Page 1

DBK215 16-Connector BNC Connection Module
With 68-Pin SCSI Adaptability for Analog I/O, Digital I/O, & Pulse/Frequency
Overview …… 1
Block Diagram …… 2
Connection Tips…… 3
System Examples …… 4
Using the Screw-Terminal Blocks …… 5
Adding RC Filter Networks …… 11
Specifications …… 13
DBK215 Front Panel
Upper Slot for Terminal Board Wiring Pass-Through
Lower section of 16 BNC Connectors
Overview
The DBK215 module is compatible with the following products:
•
DaqBoard/500 Series • DaqBoard/1000 Series
Includes a 68-pin SCSI connector designated as P5.
The DBK215 module includes:
o BNC Access to 16 inputs or outputs (on front panel)
o on-board screw-terminal blocks*
o on-board socket locations for custom RC Filter networks*
o 68-pin SCSI connector (on rear panel)
* The top cover plate must be removed to access the terminal blocks and
the RC filter network section of the board.
The 68-pin SCSI connector (P5) connects to a DaqBoard/500 Series or a DaqBoard/1000 Series 68-pin
SCSI connector via a CA-G55, CA-G56, or CA-G56-6 cable. Cable descriptions are provided on page 2.
The DBK215 provides BNC and screw-terminal access to all analog and digital I/O from the host data
acquisition device. Related to the screw-terminals is a front panel slot for routing all I/O wiring.
Reference Note:
DBK215 is intended for DaqBoard/500 Series and DaqBoard/1000 Series applications. Refer
to the DaqBoard/500 Series and DaqBoard/1000 Series documentation for detailed
information on those devices. For information concerning similar16 channel BNC
connectivity/interface boards, designed for use with other products, refer to the DBK213 and
DBK214 sections of the DBK Options manual (p/n 457-0905).
DBK215 Rear Panel
DBK Option Cards and Modules 967894 DBK215 pg. 1
Page 2
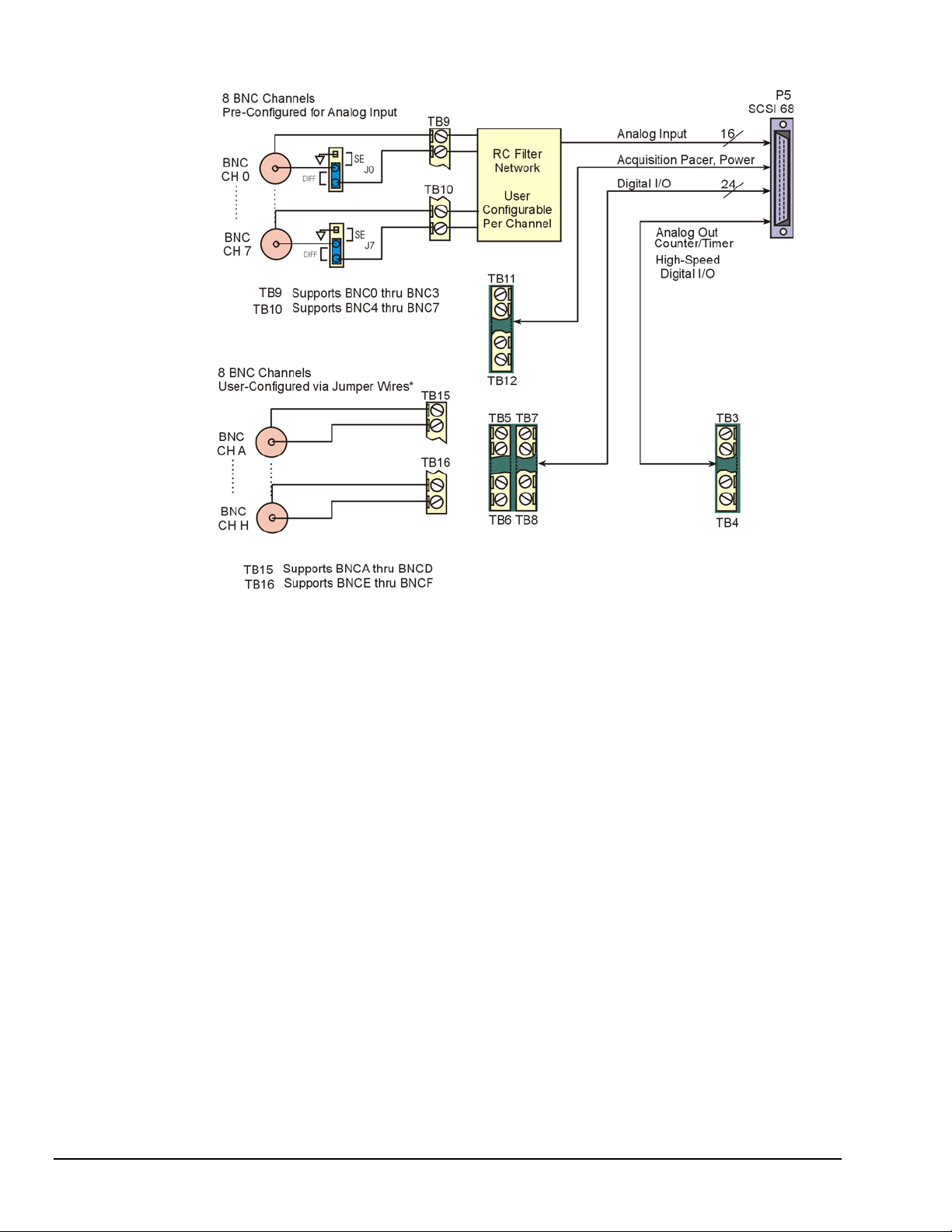
DBK215 Block Diagram
* Accessory Kit p/n 1139-0800 includes jumper wires and a screw driver.
Note that the 68-pin SCSI (P5) connector typically connects to a DaqBoard/500 Series or
DaqBoard/1000 Series board’s SCSI connector via a CA-G55, CA-G56, or CA-G56-6 cable.
o CA-G55 is a 3-foot long cable.
o CA-G56 is a 3-foot long shielded cable.
o CA-G56-6 is a 6-foot long shielded cable.
DBK215, pg. 2
967894 DBK Option Cards and Modules
Page 3

Connection Tips
CAUTION
Turn off power to the host PC and externally connected equipment prior to connecting
cables or signal lines to DBKs. Electric shock or damage to equipment can result even
under low-voltage conditions.
Take ESD precautions (packaging, proper handling, grounded wrist strap, etc.)
Use care to avoid touching board surfaces and onboard components. Only handle
boards by their edges (or ORBs, if applicable). Ensure boards do not come into
contact with foreign elements such as oils, water, and industrial particulate.
1. Ensure power is removed from all device(s) to be connected.
2. As soon as the DBK215 cover is removed, verify that the Host
Power LED is “Off.” See figure at right for location.
3. Observe ESD precautions when handling the board and making
connections.
4. You do not need to remove the cover unless you need to
access a terminal block, customize an RC filter network,
or set a BNC channel to Single-Ended mode or to Differential
mode (via Jumpers J0 through J7). Information regarding these
tasks follows shortly.
5. DBK215’s 68-pin SCSI (P5) connector typically connects to a DaqBoard/500 Series or
DaqBoard/1000 Series board’s SCSI connector via a CA-G55, CA-G56, or CA-G56-6 cable.
o CA-G55 is a 3-foot long cable.
o CA-G56 is a 3-foot long shielded cable.
o CA-G56-6 is a 6-foot long shielded cable.
6. Refer to the separate CE Cable Kit instructions that are included with the associated CE cable
kit. Refer to the Declaration of Conformity in regard to meeting CE requirements.
Location of DBK215’s
Host Power LED
DBK Option Cards and Modules 967894 DBK215 pg. 3
Page 4
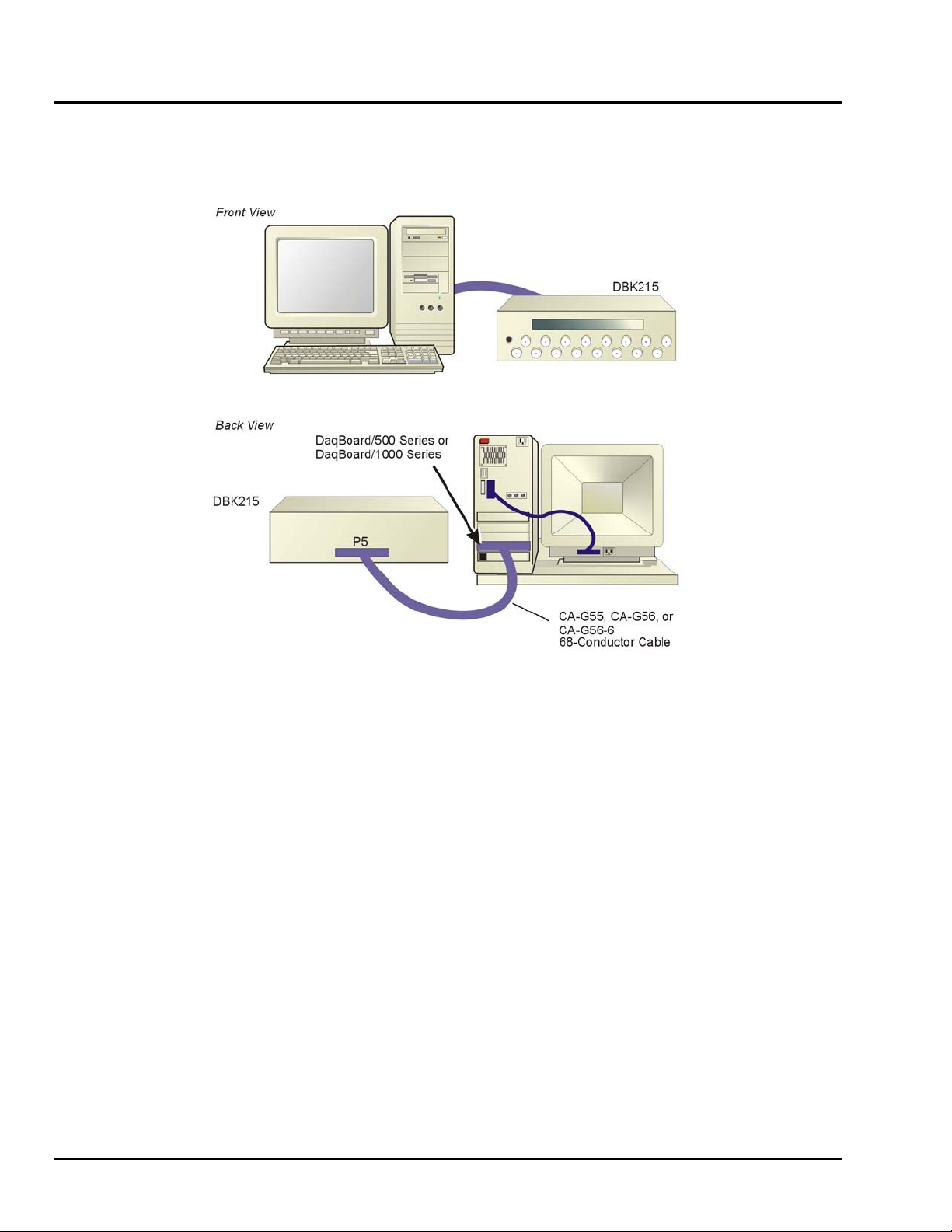
System Example
DBK215 Connection to a DaqBoard/500 Series or DaqBoard/1000 Series Board
Notes regarding the above system example:
1) Any of three 68-conductor SCSI ribbon cables can be used.
o CA-G55 is a 3-foot long cable.
o CA-G56 is a 3-foot long shielded cable.
o CA-G56-6 is a 6-foot long shielded cable.
2) Signal lines connect to front panel BNC connectors or to the internal screw-terminal board.
3) When signal lines are connected to terminal blocks (instead of the BNC connectors) the wires are routed out through
the upper slot of the front panel.
DBK215, pg. 4
967894 DBK Option Cards and Modules
Page 5

Using the Screw-Terminal Blocks
You must remove the DBK215 module’s cover plate to access the screw terminal blocks.
This is described in steps 1 and 2 below.
1. Remove the top inward screws from each of the 4 mounting brackets. See following figure.
To remove the cover plate you
must first remove the top
inward screw from each of the
4 mounting brackets.
The Cover Plate is Secured by 4 Srews
[2 Screws per-side]
2. After the 4 screws have been removed, carefully remove the cover plate.
3. As soon as the DBK215 cover is removed, verify that the Host Power LED is “Off.”
See following figure for location.
Host Power LED Location
4. Make the wiring connections to the terminals. Refer to the board’s silkscreen and to
the pin correlations on the next few pages.
5. Tighten the terminal block screws snug; but do not over-tighten.
6. After all terminal connections are made and verified correct, return the cover to the unit and
secure in place with the 4 screws removed earlier. Tighten snug, but do not over-tighten.
DBK Option Cards and Modules 967894 DBK215 pg. 5
Page 6

In general, the following terminal block-to-signal relationships apply:
DBK215
Terminal
Blocks
TB9
TB10
TB11
TB12
TB5
TB6
TB7
TB8
TB13**
TB14**
TB15
TB16
(Note 1)
TB1
TB2
TB3
TB4
Used for . . . Alternative
ANALOG INPUT BNC 0 thru 7
ANALOG INPUT N/A
DIGITAL I/O N/A
ANALOG INPUT
BNC Channels
0 thru 7**
USER
CONFIGURABLEB
NC Channels
A thru H
-- Not Used--- N/A
PULSE/
FREQUENCY
ANALOG OUTPUT
TB9,TB10
(See Note 1)
N/A
DBK215 Board
* P4 is used for connecting to DaqBoard/2000 Series devices.
** TB13 and TB14 are “virtual” terminal blocks which are routed in the printed circuit board to TB9 and TB10. The TB13 and TB14
silk-screened locations on the DBK215 board do not have physical screw terminal blocks.
Note 1: TB15 and TB16 are used for optional user-configured BNC connectors A through H. These connectors can be configured
on a per-channel basis as Analog [Input or Output], Digital I/O, or Counter/Timer. When BNC A through H are used, the
user must route wires from the “BNC routing terminal blocks” (TB15 and TB16) to the appropriate functional TB
termination points.
Accessory Wire Kit, p/n 1139-0800 includes jumper wires and a screwdriver.
The following pages correlate the DBK215 terminal block connectors with the 68-pin SCSI connector.
DBK215, pg. 6
967894 DBK Option Cards and Modules
Page 7

Analog I/O Correlation to 68-pin SCSI
Also see “Correlation to BNC Terminations (TB13 and TB14) on page DBK215-10.”
TB9 Pin Number and Description
DIFF SE
0H 0 68 CH 0 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 0 HI IN (Differential Mode)
0L 8 34 CH 8 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 0 LO IN (Differential Mode)
1H 1 33 CH 1 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 1 HI IN (Differential Mode)
1L 9 66 CH 9 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 1 LO IN (Differential Mode)
2H 2 65 CH 2 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 2 HI IN (Differential Mode)
2L 10 31 CH 10 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 2 LO IN (Differential Mode)
3H 3 30 CH 3 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 3 HI IN (Differential Mode)
3L 11 63 CH 11 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 3 LO IN (Differential Mode)
FILT CAP LO
SGND 62 Signal Ground, Sense Common; reference ground, not for general use.
For RC filter networks install a wire jumper between the relevant FILT CAP LO and
N/A
AGND. Note that there is no association between FILT CAP LO and P4.
P1 – TB9
(Note 2)
TB10 Pin Number and Description
DIFF SE
4H 4 28 CH 4 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 4 HI IN (Differential Mode)
4L 12 61 CH 12 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 4 LO IN (Differential Mode)
5H 5 60 CH 5 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 5 HI IN (Differential Mode)
5L 13 26 CH 13 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 5 LO IN (Differential Mode)
6H 6 25 CH 6 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 6 HI IN (Differential Mode)
6L 14 58 CH 14 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 6 LO IN (Differential Mode)
7H 7 57 CH 7 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 7 HI IN (Differential Mode)
7L 15 23 CH 15 IN (Single-Ended Mode) / CH 7 LO IN (Differential Mode)
FILT CAP LO
SGND 62 Signal Ground, Sense Common; reference ground, not for general use.
TB11 Pin Number and Description
TTL TRIG 6 TTL Trigger, Digital IN, External TTL Trigger Input
A/I CLK 2 A/I Clock, External ADC Pacer Clock Input/ Internal ADC Pacer Clock Output
EXP 5
EXP 6
EXP 7
EXP 8
EXP 9
EXP 10
EXP 11
AGND * Analog Ground, Common
For RC filter networks install a wire jumper between the
N/A
relevant FILT CAP LO and AGND.
Expansion 5. Digital OUT, external GAIN select bit 1
N/A
Expansion 6. Digital OUT, external GAIN select bit 0
N/A
Expansion 7. Digital OUT, external ADDRESS, select bit 3
N/A
Expansion 8. Digital OUT, external ADDRESS, select bit 2
N/A
Expansion 9. Digital OUT, external ADDRESS, select bit 1
N/A
Expansion 10. Digital OUT, external ADDRESS, select bit 0
N/A
Expansion 11. Simultaneous Sample and Hold (SSH)
N/A
P1 – TB10
(Note 2)
P1 – TB11
TB12 Pin Number and Description
AGND * Analog Ground, Common
AGND * Analog Ground, Common
AGND * Analog Ground, Common
AGND * Analog Ground, Common
AGND * Analog Ground, Common
AGND * Analog Ground, Common
+ 15 V
- 15 V
AGND * Common Ground
+ 5 V 19 Expansion, +5 V Power
*The following SCSI Pins connect to Analog Common: 24, 27, 29, 32, 55, 56, 59, 64, and 67.
Note 2: For TB9 and TB10, the filter network portion of the silkscreen is not shown. Instead, the DIFF and SE channel
identifiers have been moved next to the screws for ease in identification.
Expansion, +15 V Power
N/A
Expansion, -15 V Power
N/A
P1 – TB12
DBK Option Cards and Modules 967894 DBK215 pg. 7
Page 8

Digital I/O Correlation to 68-pin SCSI
TB5 Pin Number and Description
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
A7 49 Digital I/O: Port A, Bit 7
A6 15 Digital I/O: Port A, Bit 6
A5 50 Digital I/O: Port A, Bit 5
A4 16 Digital I/O: Port A, Bit 4
A3 51 Digital I/O: Port A, Bit 3
A2 17 Digital I/O: Port A, Bit 2
A1 52 Digital I/O: Port A, Bit 1
A0 18 Digital I/O: Port A, Bit 0
TB6 Pin Number and Description
+5 V 19 Expansion +5 V Power
+5 V 19 Expansion +5 V Power
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
TB7 Pin Number and Description
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
C7 41 Digital I/O: Port C, Bit 7
C6 7 Digital I/O: Port C, Bit 6
C5 42 Digital I/O: Port C, Bit 5
C4 8 Digital I/O: Port C, Bit 4
C3 43 Digital I/O: Port C, Bit 3
C2 9 Digital I/O: Port C, Bit 2
C1 44 Digital I/O: Port C, Bit 1
C0 10 Digital I/O: Port C, Bit 0
TB8 Pin Number and Description
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
B0 14 Digital I/O: Port B, Bit 0
B1 48 Digital I/O: Port B, Bit 1
B2 13 Digital I/O: Port B, Bit 2
B3 47 Digital I/O: Port B, Bit 3
B4 12 Digital I/O: Port B, Bit 4
B5 46 Digital I/O: Port B, Bit 5
B6 11 Digital I/O: Port B, Bit 6
B7 45 Digital I/O: Port B, Bit 7
* The following SCSI Pins connect to Analog Common: 24, 27, 29, 32, 55, 56, 59, 64, and 67.
** The following SCSI Pins connect to Digital Common: 35, 36, 40, and 53.
P2 – TB5
P2 – TB6
P2 – TB7
P2 – TB8
DBK215, pg. 8
967894 DBK Option Cards and Modules
Page 9

Pulse/Frequency Correlation to 68-pin SCSI
TB1 Pin Number and Description
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
DGND
+5V
TB2 Pin Number and Description
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
DGND
DGND
TB3 Pin Number and Description
CH0 (DAC0) 22 Analog Out; Analog DAC 0 Output
AGND * Analog Ground, Common; intended for use with DACs
EXP 0 (DAC2)
AGND * Analog Ground, Common; intended for use with DACs
CH1 (DAC1) 21 Analog Out; Analog DAC 1 Output
A/O CLK 1 Analog Out Clock; External DAC Pacer Clock Input/
EXP 1 (DAC3)
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
+15 V
-15 V
TB4 Pin Number and Description
EXP 2
EXP 3
EXP 4
TMR 0 3 P3 Timer 0 Output
TMR 1 37 P3, Timer 1 Output
CNT 3 38 P3 Counter 3 Input
CNT 2 4 P3 Counter 2 Input
CNT 1 39 P3 Counter 1 Input
CNT0 5 P3 Counter 0 Input
DGND ** Digital Ground, Common
* The following SCSI Pins connect to Analog Common: 24, 27, 29, 32, 55, 56, 59, 64, and 67.
** The following SCSI Pins connect to Digital Common: 35, 36, 40, and 53.
P3 Digital Port Bit 0
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 1
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 2
N/A
N/A P3 Digital Port Bit 3 TB1 is NOT USED
P3 Digital Port Bit 4
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 5
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 6
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 7
N/A
Digital Ground, Common
N/A
Expansion, +5 Volt Power
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 8
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 9
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 10
N/A
N/A P3 Digital Port Bit 11 TB2 is NOT USED
P3 Digital Port Bit 12
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 13
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 14
N/A
P3 Digital Port Bit 15
N/A
Digital Ground, Common
N/A
Digital Ground, Common
N/A
Analog Out; Analog DAC 2 Output
N/A
Internal DAC Pacer Clock Output
Analog Out; Analog DAC 3 Output
N/A
Expansion, + 15 VDC
N/A
Expansion, -15 VDC
N/A
Reserved
N/A
Reserved
N/A
Reserved
N/A
P3 – TB1 (not used)
P3 – TB2 (not used)
P3 – TB3
P3 – TB4
DBK Option Cards and Modules 967894 DBK215 pg. 9
Page 10

Correlation to Analog Input BNC Terminations – BNC 0 through BNC 7
“Virtual” Terminal Blocks TB13 and TB14 for ANALOG INPUT connect to TB9 and TB10 through the printed circuit board.
TB13 (“Virtual” Terminal Block) 68-Pin SCSI Connector, Pin Number and Description
BNC CH DIFF SE Pin SE = Single Ended ; DIFF = Differential Jumper Used
BNC0+ 0H 0 68 CH 0 IN (SE) / CH 0 HI IN (DIFF)
BNC0- 0L 8 34 CH 8 IN (SE) / CH 0 LO IN (DIFF)
BNC1+ 1H 1 33 CH 1 IN (SE) / CH 1 HI IN (DIFF)
BNC1- 1L 9 66 CH 9 IN (SE) / CH 1 LO IN (DIFF)
BNC2+ 2H 2 65 CH 2 IN (SE) / CH 2 HI IN (DIFF)
BNC2- 2L 10 31 CH 10 IN (SE) / CH 2 LO IN (DIFF)
BNC3+ 3H 3 30 CH 3 IN (SE) / CH 3 HI IN (DIFF)
BNC0+ 3L 11 63 CH 11 IN (SE) / CH 3 LO IN (D DIFF)
AGND N/A N/A * Analog Ground N/A
AGND N/A N/A * Analog Ground N/A
TB14 (“Virtual” Terminal Block) 68-Pin SCSI Connector, Pin Number and Description
BNC CH DIFF SE Pin SE = Single Ended ; DIFF = Differential Jumper Used
BNC4+ 4H 4 28 CH 4 IN (SE) / CH 4 HI IN (DIFF)
BNC4- 4L 12 61 CH 12 IN (SE) / CH 4 LO IN (DIFF)
BNC5+ 5H 5 60 CH 5 IN (SE) / CH 5 HI IN (DIFF)
BNC5- 5L 13 26 CH 13 IN (SE) / CH 5 LO IN (DIFF)
BNC6+ 6H 6 25 CH 6 IN (SE) / CH 6 HI IN (DIFF)
BNC6- 6L 14 58 CH 14 IN (SE) / CH 6 LO IN (DIFF)
BNC7+ 7H 7 57 CH 7 IN (SE) / CH 7 HI IN (DIFF)
BNC7+ 7L 15 23 CH 15 IN (SE) / CH 7 LO IN (DIFF)
AGND N/A N/A * Analog Ground N/A
AGND N/A N/A * Analog Ground N/A
J0
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J7
TB13 does not physically exist on
DBK215. A silkscreen of TB13 is
present as a visual aid to signal
routing and configuration.
A header located beneath TB14 and
TB16 is used to set the BNC
channels to Single-Ended or to
Differential. Simply place channel’s
2-pin jumper in the appropriate
position (SE or DIFF).
TB14 does not physically exist on
DBK215. A silkscreen of TB14 is
present as a visual aid to signal
routing and configuration.
A header located beneath TB14 and
TB16 is used to set the BNC
channels to Single-Ended or to
Differential. Simply place channel’s
2-pin jumper in the appropriate
position (SE or DIFF).
Correlation to Custom BNC Terminations – BNC A through BNC H
Pertains to Terminal Blocks TB15 and TB16 for Custom Configuration on a per-channel basis.
TB15 (“Routing” Terminal Block)
BNC CH Description
BNCA+
BNCABNCB+
BNCBBNCC+
BNCCBNCD+
BNCD+
AGND Analog Ground *
AGND Analog Ground *
TB16 (“Routing” Terminal Block)
BNC CH Description
BNCA+
BNCABNCB+
BNCBBNCC+
BNCCBNCD+
BNCD+
AGND Analog Ground *
AGND Analog Ground *
* The following SCSI Pins connect to Analog Common: 24, 27, 29, 32, 55, 56, 59, 64, and 67.
BNC channels A through D are configured on a per-channel basis by the user. TB15 is a routing
terminal block used to connect BNCs (A thru D) to the desired signals, which are selected via a second
DBK215 terminal block. For example: a user could run a wire from BNCA+ to TB4 screw terminal
“TMR0” and BNCA- to TB4 DGND to create a BNC timer connection.
Accessory Wire Kit, p/n 1139-0800 includes jumper wires and a screwdriver.
BNC channels E through H are configured on a per-channel basis by the user. TB16 is a routing
terminal block used to connect BNCs (E thru H) to the desired signals, which are selected via a second
DBK215 terminal block.
Customizing is as described for BNCA through BNCD above.
Accessory Wire Kit, p/n 1139-0800 includes jumper wires and a screwdriver.
DBK215, pg. 10
967894 DBK Option Cards and Modules
TB15
TB16
Page 11

Adding Resistor/Capacitor Filter Networks
WARNING
Disconnect the DBK215 from power and signal sources prior to installing capacitors or
resistors.
Ensure wire strands do not short power supply connections to any terminal potential.
Failure to do so could result in damage to equipment.
Do not exceed maximum allowable inputs (as listed in product specifications). There
should never be more than 30 V with reference to analog ground (AGND) or earth
ground.
You must provide strain-relief (lead slack) to all leads leaving the module. Use tie-wraps
[not included] to secure strain-relief.
Always connect the CHASSIS terminal to earth ground. This will maximize static
protection.
If a channel is not associated with a DBK expansion option you can install a customized RC filter network
to improve the signal-to noise ratio, assuming that an unacceptable level of noise exists. DBK215’s
internal board includes silk-screened sockets for installing RC filter networ ks. The following table
contains values that are typical for RC filter network components.
CAUTION
Typical One-Pole Low Pass Filter
Values
for DBK215
Do not use RC filters in conjunction with additional DBK expansion
accessories.
R C f f
Ohms µF Hertz
(-3dB)
kHz
(-3dB)
510 1 312 0.31
510 0.47 664 0.66
510 0.22 1419 1.42
510 0.1 3122 3.12
510 0.047 6643 6.64
510 0.022 14192 14.19
510 0.01 31223 31.22
510 0.0047 66431 66.43
470 0.0033 102666 102.67
In this example Channels 0 and 8 are shown as Single-Ended.
Channel 1 is Differential, i.e., using 1H and 1L (channel High and Low).
The following three notes pertain to the above figure.
Note 1: The 3 horizontal capacitors [as oriented in the illustration] are optional filter capacitors.
Note 2: The vertical capacitor [as oriented in the illustration] is an optional isolation capacitor used for the
reduction of Differential noise. Such capacitor placement is
Note 3: If installing filter resistors, carefully drill out the indicated centers with a 1/16 inch drill-bit. Otherwise
the resistor will be short-circuited.
An Example of Customer-Installed
Capacitors and Filters for RC Networks
not used in Single-Ended applications.
Prior to installing RC components, review the previous Warning and Caution
statements, then read over the following information regarding resistors and
capacitors.
DBK Option Cards and Modules 967894 DBK215 pg. 11
Page 12

• Do not use RC filters in conjunction with additional DBK expansion accessories.
• Prior to installing a resistor to the filter network you must drill a 1/16” hole through
the center pinhole [beneath the board’s silkscreen resistor symbol] as indicated in the
preceding figure. Failure to do so will short-circuit the resistor.
• Do not drill holes on the board for channels, unless those channels are to receive a
filter network (see preceding statement).
• Resistors should be ¼ watt, film-type with up to 5% tolerance. Do not use wire-
wound resistor types.
• A resistor value of 510 Ω is recommended. Do not exceed 510 Ω.
• Capacitors used are to be of the film dielectric type (e.g., polycarbonate or
NPO ceramic), above 0.001 µF.
• RECOMMENDED: For reduction of both Common Mode Noise and Differential
Mode Noise, use one capacitor between Channel High and AGND; and use a second
capacitor between Channel Low and AGND.
• For reduction of Differential Noise [when no reduction of Common Mode Noise is
needed] position a capacitor across the respective Channel High and Channel Low.
• When in Differential Mode, using capacitors between Channel High, Channel Low,
and AGND may cause a slight degradation of wideband Common Mode rejection.
• When making a RC filter network, always install a wire jumper between the relevant
FILT CAP LO and AGND. FILT CAP LO terminals are located on TB9 and TB10.
DBK215, pg. 12
967894 DBK Option Cards and Modules
Page 13

Specifications for DBK215
Operating Environment:
Temperature: -30°C to 70°C
Relative Humidity: 95% RH, non-condensing
Connectors:
P5: 68-Pin SCSI
Screw Terminals: 14 banks of 10-connector blocks
Wire Size: 12 TO 28 AWG
Dimensions:
285 mm W x 220 mm D x 45 mm H (11” x 8.5” x 2.7”)
Weight:
1.36 kg (3 lbs)
Cables and Accessories:
Item Description Part Number
Rack Mount Kit, p/n RackDBK4
68-conductor expansion cables; mate with P5 (SCSI, 68-pin) connectors:
3 ft., non-shielded CA-G55
3 ft., shielded CA-G56
6 ft., shielded CA-G56-6
Accessory Wire Kit 1139-0800
Includes jumper wires and a
screwdriver.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
DBK Option Cards and Modules 967894 DBK215 pg. 13
Page 14

DBK215, pg. 14
967894 DBK Option Cards and Modules
 Loading...
Loading...