Page 1

Page 2

Universal Library
for
NI LabVIEW™
User’s Guide
Document Revision 9, March, 2007
Copyright 2007, Measurement Computing Corporation
Page 3
Your new Measurement Computing product comes with a fantastic extra —
3
Management committed to your satisfaction!
Thank you for choosing a Measurement Computing product—and congratulations! You own the finest, and you can now enjoy
the protection of the most comprehensive warranties and unmatched phone tech support. It’s the embodiment of our mission:
To provide data acquisition hardware and software that will save time and save money.
Simple installations minimize the time between setting up your system and actually making measurements. We offer quick and
simple access to outstanding live FREE technical support to help integrate MCC products into a DAQ system.
Limited Lifetime Warranty: Most MCC products are covered by a limited lifetime warranty against defects in materials or
workmanship for the life of the product, to the original purchaser, unless otherwise noted. Any products found to be defective in
material or workmanship will be repaired, replaced with same or similar device, or refunded at MCC’s discretion. For specific
information, please refer to the terms and conditions of sale.
Harsh Environment Program: Any Measurement Computing product that is damaged due to misuse, or any reason, may be
eligible for replacement with the same or similar device for 50% of the current list price. I/O boards face some harsh
environments, some harsher than the boards are designed to withstand. Contact MCC to determine your product’s eligibility for
this program.
30 Day Money-Back Guarantee: Any Measurement Computing Corporation product may be returned within 30 days of
purchase for a full refund of the price paid for the product being returned. If you are not satisfied, or chose the wrong product by
mistake, you do not have to keep it.
These warranties are in lieu of all other warranties, expressed or implied, including any implied warranty of merchantability or
fitness for a particular application. The remedies provided herein are the buyer’s sole and exclusive remedies. Neither
Measurement Computing Corporation, nor its employees shall be liable for any direct or indirect, special, incidental or
consequential damage arising from the use of its products, even if Measurement Computing Corporation has been notified in
advance of the possibility of such damages.
Trademark and Copyright Information
Measurement Computing Corporation, InstaCal, Universal Library, and the Measurement Computing logo are either trademarks
or registered trademarks of Measurement Computing Corporation. Refer to the Copyrights & Trademarks section on
mccdaq.com/legal for more information about Measurement Computing trademarks. Other product and company names
mentioned herein are trademarks or trade names of their respective companies.
© 200 Measurement Computing Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form by any means, electronic, mechanical, by photocopying, recording, or otherwise
without the prior written permission of Measurement Computing Corporation.
Notice
Measurement Computing Corporation does not authorize any Measurement Computing Corporation product for use
in life support systems and/or devices without prior written consent from Measurement Computing Corporation.
Life support devices/systems are devices or systems that, a) are intended for surgical implantation into the body, or
b) support or sustain life and whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to result in injury. Measurement
Computing Corporation products are not designed with the components required, and are not subject to the testing
required to ensure a level of reliability suitable for the treatment and diagnosis of people.
Page 4

Table of Contents
4
Introducing the Universal Library for LabVIEW™............................................
Installing and Configuring UL for LabVIEW......................................................
Installing the software........................................................................................................................
Configuring your MCC hardware for use with UL for LabVIEW VIs ...................................................
Overview of the Universal Library VIs...............................................................
Analog I/O VIs....................................................................................................................................
Signal conditioning VIs.....................................................................................................................
Counter VIs......................................................................................................................................1
Digital I/O VIs...................................................................................................................................1
Streamer file VIs..............................................................................................................................1
Memory board VIs ...........................................................................................................................1
Miscellaneous VIs............................................................................................................................1
How to use the LabVIEW Extensions (VIs) .....................................................1
Using the Library with LabVIEW......................................................................................................1
UL function contexts: foreground (__Fg) and background (__Bg) ...............................................1
UL Extension VI example programs ................................................................................................1
Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs).....................................................1
Analog Input VIs ..............................................................................................................................1
AIn.VI...........................................................................................................................................1
AInScBg.VI...................................................................................................................................
AInScFg.VI...................................................................................................................................2
APretrBg.VI..................................................................................................................................2
APretrFg.VI ..................................................................................................................................2
ATrigger.VI...................................................................................................................................2
ALoadQue.VI ...............................................................................................................................2
OptAIn.VI .....................................................................................................................................
SetTrig.VI.....................................................................................................................................3
TIn.VI ...........................................................................................................................................3
TInScan.VI ...................................................................................................................................3
Analog Output VIs............................................................................................................................3
AOut.VI ........................................................................................................................................3
AOutScFg.VI................................................................................................................................
AOutScBg.VI................................................................................................................................4
Signal conditioning VIs.....................................................................................................................4
ACvtData.VI .................................................................................................................................4
ACnvPrDt.VI.................................................................................................................................4
ACal.VI.........................................................................................................................................4
FromEng.VI..................................................................................................................................4
ToEng.VI......................................................................................................................................4
ScaleArr.VI...................................................................................................................................4
ScalePnt.VI ..................................................................................................................................
Counter VIs......................................................................................................................................5
C8254Cfg.VI ................................................................................................................................5
C7266Config.VI............................................................................................................................5
C8536Cfg.VI ................................................................................................................................5
C8536Init.VI .................................................................................................................................5
C9513Config.VI............................................................................................................................5
C9513Init.VI .................................................................................................................................
CFreqIn.VI....................................................................................................................................6
CIn.VI...........................................................................................................................................6
CIn32.VI.......................................................................................................................................6
CLoad.VI......................................................................................................................................6
CLoad32.VI..................................................................................................................................6
CStatus.VI....................................................................................................................................6
CStore.VI .....................................................................................................................................6
Digital I/O VIs...................................................................................................................................7
Page 5

Universal Library for NI LabVIEW™ User's Guide
5
DBitIn.VI.......................................................................................................................................7
DBitOut.VI....................................................................................................................................7
DCfgBit.VI ....................................................................................................................................7
DCfgPort.VI..................................................................................................................................7
DIn.VI...........................................................................................................................................7
DInScBg.VI ..................................................................................................................................7
DInScFg.VI...................................................................................................................................7
DOut.VI........................................................................................................................................
DOutScBg.VI................................................................................................................................8
DOutScFg.VI................................................................................................................................8
Streamer File VIs.............................................................................................................................8
FileAInScan.VI .............................................................................................................................8
FileInfo.VI.....................................................................................................................................8
FilePret.VI ....................................................................................................................................8
FileRead.VI ..................................................................................................................................8
Memory board VIs ...........................................................................................................................
MemRdPrt.VI................................................................................................................................
MemRead.VI................................................................................................................................9
MemReset.VI ...............................................................................................................................9
MemSetDT.VI...............................................................................................................................9
MemWrite.VI ................................................................................................................................9
Serial VIs .........................................................................................................................................9
RS485.VI......................................................................................................................................9
Miscellaneous VIs............................................................................................................................9
ErrHdlng.VI ..................................................................................................................................9
ErrMsg.VI.....................................................................................................................................9
GetBoard.VI .................................................................................................................................9
GetCfg.VI.....................................................................................................................................9
GetStatus.VI...............................................................................................................................10
SelChan.VI.................................................................................................................................10
SetCfg.VI....................................................................................................................................10
StopBg.VI...................................................................................................................................10
InByte.VI / InWord.VI..................................................................................................................10
OutByte.VI / OutWord.VI............................................................................................................10
Page 6

1
6
Introducing the Universal Library for LabVIEW™
With the Universal Library for LabVIEW (UL for LabVIEW) software, you can construct your own
LabVIEW programs using UL Extension VIs with supported Measurement Computing’s data acquisition and
control devices.
The UL for LabVIEW Extension VIs are supported with LabVIEW version 6 and greater.
The UL for LabVIEW includes a set of LabVIEW virtual instruments (VIs) that you use to construct your
own programs in LabVIEW using Measurement Computing’s data acquisition and control boards. Each lowlevel VI corresponds to one UL function.
This manual details the syntax of each VI. Although the LabVIEW extensions closely follow the syntax of the
UL, there are some differences. For informat ion on the UL functions, refer to the Universal Library Function
Reference (this manual is available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-functions.pdf)
To use the UL with another language, refer to the Universal Library User's Guide (available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
(available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-functions.pdf
) and the Universal Library Function Reference
).
.
Page 7

2
7
Installing and Configuring UL for LabVIEW
This chapter explains how to install the software on your computer, and how to configure the software for the
boards that you will be using with it.
The UL for LabVIEW software contains the following compone nts:
UL for LabVIEW rev. 7.11 software, which includes the UL Extension VIs
Sample programs for use with Extension VIs and MCC hardware
readme.txt
You can install this software on all operating systems that are supported by the UL and your version of
LabVIEW.
Installing the software
The UL for LabVIEW software is installed from the Measurement Computing Data Acquisition Software CD.
Refer to the Quick Start Guide for instructions on installing the software on the Measurement Computing
Data Acquisition Software CD. This booklet is available in PDF at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/DAQ-
Software-Quick-Start.pdf.
Configuring your MCC hardware for use with UL for LabVIEW VIs
Before starting the LabVIEW environment, configure your Measurement Computing data acquisition board(s)
using InstaCal. InstaCal stores all board-specific configuration information in a configuration file named
CB.CFG. InstaCal creates and/or modifies the CB.CFG file when board configurations are added or updated.
The CB.CFG file is read by the UL. The LabVIEW Extension VIs use the CB.CFG file to access the
hardware.
Page 8

3
8
Overview of the Universal Library VIs
The Universal Library for LabVIEW contains a set of low-level VIs that you "wire" together to build your
application. These VIs are grouped according to their purpose. All of the groups except for "Miscellaneous"
are based on the type of devices they are used with.
Analog I/O VIs
The analog I/O VIs perform analog input and output and convert analog data.
AIn.VI - Single analog input
Takes a single reading from an analog input channel (A/D).
AInScBg.VI - Background analog input scan
Repeatedly scans a range of analog input (A/D) channels in the background. The channel range, the number of
samples, the sampling rate, and the A/D range can all be specified. The collected data is stored in an array.
AInScFg.VI - Foreground analog input scan
Repeatedly scans a range of analog input (A/D) channels in the foreground. The channel range, the number of
samples, the sampling rate, and the A/D range can all be specified. The data that is collected is stored in an
array.
ALoadQue.VI - Load channel/gain queue
Loads a series of channel/gain pairs into A/D board's queue. These channel/gains will be used with all
subsequent analog input VIs.
AOut.VI - Single analog output
Outputs a single value to an analog output (D/A).
AOutScBg.VI - Background analog output scan
Repeatedly updates a range of analog output (D/A) channels in the background. The channel range, the
number of samples, and the rate can all be specified. The data values from consecutive elements of an array
are sent to each D/A channel in the scan.
AOutScFg.VI - Foreground analog output scan
Repeatedly updates a range of analog output (D/A) channels in the foreground. The channel range, the number
of samples, and the rate can all be specified. The data values from consecutive elements of an array are sent to
each D/A channel in the scan.
APretrBg.VI - Analog pre-triggered input in the background
Repeatedly scans a range of analog input (A/D) channels in the background while waiting for a trigger signal.
When a trigger occurs, it returns the specified number of samples before and after the trigger occurred. The
channel range, the sampling rate, and the A/D range can all be specified. The data that is collected is stored in
an array.
APretrFg.VI - Analog pre-triggered input in the foreground
Repeatedly scans a range of analog input (A/D) channels in the foreground while waiting for a trigger signal.
When a trigger occurs it returns the specified number of samples before and after the trigger occurred. The
channel range, the sampling rate, and the A/D range can all be specified. The data that is collected is stored in
an array.
ATrig.VI - Analog trigger
Reads the specified analog input until it goes above or below a specified threshold. When the trigger condition
is met the current sample is returned.
Page 9

Overview of the Universal Library VIs Signal conditioning VIs
9
OptAIn.VI – Specifies analog input options.
Both AInScBg.VI and AInScFg.VI have an input called
options which should be wired to this VIs output. It
generates a value based on the Anded values of its inputs.
SetTrig.VI - Set the trigger source.
Configures the type and threshold value of external trigger signals.
TIn.VI - Single temperature input
Reads a temperature input channel and, as necessary, filters it, performs cold junction compensation, and
linearization.
TInScan.VI - Scans a range of thermocouple inputs.
Reads the temperature from a range of channels as described above. Returns the temperature values to an
array.
Signal conditioning VIs
ACvtData.VI - Converts analog data
Each raw sample from an analog input is a 16-bit value. On some 12-bit A/D boards it consists of a 12-bit
A/D value along with a four bit channel number. On 16-bit A/D boards it contains the 16-bit A/D value.
This conversion is done automatically by the AIn VI. It can also be done automatically by the AInScBg.VI or
the AInScFg.VI with the
the data and then do the conversion sometime later. The ACvtData.VI takes a buffer full of unconverted data
and converts it.
ACnvPrDt.VI - Convert pre-trigger data
CONVERTDATA option. In some cases though, it may be useful or necessary to collect
When data is collected by either APretrBg.VI or APretrFg.VI, the s ame conversion needs to be done as
described above for ACvtData.VI.
However, both APretrBg.VI and APretrFg.VI collect analog data into an array. They treat the array like a
circular buffer. While they are waiting for the trigger to occur, they fill the buffer. When the end of the buffer
is reached, they return to the beginning of the buffer. When the trigger signal occurs, the VIs continue
collecting data into the circular buffer until the requested number of samples have been collected.
When the data acquisition is complete, all of the data is in the array, but it is in the wrong order. The first
element of the array does not contain the first data point. The data has to be rotated to the correct order.
This conversion can be done automatically by the APretrB g. VI or APretrFg.VI with the
CONVERTDATA option.
In some cases, though, it may be useful or necessary to collect the data and then do the conversion sometime
later. The ACnvPrDt.VI takes a buffer full of unconverted data and converts it.
ACalData.VI - Calibrates raw data.
Calibrates raw data collected by
cbAInScan() when the real-time software calibration is turned off.
FromEng.VI - Convert to raw data.
Converts one data sample or an array of data samples from engineering units to raw data format. Can also
convert a single voltage (or current) to a D/A count value for use as an analog trigger threshold value.
ToEng.VI - Convert to engineering units.
Converts one data sample or an array of data samples from raw data format to engineering units.
ScalePnt.VI - Converts a raw data point to engineering units.
ScaleArray.VI - Converts raw data in an array to engineering units data in an array.
Page 10

Overview of the Universal Library VIs Counter VIs
10
Counter VIs
The counter VIs load, read, and configure counters. There are four types of counter chips used in
Measurement Computing products - 8254s, 8536s, 7266s, and 9513s. Some of the counter commands only
apply to one type of counter. To gain full access to the power of these counter VIs, you should refer to the
data sheet for the type of counter you are using:
82C54 data sheet (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/82C54.pdf
LS7266 data sheet (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/LS7266R1.pdf
9513A data sheet (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/9513A.pdf
C7266Config.VI – Configures an LS7266 counter.
Selects all of the programmable options that are associated with the LS7266 counter.
C8254Cfg.VI - Configures an 8254 counter.
Selects the basic operating mode of an 8254 counter.
C8536Cfg.VI - Sets the operating mode of an 8536 counter.
Sets all of the programmable options associated with an 8536 counter chip.
C8536Ini.VI - Initializes an 8536 counter.
Initializes and selects all of the chip level features for an 8536 counter board. The options that are set by this
command are associated with each counter chip, and not the individual counters within it.
C9513Cfg.VI - Sets the operating mode of a 9513 counter.
Sets all of the programmable options associated with a 9513 counter chip. It is similar in purpose to
C8254Cfg.VI, except that it is used with a 9513 counter.
C9513Ini.VI - Initializes a 9513 counter.
Initializes and selects all of the chip level features for a 9513 counter board. The options that are set by this
command are associated with the specified counter chip, and not the individual counters within it.
)
)
)
CFreqIn.VI - Measures the frequency of a signal.
Measures the frequency of a signal by counting it for a specified period of time (
converting the count to counts/sec (Hz). This VI only works with 9513 coun ters.
CIn.VI - Reads a counter.
Reads a counter’s current value and returns the value as a 16-bit integer.
CIn32.VI - Reads a counter.
Reads a counter’s current value and returns the value as a 32-bit integer.
CLoad.VI - Loads a counter.
Loads a counter with an initial 16-bit count value.
CLoad32.VI - Loads a coun ter.
Loads a counter with an initial 32-bit count value.
CStatus.VI – Gets a counter status.
Retrieves status information about a LS7266 based counter. This VI only works with LS7266 counters.
CStore.VI - Stores the counter value when an interrupt occurs.
Installs an interrupt handler that stores the current count whenever an interrupt occurs. This VI only works
with 9513 counters.
GatingInterval) and then
Page 11

Overview of the Universal Library VIs Digital I/O VIs
11
Digital I/O VIs
To gain full access to the power of these digital I/O VIs, you should refer to the data sheet for the type of
digital interface you are using:
the 82C55 data sheet (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/82C55.pdf
the 8536 data sheet (not available on our web site)
DBitIn.VI - Digital bit input.
Reads a single bit from a digital input port.
DBitOut.VI - Digital bit output.
Sets a single bit on a digital output port.
DCfgBit.VI - Configures a specific digital bit within a digital port.
Configures a specific bit within a digital port as an input or an output.
DCfgPort.VI - Configures digit a l out put s.
Configures a digital port as an input or an output.
DIn.VI - Digital input.
Reads a specified digital input port.
DInScBg.VI - Digital multiple byte or word input in the background.
Reads a specified number of bytes or words from a digital input port at a specified rate.
DInScFg.VI - Digital multiple byte or word input in the foreground.
Reads a specified number of bytes or words from a digital input port at a specified rate.
DOut.VI - Digital output.
)
Writes a byte or word to a digital output port.
DOutScBg.VI - Digital multiple byte or word output in the background.
Writes a series of bytes or words to a digital output port at a specified rate.
DOutScFg.VI - Digital multiple byte or word output in the foreground.
Writes a series of bytes or words to a digital output port at a specified rate.
Streamer file VIs
These VIs create, fill, and read "streamer" files. These VIs also let you collect and store large amounts of
analog input data. The amount of data is limited only by available disk space.
FileAInS.VI - Transfer analog input data directly to file.
Very similar to AInScFg.VI, except that data is stored in a file instead of an array.
FilePret.VI - Pre-triggered analog input to a file.
Very similar to APretrFg.VI, except that data is stored in a file instead of an array.
FileInfo.VI - Reads "streamer" file information.
Each streamer file contains information about how much data is in the file and the conditions under which it
was collected (sampling rate, channels, etc.). This VI reads that information.
FileRead.VI - Reads data from a "streamer" file.
Reads a selected number of data points from a streamer file into an array.
Page 12

Overview of the Universal Library VIs Memory board VIs
12
Memory board VIs
The memory board VIs read from, write to, and control memory boards (MEGA-FIFO). The most common
use for the memory boards is to store large amounts of data from an A/D board via a DT-Connect cable
between the two boards. To do this, you should use the
APretrBg.VI, or APretrFg.VI.
After data is transferred to the memory board, you can use the memory VIs to retrieve the data.
MemSetDT.VI - Sets DT-Connect mode on a memory board
The memory boards have a DT-Connect interface which can be used to transfer data through a cable between
two boards rather than through the PC's system memory. The DT-Connect port on the memory board can be
configured as either an input (from an A/D) or as an output (to a D/A). This VI configures the port.
MemReset.VI - Resets the memory board address
The memory board is organized as a sequential device. When data is transferred to the memory board it is
automatically put in the next address location. This VI resets the current address to the location 0.
MemRead.VI - Reads data from a memory board.
Reads a specified number of points from a memory board starting at a specified address.
MemWrite.VI - Writes data to a memory board.
Writes a specified number of points to a memory board starting at a specified address.
EXTMEMORY option with AInScBg.VI, AInScFg.VI,
MemRdPrt.VI - Reads data collected with APretrBg.VI or APretrFg.VI.
Both APretrBg.VI and APretrFg.VI write the pre-triggered data to the memory board in a shifted order. This
VI shifts the data and returns it in the correct order.
Miscellaneous VIs
These VIs perform error handling, configuration, and other miscellaneous operati o ns.
ErrHdlng.VI - Selects the type of error handling.
The Universal Library has a number of different methods of handling errors. This VI selects which of these
methods will be used with all subsequent library calls. The options include stopping the program when an
error occurs and printing error messages.
ErrMsg.VI - Returns an error message for a given error.
All library VIs return error codes. This VI converts an error code to an error message.
GetBoard.VI - Get the board name.
Returns the name of the selected target board.
GetCfg.VI - Get configuration options.
Extracts hardware configuration options from board configuration file.
GetStatus.VI - Returns the status of backgroun d operations.
After a background operation is started your program will need to periodically check on its progress. This VI
returns the current status of the process that is running.
InByte.VI - Read one byte.
Reads one byte of data from the specified port.
InWord.VI - Read one word.
Reads one word of data from the specified port.
Page 13

Overview of the Universal Library VIs Miscellaneous VIs
13
OutByte.VI - Write one byte.
Writes one byte of data to the specified port.
OutWord.VI - Write one word.
Writes one word of data to the specified port.
SelChan.VI – Selects specific channel data from an array.
Allows one channel of data to be extracted from an array of interleaved data for multiple channels.
SetCfg.VI - Set configuration options.
Sets hardware configuration options for a selected board.
StopBg.VI - Stop a background process.
It is sometimes necessary to stop a background process in the case of an error or if the process has been set up
to run continuously. This VI will stop a background process.
Page 14

4
14
How to use the NI LabVIEW Extensions (VIs)
Using the Library with NI LabVIEW
The Universal Library NI LabVIEW extensions provide a complete set of virtual instruments (VIs) for
interfacing all Measurement Computing data acquisition hardware . Eac h l ow-l e vel VI c or res po nds to one
Universal Library function. All of the VIs are combined into a LabVIEW Library named DAS16.LLB. There
are two approaches you can use in developing new LabVIEW applications that can interface to Measurement
Computing hardware.
Modify one of the example applications.
Build a new application from scratch using the low-level VIs supplied in the DAS16.LLB library.
The easiest way to get started is to modify one of the sample applications. Select an example application that
contains the operating behavior you are looking for. The example applications contain the basic requirements
for transferring data to and from the target hardware. Additional capability can be added by selecting new
functions and placing them on the diagram window. The corresponding controls can then be selected and
placed on the panel window. Wire the new functions to the existing application and test the program.
If you prefer to build an application from scratch, you can wire any LabVIEW functions together to build your
application. When the application requires interaction with the data acquisition hardware, simply select the
appropriate VI from the DAS16.LLB and add it to the working diagram.
To access the DAS16.LLB library VIs, do the following:
1. Make the Diagram window of the project the active window. If the Panel window is currently active, select the
Show Diagram option from the Window menu.
2. From the Diagram window, select the Show Functions Palette option from the Window menu to open the
Functions palette.
3. From the Functions palette, click on the User Libraries icon to open the User Libraries palette.
4. From the User Libraries palette, click on the MCC icon to open the MCC Data Acquisition palette.
5. Select the VI you want to use by clicking on the appropriate icon. Move the cursor back to the Diagram window and
click to place the VI.
After placing the VIs you want to use on the Diagram window, you can wire them together. Save the
application prior to testing. Refer to the documentation of each VI for specifics on the input and output
parameters.
Page 15
How to use the NI LabVIEW Extensions (VIs) UL Extension VI example programs
15
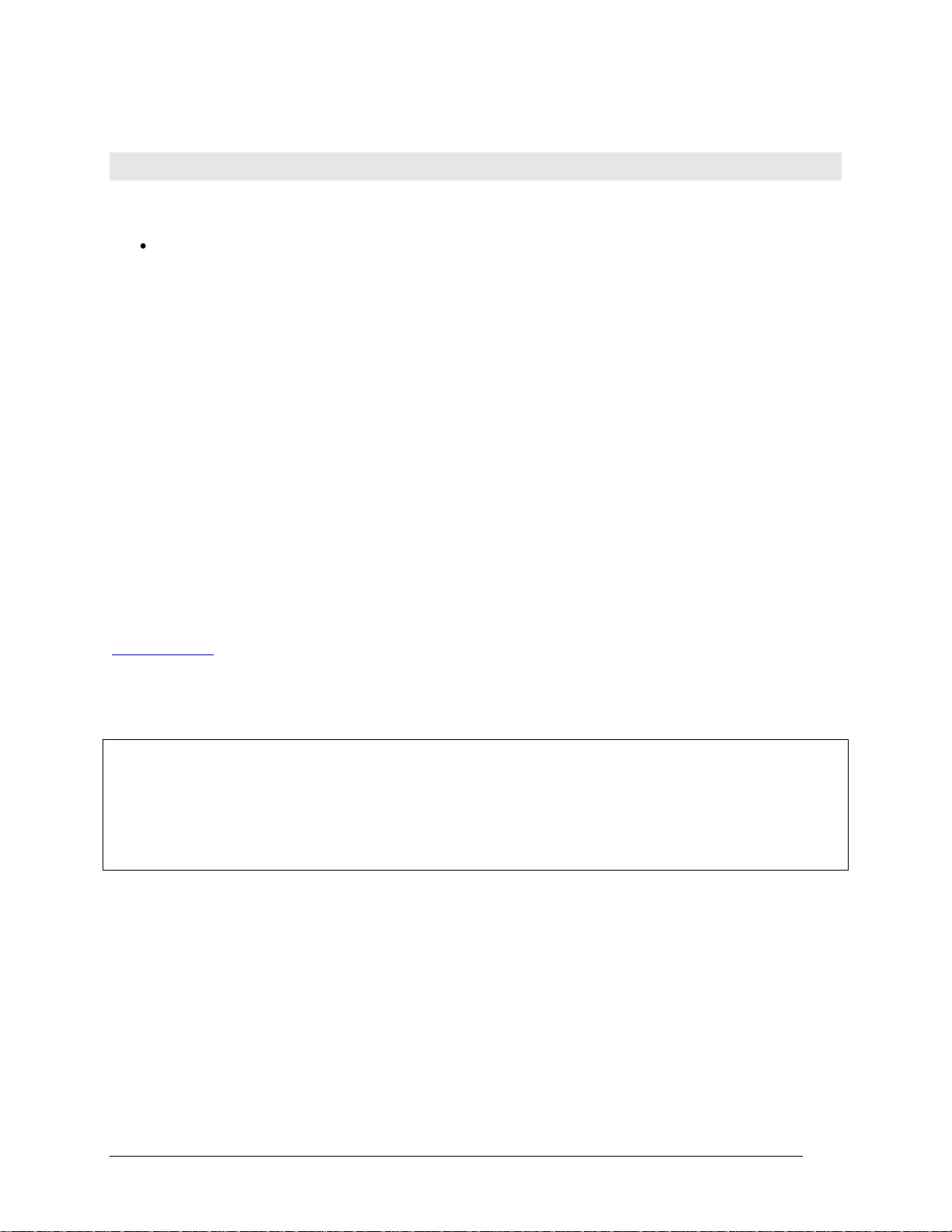
UL function contexts: foreground (__Fg) and background (__Bg)
There are two distinct VIs for every UL function featur ing background operation. One is for foreground
operation only, and the other is for background operation only. The last two letters of the function names are
"Fg" and "Bg" for foreground and background, respectively. Their parameter lists differ, in that background
VIs have a
Context is an output data structure that contains information such as the board number, the data array, the size
of the data array, the initial status of the operation, and the error code. Connecting a probe to the
displays the elements in the data structure. You can check the intermediate values if desired. In general, the
background VIs should conform to the wiring pattern shown in Figure 1. There are severa l example programs
that effectively demonstrate the correct wiring and use of Contexts. Please refer to example VIs whose names
end in "BG."
Context output that must be wired to subsequent VIs (GetStatus.VI and StopBg.VI).
Context wire
Figure 1. Background VIs General Wiring Pattern
UL Extension VI example programs
The UL for LabVIEW software package includes example programs which demonstrate how to use the
Universal Library low-level extension VIs. We strongly suggest that you review the example programs to help
you understand how to integrate the VIs into your program. The following example programs are included to
demonstrate the LabVIEW interface:
Example VI explanation
XAIN Single analog input in a while loop with a metered display.
XAINSCBG Analog input scan in the background. Display data on a graph. Uses GetStatus.VI,
StopBg.VI and OptAIn.VI.
XAICNBG Analog input scan in the background in the CONTINUOUS mode. Same as
XAINSCBG but runs continuously displaying data in real time.
XAINSCFG Analog input scan in the foreground. Displays data on a graph. Uses SelChan.VI
and OptAIn.VI.
XAIOSCB Demonstrates concurrent analog input and output scans.
XAOUT Single analog output. Demonstrates sequences, case statements, for loops, and
while loops.
XAOUTSCB Analog output scan in the background. Uses GetStatus.VI and StopBg.V I.
XAOUTSCF Analog output scan in the foreground. Generates sinusoidal data.
XAPRETRB Analog pre-trigger in the background. Display data on a graph. Uses GetStatus.VI,
StopBg.VI and ACnvPrDt.VI.
XAPRETRF Analog pre-trigger in the foreground. Displays data on a graph. Uses SelChan.VI
and ACnvPrDt.VI.
XASCFILE Analog input to a file. Displays data on a graph. Uses Fil eAInS.VI and
FileRead.VI.
XASCMEM Analog input to memory board. Displays data on a graph. Uses MemReset.VI and
MemRead.VI.
XCFREQ Displays frequency of signal at counter input. Uses C9513Init.VI and CFreqIn.VI.
Page 16

How to use the NI LabVIEW Extensions (VIs) UL Extension VI example programs
16
XCSTORE Stores counter values when interrupts occur and displays the m. Uses CStore.VI,
GetStatus.VI, and StopBg.VI.
XCTR8254 Configures, loads and reads the counter. Displays the count. Uses C8254Cfg.VI,
CLoad.VI, and CIn.VI.
XCTR8536 Initializes, configures, loads, and reads the counter. Displays the count. Uses
C8536Cfg.VI, CLoad.VI, and CIn.VI.
XCTR9513 Initializes, configures, loads, and reads the counter. Displays the count. Uses
C9513Cfg.VI, CLoad.VI, and CIn.VI.
XCTR7266 Configures, loads, and reads the counter. Displays count and status. Uses
C7266Cfg.VI, CLoad32.VI, CIn32.VI, and CStatus.VI.
XDBITIN Configures and reads a digital bit. Toggles an LED accordingly. Uses DCfgPort.VI
and DBitIn.VI.
XDBITOUT Configures and writes a digital bit. Uses DCfgPort.VI and DBitOut.VI.
XDIN Configures and reads a digital port. Toggles eight LEDs accordingly. Uses
DCfgPort.VI and DIn.VI.
XDCFGBIT Configures a bitwise configurable digital port.
XDINSCBG Reads multiple bytes in the background. Uses DCfgPort.VI, DInScBg.VI,
GetStatus.VI, and StopBg.VI.
XDINSCFG Reads multiple digital bytes or words in the foreground. Uses DCfgPort.VI and
DInScFg.VI.
XDOUT Configures and writes to a digital port. Uses DCfgPort.VI and DOut.VI.
XDOUTSCB Writes multiple digital bytes or words in the background. Uses DCfgPort.VI,
DOutScBg.VI, GetStatus.VI, and StopBg.VI.
XDOUTSCF Writes multiple digital bytes or words in the foreground. Uses DCfgPort.VI and
DOutScFg.VI.
XEVENTCTR Uses the event counters available from MCC's Personal Measurement Device™
and Measurement Advantage™ USB devices. Uses CIn32.VI.
XTIN Single temperature input in a while loop with a metered display. Uses TIn VI.
XTINSCAN Temperature input scan across multiple channels in a while loop. Data is displayed
on a strip chart. Uses TInScan VI.
Page 17

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs)
17
Analog Input VIs
AIn.VI
Reads an A/D input channel. This VI reads the specified A/D channel from the specified board. If the A/D
board has programmable gain, it sets the gain to the specified range. The raw A/D value is converted to an
A/D value and returned to
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number when installed with InstaCal; can be 0 to
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
Channel The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of A/D board is being
Range If the selected A/D board does not have a programmable gain feature, this
The
DataValue.
100.
Channel [I32] - A/D channel number
Range [I32] - A/D Range
DataValue [U16] - Value of A/D sample
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI on page 97.
specified board must have an A/D. BoardNum can be from 0 to 100.
used. For boards that have both single ended and differential inputs, the maximum
allowable channel number also depends on how the board is configured. For
example, a PCI-DAS6025 has eight channels for differential, 16 for single-ended
input mode.
argument is ignored. If the A/D board does have programmable gain, set the
argument to the desired A/D range.
Range input values table on page 19 lists the constants you can use in the
Range argument for most functions. Not all A/D boards support the same A/D
ranges. Refer to the board’s hardware manual for a list of supported A/D ranges.
Range
5
Page 18
Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
18
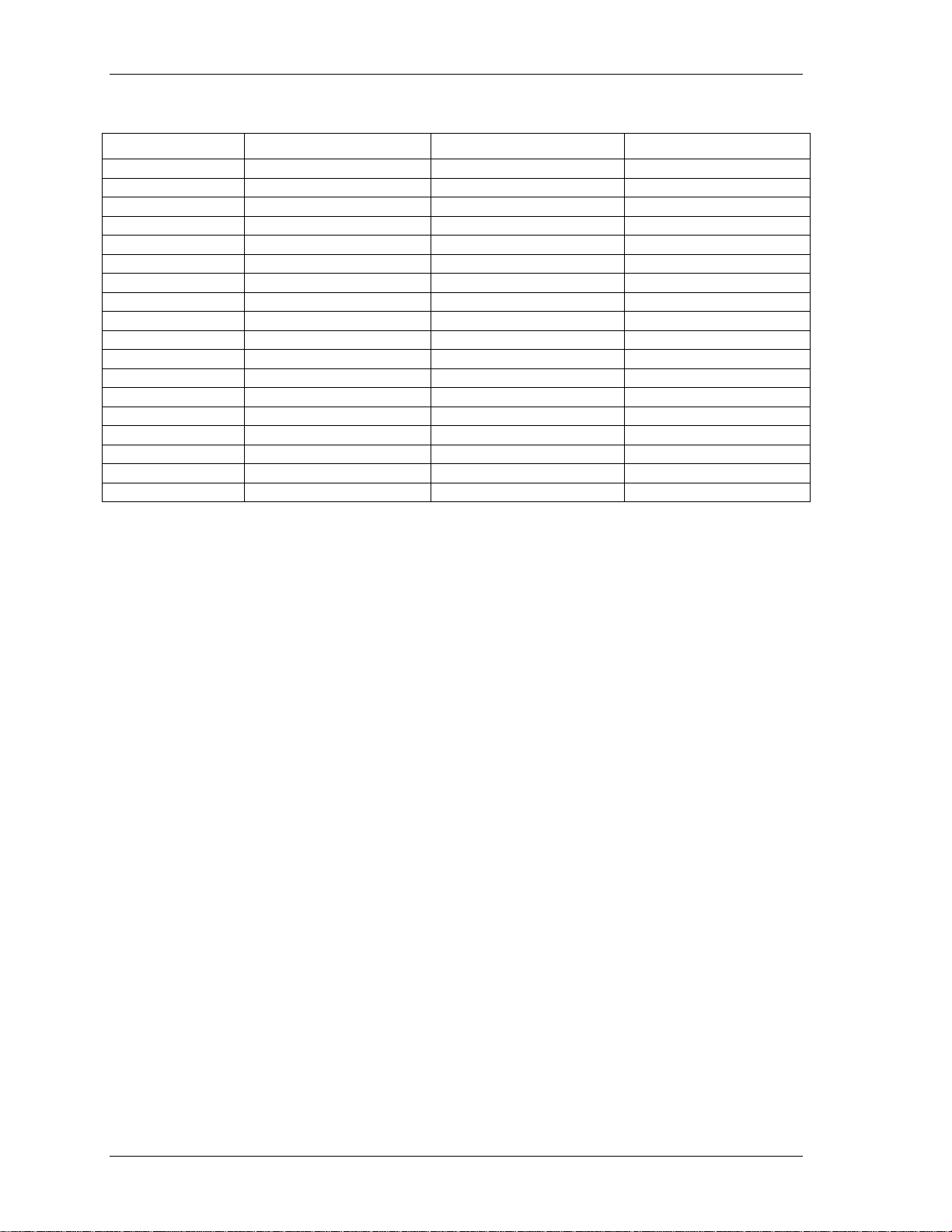
Range input values
Range Input value Range Input value
±20 V 27 0 to 5 V 14
±10 V 1 0 to 4 V 36
±5 V 2 0 to 2.5 V 15
±4 V 28 0 to 2 V 16
±2.5 V 3 0 to 1.67 V 17
±2 V 29 0 to 1.25 V 18
±1.67 V 4 0 to 1 V 19
±1.25 V 5 0 to 0.5 V 32
±1 V 6 0 to 0.25 V 33
±0.625 V 7 0 to 0.2 V 34
±0.5 V 8 0 to 0.1 V 20
±0.25 V 30 0 to 0.01 V 21
±0.2 V 31 0 to 0.02 V 35
±0.1 V 9 4 to 20 mA 22
±0.05 V 10 0 to 20 mA 26
±0.01 V 11 2 to 10 mA 23
±0.005 V 12 1 to 5 mA 24
0 to 10 V 13 0.5 to 2.5 mA 25
DataValue Value of A/D measurement in binary counts. Use ToEng.VI (on page 48) to
convert into engineering units (volts or milliamps).
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI (on page 97) to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 19

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
19
AInScBg.VI
Changed R3.3 ID, R5.4 ID'
Scans a range of A/D channels in the background and stores the samples in an array. This VI reads the
specified number of A/D samples at the specified sampling rate from the specified range of A/D channels
from the specified board. If the A/D board has programmable gain, it sets the gain to the specified range. The
collected data is returned to the data array. This VI immediately returns control to your program and the data
transfer from the A/D board into ADData will continue in the background. ADData is the array contained in
the context output. Use the GetStatus.VI to check on the status of the background operation and to get data as
it is being collected. Use StopBg.VI to terminate the background process before it has completed. Always
execute StopBg.VI after any background operation has terminated normally to clear variables and flags.
Revision 3.3: added an option to disable real-t ime calibration. See OptAIn.VI on page 30 for detail s .
Revision 5.4: added InterChannel Delay input.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
LowChan [I32] - First A/D channel of scan
HighChan [I32] - Last A/D channel of scan
Count [I32] - Number of A/D samples to collect
Rate [I32]- Sample rate in scans per second
Range [I32]- A/D range code
Continuous [TF] - Run the VI in an endless loop
Options [I32] - Bit fields that control various options.
InterChannel Delay [SGL] - Delay in seconds between channels in a scan.
Rate [I32] - Actual rate the board sampled
Context [cluster] - Output data structure.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI on page 97.
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have an A/D. Can be from 0 to 100.
LowChan First A/D channel of scan.
HighChan Last A/D channel of scan.
Low/High Channel #: The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of
A/D board is being used. For boards that ha v e bot h si n gl e-ended and differential
inputs, the maximum allowable channel number also depends on how the board is
configured. For example, a PCI-DAS6025 has 8 channels for differential, 16 for
single-ended mode.
Count Specifies the total number of A/D samples that will be collected. If more than one
channel is being sampled then the number of samples collected per channel is
equal to
Count / (HighChan- LowChan+1).
Page 20

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
20
Rate (input) This is the rate at which scans are triggered. If you are sampling four channels, 0-3,
specifying a rate of 10,000 scans per second (10 kS/s) will result in the A/D
converter rate of 40 kS/s: (4 channels at 10,000 samples per channel per second).
This is different from some software where you specify the total A/D chip rate. In
those systems, the per channel rate is equal to the A/D rate divided by the number
of channels in a scan. This argument also returns the value of the actual rate set.
This may be different from the requested rate because of pacer limitations.
Caution! You will generate an error if you specify a total A/D rate beyond the capability of the board.
For example; if you specify LowChan = 0, HighChan = 7 (8 channels total) and Rate = 40,000
and you are using a PCI-DAS6025, you will get an error. You have specified a total rate of 8
x 40,000 = 320,000.
The PCI-DAS6025 is capable of converting 200,000 samples per second. The maximum
sampling rate depends on the A/D board that is being used and on the sampling mode options.
Range If the selected A/D board does not have a programmable range feature, this
argument is ignored. Otherwise the gain can be set to any of the following ranges
that are supported by the selected A/D board. Refer to the board-specific
information for the list of ranges supported by each board. See the "
" table on page 19 for valid values. Refer to board-specific information
values
Range input
contained in the Universal Library User's Guide (available at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
) for a list of the A/D ranges
supported by each board.
Continuous This option (True) puts the VI in an endless loop. After it collects the required
number of samples, it resets to the start of the buffer and begins again. The only
way to stop this operation is with StopBg.VI.
Options For a detailed explanation of the Options field, refer to OptAIn.VI on page 30. The
OptAIn.VI must be wired to this input.
InterChannel Delay Delay in seconds between channels in a scan. Negative values indicate that the
interchannel delay will automatically be minimized. Currently, positive values will
result in interchannel delays corresponding to the
Rate*(HighChan-LowChan+1)).
1/(
Rate (output) Actual sampling rate in channel scans per second. This may be different from the
requested rate because of pacer limitations.
Context
Data structure containing information from a background operation. Some of the
Rate sampling rate. For example:
information included is the board number, the data array, the array size, and the
initial status of the background operation.
Follow the steps below when wiring this VI:
1. Start a background operation.
2. GetStatus.VI checks for completion (boolean output called
"Running").
3. StopBg.VI terminates the operation, if not already done, and
frees memory aliases.
4. Data output from the background operation is passed to
GetStatus.VI and StopBg.VI via "Context", and can be wired
from one or both of them for intermediate or final actions,
respectively.
The demo VIs illustrate this process effectively.
ErrCode
Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert Err Code into a readable string.
Important - Read board-specific information in UL User's Guide
In order to understand the functions, read the board-specific information contained in the Universal Library
User's Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf). The
example programs should be exami ned and run prior to attempting any programmi ng of y ou r ow n.
Page 21

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
21
AInScFg.VI
Changed R3.3 ID, R5.4 ID
Scans a range of A/D channels in the foreground and stores the sample s in an array. This VI reads the
specified number of A/D samples at the specified sampling rate from the specified range of A/D channels
from the specified board. If the A/D board has programmable gain, it sets the gain to the specified range. The
collected data is returned to the data array. This VI will not return control to your program until all requested
data has been collected and returned to ADData.
Revision 3.3: added an option to disable real-t ime calibration. See OptAIn.VI on page 30 for detail s .
Revision 5.4: added InterChannel Delay input.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
LowChan [I32] - First A/D channel of scan
HighChan [I32] - Last A/D channel of scan
Count [I32] - Number of A/D samples to collect
Rate [I32] - Sample rate in scans per second
Range [I32] - A/D range code
Options [I32] - Bit fields that control various options. See Note 1.
InterChannel Delay [SGL]- Delay in seconds between channels in a scan.
Rate [I32] - Actual rate the board sampled
ADData [U16] - Data array that stores A/D values
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI on page 97.
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have an A/D.
LowChan First A/D channel of scan.
HighChan Last A/D channel of scan.
Low/High Channel #: The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of
A/D board is being used. For boards that ha v e bot h si n gl e-ended and differential
inputs, the maximum allowable channel number also depends on how the board is
configured. For example, a PCI-DAS6025 has 8 channels for differential, 16 for
single-ended mode.
Count Specifies the total number of A/D samples that will be collected. If more than one
channel is being sampled then the number of samples collected per channel is
equal to Count / (HighChan- LowChan+1).
Rate This is the rate at which scans are triggered. If you are sampling four channels, 0-3,
then specifying a rate of 10,000 scans per second (10 kS/s) will result in the A/D
converter rate of 40 kS/s: (4 channels at 10,000 samples per channel per second).
This is different from some software where you specify the total A/D chip rate. In
those systems, the per channel rate is equal to the A/D rate divided by the number
of channels in a scan. This argument also returns the value of the actual rate set.
This may be different from the requested rate because of pacer limitations.
Page 22

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
22
Caution! You will generate an error if you specify a total A/D rate beyond the capability of the board.
For example, if you specify LowChan = 0, HighChan = 7
(8 channels total) and Rate = 40,000 and you are using a PCI-DAS6025, you will get an error.
You have specified a total rate of 8 x 40,000 = 320,000. The PCI-DAS6025 is capable of
converting 200,000 samples per second. The maximum sampling rate depends on the A/D
board that is being used. It is also dependent on the sampling mode options.
Range If the selected A/D board does not have a programmable range feature, then this
argument will be ignored. Otherwise the gain can be set to any of the following
ranges that are supported by the selected A/D board. Refer to board-specific
information for the list of ranges supported by each board. See the "
" table on page 19 for valid values.
values
Range input
Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's
Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-
guide.pdf) for a list of the A/D ranges supported by each board.
Options For a detailed explanation of the Options field refer to OptAIn.VI on page 30.
The OptAIn.VI must be wired to this input.
InterChannel Delay Delay in seconds between channels in a scan. Negative values indicate that the
interchannel delay will automatically be minimized. Currently, positive values will
result in interchannel delays corresponding to the
Rate*(HighChan-LowChan+1)).
1/(
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Rate sampling rate. For example:
Important - Read board-specific information in UL User's Guide
In order to understand the functions, read the board-specific information contained in the Universal Library
User's Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf). The
example programs should be exami ned and run prior to attempting any programmi ng of y ou r ow n.
Page 23
Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
23
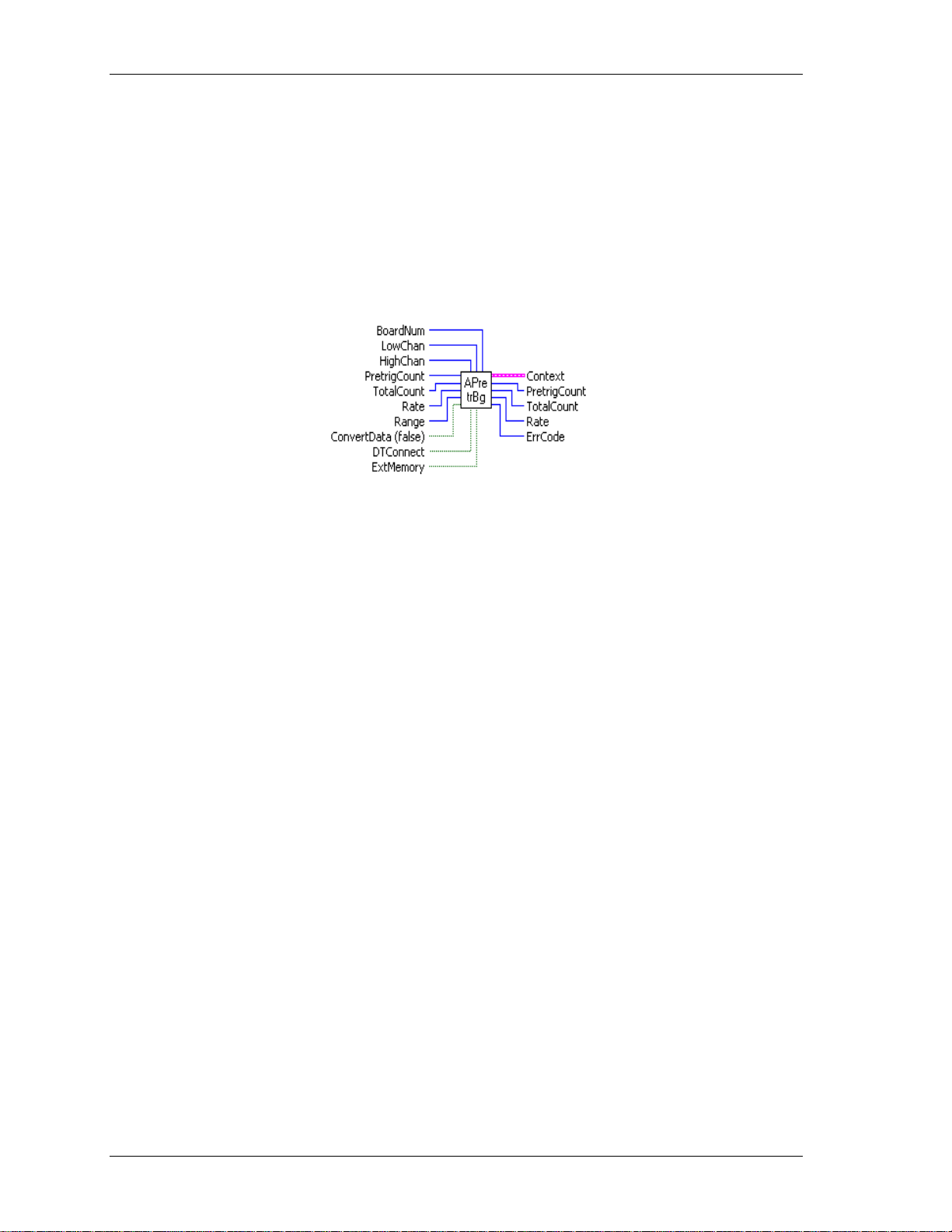
APretrBg.VI
Waits for a trigger to occur and then returns a specified number of analog samples before and after the trigger
occurred. If only 'polled gate' triggering is supported, the trigger input line (see board user's manual) must be
at TTL low before this VI is called or a
condition is met. See SetTrig.VI and board-specific information. After this VI is called, execution will return
immediately to the next point in your program and the data collection —from the A/D into the
Context cluster—will continue in the background. Use GetStatus.VI to check on the status of the
the
background operation. Use StopBg.VI to terminate the background process before or after it has completed its
function.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
LowChan [I32] - First A/D channel of scan
HighChan [I32] - Last A/D channel of scan
PretrigCount [I32] - Number of pre-trigger A/D samples to collect
TotalCount [I32] - Total number of A/D samples to collect
Rate [I32] - Sample rate in scans per second
Range [I32] - A/D Range code or 0
ConvertData [TF] - Convert data option (Boolean)
DTConnect [TF] - DT connect option (Boolean)
ExtMemory [TF] - External memory option (Boolean)
Context [cluster] - Output data structure.
PretrigCount [I32] - Number of pre-trigger A/D samples collected
TotalCount [I32] - Total number of A/D samples collected
Rate [U32] - Actual sample rate in scans per second
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI on page 97.
TRIGSTATE error will occur. The trigger occurs when the trigger
Data portion of
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have an A/D.
LowChan First A/D channel of scan.
HighChan Last A/D channel of scan.
Low/High Channel #: The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of
A/D board is being used. For boards that ha v e bot h si n gl e-ended and differential
inputs, the maximum allowable channel number also depends on how the board is
configured. For example, a PCI-DAS6025 has 8 channels for differential, 16 for
single-ended mode.
Page 24

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
24
PretrigCount Specifies the number of samples before the trigger that will be returned.
PretrigCount must be less than TotalCount - 512. If the trigger occurs too early,
then fewer than the requested number of pre-trigger samples will be collected. In
that case a
TOOFEW error will occur. The PretrigCount will be set to indicate how
many pretrigger samples were collected and the post-trigger samples will still be
collected.
TotalCount Specifies the total number of samples that will be collected and stored in
DataArray. TotalCount must be greater than or equal to PretrigCount + 512. If the
trigger occurs too early, then fewer than the requested number of samples will be
collected. In that case a
TOOFEW error will occur. The TotalCount will be set to
indicate how many total samples were actually collected.
Rate Desired sample rate in samples per channel per second.
Range If the selected A/D board does not have a programmable gain feature, this
argument will be ignored. Otherwise the
are supported by the selected A/D board. See the "
Range can be set to any of the ranges that
Range input values" table on
page 19 for valid values.
Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's
Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-
guide.pdf) for a list of the A/D ranges supported by each board.
ConvertData Set this option to False (default) when using APretrBg.VI.
DTConnect When the DTCONNECT option (True) is used with this VI, the data from ALL
A/D conversions is sent out the DT-CONNECT interface. While this VI is waiting
for a trigger to occur, it will send data out the DT-CONNECT interface
continuously. If you have a MCC memory board plugged into the DT-CONNECT
interface then you should use
ExtMemory If you use this option (True) to send the data to a connected memory board then
EXTMEMORY option rather than this option.
you must use MemRdPrt.VI to later read the pre-trigger data from the memory
board. If you use MemRead.VI, the data will NOT be in the correct order. Every
time this option is used it will overwrite any data that is already stored in the
memory board. Read all data from the board (with MemRdPrt.VI) before
collecting any new data. The Mega Fifo memory must be fully populated to use the
APretrBg.VI or APretrFg.VI.
Context The data array for the pretrigger data. This is a data structure containing output
information including the board number, the contents of
DataArray, and the initial status of the background operation. CONTEXT must be
DataArray, the size of
wired to subsequent VIs in order to process this VI correctly.
Follow the steps below when wiring this VI:
PretrigCount
TotalCount Total number of A/D samples collected.
Rate Actual sample rate in scans per second .
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
Actual number of pre-trigger A/D samples collected.
1. Start a background operation.
2. GetStatus.VI checks for completion (boolean output called "Running").
3. StopBg.VI terminates the operation, if not already done, and frees memory aliases.
4. Data output from the background operation is passed to GetStatus.VI and StopBg.VI
via Context, and can be wired from one or both of them for intermediate or final
actions, respectively.
The demo VIs illustrate this process effectively.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 25

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
25
APretrFg.VI
Waits for a trigger to occur and then returns a specified number of analog samples before and after the trigger
occurred. If only 'polled gate' triggering is supported, the trigger input line (refer to the hardware user's
manual) must be at TTL low before this VI is called or a
the trigger condition is met. See SetTrig.VI on page 33 and board-specific information for details. This VI will
not return to your program until all of the requested data has been collected and returned to
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
LowChan [I32] - First A/D channel of scan
HighChan [I32] - Last A/D channel of scan
PretrigCount [I32] - Number of pre-trigger A/D samples to collect
TotalCount [I32] - Total number of A/D samples to collect
Rate [U32] - Sample rate in scans per second
Range [I32] - A/D range code or 0
ConvertData [TF] - Convert data option (Boolean)
DTConnect [TF] - DT connect option (Boolean)
ExtMemory [TF] - External memory option (Boolean)
DataArray [U32] - Data array that stores A/D values
PretrigCount [I32]- Actual number of pre-trigger A/D samples collected
TotalCount [I32] - Total number of A/D samples collected
Rate [U32] - Actual sample rate in scans per second
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
TRIGSTATE error will occur. The trigger occurs when
DataArray.
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have an A/D.
LowChan/HighChan The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of A/D board is being
used. For boards that have both single ended and differential inputs, the maximum
allowable channel number also depends on how the board is configured (8
channels for differential, 16 for single -ended).
PretrigCount Specifies the number of samples before the trigger that will be returned.
PretrigCount must be less than TotalCount - 512. If the trigger occurs too early,
fewer than the requested number of pre-trigger samples will be collected. In that
TOOFEW error will occur. The PretrigCount will be set to indicate how many
case a
samples were collected and the post trigger samples will still be collected.
TotalCount The total number of samples that will be collected and stored in DataArray.
TotalCount must be greater than or equal to PretrigCount + 512. If the trigger
occurs too early then fewer than the requested number of samples will be collected.
In that case, a
TOOFEW error will occur. The TotalCount will be set to indicate how
many samples were actually collected.
Page 26

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
26
Range If the selected A/D board does not have a programmable gain feature, this
argument is ignored. Otherwise the
supported by the selected A/D board. See the "
Range can be set to any of the ranges that are
Range input values" table on page
19 for valid values.
Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's
Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-
guide.pdf) for a list of the A/D ranges supported by each board.
ConvertData The data is collected into a "circular" buffer. When the data collection is complete,
the data is in the wrong order. If using the
CONVERTDATA option (True), when
data acquisition is complete, the data is automatically rotated into the correct order
and converted to 12-bit values. Otherwise, you must call ACnvPrDt.VI to rotate
the data.
DTConnect When the DTConnect option (True) is used with this VI, the data from all A/D
conversions is sent out the DT-CONNECT interface. While this VI is waiting for a
trigger to occur, it will send data out the DT-CONNECT interface continuously. If
you have a memory board plugged into the DT-CONNECT interface, use the
ExtMemory option rather than this option.
ExtMemory If using this option (True) to send the data to a connected memory board, you must
use MemRdPrt.VI to read the pre-trigger data from the memory board later. If you
use the MemRead.VI, the data will not be in the correct order. Every time this
option is used it will overwrite any data that is already stored in the memory board.
All data should be read from the board (with MemRdPrt.VI before collecting any
new data. The Mega-Fifo memory must be fully populated to use the APretrBg.VI
or APretrFg.VI.
DataArray
PretrigCount [ Actual number of pre-trigger A/D samples collected.
TotalCount Total number of A/D samples collected.
Rate Actual sample rate in scans per second.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
The data array for the pretrigger data.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 27

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
27
ATrigger.VI
Waits for a specified analog input channel to go above or below a specified value. This VI continuously reads
the specified channel and compares its value to
BELOW it waits for the first A/D sample that is above or below TrigValue. It returns the first sample that
meets the trigger criteria to DataValue.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Channel [I32] - A/D channel number
TrigType [TF] - TRIGABOVE (True) or TRIGBELOW (False) - Specifies whether to wait
for the analog input to be above or below the specified trigger value.
Outputs:
TrigValue [I32] - The threshold value that all A/D values are compared to
DataValue [U16] - The value of the first A/D sample that met the trigger criteria is
returned here.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
TrigValue. Depending on whether TrigType is ABOVE or
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have an A/D.
Channel The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of A/D board is being
used. For boards that have both single ended and differential inputs, the maximum
allowable channel number also depends on how the board is configured. For
example, a PCI-DAS6025 has 8 channels for differential, 16 for single-ended.
TrigType Specifies whether to wait for the analog input to be ABOVE or BELOW the
specified trigger value.
TRIGABOVE - Wait for analog input to be above the specified trigger value.
TRIGBELOW - Wait for analog input to be below the specified trigger value.
TrigValue Must be in the range 0 to 40 9 5 fo r 12 - bi t A/ D boards, or 0 to 65,535 for 16-bit
A/D boards.
Use this VI with caution in Windows programs. All active windows will be locked
on the screen until the trigger condition is satisfied. All keyboard and mouse
actions will also be locked until the trigger condition is satisfied.
DataValue First sample that meets trigger criteria. Use ToEng.VI to convert from binary
counts to engineering units (volts or milliamps).
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 28

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
28
ALoadQue.VI
Loads the A/D board's channel/gain queue. This VI only works with A/D boards that have channel/gain queue
hardware.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed. The specified
ChanArray This array should contain all of the channels th at will be loaded into the channel
GainArray This array should contain each of the A/D ranges that will be loaded into the
Count Specifies the total number of channel/gain pairs that will be loaded into the queue.
Normally the AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI scans a fixed range of channels (from
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ChanArray [I16] - Array containing channel values
GainArray [I16] - Array containing A/D range values
Count [I32] - Number of elements in ChanArray and GainArray, or (0) to disable
the board's channel/gain queue.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
board must have an A/D and a channel/gain queue.
gain queue.
channel gain queue.
ChanArray and GainArray should contain at least Count elements. Set Count=0 to
disable the board's channel/gain queue. The maximum value is specific to the
queue size of the A/D boards channel gain queue.
LowChan to HighChan) at a fixed A/D range. If you load the channel gain queue
with this VI, all subsequent calls to AInScFg.VI or AInScBg.VI cycle through the
channel/gain pairs that you have loaded into the queue.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 29

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
29
OptAIn.VI
Changed R3.3ID
Generates option input for AInScBg.V I o r AInS cFg .V I.
Rev.3.3: Added NoCalibrateData option.
Rev. 7.1: Added BurstIO setting for
Mode option
Summary:
Inputs: ExtClock [TF] - External (True) or internal clock (False = "TIMED")
BurstMode [TF] - Burst mode option (board-specific) (True). (False =
Output:
ConvertData [TF] - Separate data and channel tags (True).
(False =
DTConnect [TF] - DT connect option (True). (False = "NO DTCONNECT")
ExtMemory [TF] - External memory option (Mega Fifo board) (True).
False= "
Mode [I32] - Sampling mode used.
NOBURSTMODE")
"
ExtTrigger [TF] - External trigger option (True). (False = "NOEX TRIGGER")
NoToDints [TF] - Option to disable time of day interrupts (True).
(False = "
NoCalData [TF] - Option to disable real time software calibration (True).
(False = "
AInScanOptions [I32] - Anded value of input options.
NOCONVERTDATA")
NORMMEMORY")
TODInts")
CalData")
Arguments:
ExtClock If this option is used , then conversions will be controlled by the signal on the
trigger input line rather than by the internal pacer clock. Each conversion will be
triggered on the appropriate edge of the trigger input signal (refer to board-specific
information). When this option is used, the
Rate argument is ignored. The
sampling rate is dependent on the trigger signal. Options for the board will default
to a transfer mode that will allow the maximum conversion rate to be attained
unless otherwise specified.
ConvertData If the CONVERTDATA option is used for 12-bit boards, then the data that is
returned to data buffer (array) will automatically be converted to 12-bit A/D
values. If
NOCONVERTDATA is used, data from 12-bit A/D boards will be returned as
16-bit values that will contain both a 12-bit A/D value and a 4-bit channel number.
After the data collection is complete, you can call ACvtData.VI to convert the data
after the fact.
CONVERTDATA cannot be specified if you are using a background
VI and DMA transfers. This option is ignored for 16-bit boards.
DTConnect All A/D values will be sent to the A/D board's DT CONNECT port. This option is
incorporated into the
EXTMEMORY option. Use DTCONNECT only when the
external board is not supported by the Universal Library.
Page 30
Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
30
ExtMemory Data is returned to a data buffer (array). EXTMEMORY causes the command to
send the data to a connected memory board via the DT-Connect interface rather
than returning the data to data buffer (array). Every time this option is used it
overwrites any data already stored in the memory board. The data should be
unloaded with the MemRead.VI before coll ect i ng new data .
Do not use
Mode Trigger and transfer method options
Mode Setting Explanation
DEFAULTIO
SINGLEIO
DMAIO
BLOCKIO
BURSTIO
BurstMode Enables burst mode sampling. Scans from LowChan to HighChan are clocked at the
EXTMEMORY and DTCONNECT together.
0
1
2
3
4
Default and recommended sampling mode. The optimum
sampling mode is chosen based on board type and sampling
speed.
A/D conversions and transfers to memory are initiated by an
interrupt. One interrupt per conversion.
A/D conversions are initiated by a trigger. Transfers are
initiated by a DMA request.
A/D conversions are initiated by a trigger. Transfers are
handled by REP-INSW.
Allows higher sampling rates for sample counts up to full
FIFO. Data is collected into the local FIFO. Data transfers to
the PC are held off until after the scan is complete.
BURSTIO is the default mode for non-Continuous fast scans
(aggregate sample rates above 1000 Hz) with sample counts up
to full-FIFO. To avoid the BURSTIO default, specify
BLOCKIO.
BURSTIO is not a valid option for most boards. It is used
mainly for USB products.
maximum A/D rate between samples to minimize channel-to-channel skew. Scans
are initiated at the rate specified by
ExtTrigger If this option is specified, the sampling will not begin until the trigger condition is
Rate.
met. On many boards, this trigger condition is programmable (see SetTrig.VI on
page 33 and board-specific information for details). On other boards, only 'polled
gate' triggering is supported. In this case, assuming active high operation, data
acquisition will commence immediately if the trigger input is high. If the trigger
input is low, acquisition will be held off until it goes high. If only 'polled gate'
triggering is supported, this option is most useful if the signal is a pulse with a very
low duty cycle (trigger signal in TTL low state most of the time) so that triggering
will be held off until the occurrence of the pulse.
NoToDints If this option is specified, the system's time-of-day interrupts are disabled for the
duration of the scan. These interrupts are used to update the system’s real time
clock and are also used by various other programs. These interrupts can limit the
maximum sampling speed of some boards - particularly the PCM-DAS08. If the
interrupts are turned off using this option, the real-time clock will fall behind by
the length of time that the scan takes.
NoCalData Turns off real-time software calibration for boards which are software-calibrated
by applying calibration factors to the data on a sample by sample basis as it is
acquired. Examples are the PC-CARD-DAS16/330 and PC-CARD-DAS16x/12.
Turning off software calibration saves CPU time during a high speed acquisition
run. This may be required if your processor is less than a 150 MHz Pentium and
you desire an acquisition speed in excess of 200 kHz. These numbers may not
apply to your system. Only trial and error testing will tell for sure.
DO NOT use this option if it is not necessary. If this option is used, the data must
be calibrated after the data acquisition with the ACalData.VI.
Page 31

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
31
AInScanOptions All of the inputs are Anded together and the result is passed to this parameter for
input to AInScBg.VI and AInScFg.VI. The
AInScanOptions output of this VI must
be wired to the options input of the AInScFg.VI or AInScBg.VI.
Page 32

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
32
SetTrig.VI
Selects the trigger source and sets up its parameters. This trigger is used to initiate analog to digital
conversions using the following UL for NI LabVIEW VIs:
AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI, if the
EXTRIGGER option is selected.
APretrFg.VI or APretrBg.VI
FilePret.VI
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Type [U32] -Trigger type (see table below)
LowThreshold [U32] - Low threshold for analog trigger
HighThreshold [U32] - High threshold for analog trigger
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
board must have the software-selectable triggering source and/or options.
Type Specifies the trigger or gate type to configure. This can be one of the constants
specified in the
Trigger
Source
Analog GATE_NEG_HYS
Analog GATE_POS_HYS
Analog GATE_ABOVE
Analog GATE_BELOW
Analog TRIG_ABOVE
Analog TRIG_BELOW
Analog GATE_IN_WINDOW
Analog GATE_OUT_WINDOW
Digital GATE_HIGH
Digital GATE_LOW
Type Explanation
Type column below.
A/D conversions are enabled when the external analog trigger input is more
positive than HighThreshold. A/D conversions are disabled when the
external analog trigger input is more negative than LowThreshold.
Hysteresis is the level between LowThreshold and HighThreshold.
A/D conversions are enabled when the external analog trigger input is more
negative than LowThreshold. A/D conversions are disabled when the
external analog trigger input is more positive than HighThreshold.
Hysteresis is the level between LowThreshold and HighThreshold.
A/D conversions are enabled as long as the external analog trigger input is
more positive than HighThreshold.
A/D conversions are enabled as long as the external analog trigger input is
more negative than LowThreshold.
A/D conversions are enabled when the external analog trigger makes a
transition from below HighThreshold to above. After conversions are
enabled, the external trigger is ignored.
A/D conversions are enabled when the external analog trigger input makes
a transition from above LowThreshold to below. After conversions are
enabled, the external trigger is ignored.
A/D conversions are enabled as long as the external analog trigger is inside
the region defined by LowThreshold and HighThreshold.
A/D conversions are enabled as long as the external analog trigger is
outside the region defined by LowThreshold and HighThreshold.
A/D conversions are enabled as long as the external digital trigger input is
5V (logic HIGH or "1").
A/D conversions are enabled as long as the external digital trigger input is
0V (logic LOW or "0").
Page 33

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
33
Trigger
Source
Digital TRIG_HIGH
Digital TRIG_LOW
Digital TRIG_POS_EDGE
Digital TRIG_NEG_EDGE
LowThreshold
Type Explanation
A/D conversions are enabled when the external digital trigger is 5 V (logic
HIGH or "1"). After conversions are enabled, the external trigger is
ignored.
A/D conversions are enabled when the external digital trigger is 0 V (logic
LOW or "0"). After conversions are enabled, the external trigger is ignored.
A/D conversions are enabled when the external digital trigger makes a
transition from 0 V to 5 V (logic LOW to HIGH). After conversions are
enabled, the external trigger is ignored.
A/D conversions are enabled when the external digital trigger makes a
transition from 5 V to 0 V (logic HIGH to LOW). After conversions are
enabled, the external trigger is ignored.
Selects the low threshold used when the trigger input is analog. The value must be
(unsigned)
specified in counts within the range of the board's A/D trigger circuit resolution.
Refer below to "Notes."
This parameter is ignored when the trigger input is digital.
HighThreshold
Selects the high threshold used when the trigger input is analog. The value must be
(unsigned)
specified in counts within the range of the board's A/D trigger circuit resolution.
Refer below to "Notes."
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
Notes:
The value of the threshold must be within the range of the analog trigger circuit associated with the board.
Please refer to board-specific information. For example, on the PCI-DAS1602/16 the analog trigger circuit
handles ±10 V. Therefore, a value of 0 corresponds to -10 V and a value of 65535 corresponds to +10 V.
Page 34

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
34
TIn.VI
Changed R3.3 ID
Reads a temperature input channel, linearizes it according to the configured temperature sensor type, and
returns the temperature in degrees. The CJC channel, gain, and sensor type are read from the configuration
file. They should be set by running the InstaCal configuration program.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100..
Outputs:
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
Chan Input channel to read. For EXP boards, the channel number is calculated using the
A/DChan = A/D channel the multiplexer ("mux") is connected to
For example, if you had an EXP16 connected to a PCI-DAS08 via the PCI-DAS08
Scale Specifies the temperature scale that the input will be converted to. Choices are
Options FILTER: The TIn.VI applies a smoothing function to thermocouple readings very
Temperature The temperature in degrees is returned here. Resolution is hardware dependent.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
Chan [U32] - Channel to read
Scale [U32] - The temperature scale used to calculate the temperature in degrees.
Options [TF] - Bit that controls data smoothing (averaging) option (True).
FILTER" (True) is default.
"
Temperature [SGL] - Temperature return ed here.
following formula:
MuxChan = Mux board input channel number
Chan = (ADChan+1) * 16 + MuxChan
channel 0 (remember, DAS08 channels are num bered 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7) , a nd
if you had a thermocouple connected to channel 5 of the EXP16, the value for
Chan would be (0 + 1) x 16 + 5 = 21.
CELSIUS, FAHRENHEIT and KELVIN.
much like the electrical smoothing inherent in all thermocouple instruments. When
selected, 10 samples are read from the specified channel and averaged. The
average is the reading returned. This is the default.
NOFILTER: If you use the NOFILTER option (False), the thermocouple readings will
not be smoothed and you will see a scattering of readings around a mean.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
A/D Range – IMPORTANT
If an EXP board is connected to an A/D that does not have programmable gain then the A/D board input range
is read from the configuration file (CB.CFG). In most cases, hardware-selectable ranges should be set for
±5 V for thermocouples and 0 to 10 V for RTDs. If the board does have programmable gains, the TIn.VI will
set the appropriate A/D range. Refer to the board-specific information for details.
Page 35

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
35
Note on CJC Channel: The CJC channel is set in the InstaCal program. If you have multiple EXP boards, the
LabVIEW VI will apply the CJC reading to the linearization formula in the following manner:
If you have chosen a CJC channel for the EXP board that the channel you are reading is on, it will use the
CJC temp reading from that board.
If you have left the CJC channel for the EXP board that the channel you are reading is on to NOT SET,
the VI will use the CJC reading from the next lower EXP board with a CJC channel selected.
For example: Assume you have four CIO-EXP16 boards connected to a PCI-DAS08 on channel 0, 1, 2, and 3,
and you have chosen CIO-EXP16 #1 (connected to PCI-DAS08 channel 0) to have its CJC read on PCIDAS08 channel 7.
If you have left CIO-EXP16 CJC channels 2, 3, and 4 to NOT SET, those CIO-EXP boards will all use
the CJC reading from CIO-EXP16 #1, connected to channel 7 for linearization.
Note that it is important to keep the CIO-EXP boards in the same case and out of any breezes to ensure valid
CJC readings.
Important - Read board-specific information in UL User's Guide
In order to understand the functions, read the board-specific information contained in the Universal Library
User's Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf). The
example programs should be exami ned and run prior to attempting any programmi ng of y ou r ow n.
Page 36

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
36
TInScan.VI
Changed R3.3 ID
Reads a range of temperature input channels, linearizes them according to temperature sensor type, and
returns the temperatures to an array in degrees. The CJC channel, the gain, and sensor type are read from the
configuration file. Use InstaCal to change any of these options.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
LowChan {U32] - Low mux channel of scan.
HighChan [U32] - High mux channel of scan.
Scale [U32] - The temperature scale used to calculate the temperature in degrees.
Options [TF] -Bit that controls data smoothing (averaging) option (T). "FILTER"
(T) is default
DataValues [SGL] – Array of temperatures returned here.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
LowChan First A/D channel of scan.
HighChan Last A/D channel of scan.
Low/High Channel #: Specify the range of multiplexer channels that will be
scanned. For EXP boards, these channel numbers are calculated using the
following formula:
A/DChan = A/D channel that mux is connected to
MuxChan = Mux board input channel number
Chan = (ADChan+1) * 16 +
MuxChan (where MuxChan ranges from 0 to 15,
indicating which channel on a particul ar b o a rd ).
For example, if you had an EXP16 connected to a PCI-DAS08 via the PCI-DAS08
channel 0 (remember, DAS08 channels are num bered 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7) , a nd
if you had a thermocouple connected to channel 5 of the EXP16, the value for
would be (0 + 1) x 16 + 5 = 21. For 6 and 7 of the EXP16, the value for
would be (0 + 1) x 16 + 6 = 22 and the value for
HighChan would be (0 + 1) x 16 +
LowChan
7 = 23.
Scale Specifies the temperature scale that the input will be converted to. Choices are
CELSIUS, FAHRENHEIT and KELVIN.
Options FILTER (T) - The TInScan.VI applies a smoothing fun c tion to thermocouple
readings very much like the electrical smoothing inherent in all thermocouple
instruments. When selected, 10 samples are read and averaged on each channel.
The average is the reading returned. This is the default.
NOFILTER (F) - If you use the NOFILTER option then the thermocouple readings
will not be smoothed and you will see a scattering of readings around a mean.
DataValues[] The temperature is returned in degrees. Each element in the array corresponds to a
channel in the scan.
LowChan + 1 temperature values.
DataValues must be at least large enough to hold HighChan -
Chan
Page 37

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Input VIs
37
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
A/D Range – IMPORTANT
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
If an EXP board is connected to an A/D board that does not have programmable gain then the A/D board input
range is read from the configuration file (CB.CFG). In most cases, hardware-selectable ranges should be set
for ±5 V for thermocouples and 0 to 10 V for RTDs. If the board does have programmable gains, the
TInScan.VI will set the appropriate A/D range. Refer to the board-specific information for details.
Note on CJC Channel: The CJC channel is set in the install p rogram. If you have multiple EXP boards, the
LabVIEW VI will apply the CJC reading to the linearization formula in the following manner:
If you have chosen a CJC channel for the EXP board that the channel you are reading is on, it will use the
CJC temp reading from that board.
If you have left the CJC channel for the EXP board that the channel you are reading is on to NOT SET,
the VI will use the CJC reading from the next lower EXP board with a CJC channel selected.
For example: Assume you have four CIO-EXP16 boards connected to a PCI-DAS08 on chan nel 0, 1, 2,
and 3, and you have chosen CIO-EXP16 #1 (connected to PCI-DAS08 channel 0) to have its CJC read on
PCI-DAS08 channel 7.
If you have left CIO-EXP16 CJC channels 2, 3, and 4 to NOT SET, those CIO-EXP boards will all use
the CJC reading from CIO-EXP16 #1, connected to channel 7 for linearization.
Note that it is important to keep the CIO-EXP boards in the same case and out of any breezes to ensure valid
CJC readings.
Page 38

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Output VIs
38
Analog Output VIs
AOut.VI
Sets the value of a D/A output.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
Channel The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of D/A board is being
DataValue Must be in the range 0 – N, where N is the value 2
Range If the selected D/A board does not have a programmable range feature, this
For simultaneous-update boards: If you have set the simultaneous update jumper for simultan eous operation,
you should use AOutScBg.VI or AOutScFg.VI for simultaneous update of multiple channels. AOut.VI always
writes the D/A data then reads the D/A, which causes the D/A output to be updated.
Channel [I32] - Number of D/A channel to update.
Range [I32] - A/D Range code
DataValue [U16] - Value to update D/A.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
specified board must have a D/A.
used.
Resolution
- 1 of the converter.
argument will be ignored. Otherwise, the gain can be set to any of the ranges that
are supported by the selected D/A board. See the "
Range input values" table on
page 19 for valid values. Refer to board-specific information contained in the
Universal Library User's Guide (available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
) for the list of ranges
supported by each board.
Page 39

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Output VIs
39
AOutScFg.VI
Outputs the values to a range of D/A channels in the foreground.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Data Array [U16] - Data array to output D/A values from.
Outputs:
LowChan [I32] - First D/A channel of scan.
HighChan [I32] - Last D/A channel of scan
Rate [I32] - Sample rate in scans per second [U32]
Range [I32] - D/A range code
Simultaneous [TF] - Simultaneous update mode
ExtClock [TF] - Pace conversions externally
ErrCode [I32] -Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Rate [I32] - Actual output rate in samples per second
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have a D/A.
LowChan First D/A channel of scan.
HighChan Last D/A channel of scan.
Low/High Channel #:The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of
D/A board is being used.
Rate (input) Sample rate in scans per second. For many D/A boards the Rate is ignored and can
be set to
fast output rates, such as the CIO-DAC04/12-HS,
NOTUSED. For D/A boards with trigger and transfer methods which allow
Rate should be set to the D/A
output rate (in scans/sec). This argument also returns the value of the actual rate
set. This value may be different from the user specified rate because of pacer
limitations.
If supported, scans are triggered at this rate. If you are updating four channels, 0-3,
specifying a rate of 10,000 scans per second (10 kS/s) will result in the D/A
converter rates of 10 kS/s: (one D/A per channel). The data transfer rate will be
40,000 words per second; (4 channels x 10,000 updates per scan).
The maximum update rate depends on the D/A board that is being used.
Range
(input) If the selected D/A board does not have a programmable range feature, then this
argument will be ignored. Otherwise the gain can be set to any of the ranges that
are supported by the selected board. See the "
Range input values" on page 19 for
valid values. Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal
Library User's Guide (available on our web site at
) for the list of ranges
Resolution
- 1 of the converter.
DataArray
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
supported by each board.
Must be in the range 0 – N, where N is the value 2
There should be at least
HighChan-LowChan+1 elements in the array.
Page 40

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Output VIs
40
Simultaneous When this option is set (True) (if the board supports it and the appropriate switches
are set on the board) all of the D/A voltages will be updated simultaneously when
the last D/A in the scan is updated. This generally means that all the D/A values
will first be written to the board, then a read of a D/A address causes all D/As to be
updated with new values simultaneously.
ExtClock If this option (True) is used, conversions will be paced by the signal on the external
clock input line rather than by the internal pacer clock. Each conversion will be
triggered on the appropriate edge of the external clock input signal (see board-
specific info). When this option is used, the
Rate argument is ignored. The
sampling rate is dependent on the trigger signal. Options for the board will default
to transfer types that allow the maximum conversion rate to be attained unless
otherwise specified.
Rate (output Actual output rate (in samples per channel per second).
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
Page 41

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Output VIs
41
AOutScBg.VI
Outputs the values to a range of D/A channels in the backgroun d. This V I can onl y be us ed wi t h boards that
support interrupt, DMA or REP-INSW transfer methods. When this option is used the D/A operations will
begin running in the background and control will immediately return to the VI. Use GetStatus.VI to check the
status of a background operation. Use StopBg.VI to terminate background operations before they are
completed. Always run StopBg.VI after running a background operation to clear variables and flags.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
LowChan [I32] - First D/A channel of scan
HighChan [I32] - Last D/A channel of scan
Rate [I32] - Sample rate in scans per second
Range [I32] - D/A range code
DataArray [U16] - Data array to output D/A values from.
Continuous [TF] - Run the VI in an endless loop
Simultaneous [TF] - Simultaneous update mode
ExtClock [TF] - Pace conversions externally
Error code [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Context [cluster] - Output data structure..
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have a D/A.
LowChan First D/A channel of scan.
HighChan Last D/A channel of scan.
Low/High Channel # The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of D/A board is being
used.
Rate (input) For many D/A boards, the Rate is ignored and can be set to NOTU SED. For D/A
boards with trigger, and transfer method s w hi ch allow fast output rates, set
Rate to
the D/A output rate (in scans/sec). A typical fast board is the CIO-DAC04/12-HS.
If supported, this is the rate at which scans are triggered. If you are updating 4
channels, 0-3, then specifying a rate of 10,000 scans per second (10 kHz) will
result in the D/A converter rates of 10 kHz: (one D/A per channel). The data
transfer rate will be 40,000 words per second; (4 channels x 10,000 updates per
scan).
The maximum update rate depends on the D/A board that is being used.
DataArray The data array should be filled with D/A values in the range 0 – n, where n is the
value 2
Resolution
- 1 of the converter. There should be at least HighChan-LowChan +
1 elements in the array.
Page 42

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Analog Output VIs
42
Continuous This option (True) can only be used with boards which support interrupt, DMA or
REP-INSW transfer methods. This option puts the VI in an endless loop. After it
outputs the specified (by Count) number of D/A values, it resets to the start of
DataArray and begins again. The only way to stop this operation is with
StopBg.VI.
Simultaneous When this option is set (True) (if the board supports it and the appropriate switches
are set on the board) all of the D/A voltages will be updated simultaneously when
the last D/A in the scan is updated. This generally means that all the D/A values
will be written to the board, then a read of a D/A address causes all D/As to be
updated with new values simultaneously.
ExtClock If this option (True) is used then conversions will be paced by the signal on the
external clock input line rather than by the internal pacer clock. Each conversion
will be triggered on the appropriate edge of the external clock input signal (refer to
the board-specific information). When this option is used the
ignored. The sampling rate is dependent on the trigger signal.
Rate argument is
Options for the board
will default to transfer types that allow the maximum conversion rate to be attained
unless otherwise specified.
Range If the selected D/A board does not have a programmable range feature, this will be
ignored. Otherwise the gain can be set to any of the ranges that are supported by
the selected D/A board. See the "
Range input values" table on page 19 for valid
values. Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library
User's Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-
user-guide.pdf) for the list of ranges supported by each board.
Rate (output) Actual sampling rate in channel scans per second. This may be different from the
requested rate because of pacer limitations.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
Context Data structure containing information from a background operation. Some of the
ErrCode into a readable string.
information included is the board number, the data array, the array size, and the
initial status of the background operation.
Follow the steps below when wiring this VI:
1. Start a background operation.
2. GetStatus.VI checks for completion (boolean output called "Running").
3. StopBg.VI terminates the operation, if not already done, and frees memory aliases.
4. Data output from the background operation is passed to GetStatus.VI and StopBg.VI
via "Context", and can be wired from one or both of them for intermediate or final
actions, respectively.
The demo VIs illustrate this process effectively.
Page 43

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Signal conditioning VIs
43
Signal conditioning VIs
ACvtData.VI
Changed R3.3 RW (MOD)
Converts the raw data collected by AInScFg.VI or AInScBg.VI into 12-bit A/D values. Th e AInS cFg .V I and
AInScBg.VI can return either raw A/D data or converted data depending on whether or not the
CONVERTDATA option was set. For many 12-bit A/D boards, the raw data is a 16-bit value that contains a
12-bit A/D value and a 4-bit channel tag (refer to board-specific information or the board’s hardware manual).
The converted data consists of just the 12-bit A/D value.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
ADDataRaw [U16] - Data and channel tags from AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI.
ADData [U16] - Converted A/D values.
ChanTags [U16] - Channel tags if available.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI.
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have an A/D.
ADDataRaw
ADData Array of converted A/D values.
ChanTags Array of channel tags, if available.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
Array of raw A/D values that include data and channel tags.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
Notes:
When you collect data with AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI and you don't use the CONVERTDATA option, you
may need to use this VI to convert the data after it is collected. There are cases where the CONVERTDATA
option is not allowed—for example, if you are using the DMAIO option with AInScBg.VI. In this case, use
this VI to convert the data after the data collection is complete.
On some boards, each raw data point consists of a 12-bit A/D value with a 4-bit channel number. This VI
separates the two and puts the A/D value into the ADData array and the channel number into the
ChanTags
array.
12-bit A/D boards: Upon returning from ACvtData.VI,
ADData array contains only 12-bit A/D data.
16-bit A/D boards: Do not use this VI is with 16-bit A/D boards. If this function is called for a 16-bit board,
it is simply ignored. No error is returned.
Page 44

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Signal conditioning VIs
44
ACnvPrDt.VI
Changed R3.3 RW (MOD)
Converts the raw data collected by APretrFg.VI or APretrBg.VI. APretrBg.VI and APretrFg.VI can return
either raw A/D data or converted data depending on whet h er or not the CONVERTDATA option was used.
The raw data as it is collected is not in the correct order. After the data collection is completed it must be
rearranged into the correct order. This VI correctly orders the data, starting with the first pretrigger data point
and ending with the last post-trigger point.
Change at revision 3.3 to support multiple background operations.
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
PreTrigCount [I32] - Number of pre-trigger samples
TotalCount [I32] - Total number of A/D samples that were collected
DataArray [U32] - Data and channel tags
DataArray [U32] - Converted data
ChanTags [I16] - Channel tags if available
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have an A/D. Can be 0 to 100.
PreTrigCount Number of pre-trigger samples.
TotalCount Total number of A/D samples that were collected.
DataArray (In) Array of raw samples that require ordering.
DataArray (Out) Array of converted samples ordered with oldest samples first.
ChanTags Array of channel tags, if available.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
Notes:
When you collect data with APretrFg.VI or APretrBg.VI and you don't use the
use this VI to convert the data after it is collected. There are cases where the
allowed—for example, if you use the
BACKGROUND option with APretrBg.VI or APretrFg.VI. In those cases,
CONVERTDATA option, you must
CONVERTDATA option is not
use this VI to convert the data after the data collection is complete.
12-bit A/D boards: On some 12-bit boards, each raw data point consists of a 12-bit A/D value with a 4-bit
channel number. This VI separates the two and puts the A/D value into the
into the
ChanTags array. Upon returning from APretrBg.VI or APretrFg.VI, DataArray contains only 12-bit
DataArray, and the channel number
A/D data.
16-bit A/D boards: This VI is used with 16-bit A/D boards only corrects the order of the data. No channel
tags are returned.
Page 45

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Signal conditioning VIs
45
ACal.VI
New R3.3
Calibrates the raw data collected by AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI from boards with real-time software
calibration capability but the real-time calibration has been turned off. AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI can return
either raw A/D data or calibrated data depen din g on whet h e r or n ot the
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Range [I32] - The programmable gain/range used when the data was collected
ADDataRaw [U16] - Raw A/D data
ADData [U16] - Pointer to data array
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed. The specified
board must have an A/D. Can be 0 to 100.
ADDataRaw Array of raw A/D measurements that require calibration.
Range If the selected A/D board does not have a programmable range feature, this will be
ignored. Otherwise the gain can be set to any of the ranges that are supported by
the selected A/D board. See the "
Range input values" table on page 19 for valid
values. Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library
User's Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-
user-guide.pdf) for the list of ranges supported by each board.
ADData Array of calibrated data.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
NOCALIBRATEDATA option was used.
Notes:
When you collect data with AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI, and you use the
must use this VI to calibrate the data after it is collected.
NOCALIBRATEDATA option, then you
Page 46

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Signal conditioning VIs
46
FromEng.VI
Changed R5.4 ID, R7.1 ID
Performs the following conversion operations:
Converts a single voltage (or current) in engineering units to a D/A count value for output to a D/A.
Converts an array of voltages (or currents) in engineering units to an array of D/A count values for output
to a D/A.
Converts a single voltage (or current) in engineering units to a D/A count value for output as an analog
trigger threshold based on the hardware's trigger circuit. If hardware does not support analog triggering,
output is 0.
To use FromEng.VI to output an analog trigger threshold to the SetTrig.VI, right-mouse-click on the VI
and select the
Change at revision 5.4 to support processing of single values and arrays of values.
Select Type ► FromEng(trigger) option from the menu.
Change at revision 7.1 to support processing of analog trigger values.
Summary:
Inputs BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs
Range [I32] - D/A range to use in conversion
EngUnits [SGL] - Voltage (or current) value or array of values to convert
DA Data [I16] - D/A count equivalent to voltage returned here
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg VI.
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a D/A board when it was installed with
InstaCal. This function uses the board number to determine whether to do a 12-bit
or 16-bit conversion.
Range If the selected D/A board does not have a programmable range feature, this will be
ignored. Otherwise the gain can be set to any of the ranges that are supported by
the selected D/A board. See the "
Range input values" table on page 19 for valid
values. Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library
User's Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-
user-guide.pdf) for the list of ranges supported by each board.
EngUnits Either a single voltage/current value or an array of voltage/current values that you
want to set the D/A to. Values should be within the range specified by the
Range
argument.
DA Data Returns a D/A count or an array of D/A counts to this output that is equivalent to
EngUnits argument.
the
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
Page 47

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Signal conditioning VIs
47
ToEng.VI
Changed R5.4 ID
Converts a single A/D count value to an equivalent voltage valu e, or converts an array of A/D counts to an
array of equivalent voltage values.
Change at revision 5.4 to support processing of single values and arrays of values.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can be 0 to
100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with an A/D board when it was installed with
Range A/D voltage (or current) range. Some A/D boards have programmable voltage
AD Data A/D measurement in binary counts to be converted to engineering units.
EngUnits The voltage (or current) value that is equivalent to AD Data is returned to this
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
Range - A/D range to use in conversion
AD Data - A/D count value returned from an A/D board
EngUnits - Equivalent voltage (or current) value returned to this variable
ErrCode - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
InstaCal. This function uses the board number to determine whether to do a 12-bit
or 16-bit conversion.
ranges, others set the voltage range via switches on the board. In either case the
selected range must be passed to this function. Each A/D board supports different
voltage and/or current ranges. See the "
Range input values" table on page 19 for
valid values. Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal
Library User's Guide (available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
) for the list of ranges
supported by each board.
variable. The value will be within the range specified by the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
Range argument.
Page 48

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Signal conditioning VIs
48
ScaleArr.VI
Scales raw data from an entire array to a user-specified range.
Summary:
Inputs: Min [SGL] - Lower limit of range
Output:
Arguments:
Min Lower limit of selected range.
Max Upper limit of selected range.
16 or 12 bit Length of data to be converted. Depends on the type of har dware being used.
ADData Array with unconverted raw data.
Val Array with converted engineering data.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
Max [SGL]- Upper limit of range
16 or 12 bit [TF] - Length of raw data; 1 to 16 bits (True), 0 to 12 bits (False =
default).
ADData [U16] - Unconverted data array
Val [SGL] - Converted data array
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
Page 49

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Signal conditioning VIs
49
ScalePnt.VI
Scales raw data point to a user-specified range.
Summary:
Inputs: Min [SGL] - Lower limit of range
Output:
Arguments:
Min Lower limit of selected range.
Max Upper limit of selected range.
16 or 12 bit Length of data to be converted. Depends on the type of har dware being used.
ADData Array element with unconverted raw data.
Val Converted engineering data.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
Max [SGL] - Upper limit of range
16 or 12 bits [TF] - Length of raw data; 1-16 bits (T), or 1 to 12 bits
(F = default)
ADData [U16] - Unconverted data array single element.
Val [SGL] - Converted data array element
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
Page 50

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
50
Counter VIs
The Universal Library for NI LabVIEW extensions provides VIs for the initialization and configuration of
counter chips. It is important to note what this means:
VIs can configure a counter for any of the counter's operations.
Counter configuration does not include the use of counters —such as event counting and pulse width.
Counter use is accomplished by programs which use the counter VIs. Some counter-use VIs are available.
To use a counter for any but the simplest counting VI, you must use the information contained in the chip
manufacturer's data sheet. Technical support of the VIs does not include providing, interpreting or explaining
the counter chip data sheet.
82C54 counter chip
The 82C54 data sheet is available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/82C54.pdf
AM9513 counter chip
The 9513A data sheet is available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/9513A.pdf
Z8536 counter chip
As of this writing, the only Measurement Computing boards that use the Z8536 are the PCI/CIO-INT32
products. The data book for the chip is included with these produc ts.
LS7266 counter chip
The LS7266 data sheet is available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/LS7266R1.pdf
contact US Digital at www.usdigital.com
.
.
, or
Page 51

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
51
C8254Cfg.VI
Configures an 8254 counter for desired operation. This VI can only be used with 8254 counters.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum (input) The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
CounterNum Selects a counter channel. An 8254 has three counters. The value can be 1-n, where
Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's
Config Sets the mode of the counter which defines the terminal count behavior and/or the
BoardNum (output) The board number used when installed with InstaCal. This parameter can be used
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
CounterNum [U32] - The counter number to configure
Config [U32] - Sets the mode of the counter.
BoardNum (Out) [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal.
Can be 0 to 100. Can be used to pass
ErrCode [U32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
BoardNum parameter to another VI.
specified board must have an 8254 counter.
n is the number of 8254 counters on the board.
Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-
guide.pdf).
waveform of the counter OUT pin. Refer to the 8254 data sheet for a detailed
description of each of the configurations.
Config can be set to one of the following
constants:
HIGHONLASTCOUNT: Output of the counter (OUT N) transitions from low to high on
terminal count and remains high until reset. See mode 0 on the 8254 data sheet.
ONESHOT: Output of the counter (OUT N) transitions from high to low on rising
edge of GATE N, then back to high on terminal count. See mode 1 on the 8254
data sheet.
RATEGENERATOR: Output of the counter (OUT N) pulses low for one clock cycle on
terminal count and reloads the counter and recycles. See mode 2 on the 8254 data
sheet.
SQUAREWAVE: Output of the counter (OUT N) is high for count < 1/2 terminal count
then low until terminal count, whereupon it recycles. This mode generates a square
wave. See mode 3 on the 8254 data sheet.
SOFTWARESTROBE O utput of the counter (OUT N) pulses low for one clock cycle on
terminal count. Count starts after counter is loaded. See mode 4 on the 8254 data
sheet.
HARDWARESTROBE : Output of the counter (OUT N) pulses low for one clock cycle
on terminal count. Count starts on rising edge at GATE N input. See mode 5 on the
8254 data sheet.
to serialize VIs such that this VI precedes the next VI whose
BoardNum is attached
to this output.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable str i ng.
Page 52

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
52
C7266Config.VI
Configures a 7266 counter for desired ope ra t i on. Thi s f unction can only be used with boards that contain a
7266 counter chip (Quadrature Encoder boards).
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
CounterNum [I32] - Counter number (1 n) to configure
Quadrature [I32] - NO_QUAD, X1_QUAD, X2_QUAD or X4_QUAD
CountingMode [I32] - NORMAL_MODE, RANGE_LIMIT, NO_RECYCLE , MODULO_N
DataEncoding [I32] - BCD_ENCODING, BINARY_ENCODING
IndexMode [I32] - INDEX_DISABLED, LOAD_CTR, LOAD_OUT_ LATCH, RESET_CTR
InvertIndex [I32] - DISABLED or ENABLED
FlagPins [I32] - Selects function for X1FLG and X2FLG pins. CARR Y_BORROW,
COMPARE_BORROW, CARRYBORROW_UPDOWN, INDEX_ERR OR.
Gating [TF] - DISABLED or ENABLED
ErrCode – Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error
occurred. Use the ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have an LS7266 counter.
CounterNum Counter number (1n) where n is the number of counters on the board. A PCM-
QUAD02 has two counters. A PCI-QUAD04 has four counters.
Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's
Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-
guide.pdf).
Quadrature Selects the resolution multiplier (X1_QUAD, X2_QUAD, or X4_QUAD) for quadrature
input or disables quadrature input (
NO_QUAD) so that the counters can be used as
standard TTL counters.
CountingMode Selects one of the following operating modes for the counter:
NORMAL_MODE - Each counter operates as a 24-bit counter that rolls over to 0 when
the maximum count is reached.
RANGE_LIMIT - In range limit count mode, an upper and lower limit is set,
mimicking limit switches in the mechanical counterpart. The upper limit is set by
loading the
PRESET register with the cbCLoad function after the counter has been
configured. The lower limit is always 0. When counting up, the counter freezes
whenever the count reaches the value loaded into the
PRESET register. When
counting down, the counter freezes at 0. In each case the counting is resumed only
when the count direction is reversed.
NO_RECYCLE - In non-recycle mode, the counter is disabled whenever a count
overflow or underflow takes place. The counter is re-enabled when a reset or load
operation is performed on the counter.
Page 53

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
53
MODULO_N - In modulo-n mode, an upper limit is set by loading the PRESET register
with a maximum count. When counting up, if the maximum count is reached, the
counter will roll-over to 0 and continue counting up. Likewise, when counting
down, if the count reaches 0, it will roll over to the maximum count (in the
PRESET
register) and continue counting down.
DataEncoding Selects the format of the data that is returned by the coun ter (Binary or BCD).
IndexMode Selects which action will be taken when the Index signal is received. IndexMode
must be set to
Gating is set to ENABLED.
INDEX_DISABLED - The Index signal is ignored.
LOAD_CTR - The counter is loaded whenever the Index signal ON the LCNTR pin
INDEX_DISABLED whenever Quadrature is set to NON_QUAD or when
occurs
LOAD_OUT_LATCH - The current count is latched whenever the Index signal on the
LCNTR pin occurs. When this mode is selected, the
CIn() function returns the
same count each time it is called until the Index signal occurs.
RESET_CTR - The counter is reset to 0 whenever the Index signal on the RCNTR
pin occurs
InvertIndex Selects the polarity of the Index signal. If set to DISA BLED the Index signal is
assumed to be positive polarity. If set to
ENABLED the Index signal is assumed to be
negative polarity.
FlagPins Selects which signals will be routed to the FLG1 and FLG2 pins.
CARRY_BORROW - FLG1 pin is CARRY outpu t , FL G2 is BOR ROW output
COMPARE_BORROW - FLG1 pin is COMPARE output, FLG2 is BORROW output
CARRYBORROW_UPDOWN - FLG1 pin is CARRY/BORROW output, FLG2 is UP/DOWN
signal
INDEX_ERROR - FLG1 is INDEX output, FLG2 is error output
Gating If Gating is set to ENABLED (True), the RCNTR pin will be used as a gating signal
for the counter. Whenever
DISABLE_INDEX.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
Gating=ENABLED, IndexMode must be set to
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 54

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
54
C8536Cfg.VI
Configures an 8536 counter for desired operation. This VI can only be used with 8536 counters.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum (input) The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
CounterNum Selects one of the counter channels. An 8536 has three counters. The value can be
Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's
OutputControl Specifies one of the following the actions of the output signal.
RecycleMode If set to RECYCLE (False, as opposed to ONET IME), the counter will automatically
Retrigger If set to ENABLED (True), every trigger on the counter's trigger input will initiate
BoardNum (output) The board number used when installed with InstaCal. This parameter can be used
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
CounterNum [U32] - Counter number to configure
OutputControl [U32] - Specifies counter output signal used.
Recycle [TF] - Execute once or reload and re-execute until stopped.
Retrigger [TF] - Enable or disable retriggering.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100. Can be used to pass
BoardNum parameter to another VI.
specified board must have an 8536 counter
1-n, where n is the number of 8536 counters on the board.
Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-
guide.pdf).
HIGHPULSEONTC - Output will transition from low to high for one clock pulse on
terminal count.
TOGGLEONTC - Output will change state on terminal count.
HIGHUNTILTC - Output will transition to high at the start of counting then go low on
terminal count.
reload to the starting count every time it reaches 0, then continue counting.
loading of the initial count. Counting will proceed from initial count.
to serialize VIs such that this VI precedes the next VI whose
BoardNum is attached
to this output.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 55

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
55
C8536Init.VI
Initializes the counter linking features of an 8536 counter chip. Refer to the "Counter/Timer Link Controls"
section on the 8536 data sheet, for a complete description of the hardware affected by this mode. Counters 1
and 2 must be linked before enabling the counters.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32]: Board number when installed with InstaCal. Can be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum (input) The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
ChipNum Selects one of the 8536 chips on the board, 1 to n.
Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's
CtrlOutput Specifies how counter 1 is to be linked to counter 2, based on the follo wing
NOTLINKED -Counter 1 is not connected to any other counters inputs.
GATECTR2 - Output of counter 1 is connected to the GATE of counter #2.
TRIGCTR2 - Output of counter 1 is connected to the trigger of counter #2.
INCTR2 - Output of counter 1 is connected to counter #2 clock input.
BoardNum (output) The board number used when installed with InstaCal. This parameter can be used
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ChipNum [U32] - Chip number to configure
CtrlOutput [U32] - Specifies counter output signal used.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100. Can be used to pass
BoardNum parameter to another VI.
specified board must have an 8536 counter.
Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-
guide.pdf).
options.
to serialize VIs such that this VI precedes the next VI whose
BoardNum is attached
to this output.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 56

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
56
C9513Config.VI
Sets all of the configurable options of a 9513 counter.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
CounterNum [U32] - Counter number (1 - n)
GateControl [U32] - Gate control
CountEdge [TF] - Which edge to count
CountSource [U32] - Which of the available count sources to use.
SpecialGate [TF] - Special gate can be enabled or disabled.
Reload [TF] - Load or load and hold.
Recycle [TF] - Execute once or reload and recycle.
BCDMode [TF] - Counter can operate in Binary Coded Decimal if desired.
CountDirection [TF]- AM9513 can count up or down.
OutputControl [U32] - The type of output desired.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments:
Important
The information provided here will only help you understand how Universal Library syntax corresponds to
the 9513 data sheet. It is not a substitute for the data sheet. You cannot program a 9513 without the
manufacturer's data sheet. The 9513 data sheet is available from out web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/9513A.pdf.
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have a 9513 counter.
CounterNum Counter number (1 n) where n is the number of counters on the board. (For
example, a PCI-CTR05 has five, a PCI-CTR20HD has 20, etc.). Refer to board-
specific information contained in the Universal Library User's Guide (available on
our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
GateControl Gate control variables are:
NOGATE No gating
AHLTCPREVCTR Active high TCN-1
AHLNEXTGATE Active High Level GATE N + 1
AHLPREVGATE Active High Level GATE N - 1
AHLGATE Active High Level GATE N
ALLGATE Active Low Level GATE N
AHEGATE Active High Edge GATE N
ALEGATE Active Low Edge GATE N
).
Page 57

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
57
CountEdge The edge to count. Refer to as Source Edge in 9513 data book. Corresponds to the
9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description. Edge control variables
are:
POSITIVEEDGE Count on Rising Edge (False)
NEGATIVEEDGE Count on Falling Edge
CountSource Corresponds to the 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description
TCPREVCTR TCN - 1 (Terminal count of previous counter)
CTRINPUT1 SRC 1 (Counter Input 1)
CTRINPUT2 SRC 2 (Counter Input 2)
CTRINPUT3 SRC 3 (Counter Input 3)
CTRINPUT4 SRC 4 (Counter Input 4)
CTRINPUT5 SRC 5 (Counter Input 5)
GATE1 GATE 1
GATE2 GATE 2
GATE3 GATE 3
GATE4 GATE 4
GATE5 GATE 5
FREQ1 F1
FREQ2 F2
FREQ3 F3
FREQ4 F4
FREQ5 F5
SpecialGate Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description.
ENABLED Enable Special Gate
DISABLED Disable Special Gate (False)
Reload Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description.
LOADREG Reload from Load (False)
LOADANDHOLDREG Reload from Load or Hold except in Mode X which reloads only
from Load.
RecycleMode Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description.
ONETIME Count Once (False)
RECYCLE Count Repetitively
BCDMode Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description:
DISABLED
ENABLED BCD Count
CountDirection Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description.
COUNTDOWN Count Down
COUNTUP Count Up (False)
Binary Count (False)
Page 58

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
58
OutputControl Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description.
ALWAYSLOW Inactive, Output Low
HIGHPULSEONTC Active High Terminal Count Pulse
TOGGLEONTC TC Toggled
DISCONNECTED Inactive, Output High Impedance
LOWPULSEONTC Active Low Terminal Count Pulse
3, 6, 7 (numeric values) Illegal
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 59

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
59
C9513Init.VI
Initializes all of the chip level features of a 9513 counter chip.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Output:
ChipNum [U32] - Specifies which 9513 chip is to be initialized. FoutDivider [U32]
- F-Out divider (0-15)
FoutSource [U32] - Specifies source of the signal for F-Out signal.
Compare1 [TF] - ENABLED or DISABLED
Compare2 [TF]- ENABLED or DISABLED
TimeOfDay [U32] - DISABLED (0) or 1-3
ErrCode [U32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have a 9513 counter.
ChipNum Specifies which 9513 chip is to be initialized. For a CTR05 board, this should be
set to 1. For a CTR10 board, it should be either 1 or 2. For a CTR20, it should be 1
to 4.
Refer to board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's
Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-
guide.pdf).
FoutDivider Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description
0 Divide by 16
1 Divide by 1
2 ... 15 Divide by the number 2 ... 15
FoutSource Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description
TCPREVCTR TCN - 1 (Terminal count of previous counter)
CTRINPUT1 SRC 1 (Counter Input 1)
CTRINPUT2 SRC 2 (Counter Input 2)
CTRINPUT3 SRC 3 (Counter Input 3)
CTRINPUT4 SRC 4 (Counter Input 4)
CTRINPUT5 SRC 5 (Counter Input 5)
GATE1 GATE 1
GATE2 GATE 2
GATE3 GATE 3
GATE4 GATE 4
GATE5 GATE 5
FREQ1 F1
FREQ2 F2
Page 60

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
60
FREQ3 F3
FREQ4 F4
FREQ5 F5
Compare1 Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description.
DISABLED Disabled (False)
ENABLED Enabled
Compare2 Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description.
DISABLED Disabled (False)
ENABLED Enabled
TimeOfDay Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description
0 TOD Disabled
1 TOD Enabled / 5 Input
2 TOD Enabled / 6 Input
3 TOD Enabled / 10 Input
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
No Arguments for:
VI Set To: Corresponds to 9513 description in Counter Mode Register Description.
0 (FOUT on) FOUT Gate
0 (Data bus matches board) Data Bus Width
1 (Disable Increment) Data Pointer Control
1 (BCD Scaling) Scalar Control
Page 61

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
61
CFreqIn.VI
Measures the frequency of a signal. This VI can only be used with 9513 counters, and uses internal counters
#5 and #4.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
SigSource Specifies the source of the signal from which the frequency will be calculated.
The signal to be measured is routed internally from the source specified by
The SigSource value determines which chip is used. CTRINPUT6 through
GateInterval Specifies the time (in milliseconds) that the counter will be counting. The optimum
If the gating interval is too low, then the count will be too low and the resolution of
If the gating interval in too long then the counter will overflow and a
Count The counts reached during the gating interval.
Freq
ErrCode
Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
SigSource [U32] - Specifies which signal will be measured
GateInterval [I16] - Gating interval in milliseconds
Count [U32] - The raw count is returned here
Freq [U32] - The measured frequency in Hz returned here.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
specified board must have a 9513 counter.
SigSource to the clock input of counter 5. On boards with more than one 9513
chip, there is more than one counter 5. Which counter 5 is used is also determined
SigSource. SigSource can be set to one of the following values:
by
One 9513
chip:
Two 9513
chips:
Four 9513
chips:
CTRINPUT1 through CTRINPUT5
GATE1 through GATE4
FREQ1 through FREQ5
CTRINPUT1 through CTRINPUT10
GATE 1 through GATE 9 (excluding gate 5)
FREQ1 through FREQ10
CTRINPUT1 through CTRINPUT20
GATE1 through GATE19 (excluding gates 5, 10 & 15)
FREQ1 through FREQ20
Chip 1 used
Chip 1 or Chip 2
used
Chips 1- 4 can
be used
CTRINPUT10, FREQ6 through FREQ10 and GATE6 through GATE9 indicate
chip 2 will be used. The signal to measure must be present at the chip 2 input
specified by
SigSource. Also, the gating connection from counter 4 output to
counter 5 gate must be made between counters 4 and 5 of this chip (see "Notes" on
page 63). See board-specific information to determine valid values for your board.
GateInterval depends on the frequency of the measured signal. The counter can
count up to 65535.
the frequency measurement will be poor. For example, if the count changes from 1
to 2 the measured frequency doubles.
FREQOVERRUN
error will occur.
The measured frequency in Hz.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 62

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
62
Notes:
This function requires an electrical connection between counter 4 output and counter 5 gate. This connection
must be made between counters 4 and 5 on the chip determined by
SigSource.
Also, C9513Init.VI must be called for each
FoutDivider, FoutSource, Compare1, Compare2, and Time of Day are irrelevant to this function and can be any
ChipNum that will be used by this function. The values of
value shown in the C9513Init.VI description.
Page 63

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
63
CIn.VI
Reads the current count from a counter.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
CounterNum The counter to read current count from. Valid values are 1 to 20, up to the number
Count Current count value from selected counter is returned here.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
CounterNum [I32] - Counter number to read
Count [I32] - Count returned here
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
specified board mus t have a counter.
of counters on the board.
1 Counter input to counter 1.
2 ...20 Counter inputs 2 through 20
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes:
CIn.VI vs. CIn32.VI: Although the CIn.VI and CIn32.VI perform the same operation , CIn32.VI is the
preferred function to use.
The only difference between the two is that CIn.VI returns a 16-bit count value and CIn32.VI returns a 32-bit
value. Both CIn.VI and CIn32.VI can be used, but CIn32.VI is required whenever you need to read count
values greater than 16 bits (counts > 65535). For instance, LS7266 based counters are 24-bit counters and can
return values larger than a 16-bit value.
Page 64

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
64
CIn32.VI
Reads the current count from a counter and returns it as a 32-bit integer.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed. The specified
CounterNum The counter to read current count from. Valid values are 1 to N, where N is the
Count Current count value from selected counter is returned here.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
CounterNum [I32] - Counter number (1 n) to read.
Count [I32] - Current count is returned here
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
board must have a counter.
number of counters on the board.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes:
CIn.VI() vs. CIn32.VI: Although the CIn.VI and CIn32.VI perform the same operation, CIn32.VI is the
preferred function to use.
The only difference between the two is that CIn.VI returns a 16-bit count value and CIn32.VI returns a 32-bit
value. Both CIn.VI and CIn32.VI can be used, but CIn32.VI is required whenever you need to read count
values greater than 16 bits (counts > 65535). For instance, LS7266 based counters are 24-bit counters and can
return values larger than a 16-bit value.
Page 65

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
65
CLoad.VI
Loads the specified counter's register with a count value. The counter and register are specified by the
RegName argument. When you want to load a counter with a value to count from, it is never loaded directly
into the counter's count register. It is loaded into the load or hold register. From there, the counter, after
enabled, loads the count from the appropriate register, generally on the first valid pulse.
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed.
RegName The register to load the count to. Valid values are:
LoadValue The value to be loaded. Must be between 0 and 2
BoardNum (output) The board number used when installed with InstaCal. This parameter can be used
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
RegName [U32] - Register to load with LoadValue.
LoadValue [U16] - Value to load into RegName register.
BoardNum [U32] The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can be
0 to 100. Can be used to pass
ErrCode [U32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
LOADREG1 .. 20: Load registers 1 through 20. This may span several chips.
HOLDREG1 .. 20: Hold registers 1 through 20. This may span several chips. (9513
BoardNum parameter to another VI..
only)
ALARM1CHIP1: Alarm register 1 of the first counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM2CHIP1: Alarm register 2 of the first counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM1CHIP2: Alarm register 1 of the second counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM2CHIP2: Alarm register 2 of the second counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM1CHIP3: Alarm register 1 of the third counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM2CHIP3: Alarm register 2 of the third counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM1CHIP4: Alarm register 1 of the four counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM2CHIP4: Alarm register 2 of the four counter chip. (9513 only)
COUNT1...4: Current Count (LS7266 only)
PRESET1...4: Preset register (LS7266 only)
PRESCALER1...4: Prescaler register (LS7266 only)
Resolution
16
example, a 16-bit counter is 2
- 1, or 65,535.
to serialize VIs such that this VI precedes the next VI whose
- 1 of the counter. For
BoardNum is attached
to this output.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes:
CLoad.VI vs. CLoad32.VI: Although the CLoad.VI and CLoad32.VI perform the same operation,
CLoad32.VI is the preferred function to use.
The only difference between the two is that CLoad.VI loads a 16-bit count value and CLoad32.VI loads a 32bit value. Both CLoad.VI and CLoad32.VI can be used, but CLoad32.VI is required whenever you need to
load count values greater than 16 bits (counts > 65535).
Page 66

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
66
CLoad32.VI
Loads the specified counter’s COUNT, PRESET or PRESCALER register with a count.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
RegName The register to load the value into. Valid register names are:
LoadValue The value to be loaded.
BoardNum (Out) The board number used when installed with InstaCal. This parameter can be used
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
RegName [U32] - Register to load LoadValue into.
LoadValue [U32] - Value to be loaded into RegName.
BoardNum [U32] The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can be
0 to 100. Can be used to pass
ErrCode [U32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
LOADREG1 .. 20: Load registers 1 through 20. This may span several chips.
HOLDREG1 .. 20: Hold registers 1 through 20. This may span several chips. (9513
BoardNum parameter to another VI.
only)
ALARM1CHIP1: Alarm register 1 of the first counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM2CHIP1: Alarm register 2 of the first counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM1CHIP2: Alarm register 1 of the second counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM2CHIP2: Alarm register 2 of the second counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM1CHIP3: Alarm register 1 of the third counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM2CHIP3: Alarm register 2 of the third counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM1CHIP4: Alarm register 1 of the four counter chip. (9513 only)
ALARM2CHIP4: Alarm register 2 of the four counter chip. (9513 only)
COUNT1...4: Current Count (LS7266 only)
PRESET1...4: Preset register (LS7266 only)
PRESCALER1...4: Prescaler register (LS7266 only)
to serialize VIs such that this VI precedes the next VI whose
BoardNum is attached
to this output.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes:
CLoad.VI vs. CLoad32.VI: Although the CLoad.VI and CLoad32.VI perform the same operation,
CLoad32.VI is the preferred function to use.
The only difference between the two is that CLoad.VI loads a 16-bit count value and CLoad32.VI loads a 32bit value. Both CLoad.VI and CLoad32.VI can be used, but CLoad32.VI is required whenever you need to
load count values greater than 16 bits (counts > 65535).
Page 67

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
67
CStatus.VI
Returns status information about the specified counter (7266 counters only)
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
CounterNum The counter to read current count from. Valid values are 1 to n, where n is the
StatusBits Current status from selected counter is returned here. The status consists of
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
CounterNum [I32] - Counter number (1 - n) to read.
StatusBits [U32] - Status information is returned here.
ErrCode [U32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI.
specified board must have an LS7266 counter.
number of counters on the board.
individual bits that indicate various conditions within the counter. The currently
defined status bits are:
C_UNDERFLOW - Is set to 1 whenever the co unt decrements past 0. Is cleared to 0
whenever CStatus.VI is called.
C_OVERFLOW - Is set to 1 whenever the count increments past it’s upper limit. Is
cleared to 0 whenever CStatus.VI is called.
C_COMPARE - Is set to 1 whenever the count matches the preset register. Is cleared to
0 whenever CStatus.VI is called.
C_SIGN - Is set to 1 when the MSB of the count is 1. Is cleared to 0 whenever the
MSB of the count is set to 0.
C_ERROR - Is set to 1 whenever an error occurs due to excessive noise on the input.
Is cleared to 0 by calling C7266Config.VI.
C_UP_DOWN - Is set to 1 when counting up. Cleared to 0 when c ou nti n g down
C_INDEX - Is set to 1 when index is valid. Cleared to 0 when index is not valid.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 68

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
68
CStore.VI
Changed R4.0 RW (MOD)
Installs an interrupt handler that will store the current count whenever an interrupt occurs. This VI can only be
used with 9513 counters. This VI will continue to operate in the background until either
or StopBg.VI is called.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
IntCount [I16] - Number of interrupts.
CntrControl [TF] - Array with each element set to either ENABLED or DISABLED.
Context [cluster] - Output data structure
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have a 9513 counter.
IntCount The counters will be read every time an interrupt occurs until IntCount interrupts
have occurred. If
CntrControl The array should have an element for each counter on the board (five elements for
IntCount is = 0 then the VI will run until StopBg.VI is called.
CTR-05 board, 10 elements for a CTR-10, etc.). Each element corresponds to a
possible counter channel. Each element should be set to either
ENABLED (True). All channels that are set to ENABLED will be read when an interrupt
occurs.
Context Data structure containing information from a background operation. Some of the
information included is the board number, the data array, the array size, and the
initial status of the background operation.
Follow the steps below when wiring this VI:
1. DInScBg.VI starts a background operation.
2. GetStatus.VI checks for completion (boolean output called "Running").
3. StopBg.VI terminates the operation, if not already done, and frees memory aliases.
4. Data output from the background operation is passed to GetStatus.VI and
StopBg.VI via Context, and can be wired from one or both of them for
intermediate or final actions, respectively.
The demo VIs illustrate this process effectively.
ErrCode
Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
IntCount is satisfied
DISABLED (False) or
New Functionality:
If the Library Revision is set to 4.0 or greater then the following code changes are required.
If
IntCount is non-zero then the Context object will contain IntCount samples for each counter. Counter
elements that are
For example, if
DISABLED will return 0.
IntCount is set to 100 for a CTR-05 board, then the new functionality keeps the user
application from having to move the data out of the context buffer for every interrupt, befo re it is overwritten.
Now, for each interrupt the counter values will be stored in adjacent memory locations within the context.
Page 69

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Counter VIs
69
Note:
Specifying IntCount to be a non-zero value and failing to allocate the proper sized array will result in a
runtime error. There is no way for the Universal Library to determine if the array has been allocated with the
proper size. If IntCount = 0, the functionality is unchanged.
Page 70

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
70
Digital I/O VIs
DBitIn.VI
Reads the state of a single digital input bit. This VI treats all of the digital I/O ports on a board as a single very
large port. It lets you read the state of any individual bit within this large port. If the bit or port direction is
programmable, you must first use DCfgPort.VI or DCfgBit.VI to con figure the bit or port for input.
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
PortType There are two general types of digital I/O: 8255 and other. Some boards (DIO
BitNum Specifies the bit number within the single large port. The specified bit must be in a
The table below shows which bit numbers are in which 82C55 and 8536 dig ital
PortType [I32] - Specifies the type of digital port to read.
BitNum [I32] - Specifies the bit where BitValue is read.
BitValue [TF] - Placeholder for return value of bit - the bit's value (0 or 1)
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Series) use an 8255 for digital I/O. For these boards
FIRSTPORTA. Other boards don't use an 8255. For these boards, PortType should be
AUXPORT. Some boards have both types of digital I/O (PCI-DAS6025). Set
set to
PortNum to either FIRSTPORTA or AUXPORT depending on which digital inputs
PortType should be set to
you wish to read.
port that is currently configured as an input.
chips. The CIO-DIO192 supports eight 82C55 chips—the most available on a
single board. The PCI-INT32 supports two 8536 chips—the most available on a
single board.
82C55 Bit# Chip # Address 8536 Bit# Chip # Address
0 - 23 1 Base + 0 0 - 19 1 Base + 0
24 - 47 2 Base + 4 20 - 39 2 Base + 4
48 - 71 3 Base + 8
72 - 96 4 Base + 12
96 - 119 5 Base + 16
120 - 143 6 Base + 20
144 - 167 7 Base + 24
168 - 191 8 Base + 28
BitValue Placeholder for return value of bit. Value will be 0 or 1. A 0 indicates a low
reading, a 1 indicates a logic high reading. Logic high does not necessarily mean
5 V. See the board manual for chip input specifications.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 71

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
71
DBitOut.VI
Sets the state of a single digital output bit. This VI treats all of the DIO chips on a board as a single very large
port. It lets you set the state of any individual bit within this large port. If the bit or port direction is
programmable you must first use DCfgBit.VI or DCfgPort.VI to configure the bit or port for output.
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Output:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
PortType There are two general types of digital I/O - 8255 and other. Some boards (DIO
BitNum Specifies the bit number within the single large port. The specified bit must be in a
The table below shows which bit numbers are in which 82C55 and 8536 dig ital
PortType [U32] - Specifies which digital port (AUXPORT, FIRSTP ORTA).
BitNum [U32] - Specifies the bit to set.
BitValue [TF] - The bit's value (0 or 1)
ErrCode - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Series) use an 8255 for digital I/O. For these boards,
FIRSTPORTA. Other boards don't use an 8255. For these boards PortType should be
AUXPORT. Some boards have both types of digital I/O (PCI-DAS6025). Set
set to
PortType to either FIRSTPORTA or AUXPORT depending on which digital outputs you
PortType should be set to
wish to write.
port that is currently configured as an output.
chips. The CIO-DIO192 supports eight 82C55 chips—the most available on a
single board. The PCI-INT32 support two 8536 chips— the most available on a
single board.
82C55 Bit# Chip # Addre ss 8536 Bit# Chip # Address
0 - 23 1 Base + 0 0 - 19 1 Base + 0
24 - 47 2 Base + 4 20 - 39 2 Base + 4
48 - 71 3 Base + 8
72 - 96 4 Base + 12
96 - 119 5 Base + 16
120 - 143 6 Base + 20
144 - 167 7 Base + 24
168 - 191 8 Base + 28
BitValue The output value of the bit. Value will be 0 or 1. A (0) indicates a logic-low output;
a (1) indicates a logic high output. Logic-high does not necessarily mean 5 V. See
the board manual for chip specifications.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 72

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
72
DCfgBit.VI
Configures a specific digital bit within a digital port for input or output. This function treats all DIO ports on a
board as a single port (AUXPORT). This function is not supported by 8255 type DIO ports. Please refer to
board-specific information for details.
Summary:
Input: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Output:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
PortType Specifies the digital I/O port whose bit to configure. The DCfgBit.VI supports
BitNum The bit number to configure as input or output. Can be 0 to 7 for AUXPORT types.
Bit Direction DIGITALOUT (True) or DIGITALIN (False - default) sets the digital bit as input
BoardNum (Out) The board number used when installed with InstaCal. This parameter can be used
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use
PortType [I32] - Digital I/O port containing the bit to configure.
BitNum - The bit number to configure as input or output.
Bit Direction [TF] - DIGITALOUT or DIGITALIN
BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100. Can be used to pass
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
AUXPORT types only.
BoardNum parameter to another VI.
or output.
to serialize VIs such that this VI precedes the next VI whose
BoardNum is attached
to this output.
ErrMsg.VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 73

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
73
DCfgPort.VI
Configures a digital port as Input or Output . Thi s mode is primarily for use with 82C55 chips and 8 53 6 chips.
See the board user's manual for details of chip operation.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
PortNum The specified port must be configurable.
For many boards, AUXPORT is not configurable. However, some later boards do
The table below shows which ports and bit numbers are in which 82C55 and 8536
PortNum [I32] - Specifies which digital I/O port to configure.
Direction [TF]- DIGITALOUT or DIGITALIN
BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100. Can be used to pass
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
BoardNum parameter to another VI.
require that the AUXPORT be configured using DCfg Port.VI or DCfgBit.VI.
Please see board details for more information.
digital chips. The CIO-DIO192 supports eight 82C55 chips—the most available on
a single board. The PCI-INT32 support two 8536 chips— the most available on a
single board.
Mnemonic Bit # 8255 Chip # Chip Address 8536 Chip # Chip Address
FIRSTPORTA 0 - 7 1A Base + 0 1A Base + 0
FIRSTPORTB 8 - 15 1B 1B
FIRSTPORTCL 16 - 19 1CL 1C
FIRSTPORTCH 20 - 23 1CH Not present
SECONDPORTA 24 - 31 2A Base + 4 2A Base + 4
SECONDPORTB 32 - 39 2B 2B
SECONDPORTCL 40 - 43 2CL 2C
SECONDPORTCH 44 - 47 2CH No port C High in 8536 chips
and so on, to the last chip on the board as: THIRDPORTx, FOURTHPORTx, FIFTHPORTx, SIXTHPORTx,
SEVENTHPORTx and...
EIGHTHPORTA 168 - 175 8A Base + 28
EIGHTHPORTB 176 - 183 8B
EIGHTHPORTCL 184 - 187 8CL
EIGHTHPORTCH 188 - 191 8CH
Direction DIGITALOUT (True) or DIGITALIN (False - default) configures an entire eight-
or four-bit port for output or input.
BoardNum (Out) The board number used when installed with InstaCal. This parameter can be used
to serialize VIs such that this VI precedes the next VI whose
BoardNum is attached
to this output.
Notes
Using this function will reset all ports on a chip configured for output to a zero state. This means that if you
set an output value on
the output value at
FIRSTPORTA and then change the configuration on FIRSTPOR TB from OUTPUT to INPUT,
FIRSTPORTA will be all zeros. You can, however, set the configuration on SECONDPORTX
Page 74

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
74
without affecting the value at FIRSTPORTA. For this reason, this function is usually called at the beginning of
the program for each port requiring configuration.
Page 75

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
75
DIn.VI
Reads a digital input port.
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
PortNum If the port type is not AUXPORT, the specified port must be configured for input.
For many boards, AUXPORT is not configurable. However, some later boards do
The table below shows which ports are in which 82C55 and 8536 digital chips. The
PortNum [I32] - Specifies which digital I/O port to read.
DataValue [I16] - Digital input value.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
require that the AUXPORT be configured using DCfg Port.VI or DCfgBit.VI.
Please see board details for more information.
CIO-DIO192 supports eight 82C55 chips—the most available on a single board.
The PCI-INT32 support two 8536 chips— the most available on a single board.
Mnemonic Bit # 8255 Chip # Chip Address 8536 Chip # Chip Address
FIRSTPORTA 0 - 7 1A Base + 0 1A Base + 0
FIRSTPORTB 8 - 15 1B 1B
FIRSTPORTCL 16 - 19 1CL 1C
FIRSTPORTCH 20 - 23 1CH Not present
SECONDPORTA 24 - 31 2A Base + 4 2A Base + 4
SECONDPORTB 32 - 39 2B 2B
SECONDPORTCL 40 - 43 2CL 2C
SECONDPORTCH 44 - 47 2CH No port C High in 8536 chips
and so on, to the last chip on the board as: THIRDPORTx, FOURTHPORTx, FIFTHPORTx, SIXTHPORTx,
SEVENTHPORTx and...
EIGHTHPORTA 168 - 175 8A Base + 28
EIGHTHPORTB 176 - 183 8B
EIGHTHPORTCL 184 - 187 8CL
EIGHTHPORTCH 188 - 191 8CH
DataValue Digital input value. The size of the ports vary. If it is an eight-bit port, then the
returned value will be in the range 0- 255. If it is a four bit port the value will be in
the range 0
ErrCode
Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
Important - Read board-specific information in UL User's Guide
-15.
ErrCode into a readable string.
Refer to the example programs and the board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's
Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf) for clarification of
valid PortNum values.
Page 76

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
76
DInScBg.VI
Performs multiple reads of digital input port of a high speed digital port on a board with a pacer clock such as
the CIO-PDMA16.
When this VI is used, control will return immediately to the next point in your program and the transfer from
the digital input port to the array in the Context will continue in the background. Use GetStatus.VI to check on
the status of the background operation. Use StopBg.VI to terminate the background process before it has
completed. StopBg.VI should be used after any background operation to clear variables and flags.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
PortNum [I32] - Specifies which digital I/O port to read.
Count [I32] - Number of times to read digital input.
Rate [I32] - Number of times per second (Hz) to read.
Continuous [TF] - Continuous or single
ExtClock [TF] - External or internal clock
WordXfer [TF] - Word or byte transfer
Context [cluster] - Output data structure.
Rate [I32]- Actual rate returned here
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
PortNum If the port type is not AUXPORT, the specified port must be configured for input.
For many boards, AUXPORT is not configurable. However, some later boards do
require that the AUXPORT be configured using DCfg Port.VI or DCfgBit.VI.
Please see board details for more information.
Count The number of times to read digital input.
Rate Number of times per second (Hz) to read the port. The actual sampling rate in
some cases will vary a small amount from the requested rate. The actual rate will
be returned to the
Continuous This option (if True) puts the VI in an endless loop. After it transfers the required
Rate output argument.
number of bytes it resets to the start of the input array and begins again. The only
way to stop this operation is with StopBg.VI (a single execution is False).
ExtClock If this option is used (True) then transfers will be controlled by the signal on the
trigger input line rather than by the internal pacer clock. Each transfer will be
triggered on the appropriate edge of the trigger input signal (see board-specific
info). When this option is used, the
dependent on the trigger signal. The default is
WordXfer Normally (default is False) this VI reads a single (byte) port (BYTEXFER). If
WORDXFER is specified, it will read two adjacent ports on each read and store the
Rate argument is ignored. The transfer rate is
TIMED (False).
value of both ports together as the low and high byte of a single array element in
the input array.
Rate (output) Actual sampling rate in samples per second.
Page 77

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
77
Context Data structure containing information from a background operation. Some of the
information included is the board number, the data array, the array size, and the
initial status of the background operation.
Follow the steps below when wiring this VI:
1. DInScBg.VI starts a background operation.
2. GetStatus.VI checks for completion (boolean output called "Running").
3. StopBg.VI terminates the operation, if not already done, and frees memory aliases.
4. Data output from the background operation is passed to GetStatus.VI and
StopBg.VI via Context, and can be wired from one or both of them for
intermediate or final actions, respectively.
The demo VIs illustrate this process effectively.
ErrCode
Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 78

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
78
DInScFg.VI
Multiple reads of digital input port of a high-speed digital port on a board with a pacer clock such as the CIOPDMA16. The DInScFg.VI will not return to your program until all of the requested data has been collected
and returned to input array.
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
PortNum [I32] - Specifies the digital I/O port to read.
Count [I32] - Number of times to read digital input
Rate [I32]- Number of times per second (Hz) to read
ExtClock [TF] - External or internal clock
WordXfer [TF] - Word or byte transfer
Rate [I32] - Actual rate returned here
DataArray [I16] - Data from scan is returned here
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated when it was installed with InstaCal.
PortNum If the port type is not AUXPORT, the specified port must be configured for input.
For many boards, AUXPORT is not configurable. However, some later boards do
require that the AUXPORT be configured using DCfg Port.VI or DCfgBit.VI.
Please see board details for more information.
Count The number of times to read digital input
Rate Number of times per second (Hz) to read the port. The actual sampling rate in
some cases will vary a small amount from the requested rate. The actual rate will
be returned to the
ExtClock If this option (True) is used, transfers are controlled by the signal on the trigger
Rate argument.
input line, rather than by the internal pacer clock. Each transfer is triggered on the
appropriate edge of the trigger input signal. When this option is used the
Rate
argument is ignored. The transfer rate is dependent on the trigger signal. The
default is
WordXfer Normally, this VI reads a single (byte) port (default is False). If WORDXFER is
TIMED (False).
specified (True), it will read two adjacent ports on each read and store the value of
both ports together as the low and high byte of a single array element in
DataArray[].
Rate (output) Actual input rate in samples per second.
DataArray Data from the scan is returned here.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 79

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
79
DOut.VI
Writes a byte to a digital output port.
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Output:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed.
PortNum If the port type is not AUXPORT, the specified port must be configured for output.
For many boards, AUXPORT is not configurable. However, some later boards do
The table below shows which ports are in which 82C55 and 8536 digital chips. The
PortNum [I32] - Specifies which digital I/O port to set.
DataValue [I32] - Byte value to output to port.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
require that the AUXPORT be configured using DCfg Port.VI or DCfgBit.VI.
Please see board details for more information.
most 82C55 chips on a single board is eight (8), on the CIO-DIO192. The most (2)
8536 chips occur on the CIO-INT32.
Mnemonic Bit # 8255 Chip # Chip Address 8536 Chip # Chip Address
FIRSTPORTA 0 - 7 1A Base + 0 1A Base + 0
FIRSTPORTB 8 - 15 1B 1B
FIRSTPORTCL 16 - 19 1CL 1C
FIRSTPORTCH 20 - 23 1CH Not present
SECONDPORTA 24 - 31 2A Base + 4 2A Base + 4
SECONDPORTB 32 - 39 2B 2B
SECONDPORTCL 40 - 43 2CL 2C
SECONDPORTCH 44 - 47 2CH No port C High in 8536 chips
and so on, to the last chip on the board as: THIRDPORTx, FOURTHPORTx, FIFTHPORTx, SIXTHPORTx,
SEVENTHPORTx and...
EIGHTHPORTA 168 - 175 8A Base + 28
EIGHTHPORTB 176 - 183 8B
EIGHTHPORTCL 184 - 187 8CL
EIGHTHPORTCH 188 - 191 8CH
Data Value Value to write to the specified port. The size of the ports varies. If it is an eight-bit
port, then the output value must be in the range 0 to 255. If it is a four-bit port, the
value must be in the range 0 to 15.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
Important - Read board-specific information in UL User's Guide
ErrCode into a readable string.
Refer to the example programs and the board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's
Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf) for clarification of
valid PortNum values.
Page 80

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
80
DOutScBg.VI
Performs multiple writes to the digital output port of a high speed digital port on a board with a pacer clock
like the CIO-PDMA16. When this VI is used, control will return immediately to the next point in your
program and the transfer to the digital output port from
GetStatus.VI to check on the status of the background operation. Use StopBg.VI to terminate the background
process before it has completed. Always use the StopBg.VI after all background operations to clear variables
and flags.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
ExtClock [TF] - External (True) or internal clock (False).
Outputs:
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI.
PortNum [I32] - Specifies the digital I/O port to set.
Rate [U32] - Number of times per second (Hz) to write.
DataBuffer [I16] - Digital output values.
Continuous [TF] - Run the VI in an endless loop (True).
WordXfer [TF] - Word (True) or byte transfer (False).
Rate [I32] - Actual scan rate.
Context - [cluster] - Output data structure.
DataBuffer will continue in the background. Use
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
PortNum If the port type is not AUXPORT, the specified port must be configured for output.
For many boards, AUXPORT is not configurable. However, some later boards do
require that the AUXPORT be configured using DCfg Port.VI or DCfgBit.VI.
Please see board details for more information.
Rate Number of times per second (Hz) to write to the port. The actual update rate in
some cases will vary a small amount from the requested rate. The actual rate will
be returned to the
DataBuffer Array of digital values to output.
Continuous This option puts the VI in an endless loop. After it transfers the required number of
bytes it resets to the start of
Rate argument.
DataBuffer and begins again. The only way to stop this
operation is with StopBg.VI.
ExtClock If this option is used, then transfers will be controlled by the signal on the trigger
input line rather than by the internal pacer clock. Each transfer will be triggered on
the appropriate edge of the trigger input signal (see board-specific info). When this
option is used, the
Rate argument is ignored. The transfer rate is dependent on the
trigger signal.
WordXfer Normally, this VI sets a single (byte) port (default is False). If WORDXFER is
specified (True), it will set two adjacent ports on each write and store the value of
both ports together as the low and high byte of a single array element in
DataBuffer[].
Page 81

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
81
Context Data structure containing information from a background operation. Some of the
information included is the board number, the data array, the array size, and the
initial status of the background operation.
Follow the steps below when wiring this VI:
1. DInScBg.VI starts a background operation.
2. GetStatus.VI checks for completion (boolean output called "Running").
3. StopBg.VI terminates the operation, if not already done, and frees memory aliases.
4. Data output from the background operation is passed to GetStatus.VI and StopBg.VI
via Context, and can be wired from one or both of them for intermediate or final
actions, respectively.
The demo VIs illustrate this process effectively.
(output) Actual update rate in samples per second.
Rate
ErrCode
Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 82

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Digital I/O VIs
82
DOutScFg.VI
Multiple writes to digital output port of a high speed digital port on a board with a pacer clock, like the CIOPDMA16. The DOutScFg.VI will not return to your program until all of the requested data has been output.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with Inst aCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
PortNum [I32] - Specifies the digital I/O port to set.
Rate [I32] - Number of times per second (Hz) to write.
DataBuffer [I16] - Digital output values.
ExtClock [TF] - External (True) or internal clock (False).
WordXfer [TF] - Word (True) or byte transfer (False).
Rate [I32] - Actual rate is returned here.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
PortNum If the port type is not AUXPORT, the specified port must be configured for output.
For many boards, AUXPORT is not configurable. However, some later boards do
require that the AUXPORT be configured using DCfg Port.VI or DCfgBit.VI.
Please see board details for more information.
Rate (input) Number of times per second (Hz) to write to the port. The actual update rate in
some cases will vary a small amount from the requested rate. The actual rate will
be returned to the
DataBuffer Array of digital values to output.
ExtClock If this option is used, then transfers will be controlled by the signal on the trigger
Rate argument.
input line rather than by the internal pacer clock. Each transfer will be triggered on
the appropriate edge of the trigger input signal (see board-specific info). When this
option is used, the
Rate argument is ignored. The transfer rate is dependent on the
trigger signal.
WordXfer Normally, this VI sets a single (byte) port (default is False). If WORDXFER is
specified (True), it will set two adjacent ports on each write and store the value of
both ports together as the low and high byte of a single array element in
DataBuffer[].
Rate (output) Actual update rate in samples per second.
ErrCode
Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 83

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Streamer File VIs
83
Streamer File VIs
FileAInScan.VI
Scan a range of A/D channels and store the samples in a disk file. This VI reads the specified number of A/D
samples at the specified sampling rate from the specified range of A/D channels from the specified board. If
the A/D board has programmable gain then it sets the gain to the specified range. The collected data is
returned to a file in binary format. Use FileRead.VI to load data from that file into an array. Refer to the
board-specific information contained in the Universal Libr ary User's Guide (available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
board.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
LowChan [I32] - First A/D channel of scan.
HighChan [I32] - Last A/D channel of scan.
Count [I32] - Number of samples to collect.
Rate [I32] - Sample rate in samples per second (Hz) per channel.
Range [I32] - Range code.
FileName [abc] - Name of disk file.
ExtClock [TF] - External (True) or internal clock (False).
DTConnect [TF] - DT connect option (True). No DTConnect is (False).
ExtTrigger [TF] - External trigger (True). Internal is (False).
Rate - Actual sampling rate
ErrCode - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
) to determine if this function is supported on your
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have an A/D.
LowChan First A/D channel of scan.
HighChan Last A/D channel of scan.
Low/High Channel #: The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of
A/D board is being used. For boards that ha v e bot h si n gl e-ended and differential
inputs, the maximum allowable channel number also depends on how the board is
configured. For example, a PCI-DAS6025 has 8 channels for differential, 16 for
single-ended mode.
Count Specifies the total number of A/D samples that will be collected. If more than one
channel is being sampled then the number of samples collected per channel is
equal to
Rate (input) The maximum sampling rate depends on the A/D board that is being used.
Count/(HighChan - LowChan + 1).
Page 84

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Streamer File VIs
84
Range If the selected A/D board does not have a programmable range feature, then this
argument will be ignored. Otherwise the gain can be set to any of the ranges that
are supported by the selected A/D board. See the "
Range input values" table on
page 19 for valid values. Refer to board-specific information contained in the
Universal Library User's Guide (available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
) for the list of ranges
supported by each board.
FileName Name of the streamer file to create.
Use FileRead.VI
to read the data from this file.
Refer to the Universal Library User's Guide (available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
) for information on the
streamer file functions.
ExtClock If this option is used , then conversions will be controlled by the signal on the
external clock input line rather than by the internal pacer clock. Each conversion
will be triggered on the appropriate edge of the external clock input signal (see
board-specific information). When t his opt ion is used, the
Rate argument is
ignored. The sampling rate is dependent on the trigger signal.
DTConnect If True, samples are sent to the DT-Connect port if the board is equipped with one.
If False, samples are not output to the DT-Connect port. This is the default.
ExtTrigger Wait until trigger input line is asserted. When set to True, the sampling will not
begin until the trigger condition is met.
Rate (output) Actual update rate in samples per second.
ErrCode
Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes:
OVERRUN Error: This error indicates that the data was not written to the file as fast as the data was sampled.
Consequently, some data was lost. The value returned from FileInfo.VI in
Count will be the number of points
that were successfully collected.
Important - Read board-specific information in UL User's Guide
In order to understand the functions, read the board-specific information contained in the Universal Library
User's Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf). The
example programs should be exami ned and run prior to attempting any programmi ng of y ou r ow n.
Page 85

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Streamer File VIs
85
FileInfo.VI
Returns information about a streamer file. When FileAInS.VI or FilePret.VI fill the streamer file, information
is stored about how the data was collected (sample rate, channels sampled etc.). This VI returns that
information.
Refer to the board-specific information contained in the Universal Library User's Guide (available on our web
site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
your board.
Summary:
Inputs: FileName [abc] - Name of streamer file.
Outputs:
PreTrigCount [I32] - Number of pre-trigger samples collected.
LowChan [I32] - First A/D channel of scan.
HighChan [I32] - Last A/D channel of scan.
TotalCount [I32] - Total number of samples collected.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI.
Range [I32] - A/D range used to collect samples.
Rate [I32] - Sampling rate used to collect samples.
) to determine if this function is supported on
Arguments:
FileName The name of the streamer file to read information from.
PreTrigCount Number of pre-trigger samples collected.
LowChan First A/D channel of scan.
HighChan Last A/D channel of scan.
TotalCount Total number of samples collected.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
Range A/D range of the collected data.
Rate Sampling rate of the collected data.
ErrCode into a readable string.
Page 86

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Streamer File VIs
86
FilePret.VI
Scan a range of channels continuously while waiting for a trigger. After the trigger occurs, return the specified
number of samples including the specified number of pre-trigger samples to a disk file. This VI waits for a
trigger signal to occur on the Trigger Input. After the trigger occurs, it returns the specified number
(TotalCount) of A/D samples including the specified number of pre-trigger points. It collects the data at the
specified sampling rate (Rate) from the specified range (LowChan-HighChan) of A/D channels from the
specified board. If the A/D board has programmable gain then it sets the gain to the specified range. The
collected data is returned to a file. Refer to the board-specific information contained in the Universal Library
User's Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
if this function is supported by your b oar d.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
LowChan [I32] - First A/D channel of scan.
HighChan [I32] - Last A/D channel of scan.
PretrigCount [I32] - Number of pre-trigger samples to collect.
TotalCount [I32] - Total number of samples to collect.
Rate [I32] - Sample rate in samples per second (Hz) per channel.
Range [I32] - A/D range.
FileName [abc] - Name of disk file.
ExtClock [TF] - External (True) or internal clock (False - default).
DTConnect [TF] - DT connect option (True).
PretrigCount [I32] - Number of pre-trigger sample collected.
TotalCount [I32] - Total number of samples collected.
Rate [I32] - Actual sampling rate.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI.
) to determine
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal. The
specified board must have an A/D and pretrigger capability.
LowChan First A/D channel of scan.
HighChan Last A/D channel of scan.
Low/High Channel #: The maximum allowable channel depends on which type of
A/D board is being used. For boards that ha v e bot h si n gl e-ended and differential
inputs, the maximum allowable channel number also depends on how the board is
configured. For example, a PCI-DAS6025 has 8 channels for differential, 16 for
single-ended mode.
PretrigCount Specifies the number of samples before the trigger that will be returned.
PreTrigCount must be less than TotalCount - 512.
Page 87

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Streamer File VIs
87
If the trigger occurs too early, then fewer than the requested number of pre-trigger
samples will be collected. In that case a
TOOFEW error will occur. The PretrigCount
will be set to indicate how many samples were collected and the post trigger
samples will still be collected.
TotalCount Specifies the total number of samples that will be collected and stored in the file.
TotalCount must be greater then or equal to PretrigCount + 512. If the trigger
occurs too early then fewer than the requested number of samples will be collected.
In that case a
TOOFEW error will occur. The TotalCount will be set to indicate how
many samples were actually collected.
Rate (input) The maximum sampling rate depends on the A/D board that is being used.
Range If the selected A/D board does not have a programmable range feature, then this
argument will be ignored. Otherwise the gain can be set to any of the ranges that
are supported by the selected A/D board. See the "
Range input values" table on
page 19 for valid values. Refer to board-specific information contained in the
Universal Library User's Guide (available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
) for the list of ranges
supported by each board.
FileName The name of the streamer file to create.
Use FileRead.VI
to read the data from this file.
Refer to the Universal Library User's Guide (available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
) for information on the
streamer file functions.
ExtClock If this option is used , then conversions will be controlled by the signal on the
external clock input line rather than by the internal pacer clock. Each conversion
will be triggered on the appropriate edge of the external clock input signal (see
board-specific information). When t his opt ion is used, the
Rate argument is
ignored. The sampling rate is dependent on the trigger signal.
DTConnect If True, samples are sent to the DT-Connect port if the board is equipped with one.
If False, samples are not output to the DT-Connect port. This is the default.
PretrigCount Actual number of pre-trigger A/D samples collected.
TotalCount Total number of A/D samples collected.
Rate (output) The maximum sampling rate depends on the A/D board that is being used. This is
the rate at which scans are triggered. If you are sampling four channels, 0 to 3, then
specifying a rate of 10,000 scans per second (10 kS/s) will result in the A/D
converter rate of 40 kS/s (four channels at 10,000 samples per channel per second).
This is different from some software where you specify the total A/D chip rate. In
those systems, the per channel rate is equal to the A/D rate divided by the number
of channels in a scan. This argument also returns the value of the actual set. This
may be different from the requested rate because of pacer limitations.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes:
OVERRUN error: This error indicates that the data was not written to the file as fast as the data was sampled.
Consequently, some data was lost. The value in
TotalCount will be the number of points that were
successfully collected.
Page 88

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Streamer File VIs
88
FileRead.VI
Reads data from a streamer file. Refer to the board-specific information contained in the Universal Library
User's Guide (available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
if this function is supported on your board.
Summary:
Inputs: FileName [abc] - Name of streamer file.
Outputs:
FirstPoint [I32] - Index of first sample to read.
NumPoints [I32] - Number of samples to read.
NumPoints [I32] - Number of samples read.
DataBuffer [I32] - Data buffer that data is read into.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI.
Arguments:
FileName Name of streamer file in which the A/D measurements are stored.
FirstPoint Index of first sample to read from the streamer file.
NumPoints (input) Number of samples to read from the streamer file.
NumPoints (output) Number of samples actually read.
DataBuffer Array of A/D measurements in binary counts read from the file. Use ToEng.VI to
convert from binary counts to engineering units (volts or mAmps).
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
) to determine
Notes:
Data format: The data is returned as 16 bits. The 16 bits can represent 12 bits of analog, 12 bits of analog plus
4 bits of channel, or 16 bits of analog. Use ACvtData.VI to correctly load the data into an array.
Loading portions of files: The file can contain much more data than can fit in
TotalCount and FirstPoint to read a selected piece of the file into DataBuffer. Call FileInfo.VI first to find out
DataBuffer. In those cases, use
how many points are in the file.
Page 89

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Memory board VIs
89
Memory board VIs
MemRdPrt.VI
Reads pre-trigger data from a memory board that has been collected with either APretrBg.VI or APretrFg.VI
and arranges the data in the correct order (pre-trigger data first, then post-trigger data). This VI can only be
used to retrieve data that has been collected by either APretrBg.VI or APretrFg.VI with the ExtMemory
option set to TRUE. After each APretrFg.VI or APretrBg.VI call, all data must be unloaded from the memory
board with this VI. If any more data is sent to the memory board then the pre-trigger data will be lost.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
FirstPoint Use the FirstPoint argument to specify the first point to be read. For example, to
If you are going to read a large amount of data from the board in small chunks then
Count Number of points (words) to read.
DataArray Data read from memory board.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
FirstPoint [I32] - Index of first point to read or FROMHERE.
Count [U32] - Number of points (words) to read.
DataArray [U16] - Output data array.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI.
read points #200 - #250, set
FirstPoint to FROMHERE (-1) to read each successive chunk. Using
set
FROMHERE (-1) speeds up the operation of MemRdPrt.VI when working with
FirstPoint=200 and Count=50.
large amounts of data.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes:
DT Connect conflicts - The .MemRdPrt.VI can not be called while a DT Connect transfer is in progress. For
example, if you start collecting A/D data to the memory board in the background (by calling AInScBg.VI or
AInScFg.VI with the
or AInScFg.VI has completed. If you do, you will get a
DTCONNECT + BACKGROUND options), you can not call MemRdPrt.VI until the AInScBg.VI
DTACTIVE error.
Page 90

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Memory board VIs
90
MemRead.VI
Reads data from a memory board into an array.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum The memory board number associated with a board when it was installed with
FirstPoint Use the FirstPoint argument to specify the first point to be read. For example, to
To read a large amount of data from the board in small portions, set
Count Number of samples (words) to read.
DataBuffer Data read from memory board.
ErrCode Error code returned from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the
FirstPoint [I32] - Index of first point to read or FROMHERE.
Count [U32] - Number of samples (words) to read
DataBuffer [U16] - Output data array.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI.
InstaCal.
read points #200 - #250, set
FROMHERE (-1) to read each successive portion. Using FROMHERE (-1) speeds up the
FirstPoint=200 and Count=50.
FirstPoint to
operation of MemRead VI when working with large amounts of data.
ErrMsg VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes:
DT-Connect conflicts - The MemRead.VI can not be called while a DT-CONNECT transfer is in progress.
For example, if you start collecting A/D data to the memory board in the background (by calling AInScBg.VI
or AInScFg.VI with the
AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI has completed. If you do, you will get a
DTCONNECT + BACKGROUND options). You cannot call MemRead.VI until the
DTACTIVE error.
Page 91

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Memory board VIs
91
MemReset.VI
Resets the memory board pointer to the start of memory. The memory boards are sequential devices. They
contain a counter which points to the 'current' word in memory. Every time a word is read or written, this
counter increments to the next word.
Summary:
Input: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Outputs:
Arguments:
BoardNum (input) The memory board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can be 0 to 100.
BoardNum (output) The memory board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. This parameter
ErrCode Error code from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the ErrMsg
BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100. Can be used to pass
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
BoardNum parameter to another VI.
can be used serialize VIs such that this VI precedes the next VI whose BoardNum
is attached to this output.
VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes
This VI is used to reset the counter back to the start of the memory. Between successive calls to AInScBg.VI
or AInScFg.VI you would call this VI so that the second AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI overwrites the data from
the first call. Otherwise the data from the first AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI will be followed by the data from
the second AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI in the memory on the card.
Likewise, anytime you call MemRead.VI or MemWrite.VI, the counter is left pointing to the next memory
location after the data that you read or wrote. Call MemReset.VI to reset back to the start of the memory
buffer before the next call to AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI.
Page 92

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Memory board VIs
92
MemSetDT.VI
Sets the DT Connect mode of a memory board.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Output:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
Mode Must be set to either DTIN (default) or DTOUT. Set the Mode on the memory board to
ErrCode Error code from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the ErrMsg
Notes:
Mode [TF] - Direction of memory board DT transfer.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
DTIN to transfer data from an A/D board to the memory board. Set Mode=DTOUT
(True) to transfer data from a memory board to a D/A board.
VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
This command only controls the direction of data transfer between the memory board and another board that
is connected to it via a DT Connect cable.
Do not use this VI when you are using the
memory board mode is already set through AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI
EXTMEMORY option with AInScBg.VI or AInScFg.VI, etc., as the
EXTMEMORY option.
Use this VI only if the parent board is not supported by the Universal Library .
Page 93

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Memory board VIs
93
MemWrite.VI
Writes data from an array to the memory card.
Summary:
Inputs: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Output:
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
DataBuffer Buffer containing data to be written to the external memory board.
FirstPoint Use the FirstPoint argument to specify where in the board's memory to write the
To write a large amount of data to the board in small portions, set
Count Specifies the number of words to be written to the external memory card. Count
ErrCode Error code from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the ErrMsg
DataBuffer [U16] - Pointer to the data array.
FirstPoint [I32] - Index of first point to write or FROMHERE.
Count [I32] - Number of samples (words) to write.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
first point. For example, to write to locations #200 - #250, set
Count=50.
FROMHERE (-1) to write each successive portion. Using FROMHERE (-1) speeds up the
FirstPoint=200 and
FirstPoint to
operation of MemWrite when working with large amounts of data.
must be equal to or less than the size of
VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
DataBuffer.
Notes:
DT Connect conflicts - The MemWrite VI can not be called while a DT Connect transfer is in progress. For
example, if you start collecting A/D data to the memory board in the background (by calling AInScBg.VI or
AInScFg.VI with the
AInScFg.VI has completed. If you do you will get a
DTCONNECT + BACKGROUND options). You can not call MemWrite until the AInScBg.VI or
DTACTIVE error.
Page 94

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Serial VIs
94
Serial VIs
RS485.VI
Sets the direction of RS-485 communications port buffers..
Summary:
Input: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
Transmit [I32] - Enable (1) or disable (0) the transmit RS-485 line driver.
Receive [I32] - Enable (1) or disable (0) the receive RS-485 buffer.
Output:
Arguments:
BoardNum The number associated with the board when it was installed with the InstaCal
Transmit Set to enabled (1) or disabled (0). The transmit RS-485 line driver is turned on.
Receive Set to enabled (1) or disabled (0). The receive RS-485 buffer is turned on. Data
ErrCode Error code from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the ErrMsg
BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
configuration program. BoardNum may be 0 to 99.
Data written to the RS-485 UART chip is transmitted to the cable connected to that
port.
present on the cable connected to the RS-485 port is received by the UART chip.
VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes:
You can simultaneously enable or disable the transmit and receive buffers. If both ar e enabled, data written to
the port is also received by the port. For a complete discussion of RS485 network construction and
communication, refer to the CIO-COM485 User's Manual (
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/cio-com485.pdf).
Page 95

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Miscellaneous VIs
95
Miscellaneous VIs
ErrHdlng.VI
Sets the error handling for all subsequent VI calls. Most VIs return error codes after each call. In addition
other error handling features have been built into the library. This VI controls those features. If the UL
LabVIEW Extension cannot find the configuration file CB.CFG, it always terminates the program regardless
of the ErrHdlng.VI setting.
Summary:
Input: ErrReporting [I32] - Type of error reporting.
Output:
Arguments:
ErrReporting This argument controls when the library will print error messages on the screen.
ErrCode Error code from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the ErrMsg
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
The default is
DONTPRINT - Errors will not generate a message to the screen. In that case your
DONTPRINT. If it is set to:
program must always check the returned error code after each library call to
determine if an error occurred.
PRINTWARNINGS - Only warning errors will generate a message to the screen. Your
program will have to check for fatal errors.
PRINTFATAL - Only fatal errors will generate a message to the screen. Your
program must check for warning errors.
PRINTALL - All errors will generate a message to the screen.
VI to convert
ErrCode into a readable string.
Warnings vs. Fatal Errors: All errors that can occur are classified as either "warnings" or "fatal." Errors that
can occur in normal operation in a bug free program (disk is full, too few samples before trigger occurred) are
classified as "warnings." All other errors indicate a more serious problem and are classified as "fatal."
Page 96

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Miscellaneous VIs
96
ErrMsg.VI
Returns the error message associated with an error code. Each VI returns an error code. If the error code is not
equal to 0 it indicates that an error occurred. Call this VI to convert the returned error code to a descriptive
error message.
Summary:
Input: ErrCode [I32] - Error code that was returned by any VI.
Outputs:
ErrMsg [abc] - Error message.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code, or 0 if no error.
Page 97

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Miscellaneous VIs
97
GetBoard.VI
Returns the board name of a specified board.
Summary:
Input: BoardNum [U32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can
be 0 to 100, or
Outputs:
BoardName [abc] - Name of the specified board.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
Arguments:
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal, or
GETFIRST or GETNEXT.
BoardName A string variable that the board name will be returned to. This string variable must
be pre-allocated to be at least as large as
be large enough to hold the longest board name string.
ErrCode Error code from the Universal Library. Zero if no error occurred. Use the ErrMsg
VI to convert
GETFIRST or GETNEXT
BOARDNAMELEN. This size is guaranteed to
ErrCode into a readable string.
Notes:
There are two distinct ways of using this function:
Pass a board number as the
BoardNum argument. In that case the string that is returned will describe the
board type of the installed board.
Set
BoardNum to GETFIRST(-2) or GETNEXT(-3), to get a list of all board types that are supported by the
library. If
Subsequent calls with
library. When you reach the end of the list
BoardNum is set to GETFIRST, it will return the first board type in the list of supported boards.
BoardNum=GETNEXT will return each of the other board types supported by the
BoardName will be set to an empty string.
Page 98

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Miscellaneous VIs
98
GetCfg.VI
Returns a configuration option for a board. Th e configuration information for all boards is stored in the
CB.CFG file. This information is loaded from CB.CFG by all programs that use the library. The current
configuration can be changed within a running program with the SetCfg.VI VI function. This GetCfg.VI
returns the current configuration information.
Inputs: InfoType [I32] - The class of configuration information that you want to retrieve.
Outputs:
Arguments:
InfoType The configuration information for each board is grouped into different categories.
BoardNum The board number associated with a board when it was installed with InstaCal.
DevNum Selects a particular device. If InfoType=DIGITALINFO then DevNum specifies which
ConfigItem Specifies the configuration item you want to retrieve.
The
ConfigVal The specified configuration item is returned to this variable.
BoardNum [I32] - The board number assigned when installed with InstaCal. Can be
0 to 100.
DevNum [I32] - Specifies the board device.
ConfigItem [I32] - Specifies the configuration item.
ConfigVal [I32] - Current configuration value.
ErrCode [I32] - Error code. See ErrMsg.VI
This argument specifies which category you want. It should be set to one of the
following constants:
GLOBALINFO - Information about the configuration file.
BOARDINFO - General information about a board.
DIGITALINFO - Information about a digital device.
COUNTERINFO - Information about a counter device.
EXPANSIONINFO - Information about an expansion device.
MISCINFO - One of the miscellaneous options for the board.
of the board's digital devices you want information on. If
DevNum specifies which of the board's counter devices.
then
ConfigItem value depends on the InfoType value. Refer to the "Notes" section
for a list of all possible values for
ConfigItem.
InfoType=COUNTERINFO
Notes:
The list of
InfoType = GLOBALINFO
InfoType = BOARDINFO
ConfigItem values for each category of configuration information is:
GIVERSION - CB.CFG file format. This information is used by the library to determine compatibility.
GINUMBOARDS - Maximum number of installable boards
GINUMEXPBOARDS - Maximum number of expansion boards allowed to be installed.
BIBASEADR - Base address of board
BIBOARDTYPE - Returns a number in the range of 0 to 8000 Hex.
BIINTLEVEL - Interrupt level. 0 for none or 1 - 15
Page 99

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Miscellaneous VIs
99
BIDMACHAN - DMA channel. 0, 1 or 3
BIINITIALIZED - TRUE (non-zero) or FALSE (0)
BICLOCK - Clock frequency in MHz (1, 4, 6, or 10); or (0) for not supported.
BIRANGE - Selected voltage range. For switch-selectable gains only. If the selected A/D board does not
have a programmable gain feature, this argument returns the range as defined by the installed InstaCal
settings which correspond to the input range as set via the switches on the board. Refer to board-specific
information for a list of the A/D ranges supported by each board.
Range Value Range Value
±20 V 15 0 - 5 V 101
±10 V 1 0 - 4 V 114
±5 V 0 0 - 2.5 V 102
±4 V 16 0 - 2 V 103
±2.5 V 2 0 - 1.67 V 109
±2 V 14 0 - 1.25 V 104
±1.67 V 11 0 - 1 V 105
±1.25 V 3 0 - 0.5 V 110
±1 V 4 0 - 0.25 V 111
±0.625 V 5 0 - 0.2 V 112
±0.5 V 6 0 - 0.1 V 106
±0.25 V 12 0 - 0.01 V 107
±0.2 V 13 0 - 0.02 V 108
±0.1 V 7 4 -20 mA 200
±0.05 V 8 0 -20 mA 204
±0.01 V 9 2 -10 mA 201
±0.005 V 10 1- 5 mA 202
0 - 10 V 100 0.5 to 2.5 mA 203
BINUMADCHANS - Number of A/D channels
BIUSESEXPS - Supports expansion boards TRUE/FALSE
BIDINUMDEVS - Number of digital devices
BIDIDEVNUM - Index into digital inf ormation for first device
BICINUMDEVS - Number of counter devices
BICIDEVNUM - Index into counter information for first device
BINUMDACHANS - Number of D/A channels
BIWAITSTATE - Setting of Wait State jumper. 1 = enabled, 0 = disabled
BINUMIOPORTS - Number of IO ports used by boar d
BIPARENTBOARD - Board number of parent board
BIDTBOARD - Board number of connected DT board
Page 100

Universal Library Virtual Instruments (VIs) Miscellaneous VIs
100
InfoType = DIGITALINFO
DIBASEADR - Base address
DIINITIALIZED - TRUE (non-zero) or FALSE (0)
DIDEVTYPE - Device Type - AUXPORT, FIRSTPORTA etc
DIMASK - Bit mask for this port
DIREADWRITE - Read required before write TRUE/FALSE
DICONFIG - Current configuration INPUT or OUTPUT
DINUMBITS - Number of bits in port
DICURVAL - Current value of outputs
InfoType = COUNTERINFO
CIBASEADR - Base address
CIINITIALIZED - TRUE (non-zero) or FALSE (0)
CICTRTYPE - 1 = 8254, 2 = 9513, 3 = 8536, 4 = 7266 type counter chip.
CICTRNUM - Which counter on chip
CICONFIGBYTE - Configuration byte
InfoType = EXPANSIONINFO
XIBOARDTYPE - Board type
XIMUXADCHAN1 - A/D channel board is connect to
XIMUXADCHAN2 - 2nd A/D channel board is connected to
XIRANGE1 - Range (gain) of low 16 channels
XIRANGE2 - Range (gain) of high 16 channels
XICJCCHAN - A/D channel that CJC is connected to
XITHERMTYPE - Thermocouple type
XINUMEXPCHANS - Number of expansion channels on board
XIPARENTBOARD - Board number of parent A/D board
 Loading...
Loading...