 2.0 mm, 2.25 mm, and 2.5 mm stents to greater
than 3.5 mm, 2.75 mm and 3.0 mm stents to greater than 4.0 mm, 3.5 mm and 4.0 mm
stents to greater than 5.0 mm, and 4.5 mm and 5.0 mm stents to greater than 6.0 mm.
14.10 Instructions for simultaneous use of 2 devices in guide catheter (kissing balloon technique)
RX only:
6 Fr (2 mm) compatibility: Any combination of one Resolute Onyx™ RX stent (models 2.0
mm to 4.0 mm) and one balloon catheter (Sprinter Legend™ RX models 1.25 mm to 3.5 mm
up to 30 mm length, Euphora™ RX models 1.5 to 3.5 mm up to 30 mm length, or NC
Euphora™ RX models 2.0 mm to 3.5 mm up to 27 mm length) can be used simultaneously
within a 6 Fr (2 mm)/GC/MID 1.8 mm (0.070 in) guide catheter.
The technique can be performed as per the instructions listed below:
1. Insert the Resolute Onyx™ RX stent using the instructions provided (refer to Section
14.5).
69
Page 71

2. Insert a second guidewire and a balloon catheter, track to the target site and inflate
the balloon.
3. Removing the catheters: Remove one catheter and its associated guidewire
completely before removing the other catheter and its associated guidewire.
15 Reuse precaution statement
For single use only.
Do not resterilize or reuse.
70
Page 72

Disclaimer of warranty
The warnings contained in the product labeling provide more detailed information and are
considered an integral part of this disclaimer of warranty. Although the product has been
manufactured under carefully controlled conditions, Medtronic has no control over the
conditions under which this product is used. Medtronic, therefore, disclaims all warranties,
both express and implied, with respect to the product, including, but not limited to, any
implied warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Medtronic shall not be
liable to any person or entity for any medical expenses or any direct, incidental, or
consequential damages caused by any use, defect, failure, or malfunction of the product,
whether a claim for such damages is based upon warranty, contract, tort, or otherwise. No
person has any authority to bind Medtronic to any representation or warranty with respect to
the product.
The exclusions and limitations set out above are not intended to, and should not be construed so as
to, contravene mandatory provisions of applicable law. If any part or term of this disclaimer of
warranty is held to be illegal, unenforceable, or in conflict with applicable law by a court of competent
jurisdiction, the validity of the remaining portions of this disclaimer of warranty shall not be affected,
and all rights and obligations shall be construed and enforced as if this disclaimer of warranty did not
contain the particular part or term held to be invalid.
71
Page 73

Medtronic, Inc.
710 Medtronic Parkway
Minneapolis, MN 55432
USA
+1 763 514 4000
www.medtronic.com
US Customer Service / Product Inquiries
+1 888 283 7868
*M055193T001* Rev AC
© 2021 Medtronic
 Loading...
Loading...