Page 1
Engine
CONTENTS
Workshop
Manual
L8
LF
L3
FOREWORD
This manual explains the disassembly,
inspection, repair, and reassembly
procedures for the above-indicated engine.
In order to do these procedures safety,
quickly, and correctly, you must first read
this manual and any other relevant service
materials carefully.
Title Section
General Information GI
Engine B
Technical Data TD
Special Tools ST
© 2002 Mazda Motor Corporation
PRINTED IN The Netherlands, MARCH 2002
1731–1E–02C
The information in this manual is current
up to March, 2002. Any changes that occur
after that time will not be reflected in
this particular manual. Therefore, the contents
of this manual may not exactly match
the mechanism that you are currently
serving.
Mazda Motor Corporation
HIROSHIMA, JAPAN
Page 2
WARNING
Servicing a vehicle can be dangerous. If you have not received
service-related training, the risks of injury, property damage, and
failure of servicing increase. The recommended servicing procedures
for the vehicle in this workshop manual were developed with
Mazda-trained technicians in mind. This manual may be useful to
non-Mazda trained technicians, but a technician with our
service-related training and experience will be at less risk when
performing service operations. However, all users of this manual are
expected to at least know general safety procedures.
This manual contains "Warnings" and "Cautions" applicable to risks
not normally encountered in a general technician's experience.
They should be followed to reduce the risk of injury and the risk that
improper service or repair may damage the vehicle or render it unsafe.
It is also important to understand that the "Warnings" and "Cautions"
are not exhaustive. It is impossible to warn of all the hazardous
consequences that might result from failure to follow the procedures.
The procedures recommended and described in this manual are
effective methods of performing service and repair. Some require tools
specifically designed for a specific purpose. Persons using procedures
and tools which are not recommended by Mazda Motor Corporation
must satisfy themselves thoroughly that neither personal safety nor
safety of the vehicle will be jeopardized.
The contents of this manual, including drawings and specifications, are
the latest available at the time of printing, and
reserves the right to change the vehicle designs and alter the contents
of this manual without notice and without incurring obligation.
Parts should be replaced with genuine Mazda replacement parts or
with parts which match the quality of genuine Mazda replacement
parts. Persons using replacement parts of lesser quality than that of
genuine Mazda replacement parts must satisfy themselves thoroughly
that neither personal safety nor safety of the vehicle will be
jeopardized.
Mazda Motor Corporation is not responsible for any problems which
may arise from the use of this manual. The cause of such problems
includes but is not limited to insufficient service-related training, use of
improper tools, use of replacement parts of lesser quality than that of
genuine Mazda replacement parts, or not being aware of any revision
of this manual.
Mazda Motor Corporation
Page 3

GI
GENERAL INFORMATION
GI
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
RANGE OF TOPICS.......................................... GI-2
SERVICE PROCEDURE ................................... GI-2
SYMBOLS.......................................................... GI-3
ADVISORY MESSAGES ................................... GI-4
UNITS
FUNDAMENTAL PROCEDURES
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
NEW STANDARDS
ABBREVIATIONS
................................................................... GI-5
UNITS ................................................................ GI-5
PREPARATION OF TOOLS AND
MEASURING EQUIPMENT............................ GI-6
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOLS.............................. GI-6
DISASSEMBLY.................................................. GI-6
INSPECTION DURING REMOVAL,
DISASSEMBLY............................................... GI-7
ARRANGEMENT OF PARTS ............................ GI-7
CLEANING OF PARTS...................................... GI-7
REASSEMBLY................................................... GI-7
ADJUSTMENT................................................... GI-8
RUBBER PARTS AND TUBING........................ GI-8
HOSE CLAMPS ................................................. GI-8
TORQUE FORMULAS....................................... GI-9
VISE................................................................... GI-9
SST.................................................................... GI-9
ELECTRICAL PARTS...................................... GI-10
CONNECTORS................................................ GI-10
............................................ GI-13
NEW STANDARDS.......................................... GI-13
.............................................. GI-15
ABBREVIATIONS............................................ GI-15
............................. GI-2
........................ GI-6
...................................... GI-10
GI–1
Page 4

HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
RANGE OF TOPICS
A6E201000001E01
• This manual contains procedures for performing all required service operations. The procedures are divided
into the following five basic operations:
— Removal/Installation
— Disassembly/Assembly
— Replacement
— Inspection
— Adjustment
• Simple operations which can be performed easily just by looking at the vehicle (i.e., removal/installation of
parts, jacking, vehicle lifting, cleaning of parts and visual inspection) have been omitted.
End Of Sie
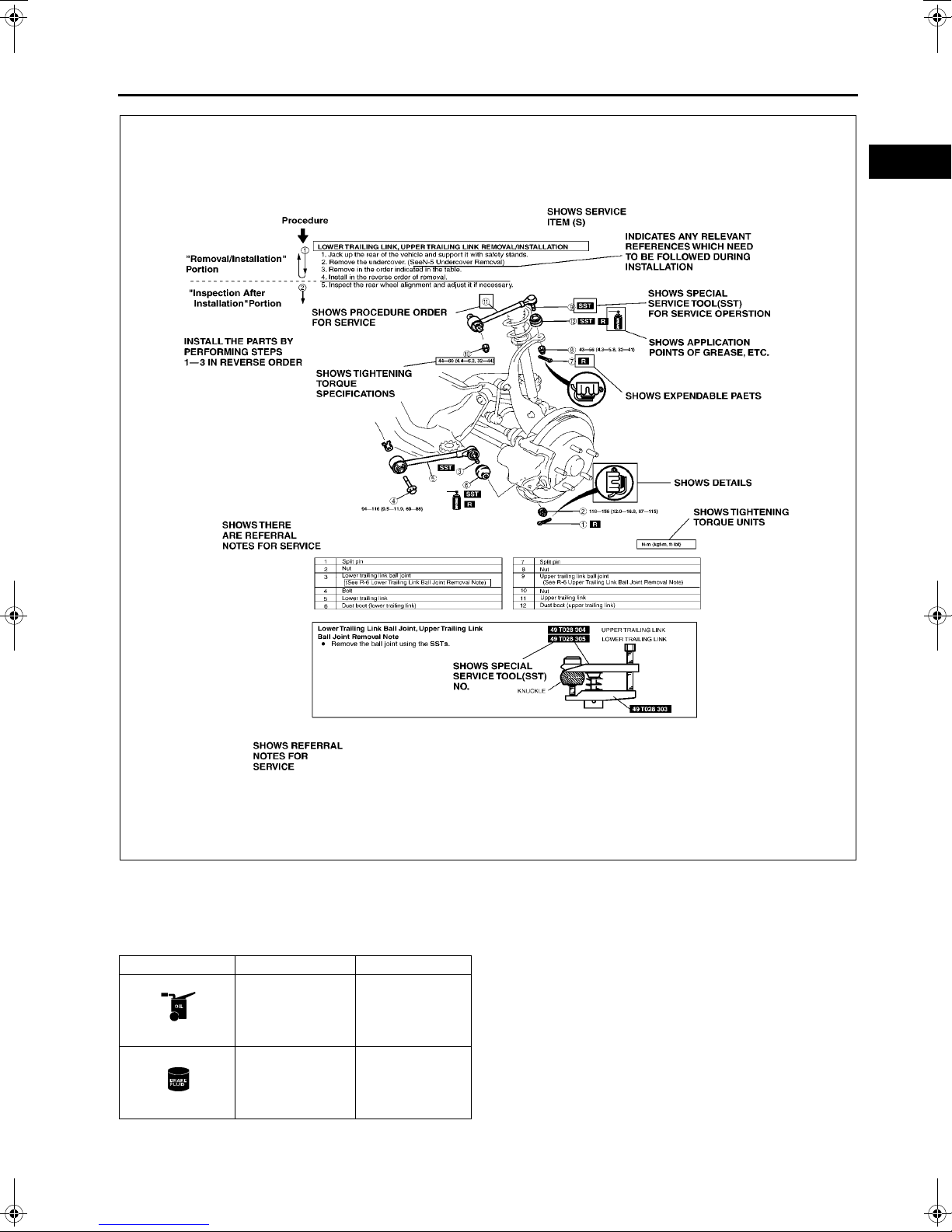
SERVICE PROCEDURE
Inspection, adjustment
• Inspection and adjustment procedures are divided into steps. Imp ortant points regarding the location and
contents of the procedures are explained in detail and shown in the illustrations.
A6E201000001E02
XME2010001
Repair procedure
1. Most repair operations begin with an overview illustration. It identifies the components, shows how the parts fit
together and describes visual part inspection. However, only removal/installation procedures that need to be
performed methodically have written instructions.
2. Expendable parts, tightening torques and symbols for oil, grease, and sealant are shown in the overview
illustration. In addition, symbols indicating parts requiring the use of special service tools or equivalent are also
shown.
3. Procedure steps are numbered and the part that is the main point of that procedure is shown in the illustration
with the corresponding number. Occasionally, there a re important points or additio nal information concerning a
procedure. Refer to this information when servicing the related part.
GI–2
Page 5
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
4.
GI
End Of Sie
SYMBOLS
• There are eight symbols indicating oil, grease, fluids , sealant, and
application points or use of these materials during service.
Symbol Meaning Kind
Apply oil
Apply brake fluid
New appropriate
engine oil or gear
oil
New appropriate
brake fluid
or equivalent use. These symbols show
SST
A6E201000001E03
XME2010010
GI–3
Page 6
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
Symbol Meaning Kind
Apply automatic
transaxle/
transmission fluid
New appropriate
automatic
transaxle/
transmission fluid
Apply grease
Apply sealant
Apply petroleum
jelly
Replace part
Use SST or
equivalent
Appropriate
grease
Appropriate
sealant
Appropriate
petroleum jelly
O-ring, gasket,
etc.
Appropriate tools
End Of Sie
ADVISORY MESSAGES
• You'll find several
Warnings, Cautions, Notes, Specifications
Warning
• A Warning indicates a situation in which serious injury or death could result if the warning is ignored.
and
Upper and Lower Limits
in this manual.
A6E201000001E04
Caution
• A Caution indicates a situation in which damage to the vehicle or parts could result if the caution is ignored.
Note
• A Note provides added information that will help you to complete a particular procedure.
Specification
• The values indicate the allowable range when performing inspections or adjustments.
Upper and lower limits
• The values indicate the upper and lower limits that must not be exceeded when performing inspections or
adjustments.
End Of Sie
GI–4
Page 7
UNITS
UNITS
UNITS
Electrical current A (ampere)
Electric power W (watt)
Electric resistance ohm
Electric voltage V (volt)
Length
Negative pressure
Positive pressure
Torque
Volume
Weight
mm (millimeter)
in (inch)
kPa (kilo pascal)
mmHg (millimeters of mercury)
inHg (inches of mercury)
kPa (kilo pascal)
2
(kilogram force per square
kgf/cm
centimeter)
psi (pounds per square inch)
N·m (Newton meter)
kgf·m (kilogram force meter)
kgf·cm (kilogram force centimeter)
ft·lbf (foot pound force)
in·lbf (inch pound force)
L (liter)
US qt (U.S. quart)
Imp qt (Imperial quart)
ml (milliliter)
cc (cubic centimeter)
cu in (cubic inch)
fl oz (fluid ounce)
g (gram)
oz (ounce)
GI
A6E201200002E01
Conversion to SI Units (Système International d'Unités)
• All numerical values in this manual are based on SI units. Numbers shown in conventional units are converted
from these values.
Rounding Off
• Converted values are rounded off to the same number of places as th e SI unit value. Fo r example, if the SI u nit
value is 17.2 and the value after conversion is 37.84, the converted value will be rounded off to 37.8.
Upper and Lower Limits
• When the data indicates upper and lower limits, the converted values are rounded down if the SI unit value is
an upper limit and rounded up if the SI unit value is a lower limit. Therefore, converted values for the same SI
unit value may differ after conversion. For ex am p l e, co ns ide r 2. 7 k gf /cm
210—260 kPa {2.1—2.7 kgf/cm
270—310 kPa {2.7—3.2 kgf/cm
• The actual converted values for 2.7 kgf/cm
2
, 30—38 psi}
2
, 39—45 psi}
2
are 264 kPa and 38.4 psi. In the first specification, 2.7 is used as
2
in the following specifications:
an upper limit, so the converted values are rounded down to 260 and 38. In the second specification, 2.7 is
used as a lower limit, so the converted values are rounded up to 270 and 39.
End Of Sie
GI–5
Page 8
FUNDAMENTAL PROCEDURES
FUNDAMENTAL PROCEDURES
PREPARATION OF TOOLS AND MEASURING EQUIPMENT
• Be sure that all necessary tools and measuring
equipment are available before starting any work.
End Of Sie
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOLS
• Use special service tools or equivalent when they
are required.
A6E201400004E02
X3U000WAH
A6E201400004E03
End Of Sie
DISASSEMBLY
• If the disassembly procedure is complex,
requiring many parts to be disassembled, all parts
should be marked in a place that will not affect
their performance or external appearance and
identified so that reassembly can be performed
easily and efficiently.
End Of Sie
X3U000WAJ
A6E201400004E07
X3U000WAL
GI–6
Page 9
FUNDAMENTAL PROCEDURES
INSPECTION DURING REMOVAL, DISASSEMBLY
• When removed, each part should be carefully
inspected for malfunction, deformation, damage,
and other problems.
End Of Sie
ARRANGEMENT OF PARTS
• All disassembled parts should be carefully
arranged for reassembly.
• Be sure to separate or otherwise identify the par ts
to be replaced from those that will be reused.
A6E201400004E08
GI
X3U000WAM
A6E201400004E09
End Of Sie
CLEANING OF PARTS
• All parts to be reused should be carefully and
thoroughly cleaned in the appropriate method.
Warning
••••
Using compressed air can cause dirt and
other particles to fly out causi ng injury to
the eyes. Wear protective eye wear
whenever using compressed air.
End Of Sie
REASSEMBLY
• Standard values, such as torques and certain
adjustments, must be strictly observed in the
reassembly of all parts.
• If removed, these parts should be replaced with
new ones:
— Oil seals
— Gaskets
— O-rings
— Lockwashers
— Cotter pins
— Nylon nuts
X3U000WAN
A6E201400004E10
WGIWXX0030J
A6E201400004E11
WGIWXX0031J
GI–7
Page 10
FUNDAMENTAL PROCEDURES
• Depending on location:
— Sealant and gaskets, or both, should be
applied to specified locations. When sealant
is applied, parts should be installed before
sealant hardens to prevent leakage.
— Oil should be applied to the moving
components of parts.
— Specified oil or grease should be applied at
the prescribed locations (such as oil seals)
before reassembly.
End Of Sie
ADJUSTMENT
• Use suitable gauges and/or testers when making
adjustments.
WGIWXX0032J
A6E201400004E12
End Of Sie
RUBBER PARTS AND TUBING
• Prevent gasoline or oil from getting on rubber
parts or tubing.
End Of Sie
HOSE CLAMPS
• When reinstalling, position the hose clamp in the
original location on the hose and squeeze the
clamp lightly with large pliers to ensure a good fit.
X3U000WAS
A6E201400004E13
WGIWXX0034E
A6E201400004E14
End Of Sie
GI–8
WGIWXX0035J
Page 11

FUNDAMENTAL PROCEDURES
TORQUE FORMULAS
• When using a torque wrench-
or equivalent
SST
combination, the written torque must be
recalculated due to the extra length that the
or equivalent adds to the torque wrench.
Recalculate the torque using the following
formulas. Choose the formula that applies to you.
Torque Unit Formula
N·mN·m × [L/(L+A)]
kgf·mkgf·m × [L/(L+A)]
kgf·cm kgf·cm × [L/(L+A)]
ft·lbf ft·lbf × [L/(L+A)]
in·lbf in·lbf × [L/(L+A)]
A : The length of the
past the torque wrench drive
SST
L : The length of the torque wrench
End Of Sie
VISE
• When using a vise, put protective plates in the
jaws of the vise to prevent damage to parts.
SST
A6E201400004E15
WGIWXX0036E
A6E201400004E16
GI
End Of Sie
SST
• Some Ford
marked with Ford
• Note that a Ford
or equivalent are used as
SST
numbers.
SST
number is written together with a corresponding Mazda
SST
Example (section ST)
Example (except section ST)
End Of Sie
necessary for engine repair. Note that these
SSTs
SST
X3U000WAW
A6E201400004E18
are
SSTs
number as shown below.
XME2014002
XME2014001
GI–9
Page 12
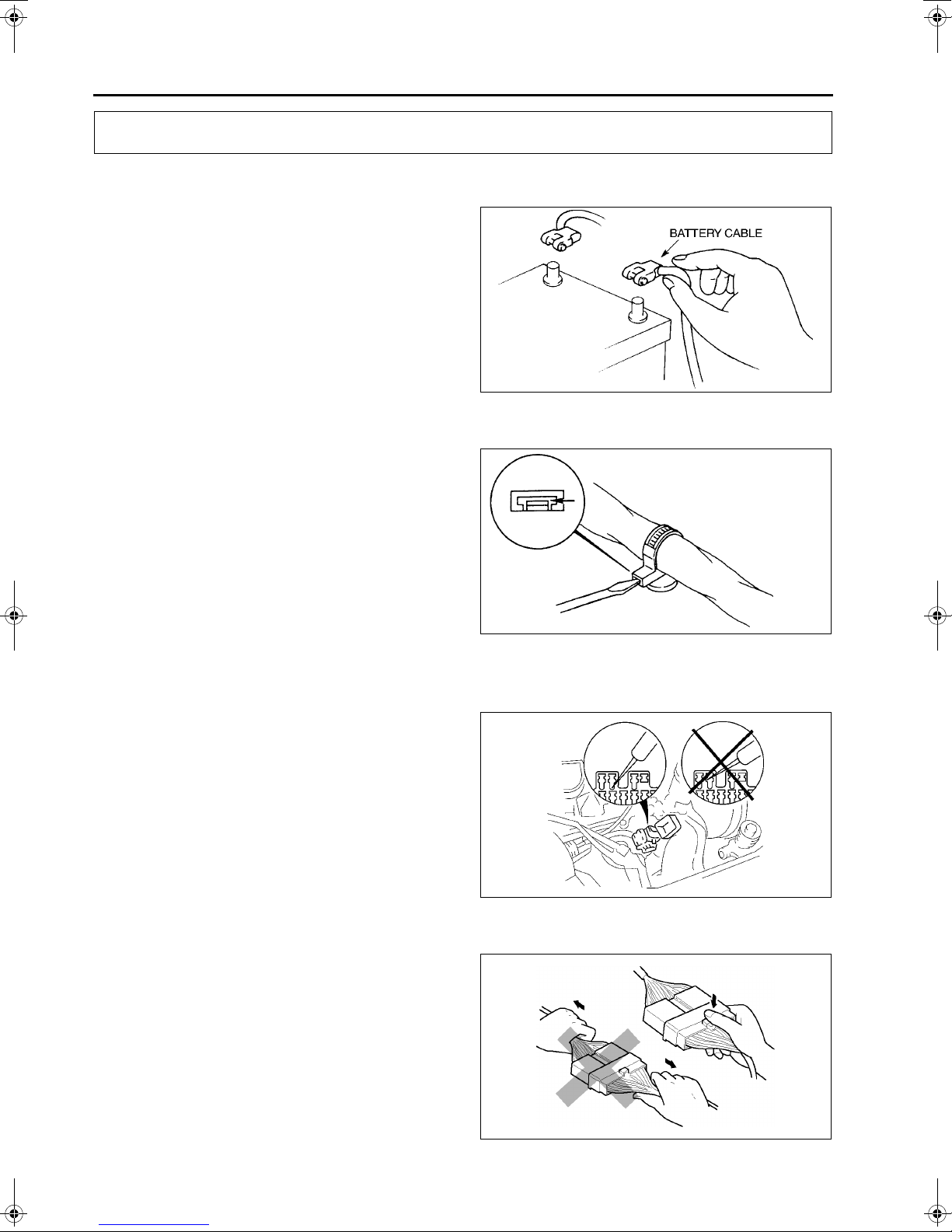
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
ELECTRICAL PARTS
Battery cable
• Before disconnecting connectors or removing
electrical parts, disconnect the negative battery
cable.
Wiring Harness
• To remove the wiring harness from the clip in the
engine room, pry up the hook of the clip using a
flathead screwdriver.
A6E201700006E01
WGIWXX0007E
End Of Sie
CONNECTORS
Data link connector
• Insert the probe into the terminal when
connecting a jumper wire to the data link
connector.
Caution
••••
Inserting a jumper wire probe into the
data link connector terminal may damage
the terminal.
Disconnecting connectors
• When disconnecting connector, grasp the
connectors, not the wires.
X3U000WBU
A6E201700006E02
X3U000WAY
GI–10
WGIWXX0041E
Page 13
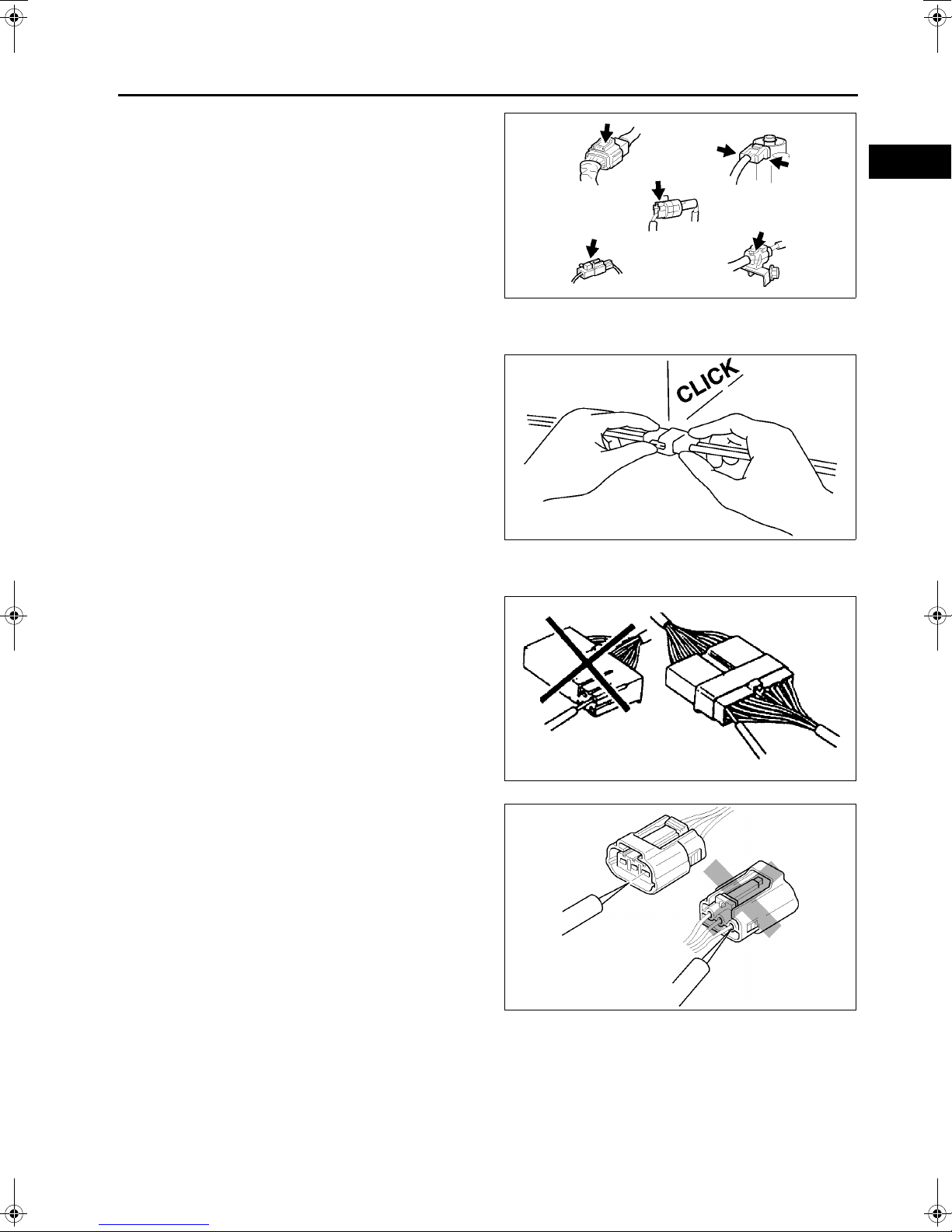
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
• Connectors can be disconnected by pressing or
pulling the lock lever as shown.
Locking connector
• When locking connectors, listen for a click
indicating they are securely locked.
GI
WGIWXX0042E
Inspection
• When a tester is used to inspect for continuity or
measuring voltage, insert the tester probe from
the wiring harness side.
• Inspect the terminals of waterproof connectors
from the connector side since they cannot be
accessed from the wiring harness side.
Caution
••••
To prevent damage to the terminal, wrap
a thin wire around the tester probe before
inserting into terminal.
X3U000WB1
X3U000WB2
WGIWXX0045E
GI–11
Page 14
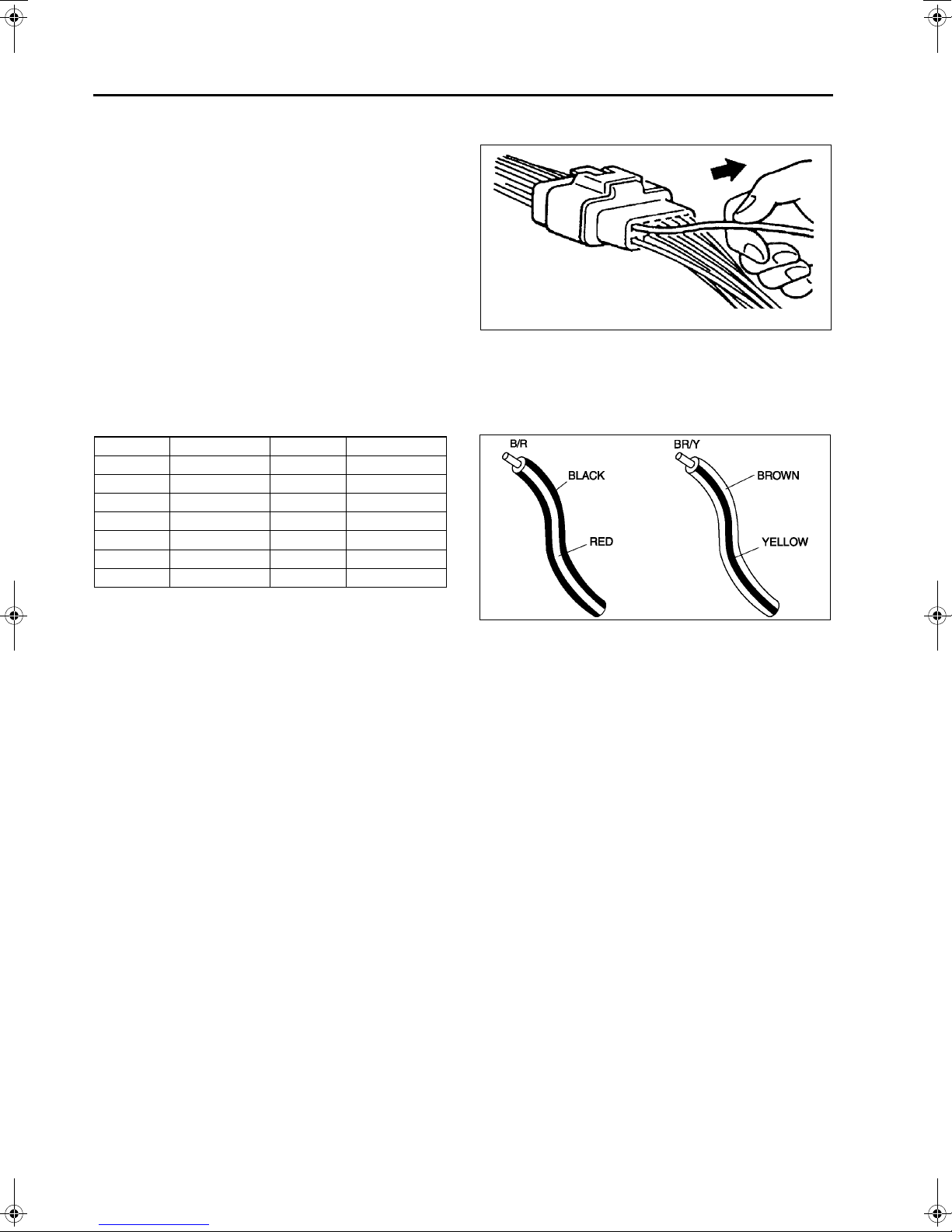
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Terminals
Inspection
• Pull lightly on individual wires to verify that they
are secured in the terminal.
Wiring Harness
Wiring color codes
• Two-color wires are indicated by a two-color code symbol.
• The first letter indicates the base color of the wire and the second the color of the stripe.
CODE COLOR CODE COLOR
B Black O Orange
BR Brown P Pink
G Green R Red
GY Gray V Violet
LBlueWWhite
LB Light Blue Y Yellow
LG Light Green
X3U000WB4
End Of Sie
X3U000WB7
GI–12
Page 15
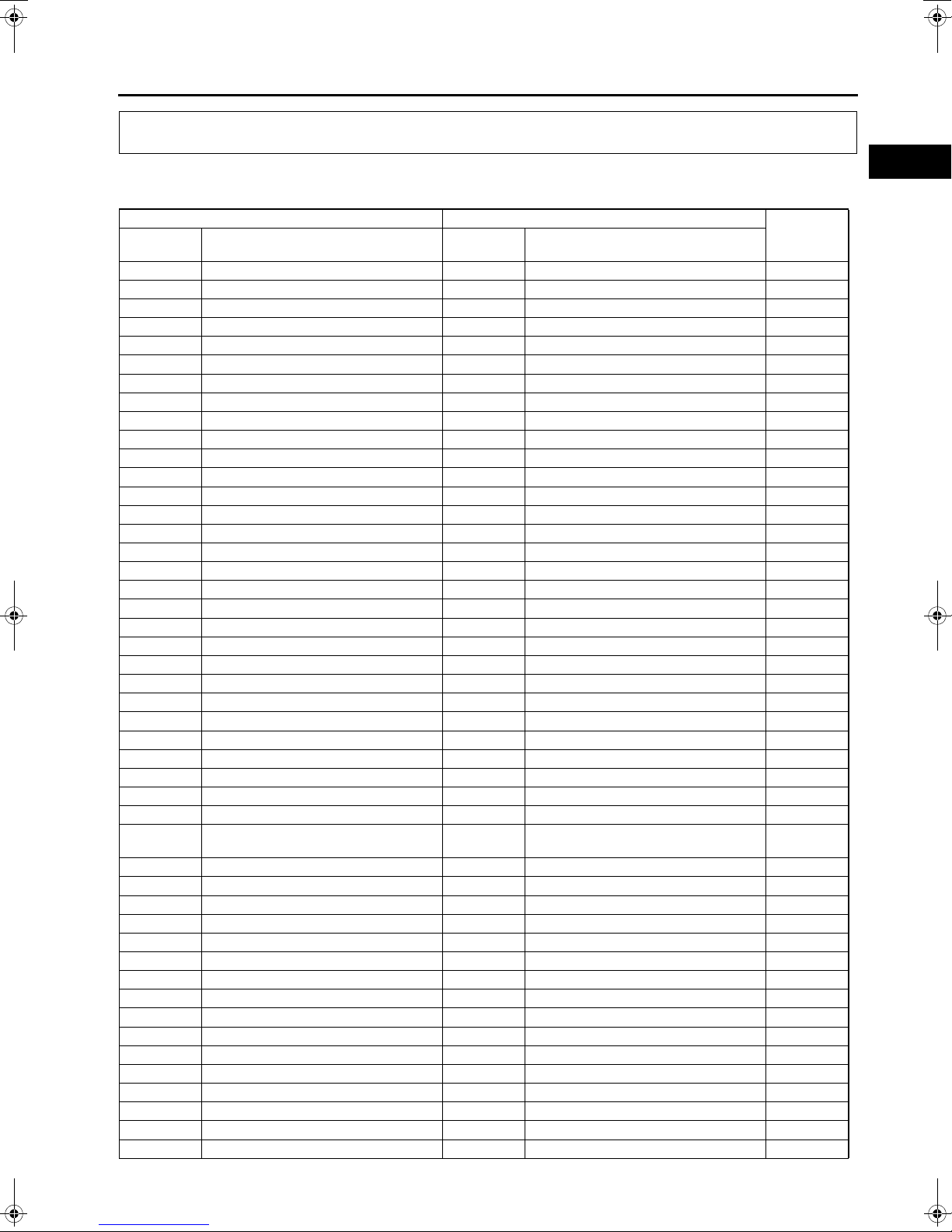
NEW STANDARDS
NEW STANDARDS
NEW STANDARDS
• Following is a comparison of the previous standard and the new standard.
New Standard Previous Standard
Abbrevi-
ation
AP Accelerator Pedal — Accelerator Pedal
ACL Air Cleaner — Air Cleaner
A/C Air Conditioning — Air Conditioning
BARO Barometric Pressure — Atmospheric Pressure
B+ Battery Positive Voltage Vb Battery Voltage
— Brake Switch — Stoplight Switch
— Calibration Resistor — Corrected Resistance #6
CMP sensor Camshaft Position Sensor — Crank Angle Sensor
CAC Charge Air Cooler — Intercooler
CLS Closed Loop System — Feedback System
CTP Closed Throttle Position — Fully Closed
CPP Clutch Pedal Position — Idle Switch
CIS Continuous Fuel Injection System — Clutch Position
CS sensor Control Sleeve Sensor CSP sensor Control Sleeve Position Sensor #6
CKP sensor Crankshaft Position Sensor — Crank Angle Sensor 2
DLC Data Link Connector — Diagnosis Connector
DTM Diagnostic Test Mode — Test Mode #1
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code(s) — Service Code(s)
DI Distributor Ignition — Spark Ignition
DLI Distributorless Ignition — Direct Ignition
EI Electronic Ignition — Electronic Spark Ignition #2
ECT Engine Coolant Temperature — Water Thermo
EM Engine Modification — Engine Modification
— Engine Speed Input Signal — Engine RPM Signal
EVAP Evaporative Emission — Evaporative Emission
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation — Exhaust Gas Recirculation
FC Fan Control — Fan Control
FF Flexible Fuel — Flexible Fuel
4GR Fourth Gear — Overdrive
— Fuel Pump Relay — Circuit Opening Relay #3
FSO
solenoid
GEN Generator — Alternator
GND Ground — Ground/Earth
HO2S Heated Oxygen Sensor — Oxygen Sensor With heater
IAC Idle Air control — Idle Speed Control
— IDM Relay — Spill Valve Relay #6
— Incorrect Gear Ratio ——
— Injection Pump FIP Fuel Injection Pump #6
— Input/Turbine Speed Sensor — Pulse Generator
IAT Intake Air Temperature — Intake Air Thermo
KS Knock Sensor — Knock Sensor
MIL Malfunction Indicator Lamp — Malfunction Indicator Light
MAP Manifold Absolute Pressure — Intake Air Pressure
MAF sensor Mass Air Flow Sensor — Airflow Sensor
MFL Multiport Fuel Injection — Multiport Fuel Injection
OBD On-Board Diagnostic — Diagnosis/SelfDiagnosis
OL Open Loop — Open Loop
Fuel Shut Off Solenoid FCV Fuel Cut Valve #6
Name
Abbreviation
Name
GI
A6E202800020E01
Remark
GI–13
Page 16
NEW STANDARDS
New Standard Previous Standard
Abbrevi-
ation
— Output Speed Sensor — Vehicle Speed Sensor 1
OC Oxidation Catalytic Converter — Catalytic Converter
O2S Oxygen Sensor — Oxygen Sensor
PNP Park/Neutral Position — Park/Neutral Range
— PCM Control Relay — Main Relay #6
PSP Power Steering Pressure — Power Steering Pressure
PCM Powertrain Control Module ECU Engine Control Unit #4
— Pressure Control Solenoid — Line Pressure Solenoid Valve
PAIR Pulsed Secondary Air Injection — Secondary Air Injection System
— Pump Speed Sensor — NE Sensor #6
AIR Secondary Air Injection — Secondary Air Injection System
SAPV Secondary Air Pulse Valve — Reed Valve
SFI Sequential Multipoint Fuel In jection — Sequential Fuel Injection
— Shift Solenoid A
— Shift Solenoid B
— Shift Solenoid C — 3–4 Shift Solenoid Valve
3GR Third Gear — 3rd Gear
TWC Three Way Catalytic Converter — Catalytic Converter
TB Throttle Body — Throttle Body
TP sensor Throttle Position Sensor — Throttle Sensor
TCV Timer Control Valve TCV Timing Control Valve #6
TCC Torque Converter Clutch — Lockup Position
TCM
—
TR Transmission (Transaxle) Range — Inhibitor Position
TC Turbocharger — Turbocharger
VSS Vehicle Speed Sensor — Vehicle Speed Sensor
VR Voltage Regulator — IC Regulator
VAF sensor Volume Air Flow Sensor — Air flow Sensor
WUTWC
WOT Wide Open Throttle — Fully Open
Transmission (Transaxle) Control
Module
Transmission (Transaxle) Fluid
Temperature Sensor
Warm Up Three Way Catalytic
Converter
Name
Abbreviation
— 1–2 Shift Solenoid Valve
— Shift A Solenoid Valve
— 2–3 Shift Solenoid Valve
— Shift B Solenoid Valve
— ECAT Control Unit
— ATF Thermosensor
— Catalytic Converter #5
Name
Remark
Pulsed
injection
Injection
with air
pump
#1 : Diagnostic trouble codes depend on the diagnostic test mode
#2 : Controlled by the PCM
#3 : In some models, there is a fuel pump relay that controls pump speed. That relay is now called the fuel pump
relay (speed).
#4 : Device that controls engine and powertrain
#5 : Directly connected to exhaust manifold
#6 : Part name of diesel engine
End Of Sie
GI–14
Page 17
ABBREVIATIONS
ABBREVIATIONS
ABBREVIATIONS
MTX Manual transaxle
ATX Automatic transaxle
ATDC After top dead center
TDC Top dead center
IN Intake
EX Exhaust
EGR Exhaust gas recirculation
OCV Oil control valve
SST Special service tool
End Of Sie
GI
A6E203000011E01
GI–15
Page 18

B
ENGINE
B
ENGINE
ENGINE OVERHAUL SERVICE WARNING .......B-2
ENGINE MOUNTING/DISMOUNTING ................B-2
TIMING CHAIN DISASSEMBLY..........................B-3
CYLINDER HEAD (I) DISASSEMBLY.................B-5
CYLINDER HEAD (II) DISASSEMBLY ................B-7
CYLINDER BLOCK (I) DISASSEMBLY...............B-9
CYLINDER BLOCK (II) DISASSEMBLY............B-10
CYLINDER HEAD INSPECTION.......................B-11
VALVE, VALVE GUIDE INSPECTION...............B-12
VALVE GUIDE REPLACEMENT .......................B-13
VALVE SEAT INSPECTION/REPAIR................B-15
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION..........................B-15
CAMSHAFT INSPECTION ................................B-16
TAPPET INSPECTION......................................B-17
CYLINDER BLOCK INSPECTION.................. ...B-18
OIL JET VALVE INSPECTION ..........................B-19
PISTON INSPECTION.......................................B-19
CRANKSHAFT INSPECTION............................B-20
CONNECTING ROD INSPECTION...................B-22
BOLT INSPECTION...........................................B-22
VARIABLE VALVE TIMING ACTUATOR
OIL CONTROL VALVE (OCV) INSPECTION....B-23
VALVE CLEARANCE INSPECTION..................B-24
VALVE CLEARANCE ADJUSTMENT ...............B-25
CYLINDER BLOCK (I) ASSEMBLY...................B-29
CYLINDER BLOCK (II) ASSEMBLY..................B-34
CYLINDER HEAD (I) ASSEMBLY .. ... ... .... ... ... ...B-37
CYLINDER HEAD (II) ASSEMBLY....................B-39
TIMING CHAIN ASSEMBLY..............................B-41
..................................................................B-2
INSPECTION..................................................B-23
B–1
Page 19
ENGINE
ENGINE
ENGINE OVERHAUL SERVICE WARNING
Warning
••••
Continuous exposure with USED engine oil has caused skin cancer in laboratory mice. Protect
your skin by washing with soap and water immediately after this work.
End Of Sie
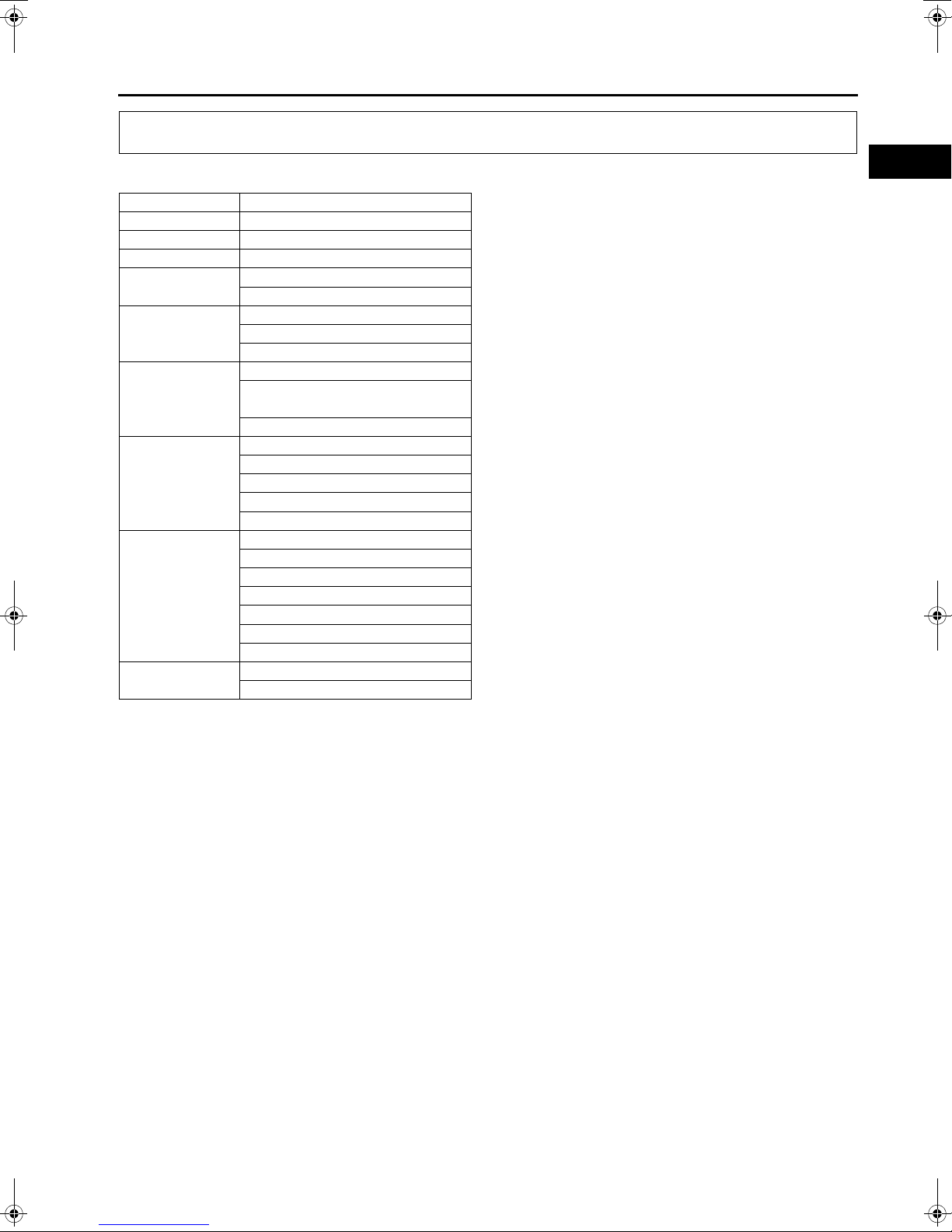
ENGINE MOUNTING/DISMOUNTING
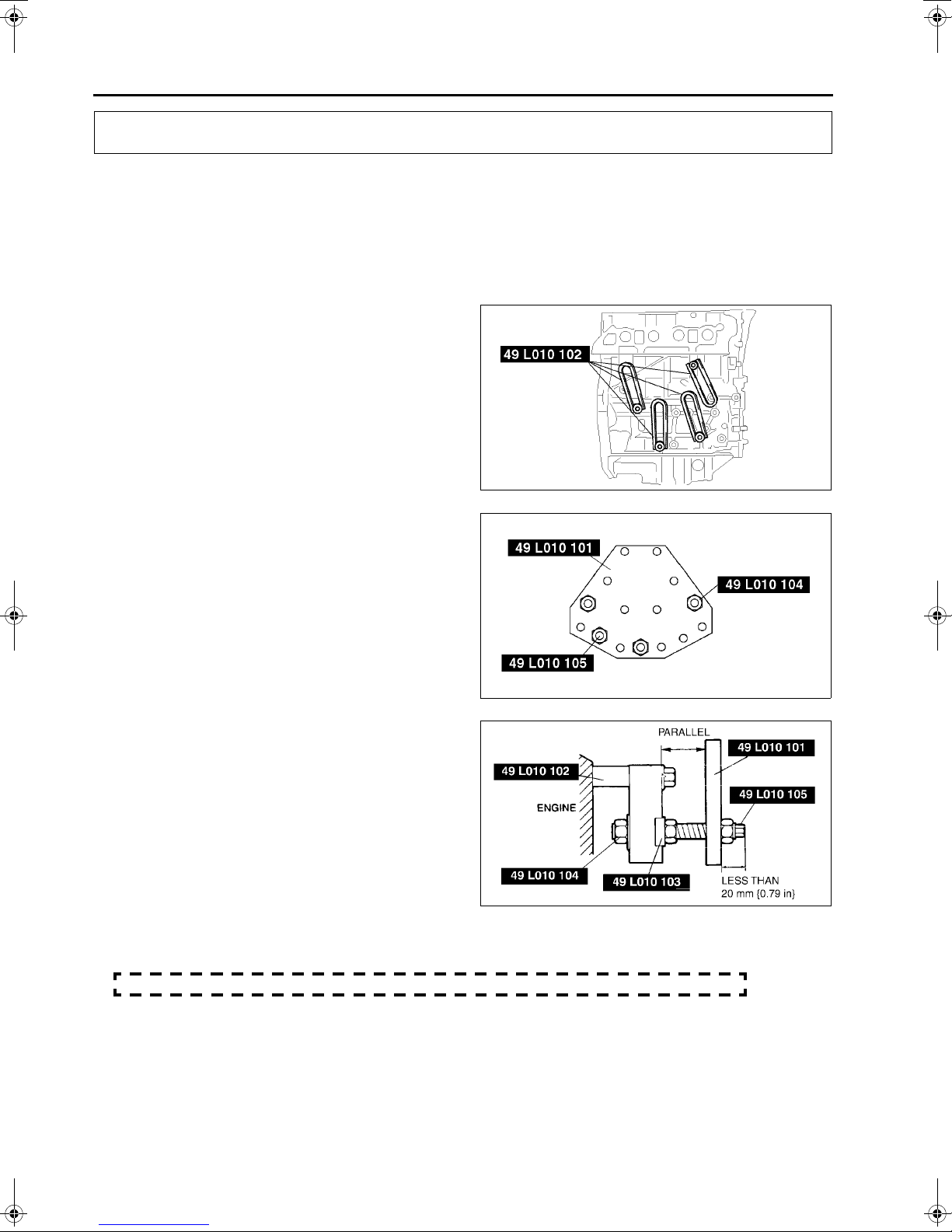
1. Install the
as shown, and hand-tighten the bolts
9YA20-1003) or M10
.
in}
2. Assemble the
specified positions.
3. Adjust the
{0.79 in}
4. Make the
adjusting the
(arms) to the cylinder block holes
SSTs
××××
1.5T length 90 mm {3.55
(bolts, nuts and plate) to the
SSTs
(bolts) so that less than
SSTs
of thread is exposed.
(arms and plate) parallel by
SSTs
(bolts and nuts).
SSTs
(part No.:
A6E242402000E01
A6E242402000E02
AME2224E065
20 mm
5. Tighten the
firmly.
SSTs
(bolts and nuts) to affix the
SSTs
Warning
••••
Self-locking brake system of the engine
stand may not be effective when the
engine is held in an unbalanced position.
This could lead to sudden, rapid
movement of the engine and mounting
stand handle and cause serious injury.
Never keep the engine in an unbalanced
position, and always hold the rotating
handle firmly when turning the engine.
6. Mount the engine on the
(engine stand).
SST
7. Drain the engine oil into a container.
8. Clean the flange surface (seal rubber) of the oil pan drain plug, then install the oil pan drain plug.
Tightening torque
20—30 N·m {2.1—3.0 kgf·m, 15—22 ft·lbf}
DISMOUNTING
• Dismount in the reverse order of mounting.
End Of Sie
AME2224E300
AME2224E301
B–2
Page 20
ENGINE
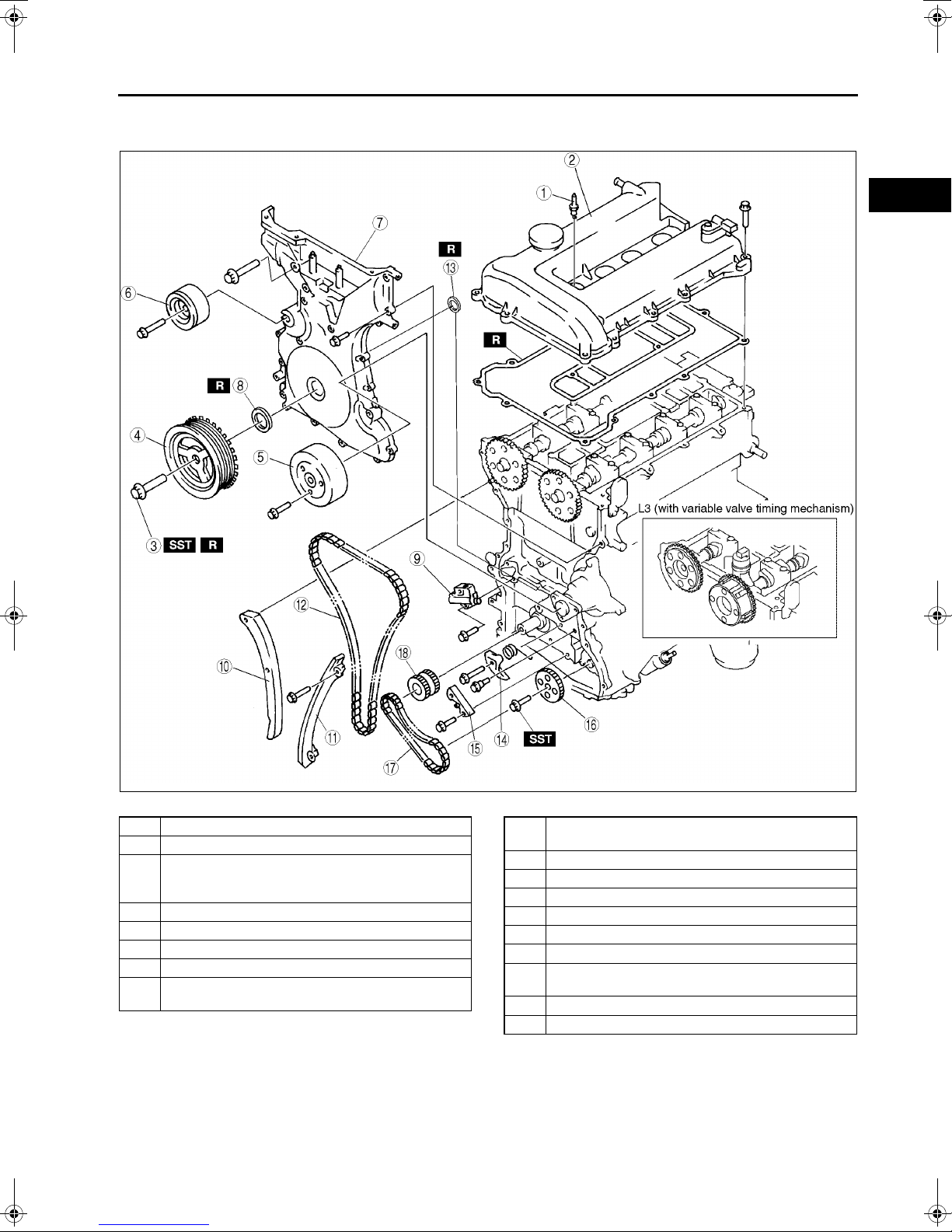
TIMING CHAIN DISASSEMBLY
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
.
A6E242402000E04
B
1 Spark plug
2 Cylinder head cover
3 Crankshaft pulley lock bolt
(See B–4 Crankshaft Pulley Lock Bolt Disassembly
Note)
4 Crankshaft pulley
5 Water pump pulley
6 Drive belt idler pulley
7 Engine front cover
8 Front oil seal
(See B–4 Front Oil Seal Disassembly Note)
AME2224E337
9 Chain tensioner
(See B–4 Chain Tensioner Disassembly Note)
10 Tensioner arm
11 Chain guide
12 Timing chain
13 Seal (L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism))
14 Oil pump chain tensioner
15 Oil pump chain guide
16 Oil pump sprocket
(See B–4 Oil Pump Sprocket Disassembly Note)
17 Oil pump chain
18 Crankshaft sprocket
B–3
Page 21
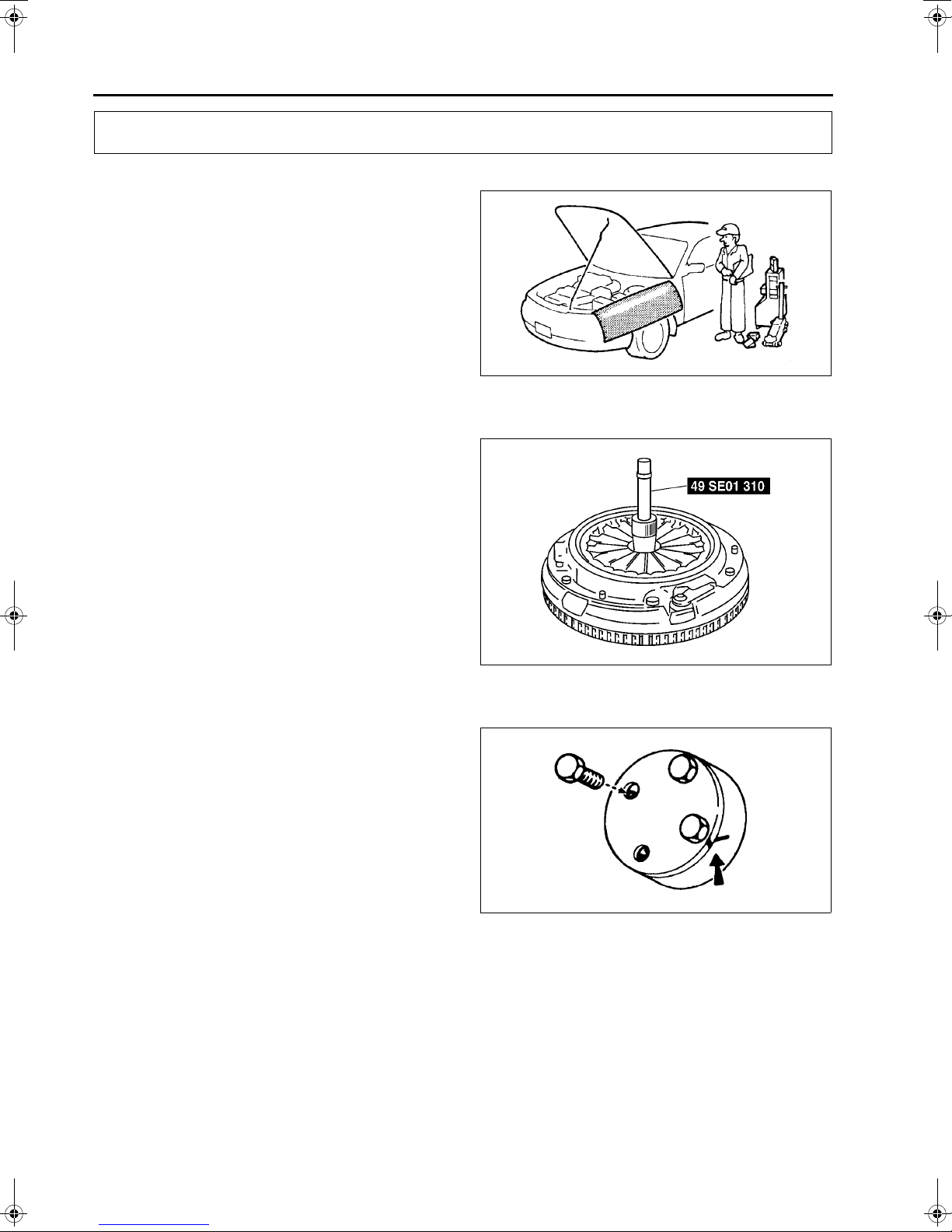
Crankshaft Pulley Lock Bolt Disassembly Note
1. Hold the crankshaft using the SST.
2. Remove the crankshaft pulley lock bolt.
Front Oil Seal Disassembly Note
1. Remove the oil seal using a screwdriver.
ENGINE
AME2224E106
Chain Tensioner Disassembly Note
1. Hold the chain tensioner ratchet lock mechanism
away from the ratchet stem with a thin
screwdriver.
2. Slowly press the tensioner piston.
3. Hold the chain tensioner piston with a
{0.06 in}
wire or paper clip.
1.5 mm
Oil Pump Sprocket Disassembly Note
1. Hold the oil pump sprocket using the
SST
.
AME2224E338
AME2224E339
End Of Sie
B–4
AME2224E340
Page 22

ENGINE
CYLINDER HEAD (I) DISASSEMBLY
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
2.
A6E242402000E05
B
.
1 Camshaft sprocket lock bolt,Variable valve timing
actuator lock bolt (L3 (with variable valve timing
mechanism))
(See B–6 Camshaft Sprocket Lock Bolt, Variable
Valve Timing Actuator Lock Bolt (L3 (with variable
valve timing mechanism)) Disassembly Note)
2 Camshaft sprocket,Variable valve timing actuator
(L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism))
3 Oil control valve (OCV) (L3 (with variable valve
timing mechanism))
AME2224E001
4 Camshaft cap
(See B–6 Camshaft Cap Disassembly Note)
5 Camshaft
6 Tappet
(See B–7 Tappet Disassembly Note)
7 Cylinder head bolt
(See B–7 Cylinder Head Bolt Disassembly Note)
8 Cylinder head
9 Cylinder head gasket
10 Cylinder block
B–5
Page 23

ENGINE
Camshaft Sprocket Lock Bolt, Variable Valve Timing Actuator Lock Bolt (L3 (with variable valve timing
mechanism)) Disassembly Note
1. Hold the camshaft by using a wrench on the cast hexagon as shown, and loosen the camshaft sprocket lock
bolt or variable valve timing actuator lock bolt (L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism)).
L8, LF, L3
L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism)
Camshaft Cap Disassembly Note
1. Before removing the camshaft caps, inspect the following.
— Camshaft end play and camshaft journal oil clearance (See B–16 CAMSHAFT INSPECTION.)
Note
• The camshaft caps are numbered to make sure they are assembled in their original positions. When
removed, keep the caps with the cylinder head they were removed from. Do not mix the caps.
2. Loosen the camshaft caps bolts in two or three
steps in the order shown.
AME2224E077
AME2224E078
B–6
AME2224E006
Page 24

ENGINE
Tappet Disassembly Note
Note
• The tappets are numbered to make sure they are assembled in their original positions. When removed,
keep the tappets with the cylinder head they were removed from. Do not mix the tappets.
Cylinder Head Bolt Disassembly Note
1. Loosen the cylinder head bolts in two or three
steps in the order shown.
End Of Sie
CYLINDER HEAD (II) DISASSEMBLY
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
2.
B
AME2224E005
A6E242402000E06
.
1 Engine hanger
2 Valve keeper
(See B–8 Valve Keeper Disassembly Note)
3 Upper valve spring seat
4 Valve spring
AME2224E008
5Valve
6 Valve seal
(See B–8 Valve Seal Disassembly Note)
7 EGR pipe
8 Water outlet case
B–7
Page 25

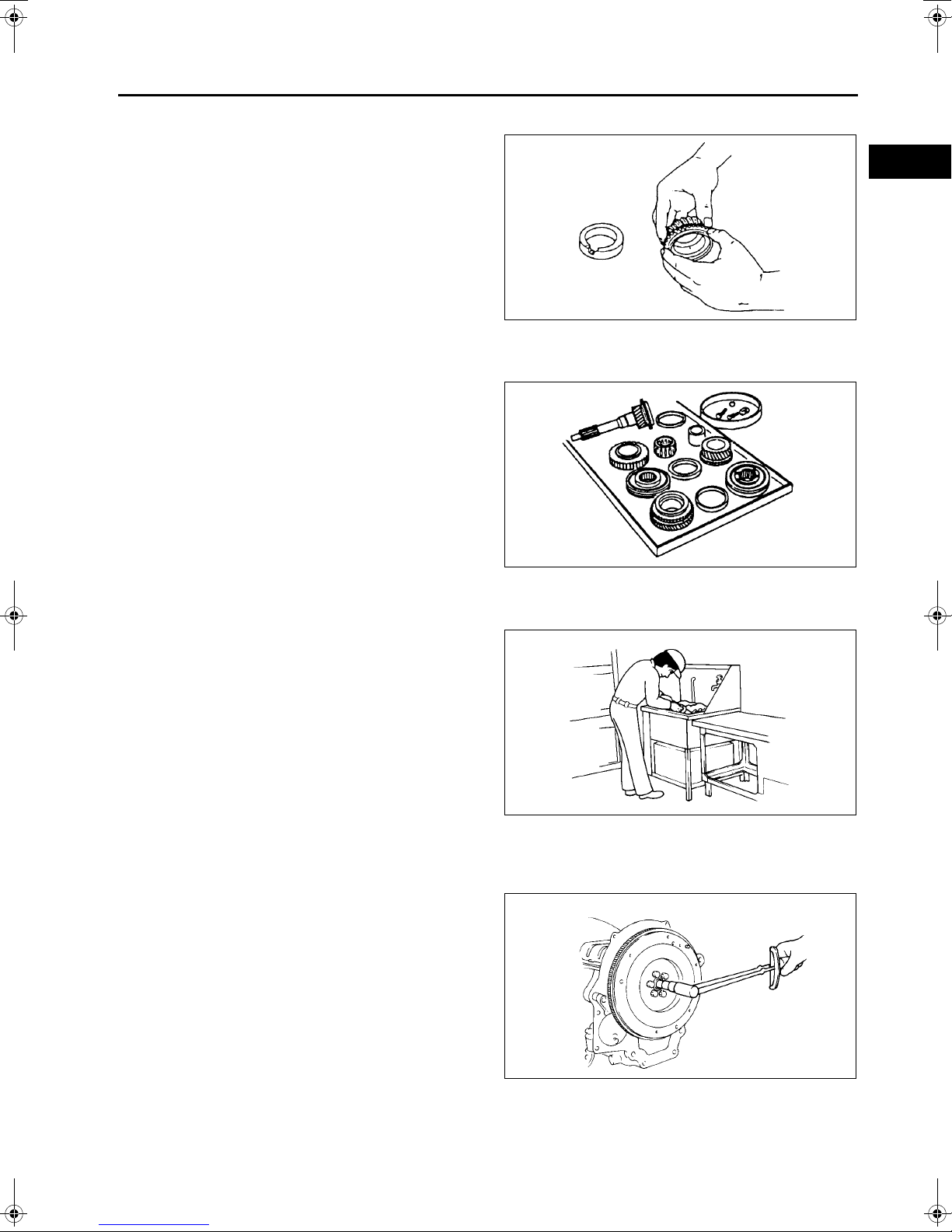
Valve Keeper Disassembly Note
1. Remove the valve keeper using the SSTs.
Valve Seal Disassembly Note
1. Remove the valve seal using the SST.
ENGINE
AME2224E302
End Of Sie
AME2224E303
B–8
Page 26

ENGINE
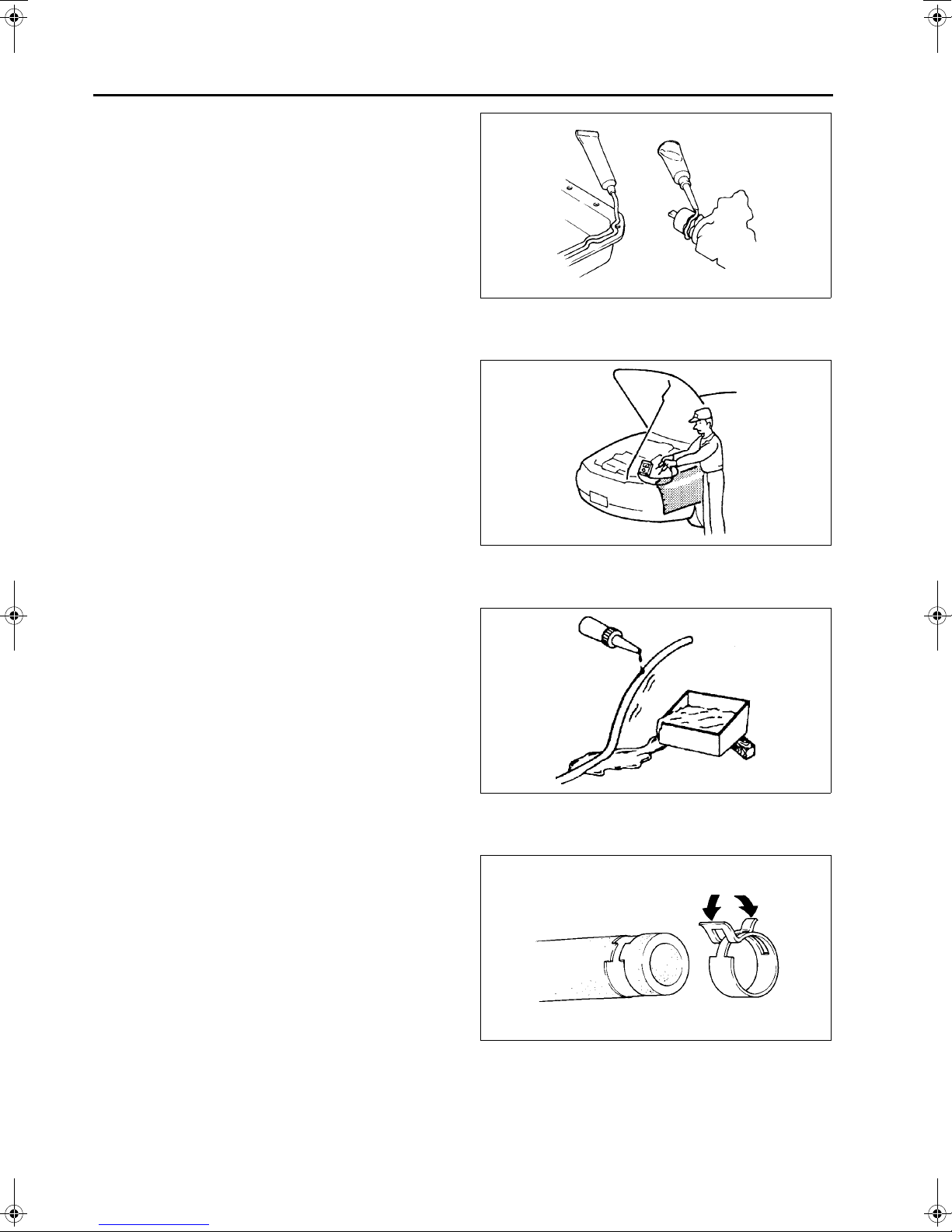
CYLINDER BLOCK (I) DISASSEMBLY
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
2.
A6E242402000E07
B
.
1 Oil pan
2 Oil filter cover
3 Oil filter
4 Oil filter adapter
5 Oil cooler
AME2224E011
6 Knock sensor
7 Oil separator
8 Thermostat
9 Water pump
10 Oil strainer
B–9
Page 27

ENGINE
11 Oil pump
12 Flywheel (MTX ), Drive plate (ATX) (See B–10 Drive
Plate (ATX), Flywheel (MTX) Disassembly Note)
13 End plate (MTX)
14 Rear oil seal
Drive Plate (ATX), Flywheel (MTX) Disassembly Note
1. Hold the crankshaft using the SST.
2. Remove the bolts in several passes.
End Of Sie
CYLINDER BLOCK (II) DISASSEMBLY
1. Disassemble in the order indicated in the table.
2.
AME2224E106
A6E242402000E08
B–10
AME2224E012
Page 28

ENGINE
.
1 Balancer unit (L3, L3 (with variable valve timing
mechanism))
2 Connecting rod cap
(See B–11 Connecting Rod Cap Disassembly Note)
3 Lower connecting rod bearing
4 Upper connecting rod bearing
5 Connecting rod, Piston assembly
6 Piston ring
Connecting Rod Cap Disassembly Note
1. Inspect the connecting rod side clearance. (See B–22 CONNECTING ROD INSPECTION .)
2. Remove the connecting rod bolt from the connecting rod cap by tapping the bolt with a plastic hammer.
Note
• The tappets are numbered to make sure they are assembled in their original positions. When removed,
keep the tappets with the cylinder head they were removed from. Do not mix the tappets.
Main Bearing Cap Disassembly Note
1. Inspect the crankshaft end play. (See B–20 CRANKSHAFT INSPECTION .)
2. Loosen the main bearing cap bolts in two or three
steps in the order shown.
7 Main bearing cap
(See B–11 Main Bearing Cap Disassembly Note)
8 Lower main bearing, thrust bearing
9 Crankshaft
10 Upper main bearing, thrust bearing
11 Oil jet valve
12 Cylinder block
13 Adjustment shim
B
End Of Sie
AME2224E341
B–11
Page 29

ENGINE
CYLINDER HEAD INSPECTION
1. Carry out color contrast penetrate examination on the cylinder head surface.
• Replace the cylinder head if necessary.
2. Inspect for the following and repair or replace if necessary.
(1) Sunken valve seats
(2) Excessive camshaft oil clearance and end play
3. Measure the cylinder head for distortion in the six
directions as shown.
• If the distortion exceeds the maximum,
replace the cylinder head.
Maximum distortion:
0.10 mm {0.004 in}
4. Measure the manifold contact surface distortion
as shown.
• If the distortion exceeds the maximum, grind
the surface or replace the cylinder head.
Maximum distortion:
0.10 mm {0.004 in}
Maximum grinding:
0.15 mm {0.006 in}
A6E242410100E01
AME2224E317
End Of Sie
VALVE, VALVE GUIDE INSPECTION
1. Measure the valve head margin thickness of each
valve.
• If not specified, replace the valve.
Margin thickness:
IN: 1.62 mm {0.0637 in}
EX: 1.82 mm {0.0716 in}
2. Measure the length of each valve. Replace the
valve if necessary.
• If not specified, replace the valve.
Standard length L:
IN: 102.99—103.79 mm {4.055—4.086 in}
EX: 104.25—105.05 mm {4.105—4.135 in}
Minimum length L:
IN: 102.99 mm {4.055 in}
EX: 103.79 mm {4.086 in}
AME2224E318
A6E242412111E01
AME2224E070
AME2224E071
B–12
Page 30

3. Measure the stem diameter of each valve in X
and Y directions at the three points (A, B, and C)
as indicated in the figure.
• If not as specified, replace the valve.
ENGINE
Standard diameter:
IN: 5.470—5.485 mm {0.2154—0.2159 in}
EX: 5.465—5.480 mm {0.2152—0.2157 in}
Maximum diameter:
IN: 5.440 mm {0.2142 in}
EX: 5.435 mm {0.2140 in}
4. Measure the inner diameter of each valve guide
in X and Y directions at the three points (A, B, and
C) as indicated in the figure.
• If not as specified, replace the valve guide.
Standard Inner diameter:
IN: 5.509—5.539 mm {0.2169—0.2180 in}
EX: 5.509—5.539 mm {0.2169—0.2180 in}
5. Calculate the valve stem to guide clearance by
subtracting the outer diameter of the valve stem
from the inner diameter of the corresponding
valve guide.
• If not as specified, replace the valve and/or
the valve guide.
B
AME2224E313
AME2224E314
Standard clearance:
IN: 0.024—0.069 mm {0.0009—0.0027 in}
EX: 0.029—0.074 mm {0.0012—0.0029 in}
Maximum clearance:
0.10 mm {0.004 in}
6. Measure the protrusion height (dimension A) o f
each valve guide without lower valve spring seat.
• If not as specified, replace the valve guide.
Standard diameter:
IN: 12.2—12.8 mm {0.481—0.503 in}
EX: 12.2—12.8 mm {0.481—0.503 in}
End Of Sie
AME2224E315
AME2224E073
B–13
Page 31

ENGINE
VALVE GUIDE REPLACEMENT
Valve Guide Removal
1. Remove the valve guide from the combustion
chamber side using the SST.
Valve Guide Installation
1. Assemble the SSTs so that depth L is as
specified.
Depth L:
IN: 12.2—12.8 mm {0.481—0.501 in}
EX: 12.2—12.8 mm {0.481—0.501 in}
A6E242412111E04
AME2224E312
2. Tap the valve guide in from the side opposite the
camshaft side until the SSTs contacts the cylinder
head.
3. Verify that the valve guide projection height
(dimension A ) is within the specification.
Standard height:
IN: 12.2—12.8 mm {0.481—0.501 in}
EX: 12.2—12.8 mm {0.481—0.501 in}
AME2224E107
AME2224E018
AME2224E073
End Of Sie
B–14
Page 32

ENGINE
VALVE SEAT INSPECTION/REPAIR
1. Measure the seat contact width.
• If necessary, resurface the valve seat using a
45° valve seat cutter and/or resurface the
valve face.
Standard width:
1.2—1.6 mm {0.048—0.062 in}
2. Verify that the valve seating position is at the
center of the valve face.
(1) If the seating position is too out side, correct
the valve seat using a 70°°°° (IN) or 65°°°° (EX)
cutter, and a 45°°°° cutter.
(2) If the seating position is too inner side, correct
the valve seat using a 30°°°° (IN) cutter, and a
0°°°° (EX) cutter, and a 45°°°° cutter.
3. Inspect the sinking of the valve seat. Measure the
protruding length (dimension L) of the valve stem.
• If not specified, replace the cylinder head.
A6E242410102E01
B
AME2224E316
AME2224E020
Standard dimension L:
IN: 40.64—42.24 mm {1.600—1.662 in}
EX: 40.50—42.10 mm {1.595—1.657 in}
End Of Sie
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION
1. Apply pressing force to the pressure spring and
inspect the spring height.
• If not as specified, replace the valve spring.
Pressing force:
494.9 N {50.47 kgf, 111.2 lbf}
Standard height:
27.80 mm {1.094 in}
AME2224E079
A6E242412125E01
AME2224E308
B–15
Page 33

2. Measure the out-of-square of the va lve sp rin g,
using a square, as shown.
(1) Rotate the valve spring one full turn and
measure "A" at the point where the gap is the
largest.
• If not as specified, replace the valve
spring.
Valve spring maximum out-of-square:
1% (2.10 mm {0.0826 in})
End Of Sie
CAMSHAFT INSPECTION
1. Set the No.1 and No.5 journals on V-blocks.
2. Measure the camshaft runout.
• If not as specified, replace the camshaft.
Maximum runout:
0.03 mm {0.0012 in}
ENGINE
AME2224E309
A6E242412420E01
3. Measure the cam lobe height at the two points as
shown.
• If not as specified, replace the camshaft.
Standard height (mm) {in}
L3 (with
Camshaft L8 LF, L3
INT 40.79 {1.606} 42.12 {1.659} 42.44 {1.671}
EXH 41.08 {1.618} 41.08 {1.618} 41.18 {1.622}
variable
valve timing
mechanism)
Minimum height (mm) {in}
L3 (with
Camshaft L8 LF, L3
INT
EXH
40.692
{1.603}
40.982
{1.614}
42.022
{1.655}
40.982
{1.614}
variable
valve timing
mechanism)
42.342
{1.667}
41.082
{1.618}
AME2224E082
AME2224E343
B–16
Page 34

4. Measure the journal diameters in X and Y
directions at the two points (A and B) as indicated
in the figure.
• If not as specified, replace the camshaft.
ENGINE
Standard diameter:
24.96—24.98 mm {0.9827—0.9834 in}
Minimum diameter:
24.95 mm {0.982 in}
5. Remove the tappet.
6. Position plasticgage atop the journals in the axial
direction.
7. IInstall the camshaft cap. (See B–40 Camshaft Assembly Note.)
8. Remove the camshaft cap. (See B–6 Camshaft Cap Disassembly Note.)
9. Measure the oil clearance.
• If not as specified, replace the cylinder head.
Standard clearance:
0.04—0.08 mm {0.002—0.003 in}
Maximum clearance:
0.09 mm {0.0035 in}
10. Install the camshaft cap. (See B–40 Camshaft
Assembly Note)
11. Measure the camshaft end play.
• If not as specified, replace the cylinder head
or camshaft.
B
AME2224E344
AME2224E307
Standard end play:
0.09—0.24 mm {0.0035—0.0094 in}
Maximum end play:
0.25 mm {0.0099 in}
12. Remove the camshaft cap. (See B–6 Camshaft
Cap Disassembly Note.)
End Of Sie
AME2224E025
B–17
Page 35

ENGINE
TAPPET INSPECTION
1. Measure the tappet hole inner diameter in X and
Y directions at the two points (A and B) shown.
Inner diameter:
31.000—31.030 mm {1.2205—1.2216 in}
2. Measure the tappet body outer diameter in X an d
Y directions at the two points (A and B) shown.
Outer diameter:
30.970—30.980 mm {1.2193—1.2196 in}
3. Subtract the tappet body outer diame ter from the
tappet hole inner diameter.
• If not as specified, replace the tappet or
cylinder head.
Clearance
Standard:
0.02—0.06 mm {0.0008—0.0023 in}
A6E242412310E01
AME2224E319
AME2224E320
Maximum:
0.15 mm {0.006 in}
End Of Sie
CYLINDER BLOCK INSPECTION
1. Measure the distortion of the cylinder block top
surface in the six directions as indicated in the
figure.
• If the distortion exceeds the maximum,
replace the cylinder block.
Maximum cylinder block distortion:
0.10 mm {0.004 in}
2. Measure the cylinder bores in X and Y directions
at 42 mm {1.65 in} below the top surface.
• If the cylinder bore exceeds the wear limit,
replace the cylinder block.
Standard diameter limit
L8:
83.000—83.030 mm {3.2677—3.2689 in}
LF, L3, L3 (with variable valve timing
mechanism):
87.500—87.530 mm {3.4449—3.4460 in}
Minimum / maximum bore diameter limit
L8:
82.940—83.090 mm {3.2653—3.2712 in}
LF, L3, L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism):
87.440—87.590 mm {3.4425—3.4484 in}
A6E242410300E01
AME2224E089
AME2224E090
B–18
Page 36

ENGINE
End Of Sie
OIL JET VALVE INSPECTION
1. Apply compressed air to oil jet valve A and verify
that air passes through oil jet valve B.
• If not ventilation,replace the oil jet valve.
Air pressure:
216—274 kPa {2.2—2.7kgf•cm
psi}
End Of Sie
PISTON INSPECTION
Caution
•••• The piston, piston ring and connecting rod cannot be disassembled.
•••• When replacing the piston, piston pin, piston ring and connecting rod, replac e them t oge the r as a
single unit.
1. Measure the outer diameter o f each piston at right
angle 90° to the piston pin, 10.0 mm {0.40 in}
above the under of the piston.
• If the piston diameter is below the standard
diameter, replace the piston, piston pin, piston
ring and connecting rod as a single unit.
2
31.4—39.7
A6E242410730E02
B
AME2224E105
A6E242411010E01
Piston diameter
L8:
82.965—82.995 mm {3.2664—3.2675 in}
LF, L3, L3 (with variable valve timing
mechanism):
87.465—87.495 mm {3.4435—3.4446 in}
2. Measure the piston-to-cylinder clearance.
• If not as specified, replace the piston, piston pin, piston ring and connecting rod as a single unit.
Standard clearance:
0.025—0.045 mm {0.0010—0.0017 in}
Maximum clearance:
0.11 mm {0.0043 in}
3. Measure the piston ring-to-ring groove clea rance
around the entire circumference.
• If the piston ring-to-ring groove clearance
exceeds the maximum clearance, repl ace the
piston, piston pin, piston ring and connecting
rod as a single unit.
Standard clearance:
Top: 0.03—0.08 mm {0.0012—0.0031 in}
Second: 0.03—0.07 mm {0.0012—0.0027in}
Oil: 0.03—0.07 mm {0.0012—0.0027 in}
Maximum clearance:
Top: 0.17 mm {0.0067 in}
Second, Oil: 0.15 mm {0.0059 in}
AME2224E030
AME2224E029
B–19
Page 37

ENGINE
4. Insert the piston ring into the cylinder by hand and
use the piston to push it to the bottom of the ring
travel.
5. Measure each piston ring end gap with a feeler
gauge.
• If the piston ring end gap exceeds the
maximum end gap, replace the piston, piston
pin, piston ring and connecting rod as a single
unit.
Standard end gap:
Top: 0.16—0.31 mm {0.0063—0.012 in}
Second: 0.33—0.48 mm {0.0130—0.0189 in}
Oil (rail): 0.20—0.70 mm {0.0079—0.0275 in}
Maximum end gap:
1.0 mm {0.0393 in}
End Of Sie
CRANKSHAFT INSPECTION
1. Install the main bearing cap. (See B–30 Main Bearing Caps Assembly Note.)
2. Measure the crankshaft end play.
• If not as specified, replace the thrust bearing
or crankshaft so that the specified end play is
obtained.
AME2224E104
A6E242411301E01
Standard end play:
0.22—0.45 mm {0.0087—0.0177 in}
Maximum end play:
0.55 mm {0.022 in}
3. Remove the main bearing cap. (See B–11 Main
Bearing Cap Disassembly Note.)
4. Measure the crankshaft runout.
• If the crankshaft runout exceeds th e ma xim u m ru no u t, re pla ce the cran ksh a ft.
Maximum runout:
0.05 mm {0.0019 in}
L8, LF
L3, L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism)
AME2224E034
AME2224E035
B–20
AME2224E311
Page 38

5. Measure the journal diameter in X and Y
directions at the two points (A and B) as indicated
in the figure.
• If not as specified, replace the crankshaft or
grind the journal and install the undersize
bearing.
ENGINE
B
Main journal
mm {in}
Bearing size Standard diameter
Standard 51.980—52.000 {2.0464—2.0472}
0.25 {0.01}
undersize
51.730—51.750 {2.0366—2.0373}
Maximum out-of-round:
0.05 mm {0.0019 in}
Crank pin
mm {in}
Bearing size Standard diameter
Standard 49.980—50.000 {1.9677—1.9685}
0.25 {0.01}
undersize
49.730—49.750 {1.9579—1.9586}
Maximum out-of-round:
0.05 mm {0.0019 in}
6. Install the main bearing caps and crankshaft.
7. Position a plastigage atop the journals in the axial direction.
8. Install the main bearing caps and cylinder block. (See B–30 Main Bearing Caps Assembly Note.)
9. Remove the main bearing caps. (See B–11 Main Bearing Cap Disassembly Note.)
10. Measure the main journal oil clearance.
• If the clearance exceeds the maximum,
replace the main bearing using the main
bearing selection table or grind the main
journal and install the oversize bearings so
that the specified oil clearance is obtained.
AME2224E036
Standard clearance:
0.019—0.035 mm {0.0007—0.0013 in}
Maximum clearance:
0.10 mm {0.0039 in}
Bearing
size
Standard Green 2.506—2.509 {0.0987—0.0988}
0.25 {0.01}
oversize
0.50 {0.02}
oversize
Color Bearing thickness
2.628—2.634 {0.1034—0.1037}
2.753—2.759 {0.1084—0.1086}
AME2224E038
mm {in}
B–21
Page 39

ENGINE
End Of Sie
CONNECTING ROD INSPECTION
Caution
•••• The piston, piston ring and connecting rod cannot be disassembled.
•••• When replacing the piston, piston pin, piston ring and connecting rod, re pla ce the m to get her as a
single unit.
1. Install the connecting rod cap. (See B–31 Connecting Rod Cap Assembly Note.)
2. Measure the connecting rod la r ge end si de
clearance.
• If the connecting rod large end side clearan ce
exceeds the maximum clearance, replace the
piston, piston pin, piston ring and connecting
rod as a single unit.
Standard clearance:
0.14—0.36 mm {0.0056—0.0141 in}
Maximum clearance:
0.435 mm {0.0172 in}
3. Remove the connecting rod cap.
4. Position plastigage atop the journals in the axial direction.
5. Install the connecting rod bearing and conn ecting rod cap. (See B–31 Connecting Rod Cap Assembly Note.)
6. Remove the connecting rod cap.
7. Measure the connecting rod oil cleara n ce .
• If not as specified, replace the connecting rod
bearing or grind the crank pin and use
oversize bearings so that the specified
clearance is obtained.
A6E242411211E01
AME2224E059
Standard clearance:
0.026—0.052 mm {0.0011—0.0020 in}
Maximum clearance:
0.1 mm {0.0039 in}
Bearing size Color Bearing thickness
Standard Green
0.50 {0.02}
oversize
0.25 {0.01}
oversize
1.748—1.754 {0.0688—0.0690}
1.623—1.629 {0.0639—0.0641}
1.496—1.502
{0.0589—0.0591}
End Of Sie
BOLT INSPECTION
1. Measure the length of each bolt.
• Replace any that exceeds maximum length.
mm {in}
AME2224E310
A6E242410135E01
B–22
AME2224E050
Page 40

ENGINE
Length L
bolt Standard (mm) {in} Maximum (mm) {in}
Cylinder
head bolt
Connecting
rod bolt
Main bearing
cap bolt
End Of Sie
VARIABLE VALVE TIMING ACTUATOR INSPECTION
L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism)
Caution
•••• Variable valve timing actuator can not be disassembled it is a precision unit /
1. Confirm that notch of the rotor and bump of the
cover at the variable valve timing actuator are
aligned and fitted.
• If the notch and the bump are not aligned,
rotate the rotor toward the bulb timing re tard
position by hand until they are in place.
• If the rotor and cover are not secured even
though their notch and groove are aligned,
replace the variable valve timing actuator.
149.0—150
{5.86—5.90}
44.7—45.3
{1.75—1.78}
110.0—110.6
{4.33—4.35}
150.5 {5.92}
46.0 {1.81}
111.3 {4.38}
B
A6E242400142E02
End Of Sie
OIL CONTROL VALVE (OCV) INSPECTION
L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism)
Coil resistance inspection
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the oil control valve (OCV) connecto r.
3. Measure the resistance between terminals A and
B using an ohmmeter.
• If not as specified, replace the oil control valve
(OCV).
Specification
6.9—7.9 ohms
4. Connect the oil control valve (OCV) connector.
AME2224E342
A6E242414420E02
A6E2226W002
B–23
Page 41

Spool valve operation inspection
1. Disconnect the negative battery cab le.
2. Remove the oil control valve (OCV).
3. Verify that the spool valve in the oil control valve
(OCV) is in the maximum valve timing retard
position as indicated in the figure.
• If not as specified, replace the oil control valve
(OCV).
4. Verify that the battery is fully charged.
• If not as specified, recharge the battery.
ENGINE
5. Apply battery positive voltage between the oil
AME2226W003
control valve (OCV) terminals and verify that the
spool valve operates and moves to the maximum
valve timing advance position.
• If not as specified, replace the oil control valve
(OCV).
Note
• When applying battery positive voltage
between the oil control valve (OCV)
terminals, the connection can be either of
the following:
— Positive battery cable to terminal A,
AME2226W004
negative battery cable to terminal B
— Positive battery cable to terminal B, negative battery cable to terminal A
6. Stop applying battery positive voltage and verify that the spool valve returns to the maximum valve timing
retard position.
• If not as specified, replace the oil control valve (OCV).
End Of Sie
VALVE CLEARANCE INSPECTION
1. Measure the valve clearance as follo ws.
(1) Turn the crankshaft clockwise so that the
No.1 piston is at TDC of the compression
stroke.
(2) Measure the valve clearance at A in the
figure.
• If the valve clearance exceeds the space
the tappet. (See B–25 VALVE
CLEARANCE ADJUSTMENT.)
A6E242412111E02
Note
• Make sure to note the measured values for
choosing the suitable replacement tappets.
Standard [Engine cold]
IN: 0.22—0.28 mm {0.0087—0.0110 in} (0.25±±±±0.03 mm {0.0098±±±±0.0011 in})
EX: 0.27—0.33 mm {0.0106—0.0130 in} (0.30±±±±0.03 mm {0.0118±±±±0.0011 in})
(3) Turn the cra n kshaft 360°°°° clockwise so that the No.4 piston is at TDC of the compression stroke.
(4) Measure the valve clearance at B in the figure.
• If the valve clearance exceeds the standard, replace the tappet. (See B–25 VALVE CLEARANCE
ADJUSTMENT.)
Note
• Make sure to note the measured values for choosing the suitable replacement tappets.
Standard [Engine cold]
IN: 0.22—0.28 mm {0.0087—0.0110 in} (0.25±±±±0.03 mm {0.0098±±±±0.0011 in})
EX: 0.27—0.33 mm {0.0106—0.0130 in} (0.30±±±±0.03 mm {0.0118±±±±0.0011 in})
B–24
AME2212W001
Page 42

End Of Sie
VALVE CLEARANCE ADJUSTMENT
1. Remove the engine front cover lower blind plug.
2. Remove the engine front cover upper blind plug.
3. Remove the cylinder block lower blind plug.
4. Install the SST as shown.
5. Turn the crankshaft clockwise the crankshaft is in
the No.1 cylinder TDC position.
ENGINE
A6E242412111E03
B
AMJ2212E004
6. Loosen the timing chain.
(1) Using a suitable screwdriver or equivalent
tool, unlock the chain tensioner ratchet.
(2) Turn the exhaust camshaft clockwise using a
suitable wrench on the cast hexagon and
loosened the timing chain.
(3) Placing the suitable bolt (M6 X 1.0 Length
25—35 mm {0.9—1.3 in}) at the engine front
cover upper blind plug, secure the chain
guide at the position where the tension is
released.
AME2212W004
AME2212W005
B–25
Page 43

7. Hold the exhaust camshaft using a suitable
wrench on the cast hexagon as shown.
8. Remove the exhaust camshaft sprocket.
9. Loosen the camshaft cap bolts in several passes
in the order shown.
ENGINE
AME2212W006
AME2212W007
Note
• The cylinder head and the camshaft caps
are numbered to make sure they are
reassembled in their original position. When
removed, keep the caps with the cylinder
head they were removed from. Do not mix
the caps.
10. Remove the camshaft.
11. Remove the tappet.
12. Select proper adjustment shim.
New adjustment shim
= Removed shim thickness + Measured valve clearance - Standard valve clearance (IN: 0.25 mm
{0.0098 in}, EX: 0.30 mm {0.0118 in})
Standard [Engine cold]
IN: 0.22—0.28 mm {0.0087—0.0110 in} (0.25±±±±0.03 mm {0.0098±±±±0.0011 in})
EX: 0.27—0.33 mm {0.0106—0.0130 in} (0.30±±±±0.03 mm {0.0118±±±±0.0011 in})
13. Install the camshaft with No.1 cylinder aligned with the TDC position.
14. Tighten the camshaft cap bolt using the following
two steps.
(1) Tighten to 5.0—9.0 N·m {51.0—91.7 kgf·cm,
44.3—79.5 in·lbf}.
(2) Tighten to 14.0—17.0 N·m {1.5—1.7 kgf·m,
10.4—12.5 ft·lbf}.
AME2212W008
B–26
AME2212W009
Page 44

15. Install the exhaust camshaft sprocket.
Note
• Do not tighten the bolt for the camshaft
sprocket during this step. First confirm the
valve timing, then tighten the bolt.
16. Install the SST to the camshaft as shown.
Europe
ENGINE
B
AME2212W007
Except Europe
17. Remove the M6 x 1.0 bolt from the engine front cover to apply tension to the timing chain.
18. Turn the crankshaft clockwise the crankshaft is in the No.1 cylinder TDC position.
19. Hold the exhaust camshaft using a suitable
wrench on the cast hexagon as shown.
20. Tighten the exhaust camshaft sprocket lock bolt
Tightening torque
69—75 N·m {7.10—7.6 kgf·m,
50.9—55.3 ft·lbf}
21. Remove the SST from the camshaft.
22. Remove the SST from the block lower blind plug.
23. Rotate the crankshaft clockwise two turns until
the TDC position.
• If not aligned, loosen the crankshaft pulley
lock bolt and repeat from Step 14.
24. Apply silicone sealant to the engine front cover upper blind plug.
AME2212W010
AME2212W011
AME2212W006
B–27
Page 45

25. I ns ta ll the en g ine fron t co ve r up per blin d plu g .
Tightening torque:
10 N·m {1.0 kgf·m, 7.4 ft·lbf}
26. Install the cylinder block lower blind plug.
Tightening torque:
20 N·m {2.0 kgf·m, 14.8 ft·lbf}
ENGINE
AME2212W003
27. Install the new engine front cover lower blind
plug.
Tightening torque:
12 N·m {1.2 kgf·m, 8.9 ft·lbf}
End Of Sie
AME2212W012
AME2212W002
B–28
Page 46

ENGINE
CYLINDER BLOCK (I) ASSEMBLY
1. Assemble in the order indicated in the table.
2.
A6E242402000E09
B
.
1 Oil jet valve
2 Upper main bearing, thrust bearing
3 Crankshaft
4 Lower main bearing, thrust bearing
5 Main bearing cap
(See B–30 Main Bearing Caps Assembly Note)
Piston ring
6
(See B–30 Piston Ring Assembly Note)
7 Connecting rod, Piston assembly
(See B–30 Piston Assembly Note)
AME2224E039
8 Upper connecting rod bearing
(See B–31 Connecting Rod Bearing Assembly
Note)
9 Lower connecting rod bearing
(See B–31 Connecting Rod Bearing Assembly
Note)
10 Connecting rod cap
(See B–31 Connecting Rod Cap Assembly Note)
11 Engine balancer (L3 (with variable valve timing
mechanism))
(See B–31 Balancer Unit Assembly Note)
12 Adjustment shim
B–29
Page 47

Main Bearing Caps Assembly Note
1. Install the main bearing caps in the order
indicated in the figure.
Tightening torque:
(1) 44—46 N·m
{4.5—4.6 kgf·m, 32.5—33.9 ft·lbf}
(2) 175°°°°—185°°°°
Piston Ring Assembly Note
1. Install the two oil control ring segments and
spacer.
2. Verify that the second ring is installed with
scraper face side downward.
3. Verify that the top ring is installed with scraper
face side inner of upper.
ENGINE
AME2224E052
Piston Assembly Note
1. Position the end gap of each ring as indicated in
the figure.
2. Insert the piston and connecting rod into the
cylinder with the arrow mark to front of t he engine.
AME2224E322
AME2224E323
AME2224E042
B–30
Page 48

ENGINE
Connecting Rod Bearing Assembly Note
1. Install the connecting rod bearing to the
connecting rod and connecting rod caps, as
shown in the figure.
Connecting Rod Cap Assembly Note
Caution
•••• When assembling the connecting rod caps, align the broken, rough faces of the connecting rods
and connecting rod caps.
1. Tighten the connecting rod bolts in two steps.
Tightening torque:
(1) 26—32 N·m
{2.7—3.2 kgf·m, 19.2—23.6 ft·lbf}
(2) 80°°°°—100°°°°
B
AME2224E053
Balancer Unit Assembly Note
1. Confirm by visual inspection that there is no damage to the balancer unit gear and verify that the shaft turns
smoothly.
• If there is any damage or malfunction, replace the balancer unit.
Caution
•••• Due to the precision interior construction of the balancer unit, it cannot be disassembled.
2. Rotate the crankshaft clockwise and align the No. 1 cylinder to the TDC.
3. Install the adjustment shim to the seat face of the balancer unit.
4. With the balancer unit marks at the exact top
center, assemble the unit to the cylinder block.
AME2224E061
5. Insert a screwdriver into the crankshaft No. 1
crankweight area and set both the rotation and
the thrust direction with the screwdriver, using a
prying action, as shown.
AME2224E080
B–31
Page 49

ENGINE
6. Set the SST as shown, then measure the gear
backlash using a dial gauge.
• If the backlash exceeds the specified range,
remeasure the backlash and, using the
adjustment shim selection table, select the
proper shim, according to the following
procedure.
Caution
•••• When measuring the backlash, rotate the
crankshaft one full rotation and verify
that it is within the specified range at all
of the following six positions: 10°°°°, 30°°°°,
100°°°°, 190°°°°, 210°°°°, 280°°°° ATDC.
Value range:
0.005—0.101 mm {0.00019—0.0039 in}
(1) Using master adjustment shim (No.50), assemble the balancer unit to the cylind er blo ck, then me asure the
backlash.
(2) Select the proper adjustment shim according to the measured value.
(3) Install the selected adjustment shim to the balancer unit, then assemble the balancer unit to the cylinder
block.
Adjustment shim selection table
Backlash
mm {in}
0.256—0.262
{0.0100—0.01031}
0.249—0.255
{0.0098—
0.010039}
0.242—0.248
{0.0096—0.00976}
0.235—0.241
{0.0093—0.0948}
0.228—0.234
{0.00897—
0.00921}
0.221—0.227
{0.00870—
0.00893}
0.214—0.220
{0.00842—
0.00874}
0.207—0.213
{0.00814—
0.00838}
0.200—0.206
{0.00787—
0.00811}
0.193—0.199
{0.00759—
0.00783}
0.186—0.192
{0.00732—
0.00755}
0.179—0.185
{0.00704—
0.00728}
Selection shim
(No.)
15 1.15 {0.0452}
16 1.16 {0.0456}
17 1.17 {0.0460}
18 1.18 {0.0464}
19 1.19 {0.0468}
20 1.20 {0.0472}
21 1.21 {0.0476}
22 1.22 {0.0480}
23 1.23 {0.0484}
24 1.24 {0.0488}
25 1.25 {0.492}
26 1.26 {0.496}
Shim thickness
mm {in}
Backlash
mm {in}
0.116—0.122
{0.00456—
0.00480}
0.109—0.115
{0.00429—
0.00452}
0.102—0.108
{0.00401—
0.00425}
0.095—0.101
{0.00374—
0.00397}
0.088—0.094
{0.00346—
0.00370}
0.081—0.087
{0.00318—
0.00342}
0.074—0.080
{0.00291—
0.00314}
0.067—0.073
{0.00263—
0.00287}
0.060—0.066
{0.00236—
0.00259}
0.053—0.059
{0.00208—
0.00232}
0.046—0.052
{0.00181—
0.00204}
0.039—0.045
{0.00153—
0.00177}
Selection shim
(No.)
35 1.35 {0.0531}
36 1.36 {0.0535}
37 1.37 {0.0539}
38 1.38 {0.0543}
39 1.39 {0.0547}
40 1.40 {0.0551}
41 1.41 {0.0555}
42 1.42 {0.0559}
43 1.43 {0.0562}
44 1.44 {0.0566}
45 1.45 {0.0570}
46 1.46 {0.0574}
Shim thickness
mm {in}
AME2224E060
B–32
Page 50

ENGINE
Backlash
mm {in}
0.172—0.178
{0.00677—
0.00700}
0.165—0.171
{0.00649—
0.00673}
0.158—0.164
{0.00622—0.00645
0.151—0.157
{0.00594—
0.00618}
0.144—0.150
{0.0566—0.0590}
0.137—0.143
{0.00539—
0.00562}
0.130—0.136
{0.00511—
0.00535}
0.123—0.129
{0.00484—
0.00507}
End Of Sie
Selection shim
(No.)
27 1.27 {0.499}
28 1.28 {0.503}
29 1.29 {0.507}
30 1.30 {0.511}
31 1.31 {0.515}
32 1.32 {0.519}
33 1.33 {0.523}
34 1.34 {0.527}
Shim thickness
mm {in}
Backlash
mm {in}
0.032—0.038
{0.00125—
0.00149}
0.025—0.031
{0.000984—
0.00122}
0.018—0.024
{0.000708—
0.000944}
0.011—0.017
{0.000433—
0.000669}
0.004—0.010
{0.00015—
0.000393}
0.000—0.004
{0.000—0.000157}
0.000—0.000
{0.000—0.000}
0.000—0.000
{0.000—0.000}
Selection shim
(No.)
47 1.47 {0.0578}
48 1.48 {0.0582}
49 1.49 {0.0586}
50 (master) 1.50 {0.0590}
51 1.51 {0.0594}
52 1.52 {0.0598}
53 1.53 {0.0602}
54 1.54 {0.0606}
Shim thickness
mm {in}
B
B–33
Page 51

ENGINE
CYLINDER BLOCK (II) ASSEMBLY
1. Assemble in the order indicated in the table.
2.
A6E242402000E10
.
B–34
AME2224E043
Page 52

ENGINE
1 Rear oil seal
(See B–35 Rear Oil Seal Assembly Note)
2 End plate (MPV)
3 Flywheel (MTX), Drive plate (ATX) (See B–36 Drive
Plate (ATX), Flywheel (MTX) Assembly Note)
4 Oil pump
5 Oil strainer
6 Water pump
7 Thermostat
Rear Oil Seal Assembly Note
1. Apply silicone sealant to the mating faces as
shown.
Dot diameter:
4.0—6.0 mm {0.16—0.23 in}
2. Apply clean engine oil to the new oil seal lip.
3. Install the rear oil seal using the installer as
shown.
8 Oil separator
9 Knock sensor
10 Oil cooler
11 Oil filter adapter
12 Oil filter
13 Oil filter cover
14 Oil pan
(See B–36 Oil pan Assembly Note)
15 MTX
B
AME2224E325
4. Tighten the rear oil seal bolts in the order as
shown.
Tightening torque:
8.0—11.5 N·m {81.6—117.2 kgf·m, 70.9—
101.7 in·lbf}
AME2224E326
AME2224E002
B–35
Page 53

Drive Plate (ATX), Flywheel (MTX) Assembly Note
1. Hold the crankshaft using the SST.
2. Tighten the bolts in the order indicated in the
figure in several passes.
Oil pan Assembly Note
1. Apply a continuous bead of silicone sealant to the
oil pan as indicated in the figure.
ENGINE
AME2224E102
2. Use a square ruler to unite the oil pan and the
cylinder block junction side on the engine front
cover side.
B–36
AME2224E555
AME2224E054
Page 54

3. Tighten the rear oil pan bolts in the order as
shown.
Tightening torque:
20—30 N·m {2.1—3.0 kgf·m, 15.2—21.6
in·lbf}
End Of Sie
CYLINDER HEAD (I) ASSEMBLY
1. Assemble in the order indicated in the table.
ENGINE
B
AME2224E056
A6E242402000E11
.
1 Water outlet case
2 EGR pipe
3 Valve seal
(See B–38 Valve Seal Assembly Note)
4Valve
AME2224E044
5 Valve spring
6 Upper valve spring seat
7 Valve keeper
(See B–38 Valve Keeper Assembly Note)
8 Engine hanger
B–37
Page 55

Valve Seal Assembly Note
1. Press the valve seal onto the valve guide by
hand.
2. Lightly tap the SST using a plastic hammer.
Valve Keeper Assembly Note
1. Install the valve keeper using the SSTs.
ENGINE
AME2224E321
End Of Sie
AME2224E302
B–38
Page 56

ENGINE
CYLINDER HEAD (II) ASSEMBLY
1. Assemble in the order indicated in the table.
2.
A6E242402000E12
B
.
1 Cylinder head gasket
2 Cylinder head
3 Cylinder head bolt
(See B–40 Cylinder Head Bolt Assembly Note)
4 Tappet
5 Camshaft
(See B–40 Camshaft Assembly Note)
AME2224E046
6 Camshaft cap
7 Camshaft sprocket, Variable valve timing actuator
(L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism))
(See B–40 Camshaft Sprocket, Variable Valve
Timing Actuator (L3 (with variable valve timing
mechanism)) Assembly Note)
8 Oil control valve (OCV) (L3 (with variable valve
timing mechanism))
B–39
Page 57

ENGINE
Cylinder Head Bolt Assembly Note
1. Tighten the cylinder head bolts in the order
indicated in the figure in six steps.
(1) Tighten to 5.0 N·m {51 kgf·cm, 44.3 in·lbf}.
(2) Tighten to 13— 17 N·m {1.4 —1.7 kgf·m,
9.6—12.5 ft·lbf}.
(3) Tighten to 44— 46 N·m {4.5 —4.6 kgf·m,
32.5—33.9 ft·lbf}.
(4) Tighten 88°°°°—92°°°°.
(5) Tighten 88°°°°—92°°°°.
Camshaft Assembly Note
1. Install the camshaft with No.1 cylinder aligned with TDC position.
2. Tighten the camshaft cap bolt using the following
two steps.
(1) Tighten to 5.0—9.0 N·m {51.0—91.7 kgf·cm,
44.3—79.5 in·lbf}.
(2) Tighten to 14.0—17.0 N·m {1.5—1.7 kgf·m,
10.4—12.5 ft·lbf}.
AME2224E047
AME2224E048
Camshaft Sprocket, Variable Valve Ti mi ng Actuat or (L 3 ( wit h v ari ab le val ve ti ming mech ani sm) ) Asse mb ly
Note
1. Camshaft sprocket or variable valve timing actuator (L3 (with vari able valve timing mechanism)) attachment
bolt is changed into the state of a temporary bundle by hand until it attaches timing chain.
2. The attachment bolt of camshaft sprocket or variable valve timing actuator (L3 (with variable valve timing
mechanism)) is bound tight for timing chain after attachment.
Tightening torque
69—75 N·m {7.10—7.60 kgf·m, 50.9—55.3 ft·lbf}
L8, LF, L3
AME2224E077
L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism)
B–40
AME2224E078
Page 58

End Of Sie
TIMING CHAIN ASSEMBLY
1. Assemble in the order indicated in the table.
2.
ENGINE
A6E242402000E13
B
.
1 Crankshaft sprocket
2 Oil pump chain
3 Oil pump sprocket
(See B–42 Oil Pump Sprocket Assembly Note)
4 Oil pump chain guide
5 Oil pump chain tensioner
6 Seal (L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism))
7 Timing chain
(See B–42 Timing Chain Aassembly Note)
8 Chain guide
9 Tensioner arm
10 Chain tensioner
11 Camshaft sprocket, Variable Valve Timing Actuator
(L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism))
(See B–43 Camshaft Sprocket, Variable Valve
Timing Actuator (L3 (with variable valve timing
mechanism)) Assembly Note)
AME2224E327
12 Front oil seal
(See B–44 Front Oil Seal Aassembly Note)
13 Engine front cover
(See B–44 Engine Front Cover Aassembly Note)
14 Drive belt idler pulley
15 Water pump pulley
16 Crankshaft pulley
17 Crankshaft pulley lock bolt
(See B–45 Crankshaft Pulley Lock Bolt Aassembly
Note)
18 Cylinder head cover
(See B–46 Cylinder Head Cover Aassembly Note)
19 Spark plug
B–41
Page 59

ENGINE
Oil Pump Sprocket Assembly Note
1. Hold the oil pump sprocket using the SST.
Timing Chain Aassembly Note
1. Install the SST to the camshaft, then align the No. 1 camshaft position with the TDC.
Europe
AME2224E340
Except Europe
2. Remove the cylinder block lower blind plug.
3. Install the SST as shown.
4. Turn the crankshaft clockwise so that the
crankshaft is in the No.1 cylinder TDC position.
5. Install the timing chain.
AME2224E329
AME2224E328
AMJ2224E666
B–42
Page 60

ENGINE
6. Install the chain tensioner and remove the
retaining wire.
AME2224E330
Camshaft Sprocket, Variable Valve Timing Actuator (L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism)) Assembly
Note
1. Hold the camshaft using a suitable wrench on the cast hexagon as shown.
L8, LF, L3
B
L3 (with variable valve timing mechanism)
2. Tighten the camshaft sprocket lock bolt.
Tightening torque: 69—75 N·m {7.10—7.6 kgf·m, 50.9—55.3 ft·lbf}
AME2224E077
AME2224E078
B–43
Page 61

Front Oil Seal Aassembly Note
1. Apply clean engine oil to the oil seal.
2. Push the oil seal slightly in by hand.
3. Compress the oil seal using the SST and a
hammer.
ENGINE
AME2224E331
Engine Front Cover Aassembly Note
1. Apply silicone sealant to the engine front cover as
shown.
Caution
•••• Install the cylinder head cover within 10
minutes of applying the silicone sealant.
•••• Silicone sealant is not need in area C as
indicated below due to an existing. (L3
(with variable valve timing mechanism))
Thickness
A: 2.0—3.0 mm {0.079—0.118 in}
B: 1.5—2.5 mm {0.059—0.098 in}
AME2224E332
AME2224E333
B–44
Page 62

2. Install the cylinder head cover bolts in the order
as shown.
Bolt No. Tigtining torque N·m {kgf·m, ft·lbf}
1—18 8.0—11.5 N·m
{81.6—117.2 kgf·cm, 70.9—101.7 in·lbf}
19—22 40—55 {4.1—5.6, 29.7—40.5}
Crankshaft Pulley Lock Bolt Aassembly Note
1. Install the SST to the camshaft as shown.
Europe
ENGINE
B
AME2224E334
Except Europe
2. Install the M6 x 1.0 bolt in by hand.
3. Turn the crankshaft clockwise so that the
crankshaft is in the No.1 cylinder TDC position.
AME2224E329
AME2224E328
AME2224E009
B–45
Page 63

4. Hold the crankshaft pully using the SST.
5. Tighten the crankshaft pulley lock bolt in the
following two steps.
(1) Tighten to 96—104 N·m {9.8—10.6 kgf·m,
70.9—76.7 ft·lbf}
(2) Tighten 87°°°°—93°°°° .
6. Remove the M6 x 1.0 bolt.
7. Remove the SST from the camshaft.
8. Remove the SST from the block lower blind plug.
9. Rotate the crankshaft clockwise two turns until
the TDC position.
• If not aligned, loosen the crankshaft pulley
lock bolt and repeat from Step 1.
10. Install the cylinder block lower blind plug.
Tightening torque: 20 N·m {2.0 kgf·m, 14.8 ft·lbf}
Cylinder Head Cover Aassembly Note
1. Apply silicone sealant to the mating faces as
shown.
Caution
•••• Install the cylinder head cover within 10
minutes of applying the silicone sealant.
Dot diameter: 4.0—6.0 mm {0.16—0.23 in}
ENGINE
AME2224E015
2. Install the cylinder head cover with a new gasket.
3. Tighten the bolts in the order shown.
Tightening torque: 8.0 —12 N·m {81.6—122.3
kgf·cm, 70.9—106.2 in·lbf}
End Of Sie
AME2224E335
AME2224E336
B–46
Page 64

TD
TECHNICAL DATA
TECHNICAL DATA ............................................. TD-2
ENGINE TECHNICAL DATA ............................ TD-2
TD
TD–1
Page 65

TECHNICAL DATA
TECHNICAL DATA
ENGINE TECHNICAL DATA
Engine
Item
Cylinder head
Cylinder head gasket
contact surfaces distortion
Manifold contact surfaces
distortion
Valve clearance [Engine cold] (mm {in})
Valve and valve guide
Valve stem diameter (mm {in})
Valve stem to guide
clearance
Valve length (mm {in})
Valve guide inner diameter (mm {in}) Standard
Valve guide protrusion
height
Valve head margin thickness (mm {in}) Minimum
Valve seat
Valve seat contact width (mm {in}) Standard
Valve seat angle (°)
Valve seat sinking
(Valve protrusion height)
Valve spring
Out-of-square (mm {in}) Maximum 1% (2.10 {0.082})
Pressing force at valve
spring height H
OCV (Oil control valve)
Coil resistance [20° C{68°F}] (ohm) Standard –
(mm {in}) Maximum 0.10 {0.004}
(mm {in})
(mm {in})
(mm {in})
(mm {in}) Standard
(N {kgf, lbf})
Maximum 0.10 {0.004}
Maximum grinding 0.15 {0.006}
IN 0.22—0.28 {0.0087—0.0110}
EX 0.27—0.33 {0.0106—0.0130}
Standard
Minimum
Standard
Maximum
Standard
Minimum
IN
EX
H: 27.8 mm
{1.094 in}
IN 5.470—5.485 {0.2154—0.2159}
EX 5.465—5.480 {0.2152—0.2157}
IN 5.440 {0.2142}
EX 5.435 {0.2140}
IN 0.024—0.069 {0.0009—0.0027}
EX 0.029—0.074 {0.0012—0.0029}
IN 0.10 {0.004}
EX 0.10 {0.004}
IN 102.99—103.79 {4.055—4.086}
EX 104.25—105.05 {4.105—4.135}
IN 102.99 {4.055}
EX 103.79 {4.086}
IN 5.509—5.539 {0.2169—0.2180}
EX 5.509—5.539 {0.2169—0.2180}
IN 1.62 {0.0637}
EX 1.82 {0.0716}
IN 1.2—1.6 {0.048—0.062}
EX 1.2—1.6 {0.048—0.062}
IN 45
EX 45
IN 40.64—42.24 {1.600—1.662}
EX 40.50—42.10{1.595—1.657}
L8 LF
12.2—12.8 {0.481—0.503}
12.2—12.8 {0.481—0.503}
494.9 {50.47,111.2}
A6E931001001E01
L3,
L3 (with variable
valve timing
mechanism)
6.9—7.9
*
TD–2
Page 66

TECHNICAL DATA
Engine
Item
Camshaft
Camshaft runout (mm {in}) Maximum 0.03 {0.0012}
IN 40.79 {1.606} 42.12{1.659}
Standard
EX 41.08 {1.618} 41.08{1.618}
Cam lobe height (mm {in})
IN 40.692{1.603} 42.022{1.655}
Minimum
EX 40.982 {1.614} 40.982{1.614}
Journal diameter (mm {in})
Journal oil clearance (mm {in})
End play (mm {in})
Tappet
Tappet bore diameter (mm {in}) Standard 31.000—31.030 {1.2205—1.2216}
Tappet diameter (mm {in}) Standard 30.970—30.980 {1.2193—1.2196}
Tappet-to-Tappet bore oil
clearance
Cylinder block
Cylinder head gasket
contact surfaces distortion
Cylinder bore diameter
[Measure the cylinder bore
at 42 mm
{1.65 in} below the top
surface]
Minimum / maximum bore
diameter Limit
Piston
Piston diameter (mm {in}) Standard
Piston-to-cylinder clearance (mm {in})
Piston ring
Piston ring-to-ring groove
clearance
End gap
(measured in cylinder)
(mm {in})
(mm {in}) Maximum 0.10 {0.004}
(mm {in}) Standard
(mm {in})
(mm {in})
Standard 24.96—24.98 {0.9827—0.9834}
Minimum 24.95 {0.982}
Standard 0.04—0.08 {0.002—0.003}
Maximum 0.09 {0.0035}
Standard 0.09—0.24 {0.0035—0.0094}
Maximum 0.25 {0.009}
Standard 0.02—0.06{0.0008—0.0023}
Maximum 0.15 {0.006}
(mm {in})
Standard 0.025—0.045 {0.0010—0.0017}
Maximum 0.11 {0.0043}
Standard
Maximum
Standard
Maximum
Top 0.03—0.08 {0.0012—0.0031}
Second 0.03—0.07 {0.0012—0.0027}
Oil (rail) 0.03—0.07 {0.0012 —0.0027}
Top 0.17 {0.0067}
Second 0.15 {0.0059}
Oil (rail) 0.15 {0.0059}
Top 0.16—0.31 {0.0063—0.0122}
Second 0.33—0.48 {0.0130—0.0189}
Oil (rail) 0.20—0.70 {0.0079 —0.0275}
Top 1.0 {0.0393}
Second 1.0 {0.0393}
Oil (rail) 1.0 {0.0393}
L8 LF
83.000—83.030
{3.2677—3.2689}
82.940—83.090
{3.2653—3.2712}
82.965—82.995
{3.2664—3.2675}
87.500—87.530 {3.4449—3.4460}
87.440—87.590 {3.4425—3.4484}
87.465—87.495 {3.4435—3.4446}
L3 (with variable
valve timing
mechanism)
42.12 {1.659}
42.44{1.671}
41.08 {1.618}
41.18 {1.622}
42.022{1.655}
42.342 {1.667}
40.982 {1.614}
41.082 {1.618}
L3,
TD
*
*
*
*
TD–3
Page 67

TECHNICAL DATA
Engine
Item
Connecting rod and connecting rod bearing
Connecting rod side
clearance
Connecting rod bearing size (mm {in})
Connecting rod bearing oil
clearance
Crankshaft
Crankshaft runout (mm {in}) Maximum 0.05 {0.0019}
Main journal diameter (mm {in})
Main journal oil clearance (mm {in})
Main journal out of round (mm {in}) Maximum 0.05 {0.0019}
Main bearing size (mm {in})
Crank pin journal diameter (mm {in})
Crank pin out of round (mm {in}) Maximum 0.05 {0.022}
Crankshaft end play (mm {in})
Front oil seal
Pushing distance of the front oil seal
[from the edge of the engine front cover]
Bolt
Cylinder head bolt length
Connecting rod bolt length
Main bearing cap bolt length
Balance shaft
Gear backlash (mm {in}) Maximum –
*:
With variable valve timing mechanism
(mm {in})
(mm {in})
Standard 0.14—0.36 {0.0056—0.0141}
Maximum 0.435 {0.0172}
Standard 1.496—1.502 {0.0589—0.0591}
0.25 {0.01} Oversize 1.623—1.629 {0.0639—0.0641}
0.50 {0.02} Oversize 1.748—1.754 {0.0688—0.0690}
Standard 0.026—0.052{0.0011—0.0020}
Maximum 0.10{0.0039}
Standard 51.980—52.000 {2.0464—2.0472}
0.25 {0.01}
undersize
Standard 0.019—0.035{0.0007—0.0013}
Maximum 0.10 {0.0039}
Standard 2.506—2.509 {0.0987—0.0988}
0.25 {0.01} Oversize 2.628—2.634 {0.1034—0.1037}
0.50 {0.02} Oversize 2.753—2.759 {0.1084—0.1086}
Standard 49.980—50.000 {1.9677—1.9685}
0.25 {0.01}
undersize
Standard 0.22—0.45{0.0087—0.0177}
Maximum 0.55 {0.0216}
(mm {in}) 0—0.5 {0—0.019}
Standard 149.0—150.0 {5.86—5.90}
Maximum 150.5 {5.92}
Standard 44.7—45.3 {1.75—1.78}
Maximum 46.0 {1.81}
Standard 110.0—110.6 {4.33—4.35}
Maximum 111.3 {4.38}
End Of Sie
L8 LF
51.730—51.750 {2.0366—2.0373}
49.730—49.750 {1.9579—1.9586}
L3,
L3 (with variable
valve timing
mechanism)
0.005-0.101
{0.00019—
0.0039}
TD–4
Page 68

ST
SPECIAL TOOLS
SPECIAL TOOLS
ENGINE SST .....................................................ST-2
.................................................ST-2
ST
ST–1
Page 69

SPECIAL TOOLS
SPECIAL TOOLS
ENGINE SST
Ford SST numbers are collated with Mazda SST numbers in the example below.
Ford SSTs are marked with Ford SST number.
Example
1:49 JE01 061
2:303-507
Peg
1: Mazda SST number
2: Ford SST number
1:49 JE01 061
2:303–507
Peg
1:49 G032 354
2: –
Adjusting
wrench
1:49 UN20 5072
2:205–072
Holder
1:49 E011 1A0
2: –
Ring gear brake
set
1:49 UN20
507202
2:205–072–02
Adapter
1:49 0636 100B
2: –
Valve spring
lifter arm
A6E941001001E01
1:49 B012 0A2
2: –
Pivot
1:49 0107 680A
2: –
Engine stand
1:49 L012 0A0B
2: –
Valve seal and
valve guide
installer set
1:49 B012 015
2: –
Valve guide
installer
1:49 L010 1A0
2: –
Engine hanger
set
1:49 T032 302
2: –
Bearing installer
1:49 H010 401
2: –
Oil seal installer
1:49 S120 170
2: –
Valve seal
remover
1:49 D032 316
2: –
Protractor
ST–2
Page 70

SPECIAL TOOLS
1:49 JE01 054
(Europe)
49 UN30 3376
(Except Europe)
2: 303–376
Plate
End Of Sie
1:49 G011 201
2: –
Attachment
–
ST
ST–3
 Loading...
Loading...