Page 1

(3',62
User's Guide
,VRODWHG,QSXWDQG5HOD\2XWSXW(WKHUQHW,QWHUIDFH0RGXOH
Page 2

E-PDISO16
Isolated Input and Relay Output
Ethernet Interface Module
User's Guide
Document Revision 4, June, 2006
© Copyright 2006, Measurement Computing Corporation
Page 3
+0(3',62GRF
Your new Measurement Computing product comes with a fantastic extra —
Management committed to your satisfaction!
Thank you for choosing a Measurement Computing product—and congratulations! You own the finest, and you can now enjoy
the protection of the most comprehensive warranties and unmatched phone tech support. It’s the embodiment of our mission:
To provide data acquisition hardware and software that will save time and save money.
Simple installations minimize the time between setting up your system and actually making measurements. We offer quick and
simple access to outstanding live FREE technical support to help integrate MCC products into a DAQ system.
Limited Lifetime Warranty: Most MCC products are covered by a limited lifetime warranty against defects in materials or
workmanship for the life of the product, to the original purchaser, unless otherwise noted. Any products found to be defective in
material or workmanship will be repaired, replaced with same or similar device, or refunded at MCC’s discretion. For specific
information, please refer to the terms and conditions of sale.
Harsh Environment Program: Any Measurement Computing product that is damaged due to misuse, or any reason, may be
eligible for replacement with the same or similar device for 50% of the current list price. I/O boards face some harsh
environments, some harsher than the boards are designed to withstand. Contact MCC to determine your product’s eligibility for
this program.
30 Day Money-Back Guarantee: Any Measurement Computing Corporation product may be returned within 30 days of
purchase for a full refund of the price paid for the product being returned. If you are not satisfied, or chose the wrong product by
mistake, you do not have to keep it.
These warranties are in lieu of all other warranties, expressed or implied, including any implied warranty of merchantability or
fitness for a particular application. The remedies provided herein are the buyer’s sole and exclusive remedies. Neither
Measurement Computing Corporation, nor its employees shall be liable for any direct or indirect, special, incidental or
consequential damage arising from the use of its products, even if Measurement Computing Corporation has been notified in
advance of the possibility of such damages.
Trademark and Copyright Information
Measurement Computing Corporation, InstaCal, Universal Library, and the Measurement Computing logo are either trademarks
or registered trademarks of Measurement Computing Corporation. Refer to the Copyrights & Trademarks section on
mccdaq.com/legal for more information about Measurement Computing trademarks. Other product and company names
mentioned herein are trademarks or trade names of their respective companies.
© 2006 Measurement Computing Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form by any means, electronic, mechanical, by photocopying, recording, or otherwise
without the prior written permission of Measurement Computing Corporation.
Notice
Measurement Computing Corporation does not authorize any Measurement Computing Corporation product for use
in life support systems and/or devices without prior written consent from Measurement Computing Corporation.
Life support devices/systems are devices or systems that, a) are intended for surgical implantation into the body, or
b) support or sustain life and whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to result in injury. Measurement
Computing Corporation products are not designed with the components required, and are not subject to the testing
required to ensure a level of reliability suitable for the treatment and diagnosis of people.
Page 4

Table of Contents
About this User's Guide ......................................................................................................................vi
What you will learn from this user's guide ........................................................................................................vi
Conventions in this user's guide ........................................................................................................................vi
Where to find more information........................................................................................................................vi
Chapter 1
Introducing the E-PDISO16 .............................................................................................................. 1-1
Overview: E-PDISO16 features ..................................................................................................................... 1-1
Ethernet interface............................................................................................................................................ 1-2
Software features............................................................................................................................................ 1-2
E-PDISO16 block diagram............................................................................................................................. 1-3
Chapter 2
Installing the E-PDISO16 .................................................................................................................. 2-1
What comes with your E-PDISO16 shipment? .............................................................................................. 2-1
Hardware ....................................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
Additional documentation.............................................................................................................................................. 2-1
Unpacking the E-PDISO16............................................................................................................................. 2-2
Installing the software .................................................................................................................................... 2-2
Connecting the external power supply............................................................................................................ 2-2
Connecting the Ethernet cable........................................................................................................................ 2-2
Configuring the E-PDISO16........................................................................................................................... 2-3
If your network does not have a DHCP server............................................................................................................... 2-3
If your network does have a DHCP server..................................................................................................................... 2-3
Run InstaCal .................................................................................................................................................................. 2-3
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).............................................................................................................2-3
IP address....................................................................................................................................................................... 2-4
Subnet mask................................................................................................................................................................... 2-4
Gateway......................................................................................................................................................................... 2-4
Chapter 3
Functional Details ............................................................................................................................. 3-1
Internal components ....................................................................................................................................... 3-1
Ethernet port ..................................................................................................................................................................3-1
External power connectors............................................................................................................................................. 3-1
POWER LED................................................................................................................................................................. 3-2
LINK LED..................................................................................................................................................................... 3-2
ACTIVITY LED............................................................................................................................................................ 3-2
TEST LED..................................................................................................................................................................... 3-2
Factory default button.................................................................................................................................................... 3-3
Screw terminal wiring.................................................................................................................................................... 3-3
Relay output terminals (NO0 to NC15) ......................................................................................................................... 3-4
Digital input terminals (IP0A to IP15B) ........................................................................................................................ 3-5
Power limitations using multiple E-PDISO16 modules ................................................................................. 3-6
Chapter 4
Ethernet Troubleshooting ................................................................................................................ 4-1
Deleting an ARP table entry........................................................................................................................... 4-3
Getting help .................................................................................................................................................... 4-4
Chapter 5
Specifications.................................................................................................................................... 5-1
Output relay specifications ............................................................................................................................. 5-1
Isolated inputs................................................................................................................................................. 5-1
iv
Page 5

E-PDISO16 User's Guide
Power consumption ........................................................................................................................................ 5-2
External power output .................................................................................................................................... 5-2
Ethernet compliance ....................................................................................................................................... 5-2
Ethernet connection ........................................................................................................................................ 5-2
EEProm memory ............................................................................................................................................ 5-2
Ethernet and input filter "Factory Default" settings........................................................................................ 5-3
LED displays and the "Factory Default" button ............................................................................................. 5-3
Mechanical ..................................................................................................................................................... 5-3
Environmental ................................................................................................................................................ 5-3
Main connector............................................................................................................................................... 5-3
Screw terminal pin out................................................................................................................................................... 5-4
v
Page 6

Preface
About this User's Guide
What you will learn from this user's guide
This user's guide explains how to install and configure the E-PDISO16 so that you get the most out of its
isolated input and relay output features.
Conventions in this user's guide
For more information on …
Text presented in a box signifies additional information and helpful hints related to the subject matter you are
reading.
Caution! Shaded caution statements present information to help you avoid injuring yourself and others,
damaging your hardware, or losing your data.
<#:#> Angle brackets that enclose numbers separated by a colon signify a range of numbers, such as those assigned
to registers, bit settings, etc.
bold text Bold text is used for the names of objects on the screen, such as buttons, text boxes, and check boxes. For
example:
1. Insert the disk or CD and click the OK button.
italic text Italic text is used for the names of manuals and help topic titles, and to emphasize a word or phrase. For
example:
The InstaCal® installation procedure is explained in the Quick Start Guide.
Never touch the exposed pins or circuit connections on the board.
Where to find more information
The following electronic documents provide information relevant to the operation of the E-PDISO16.
! MCC's Specifications: E-PDISO16 (the PDF version of the Electrical Specification Chapter in this guide) is
available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/pdfs/E-PDISO16.pdf
! MCC's Quick Start Guide is available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/DAQ-Software-Quick-Start.pdf
! MCC's Guide to Signal Connections is available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/signals/signals.pdf
! MCC's Universal Library User's Guide is available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf
! MCC's Universal Library Function Reference is available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-functions.pdf
! MCC's Universal Library for LabVIEW
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/SM-UL-LabVIEW.pdf
E-PDISO16 User's Guide (this document) is also available on our web site at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/E-PDISO16.pdf
.
.
™
User’s Guide is available on our web site at
.
.
.
.
.
vi
Page 7

Chapter 1
Introducing the E-PDISO16
Overview: E-PDISO16 features
This user's guide contains all of the information you need to connect the E-PDISO16 to your network or
computer and to the external devices you want to control. You can use the E-PDISO16 in your control
applications to switch on and off a variety of devices, such as fans, blowers, pumps, etc.
®
The E-PDISO16 is a data acquisition Ethernet interface module supported under Microsoft
and Windows XP.
The E-PDISO16 provides 16 relay outputs and 16 isolated digital inputs. All I/O connections are made to three
sets of screw terminals on the module.
The 16 individual, optically isolated (500 V) digital inputs can be driven by either AC (50 to 1000 Hz) or DC at
levels up to 30 volts. Each input channel has a software-enabled low-pass AC filter with a time constant of 5 ms
(200 Hz). The 16 inputs can be read back as a single byte.
The 16 outputs are single-pole double-throw (SPDT) dry contact, Form-C electromechanical relays. The screw
terminals provide three connections to each relay – normally open (NO), normally closed (NC), and common
(C). The relays are in a non-energized state (NC) upon power up.
Windows® 2000
The E-PDISO16 is powered by an external +9 V regulated power supply that is shipped with the module. A
power output lets you power additional Measurement Computing products from one external power supply.
Depending on your load requirement, daisy-chained modules may require a separate power supply.
On-board LEDs display the status of communication, external power, and the Ethernet connection. A fourth
LED is used for testing purposes.
The E-PDISO16 is shipped in a rugged metal enclosure that you can mount on a DIN rail or on a bench.
1-1
Page 8
E-PDISO16 User's Guide Introducing the E-PDISO16
Ethernet interface
The E-PDISO16 has one built-in 10/100 BASE-T auto-negotiation, high-speed communication port. With the
Ethernet interface, you can remotely access and configure your E-PDISO16 from anywhere on the network.
Only one computer can control the E-PDISO16 at one time. The networking protocol is TCP/IP. You can send
your data over 100 meters at data speeds of up to 100 Mbps using only one Ethernet cable connected to your
computer.
You configure the Ethernet connection settings with InstaCal. MCC assigns a unique physical (MAC) address
to each module you connect to your network. You can restore the factory-default Ethernet connection settings
with an on-board RESET button.
Max number of TCP connections to the E-PDISO16
The maximum number of TCP connections that may concurrently be connected to the E-PDISO16 is three. The
first user to establish a TCP connection can change the configurations and write to the outputs. The remaining
two users may access the unit on a "read-only" basis. An attempt by a fourth user to gain a connection with the
E-PDISO16 will not be acknowledged. Performance of these three concurrent connections will be subject to the
limitations of the network topology and the network traffic that they are connected to.
Configuration information
For more information on InstaCal and the Ethernet configuration settings for your E-PDISO16, refer to the
"PDISO8 and PDISO16 Series" section of the "Digital Input/Output Boards" chapter in the Universal Library
User's Guide. This document is available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-
guide.pdf.
Software features
For information on the features of InstaCal and the other software included with your E-PDISO16, refer to the
Quick Start Guide that shipped with your device. The Quick Start Guide is also available in PDF at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/DAQ-Software-Quick-Start.pdf
Check http://www.mccdaq.com/download.htm
supported under less commonly used operating systems.
for the latest software version or versions of the software
.
1-2
Page 9
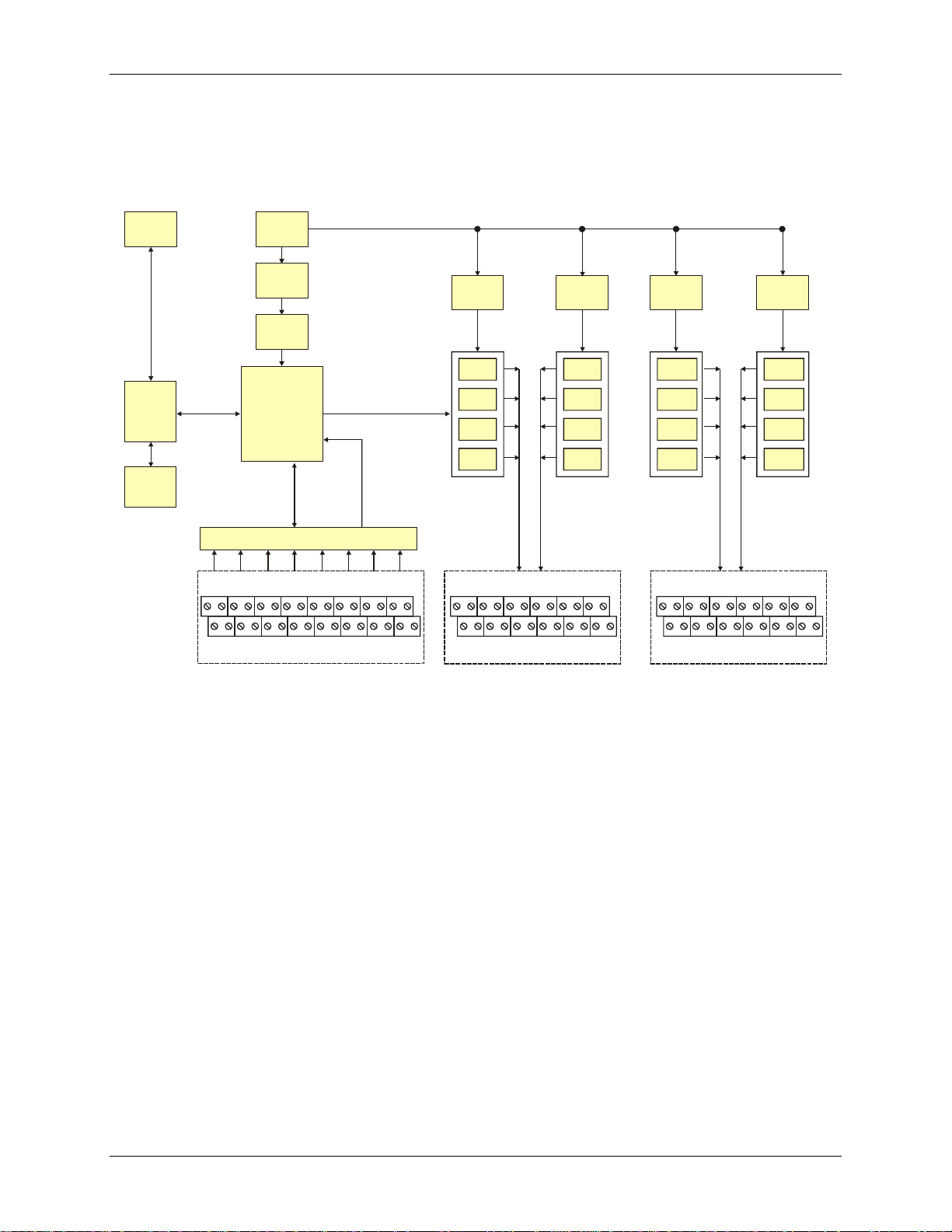
E-PDISO16 User's Guide Introducing the E-PDISO16
E-PDISO16 block diagram
E-PDISO16 functions are illustrated in the block diagram shown here.
RJ-45
Ethernet
Port
Ethernet
MAC/PHY
3V
Power
Regulator
8-bit
Host Interface
IP1A
IP0A
IP0B
9.0 V
External
Power
Power
Monitor
5V
Power
Regulator
PIC18F8520
Microcontroller
I2C
Interface
for filter control
Isolation and Fi lter
IP2A
IP3A
IP4A
IP1B
IP2B
IP3B
IP4B
16 Digital inputs
5V
Power
Regulator
Relay 4
16 channels
Relay 3
Relay 2
Relay 1
16
channels
IP5A
IP6A
IP7A
IP8A
IP9A
IP10A
IP11A
IP12A
IP13A
IP14A
IP15A
IP5B
IP6B
IP7B
IP8B
IP9B
IP11B
IP10B
IP12B
IP13B
IP14B
4 SPDT
relays
NO0
NC0
C1
NO2
NC2C3NO4
C0
C2
NC1
NO1
IP15B
NO3
8 Relay outputs
NC3
Regulator
NC4C5NO6
C4
NO5
5V
Power
Relay 5
Relay 6
Relay 7
Relay 8
4 SPDT
relays
NC5
5V
Power
Regulator
Relay 12
Relay 11
Relay 10
Relay 9
4 SPDT
relays
NC6
C7
C6
NC7
NO7
NO8
NC8
C9
NO10
NC10
C8
C10
NC9
NO9
NO11
8 Relay outputs
C11
NO12
C12
NC11
5V
Power
Regulator
Relay 13
Relay 14
Relay 15
Relay 16
4 SPDT
relays
NC12
C13
NO14
NC13
NO13
NC14
C15
C14
NC15
NO15
Figure 1-1. E-PDISO16 functional block diagram
1-3
Page 10

Installing the E-PDISO16
What comes with your E-PDISO16 shipment?
As you unpack your E-PDISO16, make sure that the following components are included.
Hardware
! E-PDISO16 (shown removed from case)
Chapter 2
! External power supply and cord (CB-PWR-9V3A) – 9 volt, 3 amp DC power supply
Additional documentation
In addition to this hardware user's guide, you should also receive the Quick Start Guide (available in PDF at
www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/DAQ-Software-Quick-Start.pdf
the software you received with your E-PDISO16 and information regarding installation of that software. Please
read this booklet completely before installing any software or hardware.
). This booklet supplies a brief description of
2-1
Page 11

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Installing the E-PDISO16
Unpacking the E-PDISO16
As with any electronic device, you should take care while handling to avoid damage from static
electricity. Before removing the E-PDISO16 from its packaging, ground yourself using a wrist strap or by
simply touching the computer chassis or other grounded object to eliminate any stored static charge.
If your E-PDISO16 arrives already damaged, notify Measurement Computing Corporation immediately by
phone, fax, or email. For international customers, contact your local distributor where you purchased the EPDISO16.
! Phone: 508-946-5100 and follow the instructions for reaching Tech Support.
! Fax: 508-946-9500 to the attention of Tech Support
! Email: techsupport@mccdaq.com
Installing the software
Refer to the Quick Start Guide for instructions on installing the software on the Measurement Computing Data
Acquisition Software CD. This booklet is available in PDF at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/DAQ-Software-
Quick-Start.pdf.
Connecting the external power supply
Power to the E-PDISO16 is provided with the +9 V, 3 A external power supply (CB-PWR-9V3A). It does not
matter if you connect the external power cable before or after you connect the Ethernet cable. To connect the
power supply to your E-PDISO16, do the following.
1.
Connect the +9 V DC power supply cord to the connector labeled
IN on the module). Refer to on page 3-1 for the location of this connector. Figure 3-1
(
Plug the power cord into an electrical outlet.
2.
POWER LED illuminates when +9 V power is supplied to the E-PDISO16. If the voltage supply is less
The
than +6.0 V or more than +12.5 V, the
Do not connect external power to the POWER OUT connector
The power connector labeled POWER OUT on the enclosure (OUT on the module) is used to power an
additional Measurement Computing product. If you connect the external power supply to the POWER OUT
connector, the E-PDISO16 does not receive power, and the POWER LED does not illuminate.
POWER LED does not light.
POWER IN on the E-PDISO16 enclosure
Connecting the Ethernet cable
Your computer communicates with the E-PDISO16 remotely via the Ethernet cable. To connect the Ethernet
cable to the E-PDISO16 and to the network, do the following:
1.
Connect the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet communication port on the E-PDISO16.
Use a standard Ethernet CAT-5 shielded or unshielded twisted pair Ethernet cable.
Plug the cable into your network's Ethernet connection.
2.
The
LINK LED illuminates steady green to indicate that you have established an Ethernet connection
between your E-PDISO16 and the network.
2-2
Page 12

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Installing the E-PDISO16
Connecting the E-PDISO16 to your computer's Ethernet port
If your computer is not connected to a network, or if you just want to connect the E-PDISO16 directly to your
computer, use a standard cross-over cable for your Ethernet connection (such as a BELKIN A3X126-07-YLWM CAT cross-over cable). Connect the cross-over cable between the unused Ethernet port on your computer
and the Ethernet port on the E-PDISO16. Once connected, set up your TCP/IP address using InstaCal.
If the LINK LED is not illuminated, you cannot communicate with the network (or with the computer if you are
connected directly). Refer to Chapter 5 Ethernet Troubleshooting
for possible solutions to connection problems.
Configuring the E-PDISO16
What you need to do to configure the Ethernet parameters of the E-PDISO16 will depend on whether or not you
have a DHCP server enabled on the network you are connecting to. If you don’t know if the network has a
DHCP server, consult your network administrator.
If your network does not have a DHCP server
If your network does not have a DHCP server, it will be necessary to set up a subnet that is compatible with the
default settings of the E-PDISO16. If you are not familiar with TCP/IP configuration, consult your network
administrator. Once you have set up your network to be compatible with the default settings of the E-PDISO16,
connect one E-PDISO16 to the network. The next step is to assign a unique IP address to this module. To do
this, proceed to the Run InstaCal section below. You’ll need to assign a unique IP address to each E-PDISO16
you want to connect to your network.
If configuring a second device, you may need to delete the arp entry on your PC for the first device. The default
IP address will be associated with the MAC address of the first device you configured. The second device will
have the same default IP address, but a different MAC address. Because of this, the device at the default IP
address may be reported as “unreachable”. To resolve this conflict, refer to Chapter 5 Deleting an ARP table
entry.
If your network does have a DHCP server
If your network has a DHCP server, the E-PDISO16 should be assigned an IP address shortly after being
powered up and attached to the network. Proceed to the Run InstaCal section below. InstaCal will display the
ethernet settings assigned to the E-PDISO16.
Run InstaCal
After connecting the external power and the Ethernet cable to the E-PDISO16 module, run the InstaCal
software and add the module to InstaCal's configuration file. Refer to the Quick Start Guide that shipped with
the module for instructions.
After adding the E-PDISO16 to InstaCal's configuration file, configure your Ethernet connection and AC filter
settings with InstaCal. If your network does not have a DHCP server, disable DHCP on the E-PDISO16.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a service that automatically assigns IP addresses to clients
supporting the protocol. The default DHCP setting for the E-PDISO16 is Enabled.
A DHCP-based device does not have a permanently assigned IP address. When you power-up or reboot the
computer, the DHCP client requests an IP address from the DHCP server. The DHCP server assigns and keeps
track of all IP addresses for that sub-net.
2-3
Page 13

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Installing the E-PDISO16
When a DHCP device requests an IP address, the DHCP server assigns, or "leases", a unique IP address to the
requesting device. The assigned IP address remains assigned to that device for a specified period, called the
lease duration. At the end of the lease duration, the lease is either renewed or the IP address becomes available
for assignment to another client.
If the DHCP client assigned to an IP address either reboots or powers down and up again, the client requests
another IP address from the DHCP server, and the DHCP server assigns an IP address as before. There is no
guarantee that the IP address is the same address previously assigned.
DHCP is a practical and efficient way of assigning and keeping track of IP addresses. If two clients are assigned
the same IP address, a communication failure will result that affects both devices.
If DHCP is disabled
If DHCP is not enabled, enter a static IP address into your E-PDISO16. The default DHCP setting is Enabled.
Unless you have a reason to disable DHCP (such as your network server is not DHCP-enabled), we recommend
that you leave DHCP enabled.
If you are not familiar with networks and their configurations, consult your network administrator prior to
installing the E-PDISO16. They can tell you if your network has a DHCP server, and if not, what static IP
address to use.
Caution! Assigning an arbitrary IP address could result in duplicate IP addresses on the network. This
condition can cause a communication failure that affects both devices.
Detecting a duplicate IP address
The E-PDISO16 can detect a duplicate IP address on the network. If the E-PDISO16 detects a duplicate IP
address, its TEST LED will flash continuously.
The only way to return the module to a stable state is to press the factory default button. This will reset the
module to the factory default configuration.
IP address
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a unique 32-bit address that identifies a device on a TCP/IP network. An IP
address can be set dynamically (by a DHCP-enabled server), or you can enter a "static" address. The address is
typically represented in dotted decimal notation, which is defined as four groups of decimal numbers separated
by periods. The numbers can be between 0 and 255, inclusive. The default IP address is 10.0.2.251.
Subnet mask
A subnet mask is a code that helps a network device determine how a network's subnet is structured. The code
is represented in dotted decimal notation. The default subnet mask is 255.255.255.252.
Gateway
A gateway is the IP address of the device that bridges subnets within a network. The gateway address is
typically represented in dotted decimal notation. The default gateway address is 10.0.2.1.
Configuration information
For more information on the Ethernet configuration settings for your E-PDISO16, refer to the "PDISO8 and
PDISO16 Series" section of the "Digital Input/Output Boards" chapter in the Universal Library User's Guide.
This document is available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/PDFmanuals/sm-ul-user-guide.pdf.
2-4
Page 14

Functional Details
Internal components
The E-PDISO16 has the following external components, as shown in Figure 3-1.
! Ethernet port
! Two (2) external power connectors
! Four status LEDs (POWER, LINK, ACTIVITY, and TEST)
! Factory default button
! Screw terminal bank for 16 digital input connections (IP0A through IP15B)
! Screw terminal bank for eight relay output connections (NO0 through NC7)
! Screw terminal bank for eight relay output connections (NO8 through NC15)
Ethernet
Port
Power
OUT
Power
IN
Chapter 3
Factory
Default
button
Stat us
LEDs
Screw terminals for
digital inputs IP0A to IP15B
Figure 3-1. E-PDISO16 module components
Screw terminals for
relays N07 - NC7
Screw terminals for
relays N08 - Nc15
Ethernet port
The E-PDISO16 has one 10/100 BASE-T, auto-negotiation, high-speed communication port. The port
connector is an RJ-45, eight-position connector. The Ethernet port accepts CAT-5 shielded or unshielded
twisted pair cable. The maximum communication distance without using a repeater is 100 meters. You can send
your data 100 meters at data speeds of up to 100 Mbps using only one Ethernet cable connected to your
computer.
External power connectors
The E-PDISO16 has two external power connectors labeled Power IN and Power OUT. Connect the Power IN
connector to the supplied +9 V, external power supply (CB-PWR-9V3A). The
power additional Measurement Computing products from a single external power supply.
The maximum output current is 3 A. When running at full load, that is, when all relays are on and the Ethernet
is transferring data, the E-PDISO16 draws 1.7 A from the supply. Depending on your load requirements,
additional products may require a separate power supply.
Power OUT connector lets you
3-1
Page 15

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Functional Details
POWER LED
The POWER LED is steady green when external power is supplied. The E-PDISO16 has an on-board voltage
supervisory circuit that monitors the 9 V external power supply. explains the function of the
Table 3-1
POWER
LED.
Table 3-1. POWER LED indicators
When the LED is… It indicates…
Steady green 6.0 V to 12.5 V external power is supplied to the E-PDISO16.
Off
! Power is not supplied by the external supply (verify that the supply is connected to the
power connector labeled Power IN.)
! A power fault has occurred. A power fault occurs when the input power falls outside of
the specified voltage range of the external supply (6.0 V to 12.5 V).
LINK LED
The LINK LED is steady green when a connection is made between the E-PDISO16 and your network, or the EPDISO16 and your computer if you are connected directly. explains the function of the
Table 3-2. LINK LED indicators
When the LED is… It indicates…
Steady green A valid Ethernet connection is established between the E-PDISO16 and the network.
Off Check the following:
! The Ethernet cable is not connected to the E-PDISO16
! The Ethernet cable is not connected to the network
! The Ethernet cable is damaged
! External power is not supplied
LINK LED. Table 3-2
ACTIVITY LED
The ACTIVITY LED blinks green when a data packet is sent or received over the Ethernet connection.
explains the function of the
When the LED is… It indicates…
Blinking green Data is being transmitted or received over the Ethernet connection.
Steady green
Off The Ethernet is idle.
ACTIVITY LED.
Table 3-3. ACTIVITY LED indicators
Your network traffic has reached its maximum limit, and no communication is possible.
Check with your Network Administrator.
During normal operation, the ACTIVITY LED flashes periodically, depending on the traffic on your network.
If the
ACTIVITY LED is solid green, then your network’s traffic has reached its limit and no communication is
possible. Check with your network administrator.
Table 3-3
TEST LED
The TEST LED blinks green when commanded to by software, and when you are performing InstaCal testing
procedures on the E-PDISO16.
The
TEST LED flashes continuously when a duplicate IP address is detected on the network by the E-PDISO16.
Press the factory default button to reset the module to the factory default configuration.
3-2
Page 16

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Functional Details
Factory default button
The factory default button resets the Ethernet parameters, filter, and relay conditions on the E-PDISO16 to the
factory default settings. Press and hold this button for three seconds to reset the E-PDISO16 to the factory
default configuration.
Screw terminal wiring
The E-PDISO16 has three rows of screw terminals for digital input and relay output connections. Use 14 AWG
to 20 AWG wire for your signal connections.
Caution! Keep the length of stripped wire at a minimum to avoid a short to the enclosure. When
connecting your field wiring to the screw terminals, use the strip gage on the terminal strip, or
strip to 5.5 - 7.0 mm (0.215" to 0.275") long.
Each screw terminal is identified with a label on the module and on the underside of the enclosure lid. Refer to
Table 3-4 for the signal name associated with each module label.
Table 3-4. Module labels and associated signal names
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
IP0A Input 0 terminal A IP8A Input 8 terminal A
IP0B Input 0 terminal B IP8B Input 8 terminal B
IP1A Input 1 terminal A IP9A Input 9 terminal A
IP1B Input 1 terminal B IP9B Input 9 terminal B
IP2A Input 2 terminal A IP10A Input 10 terminal A
IP2B Input 2 terminal B IP10B Input10 terminal B
IP3A Input 3 terminal A IP11A Input 11 terminal A
IP3B Input 3 terminal B IP11B Input 11 terminal B
IP4A Input 4 terminal A IP12A Input 12 terminal A
IP4B Input 4 terminal B IP12B Input 12 terminal B
IP5A Input 5 terminal A IP13A Input 13 terminal A
IP5B Input 5 terminal B IP13B Input 13 terminal B
IP6A Input 6 terminal A IP14A Input 14 terminal A
IP6B Input 6 terminal B IP14B Input 14 terminal B
IP7A Input 7 terminal A IP15A Input 15 terminal A
IP7B Input 7 terminal B IP15B Input 15 terminal B
NO0 Relay 0 Normally Open contact NO8 Relay 8 Normally Open contact
C0 Relay 0 Common contact C8 Relay 8 Common contact
NC0 Relay 0 Normally Closed contact NC8 Relay 8 Normally Closed contact
NO1 Relay 1 Normally Open contact NO9 Relay 9 Normally Open contact
C1 Relay 1 Common contact C9 Relay 9 Common contact
NC1 Relay 1 Normally Closed contact NC9 Relay 9 Normally Closed contact
NO2 Relay 2 Normally Open contact NO10 Relay 10 Normally Open contact
C2 Relay 2 Common contact C10 Relay 10 Common contact
NC2 Relay 2 Normally Closed contact NC10 Relay 10 Normally Closed contact
NO3 Relay 3 Normally Open contact NO11 Relay 11 Normally Open contact
C3 Relay 3 Common contact C11 Relay 11 Common contact
NC3 Relay 3 Normally Closed contact NC11 Relay 11 Normally Closed contact
NO4 Relay 4 Normally Open contact NO12 Relay 12 Normally Open contact
C4 Relay 4 Common contact C12 Relay 12 Common contact
NC4 Relay 4 Normally Closed contact NC12 Relay 12 Normally Closed contact
NO5 Relay 5 Normally Open contact NO13 Relay 13 Normally Open contact
C5 Relay 5 Common contact C13 Relay 13 Common contact
NC5 Relay 5 Normally Closed contact NC13 Relay 13 Normally Closed contact
NO6 Relay 6 Normally Open contact NO14 Relay 14 Normally Open contact
C6 Relay 6 Common contact C14 Relay 14 Common contact
NC6 Relay 6 Normally Closed contact NC14 Relay 14 Normally Closed contact
NO7 Relay 7 Normally Open contact NO15 Relay 15 Normally Open contact
C7 Relay 7 Common contact C15 Relay 15 Common contact
NC7 Relay 7 Normally Closed contact NC15 Relay 15 Normally Closed contact
3-3
Page 17

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Functional Details
Relay output terminals (NO0 to NC15)
The E-PDISO16 provides 16 Form C electromechanical relay outputs. The Form C relay has a common (C),
normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) contact.
The screw terminals labeled
screw terminals labeled
NO0 to NC7 connect to the NO, C, and NC contacts for relays 0 through 7. The
NO8 to NC15 connect to the NO, C, and NC contacts for relays 8 through 15.
Form C relay output
A schematic for Form C relay contacts is shown in . Figure 3-2
Figure 3-2. Form C relay contacts
Two 4.7 k pull-down resistor networks on the E-PDISO16 control the power-up state of each relay bank. At
power-up, the relays are put into a non-energized state (NC in contact to Common).
Relay contact protection circuit for inductive loads
If you are using the relays to control inductive loads, place a diode across the load terminals to suppress the
kickback voltage. If the diode is not present, the kickback voltage could cause the on-board processor to enter
an unstable state. To return the processor to a stable state, unplug the power cable from the E-PDISO16 and
then reconnect.
A contact protection circuit is shown in . For AC loads, install a metal oxide varistor (MOV). Figure 3-3
Relay
C
+
V
-
Figure 3-3. Relay contact protection circuit
Inductive
Load
NO
NC
Kickback
Diode
3-4
Page 18

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Functional Details
,000
Digital input terminals (IP0A to IP15B)
The E-PDISO16 has 16 isolated digital inputs. Connect up to 16 isolated differential digital input signals using
the following screw terminal pairs:
! IP0A and IP0B ! IP8A and IP8B
! IP1A and IP1B ! IP9A and IP9B
! IP2A and IP2B ! IP10A and IP10B
! IP3A and IP3B ! IP11A and IP11B
! IP4A and IP4B ! IP12A and IP12B
! IP5A and IP5B ! IP13A and IP13B
! IP6A and IP6B ! IP14A and IP14B
! IP7A and IP7B ! IP15A and IP15B
A schematic of a single channel is shown in . The signals are routed through a bridge rectifier so that
Figure 3-4
the inputs are not polarity-sensitive. It can be driven by either AC (50 - 1000 Hz) or DC voltage up to ±30
VDC.
+5V
100K
1.6 K
Isolated Input
Not Polarized Circuitry Sharing
PC Ground
Figure 3-4. Single-channel configuration
47K
Filter Switch
0.1uF
The 16 optically-isolated (500 V) inputs can be read back as a single byte. Each input has a software-controlled
filter with a time constant of 5 ms (200 Hz). The filter is required for AC inputs, and recommended for almost
all DC inputs. Unless you have a good reason to turn off a filter, we recommend that you enable it.
Extending the input range
To extend the input range beyond the 5 to 30 V specified, add an external resistor. shows the external
resistor (R
30) calculates the resistor value for a given V
) and the equations used to calculate resistor values for a given Vin. The equation R
ext
.
in
Figure 3-5
= 100 * (Vin –
ext
Make sure the external resistor is capable of handling the power generated by the input. Calculate the power
requirement in watts (P
) using the equation Pw = R
w
R ext
/10000.
ext
1.6 K
V in
R ext = 100 * (Vin - 30)
Pw = R ext / 10
Figure 3-5. External resistor added to extend input range
Isolated Input
Not Polarized
3-5
Page 19

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Functional Details
Digital I/O Techniques
For more information about digital I/O techniques, refer to the Guide to Signal Connections. This document is
available on our web site at www.mccdaq.com/signals/.
Power limitations using multiple E-PDISO16 modules
The maximum output current of the supplied CB-PWR-9V3A power supply is 3 A. When running at full load
(all relays on and the Ethernet is active), the E-PDISO16 draws 1.7 A from the supply. If you daisy chain
additional Measurement Computing products to the E-PDISO16, make sure you provide adequate power to
each module that you connect.
A drop in voltage occurs with each module connected in a daisy chain system. The voltage drop between the
external power supply and the daisy chain output is 0.5 V max. Factor in this voltage drop when you configure a
daisy chain system to ensure that at least 6.0 VDC is provided to the last module in the chain.
3-6
Page 20

Chapter 4
Ethernet Troubleshooting
There are typically only two reasons when you cannot attach and communicate with your E-PDISO16. These
are:
! The E-PDISO16 is configured incorrectly, or is operating incorrectly.
! Your network is configured incorrectly. Though the E-PDISO16 is functioning normally, you are
unable to communicate with it.
Though a detailed treatment of debugging your network is beyond the scope of this manual, there are a few
things you can try to determine if the problem you are experiencing is a problem with the board or with your
network configuration. If you are unable to communicate with the E-PDISO16, perform this troubleshooting
procedure to try and identify the problem:
1.
Check to see if the
external power is supplied to the E-PDISO16.
If the POWER LED is off, check the power cable and the socket that the cable is plugged into.
o
If the cable is good, plugged in, and the power to the socket is on, then the E-PDISO16 is not powering
o
up correctly. Contact MCC technical support. Refer to Getting help
information.
2.
Check to see if the
between the E-PDISO16 and the server/hub/switch it is connected to. If the LINK LED is off, check the
following:
o
Check the Ethernet cable — verify that the Ethernet cable is the correct type, is not damaged, and that
it is connected correctly between the E-PDISO16 and a known functional server/hub/switch (or
connected to your computer if you are connected directly).
o
If the Ethernet cable is plugged into a wall socket, check with your Network Administrator that the
wall socket is active and that it is connected to an active server/hub/switch.
If you are properly connected to an active server/hub/switch and the LINK LED is still off, there is a
problem with the E-PDISO16. Contact MCC technical support. Refer to Getting help
contact information.
3.
If your E-PDISO16 is connected to a network, check to see if the
ACTIVITY LED is an indication of transmitted and received data to and from the network. If the LED is
solid green or not flashing at all, check the following:
o
If the ACTIVITY LED is solid green, your network’s traffic is at its maximum limit and no
communication is possible. Check with your network administrator.
POWER LED on the E-PDISO16 is on (steady green). The POWER LED indicates that
on page 4-3 for contact
LINK LED is on (steady green). The LINK LED indicates a valid Ethernet connection
on page 4-3 for
ACTIVITY LED is flashing green. The
o
If the ACTIVITY LED is not flashing at all, there are two possibilities:
Even though the E-PDISO16 is connected to a good server/hub/switch, it is not connected to your
network. An average network has at least some traffic that causes the
with your network administrator.
If the network administrator verifies the network connection, the E-PDISO16 is not receiving. Contact
MCC technical support. Refer to Getting help
on page 4-3 for contact information.
4-1
ACTIVITY LED to blink. Check
Page 21

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Ethernet Troubleshooting
4. o If your E-PDISO16 is connected directly to a computer via a cross-over cable or a single hub/switch, check
to see if the
ACTIVITY LED flashes when you try to communicate with the module. The ACTIVITY LED
flashes if there is any traffic coming from the computer. If it is not flashing at all, there are two
possibilities:
There is an issue with the TCP/IP settings that is keeping your computer from transmitting. Verify that
your TCP/IP settings are correct, and that you are using a valid IP address for both your computer and
E-PDISO16. A simple way to do this is to open a DOS Command Prompt window from your
computer. Run the DOS prompt from Start►Programs►Accessories►Command Prompt. When the
DOS window opens, type in "IPCONFIG" and press the
Return key.
Your computer should return a message similar to the message shown here.
If the IP Address or Subnet Mask information are all 0’s, or if the first three numbers in either the IP
address or IP Mask do not match the settings set in the E-PDISO16, then the computer will not be able
to communicate with the E-PDISO16. If you are unfamiliar with how to set these parameters on your
computer, check with your network administrator.
o The E-PDISO16 is not receiving. Contact MCC technical support. Refer to Getting help
for contact information.
5. o If the
ACTIVITY LED is flashing, do the following:
Verify that your TCP/IP settings are correct, and that you are using a valid IP address for both your
computer and E-PDISO16. A simple way to do this is to open a DOS Command Prompt window from
your computer. Run the DOS prompt from Start►Programs►Accessories►Command Prompt. When
the DOS window opens, type in "IPCONFIG" and press the Return key.
Your computer should return a message similar to the message shown here.
on page 4-3
o If the IP Address, Subnet Mask or Default Gateway information are all 0’s, or that they do not match
the settings for your network, then the computer will not be able to communicate with the E-PDISO16.
If you are unfamiliar with how to set these parameters on your computer or do not know if they are
correct for your network, check with your network administrator.
4-2
Page 22

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Ethernet Troubleshooting
o Try to PING (Packet InterNet Groper) the Default Gateway with the IP Address listed. To use the
PING command, type in "PING <Default Gateway’s IP Address listed in IPCONFIG>" and press the
Return key.
A successful attempt to communicate with the Default Gateway returns this message.
If you receive either a "Request timed out" error or a "Destination host unreachable" error (shown
below), then there is a problem with your computer connecting to your network. Check with your
network administrator.
o If you know the IP address of the E-PDISO16, try to PING the unit. Use the same procedure listed
previously, type in "PING <E-PDISO16’s IP Address>" and press the
then there are two possibilities:
There is an issue with the settings on the E-PDISO16. Press the
RESET button on the E-PDISO16 to
reset the IP configuration settings to factory default. If you are using DHCP, the module will acquire
an IP address. If you are not using DHCP, enter a valid IP address and re-establish communication.
RESET button does not work, the microcontroller on the E-PDISO16 is not working. This is an
If the
E-PDISO16 problem. Contact MCC technical support. Refer to Getting help
information.
Deleting an ARP table entry
To clear previous entries of the default IP address from the ARP table, do the following:
1.
Open a Command Prompt (DOS) window.
2.
Type “arp –a” at the prompt.
3.
You should see an entry that includes the default IP address of the E-PDISO16 (10.0.2.251). This is the
entry you need to remove.
4.
To remove the default IP entry, type “arp –d 10.0.2.251” and press enter.
5.
You should now be able to communicate with a new device at the default IP settings.
Return key. If you get an error,
on page 4-3 for contact
4-3
Page 23

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Ethernet Troubleshooting
Getting help
If you are unable to communicate with the E-PDISO16, first contact your network administrator to verify that
you are using the correct TCP/IP network settings, and that your network configuration is working.
If your network administrator has verified your network configuration and settings, and you still cannot
communicate with the E-PDISO16, the problem may be with the E-PDISO16. For E-PDISO16-related issues,
contact Measurement Computing Corporation technical support by phone, fax, or email. For international
customers, contact your local distributor where you purchased the E-PDISO16.
! Phone: 508-946-5100 and follow the instructions for reaching Tech Support.
! Fax: 508-946-9500 to the attention of Tech Support
! Email: techsupport@mccdaq.com
4-4
Page 24

Specifications
Typical for 25 °C unless otherwise specified.
Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design.
Output relay specifications
Table 1. Output relay specifications
Number 16
Contact configuration 16 Form C (SPDT) NO, NC and Common available at connector
Contact rating 6 amperes (A) @ 240 volts AC (VAC) or 28 volts DC (VDC) resistive
Contact resistance 100 milliohms (mΩ) max.
Operate time 10 milliseconds (ms) max.
Release time 5 ms max.
Vibration 10 to 55 hertz (Hz) (Dual amplitude 1.5 millimeters (mm))
Shock 10 G (11 ms)
Dielectric isolation 500 V (1 minute)
Life expectancy 10 million mechanical operations, min.
Power on state Not energized. NC in contact to Common.
State after RESET
button activated
Not energized. NC in contact to Common.
Chapter 5
Isolated inputs
Number 16
Isolation 500 volts (V)
Resistance 1.6 K ohms (Ω) min.
Voltage range
Filters
DC
AC (with filter)
Without filter 20 µs Response
With filter 5 ms
Time constant 5 ms (200 Hz)
Filter control Software programmable at each input
Power-up
After RESET button activated Filters off
Table 2. Isolated inputs specifications
Input high: +5.0 VDC min. or –5.0 VDC min.
Input low: +1.5 VDC max. or –1.5 VDC max.
Input range: ! 30 VDC max.
Input high: 4.0 V
Input low: 1.5 V
Filter setting is stored on-board and will remain at the
last stored configuration
min. (50-1000 Hz)
rms
max. (50-1000 Hz)
rms
5-1
Page 25

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Specifications
Power consumption
Table 3. Power consumption specifications
External power input
External power supply (included) MCC p/n CB-PWR-9V3A 9 V ±10% @ 3 A
Operating current
Note 1: The E-PDISO16 monitors the external power supply with a voltage supervisory circuit. If this
All relays off, Ethernet idle 250 mA typical, 320 mA max.
All relays on, Ethernet idle 1.3 A typical, 1.6 A max.
All relays on, Ethernet active 1.45 A typical, 1.7 A max.
6.0 VDC to 12.5 VDC (9 VDC
power supply provided)
power supply exceeds the supervisor limits, the POWER LED will turn off, indicating a power
fault condition.
External power output
Table 4. External power output specifications
Parameter Conditions Specification
External power output - current range See Note 2 4.0 A max.
External power output - voltage range
Compatible cable(s) for daisy chain C-MAPWR-x x = 2, 3, or 6 feet
Note 2: The daisy chain power output option allows multiple Measurement Computing boards to be
The input voltage minus the output
voltage at the daisy chain output.
powered from a single external power source in a daisy chain fashion. The voltage drop between
the module’s power supply and the daisy chain output is 0.5 V max. Users must plan for this drop
to ensure the last module in the chain will receive at least 6.0 V.
0.5 V max.
Ethernet compliance
Table 5. Ethernet compliance specifications
Device type IEEE 802.3 Ethernet 10/100Base-T
Device compatibility IEEE 802.3-2003 10/100 Media Access Control
Ethernet connection
Table 6. Ethernet connection specifications
Ethernet type 10Base-T, 100Base-T
Connector RJ-45, 8 position
Cable CAT-5 shielded, unshielded twisted pair
Length 100 meters max.
Max connections 3 (one control port and two monitoring ports)
MAC address 00:12:71:XX:XX:XX
EEProm memory
Table 7. EEProm memory specifications
EEProm memory 1024 bytes residing in the processor
Reserved space 128 bytes, Address 0x00 to 0x7F
User space 896 bytes, Address 0x80 to 0x3FF
5-2
Page 26

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Specifications
Ethernet and input filter "Factory Default" settings
Table 8. Factory default specifications
Default IP address 10.0.2.251
Default IP mask 255.255.255.252
Default Gateway 10.0.2.1
Default DHCP setting Enabled
Default Filter setting All Filters Off
LED displays and the "Factory Default" button
Table 9. LED and button configurations
POWER LED 6.0 V < V
V
ext
TEST LED Blinks when commanded to by software.
LINK LED On when there is a valid Ethernet connection.
ACTIVITY Blinks when an Ethernet packet is sent or received.
Factory default button
Returns the device to its factory default condition including resetting all Ethernet, filter
and relay conditions.
< 12.5 V On
ext
<6.0 V, V
> 12.5 V Off (power fault)
ext
Mechanical
Table 10. Mechanical specifications
17.0" (L) x 4.8" (W) x 0.8" (H) Card dimensions
431.8 mm (L) x 121 mm (W) x 20.3 mm (H)
17.2" (L) x 5.2” (H) x 1.6” (H) Case dimensions
436.9 mm (L) x 132.1 mm (W) x 40.6 mm (H)
Environmental
Table 11. Environmental specifications
Operating temperature range
Storage temperature range -40 to 100 °C
Humidity 0 to 95% non-condensing
0 to 70 °C
Main connector
Table 12. Main connector specifications
Connector type Screw terminal
Wire gauge range 14-30 AWG
5-3
Page 27

E-PDISO16 User's Guide Specifications
Screw terminal pin out
Table 13. Screw terminal pin out specifications
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
IP0A Input 0 terminal A IP8A Input 8 terminal A
IP0B Input 0 terminal B IP8B Input 8 terminal B
IP1A Input 1 terminal A IP9A Input 9 terminal A
IP1B Input 1 terminal B IP9B Input 9 terminal B
IP2A Input 2 terminal A IP10A Input 10 terminal A
IP2B Input 2 terminal B IP10B Input10 terminal B
IP3A Input 3 terminal A IP11A Input 11 terminal A
IP3B Input 3 terminal B IP11B Input 11 terminal B
IP4A Input 4 terminal A IP12A Input 12 terminal A
IP4B Input 4 terminal B IP12B Input 12 terminal B
IP5A Input 5 terminal A IP13A Input 13 terminal A
IP5B Input 5 terminal B IP13B Input 13 terminal B
IP6A Input 6 terminal A IP14A Input 14 terminal A
IP6B Input 6 terminal B IP14B Input 14 terminal B
IP7A Input 7 terminal A IP15A Input 15 terminal A
IP7B Input 7 terminal B IP15B Input 15 terminal B
NO0 Relay 0 Normally Open contact NO8 Relay 8 Normally Open contact
C0 Relay 0 Common contact C8 Relay 8 Common contact
NC0 Relay 0 Normally Closed contact NC8 Relay 8 Normally Closed contact
NO1 Relay 1 Normally Open contact NO9 Relay 9 Normally Open contact
C1 Relay 1 Common contact C9 Relay 9 Common contact
NC1 Relay 1 Normally Closed contact NC9 Relay 9 Normally Closed contact
NO2 Relay 2 Normally Open contact NO10 Relay 10 Normally Open contact
C2 Relay 2 Common contact C10 Relay 10 Common contact
NC2 Relay 2 Normally Closed contact NC10 Relay 10 Normally Closed contact
NO3 Relay 3 Normally Open contact NO11 Relay 11 Normally Open contact
C3 Relay 3 Common contact C11 Relay 11 Common contact
NC3 Relay 3 Normally Closed contact NC11 Relay 11 Normally Closed contact
NO4 Relay 4 Normally Open contact NO12 Relay 12 Normally Open contact
C4 Relay 4 Common contact C12 Relay 12 Common contact
NC4 Relay 4 Normally Closed contact NC12 Relay 12 Normally Closed contact
NO5 Relay 5 Normally Open contact NO13 Relay 13 Normally Open contact
C5 Relay 5 Common contact C13 Relay 13 Common contact
NC5 Relay 5 Normally Closed contact NC13 Relay 13 Normally Closed contact
NO6 Relay 6 Normally Open contact NO14 Relay 14 Normally Open contact
C6 Relay 6 Common contact C14 Relay 14 Common contact
NC6 Relay 6 Normally Closed contact NC14 Relay 14 Normally Closed contact
NO7 Relay 7 Normally Open contact NO15 Relay 15 Normally Open contact
C7 Relay 7 Common contact C15 Relay 15 Common contact
NC7 Relay 7 Normally Closed contact NC15 Relay 15 Normally Closed contact
5-4
Page 28

Measurement Computing Corporation
10 Commerce Way
Suite 1008
Norton, Massachusetts 02766
(508) 946-5100
Fax: (508) 946-9500
E-mail: info@mccdaq.com
www.mccdaq.com
 Loading...
Loading...