Page 1

PCI-DAS6052
Analog and Digital I/O Board
User’s Guide
Document Revision 2, November, 2003
© Copyright 2003, Measurement Computing Corporation
Page 2

Lifetime warranty
Every hardware product manufactured by Measurement Computing Corp. is warranted against defects in
materials or workmanship for the life of the product, to the original purchaser. Any products found to be
defective will be repaired or replaced promptly.
30 Day Money Back Guarantee
Any Measurement Computing Corp. product may be returned within 30 days of purchase for a full refund of
the price paid for the product being returned. If you are not satisfied, or chose the wrong product by mistake,
you do not have to keep it. Please call for an RMA number first. No credits or returns accepted without a
copy of the original invoice. Some software products are subject to a repackaging fee.
These warranties are in lieu of all other warranties, expressed or implied, including any implied warranty of
merchantability or fitness for a particular application. The remedies provided herein are the buyer’s sole
and exclusive remedies. Neither Measurement Computing Corp., nor its employees shall be liable for any
direct or indirect, special, incidental or consequential damage arising from the use of its products, even if
Measurement Computing Corp. has been notified in advance of the possibility of such damages.
MEGA-FIFO, the CIO prefix to data acquisition board model numbers, the PCM prefix to data acquisition
board model numbers, PCM-DAS08, PCM-D24C3, PCM-DAC02, PCM-COM422, PCM-COM485, PCMDMM, PCM-DAS16D/12, PCM-DAS16S/12, PCM-DAS16D/16, PCM-DAS16S/16, PCI-DAS6402/16,
Universal Library, InstaCal, Harsh Environment Warranty and Measurement Computing Corporation are
either trademarks or registered trademarks of Measurement Computing Corporation.
IBM, PC, and PC/AT are trademarks of International Business Machines Corp. Windows is a trademark of
Microsoft Corp. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Information furnished by Measurement Computing Corp. is believed to be accurate and reliable. However,
no responsibility is assumed by Measurement Computing Corporation neither for its use; nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties, which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or copyrights of Measurement Computing Corporation.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted, in any form by any means, electronic, mechanical, by photocopying, recording or otherwise
without the prior written permission of Measurement Computing Corporation.
Notice
Measurement Computing Corporation does not authorize any Measurement Computing
Corporation product for use in life support systems and/or devices without the written approval of
the CEO of Measurement Computing Corporation. Life support devices/systems are devices or
systems which, a) are intended for surgical implantation into the body, or b) support or sustain
life and whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to result in injury. Measurement
Computing Corp. products are not designed with the components required, and are not subject to
the testing required to ensure a level of reliability suitable for the treatment and diagnosis of
people.
ii
HM PCI-DAS6052.doc
Page 3

Lifetime Harsh Environment Warranty ™
Any product manufactured by Measurement Computing Corp. that is damaged (even
due to misuse) may be replaced for only 50% of the current list price. I/O boards face
some tough operating conditionssome more severe than the boards are designed to
withstand. When a board becomes damaged, just return the unit with an order for its
replacement at only 50% of the current list price. We don’t need to profit from your
misfortune. By the way, we honor this warranty for any manufacturer’s board that we
have a replacement for!
iii
Page 4

Page 5

Table of Contents
Preface
About this User's Guide ..................................................................................... ix
What you will learn from this user's guide.................................................................... ix
Conventions in this user's guide ............................................................................................... ix
Where to find more information.................................................................................................x
Chapter 1
Introducing the PCI-DAS6052 Series Board................................................... 1-1
Overview: PCI-DAS6052 features.............................................................................. 1-1
Software features–InstaCal and Universal Library.............................................. 1-2
Chapter 2
Installing the Board ..........................................................................................2-1
What is included with your board ............................................................................... 2-1
Standard components .............................................................................................................2-1
Optional components.............................................................................................................. 2-2
Unpacking the board ................................................................................................... 2-3
Installing the software................................................................................................. 2-3
Installing the hardware................................................................................................ 2-4
Configuring the hardware............................................................................................ 2-5
Differential input mode .......................................................................................................... 2-5
Single-ended input mode........................................................................................................ 2-5
Non-referenced single-ended input mode............................................................................... 2-6
DAQ-Sync configuration ....................................................................................................... 2-6
Connecting the board for I/O operations..................................................................... 2-7
Connectors, cables – main I/O connector ............................................................................... 2-7
Pinout – main I/O connector................................................................................................... 2-8
DAQ-Sync Connector and Pinout ........................................................................................ 2-11
Field wiring, signal termination and conditioning................................................................ 2-12
Chapter 3
Programming and Developing Applications.................................................. 3-1
Programming languages.............................................................................................. 3-1
Packaged applications programs ................................................................................. 3-1
Register-level programming........................................................................................ 3-2
Chapter 4
Functional Details .............................................................................................4-1
Basic architecture........................................................................................................ 4-1
Auxiliary input & output interface ......................................................................................... 4-1
DAQ-Sync signals.................................................................................................................. 4-3
DAQ signal timing ...................................................................................................... 4-5
v
Page 6

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide
SCANCLK signal................................................................................................................... 4-5
A/D START TRIGGER signal............................................................................................... 4-6
A/D STOP TRIGGER signal.................................................................................................. 4-7
STARTSCAN signal .............................................................................................................. 4-8
SSH signal.............................................................................................................................. 4-9
A/D CONVERT signal........................................................................................................... 4-9
A/D PACER GATE signal ................................................................................................... 4-10
A/D EXTERNAL TIME BASE signal................................................................................. 4-10
A/D STOP signal.................................................................................................................. 4-11
ATRIG signal ....................................................................................................................... 4-12
Waveform generation timing signals ........................................................................ 4-21
D/A START TRIGGER signal............................................................................................. 4-21
D/A CONVERT signal......................................................................................................... 4-22
D/A EXTERNAL TIME BASE signal................................................................................. 4-23
General-purpose counter signal timing ..................................................................... 4-23
CTR1 CLK signal.................................................................................................................4-24
CTR1 GATE signal.............................................................................................................. 4-24
CTR1 OUT signal.................................................................................................................4-25
CTR2 CLK signal.................................................................................................................4-25
CTR2 GATE signal.............................................................................................................. 4-26
CTR2 OUT signal.................................................................................................................4-26
Chapter 5
Calibrating the Board ....................................................................................... 5-1
Introduction................................................................................................................. 5-1
Calibration theory ....................................................................................................... 5-1
Chapter 6
Specifications ................................................................................................... 6-1
Analog Input Section .................................................................................................. 6-1
Accuracy................................................................................................................................. 6-2
Settling Time.......................................................................................................................... 6-5
Parametrics............................................................................................................................. 6-6
Noise Performance ................................................................................................................. 6-7
Analog Output Section................................................................................................ 6-8
Analog Output Pacing and Triggering.................................................................................... 6-9
Analog Output External Reference Input (D/A EXTREF) ..................................................... 6-9
Analog Trigger.......................................................................................................... 6-10
Analog Input / Output Calibration ............................................................................ 6-10
Digital Input / Output................................................................................................ 6-10
Interrupt Section........................................................................................................ 6-11
Counter Section......................................................................................................... 6-11
Configurable AUXIN<5:0>, AUXOUT<2:0> External Trigger/Clocks .................. 6-12
DAQ-Sync inter-board Triggers/Clocks ................................................................... 6-13
Power Consumption.................................................................................................. 6-13
vi
Page 7

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide
Environmental........................................................................................................... 6-13
Mechanical ................................................................................................................ 6-13
DAQ-Sync Connector and Pin Out........................................................................... 6-14
Main Connector and Pin Out..................................................................................... 6-14
vii
Page 8

Page 9

Preface
About this User's Guide
What you will learn from this user's guide
This user's guide explains how to install, configure, and use the PCI-DAS6052 so that
you get the most out of the analog, digital, and timing I/O features.
This user's guide also refers you to related documents available on our web site, and to
technical support resources that can also help you get the most out of these boards.
Conventions in this user's guide
For more information on …
Text presented in a box signifies additional information and helpful hints related to the
subject matter you are reading.
Caution! Shaded caution statements present information to help you avoid injuring
yourself and others, damaging your hardware, or losing your data.
<#:#>
Angle brackets that enclose numbers separated by a colon signify a range
of numbers, such those assigned to registers, bit settings, etc.
bold text Bold text is used for the names of objects on the screen, such as buttons,
text boxes, and check boxes. For example:
1. Insert the disk or CD and click the OK button.
italic text
Italic text is used for the names of manuals and help topic titles, and to
emphasize a word or phrase. For example:
The InstaCal installation procedure is explained in the Software
Installation Manual.
Never touch the exposed pins or circuit connections on the board.
ix
Page 10

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide About this User's Guide
Where to find more information
The following electronic documents provide information that can help you get the most
out of your PCI-DAS6052 board.
MCC's Guide to Signal Connections is available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/signals/signals.pdf
.
The STC Register Map for the PCI-DAS6000 Series is available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/registermaps/RegMapSTC6000.pdf.
The Specifications: PCI-DAS6052 (the PDF version of Chapter 6 in this guide) is
available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/pdfs/pci-DAS6052.pdf
.
The Universal Library User's Guide is available on our web site at
.
The Universal Library Function Reference is available on our web site at
This user's manual is also available on our web site at
.
x
Page 11

Chapter 1
Introducing the PCI-DAS6052 Series Board
Overview: PCI-DAS6052 features
This manual explains how to install and use the PCI-DAS6052 board.
The PCI-DAS6052 board has eight lines of digital I/O, and two digital-to-analog
outputs. It provides either eight differential or 16 single-ended analog inputs with 16 bit
resolution. Input ranges are either Bipolar or Unipolar. Bipolar input ranges are ±10V,
±5V, ±2.5V, ±1V, ±0.5V, ±0.25V, ±0.1V and ±0.05V. Unipolar input ranges are 0 to
10V, 0 to 5V, 0 to 2V, 0 to 1V, 0 to 0.5V, 0 to 0.2V and 0 to 0.1V. The input ranges are
software-selectable.
The board has nine user-configurable trigger/clock/gate pins that are available at a
100-pin I/O connector. Six pins are configurable as inputs and three are configurable as
outputs. Refer to Chapter 4 ("Functional Details") and Chapter 6 ("Specifications") for
more information.
The PCI-DAS6052 provides triggering and synchronization capability. There are five
trigger/strobes and a synchronizing clock provided on a 14-pin header. Refer to Chapter
2 ("Installing the Board") and Chapter 6 ("Specifications") for more information on
these signals.
Interrupts can be generated by up to seven ADC sources and four DAC sources.
Interrupt sources are listed in Chapter 6 ("Specifications").
The PCI-DAS6052 board contains an 82C54 counter chip, which consists of three 16-bit
counters. Clock, gate, and output signals from two of the three counters are available on
the 100-pin I/O connector. The third counter is used internally.
1-1
Page 12

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Introducing the PCI-DAS6052 Series Board
Software features–InstaCal and Universal Library
The optional Universal Library fully supports the PCI-DAS6052 board. The Universal
Library is a complete set of I/O libraries and drivers for all MCC boards, and for all
Windows-based languages. When using the Universal Library, you can switch boards or
even programming languages and the syntax remains constant.
1-2
Page 13

Chapter 2
Installing the Board
What is included with your board
As you unpack your board, make sure each of the items shown below is included:
Standard components
The following items should be included with your shipment:
PCI-DAS6052
InstaCal installation CD.
If you ordered the optional Universal Library, use that CD to install both InstaCal
and the Universal Library.
2-1
Page 14

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
MCC's Software Installation Manual
Optional components
If you ordered any of the following products with your board, they should be included
with your shipment.
Universal Library
Universal Library™ Data Acquisition and Control Programming Tools (also
includes InstaCal installation package)
Universal Library User's Guide and Universal Library Function Reference
Cables
C100HD50-x
C100MMS-x
2-2
Page 15
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
Signal conditioning accessories
MCC provides signal termination products for use with the PCI-DAS6052. Refer to the
"Field wiring, signal termination and conditioning
" section on page 12 for a complete
list of compatible accessory products.
If any items are missing or damaged, notify Measurement Computing Corp. immediately
by phone, fax, or e-mail:
Phone: 508-946-5100 and follow the instructions for reaching Tech Support.
Fax: 508-946-9500 to the attention of Tech Support
Email: techsupport@measurementcomputing.com
Unpacking the board
The PCI-DAS6052 boards are shipped in an antistatic container to prevent damage by an
electrostatic discharge. To avoid such damage, perform the following procedure when
unpacking and handling your board.
1.
2.
3.
Before opening the antistatic container, ground yourself with a wrist-grounding
strap or by holding onto a grounded object (such as the computer chassis).
Touch the antistatic container to the computer chassis before removing the board
from the container.
Remove the board from the container. Never touch the exposed pins or circuit
connections on the board.
Installing the software
Install the InstaCal software included with your board before you install the hardware. If
you ordered the Universal Library software, install that software instead. InstaCal is
installed at the same time as the Universal Library.
).
If you ordered the Universal Library…
If you ordered the optional Universal Library, use that CD to install both InstaCal and
the Universal Library.
2-3
Page 16

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
Installing the hardware
The PCI-DAS6052 board is completely plug-and-play. There are no switches or jumpers
to set on the board. Configuration is controlled by your system's BIOS. To install your
board, follow the steps below.
Install InstaCal before you install your board
The driver needed to run your board is installed with InstaCal. Therefore, you need to
install InstaCal before you install your board. Follow the directions for installing
InstaCal in the Software Installation Manual shipped with your board.
1.
2.
3.
Turn your computer off, open it up, and insert your board into an available PCI slot.
Close your computer and turn it on.
If you are using an operating system with support for plug-and-play (such as
Windows 95 or Windows 2000), a dialog box displays as the system loads,
indicating that new hardware has been detected.
If the information file for this board is not already loaded onto your PC, you are
prompted for the disk containing this file. The InstaCal software supplied with your
board contains this file. If required, insert the disk or CD and click
OK.
4. If your board has been powered-off for more than 10 minutes, in order for it to
achieve its rated accuracy, allow your computer to warm up for at least 15 minutes
before acquiring data with this board. The high speed components used on the board
generates heat, and it takes this amount of time for a board to reach steady state if it
has been powered off for a significant amount of time.
2-4
Page 17

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
Configuring the hardware
All hardware configuration options on the PCI-DAS6052 are software controlled. You
can select some of the configuration options using InstaCal, such as the analog input
configuration (16 single-ended or eight differential channels), the edge used for
triggering when using an external pacer, and the source for the two independent
counters. Once selected, any program that uses the Universal Library will initialize the
hardware according to these selections.
Following is an overview of the available hardware configuration options for this board.
There is additional general information regarding analog signal connection and
configuration in the Guide to Signal Connections (available on our web site at
http://www.measurementcomputing.com/signals/signals.pdf
).
Differential input mode
When all channels are configured for differential input mode, eight analog input
channels are available. In this mode, the input signal is measured with respect to the low
input. The input signal is delivered through three wires:
The wire carrying the signal to be measured connects to CH# IN HI.
The wire carrying the reference signal connects to CH# IN LO.
The third wire is connected to LLGND.
Differential input mode is the preferred configuration for applications in noisy
environments, or when the signal source is referenced to a potential other than PC
ground.
Single-ended input mode
When all channels are configured for single-ended input mode, 16 analog input channels
are available. In this mode, the input signal is referenced to the board’s signal ground
(LLGND). The input signal is delivered through two wires:
The wire carrying the signal to be measured connects to CH# IN HI.
The other wire is connected to LLGND.
2-5
Page 18

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
Non-referenced single-ended input mode
This mode is a compromise between differential and single-ended modes. It offers some
of the advantages of each mode. Using non-referenced single-ended mode, you can still
get noise rejection, but not the limitation in the number of channels resulting from a
fully differential configuration. The possible downside is that the external reference
input must be the same for every channel. It is equivalent to configuring the inputs for
differential mode and then tying all of the low inputs together and using that node as the
reference input.
When configured for non-referenced single-ended input mode, 16 analog input channels
are available. In this mode, each input signal is not referenced to the board’s ground, but
to a common reference signal (AISENSE). The input signal is delivered through three
wires:
The wire carrying the signal to measure connects to CH# IN HI.
The wire carrying the reference signal connects to AISENSE.
The third wire is connected to LLGND.
This mode is useful when the application calls for differential input mode but the
limitation on channel count prevents it.
DAQ-Sync configuration
Multiple boards in the PCI-DAS6000 series may be interconnected to synchronize data
acquisition or data output. To do this, order and install a CDS-14-x cable at the
DAQ-Sync connectors (P2) between the boards to be synchronized.
The “x” in the CDS-14-x part number identifies the number of connectors available on
the cable and therefore, the number of boards that may be interconnected. Using a
CDS-14-2, two PCI-DAS6000 series boards may be connected together for I/O
synchronization. Using a CDS-14-3, three boards may be synchronized and so on up to
five PCI-DAS6000 series boards. A CDS-14-3 cable is shown in Fi on
page 2-11.
gure 2-3
By default, all DAQ-Sync connectors are configured as inputs (slave mode). In order to
be useful, one board must be set through software to serve as the master and the signal
sources of the slave boards must be defined. Detailed information regarding software
configuration of these functions is available in the STC Register Map for the PCI-DAS
6000 Series. This document is available from our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/registermaps/RegMapSTC6000.pdf
.
2-6
Page 19

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
Connecting the board for I/O operations
Connectors, cables – main I/O connector
Table 2-1
Table 2-1. Board Connectors, Cables, Accessory Equipment
lists the board connectors, applicable cables and compatible accessory boards
that can be used with the PCI-DAS6052 board.
Connector type Shielded SCSI 100 D-Type
C100HD50-x, unshielded ribbon cable. x = 3 or 6 feet
Compatible Cables
C100MMS-x, shielded round cable. x = 1, 2, or 3 meters
Compatible accessory products
(with C100HD50-x cable)
ISO-RACK16/P
ISO-DA02/P
BNC-16SE
BNC-16DI
CIO-MINI50
CIO-TERM100
SCB-50
Compatible accessory products
(with C100MMS-x cable)
SCB-100
2-7
Page 20

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
GND 100
•
•
50 GND
CTR2 OUT 99
•
•
49 AUXIN5 / A/D PACER GATE
CTR2 GATE 98
•
•
48 AUXIN4 / D/A START TRIGGER
CTR2 CLK 97
•
•
47 AUXIN3 / D/A UPDATE
GND 96
•
•
46 AUXIN2 / A/D STOP TRIGGER
CTR1 OUT 95
•
•
45 AUXIN1 / A/D START TRIGGER
CTR1 GATE 94
•
•
44 D/A EXTREF
CTR1 CLK 93
•
•
43 AUXIN0 / A/D CONVERT / ATRIG
DIO7 92
•
•
42 AUXOUT2 / SCANCLK
DIO6 91
•
•
41 AUXOUT1 / A/D PACER OUT
DIO5 90
•
•
40 AUXOUT0 / D/A PACER OUT
DIO4 89
•
•
39 PC +5 V
DIO3 88
•
•
38 D/A OUT1
DIO2 87
•
•
37 D/A GND
DIO1 86
•
•
36 D/A OUT 0
DIO0 85
•
•
35 AISENSE
n/c 84
•
•
34 n/c
n/c 83
•
•
33 n/c
n/c 82
•
•
32 n/c
n/c 81
•
•
31 n/c
n/c 80
•
•
30 n/c
n/c 79
•
•
29 n/c
n/c 78
•
•
28 n/c
n/c 77
•
•
27 n/c
n/c 76
•
•
26 n/c
n/c 75
•
•
25 n/c
n/c 74
•
•
24 n/c
n/c 73
•
•
23 n/c
n/c 72
•
•
22 n/c
n/c 71
•
•
21 n/c
n/c 70
•
•
20 n/c
n/c 69
•
•
19 n/c
n/c 68
•
•
18 LLGND
n/c 67
•
•
17 CH7 IN LO
n/c 66
•
•
16 CH7 IN HI
n/c 65
•
•
15 CH6 IN LO
n/c 64
•
•
14 CH6 IN HI
n/c 63
•
•
13 CH5 IN LO
n/c 62
•
•
12 CH5 IN HI
n/c 61
•
•
11 CH4 IN LO
n/c 60
•
•
10 CH4 IN HI
n/c 59
•
•
9 CH3 IN LO
n/c 58
•
•
8 CH3 IN HI
n/c 57
•
•
7 CH2 IN LO
n/c 56
•
•
6 CH2 IN HI
n/c 55
•
•
5 CH1 IN LO
n/c 54
•
•
4 CH1 IN HI
n/c 53
•
•
3 CH0 IN LO
n/c 52
•
•
2 CH0 IN HI
Pinout –
main I/O
connector
Table 2-2.
8-channel
differential mode
n/c 51
•
•
1 LLGND
PCI slot
↓
2-8
Page 21

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
Signal Name Pin Pin Signal Name
GND 100
•
•
50 GND
CTR2 OUT 99
•
•
49 AUXIN5 / A/D PACER GATE
CTR2 GATE 98
•
•
48 AUXIN4 / D/A START TRIGGER
CTR2 CLK 97
•
•
47 AUXIN3 / D/A UPDATE
GND 96
•
•
46 AUXIN2 / A/D STOP TRIGGER
CTR1 OUT 95
•
•
45 AUXIN1 / A/D START TRIGGER
CTR1 GATE 94
•
•
44 D/A EXTREF
CTR1 CLK 93
•
•
43 AUXIN0 / A/D CONVERT / ATRIG
DIO7 92
•
•
42 AUXOUT2 / SCANCLK
DIO6 91
•
•
41 AUXOUT1 / A/D PACER OUT
DIO5 90
•
•
40 AUXOUT0 / D/A PACER OUT
DIO4 89
•
•
39 PC +5 V
DIO3 88
•
•
38 D/A OUT1
DIO2 87
•
•
37 D/A GND
DIO1 86
•
•
36 D/A OUT 0
DIO0 85
•
•
35 AISENSE
n/c 84
•
•
34 n/c
n/c 83
•
•
33 n/c
n/c 82
•
•
32 n/c
n/c 81
•
•
31 n/c
n/c 80
•
•
30 n/c
n/c 79
•
•
29 n/c
n/c 78
•
•
28 n/c
n/c 77
•
•
27 n/c
n/c 76
•
•
26 n/c
n/c 75
•
•
25 n/c
n/c 74
•
•
24 n/c
n/c 73
•
•
23 n/c
n/c 72
•
•
22 n/c
n/c 71
•
•
21 n/c
n/c 70
•
•
20 n/c
n/c 69
•
•
19 n/c
n/c 68
•
•
18 LLGND
n/c 67
•
•
17 CH15 IN
n/c 66
•
•
16 CH7 IN
n/c 65
•
•
15 CH14 IN
n/c 64
•
•
14 CH6 IN
n/c 63
•
•
13 CH13 IN
n/c 62
•
•
12 CH5 IN
n/c 61
•
•
11 CH12 IN
n/c 60
•
•
10 CH4 IN
n/c 59
•
•
9 CH11 IN
n/c 58
•
•
8 CH3 IN
n/c 57
•
•
7 CH10 IN
n/c 56
•
•
6 CH2 IN
n/c 55
•
•
5 CH9 IN
n/c 54
•
•
4 CH1 IN
n/c 53
•
•
3 CH8 IN
n/c 52
•
•
2 CH0 IN
Table 2-3.
16-Channel
Single-Ended
Mode
n/c 51
•
•
1 LLGND
PCI slot ↓
2-9
Page 22

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
Cabling – main I/O connector
1
50
2
49
51
100
52
99
10050
511
Strain relief is
stamped “Pins 1-50”.
Pins 1-50 are on the long side
of the “D” connector.
Pins 51-100 are on
the short side of
the “D” connector.
Key
Key
The red stripe
identifies pin # 1
The red stripe
identifies pin # 51
Strain relief is
Stamped “Pins 51-100”.
Figure 2-1. C100HD50-x Cable Connections
Details on the C100HD50-x cable are available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=104&pf_id=1203.
10050
511
10050
511
Figure 2-2. C100MMS-x Cable
Details on the C100MMS-x cable are available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=104&pf_id=1514.
2-10
Page 23

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
DAQ-Sync Connector and Pinout
Table 2- 4. DAQ-Sync Connector and cable types
Connector type 14-pin right-angle 100 mil box header
Compatible cable
MCC p/n: CDS-14-x, 14 pin ribbon cable for board-to board DAQ-Sync
connection; x = number of boards (Figure 2-3 shows a CDS-14-3 cable)
Table 2-5. DAQ-sync connector pinout (view from top)
Signal Name
Pin Pin Signal Name
DS A/D STOP TRIGGER 3 ■ ■ 4GND
DS A/D CONVERT 5 ■ ■ 6GND
DS D/A UPDATE 7 ■ ■ 8GND
DS D/A START TRIGGER 9 ■ ■ 10 GND
RESERVED 11 ■ ■ 12 GND
SYNC CLK 13
■ ■
14 GND
14-pin Ribbon Cable
The red stripe
identifies pin # 1
14
2
1
13
14
2
1
13
14
2
1
13
Figure 2-3. CDS-14-3 cable
Details on the CDS-14-x cable are available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=104&pf_id=1528.
2-11
Page 24

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Installing the Board
Field wiring, signal termination and conditioning
You can use the following BNC and screw terminal boards to terminate field signals and
route them into the PCI-DAS6052 using the C100HD50-x cable:
BNC-16SE – Brings analog signals to standard BNC connectors. Designed for
boards operating in single-ended mode. Details on this product are available on our
web site at www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=101&pf_id=713.
BNC-16DI – Brings analog signals to standard BNC connectors. Designed for
boards operating in differential mode. Details on this product are available on our
web site at www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=101&pf_id=714
.
CIO-MINI50 – 50-pin screw terminal board. Two boards are required. Details on
this product are available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=102&pf_id=258
.
CIO-TERM100 – 100-pin screw terminal board (daisy-chained 50-pin IDC
connectors). Details on this product are available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=102&pf_id=281.
SCB-50 – 50 conductor, shielded signal connection/screw terminal box provides
two independent 50-pin connections. Details on this product are available on our
web site at www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=196&pf_id=1168.
You can use the following screw terminal box to terminate field signals and route them
into the PCI-DAS6052 board using the C100MMS-x cable:
SCB-100 – 100 conductor, shielded signal connection/screw terminal box provides
two independent 50-pin connections. Details on this product are available on our
web site at www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=196&pf_id=1169
Analog signal conditioning and expansion
You can use the following signal conditioning accessory products with the C100HD50-x
cable:
ISO-RACK-16/P – 16-channel ISO-5B module rack for connecting an ISO-5B
module to an analog input. Details on this product are available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=127&pf_id=1111
.
ISO-RACK-DA02/P – 2-channel, 5B module rack for 50-pin DA02 & 100-pin
series, detachable terminals are available. Details are available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/cbicatalog/cbiproduct.asp?dept_id=128&pf_id=711
.
2-12
Page 25

Chapter 3
Programming and Developing Applications
After following the installation instructions in Chapter 2, your board should now be
installed and ready for use. Although the board is part of the larger DAS family, in
general there may be no correspondence among registers for different boards1. Software
written at the register level for other DAS models will not function correctly with your
board.
Programming languages
Measurement Computing’s Universal Library® provides access to board functions from
a variety of Windows programming languages. If you are planning to write programs, or
would like to run the example programs for Visual Basic
or any other language, please
refer to the Universal Library User's Guide (available on our web site at
Packaged applications programs
Many packaged application programs, such as SoftWIRE, Labtech Notebook™, and
HP-VEE™, now have drivers for your board. If the package you own does not have
drivers for the board, please fax or e-mail the package name and the revision number
from the install disks. We will research the package for you and advise how to obtain
drivers.
Some application drivers are included with the Universal Library package, but not with
the application package. If you have purchased an application package directly from the
software vendor, you may need to purchase our Universal Library and drivers. Please
contact us by phone, fax or e-mail:
Phone: 508-946-5100 and follow the instructions for reaching Tech Support.
Fax: 508-946-9500 to the attention of Tech Support
Email: techsupport@measurementcomputing.com
1
An exception to this is the DAQ Sync capability of these boards that permit synchronized data
acquisition by multiple boards in this series.
3-1
Page 26

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Programming and Developing Applications
Register-level programming
You should use the Universal Library or one of the packaged application programs
mentioned above to control your board. Only experienced programmers should try
register-level programming. If you need to program at the register level in your
application, refer to the STC Register Map for the PCI-DAS6000 Series (available at
http://www.measurementcomputing.com/registermaps/RegMapSTC6000.pdf
).
3-2
Page 27

Chapter 4
Functional Details
Basic architecture
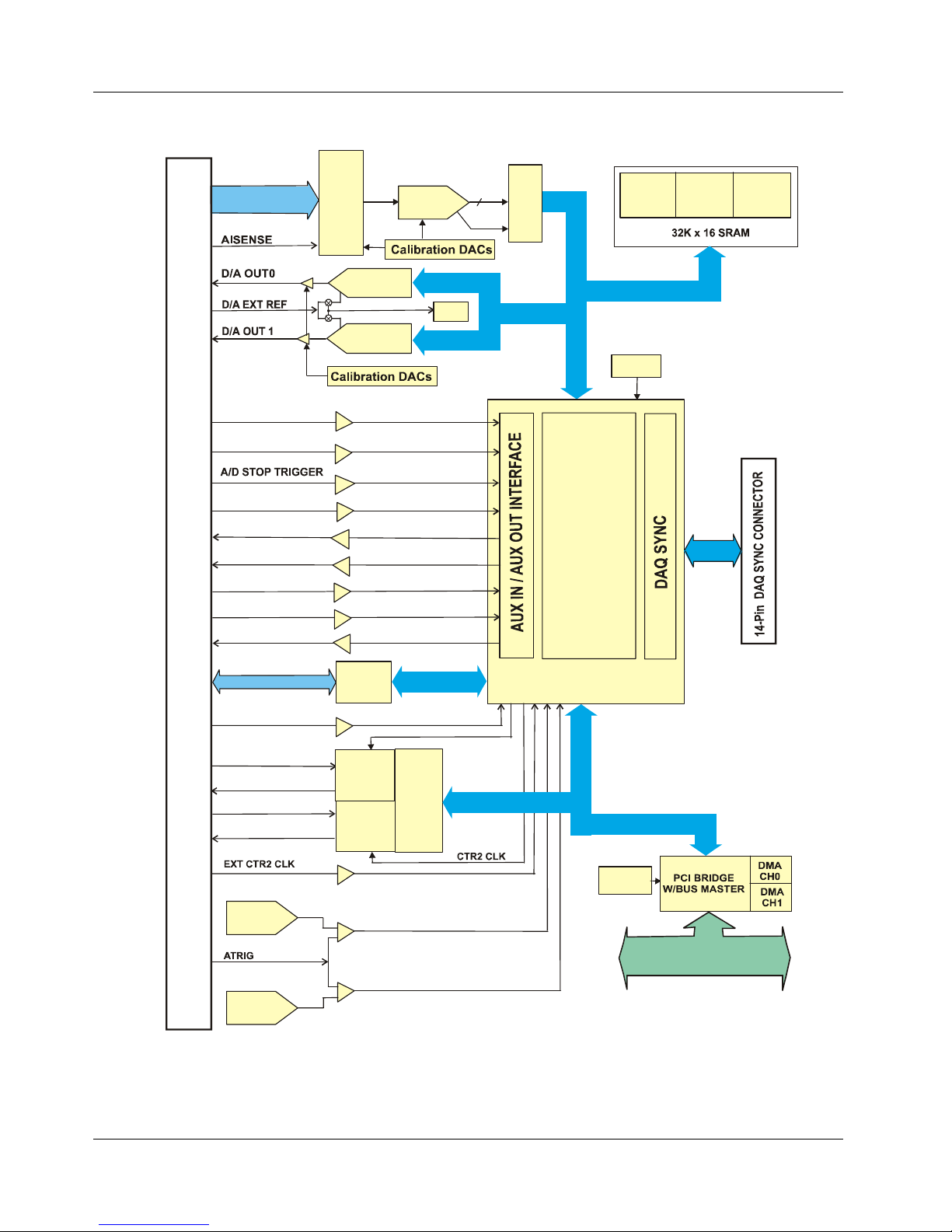
Figure 4-1 on page 4-4 is a simplified block diagram of the PCI-DAS6052. This board
provides all of the functional elements shown in the figure.
The System Timing and Control (STC) is the logical center for all DAQ, DIO, and DAC
(if applicable) operations. It communicates over two major busses: a local bus and a
memory bus.
The local bus carries digital I/O data and software commands from the PCI Bus Master.
There are two Direct Memory Access (DMA) channels provided for data transfers to the
PC.
Primarily, the memory bus carries A/D and D/A related data and commands. There are
three buffer memories provided on the memory bus:
The queue buffer (8K configuration memory) stores programmed channel numbers,
gains, and offsets.
The ADC buffer (8K FIFO [First In, First Out]) temporarily stores scanned and
converted analog inputs.
The DAC 16K buffer stores data to be output as analog waveforms.
Auxiliary input & output interface
The board's 100-pin I/O connector provides six software-selectable inputs, and three
software-selectable outputs. The signals are user-configurable clocks, triggers and gates.
Refer to the "DAQ signal timing
" on page 4-5 for information about these signals and
their timing requirements.
Table 4-1 lists all of the possible signals and the default signals you use on the nine pins.
4-1
Page 28

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
Table 4-1. Auxiliary I/O Signals
I/O Type Signal Name Function
A/D CONVERT External ADC Convert Strobe (default)
A/D TIMEBASE IN External ADC Pacer Time Base
A/D START TRIGGER ADC Start Trigger (default)
A/D STOP TRIGGER ADC Stop Trigger (default)
A/D PACER GATE External ADC Gate (default)
D/A START TRIGGER DAC Trigger/Gate (default)
D/A UPDATE DAC Update Strobe (default)
AUXIN<5:0>
Sources
(SW selectable)
D/A TIMEBASE IN External DAC Pacer Time Base
STARTSCAN A pulse indicating the start of conversion.
SSH
An active signal that terminates at the start of the
last conversion in a scan.
A/D STOP Indicates the end of a scan
A/D CONVERT ADC convert pulse (default)
SCANCLK Delayed version of ADC convert (default)
CTR1 CLK CTR1 clock source
D/A UPDATE D/A update pulse (default)
CTR2 CLK CTR2 clock source
A/D START TRIGGER ADC Start Trigger Out
A/D STOP TRIGGER ADC Stop Trigger Out
A/D PACER GATE External ADC gate
AUXOUT<2:0>
Sources
(SW selectable)
D/A START TRIGGER DAC Start Trigger Out
AUXIN0: A/D CONVERT
AUXIN1: A/D START TRIGGER
AUXIN2: A/D STOP TRIGGER
AUXIN3: D/A UPDATE
AUXIN4: D/A START TRIGGER
AUXIN5: A/D PACER GATE
AUXOUT0: D/A UPDATE
AUXOUT1: A/D CONVERT
Default
Selections
Summary
AUXOUT2: SCANCLK
4-2
Page 29
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
DAQ-Sync signals
The DAQ-Sync hardware provides the capability of triggering or clocking up to four
slave boards from a master board to synchronize data input and/or output.
The PCI-DAS6052 board provides the capability of inter-board synchronization between
boards in the PCI-DAS6000 family. There are five trigger/strobes and a synchronizing
clock provided on a 14-pin header. lists the available signals. Table 4-2
Table 4-2. DAQ-Sync Signals
DS A/D START TRIGGER
DS A/D STOP TRIGGER
DS A/D CONVERT
DS D/A UPDATE
DS D/A START TRIGGER
SYNC CLK
Except for the SYNC CLK signal, the DAQ-Sync timing and control signals are a subset
of the AUXIO signals available at the 100-pin I/O connector. These versions of the
signals are used for board-to-board synchronization and have the same timing
specifications as their I/O connector counterparts. Refer to "DAQ signal timing" on
page 4-5 for explanations of signals and timing.
Use the SYNC CLCK signal to determine the master/slave configuration of a
DAQ-Sync-enabled system. Each system can have one master and up to three slaves.
SYNC CLK is the 40 MHz time-base used to derive all board timing and control. The
master provides this clock to the slave boards so that all boards in the DAQ-syncenabled system are timed from the same clock.
4-3
Page 30
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
MEMORY BUS
ADC
16-BIT
Mux
&
Gain
Analog In
16 CH S-E or
8 CH DIFF.
DQ
EOC
16
HOLDING
REGISTER
40 MHz
A/D PACER OUT
SCANCLK
D/A PACER OUT
A/D CONVERT
A/D START TRIGGER
D/A UPDATE
D/A START TRIGGER
A/D PACER GATE
LOCAL BUS
PCI BUS (5V, 32-BIT, 33 MHZ)
Boot
EEPROM
EXT CTR1 CLK
CTR1 CLK
USER
COUNTER
2
C
ontrol
82C54
USER
COUNTER
1
CTR2 GATE
CTR1 GATE
CTR2 OUT
CTR1 OUT
DIO
8-BIT
DIO (7:
0
)
DAC1
16-BIT
DAC0
16-BIT
DAC
Buffer
(16K)
Queue
Buffer
(8K)
ADC
Buffer
(8K)
1
0
0
-
P
i
n
I
/
O
C
O
N
N
E
C
T
O
R
SYSTEM
TIMING
&
CONTROL
STC
THRESH-HI
12-BIT
THRESH-LO
12-BIT
REF.
Figure 4-1. Block Diagram – PCI-DAS6052
4-4
Page 31
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
DAQ signal timing
The DAQ timing signals are:
SCANCLK
A/D START TRIGGER
A/D STOP TRIGGER
STARTSCAN
SSH
A/D CONVERT
A/D PACER GATE
A/D EXTERNAL TIME BASE
A/D STOP
ATRIG
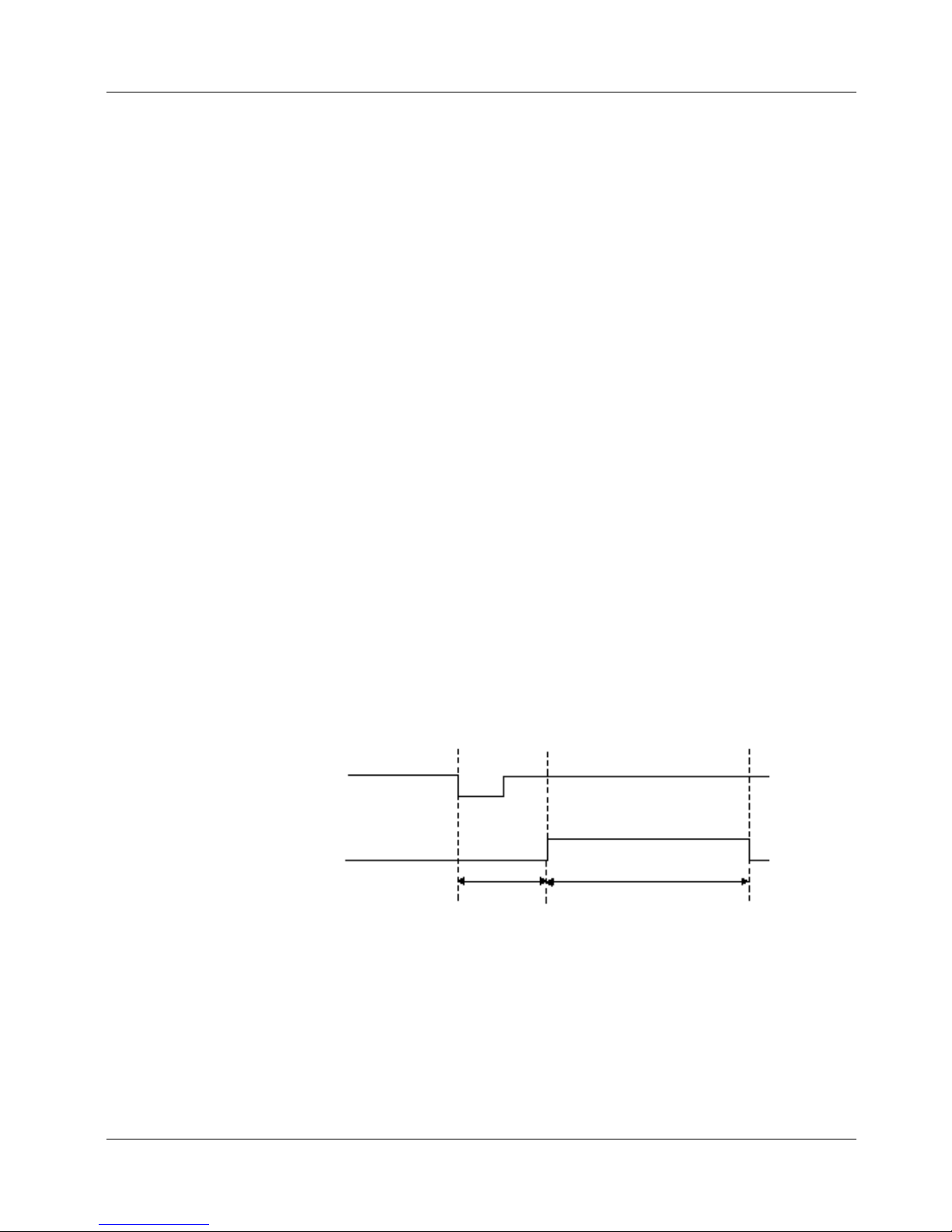
SCANCLK signal
SCANCLK is an output signal that may be used for switching external multiplexers. It is
a 400 ns wide pulse that follows the CONVERT signal after a 50 ns delay. This is
adequate time for the analog input signal to be acquired so that the next signal may be
switched in. The polarity of the SCANCLK signal is programmable. The default output
pin for the SCANCLK signal is AUXOUT2, but any of the AUXOUT pins may be
programmed as a SCANCLK output.
CONVERT
SCANCLK
tdt
d
t
w
td = 50 ns tw = 400 ns
Figure 4-2. SCANCLK Signal Timing
4-5
Page 32

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
A/D START TRIGGER signal
Use the A/D START TRIGGER signal for conventional triggering (when you only need
to acquire data after a trigger event). shows the A/D START TRIGGER
signal timing for a conventionally triggered acquisition.
Figure 4-3
Figure 4-3. Data Acquisition Example for Conventional Triggering
A/D Start Trigger
Start Scan
Convert
12340Scan Counter
The A/D START TRIGGER source is programmable and may be set to any of the
AUXIN inputs or to the DAQ-Sync DS A/D START TRIGGER input. The polarity of
this signal is also programmable to trigger acquisitions on either the positive or negative
edge.
The A/D START TRIGGER signal is also available as an output and can be
programmed to appear at any of the AUXOUT outputs. See and
for A/D START TRIGGER input and output timing requirements.
Figure 4-4
Figure 4-4. A/D START TRIGGER Input Signal Timing
Figure 4-5
Figure 4-5. A/D START TRIGGER Output Signal Timing
Rising Edge Polarity
t
w
tw = 37.5 ns minimum
Falling Edge Polarity
t
w
tw = 50 ns
4-6
Page 33

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
The A/D START TRIGGER signal is also used to initiate pre-triggered DAQ operations
(when you need to acquire data just before a trigger event). In most pre-triggered
applications, the A/D START TRIGGER signal is generated by a software trigger. The
use of A/D START TRIGGER and A/D STOP TRIGGER in pre-triggered DAQ
applications is explained next.
A/D STOP TRIGGER signal
Pre-triggered data acquisition continually acquires data into a circular buffer until a
specified number of samples have been collected after the trigger event.
illustrates a typical pre-triggered DAQ sequence.
Figure 4-6
Figure 4-6. Pre-triggered Data Acquisition Example
A/D Start Trigger
Start Scan
Convert
3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0 3 2 1
A/D Stop Trigger
Scan Counter
Don't care
The A/D STOP TRIGGER signal signifies when the circular buffer should stop and
when the specified number of post trigger samples should be acquired. It is available as
an output and an input. By default, it is available at AUXIN2 as an input but may be
programmed for access at any of the AUXIN pins or the DAQ-Sync “DS A/D STOP
TRIGGER” input. It may be programmed for access at any of the AUXOUT pins as an
output.
When using the A/D STOP TRIGGER signal as an input, the polarity may be configured
for either rising or falling edge. The selected edge of the A/D STOP TRIGGER signal
initiates the post-triggered phase of a pre-triggered acquisition sequence.
As an output, the A/D STOP TRIGGER signal indicates the event separating the
pre-trigger data from the post-trigger data. The output is an active high pulse with a
pulse width of 50 ns. and show the input and output timing
requirements for the A/D STOP TRIGGER signal.
Figure 4-7 Figure 4-8
4-7
Page 34

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
Rising Edge Polarity
t
w
tw = 37.5 ns minimum
Falling Edge Polarity
Figure 4-7. A/D STOP TRIGGER Input Signal Timing
t
w
tw = 50 ns
Figure 4-8. A/D STOP TRIGGER Output Signal Timing
STARTSCAN signal
The STARTSCAN output signal indicates when a scan of channels has been initiated.
You can program this signal to be available at any of the AUXOUT pins. The
STARTSCAN output signal is a 50 ns wide pulse the leading edge of which indicates
the start of a channel scan.
t
w
tw = 50 ns
Figure 4-9. STARTSCAN Start of Scan Timing
4-8
Page 35

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
SSH signal
The SSH signal can be used as a control signal for external sample/hold circuits. The
SSH signal is a programmable polarity pulse that is asserted throughout a channel scan.
The state of this signal changes after the start of the last conversion in the scan. The SSH
signal may be routed via software selection to any of the AUXOUT pins.
shows the timing for the SSH signal.
Figure 4-10
Figure 4-10. SSH Signal Timing
Start Pulse
t
off
= 10 ns minimum
CONVERT
SSH
t
off
A/D CONVERT signal
The A/D CONVERT signal indicates the start of an A/D conversion. It is available
through software selection as an input to any of the AUXIN pins (defaulting to
AUXIN0) or the DAQ-Sync DS A/D CONVERT input and as an output to any of the
AUXOUT pins.
When used as an input, the polarity is software selectable. The A/D CONVERT signal
starts an acquisition on the selected edge. The convert pulses must be separated by a
minimum of 5 µs to remain within the 200 kS/s conversion rate specification.
Refer to (page 4-6) and (page 4-7) for the relationship of
A/D CONVERT to the DAQ sequence. and show the input and
output pulse width requirements for the A/D CONVERT signal.
Figure 4-3 Figure 4-6
Figure 4-11 Figure 4-12
4-9
Page 36

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
Rising Edge Polarity
t
tw = 37.5 ns minimum
Falling Edge Polarity
Figure 4-11. A/D CONVERT Signal Input Timing Requirement
tw = 50 ns
t
w
Figure 4-12. A/D CONVERT Signal Output Timing Requirement
The A/D CONVERT signal is generated by the on-board pacer circuit unless the
external clock option is in use. This signal may be gated by hardware (A/D PACER
GATE) or software.
A/D PACER GATE signal
The A/D PACER GATE signal is used to disable scans temporarily. This signal may be
programmed for input at any of the AUXIN pins.
If the A/D PACER GATE signal is active, no scans can occur. If the A/D PACER
GATE signal becomes active during a scan in progress, the current scan is completed
and scans are then held off until the gate is de-asserted.
A/D EXTERNAL TIME BASE signal
The A/D EXTERNAL TIME BASE signal can serve as the source for the on-board
pacer circuit rather than using the 40 MHz internal time base. Any AUXIN pin can be
set programmatically as the source for this signal. The polarity is programmable.
The maximum frequency for the A/D EXTERNAL TIME BASE signal is 20 MHz. The
minimum pulse width is 23 ns high or low. There is no minimum frequency
specification.
Figure 4-13 shows the timing specifications for the A/D EXTERNAL TIME BASE
signal.
4-10
Page 37

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
t
w
tw =23 ns minimum
t
p
t
w
tp =50 ns minimum
Figure 4-13. A/D EXTERNAL TIME BASE Signal Timing
A/D STOP signal
The A/D STOP signal indicates a completed acquisition sequence. You can program this
signal to be available at any of the AUXOUT pins. The A/D STOP output signal is a
50 ns wide pulse whose leading edge indicates a DAQ done condition.
t
w
tw = 50 ns
Figure 4-14. A/D STOP Signal Timing
4-11
Page 38

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
ATRIG signal
In addition to standard digital trigger features, the PCI-DAS6052 also provides analog
triggering capability. When using the analog trigger, acquisitions may be started and
controlled via an analog signal. There are four trigger/gate modes available using the
analog trigger feature:
Trigger – positive or negative slope.
Gate – above reference or below reference.
Hysteresis – positive or negative hysteresis.
Window – inside or outside window.
The Trigger mode is used to start an acquisition sequence. The remaining modes provide
gating functions during an acquisition sequence which start and stop the acquisition
based on the gate condition.
There are two possible inputs for the analog trigger source. The first is the
AUXIN0/ATRIG pin on the 100-pin I/O connector. This is a software selectable
dual-purpose pin that supports either digital or analog trigger inputs. The source
selection defaults to analog trigger on power-up and may be modified at any time using
InstaCal. The input range on the ATRIG pin is always ±10V. 12-bit DACs are used to
set the HI and LO levels for the threshold(s). The threshold resolution in this mode is
4.88mV per step.
Caution! Remove all analog inputs before configuring this pin as a digital input. Any
voltage levels above ±15V in this configuration may cause damage to the product!
The post-gain version of any one of the 16 analog inputs may also be used as the analog
trigger source. In this mode, the voltage present on the first channel in the scan may be
used initiate the acquisition sequence.
Since the input to the analog trigger circuit has been scaled by the selected range, the
effective resolution of the thresholds is equal to the A/D's full-scale-range (±2.5V)
divided by 4096. For example, the ±2.5V range allows for 5V/4096, or 1.2 mV of
threshold resolution.
The following is a detailed description of each mode of operation. In each case a ±2V
triangle waveform is used as the ATRIG input source. The THRESH_HI is set to 1.0V
and the THRESH_LO signal is set to -1.0V.
In the following analog trigger signal diagrams, the bold portion of the waveform
indicates the data acquired for the given ATRIG mode.
4-12
Page 39

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
Trigger Above
The acquisition will begin when the ATRIG signal first goes above the THRESH_HI.
This mode is non-retriggerable.
Thresh_HI
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Trigger
Acquired Data
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Figure 4-15. Trigger Positive Slope
4-13
Page 40

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
Trigger Below
The acquisition will begin when ATRIG signal fist goes below the THRESH_LO level.
This mode is non-retriggerable.
Thresh_LO
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Trigger
Acquired Data
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Figure 4-16. Trigger Negative Slope
4-14
Page 41

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
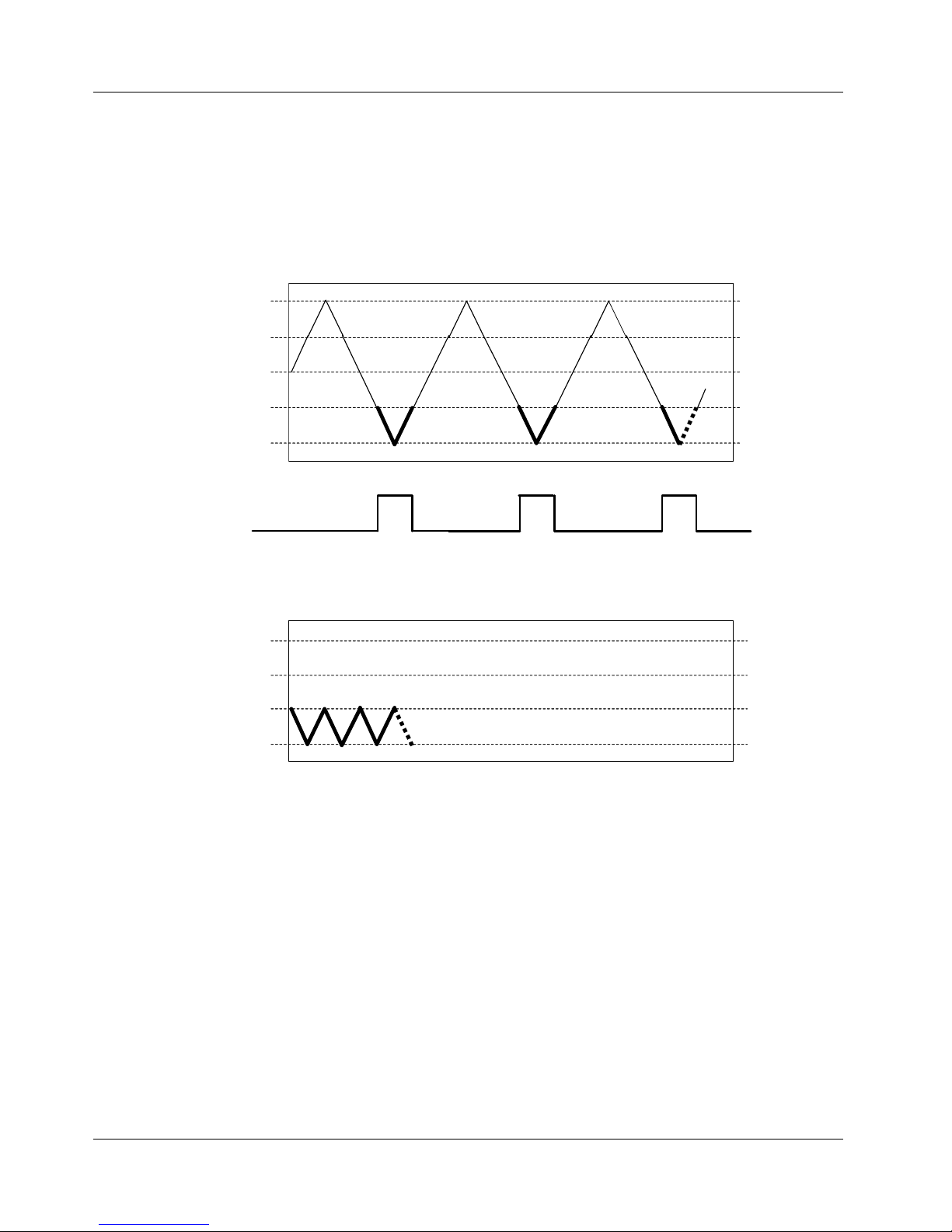
Gate Above
Data acquisition is enabled whenever ATRIG goes above the THRESH_HI level.
Acquisition is suspended whenever the ATRIG signal goes below the THRESH_HI
level. This is a level-sensitive gating mode.
Trigger
Result
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Thresh_HI
+2
+1
0
-1
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Figure 4-17. Gate Above
4-15
Page 42
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
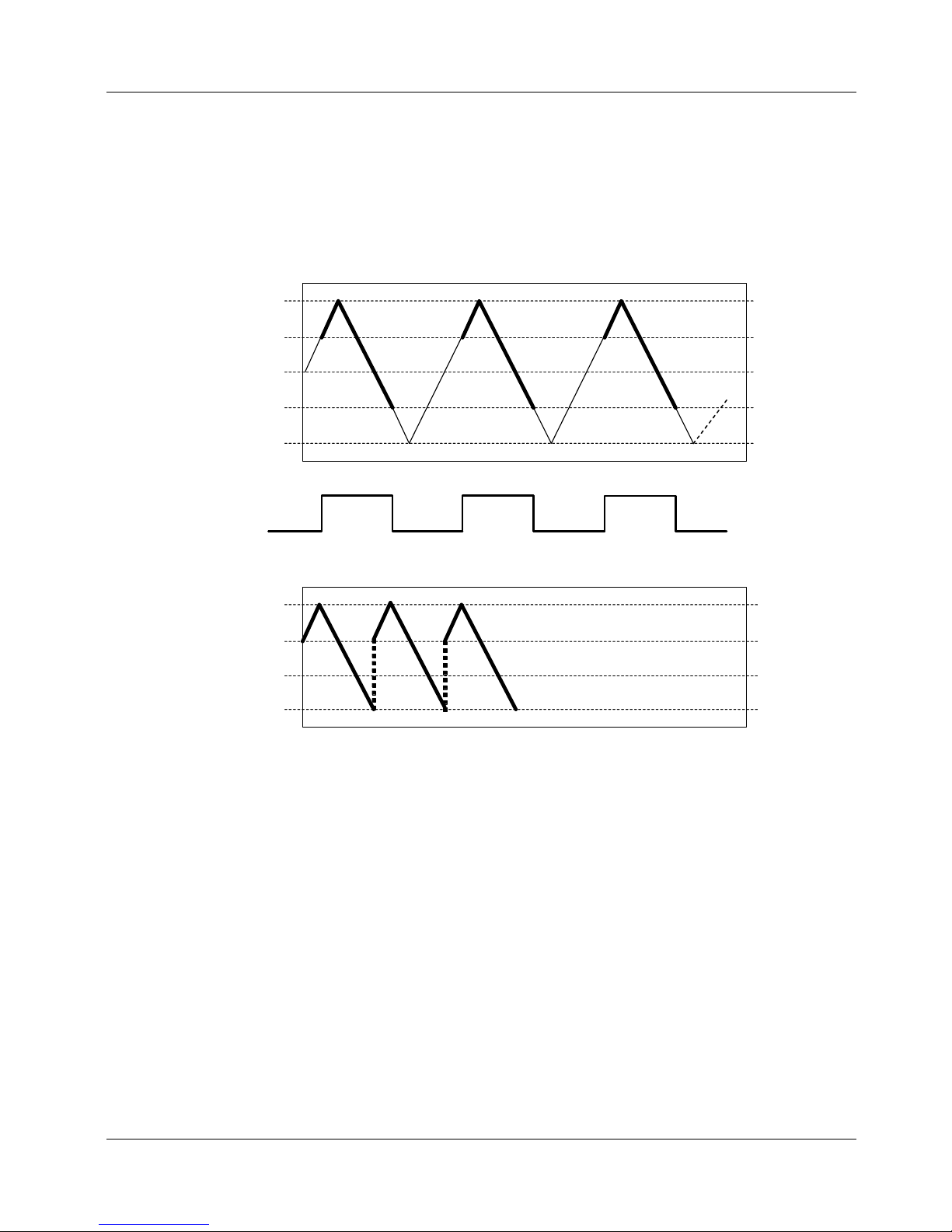
Gate Below
Data acquisition is enabled whenever ATRIG goes below the THRESH_LO level.
Acquisition is suspended whenever the ATRIG signal goes above the THRESH_LO
level. This is a level-sensitive gating mode.
Trigger
Acquired Data
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Thresh_LO
+1
0
-1
-2
Figure 4-18. Gate Below
4-16
Page 43
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
Gate Negative Hysteresis
Data acquisition is enabled whenever ATRIG goes above the THRESH_HI level.
Acquisition is suspended whenever the ATRIG signal goes below the THRESH_LO
level. The hysteresis level is set by THRESH_LO. This is a level-sensitive gating mode.
Trigger
Acquired Data
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Thresh_HI
+2
+1
0
-1
Thresh_LO
Figure 4-19. Gate Negative Hysteresis
4-17
Page 44

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
Gate Positive Hysteresis
Data acquisition is enabled whenever ATRIG goes below the THRESH_LO level.
Acquisition is suspended whenever the ATRIG signal goes above the THRESH_HI
level. The hysteresis level is set by THRESH_HI. This is a level-sensitive gating mode.
Trigger
Acquired Data
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Thresh_HI
Thresh_LO
+2
+1
0
-1
-2
Figure 4-20. Gate Positive Hysteresis
4-18
Page 45

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
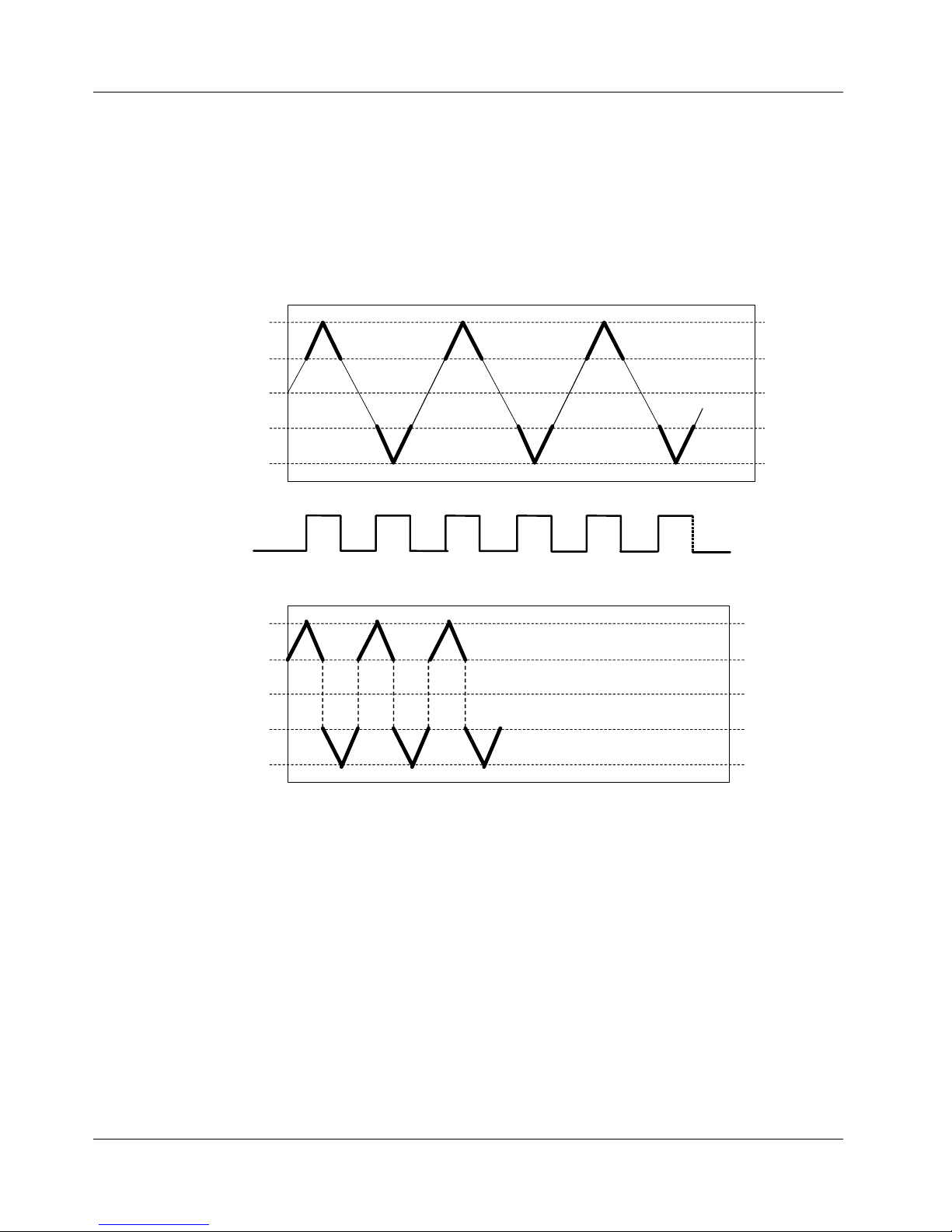
Gate Inside Window
Data acquisition is enabled whenever ATRIG is below the THRESH_HI level and above
the THRESH_LO level. Acquisition is suspended whenever the ATRIG signal is outside
of this region. This is a level-sensitive gating mode
Thresh_HI
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Trigger
Acquired Data
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Thresh_LO
Figure 4-21. Gate Inside Window
4-19
Page 46
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
Gate Outside Window
Data acquisition is enabled whenever ATRIG is above the THRESH_HI level or below
the THRESH_LO level. Acquisition is suspended whenever the ATRIG signal is
between the THRESH_HI and THRESH_LO levels. This is a level-sensitive gating
mode
Thresh_HI
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Trigger
Acquired Data
+2
-2
+1
0
-1
Thresh_LO
Figure 4-22. Gate Inside Window
4-20
Page 47
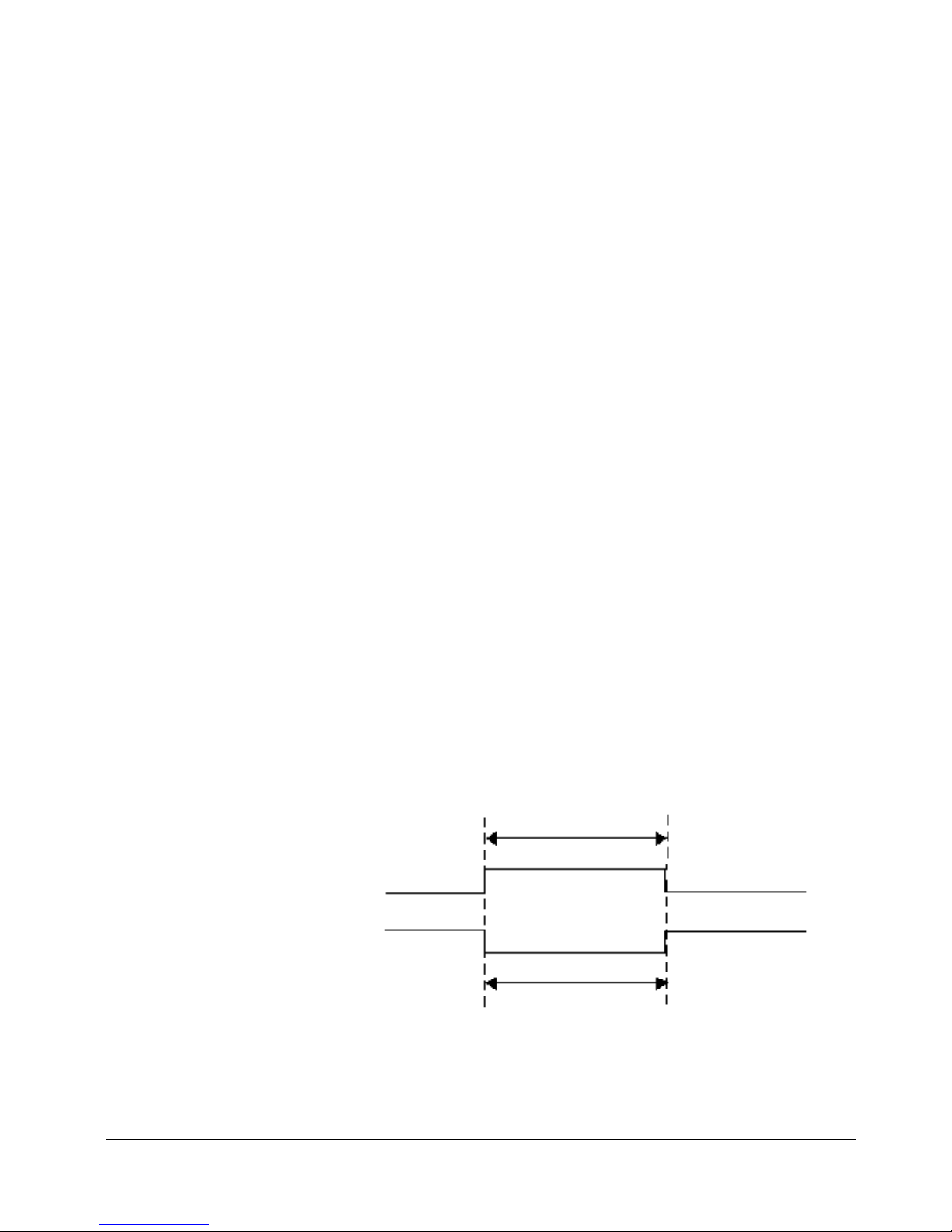
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
Waveform generation timing signals
The signals that control the timing for the analog output functions on the PCI-DAS6052
are:
D/A START TRIGGER
D/A UPDATE
D/A EXTERNAL TIME BASE
D/A START TRIGGER signal
The D/A START TRIGGER signal is used to hold off output scans until after a trigger
event. The DAQ-Sync “DS D/A START TRIGGER” input or any AUXIN pin can be
programmed to serve as the D/A START TRIGGER signal. It is also available as an
output on any AUXOUT pin.
When used as an input, the D/A START TRIGGER signal may be software selected as
either a positive or negative edge trigger. The selected edge of the D/A START
TRIGGER signal causes the DACs to start generating the output waveform.
The D/A START TRIGGER signal can be used as an output to monitor the trigger that
initiates waveform generation. The output is an active-high pulse having a width of
50 ns.
Figure 4-23
Figure 4-23. D/A START TRIGGER Input Signal Timing
and Fi show the input and output timing requirements for the
D/A START TRIGGER signal.
gure 4-24
Rising Edge Polarity
t
w
tw = 37.5 ns minimum
Falling Edge Polarity
4-21
Page 48

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
t
w
tw = 50 ns
Figure 4-24. D/A START TRIGGER Output Signal Timing
D/A CONVERT signal
The D/A CONVERT signal causes a single output update on the D/A converters. You
can program the DAQ-Sync DS D/A UPDATE input or any AUXIN pin to accept the
D/A CONVERT signal. It is also available as an output on any AUXOUT pin.
The D/A CONVERT input signal polarity is software selectable. DAC outputs update
within 100ns of the selected edge. The D/A CONVERT pulses should be no less than
100 µs apart.
When used as an output, the D/A CONVERT signal may be used to monitor the pacing
of the output updates. The output has a pulse width of 225 ns with selectable polarity.
Figure 4-25
Rising Edge Polarity
t
w
tw = 37.5 ns minimum
Falling Edge Polarity
Figure 4-25. D/A CONVERT Input Signal Timing
and Fi show the input and output timing requirements for the
D/A CONVERT signal.
gure 4-26
Figure 4-26. D/A CONVERT Output Signal Timing
t
w
tw = 225 ns
4-22
Page 49

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
D/A EXTERNAL TIME BASE signal
The D/A EXTERNAL TIME BASE signal can serve as the source for the on-board
DAC pacer circuit rather than using the internal time base. Any AUXIN pin can be set
programmatically as the source for this signal. The polarity is programmable.
The maximum frequency for the D/A EXTERNAL TIME BASE signal is 20 MHz. The
minimum pulse width is 23 ns high or low. There is no minimum frequency
specification.
Figure 4-27
Figure 4-27. D/A EXTERNAL TIME BASE Signal Timing
shows the timing requirements for the D/A EXTERNAL TIME BASE
signal.
t
w
tw =23 ns minimum
t
p
t
w
tp =50 ns minimum
General-purpose counter signal timing
The general-purpose counter signals are:
CTR1 CLK
CTR1 GATE
CTR1 OUT
CTR2 CLK
CTR2 GATE
CTR2 OUT
4-23
Page 50

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
CTR1 CLK signal
The CTR1 CLK signal can serve as the clock source for independent user counter 1. It
can be selected through software at the CTR1 CLK pin rather than using the on-board
10 MHz or 100 kHz sources. It is also polarity programmable. The maximum input
frequency is 10 MHz. There is no minimum frequency specified.
Figure 4-28
Figure 4-28. CTR1 CLK Signal Timing
shows the timing requirements for the CTR1 CLK signal.
t
w-L
t
w-H
=15 ns minimum
t
w-H
tp =100 ns minimum
t
w-L
=25 ns minimum
CTR1 GATE signal
You can use the CTR1 GATE signal for starting and stopping the counter, saving
counter contents, etc. It is polarity programmable and is available at the CTR1 GATE
pin.
Figure 4-29
Figure 4-29. CTR1 GATE Signal Timing
shows the minimum timing requirements for the CTR1 GATE signal.
Rising Edge Polarity
t
w
tw = 25 ns minimum
Falling Edge Polarity
4-24
Page 51

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
CTR1 OUT signal
This signal is present on the CTR1 OUT pin. The CTR1 OUT signal is the output of one
of the two user’s counters in an industry-standard 82C54 chip.
.
Figure 4-30
Figure 4-30. CTR1 OUT Signal Timing
shows the timing requirements for the CTR1 OUT signal for counter mode
0 and mode 2.
CTR1 CLK
TC
CTR1 OUT (Mode 2)
CTR1 OUT (Mode 0)
CTR2 CLK signal
The CTR2 CLK signal can serve as the clock source for independent user counter 2. It
can be selected through software at the CTR2 CLK pin rather than using the on-board
10 MHz or 100 kHz sources. It is also polarity programmable. The maximum input
frequency is 10 MHz. There is no minimum frequency specified.
Figure 4-31
Figure 4-31. CTR2 CLK Signal Timing
shows the timing requirements for the CTR2 CLK signal.
t
w-L
t
w-H
=15 ns minimum
t
w-H
tp =100 ns minimum
t
w-L
=25 ns minimum
4-25
Page 52

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Functional Details
CTR2 GATE signal
You can use the CTR2 GATE signal for starting and stopping the counter, saving
counter contents, etc. It is polarity programmable and is available at the CTR2 GATE
pin.
Figure 4-32
Figure 4-32. CTR2 GATE Signal Timing
shows the timing requirements for the CTR2 GATE signal.
Rising Edge Polarity
t
w
tw = 25 ns minimum
Falling Edge Polarity
CTR2 OUT signal
This signal is present on the CTR2 OUT pin. The CTR2 OUT signal is the output of one
of the two user’s counters in an industry-standard 82C54 chip.
.
Figure 4-33
Figure 4-33. CTR2 OUT Signal Timing
shows the timing of the CTR1 OUT signal for mode 0 and for mode 2.
CTR2 CLK
TC
CTR2 OUT (Mode 2)
CTR2 OUT (Mode 0)
4-26
Page 53

Chapter 5
Calibrating the Board
Introduction
You should calibrate the board (using the InstaCal utility) after the board has fully
warmed up. The recommended warm-up time is 15 minutes. For best results, calibrate
the board immediately before making critical measurements. The high resolution analog
components on the board are somewhat sensitive to temperature. Pre-measurement
calibration ensures that your board is operating at optimum calibration values.
Calibration theory
Analog inputs are calibrated for offset and gain. Offset calibration for the analog inputs
is performed directly on the input amplifier (PGIA) with coarse and fine trim DACs
acting on the amplifier.
For input gain calibration, a precision calibration reference is used with coarse and fine
trim DACs acting on the ADC (see ). Figure 5-1
Figure 5-1. Analog Input Calibration - Basic Elements
Trim DAC
Coarse
Trim DAC
Fine
Gain
Adjust
PGIA
Analog In
A/D
Trim DAC
Coarse
Trim DAC
Fine
Pre-Gain
Offset
Trim DAC
Coarse
Trim DAC
Fine
Post-Gain
Offset
5-1
Page 54

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Calibrating the Board
A similar method is used to calibrate the analog output components. A trim DAC is used
to adjust the gain of the DAC. A separate DAC is used to adjust offset on the final
output amplifier. The calibration circuits are duplicated for both analog outputs (see
). Figure 5-2
Figure 5-2. Analog Output Calibration – Basic Elements
Trim DAC
Ref
D/A
Gain
Adjust
A
nalog Out
Trim DAC
Offset
Adjust
5-2
Page 55
Chapter 6
Specifications
Analog Input Section
A/D converter Successive Approximation type, 333kS/s conversion rate.
Resolution 16 bits, 1 in 65536
Maximum Sample Rate 333kS/s
Number of channels 16 single ended / 8 differential, software selectable
Input ranges
Bipolar: ±10V, ±5V, ±2.5V, ±1V, ±0.5V, ±0.25V, ±0.1V,
±0.05V,
Unipolar: 0 to 10V, 0 to 5V, 0 to 2V, 0 to 1V, 0 to 0.5V, 0 to
0.2V, 0 to 0.1V
Software selectable
Internal counter – ASIC. Software selectable time base:
Internal 40MHz, 50ppm stability
External Source via AUXIN<5:0>, Software selectable.
External convert strobe: A/D CONVERT
A/D pacing
Software paced
Burst mode Software selectable option, burst rate = 3µS.
External digital: A/D GATE
A/D Gate Sources
External analog: ATRIG input
CH0 IN through CH15 IN
External digital: Programmable, active high or active low, level or
edge
A/D gating modes
External analog: See Analog Trigger section
External digital: A/D START TRIGGER
A/D STOP TRIGGER
A/D trigger sources
External analog: ATRIG input
CH0 IN through CH15 IN
External digital: Software-configurable for rising or falling edge.
External analog: See Analog Trigger section
A/D triggering modes
Pre-/Post-trigger: Unlimited number of pre-trigger samples, 16 Meg
post-trigger samples.
ADC Pacer Out Available at user connector: A/D PACER OUT
RAM buffer size 8K samples
DMA
Data transfer
Programmed I/O
DMA Modes Demand or Non-Demand using scatter-gather.
Configuration Memory Up to 8K elements. Programmable channel, gain, and offset.
Streaming-to-disk rate 333kS/s, system dependent
6-1
Page 56

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Accuracy
333 kS/s sampling rate, single channel operation and a 15-minute warm-up. Accuracies
listed are for measurements made following an internal calibration. They are valid for
operational temperatures within ±1°C of internal calibration temperature and ±10°C of
factory calibration temperature. Calibrator test source high side tied to Channel 0 High
and low side tied to Channel 0 Low. Low-level ground is tied to Channel 0 Low at the
user connector.
Table 6-1. Absolute Accuracy
Range Absolute Accuracy
±10V ±15.6 LSB
±5V ±5.7 LSB
±2.5V ±15.6 LSB
±1V ±15.7 LSB
±500mV ±15.9 LSB
±250mV ±18.0 LSB
±100mV ±21.0 LSB
±50mV ±23.0 LSB
0 to 10V ±8.1 LSB
0 to 5V ±27.8 LSB
0 to 2V ±28.0 LSB
0 to 1V ±28.0 LSB
0 to 500mV ±31.7 LSB
0 to 200mV ±36.4 LSB
0 to 100mV ±38.7 LSB
6-2
Page 57

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Table 6-2. Absolute Accuracy Components – All values are (±)
Noise +Quantization
(µV)
Range
% of
Reading
Offset
(µV)
Single Pt Averaged
1
Temp Drift
(%/DegC)
Absolute
Accuracy at
FS (mV)
±10V 0.0371 947 981 87.0 0.0006 4.747
±5V 0.0071 476 491 43.5 0.0001 0.876
±2.5V 0.0371 241 245 21.7 0.0006 1.190
±1V 0.0371 99.2 98.1 8.7 0.0006 0.479
±500mV 0.0371 52.1 56.2 5.0 0.0006 0.243
±250mV 0.0421 28.6 32.8 3.0 0.0006 0.137
±100mV 0.0471 14.4 22.4 2.1 0.0006 0.064
±50mV 0.0471 9.7 19.9 1.9 0.0006 0.035
0 to 10V 0.0071 476 491 43.5 0.0001 1.232
0 to 5V 0.0371 241 245 21.7 0.0006 2.119
0 to 2V 0.0371 99.2 98.1 8.7 0.0006 0.850
0 to 1V 0.0371 52.1 56.2 5.0 0.0006 0.428
0 to
500mV
0.0421 28.6 39.8 3.0 0.0006 0.242
0 to
200mV
0.0471 14.4 22.4 2.1 0.0006 0.111
0 to
100mV
0.0471 9.7 19.9 1.9 0.0006 0.059
1. Averaged measurements assume averaging of 100 single-channel readings
6-3
Page 58
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Each PCI-DAS6052 is tested at the factory to assure the board’s overall error does not
exceed accuracy limits described in Table 6-1on page 6-2.
Table 6-3. Relative Accuracy – All values are (±)
Relative Accuracy (µV)
Range
Single Point Averaged
1
±10V 1145 115
±5V 573 57.3
±2.5V 286 28.6
±1V 115 11.5
±500mV 66.3 6.6
±250mV 39.2 3.9
±100mV 27.7 2.8
±50mV 25.3 2.5
0 to 10V 573 57.3
0 to 5V 286 28.6
0 to 2V 115 11.5
0 to 1V 66.3 6.6
0 to 500mV 48.2 3.9
0 to 200mV 27.7 2.8
0 to 100mV 25.3 2.5
1. Averaged measurements assume averaging of 100 single-channel readings
Relative accuracy is defined as the measured deviation from a straight line drawn
between measured endpoints of the transfer function. ADC resolution, noise and frontend non-linearity are included in this measurement.
Table 6-4. Differential non-linearity
All Ranges
±0.5 LSB typ ±1.0 LSB max
6-4
Page 59
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Settling Time
Settling time is defined as the time required for a channel to settle to within a specified
accuracy in response to a full-scale (FS) step. Two channels are scanned at the specified
rate. A –FS DC signal is presented to Channel 1; a +FS DC signal is presented to
Channel 0.
Accuracy
Condition Range
±0.00076%
(±0.5 LSB)
±0.0015%
(±1 LSB)
±0.0031%
(±2 LSB)
±0.0061%
(±4 LSB)
±0.024%
(±16 LSB)
±10V 20µS typ 10µS max 5µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
±5V 20µS typ 10µS max 5µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
±2.5V 20µS typ 10µS max 5µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
±1V 20µS typ 10µS max 5µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
±500mV 20µS typ 15µS max 5µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
±250mV 20µS typ 15µS max 8µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
±100mV 20µS typ 15µS max 8µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
±50mV 20µS typ 15µS max 10µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
0 to 10V 20µS typ 10µS max 5µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
0 to 5V 20µS typ 10µS max 5µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
0 to 2V 20µS typ 10µS max 5µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
0 to 1V 20µS typ 15µS max 5µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
0 to
500mV
20µS typ 15µS max 8µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
0 to
200mV
20µS typ 15µS max 8µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
Same range
to same
range
0 to
100mV
20µS typ 15µS max 10µS max 4µS max 3µS typ
6-5
Page 60
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Parametrics
Max working voltage
(signal + common-mode)
±11V
±10V Range: 92dB
0 to 10V & ±5V Range: 97dB
0 to 5V & ±2.5V Range: 101dB
0 to 2V & ±1V Range: 104dB
0 to 1V & ±0.5V Range: 105dB
0 to 0.5V & ±0.25V Range: 105dB
0 to 0.5V & ±0.1V Range: 105dB
CMRR @ 60Hz
0 to 0.1V & ±0.05V Range: 105dB
Small signal bandwidth, all ranges 480 kHz
Input coupling DC
100 Gohm in parallel with 100pF in normal operation.
Input impedance
820 Ohm typ in powered off or overload condition.
Input bias current ±200pA
Input offset current ±100pA
Absolute maximum input voltage
±25 power on, ±15V power off. Protected Inputs:
CH0 IN through CH15 IN
AISENSE
Adjacent Channels: -75dB
Crosstalk
All other Channels: -90dB
6-6
Page 61
PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Noise Performance
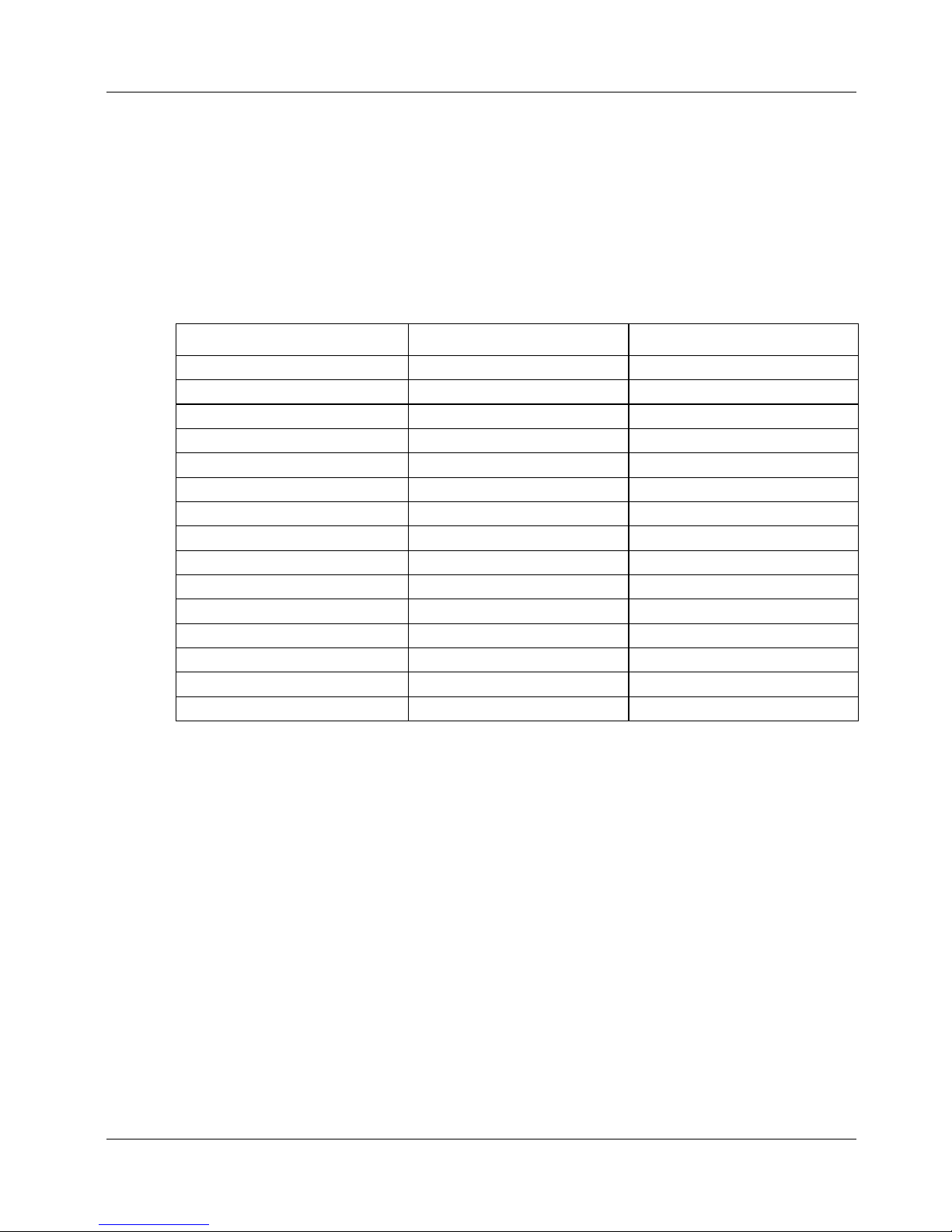
Table 6-5 summarizes the noise performance for the PCI-DAS6052. Noise distribution
is determined by gathering 50K samples with inputs tied to ground at the user connector.
Samples are gathered at the maximum specified single channel sampling rate.
Specification applies to differential mode operation.
Table 6-5. Analog Input Noise Performance
Range LSBrms Typical Counts
±10V 0.95 11
±5V 0.95 11
±2.5V 0.95 11
±1V 0.95 11
±500mV 1.1 11
±250mV 1.3 13
±100mV 2.3 23
±50mV 4.2 42
0 to 10V 0.95 11
0 to 5V 0.95 11
0 to 2V 0.95 11
0 to 1V 1.1 11
0 to 500mV 1.3 13
0 to 200mV 2.3 23
0 to 100mV 4.2 42
6-7
Page 62

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Analog Output Section
D/A Converter type Double-buffered, multiplying
Resolution 16-bits, 1 in 65536
Number of Channels 2, voltage output type
Voltage Range
±10V, 0 to 10V, ±EXT REF., 0 to EXT REF.,
software selectable
Monotonicity 16-bits, guaranteed
Slew Rate 15V/µs typ.
Settling Time (full scale step) 3.5µs max to ±1LSB
Noise 60µVrms, DC to 1MHz BW
Glitch Energy ±10mVwith 1µS duration (measured at mid-scale transition)
Current Drive ±5 mA
Output short-circuit duration Indefinite @25mA
Output coupling DC
Output impedance 0.1ohms max.
Power up and reset DACs cleared to 0 volts ±20mV max.
Table 6-6. Analog Output Absolute Accuracy
Range Absolute Accuracy
±10V ±4.6 LSB
0 to 10V ±7.7 LSB
Table 6-7. Absolute Accuracy Components - All values are (±)
Range % of Reading
Offset
(µV)
Temp Drift
(%/DegC)
Absolute Accuracy at FS
(mV)
±10V 0.0061 798 0.0001 1.405
0 to 10V 0.0061 569 0.0001 1.176
Each PCI-DAS6052 is tested at the factory to assure the board’s overall error does not
exceed the values specified in Table 6-6.
Table 6-8. Relative Accuracy
Range Relative Accuracy
All Ranges
±0.35 LSB, typical ±1.0 LSB, max
Relative accuracy is defined as the measured deviation from a straight line drawn
between measured endpoints of the transfer function.
6-8
Page 63

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Analog Output Pacing and Triggering
Internal counter – ASIC. Selectable time base:
Internal 40MHz, 50ppm stability.
External Source via AUXIN<5:0>, SW selectable.
External convert strobe: D/A UPDATE
DAC pacing
(SW programmable)
Software paced
External digital: D/A START TRIGGER
External analog: ATRIG input
CH0 IN through CH15 IN
DAC gate Sources
(Software
programmable)
Software gated
External digital: Programmable, active high or active low, level or
edge
DAC gating modes
External analog: See Analog Trigger section
External digital: D/A START TRIGGER
External analog: ATRIG input
CH0 IN through CH15 IN
DAC trigger sources
Software triggered
External digital: Software-configurable for rising or falling edge.
DAC triggering modes
External analog: See Analog Trigger section
DAC pacer Out Available at user connector D/A PACER OUT
RAM Buffer Size 16K samples
DMA
Programmed I/O
Data transfer
Update DACs individually or simultaneously, software selectable.
DMA Modes Demand or Non-Demand using scatter gather.
Waveform generation
Throughput
333 kS/s max per channel, 2 channels simultaneous
Analog Output External Reference Input (D/A EXTREF)
Range ±11V
Overvoltage Protection ±25V powered on, ±15V powered off
Input Impedance 10k ohms, min
Bandwidth (-3dB) 3 kHz
Slew rate 0.3V/µS
6-9
Page 64

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Analog Trigger
Analog Trigger Sources
Software selectable
External: ATRIG input
CH0 IN through CH15 IN, first channel in scan
ATRIG input: ±10V
Analog Trigger Levels
CH0 IN through CH15 IN: ± Full-scale, range dependent
Analog Trigger Modes
External analog: Software-configurable for:
Positive or Negative slope
Analog Gate Modes
External analog: Software-configurable for:
Above or Below reference
Positive or Negative hysteresis
In or Out of window
Resolution 12-bits, 1-in-4096
Accuracy ±1% Full-scale range max
ATRIG input 700 kHz
Bandwidth (-3dB)
CH0 IN through CH15 IN 700 kHz
Analog Input / Output Calibration
Recommended warm-up time 15 minutes
Calibration
Auto-calibration, calibration factors for each range stored
on board in non-volatile RAM.
DC Level: 5.000V± 1mV. Actual measured values stored
in EEPROM.
Tempco: 0.6ppm/°C max
Onboard calibration reference
Long-term stability: ±6ppm/sqrt(1000 hrs)
Calibration interval 1 year
Digital Input / Output
Digital Type Discrete, 5V/TTL compatible
Number of I/O 8
Configuration
8 bits, independently programmable for input or output. All pins
pulled up to +5V via 47K resistors (default). Positions available for
pull down to ground. Hardware selectable via solder gap.
Input high voltage 2.0V min, 7.0V absolute max
Input low voltage 0.8V max, –0.5V absolute min
Output high voltage
(IOH = -32mA)
3.80V min, 4.20V typ
Output low voltage
(IOL = 32mA)
0.55V max, 0.22V typ
Data Transfer Programmed I/O
Power-up / reset state Input mode (high impedance)
6-10
Page 65

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Interrupt Section
Interrupts PCI INTA# - mapped to IRQn via PCI BIOS at boot-time
Interrupt enable Programmable through PLX9080
DAQ_ACTIVE: Interrupt is generated when a DAQ sequence is active.
DAQ_STOP: Interrupt is generated when A/D Stop Trigger In is
detected.
DAQ_DONE: Interrupt is generated when a DAQ sequence completes.
DAQ_FIFO_1/4_FULL: Interrupt is generated when ADC FIFO is ¼ full.
DAQ_SINGLE: Interrupt is generated after each conversion completes.
DAQ_EOSCAN: Interrupt is generated after the last channel is converted in
multi-channel scans.
ADC Interrupt
sources
(Software
Programmable)
DAQ_EOSEQ: Interrupt is generated after each interval delay during
multi-channel scans.
DAC_ACTIVE: Interrupt is generated when DAC waveform circuitry is
active.
DAC_DONE: Interrupt is generated when a DAC sequence completes.
DAC_FIFO_1/4_EMPTY: Interrupt is generated DAC FIFO is ¼ empty.
DAC Interrupt
sources
(Software
Programmable)
DAC_HIGH_CHANNEL: Interrupt is generated when the DAC high
channel output is updated.
Counter Section
User counter type 82C54
Number of Channels 2
Resolution 16-bits
Compatibility 5V/TTL
CTRn base clock source
(Software selectable)
Internal 10MHz, Internal 100kHz or External
connector (CTRn CLK)
Internal 10MHz clock source stability 50ppm
Counter n Gate Available at connector (CTRn GATE).
Counter n Output Available at connector (CTRn OUT).
Clock input frequency 10 MHz max
High pulse width (clock input) 15ns min
Low pulse width (clock input) 25ns min
Gate width high 25ns min
Gate width low 25ns min
Input low voltage 0.8V max
Input high voltage 2.0V min
Output low voltage 0.4V max
Output high voltage 3.0V min
6-11
Page 66

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
Configurable AUXIN<5:0>, AUXOUT<2:0> External
Trigger/Clocks
The PCI-DAS6052 provides nine user-configurable Trigger/Clock pins available at the
100-pin I/O connector. Of these, six are configurable as inputs while three are
configurable as outputs.
AUXIN<5:0> Sources
(SW selectable)
A/D CONVERT: External ADC convert strobe
A/D TIMEBASE IN: External ADC pacer time base
A/D START TRIGGER: ADC Start Trigger
A/D STOP TRIGGER: ADC Stop Trigger
A/D PACER GATE: External ADC gate
D/A START TRIGGER DAC trigger/gate
D/A UPDATE: DAC update strobe
D/A TIMEBASE IN: External DAC pacer time base
AUXOUT<2:0> Sources
(SW selectable)
STARTSCAN: A pulse indicating start of conversion
SSH: Active signal that terminates at the
start of the last conversion in a scan.
A/D STOP: Indicates end of scan
A/D CONVERT: ADC convert pulse
SCANCLK: Delayed version of ADC convert
CTR1 CLK CTR1 clock source
D/A UPDATE D/A update pulse
CTR2 CLK CTR2 clock source
A/D START TRIGGER: ADC Start Trigger Out
A/D STOP TRIGGER: ADC Stop Trigger Out
A/D PACER GATE: External ADC gate
D/A START TRIGGER: DAC Start Trigger Out
AUXIN0: A/D CONVERT
AUXIN1: A/D START TRIGGER
AUXIN2: A/D STOP TRIGGER
AUXIN3: D/A UPDATE
AUXIN4: D/A START TRIGGER
AUXIN5: A/D PACER GATE
AUXOUT0: D/A UPDATE
AUXOUT1: A/D CONVERT
Default Selections:
AUXOUT2: SCANCLK
Compatibility 5V/TTL
Edge-sensitive polarity Rising/falling, software selectable
Level-sensitive polarity Active high/active low, software selectable
Minimum pulse width 3.75nS
6-12
Page 67

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
DAQ-Sync inter-board Triggers/Clocks
The DAQ-Sync bus provides inter-board triggering and synchronization capability. Five
trigger/strobe I/O pins and one clock I/O pin are provided on a 14-pin header. The
DAQ-Sync signals use dedicated pins. Only the direction may be set.
DS A/D START TRIGGER
DS A/D STOP TRIGGER
DS A/D CONVERT
DS D/A UPDATE
DS D/A START TRIGGER
DAQ-Sync Signals:
SYNC CLK
Power Consumption
+5V
1.25 A typical, 1.5A max. Does not include power consumed
through the I/O connector.
+5V available at I/O connector 1A max, protected with a resettable fuse
Environmental
Operating Temperature Range 0 to 55°C
Storage Temperature Range -20 to 70°C
Humidity 10 to 90% non-condensing
Mechanical
Card dimensions PCI half card: 174.4mm(L) x 106.9mm(W) x11.65mm(H)
6-13
Page 68

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
DAQ-Sync Connector and Pin Out
Connector type 14-Pin right-angle 100mil box header
Compatible cables MCC p/n: CDS-14-x, 14 pin ribbon cable. x = number of boards (2 - 5)
Pin Signal Name
1 DS A/D START TRIGGER
2 GND
3 DS A/D STOP TRIGGER
4 GND
5 DS A/D CONVERT
6 GND
7 DS D/A UPDATE
8 GND
9 DS D/A START TRIGGER
10 GND
11 RESERVED
12 GND
13 SYNC CLK
14 GND
Main Connector and Pin Out
Connector type Shielded SCSI 100 D-Type
C100HD50-x, unshielded ribbon cable. x = 3 or 6 feet
Compatible Cables
C100MMS-x, shielded round cable. x = 1, 2, or 3 meters
Compatible accessory products
(with C100HD50-x cable)
ISO-RACK16/P
ISO-DA02/P
BNC-16SE
BNC-16DI
CIO-MINI50
CIO-TERM100
SCB-50
Compatible accessory products
(with C100MMS-x cable)
SCB-100
6-14
Page 69

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
8 Channel Differential Mode
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 LLGND 51 n/c
2 CH0 IN HI 52 n/c
3 CH0 IN LO 53 n/c
4 CH1 IN HI 54 n/c
5 CH1 IN LO 55 n/c
6 CH2 IN HI 56 n/c
7 CH2 IN LO 57 n/c
8 CH3 IN HI 58 n/c
9 CH3 IN LO 59 n/c
10 CH4 IN HI 60 n/c
11 CH4 IN LO 61 n/c
12 CH5 IN HI 62 n/c
13 CH5 IN LO 63 n/c
14 CH6 IN HI 64 n/c
15 CH6 IN LO 65 n/c
16 CH7 IN HI 66 n/c
17 CH7 IN LO 67 n/c
18 LLGND 68 n/c
19 n/c 69 n/c
20 n/c 70 n/c
21 n/c 71 n/c
22 n/c 72 n/c
23 n/c 73 n/c
24 n/c 74 n/c
25 n/c 75 n/c
26 n/c 76 n/c
27 n/c 77 n/c
28 n/c 78 n/c
29 n/c 79 n/c
30 n/c 80 n/c
31 n/c 81 n/c
32 n/c 82 n/c
33 n/c 83 n/c
34 n/c 84 n/c
35 AISENSE 85 DIO0
36 D/A OUT 0 86 DIO1
37 D/A GND 87 DIO2
38 D/A OUT1 88 DIO3
39 PC +5 V 89 DIO4
40 AUXOUT0 / D/A PACER OUT 90 DIO5
41 AUXOUT1 / A/D PACER OUT 91 DIO6
42 AUXOUT2 / SCANCLK 92 DIO7
43 AUXIN0 / A/D CONVERT / ATRIG 93 CTR1 CLK
44 D/A EXTREF 94 CTR1 GATE
45 AUXIN1 / A/D START TRIGGER 95 CTR1 OUT
46 AUXIN2 / A/D STOP TRIGGER 96 GND
47 AUXIN3 / D/A UPDATE 97 CTR2 CLK
48 AUXIN4 / D/A START TRIGGER 98 CTR2 GATE
49 AUXIN5 / A/D PACER GATE 99 CTR2 OUT
50 GND 100 GND
6-15
Page 70

PCI-DAS6052 User's Guide Specifications
16-Channel Single-Ended Mode
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 LLGND 51 n/c
2 CH0 IN 52 n/c
3 CH8 IN 53 n/c
4 CH1 IN 54 n/c
5 CH9 IN 55 n/c
6 CH2 IN 56 n/c
7 CH10 IN 57 n/c
8 CH3 IN 58 n/c
9 CH11 IN 59 n/c
10 CH4 IN 60 n/c
11 CH12 IN 61 n/c
12 CH5 IN 62 n/c
13 CH13 IN 63 n/c
14 CH6 IN 64 n/c
15 CH14 IN 65 n/c
16 CH7 IN 66 n/c
17 CH15 IN 67 n/c
18 LLGND 68 n/c
19 n/c 69 n/c
20 n/c 70 n/c
21 n/c 71 n/c
22 n/c 72 n/c
23 n/c 73 n/c
24 n/c 74 n/c
25 n/c 75 n/c
26 n/c 76 n/c
27 n/c 77 n/c
28 n/c 78 n/c
29 n/c 79 n/c
30 n/c 80 n/c
31 n/c 81 n/c
32 n/c 82 n/c
33 n/c 83 n/c
34 n/c 84 n/c
35 AISENSE 85 DIO0
36 D/A OUT 0 86 DIO1
37 D/A GND 87 DIO2
38 D/A OUT1 88 DIO3
39 PC +5 V 89 DIO4
40 AUXOUT0 / D/A PACER OUT 90 DIO5
41 AUXOUT1 / A/D PACER OUT 91 DIO6
42 AUXOUT2 / SCANCLK 92 DIO7
43 AUXIN0 / A/D CONVERT / ATRIG 93 CTR1 CLK
44 D/A EXTREF 94 CTR1 GATE
45 AUXIN1 / A/D START TRIGGER 95 CTR1 OUT
46 AUXIN2 / A/D STOP TRIGGER 96 GND
47 AUXIN3 / D/A UPDATE 97 CTR2 CLK
48 AUXIN4 / D/A START TRIGGER 98 CTR2 GATE
49 AUXIN5 / A/D PACER GATE 99 CTR2 OUT
50 GND 100 GND
6-16
Page 71

EC Declaration of Conformity
We, Measurement Computing Corporation, declare under sole responsibility that the
products
PCI-DAS6052 High speed analog and digital I/O board for the PCI bus.
Part Number Description
to which this declaration relates, meets the essential requirements, is in conformity with,
and CE marking has been applied according to the relevant EC Directives listed below
using the relevant section of the following EC standards and other informative
documents:
EU EMC Directive 89/336/EEC: Essential requirements relating to electromagnetic
compatibility.
EN 55022 Class B (1995): Radiated and conducted emission requirements for
information technology equipment.
ENV 50204 (1995): Radio-frequency electromagnetic field immunity.
EN 55024 (1998): EC generic immunity requirements.
EN 50082-1 (1997): EC generic immunity requirements.
EN 61000-4-2 (1995): Electrostatic discharge immunity.
EN 61000-4-3 (1997) ENV 50204 (1996): RF immunity.
EN 61000-4-4 (1995): Electric fast transient burst immunity.
EN 61000-4-5 (1995): Surge immunity.
EN 61000-4-6 (1996): Radio frequency common mode immunity.
EN 61000-4-8 (1994): Power frequency magnetic field immunity.
EN 61000-4-11 (1994): Voltage dip and interrupt immunity.
Carl Haapaoja, Vice-President of Design Verification
Page 72

Measurement Computing Corporation
16 Commerce Boulevard,
Middleboro, Massachusetts 02346
(508) 946-5100
Fax: (508) 946-9500
E-mail: info@mccdaq.com
www.mccdaq.com
 Loading...
Loading...