Page 1

DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Measurement Computing
10 Commerce Way
Norton, MA 02766
(508) 946-5100
Fax: (508) 946-9500
info@mccdaq.com
www.mccdaq.com
For PCI-bus & Compact PCI-bus Data Acquisition Boards
DaqBoard/1000 & /2000 Series
User’s Manual
For PCI-bus & Compact PCI-bus
Data Acquisition Boards
p/n 1033-0901 Rev. 8.0
© 1999 through 2005 by 0HDVXUHPHQW&RPSXWLQJ&RUS 889094 Printed in the United States of America
Page 2

ii
Page 3
Warranty Information
Contact Measurement Computing by phone, fax, or e-mail in regard to warranty-related issues:
Phone: (508) 946-5100, fax: (508) 946-9500, e-mail: info@mccdaq.com
Many Measurement Computing products carry the CE marker indicating they comply with the safety and emissions
standards of the European Community. When applicable these products have a Declaration of Conformity stating which
specifications and operating conditions apply. You can view the Declarations of Conformity at
www.mccdaq.com/legal.aspx (CE Information page).
Refer all service to qualified personnel. This caution symbol warns of possible personal injury or equipment damage
under noted conditions. Follow all safety standards of professional practice and the recommendations in this manual.
Using this equipment in ways other than described in this manual can present serious safety hazards or cause equipment
damage.
This warning symbol is used in this manual or on the equipment to warn of possible injury or death from electrical
shock under noted conditions.
This ESD caution symbol urges proper handling of equipment or components sensitive to damage from electrostatic
discharge. Proper handling guidelines include the use of grounded anti-static mats and wrist straps, ESD-protective bags
and cartons, and related procedures.
This symbol indicates the message is important, but is not of a Warning or Caution category. These notes can be of great
benefit to the user, and should be read.
In this manual, the book symbol always precedes the words “Reference Note.” This type of note identifies the location
of additional information that may prove helpful. References may be made to other chapters or other documentation.
Tips provide advice that may save time during a procedure, or help to clarify an issue. Tips may include additional
reference.
Limitation of Liability
Measurement Computing cannot be held liable for any damages resulting from the use or misuse of this product.
Copyright, Trademark, and Licensing Notice
All Measurement Computing documentation, software, and hardware are copyright with all rights reserved. No part of
this product may be copied, reproduced or transmitted by any mechanical, photographic, electronic, or other method
without Measurement Computing’s prior written consent. IOtech product names are trademarked; other product names, as
applicable, are trademarks of their respective holders. All supplied IOtech software (including miscellaneous support
files, drivers, and sample programs) may only be used on one installation. You may make archival backup copies.
CE Notice
Warnings, Cautions, Notes, and Tips
Specifications and Calibration
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Significant changes will be addressed in an addendum or revision to
the manual. As applicable, the hardware is calibrated to published specifications. Periodic hardware calibration is not
covered under the warranty and must be performed by qualified personnel as specified in this manual. Improper
calibration procedures may void the warranty.
Page 4
Your order was carefully inspected prior to shipment. When you receive your system, carefully
unpack all items from the shipping carton and check for physical signs of damage that may have
occurred during shipment. Promptly report any damage to the shipping agent and your sales
representative. Retain all shipping materials in case the unit needs returned to the factory.
CAUTION
Using this equipment in ways other than described in this manual can cause
personal injury or equipment damage. Before setting up and using your
equipment, you should read all documentation that covers your system.
Pay special attention to Warnings and Cautions.
Note:
PDF
1033-0901
During software installation, Adobe
®
PDF versions of user manuals will automatically
install onto your hard drive as a part of product support. The default location is in the
Programs group, which can be accessed from the Windows Desktop. Initial
navigation is as follows:
Start [Desktop “Start” pull-down menu]
⇒ Programs
⇒ IOtech DaqX Software
You can also access the PDF documents directly from the data acquisition CD by using
the <View PDFs> button located on the opening screen.
Refer to the PDF documentation for details regarding both hardware and software.
®
A copy of the Adobe Acrobat Reader
is included on your CD. The Reader provides
a means of reading and printing the PDF documents. Note that hardcopy versions of
the manuals can be ordered from the factory.
DaqBoard 1000 and 2000 Series.pdf
Contains the DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series hardware-related and software-related
chapters, as well as links to the .pdf files listed below. This pdf file, plus the
following constitute a complete set of documentation for the DaqBoards discussed.
Note that the Programmer’s Manual (1008-0901) and the DBK Option Cards &
Modules
(457-0905) are completely separate documents. The later does not apply to
DaqBoard/1000 Series boards.
DaqView.pdf
Discusses how to install and use this “out-of-the-box” data acquisition program.
PDF
457-0909
PostAcquisition Analysis.pdf
This pdf consists of two documents. The first discusses eZ-PostView, a post data
acquisition analysis program. The application is included free as a part of DaqTemp
PDF
1086-0926
1086-0922
iv DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
product support. The second includes information regarding eZ-FrequencyView and
eZ-TimeView. These two applications have more features than does eZ-PostView and
are available for purchase. They can; however, be used freely during a 30-day trial
period.
Page 5
DBK Options.pdf
The DBK Option Cards and Modules Manual discusses each of the DBK products
available at the time of print. The DBK Options document does not apply to
PDF
457-0905
DaqBoard/1000 Series boards.
Programmers Manual.pdf
The programmer’s manual pertains to developing custom programs using
Applications Program Interface (API) commands.
PDF
1008-0901
Programmers should check the readme.file on the install CD-ROM for the location of
program examples included on the CD.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual v
Page 6

vi DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 7

Manual Layout
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series, Installation Guide (p/n 1033-0940)
DaqBoard/2000c Series, Installation Guide (p/n 1061-0940)
Chapter 1 – Daq Systems and Device Overviews. This chapter begins with a discussion of the “modular
Chapter 2 –Connections and Pinouts, DaqBoard/1000 Series - This chapter includes board pinouts for
Chapter 3 - Connections and Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series - This chapter includes board pinouts
Chapter 4 - CE Compliance pertains to CE standards and conditions that are relevant to DaqBoard/1000
Chapter 5 - Calibration lists the order in which to perform calibration-related adjustments and briefly
concept” that is associated with Daq data acquisition systems. The chapter then goes on to provide
an overview for each DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series board.
the DaqBoard/1000 Series 68-pin connector. It includes screw terminal identification for TB-100,
which is an optional terminal board connector.
for the DaqBoard/2000 Series boards’ 100-pin connector (P4). The chapter includes an overview of
the DBK200 Series P4 adapters that can be used to obtain DB37 type connectors (P1, P2, and P3).
and /2000 Series boards. A CE Kit, which can be used for DaqBoard/2000 Series boards, is also
discussed.
discusses DaqCal.exe, a program that provides on-screen instruction, graphics, and prompts.
Chapter 6 – Specifications, DaqBoard/1000 Series Boards
Chapter 7 – Specifications, DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards
Glossary
Reference Notes:
During software installation, Adobe
®
PDF versions of user manuals are automatically
installed onto your hard drive as a part of product support. The default location is in the
Programs directory, which can be accessed from the Windows Desktop.
®
A copy of the Adobe Acrobat Reader
is included on your CD. The Reader provides
a means of reading and printing the PDF documents. Note that hardcopy versions of manuals
can be ordered from the factory.
¾ DaqView and DaqViewXL – explains the use and features of the included out-of-the-
box data acquisition software.
¾ Post Acquisition Data Analysis User’s Guide – discusses three post-acquisition data
analysis programs: eZ-PostView, eZ-TimeView, and eZ-FrequencyView.
¾ For detailed information regarding specific DBKs, refer to the DBK Option Cards
and Modules User’s Manual, p/n 457-0905. Each DBK section includes device-
specific hardware and software information. The document includes a chapter on
power management. DaqBoard/1000 Series boards do not support DBK options.
¾ For programming-related information refer to the separate Programmer’s Manual,
p/n 1008-0901.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 vii
Page 8

This page is intentionally blank.
viii 889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 9

Table of Contents
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series, Installation Guide (p/n 1033-0940)
DaqBoard/2000c Series, Installation Guide (p/n 1061-0940)
1 – Daq Systems and Device Overviews
Daq Systems, the Modular Concept ……1-1
Theory of Operation, DaqBoard/1000 and/2000 Series Boards…… 1-3
Using DBK Cards & Modules for Signal Conditioning ……1-23
Note: DBK options do not apply to DaqBoard/1000 Series Boards
Daq Software …… 1-23
2 – Connections and Pinouts, DaqBoard/1000 Series
Overview …… 2-1
TB-100 Terminal Connector Option …… 2-2
Pinouts for DaqBoard/1000 Series Boards …… 2-3
3 – Connections and Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series
Overview …… 3-1
DBK200 Series, P4 Connector Options …… 3-2
Pinouts for DaqBoard/2000 Series and /2000c Series Boards …… 3-8
4 – CE-Compliance
Overview …… 4-1
CE Standards and Directives …… 4-1
Safety Conditions …… 4-2
Emissions/Immunity Conditions …… 4-2
CE Enhancements for DBKs ...... 4-3
CE Cable Kits for DaqBoard/2000 Series and /2000c Series Boards…… 4-3
5 – Calibration
6 – Specifications, DaqBoard/1000 Series Boards
7 – Specifications, DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards
Glossary
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 ix
Page 10

This page is intentionally blank.
x 889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 11
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation
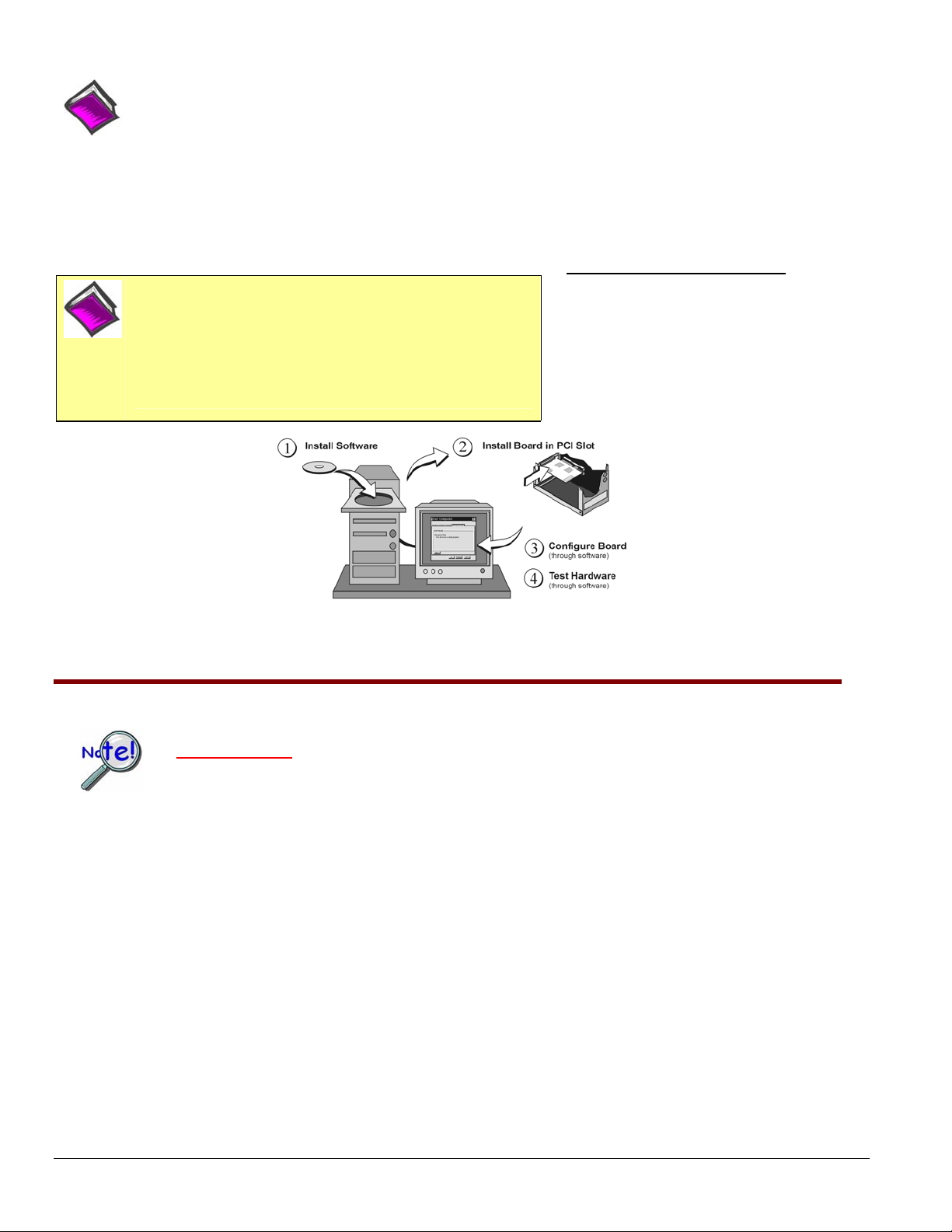
This guide tells how to complete the following steps for a successful installation.
Step 1 – Install Software …… page 2
Step 2 – Install Boards in Available PCI Bus-Slots …… page 3
Step 3 – Configure Boards ….. page 5
Step 4 – Test Hardware ….. page 6
Reference Note:
After you have completed the installation you should refer to the electronic documents that
were automatically installed onto your hard drive as a part of product support. The default
location is in the Programs group, which can be accessed from the Windows Desktop.
You should keep your DaqBoard’s serial number and your DaqView/2000 authorization code (if
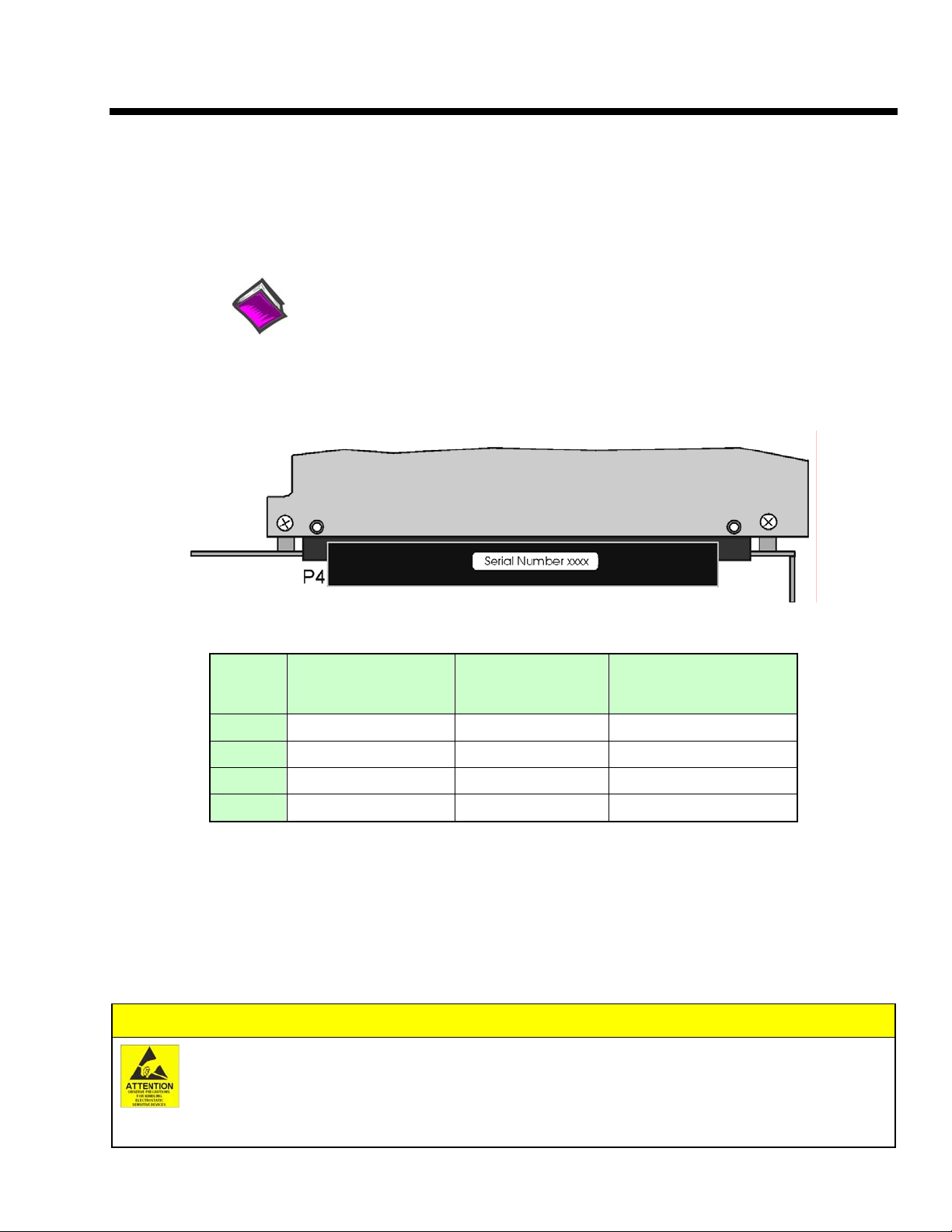
applicable) with this document. Space is provided below for recording up to 4 board numbers and their
PCI bus-slot locations. The board serial number is located on the connector as indicated
figure.
in the following
Serial Number Location on DaqBoard/2000 Series Connector
The location is similar for DaqBoard/1000 Series Board.
Board 1
Board 2
Board 3
Board 4
The host PC can support up to four Boards.
Board Type (e.g.,
1000, 1005, 2000,
2001, etc.)*
Serial Number PCI Bus-Slot Location
*Note: DaqBoards have device labels which read, for example, “DaqBoard/1000,” “DaqBoard/2001,” “DaqBoard/2002,”
etc. The name labels are convenient for users of more than one board type.
DaqView/2000 Authorization Code ____________________________
Customers who ordered DaqView/2000 can find their authorization code on the authorization code sheet located inside the sleeve of the install CD.
Note that earlier documents may refer to this as a “registration code” or “registration ID.”
Customers who did not order DaqView/2000 can run a 30-day free trial version, as discussed elsewhere in the User’s Manual.
CAUTION
Take ESD precautions (packaging, proper handling, grounded wrist strap, etc.)
Use care to avoid touching board surfaces and onboard components. Only handle boards by their
edges (or ORBs, if applicable). Ensure boards do not come into contact with foreign elements such as
oils, water, and industrial particulate.
© 1999 through 2004 by 0HDVXUHPHQW&RPSXWLQJ&RUS 898195 1033-0940, rev. 8.0 IG-1
Page 12
Reference Notes:
(1) Each DaqBoard plugs into a PCI bus-slot. Consult your PC owner’s manual as needed.
(2) DaqBoard/2000 Series users should read about the DBK cards and modules applicable to their acquisition system.
Specific DBK information can be found in the world wide web at http://www.daqboard.com; and in the DBK Option Cards
and Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905). After the install you can navigate to the DBK manual and other relevant
electronic documents from your desktop as follows: Start ⇒ Programs ⇒ IOtech DaqX Software ⇒ DaqBoard 2000
Series Users
Note: DaqBoard/1000 Series boards do not support DBK options.
Minimum System Requirements
Reference Note: Adobe PDF versions of user manuals will
automatically install onto your hard drive as a part of product
support. The default location is in the Programs group, which
can be accessed from the Windows Desktop. Refer to the PDF
documentation for details regarding both hardware and
software. Note that hardcopy versions of the manuals can be
ordered from the factory.
PC system with Pentium® Processor
Windows Operating System
RAM, as follows:
32 Mbytes of RAM for Windows 95/98/NT
64 Mbytes of RAM for Windows Me
64 Mbytes of RAM for Windows 2000
64 Mbytes of RAM for Windows XP
Step 1 – Install Software
IMPORTANT: Software must be installed before installing hardware.
1. Remove previous version Daq drivers, if present. You can do this through Microsoft’s Add/Remove
Programs feature.
2. Place the Data Acquisition CD into the CD-ROM drive. Wait for PC to auto-run the CD. This may
take a few moments, depending on your PC. If the CD does not auto-run, use the Desktop’s
Start/Run/Browse feature and run the Setup.exe file.
3. After the intro-screen appears, follow the screen prompts.
Upon completing the software installation, continue with step 2, Install Boards in available
PCI Bus-slots.
Installation, A Pictorial Overview
IG-2 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide 898195 1033-0940, rev 8.0
Page 13
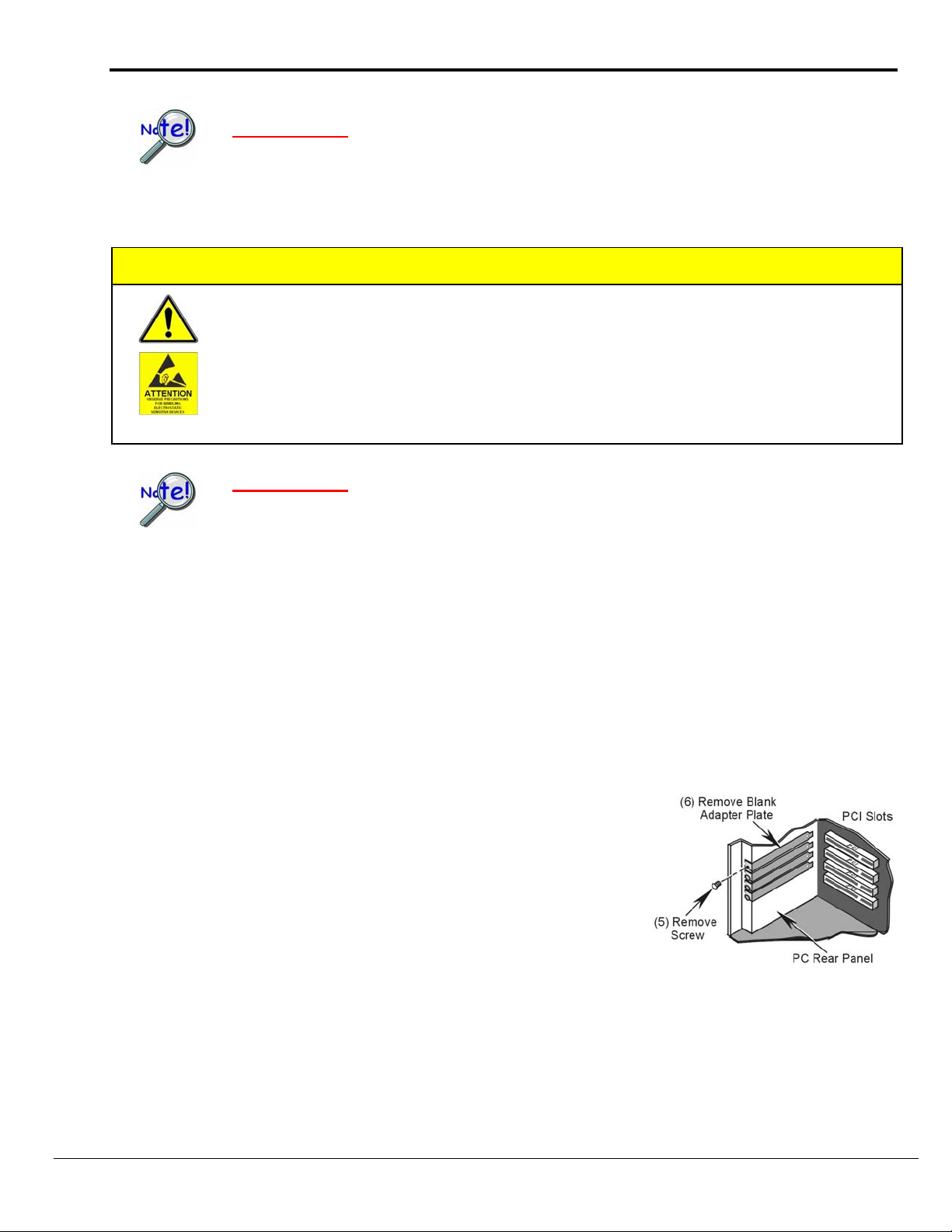
Step 2 – Install Boards in available PCI Bus-slots
IMPORTANT: Software must be installed before installing hardware.
CAUTION
Turn off power to, and UNPLUG the host PC and externally connected equipment prior to
removing the PC’s cover and installing the DaqBoard. Electric shock or damage to equipment
can result even under low-voltage conditions.
Take ESD precautions (packaging, proper handling, grounded wrist strap, etc.)
Use care to avoid touching board surfaces and onboard components. Only handle boards by their
edges (or ORBs, if applicable). Ensure boards do not come into contact with foreign elements such
as oils, water, and industrial particulate.
IMPORTANT: Bus Mastering DMA must be Enabled.
For a DaqBoard/1000 or /2000 Series board to operate properly, Bus Mastering DMA must be
Enabled on the PCI slot [for which the board is to be installed]. Prior to installation, verify that
your computer is capable of performing Bus Mastering DMA for the applicable PCI slot. Note that
some computers have BIOS settings that enable [or disable] Bus Mastering DMA. If your
computer has this BIOS option, ensure that Bus Mastering DMA is Enabled on the appropriate
PCI slot.
Refer to your PC Owner's Manual for additional information regarding your PC and enabling
Bus Mastering DMA for PCI slots.
1. Turn off power to, and UNPLUG the host PC and externally connected equipment.
2. Remove the PC’s cover. Refer to your PC Owner’s Manual as needed.
3. Choose an available PCI bus-slot.
4. Carefully remove the DaqBoard from its anti-static protective bag. If you have not already done so,
write down the serial number of your board at this time.
5. Refer to the figure at the right. Remove the screw that
secures the blank adapter plate, which is associated with the
PCI slot you will be using. Refer to your PC Owner’s
Manual if needed.
6. Remove the blank adapter plate.
Removing a Blank Adapter Plate
1033-0940, rev 8.0 898195 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide IG-3
Page 14

7. Refer to the figure at the right. Align the groove in the
DaqBoard’s PCI edge-connector with the ridge of the
desired PCI slot, and with the PC’s corresponding rearpanel slot.
8. Push the board firmly into the PCI slot. The board will
snap into position.
9. Secure the board by inserting the rear-panel adapter-plate
screw.
10. Using the previous steps, install additional boards into
available PCI bus-slots, if applicable to your application.
11. Replace the computer’s cover.
12. Plug in all cords and cables that were removed in step 1.
13. Apply power to, and start up the PC.
Note: At this point some PCs may prompt you to insert an
installation disk. While this is rare, if you do receive such a
prompt simply place the install CD-ROM into the disk drive
and follow additional screen prompts.
Installing a DaqBoard/2000 Series Board
IG-4 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide 898195 1033-0940, rev 8.0
Page 15
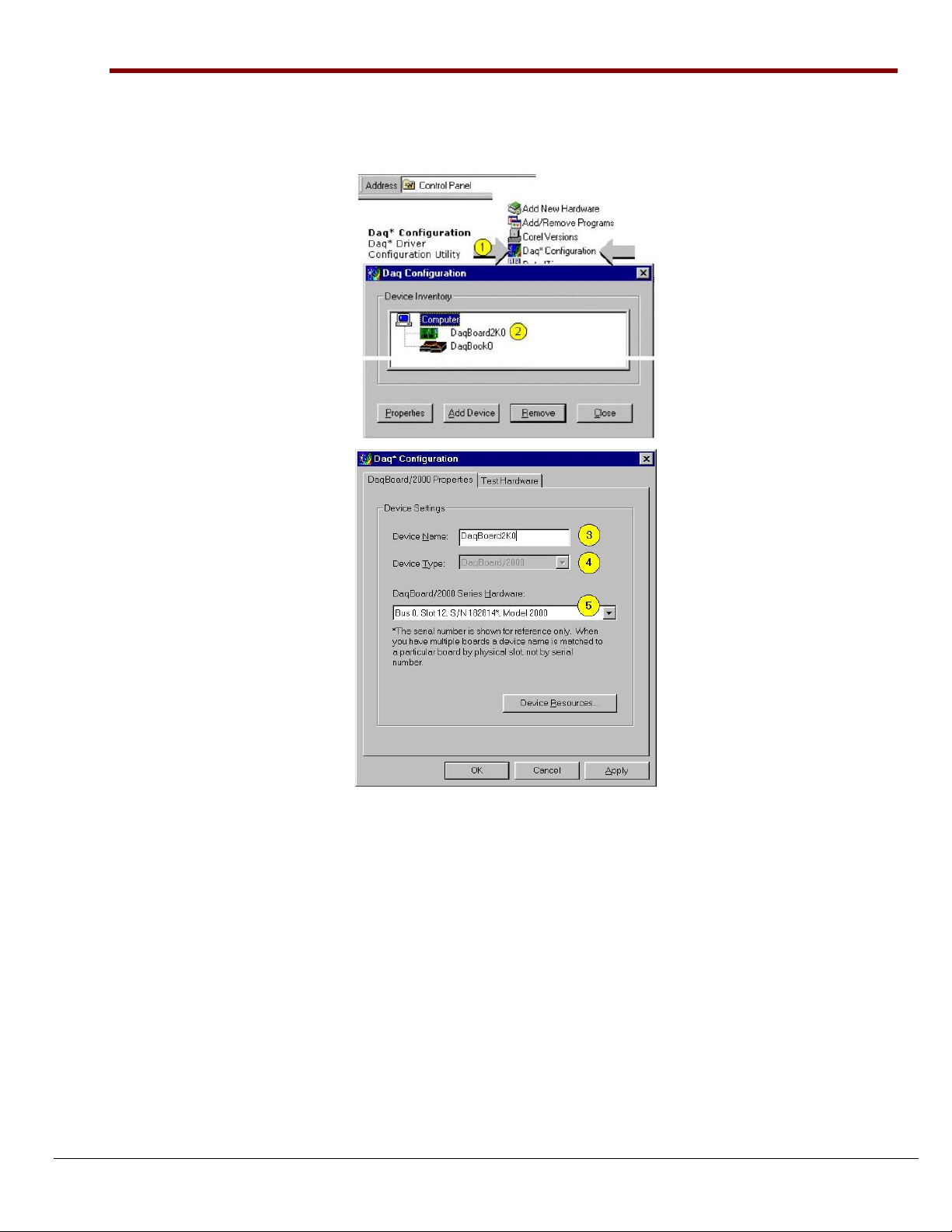
Step 3 – Configure Boards
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Boards have no jumpers or switches to set. Configuration is performed,
in its entirety, through software. Refer to the following figure and steps to complete the configuration.
The numbers in the figure correspond to the numbered steps immediately following the figure.
Accessing the DaqBoard/2000 Properties Tab
Note: Images are similar for DaqBoard/1000 Series.
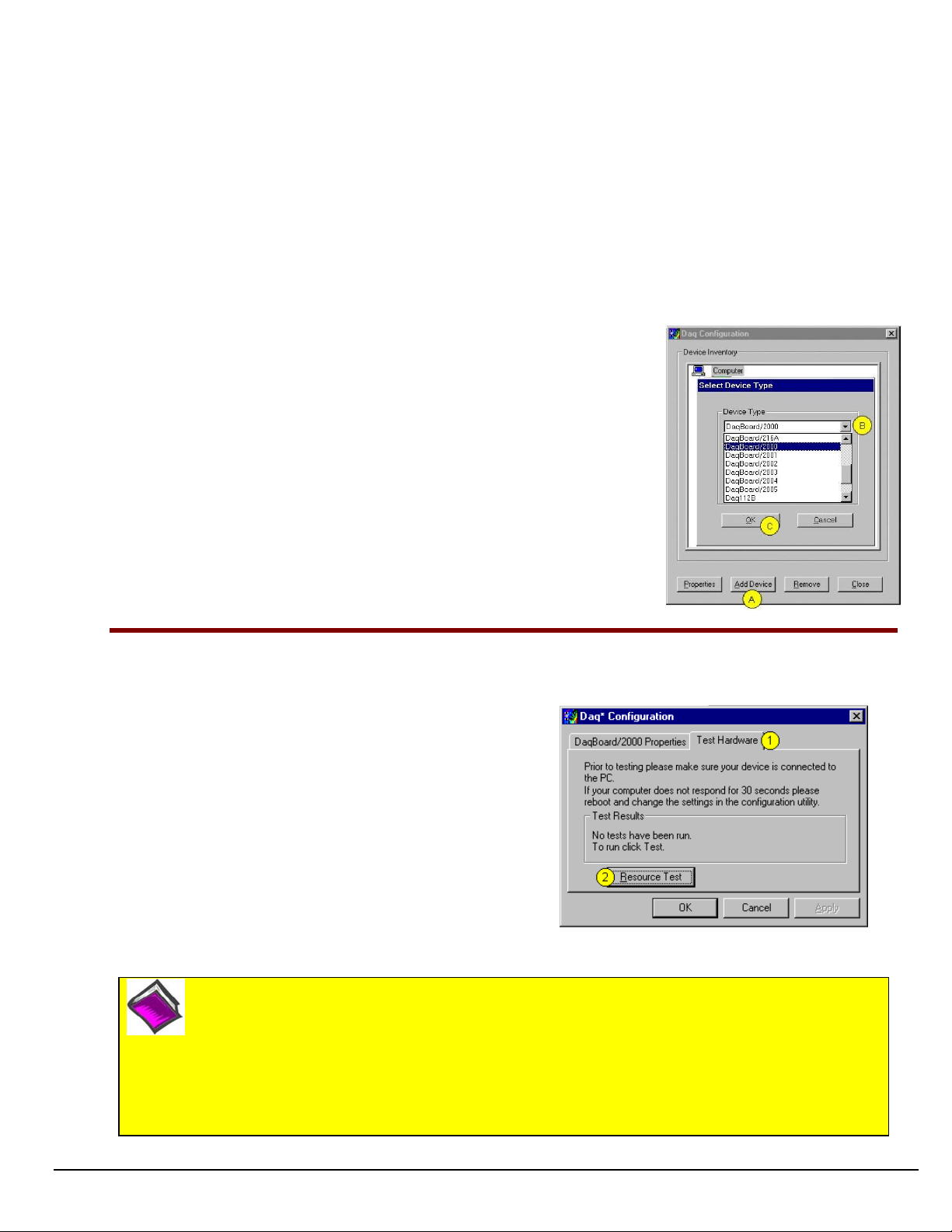
1. Run the Daq Configuration control panel applet. Navigation from the desktop to the applet is as follows:
Start ⇒ Settings ⇒ Control Panel ⇒ Daq*Configuration (double-click)
2. Double-click on the Device Inventory’s DaqBoard2K0 or DaqBoard1K0 icon, as applicable. The DaqBoard’s
Properties tab will appear. If the DaqBoard icon is not present, skip to the upcoming Using ‘Add Device’
section.
3. Enter a “Device Name” in the text box, or use the default, e.g., DaqBoard2K0. The Name is for identifying the
specific DaqBoard, but actually refers to the PCI slot.
4. Verify that the “Device Type” shows the correct board, e.g., “DaqBoard/1000, DaqBoard/2001, etc.”
Note that available device types can be viewed via the pull-down list.
5. Confirm that the DaqBoard’s text box shows a Bus #, Slot #, and Serial Number.
If this text box is empty, use its pull-down list and select the serial number that matches the one for your board.
1033-0940, rev 8.0 898195 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide IG-5
Page 16
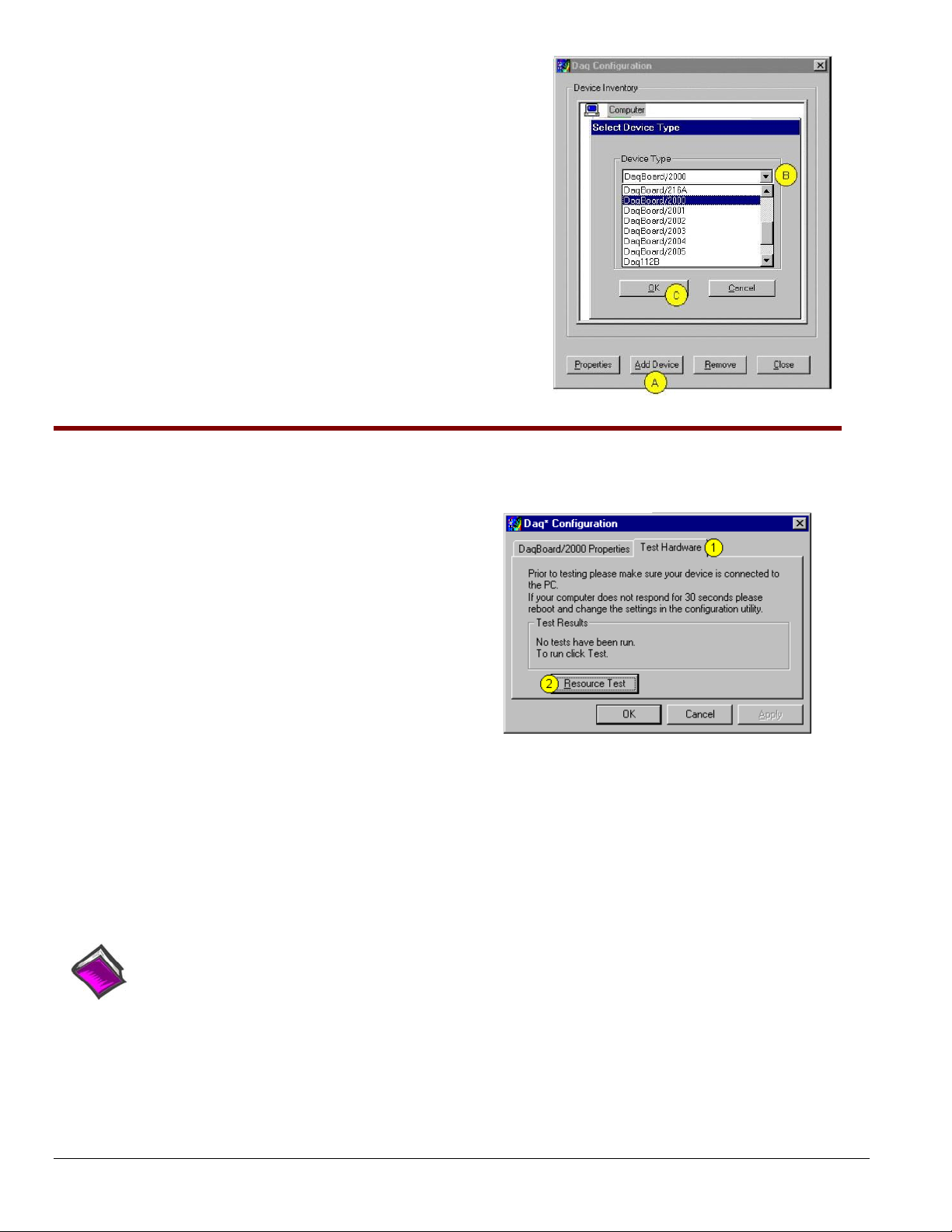
Using “Add Device”
This method is for users who have accessed the Daq Configuration
control panel applet, but have no DaqBoard1K icon or DaqBoard2K icon
[as described on page IG-5, step 2].
(A) After accessing the Daq Configuration control panel applet, click on
the <Add Device> button (see figure, right). The Select Device Type
window will appear.
(B) Using the Device Type’s pull-down list, select the applicable board.
In the example at the right DaqBoard/2000 is selected.
(C) Click the <OK> button. The board’s Properties tab will appear.
Note that this tab will apply to all boards in the series.
At this point, complete steps 3 through 5 from page IG-5.
Using “Add Device”
Step 4 – Test Hardware
Use the following steps to test the DaqBoard board. Note that these steps are continued from those listed under the
previous section, “Configure Board.”
1. Select the “Test Hardware” tab.
2. Click the “Resource Test” button.
3. After the test is complete, click “OK.”
System capability is now tested for the DaqBoard and a list
of test results appears on screen.
Note: If you experience difficulties, please consult your user
documentation (included on your CD) before calling for
technical support. Note that the user documentation
includes a troubleshooting chapter, as well as a great
deal of information regarding specific DBK cards and
modules, which can be used with DaqBoard/2000
systems.
At this point we are ready to connect signals.
• For DaqBoard/2000 Series boards, signal connection is typically accomplished with the use of a
DBK200 Series option.
Test Hardware Tab
(Condensed Screen Image)
• For DaqBoard/1000 Series boards, connection is typically made via a terminal board, such as the
optional TB-100.
Reference Notes:
¾ DaqBoard/2000 Series users: For detailed information regarding the DBK200 Series options, refer
¾ During software installation, Adobe
to the DBK Option Cards and Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905).
®
PDF versions of user manuals are automatically installed onto
your hard drive as a part of product support. The default location is in the Programs group, which
can be accessed from the Windows Desktop. A copy of the Adobe Acrobat Reader
®
is included on
your CD. The Reader provides a means of reading and printing the PDF documents. Note that
hardcopy versions of manuals can be ordered from the factory.
IG-6 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide 898195 1033-0940, rev 8.0
Page 17
DaqBoard/2000c Series Installation
This guide tells you how to complete the following steps for a successful installation.
Step 1 – Install Software …… page 2
Step 2 – Install Boards into Available, 5 Volt, Compact-PCI Bus-Slots …… page 2
Step 3 – Configure Boards ….. page 4
Step 4 – Test Hardware ….. page 5
Reference Note:
After you have completed the installation you should refer to the electronic documents that
were automatically installed onto your hard drive as a part of product support. The default
location is in the Programs group, which can be accessed from the Windows Desktop.
You should keep your DaqBoard/2000c Series board’s serial number and your DaqView/2000
authorization code (if applicable) with this document. Space is provided below for recording up to 4 board
numbers and their compact-PCI bus-slot location. Board serial numbers are located on the 100-pin P4
connector.
Board 1
Board 2
Board 3
Board 4
Compact PC support for DaqBoard/2000c Series boards varies. A system can support no more than four boards.
Board Type
e.g., DaqBoard/2005c
Serial Number Compact-PCI Bus-Slot Location
*Note: The DaqBoard/2000c Series boards have their board identity indicated on the latch, as indicated in
the photo on the front page of this guide. This identification is provided since the boards look very
much alike and are visually identical once installed.
DaqView/2000 Authorization Code ____________________________
Customers who ordered DaqView/2000 can find their authorization code on the authorization code sheet located inside the
sleeve of the install CD. Customers who did not order DaqView/2000 can run a 30-day free trial version, as discussed in the
user’s manual.
CAUTION
Take ESD precautions (packaging, proper handling, grounded wrist strap, etc.)
Use care to avoid touching board surfaces and onboard components. Only handle
boards by their edges (or ORBs, if applicable). Ensure boards do not come into contact
with foreign elements such as oils, water, and industrial particulate.
Reference Note:
During software installation, Adobe
®
PDF versions of user manuals are automatically installed
onto your hard drive as a part of product support. The default location is in the Programs
group, which can be accessed from the Windows Desktop. A copy of the Adobe Acrobat
®
Reader
is included on your CD. The Reader provides a means of reading and printing the
PDF documents. Note that hardcopy versions of manuals can be ordered from the factory.
Note: In regard to functionality, the DaqBoard/2000c Series boards are identical to their
DaqBoard/2000 Series counterparts.
© 2001 through 2004 by 0HDVXUHPHQW&RPSXWLQJ&RUS 979294 061-0940, rev. 4.0 IG-1
Page 18
Reference Notes:
¾ Each DaqBoard/2000c Series Board plugs into a 5 volt, compact-PCI bus-slot located on the PC’s backplane. Note
that the 5 V compact-PCI bus-slot contains a blue key (see page 3). Consult your PC owner’s manual as needed.
¾ Be sure to read about the DBK cards and modules applicable to your acquisition system. Specific DBK information
can be found in on the world wide web at http://www.daqboard.com; and in your DBK Option Cards and Modules
User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905). After the install you can navigate to the DBK manual and other relevant electronic
documents from your desktop as follows:
Start ⇒ Programs ⇒ IOtech DaqX Software ⇒ DaqBoard 2000 Series Users
Reference Note: Adobe PDF versions of user manuals will
automatically install onto your hard drive as a part of product
support. The default location is in the Programs group, which
can be accessed from the Windows Desktop. Refer to the PDF
documentation for details regarding both hardware and
software. Note that hardcopy versions of the manuals can be
ordered from the factory.
Step 1 – Install Software
Minimum System Requirements
PC system with Pentium® Processor
Windows Operating System
RAM, as follows:
32 Mbytes of RAM for Windows 95/98/NT
64 Mbytes of RAM for Windows Me
64 Mbytes of RAM for Windows 2000
64 Mbytes of RAM for Windows XP
IMPORTANT: Software must be installed before installing hardware.
1. Remove previous version Daq drivers, if present. You can do this through Microsoft’s Add/Remove
Programs feature.
2. Place the Data Acquisition CD into the CD-ROM drive. Wait for PC to auto-run the CD. This may
take a few moments, depending on your PC. If the CD does not auto-run, use the Desktop’s
Start/Run/Browse feature.
3. After the intro-screen appears, follow the screen prompts.
Upon completing the software installation, continue with step 2, Install Boards in available 5 Volt,
Compact-PCI Bus-slots.
Step 2 – Install Boards in available 5 Volt, Compact-PCI Bus-slots
IMPORTANT: Software must be installed before installing hardware.
IMPORTANT: Bus Mastering DMA must be Enabled.
For a DaqBoard/2000c Series board to operate properly, Bus Mastering DMA must be enabled.
Prior to installation, verify that your computer is capable of performing Bus Mastering DMA for
the applicable compact-PCI bus-slot. Note that some computers have BIOS settings that enable
[or disable] Bus Mastering DMA. If your computer has this BIOS option, ensure that Bus
Mastering DMA is Enabled on the appropriate compact-PCI bus-slot.
Refer to your PC’s owner manual for additional information regarding Bus Mastering DMA.
IMPORTANT: The Compact-PCI Bus-Slot must be keyed for 5 Volt use.
Note: The 5 Volt Key location is indicated in the first photograph on page 3.
IG-2 DaqBoard/2000c Series Installation Guide 979294 1061-0940, rev 4.0
Page 19

Turn power OFF, and UNPLUG the host PC and externally connected equipment prior to
removing any cover plates or modules. Electric shock or damage to equipment can result even
under low-voltage conditions.
Take ESD precautions (packaging, proper handling, grounded wrist strap, etc.)
Use care to avoid touching board surfaces and onboard components. Only handle boards by their
edges or ORBs. Ensure boards do not come into contact with foreign elements such as oils, water,
and industrial particulate.
1. Turn the PC’s power OFF.
CAUTION
2. Turn power OFF to externally connected equipment.
3. UNPLUG the host PC and all externally connected
equipment.
4. Remove the computer’s compact-PCI bus-slot cover plate
[or remove an unwanted module, if applicable].
Refer to your PC Owner’s Manual as needed.
5. Verify that the available compact-PCI bus slot is for
5 volt applications.
The computer’s 5 volt compact-PCI bus-slots can be
recognized by a blue voltage key that is located in the
center of the slot (see figure).
6. Carefully remove the DaqBoard/2000c Series Board
from its anti-static protective bag. If you have not
already done so, write down the serial number of your
board at this time. The serial number is located on the
100-pin P4 connector.
7. With the board’s injector/ejector down, guide the board
into the PC’s slot. Note that the top and bottom edges of
the board locate in edge-guides, within the PC.
8. Push the board back into the PC to engage the board’s
compact-PCI connector with the computer’s compactPCI bus-slot.
9. Pull the board’s injector/ejector up. This will fully
engage the connectors.
10. Secure the board by tightening the upper and lower lock
screws.
11. Using the previous steps, install additional boards into
available compact-PCI bus-slots, if applicable to your
application.
Note: The lower lock screw is accessed through an opening
on the injector/ejector as indicated in the right-hand
figure.
Voltage
Key
Compact-PCI Bus-Slot with Blue 5 Volt Identifier Key
Upper Lock Screw
Injector/
Ejector
Lower Lock Screw
(see note)
Installing a DaqBoard/2000c Series Board
Lower Lock
Screw
Injector/Ejector and Lower Lock Screw
1061-0940, rev 4.0 979294 DaqBoard/2000c Series Installation Guide IG-3
Page 20

12. Plug in all cords and cables that were removed in step 3.
S
13. Apply power to, and start up the PC.
Note: At this point some PCs may prompt you to insert an
installation disk. While this is rare, if you do receive
such a prompt simply place the install CD into the disk
drive and follow the screen prompts.
ecuring a DaqBoard/2000c Series Board
Step 3 – Configure Boards
DaqBoard/2000c Series boards have no jumpers or switches to set. Configuration is performed entirely through software.
Refer to the following figure and steps to complete the configuration. The numbers in the figure correspond to the numbered
steps immediately following the figure.
Accessing the DaqBoard/2000 Properties Tab
IG-4 DaqBoard/2000c Series Installation Guide 979294 1061-0940, rev 4.0
Page 21
1. Run the Daq Configuration control panel applet. Navigation from the desktop to the applet is as follows:
Start ⇒ Settings ⇒ Control Panel ⇒ Daq*Configuration (double-click)
2. Double-click on the Device Inventory’s DaqBoard2K0 icon. The DaqBoard/2000 Properties tab (used for the entire
DaqBoard/2000 Series) will appear. If the DaqBoard2K0 icon is not present, skip to the Using ‘Add Device’ section
provided below.
3. Enter a “Device Name” in the text box, or use the default “DaqBoard2K0.” Device Name is for identifying the specific
DaqBoard/2000 Series board. Note that Device Name actually refers to the PCI slot and not to the actual board.
4. Verify that the “Device Type” shows the correct DaqBoard/2000 Series board, e.g., “DaqBoard/2000, DaqBoard/2001,
etc.” Note that available device types can be viewed via the pull-down list ().
5. Confirm that the DaqBoard/2000 Series text box shows a Bus #, Slot #, and Serial Number.
If this text box is empty, use its pull-down list () and select the serial number that matches the one for your board.
Refer to the inside front cover page for serial number information.
Using “Add Device”
This method is for users who have accessed the Daq Configuration control panel
applet, but have no DaqBoard2K icon (as described in
step 2, above).
(A) After accessing the Daq Configuration control panel applet, click on the Add
Device button (see figure, right). The Select Device Type window will appear.
(B) Using the Device Type’s pull-down list, select the applicable board. In the
example at the right DaqBoard/2000 is selected.
(C) Click the OK button. The DaqBoard/2000 Properties tab will appear. This tab
applies to all boards in the DaqBoard/2000 Series.
At this point, complete steps 3 through 5 from above.
Using “Add Device’
Step 4 – Test Hardware
Use the following steps to test the DaqBoard/2000 Series board. Note that these steps are continued from those listed
under the previous section, “Configure Board.”
1. Select the “Test Hardware” tab.
2. Click the “Resource Test” button.
3. After the test is complete, click “OK.”
System capability is now tested for the DaqBoard/2000
Series board and a list of test results appears on screen.
Note: If you experience difficulties, please consult your user
documentation (included on your CD) before calling for
technical support. Note that the user documentation
includes a troubleshooting chapter, as well as a great
deal of information regarding specific DBK cards and
modules.
At this point we are ready to connect signals. This is typically accomplished with the use of a DBK200 Series option.
Reference Note:
For detailed information regarding the DBK200 Series options, refer to the DBK Option Cards and Modules
User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905).
During software installation, Adobe® PDF versions of user manuals are automatically installed onto your
hard drive as a part of product support. The default location is in the Programs group, which can be
accessed from the Windows Desktop. A copy of the Adobe Acrobat Reader® is included on your CD. The
Reader provides a means of reading and printing the PDF documents. Note that hardcopy versions of
manuals can be ordered from the factory.
Test Hardware Tab
(Condensed Screen Image)
1061-0940, rev 4.0 979294 DaqBoard/2000c Series Installation Guide IG-5
Page 22

IG-6 DaqBoard/2000c Series Installation Guide 979294 1061-0940, rev 4.0
Page 23

Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1
Daq Systems, the Modular Concept …… 1-1
Theory of Operation, DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Boards …… 1-3
DaqBoard/1000 …… 1-7
DaqBoard/1005 …… 1-9
DaqBoard/2000 ….… 1-11
DaqBoard/2001……. 1-13
DaqBoard/2002…… 1-15
DaqBoard/2003…… 1-17
DaqBoard/2004…… 1-19
DaqBoard/2005…… 1-21
Using DBK Cards and Modules for Signal Conditioning ….. 1-23
Daq Software ……1-23
Daq Systems, the Modular Concept
Daq equipment and software form a modular, interrelated family of products that provide great flexibility
in data acquisition system design. This flexibility allows for the development of custom systems that are
unique to the user, and which can be optimized for his or her specific application needs. With the Daq
product line, system expansion or redesign can typically be accomplished with relative ease.
• Primary Acquisition Device. This is the main data acquisition device, e.g., a DaqBook, DaqBoard,
or Daq PC-Card. These devices provide a vital data conversion and communications link between
the data source of transducers and signal conditioners and the data processor of the host computer.
Note that a DaqBoard can be one of three types: (1) ISA, (2) PCI, or (3) compact-PCI.
• DBK Option Cards and Modules. Over 35 DBK cards and modules (the number is constantly
growing) provide various types of signal conditioning and system expansion. Note that certain DBK
modules exist for the purpose of supplying power to other members of the acquisition system. The
DBK options are discussed in a DBK Basics document module and in the detailed DBK Option
Cards and User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905). DaqBoard/1000 Series boards do not support DBK
options.
Note: Only passive DBKs, such as the DBK1 BNC module, the DBK11A screw terminal card, and
the DBK40 BNC analog interface, can be used with a Daq PC-Cards.
Reference Note:
DBK options are discussed in the DBK Option Cards and Modules User’s Manual
(p/n 457-0905). As a part of product support, this manual is automatically loaded onto
your hard drive during software installation. The default location is the Programs
directory, which can be accessed through the Windows Desktop.
• Software. DaqView out-of-the-box software provides a graphical user interface with easy to read
spreadsheet formats for viewing channel data, as well as a choice of analog, digital, and bar-graph
meters. Waveform analysis can be performed, when applicable. A product support option, included
on the data acquisition CD, provides a means of performing post data analysis. More information is
included in the software-specific PDF documents that are installed on your hard-drive as a part of
product support.
In addition to the included out-of-the-box software, Daq products can be controlled via user-written
custom programs through Applications Program Interface (API). Several languages are supported,
including C/C++ and VisualBASIC.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-1
Page 24
DaqView and DASYLab can only be used with one DaqBoard at a time.
LabView can be used with multiple boards. For multiple board use (via custom
programming) refer to the Using Multiple Devices section of the Programmer’s Manual.
Reference Note:
Programming topics are covered in the Programmer’s User Manual (p/n 1008-0901). As a part
of product support, this manual is automatically loaded onto your hard drive during software
installation. The default location is the Programs group, which can be accessed through the
Windows Desktop.
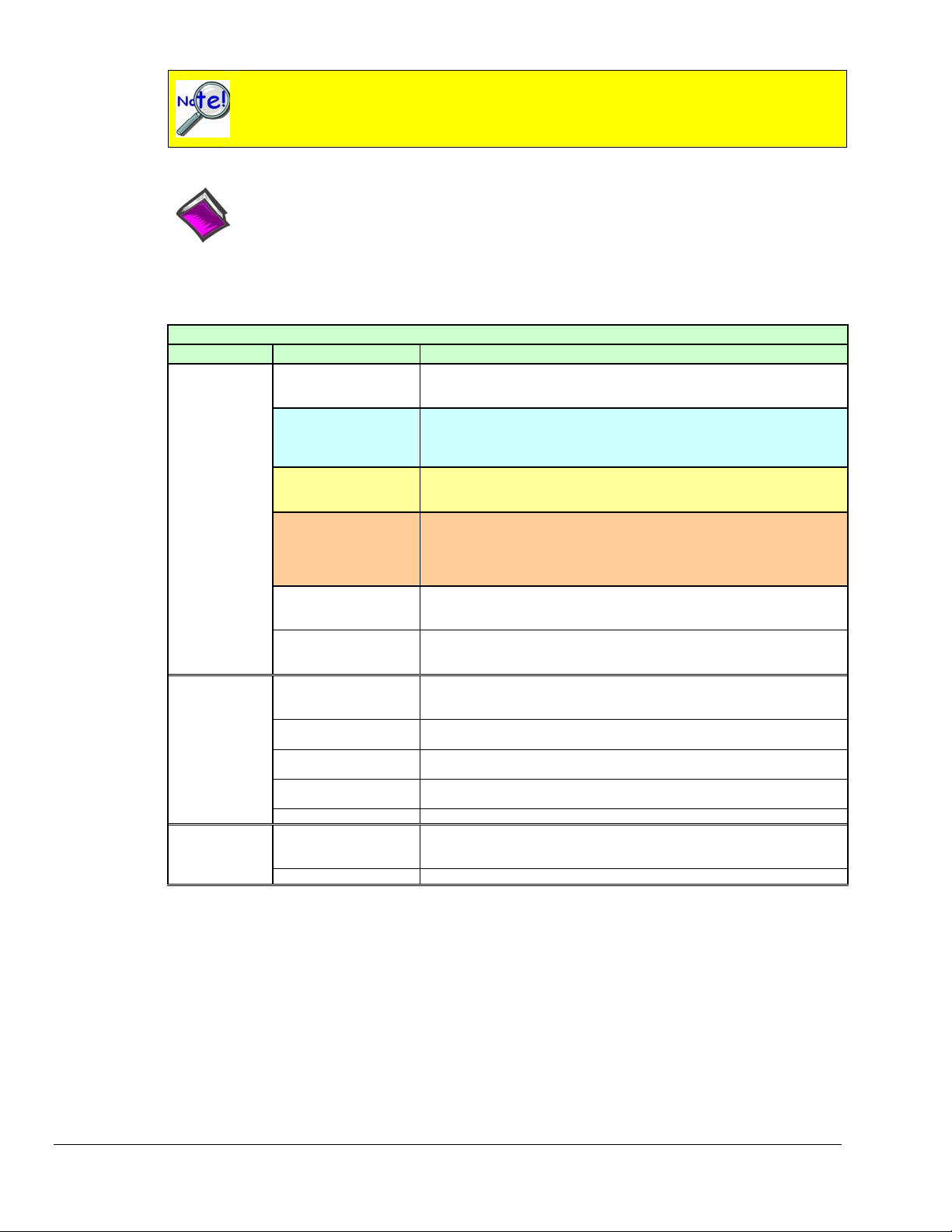
Daq Data Acquisition Devices
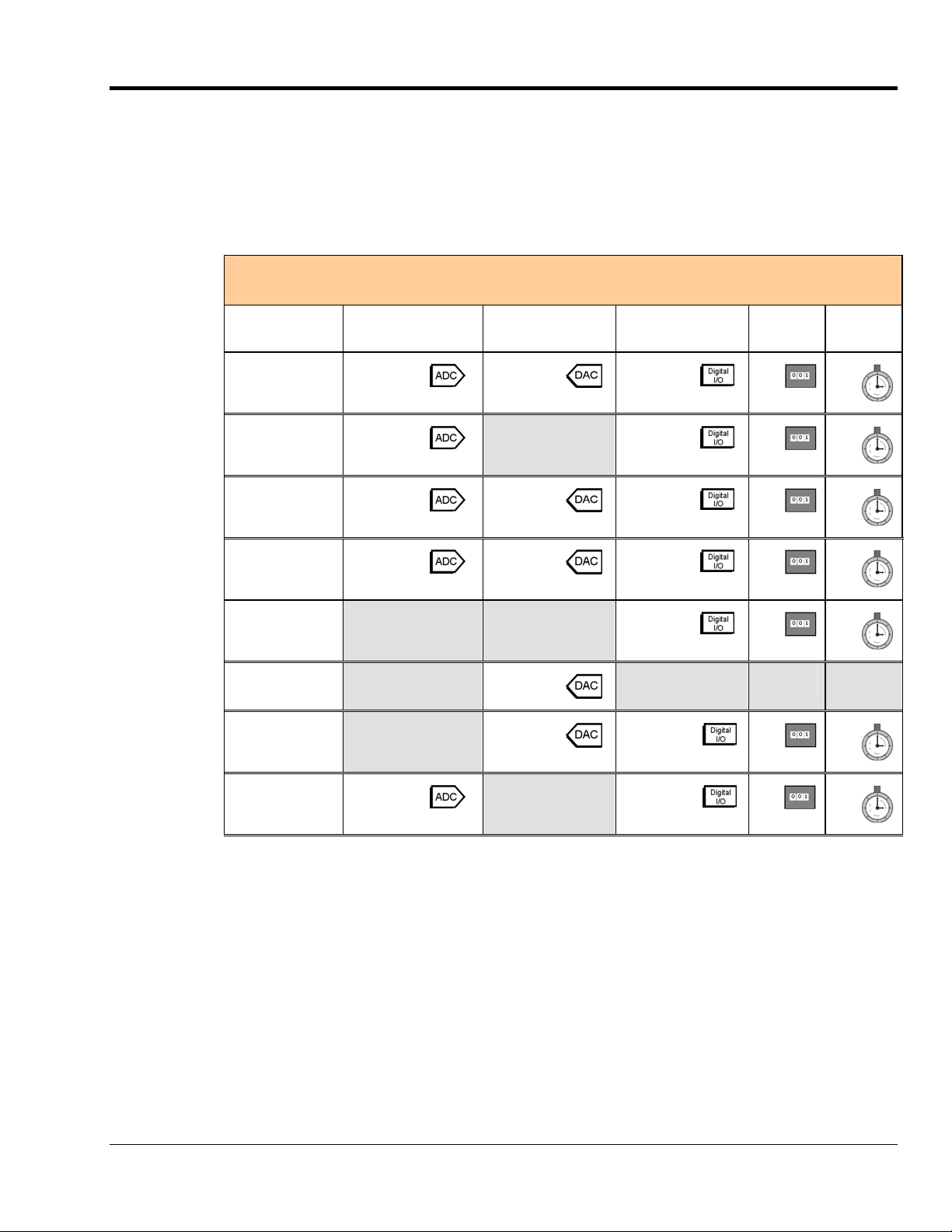
Category Device Description
Primary
Acquisition
Device
DBK Option
Cards and
Modules*
Software
DaqBook
DaqBoard/1000
Series*
DaqBoard/2000
Series
DaqBoard/2000c
Series
DaqBoard (ISA types)
Daq PC-Card
Analog Signal
Conditioning
Analog Output
Digital I/O and Control
Expansion
Connections
Power Supply DBKs: 30A, 32A, 33, 34
Included Software DaqView, Post Data Acquisition Analysis Program (actual application not
Optional Software DaqView/2000, DaqViewXL, DASYLab
Portable Data Acquisition Modules
12-bit: DaqBook/100, /112, /120
16-bit: DaqBook/200, /216, /260, /2001, /2005, /2020
Plug-In Boards for PCI Bus-Slots
16-bit , 200 kHz. 2 boards identified as /1000 and /1005
Make use of a 68-pin SCSI III connector.
The DaqBoard/1000 Series boards do not support DBK options.
Plug-In Boards for PCI Bus-Slots
16-bit , 200 kHz. Six boards identified as /2000 through /2005.
Make use of a 100-pin connector (P4).
Plug-In Boards for Compact-PCI Bus-Slots
16-bit , 200 kHz. Six boards identified as /2000c through /2005c.
Make use of a 100-pin connector (P4).
Unless otherwise specified, documentation discussing a DaqBoard/2000
series board also applies to a DaqBoard/2000c Series board.
Plug-In Boards for ISA Bus-Slots
12-bit: DaqBoard/100A, /112A
16-bit: DaqBoard/200A, /216A, /2000
Plug-In PCMCI Card
12-bit: Daq/112B
16-bit: Daq/216B
Cards and modules used to condition Analog Signals
DBK/ 4, 7, 8, 9, 12, 13, 15, 17, 18, 19, 42, 43A, 44, 45, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54,
55, 65, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 90, 100, 207, 207/CJC
Cards used to modify Analog Output Signals
DBK/ 2, 5
Cards and modules used to condition Digital I/O
DBK/ 20, 21, 23, 24, 25, 208, 210
Cards and modules used to expand the acquisition system.
DBK/ 1, 10, 11A, 35, 40, 41, 60, 200, 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206, 209
specified), Visual Basic extensions, Application Programming Interface
(API)
* DBK Option cards and modules are not supported by DaqBoard/1000 Series boards.
1-2 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 25
Theory of Operation for DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Boards
As implied by the following matrix, the operational material does not apply globally to every board. For
example, DaqBoard/1005, /2002, and /2005 have no analog output channels.
For ease of understanding, each board is discussed independently, following the matrix. Note that pinouts
are provided in chapter 2 for the DaqBoard/1000 Series and in chapter 3 for the DaqBoard/2000 Series.
I/O Comparison Matrix
I/O Comparison Matrix
for DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Boards
DaqBoard
Identity
1000 16
1005 16
2000 16
2001 16
2002 -- -- 40
2003
2004 -- 4
Analog Input
Channels
-- 4
Analog Output
Channels
2
2
4
Digital I/O
Channels
24
-- 24
40
40
-- -- --
40
Counter
Inputs
4
4
4
4
4
4
Timer
Outputs
2
2
2
2
2
2
2005 16
-- 40
4
2
Note: DaqBoard/1000 Series boards do not support DBK options.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-3
Page 26

Synchronous Input Operations for DaqBoard/1000 and DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards
As indicated in the I/O matrix, applicable DaqBoards allow for synchronous scanning and acquisition of
Analog Input, Digital Input and Counter Input Data at up to 200kHz aggregate scanning rates.
For applicable DaqBoard/2000 Series devices, the Analog Input data can be either directly to the board or
expansion anal
from
P2 (8255) digital inputs, 16-bit P3 digital inputs or P2 compatible DBK digital input expansion modules.
Refer to the applicable pinouts to see how P1, P2, and P3 relate to the 100-pin P4 connector.
DaqBoard/1000 Series boards do not support DBK options.
Analog Input Channels
The boards that offer analog input (see previous matrix) allow analog input configuration for the board.
og input modules connected to P1. The Digital Input data can be to the board’s 8-bit
For applicable DaqBook/2000 Series boards, analog input can be received from
P1 comp
atible DBK
analog input expansion modules.
Channel Selection and Mode Settings
The main unit accepts up to 16 single ended or up to 8 differential-ended inputs and can be programme
for single-ended or differential-ended on a per channel basis. In regard to DaqBoard/2000 Series boards,
just one analog channel is sacrificed when a DBK expansion module is enabled. See DBK documentation
in the DBK Option Cards & Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905) for further information.
Channel Range and Polarity
d for either unipolar or bipolar mode with gain
DaqBoard/2000 Series board channels can be program
me
settings of 1,2,4,8,16,32 and 64. DaqBoard/1000 Series boards have the same gains but are only bipolar.
Channel Sampling Interval
The boards allow programmable sampling intervals of 5us or 10us on a per channel basis. Thi
s mode
allows some channels which change slowly but a higher degree of accuracy is desirable to be sampled at a
longer interval while channels that change more rapidly to be sampled using a shorter interval. Each 5us or
10us interval reduces the maximum aggregate acquisition rate for the entire scan by that amount.
Digital Input Channels
Associated boards allow either synchronous scanning of digital input channels or asynchronous I/O
operations for all configured digital channels.
Counter Input Channels
d
Associated boards allow synchronous scanning of the 4 16-bit counter input channels. The four 16-bit
counter channels can also be cascaded into two 32-bit counter channels. For either cascaded or
non-cascaded counter channels each channel can be configured for:
• Pulse Counting Mo
the input scan.
talize Counting Mode – specifies that each counter is to free-run and not be cleared during the input
• To
acquisi
tion.
Synchronous Input Acquisition Clocking
Associated boards allow clocking of the synchronized inputs either by an internal, programmable pacer
clock or by external clocking. These products use a sequencer to implement a multiplexing approach to
gathering the input data. This means that with either internal or external clocking the entire channel scan
(including the sampling time for each channel) may not exceed the maximum aggregate rate of 200kHz.
1-4 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
de – specifies that each counter should be cleared upon being read and placed into
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 27

Synchronous Output Operations
The DaqBoard/1000 allows synchronous output of any D/A channels available at up to 100kHz for each
channel. All D/A channels available may have output streamed to them and clocked out synchronously.
The D/A channels may be configured for waveform output.
The DaqBoard/2000 Series boards allow synchronous output
available at up to 100kHz for each channel. All D/A channels available and the 16-bit P3 Digital channel
may have output streamed to them and clocked out synchronously. The D/A channels may be configured
for waveform output and the P3 digital channel may be configured for streamed digital pattern output using
the same clock sources.
Output Channel Configuration
Analog Output Channels
Each D/A channel can be configured for waveform output individually. If the D/A channel is not
configured for waveform output it then is available for asynchronous output operations.
Digital Pattern Output Channel (DaqBoard/2000 Series Only)
In regard to DaqBook/2000 Series boards, the 16-bit P3 Digital Port can be configured for streamed digital
pattern output. If not configured for streamed digital pattern output operations it then may be used for
asynchronous digital I/O operations.
Synchronous Output Clocking
Associated boards allow clocking of the synchronized output by the acquisition clock source, an internal,
programmable pacer clock or by an external clock source. When the clock source generates a new clock
signal all outputs are updated concurrently. Regardless of the clock source, the clock may not exceed the
maximum update rate of 100kHz.
Synchronous Output Data Source
of any D/
A or P3 16-bit Digital channels
Associated boards allow the data source for synchronized output operations to be that of a memory based
buffer or a file located on a mass storage medium. With either type of output data source, the output data
for all the channels are contained in the buffer and/or file. The file path may be any file located on the
machine or network accessible file.
Asynchronous I/O Operations
Associated boards allow asynchronous input of any counter or digital channel that is not currently
configured for synchronous acquisition. The boards also allow for asynchronous output to any D/A
channels not currently configured for waveform output.
In addition, for DaqBoard/2000 Series boards, the 16-bit P3 digital port can be used for both asynchronous
nput and out
i
the timer outputs can be programmed at any time regardless of the current state of synchronous or
asynchronous operations on other channels.
Digital I/O Channels
Local 8255 Channels
The boards [which have digital I/O capabilities] have an implemented Intel 8255 core in the digital I/O
ogic. For DaqBoard/2000 Series boards, this is applicable to the P2 port [see pinouts for P2 to P4
l
relationship]. With the Intel 8255 there are three 8-bit wide ports available for I/O and one 8-bit wide port
for configuration purposes. The configuration port is used to configure the other three 8-bit ports for either
input or output operations.
Local 16-bit P3 Port (DaqB
For DaqBoard/2000 series devices, the 16-bit P3 Digital Port can be used as eit
port. With this port, no configuration is required as the port simply outputs when written to and inputs
when read.
put operations if it is not currently configured for streamed pattern output operations. Also,
oard/2000 Seri
es only)
her an input, or an output
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-5
Page 28

Expansion Digital I/O (DaqBoard/2000 Series only)
The DaqBoard/2000 Series boards that have digital I/O capabilities have the ability to expand these
through t
discussed in the DBK Option Cards & Modules User’s Manual. When using the digital I/O expansion
modules the local P2 Intel 8255 digital I/O becomes inaccessible in lieu of the expansion modules. These
expansion modules provide additionally Intel 8255 ports as well as input isolation for applications that
require the expanded capabilities.
he P2 port and the connection of applicable digital I/O expansion modules. These modules are
Pulse Stream Output Using Timers
The boards allow the generation of output pulses based upon a programmable setting. These output timers
can be set at any time regardless of the state of any synchronous or asynchronous operations which are
currently taking place on other channels.
Analog Output Channels
The boards that have analog output capabilities hav e the ability to output analog data to any of the
available (up to four) D/A channels. Each D/A channel may be asynchronously updated by an application
if the D/A channel is not currently being used for waveform output operations.
Counter Input Channels
With exception of DaqBoard/2003, the boards have counter input capabilities and have the ability to read
counter input [if the counter channel is not configured for synchronous acquisition]. As in the case of
synchronous operations the 4 16-bit counter input channels can be used individually or cascaded into two
32-bit counter channels. For either cascaded or non-cascaded counter channels each channel can be
configured for:
• C
• Continuous Totalize Mode – specifies that each counter is to free-run and not be cl
Operation Matrix*
Synchronous Input
Analog Main Unit Inputs Yes Yes Yes Yes No No No Yes
Analog Expansion Input No No Yes Yes No No No Yes
Counter Inputs Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Digital Main Unit Inputs Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Digital Expansion Inputs No No Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Synchronous Output
Analog D/A Waveform Output Yes No Yes Yes No Yes Yes No
Streamed Digital Output (16-bit) No No Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Asynchronous IO
Main Unit Digital I/O Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Expansion Digital I/O No No Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Timer Output (Pulse Generation) Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Analog Output Yes No Yes Yes No Yes Yes No
* A similar matrix, intended to highlight board differences at a glance, is presented on page 1-3.
lear on Read Mode - specifies that each counter should be cleared (reset to 0) upon being read.
eared during
the read operation.
Operation
1000 1005 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005
1-6 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 29

DaqBoard/1000
Outputs
2 Timer
16 Analog
Input
2 Analog
Output
24 Digital
I/O
4 Counter
Inputs
DaqBoard/1000 is a high-speed, multi-function, plug-and-play data acquisition board for PCI bus
computers. It features a 16-bit, 200-kHz A/D converter, digital calibration, bus mastering DMA, two
16-bit, 100-kHz D/A converters, 24 digital I/O lines, four counters, and two timers.
Up to four boards can be installed into a PC.
One 68-pin SCSI III connector on the board provides access to all of the input and output signals. The
DaqBoard/1000 accommodates all I/O with one cable and one PCI slot.
The 68-pin I/O connector is logically divided into three functions:
• Analog input for16 single-ended or 8 differential analog inputs with 7 software programmable bipolar
ranges (±10 V to ±156 mV full scale).
• 24 lines of general purpose digital I/O.
• 4 counter inputs, 2 timer outputs, and 2 analog outputs.
The on-board scan sequencer lets you select up to 512 channel/range combinations. The sequencer scans
all channels of the scan at 5µs or 10 µs/channel.
Bus mastering allows analog and digital/counter input data, as well as analog and digital output data, to
flow between the PC and the DaqBoard without consuming CPU time.
DaqBoard/1000 supports trigger modes that include:
• Digital and pattern triggering – The boards have separate digital trigger input line, allowing TTL-
level triggering and latencies less than 5 µs. The trigger can be programmed for logic level or edge
triggering. In pattern triggering, any of the digital input ports acts as the trigger port. You can program
the digital pattern.
• Software-based triggering – The PC detects the trigger event from analog, digital, or counter
readings. Six pre- and post-triggering modes are supported.
The two 16-bit, 100-kHz analog output channels have an output from –10 V to +10 V. Using Bus
Mastering DMA, each D/A can output a waveform.
Other features of the DaqBoard/1000 include:
• 24 TTL-level digital I/O lines. They are divided into three 8-bit ports.
• Four 16-bit counters. Each can accept frequency inputs up to 10 MHz. The counters can be cascaded
into two 32-bit counters.
• Two 16-bit timer outputs. Each can generate square waves from 16 Hz to 1 MHz.
• Configuration through software. There are no switches or jumpers on the DaqBoard/1000.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-7
Page 30

DaqBoard/1000 Block Diagram
Connections
Installation
I/O Connectors
Reference Note:
For the DaqBoard/1000 installation procedure, refer to the DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series
Installation Guide. A copy of the guide is included at the beginning of this manual.
All input and output signals are available at the board’s 68-pin SCSI III connector. Chapter 2 includes a
pinout. The following cable and terminal board options can be used to provide convenient screw terminal
connections for all signal I/O lines.
Mating Cable: The CA-G56 is a 68-conductor shielded cable. It is used to connect a DaqBoard/1000
Series board to a TB-100 termination board. The cable length is 3 feet.
TB-100: TB-100 is an optional termination board. It provides convenient screw terminal
connections for all signal I/O lines of a DaqBoard/1000 Series board.
Reference Note:
The TB-100 terminal board connection option is discussed in chapter 2.
1-8 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 31

DaqBoard/1005
Outputs
2 Timer
16 Analog
Inputs
I/O
4 Counter
Inputs
24 Digital
DaqBoard/1005 is a high-speed, multi-function, plug-and-play data acquisition board for PCI bus
computers. It features a 16-bit, 200-kHz A/D converter, digital calibration, bus mastering DMA, 24 digital
I/O lines, four counters, and two timers.
Up to four boards can be installed into a PC.
One 68-pin SCSI III connector on the board provides access to all of the input and output signals. The
DaqBoard/1000 accommodates all I/O with one cable and one PCI slot. The 68-pin I/O connector is
logically divided into three functions:
• Analog input for16 single-ended or 8 differential analog inputs with 7 software programmable bipolar
ranges (±10 V to ±156 mV full scale).
• 24 lines of general purpose digital I/O.
• 4 counter inputs and 2 timer outputs
The on-board scan sequencer lets you select up to 512 channel/range combinations. The sequencer scans
all channels of the scan at 5µs/channel or 10 µs/channel.
Bus mastering allows analog and digital/counter input data, as well as digital output data, to flow between
the PC and the DaqBoard without consuming CPU time.
DaqBoard/1005 supports trigger modes that include:
• Digital and pattern triggering – The boards have separate digital trigger input line, allowing TTL-
level triggering and latencies less than 5 µs. The trigger can be programmed for logic level or edge
triggering. In pattern triggering, any of the digital input ports acts as the trigger port. You can program
the digital pattern.
• Software-based triggering – The PC detects the trigger event from analog, digital, or counter
readings. Six pre- and post-triggering modes are supported.
Other features of the DaqBoard/1000 include:
• 24 TTL-level digital I/O lines. They are divided into three 8-bit ports.
• Four 16-bit counters. Each can accept frequency inputs up to 10 MHz. The counters can be cascaded
into two 32-bit counters.
• Two 16-bit timer outputs. Each can generate square waves from 16 Hz to 1 MHz.
• Configuration through software. There are no switches or jumpers on the DaqBoard/1005.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-9
Page 32

DaqBoard/1005 Block Diagram
Connections
Installation
I/O Connectors
Reference Note:
For the DaqBoard/1005 installation procedure, refer to the DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series
Installation Guide. A copy of the guide is included at the beginning of this manual.
All input and output signals are available at the board’s 68-pin SCSI III connector. Chapter 2 includes a
pinout. The following cable and terminal board options can be used to provide convenient screw terminal
connections for all signal I/O lines.
Mating Cable: The CA-G56 is a 68-conductor shielded cable. It is used to connect a DaqBoard/1000
Series board to a TB-100 termination board. The cable length is 3 feet.
TB-100: TB-100 is an optional termination board. It provides convenient screw terminal
connections for all signal I/O lines of a DaqBoard/1000 Series board.
Reference Note:
The TB-100 terminal board connection option is discussed in chapter 2.
1-10 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 33

DaqBoard/2000
Outputs
2 Timer
16 Analog
Input
2 Analog
Output
40 Digital
I/O
4 Counter
Inputs
DaqBoard/2000 and DaqBoard/2000c are high-speed, multi-function, plug-and-play data acquisition
boards for PCI and compact-PCI bus computers, respectively. They feature a 16-bit, 200-kHz A/D
converter, digital calibration, bus mastering DMA, two 16-bit, 100-kHz D/A converters, 40 digital I/O
lines, four counters, and two timers.
Up to 470 channels of analog and digital I/O can be accessed with one DaqBoard/2000. Up to four boards
can be installed into a PC.
A 100-pin connector on the boards provides access to all of the input and output signals. The
DaqBoard/2000 and /2000c accommodate all I/O with one cable and one PCI [or compact-PCI] slot.
The 100-pin I/O connector, P4, is logically divided into three ports:
• P1 – Analog input port for16 single-ended or 8 differential analog inputs with 13 software
programmable ranges (±10 V to ±156 mV full scale).
• P2 – General purpose digital I/O port with 24 lines, or digital I/O expansion port controlling up to 192
external lines.
• P3 – 16-bit digital I/O port, counter inputs, timer outputs, and analog outputs.
The on-board scan sequencer lets you select up to 512 channel/range combinations. The sequencer scans
all channels of the scan at 5µs or 10 µs/channel.
Bus mastering allows analog and digital/counter input data, as well as analog and digital output data, to
flow between the PC and the DaqBoard/2000 without consuming CPU time.
DaqBoard/2000 supports a full complement of trigger modes including:
• Hardware analog triggering – A user-programmed trigger level sets an analog DAC, which is
compared in hardware to the analog input level on the selected channel. Trigger latency is < 5 µs.
• Digital and pattern triggering – The boards have separate digital trigger input line, allowing TTL-
level triggering and latencies less than 5 µs. The trigger can be programmed for logic level or edge
triggering. In pattern triggering, any of the digital input ports acts as the trigger port. You can program
the digital pattern.
• Software-based triggering – The PC detects the trigger event from readings, either analog, digital, or
counter. Six pre- and post-triggering modes are supported.
The two 16-bit, 100-kHz analog output channels have an output from –10 V to +10 V. (These channels are
separate from the D/As used to determine analog trigger levels.) Using Bus Mastering DMA, each D/A can
output a waveform. Bus Mastering DMA also allows for digital pattern generation on the 16-bit high-speed
digital I/O port.
Other features of the DaqBoard/2000 include:
• 40 TTL-level digital I/O lines. They are divided into three 8-bit ports and one 16-bit port.
• Four 16-bit counters. Each can accept frequency inputs up to 10 MHz. The counters can be cascaded
into two 32-bit counters.
• Two 16-bit timer outputs. Each can generate square waves from 16 Hz to 1 MHz.
• Configuration through software. There are no switches or jumpers on the DaqBoard/2000.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-11
Page 34

DaqBoard/2000 Block Diagram*
Connections
Installation
I/O Connectors
* The DaqBoard/2000c Block Diagram is the same, with exception that the /2000c board uses a
compact-PCI Bus instead of a standard PCI bus.
Reference Note: For the DaqBoard/2000 and DaqBoard/2000c installation procedure, refer to
either the DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide or to the DaqBoard/2000c
Series Installation Guide, as applicable. The guides are included at the beginning of this
manual.
All input and output signals are available at the board’s 100-pin P4 connector. A 3-foot, 100-conductor
ribbon cable, part number CA-195, mates with connector P4.
Reference Note: There are several P4-connector board options available for connecting the
100 pins of P4 to typical DB37 connectors (P1, P2, and P3). In addition to being briefly
discussed in chapter 3 of this manual, these options, referred to as DBK200 Series, are
detailed in the DBK Cards and Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905).
1-12 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 35

DaqBoard/2001
Outputs
2 Timer
16 Analog
Input
4 Analog
Output
40 Digital
I/O
4 Counter
Inputs
DaqBoard/2001 and DaqBoard/2001c are high-speed, multi-function, plug-and-play data acquisition
boards for PCI or compact-PCI bus computers, respectively. They feature a 16-bit, 200-kHz A/D
converter, digital calibration, bus mastering DMA, four 16-bit, 100-kHz D/A converters, 40 digital I/O
lines, four counters, and two timers.
Up to 470 channels of analog and digital I/O can be accessed with one DaqBoard/2001 board. Up to four
boards can be installed into a PC.
A 100-pin connector on the DaqBoard/2001 provides access to all of the input and output signals. The
boards accommodate all I/O with one cable and one PCI [or compact-PCI] slot. The 100-pin I/O connector,
P4, is logically divided into three ports:
• P1 – Analog input port for16 single-ended or 8 differential analog inputs with 13 software
programmable ranges (±10 V to ±156 mV full scale).
• P2 – General purpose digital I/O port with 24 lines, or digital I/O expansion port controlling up to 192
external lines.
• P3 – 16-bit digital I/O port, counter inputs, timer outputs, and analog outputs.
The on-board scan sequencer lets you select up to 512 channel/range combinations. The sequencer scans
all channels of the scan at 5µs/channel or 10µs/channel.
Bus mastering allows analog and digital/counter input data, as well as analog and digital output data, to
flow between the PC and the DaqBoard/2001 without consuming CPU time.
DaqBoard/2001 supports a full complement of trigger modes including:
• Hardware analog triggering – A user-programmed trigger level sets an analog DAC, which is
compared in hardware to the analog input level on the selected channel. Trigger latency is < 5 µs.
• Digital and pattern triggering – The DaqBoard/2001 has a separate digital trigger input line,
allowing TTL-level triggering and latencies less than 5 µs. The trigger can be programmed for logic
level or edge triggering. In pattern triggering, any of the digital input ports acts as the trigger port.
You can program the digital pattern.
• Software-based triggering – The PC detects the trigger event from readings, either analog, digital, or
counter. Six pre- and post-triggering modes are supported.
The four 16-bit, 100-kHz analog output channels have an output from –10 V to +10 V. (These channels
are separate from the D/As used to determine analog trigger levels.) Using Bus Mastering DMA, each D/A
can output a waveform. Bus Mastering DMA also allows for digital pattern generation on the 16-bit highspeed digital I/O port.
Other features of the DaqBoard/2001 include:
• 40 TTL-level digital I/O lines. They are divided into three 8-bit ports and one 16-bit port.
• Four 16-bit counters. Each can accept frequency inputs up to 10 MHz. The counters can be cascaded
into two 32-bit counters.
• Two 16-bit timer outputs. Each can generate square waves from 16 Hz to 1 MHz.
• Configuration through software. There are no switches or jumpers on a DaqBoard/2001.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-13
Page 36

Connections
Installation
I/O Connector
DaqBoard/2001 Block Diagram*
* The DaqBoard/2001c Block Diagram is the same, with exception that the /2001c board uses a
compact-PCI Bus instead of a standard PCI bus.
Reference Note: For the DaqBoard/2001 and /2001c installation procedure, refer to either the
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide or to the DaqBoard/2000c Series
Installation Guide, as applicable. The guides are included at the beginning of this manual.
All input and output signals are available at the board’s 100-pin P4 connector. A 3-foot, 100-conductor
ribbon cable, part number CA-195, mates with connector P4.
Reference Note: There are several P4-connector board options available for connecting the
100 pins of P4 to typical DB37 connectors (P1, P2, and P3). In addition to being briefly
discussed in chapter 3 of this manual, these options, referred to as DBK200 Series, are
detailed in the DBK Cards and Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905).
1-14 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 37

DaqBoard/2002
Outputs
2 Timer
40 Digital
I/O
4 Counter
Inputs
DaqBoard/2002 and /2002c are high-speed, multi-function, plug-and-play data acquisition boards for PCI
and compact-PCI bus computers, respectively. They feature digital calibration, bus mastering DMA,
40 digital I/O lines, four counters, and two timers.
Up to 470 channels of analog and digital I/O can be accessed with one board. Up to four boards can be
installed into a PC.
A 100-pin connector on the boards provides access to all of the input and output signals. The boards
accommodate all I/O with one cable and one PCI [or compact-PCI] slot. The 100-pin I/O connector, P4, is
logically divided into three ports:
• P1 – Not used by DaqBoard/2002
• P2 – General purpose digital I/O port with 24 lines, or digital I/O expansion port controlling up to
192 external lines.
• P3 – 16-bit digital I/O port, counter inputs, timer outputs, and analog outputs.
The on-board scan sequencer lets you select up to 512 channel/range combinations. The sequencer scans
all channels of the scan at 5 µs/channel or 10 µs/channel.
Bus mastering allows digital/counter input data and digital output data to flow between the PC and the
DaqBoard/2002 board without consuming CPU time.
DaqBoard/2002 supports a complement of trigger modes including:
• Digital and pattern triggering – The boards have separate digital trigger input line, allowing TTL-
level triggering and latencies less than 5 µs. The trigger can be programmed for logic level or edge
triggering. In pattern triggering, any of the digital input ports acts as the trigger port. You can program
the digital pattern.
• Software-based triggering – The PC detects the trigger event from readings [digital, or counter].
Six pre- and post-triggering modes are supported.
Other features of the DaqBoard/2002 include:
• 40 TTL-level digital I/O lines. They are divided into three 8-bit ports and one 16-bit port.
• Four 16-bit counters. Each can accept frequency inputs up to 10 MHz. The counters can be cascaded
into two 32-bit counters.
• Two 16-bit timer outputs. Each can generate square waves from 16 Hz to 1 MHz.
• Configuration through software. There are no switches or jumpers on a DaqBoard/2002.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-15
Page 38

DaqBoard/2002 Block Diagram*
*The DaqBoard/2002c Block Diagram is the same, with exception that the /2002c board uses a
compact-PCI Bus instead of a standard PCI bus.
Connections
Installation
I/O Connector
Reference Note: For the DaqBoard/2002 and compact-PCI DaqBoard/2002c installation
procedure, refer to either the DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide or to the
DaqBoard/2000c Series Installation Guide, as applicable. The guides are included at the
beginning of this manual.
All input and output signals are available at the board’s 100-pin P4 connector. A 3-foot, 100-conductor
ribbon cable, part number CA-195, mates with connector P4.
Reference Note: There are several P4-connector board options available for connecting the
100 pins of P4 to typical DB37 connectors (P1, P2, and P3). In addition to being briefly
discussed in chapter 3 of this manual, these options, referred to as DBK200 Series, are
detailed in the DBK Cards and Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905).
1-16 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 39

DaqBoard/2003
DBK205
Terminations
TB1-1 AGND
TB1-2 DAC0
TB1-3 AGND
TB1-4 DAC1
TB1-5 AGND
TB1-6 DAC2
TB1-7 AGND
TB1-8 DAC3
TB1-9 AGND
TB1-10 XTTL
TB1-11 CLK
TB1-12 DGND
4 Analog Outputs
DaqBoard/2003 and /2003c are high-speed plug-and-play data acquisition boards for PCI and compact-PCI
bus computers, respectively. The boards are used for analog output and include four 16-bit, 100-kHz D/A
converters. Up to four boards can be installed into a PC.
A 100-pin connector on the boards provides access to the DAC analog output signals. The boards plug
directly into a PCI or compact-PCI bus slot, as applicable. The DAC analog output leaves the board
through “P3-designated” pins located on the board’s 100-pin P4 connector.
Both boards support Software-based triggering. In “Software-based” triggering the PC detects the
trigger event from the readings. Six pre- and post-triggering modes are supported.
DBK205 Adapter DaqBoard/2003 Block Diagram
Connections
Installation
I/O Connector
Note: DaqBoard/2003 and DaqBoard/2003c are shipped with one DBK205 adapter. The adapter has twelve screw
terminals as follows: DAC0, DAC1, DAC2, DAC3, 1 digital ground, 5 analog grounds, 1 external clock (CLK), and
1 external trigger (XTTL). DBK205 connects directly to DaqBoard/2003’s P4 connector.
Reference Note: For the DaqBoard/2003 and DaqBoard/2003c installation procedure, refer to
either the DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide or to the DaqBoard/2000c
Series Installation Guide, as applicable. The guides are included at the beginning of this
manual.
Analog output signals are available at the board’s 100-pin P4 connector. A 3-foot, 100-conductor ribbon
cable, part number CA-195, mates with connector P4; however, a DBK205 adapter board is included for
connecting the 100 pins of P4 to a terminal block (TB1).
DBK205’s TB1 includes screw terminals for: DAC0, DAC1, DAC2, and DAC3, 1 digital ground,
5 analog grounds, 1 external clock (CLK), and 1 external trigger (XTTL). DBK205 connects directly to
DaqBoard/2003’s P4 connector or to a compact-PCI DaqBoard/2003c’s P4 connector.
DBK205 is depicted as part of the block diagram above and is discussed briefly in chapter 3 of this manual.
DBK205 is also discussed in the DBK Cards and Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905).
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-17
Page 40

1-18 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 41

DaqBoard/2004
4 Analog
Output
40 Digital
I/O
4 Counter
Inputs
2 Timer
Outputs
DaqBoard/2004 and /2004c are high-speed, multi-function, plug-and-play data acquisition boards for PCI
and compact-PCI bus computers, respectively. They feature bus mastering DMA, four 16-bit, 100-kHz
D/A converters, 40 digital I/O lines, four counters, and two timers.
Up to four boards can be installed in one PC.
A 100-pin connector on the boards provides access to all of the input and output signals. Each board
accommodates all I/O with one cable and one PCI [or compact-PCI] slot, as applicable. The 100-pin I/O
connector, P4, is logically divided into three ports: P1, P2, and P3; however, DaqBoard/2004 only makes
use of the P2 and P3 pin designations.
• P1 – Not used by DaqBoard/2004
• P2 – General purpose digital I/O port with 24 lines, or digital I/O expansion port controlling up to 192
external lines.
• P3 – 16-bit digital I/O port, counter inputs, timer outputs, and analog outputs.
The on-board scan sequencer lets you select up to 512 channel/range combinations. The sequencer scans
all channels of the scan at 5 µs or 10 µs per channel.
Bus mastering allows the digital/counter input data and analog and digital output data to flow between the
PC and the DaqBoard/2004 without consuming CPU time.
DaqBoard/2004 supports several trigger modes, including:
• Digital and pattern triggering – Each board has a separate digital trigger input line, allowing TTL-
level triggering and latencies less than 5 µs. The trigger can be programmed for logic level or edge
triggering. In pattern triggering, any of the digital input ports acts as the trigger port. You can
program the digital pattern.
• Software-based triggering – The PC detects the trigger event from readings, either analog, digital, or
counter. Six pre- and post-triggering modes are supported.
The four 16-bit, 100-kHz analog output channels have an output from -10 V to +10 V. Using Bus
Mastering DMA, each D/A can output a waveform. Bus Mastering DMA also allows for digital pattern
generation on the 16-bit high-speed digital I/O port.
Other features of the DaqBoard/2004 include:
• 40 TTL-level digital I/O lines. They are divided into three 8-bit ports and one 16-bit port.
• Four 16-bit counters. Each can accept frequency inputs up to 10 MHz. The counters can be cascaded
into two 32-bit counters.
• Two 16-bit timer outputs. Each can generate square waves from 16 Hz to 1 MHz.
• Configuration through software. There are no switches or jumpers on a DaqBoard/2004.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-19
Page 42

DaqBoard/2004 Block Diagram*
Connections
Installation
I/O Connector
* The DaqBoard/2004c Block Diagram is the same, with exception that the /2004c board uses a
compact-PCI Bus instead of a standard PCI bus.
Reference Note: For the DaqBoard/2004 and DaqBoard/2004c installation procedure, refer to
either the DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide or to the DaqBoard/2000c
Series Installation Guide, as applicable. The guides are included at the beginning of this
manual.
All input and output signals are available at the board’s 100-pin P4 connector. A 3-foot, 100-conductor
ribbon cable, part number CA-195, mates with connector P4.
Reference Note: There are several P4-connector board options available for connecting the
100 pins of P4 to typical DB37 connectors (P1, P2, and P3). In addition to being briefly
discussed in chapter 3 of this manual, these options, referred to as DBK200 Series, are
detailed in the DBK Cards and Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905).
1-20 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 43

DaqBoard/2005
16 Analog
Input
40 Digital
I/O
4 Counter
Inputs
2 Timer Outputs
DaqBoard/2005 and DaqBoard/2005c are high-speed, multi-function, plug-and-play data acquisition
boards for PCI and compact-PCI bus computers, respectively. They feature a 16-bit, 200-kHz A/D
converter, digital calibration, bus mastering DMA, 40 digital I/O lines, four counters, and two timers.
Up to 470 channels of analog and digital I/O can be accessed with one board. Up to four boards can be
installed in one PC.
A 100-pin connector on the board provides access to all of the input and output signals. The Each board
accommodates all I/O with one cable and one PCI [or compact-PCI] bus-slot, as applicable. The 100-pin
I/O connector, P4, is logically divided into three ports:
• P1 – Analog input port for 16 single-ended or 8 differential analog inputs with 13 software
programmable ranges (±10 V to ±156 mV full scale).
• P2 – General purpose digital I/O port with 24 lines, or digital I/O expansion port controlling up to 192
external lines.
• P3 – 16-bit digital I/O port, counter inputs, and timer outputs.
The on-board scan sequencer lets you select up to 512 channel/range combinations. The sequencer scans
all channels of the scan at 5 µs/channel or 10 µs/channel.
Bus mastering allows analog and digital/counter input data, as well as analog and digital output data, to
flow between the PC and the board without consuming CPU time.
DaqBoard/2005 supports a full complement of trigger modes, including:
• Hardware analog triggering – A user-programmed trigger level sets an analog DAC, which is
compared in hardware to the analog input level on the selected channel. Trigger latency is < 5 µs.
• Digital and pattern triggering – Both boards have a separate digital trigger input line, allowing TTL-
level triggering and latencies less than 5 µs. The trigger can be programmed for logic level or edge
triggering. In pattern triggering, any of the digital input ports acts as the trigger port. You can program
the digital pattern.
• Software-based triggering – The PC detects the trigger event from readings, either analog, digital, or
counter. Six pre- and post-triggering modes are supported.
Bus Mastering DMA also allows for digital pattern generation on the 16-bit high-speed digital I/O port.
Other features of the DaqBoard/2005 include:
• 40 TTL-level digital I/O lines. They are divided into three 8-bit ports and one 16-bit port.
• Four 16-bit counters. Each can accept frequency inputs up to 10 MHz. The counters can be cascaded
into two 32-bit counters.
• Two 16-bit timer outputs. Each can generate square waves from 16 Hz to 1 MHz.
• Configuration through software. There are no switches or jumpers on a DaqBoard/2005.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-21
Page 44

DaqBoard/2005 Block Diagram*
Connections
Installation
I/O Connector
*The DaqBoard/2005c Block Diagram is the same, with exception that the /2005c board uses a
compact-PCI Bus instead of a standard PCI bus.
Reference Note:
For the DaqBoard/2005 and compact-PCI DaqBoard/2005c installation procedure, refer to
either the DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series Installation Guide or to the DaqBoard/2000c
Series Installation Guide, as applicable. The guides are included at the beginning of this
manual.
All input and output signals are available at the board’s 100-pin P4 connector. A 3-foot, 100-conductor
ribbon cable, part number CA-195, mates with connector P4.
Reference Note:
There are several P4-connector board options available for connecting the 100 pins of P4 to
typical DB37 connectors (P1, P2, and P3). In addition to being briefly discussed in chapter 3
of this manual, these options, referred to as DBK200 Series, are detailed in the DBK Cards
and Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905).
1-22 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 45

Using DBK Cards and Modules for Signal Conditioning
The DBK signal-conditioning cards and module are designed for use with DaqBooks, LogBooks, and
various types of data acquisition boards, i.e., ISA, PCI, and compact-PCI types. The DBKs perform best
when used with an acquisition device that can dynamically select channel, gain, and range. DBK cards and
modules with dynamic channel and gain/range selection allow for high channel-to-channel scan rates with
a variety of transducers.
Note: Only passive DBKs, such as the DBK1 BNC module, the DBK11A screw terminal card, and the
DBK40 BNC analog interface, can be used with Daq PC-Cards.
DBK output signals can be bipolar, e.g., -5 to +5 V, or unipolar, e.g., 0 to 10 V. The user can select a
range of relevant values to correspond to the lowest signal (e.g., -5 or 0 V) and the highest signal (e.g., 5 or
10 V) signal. This type of range selection guarantees the highest resolution in 12-bit or 16-bit conversion.
DBK modules share the same footprint as the DaqBook and a typical notebook PCs; allowing for
convenient stacking. The majority of these modules have their own power supply; however, several
options exist for packaging and powering the DBKs.
Reference Note:
DBK options are detailed in the DBK Option Cards and Modules User’s Manual
(p/n 457-0905). As a part of product support, this manual is automatically loaded onto your
hard drive during software installation. The default location is the Programs directory, which
can be accessed through the Windows Desktop.
Daq Software
The Daq devices have software options capable of handling most applications. Three types of software are
available:
Ready-to-use programs are convenient for fill-in-the-blank applications that do not require programming
for basic data acquisition and display:
• ready-to-use graphical programs, e.g., DaqView, DaqViewXL, and post acquisition data analysis
programs such as PostView, DIAdem, and eZ-PostView
• drivers for third-party, icon-driven software such as DASYLab and LabView
• various language drivers to aid custom programming using API
• DaqView is a Windows-based program for basic set-up and data acquisition. DaqView lets you
select desired channels, gains, transducer types (including thermocouples), and a host of other
parameters with a click of a PC’s mouse. DaqView lets you stream data to disk and display data
in numerical or graphical formats. PostView is a post-acquisition waveform-display program
within DaqView.
• DaqViewXL allows you to interface directly with Microsoft Excel to enhance data handling and
display. Within Excel you have a full-featured Daq control panel and all the data display
capabilities of Excel.
• Post acquisition data analysis programs, e.g., PostView, DIAdem, and eZ-PostView, typically
allow you to view and edit post-acquisition data.
• The Daq Configuration control panel allows for interface configuration, testing, and
troubleshooting.
Each Daq system comes with an Application Programming Interface (API). API-language drivers include
C/C++ and Visual Basic. The latest software is a 32-bit version API.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Daq Systems and Device Overviews 1-23
Page 46

Reference Notes:
Data Analysis User’s Guide, are not included as part of the hardcopy manual, but
are available in PDF version. See the PDF Note, below.
¾ Programming topics are covered in the Programmer’s User Manual (1008-0901).
As a part of product support, this manual is automatically loaded onto your hard
drive during software installation. The default location is the Programs directory,
which can be accessed through the Windows Desktop.
¾ The software document modules, DaqView, DaqViewXL, and Post Acquisition
®
PDF
Note:
During software installation, Adobe
install onto your hard drive as a part of product support. The default location is in the
PDF versions of user manuals will automatically
Programs directory, which can be accessed from the Windows Desktop. Refer to the PDF
documentation for details regarding both hardware and software.
A copy of the Adobe Acrobat Reader
®
is included on your CD. The Reader provides
a means of reading and printing the PDF documents. Note that hardcopy versions of the
manuals can be ordered from the factory.
1-24 Daq Systems and Device Overviews
889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 47

Connections and Pinouts, DaqBoard/1000 Series 2
Overview …… 2-1
TB-100 Terminal Connector Option …… 2-2
Pinout for DaqBoard/1000 and DaqBoard/1005 …… 2-3
Turn off power to all devices connected to the system before connecting cables or
setting configuration jumpers and switches. Electrical shock or damage to
equipment can result even under low-voltage conditions.
The discharge of static electricity can damage some electronic components.
Semiconductor devices are especially susceptible to ESD damage. You should
always handle components carefully, and you should never touch connector pins or
circuit components unless you are following ESD guidelines in an appropriate ESD
controlled area. Such guidelines include the use of properly grounded mats and
wrist straps, ESD bags and cartons, and related procedures.
CAUTION
CAUTION
Overview
DaqBoard/1000 Series boards communicate [external from the host PC] through a 68-pin SCSI III
connector. The TB-100 board is used to provide convenient screw-terminal connections for all signal I/O.
Pinouts for both the TB-100 and the DaqBoard/1000 Series boards follow.
Note that a TB-100 board can be easily connected to a DaqBopard/1000 or DaqBoard/1005 via a 68-
conductor, shielded cable, p/n CA-G56. The cable has a length of three feet.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 889094 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/1000 Series 2-1
Page 48

TB-100 Terminal Connector Option
The TB-100 Terminal Connector option can be used to connect all
signal I/O lines that are associated with a DaqBoard/1000 Series
device. TB-100 connects to the DaqBoard’s 68-pin SCSI III
connector via a shielded 3 ft., 68 conductor cable, p/n CA-G56.
TB-100 Pinout The “Pin” column refers to the pin no. on the 68-Pin SCSI III Connector.
TB2 Side Pin TB1 Side
+5V Vcc (+5 VDC) 19 ACH0 Analog Input CH 0 0 HI 68
GND Digital Common
A0 Digital I/O Line A0 18 AGND Analog Com
A1 Digital I/O Line A1 52 ACH1 Analog Input CH 1 1 HI 33
A2 Digital I/O Line A2 17 ACH9 Analog Input CH 9 1 LO 66
A3 Digital I/O Line A3 51 AGND Analog Com
A4 Digital I/O Line A4 16 ACH2 Analog Input CH 2 2 HI 65
A5 Digital I/O Line A5 50 ACH10 Analog Input CH 10 2 LO 31
A6 Digital I/O Line A6 15 AGND Analog Com
A7 Digital I/O Line A7 49 ACH3 Analog Input CH 3 3 HI 30
B0 Digital I/O Line B0 14 ACH11 Analog Input CH 11 3 LO 63
B1 Digital I/O Line B1 48 AGND Analog Com
B2 Digital I/O Line B2 13 ACH4 Analog Input CH 4 4 HI 28
B3 Digital I/O Line B3 47 ACH12 Analog Input CH 12 4 LO 61
B4 Digital I/O Line B4 12 AGND Analog Com
B5 Digital I/O Line B5 46 ACH5 Analog Input CH 5 5 HI 60
B6 Digital I/O Line B6 11 ACH13 Analog Input CH 13 5 LO 26
B7 Digital I/O Line B7 45 AGND Analog Com
C0 Digital I/O Line C0 10 ACH6 Analog Input CH 6 6 HI 25
C1 Digital I/O Line C1 44 ACH14 Analog Input CH 14 6 LO 58
C2 Digital I/O Line C2 9 AGND Analog Com
C3 Digital I/O Line C3 43 ACH7 Analog Input CH 7 7 HI 57
C4 Digital I/O Line C4 8 ACH15 Analog Input CH 15 7 LO 23
C5 Digital I/O Line C5 42 AGND Analog Common
C6 Digital I/O Line C6 7 SGND Low Level Sense Common 62
C7 Digital I/O Line C7 41 POSREF +5 VDC Positive Reference 20
TTLTRG TTL Trigger Input 6 AGND Analog Common
GND Digital Common
CNT0 Counter Input CTR0 5 AGND Analog Common
CNT1 Counter Input CTR1 39 XDAC0 Analog Output, DAC0 22
CNT2 Counter Input CTR2 4 AGND Analog Common
CNT3 Counter Input CTR3 38 XDAC1 Analog Output, DAC1 21
TMR0 Timer Output 0 3 AGND Analog Common
TMR1 Timer Output 1 37 XAPCR A/D Pacer Clock I/O 2
XDPCR DAC Pacer Clock I/O 1 GND Digital Common
GND Digital Common
Note 1: Digital Common Pins on the SCSI III connector are: 35, 36, and 40.
Note 2: Analog Common Pins on the SCSI III connector are: 24, 27, 29, 32, 56, 59, 64, and 67
Note 1
Note 1
Note 1
SE DIFF
ACH8 Analog Input CH 8 0 LO 34
NEGREF - 5 VDC Negative Reference 54
EGND Earth Ground N/A
Pin
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
Note 1
2-2 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/1000 Series 889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 49

Pinout for DaqBoard/1000 and DaqBoard/1005
Pin numbers refer to the 68-pin SCSI III female connector, lo c ate d o n the DaqBoard/1000
and DaqBoard/1005 boards.
Function SE DIFF Pin Pin Function SE DIFF
Analog Input CH 8 CH 0 LO 34 68 Analog Input CH 0 CH 0 HI
Analog Input CH 1 CH 1 HI 33 67 Analog Com
Analog Com 32 66 Analog Input CH 9 CH 1 LO
Analog Input CH 10 CH 2 LO 31 65 Analog Input CH 2 CH 2 HI
Analog Input CH 3 CH 3 HI 30 64 Analog Com
Analog Com 29 63 Analog Input CH 11 CH 3 LO
Analog Input CH 4 CH 4 HI 28 62
Analog Com 27 61 Analog Input CH 12 CH 4 LO
Analog Input CH 13 CH 5 LO 26 60 Analog Input CH 5 CH 5 HI
Analog Input CH 6 CH 6 HI 25 59 Analog Com
Analog Com 24 58 Analog Input CH 14 CH 6 LO
Analog Input CH 15 CH 7 LO 23 57 Analog Input CH 7 CH 7 HI
Analog Output 0 (DAC0) Note 1 22 56 Analog Common
Analog Output 1 (DAC1) Note 1 21 55 Analog Common
5 VDC Positive Reference 20 54 -5 VDC Negative Reference
Vcc (+5 VDC) 19 53 Digital Common
Digital I/O line A0 18 52 Digital I/O line A1
Digital I/O line A2 17 51 Digital I/O line A3
Digital I/O line A4 16 50 Digital I/O line A5
Digital I/O line A6 15 49 Digital I/O line A7
Digital I/O line B0 14 48 Digital I/O line B1
Digital I/O line B2 13 47 Digital I/O line B3
Digital I/O line B4 12 46 Digital I/O line B5
Digital I/O line B6 11 45 Digital I/O line B7
Digital I/O line C0 10 44 Digital I/O line C 1
Digital I/O line C2 9 43 Digital I/O line C3
Digital I/O line C4 8 42 Digital I/O line C5
Digital I/O line C6 7 41 Digital I/O line C7
TTL Trigger Input 6 40 Digital Common
Counter Input CTR0 5 39 Counter Input CTR1
Counter Input CTR2 4 38 Counter Input CTR3
Timer Output 0 3 37 Timer Output 1
A/D Pacer Clock Input/Output 2 36 Digital Common
DAC Pacer Clock I/O 1
Note 1: DAC0 and DAC1 apply to DaqBoard/1000. They do not apply to DaqBoard/1005.
35 Digital Common
Low Level Sense Common
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
889094 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/1000 Series 2-3
Page 50

2-4 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/1000 Series 889094 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 51

Connections and Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 3
Overview …… 3-1
DBK200 Series, P4 Connector Options …… 3-2
Pinouts for DaqBoard/2000 Series and /2000c Series Boards …… 3-8
CAUTION
CAUTION
Overview
Turn off power to all devices connected to the system before connecting cables or
setting configuration jumpers and switches. Electrical shock or damage to
equipment can result even under low-voltage conditions.
The discharge of static electricity can damage some electronic components.
Semiconductor devices are especially susceptible to ESD damage. You should
always handle components carefully, and you should never touch connector pins or
circuit components unless you are following ESD guidelines in an appropriate ESD
controlled area. Such guidelines include the use of properly grounded mats and
wrist straps, ESD bags and cartons, and related procedures.
DaqBoard/2000 Series and DaqBoard/2000c Series boards communicate [external from the host PC]
through the board’s 100-pin P4 connector. Typically, a DBK200 Series P4-adapter is used to provide one
or more DB37 connectors (P1, P2, P3), which are subsets of the 100-pin P4 connector.
Pinouts for P1, P2, P3, and P4 are located after the following DBK200 Series board descriptions.
DaqBoard/2000 Series and cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series boards communicate [external from the host PC]
through the board’s 100-pin P4 connector. Typically a DBK200 Series P4-adapter is used to provide one or
more DB37 connectors (P1, P2, P3).
Using a DBK201 P4-to-P1/P2/P3 Adapter
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual 898195 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 3-1
Page 52

The following matrix provides a quick comparison of the DBK200 Series adapter boards. Details for each
board are provided in the DBK Option Cards and Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905). An illustration and
brief discussion of each DBK200 Series adapter board is presented after the following table.
DBK200 Series, Adapter Board Matrix
DBK P1
Analog
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
207/CJC
208
209
210
Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes 40-pin
No No 12
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes
(Qty. 2)
No
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes
P2
Digital
No No
No
Yes
(Qty. 2)
(Qty. 2)
P3
Pulse,
Freq.,
Digital
header
for P3
screw-
term.
No
No
No
Screw
P4
Terminals
Yes
Yes Yes Custom RC
Yes Yes
Yes Yes Can carry
Yes Yes Can carry
Yes Yes Can carry
Special
Features
No
No
No No
Filter Setup.
No
No
5B modules.
relay modules.
No No
digital I/O
modules.
Comments
Analog I/O use only.
Like DBK209, except for form-factor.
DBK202 is a bare board. DBK203
consists of a DBK202 mounted in a
chassis. DBK204 consists of a DBK203
and a CA-209 CE cable kit.
Only used with DaqBoard/2003 or /2003c.
Can plug directly into P4. Screw terminals
are related to P3.
Similar to DBK202, but has a different
form-factor and has no RC filter setup.
Supports 5B-compatible Analog I/O
modules. DBK207/CJC includes Cold
Junction Compensation. Includes two P1
connectors. Screw terminals are for 5B
module connections.
Supports Opto-22 compatible Solid-StateRelay (SSR) digital modules. Includes two
P2 connectors.
Like DBK201, except for form-factor.
Supports 32 channels of digital I/O via
GrayhillTM 70M-Series mini-modules.
DBK200 Series, P4 Connector Options
Reference Note: Prior to connecting a DBK to a DaqBoard/2000 Series or /2000c Series board, refer to
the applicable DBK document module(s), in the DBK Option Cards and Modules User’s Manual
(p/n 457-0905). During software installation, the manual is automatically installed onto your hard drive as
a part of product support. The default location is the Programs directory, which can be accessed through
the Windows Desktop.
DBK200
The DBK200 P4-to-P1 adapter board provides a DB37 P1
connector.
P1 is suitable for ANALOG/IO.
DBK200 does not support Digital I/O or frequency signals.
DBK200’s P4 (100-pin connector) connects to the DaqBoard/2000
Series or DaqBoard/2000c Series board’s P4 connector via a
CA-195 Cable.
DBK200 Adapter with P1
3-2 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 898195 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual
Page 53

DBK201
The DBK201 P4-to-P1/P2/P3 adapter provides DB37 P1, P2, and
P3 connectors.
• P1 is used for ANALOG I/O.
• P2 is used for DIGITAL I/O.
• P3 is used for Pulse/Frequency
(Digital and Counter/Timer) I/O.
DBK201’s P4 (100-pin connector) connects to a DaqBoard/2000
Series or /2000c Series board’s P4 connector via a CA-195 Cable.
DBK201, P4-to-P1/P2/P3 Adapter
DBK202, DBK203, and DBK204
DBK202
P4-to-P1/P2/P3 Adapter with Screw-Terminals
and Locators for RC Filter Setup
1
Note: The DBK203, DBK204, and DBK204c modules are identical. The DBK204 designation indicates
DBK203, with Cover Plate Removed
Chassis-Mounted P4-to-P1/P2/P3 Adapter with
Screw-Terminals and Locators for RC Filter Setup
1
that the module includes a CE cable kit for use with DaqBoard/2000 Series boards that are of the
standard PCI type. The DBK204c designation indicates that the module includes a CE cable kit for
use with the compact-PCI type boards, i.e., the DaqBoard/2000c Series.
The DBK202, DBK203, DBK204, and DBK204c adapters each provide a DB37 P1 connector, DB37 P2
connector, and a 40-pin header (designated as P3).
P1 is used for ANALOG I/O •
•
P2 for DIGITAL I/O
•
P3 for Pulse/Frequency (Digital and Counter/Timer) I/O
In addition to the P1, P2, and P3 connectors, these boards include terminal blocks designated TB1 through
TB12. The blocks provide a screw-terminal connection option for P1, P2, and P3.
Each of the three adapters can be connected to the DaqBoard/2000 Series or /2000c Series 100-pin P4
connector via a CA-195 cable.
Note: These screw-terminal adapter boards provide a means of connecting signals to a DaqBoard/2000
Series or a /2000c Series board through one of three methods:
• Cables connected to P1, P2, and P3 connectors, as applicable.
• Signal wires connected to the appropriate screw-terminal blocks (TB1 through TB12).
The board’s silkscreen identifies all screw terminals.
• With a combination of the above two methods.
Note: Board images are not to the same scale.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual 898195 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 3-3
Page 54

DBK205
The DBK205 provides 12 screw-terminal connections on one terminal block (TB1) for DaqBoard/2003
and DaqBoard/2003c. The signal lines on DBK205’s P4 connector correspond with P3-associated pins on
the P4 connector of DaqBoard/2003 and /2003c. The DBK205 can connect directly to the 100-pin P4
connector on the DaqBoard/2003, or DaqBoard/2003c.
DBK205
Terminations
TB1-1 AGND
TB1-2 DAC0
TB1-3 AGND
TB1-4 DAC1
TB1-5 AGND
TB1-6 DAC2
TB1-7 AGND
TB1-8 DAC3
TB1-9 AGND
TB1-10 XTTL
TB1-11 CLK
TB1-12 DGND
DBK205 Adapter DaqBoard/2003 Block Diagram
Note: DBK205 connects directly to
DaqBoard/2003’s or /2003c’s
P4 connector.
DBK206
The DBK206 provides a P1, P2, and P3 connector and corresponding screw-terminal blocks.
P1 is used for ANALOG I/O •
•
P2 for DIGITAL I/O
•
P3 for Pulse/Frequency (Digital and Counter/Timer) I/O
DBK206, P4-to-P1/P2/P3 Adapter with Screw-Terminals
The DBK206 is suitable for both analog and digital expansion. Signal connection to a DaqBoard/2000
Series or to a DaqBoard/2000c Series board can be made as follows:
• With cables connected to P1, P2, and P3 connectors, as applicable.
• With signal wires connected to the appropriate screw-terminal blocks (TB1 through TB12).
Note that the DBK206 board’s silkscreen identifies all screw terminals.
• With a combination of the above two methods.
Regardless of which method is used, the DBK206 connects to the 100-pin P4 connector of a
DaqBoard/2000 Series or a /2000c Series board. The connection is made via a CA-195 cable. The board
contains mounting holes that allow the board to be secured inside a user-provided enclosure.
Note: Board images are not to the same scale.
3-4 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 898195 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual
Page 55

DBK207 and DBK207/CJC
The DBK207 and DBK207/CJC are carrier boards for 5B-compatible analog input modules. They
each provide:
two P1 connectors – for ANALOG I/O
•
a 5 VDC power terminal
•
footprints for sixteen 5B Modules
•
16 terminal blocks.
•
In addition, DBK207/CJC provides Cold Junction Compensation. The DBK207 and DBK207/CJC
each include a 100-pin P4 connector for use with DaqBoard/2000 Series and cPCI DaqBoard/2000c
Series Boards.
DBK207/CJC Carrier Board for 5B Compatible Modules
WARNING
Ensure that hard-wire emergency over-ride circuitry exists for all applications that
make use of dangerous switch-loads. Do not operate such switch-loads unless
emergency over-ride circuitry is present.
DBK207 and DBK207/CJC are typically installed in NEMA-type panels; however, they may be installed
on DIN rails. Separate mounting instructions are included with Rack Mount Kit (part no. Rack-DBK-3)
and with DIN-rail Mount Kit (part no. DIN-DBK-1).
DBK207 and DBK207/CJC allow Daq-based acquisition systems to use various combinations of sixteen
5B signal-conditioning modules. 5B modules can accommodate a variety of signals, including low-level
thermocouple and strain-gage signals. Configuration options are flexible. You can select the type of signal
attached to each channel. One Daq device can support up to 16 DBK207 [or DBK207/CJC] boards,
providing a maximum of 256 isolated, analog input channels. Note that Daq devices scan the channels at
the same 10 µs/channel rate as other DBKs (256 scans in 2.56 ms in a full system).
Each user-installed 5B module offers 500 V isolation from the system and between channels. Both
DBK207 and DBK207/CJC include 16 screw-terminal blocks for signal inputs. In addition, the
DBK207/CJC includes cold junction compensators (CJCs) for use with thermocouple 5B modules.
Sockets are provided for user-installed AC1362 current-sense resistor modules, as discussed in
5B Module Connection in the DBK207 section of the DBK Option Cards and Modules User’s Manual
(p/n 457-0905).
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual 898195 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 3-5
Page 56

DBK208
DBK208 is a two-bank carrier board for optically-isolated Solid-State-Relay (SSR) modules. Each
bank supports up to eight digital I/O modules. The banks can be independently set as “input” or
“output” via jumpers (JP0 for Bank 0, and JP1 for Bank 1). The I/O modules are industry standard
Opto-22 compatible, 5-volt logic level modules.
The DBK208 provides:
•
two P2 connectors for DIGITAL I/O
•
footprints for sixteen optically-isolated Solid-State-Relay (SSR) Modules
•
16 dual-screw terminal blocks.
DBK208 includes a 100-pin P4 connector for use with DaqBoard/2000 Series and /2000c Series
Boards.
DBK208 Carrier Board for Opto-22 Compatible Solid-State-Relays
WARNING
Ensure that hard-wire emergency over-ride circuitry exists for all applications that
make use of dangerous switch-loads. Do not operate such switch-loads unless
emergency over-ride circuitry is present.
Note: DBK208 is not used with DaqBoard/2003.
DBK208 boards are typically installed in NEMA-type panels; however, they may alternatively be installed
on DIN rails. Separate mounting instructions are included with Rack Mount Kit (part no. Rack-DBK-3)
and with DIN-rail Mount Kit (part no. DIN-DBK-1).
In regard to the DaqBoard/2000 Series and DaqBoard/2000c Series boards, control originates in the
board’s 100-pin P4 connector. Connection of these boards to DBK208 can be made directly or indirectly
as follows:
• Direct connection can be made from the DaqBoard/2000 Series or /2000c Series board’s
100-pin P4 connector to a DBK208’s P4 connector via a CA-195 cable.
• Indirect connection can be made using an additional DBK200 Series P4-adapter that includes
a 37-pin P2 connector. For example, one of the following could be used: DBK201, DBK202,
DBK203, DBK204, DBK206, DBK209, or another DBK208. CA-37 cables are used to
connect from P2 to P2.
Note that a single Daq-based data acquisition system can support up to 16 DBK208 boards, providing a
total of 256 channels. DBK208 boards contain two DB37 P2 connectors for the purpose of daisy-chaining
to other DBK208s or to other P2-supported devices.
3-6 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 898195 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual
Page 57

DBK209
The DBK209 is a mini-adapter board suitable for both
analog and digital expansion. The board provides three
DB37 connectors (P1, P2, and P3).
DBK209 connects to DaqBoard/2000 Series or /2000c Series
P4 connector via a CA-195 cable.
Other than the form factor, DBK209 is identical to DBK201.
• P1 is used for ANALOG I/O.
• P2 is used for DIGITAL I/O.
• P3 is used for Pulse/Frequency (Digital and
Counter/Timer) I/O.
DBK209’s P4 (100-pin connector) connects to the
DaqBoard/2000 Series or /2000c Series board’s P4
connector via a CA-195 Cable.
DBK209
P4-to-P1/P2/P3 Mini-adapter Board
DBK210
DBK210 is a four-bank carrier board for optically-isolated Grayhill 70M-Series mini-modules. Each
bank supports up to eight digital I/O modules. Each bank can be independently set to input or output.
The settings are made via micro-switches. The Grayhill 70M-Series I/O modules are industry
standard, 5-volt logic level modules.
DBK210 boards are typically installed in NEMA-type panels; however, they can be installed on DIN
rails. Separate mounting instructions are included with Rack Mount Kit (part no. Rack-DBK-3) and
with DIN-rail Mount Kit (part no. DIN-DBK-1).
DBK210 boards contain three DB37 connectors, as follows: two P2 connectors for daisy-chaining to
other DBK210s or to other P2-supported devices; one P1 connector for convenient access to the
analog input channels of a DaqBook/2000 Series or a DaqBoard/2000 Series device.
DBK210 Carrier Board for Grayhill 70M-Series Mini-Modules
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual 898195 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 3-7
Page 58

Pinouts for DaqBoard/2000 Series and /2000c Series Boards
Reference Notes: You must set up DaqView for the particular DBKs in your system. If
you are unfamiliar with the method of setting up DBKs in DaqView, or if you need a
refresher, refer to the following documents as needed.
¾ The DBK Set Up in DaqView chapter of the DBK Option Cards Modules User’s
Manual (p/n 457-0905),
¾ The DBK Option Cards Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905), for the applicable
DBK document module(s). The documentation discusses hardware configuration
aspects that require setup in software.
¾ The DaqView document module.
During software installation, documentation is automatically installed onto your hard drive
as a part of product support. The default location is the Programs directory, which can be
accessed through the Windows Desktop.
Note: As new DBKs become available, be sure to use the latest revision of DaqView with the proper
configuration options.
The following P1, P2, and P3 connector pinouts pertain to the DBK200 Series adapter boards that were
discussed in the first part of this chapter. P1, P2, and P3 are subset connectors of the 100-pin P4 connector
found on the DaqBoard/2000 Series and /2000c Series boards, and for that reason P4 pin-correlation is
provided.
CAUTION
Do not confuse connectors. Ensure that you only connect P1 I/Os to P1,
P2 I/Os to P2, and P3 I/Os to P3. Improper connection may result in equipment
damage.
Note: In the pinouts that follow, some pins are irrelevant to certain DaqBoards. For example:
DaqBoard/2002, /2002c, /2004, and 2004c have no P1 correlation; and for those boards P1 and the
associated P4 pins should be ignored. The DaqBoard/2003 and /2003c only relate to P3 and the
associated P4 pins; but for these two boards, a DBK205 screw-terminal adapter is typically used
(see page 3-3). Note that chapter 1, Device Systems and Device Overviews, contains detailed
information that is specific to each board.
3-8 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 898195 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual
Page 59

P1 for DaqBoard/2000 Series and /2000c Series Boards Analog I/O
P1
The P1 DB37 connector is
obtained with the use of
one of the following:
DBK200
DBK201
DBK202
DBK203
DBK204
DBK206
DBK207
DBK207/CJC
DBK209
The P1 DB37 connector
does not apply to DBK205
or to DBK208.
Pin Signal Name Description for P1 Pin Use P4
1 +5 Volts Expansion +5 V power (Refer to Power Management, chapter 2, in DBK Manual) A1
2 -15 Volts Expansion -15 VDC power (Refer to Power Management, ch. 2, in DBK Manual) A48
3 Expansion 7 Digital OUT, external ADDRESS select bit 3 B32
4 Expansion 9 Digital OUT, external ADDRESS select bit 1 B33
5 Expansion 5 Digital OUT, external GAIN select bit 1 B31
6 Expansion 6 Digital OUT, external GAIN select bit 0 A32
7 Ground Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3-15.
8 Negative Reference Analog, -5 V reference A36
9 Positive Reference Analog +5V reference B35
10 Not Connected N/A N/A
11 CH 15 (SE), or CH 7 LO DIFF Ch 15 HI IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 7 LO IN (differential mode) B36
12 CH 14 (SE), or CH 6 LO DIFF Ch 14 HI IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 6 LO IN (differential mode) A38
13 CH 13 (SE), or CH 5 LO DIFF Ch 13 HI IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 5 LO IN (differential mode) B39
14 CH 12 (SE), or CH 4 LO DIFF Ch 12 HI IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 4 LO IN (differential mode) A41
15 CH 11 (SE), or CH 3 LO DIFF Ch 11 HI IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 3 LO IN (differential mode) B42
16 CH 10 (SE), or CH 2 LO DIFF Ch 10 HI IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 2 LO IN (differential mode) A44
17 CH 9 (SE), or CH 1 LO DIFF Ch 9 HI IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 1 LO IN (differential mode) B45
18 CH 8 (SE), or CH 0 LO DIFF Ch 8 HI IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 0 LO IN (differential mode) A47
19 Signal Ground (SGND) Sense Common (SGND) A45
20 A/I Clock External ADC Pacer Clock Input / Internal ADC Pacer Clock Output B26
21 +15 Volts Expansion +15 V power (Refer to Power Management, chapter 2, in DBK Manual) B48
22 Expansion 8 Digital OUT, external ADDRESS select bit 2 A33
23 Expansion 10 Digital OUT, external ADDRESS select bit 0 A34
24 Not Connected N/A N/A
25 TTL Trigger Digital IN, External TTL Trigger Input A27
26 Expansion 11 Digital OUT, Simultaneous sample and hold (SSH) B34
27 Not Connected N/A N/A
28 Ground Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3- 15.
29 Ground Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3-15.
30 CH 7 (SE), or CH 7 HI DIFF Ch 7 IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 7 HI IN (differential mode) A37
31 CH 6 (SE), or CH 6 HI DIFF Ch 6 IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 6 HI IN (differential mode) B38
32 CH 5 (SE), or CH 5 HI DIFF Ch 5 IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 5 HI IN (differential mode) A40
33 CH 4 (SE), or CH 4 HI DIFF Ch 4 IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 4 HI IN (differential mode) B41
34 CH 3 (SE), or CH 3 HI DIFF Ch 3 IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 3 HI IN (differential mode) A43
35 CH 2 (SE), or CH 2 HI DIFF Ch 2 IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 2 HI IN (differential mode) B44
36 CH 1 (SE), or CH 1 HI DIFF Ch 1 IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 1 HI IN (differential mode) A46
37 CH 0 (SE), or CH 0 HI DIFF Ch 0 IN (single-ended mode) / Ch 0 HI IN (differential mode) B47
Correlation
⇐
⇐
⇐
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual 879194 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 3-9
Page 60

P2 for DaqBoard/2000 Series and /2000c Series Boards Digital I/O
P2
The P2 DB37 connector is
obtained with the use of
one of the following:
DBK201
DBK202
DBK203
DBK204
DBK206
DBK208
DBK209
Pin Signal Name Description for P2 Pin Use P4
1 Not Connected N/A N/A
2 Not Connected N/A N/A
3 Port B - B7 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port B, Bit 7; or, P2 Expansion Address Bit 0 Out B10
4 Port B - B6 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port B, Bit 6; or, P2 Expansion Address Bit 1 Out A11
5 Port B - B5 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port B, Bit 5; or, P2 Expansion Address Bit 2 Out B11
6 Port B - B4 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port B, Bit 4; or, P2 Expansion Address Bit 3 Out A12
7 Port B - B3 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port B, Bit 3; or, P2 Expansion Address Bit 4 Out B12
8 Port B - B2 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port B, Bit 2; or, P2 Expansion RESET Output A13
9 Port B - B1 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port B, Bit 1; or, P2 Expansion WRITE Output B13
10 Port B - B0 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port B, Bit 0; or, P2 Expansion READ Output A14
11 Ground Digital Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3- 15.
12 Not Connected N/A N/A
13 Ground Digital Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3- 15.
14 Not Connected N/A N/A
15 Ground Digital Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3- 15.
16 Not Connected N/A N/A
17 Ground Digital Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3- 15.
18 + 5 Volt Supply Expansion +5 Volt Power (Refer to Power Management, ch. 2, in DBK Manual) A1, B1
19 Ground Digital Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3- 15.
20 + 5 Volt Supply Expansion +5 Volt Power (Refer to Power Management, ch. 2, in DBK Manual) A1, B1
21 Ground Digital Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3- 15.
22 Port C - C7 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port C, Bit 7; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 7 A6
23 Port C - C6 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port C, Bit 6; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 6 B6
24 Port C - C5 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port C, Bit 5; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 5 A7
25 Port C - C4 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port C, Bit 4; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 4 B7
26 Port C - C3 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port C, Bit 3; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 3 A8
27 Port C - C2 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port C, Bit 2; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 2 B8
28 Port C - C1 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port C, Bit 1; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 1 A9
29 Port C - C0 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port C, Bit 0; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 0 B9
30 Port A - A7 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port A, Bit 7; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 15 A2
31 Port A - A6 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port A, Bit 6; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 14 B2
32 Port A - A5 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port A, Bit 5; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 13 A3
33 Port A - A4 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port A, Bit 4; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 12 B3
34 Port A - A3 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port A, Bit 3; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 11 A4
35 Port A - A2 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port A, Bit 2; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 10 B4
36 Port A - A1 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port A, Bit 1; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 9 A5
37 Port A - A0 Digital I/O: P2 Digital Port A, Bit 0; or, P2 Expansion Data Bit 8 B5
The P2 DB37 connector
does not apply to DBK200,
DBK205, DBK207, or
DBK207/CJC.
Correlation
⇐
⇐
⇐
⇐
⇐
⇐
3-10 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 898195 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual
Page 61

P3 for DaqBoard/2000 Series and /2000c Series Boards Pulse/Frequency/Digital I/O
(
P3
Note 2)
The P3 DB37
connector is
obtained with
the use of one
of the
following:
DBK201
DBK202
DBK203
DBK204
(Note 1)
(Note 1)
(Note 1)
(Analog Out DAC 3)
(Analog Out DAC 2)
DBK206
DBK209
Note: There is no direct pin number correlation between the
40-pin header and the DB37 P3 connector.
In regard to pins 31 through 34, see Note 3.
*
DB37 P3 Connector
DBK202, DBK203, DBK204
“On-Board” 40-Pin Header
The P3 DB37 connector does not apply to DBK200, DBK205, DBK207, DBK207/CJC, or DBK208.
Pin Signal Name Description for P3 Pin Use P4
1 Digital Ground (Note 1) Digital Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3-15.
2 Digital Ground (Note 1) Digital Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3-15.
3 Digital 7 P3 Digital Port Bit 7 B19
4 Digital 6 P3 Digital Port Bit 6 A19
5 Digital 5 P3 Digital Port Bit 5 B20
6 Digital 4 P3 Digital Port Bit 4 A20
7 Digital 3 P3 Digital Port Bit 3 B21
8 Digital 2 P3 Digital Port Bit 2 A21
9 Digital 1 P3 Digital Port Bit 1 B22
10 Digital 0 P3 Digital Port Bit 0 A22
11 Digital Ground Digital Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3-15.
12 Expansion 2 Reserved --13 Expansion 3 Reserved --14 Expansion 4 Reserved --15 Timer 0 P3 Timer 0 Output B24
16 Timer 1 P3 Timer 1 Output A25
17 Counter 2 P3 Counter 2 Input B28
18 Counter 0 P3 Counter 0 Input B29
19 + 15 Volts Expansion, +15 VDC B48
20 + 5 Volt Supply Expansion, +5 Volt Power (Refer to Power Management, ch. 2, in DBK Manual) A1, B1
21 Analog Out Clock External DAC Pacer Clock Input/Internal DAC Pacer Clock Output A26
22 Digital 15 Digital I/O; P3 Digital Port Bit 15 B15
23 Digital 14 Digital I/O; P3 Digital Port Bit 14 A15
24 Digital 13 P3 Digital Port Bit 13 B16
25 Digital 12 P3 Digital Port Bit 12 A16
26 Digital 11 P3 Digital Port Bit 11 B17
27 Digital 10 P3 Digital Port Bit 10 A17
28 Digital 9 P3 Digital Port Bit 9 B18
29 Digital 8 P3 Digital Port Bit 8 A18
30 Digital Ground Digital Common See Ground Correlation Tables, page 3-15.
31 Analog Out DAC 3 (Note 3) Analog DAC 3 Output B50
32 Analog Out DAC 2 (Note 3) Analog DAC 2 Output B49
33 Analog Out DAC 1 (Note 3) Analog DAC 1 Output A50
34 Analog Out DAC 0 (Note 3) Analog DAC 0 Output A49
35 Counter 3 P3 Counter 3 Input A28
36 Counter 1 P3 Counter 1 Input A29
37 - 15 Volts Expansion, - 15 VDC Power (Refer to Power Management, ch. 2, in DBK
Note 1: P3 pins 1 and 2 are not connected on DBK201.
Note 2: For DBK202, DBK203, and DBK204, the 37-pin P3 connector is obtained by connecting a CA-60 cable to an
“On-Board” 40-pin header.
Note 3: Pins 31, 32, 33, and 34 on the P3 DB37 connector are used for Analog Out DACs. DaqBoard/2001, /2003 & /2004 can utilize
all four pins. DaqBoard/2000 does not make use of pins 31 or 32. DaqBoard/2002 and DaqBoard/2005 boards do not make
use of pins 31 through 34 as these series two boards have no Analog Out DAC.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual 898195 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 3-11
Manual)
Correlation
⇐
⇐
⇐
⇐
A48
Page 62

P4 to P1, P2 and P3 Correlation
The following table lists the correlation between the P4 I/O lines and their respective P1, P2 an d P3 pin
locations on the DBK200 Series boards. Ground correlation is provided in a subsequent table.
P4 Pin Signal Type Description P1, P2, P3 Correlation
A1 +5VDC Power Expansion +5 Volts P1 pin 1
B1 +5VDC Power Expansion +5 Volts P1 pin 1
A2 Port A bit 7 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port A, bit 7 -or-
B2 Port A bit 6 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port A, bit 6 -or-
A3 Port A bit 5 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port A, bit 5 -or-
B3 Port A bit 4 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port A, bit 4 -or-
A4 Port A bit 3 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port A, bit 3 -or-
B4 Port A bit 2 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port A, bit 2 -or-
A5 Port A bit 1 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port A, bit 1 -or-
B5 Port A bit 0 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port A, bit 0 -or-
A6 Port C bit 7 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port C, bit 7 -or-
B6 Port C bit 6 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port C, bit 6 -or-
A7 Port C bit 5 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port C, bit 5 -or-
B7 Port C bit 4 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port C, bit 4 -or-
A8 Port C bit 3 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port C, bit 3 -or-
B8 Port C bit 2 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port C, bit 2 -or-
A9 Port C bit 1 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port C, bit 1 -or-
B9 Port C bit 0 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port C, bit 0 -or-
A10 Ground Dig I/O Digital Common See Ground Tables
B10 Port B bit 7 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port B, bit 7 -or-
A11 Port B bit 6 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port B, bit 6 -or-
B11 Port B bit 5 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port B, bit 5 -or-
A12 Port B bit 4 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port B, bit 4 -or-
B12 Port B bit 3 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port B, bit 3 -or-
This table is continued.
P2 pin 18, 20
P3 pin 20
P2 pin 18, 20
P3 pin 20
P2 pin 30
P2 expansion Data bit 15
P2 pin 31
P2 expansion Data bit 14
P2 pin 32
P2 expansion Data bit 13
P2 pin 33
P2 expansion Data bit 12
P2 pin 34
P2 expansion Data bit 11
P2 pin 35
P2 expansion Data bit 10
P2 pin 36
P2 expansion Data bit 9
P2 pin 37
P2 expansion Data bit 8
P2 pin 22
P2 expansion Data bit 7
P2 pin 23
P2 expansion Data bit 6
P2 pin 24
P2 expansion Data bit 5
P2 pin 25
P2 expansion Data bit 4
P2 pin 26
P2 expansion Data bit 3
P2 pin 27
P2 expansion Data bit 2
P2 pin 28
P2 expansion Data bit 1
P2 pin 29
P2 expansion Data bit 0
P2 pin 3
P2 expansion address bit 0
P2 pin 4
P2 expansion address bit 1
P2 pin 5
P2 expansion address bit 2
P2 pin 6
P2 expansion address bit 2
P2 pin 7
P2 expansion address bit 3
3-12 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 898195 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual
Page 63

P4 Pin Signal Type Description P1, P2, P3 Correlation
A13 Port B bit 2 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port B, bit 2 -or-
P2 expansion RESET
B13 Port B bit 1 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port B, bit 1 -or-
P2 expansion WRITE
A14 Port B bit 0 Dig I/O P2 Digital Port B, bit 0 -or-
P2 expansion READ
B14 Ground Dig I/O Digital Common See Ground Tables
A15 P3 Dig bit 14 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 14 P3 pin 23
B15 P3 Dig bit 15 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 15 P3 pin 22
A16 P3 Dig bit 12 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 12 P3 pin 25
B16 P3 Dig bit 13 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 13 P3 pin 24
A17 P3 Dig bit 10 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 10 P3 pin 27
B17 P3 Dig bit 11 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 11 P3 pin 26
A18 P3 Dig bit 8 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 8 P3 pin 29
B18 P3 Dig bit 9 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 9 P3 pin 28
A19 P3 Dig bit 6 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 6 P3 pin 4
B19 P3 Dig bit 7 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 7 P3 pin 3
A20 P3 Dig bit 4 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 4 P3 pin 6
B20 P3 Dig bit 5 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 5 P3 pin 5
A21 P3 Dig bit 2 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 2 P3 pin 8
B21 P3 Dig bit 3 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 3 P3 pin 7
A22 P3 Dig bit 0 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 0 P3 pin 10
B22 P3 Dig bit 1 Dig I/O P3 Digital Port bit 1 P3 pin 9
A23 Ground Dig I/O Digital Common See Ground Tables
B23 XCK Dig I/O Reserved No Connection
A24 Ground Dig I/O Digital Common See Ground Tables
B24 Timer 0 Dig OUT P3 Timer 0 Output P3 pin 15
A25 Timer 1 Dig OUT P3 Timer 1 Output P3 pin 16
B25 Ground Dig I/O Digital Common See Ground Tables
A26 DAC Pacer Dig I/O External DAC Pacer Clock Input /
Internal DAC Pacer Output
B26 ADC Pacer Dig I/O External ADC Pacer Clock Input /
Internal ADC Pacer Output
A27 TTL Trigger Dig IN External TTL Trigger Input P1 pin 25
B27 Ground Dig I/O Digital Common See Ground Tables
A28 Counter 3 Dig IN P3 Counter 3 Input P3 pin 35
B28 Counter 2 Dig IN P3 Counter 2 Input P3 pin 17
A29 Counter 1 Dig IN P3 Counter 1 Input P3 pin 36
B29 Counter 0 Dig IN P3 Counter 0 Input P3 pin 18
A30 CD ACK- Dig IN Reserved No Connection
B30 SDI Dig IN Reserved No Connection
A31 Ground Analog Analog Signal Common See Ground Tables
B31 XI/O Gain 1 Dig OUT Analog Expansion Gain Select bit 1 P1 pin 5
A32 XI/O Gain 0 Dig OUT Analog Expansion Gain Select bit 0 P1 pin 6
B32 XI/O Address 3 Dig OUT Analog Exp. Address Select bit 3 P1 pin 3
A33 XI/O Address 2 Dig OUT Analog Exp. Address Select bit 2 P1 pin 22
B33 XI/O Address 1 Dig OUT Analog Exp. Address Select bit 1 P1 pin 4
A34 XI/O Address 0 Dig OUT Analog Exp. Address Select bit 0 P1 pin 23
B34 External SSH Dig OUT Analog Expansion Simultaneous
Sample/Hold Signal
A35 Ground Analog Analog Signal Common See Ground Tables
B35 Positive Ref Analog Analog +5 Volt Reference P1 pin 9
A36 Negative Ref Analog Analog -5 Volt Reference P1 pin 8
B36 Analog In Ch15 Analog Analog Input Chan 15 (SE)
Analog Input Chan 7L (DIF)
A37 Analog In Ch7 Analog Analog Input Chan 7 (SE)
Analog Input Chan 7H (DIF)
B37 Ground Analog Analog Signal Common See Ground Tables
A38 Analog In Ch14 Analog Analog Input Chan 14 (SE)
Analog Input Chan 6L (DIF)
B38 Analog In Ch6 Analog Analog Input Chan 6 (SE)
Analog Input Chan 6H (DIF)
A39 Ground Analog Analog Signal Common See Ground Tables
P2 pin 8
P2 pin 9
P2 pin 10
P3 pin 21
P1 pin 20
P1 pin 26
P1 pin 11
P1 pin 30
P1 pin 12
P1 pin 31
This table is continued.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual 898195 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 3-13
Page 64

P4 Pin Signal Type Description P1, P2, P3 Correlation
B39 Analog In Ch13 Analog Analog Input Chan 13 (SE)
A40 Analog In Ch5 Analog Analog Input Chan 5 (SE)
B40 Ground Analog Analog Signal Common See Ground Tables
A41 Analog In Ch12 Analog Analog Input Chan 12 (SE)
B41 Analog In Ch Analog Analog Input Chan 4 (SE)
A42 Ground Analog Analog Signal Common See Ground Tables
B42 Analog In Ch11 Analog Analog Input Chan 11 (SE)
A43 Analog In Ch3 Analog Analog Input Chan 3 (SE)
B43 Ground Analog Analog Signal Common See Ground Tables
A44 Analog In Ch10 Analog Analog Input Chan 10 (SE)
B44 Analog In Ch2 Analog Analog Input Chan 2 (SE)
A45 Signal Ground Analog Sense Common (SGND) P1-19
B45 Analog In Ch9 Analog Analog Input Chan 9 (SE)
A46 Analog In Ch1 Analog Analog Input Chan 1 (SE)
B46 Ground Analog Analog Signal Common See Ground Tables
A47 Analog In Ch8 Analog Analog Input Chan 8 (SE)
B47 Analog In Ch0 Analog Analog Input Chan 0 (SE)
A48 -15VDC Power Expansion -15 Volts P1 pin 2
B48 +15VDC Power Expansion +15 Volts P1 pin 21
A49 DAC 0 Analog DAC 0 Output P3 pin 34
B49 *
A50 DAC 1 Analog DAC 1 Output P3 pin 33
B50 *
DAC 2 Analog DAC 2 Output P3 pin 32
DAC 3 Analog DAC 3 Output P3 pin 31
Analog Input Chan 5L (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 5H (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 4L (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 4H (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 3L (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 3H (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 2L (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 2H (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 1L (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 1H (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 0L (DIF)
Analog Input Chan 0H (DIF)
P1 pin 13
P1 pin 32
P1 pin 14
P1 pin 33
P1 pin 15
P1 pin 34
P1 pin 16
P1 pin 35
P1 pin 17
P1 pin 36
P1 pin 18
P1 pin 37
P3 pin 37
P3 pin 19
* DAC 2 and DAC 3 (from P4 pins B49 and B50, respectiv
ely) only apply to DaqBoard/2001, /2003 /2004
and the equivalent cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Boards.
3-14 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 898195 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual
Page 65

Ground Tables – P4 Pin to P1, P2, and P3 Ground Correlation
P2-13
P2-15
P2-17
P2-19
P2-21
------P3-11
-------
P1-7
P1-28
P1-29
DBK203
DBK204
P2-11
P2-13
P2-15
P2-17
P2-19
P2-21
P3-1
P3-2
P3-11
P3-30
DBK203
DBK204
P1-7
P1-28
P1-29
DBK206 DBK207 DBK208 DBK209
P2-11
P2-13
P2-15
P2-17
P2-19
P2-21
P3-1
P3-2
P3-11
P3-30
DBK206 DBK207 DBK208 DBK209
------P1-28
P1-29
-------
------- ------- P3-1
P1-7
P1-28
P1-29
P2-11
P2-13
P2-15
P2-17
P2-19
P2-21
------- -------
Digital Common (DGND)
P4 Pin DBK200 DBK201 DBK202
A10
B14
A23
A24
B25
B27
------- ------- ------- P1-7 ------- ------- P1-7
------- P2-11
------- -------
Analog Common (AGND)
P4 Pin DBK200 DBK201 DBK202
A31
A35
B37
A39
B40
A42
B43
B46
P1-7
P1-28
P1-29
------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
------- P3-30 ------- ------- ------- ------- -------
P2-11
P2-13
P2-15
P2-17
P2-19
P2-21
P3-2
P3-11
P3-30
P1-28
P1-29
P1
P2
P3
P1
P2
P3
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual 898195 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 3-15
Page 66

3-16 Connections & Pinouts, DaqBoard/2000 Series 898195 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 User’s Manual
Page 67

CE-Compliance 4
Overview ……4-1
CE Standards and Directives …… 4-1
Safety Conditions ……4-2
Emissions/Immunity Conditions ……4-2
CE Enhancements for DBKs .…… 4-3
CE Cable Kits for DaqBoard/2000 Series and /2000c Series Boards…… 4-3
Overview
CE standards were developed by the European Union (EU) dating from 1985 and include specifications
both for safety and for EMI emissions and immunity. Now, all affected products sold in EU countries must
meet such standards. Although not required in the USA, these standards are considered good engineering
practice since they enhance safety while reducing noise and ESD problems.
In contracted and in-house testing, most Daq* products met the required specifications. Those products
not originally in compliance were redesigned accordingly. In some cases, alternate product versions, shield
plates, edge guards, special connectors, or add-on kits are required to meet CE compliance.
CE-compliant products bear the “CE” mark and include a Declaration of Conformity stating the
particular specifications and conditions that apply. The test records and supporting documentation
that validate the compliance are kept on file at the factory.
CE Standards and Directives
The electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) directives specify two basic requirements:
1. The device must not interfere with radio or telecommunications.
2. The device must be immune from electromagnetic interference from RF transmitters, etc.
The standards are published in the Official Journal of European Union under direction of CENELEC
(European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization). The specific standards relevant to Daq*
equipment are listed on the product’s Declaration of Conformity and include: CISPR22:1985;
EN55022:1988 (Information Technology Equipment, Class A for commercial/industrial use); and
EN50082-1:1992 for various categories of EMI immunity.
The safety standard that applies to Daq* products is EN 61010-1 : 1993 (Safety Requirements for
Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control, and Laboratory Use, Part 1: General Requirements).
Environmental conditions include the following:
• indoor use
• altitude up to 2000 m
• temperature 5°C to 40°C (41°F to 104°F)
• maximum relative humidity 80% for temperatures up to 31°C (87.8°F) decreasing linearly
to 50% relative humidity at 40°C (104°F)
• mains supply voltage fluctuations not to exceed ±10% of the nominal voltage
• other supply voltage fluctuations as stated by the manufacturer
• transient overvoltage according to installation categories (overvoltage categories) I, II and III
For mains supply, the minimum and normal category is II
• pollution degree I or II in accordance with IEC 664
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 959495 CE-Compliance 4-1
Page 68

For clarification, terms used in some Declarations of Conformity include:
• pollution degree: any addition of foreign matter, solid, liquid or gaseous (ionized gases) that may
produce a reduction of dielectric strength or surface resistivity. Pollution Degree I has no influence
on safety and implies: the equipment is at operating temperature with non-condensing humidity
conditions; no conductive particles are permitted in the atmosphere; warm-up time is sufficient to
avert any condensation or frost; no hazardous voltages are applied until completion of the warm-up
period. Pollution Degree II implies the expectation of occasional condensation.
• overvoltage (installation) category: classification with limits for transient overvoltage, dependent
on the nominal line voltage to earth. Category I implies signals without high transient values.
Category II applies to typical mains power lines with some transients.
Safety Conditions
Users must comply with all relevant safety conditions in the user’s manual and the Declarations of
Conformity. This manual and Daq* hardware make use of the following Warning and Caution symbols:
If you see either of these symbols on a product, carefully read the related information and be alert to the
possibility of personal injury.
Daq* products contain no user-serviceable parts; refer all service to qualified personnel. The
specific safety conditions for CE compliance vary by product; but general safety conditions include:
• The operator must observe all safety cautions and operating conditions specified in the
documentation for all hardware used.
• The host computer and all connected equipment must be CE compliant.
• All power must be off to the device and externally connected equipment before internal access to the
device is permitted.
• Isolation voltage ratings: do not exceed documented voltage limits for power and signal inputs.
All wire insulation and terminal blocks in the system must be rated for the isolation voltage in use.
Voltages above 30 Vrms or ±60 VDC must not be applied if any condensation has formed on the
device.
• Current and power use must not exceed specifications. Do not defeat fuses or other over-current
protection.
This warning symbol is used in this manual or on the equipment to warn of possible
injury or death from electrical shock under noted conditions.
This warning/caution symbol is used to warn of possible personal injury or
equipment damage under noted conditions.
Emissions/Immunity Conditions
The specific immunity conditions for CE compliance vary by product; but general immunity conditions
include:
• Cables must be shielded, braid-type with metal-shelled connectors. Input terminal connections are to
be made with shielded wire. The shield should be connected to the chassis ground with the hardware
provided.
• The host computer must be properly grounded.
• In low-level analog applications, some inaccuracy is to be expected when I/O leads are exposed to
RF fields or transients over 3 or 10 V/m as noted on the Declaration of Conformity.
4-2 CE-Compliance 959495 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 69

CE Enhancements for DBKs
The following CE enhancements are described in the individual document modules of the
DBK Cards and Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905).
• DBK41/CE
• Edge Guard (for DBK5, DBK8, and DBK44)
• Applicable cables and connectors
CE Cable Kits for DaqBoard 2000 Series and /2000c Series Boards
CAUTION
Turn OFF the power to, and UNPLUG the host PC and externally connected equipment prior to
removing the PC’s cover and removing (or installing) the DaqBoard/2000 Series [or /2000c Series]
Board. Electric shock or damage to equipment can result even under low-voltage conditions.
Take ESD precautions (packaging, proper handling, grounded wrist strap, etc.)
Use care to avoid touching board surfaces and onboard components. Only handle boards by their
edges (or ORBs, if applicable). Ensure boards do not come into contact with foreign elements such
as oils, water, and industrial particulate.
Note: The CE Cable Kit used with DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards is p/n CA-209.
The CE Cable Kit used with cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Boards is p/n CA-209c.
By following these instructions correctly, your DaqBoard/2000 Series [or /2000c Series] Board will be
CE Compliant in accordance with the conditions stated on your board’s Declaration of Conformity.
If your board is already installed, you will need to remove it from the PC before proceeding. If your board
is not yet installed, proceed to the section entitled, Install the CE ORB.
Remove DaqBoard/2000 Series or /2000c Series Board from the Host PC
For DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards [PCI type]
1. Turn the host PC’s power OFF.
2. Turn power OFF to externally connected equipment.
3. UNPLUG the host PC and all externally connected equipment.
4. Remove the PC’s cover. Refer to your PC Owner’s Manual as needed.
5. Locate the DaqBoard/2000 Series Board and carefully remove the board from its PCI slot.
For cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Boards [cPCI Type]
1. Turn the compact PC’s power OFF.
2. Turn power OFF to externally connected
equipment.
3. UNPLUG the compact PC and all
externally connected equipment.
4. Loosen the upper and lower lock screws
(see figure).
5. Push the cPCI board’s injector/ejector
down to disengage the board.
6. Slide the board free of the compact PC.
Injector/
Ejector
Lower Lock Screw
Upper Lock Screw
Removing a cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Board
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 959495 CE-Compliance 4-3
Page 70

Install the CE ORB
1. Remove the two screws that secure the standard [non-CE] ORB to the board (see figures).
2. Using the same screws, mount the CE ORB to the board. Tighten the screws snug, but do not over
tighten.
Note: For the cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Boards, the board’s edge will locate between the
Mounting DaqBoard/2000 Series and cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Boards to CE ORBs
ORB’s Retaining Edge and the two screw mounts.
Install the Board with its CE ORB
For DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards [PCI type]
If you a installing the DaqBoard/2000 Series Board for the first time, refer to chapter 1 of this manual;
or to the DaqBoard/2000 Series Quick Start Guide, prior to installing the board.
1. If you have not already done so, turn off power to, and
UNPLUG the host PC and externally connected
equipment. Then remove the PC’s cover. Refer to your
PC Owner’s Manual as needed.
2. Install the DaqBoard/2000 Series Board[with CE ORB]
as follows:
(a) Align the groove in the edge connector with the
ridge on the PCI slot.
(b) Push the DaqBoard/2000 Series Board firmly
into the PCI slot.
(c) Replace the rear panel adapter screw.
Installing a DaqBoard/2000 Series Board
3. Replace the PC’s cover.
4-4 CE-Compliance 959495 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 71

For cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Boards [cPCI Type]
If you a installing the cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Board for the first time, refer to chapter 2 of this
manual; or to the cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Quick Start Guide, prior to installing the board.
1. Turn the compact PC’s power OFF.
2. Turn power OFF to externally connected
equipment.
3. UNPLUG the compact PC and all
externally connected equipment.
4. With the board’s injector/ejector down,
slide the board into the compact PC.
Make sure you use the PCs card guides.
5. After the board is inserted, pull the cPCI
board’s injector/ejector up to engage the
board.
6. Tighten the upper and lower lock screws.
Connect the CA-195CE Cable to the Board
Note: This section includes illustrations depicting the DaqBoard/2000; but apply to both the
DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards and the cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Boards.
Upper Lock Screw
Injector/
Ejector
Lower Lock Screw
Installing a cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Board
Note: When mating P4 connectors, ensure that the P4 white locator triangles
point to each other. The triangles locate pin A1.
1. Connect one end of the CA-195CE Cable to DaqBoard/2000 Series [or /2000c Series] Board’s P4
connector. Note that either end of the cable can be connected to the board; however, the white locator
triangles must align with each other.
2. Align the Cable Clamp (1033-2009) with the
CE ORB and secure the items with two
4-40 x 3/16 screws (provided).
Note: In the right hand figure, the cable is not shown to
allow for greater clarity of parts.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 959495 CE-Compliance 4-5
Page 72

Secure the Grounding Pigtail to Cable CA-195CE
Using Cable Clamps 1033-2009, 1033-2010, and two 4_40 x 5/16 screws, secure the Grounding Pigtail to
the cable. Note that the Clamps must be positioned over the cable’s Copper Band as shown in the figure
on page 4-5. Tighten screws snug, but do not over tighten.
Note: In the following figure, the cable is not shown to allow for greater clarity of p arts.
Connect Cable and Grounding Pigtail to DBK203
Note: DBK204 [for use with DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards] consists of a DBK203 and a CA-209 CE
cable kit. DBK204c [for use with cPCI DaqBoard/2000c Series Boards] consists of a DBK203 and
a CA-209c CE cable kit.
1. Verify correct P4 connector alignment of the CA-195CE Cable and DBK203’s P4 connector.
2. Complete the connection.
3. Connect the open end of the Grounding Pigtail to the threaded insert located to the right of
DBK203’s P4 connector. See figure on page 4-5.
Note: When mating P4 connectors, ensure that the P4 white locator triangles
point to each other. The triangles locate pin A1.
At this point your board will be CE compliant, providing that the conditions listed on your board’s
Declaration of Conformity are satisfied. You can return power to the system and commence with normal
operation of your DaqBoard/2000 Series [or /2000c Series] Board.
4-6 CE-Compliance 959495 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 73

Calibration 5
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series boards are factory-calibrated. However, if adjustments are needed they
should be completed in the following order:
1. PGA Input and Output
2. Sample/Ho
3. A/D Offset and Gain
4. VDC Voltage Reference
5. DAC0 Full-Scale*
6. DAC1 Full-Scale*
7. DAC2 Full-Scale*
8. DAC3 Full-Scale*
*In regard to the various DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series boards, DAC applicability is as follows:
DaqBoard/1000 – DAC0 and DAC1 apply
DaqB
oard/1005 – No DAC
DaqBoard/2000 and /2000c– DAC0 and DAC1 apply
DaqBoard/2001 and /2001c– DAC0, DAC1, DAC2, and DAC3 apply
DaqBoard/2002 and /2002c– No DACs apply
DaqBoard/2003 and /2003c– DAC0, DAC1, DAC2, and DAC3 apply
DaqBoard/2004 and /2004c– DAC0, DAC1, DAC2, and DAC3 apply
DaqBoard/2005 and /2005c – No DACs apply
A Windows-based program, DaqCal.exe, is used to calibrate Daq systems, including analog expansion
s used in conjunction with:
cards. DaqC
al.exe i
ld Offset
Offset
s apply
• a 4.5-digit, digital multi-meter
• an adjustable voltage calibrator
• an ambient tem
To use the calibration program:
1. Launch DaqCal.
Note:
DaqCal is installed automatically from your data acquisition CD as a part of product
support. This takes place during software installation. DaqCal’s default location is the
IOtech DaqX Software fo
2. When DaqCal opens you will be prompted to select your device from a list. After doing so,
ly follow the illustrated on-screen instructions.
simp
erature meter.
p
lder, in the Programs group.
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual 959495 Calibration 5-1
Page 74

5-2 Calibration 959495 DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual
Page 75

Specifications – DaqBoard/1000 Series Boards 6
I/O Comparison Matrix
for DaqBoard/1000 Series Boards
DaqBoard
Identity
1000 16
1005 16
Analog Input
Channels
Analog Output
Channels
2
-- 24
General Specifications Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
Warm-up: 1 hour to rated specifications
Supply voltage range: 4.75 VDC to 5.25 VDC (PCI bus)
Power consumption (per board): 3.5 W
Operating temperature: 0 to +60°C
Storage temperature: -40 to +80°C
Relative Humidity: 0 to 95% non-condensing
Vibration: MIL STD 810E
Signal I/O Connector: 68-pin SCSI type III, carries all analog I/O and digital I/O
Dimensions: 165 mm W x 15 mm D x 108 mm H (6.5” x 0.6” x 4.2”)
Weight: 160 g (0.35 lbs)
Digital I/O
Channels
24
Counter
Inputs
4
4
Timer
Outputs
2
2
Analog Inputs Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
Channels: 16 single-ended or 8 differential, programmable on a per-channel basis as single-
ended or differential bipolar.
Bandwidth: 500 kHz
Settling Time: 5 µs maximum to 1 LSB for full-scale step
Maximum Input Voltage: +11V relative to analog common
Over-Voltage Protection: ±35V
Ranges:
Voltage Range
(Note 1)
-10 to +10 V 0.015+.005 1
-5 to +5 V 0.015+.005 1
-2.5 to +2.5 V 0.015+.005 1
-1.25 to +1.25 V 0.015+.005 2
-0.625 to +0.625 V 0.015+.008 2
-0.3125 to +0.3125 V 0.015+.008 3
-0.156 to +0.156 V 0.02+.008 3
Notes:
1) Specifications assume differential input single channel scan, 200 kHz scan rate, unfiltered.
2) Accuracy specification is exclusive of noise. Measurements were taken at P1.
3) Inputs shorted to signal ground (SGND). 8192 samples.
Software programmable via sequencer on a per-channel basis.
Accuracy (Note 2)
One Year, 0 to 35°C
±(% reading + % range)
Absolute Typical
Input Noise (Note 3)
(LSB rms)
10 Hz to 200 kHz
Note: Specifications subject to change without notice. 889094 Specifications – DaqBoard/1000 Series 6-1
Page 76

A/D Specifications Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
Type: Successive approximation, 200 kHz maximum conversion rate
Resolution: 16 bits
Conversion Time: 5 µs
Maximum Sample Rate: 200 kHz
Differential Nonlinearity: ±2 LSB maximum
Integral Nonlinearity: ±1 LSB maximum
Missing Codes: None, over full operating temperature range
Input Sequencer Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
Analog, digital and counter inputs can be scanned synchronously based either on an internal
programmable timer, or an external clock source. Analog and digital outputs can be synchronized to
either of these clocks.
Scan Clock Sources: 2
1. Internal, programmable from 5 µs to 5.96 hours maximum in 1 µs steps
2. External, TTL level input up to 200 kHz maximum
Programmable parameters per scan: channel (random order), gain
Depth: 512 location
On-board Channel to channel scan rate: 5 or 10 µs per channel, programmable
External Acquisition Scan Clock Input Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
Maximum rate: 200 kHz
Clock Signal Range: 0V to +5V
Minimum pulse width: 50 ns high, 50 ns low
Triggering Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
Trigger Sources:4, individually selectable for starting and stopping an acquisition. Stop acquisition
can occur on a different channel than start acquisition; stop acquisition can be triggered via modes 2,
3, or 4 described below. Pre-trigger is supported with fixed or variable pre-trigger periods.
1. Single-Channel Digital Trigger: A separate digital input is provided for digital triggering.
Latency: 5 µs max.
2. Digital Pattern Triggering: 8 or 16-bit pattern triggering on any digital input. Programmable for
trigger on equal, above, below, or within or outside of a window. Individual bits can be masked for
“don’t care” condition. Latency: One scan period maximum.
3. Counter/Totalizer Triggering: Counter/totalizer inputs can trigger an acquisition. User can select
to trigger on a frequency or on total counts that are equal, above, below, or within/outside of a
window. Latency: One scan period maximum.
4. Software Triggering: Trigger can be initiated under program control.
6-2 Specifications – DaqBoard/1000 Series
889094 Note: Specifications subject to change without notice.
Page 77

Analog Outputs Applicable to DaqBoard/1000; does not apply to DaqBoard/1005
Two analog output channels are updated synchronously relative to scanned inputs, and clocked from
either an internal onboard clock, or an external clock source. Analog outputs can also be updated
asynchronously, independent of any other scanning in
CPU and system-independent data transfers, ensuring accurate outputs that are irrespective of other
system activities. Streaming from disk or memory is supported, allowing continuous, nearly-infinite
length, waveform outputs (limited only by available PC system resources).
Channels: 2 DAC channels (DAC0, DAC1)
Resolution: 16 bits
Output v
oltage range: ±10 V
Digital Feedthru: 50 mV when updated
Output current: ±10 mA
Offset error: ±0.0045 V maximum
Gain error: ±0.01%
Update rate: 100 kHz maximum, 1.5 Hz minimum (no minimum with external clock)
Settling Time: 10 µs
maximum to 1 LSB for full-sc
Clock Sources: 4 programmable
1. Onboard D/A clock, independent of scanning input clock
2. Onboard scanning input clock
3. External D/A input clock, independent of external scanning input clock
4. External scanning input clock
the system. Bus mastering DMA provides
ale step
Digital I/O Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
Channels: 24, expandable to 208 with external DBK options
Input Scanning Modes: 2 programmable
1. Asynchronous, under program control at any time relative to input scanning
2. Synchronous with input scanning
Ports: 3 x 8-bit (82C55 emulation). Each port is programmable as input or output.
Input Characteristics: 100 Ω series, 20 pF to common
Input protection: ±8 kV ESD clamp diodes parallel
I/O leve
ls: TTL
Sampling/Update rate: 200 kHz maximum
Output Characteristics: Output 12 mA per pin, 200 mA total continuous (per bank of 24 outputs)
Counters Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
Counter inputs can be scanned synchronously along with analog and digital scanned inputs, based
either on internal programmable timer, or an external clock source. Bus mastering DMA provides
CPU and system-independent data transfers, insuring data acquisition performance irrespective of
other system activities. Counters can be configured to clear when read, or to totalize and clear under
program control.
Channels: 4 x 16-bit, cascadable as 2 x 32-bit
Frequency Measurement Rate: 10 MHz maximum
Input Signal Range: -15 V to +15 V
Input Characteristics: 2.7 kΩ series in parallel with 20 pF to common and 10 kΩ to +5 V
Input protection: ±8 kV ESD clamp diodes parallel
Trigger Lev
Minimum pulse width: 50 ns high, 50 ns low
el: TTL
Note: Specifications subject to change without notice. 889094 Specifications – DaqBoard/1000 Series 6-3
Page 78

Frequency/Pulse Generators Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
Channels: 2 x 16-bit
Output Waveform: Square wave
Output rate: 1 MHz base rate divided by 1 to 65535 (programmable)
High level output voltage: 2.0 V minimum @ -3.75 mA, 3.0 V minimum @ -2.5 mA
Low level output voltage: 0.4 V maximum @ 2.5 mA
Accessories and Cables Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
Termination Board (TB-100)
Termination board with screw terminals for accessing all I/O for one DaqBoard/1000 or
DaqBoard/1005. The terminal board connects to the DaqBoard/1000 Series board’s 68-pin
connector via a CA-G56 cable.
Rack Mount Kit (Rack3)
This is a kit for mounting the TB-100 termination board to a rack.
68-Conductor Cable (CA-G56)
68-conductor, 3 ft. shielded cable. Used to connect a TB-100 terminal board to a DaqBoard/1000 or
a DaqBoard/1005.
Manual Set (Set #1033), p/n 1033-0900
This is a hardcopy set of the following 3 manuals, available for purchase.
o DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual (p/n 1033-0901)
o Programmer’s Manual for developing custom programs using API commands (p/n 1008-0901)
o DBK Option Cards & Modules User’
Note: DaqBoard/1000 Series boards do not support DBK options.
s Manual (p/n 457-0905)
Software Applicable to DaqBoard/1000, /1005
DaqView for setup, data acquisition display and analysis.
DaqViewXL for seamless execution within Microsoft Excel’s tool palette.
eZ-PostView for post acquisition viewing and analysis.
6-4 Specifications – DaqBoard/1000 Series
889094 Note: Specifications subject to change without notice.
Page 79

Specifications – DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards 7
I/O Comparison Matrix
for DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards
DaqBoard
Identity
2000 16
2001 16
2002 -- -- 40
2003
2004 -- 4
2005 16
Analog Input
Channels
-- 4
Analog Output
Channels
2
4
Digital I/O
Channels
40
40
-- 40
-- -- --
40
General Specifications Applicable to all DaqBoard/2000 Series Boards
Warm-up: 1 hour to rated specifications
Supply voltage range: 4.75 VDC to 5.25 VDC (PCI bus)
Power consumption (per board): 3.5 W (up to 10 W with external accessories)
Power Available for External Signal Conditioning and Expansion Options:
5 V at 1 A (all boards); ±15 V at 75 mA each (with exception of DaqBoard/2002)
Operating temperature: 0 to +60°C
Storage temperature: -40 to +80°C
Relative Humidity: 0 to 95% non-condensing
Vibration: MIL Std 810E
Dimensions:
DaqBoard/2000 Series: 165 mm W x 15 mm D x 108 mm H (6.5” x 0.6” x 4.2”)
DaqBoard/2000c Series: 160mm W x 19 mm D x 100 mm H (6.3” x 0.7” x 3.9”)
Weight:
DaqBoard/2000 Series: 160 g (0.35 lbs)
DaqBoard/2000c Series: 178.95 g (0.39 lbs)
Counter
Inputs
4
4
4
4
4
Timer
Outputs
2
2
2
2
2
Note: Specifications subject to change without notice. 889094 Specifications – DaqBoard/2000 Series 7-1
Page 80

Analog Specifications Applicable to DaqBoard/2000, /2001, /2005
A/D: Successive approximation, 200 kHz maximum conversion rate
Resolution: 16 bits
Channels: 16 single-ended or 8 differential, expandable up to 256 differential
Conversion Time: 5 µs
Connector: 100-pin high-density edge-type
Missing Codes: None, over full operating temperature range
Input Voltage Ranges (software programmable via sequencer):
Voltage Range
0 to +10 V 0.015+.005 1
0 to +5 V 0.015+.005 1
0 to +2.5 V 0.015+.005 1
0 to +1.25 V 0.015+.008 2
0 to +0.625 V 0.015+.008 2
0 to +0.3125 V 0.015+.008 2
-10 to +10 V 0.015+.005 1
-5 to +5 V 0.015+.005 1
-2.5 to +2.5 V 0.015+.005 1
-1.25 to +1.25 V 0.015+.005 2
-0.625 to +0.625 V 0.015+.008 2
-0.3125 to +0.3125 V 0.015+.008 3
-0.156 to +0.156 V 0.02+.008 3
Accuracy (Note 2)
One Year,
0 to 35°C
±(% reading+% range)
Absolute Typical
Input Noise
(LSB rms)
10 Hz-200 kHz
(Note 3)
Notes
(1) Specifications assume
differential input single
channel scan, 200 kHz
scan rate, unfiltered.
(2) Accuracy specification is
exclusive of noise.
(3) Inputs shorted to P4-45A,
differential input, 8192
samples.
Voltage Specifications (one year, 0-35°C) Applicable to DaqBoard/2000, /2001, /2005
Differential Nonlinearity: ±2 LSB maximum
Integral Nonlinearity: ±1 LSB maximum
Temperature Coefficient: ±(10 ppm + 0.3 LSB)/°C typical
Input Impedance: 10 MΩ (single ended); 20 MΩ (differential), in parallel with 50 pF
Bias Current: <
Common Mode Rejection: 86 dB typical, from DC to 60 Hz for gains ≤8; 95 dB typical, from DC to
60 Hz for gains ≥16
Hostile Channel-to-channel Crosstalk: 100 dB DC to 60 Hz; 86 dB @10 kHz
Maximum Input Voltage: ±11 V relative to analog common
Over-Voltage Protection: ±35 V relative to analog common
1 nA (0 to 35°C)
7-2 Specifications – DaqBoard/2000 Series
889094 Note: Specifications subject to change without notice.
Page 81

Input Sequencer Applicable to DaqBoard/2000, /2001, /2002, /2004, /2005
Analog, digital and counter inputs can be scanned synchronously based either on an internal
programmable timer, or an external clock source. Analog and digital outputs can also be
synchronized to either of these clocks. Bus Mastering DMA is utilized to provide CPU and systemindependent data transfers, insuring data acquisition performance irrespective of other system
activities.
Scan Clock Sources: 2
1. Internal, programmable from 5 µs to 5.96 hours maximum in 5 µs steps
2. External, TTL level input up to 200 kHz maximum
Programmable parameters per scan: channel (random order), gain, unipolar/bipolar
Depth: 512 locations
On-board Channel to channel scan rate: 5 or 10 µs per channel, programmable
Expansion channel scan rate: 5 or 10 µs per channel, programmable
External Acquisition Scan Clock Input Applicable to DaqBoard/2000, /2001, /2005
Maximum rate: 200 kHz
Signal Range: 0V to +5V
Input Characteristics: 100 Ω series, 20 pF to common and 10 kΩ to +5V
Input protection: ±8 kV ESD clamp diodes parallel
Trigger Lev
Slew Rate Requirement: 14 V/µs minimum
Minimum pulse width: 50 ns high, 50 ns low
el: TTL
Triggering Applicable to DaqBoard/2000, /2001, /2005
Trigger Sources: 6, individually selectable for starting and stopping an acquisition. Stop acquisition
can occur on a different channel than start acquisition; stop acquisition can be triggered via modes 2,
4, 5, or 6 described below. Pre-trigger is supported with fixed or variable pre-trigger periods.
1. Single-Channel Analog Hardwa
programmed as the analog trigger channel, including any of the 256 analog expansion channels.
Input Signal Range: Anywhere within range of the selected input channel
Trigger level: Programmable (11-bit resolution), including “window triggering.”
Hysteresis: Programmable (11-bit resolution)
Latency: 5 µs maximum
2. Single-Channel Analog Software Trigger: Any analog input channel, including any of the 256
analog expansion channels, can be selected as the software trigger channel. If the trigger channel
involves a calculation, such as with temperature, then the driver automatically compensates for the
delay required to calculate the reading, resulting in a maximum latency of one scan period.
Input Signal Range: Anywhere within the range of the selected trigger channel
Trigger lev
el: Programmable (16-bit resolution), including “window triggering”
Latency: One scan period maximum
3. Single-Channel Digital Trigger: A separate digital input is provided for digital triggering
Input Signal Range: -15V to +15V
Trigger level: TTL
Minimum pulse width: 50 ns high, 50 ns low
Latency: 5 µs maximum
re Trigger: Any analog input channel can be software
Note: Specifications subject to change without notice. 889094 Specifications – DaqBoard/2000 Series 7-3
Page 82

4. Digital Pattern Triggering: 8 or 16-bit pattern triggering on any of the digital input ports.
Programmable for trigger on equal, above, below, or within or outside of a window. Individual bits
can be masked for “don’t care” condition.
Latency: One scan period maximum
5. Counter/Totalizer Triggering: Counter/totalizer inputs can trigger an acquisition. User can select
to trigger on a frequency or on total counts that are equal, above, below, or within/outside of a
window.
Latency: One scan period maximum
6. Software Triggering: Trigger can be initiated under program control.
Analog Output Applicable to DaqBoard/2000, /2001, /2003, /2004
The analog output channels are updated synchronously relative to scanned inputs, and clocked from
either an internal onboard clock, or an external clock source. Analog outputs can also be updated
asynchronously, independent of any other scanning in
CPU and system-independent data transfers, ensuring accurate outputs that are irrespective of other
system activities. Streaming from disk or memory is supported, allowing continuous, nearly-infinite
length, waveform outputs (limited only by available PC system resources).
Channels: DaqBoard/2000: 2 DAC channels (DAC0, DAC1)
DaqBoard/2001, /2003, /2004: 4 DAC channels each (DAC0, DAC1, DAC2, and DAC3)
Resolution: 16 bits
Output voltage range: ±10 V
Output current: ±10 mA
Offset error: ±0.0045 V maximum
Digital Feedthru: 50 mV when updated
Gain error: ±0.01%
Update rate: 100 kHz maximum, 1.5 Hz minimum (no minimum with external clock)
Settling Time: 10 µs
maximum to 1 LSB for full-sc
Clock Sources: 4
1. Onboard D/A clock, independent of scanning input clock
2. Onboard scanning input clock
3. External D/A input clock, independent of external scanning input clock
4. External scanning input clock
the system. Bus mastering DMA provides
ale step
Digital I/O Applicable to DaqBoard/2000, /2001, /2002, /2004, /2005
Channels: 40, expandable to 208 with external DBK options
Input Scanning Modes: 2
1. Asynchronous, under program control at any time relative to input scanning
2. Synchronous with input scanning
Ports: 3 x 8-bit (82C55 emulation), and 1 x 16-bit. Each port is programmable as input or output.
Input Characteristics: 100 Ω series, 20 pF to common
Input protection: ±8 kV ESD clamp diodes parallel
I/O levels: TTL
Sampling/Update rate: 200 kHz maximum
7-4 Specifications – DaqBoard/2000 Series
889094 Note: Specifications subject to change without notice.
Page 83

Pattern Generation Output Applicable to DaqBoard/2000, /2001, /2002, /2004, /2005
The P3 16-bit digital I/O port can be configured for 16-bit pattern generation. The pattern can be
updated synchronously with an acquisition from a file. If pattern generation mode is utilized, then the
D/A outputs can only be used in an asynchronous
system-independent data transfers, insuring data acquisition performance irrespective of other
system activities. Streaming from disk or memory is supported, allowing
length, pattern outputs (limited only by available PC system resources)
mode. Bus mastering DMA provides CPU and
continuous, nearly-infinite
Frequency/Pulse Generators Applicable to DaqBoard/2000, /2001, /2002, /2004, /2005
Channels: 2 x 16-bit
Output Waveform: Square wave
Output rate: 1 MHz base rate divided by 1 to 65535 (programmable)
High level output voltage: 2.0 V minimum @ -3.75 mA, 3.0 V minimum @ -2.5 mA
Low level output voltage: 0.4 V maximum @ 2.5 mA
Frequency/Pulse Counters Applicable to DaqBoard/2000, /2001, /2002, /2004, /2005
Counter inputs can be scanned synchronously along with analog and digital scanned inputs, based
either on internal programmable timer, or an external clock source. Bus mastering DMA provides
CPU and system-independent data transfers, insuring data acquisition performance irrespective of
other system activities. Counters can be configured to clear when read, or to totalize and clear under
program control.
Channels: 4 x 16-bit, cascadable as 2 x 32-bit
Input rate: 10 MHz maximum
Input Signal Range: -15 V to +15 V
Input Characteristics: 2.7 kΩ series in parallel with 20 pF to common and 10 kΩ to +
Input protection: ±8 kV ESD clamp diodes parallel
Trigger Lev
Minimum pulse width: 50 ns high, 50 ns low
el: TTL
5 V
Included Accessories and Software for DaqBoard/2000 Series
Software: Windows Drivers (32-bit), 90-day Getting Started DaqView
Hardware: DBK205 is included with only DaqBoard/2003 and DaqBoard/2003c. This adapter option
provides screw-terminal access to the board’s four analog outputs (DAC0, DAC1, DAC2,
and DAC3), 1 digital ground, 5 analog grounds, an
trigger (XTTL).
external clock (CLK), and an external
Note: Specifications subject to change without notice. 889094 Specifications – DaqBoard/2000 Series 7-5
Page 84

Optional Accessories for DaqBoard/2000 Series
Software: DaqView including drivers for DasyLab and LabView, eZ-PostView post-acquisition software,
DasyLab
Hardware:
CA-37-x - Expansion cable. The “x” indicates number of devices on expansion side, for example, CA-
37-1 is a DB37-to-DB37 cable that provides expansion to 1 card. CA-37 cables are used
to connect from P1 to P1, P2 to P2, or P3 to P3.
CA-195 - Interconnect cable, 3-ft, 100-conductor, mates with all above options and with
DaqBoard/2000 Series P4 connectors.
DBK200 - Adapter panel, for connection of DBK signal conditioning and expansion options (analog)
DBK201 - Adapter panel, connects DBK signal conditioning and expansion options
DBK202 - Adapter panel with screw terminals, connects DBK signal conditioning and expansion
options
DBK203 - Adapter module with screw terminals, connects DBK signal conditioning and expansion
options
DBK204 - Consists of a DBK203 and a CA-209 CE cable kit for meeting CE compliance
DBK205 - This adapter provides screw-terminal access to DaqBoard/2003’s [and DaqBoard/2003c’s]
four analog outputs (DAC0, DAC1, DAC2, and DAC3) 1 digital ground, 5 analog grounds,
an external clock (CLK), and an external trigger (XT
DBK206 - Screw-terminal board suitable for both analog and digital expansion. It provides three
DB37 connectors
(P1, P2, and P3) and corresponding terminal blocks.
DBK207 - Carrier board for 5B-compatible analog input modules. The DBK207 board includes two
P1 connectors for analog expansion, a power connection terminal, and 16 signal terminal
blocks.
DBK207/CJC - Carrier board for 5B-compatible analog input modules. T
two P1 connectors for analog expansion, a pow
16 signal terminal blocks, and cold junction sensors for cold junction compensation (CJC)
for thermocouple applications.
DBK208 - Carrier board for Opto-22 compatible solid-state-relay
board includes tw
16 signal terminal blocks.
DBK209 - mini-adapter board suitable for both analog and digital expansion. T
three DB37 connectors (P1, P2, and P3).
DBK210 - 32 channel digital I/O carrier board. The DBK210 provides: tw
connector, footprints for 32 optically-isolated Grayhill 70M-Series mini-modules, a
100-pin P4 connector, and 4 removable screw
mini-modules.
DIN-DBK-1 – DIN-rail mount kit for DBK206, DBK207, and DBK208 applications.
Rack-DBK-3 – Rack mount kit for DBK206, DBK207, DBK208, and DBK209 applications.
Manuals
Manual Set (Set #1033), p/n 1033-0900.
This is a hardcopy set of manuals that is available for purchase.
The set includes the following three manuals.
o P2 connectors for digital expansion, a power connection terminal, and
).
TL
he DBK207 board includes
er connection terminal,
(SSR) digital modules. The DBK208
he board provides
o P2 connectors, one P1
terminal blocks. Each block supports 8
DaqBoard/1000 and /2000 Series User’s Manual (p/n 1033-0901)
Programmer’s Manual for developing custom programs using API commands.
(p/n 1008-0901)
DBK Option Cards & Modules User’s Manual (p/n 457-0905)
7-6 Specifications – DaqBoard/2000 Series
889094 Note: Specifications subject to change without notice.
Page 85

Glossary
Acquisition
Analog
Analog-to-Digital
Converter (ADC)
API
Bipolar
Buffer
A collection of scans acquired at a specified rat
e as cont
rolled by the sequencer.
A signal of varying voltage or current that communicates data.
A circuit or device that converts analog values into digital values, such as binary bits, for use in
digit
al computer processing.
Application Program Interface. The interface program within the Daq system’s driver that
cludes function calls specific to Daq hardware and can be used with user-written prog r ams
in
(several languages supported).
A range of analog signals with positive and negative values (e.g., -5 to +5 V); see unipolar.
ffer refers to a ci
Bu
rcuit or device that allows a signal to pass through it, while providing
isolation, or another function, without altering the signal. Buffer usually refers to:
(a) A device or circuit that allows for the temporary storage of data during data transfers. Such
storage can compensate for differences in data flow rates. In a FIFO (First In - First Out)
buffer, the data that is stored first is also the first data to leave the buffer.
(b) A follower stage used to drive a number of gates without overloading the preceding stage.
(c) An amplifier which accepts high source impedance input and results in low source
impedance output (effectively, an impedance buffer).
Buffer Amplifier
Channel
Common mode
Common mode
voltage
Crosstalk
Digital
An amplifier used primarily to match two different impedance points, and isolate one stage from
a succeeding stage in order to prevent an undesirable interaction between the two stages. (Also
ffer).
see, Bu
In reference to Daq devices, channel sim
In a broader sense, an input channel is a signal p
refers to a single input, or output entity.
ply
ath between the transducer at the point of
measurement and the data acquisition system. A channel can go through various stages
(buffers, multiplexers, or signal conditioning amplifiers and filters). Input channels are
periodically sampled for readings.
put channel from a devi
An out
ce can be digital or analog. Outputs can vary in a programmed
way in response to an input channel signal.
Common mode pertains to signals that are identical in amplitude and duration; also can be used
in reference t
mmon mode voltage refers to a voltage magnitude (referenced t
Co
o signal components.
o a common point) that is
shared by two or more signals. Example: referenced to common, Signal 1 is +5 VDC and
Signal 2 is +6 VDC. The common mode voltage for the two signals is +5.5 VDC [(5 + 6)/2].
An undesired transfer of signals between systems or system components. Crosstalk causes
signal interference, more com
A digital signal is one of discrete value, in contrast to
monly referred to as noise.
a varying signal. Combinations of binary
digits (0s and 1s) represent digital data.
Glossary 959395 G-1
Page 86

Digital-to-Analog
Converter (DAC)
A circuit or device that converts digital values (binary bits), into analog signals.
DIP switch
Differential mode
Differential mode
voltage
ESD
Excitation
Gain
A DIP switch is a group of miniature switches in a small Dual In-li
ne Package (DIP). Typically,
users set these switches to configure their particular application.
The differential mode measures a voltage between 2 signal lines for a single channel. (Also see
single-ended mode).
Different
to a com
ial mode voltage refers to a voltage difference between two signals that are referenced
mon point. Example: Signal 1 is +5 VDC referenced to common. Signal 2 is +6 VDC
referenced to common.
If the +5 VDC signal is used as the reference, the differential mode voltage is +1 VDC
(+ 6 VDC - +5 VDC = +1 VDC).
If the +6 VDC signal is used as the reference, the differential mode voltage is -1 VDC
(+ 5 VDC - +6 VDC = -1 VDC).
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the transfer of an electrostatic charge between bodies having
different el
ectrostatic potentials. This transfer occurs during direct contact of the bodies, or
when induced by an electrostatic field. ESD energy can damage an integrated circuit (IC).
Some transducers [e.g. strain gages, thermistors, and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs)]
re a known voltage or current. Typically, the variation of this signal through the
requi
transducer corresponds to the condition measured.
The degree to which an input signal is amplified (or attenuated) to allow greater accuracy and
ion; can be expressed as ×n or ±dB.
resolut
Isolation
Linearization
Multiplexer (MUX)
Sample (reading)
Scan
Sequencer
Simultaneous
Sample-and-Hold
Single-ended mode
The arrangement or operation of a circuit so that signal
s from another circuit or device do not
affect the isolated circuit.
In reference to Daq devices, isola
tion usually refers to a separation of the direct link between the
signal source and the analog-to-digital converter (ADC). Isolation is necessary when
measuring high common-mode voltage.
Some transducers produce a voltage in linear proportion to the condition measured. Other
ansducers (e.g., thermocouples) have a nonlinear response. To convert nonlinear signals into
tr
accurate readings requires software to calibrate several points in the range used and then
interpolate values between these points.
A device that collects signals from several inputs and outputs them on a single channel.
The value of a signal on a channel at an instant in
time. W
hen triggered, the ADC reads the
channel and converts the sampled value into a 12- or 16-bit value.
A series of measurements across a pre-selected sequence of channels.
A programmable device that manages channels and channel-specific settings.
An operation that gathers samples from multiple channels at the same instant and holds these
values until all are sequentially converted to digital values.
The single-ended mode measures a voltage between a signal line and a common reference that
may
be shared with other channels. (Also see differential mode).
G-2 959395 Glossary
Page 87

Trigger
An event to start a scan or mark an inst
ant during an acquisition. The event can be defined in
various ways; e.g., a TTL signal, a specified voltage level in a monitored channel, a button
manually or mechanically engaged, a software command, etc. Some applications may use preand post-triggers to gather data around an instant or based on signal counts.
TTL
Unipolar
Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) is a circuit in which a multiple-emitter transistor has replaced
e mu
ltiple diode cluster (of the diode-transistor logic circuit); typically used to communicate
th
logic signals at 5 V.
A range of analog signals that is always zero or positive (e.g., 0 to 10 V). Evaluating a signal in
ght range (unipolar or bipolar) allows greater resolution by using the full-range of the
the ri
corresponding digital value. See bipolar.
Glossary 959395 G-3
Page 88

G-4 959395 Glossary
 Loading...
Loading...