Page 1
- 20 -
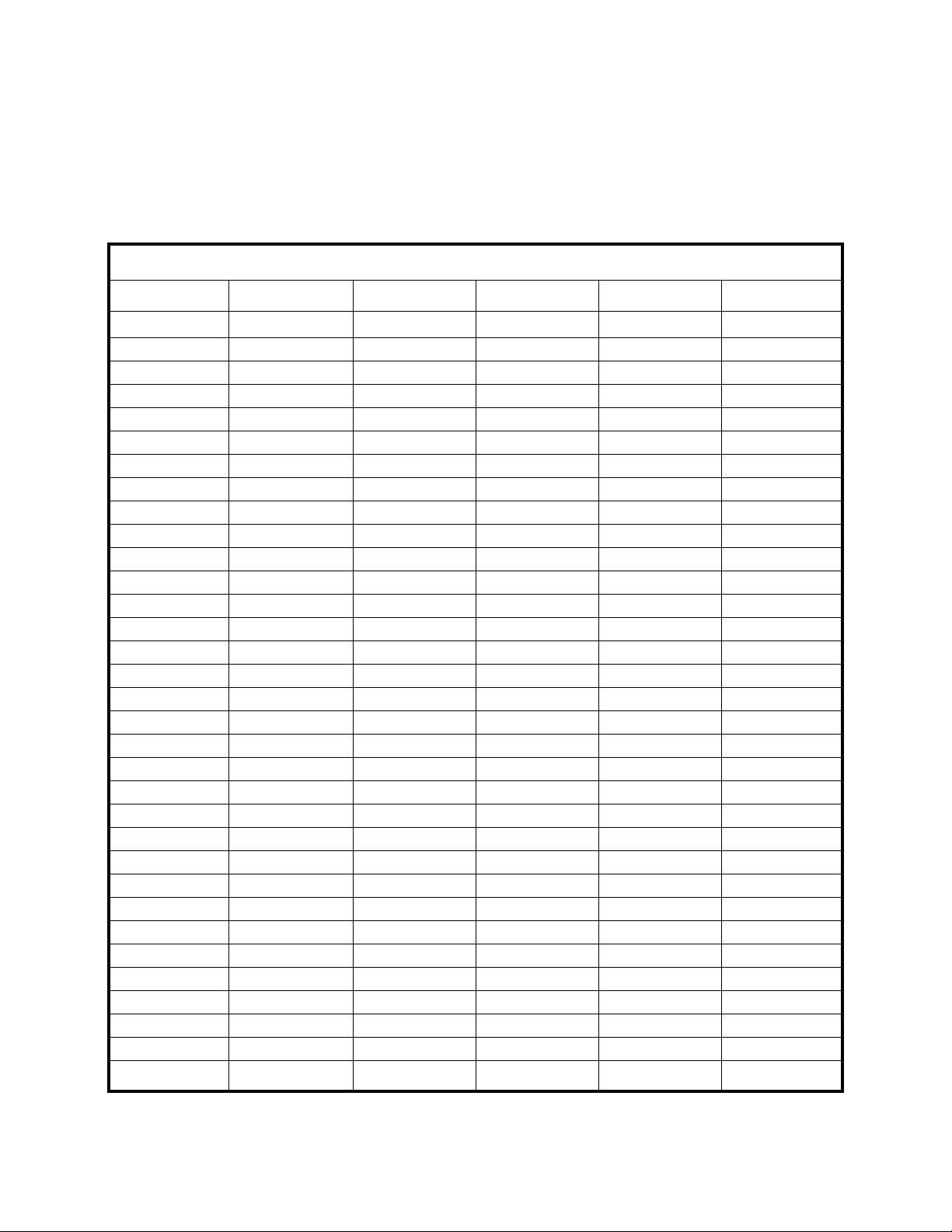
APPENDIX B: ALIGNMENT STAR LIBRARY AND STAR CHARTS:
1. Alignment Stars
The CDS utilizes 33 bright and well-known stars to calibrate the telescope’s Object Library during the
computerized alignment process. These stars were selected to allow observers from anywhere in the world
on any given night, to be able to easily and quickly make precision alignments. The CDS Alignment Star
Library and Star Charts are listed below for your reference:
CDS ALIGNMENT STAR LIBRARY
STAR NAME STAR # MAGNITUDE CONSTELL R/A DEC.
ACHERNAR 13 0.5 ERIDANUS 01 37.7 -57 14
ACRUX A 121 1.3 CRUX 12 26.6 -63 06
ALBIREO 223 3.1 CYGNUS 19 30.8 +27 58
ALKAID 140 1.9 URSA MAJOR 13 47.6 +49 19
ALDEBARAN 33 0.9 TAURUS 04 35.9 +16 31
ALNILAM 50 1.7 ORION 05 36.2 -01 12
ALPHARD 95 2.0 HYDRA 09 27.6 -08 39
ALPHEKKA 165 2.2 CORONA BOR. 15 35.5 +26 43
ALTAIR 226 0.8 AQUILA 19 50.8 +08 52
ANTARES 177 0.9 SCORPIUS 16 29.5 -26 26
ARCTURUS 147 0.0 BOOTES 14 15.7 +19 11
BETELGUESE 56 0.4 ORION 05 55.2 +07 25
BOGARDUS 58 2.6 AURIGA 05 59.8 +37 13
CANOPUS 63 -0.7 CARINA 06 24.0 -52 42
CAPELLA 42 0.1 AURIGA 05 16.6 +46 00
CASTOR A 78 1.9 GEMINI 07 34.6 +31 53
DENEB 232 1.3 CYGNUS 20 41.5 +45 17
DENEBOLA 114 2.1 LEO 11 49.1 +14 34
DIPHDA 8 2.0 CETUS 00 43.6 -17 59
ENIF 238 2.4 PEGASUS 21 44.2 +09 53
FOMALHAUT 247 1.2 PISCES AUST. 22 57.7 -29 38
HADAR 144 0.6 CENTAURUS 14 03.9 -60 24
HAMAL 17 2.0 ARIES 02 07.2 +23 28
MARKAB 249 2.5 PEGASUS 23 04.8 +15 12
MIRA 20 2.1 CETUS 02 19.4 -02 58
POLARIS 19 2.0 URSA MINOR 02 14.7 +89 17
POLLUX 81 1.1 GEMINI 07 45.4 +28 02
PROCYON 80 0.4 CANIS MINOR 07 39.3 +05 14
REGULUS 100 1.4 LEO 10 08.5 +11 58
RIGEL 41 0.1 ORION 05 14.6 -08 12
SIRIUS 67 -1.5 CANIS MAJOR 06 45.2 -16 43
SPICA 138 1.0 VIRGO 13 25.2 -11 10
VEGA 214 0.0 LYRA 18 37.0 +38 47
Page 2
- 21 -
Aldebaran
Betelgeuse
Rigel
Sirius
Overhead
Aldebaran
Betelgeuse
Rigel
Sirius
Overhead
Polaris
Alkaid
Aldebaran
Betelgeuse
Rigel
Sirius
Overhead
Polaris
Alkaid
Overhead
Alkaid
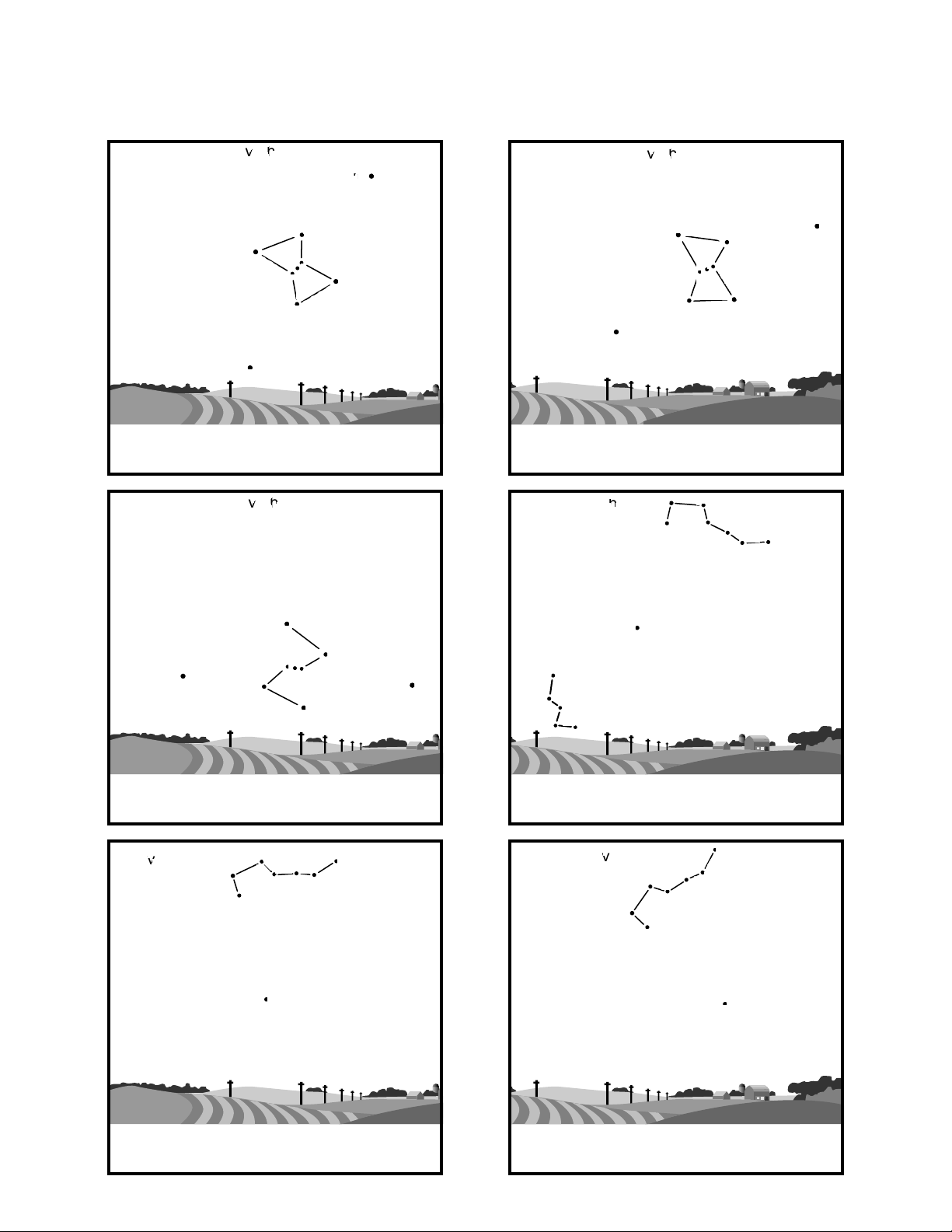
2. Star Charts (for Northern Hemisphere Observers)
SOUTHEAST
January 7:00 to 9:00
SOUTHWEST
March 7:00 to 9:00
SOUTH
February 7:00 to 9:00
NORTH
April 7:00 to 9:00
NORTH
May 7:00 to 9:00
NORTH
June 7:00 to 9:00
Page 3

- 22 -
Polaris
Alkaid
Overhead
Vega
Deneb
Polaris
Alkaid
Overhead
Vega
Deneb
Overhead
Vega
Deneb
Altair
Polaris
Alkaid
Overhead
Vega
Deneb
Overhead
Deneb
Aldebaran
Rigel
Overhead
NORTH
July 7:00 to 9:00
NORTH
September 7:00 to 9:00
NORTH
August 7:00 to 9:00
NORTH
October 7:00 to 9:00
NORTHWEST
November 7:00 to 9:00
SOUTHEAST
December 7:00 to 9:00
Page 4
- 23 -
APPENDIX C: #1697 CDS 64,359-Object Library
1. Overview: 64,359 Object Library
The CDS 64,359-Object Library is a collection of the most studied and fantastic objects in the sky.
This library consists of the following object databases:
• 110 Messier objects.
• 351 bright stars, interesting double stars and Sigma Octans (the southern star) in the star .
• 15,928 SAO (Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory) Catalog of Stars: all stars brighter than 7th
magnitude.
• 21,815 GCVS (General Catalog of Variable Stars) objects: complete catalog.
• 7,840 NGC (New General Catalog*) objects: complete catalog.
• 5,386 IC (Index Catalog*) objects: complete catalog.
• 12,921 UGC (Uppsala General Catalog) galaxies: complete catalog.
• 8 Major Planets and the Moon.
2. Accessing the Object Databases
A. Messier Catalog:
1. Press the M key.
2. Enter the number of the desired Messier object and press ENTER.
3. Object information will appear on the display.
B. Planets and Moon:
The CDS calculates the orbital positions of the Moon and the eight major planets for the current calendar
date. To access the Moon or a planet, press the STAR key and enter the appropriate number as
indicated below:
OBJECT LIBRARY PLANET LEGEND
PLANET MERCURY VENUS MOON MARS JUPITER SATURN URANUS NEPTUNE PLUTO
STAR # 901 902 903 904 905 906 907 908 909
C. Star, SAO and GCVS Catalogs:
1. Press the STAR key on the Hand Controller, then press ENTER.
2. Use the PREV and NEXT keys to cycle through the following options:
NAME Alphebetical listing of 33 bright alignment stars.
STAR 250 brightest stars, 100 interesting double stars and Sigma Octans (the southern hemisphere).
The list of stars begins on page 27.
SAO The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory catalog of stars (all stars brighter than 7th
magnitude).
GCVS The General Catalog of Variable Stars (complete catalog). Variable stars from the GCVS are
entered using a six digit number. The first two digits, refer to the constellation where the
variable star is located and is listed in the table below. The next four digits are assigned
sequentially within each constellation according to the standard sequence of variable-star
designations (R, S, ...). Therefore, the first variable star in the constellation of Virgo would be
entered as: 860001.
3. Press Enter when the desired catalog is selected. An arrow will appear to the right of the selected
catalog.
4. Press MODE to activate the curser. Using the keypad, enter the number of the desired selection
into the Hand Controler and press ENTER. The object information of the selected object then appears
on the screen.
* NGC 2000 and IC databases are copyrighted by Sky Publishing Corporation and used with their permission.
Page 5

- 24 -
D. CNGC, IC, and UGC catalogs:
1. Press the CNGC key on the Hand Controller, then press ENTER.
2. Use the PREV and NEXT keys to cycle through the following options:
NGC New General Catalog (complete catalog).
IC Index Catalog (complete catalog).
UGC Uppsala General Catalog (complete catalog).
3. Press Enter when the desired catalog is selected. An arrow will appear to the right of the selected
catalog.
4. Press MODE to activate the curser. Using the keypad, enter the number of the desired selection
into the Hand Controler and press ENTER. The object information of the selected object then appears
on the screen.
The CDS “remembers” the database you last accessed. Each time you press the CNGC key, the same
object database will be displayed on the first line of the Keypad display. To change databases, press ENTER
to bring up the database menu.
3. The Meade CNGC* Catalog
You will notice that the Messier (M) objects, and the NGC objects have been incorporated into the Meade
Instruments CNGC listing. CNGC stands for “Computerized New General Catalog of Non-Stellar
Astronomical Objects”. The CNGC is an enhancement from the RNGC (Revised New General Catalog)
in many ways. Angular sizes are given in arc-seconds on the CNGC listing, and in a convenient scaled
format on the CDS Keypad Display.
The complete CNGC contains 7,840 objects, most of which appear in the RNGC (Revised New General
Catalog) with the same number. More than 400 objects were added to the RNGC to create the CNGC. Most
of these “should have been” in the RNGC in the sense that they are bright and large enough to have been
included.
The CNGC is enhanced from the RNGC in many ways. Angular sizes are given in arc-seconds on the
CNGC listing, and in a convenient scaled format on the CDS display. Magnitudes are given to 0.1
magnitude where possible.
The coordinates in the CNGC listing are listed for the year 2000. The CDS calculates object positions upon
power up to the current date (as shown on the time/date display). This makes the CDS pointing more
accurate. Therefore, the CNGC listing and the CDS display will not exactly agree on object positions.
Objects have been assigned a “Visual Quality Rating”, henceforth called VQ. A large number of VQs have
been obtained by direct visual observations the objects. To make the VQs as useful as possible, all
observations have been made with the same telescope and eyepiece under essentially identical observing
conditions. A higher power eyepiece was used only for very small objects. Your “Visual Quality Rating” of
a particular object will vary, largely due to sky conditions.
If the object has been rated by observation, an upper-case character (ABCDEFG) is used for the VQ on the
CNGC listing. If the object has not been observed, the VQ has been estimated by a computer program from
the object type, size, and brightness and the VQ is specified in lower-case characters (abcdefg). The VQs
for visually-rated objects are a considerably more consistent guide to observability and appearance than
either the computed VQs or an examination of the type, magnitude, and size data.
All, or very nearly all, of the objects in the CNGC are visible with the standard instrumentation and observing
conditions used to obtain the visual quality ratings. It is a good indication of what can be expected with
similar equipment by experienced deep-sky observers in excellent sky conditions. Naturally smaller
telescopes and/or less optimal observing conditions will lower the apparent quality of all objects.
* The Meade CNGC Catalog is copyright by Meade Instruments Corporation.
Page 6
- 25 -
The following guide to VQs was used in the visual observing process.
SUPER Very bright object with very interesting shape or structure.
Bright object with very interesting shape or structure.
EXCEL OR
Very bright object with moderately interesting shape or structure.
Bright object with moderately interesting shape or structure.
V GOOD OR
Very bright object with little or no interesting shape or structure.
Easy to see without averted vision with some interesting shape or structure.
GOOD OR
Bright object, but little or no interesting shape or structure.
FAIR Easy to see without averted vision, but little or no interesting shape or structure.
POOR Easy to see with averted vision. Often borderline visible without averted vision.
V POOR A struggle to see with careful use of averted vision.
Not yet rated AND missing information for computer estimate.
(none) OR
Could not see despite careful use of averted vision.
The following is a description of the format of the optional CNGC listing for each object:
COLUMN NAME DESCRIPTION
1 CNGC # CNGC 0001 through CNGC 7840
2 RA Right Ascension
3 DEC Declination
4 SIZE Size of object (arc-seconds)
5 MAG Magnitude (-5.5 through 19.9)
6 TYPE Type of object
7 * * means object is not in the RNGC
8 ALT CAT Alternate catalog name and number
9 VQ Visual Quality Rating (abcdefg ) or (ABCDEFG)
10 TAGS Object Type # (0-F) : S = Sky-Cat : T = Tirion
11 COMMENTS Name, comments, other information
Page 7
- 26 -
The following types are distinguished in the CNGC.
TYPE LEGEND DESCRIPTION
0 None Unverified Southern Object
1 OPEN Open Cluster
2 GLOB Globular Cluster
3 DNEB Diffuse Nebula
4 PNEB Planetary Nebula (or SN Remnant)
5 GAL Galaxy
6 OPEN + DNEB Open Cluster + Diffuse Nebula
7 None Non-Existent Object
8 STAR Star
9 MULTI+STAR Multiple Star
A MULTI+GAL Multiple Galaxy (Usually Interacting)
B DNEB Dark Nebula in front of Diffuse Nebula
C GAL+OPEN Open Cluster in External Galaxy
D GAL+GLOB Globular Cluster in External Galaxy
E GAL+DNEB Diffuse Nebula in External Galaxy
F GAL+OPEN+DNEB Open Cluster + Diffuse Nebula in Galaxy
S Object is also listed in the Sky Catalogue 2000
T Object is also listed in the Tirion Sky Atlas 2000
Page 8

- 27 -
a. STAR CATALOG
STAR# RA DEC SIZE MAG TYPE & DESCRIPTION ALT NAME Q TAGS COMMON NAME/COMMENTS
* 1 00 08.3 +29 06 2.1v STAR B8.5p IV:(Hg+Mn) Alpha And 8 ST Alpheratz
* 2 00 09.2 +59 10 2.3v STAR F2 III-IV Beta Cas 8 ST Caph
* 3 00 13.2 +15 12 2.8v STAR B2 IV Gamma Peg 8 ST Algenib
* 4 00 25.7 -77 15 2.8v STAR G1 IV Beta Hyi 8 ST
* 5 00 26.3 -42 18 2.4v STAR K0 IIIb Alpha Phe 8 ST Ankaa
* 6 00 39.4 +30 52 3.3v STAR K3 III Delta And A 8 ST
* 7 00 40.5 +56 33 2.2v STAR K0 IIIa Alpha Cas 8 ST Shedir
* 8 00 43.6 -17 59 2.0v STAR G9.5 III Beta Cet 8 ST Diphda
* 9 00 56.7 +60 43 20 2.5v STAR B0 IVnpe(shell) + ? Gamma Cas 9 ST Marj B=8.8
* 10 01 06.1 -46 43 10 3.3v STAR G8 III Beta Phe AB 9 ST B=Similar mag & spectrum
* 11 01 09.8 +35 37 2.1v STAR M0 IIIa Beta And 8 ST Mirach
* 12 01 25.8 +60 15 2.7v STAR A5 IV Delta Cas 8 ST Ruchbah Ecl-Bin @759d
* 13 01 37.7 -57 14 0.5v STAR B3 Vnp (shell) Alpha Eri 8 ST Achernar
* 14 01 54.7 +20 49 2.6v STAR A5 V Beta Ari 8 ST Sharatan
* 15 01 58.7 -61 34 2.9v STAR A9 III-IVn Alpha Hyi 8 ST
* 16 02 04.0 +42 21 100 2.3v STAR K3 IIb + B9 V + A0 V Gamma And A 9 ST Almaak B=5.4 C=6.2
* 17 02 07.2 +23 28 2.0v STAR K2 IIIab Alpha Ari 8 ST Hamal
* 18 02 09.5 +34 59 3.0v STAR A5 IV Beta Tri 8 ST
* 19 02 14.7 +89 17 180 2.0v STAR F5-8 Ib + F3 V Alpha UMi A 9 ST Polaris B=8.2
* 20 02 19.4 -02 58 10 2.1v STAR M5.5-9 IIIe + Bpe Omicron Cet A 9 ST Mira B=9.5
* 21 02 58.3 -40 19 3.2v STAR A5 IV Theta Eri A 8 ST Acamar
* 22 03 02.3 +04 05 2.5v STAR M1.5 IIIa Alpha Cet 8 ST Menkar
* 23 03 04.8 +53 31 2.9v STAR G8 III + A2 V Gamma Per 8 ST
* 24 03 08.2 +40 58 2.1v STAR B8 V + F: Beta Per 8 ST Algol
* 25 03 24.4 +49 52 1.8v STAR F5 Ib Alpha Per 8 ST Mirphak
* 26 03 43.0 +47 48 3.0v STAR B5 IIIn Delta Per 8 ST
* 27 03 47.6 +27 06 2.9v STAR B7 IIIn Eta Tau 8 ST Alcyone
* 28 03 47.2 -74 15 3.2v STAR M2 III Gamma Hyi 8 ST
* 29 03 54.2 +31 54 130 2.9v STAR B1 Ib + B8 V Zeta Per A 9 ST B=9.2
* 30 03 57.8 +40 01 90 2.9v STAR B0.5 IV + B9.5 V Epsilon Per A 9 ST B=7.9
* 31 03 58.0 -13 30 3.0v STAR M0.5 III-IIIb Gamma Eri 8 ST Zaurak
* 32 04 34.0 -55 02 2 3.3v STAR A0p III:(Si) + B9 IV Alpha Dor AB 9 ST A=3.8 B=4.3
* 33 04 35.9 +16 31 0.9v STAR K5 III Alpha Tau A 8 ST Aldebaran
* 34 04 49.9 +06 57 3.2v STAR F6 V Pi^3 Ori 8 ST Hassaleh
* 35 04 57.0 +33 11 2.7v STAR K3 II Iota Aur 8 ST Ayn
* 36 05 02.0 +43 49 3.0v STAR A9 Iae + B Epsilon Aur A 8 ST Anz
* 37 05 05.5 -22 22 3.2v STAR K5 III Epsilon Lep 8 ST
* 38 05 06.6 +41 14 3.2v STAR B3 V Eta Ori AB 8 ST Hoedus II
* 39 05 07.9 -05 05 2.8v STAR A3 IIIn Theta Eri 8 ST Kursa
* 40 05 12.9 -16 12 3.1v STAR B9p IV: (Hg+Mn) Mu Lep 8 ST
* 41 05 14.6 -08 12 90 0.1v STAR B8 Iae + B5 V Beta Ori A 9 ST Rigel B=7.6 C=7.6
* 42 05 16.6 +46 00 0.1v STAR G6: III + G2: III Alpha Aur AB 8 ST Capella
* 43 05 24.5 -02 24 3.3v STAR B1 IV + B Eta Ori AB 8 ST
* 44 05 25.2 +06 21 1.6v STAR B2 III Gamma Ori 8 ST Bellatrix
* 45 05 26.3 +28 37 1.7v STAR B7 III Beta Tau 8 ST Alnath
* 46 05 28.3 -20 46 26 2.8v STAR G5 II + ? Beta Lep A 9 ST B=7.4
* 47 05 32.0 -00 19 2.2v STAR O9.5 II Delta Ori A 8 ST Mintaka
* 48 05 32.7 -17 49 2.6v STAR F0 Ib Alpha Lep 8 ST Arneb
* 49 05 46.5 -05 55 110 2.8v STAR O9 III + B7 IIIp Iota Ori A 9 ST Nair al Saif B=7.3
Page 9

- 28 -
STAR CATALOG
STAR# RA DEC SIZE MAG TYPE & DESCRIPTION ALT NAME Q TAGS COMMON NAME/COMMENTS
* 50 05 36.2 -01 12 1.7v STAR B0 Ia Epsilon Ori 8 ST Alnilam
* 51 05 37.6 +21 09 3.0v STAR B2 IIIpe (shell) Zeta Tau 8 ST
* 52 05 39.7 -34 04 2.6v STAR B7 IV Alpha Col A 8 ST Phaet
* 53 05 40.8 -01 56 24 2.1v STAR O9.5 Ib + B0 III Zeta Ori A 9 ST Alnitak B=4.2
* 54 05 47.8 -09 40 2.1v STAR B0.5 Ia Kappa Ori 8 ST Saiph
* 55 05 51.0 -35 46 3.1v STAR K1.5 III Beta Col 8 ST Wezn
* 56 05 55.2 +07 25 0.4v STAR M2 Iab Alpha Ori 8 ST Betelgeuse
* 57 05 59.5 +44 57 1.9v STAR A1 IV Beta Aur 8 ST Menkalinan
* 58 05 59.8 +37 13 40 2.6v STAR A0p III: (si) + G2 V Theta Aur AB 9 ST Bogardus B=7.2 G2V
* 59 06 14.9 +22 31 3.3v STAR M3 III Eta Gem 8 ST Propus
* 60 06 20.3 -30 03 3.0v STAR B2.5 V Zeta CMa 8 ST Phurud
* 61 06 22.9 +22 31 2.8v STAR M3 IIIab Mu Gem 8 ST Tejat Posterior
* 62 06 22.7 -17 58 2.0v STAR B1 II-III Beta CMa 8 ST Murzim
* 63 06 24.0 -52 42 -0.7v STAR A9 II Alpha Car 8 ST Canopus
* 64 06 37.7 +16 24 1.9v STAR A1 IVs Gamma Gem 8 ST Alhena
* 65 06 37.7 -43 12 3.2v STAR B8 IIIn Nu Pup 8 ST
* 66 06 44.0 +25 08 3.0v STAR G8 Ib Epsilon Gem 8 ST Mebsuta
* 67 06 45.2 -16 43 95 -1.5v STAR A0mA1 Va Alpha CMa A 9 ST Sirius B=8.5 50y
* 68 06 48.2 -61 56 3.3v STAR A6 Vn Alpha Pic 8 ST
* 69 06 49.9 -50 37 2.9v STAR K1 III Tau Pup 8 ST
* 70 06 58.6 -28 58 1.5v STAR B2 II Epsilon CMa A 8 ST Adara
* 71 07 03.1 -23 50 3.0v STAR B3 Iab Omicron^2 CMa 8 ST
* 72 07 08.4 -26 23 1.8v STAR F8 Ia Delta CMa 8 ST Wezen
* 73 07 13.5 -44 38 2.6v STAR M5 IIIe L2 Pup 8 ST HR2748
* 74 07 17.2 -37 05 2.7v STAR K3 Ib Pi Pup 8 ST
* 75 07 24.2 -26 19 2.5v STAR B5 Ia Eta CMa 8 ST Aludra
* 76 07 27.2 +08 17 2.9v STAR B8 V Beta CMi 8 ST Gomeisa
* 77 07 29.3 -43 17 220 3.3v STAR K5 III + G5: V Sigma Pup A 9 ST
* 78 07 34.6 +31 53 25 1.9v STAR A1 V + A2mA5 Alpha Gem A 9 ST Castor A
* 79 07 34.6 +31 53 25 2.9v STAR A2mA5 + A1 V Alpha Gem B 9 ST Castor B
* 80 07 39.3 +05 14 40 0.4v STAR F5 IV-V + ? Alpha CMi A 9 ST Procyon B=10.3
* 81 07 45.4 +28 02 1.1v STAR K0 IIIb Beta Gem 8 ST Pollux
* 82 07 49.3 -24 52 3.3v STAR G6 Ib Xi Pup 8 ST
* 83 08 03.7 -30 01 2.3v STAR O5 Iafn Zeta Pup 8 ST Naos
* 84 08 07.6 -24 19 2.7v STAR F6 IIp (var) Rho Pup 8 ST
* 85 08 09.5 -47 21 1.7v STAR WC8 + O9 I: Gamma^2 Vel 8 ST
* 86 08 22.5 -59 31 1.9v STAR K3: III Epsilon Car 8 ST Avior
* 87 08 44.7 -54 43 20 2.0v STAR A1 IV Delta Vel AB 9 ST B=5.0
* 88 08 55.5 +05 56 3.1v STAR G9 II-III Zeta Hya 8 ST
* 89 08 59.3 +48 03 40 3.1v STAR A7 IVn + M1 V Iota UMa A 9 ST Talitha BC=10.8
* 90 09 08.0 -43 25 2.2v STAR K4 Ib-IIa Lambda Vel 8 ST Suhail
* 91 09 13.3 -69 44 1.7v STAR A1 III Beta Car 8 ST Miaplacidus
* 92 09 17.1 -59 17 2.2v STAR A8 II Iota Car 8 ST Turais
* 93 09 21.1 +34 23 3.1v STAR K7 IIIab Alpha Lyn 8 ST
* 94 09 22.1 -55 01 2.5v STAR B2 IV-V Kappa Vel 8 ST
* 95 09 27.6 -08 39 2.0v STAR K3 II-III Alpha Hya 8 ST Alphard
* 96 09 31.2 -57 01 3.1v STAR K5 III N Vel 8 ST HR3803
* 97 09 33.0 +51 41 3.2v STAR F6 IV Theta UMa 8 ST
* 98 09 45.9 +23 46 3.0v STAR G1 II 1 Leo 8 ST Ras Elased Aus
* 99 09 47.2 -65 05 50 3.0v STAR A5 Ib + B7 III Nu Car AB 9 ST B=6.3
Page 10

- 29 -
STAR CATALOG
STAR# RA DEC SIZE MAG TYPE & DESCRIPTION ALT NAME Q TAGS COMMON NAME/COMMENTS
*100 10 08.5 +11 58 1.4v STAR B7 Vn Alpha Leo A 8 ST Regulus
*101 10 13.7 -70 02 3.3v STAR B8 IIIn Omega Car 8 ST
*102 10 20.0 +19 51 50 2.6v STAR K1 IIIb Fe-0.5 + * Gamma Leo A 9 ST Algieba B=3.5 G7 III Fe-1
*103 10 22.4 +41 30 3.1v STAR M0 IIIp Mu Uma 8 ST Tania Australis
*104 10 32.0 -61 42 3.3v STAR B4 Vne Rho Car 8 ST HR4140
*105 10 43.0 -64 24 2.8v STAR B0.5 Vp Theta Car 8 ST
*106 10 46.8 -49 26 20 2.7v STAR G5 III + F8: V Mu Vel AB 9 ST B=6.4
*107 10 49.7 -16 11 3.1v STAR K2 III Ny Hya 8 ST
*108 11 01.9 +56 23 2.4v STAR A0mA1 IV-V Beta UMa 8 ST Merak
*109 11 03.8 +61 45 3 1.8v STAR K0 IIIa + A8 V Alpha UMa AB 9 ST Dubhe B=4.8
*110 11 09.7 +44 30 3.0v STAR K1 III Psi UMa 8 ST
*111 11 14.2 +20 32 2.6v STAR A4 V Delta Leo 8 ST Zosma
*112 11 14.2 +15 26 3.3v STAR A2 Vs Theta Leo 8 ST Chort
*113 11 35.8 -63 02 3.1v STAR B9 III Lambda Cen 8 ST
*114 11 49.1 +14 34 2.1v STAR A3 V Beta Leo 8 ST Denebola
*115 11 53.8 +53 41 2.4v STAR A0 IV-Vn Gamma UMa 8 ST Phad
*116 12 08.4 -50 44 2.5v STAR B2 IVne Delta Cen 8 ST
*117 12 10.1 -22 37 3.0v STAR K3 IIIa Epsilon Crv 8 ST Minkar
*118 12 15.1 -58 45 2.8v STAR B2 IV Delta Cru 8 ST
*119 12 15.5 +57 01 3.3v STAR A2 IV-Vn Delta UMa 8 ST Megrez
*120 12 15.8 -17 33 2.6v STAR B8p III: (Hg+Mn) Gamma Crv 8 ST Gienah Ghurab
*121 12 26.6 -63 06 50 1.3v STAR B0.5 IV + B1 Vn Alpha Cru A 9 ST Acrux A B=1.7
*122 12 26.7 -63 07 50 1.7v STAR B1 Vn + B0.5 IV Alpha Cru B 9 ST Acrux B A=1.3
*123 12 29.9 -16 31 240 3.0v STAR B9.5 III + K2 V Delta Crv A 9 ST Algorab B=8.3
*124 12 31.2 -57 07 1.6v STAR M3.5 III Gamma Cru 8 ST Gacrux
*125 12 34.4 -23 24 2.7v STAR G5 II Beta Crv 8 ST Kraz
*126 12 37.2 -69 09 2.7v STAR B2 IV-V Alpha Mus 8 ST
*127 12 41.6 -48 58 50 2.9v STAR B9.5 III + A0 III Gamma Cen A 9 ST B=3.0
*128 12 41.5 -48 58 50 3.0v STAR A0 III + B9.5 III Gamma Cen B 9 ST A=2.9
*129 12 41.7 -01 28 40 2.8v STAR F1 V + F1 V Gamma Vir AB 9 ST Porrima B=3.5
*130 12 46.2 -68 07 10 3.1v STAR B2 V + B2.5 V Beta Mus AB 9 ST B=4.1
*131 12 47.7 -59 42 1.2v STAR B0.5 III Beta Cru 8 ST Becrux Mimosa
*132 12 54.0 +55 58 1.8v STAR A0p IV: (Cr+Eu) Epsilon UMa 8 ST Alioth
*133 12 56.1 +38 19 2.9v STAR A0p III: (Si+Eu+Sr) Alpha^2 CVn A 8 ST Cor Caroli B=5.6 F0 V
*134 13 02.2 +10 58 2.8v STAR G9 IIIab Epsilon Vir 8 ST Vindamiatrix
*135 13 19.0 -23 11 3.0v STAR G8 IIIa Gamma Hya 8 ST
*136 13 20.6 -36 43 2.8v STAR A2 V Iota Cen 8 ST
*137 13 24.0 +54 55 140 2.3v STAR A1p IV: (Si) + A1mA7 Zeta UMa A 9 ST Mizar B=3.9
*138 13 25.2 -11 10 1.0v STAR B1 V Alpha Vir 8 ST Spica
*139 13 39.9 -53 28 2.3v STAR B1 III Epsilon Cen 8 ST
*140 13 47.6 +49 19 1.9v STAR B3 V Eta UMa 8 ST Alkaid
*141 13 49.6 -42 28 3.0v STAR B2 IV-Vpne Mu Cen 8 ST
*142 13 54.7 +18 24 2.7v STAR G0 IV Eta Boo 8 ST Mufrid
*143 13 55.6 -47 17 2.6v STAR B2.5 IV Zeta Cen 8 ST
*144 14 03.9 -60 24 0.6v STAR B1 III Beta Cen AB 8 ST Hadar
*145 14 06.4 -26 41 3.3v STAR K2 IIIb Pi Hya 8 ST
*146 14 06.7 -36 22 2.1v STAR K0 IIIb Theta Cen 8 ST Menkent
*147 14 15.7 +19 11 0.0v STAR K1.5 III Fe-0.5 Alpha Boo 8 ST Arcturus
*148 14 32.1 +38 19 3.0v STAR A7 III-IV Gamma Boo 8 ST Seginus
*149 14 35.5 -42 10 2.4 STAR B1.5 IVpne Eta Cen 8 ST
Page 11

- 30 -
STAR CATALOG
STAR# RA DEC SIZE MAG TYPE & DESCRIPTION ALT NAME Q TAGS COMMON NAME/COMMENTS
*150 14 39.8 -60 51 210 0.0v STAR G2 V + K4 V Alpha Cen A 9 ST Rigil Kentaurus B=1.3
*151 14 39.8 -60 51 210 1.3v STAR K4 V + G2 V Alpha Cen B 9 ST A=0.0
*152 14 41.9 -47 24 2.3v STAR B1.5 III Alpha Lup 8 ST
*153 14 42.5 -64 59 160 3.2v STAR A7p (Sr) + K5 V Alpha Cir 9 ST B=8.6
*154 14 46.6 +27 04 30 2.4v STAR K0 II-III + A0 V Epsilon Boo 9 ST Izar B=5.1
*155 14 51.1 -51 03 2.8v STAR A3 IV Alpha Lib A 8 ST Zuben Elgenubi
*156 14 50.6 +74 10 2.1v STAR K4 III Beta UMi 8 ST Kocab
*157 14 58.5 -43 08 2.7v STAR B2 IV Beta Lup 8 ST
*158 14 59.2 -42 06 3.1v STAR B2 V Kappa Cen 8 ST
*159 15 04.1 -25 18 3.3v STAR M4 III Sigma Lib 8 ST Brachium
*160 15 17.1 -09 23 2.6v STAR B8 Vn Beta Lib 8 ST Zuben Elschemali
*161 15 18.9 -68 41 2.9v STAR A1 IIIn Gamma TrA 8 ST
*162 15 21.4 -40 39 3.2v STAR B1.5 IVn Delta Lup 8 ST
*163 15 20.7 +71 50 3.1v STAR A2.5 III Gamma UMi 8 ST Pherkad
*164 15 24.9 +58 58 3.3v STAR K2 III Iota Dra 8 ST Ed Asich
*165 15 35.5 +26 43 2.2v STAR A0 IV Gamma CrB 8 ST Alphekka
*166 15 35.1 -41 10 5 2.8v STAR B2 IVn + B2 IVn Alpha Lup AB 9 ST A=3.5 B=3.6
*167 15 54.3 +06 25 2.7v STAR K2 IIIb (CN1) Alpha Ser 8 ST Unukalhai
*168 15 55.1 -63 26 2.9v STAR F0 IV Beta Tra 8 ST
*169 15 58.9 -26 08 2.9v STAR B1 V + B2 V Pi Sco A 8 ST
*170 15 59.5 +25 54 2.0v STAR gM3: + Bep T CrB 8 ST Galt
*171 16 00.3 -22 38 2.3v STAR B0.3 IV Delta Sco AB 8 ST Dschubba
*172 16 05.5 -19 48 10 2.6v STAR B0.5 IV Beta Sco AB 9 ST Graffias B=5.0 C=4.9 @ 14"
*173 16 14.3 -03 43 2.7v STAR M0.5 III Delta Oph 8 ST Yed Prior
*174 16 18.3 -04 36 3.2v STAR G9.5 IIIb Fe-0.5 Epsilon Oph 8 ST Yed Posterior
*175 16 21.2 -25 36 200 2.9v STAR B1 III + B9 V Sigma Sco A 9 ST Alniyat B=8.3
*176 16 24.0 +61 31 60 2.7v STAR G8 IIIab Eta Dra A 9 ST Booboo B=8.7
*177 16 29.5 -26 26 30 0.9v STAR M1.5 Iab + B2.5 V Alpha Sco A 9 ST Antares B=5.4
*178 16 30.2 +21 29 2.8v STAR G7 IIIa Beta Her 8 ST Kornephoros
*179 16 35.9 -28 13 2.8v STAR B0 V Tau Sco 8 ST
*180 16 37.2 -10 34 2.6v STAR O9.5 Vn Zeta Oph 8 ST Fieht
*181 16 41.3 +31 36 11 2.8v STAR G1 IV + G7 V Zeta Her AB 9 ST B=5.5
*182 16 48.7 -69 02 1.9v STAR K2 IIb - IIIa Alpha TrA 8 ST Artia
*183 16 50.2 -34 17 2.3v STAR K2 III Epsilon Sco 8 ST
*184 16 51.9 -38 03 3.0v STAR B1.5 IVn Mu^1 Sco 8 ST
*185 16 57.7 +09 22 3.2v STAR K2 III Kappa Oph 8 ST
*186 16 58.7 -56 00 3.1v STAR K4 III Zeta Ara 8 ST
*187 17 08.7 +65 43 3.2v STAR B6 III Zeta Dra 8 ST Aldhibah
*188 17 10.4 -15 44 10 2.4v STAR A2 Vs + A3 V Eta Oph AB 9 ST Sabik A=3.0 B=3.5
*189 17 12.2 -43 14 3.3v STAR F2p V: (Cr) Eta Sco 8 ST
*190 17 14.7 +14 23 3.1v STAR M5 Ib-II Alpha Her AB 8 ST Ras Algethi
*191 17 15.1 +24 50 90 3.1v STAR A1 IVn + ? Delta Her 9 ST Sarin B=8.8
*192 17 15.1 +36 48 3.2v STAR K3 IIab Pi Her 8 ST
*193 17 22.1 -25 00 3.3v STAR B2 IV Alpha Oph 8 ST
*194 17 25.4 -55 32 2.9v STAR K3 Ib-IIa Beta Ara 8 ST
*195 17 25.5 -56 23 3.3v STAR B1 Ib Gamma Ara A 8 ST
*196 17 30.8 -37 17 2.7v STAR B2 IV Upsilon Sco 8 ST
*197 17 30.4 +52 19 40 2.8v STAR G2 Ib-IIa + ? Beta Dra A 9 ST Restaban B=11.5
*198 17 31.9 -49 52 3.0v STAR B2 Vne Alpha Ara 8 ST
*199 17 33.7 -37 07 1.6v STAR B1.5 IV Lambda Sco 8 ST Shaula
Page 12

- 31 -
STAR CATALOG
STAR# RA DEC SIZE MAG TYPE & DESCRIPTION ALT NAME Q TAGS COMMON NAME/COMMENTS
*200 17 25.0 +12 33 2.1v STAR A5 IIIn Alpha Oph 8 ST Rasalhague
*201 17 37.3 -43 00 1.9v STAR F1 II Theta Sco 8 ST Sargas
*202 17 42.6 -39 02 2.4v STAR B1.5 III Kappa Sco 8 ST
*203 17 43.5 +04 34 2.8v STAR K2 III Beta Oph 8 ST Cebalrai
*204 17 47.6 -40 07 3.0 STAR F2 Ia Iota^1 Sco 8 ST
*205 17 49.9 -37 02 3.2v STAR K2 III G Sco 8 ST HR6630
*206 17 56.6 +51 29 2.2v STAR K5 III Gamma Dra 8 ST Etamin
*207 17 59.1 -09 46 3.3v STAR K0 III Nu Oph 8 ST
*208 18 05.8 -30 26 3.0v STAR K0 III Gamma^2 Sgr 8 ST Nash
*209 18 17.7 -36 46 40 3.1v STAR M3.5 IIIab + G8: IV: Eta Sgr A 9 ST B=8.3
*210 18 21.0 -29 50 2.7v STAR K2.5 IIIa Delta Sgr 8 ST
*211 18 21.3 -02 54 3.3v STAR K0 III-IV Eta Ser 8 ST
*212 18 24.2 -34 23 1.9v STAR A0 IIInp (shell) Epsilon Sgr 8 ST Kaus Australis
*213 18 28.0 -25 25 2.8v STAR K1 IIIb Lambda Sgr 8 ST Kaus Borealis
*214 18 37.0 +38 47 0.0v STAR A0 Va Alpha Lyr 8 ST Vega
*215 18 45.7 -26 59 3.2v STAR B8.5 III Phi Sgr 8 ST
*216 18 55.3 -26 18 2.0v STAR B2.5 V Sigma Sgr 8 ST Nunki
*217 18 58.9 +32 41 3.2v STAR B9 III Gamma Lyr 8 ST Sulaphat
*218 19 02.7 -29 53 5 2.6v STAR A2.5 V + A4: V: Zeta Sgr AB 9 ST Ascella A=3.2 B=3.5
*219 19 05.5 +13 53 3.0v STAR A0 IVnn Zeta Aql A 8 ST
*220 19 07.0 -27 39 3.3v STAR K1.5 IIIb Tau Sgr 8 ST
*221 19 09.8 -21 02 6 2.9v STAR F2 II + ? + ? Pi Sgr ABC 9 ST Albaldah A=3.7 B=3.8
*222 19 12.6 +67 39 3.1v STAR G9 III Delta Dra 8 ST Nodus Secundus
*223 19 30.8 +27 58 350 3.1v STAR K3 II + B9.5 V Beta Cyg A 9 ST Albireo B=5.1
*224 19 45.0 +45 08 20 2.9v STAR B9.5 III + F1 V Delta Cyg AB 9 ST B=6.4
*225 19 46.3 +10 37 2.7v STAR K3 II Gamma Aql 8 ST Tarazed
*226 19 50.8 +08 52 0.8v STAR A7 Vn Alpha Aql 8 ST Altair
*227 20 11.3 -00 50 3.2v STAR B9.5 III Theta Aql 8 ST
*228 20 21.1 -14 46 3.1v STAR K0 II + A5 V:n Beta Cap A 8 ST Dabih
*229 20 22.2 +40 16 2.2v STAR F8 Ib Gamma Cyg 8 ST Sadr
*230 20 26.9 +15 05 1.9v STAR B2.5 V Alpha Pav 8 ST Peacock
*231 20 37.6 -47 18 3.1v STAR K0 III (Cn1) Alpha Ind 8 ST
*232 20 41.5 +45 17 1.3v STAR A2 Ia Alpha Cyg 8 ST Deneb
*233 20 46.3 +33 58 2.5v STAR K0 III Epsilon Cyg 8 ST Cat
*234 21 13.0 +30 13 3.2v STAR G8 IIIa Ba 0.6 Zeta Cyg 8 ST
*235 21 18.6 +62 36 2.4v STAR A7 IV-V Alpha Cep 8 ST Alderamin
*236 21 28.7 +70 33 3.2v STAR B1 III Beta Cep 8 ST Alphirk
*237 21 31.6 -05 35 2.9v STAR G0 Ib Beta Aqr 8 ST Sadalsuud
*238 21 44.2 +09 53 2.4v STAR K2 Ib Epsilon Peg 8 ST Enif '72 flare
*239 21 47.1 -16 07 2.9v STAR A3mF2 V: Delta Cap 8 ST
*240 21 54.0 -37 22 3.0v STAR B8 III Gamma Gru 8 ST
*241 22 05.8 -00 19 3.0v STAR G2 Ib Alpha Aqr 8 ST Sadalmelik
*242 22 08.3 -46 58 1.7v STAR B7 IV Alpha Gru 8 ST Al Nair
*243 22 18.6 -60 16 2.9v STAR K3 III Alpha Tuc 8 ST
*244 22 42.7 -46 52 2.1v STAR M5 III Beta Gru 8 ST
*245 22 43.1 +30 14 2.9v STAR G8 II + F0 V Eta Peg 8 ST Matar
*246 22 53.6 -15 50 3.3v STAR A3 IV Delta Aqr 8 ST Skat
*247 22 57.7 -29 38 1.2v STAR A3 V Alpha PsA 8 ST Fomalhaut
*248 23 03.8 +28 05 2.4v STAR M2 II-III Beta Peg 8 ST Scheat
*249 23 04.8 +15 12 2.5v STAR B9.5 V Alpha Peg 8 ST Markab
Page 13

- 32 -
STAR CATALOG
STAR# RA DEC SIZE MAG TYPE & DESCRIPTION ALT NAME Q TAGS COMMON NAME/COMMENTS
*250 23 39.4 +77 38 3.2v STAR K1 III-IV Gamma Cep 8 ST Alrai
*251 00 06.1 +58 26 15 6.4 STAR 6.4:7.2 @308 ADS 61 9 ST 1980=1.4 @287 107y
*252 00 40.0 +21 27 66 5.5 STAR 5.5:8.7 @194 ADS 558 9 ST 1964 Yellow:Blue
*253 00 42.4 +04 11 15 7.8 STAR 7.8:9.4 @207 ADS 588 9 ST 1980=1.5 @ 200
*254 00 49.9 +27 42 44 6.3 STAR 6.3:6.3 @296 ADS 683 9 ST 1959 p(Yellow:Blue)
*255 00 54.6 +19 11 5 6.2 STAR 6.2:6.9 @211 ADS 746 9 ST 1980=0.5 @ 224 400y
*256 00 55.0 +23 38 8 6.0 STAR 6.0:6.4 @292 ADS 755 9 ST 1980=0.6 @ 259
*257 01 05.7 +21 28 299 5.6 STAR 5.6:5.8 @159 ADS 899 9 ST 1964 Yellow:pBlue
*258 01 09.5 +47 15 5 4.6 STAR 4.6:5.5 @133 ADS 940 9 ST 1980=0.5 @ 140
*259 01 13.7 +07 35 230 5.6 STAR 5.6:6.6 @063 ADS 996 9 ST 1972 Yellow:pBlue
*260 01 39.8 -56 12 113 5.8 STAR 5.8:5.8 @193 p Eri 9 ST 1980=11.1 @195
*261 02 35.5 +89 35 178 2.0 STAR 2.0:8.9 @216 ADS 1477 9 ST Polaris North Star
*262 01 53.6 +19 18 78 4.6 STAR 4.6:4.7 @000 ADS 1507 9 ST 1969 1831=8.6
*263 01 55.9 +01 51 10 6.8 STAR 6.8:6.8 @057 ADS 1538 9 ST 1980=1.2 @053
*264 01 57.9 +23 36 385 4.7 STAR 4.7:7.7 @047 ADS 1563 9 ST 1973 Yellow:Blue
*265 02 02.0 +02 46 16 4.2 STAR 4.2:5.2 @273 ADS 1615 9 ST pBlue:pGreen
*266 02 03.9 +42 20 98 2.2 STAR 2.2:5.1 @063 ADS 1630 9 ST 1967 Orange:Emerald
*267 02 12.4 +30 18 39 5.3 STAR 5.3:6.9 @071 ADS 1697 9 ST 1959 Yellow:Blue
*268 02 14.0 +47 29 11 6.6 STAR 6.6:7.1 @274 ADS 1709 9 ST 1980=1.1 @266
*269 02 29.1 +67 25 25 4.6 STAR 4.6:6.9 @232 ADS 1860 9 ST 1980=2.4 @234
*270 02 37.0 +24 39 383 6.6 STAR 6.6:7.4 @276 ADS 1982 9 ST 1973 Yellow:pBlue
*271 02 43.3 +03 15 28 3.6 STAR 3.6:6.2 @297 ADS 2080 9 ST 1974 Yellow:Ashen
*272 03 14.1 +00 11 11 8.8 STAR 8.8:8.8 @139 ADS 2416 9 ST 1980=1.0 @144
*273 03 17.8 +38 38 8 7.8 STAR 7.8:8.3 @259 ADS 2446 9 ST 1980=0.9 @265
*274 03 35.0 +60 02 14 6.8 STAR 6.8:7.6 @261 ADS 2612 9 ST 1980=1.3 @258
*275 03 34.5 +24 28 7 6.6 STAR 6.6:6.7 @002 ADS 2616 9 ST 1980=0.6 @006
*276 03 50.3 +25 35 4 5.8 STAR 5.8:6.2 @211 ADS 2799 9 ST 1980=0.6 @207
*277 03 54.3 -02 57 67 4.7 STAR 4.7:6.2 @347 ADS 2850 9 ST Fixed
*278 04 09.9 +80 42 7 5.5 STAR 5.5:6.3 @120 ADS 2963 9 ST 1980=0.8 @109
*279 04 07.5 +38 05 16 7.4 STAR 7.4:8.9 @353 ADS 2995 9 ST 1980=1.4 @003
*280 04 16.0 +31 42 7 8.0 STAR 8.0:8.1 @275 ADS 3082 9 ST 1980=0.8 @270
*281 04 20.4 +27 21 496 5.1 STAR 5.1:8.5 @496 ADS 3137 9 ST 1973 Yel/Ora:Blue
*282 04 22.8 +15 03 14 7.3 STAR 7.3:8.5 @352 ADS 3169 9 ST Purple:Blue
*283 05 07.9 +08 30 7 5.8 STAR 5.8:6.5 @349 ADS 3711 9 ST 1980=0.7 @021
*284 05 14.5 -08 12 92 0.2 STAR 0.2:6.7 @206 ADS 3823 9 ST Rigel
*285 05 35.2 +09 56 43 3.6 STAR 3.6:5.5 @044 ADS 4179 9 ST 1959 Yellow:Purple
*286 05 35.3 -05 23 132 5.1 STAR 5.4:6.8:6.8 ADS 4186 9 ST Trapezium in M42
*287 06 28.8 -07 02 99 4.6 STAR 4.6:5.1:5.4 ADS 5107 9 ST Fixed White Stars
*288 06 46.3 +59 27 17 5.4 STAR 5.4:6.0 @074 ADS 5400 9 ST 1980=1.7 @079
*289 06 45.3 -16 42 45 -1.5 STAR -1.5:8.5 @005 ADS 4523 9 ST 1980=10.3 @049
*290 07 12.8 +27 14 13 7.2 STAR 7.2:7.2 @316 ADS 5871 9 ST 1980=1.3 @320 120y
*291 07 30.3 +49 59 8 8.8 STAR 8.8:8.8 @195 ADS 6117 9 ST 1980=0.8 @189
*292 07 34.6 +31 53 30 1.9 STAR 1.9:2.9 @073 ADS 6175 9 ST 1980=2.2 @095 420y
*293 08 12.2 +17 39 6 5.6 STAR 5.6:6.0 @182 ADS 6650 9 ST Yellow:Yellow:Blue
*294 09 21.1 +38 11 11 6.5 STAR 6.5:6.7 @271 ADS 7307 9 ST 1980=1.1 @254
*295 10 16.3 +17 44 14 7.2 STAR 7.2:7.5 @181 ADS 7704 9 ST 1980=1.4 @183
*296 10 20.0 +19 51 44 2.2 STAR 2.2:3.5 @124 ADS 7724 9 ST 1980=4.3 @123
*297 11 18.3 +31 32 13 4.3 STAR 4.3:4.8 @060 ADS 8119 9 ST 1980=2.9 @105
*298 11 32.4 +61 05 6 5.8 STAR 5.8:7.1 @295 ADS 8197 9 ST 1980=0.4 @211
*299 12 16.1 +40 39 115 5.9 STAR 5.9:9.0 @260 ADS 8489 9 ST 1925 Gold:Blue
Page 14

- 33 -
STAR CATALOG
STAR# RA DEC SIZE MAG TYPE & DESCRIPTION ALT NAME Q TAGS COMMON NAME/COMMENTS
*300 12 24.4 +25 35 16 6.8 STAR 6.8:7.8 @325 ADS 8539 9 ST 1980=1.5 @326
*301 12 26.6 -63 06 47 1.6 STAR 1.6:2.1 @114 Alpha Cru 9 ST 1943 White:White
*302 12 35.1 +18 22 202 5.2 STAR 5.2:6.8 @271 ADS 8600 9 ST 1963 Yellow:vBlue
*303 12 41.7 -01 28 30 3.5 STAR 3.5:3.5 @287 ADS 8630 9 ST 1980=3.9 @297 White
*304 12 53.3 +21 15 8 5.1 STAR 5.1:7.2 @194 ADS 8695 9 ST 1980=0.8 @175
*305 13 23.9 +54 55 144 2.3 STAR 2.3:4.0 @151 ADS 8891 9 ST 1967
*306 13 49.1 +26 59 34 7.6 STAR 7.6:8.0 @167 ADS 9031 9 ST 1980=3.4 @159
*307 14 15.3 +03 08 12 7.8 STAR 7.8:7.9 @239 ADS 9182 9 ST 1980=1.1 @252
*308 14 20.4 +48 30 13 8.1 STAR 8.1:8.3 @105 ADS 9229 9 ST 1980=1.2 @104 White
*309 14 40.0 -60 51 197 0.0 STAR 0.0:1.2 @214 Alpha Cen 9 ST 1980=21.8 @209
*310 14 41.2 +13 44 10 4.5 STAR 4.5:4.6 @160 ADS 9343 9 ST 1980=1.1 @305 White
*311 14 45.0 +27 04 28 2.5 STAR 2.5:5.0 @339 ADS 9372 9 ST 1971 Orange:Green
*312 14 51.4 +19 06 70 4.7 STAR 4.7:6.9 @326 ADS 9413 9 ST Orange:Blue
*313 14 51.4 +44 56 11 8.4 STAR 8.4:8.6 @348 ADS 9418 9 ST 1980=1.1 @346
*314 15 18.4 +26 50 15 7.3 STAR 7.3:7.4 @255 ADS 9578 9 ST 1980=1.4 @250
*315 15 23.2 +30 17 10 5.6 STAR 5.6:5.9 @027 ADS 9617 9 ST 1980=0.4 @321
*316 15 24.5 +37 20 22 7.0 STAR 7.0:7.6 @012 ADS 9626 9 ST 1980=2.2 @016
*317 15 34.8 +10 32 39 4.1 STAR 4.1:5.2 @179 ADS 9701 9 ST 1960 Yel-Whi:Ashen
*318 15 39.4 +36 38 63 5.1 STAR 5.1:6.0 @305 ADS 9737 9 ST 1957
*319 16 04.4 -11 22 7 4.9 STAR 4.9:4.9 @044 ADS 9909 9 ST 1980=1.2 @021
*320 16 14.7 +33 51 69 5.6 STAR 5.6:6.6 @235 ADS 9979 9 ST 1980=6.7 @233
*321 16 29.4 -26 26 24 0.9v STAR 0.9:5.5 @276 ADS 10074 9 ST Antares Red:pGreen
*322 16 28.9 +18 24 17 7.7 STAR 7.7:7.8 @129 ADS 10075 9 ST 1980=1.4 @136
*323 16 30.9 +01 59 15 4.2 STAR 4.2:5.2 @022 ADS 10087 9 ST 1980=1.3 @ 013
*324 16 56.5 +65 02 14 7.1 STAR 7.1:7.3 @069 ADS 10279 9 ST 1980=1.3 @069
*325 17 05.4 +54 28 19 5.7 STAR 5.7:5.7 @025 ADS 10345 9 ST 1980=1.9 @042
*326 17 15.4 -26 35 48 5.1 STAR 5.1:5.1 @151 ADS 10417 9 ST Orange:Orange
*327 17 14.7 +14 24 47 3.2 STAR 3.2:5.4 @107 ADS 10418 9 ST 1968 Yellow:Blue
*328 17 23.7 +37 08 40 4.6 STAR 4.6:5.5 @316 ADS 10526 9 ST 1964
*329 18 01.5 +21 36 65 5.1 STAR 5.1:5.2 @258 ADS 10993 9 ST 1953 Yellow:pRed
*330 18 03.1 -08 11 18 5.2 STAR 5.2:5.9 @280 ADS 11005 9 ST 1980=1.9 @277
*331 18 05.3 +02 32 15 4.2 STAR 4.2:6.0 @220 ADS 11046 9 ST Yel-Ora:Ora
*332 18 25.0 +27 24 7 6.5 STAR 6.5:7.5 @126 ADS 11334 9 ST 1980=0.7 @129
*333 18 35.8 +16 58 15 6.8 STAR 6.8:7.0 @155 ADS 11483 9 ST 1980=1.6 @161
*334 18 44.4 +39 40 26 5.0 STAR 5.0:6.1 @353 ADS 11635 9 ST 1980=2.7 @355 White
*335 18 44.4 +39 36 24 5.2 STAR 5.2:5.5 @080 ADS 11635 9 ST 1980=2.3 @084 White
*336 18 57.1 +32 54 10 5.4 STAR 5.4:7.5 @021 ADS 11871 9 ST 1980=1.1 @051
*337 19 06.4 -37 03 13 4.8 STAR 4.8:5.1 @109 Gamma CrA 9 ST 1980=1.5 @157
*338 19 26.5 +27 19 20 8.1 STAR 8.1:8.4 @292 ADS 12447 9 ST 1980=1.8 @293
*339 19 30.7 +27 58 344 3.2 STAR 3.2:5.4 @054 ADS 12540 9 ST 1967 Gold:Blue
*340 19 45.5 +33 37 24 8.3 STAR 8.3:8.4 @349 ADS 12889 9 ST 1980=2.0 @357
*341 20 21.0 -14 46 2050 3.1 STAR 3.1:6.2 @267 Beta Cap 9 ST Yellow:Blue
*342 20 46.6 +16 08 98 4.3 STAR 4.3:5.2 @268 ADS 14279 9 ST 1967 Gold:Blue-Gre
*343 20 47.5 +36 29 9 4.9 STAR 4.9:6.1 @011 ADS 14296 9 ST White:pBlue
*344 20 59.1 +04 18 10 6.0 STAR 6.0:6.3 @285 ADS 14499 9 ST 1980=1.1 @286
*345 21 02.3 +07 11 28 7.3 STAR 7.3:7.5 @217 ADS 14556 9 ST 1961
*346 21 06.7 +38 42 297 5.2 STAR 5.2:6.0 @148 ADS 14636 9 ST 1980=29.0 @146
*347 22 28.8 +00 15 19 4.3 STAR 4.3:4.5 @207 ADS 15971 9 ST pYellow:pBlue
*348 22 28.2 +57 42 33 9.8 STAR 9.8:11.5 @132 ADS 15972 9 ST 1980=2.6 @176 Reds
*349 22 33.0 +69 55 4 6.5 STAR 6.5:7.0 @094 ADS 16057 9 ST 1980=0.5 @086
*350 23 34.0 +31 20 4 5.6 STAR 5.6:5.7 @280 ADS 16836 9 ST 1980=0.4 @267
*351 21 12.3 -88 58 5.5 STAR VAR 5.3-5.7 F0III Sigma Oct 8 ST S-Pole * Sigma Oct
Page 15

- 34 -
b. M CATALOG
M# RA DEC SIZE MAG TYPE & DESCRIPTION ALT NAME Q TAGS COMMON NAME/COMMENTS
M 1 05 34.5 +22 01 360 8.4 PLAN NEB EMIS SN REM CNGC 1952 B 4 ST M1 Crab Nebula 4kly
M 2 21 33.5 -00 50 774 6.5v GLOB CLUS sp=F4 CNGC 7089 C 2 ST M2 40kly
M 3 13 42.3 +28 23 972 6.4v GLOB CLUS sp=F7 CNGC 5272 B 2 ST M3 35kly
M 4 16 23.7 -26 31 1578 5.9v GLOB CLUS sp=G0 CNGC 6121 B 2 ST M4 14kly
M 5 15 18.6 +02 05 1044 5.8v GLOB CLUS sp=F6 CNGC 5904 B 2 ST M5 26kly
M 6 17 40.1 -32 13 900 4.2v OPEN CLUS sp=B4 CNGC 6405 C 1 ST M6 1500ly
M 7 17 54.0 -34 49 4800 3.3v OPEN CLUS sp=B5 CNGC 6475 C 1 ST M7 800ly
M 8 18 03.2 -24 23 5400 5.2 OPEN CLUS + ENEB sp=O5 CNGC 6523 B 6 ST M8 Lagoon Nebula 5100ly
M 9 17 19.2 -18 31 558 7.9v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6333 D 2 ST M9
M 10 16 57.1 -04 07 906 6.6v GLOB CLUS sp=G1 CNGC 6254 D 2 ST M10 20kly
M 11 18 51.1 -06 16 840 5.8v OPEN CLUS sp=B8 CNGC 6705 C 1 ST M11 Very rich 5600ly
M 12 16 47.2 -01 57 870 6.6v GLOB CLUS sp=F8 CNGC 6218 D 2 ST M12 24kly
M 13 16 41.7 +36 27 996 5.9v GLOB CLUS sp=F6 CNGC 6205 B 2 ST M13 Hercules Globular
M 14 17 37.6 -03 17 702 7.6v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6402 D 2 ST M14
M 15 21 30.0 +12 10 738 6.4v GLOB CLUS sp=F2 CNGC 7078 C 2 ST M15 X-Ray Source 34kly
M 16 18 18.8 -13 47 2100 6.0v OPEN CLUS + ENEB sp=O7 CNGC 6611 D 6 ST M16 Eagle Nebula 5500ly
M 17 18 20.8 -16 11 2760 6.0v
M 18 18 20.0 -17 08 540 6.9v OPEN CLUS CNGC 6613 D 1 ST M18
M 19 17 02.6 -26 15 810 7.2v GLOB CLUS OBLATE CNGC 6273 D 2 ST M19 Oblate Shape Globular
DIFF ENEB + OPEN CLUS HII
CNGC 6618 B 6 ST M17 Omega/Swan/Horseshoe
M 20 18 02.3 -23 02 1740 6.3v
M 21 18 04.6 -22 30 780 5.9v OPEN CLUS CNGC 6531 D 1 ST M21
M 22 18 36.3 -23 56 1440 5.1v GLOB CLUS sp=F7 CNGC 6656 C 2 ST M22 10kly
M 23 17 57.0 -19 01 1620 5.5v OPEN CLUS sp=B8 CNGC 6494 D 1 ST M23 1400ly
M 24 18 20.0 -18 26 4800 4.7 OPEN CLUS CNGC 6630 c 1 T M24 Best with large field
M 25 18 33.5 -19 14 2400 6.5 OPEN CLUS SPARSE CNGC 6634 c 1 M25 IC 4725 Sparse Cluster
M 26 18 45.4 -09 24 900 8.0v OPEN CLUS CNGC 6694 D 1 ST M26
M 27 19 59.6 +22 43 910 7.6p PLAN NEB CNGC 6853 B 4 ST M27 Dumbbell Nebula 3500ly
M 28 18 24.6 -24 52 672 6.9v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6626 D 2 ST M28
M 29 20 23.9 +38 32 420 6.6v OPEN CLUS CNGC 6913 D 1 ST M29
M 30 21 40.3 -23 11 660 7.5v GLOB CLUS CNGC 7099 D 2 S M30
M 31 00 42.8 +41 17 10680 3.5 GALAXY Sb I-II UGC 454 B 5 ST M31 Andromeda Gal 178x63
M 32 00 42.8 +40 53 456 8.2 GALAXY E2 UGC 452 C 5 ST M32 Comp of M31 7.6x5.8
M 33 01 33.9 +30 40 3720 5.7 GALAXY Sc II-III UGC 1117 C 5 ST M33 Triangulum Gal 62x39
M 34 02 42.0 +42 47 2100 5.2v OPEN CLUS CNGC 1039 C 1 ST M34
M 35 06 08.9 +24 21 1680 5.1v OPEN CLUS sp=B5 CNGC 2168 C 1 ST M35 2800ly
M 36 05 36.2 +34 08 720 6.0v OPEN CLUS CNGC 1960 C 1 ST M36
M 37 05 52.4 +32 33 1440 5.6v OPEN CLUS sp=B8 CNGC 2099 C 1 ST M37 4200ly
M 38 05 28.7 +35 51 1260 6.4v OPEN CLUS sp=B5 CNGC 1912 C 1 ST M38 4600ly
M 39 21 32.2 +48 26 1920 4.6v OPEN CLUS CNGC 7092 D 1 ST M39
M 40 12 36.4 +25 59 972 9.6 GALAXY Sb I: + 3-SYS FNT UGC 7772 B A ST M40 16.2x2.8 Edge-On Lane
M 41 06 47.1 -20 45 2280 4.5v OPEN CLUS sp=B4 CNGC 2287 C 1 ST M41 2200ly
M 42 05 35.3 -05 23 3960 3.9 DIFF RNEB + ENEB CNGC 1976 A 3 ST M42 Orion Nebula Blue+Red
M 43 05 35.5 -05 16 1200 5.8 DIFF RNEB + ENEB CNGC 1982 C 3 ST M43 Orion Nebula Extension
M 44 08 40.1 +19 59 5700 3.1v OPEN CLUS sp=A0 CNGC 2632 C 1 ST M44 Praesepe/Beehive 590ly
DIFF ENEB + OPEN CLUS HII
CNGC 6514 B 6 ST M20 Trifid Nebula 3500ly
M 45 03 47.1 +24 07 7200 1.6 OPEN CLUS + RNEB sp=B6 CNGC 1457 c 6 ST M45 Pleiades 410ly
M 46 07 41.9 -14 49 1620 6.1v OPEN CLUS sp=B8 CNGC 2437 C 1 ST M46 5400ly (+CNGC 2438 PN)
M 47 07 36.6 -14 29 1800 4.4v OPEN CLUS sp=B3 CNGC 2422 D 1 ST M47 1600ly
M 48 08 13.7 -05 47 3240 5.8v OPEN CLUS CNGC 2548 D 1 ST M48
M 49 12 29.8 +08 00 534 8.4 GALAXY E4 UGC 7629 C 5 ST M49 8.9x7.4
M 50 07 02.9 -08 20 960 5.9v OPEN CLUS CNGC 2323 D 1 ST M50
M 51 13 30.0 +47 11 660 8.4 GALAXY Sc I 2-SYS FACE UGC 8493 B A ST M51 11.0x7.8 Whirlpool Gal
M 52 23 24.2 +61 36 780 6.9v OPEN CLUS CNGC 7654 D 1 ST M52
M 53 13 13.0 +18 10 756 7.7v GLOB CLUS CNGC 5024 D 2 ST M53
M 54 18 55.2 -30 28 546 7.7v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6715 D 2 ST M54
Page 16

- 35 -
M CATALOG
M# RA DEC SIZE MAG TYPE & DESCRIPTION ALT NAME Q TAGS COMMON NAME/COMMENTS
M 55 19 40.1 -30 56 1140 7.0 GLOB CLUS sp=F5 CNGC 6809 D 2 ST M55 20kly
M 56 19 16.6 +30 10 426 8.3v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6779 D 2 ST M56
M 57 18 53.5 +33 02 150 9.7p PLAN NEB RING-LIKE CNGC 6720 B 4 ST M57 Ring Nebula 5kly
M 58 12 37.8 +11 49 324 9.8 GALAXY Sb UGC 7796 C 5 ST M58 5.4x4.4 Near CNGC 4621
M 59 12 42.1 +11 38 306 9.8 GALAXY E3 UGC 7858 D 5 ST M59 5.1x3.4 Near CNGC 4579
M 60 12 43.7 +11 33 432 8.8 GALAXY E1 UGC 7898 D 5 ST M60 7.2x6.2 Near CNGC 4621
M 61 12 22.0 +04 28 360 9.7 GALAXY Sc I 2-SYS UGC 7420 D A ST M61 6.0x5.5 Face-On
M 62 17 01.3 -30 07 846 6.6v GLOB CLUS OBLATE CNGC 6266 D 2 ST M62 Non-symmetrical
M 63 13 15.8 +42 02 738 8.6 GALAXY Sb+ II UGC 8334 C 5 ST M63 12.3x7.6 Sunflower Gal
M 64 12 56.7 +21 41 558 8.5 GALAXY Sb- UGC 8062 C 5 ST M64 9.3x5.4 Black Eye Gal
M 65 11 18.9 +13 05 600 9.3 GALAXY Sb II: UGC 6328 C 5 ST M65 10.0x3.3 Near M66
M 66 11 20.2 +12 59 522 9.0 GALAXY Sb+ II: UGC 6346 C 5 ST M66 8.7x4.4 Near M65
M 67 08 51.1 +11 49 1800 6.9v OPEN CLUS sp=F2 CNGC 2682 D 1 ST M67 Very old 2700ly
M 68 12 39.4 -26 46 720 8.2v GLOB CLUS CNGC 4590 D 2 ST M68
M 69 18 31.4 -32 21 426 7.7v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6637 D 2 ST M69
M 70 18 43.2 -32 18 468 8.1v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6681 D 2 ST M70
M 71 19 53.7 +18 47 432 8.3v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6838 D 2 ST M71
M 72 20 53.5 -12 33 354 9.4v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6981 D 2 ST M72
M 73 20 59.0 -12 37 168 8.9p OPEN CLUS CNGC 6994 D 1 ST M73
M 74 01 36.7 +15 47 612 9.2 GALAXY Sc I UGC 1149 D 5 ST M74 10.2x9.5
M 75 20 06.2 -21 55 360 8.6v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6864 D 2 ST M75
M 76 01 42.0 +51 34 290 12.2 PLAN NEB PART OF 0651 CNGC 0650 C 4 ST M76 Little Dumbbell Nebula
M 77 02 42.7 -00 01 414 8.8 GALAXY Sbp SEYFERT UGC 2188 D 5 ST M77 6.9x5.9 Seyfert Galaxy
M 78 05 46.8 +00 03 480 11.3 DIFF RNEB CNGC 2068 C 3 ST M78 Blue 1500ly
M 79 05 24.2 -24 31 522 8.0v GLOB CLUS CNGC 1904 D 2 ST M79
M 80 16 17.1 -23 00 534 7.2v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6093 D 2 ST M80
M 81 09 55.7 +69 04 1542 6.9 GALAXY Sb I-II CNGC 3031 C 5 ST M81 25.7x14.1 Near M82
M 82 09 55.9 +69 41 672 8.4 GALAXY P EDGE-ON UGC 5322 C 5 ST M82 11.2x4.6 Exploding
M 83 13 37.1 -29 51 672 8.2 GALAXY Sc I-II FACE-ON CNGC 5236 B 5 ST M83 11.2x10.2
M 84 12 25.1 +12 53 300 9.3 GALAXY E1 UGC 7494 C 5 ST M84 5.0x4.4 Near M86
M 85 12 25.5 +18 11 426 9.2 GALAXY Ep 2-SYS UGC 7508 C A ST M85 7.1x5.2
M 86 12 26.3 +12 56 444 9.2 GALAXY E3 UGC 7532 C 5 ST M86 7.4x5.5
M 87 12 30.9 +12 23 432 8.6 GALAXY E1 + E0 2-SYS UGC 7654 D A ST M87 7.2x6.8 + CNGC 4471
M 88 12 32.1 +14 25 414 9.5 GALAXY Sb+ I MULTI-ARM UGC 7675 D 5 ST M88 6.9x3.9
M 89 12 35.7 +12 33 252 9.8 GALAXY E0 UGC 7760 D 5 ST M89 4.2x4.2
M 90 12 36.9 +13 09 570 9.5 GALAXY Sb+ UGC 7786 C 5 ST M90 9.5x4.7
M 91 12 35.5 +14 29 324 10.2 GALAXY SBb + Sc 2-SYS UGC 7753 D A ST M91 5.4x4.4 Near CNGC 4571
M 92 17 17.2 +43 09 672 6.5v GLOB CLUS sp=F1 CNGC 6341 D 2 ST M92 X-Ray Source 26kly
M 93 07 44.6 -23 52 1320 6.2v OPEN CLUS + DNEB CNGC 2447 D 6 ST M93 Includes dark nebula
M 94 12 50.9 +41 08 660 8.2 GALAXY Sb-p II: UGC 7996 C 5 ST M94 11.0x9.1
M 95 10 43.9 +11 42 444 9.7 GALAXY S(B)b II UGC 5850 C 5 ST M95 7.4x5.1 Near M96
M 96 10 46.7 +11 49 426 9.2 GALAXY Sbp UGC 5882 C 5 ST M96 7.1x5.1 Near M95
M 97 11 14.8 +55 02 194 12.0p PLAN NEB CNGC 3587 C 4 ST M97 Owl Nebula 12kly
M 98 12 13.9 +14 54 570 10.1 GALAXY Sb I-II: 3-SYS UGC 7231 D A ST M98 9.5x3.2
M 99 12 18.9 +14 25 324 9.8 GALAXY Sc
I NEAR FACE-ON
UGC 7345 D 5 ST M99 5.4x4.8
M100 12 23.0 +15 49 414 9.4 GALAXY Sc I FACE-ON UGC 7450 D 5 ST M100 6.9x6.2 Brite Nucleus
M101 14 03.3 +54 21 1614 7.7 GALAXY Sc I FACE-ON UGC 8981 C 5 S M101 26.9x26.3 Pinwheel
M102 15 06.5 +55 45 312 10.0 GALAXY E6p 2-SYS UGC 9723 D A ST M102 5.2x2.3
M103 01 33.3 +60 43 360 7.4v OPEN CLUS CNGC 0581 D 1 ST M103
M104 12 39.9 -11 38 534 8.3 GALAXY Sb- CNGC 4594 C 5 ST M104 8.9x4.1 “Sombrero”
M105 10 47.8 +12 35 270 9.3 GALAXY E1 2-SYS UGC 5902 C A ST M105 4.5x4.0
M106 12 19.0 +47 18 1092 8.3 GALAXY Sb+p UGC 7353 C 5 ST M106 18.2x7.9
M107 16 32.5 -13 02 600 8.1v GLOB CLUS CNGC 6171 D 2 ST M107
M108 11 11.6 +55 41 498 10.1 GALAXY Sc
M109 11 57.6 +53 22 456 9.8 GALAXY S(B)b+ I UGC 6937 D 5 ST M109 7.6x4.9
M110 00 40.4 +41 42 1044 8.0 GALAXY E6: UGC 426 C 5 ST M110 Comp of M31 17.4x9.8
NEAR EDGE-ON
UGC 6225 C 5 ST M108 8.3x2.5 Near M97
Page 17

- 36 -
142 536
APPENDIX D: PERSONAL COMPUTER (PC) CONTROL OF THE #1697 CDS
Remote operation of a computerized telescope has only been a fanciful dream for most amateur
astronomers. The realization of fully controlling a telescope through a personal computer has previously
been a staggering proposition involving high monetary cost and expert knowledge of software and hardware.
To realize this dream, the Meade #1697 Computer Drive System's internal software
supports a RS-232 interface, allowing observers to utilize a PC and software such as
Meade EPOCH 2000sk (see Optional Accessories, page, 18), other after-market
software, or a user's own custom software to control a compatible telescope.
The following sections are devoted to those interested in developing their own
software to remotely control every feature of the CDS.
An RS-232 cable is required for serial communication between the CDS and a PC. It
is possible to either purchase an RS-232 cable from your local Meade dealer, or
construct your own cable. Following is a schematic for constructing your own RS-232 cable, a program to
test the RS-232 communication line called CDS TEST, the CDS Command Set, and CDS DEMO, which is
a program that you can enter into your computer to access the Object Library, slew to the object, and center
the image. The CDS TEST and CDS DEMO programs require a serial communication program, such as
Procomm*, to communicate with a PC.
Fig. 14: EPOCH 2000sk.
1. RS-232 Cable
The input hardware uses a standard 6 line telephone jack
connector, preattached to a 6 conductor flat line telephone
style cable (of any length, up to 100' and perhaps even more,
depending on the gauge of the cable). You will also need
either a 9-pin or 25-pin RS-232 connector, whichever your
computer uses for the serial port. All of the above items are
available at most electronics hardware stores.
Fig. 15 shows the CDS pinouts for the 6 line telephone
connector. The table below shows standard IBM compatible
DB-9 and DB-25 serial port pin outs, and how they should be
connected to the CDS 6 line modular connector. Note: Only
3 wires are required.
1
4
2
5
6
3
Fig. 15: CDS Modular Connector
RS-232 CONNECTOR PIN OUT CODE LEGEND
6 WIRE MODULAR DESCRIPTION TO DB-9 CONNECTOR TO DB-25
CONNECTOR PIN#** CONNECTOR PIN#**
#1 +12 VOLTS DC NOT USED NOT USED
#2 MISC. SERIAL OUT NOT USED NOT USED
* Procomm is a product of Datastorm Industries.
** The DB-9 and DB-25 serial port pin out numbering code is representative of a widely used standard format.
Consult your computer’s instruction manual for your computer's format.
#3 PC TRANSMIT DATA #3 #2
#4 GROUND #5 #7
#5 PC RECEIVE DATA #2 #3
#6 MISC. SERIAL IN NOT USED NOT USED
Page 18

- 37 -
2. CDS Test Program
Once you have the RS-232 cable constructed, you will want to test the cable. Below is a simple program
called "CDS TEST” that is written in GW Basic programming language and will work with virtually any IBM
compatible computer. CDS Test is an effective program to fully check the RS-232 line communications from
your personal computer to the CDS, allowing you to concentrate on de-bugging your RS-232 cable.
To enter the following program, first load BASIC or GWBASIC (which ever your computer system uses), then
type in the following program. When complete, be sure to save the program as “CDSTST.BAS.”
10 CLS
20 DEFINT A-X
30 OPEN "COM1:9600,N,8,1,CD0,CS0,DS0,RS," FOR RANDOM AS #1
50 key1$ = INKEY$: IF key1$ = "" THEN GOTO 50
60 REM KEY1S
70 IF key1$ = CHR$(119) THEN GOSUB 200: REM "w" key
80 IF key1$ = CHR$(101) THEN GOSUB 200: REM "e" key
90 IF key1$ = CHR$(110) THEN GOSUB 200: REM "n" key
100 IF key1$ = CHR$(115) THEN GOSUB 200: REM "s" key
105 IF key1$ = "x" THEN END: REM To exit test.
110 GOTO 50
120 END
200 REM directions
210 REM west
220 IF key1$ = "w" THEN a$ = "#:Mw#": PRINT #1, a$: REM GO west
230 REM east
240 IF key1$ = "e" THEN a$ = "#:Me#": PRINT #1, a$: REM GO east
250 REM north
260 IF key1$ = "n" THEN a$ = "#:Mn#": PRINT #1, a$: REM GO north
270 REM south:
280 IF key1$ = "s" THEN a$ = "#:Ms#": PRINT #1, a$: REM GO south
290 key1$ = INKEY$:
300 IF key1$ = CHR$(32) THEN GOTO 400 ELSE GOTO 200
400 REM This stops motion (by hitting SPACE bar).
410 B$ = "#:Qe#": PRINT #1, B$
420 B$ = "#:Qw#": PRINT #1, B$
430 B$ = "#:Qn#": PRINT #1, B$
440 B$ = "#:Qs#": PRINT #1, B$
450 RETURN
460 END
To use the above program, connect the completed cable to your PC serial port and to the CDS RS-232 Port.
Load BASIC (or GWBASIC), if not already loaded, and run “CDSTST.BAS.” Nothing will appear on the
computer screen. Press any one of the N, S, E, or W (lower case) keys on your PC keyboard, this will move
the LXD mount North, South, East, or West respectively. Press the space bar on the PC keyboard to stop.
Press X to exit the program.
If the LXD mount does not respond to the N, S, E, or W keys, be sure the CAPSLOCK is OFF. If it still does
not work, check the PC serial port pinouts for your computer to be sure they are wired correctly to the CDS
6 line connector.
With a successful check-out of the PC link with the CDS using “TEST”, you are now ready to write your own
software program using the CDS Command Set, or to use the sample program called “DEMO” that is written
in Quick Basic software language.
Page 19

- 38 -
3. CDS Command Set
Intended for professional programmers, the CDS Command Set is used to write custom software for remote
operation of the telescope with a PC. Each command is listed in a section appropriate to its type. Each
entry in the command list includes the command name, any parameters, any return values, and a
description. The parameters and the return data are shown in a manner that indicates their format. These
formats are listed below along with examples of how the data might really appear, the legal range of values,
and a short description. Below is a detailed description:
a. Command Set Formats
HH:MM.T Example: 05:47.4
Range: 00:00.0 - 23:59.9
Hours, minutes, and tenths of minutes.
sDD*MM Example: +45*59
Range: -90*00 - +90*00
Signed degrees and minutes (the '*' represents ASCII 223 which appears on the handbox as a
degree symbol).
DDD*MM Example: 254*09
Range: 000*00 - 359*59
Unsigned degrees and minutes.
HH:MM:SS Example: 13:15:36
Range: 00:00:00 - 23:59:59
Hours, minutes, and seconds.
MM/DD/YY Example: 02/06/92
Range: 01/01/00 - 12/31/99 (see description)
Month, day, and year.
The two digit year indicates the following: 92 through 99 = 1992 through 1999
sHH Example: -5
Range: -24 - +24
Signed hour offset.
NNNN Example: 3456
Range: 0000 - 9999
Four digit object number.
sMM.M Example: -02.4
Range: -05.5 - 20.0
Signed magnitude value.
NNN Example: 134
Range: 000 - 200
Three digit object size (minutes).
00 through 91 = 2000 through 2091
DD* Example: 56*
Range: 00* - 90*
Higher' parameter (degrees).
TT.T Example: 59.2
Range: 56.4 - 60.1
Tracking 'frequency'. info
Page 20

Example: CNGC1976 SU DNEB MAG 3.9 SZ 66.0'
Range: n/a
Object information.
Ok Example: 1
Range: 0 or 1
Status value returned after setting values.
If the value is legal 1 is returned, otherwise 0 is returned.
b. General Telescope Information
Command ACK (ASCII 6)
Returns A, L, P, or G
Gets alignment status, A for alt-az, L for land, P for polar, G for German mount polar.
Command :GR#
Returns +HH:MM.T#
Gets the current Right Ascension.
Command :GD#
Returns sDD*MM#
Gets the current declination.
- 39 -
Command :GA#
Returns sDD*MM#
Gets the current altitude.
Command :GZ#
Returns DDD*MM#
Gets the current azimuth.
Command :GS#
Returns HH:MM:SS#
Gets the current sidereal time.
Command :SS HH:MM:SS#
Returns Ok
Sets the sidereal time.
Command :GL# :Ga#
Returns HH:MM:SS#
Gets the local time either in 24 hour (GL) or 12 hour (Ga) format.
Command :SL HH:MM:SS#
Returns Ok
Sets the local time.
NOTE: The parameter should always be in 24 hour format.
Command :GC#
Returns MM/DD/YY#
Gets the calendar date.
Command :SC MM/DD/YY#
Returns Ok (see description)
Sets the calendar date.
NOTE: After the Ok, if the date is valid, two strings will be sent. The first will contain the message
“Updating planetary data,” the second (sent after the planetary calculations) will contain only blanks.
Both strings will be terminated by the '#' symbol.
Page 21

Command :Gt#
Returns sDD*MM#
Gets the latitude of the currently selected site.
Command :St sDD*MM#
Returns Ok
Sets the latitude of the currently selected site.
Command :Gg#
Returns DDD*MM#
Gets the longitude of the currently selected site.
Command :Sg DDD*MM#
Returns Ok
Sets the longitude of the currently selected site.
Command :GG#
Returns sHH#
Gets the offset from Greenwich Mean Time.
Command :SG sHH#
Returns Ok
Sets the offset from Greenwich Mean Time.
- 40 -
Command :W1# :W2# :W3# :W4#
Returns Nothing
Sets the current site number.
c. Telescope Motion
Command :Mn# :Ms# :Me# :Mw#
Returns Nothing
Starts motion in the specified direction at the current rate.
Command :MS#
Returns 0, 1, 2, or 3 (see description)
Slews telescope to current object coordinates. 0 is returned if the telescope can complete the slew,
1 is returned if the object is below the horizon, and 2 is returned if the object is below the ‘higher’
limit. If 1 or 2 is returned, a string containing an appropriate message is also returned. If 3 is
returned, the telescope can hit the tripod.
Command :Qn# :Qs# :Qe# :Qw#
Returns Nothing
Stops motion in the specified direction. Also stops the telescope if a slew to object is in progress.
Command :Q#
Returns Nothing
Stops a slew to an object.
Command :RG# :RC# :RM# :RS#
Returns Nothing
Sets the motion rate to guide (RG), center (RC), find (RM), or slew (RS).
d. Library/Objects
Command :Gr#
Returns HH:MM.T#
Gets object Right Ascension.
Page 22

Command :Sr HH:MM.T#
Returns Ok
Sets object Right Ascension.
Command :Gd#
Returns sDD*MM#
Gets object Declination.
Command :Sd sDD*MM#
Returns Ok
Sets object Declination.
Command :CM#
Returns (see description)
Sync. Matches current telescope coordinates to the object coordinates and sends a string indicating
which object’s coordinates were used.
Command :Gy#
Returns GPDCO#
Gets the 'type' string for the FIND operation. A capital letter means that the corresponding type is
selected while a lower case letter indicates it is not.
Command :Sy GPDCO#
Returns Ok
Sets the 'type' string for the FIND operation.
- 41 -
Command :Gq#
Returns SU#, EX#, VG#, GD#, FR#, PR#, or VP#
Gets the current minimum quality for the FIND operation
Command :Sq#
Returns Nothing
Steps to the next minimum quality for the FIND operation.
Command :Gh#
Returns DD*#
Gets the current 'higher' limit.
Command :Sh DD#
Returns Ok
Sets the current 'higher' limit.
Command :Gb# :Gf#
Returns sMM.M#
Gets the brighter (Gb) or fainter (Gf) magnitude limit for the FIND operation.
Command :Sb sMM.M# :Sf sMM.M#
Returns Ok
Sets the brighter (Gb) or fainter (Gf) magnitude limit for the FIND operation.
Command :Gl# :Gs#
Returns NNN'#
Gets the larger (Gl) or smaller (Gs) size limit for the FIND operation.
Page 23

Command :Sl NNN# :Ss NNN#
Returns Ok
Sets the larger (Gl) or smaller (Gs) size limit for the FIND operation.
Command :GF#
Returns NNN'#
Gets the field radius of the FIELD operation.
Command :SF NNN#
Returns Ok
Sets the field radius of the FIELD operation.
Command :LF#
Returns Nothing
Starts a FIND operation.
Command :LN#
Returns Nothing
Finds the next object in a FIND sequence.
Command :LB#
Returns Nothing
Finds the previous object in a FIND sequence.
- 42 -
Command :Lf#
Returns (see description)
Performs a FIELD operation returning a string containing the number of objects in the field and the
object that is closest to the center of the field.
Command :LC NNNN# :LM NNNN# :LS NNNN#
Returns Nothing
Sets the object to the CNGC (LC), Messier (LM), or Star (LS) specified by the number. Planets are
'stars' 901-909.
Command :LI#
Returns Object Information
Gets the current object information.
e. Miscellaneous
Command :B+# :B-# :B0# :B1# :B2# :B3#
Returns Nothing
Increases (B+) or decreases (B-) reticle brightness, or sets to one of the flashing modes (B0, B1,
B2, or B3).
Command :F+# :F-# :FQ# :FF# :FS#
Returns Nothing
Starts focus out (F+), starts focus in (F-), stops focus change (FQ), sets focus fast (FF), or
Command :GM# :GN# :GO# :GP#
Returns XYZ#
Gets site name (XYZ). M through P correspond to 1 through 4.
Command :SM XYZ# :SN XYZ# :SO XYZ# :SP XYZ#
Returns Ok
Sets site name.
Page 24

Command :GT#
Returns TT.T#
Gets the current track 'frequency'.
Command :ST TT.T#
Returns Ok
Sets the current track 'frequency'.
Command :TM# :TQ# :T+# :T-#
Returns Nothing
Switch to manual (TM) or quartz (TM). Increment (T+) or decrement (T-) manual frequency by one
tenth.
Command :Gc#
Returns (12) or (24)
Get 12/24 hour status of clock.
Command :H#
Returns Nothing
Toggle 12/24 hour mode.
Command :P#
- 43 -
Returns“HIGH PRECISION” when ON
“LOW PRECISION” when OFF
Toggles the High Precision Mode ON or OFF.
Command :U#
Returns Nothing
Toggles the long format ON or OFF.
When the long format is active, whenever a request to send or receive position data, the following
format is used:
HH:MM:SS
Example: 05:47:45
Range: 00:00.0 - 23:59:59
Hours, minutes, and seconds.
sDD*MM:SS
Example: +45*59:45
Range: -90*00 - +90*00
Signed degrees, minutes, and seconds (the '*' represents ASCII 223 which appears on
the handbox as a degree symbol).
DDD*MM:SS
Example: 254*09:45
Range: 000*00 - 359*59:59
Unsigned degrees, minutes, and seconds.
Command :Lo N#
Returns Ok
Sets the NGC object library type. 0 is the NGC library, 1 is the IC library, and 2 is the UGC library.
This operation is successful only if the user has a version of the software that includes the desired
library.
Page 25

- 44 -
Command :Ls N#
Returns Ok
Sets the STAR object library type. 0 is the STAR library, 1 is the SAO library, and 2 is the GCVS
library. This operation is successful only if the user has a version of the software that includes the
desired library.
f. Keypad Hand Controller Specific
Command:D#
Returns (see description)
Gets the distance ‘bars’ string.
Command: $Q (1-5)#
Returns Nothing
Toggles Smart Drive status.
Command: ?#
Command : ?+#
Command: ?-#
Returns Page of Help Information
Starts (??) or moves through (?+ or ?-) Help.
Command: G0#
Command: G1#
Command: G2#
Returns Alignment Menu Entry
Used to implement alignment menu.
4. CDS Demo Program
The RS-232 interface communicates with your computer at 9600 Baud Rate, Parity = None, 8 Data Bits, 1
Stop Bits. For those who are familiar with programming, the CDS Command Set is written in ASCII
character format and can be used to write your own programs.
The CDS Demo Program is written in Quick Basic and is intended to demonstrate how commands can be
sent to the telescope and information received from the telescope. It is not a “polished” program and does
not incorporate all of the RS-232 features available.
The program is set-up to operate on serial port 2 (COM2:). To operate on serial port 1 (COM1:) line 4 should
be changed from “COM2:” to “COM1:”. The program is as follows:
Please note that Meade Instruments does not support these programs, or programs that you may write in
any way. For questions relating to after-market software programs, refer back to those manufacturers.
Page 26

- 45 -
CLS
DEFINT A-X
counter = 0
OPEN "COM1:9600,N,8,1,CD0,CS0,DS0,OP0,RS,TB2048,RB2048" FOR RANDOM AS #1 hourform$ = "low "
KEY ON
KEY(1) ON
KEY(2) ON
KEY(3) ON
KEY(4) ON
KEY(5) ON
KEY(6) ON
KEY(7) ON
KEY(8) ON
KEY(9) ON
KEY(10) ON
KEY(11) ON
KEY(12) ON
KEY(13) ON
KEY(14) ON
KEY 1, "GO TO":
ON KEY(1) GOSUB key1
KEY 2, " SYNC"
ON KEY(2) GOSUB KEY2
KEY 3, " SLEW"
ON KEY(3) GOSUB key3
KEY 4, " FIND"
ON KEY(4) GOSUB KEY4
KEY 5, " CNTR"
ON KEY(5) GOSUB KEY5
KEY 6, "GUIDE"
ON KEY(6) GOSUB KEY6
KEY 7, " H.P."
ON KEY(7) GOSUB key7
KEY 8, "FORMAT"
ON KEY(8) GOSUB key8
KEY 9, " PREV"
ON KEY(9) GOSUB key9
KEY 10, " NEXT"
ON KEY(10) GOSUB key10
ON KEY(11) GOSUB key11
ON KEY(12) GOSUB key12
ON KEY(13) GOSUB key13
ON KEY(14) GOSUB key14
GOSUB statis
GOSUB key3: REM puts maker over key3
GOSUB help
20 GOSUB telpos
50 key$ = INKEY$: IF key$ = "" THEN GOTO 20
REM KEYS
GOTO 20
END
PRINT #1, "#:LI#": info$ = INPUT$(33, 1): REM LOCATE 10, 20: PRINT info$;
GOSUB obdraw
GOSUB TIME
IF key$ = CHR$(119) THEN GOSUB senddir: REM a$ = "#:Mw#"
IF key$ = CHR$(101) THEN GOSUB senddir: REM a$ = "#:Me#"
IF key$ = CHR$(110) THEN GOSUB senddir: REM a$ = "#:Mn#"
IF key$ = CHR$(115) THEN GOSUB senddir: REM a$ = "#:Ms#"
IF key$ = "m" THEN GOSUB objects
IF key$ = "t" THEN GOSUB objects
IF key$ = "c" THEN GOSUB objects
IF key$ = "p" THEN GOSUB objects
IF key$ = "q" THEN GOSUB objects
IF key$ = "x" THEN CLS : END
IF key$ = "r" THEN RUN
Page 27

senddir:
west:
IF key$ = "w" THEN a$ = "#:Mw#": PRINT #1, a$: REM GOTO west
east:
IF key$ = "e" THEN a$ = "#:Me#": PRINT #1, a$: REM GOTO east
north:
IF key$ = "n" THEN a$ = "#:Mn#": PRINT #1, a$: REM GOTO north
south:
IF key$ = "s" THEN a$ = "#:Ms#": PRINT #1, a$: REM GOTO south
GOSUB telpos
key$ = INKEY$:
IF key$ = CHR$(32) THEN GOTO end1 ELSE GOTO senddir
end1:
B$ = "#:Qe#": PRINT #1, B$
B$ = "#:Qw#": PRINT #1, B$
B$ = "#:Qn#": PRINT #1, B$
B$ = "#:Qs#": PRINT #1, B$
RETURN
telpos:
LOCATE 6, 7: PRINT "TELESCOPE POSITION";
c$ = "#:GR#": PRINT #1, c$;
IF hourform$ = "high" THEN d$ = INPUT$(9, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 4, 2): RAR$ = MID$(d$, 7, 2): LOCATE 7, 10: PRINT USING "RA :
\\:\\:\ \"; RAL$; RAM$; RAR$;
IF hourform$ = "low " THEN d$ = INPUT$(8, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 4, 4): LOCATE 7, 10: PRINT USING "RA : \\:\ \ "; RAL$; RAM$;
- 46 -
TIME:
c$ = "#:GD#": PRINT #1, c$;
IF hourform$ = "high" THEN d$ = INPUT$(10, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 5, 2): RAR$ = MID$(d$, 8, 2): LOCATE 8, 10: PRINT "DEC: "; RAL$;
CHR$(248); RAM$; "'"; RAR$; CHR$(34);
IF hourform$ = "low " THEN d$ = INPUT$(7, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 5, 2): LOCATE 8, 10: PRINT "DEC: "; RAL$; CHR$(248); RAM$; "'
";
c$ = "#:GA#": PRINT #1, c$;
IF hourform$ = "high" THEN d$ = INPUT$(10, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 5, 2): RAR$ = MID$(d$, 8, 2): LOCATE 9, 10: PRINT "ALT: "; RAL$;
CHR$(248); RAM$; "'"; RAR$; CHR$(34);
IF hourform$ = "low " THEN d$ = INPUT$(7, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 5, 2): LOCATE 9, 10: PRINT "ALT: "; RAL$; CHR$(248); RAM$; "'
";
c$ = "#:GZ#": PRINT #1, c$;
IF hourform$ = "high" THEN d$ = INPUT$(10, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 5, 2): RAR$ = MID$(d$, 8, 2): LOCATE 10, 10: PRINT "AZ : "; RAL$;
CHR$(248); RAM$; "'"; RAR$; CHR$(34);
IF hourform$ = "low " THEN d$ = INPUT$(7, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 5, 2): LOCATE 10, 10: PRINT "AZ : "; RAL$; CHR$(248); RAM$; "'
";
RETURN
LOCATE 1, 32: PRINT "DATE"; : LOCATE 1, 64: PRINT "TIME";
c$ = "#:GS#": PRINT #1, c$; : d$ = INPUT$(9, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 2): RAM$ = MID$(d$,
4, 2): RAR$ = MID$(d$, 7, 2): LOCATE 3, 55: PRINT USING "Siderial Time:
\\:\\:\\"; RAL$; RAM$; RAR$;
c$ = "#:GL#": PRINT #1, c$; : d$ = INPUT$(9, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 2): RAM$ = MID$(d$,
4, 2): RAR$ = MID$(d$, 7, 2): LOCATE 2, 55: PRINT USING "Local (24hr) :
\\:\\:\\"; RAL$; RAM$; RAR$;
c$ = "#:GG#": PRINT #1, c$; : d$ = INPUT$(4, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3):
LOCATE 3, 25: PRINT USING "GMT Offset: \ \ Hours"; RAL$;
c$ = "#:GC#": PRINT #1, c$; : d$ = INPUT$(9, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 2): RAM$ = MID$(d$,
4, 2): RAR$ = MID$(d$, 7, 2): LOCATE 2, 25: PRINT USING "Date : \\/\\/\\";
RAL$; RAM$; RAR$;
RETURN
Page 28

- 47 -
objects:
obdraw:
counter = 1
LOCATE 21, 25
IF key$ = "m" THEN INPUT "Enter Messier number: "; m$: o$ = "#:LM" + m$
IF key$ = "t" THEN INPUT "Enter Star number: "; m$: o$ = "#:LS" + m$
IF key$ = "c" THEN INPUT "Enter CNGC number: "; m$: o$ = "#:LC" + m$
IF key$ = "p" THEN INPUT "Enter Planet number: "; m$: o$ = "#:LS" + m$
IF key$ = "q" THEN INPUT "Enter RA: (HH:MM:SS) "; m$: o$ = "#:Sr" + m$: REM d$=
INPUT$(1, 1)
IF key$ = "q" THEN INPUT "Enter RA: (HH:MM:SS) "; m$: o$ = "#:Sr" + m$: REM d$=
INPUT$(1, 1)
o$ = o$ + "#"
PRINT #1, o$
LOCATE 21, 15: PRINT " ";
PRINT #1, "#:LI#": info$ = INPUT$(33, 1): REM LOCATE 10, 20: PRINT info$;
counter = 1
LOCATE 6, 31: PRINT " O B J E C T I N F O R M A T I O N";
LOCATE 7, 31: PRINT "Object: "; LEFT$(info$, 9);
LOCATE 8, 31: PRINT "Rating: "; MID$(info$, 10, 7);
LOCATE 9, 31: PRINT "Magnitude: "; MID$(info$, 20, 5);
LOCATE 10, 31: PRINT "Size: "; MID$(info$, 27, 6);
IF counter = 0 THEN LOCATE 11, 31: PRINT "RA :"; : LOCATE 12, 31: PRINT "DEC:"; :
LOCATE 7, 60: PRINT "Distance to SLEW"; : LOCATE 9, 55: PRINT "RA :"; : LOCATE 10,
55: PRINT "Dec:"; : REM goto scale
c$ = "#:Gr#": PRINT #1, c$;
IF hourform$ = "high" THEN d$ = INPUT$(9, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 4, 2): RAR$ = MID$(d$, 7, 2): LOCATE 11, 31: PRINT USING "RA :
\\:\\:\ \"; RAL$; RAM$; RAR$;
IF hourform$ = "low " THEN d$ = INPUT$(8, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 4, 4): LOCATE 11, 31: PRINT USING "RA : \\:\ \ ";
RAL$; RAM$;
c$ = "#:Gd#": PRINT #1, c$;
REM c$ = "#:Gr#": PRINT #1, c$; : d$ = INPUT$(8, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 2): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 4, 4): LOCATE 11, 31: PRINT USING "RA : \\:\ \"; RAL$; RAM$;
REM c$ = "#:Gd#": PRINT #1, c$; : d$ = INPUT$(7, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 5, 2): LOCATE 12, 31: PRINT "DEC: "; RAL$; CHR$(248); RAM$; "'";
distbar:
rad$ = "": decd$ = ""
c$ = "#:D#": PRINT #1, c$: d$ = INPUT$(33, 1)
REM LOCATE 22, 20: PRINT "XXXXX"; d$; "XXXXXXX"; ASC(d$); "XXXXX";
REM LOCATE 23, 3: FOR I = 1 TO 33: PRINT ASC(MID$(d$, I, 1)); : NEXT I
LOCATE 7, 59: PRINT " Distance to SLEW ";
scale: LOCATE 8, 59: PRINT "0"; CHR$(248); " 45"; CHR$(248); " 90"; CHR$(248); " 150+";
CHR$(248);
IF counter = 0 THEN RETURN
IF hourform$ = "high" THEN d$ = INPUT$(10, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 5, 2): RAR$ = MID$(d$, 8, 2): LOCATE 12, 31: PRINT "DEC: ";
RAL$; CHR$(248); RAM$; "'"; RAR$; CHR$(34);
IF hourform$ = "low " THEN d$ = INPUT$(7, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ =
MID$(d$, 5, 2): LOCATE 12, 31: PRINT "DEC: "; RAL$; CHR$(248);
RAM$; "' ";
FOR i = 1 TO 16
IF ASC(MID$(d$, i, 1)) = 255 THEN rad$ = rad$ + CHR$(254)
NEXT i
FOR i = 17 TO 33
IF ASC(MID$(d$, i, 1)) = 255 THEN decd$ = decd$ + CHR$(254)
NEXT i
LOCATE 9, 55: PRINT " "; : LOCATE 9, 55: PRINT "RA "; rad$;
LOCATE 10, 55: PRINT " "; : LOCATE 10, 55: PRINT "DEC "; decd$;
RETURN
Page 29

- 48 -
statis:
key1:
KEY2:
clearr: FOR i = 1 TO 30000: NEXT i: FOR i = 1 TO 30000: NEXT i: FOR i = 1 TO 30000: NEXT i:
key3:
KEY4:
CHR$(219);
KEY5:
KEY6:
key7:
key8:
key9:
key10:
LOCATE 1, 7: PRINT "SITE"
c$ = "#:Gt#": PRINT #1, c$; : d$ = INPUT$(7, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ = MID$(d$,
5, 2): LOCATE 2, 3: PRINT "Lat. : "; RAL$; CHR$(248); RAM$; "'";
c$ = "#:Gg#": PRINT #1, c$; : d$ = INPUT$(7, 1): RAL$ = LEFT$(d$, 3): RAM$ = MID$(d$,
5, 2): LOCATE 3, 3: PRINT "Long.: "; RAL$; CHR$(248); RAM$; "'";
BOXSTX = 2: BOXSTY = 3: BOXWIDE = 10: boxtall = 5: GOSUB drawbox
RETURN
PRINT #1, "#:MS#"
error1$ = INPUT$(1, 1)
IF error1$ = "1" OR error1$ = "2" THEN error2$ = INPUT$(33, 1) ELSE RETURN
LOCATE 22, 20: PRINT LEFT$(error2$, 32)
GOSUB clearr
RETURN
PRINT #1, "#:CM#"
sync$ = INPUT$(33, 1)
LOCATE 22, 20: PRINT sync$;
FOR i = 1 TO 30000: NEXT i: FOR i = 1 TO 30000: NEXT i: FOR i = 1 TO 30000: NEXT i:
LOCATE 22, 20: PRINT " ";
RETURN
PRINT #1, "#:RS#"
LOCATE 24, 1: PRINT " ";
LOCATE 24, 18: PRINT CHR$(219); CHR$(178); CHR$(176); CHR$(176); CHR$(178); CHR$(219);
RETURN
PRINT #1, "#:RM#:"
LOCATE 24, 1: PRINT " ";
LOCATE 24, 26: PRINT CHR$(219); CHR$(178); CHR$(176); CHR$(176); CHR$(178);
RETURN
PRINT #1, "#:RC#"
LOCATE 24, 1: PRINT " ";
LOCATE 24, 34: PRINT CHR$(219); CHR$(178); CHR$(176); CHR$(176); CHR$(178);
CHR$(219);
RETURN
PRINT #1, "#:RG#"
LOCATE 24, 1: PRINT " ";
LOCATE 24, 42: PRINT CHR$(219); CHR$(178); CHR$(176); CHR$(176); CHR$(178);
CHR$(219);
RETURN
PRINT #1, "#:P#"
notice$ = INPUT$(14, 1): LOCATE 4, 15: PRINT notice$
RETURN
PRINT #1, "#:U#"
IF hourform$ = "high" THEN hourform$ = "low " ELSE hourform$ = "high"
LOCATE 4, 40: PRINT "Number Format= "; hourform$
RETURN
PRINT #1, "#:LN#"
PRINT #1, "#:LI#": info$ = INPUT$(33, 1): REM LOCATE 10, 20: PRINT info$;
GOSUB obdraw
RETURN
PRINT #1, "#:LB#"
PRINT #1, "#:LI#": info$ = INPUT$(33, 1): REM LOCATE 10, 20: PRINT info$;
GOSUB obdraw
RETURN
Page 30

- 49 -
key11:
key12:
key13:
key14:
drawbox:
REM LOCATE BOXSTX, BOXSTY:
REM BOX$ = CHR$(201)
REM FOR I = 1 TO BOXWIDE: BOX$ = BOX$ + CHR$(205): NEXT
REM PRINT BOX$;
help:
key$ = "n"
GOSUB north
RETURN
key$ = "w"
GOSUB west
RETURN
key$ = "e"
GOSUB east
RETURN
key$ = "s"
GOSUB south
RETURN
RETURN
LOCATE 14, 10: PRINT "E W N S keys move telescope. SPACE BAR stops.";
LOCATE 15, 10: PRINT "M key to enter Messier object.";
LOCATE 16, 10: PRINT "T key to enter sTar.";
LOCATE 17, 10: PRINT "P key to enter Planet (900 + orbit #).";
LOCATE 18, 10: PRINT "C key to enter Cngc object.";
LOCATE 19, 10: PRINT "Q key to enter Planet (900 + orbit #).";
LOCATE 20, 10: PRINT "X to End program.";
END
RETURN
Page 31

- 50 -
APPENDIX E: CARE AND MAINTENANCE OF THE CDS
1. Keeping Your Components Clean
Prevention is the best recommendation that a telescope owner can follow in keeping astronomical
equipment in top working order. Proper measures taken during observations and when storing the
equipment between observation runs can ensure many years of trouble free use.
Dust and moisture are the two main enemies to your telescope and electronics. If you live in a very moist
climate, you may find it necessary to use a silica dessicant stored with the telescope and electronics to ward
off moisture and the possibility of corrosion growing on the metal contacts of the electronics. Replace the
silica dessicant as often as necessary. All of the metal surfaces should be cleaned routinely with a soft rag
and alcohol to prevent corrosion.
Those living in coastal areas or tropic zones should also cover the electronic ports on the Control Panel and
Keypad with gaffers tape to reduce corrosion on the metal contacts. Apply a dab of water displacement
solution (such as WD-40) with a small brush on all of the interior metal contacts and the input cord metal
contacts. The Keypad and all separate accessories should be kept in sealable bags with silica dessicant.
2. Behind the Power Panel
The CDS Control Panel houses the back-up replaceable
clock/ calendar battery and a replaceable standard 1.0
amp slow blow fuse. The long-life lithium battery
(Panasonic CR2032 3 volt or Duracell DL2032B) is
stored behind the front panel of the CDS. The battery
should be replaced whenever the CDS begins to lose
time. The 1 amp slow blow fuse will fail in the event that
the telescope is prevented from completing a GO TO
function (e.g. the tube runs into something that keeps it
from slewing).
To replace either the battery or the fuse, first remove the
CDS PCB assembly from the Declination casting by
removing the four screws and unplugging the 16-pin
ribbon cable. With a thin flat-headed screwdriver, lift the
small coin-sized battery out of its’ holder. The new
battery slides back in place.
The fuse can be removed with the aid of a small screwdriver. Loosening the two upper screws on the front
side of the power panel will provide more clearance to replace the fuse if needed.
Fig. 16. CDS PCD. (1) 16-Pin Ribbon Cable.
1
Page 32

NOTICE
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a CLASS B digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions contained in this manual, may
cause harmful interference to radio and television communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio of television reception, which can be determined
by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that of the receiver.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced audio television technician.
NOTE: Connecting this device to peripheral devices that do not comply with CLASS B requirements or
using an unshielded peripheral data cable could also result in harmful interference to radio or television
reception.
The user is cautioned that any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
To ensure that the use of this product does not contribute to interference, it is necessary to use shielded
I/O cables
Page 33

Meade Instruments Corporation
World’s leading manufacturer of astronomical telescopes for the serious amateur.
6001 Oak Canyon, Irvine, California 92620-4205■(949) 451-1450
■
Fax: (949) 451-1460
www.meade.com
Ver. 0698 Part Number 14-0205-00
 Loading...
Loading...