Page 1

HSDPA Standard AT Commands Manual
VERSION 1.2
This document is the sole and
exclusive property of Maxon. Not to
be distributed or divulged without
prior written agreement
.
36A Gibson Ave
Padstow NSW 2211
Australia
URL: www.maxon.com.au
Page 2

Document Description
All data and information contained in or disclosed by this document are confidential and
proprietary information of Maxon Australia, and all rights therein are expressly reserved. By
accepting this material, the recipient agrees that this material and the information contained
therein are held in confidence and in trust and will not be copied or reproduced in whole or in
part, nor its contents revealed in any manner to others without the express written permission of
Maxon Australia.
This information provided in this document is provided on an “as is” basis.
In no event will Maxon Australia be liable for any damages arising directly or indirectly from any
use of information contained in this document.
Information in this document is subjected to change without any notice.
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 2 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 3

REVISION HISTORY
Product Name Maxon ModMax - MM-6280IND
Document Type Public
Document Number CHE-FDS-2301
Current Version Number 1.2
Status of the Document Public Release
Revision Date 2007-12-13
Total Number of Pages 60
- Revision History
Level Date History
1.0 2006-10-02 Internal Release Version
1.1 2007-12-13 Initial Version
1.2 2007-12-12 +CLCK format adjustment
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 3 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 4

CONTACT INFORMATION
Depending on the nature of your inquiry, please feel free to contact the following senior
personnel:
Sales, Marketing & Corporate:
Ray Sanders – Managing Director Email: rayws@maxon.com.au
Phone: +61 2 9707 3000
Dana Baggetto – General Manager Email: danab@maxon.com.au
Phone: +61 2 9707 3000
Technical:
Phone: +61 2 9707 3000 Email: support@maxon.com.au
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 4 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
HSDPA Standard AT Commands Manual .................................................................................... 1
Document Description .............................................................................................................. 2
REVISION HISTORY .................................................................................................................. 3
CONTACT INFORMATION .......................................................................................................... 4
TABLE OF CONTENTS ...............................................................................................................5
Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 7
1.1. General ................................................................................................................................ 7
1.2. Terms................................................................................................................................... 7
1.3. References............................................................................................................................ 8
AT INTERFACE DESCRIPTION..................................................................................................11
1.4. Basic Integration .................................................................................................................11
1.5. Serial Interface ....................................................................................................................11
1.6. Command Format ...............................................................................................................11
1.7. Message Naming Convention ...............................................................................................11
1.8. DTE-TA/DCE interface commands ......................................................................................12
Mobile Termination errors commands ......................................................................................15
1.9. Report Mobile Termination error( +CMEE) ...........................................................................15
1.9.1. Mobile Termination error result code (CME ERROR) .....................................................15
1.10. Informative examples .......................................................................................................17
General commands ..................................................................................................................18
1.11. Request manufacturer identification(+CGMI)....................................................................18
1.12. Request model identification(+CGMM ).............................................................................18
1.13. Request product serial number identification (+CGSN) .....................................................19
1.14. Select TE character set (+CSCS).......................................................................................19
1.15. ITU-T V.250 generic TA control commands.......................................................................20
1.16. PCCA STD‑101 [17] select wireless network +WS46 .........................................................21
1.17. Informative examples .......................................................................................................21
1.17.1. Phone model .............................................................................................................21
1.17.2. Phone Manufacturer .................................................................................................21
1.17.3. Checking mobile state ...............................................................................................21
1.17.4. Firmware version reading..........................................................................................21
1.17.5. IMEI number reading................................................................................................21
1.17.6. Supported alphabets.................................................................................................22
1.17.7. Supported alphabets.................................................................................................22
Network service commands......................................................................................................23
1.18. Subscriber number +CNUM .............................................................................................24
1.19. Network registration +CREG ............................................................................................24
1.20. PLMN selection +COPS.....................................................................................................25
1.21. Facility lock +CLCK..........................................................................................................27
1.22. Change password +CPWD................................................................................................29
1.23. Preferred PLMN list +CPOL...............................................................................................29
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 5 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 6

1.24. Read operator names +COPN ...........................................................................................30
1.25. Informative examples .......................................................................................................30
1.25.1. Operator information reading ....................................................................................30
1.25.2. IMSI number reading ................................................................................................31
1.25.3. GPRS Attachment .....................................................................................................31
1.25.4. Network registration .................................................................................................31
1.25.5. Own number reading ................................................................................................31
Mobile Termination control and status commands ...................................................................32
1.26. Basic TE ..........................................................................................................................32
1.27. Signal quality +CSQ.........................................................................................................33
1.28. Clock +CCLK ...................................................................................................................33
1.29. Band Selection (AT$$MBAND).........................................................................................34
1.30. Enter PIN +CPIN ..............................................................................................................34
1.31. Informative examples .......................................................................................................35
1.31.1. Signal strength reading .............................................................................................35
1.31.2. Pin registration .........................................................................................................36
Packet Domain Command(GPRS)..............................................................................................37
1.32. UMTS packet Domain commands ....................................................................................37
1.32.1. Define PDP Context +CGDCONT ...............................................................................38
1.32.2. Define Secondary PDP Context +CGDSCONT ............................................................39
1.32.3. Traffic Flow Template +CGTFT ..................................................................................40
The following parameters are defined in 3GPP TS 23.060[47] - .................................................42
1.32.4. Quality of Service Profile (Requested) +CGQREQ .......................................................43
1.32.5. Quality of Service Profile (Minimum acceptable) +CGQMIN ........................................44
1.32.6. 3G Quality of Service Profile (Requested) +CGEQREQ................................................45
The following parameters are defined in 3GPP TS 23.107 [46] - ................................................46
1.32.7. 3G Quality of Service Profile (Minimum acceptable) +CGEQMIN ................................48
The following parameters are defined in 3GPP TS 23.107 [46] - ................................................50
1.32.8. 3G Quality of Service Profile (Negotiated) +CGEQNEG ...............................................51
The following parameters are defined in 3GPP TS 23.107 [46] - ................................................52
If a value is omitted for a particular class then the value is considered to be unspecified.........53
1.32.9. PS attach or detach +CGATT .....................................................................................53
1.32.10. PDP context activate or deactivate +CGACT...............................................................54
1.32.11. PDP Context Modify +CGCMOD ................................................................................55
1.32.12. Enter data state +CGDATA........................................................................................55
1.32.13. Show PDP address +CGPADDR .................................................................................56
1.33. Modem compatibility commands......................................................................................57
1.34. Informative examples .......................................................................................................57
1.34.1. UMTS Connection .....................................................................................................57
Synchronous data mode commands .........................................................................................58
Qualcomm commands..............................................................................................................59
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 6 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 7

Introduction
1.1. General
The 3GPP TS 27.007 technical specification defines an AT command set for use in controlling devices
that operate on WCDMA networks. This document identifies which of those AT commands are
supported on the CHU628 USB modem module.
The specification document that lists the AT command set, 3GPP TS 27.007 V5.6.0(2005-03), is
available on the 3GPP web site, www.3gpp.org
The table below identifies whether each command is supported on the CHU628 USB module.
An “N/A in the support column of the table indicates that the command is related to a feature that is not
available on the modems.
.
1.2. Terms
The following terms are used throughout this document. We have provided and explanation of these
for your reference.
Table 1. Terms definition
Term Description
[ ]
{ }
<CR> Carriage return character, which value is specified with command S3
<del> Delimiter/Space. Insert a space.
Field. Contents between ‘[’ and ‘]’ indicate the name of the field or the
parameter required to complete the syntax.
Option field. Contents between ‘{‘ and ‘}’ indicate the name of the field or the
parameter which can be omitted.
AT command set
DCE Same as MT2.
DTE Same as TE2
IMEI International Mobile station Equipment Identity
MO
Mobile Station
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 7 of 60 Version 1.2
Communications command set interface between data terminal equipment
(DTE) and data circuit terminating equipment (DCE).
Mobile-Originated where the SMS or the call is originated [sent] by the Mobile
Station.
A cellular device [e.g this modem or a mobile phone handset] in the carrier’s
domestic public cellular phone network intended to be used when stationary,
while in motion or during halts at unspecified points. Mobile stations may
include fixed, portable (e.g., hand-held personal units) or vehicular units.
Page 8
Term Description
MSC Mobile Switching Centre
MT
MT2
NVM
PCCA Portable Computer and Communications Association
Rm Hardwire Interface between MT2 and TE2.
SMS Short text Message Service.
TE2
UART
Mobile-Terminated where the SMS or the call is terminated [received] at the
Mobile Station.
Mobile Termination 2An MT2 provides a non-ISDN (Rm) user interface, e.g.,
CCITT V series or CCITT X series. Same at DCE. Refers to the MM-6280IND
modem.
Non Volatile Memory. User changeable and is written at time of change or
entry to a separate section of memory unaffected by power cycles. The setting
value is available in all profiles.
Terminal Equipment 2. A TE2 is a data terminal device that has a non-ISDN
user-network interface, e.g., CCITT V series or CCITT X series. Same as DTE.
Products which can issue AT command set and handle the response through
UART or RS-232 signalling ports of the MM-6280IND. The popular examples
of MT2 are PC’s, PDA and embedded systems i.e. Data Logger, PLC etc.
Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter, the UART is a microchip
component that handles asynchronous serial communication. Every computer
contains a UART to manage the serial ports, and some internal modems such
as MM-6280IND have their own UART. UART 1(RS232 port) UART 2 (On
serial for diagnostics)
UE User Equipment
UI User Interface.
UICC Universal Integrated Circuit Card
Um Over-air interface between the MT2 and the BS.
USIM Universal Subscriber Identity Module
1.3. References
The following standards are referenced in this text.
3GPP TS 22.002
3rd Generation Partnership Project; Bearer Services (BS) supported by a GSM Public Land Mobile
Network (PLMN)
3GPP TS 22.003
3rd Generation Partnership Project; Teleservices supported by a GSM Public Land Mobile Network
(PLMN).
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 8 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 9

3GPP TS 22.081
3rd Generation Partnership Project; Line identification supplementary services - Stage 1.
3GPP TS 22.082
3rd Generation Partnership Project; Call Forwarding (CF) supplementary services - Stage 1".
3GPP TS 22.083
3rd Generation Partnership Project; Call Waiting (CW) and Call Hold (HOLD) supplementary
services - Stage 1".
3GPP TS 22.088
3rd Generation Partnership Project; Call Barring (CB) supplementary services - Stage 1.
3GPP TS 23.003
3rd Generation Partnership Project; Numbering, addressing and identification.
3GPP TS 24.008
3rd Generation Partnership Project; Mobile Radio Interface Layer 3 specification; Core Network
Protocols-Stage 3.
GSM MoU SE.13
GSM MoU Permanent Reference Document SE.13
GSM Mobile Network Codes and Names.
ITU-T Recommendation E.212
Identification plan for land mobile stations.
ITU-T Recommendation T.31
Asynchronous facsimile DCE control, service class 1.
ITU-T Recommendation T.32
Asynchronous facsimile DCE control, service class 2.
ITU-T Recommendation T.50
International Reference Alphabet (IRA) (Formerly International Alphabet No. 5 or IA5) - Information
technology - 7-bit coded character set for information exchange.
ITU-T Draft new Recommendation V.250
Serial asynchronous automatic dialling and control.
Telecommunications Industry Association TIA IS-99
Data Services Option Standard for Wideband Spread Spectrum Digital Cellular System.
Telecommunications Industry Association TIA IS-135
800 MHz Cellular Systems, TDMA Services, Async Data and Fax.
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 9 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 10

Portable Computer and Communications Association PCCA STD-101 Data Transmission
Systems and Equipment
Serial Asynchronous Automatic Dialling and Control for Character Mode DCE on Wireless Data
Services.
3GPP TS 27.060
3rd Generation Partnership Project; General requirements on Mobile Stations (MS) supporting
General Packet Radio Bearer Service (GPRS).
CCITT Recommendation V.110
Support of data terminal equipments (DTEs) with V-Series interfaces by an integrated services digital
network.
CCITT Recommendation V.120
Support by an ISDN of data terminal equipment with V-Series type interfaces with provision for
statistical multiplexing.
ITU-T Recommendation X.31
Support of packet mode terminal equipment by an ISDN.
3GPP TS 31.101
UICC-Terminal Interface; Physical and Logical Characteristics
ETSI TS 102 310
Smart Cards; Extensible Authentication Protocol support in the UICC.
ETSI TS 102 221
Smart cards; UICC-Terminal interface; Physical and logical characteristics.
RFC 3748, June 2004
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 10 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 11
AT INTERFACE DESCRIPTION
1.4. Basic Integration
The MM-6280IND supports asynchronous serial communication known as RS-232 or USB.
This chapter describes the basic integration and communication of MT2 with TE2. MT2 hereby defines
MM-6280IND and TE2 means host products which can issue AT commands and handle the response
through UART or USB signalling. The popular examples of TE2 are PC’s, PDA’s and unmanned
systems such as Data Loggers, RTU’s or PLC’s.
1.5. Serial Interface
TE2’s command and MT2’s response pair is the basic interface sequence. The pairs should keep a
pre-defined format and ignore the case of letters unless otherwise specified. MM-6280IND supports 2
serial interfaces, USB and UART. USB and UART serve an AT command set with ASCII character
sequence.
1.6. Command Format
The AT command set in USB and UART is based on ASCII text. The extended AT command set by
Qualcomm start with “AT$QC” and the extended AT command set by C-motech start with “AT$$”. All
commands should finish by <CR>, 0x0d.
Any spaces in the AT command field are ignored and the space in the parameter field should be
removed if it is not necessary unless otherwise specified.
With few exceptions the following syntax provides the given response for each AT command. Where
not applicable the response is ERROR:
Table 2. AT command Format
Command Description
AT***? reads current set value
AT***=? reads supported range of values
AT***=<value> changes current set value to new set value
ASCII commands/ACK AT$$ command = argument
ASCII
responses/notifications
$$command: result
Error(In case of not applicable command, or wrong argument input)
NOTE: *** stands for the specific AT syntax.
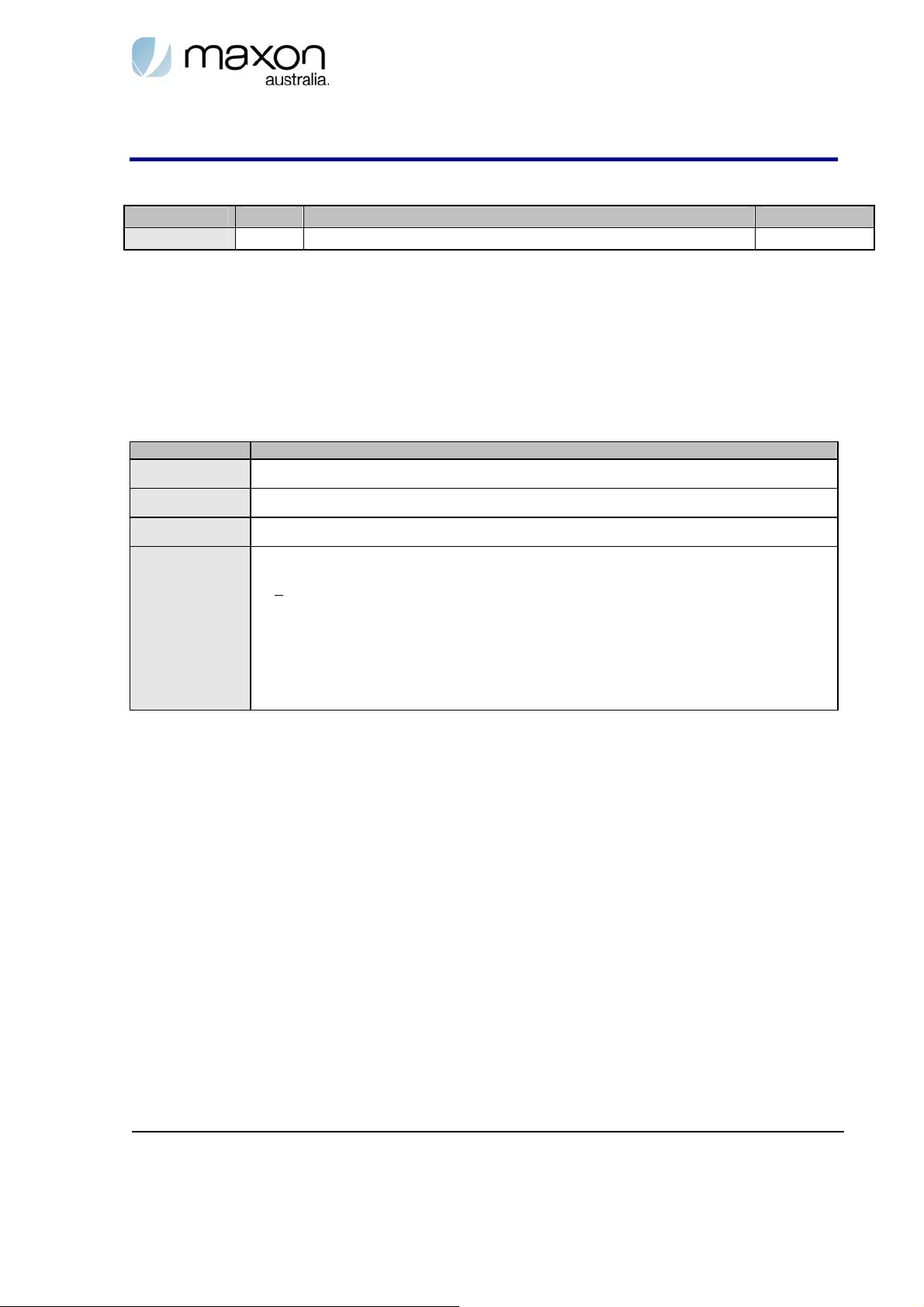
1.7. Message Naming Convention
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 11 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 12

The following diagram shows the naming convention of messages between MT2 and TE2.
Command (including AT)
TE2 MT2
Response (excluding AT)
<TE2 sends command to MT2>
Signal (H/W)
TE2
Indication (message)
<MT2 sends H/W signalling to TE2>
TE2 MT2
<MT2 sends notification message to TE2>
Notification (excluding AT)
MT2
Figure 1. Naming convention diagram
1.8. DTE-TA/DCE interface commands
Table 3. ITU-T V.250 commands relating to TE-TA interface
Command Req Description Support
E<value> Mand. Command echo
Q<value> Mand. Result code suppression
supported
supported
S3 Mand. Command line termination character supported
S4 Mand. Response formatting character
S5 Mand. Command line editing character
V<value> Mand. DCE response format
X<value> Mand. Result code selection and call progress monitoring control
&C<value> Mand. Circuit 109 DCE RLSD (DCD) behavior
&D<value> Mand. Circuit 108 DTE DTR behavior
Fixed Rm Rate. This numeric extended-format parameter
supported
supported
supported
supported
supported
supported
supported
specifies the data rate at which the MT2 will accept
command set, in addition to 1200 bit/s or 9600 bit/s (as
required in EIA/TIA-602). It may be used to select operation
at rates at which the MT2 is not capable of automatically
+IPR=<rate> Opt.
detecting the data rate being used by the TE2.
115200bps. (Default)
+IPR? Displays current set value.
+IPR=? Displays range of (supported auto detectable rates),
(list of supported fixed-only rates). e.g. +IPR: (1200, 2400,
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 12 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 13
4800, 9600, 19200), (45, 50, 75, 110, 150, 300, 600, 38400,
57600, 115200, 230400)
+IPR=<value> Set value
TE2-MT2 Character Framing. This extended-format
compound parameter is used to determine the local serial
port start-stop (asynchronous) character framing that the
MT2 shall use while accepting TE2 command set and while
transmitting information text and result codes to the TE2, if
this is not automatically determined (see +IPR).
<format> valid numeric values
0 auto detect [NOT SUPPORTED]
1 8Data 2Stop
2 8Data 1Parity 1Stop
3 8Data 1Stop (Default)
+ICF Opt.
4 7Data 2Stop
5 7Data 1Parity 1Stop
6 7Data 1Stop
<parity> defined numeric values
0 odd
1 even
supported
2 Mark [NOT SUPPORTED]
3 space (Default)
+ICF? Shows current settings
+ICF=? Shows supported range
+ICF=<format_value,parity_value> sets value
TE2-MT2 Local Flow Control. This extended-format
compound parameter is used to control the operation of
local flow control between the TE2 and MT2
<c_by_t> Description
0 None
+IFC Opt.
1 Xon/Xoff local
2 Circuit 133 (Ready for Receiving)
[1]
.
DC1/DC3 on circuit 103; do not pass
DC1/DC3 characters to the remote
DCE.
(Default)
supported
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 13 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 14
r
3 Xon/Xoff global
DC1/DC3 on circuit 103 with DC1/DC3
characters being passed through to the
remote DCE in addition to being acted
upon for local flow control
<t_by_c> Description
0 None
1 Xon/Xoff local
DC1/DC3 on circuit 104
2 Circuit 106 (Clear to Send/Ready fo
<c_by_t>: specifies the method to be used by the DTE to
control the flow of received data from the DCE;
<t_by_c>: specifies the method to be used by the DCE to
control the flow of transmitted data from the DTE.
AT+IFC=<[[c_by_t]DCE_DTE]>,<[[t_by_c]DTE_DCE]>
+IFC? Shows current settings
+IFC=? Shows supported range
+IFC=<c_by_t,t_by_c> sets value
+ILRR Opt.
determines whether the used local TE-TA data rate is
informed using intermediate result code +ILRR
Sending) (Default)
Not supported
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 14 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 15
Mobile Termination errors commands
Table 4. Mobile Termination control and status commands
Command Req Description Support
+CMEE Report Mobile Termination error supported
1.9. Report Mobile Termination error( +CMEE)
Set command disables or enables the use of result code +CME ERROR: <err> as an
indication of an error relating to the functionality of the MT. When enabled, MT related
errors cause +CME ERROR: <err> final result code instead of the regular ERROR final result
code. ERROR is returned normally when error is related to syntax, invalid parameters, or TA
functionality.
Table 5. +CMEE parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CMEE=[<n>]
+CMEE? +CMEE: <n>
+CMEE=? +CMEE: (list of supported <n>s)
value
<n>:
0
disable +CME ERROR: <err> result code and use ERROR instead
1 enable +CME ERROR: <err> result code and use numeric <err> values (refer
next subclause)
2 enable +CME ERROR: <err> result code and use verbose <err> values (refer
next subclause)
1.9.1. Mobile Termination error result code (CME ERROR)
The operation of +CME ERROR: <err> result code is similar to the regular ERROR result code: if
+CME ERROR: <err> is the result code for any of the commands in a command line, none of the
following commands in the same command line is executed (neither ERROR nor OK result code shall
be returned as a result of a completed command line execution). The format of <err> can be either
numeric or verbose. This is set with command +CMEE (refer previous subclause).
<err> values (numeric format followed by verbose format):
0 phone failure
1 no connection to phone
2 phone-adaptor link reserved
3 operation not allowed
4 operation not supported
5 PH-SIM PIN required
6 PH-FSIM PIN required
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 15 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 16

7 PH-FSIM PUK required
10 SIM not inserted (Note)
11 SIM PIN required
12 SIM PUK required
13 SIM failure (Note)
14 SIM busy (Note)
15 SIM wrong (Note)
16 incorrect password
17 SIM PIN2 required
18 SIM PUK2 required
20 memory full
21 invalid index
22 not found
23 memory failure
24 text string too long
25 invalid characters in text string
26 dial string too long
27 invalid characters in dial string
30 no network service
31 network timeout
32 network not allowed - emergency calls only
40 network personalization PIN required
41 network personalization PUK required
42 network subset personalization PIN required
43 network subset personalization PUK required
44 service provider personalization PIN required
45 service provider personalization PUK required
46 corporate personalization PIN required
47 corporate personalization PUK required
48 hidden key required
49 EAP method not supported
50 Incorrect parameters
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 16 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 17

100 Unknown
1.10. Informative examples
An example of TA responses with all three +CMEE values when MT manufacturer identification is
requested but MT is not connected to the TA:
AT+CMEE=0 (+CME ERROR shall not be used)
OK
AT+CGMI
ERROR
AT+CMEE=1 (use numeric <err>)
OK
AT+CGMI
+CME ERROR: 1
AT+CMEE=2 (use verbose <err>)
OK
AT+CGMI
+CME ERROR: no connection to phone
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 17 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 18
General commands
ITU-T Recommendation V.250 [14] includes "Generic DCE Control" commands with the prefix +G.
These commands are for the identification of the TA. Four of those commands are adapted here to be
the identification commands of the MT. Syntax is otherwise similar but the prefix is +CG. TIA
IS-99 [15] uses same commands for base station identification.
Table 6. General AT command
Command Req Description Support
+CGMI Opt. Request manufacturer identification
+CGMM Opt. Request model identification
+CGMR Opt. Request revision identification
+CGSN Opt. Request product serial number identification
+CSCS Mand. Select TE character set
+CIMI Opt. Request international mobile subscriber identity
+CMUX Multiplexing mode Not supported
supported
supported
supported
supported
supported
supported
1.11. Request manufacturer identification(+CGMI)
Execution command causes the TA to return one or more lines of information text <manufacturer>,
determined by the MT manufacturer, which is intended to permit the user of the TA to identify the
manufacturer of the MT to which it is connected to. Typically, the text will consist of a single line
containing the name of the manufacturer, but manufacturers may choose to provide more information
if desired.
Table 7. +CGMI action command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGMI <manufacturer>
+CME ERROR: <err>
+CGMI=?
value <manufacturer>: the total number of characters, including line terminators, in the
information text shall not exceed 2048 characters
1.12. Request model identification(+CGMM )
Execution command causes the TA to return one or more lines of information text <model>,
determined by the MT manufacturer, which is intended to permit the user of the TA to identify the
specific model of the MT to which it is connected to. Typically, the text will consist of a single line
containing the name of the product, but manufacturers may choose to provide more information if
desired.
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 18 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 19

Table 8. +CGMM action command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGMM <model>
+CME ERROR: <err>
+CGMM=?
value <model>: the total number of characters, including line terminators, in the information text
shall not exceed 2048 characters.
1.13. Request product serial number identification (+CGSN)
Execution command causes the TA to return one or more lines of information text <sn>, determined by
the MT manufacturer, which is intended to permit the user of the TA to identify the individual MT to
which it is connected to. Typically, the text will consist of a single line containing the IMEI (International
Mobile station Equipment Identity; refer 3GPP TS 23.003 [7]) number of the MT, but manufacturers
may choose to provide more information if desired.
Table 9. +CGSN action command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGSN <sn>
+CME ERROR: <err>
+CGSN=?
value <sn>: the total number of characters, including line terminators, in the information text
shall not exceed 2048 characters
1.14. Select TE character set (+CSCS)
Set command informs TA which character set <chset> is used by the TE. TA is then able to convert
character strings correctly between TE and MT character sets.
Table 10. +CSCS parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CSCS=[<chset>]
+CSCS? +CSCS: <chset>
+CSCS=? +CSCS: (list of supported <chset>s)
Value
<chset> (conversion schemes not listed here can be defined by
manufacturers):
"GSM" GSM 7 bit default alphabet (3GPP TS 23.038); this setting
causes easily software flow control (XON/XOFF) problems
"IRA"
international reference alphabet (ITU-T T.50 [13])
"UCS2" 16-bit universal multiple-octet coded character set
(ISO/IEC10646 [32]); UCS2 character strings are converted to
hexadecimal numbers from 0000 to FFFF; e.g.
"004100620063" equals three 16-bit characters with decimal
values 65, 98 and 99
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 19 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 20
1.15. ITU-T V.250 generic TA control commands
Table 11. ITU-T V.250 generic TA control commands
Command Req Description Support
Z[<value>] Mand. TA sets all parameters to their defaults as specified by a
user memory profile or by the manufacturer, and resets TA
&F[<value>] Mand. TA sets all parameters to their defaults as specified by the
manufacturer
I[<value>] Opt. request manufacturer specific information about the
TA (software cannot use this command to determine the
capabilities of a TA)
+GMI Mand.
+GMM Mand.
+GMR Mand.
+GSN Opt. This command causes the MT2 to transmit one or more
+GOI Opt. request ISO system global object identification of the TA
+GCAP Mand.
This command causes the MT2 to transmit one or more
lines of information text, determined by the manufacturer,
which is intended to permit the user of the MT2 to identify
the manufacturer. Typically, the text will consist of a single
line containing the name of the manufacturer, but
manufacturers may choose to provide more information if
desired (e.g., address, telephone number for customer
service, etc.).
Maxon Electronics Australia Pty. Ltd.
This command causes the MT2 to transmit one or more
lines of information text, determined by the manufacturer,
which is intended to permit the user of the MT2 to identify
the specific model of the device. Typically, the text will
consist of a single line containing the name of the product,
but manufacturers may choose to provide any information
desired.
This command causes the MT2 to transmit one or more
lines of information text, determined by the manufacturer,
which is intended to permit the user of the MT2 to identify
the version, revision level or date, or other pertinent
information of the device. Typically, the text will consist of a
single line containing the version of the product, but
manufacturers may choose to provide any information
desired.
lines of information text, determined by the manufacturer,
which is intended to permit the user of the MT2 to identify
the individual device. Typically, the text will consist of a
single line containing a manufacturer determined alphanumeric string, but manufacturers may choose to provide
any information desired.
(general format defined in ITU T Recommendation X.208;
encoding rules in ITU T Recommendation X.209)
This extended-format command causes the MT2 to
transmit one or more lines of information text in a specific
format. The content is a list of additional capabilities
supported
supported
supported
supported
supported
supported
supported
Not supported
supported
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 20 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 21

command +<name>s, which is intended to permit the user
of the MT2 to identify the minimum capabilities of the MT2.
An MT2 conforming to this standard shall include the
following items, as a minimum, in the result code for the
+GCAP command:
+CIS707, +MS, +ES, +DS, +FCLASS (Default)
+GCI=<T.35> Opt. selects the country of installation for the TA using ITU T
Recommendation T.35 Annex A country codes
Not supported
1.16. PCCA STD‑101 [17] select wireless network +WS46
Table 12. PCCA STD‑101 [17] select wireless network +WS46
Command Req Description Support
+WS46
select wireless network
1.17. Informative examples
1.17.1. Phone model
Command: AT+CGMM
Expected response: Model
1.17.2. Phone Manufacturer
Command: AT+CGMI
Expected response: Manufacturer
1.17.3. Checking mobile state
Command: AT+CPAS
Expected response:+CPAS: State
State possible values:
0: available
3: ringing
4: call in progress
1.17.4. Firmware version reading
Command: AT+CGMR
Expected response: +CGMR: Firmware
1.17.5. IMEI number reading
Command: AT+CGSN
Expected response: +CGSN: IMEI
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 21 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 22

1.17.6. Supported alphabets
Command: AT+CSCS=?
Expected response: +CSCS: (“alphabet1”,”alphabet2”,…)
Command: AT+CSCS=”Alphabet”
Expected response: OK if chosen alphabet is supported or ERROR
1.17.7. Supported alphabets
Command: AT+CSCS=?
Expected response: +CSCS: (“alphabet1”,”alphabet2”,…)
Command: AT+CSCS=”Alphabet”
Expected response: OK if chosen alphabet is supported or ERROR
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 22 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 23

Network service commands
UMTS network related commands, which are not covered in call control clause of the present
document. Commands include UMTS MSISDN query, MT and network facility locking, and network
registration information query
Table 13. Network service commands
Command
+CNUM Opt. Subscriber number Supported
+CREG=[<n>] Opt.
+COPS Opt. PLMN selection Supported
+CLCK=<fac>,
mode>,<passwd
>,<class>
+CPWD=
<fac>, <oldpwd>,
<newpwd>
+CLIP Opt. Calling line identification presentation NA
+CLIR Opt. Calling line identification restriction NA
+COLP Opt. Connected line identification presentation NA
+CDIP Opt. Called line identification presentation Not supported
+CCUG Opt. Closed user grou p NA
27.007
Req.
Mand.
Opt.
Description Support
Presentation of unsolicited network registration status Values
per spec Parameter values supported:
<n> – 0, 1
<stat> – 0 to 5
Lock, unlock, or interrogate an ME or a network facility
Values per spec Command is abortable Parameter values
supported:
<fac>:
AB
AC
AG
AI
AO
IR
OI
OX
SC
PN
PU
PP
PC
PF
<mode> – 0 to 2
<class> – 1 to 255
Set new password for a facility lock function Values per spec
Parameter values supported:
<fac>:
AB
AC
AG
AI
AO
IR
OI
OX
P2
SC
Supported
Supported
Supported
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 23 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 24

+CCFC Mand. Call forwarding number and conditions NA
+CCWA Opt. Call waiting NA
+CHLD Opt. Call related supplementary services NA
+CTFR Opt. Call deflection Not supported
+CUSD Opt. Unstructured supplementary service data NA
+CAOC Opt. Advice of Charge NA
+CSSN Opt. Supplementary service notifications NA
+CLCC Opt. List current calls NA
+CPOL=[<index>
][,
format>[,<oper>]]
Opt.
Preferred operator list Parameter values supported:
<index> – 0 to 50
<format> – 0,2
Supported
+CPLS Opt. Selection of preferred PLMN list Not supported
+COPN Opt. Read operator names Supported
+CAEMLPP Mand. eMLPP Priority Registration and Interrogation Not supported
+CPPS Mand. eMLPP subscriptions Not supported
+CFCS Mand. Fast call setup conditions Not supported
+CAAP Mand. Automatic answer for eMLPP Service Not supported
+CUUS1 Opt. User to User Signalling Service 1 Not supported
1.18. Subscriber number +CNUM
Action command returns the MSISDNs related to the subscriber (this information can be stored
in the SIM/UICC or in the MT). When storing information in the SIM/UICC, if a SIM card is
present or if a UICC with an active GSM application is present, the information is stored in the
MSISDN
under DF
EF
stored in the EF
MSISDN
. If a UICC with an active USIM application is present, the information is
Telecom
under ADF
). If subscriber has different MSISDN for different services,
USIM
each MSISDN is returned in a separate line.
Table 14. +CNUM action command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CNUM +CNUM: [<alpha1>],<number1>,<type1>[,<speed>,<service>[,<itc>]]
[<CR><LF>+CNUM: [<alpha2>],<number2>,<type2>[,<speed>,<service>
[,<itc>]]
[...]]
+CME ERROR: <err>
+CNUM=?
1.19. Network registration +CREG
Action command returns the MSISDNs related to the subscriber (this information can be stored
in the SIM/UICC or in the MT). When storing information in the SIM/UICC, if a SIM card is
present or if a UICC with an active GSM application is present, the information is stored in the
MSISDN
under DF
MSISDN
EF
stored in the EF
each MSISDN is returned in a separate line.
. If a UICC with an active USIM application is present, the information is
Telecom
under ADF
). If subscriber has different MSISDN for different services,
USIM
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 24 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 25

Table 15. +CREG parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CREG=[<n>]
+CREG? +CREG: <n>,<stat>[,<lac>,<ci>]
+CME ERROR: <err>
+CREG=? +CREG: (list of supported <n>s)
value
<n>:
0
disable network registration unsolicited result code
1 enable network registration unsolicited result code +CREG: <stat>
2 enable network registration and location information unsolicited result code +CREG:
<stat>[,<lac>,<ci>]
<stat>:
0 not registered, MT is not currently searching a new operator to register to
1 registered, home network
2 not registered, but MT is currently searching a new operator to register to
3 registration denied
4 unknown
5 registered, roaming
<lac>: string type; two byte location area code in hexadecimal format (e.g. "00C3"
equals 195 in decimal)
<ci>: string type; two byte cell ID in hexadecimal format
1.20. PLMN selection +COPS
Set command forces an attempt to select and register the GSM/UMTS network operator. <mode>
is used to select whether the selection is done automatically by the MT or is forced by this
command to operator <oper> (it shall be given in format <format>) to a certain access
technology, indicated in <AcT>. If the selected operator is not available, no other operator shall
be selected (except <mode>=4). If the selected access technology is not available, then the same
operator shall be selected in other access technology. The selected operator name format shall
apply to further read commands (+COPS?) also. <mode>=2 forces an attempt to deregister from
the network. The selected mode affects to all further network registration (e.g. after <mode>=2,
MT shall be unregistered until <mode>=0 or 1 is selected).
This command should be abortable when registration/deregistration attempt is made.
Read command returns the current mode, the currently selected operator and the current Access
Technology. If no operator is selected, <format>, <oper> and < AcT> are omitted.
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 25 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 26

Test command returns a set of five parameters, each representing an operator present in the
network. A set consists of an integer indicating the availability of the operator <stat>, long and
short alphanumeric format of the name of the operator, numeric format representation of the
operator and access technology. Any of the formats may be unavailable and should then be an
empty field. The list of operators shall be in order: home network, networks referenced in SIM or
active application in the UICC (GSM or USIM) in the following order: HPLMN selector, User
controlled PLMN selector, Operator controlled PLMN selector and PLMN selector (in the SIM or
GSM application), and other networks.
It is recommended (although optional) that after the operator list TA returns lists of supported
<mode>s and <format>s. These lists shall be delimited from the operator list by two commas.
NOTE: The access technology selected parameters, <AcT>, should only be used in terminals capable to register
to more than one access technology. Selection of <AcT> does not limit the capability to cell
reselections, even though access technology is selected, the phone may still re-select a cell in other
access technology.
Table 16. +CREG parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+COPS=[<mode>[
,<format>
[,<oper>[,<
AcT>]]]]
+COPS? +COPS: <mode>[,<format>,<oper>[,< AcT>]]
+COPS=? +COPS: [list of supported (<stat>,long alphanumeric <oper>
value
+CME ERROR: <err>
+CME ERROR: <err>
,short alphanumeric <oper>,numeric <oper>[,< AcT>])s]
[,,(list of supported <mode>s),(list of supported <format>s)]
+CME ERROR: <err>
<mode>:
automatic (<oper> field is ignored)
0
1 manual (<oper> field shall be present, and <AcT> optionally)
2 deregister from network
3 set only <format> (for read command +COPS?), do not attempt
registration/deregistration (<oper> and < AcT> fields are ignored); this value is not
applicable in read command response
4 manual/automatic (<oper> field shall be present); if manual selection fails, automatic
mode (<mode>=0) is entered
<format>:
long format alphanumeric <oper>
0
1 short format alphanumeric <oper>
2 numeric <oper>
<oper>: string type; <format> indicates if the format is alphanumeric or numeric; long
alphanumeric format can be upto 16 characters long and short format up to 8
characters (refer GSM MoU SE.13 [9]); numeric format is the GSM Location Area
Identification number (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.1.3) which consists of a
three BCD digit country code coded as in ITU-T E.212 Annex A [10], plus a two BCD
digit network code, which is administration specific; returned <oper> shall not be in
BCD format, but in IRA characters converted from BCD; hence the number has
structure: (country code digit 3)(country code digit 2)(country code digit 1)(network
code digit 3)(network code digit 2)(network code digit 1)
<stat>:
0 unknown
1 available
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 26 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 27

2 current
3 forbidden
<AcT> access technology selected:
GSM
0
1 GSM Compact
2 UTRAN
1.21. Facility lock +CLCK
Execute command is used to lock, unlock or interrogate a MT or a network facility <fac>.
Password is normally needed to do such actions. When querying the status of a network service
(<mode>=2) the response line for 'not active' case (<status>=0) should be returned only if service
is not active for any <class>.
. This command should be abortable when network facilities are set or interrogated.
Call barring facilities are based on GSM/UMTS supplementary services (refer 3GPP TS
22.088 [6]). The interaction of these with other commands based on other GSM/UMTS
supplementary services is described in the GSM/UMTS standard.
Test command returns facility values supported as a compound value.
Table 17. +CREG parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CLCK=<fac>,<mode>[,<
passwd>[,<class>]]
+CLCK=?
+CME ERROR: <err>
when <mode>=2 and command successful:
+CLCK: <status>[,<class1>
[<CR><LF>+CLCK: <status>,<class2>
[...]]
+CLCK: (list of supported <fac>s)
+CME ERROR: <err>
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 27 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 28
value
<fac> values reserved by the present document:
"CS" CNTRL (lock CoNTRoL surface (e.g. phone keyboard))
"PS" PH-SIM (lock PHone to SIM/UICC card) (MT asks password when
other than current SIM/UICC card inserted; MT may remember certain
amount of previously used cards thus not requiring password when they
are inserted)
"PF" lock Phone to the very First inserted SIM/UICC card (also referred in the
present document as PH-FSIM) (MT asks password when other than the
first SIM/UICC card is inserted)
"SC" SIM (lock SIM/UICC card) (SIM/UICC asks password in MT power-up
and when this lock command issued)
"AO" BAOC (Barr All Outgoing Calls) (refer 3GPP TS 22.088 [6] clause 1)
"OI" BOIC (Barr Outgoing International Calls) (refer 3GPP TS 22.088 [6]
clause 1)
"OX" BOIC-exHC (Barr Outgoing International Calls except to Home
Country) (refer 3GPP TS 22.088 [6] clause 1)
"AI" BAIC (Barr All Incoming Calls) (refer 3GPP TS 22.088 [6] clause 2)
"IR" BIC-Roam (Barr Incoming Calls when Roaming outside the home
country) (refer 3GPP TS 22.088 [6] clause 2)
"NT" barr incoming calls from numbers Not stored to TA memory
"NM" barr incoming calls from numbers Not stored to MT memory
"NS" barr incoming calls from numbers Not stored to SIM/UICC memory
"NA" barr incoming calls from numbers Not stored in Any memory
"AB" All Barring services (refer 3GPP TS 22.030 [19]) (applicable only for
<mode>=0)
"AG" All outGoing barring services (refer 3GPP TS 22.030 [19]) (applicable
only for <mode>=0)
"AC" All inComing barring services (refer 3GPP TS 22.030 [19]) (applicable
only for <mode>=0)
"FD" SIM card or active application in the UICC (GSM or USIM) fixed
dialling memory feature (if PIN2 authentication has not been done
during the current session, PIN2 is required as <passwd>)
"PN" Network Personalization (refer 3GPP TS 22.022 [33])
"PU" network sUbset Personalization (refer 3GPP TS 22.022 [33])
"PP" service Provider Personalization (refer 3GPP TS 22.022 [33])
"PC" Corporate Personalization (refer 3GPP TS 22.022 [33])
<mode>:
0 unlock
1 lock
2 query status
<status>:
0 not active
1 active
<passwd>: string type; shall be the same as password specified for the facility
from the MT user interface or with command Change Password +CPWD
<classx> is a sum of integers each representing a class of information
(default 7):
1 voice (telephony)
2 data (refers to all bearer services; with <mode>=2 this may refer only to
some bearer service if TA does not support values 16, 32, 64 and 128)
4 fax (facsimile services)
8 short message service
16 data circuit sync
32 data circuit async
64 dedicated packet access
128 dedicated PAD access
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 28 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 29

1.22. Change password +CPWD
Action command sets a new password for the facility lock function defined by command Facility
Lock +CLCK.
Table 18. +CPWD action command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CPWD=<fac>,<oldpwd>,
<newpwd>
+CPWD=? +CPWD: list of supported (<fac>,<pwdlength>)s
value
+CME ERROR: <err>
+CME ERROR: <err>
<fac>:
"P2" SIM PIN2
refer Facility Lock +CLCK for other values
<oldpwd>, <newpwd>: string type; <oldpwd> shall be the same as
password specified for the facility from the MT user interface or with
command Change Password +CPWD and <newpwd> is the new password;
maximum length of password can be determined with <pwdlength>
<pwdlength>: integer type maximum length of the password for the facility
1.23. Preferred PLMN list +CPOL
This command refers to the GSM/UMTS supplementary service COLP (Connected Line
Identification Presentation) that enables a calling subscriber to get the connected line identity
(COL) of the called party after setting up a mobile originated call. The command enables or
disables the presentation of the COL at the TE. It has no effect on the execution of the
supplementary service COLR in the network.
When enabled (and called subscriber allows), +COLP:
<number>,<type>[,<subaddr>,<satype> [,<alpha>]] intermediate result code is returned
from TA to TE before any +CR or V.25ter [14] responses. It is manufacturer specific if this
response is used when normal voice call is established.
Read command gives the status of <n>, and also triggers an interrogation of the provision status
of the COLP service according 3GPP TS 22.081 [3] (given in <m>).
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 29 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 30

Table 19. +COLP parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+COLP=[<n>]
+COLP? +COLP: <n>,<m>
+COLP=? +COLP: (list of supported <n>s)
value
<n> (parameter sets/shows the result code presentation status to the TE):
0
disable
1 enable
<m> (parameter shows the subscriber COLP service status in the network):
0 COLP not provisioned
1 COLP provisioned
2 unknown (e.g. no network, etc.)
<number>, <type>, <subaddr>, <satype>, <alpha>: refer +CLIP
1.24. Read operator names +COPN
Execute command returns the list of operator names from the MT. Each operator code
<numericn> that has an alphanumeric equivalent <alphan> in the MT memory shall be
returned.
Table 20. +COPN action command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+COPN +COPN: <numeric1>,<alpha1>
[<CR><LF>+COPN: <numeric2>,<alpha2>
[...]]
+CME ERROR: <err>
+COPN=?
value
<numericn>: string type; operator in numeric format (see +COPS)
<alphan>: string type; operator in long alphanumeric format (see +COPS)
1.25. Informative examples
1.25.1. Operator information reading
Command: AT+COPS?
Expected response: +COPS: mode, format, name
mode possible values:
0: automatic registration
1: manual registration
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 30 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 31

3: use for set format, see below
4: manual/automatic. If manual choice fails then make an automatic registration
Format possible values:
0: short alphanumeric format
1: long alphanumeric format
2: numeric format
name is operator name corresponding to the format.
Command: AT+COPS=3, format command used to change the name format
Expected response: OK
Format possible values:
0: short alphanumeric format
1: long alphanumeric format
2: numeric format
1.25.2. IMSI number reading
Command: AT+CIMI
Expected response: IMSINumber
1.25.3. GPRS Attachment
Command: AT+CGATT=1
Expected response: OK or ERROR
Command: AT+CGATT?
Expected response: 1 or 0 depending on GPRS attachment
1.25.4. Network registration
UI waits for registered or Roaming status before going further.
Command: AT+CREG?
Expected response: +CREG: 0,Status
Status possible values:
0 : no network found
1 : registered
2 : not registered, looking for network
3 : registration denied
4 : unknown
5 : roaming
1.25.5. Own number reading
Command: AT+CNUM
Expected response: +CNUM: “String”,”OwnNumber”
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 31 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 32
Mobile Termination control and status
commands
1.26. Basic TE
Table 21. Basic TE
Comman
d
+CPAS
+CFUN Opt. Set phone functionality Not Supported
+CMA`R Opt. Master Reset Not supported
+CSCC Opt. Secure control command Not supported
+CBC Opt. Battery charge N/A
+CSQ Opt. Signal quality Supported
+CMEC
+CKPD
+CDIS Opt. Display control Not supported
+CIND Opt. Indicator control Not supported
+CMER
+CCLK Opt. Clock Supported
+CALA Opt. Alarm Not supported
+CALD Opt. Delete alarm Not supported
+CAPD Opt. Postpone or dismiss an alarm Not supported
+CTZU Opt. Automatic Time Zone Update Not supported
+CTZR Opt. Time Zone Reporting
+CPWC Opt. Power class Not supported
+CPROT Opt. Enter protocol mode Not supported
+CEAP Opt. EAP authentication Not supported
+CERP Opt. EAP Retrieve Parameters Not supported
+CLAN Opt. Set Language Not supported
+CLAE Opt. Language Event Not supported
+CSGT Opt. Set Greeting Text Not supported
+CSVM Opt. Set Voice Mail Number Not supported
+CALM Opt. Alert sound mode Not supported
+CRSL Opt. Ringer sound level Not supported
+CVIB Opt. Vibrator mode Not supported
+CLVL Opt. Loudspeaker volume level Not supported
+CMUT Opt. Mute control N/A
+CRMC Opt. Ring Melody Control Not supported
+CRMP Opt. Ring Melody Playback Not supported
+CLAC Opt. List all available AT commands Not supported
+CSIM Opt. Generic SIM access Supported
Req Description Support
Mand
.
Mand
.
Mand
.
Mand
.
Phone activity status Not Supported
Mobile Termination control mode N/A
Keypad control N/A
Mobile Termination event reporting Not supported
Not supported
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 32 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 33
+CRSM Opt. Restricted SIM access Supported
+CPIN
+CGLA Generic UICC Logical Channel access Not suppo rted
+CRLA Opt. Restricted UICC Logical Channel access Not supported
+CCHO Opt. Open Logical Channel Not supported
+CCHC Opt. Close Logical Channel Not supported
+CUAD Opt. UICC Application Discovery Not supported
CACM Opt. Accumulated call meter N/A
+CAMM Opt. Accumulated call meter maximum N/A
+CPUC Opt. Price per unit and currency table N/A
+CCWE Opt. Call Meter maximum event Not supported
Mand
.
Enter PIN Supported
1.27. Signal quality +CSQ
Execution command returns received signal strength indication <rssi> and channel bit error rate <ber>
from the MT..
Table 22. +CSQ action command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CSQ +CSQ: <rssi>,<ber>
+CME ERROR: <err>
+CSQ=?
Value
+CSQ: (list of supported <rssi>s),(list of supported <ber>s)
<rssi>:
0 -113 dBm or less
1 -111 dBm
2...30 -109... -53 dBm
31 -51 dBm or greater
99 not known or not detectable
<ber> (in percent):
0...7 as RXQUAL values in the table in TS 45.008 [20] subclause 8.2.4
99 not known or not detectable
1.28. Clock +CCLK
Set command sets the real-time clock of the MT.
Table 23. +CCLK parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CCLK=<time> +CME ERROR: <err>
+CCLK? +CCLK: <time>
+CME ERROR: <err>
+CCLK=?
Value <time>: string type value; format is "yy/MM/dd,hh:mm:ss±zz", where
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 33 of 60 Version 1.2
characters indicate year (two last digits), month, day, hour, minutes,
seconds and time zone (indicates the difference, expressed in quarters of an
hour, between the local time and GMT; range -96...+96). E.g. 6th of May
1994, 22:10:00 GMT+2 hours equals to "94/05/06,22:10:00+08"
Page 34
1.29. Band Selection (AT$$MBAND)
This command is used to read and write of the band selection.
Table 24. AT$$MBAND Read Command
Command TE2
Response TE2
0 : auto
Result Value
Table 25. AT$$MBAND Write Command
Command TE2
Response TE2
Setting
Value
Result value
1 : 850MHz
2 : 2.1GHz
3 : Not Setting
0 : auto
1 : 850MHz
2 : 2.1GMHz
0 : Fail
1 : Success
MT2 $$MBAND? <CR>
Æ
MT2
Å
MT2 $$MBAND= <Setting value> <CR>
Æ
MT2
Å
$$MBAND: [result value] <CR>
<result_code>(OK | ERROR)
$$MBAND: [result value] <CR>
<result_code>(OK | ERROR)
1.30. Enter PIN +CPIN
Set command sends to the MT a password which is necessary before it can be operated (SIM
PIN, SIM PUK, PH-SIM, PIN, etc.). If the PIN is to be entered twice, the TA shall
automatically repeat the PIN. If no PIN request is pending, no action is taken towards MT
and an error message, +CME ERROR, is returned to TE.
Table 26. +CPIN parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CPIN=<pin>[,<newpin>] +CME ERROR: <err>
+CPIN? +CPIN: <code>
+CME ERROR: <err>
+CPIN=?
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 34 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 35
Value “READY” MT is not pending for any password
“SIM PIN” MT is waiting SIM PIN to be given
“SIM PUK” MT is waiting SIM PUK to be given
“PH-SIM PIN” MT is waiting phone-to-SIM card password
to be given
“PH-FSIM PIN” MT is waiting phone-to-very first SIM card
password to be given
“PH-FSIM PUK” MT is waiting phone-to-very first SIM card
unblocking password to be given
“SIM PIN2” MT is waiting SIM PIN2 to be given (this
<code> is recommended to be returned only
when the last executed command resulted in
PIN2 authentication failure (i.e. +CME
ERROR: 17); if PIN2 is not entered right
after the failure, it is recommended that MT
does not block its operation)
“SIM PUK2” MT is waiting SIM PUK2 to be given (this
<code> is recommended to be returned only
when the last executed command resulted in
PUK2 authentication failure (i.e. +CME
ERROR: 18); if PUK2 and new PIN2 are not
entered right after the failure, it is
recommended that MT does not
block its operation)
“PH-NET PIN” MT is waiting network personalization
password to be given
“PH-NET PUK” MT is waiting network personalization
unblocking password to be given
PH-NETSUB” PIN MT is waiting network subset
personalization password to be given
“PH-NETSUB” PUK MT is waiting network subset
personalization unblocking password to
be given
“PH-SP PIN” MT is waiting service provider
personalization password to be given
“PH-SP PUK” MT is waiting service provider
personalization unblocking password
to be given
“PH-CORP PIN” MT is waiting corporate personalization
password to be given
“PH-CORP PUK” MT is waiting corporate personalization
unblocking password to be given
1.31. Informative examples
1.31.1. Signal strength reading
Command: AT+CSQ
Expected response: +CSQ: signalstrength,BER
Signalstrength possible values:
0 -113 dBm or less
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 35 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 36

1 -111 dBm
2...30 -109... -53 dBm
31 -51 dBm or greater
1.31.2. Pin registration
The application just allows for an emergency call until PIN code is entered
Command: AT+CPIN?
Expected response: +CPIN: PinStatus
PinStatus possible values:
SIM PIN : waiting for PIN code
READY : PIN code OK
Command: AT+CPIN=”PinCode”,”NewPinCode”
Expected response: OK or ERROR
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 36 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 37

Packet Domain Command(GPRS)
1.32. UMTS packet Domain commands
This clause defines commands that a TE may use to control a MT supporting packet switched
services. Other aspects of a Packet Domain MT are described in 3GPP TS 27.060 [34].
It is anticipated that Packet Domain MTs will vary widely in functionality. At one extreme, a MT
supporting CS/PS or class-A mode of operation might support multiple PDP types as well as
circuit switched data, and use multiple external networks and QoS profiles. At the other extreme
a MT supporting only PS or class-C mode of operation might support only a single PDP type
using a single external network, and rely on the HLR to contain the PDP context definition.
A comprehensive set of Packet Domain-specifc commands is defined in clause 10.1 to provide the
flexibility needed by the more complex MT. The commands are designed to be expandable to
accommodate new PDP types and interface protocols, merely by defining new values for many of
the parameters. Multiple contexts may be activated if the interface link-layer protocol is able to
support them. The commands use the extended information and error message capabilities
described in this specification.
For MTs of intermediate complexity, most commands have simplified forms where certain
parameters may be omitted.
For the simplest MTs, and for backwards compatibility with existing communications
software, it is possible to control access to the Packet Domain using existing modemcompatible commands. A special dial-string syntax is defined for use with the D command.
This "modem compatible" mode of operation is described in subclause 10.2.
A discussion on the interaction of the AT commands, Packet Domain Management and
Packet Data Protocols, together with examples of command sequences for a number of
applications may be found in 3GPP TS 27.060 [34].
Table 27. UMTS packet Domain commands
Command Req Description Support
+CGDCONT Mand. Define PDP Context Supported
+CGDSCONT Opt. Define Secondary PDP Context Supported
+CGTFT Opt. Traffic Flow Template Supported
+CGQREQ Opt. Quality of Service Profile (Requested) Supported
+CGQMIN Opt. Quality of Service Profile (Minimum acceptable) Supported
+CGEQREQ Opt. 3G Quality of Service Profile (Requested) Supported
+CGEQMIN Opt. 3G Quality of Service Profile (Minimum acceptable) Supported
+CGEQNEG Opt. 3G Quality of Service Profile (Negotiated) Not supported
+CGATT Opt. PS attach or detach Supported
+CGACT Opt. PDP context activate or deactivate Supported
+CGCMOD Opt. PDP Context Modify Supported
+CGDATA Opt. Enter data state Supported
+CGCLOSP Opt. Configure local Octet Stream PAD parameters Not supported
+CGPADDR Opt. Show PDP address Supported
+CGAUTO Opt.
Automatic response to a network request for PDP context
activation
Not supported
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 37 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 38

_
_
(
(
(
+CGANS Opt.
Manual response to a network request for PDP context
activation
+CGCLASS Opt. GPRS mobile station class
+CGCLPAD
Opt. Configure local triple-X PAD parameters
(GPRS only)
+CGEREP Opt. Packet Domain event reporting
+CGREG Opt. GPRS network registration status
+CGSMS Opt. Select service for MO SMS messages
Not supported
Supported
Not supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
1.32.1. Define PDP Context +CGDCONT
The set command specifies PDP context parameter values for a PDP context identified by the
(local) context identification parameter, <cid>. The number of PDP contexts that may be in a
defined state at the same time is given by the range returned by the test command.
A special form of the set command, +CGDCONT= <cid> causes the values for context number
<cid> to become undefined.
The read command returns the current settings for each defined context.
The test command returns values supported as a compound value. If the MT supports several
PDP types, <PDP_type>, the parameter value ranges for each <PDP_type> are returned on a
separate line.
Table 28. +CGDCONT parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGDCONT=[<cid>
[,<PDP
[,<PDP_addr>
,<d_comp>[,<h_comp>
[,<pd1>
[,…[,pdN]]]]]]]]]
+CGDCONT? +CGDCONT: <cid>, <PDP_type>,
+CGDCONT=? +CGDCONT: (range of supported <cid>s), <PDP_type>,,,(list of supported
Value
type> [,<APN>
OK
ERROR
<APN>,<PDP_addr>,<d_comp>, <h_comp>[,<pd1>[,…[,pdN]]]
[<CR><LF>+CGDCONT:<cid>,<PDP
<h_comp>[,<pd1>[,…[,pdN]]]
[...]]
<d_comp>s),
(list of supported <h_comp>s)[,(list of supported <pd1>s)[,…[,
supported <pdN>s)]]]
[<CR><LF>+CGDCONT: (range of supported <cid>s), <PDP_type>,,,
supported <d_comp>s),
(list of supported <h_comp>s)[,(list of supported <pd1>s)[,…[,
supported <pdN>s)]]]
[...]]
<cid>: (PDP Context Identifier) a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP
context definition. The parameter is local to the TE-MT interface and is used in other
PDP context-related commands. The range of permitted values (minimum value = 1) is
type>, <APN>,<PDP_addr>,<d_comp>,
list of
list of
list of
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 38 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 39

returned by the test form of the command.
<PDP_type>: (Packet Data Protocol type) a string parameter which specifies the type of
packet data protocol
X.25 ITU-T/CCITT X.25 layer 3 (Obsolete)
IP Internet Protocol (IETF STD 5)
IPV6 Internet Protocol, version 6 (IETF RFC 2460)
OSPIH Internet Hosted Octect Stream Protocol (Obsolete)
PPP Point to Point Protocol (IETF STD 51)
<APN>: (Access Point Name) a string parameter which is a logical name that is used to
select the GGSN or the external packet data network.
If the value is null or omitted, then the subscription value will be requested.
<PDP_address>: a string parameter that identifies the MT in the address space
applicable to the PDP.
If the value is null or omitted, then a value may be provided by the TE during the PDP
startup procedure or, failing that, a dynamic address will be requested.
The read form of the command will continue to return the null string even if an address
has been allocated during the PDP startup procedure. The allocated address may be read
using the +CGPADDR command.
<d_comp>: a numeric parameter that controls PDP data compression (applicable for
SNDCP only) (refer 3GPP TS 44.065 [61])
0 - off (default if value is omitted)
1 - on (manufacturer preferred compression)
2 - V.42bis
3 - V.44
Other values are reserved.
<h_comp>: a numeric parameter that controls PDP header compression (refer 3GPP TS
44.065 [61] and 3GPP TS 25.323 [62])
0 - off (default if value is omitted)
1 - on (manufacturer preferred compression)
2 - RFC1144 (applicable for SNDCP only)
3 - RFC2507
4 - RFC3095 (applicable for PDCP only)
Other values are reserved.
<pd1>, … <pdN>: zero to N string parameters whose meanings are specific to the
<PDP_type>
1.32.2. Define Secondary PDP Context +CGDSCONT
The set command specifies PDP context parameter values for a Secondary PDP context identified
by the (local) context identification parameter, <cid>. The number of PDP contexts that may be
in a defined state at the same time is given by the range returned by the test command.
A special form of the set command, +CGDSCONT= <cid> causes the values for context number
<cid> to become undefined..
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 39 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 40
_
Table 29. +CGDCONT parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGDSCONT=[<cid> ,
<p
cid> [,<d_comp>
[,<h_comp>]]]
+CGDSCONT? +CGDSCONT: <cid>, <p_cid>, <d_comp>, <h_comp>
+CGDSCONT=? +CGDSCONT: (range of supported <cid>s), (list of <cid>s for
Value
OK
ERROR
[<CR><LF>+CGDSCONT: <cid>, <p_cid>, <d_comp>, <h_comp>
[...]]
active primary contexts), (list of supported <d_comp>s),
(list of supported <h_comp>s)
<cid>: (PDP Context Identifier) a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP
context definition. The parameter is local to the TE-MT interface and is used in other
PDP context-related commands. The range of permitted values (minimum value = 1) is
returned by the test form of the command.
<p_cid>: (Primary PDP Context Identifier) a numeric parameter which specifies a
particular PDP context definition which has been specified by use of the +CGDCONT
command. The parameter is local to the TE-MT interface. The list of permitted values is
returned by the test form of the command.
<d_comp>: a numeric parameter that controls PDP data compression (applicable for
SNDCPonly) (refer 3GPP TS 44.065 [61])
0 - off (default if value is omitted)
1 - on (manufacturer preferred compression)
2 - V.42bis
3 - V.44
Other values are reserved.
<h_comp>: a numeric parameter that controls PDP header compression (refer 3GPP TS
44.065 [61] and 3GPP TS 25.323 [62])
0 - off (default if value is omitted)
1 - on (manufacturer preferred compression)
2 - RFC1144 (applicable for SNDCP only)
3 - RFC2507
4 - RFC3095 (applicable for PDCP only)
Other values are reserved.
1.32.3. Traffic Flow Template +CGTFT
This command allows the TE to specify a Packet Filter - PF for a Traffic Flow Template - TFT that
is used in the GGSN for routing of down-link packets onto different QoS flows towards the TE.
The concept is further described in the 3GPP TS 23.060[47]. A TFT consists of from one and up
to eight Packet Filters, each identified by a unique <packet filter identifier>. A Packet
Filter also has an <evaluation precedence index> that is unique within all TFTs associated
with all PDP contexts that are associated with the same PDP address.
The set command specifies a Packet Filters that is to be added to the TFT stored in the MT and
used for the context identified by the (local) context identification parameter, <cid>. The
specified TFT will be stored in the GGSN only at activation or MS-initiated modification of the
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 40 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 41

related context. Since this is the same parameter that is used in the +CGDCONT and
+CGDSCONT commands, the +CGTFT command is effectively an extension to these commands.
The Packet Filters consist of a number of parameters, each of which may be set to a separate
value.
A special form of the set command, +CGTFT= <cid> causes all of the Packet Filters in the TFT for
context number <cid> to become undefined. At any time there may exist only one PDP context
with no associated TFT amongst all PDP contexts associated to one PDP address. At an attempt
to delete a TFT, which would violate this rule, an ERROR or +CME ERROR response is returned.
Extended error responses are enabled by the +CMEE command.
The read command returns the current settings for all Packet Filters for each defined context.
The test command returns values supported as a compound value. If the MT supports several
PDP types, the parameter value ranges for each PDP type are returned on a separate line. TFTs
shall be used for PDP-type IP and PPP only. For PDP-type PPP a TFT is applicable only when IP
traffic is carried over PPP. If PPP carries header-compressed IP packets, then a TFT cannot be
used.
Table 30. + CGTFT parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGTFT=[<cid>,
[<packet filter
identifier>,
<evaluation
precedence index>
[,<source address and
subnet mask>
[,<protocol number
(ipv4) / next header
(ipv6)>
[,<destination port
range> [,<source port
range> [,<ipsec
security parameter
index (spi)> [,<type
of service (tos)
(ipv4) and mask /
traffic class (ipv6)
and mask> [,<flow
label (ipv6)>
]]]]]]]]]
OK
ERROR
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 41 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 42

_
_
+CGTFT?
+CGTFT=?
+CGTFT: <cid>, <packet filter identifier>, <evaluation
precedence index>, <source address and subnet mask>, <protocol
number (ipv4) / next header (ipv6)>, <destination port range>,
<source port range>, <ipsec security parameter index (spi)>,
<type of service (tos) (ipv4) and mask / traffic class (ipv6)
and mask>, <flow label (ipv6)>
[<CR><LF>+CGTFT: <cid>, <packet filter identifier>, <evaluation
precedence index>, <source address and subnet mask>, <protocol
number (ipv4) / next header (ipv6)>, <destination port range>,
<source port range>, <ipsec security parameter index (spi)>,
<type of service (tos) (ipv4) and mask / traffic class (ipv6)
and mask>, <flow label (ipv6)>
[…]]
+CGTFT: <PDP
identifier>s), (list of supported <evaluation precedence
index>s), (list of supported <source address and subnet mask>s),
(list of supported <protocol number (ipv4) / next header
(ipv6)>s), (list of supported <destination port range>s), (list
of supported <source port range>s), (list of supported <ipsec
security parameter index (spi)>s), (list of supported <type of
service (tos) (ipv4) and mask / traffic class (ipv6) and
mask>s), (list of supported <flow label (ipv6)>s)
type>, (list of supported <packet filter
Value
[<CR><LF>+CGTFT: <PDP
identifier>s), (list of supported <evaluation precedence
index>s), (list of supported <source address and subnet mask>s),
(list of supported <protocol number (ipv4) / next header
(ipv6)>s), (list of supported <destination port range>s), (list
of supported <source port range>s), (list of supported <ipsec
security parameter index (spi)>s), (list of supported <type of
service (tos) (ipv4) and mask / traffic class (ipv6) and
mask>s), (list of supported <flow label (ipv6)>s)
[…]]
<cid>: a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP context definition (see the
+CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands).
The following parameters are defined in 3GPP TS 23.060[47] -
<packet filter identifier>: Numeric parameter, value range from 1 to 8.
<source address and subnet mask>: Consists of dot-separated numeric (0-255)
parameters on the form 'a1.a2.a3.a4.m1.m2.m3.m4', for IPv4 and
'a1.a2.a3.a4.a5.a6.a7.a8.a9.a10.a11.a12.a13.a14.a15.a16.
m1.m2.m3.m4.m5.m6.m7.m8.m9.m10.m11.m12.m13.m14.m15.m16', for IPv6.
<protocol number (ipv4) / next header (ipv6)>: Numeric parameter,
value range from 0 to 255.
type>, (list of supported <packet filter
<destination port range>: Consists of dot-separated numeric (0-65535)
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 42 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 43

parameters on the form 'f.t'.
<source port range>:Consists of dot-separated numeric (0-65535) parameters on the
form 'f.t'.
<ipsec security parameter index (spi)>: Hexadecimal parameter,
value range from 00000000 to FFFFFFFF.
<type of service (tos) (ipv4) and mask / traffic class (ipv6)
and mask>:
Dot-separated numeric (0-255) parameters on the form 't.m'.
<flow label (ipv6)>: Hexadecimal parameter, value range from 00000 to FFFFF.
Valid for IPv6 only.
<evaluation precedence index>: Numeric parameter, value range from 0 to 255.
Some of the above listed attributes may coexist in a Packet Filter while others mutually exclude
each other, the possible combinations are shown in 3GPP TS 23.060[47].
1.32.4. Quality of Service Profile (Requested) +CGQREQ
This command allows the TE to specify a Quality of Service Profile that is used when the MT
sends an Activate PDP Context Request message to the network.
The set command specifies a profile for the context identified by the (local) context identification
parameter, <cid>. Since this is the same parameter that is used in the +CGDCONT and
+CGDSCONT commands, the +CGQREQ command is effectively an extension to these
commands. The QoS profile consists of a number of parameters, each of which may be set to a
separate value.
A special form of the set command, +CGQREQ= <cid> causes the requested profile for context
number <cid> to become undefined.
The read command returns the current settings for each defined context.
The test command returns values supported as a compound value. If the MT supports several
PDP types, the parameter value ranges for each PDP type are returned on a separate line.
Table 31. + CGQREQ parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGQREQ=[<cid>
[,<precedence>
[,<delay>
[,<reliability.>
[,<peak>
[,<mean>]]]]]]
+CGQREQ? +CGQREQ:<cid>,<precedence>,<delay>,<reliability>,
OK
ERROR
<peak>,<mean>
[<CR><LF>+CGQREQ:<cid>,<precedence>,<delay>,
<reliability.>,<peak>,<mean>[…]]
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 43 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 44
[
+CGQREQ=? +CGQREQ: <PDP_type>, (list of supported <precedence>s), (list
Value
of supported <delay>s), (list of supported <reliability>s) ,
(list of supported <peak>s), (list of supported <mean>s)
[<CR><LF>+CGQREQ:<PDP_type>,(list of supported
<precedence>s), (list of supported <delay>s), (list of
supported <reliability>s) , (list of supported <peak>s), (list
of supported <mean>s)[…]]
<cid>: a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP context definition (see the
+CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands).
The following parameters are defined in 3GPP TS 23.107 [46]:
<precedence>: a numeric parameter which specifies the precedence class
<delay>: a numeric parameter which specifies the delay class
<reliability>: a numeric parameter which specifies the reliability class
<peak>: a numeric parameter which specifies the peak throughput class
<mean>: a numeric parameter which specifies the mean throughput class
If a value is omitted for a particular class then the value is considered to be
unspecified.
1.32.5. Quality of Service Profile (Minimum acceptable) +CGQMIN
This command allows the TE to specify a minimum acceptable profile which is checked by the
MT against the negotiated profile returned in the Activate PDP Context Accept message.
The set command specifies a profile for the context identified by the (local) context identification
parameter, <cid>. Since this is the same parameter that is used in the +CGDCONT and
+CGDSCONT commands, the +CGQMIN command is effectively an extension to these commands.
The QoS profile consists of a number of parameters, each of which may be set to a separate
value.
A special form of the set command, +CGQMIN= <cid> causes the minimum acceptable profile for
context number <cid> to become undefined. In this case no check is made against the
negotiated profile.
The read command returns the current settings for each defined context.
The test command returns values supported as a compound value. If the MT supports several
PDP types, the parameter value ranges for each PDP type are returned on a separate line.
Table 32. + CGQMIN parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGQMIN=[<cid>
,<precedence >
[,<delay>
[,<reliability.>
[,<peak>
[,<mean>]]]]]]
+CGQMIN? +CGQMIN: <cid>, <precedence >, <delay>, <reliability>,
OK
ERROR
<peak>,<mean>[<CR><LF>+CGQMIN: <cid>, <precedence >, <delay>,
<reliability.>,<peak>,<mean>[…]]
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 44 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 45

_
+CGQMIN=? +CGQMIN: <PDP_type>, (list of supported <precedence>s), (list
Value
of supported <delay>s), (list of supported <reliability>s) ,
(list of supported <peak>s), (list of supported <mean>s)
[<CR><LF>+CGQMIN: <PDP
<precedence>s), (list of supported <delay>s), (list of
supported <reliability>s) , (list of supported <peak>s), (list
of supported <mean>s)[…]]
<cid>: a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP context definition (see the
+CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands).
The following parameters are defined in -3GPP TS 23.107 [46]:
<precedence>: a numeric parameter which specifies the precedence class
<delay>: a numeric parameter which specifies the delay class
<reliability>: a numeric parameter which specifies the reliability class
<peak>: a numeric parameter which specifies the peak throughput class
<mean>: a numeric parameter which specifies the mean throughput class
If a value is omitted for a particular class then this class is not checked
type>, (list of supported
1.32.6. 3G Quality of Service Profile (Requested) +CGEQREQ
This command allows the TE to specify a UMTS Quality of Service Profile that is used when the
MT sends an Activate PDP Context Request message to the network.
The set command specifies a profile for the context identified by the (local) context identification
parameter, <cid>. The specified profile will be stored in the MT and sent to the network only at
activation or MS-initiated modification of the related context. Since this is the same parameter
that is used in the +CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands, the +CGEQREQ command is
effectively an extension to these commands. The QoS profile consists of a number of parameters,
each of which may be set to a separate value.
A special form of the set command, +CGEQREQ= <cid> causes the requested profile for context
number <cid> to become undefined.
The read command returns the current settings for each defined context.
The test command returns values supported as a compound value. If the MT supports several
PDP types, the parameter value ranges for each PDP type are returned on a separate line..
Table 33. + CGEQREQ parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGEQREQ=[<cid> [,<Traffic
class> [,<Maximum bitrate
UL> [,<Maximum bitrate DL>
[,<Guaranteed bitrate UL>
[,<Guaranteed bitrate DL>
[,<Delivery order>
[,<Maximum SDU size>
[,<SDU error ratio>
[,<Residual bit error
ratio> [,<Delivery of
erroneous SDUs>
[,<Transfer delay>
OK
ERROR
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 45 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 46

_
_
[,<Traffic handling
priority> ]]]]]]]]]]]]]
+CGEQREQ?
+CGEQREQ=?
Value
+CGEQREQ: <cid>, <Traffic class> ,<Maximum bitrate
UL> ,<Maximum bitrate DL> ,<Guaranteed bitrate UL>
,<Guaranteed bitrate DL> ,<Delivery order> ,<Maximum
SDU size> ,<SDU error ratio> ,<Residual bit error
ratio> ,<Delivery of erroneous SDUs> ,<Transfer
delay> ,<Traffic handling priority>
[<CR><LF>+CGEQREQ: <cid>, <Traffic class> ,<Maximum
bitrate UL> ,<Maximum bitrate DL> ,<Guaranteed
bitrate UL> ,<Guaranteed bitrate DL> ,<Delivery
order> ,<Maximum SDU size> ,<SDU error ratio>
,<Residual bit error ratio> ,<Delivery of erroneous
SDUs> ,<Transfer delay> ,<Traffic handling priority>
[…]]
+CGEQREQ: <PDP
class>s) ,(list of supported <Maximum bitrate UL>s),
(list of supported <Maximum bitrate DL>s), (list of
supported <Guaranteed bitrate UL>s), (list of
supported <Guaranteed bitrate DL>s),(list of
supported <Delivery order>s) ,(list of supported
<Maximum SDU size>s) ,(list of supported <SDU error
ratio>s) ,(list of supported <Residual bit error
ratio>s) ,(list of supported <Delivery of erroneous
SDUs>s) ,(list of supported <Transfer delay>s)
,(list of supported <Traffic handling priority>s)
[<CR><LF>+CGEQREQ: <PDP
<Traffic class>s) ,(list of supported <Maximum
bitrate UL>s), (list of supported <Maximum bitrate
DL>s), (list of supported <Guaranteed bitrate UL>s),
(list of supported <Guaranteed bitrate DL>s),(list
of supported <Delivery order>s) ,(list of supported
<Maximum SDU size>s) ,(list of supported <SDU error
ratio>s) ,(list of supported <Residual bit error
ratio>s) ,(list of supported <Delivery of erroneous
SDUs>s) ,(list of supported <Transfer delay>s)
,(list of supported <Traffic handling priority>s)
[…]]
<cid>: a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP context
definition (see +CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands).
type>, (list of supported <Traffic
type>, (list of supported
The following parameters are defined in 3GPP TS 23.107 [46] -
<Traffic class>: a numeric parameter that indicates the type of
application for which the UMTS bearer service is optimised.
0 - conversational
1 - streaming
2 - interactive
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 46 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 47

3 - background
4 - subscribed value
If the Traffic class is specified as conversational or streaming, then the
Guaranteed and Maximum bitrate parameters should also be
provided. Other values are reserved.
<Maximum bitrate UL>: a numeric parameter that indicates the
maximum number of kbits/s delivered to UMTS (up-link traffic) at a
SAP. As an example a bitrate of 32kbit/s would be specified as '32'
(e.g. AT+CGEQREQ=…,32, …). This parameter should be provided
if the Traffic class is specified as conversational or streaming (refer TS
24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Maximum bitrate DL>: a numeric parameter that indicates the
maximum number of kbits/s delivered by UMTS (down-link traffic) at
a SAP. As an example a bitrate of 32kbit/s would be specified as '32'
(e.g. AT+CGEQREQ=…,32, …). If the parameter is set to '0' the
subscribed value will be requested. This parameter should be provided
if the Traffic class is specified as conversational or streaming (refer TS
24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Guaranteed bitrate UL>: a numeric parameter that indicates the
guaranteed number of kbits/s delivered to UMTS (up-link traffic) at a
SAP (provided that there is data to deliver). As an example a bitrate of
32kbit/s would be specified as '32' (e.g. AT+CGEQREQ=…,32, …). If
the parameter is set to '0' the subscribed value will be requested. This
parameter should be provided if the Traffic class is specified as
conversational or streaming (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Guaranteed bitrate DL>: a numeric parameter that indicates the
guaranteed number of kbits/s delivered by UMTS (down-link traffic)
at a SAP (provided that there is data to deliver). As an example a
bitrate of 32kbit/s would be specified as '32' (e.g.
AT+CGEQREQ=…,32, …). If the parameter is set to '0' the
subscribed value will be requested. This parameter should be provided
if the Traffic class is specified as conversational or streaming (refer TS
24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Delivery order>: a numeric parameter that indicates whether the
UMTS bearer shall provide in-sequence SDU delivery or not.
0 - no
1 - yes
2 - subscribed value.
Other values are reserved.
<Maximum SDU size>: a numeric parameter (1,2,3,…) that indicates
the maximum allowed SDU size in octets. If the parameter is set to '0'
the subscribed value will be requested (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause
10.5.6.5).
<SDU error ratio>: a string parameter that indicates the target
value for the fraction of SDUs lost or detected as erroneous. SDU error
ratio is defined only for conforming traffic. The value is specified as
'mEe'. As an example a target SDU error ratio of 5•10
-3
would be
specified as '5E3' (e.g. AT+CGEQREQ=…,”5E3”,…). '0E0' means
subscribed value (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Residual bit error ratio>: a string parameter that indicates
the target value for the undetected bit error ratio in the delivered
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 47 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 48

b
SDUs. If no error detection is requested, Residual bit error ratio
indicates the bit error ratio in the delivered SDUs. The value is
specified as 'mEe'. As an example a target residual bit error ratio of
-3
would be specified as '5E3' (e.g. AT+CGEQREQ=…,”5E3”,…).
5•10
'0E0' means subscribed value (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Delivery of erroneous SDUs>: a numeric parameter that
indicates whether SDUs detected as erroneous shall be delivered or
not.
0 - no
1 - yes
2 - no detect
3 - subscribed value
Other values are reserved.
<Transfer delay>: a numeric parameter (0,1,2,…) that indicates the
targeted time between request to transfer an SDU at one SAP to its
delivery at the other SAP, in milliseconds. If the parameter is set to '0'
the subscribed value will be requested (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause
10.5.6.5).
<Traffic handling priority>: a numeric parameter (1,2,3,…)
that specifies the relative importance for handling of all SDUs
elonging to the UMTS bearer compared to the SDUs of other bearers.
If the parameter is set to '0' the subscribed value will be requested
(refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<PDP_type>: (see +CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands).
If a value is omitted for a particular class then the value is
considered to be unspecified
1.32.7. 3G Quality of Service Profile (Minimum acceptable) +CGEQMIN
This command allows the TE to specify a minimum acceptable profile, which is checked by
the MT against the negotiated profile returned in the Activate/Modify PDP Context Accept
message.
The set command specifies a profile for the context identified by the (local) context
identification parameter, <cid>. The specified profile will be stored in the MT and checked
against the negotiated profile only at activation or MS-initiated modification of the related
context. Since this is the same parameter that is used in the +CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT
commands, the +CGEQMIN command is effectively an extension to these commands. The
QoS profile consists of a number of parameters, each of which may be set to a separate
value.
A special form of the set command, +CGEQMIN= <cid> causes the minimum acceptable
profile for context number <cid> to become undefined. In this case no check is made
against the negotiated profile.
The read command returns the current settings for each defined context.
The test command returns values supported as a compound value. If the MT supports
several PDP types, the parameter value ranges for each PDP type are returned on a separate
line
.
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 48 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 49

Table 34. + CGEQMIN parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGEQMIN=[<cid> [,<Traffic
class> [,<Maximum bitrate
UL> [,<Maximum bitrate DL>
OK
ERROR
[,<Guaranteed bitrate UL>
[,<Guaranteed bitrate DL>
[,<Delivery order>
[,<Maximum SDU size> [,<SDU
error ratio> [,<Residual
bit error ratio>
[,<Delivery of erroneous
SDUs> [,<Transfer delay>
[,<Traffic handling
priority>]]]]]]]]]]]]]
+CGEQMIN?
+CGEQMIN: <cid>, <Traffic class> ,<Maximum
bitrate UL>, <Maximum bitrate DL> ,<Guaranteed
bitrate UL> ,<Guaranteed bitrate DL>, <Delivery
order> ,<Maximum SDU size> ,<SDU error ratio>
,<Residual bit error ratio> ,<Delivery of
erroneous SDUs> ,<Transfer delay> ,<Traffic
handling priority>
[<CR><LF>+CGEQMIN: <cid>, <Traffic class>
,<Maximum bitrate UL> ,<Maximum bitrate DL>
,<Guaranteed bitrate UL> ,<Guaranteed bitrate
DL>, <Delivery order> ,<Maximum SDU size> ,<SDU
error ratio> ,<Residual bit error ratio>
,<Delivery of erroneous SDUs> ,<Transfer delay>
,<Traffic handling priority>
[…]]
+CGEQMIN=?
+CGEQMIN: <PDP_type>, (list of supported
<Traffic class>s) ,(list of supported <Maximum
bitrate UL>s) ,(list of supported <Maximum
bitrate DL>s), (list of supported <Guaranteed
bitrate UL>s), (list of supported <Guaranteed
bitrate DL>s) ,(list of supported <Delivery
order>s) ,(list of supported <Maximum SDU
size>s) ,(list of supported <SDU error ratio>s)
,(list of supported <Residual bit error ratio>s)
,(list of supported <Delivery of erroneous
SDUs>s) ,(list of supported <Transfer delay>s)
,(list of supported <Traffic handling
priority>s)
[<CR><LF>+CGEQMIN: <PDP_type>, (list of
supported <Traffic class>s) ,(list of supported
<Maximum bitrate UL>s), (list of supported
<Maximum bitrate DL>s) ,(list of supported
<Guaranteed bitrate UL >s), (list of supported
<Guaranteed bitrate DL >s) ,(list of supported
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 49 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 50
T
Value
<Delivery order>s) ,(list of supported <Maximum
SDU size>s) ,(list of supported <SDU error
ratio>s) ,(list of supported <Residual bit error
ratio>s) ,(list of supported <Delivery of
erroneous SDUs>s) ,(list of supported <Transfer
delay>s) ,(list of supported <Traffic handling
priority>s)
[…]]
<cid>: a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP
context definition (see +CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT
commands).
he following parameters are defined in 3GPP TS 23.107
[46] -
<Traffic class>: a numeric parameter that indicates the type
of application for which the UMTS bearer service is optimised.
0 - conversational
1 - streaming
2 - interactive
3 - background
Other values are reserved.
<Maximum bitrate UL>: a numeric parameter that indicates
the maximum number of kbits/s delivered to UMTS (up-link
traffic) at a SAP. As an example a bitrate of 32kbit/s would be
specified as '32' (e.g. AT+CGEQMIN=…,32, …) (refer TS
24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Maximum bitrate DL>: a numeric parameter that indicates
the maximum number of kbits/s delivered by UMTS (down-link
traffic) at a SAP. As an example a bitrate of 32kbit/s would be
specified as '32' (e.g. AT+CGEQMIN=…,32, …) (refer TS
24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Guaranteed bitrate UL>: a numeric parameter that
indicates the guaranteed number of kbits/s delivered to UMTS
(up-link traffic) at a SAP (provided that there is data to deliver).
As an example a bitrate of 32kbit/s would be specified as '32'
(e.g. AT+CGEQMIN=…,32, …) (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause
10.5.6.5).
<Guaranteed bitrate DL>: a numeric parameter that
indicates the guaranteed number of kbits/s delivered by UMTS
(down-link traffic) at a SAP (provided that there is data to
deliver). As an example a bitrate of 32kbit/s would be specified
as '32' (e.g. AT+CGEQMIN=…,32, …) (refer TS 24.008 [8]
subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Delivery order>: a numeric parameter that indicates
whether the UMTS bearer shall provide in-sequence SDU
delivery or not.
0 - no
1 - yes
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 50 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 51

Other values are reserved.
<Maximum SDU size>: a numeric parameter (1,2,3,…) that
indicates the maximum allowed SDU size in octets (refer TS
24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<SDU error ratio>: a string parameter that indicates the
target value for the fraction of SDUs lost or detected as
erroneous. SDU error ratio is defined only for conforming
traffic. The value is specified as 'mEe'. As an example a target
SDU error ratio of 5•10
-3
would be specified as '5E3' (e.g.
AT+CGEQMIN=…,”5E3”,…) (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause
10.5.6.5).
<Residual bit error ratio>: a string parameter that
indicates the target value for the undetected bit error ratio in the
delivered SDUs. If no error detection is requested, Residual bit
error ratio indicates the bit error ratio in the delivered SDUs.
The value is specified as 'mEe'. As an example a target residual
bit error ratio of 5•10
-3
would be specified as '5E3' (e.g.
AT+CGEQMIN=…,”5E3”,…) (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause
10.5.6.5).
<Delivery of erroneous SDUs>: a numeric parameter
that indicates whether SDUs detected as erroneous shall be
delivered or not.
0 - no
1 - yes
2 - no detect
Other values are reserved.
<Transfer delay>: a numeric parameter (0,1,2,…) that
indicates the targeted time between request to transfer an SDU
at one SAP to its delivery at the other SAP, in milliseconds
(refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Traffic handling priority>: a numeric parameter
(1,2,3,…) that specifies the relative importance for handling of
all SDUs belonging to the UMTS bearer compared to the SDUs
of other bearers (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<PDP_type>: (see +CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT
commands).
If a value is omitted for a particular class then the value is
considered to be unspecified.
1.32.8. 3G Quality of Service Profile (Negotiated) +CGEQNEG
This command allows the TE to retrieve the negotiated QoS profiles returned in the Activate
PDP Context Accept message.
The execution command returns the negotiated QoS profile for the specified context
identifiers, <cid>s. The QoS profile consists of a number of parameters, each of which may
have a separate value.
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 51 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 52
The test command returns a list of <cid>s associated with active contexts
Table 35. +CGEQNEG action command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGEQNEG
=[<cid>[,<cid>
[,…]]]
+CGEQNEG: <cid>, <Traffic class> ,<Maximum bitrate UL>,
<Maximum bitrate DL> ,<Guaranteed bitrate UL>, <Guaranteed
bitrate DL> ,<Delivery order> ,<Maximum SDU size> ,<SDU error
ratio> ,<Residual bit error ratio> ,<Delivery of erroneous
SDUs> ,<Transfer delay> ,<Traffic handling priority>
[<CR><LF>+CGEQNEG: <cid>, <Traffic class> ,<Maximum bitrate
UL>, <Maximum bitrate DL> ,<Guaranteed bitrate UL>,
<Guaranteed bitrate DL> ,<Delivery order> ,<Maximum SDU size>
,<SDU error ratio> ,<Residual bit error ratio> ,<Delivery of
erroneous SDUs> ,<Transfer delay> ,<Traffic handling
priority>
[…]]
+CGEQNEG=? +CGEQNEG: (list of <cid>s associated with active contexts)
Value
<cid>: a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP context definition (see
+CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands).
The following parameters are defined in 3GPP TS 23.107 [46] -
<Traffic class>: a numeric parameter that indicates the type of application for
which the UMTS bearer service is optimised.
0 - conversational
1 - streaming
2 - interactive
3 - background
Other values are reserved.
<Maximum bitrate UL>: a numeric parameter that indicates the maximum
number of kbits/s delivered to UMTS (up-link traffic) at a SAP. As an example a
bitrate of 32kbit/s would be specified as '32' (e.g. +CGEQNEG:…,32, …) (refer TS
24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Maximum bitrate DL>: a numeric parameter that indicates the maximum
number of kbits/s delivered by UMTS (down-link traffic) at a SAP As an example a
bitrate of 32kbit/s would be specified as '32' (e.g. +CGEQNEG:…,32, …) (refer TS
24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Guaranteed bitrate UL>: a numeric parameter that indicates the guaranteed
number of kbits/s delivered to UMTS (up-link traffic) at a SAP (provided that there
is data to deliver). As an example a bitrate of 32kbit/s would be specified as '32'
(e.g. +CGEQNEG:…,32, …) (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Guaranteed bitrate DL>: a numeric parameter that indicates the guaranteed
number of kbits/s delivered by UMTS (down-link traffic) at a SAP (provided that
there is data to deliver). As an example a bitrate of 32kbit/s would be specified as
'32' (e.g. +CGEQNEG:…,32, …) (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Delivery order>: a numeric parameter that indicates whether the UMTS bearer
shall provide in-sequence SDU delivery or not.
0 - no
1 - yes
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 52 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 53
Other values are reserved.
<Maximum SDU size>: a numeric parameter that (1,2,3,…) indicates the
maximum allowed SDU size in octets (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<SDU error ratio>: a string parameter that indicates the target value for the
fraction of SDUs lost or detected as erroneous. SDU error ratio is defined only for
conforming traffic. The value is specified as 'mEe'. As an example a target SDU
error ratio of 5•10
-3
would be specified as '5E3' (e.g. +CGEQNEG:…,”5E3”,…)
(refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Residual bit error ratio>: a string parameter that indicates the target
value for the undetected bit error ratio in the delivered SDUs. If no error detection is
requested, Residual bit error ratio indicates the bit error ratio in the delivered SDUs.
The value is specified as 'mEe'. As an example a target residual bit error ratio of
-3
5•10
would be specified as '5E3' (e.g. +CGEQNEG:…,”5E3”,…) (refer TS
24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Delivery of erroneous SDUs>: a numeric parameter that indicates whether
SDUs detected as erroneous shall be delivered or not.
0 - no
1 - yes
2 - no detect
Other values are reserved.
<Transfer delay>: a numeric parameter (0,1,2,…) that indicates the targeted
time between request to transfer an SDU at one SAP to its delivery at the other
SAP, in milliseconds (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
<Traffic handling priority>: a numeric parameter (1,2,3,…) that specifies
the relative importance for handling of all SDUs belonging to the UMTS bearer
compared to the SDUs of other bearers (refer TS 24.008 [8] subclause 10.5.6.5).
If a value is omitted for a particular class then the value is considered to
be unspecified.
1.32.9. PS attach or detach +CGATT
The execution command is used to attach the MT to, or detach the MT from, the Packet
Domain service. After the command has completed, the MT remains in V.25ter command
state. If the MT is already in the requested state, the command is ignored and the OK
response is returned. If the requested state cannot be achieved, an ERROR or +CME ERROR
response is returned. Extended error responses are enabled by the +CMEE command.
Any active PDP contexts will be automatically deactivated when the attachment state
changes to detached.
The read command returns the current Packet Domain service state.
The test command is used for requesting information on the supported Packet Domain
service states.
NOTE: This command has the characteristics of both the V.25ter action and parameter
commands. Hence it has the read form in addition to the execution/set and test forms
.
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 53 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 54

Table 36. + CGATT parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGATT=
[<state>]
OK
ERROR
+CGATT? +CGATT: <state>
+CGATT=? +CGATT: (list of supported <state>s)
Value
<state>: indicates the state of PS attachment
0 - detached
1 - attached
Other values are reserved and will result in an ERROR response to the execution
command.
1.32.10. PDP context activate or deactivate +CGACT
The execution command is used to activate or deactivate the specified PDP context (s). After
the command has completed, the MT remains in V.25ter command state. If any PDP context
is already in the requested state, the state for that context remains unchanged. If the
requested state for any specified context cannot be achieved, an ERROR or +CME ERROR
response is returned. Extended error responses are enabled by the +CMEE command. If the
MT is not PS attached when the activation form of the command is executed, the MT first
performs a PS attach and them attempts to activate the specified contexts. If the attach fails
then the MT responds with ERROR or, if extended error responses are enabled, with the
appropriate failure-to-attach error message.
If no <cid>s are specified the activation form of the command activates all defined contexts.
If no <cid>s are specified the deactivation form of the command deactivates all active
contexts.
The read command returns the current activation states for all the defined PDP contexts.
The test command is used for requesting information on the supported PDP context
activation states.
NOTE. This command has the characteristics of both the V.25ter action and parameter
commands. Hence it has the read form in addition to the execution/set and test forms
.
Table 37. + CGACT parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGACT=[<state>
[,<cid>[,<cid>[,…
OK
ERROR
]]]]
+CGACT? +CGACT:<cid>,<state>[<CR><LF>+CGACT:<cid>,<state>[...]]
+CGACT=? +CGACT: (list of supported <state>s)
Value
<state>: indicates the state of PDP context activation
0 - deactivated
1 - activated
Other values are reserved and will result in an ERROR response to the
execution command.
<cid>: a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP context definition
(see the +CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands).
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 54 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 55

1.32.11. PDP Context Modify +CGCMOD
The execution command is used to modify the specified PDP context (s) with repect to QoS
profiles and TFTs. After the command has completed, the MT returns to V.25ter online data
state. If the requested modification for any specified context cannot be achieved, an ERROR
or +CME ERROR response is returned. Extended error responses are enabled by the +CMEE
command.
If no <cid>s are specified the activation form of the command modifies all active contexts.
The test command returns a list of <cid>s associated with active contexts
Table 38. + CGCMOD parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGCMOD=[<cid>
[,<cid>[,…]]]
+CGCMOD=? +CGCMOD: (list of <cid>s associated with active contexts)
Value
OK
ERROR
<cid>: a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP context definition (see
the +CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands).
.
1.32.12. Enter data state +CGDATA
The execution command causes the MT to perform whatever actions are necessary to
establish communication between the TE and the network using one or more Packet
Domain PDP types. This may include performing a PS attach and one or more PDP context
activations. If the <L2P> parameter value is unacceptable to the MT, the MT shall return an
ERROR or +CME ERROR response. Otherwise, the MT issues the intermediate result code
CONNECT and enters V.25ter online data state.
Commands following +CGDATA command in the AT command line shall not be processed
by the MT.
The detailed behaviour after the online data state has been entered is dependent on the PDP
type. It is described briefly in 3GPP TS 27.060[34] and in more detail in 3GPP TS 29.061[39]
and the specifications for the relevant PDPs. PS attachment and PDP context activation
procedures may take place prior to or during the PDP startup if they have not already been
performed using the +CGATT and +CGACT commands.
If context activation takes place during the PDP startup, one or more <cid>s may be
specified in order to provide the information needed for the context activation request(s).
During each PDP startup procedure the MT may have access to some or all of the following
information -
The MT may have a priori knowledge, for example, it may implement only one PDP type.
The command may have provided an <L2P> parameter value.
The TE may provide a PDP type and/or PDP address to the MT during in the PDP startup procedure.
If any of this information is in conflict, the command will fail.
Any PDP type and/or PDP address present in the above information shall be compared with
the PDP type and/or PDP address in any context definitions specified in the command in the
order in which their <cid>s appear. For a context definition to match -
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 55 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 56
The PDP type must match exactly.
The PDP addresses are considered to match if they are identical or if either or both addresses are
unspecified. For example, a PPP NCP request specifying PDP type = IP and no PDP address would cause
the MT to search through the specified context definitions for one with PDP type = IP and any PDP
address.
The context shall be activated using the matched value for PDP type and a static PDP
address if available, together with the other information found in the PDP context definition.
If a static PDP address is not available then a dynamic address is requested.
If no <cid> is given or if there is no matching context definition, the MT shall attempt to
activate the context with whatever information is available to the MT. The other context
parameters shall be set to their default values.
If the activation is successful, data transfer may proceed.
After data transfer is complete, and the layer 2 protocol termination procedure has
completed successfully, the V.25ter command state is re-entered and the MT returns the
final result code OK.
In the event of an erroneous termination or a failure to start up, the V.25ter command state
is re-entered and the MT returns the final result code NO CARRIER or, if enabled, +CME
ERROR. Attach, activate and other errors may be reported.
Table 39.
+CGDATA=[<L2P> ,[<cid>
[,<cid> [,…]]]]
+ CGDATA parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
CONNECT
ERROR
+CGDATA=? +CGDATA: (list of supported <L2P>s)
Value
<L2P>: a string parameter that indicates the layer 2 protocol to be used
between the TE and MT
NULL none, for PDP type OSP:IHOSS (Obsolete)
PPP Point-to-point protocol for a PDP such as IP
PAD character stream for X.25 character (triple X PAD) mode
(Obsolete)
X25 X.25 L2 (LAPB) for X.25 packet mode (Obsolete)
M-xxxx manufacturer-specific protocol (xxxx is an alphanumeric
string)
If the value is omitted, the layer 2 protocol is unspecified. Other values
are reserved and will result in an ERROR response.
<cid>: a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP context
definition (see the +CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands).
1.32.13. Show PDP address +CGPADDR
The execution command returns a list of PDP addresses for the specified context identifiers.
The test command returns a list of defined <cid>s
.
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 56 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 57
Table 40. + CGPADDR parameter command syntax
Command Possible response(s)
+CGPADDR=[<cid>
[,<cid> [,…]]]
+CGPADDR=? +CGPADDR: (list of defined <cid>s)
Value
+CGPADDR: <cid>,<PDP_addr>
[<CR><LF>+CGPADDR: <cid>,<PDP_addr>
[...]]
<cid>: a numeric parameter which specifies a particular PDP context definition
(see the +CGDCONT and +CGDSCONT commands). If no <cid> is
specified, the addresses for all defined contexts are returned.
<PDP_address>: a string that identifies the MT in the address
space applicable to the PDP. The address may be static or dynamic.
For a static address, it will be the one set by the +CGDCONT and
+CGDSCONT commands when the context was defined. For a
dynamic address it will be the one assigned during the last PDP
context activation that used the context definition referred to by
<cid>. <PDP_address> is omitted if none is available.
1.33. Modem compatibility commands
Table 41. Modem compatibility commands
Command Req Description Support
D Dial(request packet domain service or packet domain IP
service)
Supported
1.34. Informative examples
1.34.1. UMTS Connection
Command:
AT+CGDCONT=%CID%,"%PDPTYPE%","%APN%","%PDPADDRESS_NONE%",%DCOMP%,%H
COMP%
Expected response: OK
Command:
AT+CGEQREQ=%CID%,%REQ_TCLSS%,%REQ_MBRUL%,%REQ_MBRDL%,%REQ_GBRUL
%,%REQ_GBRDL%,%REQ_DORDR%,%REQ_MSDU%,"%REQ_SDUER%","%REQ_RBER%",%
REQ_DESDU%,%REQ_TRDELAY%,%REQ_TRHP%
Expected response: OK
Command:
AT+CGEQMIN=%CID%,%MIN_TCLSS%,%MIN_MBRUL%,%MIN_MBRDL%,%MIN_GBRUL%,
%MIN_GBRDL%,%MIN_DORDR%,%MIN_MSDU%,"%MIN_SDUER%","%MIN_RBER%",%MIN_
DESDU%,%MIN_TRDELAY%,%MIN_TRHP%
Expected response: OK
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 57 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 58

Synchronous data mode commands
Table 42. ITU-T V80ter Synchronous data mode command
Command Req Description Support
+ES=<orig_rq
st>
<orig_fbk>,<a
ns_fbk>
+ESA=<trans
_idle>,<frame
d_idle>,<fram
ed_un_ov>,<h
d_auto>,<crc_
type>,<nrzi_e
n>,<sync1>,<
sync2>
Man
Man
Enables the Synchronous Mode Values per spec
<orig_rqst> – 6
<orig_fbk> –undefined
<ans_fbk> – 1
Preferred message storage Values per spec
<trans_idle> –0
<framed_idle>– Undefined
<framed_un_ov> – Undefined
<hd_auto> –Undefined
<crc_type> –Undefined
<nrzi_en> – 0
<sync1> – 0
<sync2> – 0 to255
Supported
Supported
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 58 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 59

Qualcomm commands
Table 43. Qualcomm command
COMMAND Description
$QCCLR clear mobile error log Clears the mobile error log Supported
$QCDMG
$QCDMR=
<rate>
&V
&C2
$QCTER=
<rate>
$ $QCDNSP=
<address>
$QCDNSS=
<address>
$QCPDPP=
<cid>,
<auth_type>,
transition to diagnostics
monitor operation
set DM baud rate
dump configuration
parameters
Circuit 109 (carrier
detect pin) behavior wink
Set TE-DCE baud rate
Baud rates supported
are identical to +IPR
command.
set primary DNS IP address
Set secondary DNS IP
address
PDP-IP packet data calls
<cid> – 1 to 16
<auth_type>:
Operation
Returns OK and then transitions the
mobile’s serial port to DM mode; DM
mode runs at rate set by $QCDMR
command and uses a proprietary
halfduplex protocol; default DM rate
fixed at 115200 bps
Changes DM rate that will be used on
mobile’s serial port when mobile’s
serial port transitions to DM mode; DM
mode is entered after $QCDMG
command is issued; default DM rate is
fixed at 115200 bps; test command,
i.e., $QCDMR=?, returns rates
supported and query command, i.e.,
$QCDMR?, returns current
Rate
Dumps the status of all AT parameters
applicable to current operating mode,
including the single-letter parameters
not otherwise readable
Setting “winks” (briefly transitions off,
then back on) the Rm port Carrier
Detect pin when Data calls end
Sets TE-DCE rate at which DCE will
accept commands; this data rate also
becomes the default and is stored in
NV RAM, changing the +IPR
command default rate; test command,
i.e., $QCTER=?, returns rates
supported and query command, i.e.,
$QCTER?, returns rate last issued by
$QCTER command or default rate
Sets the default primary IP address
used for Domain Name Services;
used only if no DNS server address is
received over the air during PDP
context activation; value is stored in
NVRAM.
Sets the default secondary IP address
used for Domain Name Services;
used only if no DNS server address is
received over the air during PDP
context activation; value is stored in
NVRAM
Defines authentication parameters on
a per connection basis. Value of
<auth_type> determines what
Support
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 59 of 60 Version 1.2
Page 60

<password>,
<username>
0 None
1 PAP
2 CHAP
$QCPWRDN used to power down the ME
Generates data over
$QCDGEN=<
cid>,<data
length>
+CGACT activated PDP
context
<cid> – 1 to 16
<data length> – 21 to 2^32
$QCSLOT=
<slot>
$QCPDPLT=<
enable>
$QCPINSTAT
?
set SIM card slot commands
will operate on
Enable/disable tolerance to
long delays in PDP call setup
sends the ME the status of
all PINs for all cards
additional parameters are required, as
follows:
0 – Neither username nor password
accepted
1 – Username and password
accepted
2 – Only password (secret)
accepted
Query command, i.e., $QCPDPP?,
does not display password values and
only displays username for PAP
authentication.
Returns OK and then shuts down the
phone
Supported only during PDP context
activation by +CGACT
Slot other than 1 only available if
FEATURE_DUAL_SLOTS enabled
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Statuses listed in order: SIM PIN, PH
FSIM PIN, NET PIN, NETSUB PIN,
Supported
SP PIN, CORP PIN, SIM PIN2
HSDPA Standard At Commands Page 60 of 60 Version 1.2
 Loading...
Loading...