Page 1

Troubleshooting Guide
Revision 6.0
McAfee® Network Security Platform
version 6.0
McAfee®
Network Protection
Industry-leading network security solutions
Page 2

COPYRIGHT
Copyright ® 2001 - 2011 McAfee, Inc. All Rights Reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into
any language in any form or by any means without the written permission of McAfee, Inc., or its suppliers or affiliate companies.
TRADEMARKS
ACTIVE FIREWALL, ACTIVE SECURITY, ACTIVESECURITY (AND IN KATAKANA), ACTIVESHIELD, CLEAN-UP, DESIGN (STYLIZED E), DESIGN (STYLIZED N),
ENTERCEPT, EPOLICY ORCHESTRATOR, FIRST AID, FOUNDSTONE, GROUPSHIELD, GROUPSHIELD (AND IN KATAKANA), INTRUSHIELD, INTRUSION PREVENTION
THROUGH INNOVATION, McAfee, McAfee (AND IN KATAKANA), McAfee AND DESIGN, McAfee.COM, McAfee VIRUSSCAN, NET TOOLS, NET TOOLS (AND IN KATAKANA),
NETSCAN, NETSHIELD, NUTS & BOLTS, OIL CHANGE, PRIMESUPPORT, SPAMKILLER, THREATSCAN, TOTAL VIRUS DEFENSE, VIREX, VIRUS FORUM, VIRUSCAN,
VIRUSSCAN, VIRUSSCAN (AND IN KATAKANA), WEBSCAN, WEBSHIELD, WEBSHIELD (AND IN KATAKANA) are registered trademarks or trademarks of McAfee, Inc. and/or
its affiliates in the US and/or other countries. The color red in connection with security is distinctive of McAfee brand products. All other registered and unregistered tr ademarks
herein are the sole property of their respective owners.
LICENSE AND PATENT INFORMATION
License Agreement
NOTICE TO ALL USERS: CAREFULLY READ THE APPROPRIATE LEGAL AGREEMENT CORRESPONDING TO THE LICENSE YOU PURCHASED, WHICH SETS FORTH
THE GENERAL TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR THE USE OF THE LICENSED SOFTWARE. IF YOU DO NOT KNOW WHICH TYPE OF LICENSE YOU HAVE ACQUIRED,
PLEASE CONSULT THE SALES AND OTHER RELATED LICENSE GRANT OR PURCHASE ORDER DOCUMENTS THAT ACCOMPANIES YOUR SOFTWARE PACKAGING
OR THAT YOU HAVE RECEIVED SEPARATELY AS PART OF THE PURCHASE (AS A BOOKLET, A FILE ON THE PRODUCT CD, OR A FILE AVAILABLE ON THE WEB SITE
FROM WHICH YOU DOWNLOADED THE SOFTWARE PACKAGE). IF YOU DO NOT AGREE TO ALL OF THE TERMS SET FORTH IN THE AGREEMENT, DO NOT INSTALL
THE SOFTWARE. IF APPLICABLE, YOU MAY RETURN THE PRODUCT TO McAfee OR THE PLACE OF PURCHASE FOR A FULL REFUND.
License Attributions
This product includes or may include:
* Software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit (http://www.openssl.org/). * Cryptographic software written by Eric A. Young and software written by
Tim J. Hudson. * Some software programs that are licensed (or sublicensed) to the user under the GNU General Public License (GPL) or other similar Free Software licenses
which, among other rights, permit the user to copy, modify and redistribute certain programs, or portions thereof, and have access to the source code. The GPL requires that for
any software covered under the GPL, which is distributed to someone in an executable binary format, that the source code also be made available to those users. For any such
software covered under the GPL, the source code is made available on this CD. If any Free Software licenses require that McAfee provide rights to use, copy or modify a software
program that are broader than the rights granted in this agreement, then such rights shall take precedence over the rights and restrictions herein. * Software originally written by
Henry Spencer, Copyright 1992, 1993, 1994, 1997 Henry Spencer. * Software originally written by Robert Nordier, Copyright (C) 1996-7 Robert Nordier. * Software written by
Douglas W. Sauder. * Software developed by the Apache Software Foundatio n (http://www.apache.org/). A copy of the license agreement for this software can be found at
www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.txt. * International Components for Unicode ("ICU") Copyright (C) 1995-2002 International Business Machines Corporation and others. *
Software developed by CrystalClear Software, Inc., Copyright (C) 2000 CrystalClear Software, Inc. * FEAD(R) Optimizer(R) technology, Copyright Netopsystems AG, Berlin,
Germany. * Outside In(R) Viewer Technology (C) 1992-2001 Stellent Chicago, Inc. and/or Outside In(R) HTML Export, (C) 2001 Stellent Chicago, Inc. * Software copyrighted by
Thai Open Source Software Center Ltd. and Clark Cooper, (C) 1998, 1999, 2000. * Software copyrighted by Expat maintainers. * Software copyrighted by The Regents of the
University of California, (C) 1996, 1989, 1998-2000. * Software copyrighted by Gunnar Ritter. * Software copyrighted by Sun Microsystems, Inc., 4150 Network Circle, Santa Clara,
California 95054, U.S.A., (C) 2003. * Software copyrighted by Gisle Aas. (C) 1995-2003. * Software copyrighted by Michael A. Chase, (C) 1999-2000. * Software copyrighted by
Neil Winton, (C) 1995-1996. * Software copyrighted by RSA Data Security, Inc., (C) 1990-1992. * Software copyrighted by Sean M. Burke, (C) 1999, 2000. * Software copyrighted
by Martijn Koster, (C) 1995. * Software copyrighted by Brad Appleton, (C) 1996-1999. * Software copyrighted by Michael G. Schwern, (C) 2001. * Software copyrighted by Graham
Barr, (C) 1998. * Software copyrighted by Larry Wall and Clark Cooper, (C) 1998-2000. * Software copyrighted by Frodo Looijaard, (C) 1997. * Software copyrighted by the Python
Software Foundation, Copyright (C) 2001, 2002, 2003. A copy of the license agreement for this software can be found at www.python.org. * Software copyrighted by Beman
Dawes, (C) 1994-1999, 2002. * Software written by Andrew Lumsdaine, Lie-Quan Lee, Jeremy G. Siek (C) 1997-2000 University of Notre Dame. * Software copyrighted by Simone
Bordet & Marco Cravero, (C) 2002. * Software copyrighted by Stephen Purcell, (C) 2001. * Software developed by the Indiana University Extreme! Lab
(http://www.extreme.indiana.edu/). * Software copyrighted by International Business Machines Corporation and others, (C) 1995-2003. * Software developed by the University of
California, Berkeley and its contributors. * Software developed by Ralf S. Engelschall <rse@engelschall.com> for use in the mod_ssl project (http:// www.modssl.org/). * Software
copyrighted by Kevlin Henney, (C) 2000-2002. * Software copyrighted by Peter Dimov and Multi Media Ltd. (C) 2001, 2002. * Software copyrighted by David Abrahams, (C) 2001,
2002. See http://www.boost.org/libs/bind/bind.html
Software copyrighted by Boost.org, (C) 1999-2002. * Software copyrighted by Nicolai M. Josuttis, (C) 1999. * Software copyrighted by Jeremy Siek, (C) 1999-2001. * Software
copyrighted by Daryle Walker, (C) 2001. * Software copyrighted by Chuck Allison and Jeremy Siek, (C) 2001, 2002. * Software copyrighted by Samuel Krempp, (C) 2001. See
http://www.boost.org for updates, documentation, and revision history. * Software copyrighted by Doug Gregor (gregod@cs.rpi.edu), (C) 2001, 2002. * Software copyrighted by
Cadenza New Zealand Ltd., (C) 2000. * Software copyrighted by Jens Maurer, (C) 2000, 2001. * Software copyrighted by Jaakko Järvi (jaakko.jarvi@cs.utu.fi), (C) 1999, 2000. *
Software copyrighted by Ronald Garcia, (C) 2002. * Software copyrighted by David Abrahams, Jeremy Siek, and Daryle Walker, (C) 1999-2001. * Software copyrighted by Stephen
Cleary (shammah@voyager.net
1999. * Software copyrighted by Dr. John Maddock, (C) 1998-2002. * Software copyrighted by Greg Colvin and Beman Dawes, (C) 1998, 1999. * Software copyrighted by Peter
Dimov, (C) 2001, 2002. * Software copyrighted by Jeremy Siek and John R. Bandela, (C) 2001. * Software copyrighted by Joerg Walter and Mathias Koch, (C) 2000-2002. *
Software copyrighted by Carnegie Mellon University (C) 1989, 1991, 1992. * Software copyrighted by Cambridge Broadband Ltd., (C) 2001-2003. * Software copyrighted by
Sparta, Inc., (C) 2003-2004. * Software copyrighted by Cisco, Inc and Information Network Center of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunication s , (C) 2004. * Software
copyrighted by Simon Josefsson, (C) 2003. * Software copyrighted by Thomas Jacob, (C) 2003-2004. * Software copyrighted by Advanced Software Engineering Limited, (C)
2004. * Software copyrighted by Todd C. Miller, (C) 1998. * Software copyrighted by The Regents of the University of California, (C) 1990, 1993, with code derived from software
contributed to Berkeley by Chris Torek.
), (C) 2000. * Software copyrighted by Housemarque Oy <http://www.housemarque.com>, (C) 2001. * Software copyrighted by Paul Moore, (C)
for documentation. * Software copyrighted by Steve Cleary, Beman Dawes, Howard Hinnant & John Maddock, (C) 2000. *
Issued APRIL 2011 / Troubleshooting Guide
700-2380-00/ 6.0 - English
Page 3

Contents
Preface ........................................................................................................... v
Introducing McAfee Network Security Platform............................................................................. v
About this Guide............................................................................................................................ v
Audience ....................................................................................................................................... v
Conventions used in this book ......................................................................................................vi
Related Documentation................................................................................................................vii
Contacting Technical Support.....................................................................................................viii
Information requested for Troubleshooting ......................................................................... viii
Chapter 1 Before You Install........................................................................ 1
Pre-installation recommendations................................................................................................. 1
Planning for installation..........................................................................................................1
Functional requirements.........................................................................................................2
Using anti-virus software with the Manager ...........................................................................4
User interface responsiveness...............................................................................................5
Chapter 2 Hardening the Manager Server for Windows 2003 .................. 6
Introduction....................................................................................................................................6
Install a desktop firewall................................................................................................................6
Harden the MySQL installation......................................................................................................6
Remove test database...........................................................................................................7
Remove local anonymous users............................................................................................7
Remove remote anonymous users........................................................................................7
Secure MySQL remote access ..............................................................................................8
Rolling back your changes.....................................................................................................9
Remove debug shell at port 9001 ..........................................................................................9
Other best practices for securing Manager...................................................................................9
Chapter 3 Hardening the Manager Server for Windows 2008 ................ 10
Pre-installation.............................................................................................................................10
Installation...................................................................................................................................10
Post Installation........................................................................................................................... 10
Disabling non-required Services..........................................................................................11
Setting System Policies........................................................................................................11
Setting User Policies............................................................................................................11
Setting a Desktop Firewall ...................................................................................................11
Configuring Audit Events......................................................................................................12
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting Network Security Platform.......................... 14
Facilitating troubleshooting..........................................................................................................14
Starting your troubleshooting ...................................................................................................... 15
Difficulties connecting Sensor and Manager............................................................................... 15
Network connectivity............................................................................................................15
Inconsistency in Sensor and Manager configuration ...........................................................15
Software or signature set incompatibility..............................................................................15
Firewall between the devices...............................................................................................16
Management port configuration ...........................................................................................16
Connectivity issues between the Sensor and other network devices .........................................17
Duplex mismatches..............................................................................................................17
Valid auto-negotiation and speed configurations.................................................................17
Explanation of CatOS show port Command Counters.........................................................20
Auto-negotiation...................................................................................................................21
iii
Page 4

Checking Sensor health..............................................................................................................22
Pinging a Sensor..................................................................................................................22
Ensuring that the Sensor is receiving traffic................................................................................ 22
Checking Sensor failover status.................................................................................................. 23
Cabling failover through a network device...........................................................................23
Checking whether a signature or software update was successful............................................. 24
Checking status of a download or upload ................................................................................... 24
Conditions requiring a Sensor reboot.......................................................................................... 24
Rebooting a Sensor via the Manager...................................................................................25
Rebooting a Sensor using the reboot command..................................................................25
Sensor doesn’t boot .................................................................................................................... 25
Debugging critical Sensor issues................................................................................................ 25
Loss of connectivity between the Sensor and Manager.............................................................. 29
How Sensor handles new alerts during connectivity loss ....................................................30
Manager connectivity to the database.........................................................................................30
Manager database is full......................................................................................................31
Error on accessing the Configuration page................................................................................. 31
Sensor response if its throughput is exceeded ........................................................................... 31
MySQL issues.............................................................................................................................32
How Sensors handle various types of traffic...............................................................................32
Jumbo Ethernet frames........................................................................................................32
ISL frames............................................................................................................................32
Sensor failover issues.................................................................................................................33
External fail-open kit issues in connecting to the monitoring port ............................................... 33
XC cable connection issues for M8000 Sensors......................................................................... 33
Chapter 5 Determining False Positives .................................................... 34
Reducing false positives..............................................................................................................34
Tune your policies.......................................................................................................................34
About false positives and “noise”.........................................................................................35
Determining a false positive versus noise............................................................................36
Chapter 6 System Fault Messages............................................................ 38
Critical faults................................................................................................................................ 38
Error faults...................................................................................................................................55
Warning faults ............................................................................................................................. 61
Informational faults...................................................................................................................... 65
Other faults.................................................................................................................................. 76
Chapter 7 Error Messages.......................................................................... 77
Error messages for RADIUS servers .......................................................................................... 77
Error messages for LDAP server ................................................................................................ 78
Chapter 8 Using the InfoCollector tool..................................................... 79
Introduction..................................................................................................................................79
Running the InfoCollector............................................................................................................ 80
Using InfoCollector...................................................................................................................... 80
Chapter 9 Automatically restarting a failed Manager with Manager
Watchdog..................................................................................................... 81
Introduction..................................................................................................................................81
How the Manager Watchdog Works............................................................................................ 81
Installing Manager Watchdog...................................................................................................... 82
Starting Manager Watchdog........................................................................................................82
Using Manager Watchdog with Manager in an MDR configuration ............................................82
Tracking Manager Watchdog activities ....................................................................................... 82
Chapter 10 Utilizing the McAfee Knowledge Base .................................. 84
Index............................................................................................................. 86
iv
Page 5

Preface
This preface provides a brief introduction to the product, discusses the information in this
document, and explains how this document is organized. It also provides information such
as, the supporting documents for this guide and how to contact McAfee Technical Support.
Introducing McAfee Network Security Platform
McAfee® Network Security Platform [formerly McAfee® IntruShield®] delivers the most
comprehensive, accurate, and scalable Network Access Control (NAC), network Intrusion
Prevention System (IPS) and Network Threat Behavior Analysis (NTBA) for mission-critical
enterprise, carrier and service provider networks, while providing unmatched protectio n
against spyware; known, zero-day, and encrypted attacks.
McAfee
network traffic by analyzing NetFlow information flowing through the network in real time,
thus complementing the NAC and IPS capabilities in a scenario in which McAfee Net work
Security Sensor, NAC Sensor, and NTBA Appliance are installed and managed through a
single Manager.
®
Network Threat Behavior Analysis Appliance provides the capability of monitoring
About this Guide
This guide provides the basic troubleshooting techniques for Network Security Platform.
You get information on the key issues to be taken care of in the McAfee
Manager [formerly McAfee
Sensor [formerly McAfee
from installing Network Security Platform to troubleshooting the system.
This guide provides detailed sections on the following topics:
Pre-installation recommendations
Hardening McAfee Network Security Manager (Manager) Server
Troubleshooting techniques
How to use the InfoCollector tool and Manager Watchdog
Audience
This guide is intended for use by network technicians responsible for maintaini ng the
Network Security Platform and analyzing and disseminating the resulting data. It is
assumed that you are familiar with IPS-related tasks, the relationship between tasks, and
the commands necessary to perform particular tasks.
®
®
IntruShield® Security Manager] and McAfee® Network Security
®
IntruShield® Sensor] software in a step-by- step manner; right
Network Security
v
Page 6
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Conventions used in this book
This document uses the following typographical conventions:
Convention Example
Preface
Terms that identify fields, buttons,
tabs, options, selections, and
commands on the User Interface
(UI) are shown in
Arial Narrow bold
font.
Menu or action group selections
are indicated using a right angle
bracket.
Procedures are presented as a
series of numbered steps.
Names of keys on the keyboard
are denoted using UPPER CASE.
Text such as syntax, key words,
and values that you must type
exactly are denoted using
Courier New font.
Variable information that you must
type based on your specific
situation or environment is shown
in italics.
Parameters that you must supply
are shown enclosed in angle
brackets.
Service field on the Properties tab specifies the
The
name of the requested service.
Select My Company > Admin Domain > Summary.
1. On the Configuration tab, click Backup.
Press ENTER.
Type: setup and then press ENTER.
Type: Sensor-IP-address and then press
ENTER.
set Sensor ip <A.B.C.D>
Information that you must read
Caution:
before beginning a procedure or
that alerts you to negative
consequences of certain actions,
such as loss of data is denoted
using this notation.
Information that you must read to
Warning:
prevent injury, accidents from
contact with electricity, or other
serious consequences is denoted
using this notation.
Notes that provide related, but
Note:
non-critical, information are
denoted using this notation.
vi
Page 7

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Related Documentation
The following documents and on-line help are companions to this guide. Refer to Quick Tour
for more information on these guides.
Quick Tour
Installation Guide
Upgrade Guide
Getting Started Guide
IPS Deployment Guide
Manager Configuration Basics Guide
I-1200 Sensor Product Guide
I-1400 Sensor Product Guide
I-2700 Sensor Product Guide
I-3000 Sensor Product Guide
I-4000 Sensor Product Guide
I-4010 Sensor Product Guide
M-1250/M-1450 Sensor Product Guide
M-1250/M-1450 Quick Start Guide
M-2750 Sensor Product Guide
M-2750 Quick Start Guide
M-3050/M-4050 Sensor Product Guide
M-3050/M-4050 Quick Start Guide
M-6050 Sensor Product Guide
M-6050 Quick Start Guide
M-8000 Sensor Product Guide
M-8000 Quick Start Guide
Gigabit Optical Fail-Open Bypass Kit Guide
Gigabit Copper Fail-Open Bypass Kit Guide
10 Gigabit Fail-Open Bypass Kit Guide
M-8000/M-6050/M-4050/M-3050 Slide Rail Assembly Procedure
M-2750 Slide Rail Assembly Procedure
M-series DC Power Supply Installation Procedure
Administrative Domain Configuration Guide
Manager Server Configuration Guide
CLI Guide
Device Configuration Guide
IPS Configuration Guide
NAC Configuration Guide
Integration Guide
System Status Monitoring Guide
Reports Guide
Custom Attack Definitions Guide
Central Manager Administrator's Guide
Best Practices Guide
Special Topics Guide—In-line Sensor Deployment
Preface
vii
Page 8
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Special Topics Guide—Sensor High Availability
Special Topics Guide—Virtualization
Special Topics Guide—Denial-of-Service
NTBA Appliance Administrator's Guide
NTBA Monitoring Guide
NTBA Appliance T-200 Quick Start Guide
NTBA Appliance T-500 Quick Start Guide
Contacting Technical Support
If you have any questions, contact McAfee for assistance:
Online
Contact McAfee Technical Support http://mysupport.mcafee.com.
Registered customers can obtain up-to-date documentation, technical bulletins, and quick
tips on McAfee's 24x7 comprehensive KnowledgeBase. In addition, custom ers can also
resolve technical issues with the online case submit, software downloads, and signature
updates.
Preface
Phone
Technical Support is available 7:00 A.M. to 5:00 P.M. PST Monday-Friday. Extended 24x7
Technical Support is available for customers with Gold or Platinum service contracts.
Global phone contact numbers can be found at McAfee Contact Information
http://www.mcafee.com/us/about/contact/index.html page.
Note: McAfee requir
your system when opening a ticket with Technical Support. You will be provided with
a user name and password for the online case submission.
es that you provide your GRANT ID and the serial number of
Information requested for Troubleshooting
McAfee wants to provide you with the best possible support. When you contact Technical
Support, we will request a variety of information to use to troubleshoot your deployment.
This section describes the information we ask that you have available for troubleshooting.
General information
your GRANT ID. This was provided to you when you purchased the product.
the version number of the Manager software you are using
the version number of the McAfee Network Security Sensor (Sensor) software you are
using
Is this a new or existing issue?
any physical changes made to the environment recently
viii
Page 9

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Did you make any changes in your environment/setup/configuration that may have
introduced the issue?
Manager-specific information
We may ask you to use our troubleshooting tool, which is called InfoCollector. This tool will
collect all Manager-related log files (For example, ems.log, emsout, output.bin, config
back, and the Sensor trace file, if you have uploaded it to the Manager) and return them to
us for analysis
As of this writing, the tool is available at the following link:
http://serviceweb/McAfee/backline/escalations/MER_TOOL/IPSInfoCollector.zip
Sensor issues
the Sensor deployment configuration
information on the GBICs you are using with Sensor GE ports; this information is
extremely helpful for troubleshooting link issues
the volume of traffic through the Sensor
in some cases, a network diagram (particularly for troubleshooting asymmetric traffic
issues)
a Sensor trace file, which you can create using the process described in Providing a
Sensor diagnostics trace.
Sensor operating mode (i.e., In-line, SPAN or TAP). This information can be obtained
from:
Sensor_Name > Interface > View Details
peer device port settings (For example, for Cisco switches/routers, you would provide
the output of the show port [mod[/port] command.
Management port configuration (obtained by issuing a show mgmtport command)
Preface
Signature set issues
the signature set and software versions you are running
the frequency at which you see the false positive
whether the alert condition is reproducible
policy configuration
alert evidence reports
traffic volume, if possible
traffic type
what software and systems are on the affected systems
your network topology
ix
Page 10

C HAPTER 1
Before You Install
This chapter lists pre-installation recommendations.
Pre-installation recommendations
These McAfee® Network Security Platform [formerly McAfee® IntruShield®] pre-installation
recommendations are a compilation of the information gathered from individual interviews
with some of the most seasoned McAfee Network Security Platform System Engineers at
McAfee.
Planning for installation
Before installation, ensure that you complete the following tasks:
®
The server, on which McAfee
should be configured and ready to be placed online.
You must have administrator privileges for McAfee Network Security Manager
(Manager) server.
This server should be dedicated, hardened for security, and placed on its own subnet.
This server should not be used for programs like instant messaging or other non-
secure Internet functions.
Make sure your hardware requirements meet the requirements. See Server
requirements.
Ensure the proper static IP address has been assigned to the Manager server. For the
Manager server, McAfee strongly recommends assigning a static IP against using
DHCP for IP assignment.
If applicable, configure name resolution for the Manager.
Ensure that all parties have agreed to the solution design, including the location and
mode of all McAfee
groups, and if and how the Manager will be connected to the production network.
Get the required license file and grant number.
Accumulate the required number of wires and (supported) GBICs, SFPs, or XFPs.
Ensure these are approved hardware from McAfee or a supported vendor. Ensure
that the required number of Network Security Platform dongles, which ship with the
McAfee Network Security Sensors (Sensors), are available.
Crossover cables will be required for 10/100 or 10/100/1000 monitoring ports if they
are directly connected to a firewall, router, or end node. Otherwise, standard patch
cables are required for the Fast Ethernet ports.
If applicable, identify the ports to be mirrored, and someone who has the knowledge
and rights to mirror them.
Allocate the proper static IP addresses for the Sensor. For the Sensors, you cannot
assign IPs using DHCP.
®
Network Security Sensor, the use of sub-interfaces or interface
Network Security Manager software will be installed,
1
Page 11
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Identify hosts that may cause false positives, for example, HTTP cache servers, DNS
servers, mail relays, SNMP managers, and vulnerability scanners.
Functional requirements
Following are the functional requirements to be taken care of:
Before You Install
Install Wireshark (formerly known as Ethereal http://www.wireshark.com
http://www.wireshark.org) on the client PCs. Etherea
l is a network protocol analyzer
for Unix and Windows servers, used to analyze the packet logs created by Sensors.
Ensure the correct version of JRE is installed on the client system, as described in the
Release Notes. This can save a lot of time during deployment.
Determine a way in which the Manager maintains the correct time. To keep time from
drifting, for example, point the Manager server to an NTP timeserver. (If the time is
changed on the Manager server, the Manager will lose connectivity with all Sensors
and the McAfee
®
Network Security Update Server because SSL is time sensitive.)
If Manager Disaster Recovery (MDR) is configured, ensure that the time difference
between the Primary and Secondary Managers is less than 60 seconds. (If the spread
between the two exceeds more than two minutes, communication with the Sensors
will be lost.)
If you are upgrading from a previous version, we recommend that you follow the
instructions in the respective version’s release notes or, if applicable, the Upgrade
Guide
.
Install a desktop firewall
McAfee strongly recommends that you configure a packet-filtering firewall to block
connections to ports 8551, 3306, 8007, 8009, and 8552 of your Manager server. The
firewall can either be a host-based or a network-based.
Set your firewall to deny connections to these ports if the connections are not initiated by
the localhost. The only connections that should be allowed are those from the Manager
server itself; that is, the localhost.
For example, if another machine attempts to connect to port 8551, 8552, 3306, 8007 and
8009 the firewall should automatically block any packets sent. If you need assistanc e in
blocking these, contact Technical Support.
If a firewall will reside between the Sensor, Manager, or administrative client, which
includes a personal firewall on the Manager, the following ports must be opened:
Port # Protocol Description Direction of communication
4167 (high ports)
(source port on the Manager)
and
UDP
Default SNMPv3
(command
channel)
Manager-->Sensor
8500
(destination port on the
Sensor)
2
Page 12
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Port # Protocol Description Direction of communication
Before You Install
8501 TCP Proprietary
Sensor-->Manager
(install port)
8502 TCP Proprietary
Sensor-->Manager
(alert
channel/control
channel)
8503 TCP Proprietary
Sensor-->Manager
(packet log
channel)
8504 TCP Proprietary
Sensor-->Manager
(file transfer
channel)
8555 TCP SSL/TCP/IP
client-->Manager
(Threat Analyzer)
443 TCP HTTPS client-->Manager
80 TCP Web-based user
interface
client-->Manager
(Webstart/JNLP, Console
Applets)
22 TCP SSH Remote console access
Note: If you choose to use non-default ports for the Install port, Alert port, and Log
port, ensure that those ports are also open on the firewall.
Note that 3306/TCP is used internally by the Manager to connect to the MySQL
database.
If you have Email Notification or SNMP Forwarding configured on the Manager, and
there is firewall residing between the Manager and your SMTP or SNMP server,
ensure the following ports are available as well.
Additional communication ports
Port # Protocol Description Direction of communication
25 TCP SMTP Manager-->SMTP server
49 TCP TACACS+ Integration Sensor-->TACACS+ server
162 UDP SNMP Forwarding Manager-->SNMP server
389 TCP LDAP Integration
(without SSL)
443 TCP Secure communication
for MDR
443 TCP Secure communication
for MDR
514 UDP Syslog forwarding (ACL
logging)
636 TCP LDAP Integration (with
SSL)
3
Manager-->LDAP server
Manager 1-->Manager 2
Manager 2-->Manager 1
Manager-->Syslog server
Manager-->LDAP server
Page 13

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Port # Protocol Description Direction of communication
1812 UDP RADIUS Integration Manager-->RADIUS server
Close all open programs, including email, the
instant messaging before installation to avoid port conflicts. A port conflict may
prevent the application from binding to the port in question because it will already be
in use.
Caution: The Manager is a standalone system and should not have other
applications installed.
Using anti-virus software with the Manager
If you plan to install anti-virus software such as McAfee VirusScan on the Manager, be
sure the MySQL directory and its sub-directories are excluded from the anti-virus scanning
processes. For example selecting
entire MySQL installation directory from the anti-virus scanning processes. Otherwise,
Network Security Platform packet captures may result in the deletion of essential MySQL
files.
Also exclude the Network Security Platform installation directory and its sub-directories
because temporary files are created there that might conflict with the anti-virus scanner.
Administrative Tools > Services window, and
...\Manager\MySQL and its subdirectories will exclude the
Before You Install
Note: If you install McAfee VirusScan 8.5.0i on the Manager after the installation of
the Manager software, the MySQL scanning exceptions will be created
automatically, but the Network Security Platform exceptions will not.
McAfee VirusScan and SMTP notification
From 8.0i, VirusScan includes an option (enabled by default) to block all outbound
connections over TCP port 25. This helps reduce the risk of a compromised host
propagating a worm over SMTP using a homemade mail client.
VirusScan avoids blocking outbound SMTP connections from legitimate mail clients, such
as Outlook and Eudora, by including the processes used by these products in an exclusion
list. In other words, VirusScan ships with a list of processes it will allow to create outbound
TCP port 25 connections; all other processes are denied that access.
The Manager takes advantage of the JavaMail API to send SMTP notifications. If you
enable SMTP notification and also run VirusScan 8.0i or above, you must therefor e add
java.exe to the list of excluded processes. If you do not explicitly create the exclusion
within VirusScan, you will see a Mailer Unreachable error in the Manager Operational Status
to each time the Manager attempts to connect to its configured mail server.
To add the exclusion, follow these steps:
4
Page 14

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
1 Launch the VirusScan Console.
2 Right-click the task called
menu.
3 Highlight the rule called
4 Click
Edit.
5 Append java.exe to the list of
6 Click
OK to save the changes.
User interface responsiveness
The responsiveness of the user interface, the Threat Analyzer in particular, has a lasting
effect on your overall product satisfaction.
In this section we suggest some easy but essential steps, to ensure that Network Security
Platform responsiveness is optimal:
During Manager software installation, use the recommended values for memory and
connection allocation.
You will experience better performance in your configuration and data forensic tasks
by connecting to the Manager from a browser on a client machine. Performance may
be slow if you connect to the Manager using a browser on the server machine itself.
Perform monthly or semi-monthly database purging and tuning. The greater the
quantity of alert records stored in the database, the longer it will take the user
interface to parse through those records for display in the Threat Analyzer. T he
default Network Security Platform settings err on the side of caution and leave alerts
(and their packet logs) in the database until the user explicitly decides to remove
them. However, most users can safely remove alerts after 30 days.
Caution: It is imperative that you tune the MySQL database after each purge
operation. Otherwise, the purge process will fragment the database, which can
lead to significant performance degradation.
Defragment the disks on the Manager on a routine basis, with the exception of the
MySQL directory. The more often you run your defragmenter, the quicker the process
will be. Consider defragmenting the disks at least once a month.
Warning: Do NOT attempt to defragment the MySQL directory using an O/S
defrag utility. To defragment MySQL tables, use a MySQL-specific utility,
myisamchk available in the <mysqlinstallation>\bin directory.
Limit the quantity of alerts to view when launching the Threat Analyzer. This will
reduce the total quantity of records the user interface must parse and therefore
potentially result in a faster initial response on startup.
When scheduling certain Manager actions (backups, file maintenance, archivals,
database tuning), set a time for each that is unique and is a minimum of an hour
after/before other scheduled actions. Do not run scheduled actions concurrently.
Access Protection and choose Properties from the right-click
Prevent mass mailing worms from sending mail.
Processes to Exclude.
Before You Install
5
Page 15

C HAPTER 2
Hardening the Manager Server for Windows 2003
This section describes methods for hardening your McAfee® Network Security Manager
(Manager) server.
Introduction
Manager implementation varies between environments. The Manager server’s pos itioning
in the network, both physically and logically, may influence specific remote access and
firewall configuration requirements.
The following best practices are intended to cover the configurable features that can
impact the security of Manager. This information should be used in combination with the
McAfee
McAfee’s recommendations, at a high level:
Install a desktop firewall on the server and open the proper ports
Harden the MySQL installation
Harden the Manager host
®
Network Security Platform Release Notes and the rest of the documentation set.
Install a desktop firewall
It is recommended that you operate a desktop firewall on the Manager server. Certain
ports are used within the McAfee Network Security Platform. Some of these required for
Manager--McAfee® Network Security Sensor (Sensor) and Manager client-server
communication. All remaining unnecessary ports should be closed. The ports used by
Network Security Platform are listed in Install a desktop firewall (on page 2
).
Harden the MySQL installation
Ensure the cmd window used for making changes to database tables in the “mysql”
database stays opened in the mysql shell until validation is completed.
This is necessary to enable you to rollback the changes in case you need to. Rollback
procedures are shown at the end of this section.
Use another cmd window, where necessary, to validate hardening changes you h ave
made.
6
Page 16
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Remove test database
Remove the ‘test” database from the server.
Hardening the Manager Server for Windows 2003
1. Start My SQL.
2. Backup db table to do
dbbackup before changing it.
3. Validate that the backup table
was created and row count
matches that of the mysql.db table.
4. Check all the databases on the
Manager server.
5. Remove the test db, Keep only
the MYSQL and Network Security
Platform (for example, lf)
databases.
6. You should see only two
databases (MYSQL and LF) if you
are using the default Network
Security Platform installation of
MySQL.
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> create table db_backup as
select * from db;
mysql> select count(*) from
db_backup;
mysql> show databases;
mysql> drop database test;
mysql> show databases;
Remove local anonymous users
To remove local anonymous users:
1. Look for blank entries for user.
2. Remove anonymous access to databases
3. Remove anonymous/blank accounts
4. Validate that “localhost” replaced % entry
under the host column. You will also notice
you will now need to qualify username and
password on the local machine to get into
mysql shell from the mysql.exe CLI.
mysql> select host,db,user from db;
mysql> update db set
host="localhost" where user="";
mysql> flush privileges;
Remove remote anonymous users
To remove remote anonymous users, you harden mysql.exe CLI access by forcing the
requirement for a username and password to get into the mysql shell as follows.
7
Page 17
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Hardening the Manager Server for Windows 2003
Start MySQL.
Back up the user table to
user_backup before changing it.
Validate that the backup table was
created and row count matches that
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> create table user_backup
as select * from user;
mysql> select count(*) from
user_backup;
of the mysql.db table.
List all users and hosts.
mysql> select user,host from
user;
Remove anonymous/blank
accounts.
Validate that rows with blank user
columns have been removed.
mysql> delete from user where
user="";
mysql> select user,host from
user;
Secure MySQL remote access
This section provides two options for removing remote access.
Remove individual users’ remote access
Remove ALL remote access (Recommended)
Remove individual users’ remote access
Do ONE of the following:
Remove admin (Network Security Platform user) remote access
mysql> delete from user where host!='localhost' and
user='admin';
(The admin user cannot login remotely; however Manager root can. Use second cmd
window to validate.)
mysql>flush privileges;
Remove root remote access (Recommended minimum action)
mysql> delete from user where host!='localhost' and
user='root';
This ensures that the root user cannot login remotely; however Manager user can log
in remotely. Use second cmd window to validate.
mysql>flush privileges;
Remove ALL remote access
mysql> delete from user where host!='localhost'
ALL user access is disabled including Manager users from remote host(s).
Use another cmd window to validate; you can ONLY log in to the MySQL CLI on the
Manager server by qualifying username, password and db. For example: mysql -
uadmin -pXXX lf
8
Page 18

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Rolling back your changes
If you need to roll back your changes, use the following commands:
To roll back changes made to the mysql.db table from the mysql.db_backup table:
mysql> rename table db to db_1;
mysql> rename table db_backup to db;
mysql> flush privileges;
To roll back changes made to the "mysql.user" table from mysql.user_backup table:
mysql> rename table user to user_1
mysql> rename table user_backup to user;
mysql> flush privileges;
Remove debug shell at port 9001
In addition to denying traffic over port 9001 and 9002 (as per Install a desktop firewall) (on
), the debugging shell that runs on port 9001 can be disabled by modifying the
page 2
value o
f the iv.policymgmt.RuleEngine.BSH_Diagnostics_Port record in the iv_emsproperties table.
To disable the port, set the value in the field called “value” = -1
Hardening the Manager Server for Windows 2003
Other best practices for securing Manager
Use a clean, dedicated machine for the Manager server and perform a fresh install of
the Manager software, including the installation of the embedded MySQL database.
No other software should be available on the server, with the exception of a hostbased firewall as described in Install a desktop firewall. (on page 2
Make sure the PC is in an isolated, physically secure environment
Disallow access to the directory clumsily and all its sub-directories to anyone other
than authorized administrators. Use Microsoft Knowledge Base article # 324067 to
accomplish this procedure. Disallow the following permissions:
Read
Write
Read and Write
Modify
List folder contents
Full control
Disable HTTP TRACE request. It can be disabled with the following mod_rewrite
syntax in the Apache Server's httpd.conf file (available in the “<Network Security
Platform installation directory>/Apache/conf” directory).
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_METHOD} ^TRACE
RewriteRule .* - [F]
)
9
Page 19

C HAPTER 3
Hardening the Manager Server for Windows 2008
Implementation of Manager varies from environment to environment. The Manager's
physical and logical position in the network influences specific remote access and firewall
configuration requirements. The following best practices on managing configurable
features on Manager impacts the security of Manager.
Pre-installation
Use a dedicated machine for the Manager server and then install Manager and the
embedded MySQL database. Other than the host-based firewall, no other software should
be installed on the server. Before installation of Manager do the following:
Ensure that the server is located in a physically secure environment.
Connect the server on a protected or isolated network.
If the hard disk is old, use fdisk (a command line utility) to remove all partitions and
create new partitions.
Installation
Installation of Manager should be performed as follows:
Install the US version of Windows Server 2008.
Use NTFS on all partitions.
Post Installation
After installation of Manager perform the following installations:
Install the latest Windows Server 2008 patches, service packs, and hot fixes from
Install a Virus Scanner and update the signatures.
Also keep a check on the following:
Minimize the number of Windows roles and features that are installed.
Uninstall applications that are not necessary.
Microsoft.
Note: Exclude “Network Security Manager” and “MySQL” directories from being
scanned.
10
Page 20

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Disabling non-required Services
Disable the following services.
DHCP Client
FTP
Print spooler
Remote access auto connection manager
Remote procedure call locator
Remote registry
Server
TCP/IP NetBIOS helper service
Telephony service.
Note: Enable these services only if it is absolutely required.
Setting System Policies
Ensure to set the following system policies:
Hardening the Manager Server for Windows 2008
Implement the System key and strong encryption of the password database by
running SYSKEY.EXE
Use Microsoft security compliance toolkit or set local security policy
Display legal notice at during interactive logon window.
Do not display username that was earlier used to login.
Disable Posix
Clear virtual memory page file during shutdown
Disable autorun
Disable LMHOSTS lookup while setting the advanced TCP/IP settings.
Setting User Policies
Ensure to set the following user policies:
Rename the administrator account.
Disable guest account .
Passwords should be at least 8 ASCII characters.
Enable locking of screensaver.
Setting a Desktop Firewall
It is recommended that a desktop firewall operates on the Manager server. The following
ports are required for Manager-Sensor communication.
Note: Ensure that there are no other open ports using a scanning tool such as
Vulnerability Manager.
11
Page 21
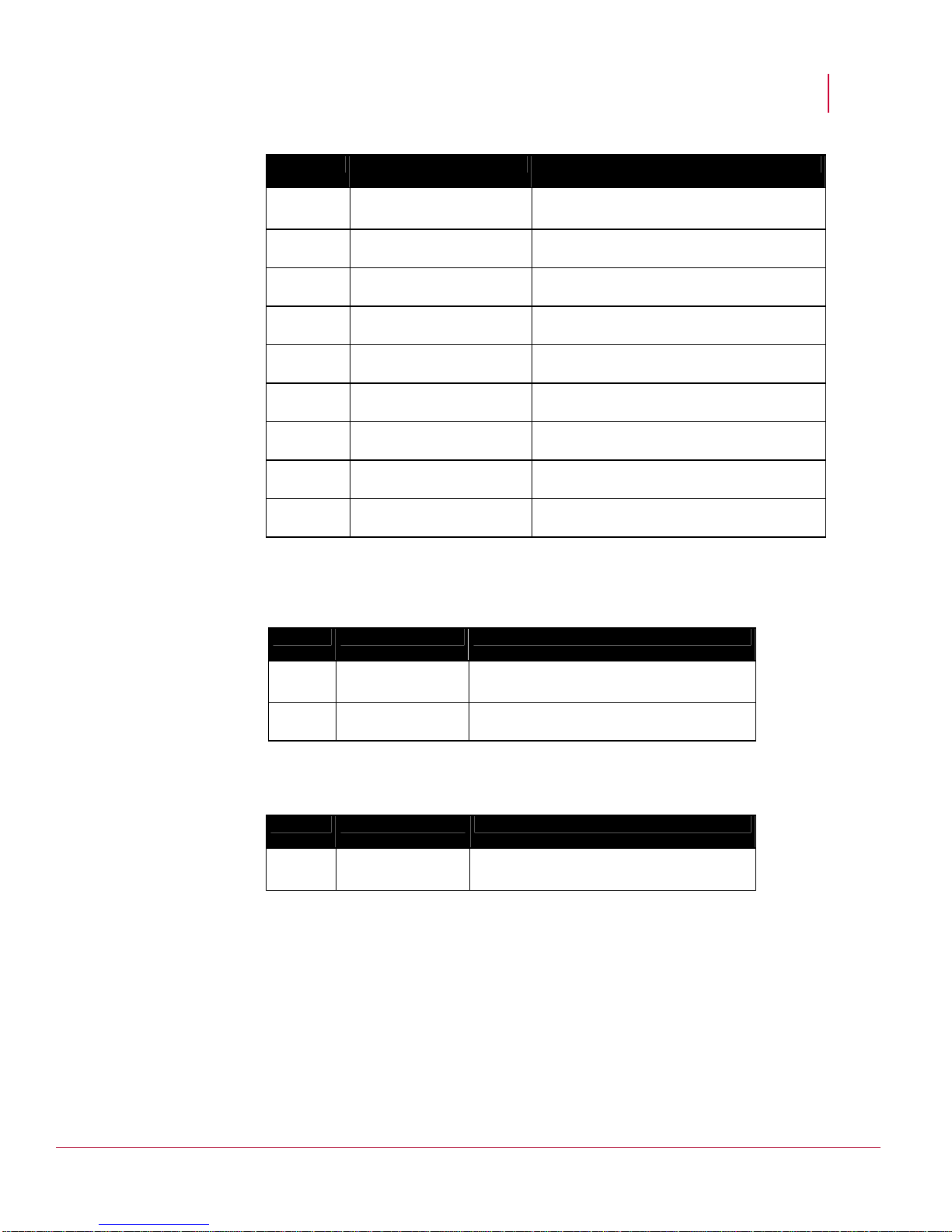
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Port Description Communication
80 HTTP port Client to Manager
443 HTTPS Client to Manager
3306 MySQL database Open only while using external SQL database
8500 Command channel(UDP) Manager to Sensor
8501 Install port(TCP) Sensor to Manager
8502 Alert channel(TCP) Sensor to Manager
8503 Packet log channel(TCP) Sensor to Manager
8504 File transfer channel(TCP) Sensor to Manager
8555 Alert viewer(TC) Client to Manager
Hardening the Manager Server for Windows 2008
When email notification or SNMP forwarding is configured on Manager and there is firewall
between Manager and SNMP Server, ensure that the following ports are allowed through
firewall.
Port Description Communication
25 SMTP port Manager to SMTP server
162 SNMP forwarding Manager to SNMP server
If you have ePO integration configured on Manager, and there is firewall between Manager
and the ePO Server, ensure the following port is also allowed through firewall.
Port Description Communication
8443 ePO
Manager to ePO server
communication port
Configuring Audit Events
Set the following events to be audited:
Audit account logon events
Audit account management
Audit logon events
Audit object access (Failure)
12
Page 22

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Audit policy change (Success)
Audit privilege use (Failure)
Audit system events (Success)
Hardening the Manager Server for Windows 2008
13
Page 23

C HAPTER 4
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
This section lists some troubleshooting tips for McAfee® Network Security Platform.
Facilitating troubleshooting
When an in-line device experiences problems, most people ’s instinct is to physically pull it
out of the path; to disconnect the cables and let traffic flow unimpeded while the device
can be examined elsewhere. McAfee recommends yo u first try the follo wing techniques to
troubleshoot a McAfee
All Sensors have a Layer2 Passthru feature. If you feel your Sensor is causing
network disruption, before you remove it from the network, issue the following
command:
layer2 mode assert
This pushes the Sensor into Layer2 Passthru (L2) mode, causing traffic to flow
through the Sensor while bypassing the detection engine. Check to see whether your
services are still affected; if they are, then you have eliminated certain Sensor
hardware issues; the problem could instead be a network issue or a configuration
issue. (The layer2 mode deassert command pushes the Sensor back to
detection mode.)
McAfee recommends that you configure Layer2 Passthru Mode on each Sensor. This
enables you to set a threshold on the Sensor that pushes the Sensor into L2 bypass
mode if the Sensor experiences a specified number of errors within a specified
timeframe. Traffic then continues to flow directly through the Sensor without passing
to the detection engine.
Connect a fail-open kit, which consists of a bypass switch and a controller, to any GE
monitoring port pairs on the Sensor. If a kit is attached to the Sensor, disabling the
Sensor ports forces traffic to flow through the bypass switch, effectively pulling the
Sensor out of the path. For FE monitoring ports, there is no need for the external kit.
Sensors with FE ports contain an internal tap; disabling the ports will send traffic
through the internal tap, providing fail-open functionality.
®
Network Security Sensor (Sensor) issue:
Caution 1: Note that the Sensor will need to reboot to move out of L2 mode only if
the Sensor entered L2 mode because of internal errors. (It does not need a reboot if
the layer2 mode assert command was used to put the Sensor into L2 mode).
Caution 2: A Sensor reboot breaks the link connecting the devices on either side of
the Sensor and requires the renegotiation of the network link between the two
devices surrounding the Sensor.
Caution 3: Depending on the network equipment, this disruption should range from
a couple of seconds to more than a minute with certain vendors’ devices. A very
brief link disruption might occur while the links are renegotiated to place the Sensor
back in in-line mode.
14
Page 24
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Starting your troubleshooting
Before you get too deep into troubleshooting techniques, it is a good practice to consider
the following questions:
Were there physical changes to your network that occurred recently?
If another device is placed in the Sensor’s position, does that device receive traffic?
If the Sensor is in L2 mode, are your network’s services still affected?
Are you using approved McAfee GBICs or SFPs or XFPs with your Sensor? [For a list
of approved hardware, see McAfee KnowledgeBase article KB56364 (Go to
http://mysupport.mcafee.com/Eservice/
Difficulties connecting Sensor and Manager
If you experience problems getting the McAfee® Network Security Manager (Manager) and
Sensor to communicate, see if one of the following situations may be the cause.
Network connectivity
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
, and click Search the KnowledgeBase)]
Ensure that the Sensor and Manager server have power and are appropriately
connected to the network.
Verify the link LEDs on both devices to indicate they have an active link.
Ping the Sensor and Manager server to ensure that they are available on the network.
Inconsistency in Sensor and Manager configuration
Check to ensure that the Sensor name that was entered in the CLI is identical to that
entered in the Manager. Ensure the same for the shared secret key value. If these
values do not match, the two cannot communicate.
Note: The Sensor name is case-sensitive.
Check the network addresses for the Manager, the Manager’s gateway, and the
Sensor to ensure everything is configured correctly by typing show at the Sensor CLI
command prompt.
Software or signature set incompatibility
Check to ensure that the Sensor software image, Manager software version, and signature
set version are compatible.
A compatibility matrix is provided in the release notes that accompany each product
release.
15
Page 25
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Firewall between the devices
If there is a firewall between the Sensor and the Manager server, make sure the devices
are able to communicate by opening the appropriate ports.
Note : Ports used by the Manager server are listed in the section Install a desktop
firewall. (on page 2)
Management port configuration
If you experience problems getting your Sensor and Manager to communicate, it may be a
communication issue between the Sensor’s Management port and the network device to
which it is connected. Check the Management Port Link LEDs on the Sensor; if the link is
down, see if any of the following suggestions enable connectivity.
Check that the network device is on-line.
Check the cable connecting the Sensor to the network device.
Ensure that the port on the device to which the Management port is connected is
enabled/active.
The port speed and duplex mode of the two devices must match. For example, if the
device connecting to the Sensor is not set to auto-negotiate, you must configure the
Management port to use the same settings as those of the device connecting to the
Management port. To troubleshoot this, use the set mgmtport command.
Note: Check the link LEDs on the devices to see if communication is
established, or use the show mgmtport command to show the link’s status.
Try each of these configuration options to see if one establishes a link:
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
1 First (if possible) set the other device’s port configuration to auto-negotiate. (The
Sensor is set to auto-negotiate by default.)
2 Using the set mgmtport command as described below in Setting the management
port speed and duplex mode, try setting the speed and port of the Sensor to speed
100 and duplex half or full.
3 If no link is established, try speed 10 and duplex half or full.
4 If none of the above attempts creates a link, try setting the port on the other device to
a speed of 100, duplex half or full, and try step 2 again.
5 If this does not establish a link, you can then do the same, setting the other device to
a speed of 10, duplex half or full , and try step 3 again.
6 If you are still experiencing difficulties, contact McAfee Technical Support.
Note: M series Sensors Management port support 1000 Mbps(1Gbps)too.Use the
set mgmtport auto command to establish a link to the connecting device(before
performing this,see to it that the other device's port configuration's speed is fixed to
1000 and also set to auto-negotiate).
16
Page 26

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Setting the management port speed and duplex mode
1 Set the speed of the Management port and whether the port should be set to half-or
full-duplex. At the prompt, type:
set mgmtport speed <10 | 100 | 1000> duplex <half | full>
where
<10> indicates 10 Mbps, <100> indicates 100 Mbps, and <1000> indicates 1000
Mbps
<half> indicates half-duplex and <full> indicates full-duplex.
Note: 1000 Mbps is applicable only for M-series Sensors. I-Series sensors
support only 10/100 Mbps for Management port
Example: set mgmtport speed 100 duplex half
Connectivity issues between the Sensor and other network
devices
The most common Sensor problems relate to configuration of the speed and duplex
settings. Speed determination issues may result in no connectivity between the Sensor
and the switch.
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Duplex mismatches
A duplex mismatch (for example, one end of the link in full-duplex and the other in halfduplex) may result in performance issues, intermittent connectivity, and loss of
communication. It can also create subtle problems in applications. For example, if a Web
server is talking to a database server through an Ethernet switch with a duplex mismatch,
small database queries may succeed, while large ones fail due to a timeout.
Manually setting the speed and duplex to full-duplex on only one link partner generally
results in a mismatch. This common issue results from disabling auto-negotiation on one
link partner and having the other link partner default to a half-duplex configuration, creating
a mismatch. This is the reason why speed and duplex cannot be hard-coded on onl y one
link partner. If your intent is not to use auto-negotiation, you must manually set both link
partners' speed and duplex settings to full-duplex.
Valid auto-negotiation and speed configurations
The table below summarizes all possible settings of speed and duplex for Sensors and
Cisco catalyst switch ports.
17
Page 27
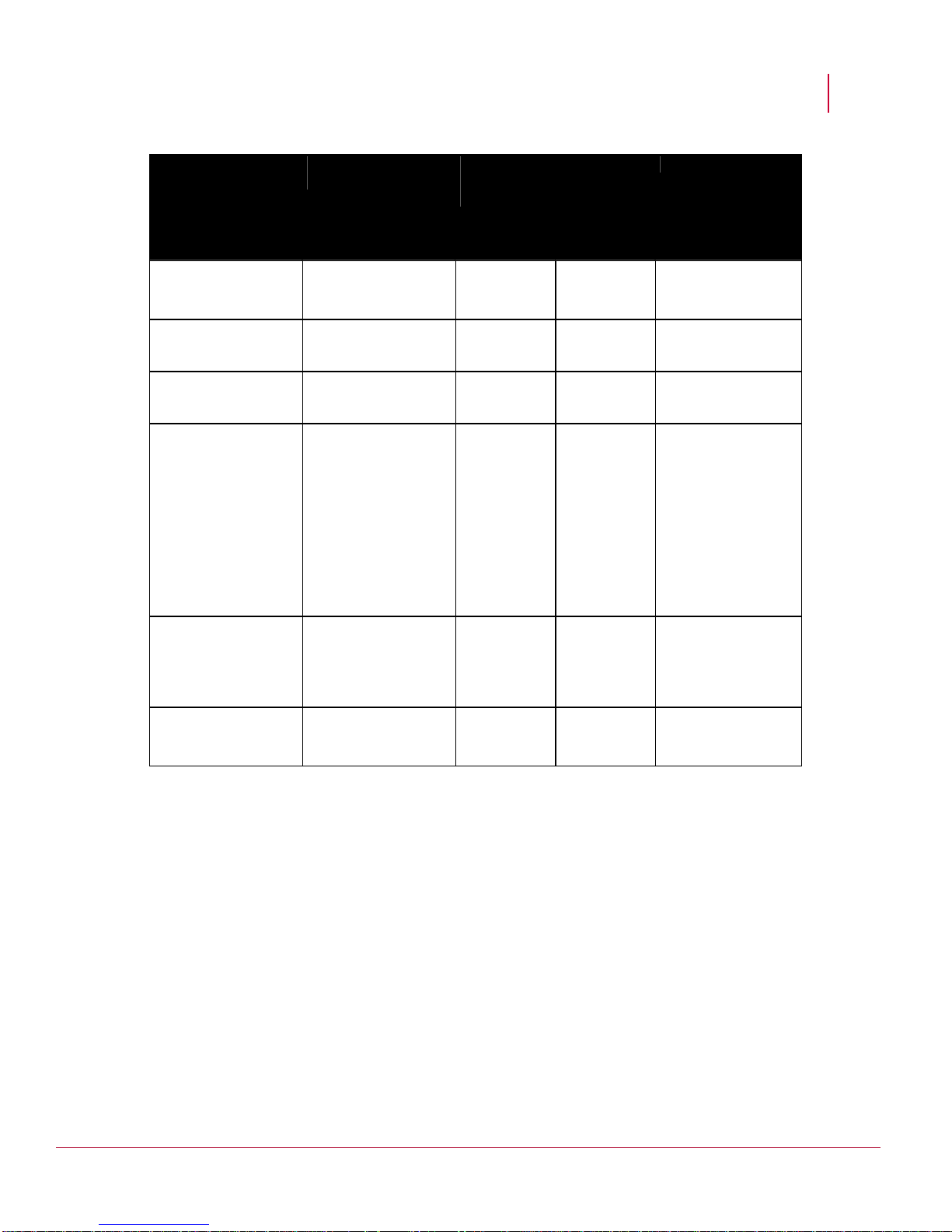
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Network Security
Platform Configuration
10/100/1000 port
(Speed/Duplex)
100 Mbps
Full-duplex
100 Mbps
Full-duplex
100 Mbps
Full-duplex
100 Mbps
Half-duplex
Configuration of Switch
(Speed/Duplex)
1000 Mbps
Resulting
Sensor
(Speed/Duplex)
Resulting
Catalyst
(Speed/Duplex)
No Link No Link Neither side
Full-duplex
AUTO 100 Mbps
Full-duplex
1000 Mbps
Full-duplex
100 Mbps
Full-duplex
AUTO 100 Mbps
Half-duplex
100 Mbps
Full-duplex
100 Mbps
Full-duplex
100 Mbps
Half-duplex
Comments
establishes link, due
to speed mismatch
Correct configuration
Correct Manual
Configuration
Link is established,
but switch does not
see any autonegotiation
information from
McAfee Network
Security Platform and
defaults to halfduplex when
operating at 10/100
Mbps.
10 Mbps
Half-duplex
10 Mbps
Half-duplex
AUTO 100 Mbps
Half-duplex
100 Mbps
Half-duplex
Link is established,
but switch does not
see Fast Link Pulse
(FLP) and defaults to
10 Mbps half-duplex.
1000 Mbps
Half-duplex
No Link No Link Neither side
establishes link, due
to speed mismatch.
Gigabit auto-negotiation (no link to connected device)
Gigabit Ethernet has an auto-negotiation procedure that is more extensive than that which
is used for 10/100 Mbps Ethernet (per Gigabit auto-negotiation specification IEEE 802.3z-
1998). The Gigabit auto-negotiation negotiates flow control, duplex mode, and rem ote fau lt
information. You must either enable or disable link negotiation on both ends of the link.
Both ends of the link must be set to the same value or the link will not connect.
If either device does not support Gigabit auto-negotiation, disabling Gigabit autonegotiation forces the link up.
Troubleshooting a Duplex Mismatch with Cisco Devices
When troubleshooting connectivity issues with Cisco switches or routers, verify that the
Sensor and the switch/routers are using a valid configuration. The show intfport <port>
command on the Sensor CLI will help reveal errors.
18
Page 28

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Sometimes there are duplex inconsistencies between Network Security Platform and the
switch port. Symptoms include poor port performance and frame check sequence (FCS)
errors that increment on the switch port. To troubleshoot this issue, manually configure the
switchport to 100 Mbps, half-duplex. If this action resolves the connectivity problems, you
may be running into this issue. Contact Cisco's TAC for assistance.
Use the following commands to verify fixed interface settings on some Cisco devices that
connect to Sensors:
Cisco PIX® Firewall
interface ethernet0 100full
Cisco CSS 11000
interface ethernet-3
phy 100Mbits-FD
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Cisco Catalyst® 2900XL, 3500XL Series (Hybrid)
interface FastEthernet0/2
duplex full
speed 100
Cisco Catalyst 4000, 5000, 6000 Series (Native)
set port speed 1/1 100
set port duplex 1/1 full
Connectivity issues with Cisco 3750-12S switch
Use the following ports when connecting a Cisco 3750-12s switch to your Sensor: 3, 4, 7,
8, 11, or 12. Connections using ports 1, 2, 5, 6, 9, or 10 may cause network jitter, which is
an inconsistent delay of packets.
Cisco IOS® for Catalyst 4000, 6000 Series
Router(config)# interface fastethernet slot/port
Router(config-if)# speed 100
Router(config-if)# duplex full
When troubleshooting Network Security Platform performance issues with Cisco switches,
view the output of the show port mod/port command, and note the counter
information.
19
Page 29
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
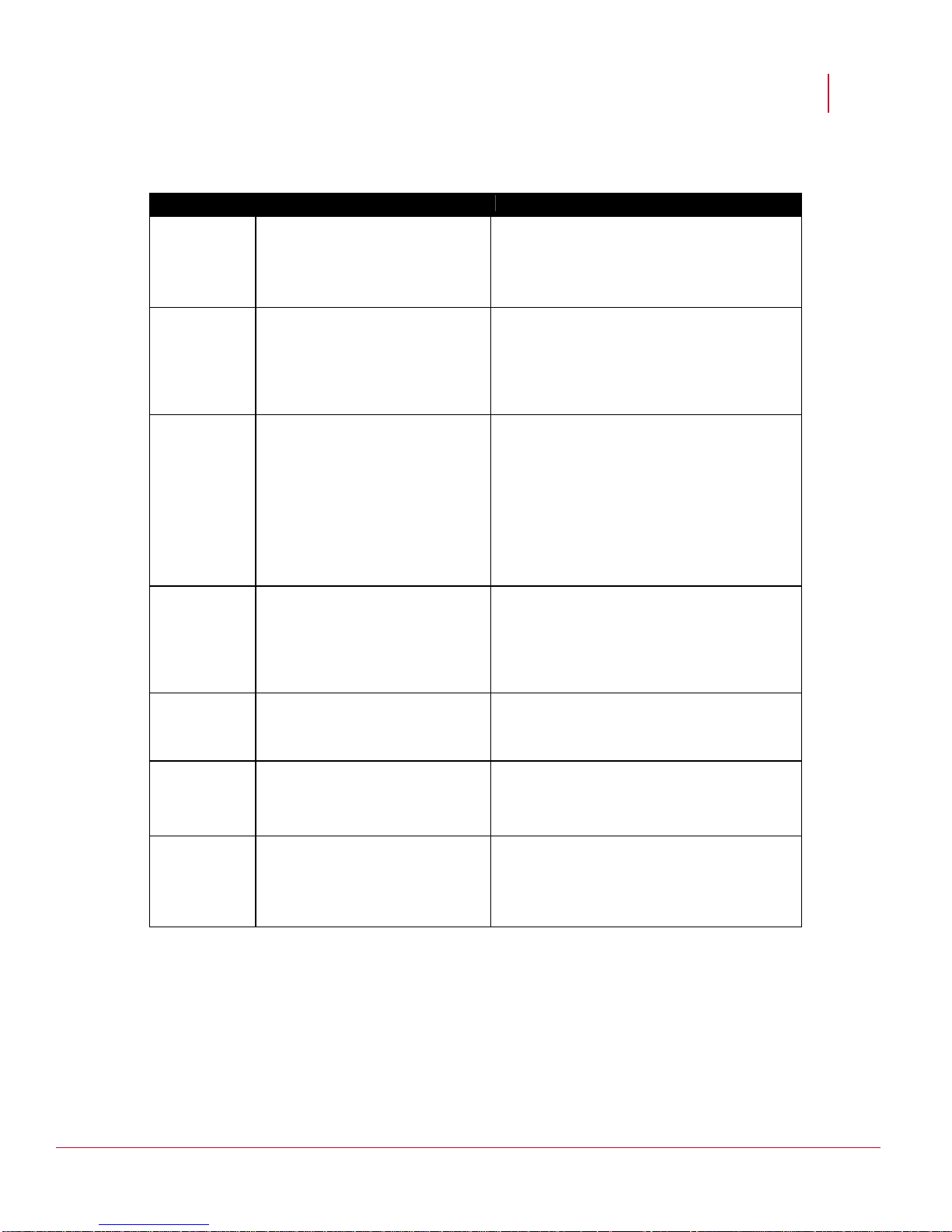
Explanation of CatOS show port Command Counters
Counter Description Possible Causes
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Alignment
Errors
Alignment errors are a count of the
number of frames received that do
not end with an even number of
octets and have a bad CRC.
FCS FCS error count is the number of
frames that were transmitted or
received with a bad checksum
(CRC value) in the Ethernet frame.
These frames are dropped and not
propagated onto other ports.
Xmit-Err This is an indication that the internal
transmit buffer is full.
Rcv-Err This is an indication that the receive
buffer is full.
These are the result of collisions at half-duplex,
duplex mismatch, bad hardware (NIC, cable, or
port), or a connected device generating frames
that do not end with on an octet and have a bad
FCS.
These are the result of collisions at half-duplex,
duplex mismatch, bad hardware (NIC, cable, or
port), or a connected device generating frames
with bad FCS.
This is an indication of excessive input rates of
traffic. This is also an indication of transmit
buffer being full. The counter should only
increment in situations in which the switch is
unable to forward out the port at a desired rate.
Situations such as excessive collisions and 10
Mb ports cause the transmit buffer to become
full. Increasing speed and moving the link
partner to full-duplex should minimize this
occurrence.
This is an indication of excessive output rates of
traffic. This is also an indication of the receive
buffer being full. This counter should be zero
unless there is excessive traffic through the
switch. In some switches, the Out-Lost counter
has a direct correlation to the Rcv-Err.
UnderSize These are frames that are smaller
than 64 bytes (including FCS) and
have a good FCS value.
Single
Collisions
Single collisions are the number of
times the transmitting port had one
collision before successfully
transmitting the frame to the media.
Multiple
Collisions
Multiple collisions are the number of
times the transmitting port had more
than one collision before
successfully transmitting the frame
to the media.
This is an indication of a bad frame generated
by the connected device.
This is an indication of a half-duplex
configuration.
This is an indication of a half-duplex
configuration.
20
Page 30

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Counter Description Possible Causes
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Late Collisions A late collision occurs when two
devices transmit at the same time
and neither side of the connection
detects a collision. The reason for
this occurrence is that the time to
propagate the signal from one end
of the network to another is longer
than the time to put the entire
packet on the network. The two
devices that cause the late collision
never see that the other is sending
until after it puts the entire packet on
the network. Late collisions are
detected by the transmitter after the
first time slot of the 64-byte transmit
time occurs. They are only detected
during transmissions of packets
longer than 64 bytes. Its detection is
exactly the same as it is for a
normal collision; it just happens later
than it does for a normal collision.
Excessive
Collisions
Excessive collisions are the number
of frames that are dropped after 16
attempts to send the packet resulted
in 16 collisions.
Carrier Sense Carrier sense occurs every time an
Ethernet controller wants to send
data and the counter is incremented
when there is an error in the
process.
This is an indication of faulty hardware (NIC,
cable, or switch port) or a duplex mismatch.
This is an indication of over utilization of the
switch port at half-duplex or duplex mismatch.
This is an indication of faulty hardware (NIC,
cable, or switch port).
Runts These are frames smaller than 64
bytes with a bad FCS value.
Giants These are frames that are greater
than 1518 bytes and have a bad
FCS value.
Auto-negotiation
Auto-negotiation issues typically do not result in link establishment issues. Instead, autonegotiation issues mainly result in a loss of performance. When auto-negotiation leaves
one end of the link in, for example, full-duplex mode and the other in half-duple x (also
known as a duplex mismatch), errors and retransmissions can cause unpr edictable
behavior in the network causing performance issues, intermittent connectivity, and loss of
communication. Generally these errors are not fatal-traffic still makes it through-but
locating and fixing them is a time-waster.
This is an indication of the result of collisions,
duplex mismatch, IEEE 802.1Q (dot1q), or an
Inter-Switch Link Protocol (ISL) configuration
issue.
This is an indication of faulty hardware, dot1q, or
an ISL configuration issue.
21
Page 31

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Situations that may lead to Auto-negotiation issues
Auto-negotiation issues with the Sensor may result from nonconforming implementation,
hardware incapability, or software defects.
Generally, if the switch used with the Sensor adheres to IEEE 802.3u auto-negotiation
specifications and all additional features are disabled, auto-neg otiation should properly
negotiate speed and duplex, and no operational issues should exist.
Problems may arise when vendor switches/routers do not conform exactly to the IEEE
specification 802.3u.
Vendor-specific advanced features that are not described in IEEE 802.3u for 10/100
Mbps auto-negotiation (such as auto-polarity or cabling integrity) can also lead to
hardware incompatibility and other issues.
Checking Sensor health
To see if your Sensor is functioning correctly, do one of the following:
On the Sensor:
At the command prompt, type status. This displays system status (such as
Operational Status, system initialization, signature version, trust, channel status, alert
counts, and so on). Sensor should be initialized and in good health.
At the command prompt, type show. This displays configuration information (such as
Sensor image version, type, name, Manager and Sensor IP addresses, and so on).
On the Manager:
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
In the Manager Home page, view the Operational Status section. Manager status
should be
Note: If you see system faults indicating that the Manager is down, see System
Fault Messages (on page 38), to interpret the fault and, if necessary, take action to
clear the fault.
UP, and Sensor status should be ACTIVE.
Pinging a Sensor
The Sensor Management port responds only to 1 ping/sec. This prevents it from
susceptibility to a ping flood.
To ping a Sensor Management port from multiple hosts, increase the time interval between
pings.
Ensuring that the Sensor is receiving traffic
Sensor Statistics can be viewed in the Threat Analyzer by creating a new dashboard and
by choosing monitors that display different type of Sensor statistics. Sensor Flow
Statistics, IP Spoofing Statistics, Packet Drop Statistics, Port Packet Drop Statistics and
Rate Limiting Statistics are the monitors available.
Follow this procedure to view Sensor Flow Statistics:
22
Page 32

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
1 Click Options > Dashboard > New to open the Create New Dashboard dialog.
2 Enter a name for the new dashboard in the
3 Click
Assign Monitor to view the Assign Monitor Dialog.
4 Select the
5 Select Default Monitors against Category (these are the default choices).
6 Select
Sensor Performance against Type to view the choice of Monitors for Sensor
Performance in the
7 Select
Statistics - Flows and click OK.
8 Select the Sensor for which you wish to view flow statistics.
9 Click
Refresh to view the flow statistics for the selected Sensor.
10 Follow a similar procedure and select other Monitors for Sensor Performance to view
the relevant Sensor Statistics.
List of Monitors for Sensor Statistics
Sensor Flow Statistics: Statistical view of the TCP and UDP flow data processed by a
Network Security Sensor. Checking your flow rates can help you determine if your
Sensor is processing traffic normally, while also providing you with a view of statistics
such as the maximum number of flows supported as well as the number of active TCP
and UDP flows.
IP Spoofing Statistics: Statistics on the number of IP spoofing attacks detected by
McAfee Network Security Platform. Statistics are displayed per direction.
Packet Drop Statistics: Packet drop rate on a Sensor. The statistics is displayed on a
per Sensor basis. The statistics includes the count of number of packets dropped by
Sensor due to set rate limiting on the Sensor and sanity check failures.
Port Packet Drop Statistics: Packet drop rate on a port.
Rate Limiting Statistics: Rate limiting statistics provides the estimated number of
packets dropped/bytes dropped by the Network Security Sensor. You can view rate
limiting statistics for each Sensor (per port), listed in the resource tree of Manager
Assign an existing Monitor radio button.
Monitor choices box.
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Dashboard Dialog.
Checking Sensor failover status
To ensure that two Sensors comprising a failover pair are communicating via their
interconnection cable, go to each Sensor's CLI and type show failover-status.
Failover should display as enabled (YES), and the peer Sensor should display as UP.
Cabling failover through a network device
Do not cable the heartbeat connection through an external network device.
To keep overhead low and throughput high, the Sensors do not include layer 2 or 3
headers on the packets they pass over the heartbeat connection, and they pass data
larger than the standard Ethernet maximum frame size (1518 bytes).
If you attempt to place a network device, such as a switch or router, between the heartbeat
ports, the heartbeat connection will fail.
23
Page 33

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Checking whether a signature or software update was
successful
To see if your Sensor successfully received a signature update or software upgrade, you
can use the status command as shown in the following procedure, or the
downloadstatus command, described later in this chapter.
To use the status command:
1 On the Sensor, type status at the command prompt before updating the signature
set on the Sensor. Note the signature version.
2 Update the signature set on the Sensor using the Manager screens.
3 On the Sensor, again type status at the command prompt after the update from
Manager is complete. Verify that the signature version number has incremented. The
new signature version should match with the signature set version that has been
updated from the Manager and applied to the Sensor.
Checking status of a download or upload
To see the progress of an upload or download, use the downloadstatus command.
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
The downloadstatus command displays the status of various download/upload
operations: signature, software image, and DoS profile downloads (from Manager to
Sensor) and DoS profile and debug trace uploads (from Sensor to Manager). It also lists
the number of times you have performed the operation, status of your previous attempt to
perform the operation (including—if the operation failed—the cause of failure), and the
time the command was executed.
Do the following:
On the Sensor, type downloadstatus at the command prompt.
Conditions requiring a Sensor reboot
The following situations either cause or require a Sensor reboot. You have two options for
rebooting the Sensor. You can reboot the Sensor from the NSM interface, or you can issue
the reboot CLI command.
Note: A Sensor reboot can take up to five minutes.
Issuing the following CLI commands causes an automatic reboot of the Sensor:
resetconfig
deletesignatures
factorydefaults
For more information on the Sensor CLI commands, see
Changing the Sensor’s management port IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) requires a manual
reboot of the Sensor, before the change takes into effect.
CLI Guide.
24
Page 34

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Certain internal software errors may cause the Sensor to reboot itself. See a
description of Sensor fault messages later in this chapter. For more information on
Operational Status Viewer, see
Enabling/disabling SSL requires a Sensor reboot.
Enabling/disabling parsing and detection of attacks in IPv6 traffic passing through the
Sensor monitoring port requires a manual reboot of the Sensor.
In the Manager user interface, you can enable/disable parsing and detection of
attacks in IPv6 traffic with the
Settings/Sensor_Name > Advanced Scanning > IP Settings
Configuring IP Settings for IPv4 and IPv6 traffic,
Upgrading Sensor software requires a manual reboot of the Sensor.
Rebooting a Sensor via the Manager
The Reboot Sensor action restarts a Sensor. You perform this action in the Manager
interface.
To reboot a Sensor, do the following:
System Status Monitoring Guide.
Scan IPv6 traffic for attacks option from the IP Settings tab (IPS
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
). For more information, see
IPS Configuration Guide.
1 Select
2 Click
Reboot Now.
Rebooting a Sensor using the reboot command
The reboot command restarts a Sensor. You perform this action in the Sensor CLI:
1 At the prompt, type:
reboot
2 Confirm the reboot.
Sensor doesn’t boot
If you cannot get the Sensor to boot, try the following:
Check to ensure that the Sensor is powered on. Check the LEDs on the front of the
Sensor.
Check the front panel LEDs to ensure that the Sensor temperature is normal. For
more information on Sensor LEDs, see the
If you receive an error message in the CLI: “OS not found,” you may have a corrupted
internal flash. If you see this error, contact Technical Support to obtain help in
recovering the Sensor.
<root admin domain>/ Device List/ Device_Name Node>Physical Device>Reboot.
Sensor Product Guide for your Sensor model.
Debugging critical Sensor issues
CLI commands in the debug mode are used to improve supportability of the Sensor for
better debugging of critical issues. This section is a detailed reference to the CLI
debugging commands available in the debug mode.
25
Page 35

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
o
s
a
d
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Debug command
name/Parameter(s)
set l3
show l3 status
set l7
Available parameters:
on/off
show l7 status
set ipfrag
Available parameters:
on/off
show ipfragstatus
set recon
Available parameters:
on/off
show recon status
Description
Enables or disables the layer 3 packet processing on datapaths.
Note: This setting should be reconfigured if the Sensor is rebooted.
Displays the layer 3 packet processing status on datapaths.
Enables or disables layer 7 packet processing and attack detection
on datapaths.
Note: This setting should be reconfigured if the Sensor is rebooted.
Displays the layer 7 protocol parsing and attack detection
status on datapaths.
Enables or disables IP fragment reassembly processing on
datapaths.
Displays the IP fragment reassembly processing status.
Enables or disables reconnaissance attacks detection.
Note: This setting should be reconfigured if the Sensor is rebooted.
Displays reconnaissance attack detection status.
Note: This setting should be reconfigured if the Sensor is rebooted.
show startup stats Displays the startup initialization information.
set intfportid
Available parameters:
1A-6B (a valid ethernet monit
port on the Sensor)
adminstatus up/down
ifo/ifc/tap/span(change
the operating mode in-line fail
open line fail-close, tap or sp
gig/auto (sets intfport spee
Gbps or auto negotiate)
Sets the adminstatus, operatingmode, flowcontrol, speed and
duplex on the specified gigabit ethernet monitoring port.
It is not mandatory to use all the parameters for this command.
Example 1
You can execute this command with only one parameter (auto)
to set the port to auto-negotiate.
set intfport id 4B auto
Example 2
You can also execute this command with multiple parameters.
set intfport id 3A adminstatus up operatingmode
span
For more information on this command, see
show sensor health
Displays the Sensor health information.
Sensor CLI Guide.
26
Page 36

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Debug command
name/Parameter(s)
show saved alerts
show saved packets
show statistics tcp
show statistics alerts
show statistics l4
show attackcount
Description
Displays the total number and size of alerts that are saved.
Displays the total number of packets that are saved.
Displays the TCP statistics of a datapath for an ID range. It includes
the following information TCP total packets
TCP total packets
TCP drop count
TCP error count.
Displays the alert statistics (signature alerts, reconnaissance alerts
and ACL logs) that are sent to the Manager.
Displays the layer 4 statistics.It includes the following information.
Total layer 4 flow blocks
Total SYN flow blocks
Total active TCP flows
Total Inactive TCP flows
Total TCP in timewait
Total active UDP flows
Total flows in SYN state
Total free TCBs
Total created flows
Total timeout flows
Displays the total number of attacks detected in a datapath.
show eccerrors
show statistics udp
show statistics icmp
Displays the number of ecc errors.
Displays the UDP statistics.It includes the following information.
UDP Total packets
UDP Dropped packets
UDP TimedOut UDP Resp(onse) packets
UDP ACL Deny count
Displays the ICMP statistics.It includes the following
information.
ICMP echo request packets
ICMP echo reply packets
ICMP unsol(icited) reply packets
ICMP other packets
ICMP total packets
ICMP dropped under load
ICMP dropped checksum error.
27
Page 37

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
m
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Debug command
name/Parameter(s)
show statistics ipfrag
show datapath
processunits
set loglevel
Available parameters:
all/dos/dp/
reset debugmode passwd
Description
Displays the IP fragment statistics in a data path. It includes the
following information.
Total number of IP
Fragments received
Total number of IP flows
Number of duplicate fragments
Number of fragments dropped
Fragments dropped for invalid options
Number of flows timeout
Number of flows dropped for invalid checksum
Number of invalid fragments
Error getting reassembled lists
Number of fragments received after timeout.
Displays the number of process units in a datapath.
Assigns the log level for modules at each sensor processing unit.
Resets the password for entering into the debug mode.
Note: This command can be executed only from
debug mode.
perf Displays the count of total watermark exceeded in the DoS
processor.
clearactiveflows
Clears the existing active TCP and UDP flows using the following
sequence of actions:
1 Configures the Sensor to layer2 mode.
2 Clears the existing TCP and UDP flows.
set aidlog
Available parameters:
Configures the Sensor back to normal mode
Sets the debugging for false positives on the Sensor for a specific
attack ID
enable/disable/attack ID
show aidlog status
Displays the status of the attack ID logging.
28
Page 38

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Debug command
name/Parameter(s)
set aidlog
Available parameters:
off
enable <WORD>
disable <WORD>
where <WORD> is the
attack ID.
layer2 forward tcp
Available parameters:
enable/disable/0-65535
/[0-65535(optional)]
layer2 forward udp
Available parameters:
enable/disable/0-65535
/[0-65535(optional)]
layer2 forward vlan
Available parameters:
Description
Sets the debugging for false positives on the Sensor for a specific
attack ID.
Configures the Layer2 forwarding to a TCP port or to a range of TCP
ports.
Configures the Layer2 forwarding to a single or range of UDP ports.
Enables or disables a single VLAN ID or a range of vlan IDs on all
the interfaces available on the Sensor.
enable/disable/0-4095
/[0-4095(optional)]
layer 2 forward vlan
interface
Available parameters:
Enables or disables a single VLAN ID or a range of VLAN IDs on
specific interfaces available on the Sensor.
enable/disable/04095/[04095(optional)]/<all |
interfaceAinterfaceB(optional)>
layer2 forward clear
Available parameters:
all/tcp/udp/vlan
Removes all the ports or VLANs that are enabled for layer2
forwarding.It removes all the port numbers ranging from 0 to 65535
that were enabled for TCP and UDP. Similarly all the VLAN IDs
ranging from 0 to 4095 are removed.
Loss of connectivity between the Sensor and Manager
If you have previously established a connection between the Sensor and the Manager and
the connection fails, try the following:
Check network connectivity.
View the system status on both the Manager and the Sensor.
29
Page 39

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Check to ensure the Management port on the Sensor is configured with the proper
speed and duplex mode as described in Management port configuration.
Has the time been reset on the Manager server? The connection between the Sensor
and Manager server is secure, and this secure communication is time-sensitive, so
the time on the devices should remain synchronized. You must set the time on the
Manager server before you install the Manager software and never change the time
on that machine. If the time changes on the Manager server, the Manager will lose its
connectivity with the Sensor and the Update Server. A time change could ultimately
cause serious database errors.
For more information, see the KnowledgeBase article KB55587 (Go to
http://mysupport.mcafee.com/Eservice/
How Sensor handles new alerts during connectivity loss
The Sensor stores alerts internally until connection is restored. Network Security Platform
classifies events and prioritizes to ensure the buffer is filled with the most meaningful
events to an analyst.
The following table lists the number of alerts that can be stored locally on the Sensor.
Number Alert Type
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
, and click Search the KnowledgeBase)
100000 Signature based alerts
2500 Throttled alerts (with source and destination IP
information)
2500 Compressed throttled alerts (alerts with no source and
destination IP information)
2500 Statistical or anomaly DoS
2500 Throttled DoS alerts
1000 Host sweep alerts
1000 Port scan alerts
Once the connection from the Sensor to the Manager has been re-established, the queued
alerts are forwarded up to the Manager. So the customer will retain them even in the event
that connectivity is disrupted for some time.
If the buffer fills up before connectivity is restored, the Sensor will drop new alerts, but if
blocking is enabled, the Sensor will continue to block irrespective of the Sensor's
connectivity with the Manager.
Manager connectivity to the database
In the event that the Manager loses connectivity to the database (i.e. the database goes
down) the alerts are stored in a flat file on the Manager server. When the database
connectivity is restored, the alerts are stored in the database.
30
Page 40

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Manager database is full
We recommend that the customer monitor the disk space on a continuous basis to prevent
this from happening.
If the Manager database or disk space is full, the Manager will unable to process any new
alerts or packet logs. In addition, the Manager may not be able to process any
configuration changes, including policy chan ges and alert acknowledgement. In fact, the
Manager may stop functioning completely.
To rectify this situation, please perform maintenance operations on the database, including
deleting unnecessary alerts and packet logs. Furthermore, please reevaluate database
capacity planning and sizing, and monitor free space proactively. The Manager is
designed with various file and disk maintenance functions. You can archive alert and
packetlog data and then delete the data to free up disk space. It also provides a
standalone tool for creating database backups that can be archived for emergency
restoration.
The Manager also provides disk maintenance alerts, which send proactive system fault
messages when certain database dependent processes exceed a user-defined threshold
(say 70%). Manager generates faults for various thresholds for database space utilization.
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
Error on accessing the Configuration page
On some occasions, accessing the Manager Configuration page can result in an error
message. This typically happens if you access various versions of the Manager from the
same client or use the Manager client to access other Web-based applications as well.
This is a Java-cache related issue.
To resolve the issue:
1 On the Manager client, go to Windows Control Panel > Java > General > Settings.
2 Click
Delete Files and then click OK in the Delete Temporary Files dialog.
This deletes all Java-related temporary files on the client.
3 Log out of the Manager and close Internet Explorer.
4 Log in to the Manager in a new instance of Internet Explorer.
Sensor response if its throughput is exceeded
Each Sensor model has a limited throughput. For example, the Network Security Platform
2700 Sensor is rated at 600Mbps performance. With the Gigabit interfaces it is
theoretically possible to oversubscribe the limit. What happens in this situation? Will it
throttle the throughput to 600Mbps or will you just lose the IPS functionality for everything
more than 600Mbps?
The answer is that the Sensor will drop packets depending on the TCP flow violation
settings.We also have the over-subscription feature where the sensor can inline-forward
traffic without IPS inspection if it is over-subscribed.There could also be false negatives
and the traffic may experience high latency.
It is very important that you stay within the operating parameters of the device you deploy.
If you are actually running at gigabit speeds, you should probably be running a n I-3000/I-
31
Page 41

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
4000/I-4010/M3050/M4050/M6050 and M8000.Sensor, which all have a much higher
throughput.
MySQL issues
The common symptoms that occur if your database tables become corrupt:
.MYI or .MYD errors reported in the ems.log file
Inability to acknowledge or delete faults in Operational Status
When trying to view packet log for in the Threat Analyzer, you receive an error
message:
You receive the message “No Packet log available for this alert at this time”
If you think that your MySQL database tables have become corrupt, follow the instructions
on verifying your tables, which is available in McAfee KnowledgeBase ar ticle KB60660 (Go
to http://mysupport.mcafee.com/Eservice/
How Sensors handle various types of traffic
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
, and click Search the KnowledgeBase).
Non-ethernet frames are forwarded without inspection.
The following are the types of special traffic.
Jumbo Ethernet frames (on page 32)
ISL frames (on page 32)
Jumbo Ethernet frames
Sensors respond differently to jumbo frames based on which ports are receiving them.
Inspection is available for jumbo frames only for M-3050, M-4050, M-6050, and M-8000
Sensors.
10/100 (FE) ports: Jumbo frames are not supported. When a 10/100 port receives a
jumbo frame, the frame is dropped.
1000 (GE) port: The frame is passed through the Sensor, but is not subjected to IPS
inspection.
ISL frames
All McAfee® Network Security Sensor (Sensor) models (running all Sensor software
versions) pass ISL frames through the Sensor without IPS inspection.
32
Page 42

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Sensor failover issues
By having a check on the following connections and settings may resolve Sensor failover
issues.
The Sensor model and Sensor image version on both the peer Sensors should be the
same.
The Sensor License and IPv6 status should be identical on the peer Sensors.
Identify the interconnect port for the selected model because the interconnect ports
vary for different models.
Check on the FO type setting on the Sensor. The failover creation would fail if the FO
type is set on the primary Sensor.
The Sensor health status should be good and normal.
External fail-open kit issues in connecting to the monitoring
port
External fail-open kit issues may occur due to disconnection of network device cables and
improper cabling or port configuration.
Troubleshooting Network Security Platform
By having a check on the following connections may resolve the issue.
Ensure that the cables are properly connected to both the network devices and the
Bypass Switch.
Ensure that the transmit and receive cables are properly connected to the Bypass
Switch.
XC cable connection issues for M8000 Sensors
XC cable connection issues may occur in the M8000 Sensors due to improper cabling of
XFP interconnect ports(XC2, XC3, XC5 and XC6).
Check the following connections in the M8000 Sensors while facing such issues.
One end of an LC-LC fiber-optic cable should be plugged into the XC2 port of the
primary Sensor and the other end of the cable to be plugged into the XC5 port of the
secondary Sensor.
One end of an LC-LC fiber-optic cable should be plugged into the XC3 port of the
primary Sensor and the other end of the cable to be plugged into the XC6 port of the
secondary Sensor.
33
Page 43

C HAPTER 5
Determining False Positives
This section lists methods for determining and reducing false positives.
Reducing false positives
Your policy determines what traffic analysis your McAfee® Network Security Sensor
(Sensor) will perform. McAfee
templates to get you started toward your ultimate goal: prevent attacks from damaging
your network, and limit the alerts displayed in the Threat Analyzer to those which are valid
and useful for your analysis.
There are two stages to this process: initial policy configuration and policy tuning.Though
these are tedious tasks, McAfee has extended its blocking options to include
SmartBlocking, which only activates blocking when high confidence signatures are
matched, thus minimizing the possibility of false positives.Network Security Platform is
replacing its present Recommended for Blocking (RFB) designation with Recommended
for SmartBlocking (RFSB) because this new level of granularity enables McAfee to
recommend many more attacks – the list of RFB attacks is a subset of the list of RFSB
attacks.
The ultimate goal of policy tuning is to eliminate false positives and noise and avoid
overwhelming quantities of legitimate, but anticipated alerts.
®
Network Security Platform provides a number of policy
Tune your policies
The default McAfee Network Security Platform policy templates are provided as a generic
starting point; you will want to customize one of these policies for your needs. So the first
step in tuning is to clone the most appropriate policy for your network and your goals, and
then customize it. (You can also modify a policy directly rather than modifying a copy.)
This process is involved, and is discussed in IPS Configuration Guide.
Some things to remember when tuning your policies:
We ask that you set your expectations appropriately regarding the elimination of false
positives and noise. A proper Network Security Platform implementation includes
multiple tuning phases. False positives and excess noise are routine for the first 3 to 4
weeks. Once properly tuned, however, they can be reduced to a rare occurrence.
When initially deployed, Network Security Platform frequently exposes unexpected
conditions in the existing network and application configuration. What may at first
seem like a false positive might actually be the manifestation of a misconfigured router
or Web application, for example.
Before you begin, be aware of the network topology and the hosts in your network, so
you can enable the policy to detect the correct set of attacks for your environment.
34
Page 44

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Take steps to reduce false positives and noise from the start. If you allow a large
number of “noisy” alerts to continue to sound on a very busy network, parsing and
pruning the database can quickly become cumbersome tasks. It is preferable to all
parties involved to put energy into preventing false positives than into working around
them.Attack filters are also an option where you can have custom rule sets specific to
his environment. You can disable all alerts that are obviously not applicable to the
hosts that you protect. For example, if you use only Apache Web servers, you can
disable IIS-related attacks.
About false positives and “noise”
The mere mention of false positives always causes concern in the mind of any securit y
analyst. However, false positives may mean quite differently things to different people. In
order to better manage the security risks using any IDS/IPS devices, it's very important to
understand the exact meanings of different types of alerts so that appropriate response
can be applied.
With Network Security Platform, there are three types of alerts which are often taken as
“false positives:”
incorrectly identified events
correctly identified events subject to interpretation by usage policy
correctly identified events uninteresting to the user.
Determining False Positives
Incorrect identification
These alerts typically result from overly aggressive signature design, special
characteristics of the user environment, or system bugs. For example, typical users will
never use nested file folders with a path more than 256 characters long; however, a
particular user may push the Windows' free-style naming to the extreme and create files
with path names more than 1024 characters. Issues in this category are rare. They can be
fixed by signature modifications or software bug fixes.
Correct identification; significance subject to usage policy
Events of this type include those alerting on activities associated with Instant Messaging
(IM), Internet Relay chat (IRC), and Peer to Peer programs (P2P). Some security policies
forbid such traffic on their network; for example, within a corporate common operation
environment (COE); others may allow them to various degrees. Universities, for example,
typically have a totally open policy for running these applications. Network Security
Platform provides two means by which to tune out such events if your policies deem these
events uninteresting. First, you can define a customized policy in which these events are
disabled. In doing so, the Sensor will not even look for these events in the traffic stream to
which the policy is applied. If these events are of interest for most of the hosts except a
few, creating attack filters to suppress alerts for the few hosts is an alternative approach.
35
Page 45

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Correct identification; significance subject to user sensitivity (also known
as noise)
There is another type of event which you may not be interested in, due to the perceived
severity of the event. For example, Network Security Platform will detect a UDP-based
host sweep when a given host sends UDP packets to a certain number of distinct
destinations within a given time interval. Although you can tune this detection by
configuring the threshold and the interval according to their sensitivity, it's still possibl e that
some or all of the host IPs being scanned are actually not live. Some users will consider
these alerts as noise, others will take notice because it indicates possible reconnaissance
activity. Another example of noise would be if someone attempted an IIS-based attack
against your Apache Web server. This is a hostile act, but it will not actually harm anything
except wasting some network bandwidth. Again, a would-be attacker learns something he
can use against your network: Relevance analysis involves the analysis of the vulnerability
relevance of real-time alerts, using the vulnerability data imported to Manager database.
The imported vulnerability data can be from Vulnerabilit y Manager or other supported
vulnerability scanners such as Nessus.The fact that the attack failed can help in zero in o n
the type of Web server you use. Users can also better manage this type of events through
policy customization or installing attack filters.
The noise-to-incorrect-identification ratio can be fairly high, particularly in the following
conditions:
the configured policy includes a lot of Informational alerts, or scan alerts which are
based on request activities (such as the All Inclusive policy)
deployment links where there is a lot of hostile traffic, such as in front of a firewall
overly coarse traffic VIDS definition that contains very disparate applications, for
example, a highly aggregated link in dedicated interface mode
Users can effectively manage the noise level by defining appropriate VIDS and customize
the policy accordingly. For dealing with exceptional hosts, such as a dedicated pe ntest
machine, alert filters can also be used.
Determining False Positives
Determining a false positive versus noise
Some troubleshooting tips for gathering the proper data to determine whether you are
dealing with a false positive or uninteresting event;
What did you expect to see? What is the vulnerability, if applicable, that the attack
indicated by the alert is supposed to exploit?
Ensure that you capture valid traffic dumps that are captured from the attack attempt
(for example, have packet logging enabled and can view the resulting packet log)
Determine whether any applications are suspected of triggering the alert—which
ones, which versions, and in what specific configurations.
If you intend to work with McAfee Technical Support on the issue, we ask that you provide
the following information to assist in troubleshooting:
If this occurred in a lab using testing tools rather than live traffic, please provide
detailed information of the attack/test tool used, including its name, version,
configuration and where the traffic originated.
If this is a testing environment using a traffic dump relay, make sure that the traffic
dumps are valid, TCP traffic follows a proper 3-way handshake, and so on
Also, please provide detailed information of the test configuration in the form of a
network diagram.
36
Page 46

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Create an Evidence Report (within Threat Analyzer) with the packet log
Be ready to tell Technical Support how often you are seeing the alerts and whether
they are ongoing
Determining False Positives
37
Page 47
C HAPTER 6
System Fault Messages
Table below lists the system fault messages visible in the Manager Operational Status
viewer, organized by severity, with Critical messages first, then Errors, then Warnings,
then Informational messages.
The faults are then listed alphabetically within those categories.
This table lists the fault messages you might encounter, their severity, and a description,
including information on what action clears the fault. In many cases, the fault clears itself if
the condition causing the fault is resolved. In some cases, the fault does not clear—you
must acknowledge or delete it to dismiss it.
Critical faults
Critical faults are the highest severity faults and generally indicate a serious issue. See the
Action column for potential troubleshooting tips.
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert update failed Critical An attempt to save alerts to the
database failed, most likely due
to insufficient database capacity.
Bootloader
upgrade failure
Critical The firmware upgrade has failed
on the Sensor.
Ensure that the disk space
allocated to the database is
sufficient, and try the
operation again.
Debug or reload the firmware
on the Sensor.
Cannot start
control channel
service (certificate)
Cannot start
control channel
service
(key store)
Critical The Manager’s certificate is
Critical The Manager’s key file is
unavailable; this could indicate
database corruption.
unavailable and possibly
corrupted. This fault could
indicate a database corruption.
38
If you have a database
backup file (and think it is not
corrupted) you can attempt a
Restore. If this does not work,
you may need to manually
repair the database. Contact
McAfee Technical Support.
If you have a database
backup file (and think it is not
corrupted) you can attempt a
Restore. If this does not work,
you may need to manually
repair the database. Contact
McAfee Technical Support.
Page 48

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Cluster software
Critical The soft ware versions on the
mismatch status
cluster primary and cluster
secondary are not the same.
System Fault Messages
Check for errors in software
image download to cluster.
Communication
failure with the
Network Security
Platform Update
Server
Communication
failure with the
proxy server
Conflict in MDR IP
address type
Conflict in MDR
Mode
Critical The Manager is unable to
communicate with the Update
Server.
Any connectivity issues with the
Update Server will generate this
fault, including DNS name
resolution failure, Update Server
failure, proxy server connectivity
failure, network connectivity
failure, and even situations
where the network cable is
detached from the Manager
server.
Critical The Manager i s unable to
communicate with the proxy
server. (This fault can occur only
when the Manager is configured
to communicate with a proxy
server.)
Critical Sensor found a conflict with
MDR IP Address type.
Critical Sensor found a conflict with
MDR mode; Manager IP address
/ MDR status.
This fault clears when
communication with the
Update Server succeeds.
If your Manager is connected
to the Internet, ensure it has
connectivity to the Internet.
Contact McAfee Technical
Support if you lost your
Update Server authentication
information.
This fault clears when
communication to the Update
Server through the proxy
succeeds.
You may need to correct the
MDR configuration.
There is a problem with MDR
configuration. Check your
MDR settings.
Conflict in MDR
Critical Sensor found a conflict with
Pair IP address
Conflict in MDR
Critical Sensor found a conflict with
Status
CRC Errors Critical A recoverable CRC error has
MDR-Pair IP Address; ManagerIP address / MDR action.
MDR status; Manager IP
address / MDR status as ...
occurred within the sensor.
39
You may need to correct the
MDR configuration.
There is a problem with MDR
configuration. Check your
MDR settings.
Reboot the Sensor, which
may then resolve the issue
causing the fault.
Page 49

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
DB Connectivity
Critical Problems Communicating To
Problems
Database
System Fault Messages
Please check if the database
service is running and
connectivity is present.
Database backup
failed
Database System
Integrity
Dropping alerts
and packet logs
Exceeding alert
capacity threshold
Critical A manual attempt to backup the
database failed.
Critical A warning is displayed: Unable
To Locate Index File For Table
Critical Manager is not communicating
with the database; the alert and
packet logs overflowing queues.
Critical As with the “Approaching alert
capacity threshold” fault
message, this message
indicates the percentage of
space occupied by alerts in the
database. This message
appears once you have
exceeded the alert threshold
specified in Manager >
Maintenance.
This can indicate insufficient
disk space for storage of the
backup file. Check your disk
capacity and clear enough
space to accommodate the
backup file, and then attempt
the backup again.
Repair the corrupt Database
tables
Perform maintenance
operations to clean and tune
the database.
Perform maintenance
operations to clean the
database. Delete unnecessary
alerts, such as alerts older
than a specific number of
days.
Failure to create additional
space could cause
undesirable behavior in the
Manager.
Failed to create
command channel
association
Fail Open Control
Module Timeout
Critical Indicates a failure to create a
secure connection between the
Manager and the McAfee®
Network Security Sensor
(Sensor). Can be caused by loss
of synchronisms between the
system time of the Manager
server and the Sensor. Can also
indicate that the Sensor is not
completely on-line after a reboot.
Critical Communication has timed out
between the Fail Open Controller
in the Sensor’s Compact Flash
port and the Fail Open Bypass
Switch. This situation has
caused the Sensor to move to
Bypass mode and traffic to
bypass the Sensor.
40
Restart the Manager. Check
the Sensor’s operating status
to ensure that the Sensor’s
health is good and status is
good.
The fault could be the result of
a cable being disconnected, or
removal of the Bypass Switch.
This fault clears automatically
when communication resumes
between the Fail Open
Controller and Fail Open
Bypass Switch.
Page 50

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Failover peer
Critical This fault indicates whether the
status
Sensor peer is up or down.
System Fault Messages
This fault clears automatically
when the Sensor peer is up.
Fan error Critical One or more of the fans inside
the Sensor have failed.
For the I-4000 and 4010, the
Manager indicates which fan has
failed.
Fail-Open Bypass
Switch timeout
Critical The Sensor is not
communicating with the FailOpen Bypass Switch.
Failed to update
the failOver sensor
configuration
Critical Monitoring port IP settings are
not configured for the ports on
which either NAC
or IBAC is enabled.
On the I-4000, you can also
check the Sensor’s front panel
LEDs to see which fan has
failed.
If a fan is not operational,
McAfee strongly recommends
powering down the Sensor
and contacting Technical
Support to schedule a
replacement unit.
In the meantime, you can use
an external fan (blowing into
the front of the Sensor) to
prevent the Sensor from
overheating until the
replacement is completed.
Check external FailOpen kit
connections or portpair
configuration to restore Inline
FailOpen mode.
Either configure the
Monitoring Port IPs for all the
above ports (or) Disable the
IBAC/NAC on those ports.
Hardware error Critical There is an error in the hardware
component on the Sensor.
41
Debug or replace the
hardware component.
Page 51

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Illegal In-line, fail-
Critical The Sensor is configured to
open configuration
of <port name>.
operate with an external FailOpen Module hardware
component, but cannot detect
the hardware.
System Fault Messages
This error applies only to
Sensors running in in-line
mode with a gigabit port in failopen mode (using the external
Fail Open Module). When this
fault is triggered, the port will
be in bypass mode and will
send another fault of that
nature to the Manager. When
appropriate configuration is
sent to the Sensor (either the
hardware is discovered or the
configuration changes), and
the Sensor begins to operate
in in-line-fail open mode.
Incompatible
custom attack
Incompatible UDS
signature
Image downgrade
detected
Critical One or more custom attack
definition is incompatible with the
Modify any invalid custom
attack definition and try again.
current update set.
Critical A user-defined signature (UD S)
is incompatible with the current
signature set.
You will need to edit your
existing UDS attacks to make
them conform to the new
signature set definitions. Bring
up the Custom Attack Editor
(IPS Settings > Advanced
Policies > Custom Attack
Editor) and manually
performing the edit /
validation.
This fault clears when a
subsequent UDS compilation
succeeds.
Critical Unsupported configuration
upgrade/downgrade, default
configurations are used.
This is an internal error.
Check the Sensor status to
see that the Sensor is online
and in good health.
42
Page 52

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Late Collision of
Critical This fault can indicate a
<count
Up/Down>
problem with the setup or
configuration of the 10/100
Ethernet ports or devices
connected to those ports. It
can also indicate a
compatibility issue between
the Sensor and the device to
which it is connected.
System Fault Messages
Check the speed and duplex
settings on the sensor ports
and the peer device ports and
ensure that they are the same.
Licence expires
soon
Critical Indicates that your Network
Security Platform license is
about to expire; this fault first
appears 7 days prior to
expiration.
Licence expired Critical Indicates that your Network
Security Platform license has
expired.
Link failure of Port
<port name>
Critical The link between a Monitoring
port on the Sensor and the
device to which it is connected is
down, and communication is
unavailable. The fault indicates
which port is affected.
Contact
licensing@mcafee.com
for a
current license. This fault
clears when the license is
current.
Contact
licensing@mcafee.com
for a
current license.
This fault clears when the
license is current.
Contact your IT department to
troubleshoot connectivity
issues: check the cabling of
the specified Monitoring port
and the device connected to it;
check the speed and duplex
mode of the connection to the
switch or router to ensure
parameters such as port
speed and duplex mode are
set correctly; check power to
the switch or router.
This fault clears when
communication is reestablished.
Low JVM Memory Critical The Manager is experiencing
Low Tomcat JVM
Critical The Manager is experiencing
Memory
Reboot the Manager server.
high memory usage. Available
system memory is low.
Reboot the Manager server.
high memory usage. Available
system memory is low.
43
Page 53

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Memory error Critical A recoverable software memory
error has occurred within the
sensor.
System Fault Messages
Reboot the sensor, which may
then resolve the issue causing
the fault.
Ondemand scan
failed because
connection was
refused to
FoundScan engine
Packet log update
failed
MPE Certificate
download failure
Network Security
Central Manager
UDS signature
synchronization
failed.
Critical This fault can be due to two
reasons- the user has not
specified the Fully Qualified
Domain Name OR the
FoundScan engine is shutdown.
Critical An attempt to save packet log
data to the database failed, most
likely due to insufficient database
capacity.
Critical Occurs when the Manag er
cannot push the MPE certificate
to the Sensor. This could result
from a network connectivity
issue.
Critical Port conflict in Network Security
Central Manager UDS
synchronization. The Port is
already in use by UDS.
Free this port for Central
Manager synchronization to
succeed.
For more information on using
Fully Qualified Domain Name,
see Integration Guide.
Ensure that the disk space
allocated to the database is
sufficient, and try the
operation again.
Check Manager connection to
NSP. Check to ensure that the
Network Security Platform has
the latest software image
compatible with the Manager
software image. If the images
are incompatible, update the
Network Security Platform
image via a tftp server.
Free this port for Network
Security Central Manager
synchronization to succeed.
Network Security
Sensor - McAfee
NAC Server
Communication
Status
Network Security
Sensor - McAfee
NAC Server
Communication
Status
Critical The link between Sensor and
McAfee NAC Server is down,
and
communication is unavailable
Critical The link between Sensor and
McAfee NAC Server is down,
and communication is
unavailable
44
Check network link between
Network Security Platform and
NAC Server.
Check network link between
Network Security Platform and
NAC Server.
Page 54
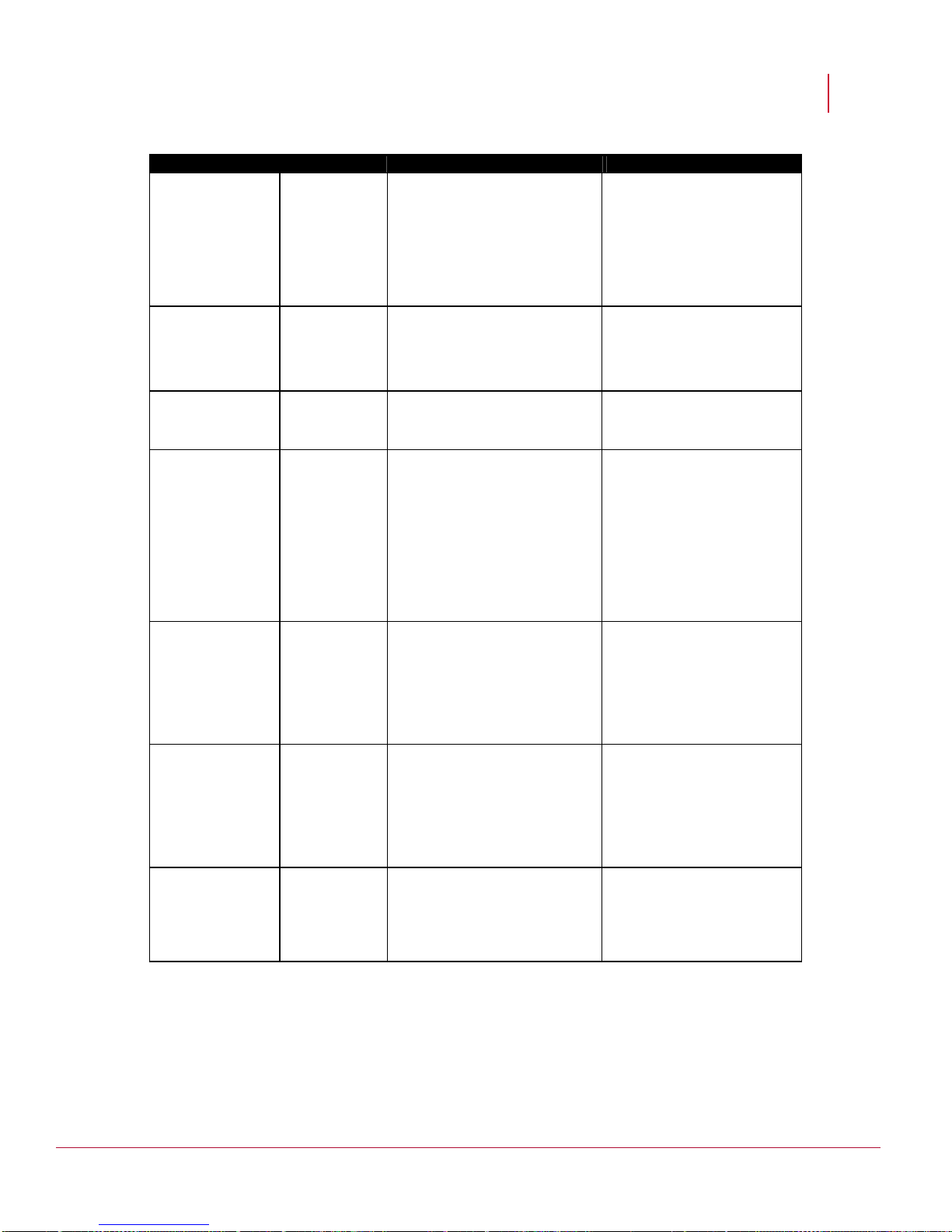
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Network Security
Critical Port conflict in Network Security
Central Manager
UDS signature
synchronization
failed
No DataBase
Critical No DataBase Connectivit y. Check the database
Connectivity
Central Manager UDS
synchronization. Port already in
use by UDS. Free this port for
Central Manager synchronization
to succeed.
System Fault Messages
Free this port for Network
Security Central Manager
synchronization to succeed.
connectivity.
Packet overflow Critical A recoverable software buffer
overflow error has occurred
within the sensor.
Port late collision Critical This fault could indicate a
problem with the setup or
configuration of the 10/100
Ethernet ports or devices
connected to those ports. It
could also indicate a
compatibility issue between the
Sensor and the device to which it
is connected.
Port certification
mismatch
Port media type
mismatch
Critical There is a mismatch in the P ort
certification.
Critical There is a mismatch in the
media or connector type on the
port that says "copper and uses
fiber or vice versa".
Reboot the Sensor. which
may then resolve the issue
causing the fault
The Sensor may be detecting
an issue with another device
located on the same network
link. Check to see if there is a
problem with one of the other
devices on the same link as
the Sensor. This situation
could cause traffic to cease
flowing on the Sensor and
may require a Sensor reboot.
Check if pluggable interface is
McAfee certified. Replace with
McAfee certified connector or
disable check-box to use non
certified connector
(recommended to use McAfee
certified).
Check if pluggable connector
matched user configuration.
Example: Copper SFP
inserted in cage configured for
Fiber.Replace the media
according to the configured
value.
Port pair <port
Critical Sensor is back to In-line, Failname> is back to
In-line, Fail-Open
Mode.
Open Mode.
45
This message indicates that
the ports have gone from
Bypass mode back to normal.
Page 55

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Port pair <port
Critical This fault indicates that the
name> is in
Bypass Mode.
indicated GBIC ports are unable
to remain in In-line Mode as
configured. This has caused failopen control to initiate and the
Sensor is now operating in
Bypass Mode. Bypass mode
indicates that traffic is flowing
through the Fail Open Bypass
Switch, bypassing the Sensor
completely.
System Fault Messages
Check the health of the
Sensor and the indicated
ports. Check the connectivity
of the Fail Open Control Cable
to ensure that the Fail Open
Control Module can
communicate with the Fail
Open Controller in the
Sensor’s Compact Flash port.
Power supply error Critical (Seen only with Sensors with a
redundant power supply). This
fault indicates a loss of power in
one of the two power supplies in
the Sensor (primary or
secondary). This fault can
indicate that the power supply
has failed; that supply has been
inserted, but there is no power to
the supply; or that the power
supply has been removed.
Sensor changed to
a different model
Critical Sensor has been replace d b y a
different model, which does not
match the original model. The
alert channel will not be able to
establish a connection.
Scheduled
Vulnerability
Manager
vulnerability data
Critical This message indicates that the
vulnerability data import by the
Scheduler from Vulnerability
Manager database has failed.
import failed
If the power supply is in place
and plugged in to a power
source, check power to the
outlet providing power to the
power supply. If the fault
indicates that there is no
power and a power
interruption is not the cause,
replace the failed power
supply. Contact McAfee
Technical Support to schedule
a replacement unit.
Ensure you replace with the
same Sensor model (For
example: Replace an I-2700
with I-2700, and not with an I-
4010).
Refer to error logs for details
Sensor changes to
Critical A Sensor was replaced with a
a different model
different model type (for
example, an I-1200 was
replaced with an I-1200-FO
(failover only) Sensor). The alert
channel will be unable to make a
connection.
46
When replacing a Sensor,
ensure that you replace it with
an identical model (for
example, replace an I-1200
with an I-1200, do not attempt
to replace a regular Sensor
with a failover-only model, and
vice-versa).
Page 56

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Sensor
Critical The Manager c annot push
configuration
download failure
original Sensor configuration to
Sensor during Sensor reinitialization, possibly because
the trust relationship is lost
between Manager and Sensor.
This can also occur when a
failed Sensor is replaced with a
new unit, and the new unit is
unable to discover its
configuration information.It
happens if the Sensor's health is
bad.
System Fault Messages
The link between Manager
and Sensor may be down, or
you may need to re-establish
the trust relationship between
Sensor and Manager by
resetting the shared key
values.
Sensor device
license expired
Sensor discovered
with cluster
secondary license.
Sensor discovered
without license.
Sensor Dropping
Packets Internally.
Critical Sensor device
license expired,and may not
detect attacks.
Critical Sensor discovered with cluster
secondary license, and must not
be connected to Manager
To obtain a permanent
license, kindly contact
Technical Support or your
local reseller.
To obtain a standard license
now, kindly contact Technical
Support or your local reseller.
directly.
Critical Sensor discovered without
license, and may not detect
attacks.
Critical Network Security Sensor
Frontend is Overloaded.
To obtain a permanent license
now, kindly contact Technical
Support or your local reseller.
Reduce the amount of traffic
passing through the sensor as
there is oversubscription of
traffic on the sensor
47
Page 57

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Sensor internal
Critical An internal communication e rror
configuration error
occurred within the Sensor.
System Fault Messages
You must manually clear this
fault.
This error may cause a reboot
of the Sensor, which may
resolve the issue causing the
fault.
If the fault persists, McAfee
recommends that you perform
the following steps to help
assist McAfee Technical
Support with troubleshooting:
execute a logstat on the
Sensor as described in the
Sensor CLI command
reference, perform a
Diagnostic Trace as described
in Uploading a diagnostics
trace from a Sensor to your
Manager,
Guide
IPS Configuration
, and submit the trace file
to Technical Support for
troubleshooting.
Sensor reboot
required for SSL
decryption
configuration
change
Sensor rediscovery failure
Critical User-configure d SSL decryption
settings for a particular Sensor
changed, requiring a Sensor
reboot.
Critical This fault occurs as a second
part to the “Sensor discovery
failure” fault. If the condition of
the Sensor changes such that
the Manager can again
communicate with it, the
Manager again checks to see if
the Sensor discovery was
successful.
This fault is issued if discovery
fails, and thus the Sensor is still
not properly initialized.
Reboot the Sensor to cause
the changes to take effect.
Check to ensure that the
Sensor has the latest software
image compatible with the
Manager software image. If
the images are incompatible,
update the Sensor image via a
TFTP server.
48
Page 58

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Sensor reports a
Critical Indicates that an error has
signature set error
occurred with a signature set
that has been successfully
applied on a Sensor.
System Fault Messages
Re-import the signature set
onto the Sensor. This can
indicate a problem within the
signature set itself that was
not detected during download;
if re-importing the same set
does not solve the problem,
providing a new signature set
may clear the fault. If this does
not solve the issue, reboot the
Sensor. If the fault persists,
contact Technical Support.
The fault will clear when the
signature set is successfully
applied on the Sensor and
continues to be error-free after
application.
Sensor switched to
Layer 2 mode
Sensor support
license expired.
Sensor switched to
Layer 2 Bypass
mode
Sensor - McAfee
NAC Server
Communication
Status
Critical The Sensor has moved from
detection mode to Layer 2
(Passthru) mode. This indicates
that the Sensor has experienced
the specified number of errors
within the specified timeframe
and Layer 2 mode has triggered.
Critical Sensor support license is
expired, and may not detect
attacks.
Critical Sensor is now operating in
Layer2 Bypass mode. Intrusion
detection/prevention is not
functioning.
Critical A Sensor sends this fault to
Manager when it is not able to
communicate with the McAfee
NAC server to which it has been
configured.
The Sensor will remain in
Layer 2 mode until it is
rebooted.
To obtain a permanent license
now, kindly contact Technical
Support or your local reseller.
The Sensor has experienced
multiple errors, surpassing the
configured Layer2 mode
threshold. Check the Sensor's
status.
Check the Condition Type
field in the Fault Detail page to
know the probable reason for
this communication failure.
49
Page 59

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Sensor is
Critical Indicates that the Sensor cannot
unreachable
communicate with the Manager,
indicating that the connection
between the Sensor and the
Manager is down, or that the
Sensor has been
administratively disconnected.
System Fault Messages
Contact your IT department to
troubleshoot connectivity
issues: check that a
connection route between the
Manager and the Sensor
exists; check the Sensor’s
status using the status
command in the Sensor
command line interface or
ping the Sensor or the Sensor
gateway to ensure
connectivity to the Sensor.
This fault clears when the
Manager detects the Sensor
again.
SGAP Certificate
download failure
Signature set
update not
successful
Signature set
download failure
Critical Cannot push SGAP Certificate to
Sensor. Kindly see the log for
details.
Critical The attempt to update the
signature set on the Manager
was not successful, and thus
signature set is not available in
the Manager.
You must re-import a signature
set
before performing any action on
the Manager.
Critical Occurs when the Manag er
cannot push the signature set file
to a Sensor. Could result from a
network connectivity issue.
Check NSM connection to
Network Security Platform.
Check to ensure that the
Network Security Platform has
the latest software image
compatible with the Manager
software image. If the images
are incompatible, update the
Network Security Platform
image via a tftp server.
A valid signature set must be
present before any action can
be taken in Network Security
Platform.
Contact your IT department to
troubleshoot connectivity
issues: check that a
connection route between the
Manager and the Sensor.
50
Page 60

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Software error Critical Indicates a recoverable software
error within the Sensor.
System Fault Messages
This error may cause a reboot
of the Sensor, which may
resolve the issue causing the
fault.
If the fault persists, McAfee
recommends that you perform
the following steps to help
assist McAfee Technical
Support with troubleshooting:
execute a logstat on the
Sensor as described in the
Sensor CLI command
reference, perform a
Diagnostic Trace as described
in the
IPS Configuration Guide,
and submit the trace file to
Technical Support for
troubleshooting.
SSL decryption key
download failure
Critical Occurs when the Manag er
cannot push a decryption key file
to a Sensor. Could result from a
network connectivity issue.
Temperature error Critical Indicates that the temperature of
the Sensor is abnormal.
The Sensor will raise a
temperature alert when the
internal temperature of the
Sensor crosses 50 degrees
Centigrade. The fault is removed
only when the temperature falls
below 40 degrees Centigrade.
Temperature
Sensor status
Critical The environment temperature for
the Manager is not appropriate.
Contact your IT department to
troubleshoot connectivity
issues: check that a
connection route between the
Manager and the Sensor.
Check for a Fan Status fault,
and also check the Sensor’s
front panel LEDs to see if the
Sensor’s fans are operational.
If a fan is not operational,
McAfee strongly recommends
contacting Technical Support
as soon as possible to
schedule a replacement unit.
In the meantime, you can use
an external fan (blowing into
the front of the Sensor) to
prevent the Sensor from
overheating until the repair is
completed.
If a fan is not the issue, please
ensure that the room where
the Sensor is located is cool
enough for the Sensor to
operate without overheating.
Check the environment
temperature for the Manager
and provide adequate
ventilation.
51
Page 61
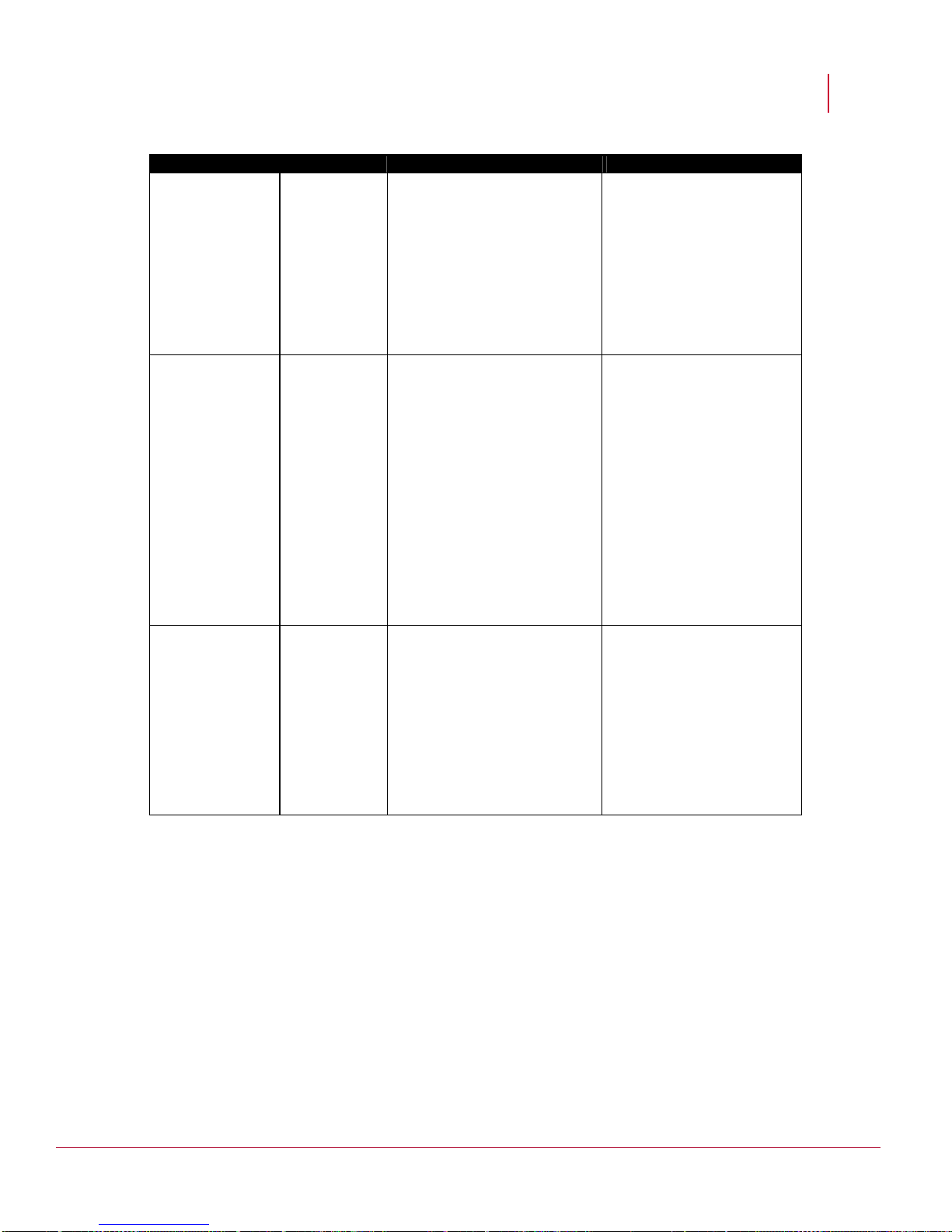
McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
The MDR pair is
Critical This fault tells about change of
changed.
The Manager <
Critical The Manager foun d InActive
Manager name>
has switched to
MDR mode, and
this Manager
cannot handle the
change.
MDR configuration for a Local
Manager or Central Manager.
The fault tells that for this
Manager, the IP addresses of
the underlying MDR pair has
changed. The fault gives the old
and new IP addresses of the
primary and secondary Manager.
(stand by) for now, the peer
Manager is either not reachable
or does not have data.
System Fault Messages
Change to the correct MDR
pair.
If the Manager that has moved
to MDR mode is Network
Security Central Manager,
then make the Central
Manager, which has all the
Network Security Manager
data as Active or reform MDR.
If the MDR moved Manager is
Network Security Manager
then make the Manager which
has Central Manager data as
active or make sure that active
Manager has Central Manager
configuration data.
The Manager
<Manager name>
is not reachable
Critical Indicates that the Network
Security Central Manager and
Manager cannot communicate
each other, the connection
between these two may be
down, or the Manager has been
administratively disconnected.
1) Check that a connection
route exists between the
Network Security Central
Manager and the Manager.
2) Access the
Manager/Network Security
Central Manager directly.
This fault clears when the
Manager detects the Sensor
again.
52
Page 62

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
The Manager
Critical No communication exists
<Manager name>
is not reachable
between Central Manager and
Manager.
System Fault Messages
Indicates that the Central
Manager server and Manager
cannot communicate with
each other. The connection
between these two may be
down, or Central Manager has
been administratively
disconnected.
1) Check that a connection
route exists between the
Central Manager and
Manager;
2) Access the Manager
directly. This fault clears when
the Manager detects the
Sensor again.
The Manager
name has moved
to MDR mode, and
this Manager
cannot handle the
change
The Manager has
moved to MDR
mode, and this
Manager cannot
handle the change
Critical The Central Manager server is in
Standby mode.The Manager
server which is configured by
Central Manager goes into
secondary Standby mode after
MDR creation or before data
dump from primary to secondary
takes place.
The Manager server configured
by Central Manager is in Active
mode but is in a disconnected
state and therefore cannot
communicate with Central
Manager.
If Manager is reconnected and
Central Manager is in Standby
mode, then the Peer Central
Manager does not have
Manager configuration.
Critical The Manager server is in
Standby mode(MDR action) and
active peer Manager does not
have Central Manager
information
If the Central Manager server
has moved to Standby ,then
the Central Manager with
latest Manager information is
moved to Active mode or
recreate MDR pair.
If the Manager has moved to
Standby, then make the
Manager with Central
Manager information as Active
or make sure that active
Central Manager or Manager
has latest configuration data.
If the Manager server has
moved to Stand by ,then make
Central Manager with latest
Manager information as Active
or reform MDR; if the Manager
has moved to Standby, then
make the Manager with
Central Manager information
as Active or make sure that
active Central Manager or
Manager has latest
configuration data.
53
Page 63

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
The Manager info
Critical If two Managers, Manager 1 and
is deleted
Manager 2 are configured to
Central Manager, and MDR pair
has to be established between
them, then, Central Manager
considers the active Manager
configuration. The Standby
Manager information is deleted
from Central Manager.
System Fault Messages
The Standby Manager
information is deleted from
Central Manager.
There is conflicts in
the MDR
configuration for
the Manager
<name>
The Trust request
failed !!
Critical The configurati on between an
existing MDR pair (Manager 1
and Manager 2 - both Managers
are Central Manager configured)
is disabled and a new MDR pair
configuration has been created
with Manager 2 and Manager 3.
Manager 2 is in Standby mode
and Manager 3 does not have
Central Manager configuration
Critical No communication exists
between Central Manager and
Manager. Central Manager may
not be configured.
Manager failed to establish trust
with Central Manager server.
Central Manager could not be
configured onto Manager or
Central Manager server is not
reachable.
The Manager IP address is not
configured.
Central Manager may already
been configured with an
Manager.
The Central Manager is in MDR
mode and no Manager is in
Active state.
The trust request failed due an
internal error.
Dissolve and recreate an
MDR pair.
Indicates that the Central
Manager and Manager cannot
communicate with each other.
The connection between
these two may be down, or
Central Manager has been
administratively disconnected.
Check whether Manager is
configured in Central
Manager.
Delete the previous
configuration and establish a
new trust with Central
Manager.
Bring any Central Manager
MDR pair into Active state.
Check the log for details.
54
Page 64

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
VIDS creation
Critical This fault generally occurs in
failure
situations where the port in
question is configured
incorrectly. For example, a pair
of ports is configured to be in
different operating modes (1A is
in-line while 1B is in SPAN).
System Fault Messages
Check the configuration of the
port pair to see if there is an
inconsistency, and make the
port pair run in the same
operating mode.
NTBA is
unreachable
Critical Indicates that the NTBA cannot
communicate with the Manager.
The connection between the
NTBA and the Manager is down,
or the NTBA has been
administratively disconnected.
Check that a connection route
exists between the Manager
and the NTBA.
Check the NTBA’s status
using the status command in
the NTBA command line
interface, or ping the NTBA or
the NTBA gateway to ensure
connectivity to the NTBA. This
fault clears when the Manager
detects the NTBA again.
Error faults
The faults listed in the following table have a severity of Error.
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert channel is
down
Approaching alert
capacity
threshold
Error Indicates a failure to communicate
with the Sensor via the channel on
which the Manager listens for
Sensor alerts.
Error Displ ays the percentage of space
occupied by alerts in the database.
As available space decreases, this
message will continue to appear—
at 50%, 70%, 90% and 100%.
Once you’ve exceeded this
threshold, an ‘Exceeding’ fault will
appear.
This fault clears when the
alert channel is back up.
Please perform maintenance
operations to clean the
database. Delete
unnecessary alerts, such as
alerts older than a specific
number of days.
Incident update
Error The Manager is unable to accept
failed
Internal packet
Error Sensor is dropping packets due to
drop error
more incidents. You have reached
the maximum number of incidents
that can be accepted by the
Manager.
extreme traffic load.
55
Delete old incidents to
provide room for incoming
incidents. The fault clears
when the Manager can
accept incoming incidents.
Reduce the amount of traffic
passing through the Sensor
as this fault indicates
oversubscription of traffic on
the Sensor
Page 65

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Invalid SSL
Error The Sensor detects that a particular
decryption key
SSL decryption key is no longer
valid; for example, it may be failing
to decrypt traffic.
System Fault Messages
Re-import the key (which is
identified within the error
message). The fault will clear
itself when the key is
determined to be valid.
Sensor
Configuration
update failed
Sensor reports a
anti-virus dat file
error
SSL decryption
key invalid
Error Sensor configuration
update failed while
transferring from the
Manager server to the
Sensor.
Error A Sensor is detecting an error on
av-dat file.
Error The Manager detects that a
particular SSL decryption key is no
longer valid. The detailed reason
why the fault is occurring is shown
in the fault message. These
reasons can range from the Sensor
re-initializing itself with a different
certificate to an inconsistency
between the decryption key
residing on a primary Sensor and
its failover peer Sensor.
See the ems.log file to isolate
reason for failure.
Ensure that the Sensor is
online and in good health.
The Manager will make
another attempt to push the
file to the Sensor. This fault
will clear when the av-dat file
is successfully pushed to the
Sensor.
Re-import the key (which is
identified within the error
message). The fault will clear
itself when the key is
determined to be valid.
Get peer DoS
Error The Manager was unable to obtain
profile failure
Get peer DoS
Error Get peer DOS profil e request from
profile failure
the requested profile from a peer
Sensor. This was likely due to the
requested profile or a valid, saved
version being unavailable.
the Sensor.
failed because the profile cannot be
pushed to the Sensor that
requested it. See log for details.
56
Check NSM connection to
peer NSP
Check NSM connection to
NSP.
Page 66

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Packet log
Error Indicates a failure to communicate
channel is down
with the Sensor via the channel on
which the Manager receives packet
logs.
System Fault Messages
This fault clears when the
pktlog channel is back up.
Put peer DoS
profile failure
Queue size full
Real-time
Scheduler signature set
update from
Manager to
Sensor failed
Error The Sensor was unable to push a
requested profile to the Manager.
Error The Manager alert queue has
reached its maximum size (default
200,000 alerts), and is unable to
process alerts until there is space in
the queue. Packets are being
detected by your Sensor(s) faster
than the Manager can process
them.
Error The Manager packet log queue has
reached its maximum size (default
200,000 alerts), and is unable to
process packet logs until there is
space in the queue.
Error Una ble to make scheduled
signature set update from the
Manager to Sensor
See the ems.log file for
details on why the error is
occurring. The fault will clear
when the Sensor is able to
push a valid DoS profile.
This is evidence of extremely
heavy activity. Check the
packets you are receiving to
see what is causing the
heavy traffic on the Sensor.
Also see the suggested
actions for the alert
Unarchived, queued alert
count full.
This is evidence of extremely
heavy activity. Check the
packet logs you are receiving
to see what is causing the
heavy traffic on the Sensor.
Also see the suggested
actions for the alert
Unarchived, queued alert
count full.
This fault can indicate
problems with network
connectivity between the
Manager and
the Sensor. This fault clears
when a signature update is
applied successfully.
Scheduled real-
Error This fault can indicate problems
time update from
Update Server to
Manager failed
with network connectivity between
the Update Server and the
Manager, invalid update sets, or
update sets that were not properly
signed.
57
This fault clears when a
signature update is applied
successfully.
Page 67

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Scheduled real-
Error Una ble to make scheduled update
time update from
Update Server to
Manager failed
of Manager signature sets. This
fault can indicate—for example,
problems with network connectivity
between the Update Server and the
Manager or between the Manager
and the Sensor; invalid update sets;
or update sets that were not
properly signed.
System Fault Messages
This fault clears when a
signature update is applied
successfully.
Scheduled
update from
Manager to
Sensor failed
Sensor is in bad
health
Sensor reports
an anti-virus dat
file error
Error Una ble to make scheduled update
of Sensor. This fault can indicate—
for example, problems with network
connectivity between the Manager
and the Sensor, incompatibility
between the update set and the
Manager software, compilation
problems with the signature update
set, or invalid update set.
Error This fault occurs with any type of
Sensor software failure, and usually
occurs in conjunction with a
‘Software error’ fault.
Error The Sensor has detected an error
on av-dat file segment
This fault clears when an
update is sent to Sensor
successfully.
If this fault persists, McAfee
recommends that you
execute a logstat from the
Sensor CLI twice (1 minute
apart), then perform a
Diagnostic Trace and submit
the trace file to McAfee
Technical Support for
troubleshooting.
Ensure that the Sensor is
online and in good health.
The Manager will make
another attempt to push the
file to the Sensor.
This fault is cleared when the
av-dat file is successfully
pushed to the Sensor.
Sensor reports
Error Sensor re ports Pktlog channel
that the packet
log channel is
down
between the EMS and Sensor is
DOWN, but the EMS detects that
the link(socket) is up. This
inconsistency may cause by
channel heartbeat timeout.
58
The Sensor will typically
recover on its own. If you are
receiving alerts and your
Sensor is otherwise
functioning normally, you can
ignore this message. Check
to see if trust is established
between the Sensor and
Manager, by issuing a show
command in the Sensor CLI.
Page 68

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Sensor reports
Error This fault indicates that the Sensor
that the alert
channel is down
is reporting that the alert channel is
down, but the physical channel is
actually up.
System Fault Messages
The Sensor will typically
recover on its own. If you are
receiving alerts with packet
logs and your Sensor is
otherwise behaving normally,
you can ignore this message.
Check to see if trust is
established between the
Sensor and Manager by
issuing a show command in
the Sensor CLI.
If this fault persists, contact
McAfee Technical Support.
Sensor reports
an out-of-range
configuration
Sensor
configuration
update failed
Sensor discovery
failure
Unable to clean
alerts and packet
logs
Error The Manager received a value from
the Sensor that is invalid. The
additional text of the message
contains details.
Error The Sensor configuration update
failed to be pushed from the
Manager Server to the Sensor.
Error The Sensor failed to discover its
configuration information, and thus
is not properly initialized. Typically,
the Manager will be unable to
display the Sensor. Could indicate
an old Sensor image on the
Sensor.
Error Mainte nance is not able to clean
alerts and packet logs
This fault does not clear
automatically; it must be
cleared manually.
Contact McAfee Technical
Support for assistance.
Please see ems.log file to
isolate reason for failure.
Check the Manager
connection to Network
Security Platform. Check to
ensure that the NSP has the
latest software image
compatible with the Manager
software image. If the images
are incompatible, update the
NSP image via a tftp server
Check your database
connections.
59
Page 69

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Unarchived,
Error Indicates that the Manager has
queued alert
count full
reached the limit (default of
100,000) of alerts that can be
queued for storage in the database.
Also indicates the number of
dropped alerts.
System Fault Messages
Alerts are being detected by
your Sensor(s) faster than the
Manager can process them.
This is evidence of extremely
heavy activity.
Try the following:
Check the alerts you are
receiving to see what is
causing the heavy traffic on
the Sensor(s). You may be
under a heavy attack.
Check your policies. You may
have enabled a very verbose
policy (for example, AllInclusive with Audit) which is
causing too many
alerts/packet logs to be sent
to the Manager, or packet
logging is excessive (for
example, packet logging is
enabled for entire flow for all
alerts).
Your Manager server may not
have sufficient disk
space/processing power to
accommodate the
number/rate of alerts your
Sensors are generating.
Rectify the situation in your
policies and let the queue
drain and write to the
database.
Unarchived,
queued packet
log count full
NTBA Sigfile
Update Error
Error Indicates that the Manager has
reached the limit (default of
100,000) of packet logs that can be
queued for storage in the database.
Also indicates the number of
dropped packet logs.
Error Indicates that there is an error in
the Signature set configuration
update.
60
See the suggestions for the
fault ‘Unarchived, queued
alert count full.'
Rre-try the NTBA
configuration update.
Page 70

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Warning faults
The faults listed in the following table have a severity of Warning.
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Attempt to disable
failover failed
Warning The Manager’s attempt to
disable failover on the
Sensor failed.
This is likely due to the
Sensor being unavailable, or
down.
System Fault Messages
Ensure that the Sensor is online. The Manager will make
another attempt to disable
failover when it detects that the
Sensor is up. The fault will clear
when the Manager is successful.
Disabled scheduled
Report Template
Failed to backup
IDS
Policy
Failed to backup
Recon Policy
Warning Report Generation has failed
for Schedule Report
Edit and save the disabled
template in Report Generation.
Template due to
unavailability of resource(s)
in the Manager.
Warning Failed to backup
Delete previous versions.
Policy.
Warning Failed to backup
Policy.
Please contact technical support
or local reseller.
Warning Failed to backup Policy. Please contact technical support
or local reseller.
Warning Failed to backup Policy. Delete previous version.
61
Page 71

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Initiating Audit Log
Warning The Audit Log capacity of the
file rotation
Manager was reached, and
the Manager will begin
overwriting the oldest records
with the newest records (i.e.
first in first out).
The fault indicates the
number of records that have
been written to the audit log;
and equal number of audit
log records are now being
overwritten.
System Fault Messages
This fault will be raised after a
configured number of records
written. No action is required.
The capacity is configured in the
iv_emsproperties table in
MySQL; this option can be
turned off. If this feature is
enabled, when disk capacity is
reached or audit log capacity is
reached, then Audit Log rotation
is initiated.
McAfee NAC
channels are
already Installed
Manager shutdown
was not graceful
MDR IPv4 and IPv6
address
configuration
Offline Sensor
Download Started
Warning This warning denotes the
failure to update the McAfee
NAC-installation-related
configuration.
Warning Reinstall McAfee NAC if you
updated the
McAfee NAC installation
parameters.
Warning The Manager experienced an
abrupt shutdown, such as a
crash.
Warning You have specified only the
peer Managers address. So
you cannot add any Sensors
to the current Manager nor
will the existing Sensors be
able to communicate to the
peer Manager.
Warning Offline Sensor download has
been initiated form the
Sensor command line
interface.
De install and try to update the
McAfee NAC- installation-related
configuration.
Reinstall McAfee NAC if you
updated the
McAfee NAC installation related
configuration.
Perform database tuning
(dbtuning) to fix possible
database inconsistencies that
may have resulted. Tuning may
take a while, depending on the
amount of data currently in the
database.
If Sensor is needed to
communicate over IPv6 to
Manager and Manager is in mdr
mode, then mdr has to be
reconfigured to include IPv6
version of the peer Manager.
Please wait for offline Sensor to
complete the download.
Offline Sensor
Warning Offline Sensor download has
Download
Completed
completed with status,
download type, time and file
name.
62
Please see log messages if
download has failed, and check
for status code.
Page 72

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Physical
Warning The physical configuration
configuration
changed
Pluggable interface
Warning Indicates that the Pluggable
is absent
has changed of
Sensor. New physical
configuration has been
discovered.
interface is absent.
System Fault Messages
Occurs when the Sensor
connects to the Manager
with a different physical
configuration.
Indicates if the pluggable
connector is absent in the cage.
Pluggable interface
certification status
Policy
Synchronization
aborted because
concurrent
processes are
running on the
Manager Server
Signature
segments out of
sync
Warning Indicates if pluggable
connector is McAfee certified
or not.
Warning Unable to synchronize policy
due to concurrent processes
are running on the Manager
Server.
Warning An attempt to update the
signature set on both
Sensors of a failover pair
was unsuccessful for one of
the pair, causing the
signature sets to be out of
sync on the two Sensors.
Indicates if pluggable connector
is McAfee certified or not.
Try again later
The Manager will make another
attempt to automatically push the
signature file down to the Sensor
on which the update operation
failed.
Ensure that the Sensor in
question is on-line and in good
health. The fault will clear when
the Manager is successful.
If the operation fails a second
time, a Critical Signature set
download failure fault will be
shown as well.
Both faults will clear when the
signature set is successfully
pushed to the Sensor.
63
Page 73

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Sensor is not
Warning The Sensor is not properly
initialized
initialized. Either it is in the
process of starting up and is
not ready, or the signature
set is missing on the Sensor.
System Fault Messages
The Sensor may have just been
rebooted and is not up yet. Wait
a few minutes to see if this is the
issue; if not, check to ensure that
a signature set is present on the
Sensor. A resetconfig
command may have been
issued, and the Sensor not yet
been reconfigured.
Sensor
Performance
<Metric Name>
Warning <Metric Name> has
<risen/fallen> to <%/count>
on
<Sensor name / Port name>,
which is <above/below> the
configured <Band Name>
threshold of <%/count>. For
example: <CPU utilization
metric> has <risen> to
<70%> on <Sensor name>
which is <above> the
configured <alarm band
value> threshold of <60%>,
then this type of warning will
be generated.
up Warning The Sensor has just
completed booting and is online.
Check NSP operation to bring
down the metrics below
configured threshold level.
This message is informational.
Acknowledge the fault.
SSL decryption
Warning The Manager was unable to
keys out of sync
System startup in
Warning System startup restored
progress; alerts
being restored
update the decryption key on
one Sensor in a failover pair,
causing the key on one
Sensor to be out of sync with
the one on its failover peer
alerts from the archive file.
Threat Analyzer may not
show all alerts.
64
The Manager will make another
attempt to update the key.
Ensure that the Sensor is online
and in good health.
The fault will clear when the
Manager successfully pushes
the key to the Sensor and both
keys are in sync.
Threat Analyzer may not show
all alerts.
Page 74

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Informational faults
The faults listed in the following table are Informational in nature. These faults indicate
system status, for example. An
message is informational.
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
Action type of “n/a” indicates that no action is required--the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
Alert Archival state has
changed
Cluster software
initialization status
Custom attacks are being
saved to the Manager
Custom attack overridden
by signature set
Custom attacks
successfully saved to the
Manager
Daily scheduled report
generation complete
Informational The alert archival process
has started.
Informational Sensor software has
initialized correctly.
Informational One or more custom
attack definition is in the
process of being saved
from the Custom Attack
Editor to the Manager.
Informational One or more custom
attack definition has been
incorporated in a new
signature set and has
been removed from the
Custom Attack Editor.
Informational One or more custom
attack definition was
successfully saved from
the Custom Attack Editor
to the Manager.
Informational Daily scheduled report
generation process
successfully completed
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
On initialization failure,
check if cluster crossconnects are present
as documented.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Daily scheduled report
generation in progress
Data dump retrieval from
peer has been completed
successfully
Data dump retrieval from
peer is in progress
Informational Daily scheduled report
generation process in
progress
Informational The data dump retrieval
from peer has been
completed successfully
Informational The data dump retrieval
from peer is in progress
65
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Page 75

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
Data dump retrieval is in
progress
Informational The Data dump retrieval
from peer Manager is in
progress
Data dump retrieval
successful
Informational The Data dump retrieval
from peer Managerhas
been completed
successfully.
Database tuning required Informational Database Tuning is
needed. "..." days have
passed since the last
database tuning.
Database archival in
progress
Database archival
successful
Informational The database archival
process is in progress.
Informational The database archival
was successful.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Shutdown the Manager
and execute the
Database Tuning Utility
at the earliest
Do not attempt to tune
the database or
perform any other
database activity such
as a backup or restore
until the archival
process successfully
completes.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Database backup failure. Informational Unable to backup
database tables.
66
This message indicates
that an attempt to
manually back up the
database backup has
failed. The most likely
cause of failure is
insufficient disk space
on the Manager server;
the backup file may be
too big. Check your
disk capacity to ensure
there is sufficient disk
space, and try the
operation again.
Page 76

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
Database backup is in
progress.
Informational A manual or scheduled
database backup process
is in progress.
Database backup
successfully completed
Database tuning in
progress
Informational The database backup was
successful.
Informational The database tuni ng
process is in progress.
Database tuning successful Informational The database tuning
process successfully
completed.
Do not attempt to tune
the database or
perform any other
database activity such
as an archive or restore
until the backup
process successfully
completes.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
The user cannot do the
following operations
during tuning process
(1) Viewing / Modifying
alerts from Threat
Analyzer (2)
Generating IDS reports
on alerts (3) Backing up
/ Restoration of all
tables OR alert and
packet log tables. (4)
Archiving alerts and
packet logs into files
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Deleted Network Security
Central Manager Attack
filter is applied on resource
Deleted Network Security
Central Manager Rule Set
is used by policy
Deleted Central Manager
policy is applied on
resources
Informational Attack filter is applied on
resource(s). Creating a
clone before delete.
Informational Rule Set is used by
policy.Create a clone
before delete
Informational Deleted Central Manager
policy is in use
67
Deleted Network
Security Central
Manager Attack filter is
applied on resource(s)
Remove the reference
and try again
Remove the reference
and try again
Page 77

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
Deleted Central Manager
Policy is applied on
resources
Manager version
mismatch. Primary
Manager has latest version
Manager version
mismatch. Secondary
Manager has latest version
Network Security Platformdefined UDS overridden by
signature set.
Informational Policy <policy name> is
applied on resources.
Creating clone <policy
name> before delete.
Informational The two Managers in an
configuration must have
the same Manager
software version installed.
The Primary Manager
software is more recent
than that of the
Secondary Manager.
Informational The two Managers in an
MDR configuration must
have the same Manager
software version installed.
The Secondary Manager
software is more recent
than that of the Primary
Manager.
Informational An Network Security
Platform-defined UDS has
been incorporated in a
new signature set and has
been removed from the
Custom Attack Editor.
Remove the reference
and try again.
Ensure the two
Managers run the same
software version.
Ensure the two
Managers run the same
software version.
This message is
informational and
indicates that an
emergency McAfeeprovided UDS
signature has been
appropriately
overwritten as part of a
signature set upgrade.
MDR manual switch over
successful; the Secondary
<Manager/Central
Manager> is in control of
<Sensors/Manager>
Informational Manager Disaster
Recovery initiated via a
manual switchover, is
successfully completed.
Secondary Manager is
now in control of Sensors.
68
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Page 78

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
MDR automatic switchover
has been completed; the
Secondary
<Manager/Central
Manager> is in control of
Informational Manager Disaster
Recovery switchover has
been completed; the
Secondary Manager is in
control of Sensors.
<Sensors/Manager>
MDR configuration
information retrieval from
Primary Manager
successful
Informational Manager Disaster
Recovery Secondary
Manager has successfully
retrieved configuration
information from the
Primary Manager.
MDR forced switch over
has been completed; the
Secondary
<Manager/Central
Manager> is in control of
Informational Manager Disaster
Recovery is completed via
a manual switchover.
Secondary Manager is
now in control of Sensors.
<Sensors/Manager>
MDR has been cancelled Informational Manager Disaster
Recovery has been
cancelled
Failover has occurred;
the Secondary
Manager is now in
control of the Sensors.
Troubleshoot problems
with the Primary
Manager and attempt
to bring it online again.
Once it is online again,
you can switch control
back to the Primary.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information, no
action required.
This message is for
user information, no
action required.
MDR has been configured Informational Manager Disaster
Recovery has been
successfully configured
MDR operations have been
resumed
Informational Manager Disaster
Recovery functionality has
been resumed. Failover
functionality is again
available.
MDR operations have been
suspended
Informational Manager Disaster
Recovery functionality has
been suspended. No
failover will take place
while MDR is suspended.
MDR switchback has been
completed; the Primary
<Manager/Central
Manager> is in control of
<Sensors/Manager>
Informational Manager Disaster
Recovery switchback has
been completed; the
Primary Manager has
regained control of
Sensors.
69
This message is for
user information, no
action required.
This message is for
user information, no
action required.
This message is for
user information, no
action required.
This message is for
user information, no
action required.
Page 79

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
MDR pair is changed Informational McAfee® Network Security
Central Manager (Central
Manager) has a MDR pair
created and the Manager
is in disconnected mode.
Network Security Manager
Type mismatch
Informational The two Managers in an
MDR
configuration must have
the same ManagerType.
No Syslog Forwarder
configured
Informational No Syslog server has
been configured to accept
ACL logs for the Admin
Domain <Admin Domain
Name>. Configure a
Syslog server for the
Manager Request is not
from Trusted IP Address
Informational The Manager Request is
not from
Trusted IP Address.
.
Packet Log archival in
progress
Informational Manager is archiving the
Packet Logs
Dissolve and recreate
an MDR pair.
Ensure both Managers
are of same Type
(Network Security
Central Manager or
Network Security
This message will
appear until a Syslog
server has been
configured for use in
forwarding ffhfjhjjjjfj
forwarding forwarding
Ensure the Peer
Manager is not already
in MDR with other
Manager.
Kindly wait for the
Packet Log archival to
complete.
Packet Log Archival state
has changed
Port pair <port name> is
back to In-line Fail-Open
Mode.
Problem retrieving the data
dump from peer
Informational Indicates that the packet
log archival state has
changed
Informational Indicates that the ports
have gone from Bypass
Mode back to normal.
Informational The data import process
is aborted as there was a
problem while retrieving
the dump from peer.
This fault is generated for
MDR pairs.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information, no
action required.
Check whether the
peer Manager machine
is reachable from this
machine
70
Page 80

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
Report creation complete Informational Report creation
successfully complete
Report generation in
progress
Informational Report generation
process in progress
Reset to standalone has
been invoked; the Primary
<Manager/Central
Manager> is in control of
<Sensors/Manager>
Informational A “Reset to Standalone”
has been invoked; the
Primary Manager is
standalone and is in
control of Sensors
Reset to standalone is
invoked; the Secondary
<Manager/Central
Manager> is in control of
<Sensors/Manager>
Reset to standalone is
invoked; the
<Manager/Central
Manager> is in control of
<Sensors/Manager>
Informational A “Reset to Standalone”
has been invoked; the
Secondary Manager is
standalone and is in
control of Sensors
Informational A "Reset to Standalone"
has been invoked; the
current Manager is
standalone and in control
of Sensors.
This message is for
user information, no
action required.
This message is for
user information, no
action required.
This message is for
user information, no
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Reset to standalone has
been invoked; the peer
<Manager/Central
Manager> is in control of
<Sensors/Manager>
Real-time signature file
update from Manager to
Sensor(s) is in progress
Informational A "Reset to Standalone"
has been invoked; the
Peer Manager is
standalone and in control
of Sensors.
Informational A real-time signature file
update to Sensor(s) is in
progress.
This action is attempted
after a scheduled
signature set update to
the Manager, and if realtime signature file updates
are enabled
71
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Page 81

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
Real-time signature file
update from Manager to
Sensor(s) successful
Informational A real-time signature file
update to Sensor(s) is
successful.
This action is attempted
after a scheduled
signature set update to
the Manager, and if realtime signature file updates
are enabled.
Sensor software image or
signature set import in
progress
Informational A Sensor software image
or signature set file is in
the process of being
imported to the Manager.
Scheduled backup failed Informational Unable to create backup
for scheduled database
Scheduled signature set
download from Update
Server to Manager in
progress
Informational A scheduled signature set
update is in the process of
downloading from the
McAfee Update Server to
the Manager server
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This fault indicates
problems such as SQL
exceptions, database
connectivity problems,
or out-of-disk space
errors.
Check your backup
configuration settings.
This fault clears when a
successful backup is
made.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Scheduled signature set
download from Update
Server to Manager is
successful
Scheduled signature file
update from Manager to
Sensor(s) is in progress
Scheduled signature file
update from Manager to
Sensor(s) successful
Informational A scheduled signature set
download from the
McAfee Update Server to
the Manager server is
Successful.
Informational A scheduled signature file
update from the Manager
to Sensor(s) is in
progress.
Informational A scheduled signature file
update from the Manager
to Sensor(s) is successful.
72
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Page 82

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
Scheduler - Signature
download from Manager to
Sensor failed
Scheduled Vulnerability
Manager vulnerability data
import failed
Sensor configuration
update in progress
Sensor configuration
successful
Sensor configuration
update successful
Sensor discovered with
license
Informational Scheduler - Signature
download from Manager
to Sensor has failed
Informational Scheduled Vulnerability
Manager vulnerability
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Refer to error logs for
details
data import has failed
Informational A Sensor configuration
update is in the process of
being pushed from the
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Manager server to the
Sensor.
Informational A Sensor configuration
update was successfully
pushed from the Manager
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
server to Sensor
Informational Sensor configuration
update successfully
pushed from the Manager
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
server to the Sensor.
Informational Sensor discovered with
license that will expire.
Renew the license
before expire
Sensor discovery is in
progress
Sensor software image
download failed
Sensor software image
download in progress
Sensor software image
download successful
Informational The Manager is
attempting to discover the
Sensor.
Informational Sensor software image
failed to download from
the McAfee Update
Server to the Manager
server.
Informational Sensor software image is
in the process of
downloading from the
McAfee Update Server to
the Manager server.
Informational Sensor software image
successfully downloaded
from the McAfee Update
Server to the Manager
server.
73
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Page 83

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
Sensor software image or
signature set import in
progress
Sensor software image or
signature
set import in progress
Sensor software update is
in progress
Sensor software update
successful
Informational A Sensor software image
or signature set file is in
the process of being
imported from the McAfee
Update Server to the
Manager server.
Informational A Sensor software image
or signature set file is in
the process of being
imported from the
Network Security Platform
Update Server to the
Manager server.
Informational
Informational A Sensor software update
is in the process of being
pushed from the Manager
Server to the Sensor.
Informational Sensor software update is
successfully pushed from
the Manager Server to
Sensor.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Signature set download
successful
Informational Signature set successfully
downloaded from the
McAfee Update Server to
the Manager server.
Signature set update failed Informational Signature set update
failed while transferring
from the Manager server
to the Sensor.
Signature set update is in
progress
Informational A signature set is in the
process of being pushed
from the Manager server
to the Sensor.
74
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Page 84

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
Signature set update not
successful.
Switchback has been
completed, the primary
Manager has got the
control of Sensors now
System startup in process;
alerts being restored
Syslog Forwarder is not
configured for the Admin
Domain: <Admin Domain
Name> to accept the ACL
logs.
The Sensor to Manager
communication IP do not
match with the peer
Manager's peer IP
configured in the MDR set
up.
Informational The attempt to update the
signature set on the
Manager was not
successful, and thus no
signature set is available
on the Manager.
You must re-import a
signature set before
performing any action
on the Manager. A valid
signature set must be
present before any
action can be taken in
Network Security
Platform.
Informational n/a This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Informational Threat Analyzer may not
show all alerts.
You need to restart
Manager, to view the
restored alerts in
Threat Analyzer.
Informational ACL logging is enabled,
but no Syslog server has
been configured to accept
Configure a Syslog
server to receive
forwarded ACL logs.
the log messages.
Informational The Sensor to Manager
communication IP does
not match with the peer
Manager's peer IP. The
peer IP configured in the
peer Manager is the IP of
Ensure that the Sensor-
Manager
communication IP
matches with the peer
Manager's peer IP in
MDR configuration.
this Manager, and this IP
should match with the
Sensor- Manager
Communication IP set in
this Manager during
installation.
UDS export to the Manager
in progress
Update Scheduler in
progress
Informational One or more UDS is in
the process of being
exported from the Custom
Attack Editor to the
Manager server.
Informational This message indictaes
that the update scheduler
is in progress
75
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Page 85

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Fault Severity Description/Cause Action
Alert archival in progress Informational Manager is archiving the
alerts, and this is in
progress
System Fault Messages
Wait for the Alert
archival to complete
Vulnerability data import
from McAfee Vulnerability
Manager database was
successful
Weekly scheduled report
generation complete
Weekly scheduled report
generation in progress
Other faults
IPS Quarantine
In the case of IPS Quarantine, an error message is raised when the number of quarantine
rules exceed the permitted limit. The Sensor raises a fault message to the Manager when
the number of quarantine rules exceeds the maximum permitted limit. The fault is
displayed as
Threat Analyzer.
Informational This message indicates
that the vulnerability data
import from McAfee
Vulnerability Manager
database is successful.
For more information on
importing vulnerability
data reports in Manager,
see Importing
Vulnerability Scanner
Reports, Integration Guide.
Informational Weekly scheduled report
generation process
successfully completed
Informational Weekly scheduled report
generation process in
progress
IP: IPS quarantine block nodes exhausted. This can be viewed as an alert in the
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
This message is for
user information. No
action required.
Note : You can have up to 1000 IPS Quarantine rules for an IPv4 addresses, and
up to 500 IPS Quarantine rules for IPv6 addresses.
For more information on quarantine and remediation functionality, see IPS
Quarantine settings in the IPS Sensor,
You can view the faults from the Operational Status menu in Manager. For more information,
see Fault messages for Vulnerability Manager Scheduler and Automatic report import
using Scheduler, Integration Guide.
IPS Configuration Guide
76
Page 86

C HAPTER 7
Error Messages
This section lists the error messages displayed in McAfee® Network Security Manager
(Manager).
Error messages for RADIUS servers
The table lists the error messages displayed in the Manager.
Error Name Description/Cause Action
RADIUS Connection
Successful
RADIUS Connection Failed Network failure, congestion at
No RADIUS server
configured
Server with IP address and
port already exists for
RADIUS server
RADIUS server host IP
address/host name is
required
Shared Secret key is
unique in case of RADIUS
server
RADIUS server is up and
running
servers or RADIUS server not
available
No server available Configure at least one RADIUS server
IP address and port connection
not unique
Field cannot be blank Enter a valid host name /IP address
Field cannot be blank Enter a valid host name /IP address
RADIUS server is up and running
Try after sometime, check IP address
and Shared Secret key
Use a different IP address and port
number
RADIUS server host IP
address/host name cannot
be resolved as entered
The table lists the error messages displayed in the User Activity Audit report.
Error Name Description/Cause Error Type
RADIUS Authentication User <user name> with login Id <login Id> failed to
Add Radius Server Added RADIUS server IP Address/Host <IP
Invalid host name /IP address Enter a valid host name /IP address
User
authenticate to RADIUS server <RADIUS server
host name /IP address> on port <port number>
due to server timeout/ network failure
Manager
address or host name> , port <port number>
enable <Yes/No>
77
Page 87

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Error Name Description/Cause Error Type
Edit RADIUS server IP Address/Host <IP address or host name> set
port <port number> ,set Enabled <Yes/No>
Error Messages
Manager
Delete RADIUS server Deleted RADIUS Server IP Address/Host <IP
Manager
address or host name> , port <port number>
Error messages for LDAP server
The table lists the error messages displayed in the Manager.
Error Name Description/Cause Action
Server with IP address and
port already exists for LDAP
server
LDAP server host IP
address/host name is
required
LDAP server host IP
address/host name cannot
be resolved as entered
LDAP Connection Successful LDAP server is up and running LDAP server is up and running
LDAP Connection Failed Network failure, congestion at
No LDAP server configured No server available Configure at least one LDAP server
IP address and port connection
not unique
Use a different IP address and port
number
Field cannot be blank Enter a valid host name /IP address
Invalid host name /IP address Enter a valid host name /IP address
Try after sometime, check IP
servers or LDAP server not
address
available
The table lists the error messages displayed in the User Activity Audit report.
Error Name Description/Cause Error Type
LDAP Authentication User <user name> with login Id <login Id>
failed to authenticate to LDAP server <LDAP
server host name /IP address> on port <port
number> due to server timeout/ network
failure.
Add LDAP server Added LDAP server IP Address/Host <IP
address or host name> , port <port number>,
enable <Yes/No>
Edit LDAP server IP Address/Host <IP address or host name>
set port <port number> ,set Enabled
<Yes/No>
Delete LDAP server Deleted LDAP Server IP Address/Host <IP
address or host name" , port<port number>
78
User
Manager
Manager
Manager
Page 88

C HAPTER 8
Using the InfoCollector tool
This section describes the following aspects of using the Infocollector tool:
Introduction (on page 79)
Running the InfoCollector (on page 80)
Using InfoCollector (on page 80)
Introduction
InfoCollector is an information collection tool, bundled with Manager that allows you to
easily provide McAfee with McAfee
McAfee can use this information to investigate and diagnose issues you may be
experiencing with the Manager.
InfoCollector can collect information from the following sources within McAfee Network
Security Platform:
Information Type Description
Ems.log Files Configurable logs containing information from various components of
the Manager. The current ems.log file is renamed when its size reaches
1MB, using the current timestamp. Another ems.log is created to collect
the latest log information.
Configuration
backup
Configuration files XML and property files within the Network Security Platform config
A collection of database information containing all Network Security
Platform configuration information.
directory.
®
Network Security Platform-related log information.
Fault log A table in the Network Security Platform database that contains
Sensor Trace A file containing various McAfee® Network Security Sensor (Sensor)-
Compiled
Signature
InfoCollector is a tool that can be used both by you and by McAfee.
McAfee systems engineers can use the InfoCollector tool to provide you with a definition
(.def) file via email. This file is configured by McAfee to automatically choose information
that McAfee needs from your installation of Network Security Platform. You simply open
the definition file within the InfoCollector and it will automatically select the information that
McAfee needs from your installation of the Manager.
Alternatively, a manual approach can also be used with InfoCollector, and you can select
information yourself to provide to McAfee. For example, McAfee may ask you to select
generated fault log messages.
related log files.
A file containing signature information and policy configuration for a
given Sensor.
79
Page 89

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
checkboxes that correspond to different sets of information available within Network
Security Platform.
Running the InfoCollector
To run InfoCollector, follow the following steps:
1. If you do not already have InfoCollector installed, download the
InfoCollector.zip file from the McAfee website and extract it to a specific
location in a specific drive:
Example
C:\[Network Security Manager_INSTALL_DIR]\App\diag
Files related to InfoCollector, such as infocollector.bat should be in a specific
location:
Example
C:\[Network Security
Manager_INSTALL_DIR]\App\diag\InfoCollector
2. Run the following batch file:
C:\[Network Security
Manager_INSTALL_DIR]\App\diag\InfoCollector\infocollecto
r.bat
Using the InfoCollector tool
Using InfoCollector
To use InfoCollector, follow these steps:
1 After you run InfoCollector, do one of the following:
If McAfee provides you with a definition file:
i. After you run InfoCollector, open the File menu and click Open Definition.
ii. Select the definition file that McAfee sent you via email and click Select.
If McAfee instructs you to select InfoCollector checkboxes:
iii. After you run InfoCollector, select the checkboxes as instructed by McAfee.
iv. Select a Duration. Select Date to specify a start and end date, or select Last X
Days and
v. Select the number of days from which InfoColl ector should gather
information.
vi. Click Browse and select the path and filename of the output ZIP file.
2 Click
3 Provide the output ZIP file to McAfee as recommended by McAfee Technical Support.
Caution: The output ZIP file contains the toolconfig.txt file, which lists the
information that you have chosen to provide McAfee.
Run.
You can send the file via email or through FTP.
80
Page 90

C HAPTER 9
Automatically restarting a failed Manager with Manager
Introduction
How the Manager Watchdog Works
This section provides the following information on starting a failed Manager with Manager
Watchdog:
Introduction (on page 81
How the Manager Watchdog Works (on page 81)
Installing Manager Watchdog (on page 82)
Starting Manager Watchdog (on page 82)
Using Manager Watchdog with Manager in an MDR configuration (on page 82)
Tracking Manager Watchdog activities (on page 82)
The Manager Watchdog feature is designed to restart the Manager if the Manager
crashes, potentially bringing the Manager back online before MDR enables.
The Manager Watchdog monitors the Manager process on the Manager server period ically
for availability. If Manager Watchdog detects that the Manager has gone down
unexpectedly, it restarts the service automatically. (It does not restart the Manager if the
Manager has been shut down intentionally.)
)
Watchdog
Manager Watchdog runs as a separate process and monitors Manager through the
Windows OS Services model. Manager Watchdog polls Manager every 10 seconds. If the
Manager Watchdog does not detect the Manager during a polling period, it waits 30
seconds and then restarts the Manager service automatically. Manager Watchdog will
make five attempts to restart the Manager and then, if it has not succeeded, it will exit.
Manager Watchdog, by default, is a manual service; you must explicitly start it.
Caution 1: You can instead change this setting to be automatic if you wish the
service to start automatically after a system reboot.
Caution 2: If you have chosen to change the Manager service setting from its
default (Auto) to "Manual," (during a troubleshooting session, for example) then
consider doing the same for Manager Watchdog. This will prevent the Manager
Watchdog from restarting Manager automatically.
81
Page 91

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Installing Manager Watchdog
Manager Watchdog is installed automatically during Manager installation, and a new OS
service called "Network Security Platform Watchdog Service" is created to enable you to
start and stop the Manager Watchdog service.
Caution: Manager Watchdog monitors only the "Network Security PlatformMgr"
service; it does not monitor services like MySQL or Apache.
Starting Manager Watchdog
The Manager watchdog process is, by default, not started after installation; you must start
the Manager watchdog process manually.
To start/stop Manager Watchdog:
Automatically restarting a failed Manager with Manager Watchdog
1. Select
2. Click
3. Do one of the following:
To start the service, select
To stop the service, select
Start > Settings > Control Panel. Double-click Administrative Tools, and then
double-click
Network Security Platform Watchdog Service.
Services.
Action > Start.
Action > Stop.
Using Manager Watchdog with Manager in an MDR
configuration
When using Manager Watchdog on an Manager that is part of an MDR configuration,
consider whether you want the Manager Watchdog to restart the Manager before failover
can occur. If so, you must ensure that the value set for the MDR setting "Downtime Before
Switchover" is greater than the Manager Watchdog setting of 30 seconds. This prevents
the initiation of MDR, wherein the peer Manager takes over if the primary Manager fails.
McAfee suggests retaining the default value of 5 minutes or greater to allow the Manager
Watchdog time to restart the Manager.
If the Manager Watchdog brings up a primary Manager after MDR has initiated, note that
the primary Manager does not come back Active; it checks first to determine whether the
secondary is Active and if so, remains as standby.
Tracking Manager Watchdog activities
The Manager Watchdog logs all controlled activities in a log file. Log files can be found at:
/<Network Security Platform install directory>/ named with the
filename convention wdout_<<time stamp>>.log
A sample log file entry follows:
82
Page 92

Sample Manager Watchdog Log
Restarting server at Mon Jun 09 14:48:53 GMT+05:30 2006
SERVER STDOUT: The Network Security Platform Manager Service is
starting.
SERVER STDOUT: The Network Security Platform Manager Service
was started successfully.
SERVER STDOUT:
SERVER STDOUT:
If the Manager Watchdog fails after five attempts to restart Manager, the following line will
appear in the log file:
SERVER STDOUT: Failed to restart Manager after five attempts.
Exiting. [kl]
83
Page 93

C HAPTER 10
Utilizing the McAfee Knowledge Base
Old Number New Number Topic
KB38000 KB55446 All signature set releases with links to signature set release notes
KB38001 KB55447 All UDS releases and release notes of the UDS’s (this is a restricted
KB38002 KB55448 Table displaying the current versions for McAfee® Network Security
KB38003 KB55449 Listing of McAfee Network Security Platform’s response to high
KB38004 KB55450 How to request coverage for a threat that isn't already covered
KB38005 KB55451 List of all McAfee Recommended for Blocking (RFB) attacks
KB37553 KB55318 Sensor heat dissipation rates (BTUs per hour)
KB37773 KB60660 Verifying MySQL Database Tables
The McAfee Knowledgebase (KB) contains a large number of useful articles design ed to
answer specific questions that might not have been addressed elsewhere in the
documentation set. We suggest checking to see if a question you have is answered in a
KB article.
To access McAfee Knowledgebase:
Go to http://mysupport.mcafee.com/Eservice/
The following list contains some of the more commonly accessed KB articles.
article and requires the user to log into service portal or be internal)
Platform
profile public vulnerabilities
, and click Search the KnowledgeBase.
KB38041 KB55470 Network Security Platform maximum number of CIDR blocks using
VIDS
KB38365 KB55549 Collecting a diagnostics trace from the McAfee® Network Security
Sensor (Sensor)
KB38487 KB55568 VLAN limitations for Network Security Platform
KB39232 KB55723 Maximum number of SSL keys for McAfee® Network Security
Manager (Manager) or Sensor
KB39353 KB55743 Submitting Net work Security Platform incorrect identifications (false
positive/incorrect detection) to support
KB39888 KB55908 Support for legacy versions
KB40570 KB55364 Asymmetric traffic
KB40571 KB56069 "Login faile d: Unab le to get the Network Security Manager license
information"
84
Page 94

McAfee® Network Security Platform 6.0
Old Number New Number Topic
Utilizing the McAfee Knowledge Base
KB40582 KB56071
Configuring authentication on the Manager for the update server
KB41752 KB56364 3rd Party Recommended Hardware for Sensors
KB61131
Error: Download Failed: Reason 42: Sensor fails to apply new
updates internally(Sensor signature updates fails)
KB65523
NAI32011 KB59347
Network Security Platform Release Notes (Master List)
Sensor is reporting false DOS attacks / New network device is
added and Sensor is now reporting DOS attacks
NAI32008 KB59344 Recover the password for the Manager
85
Page 95

S
sensor failover status............................................. 26
Index
system health......................................................... 25
A
auto-negotiation and speed configurations......19, 24
C
connectivity issues.................................................19
conventions.............................................................vii
critical faults ...........................................................42
D
duplex mismatches ................................................ 19
F
false positives.........................................................38
H
hardening the ISM server.........................................7
hardening the MySQL installation............................7
I
InfoCollector tool....................................................86
informational faults.................................................69
T
technical support...................................................... x
W
Watchdog............................................................... 89
M
management port configuration .............................18
MySQL issues........................................................36
O
other faults .............................................................82
P
problems with sensor reboot............................27, 28
R
rolling back changes ..............................................10
 Loading...
Loading...