
r
www.maxim-ic.com
DS26519
16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceive
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The DS26519 is a single-chip 16-port framer and line
interface unit (LIU) combination for T1, E1, and J1
applications. Each port is independently configurable,
supporting both long-haul and short-haul lines. The
DS26519 is nearly software compatible with the
DS26528 and its derivatives.
APPLICATIONS
Routers
Channel Service Units (CSUs)
Data Service Units (DSUs)
Muxes
Switches
Channel Banks
T1/E1 Test Equipment
FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM
T1/E1/J1
NETWORK
DS26519
T1/J1/E1
Transceiver
x16
BACKPLANE
TDM
ORDERING INFORMATION
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
DS26519G
DS26519G+
DS26519GN
DS26519GN+
+ Denotes lead-free/RoHS compliant device.
0°C to +70°C
0°C to +70°C
-40°C to +85°C
-40°C to +85°C
484 HSBGA
484 HSBGA
484 HSBGA
484 HSBGA
FEATURES
16 Complete T1, E1, or J1 Long-Haul/
Short-Haul Transceivers (LIU Plus Framer)
Independent T1, E1, or J1 Selections for Each
Transceiver
Software-Selectable Transmit- and Receive-
Side Termination for 100Ω T1 Twisted Pair,
110Ω J1 Twisted Pair, 120Ω E1 Twisted Pair,
and 75Ω E1 Coaxial Applications
Hitless Protection Switching
Crystal-Less Jitter Attenuators Can Be
Selected for Transmit or Receive Path; Jitter
Attenuator Meets ETS CTR 12/13, ITU-T
G.736, G.742, G.823, and AT&T Pub 62411
External Master Clock Can Be Multiple of
2.048MHz or 1.544MHz for T1/J1 or E1
Operation; This Clock is Internally Adapted
for T1 or E1 Usage in the Host Mode
Receive-Signal Level Indication from -2.5dB
to -36dB in T1 Mode and -2.5dB to -44dB in E1
Mode in Approximate 2.5dB Increments
Transmit Open- and Short-Circuit Detection
LIU LOS in Accordance with G.775, ETS 300
233, and T1.231
Transmit Synchronizer
Flexible Signaling Extraction and Insertion
Using Either the System Interface or
Microprocessor Port
Alarm Detection and Insertion
T1 Framing Formats of D4, SLC-96, and ESF
J1 Support
E1 G.704 and CRC-4 Multiframe
T1-to-E1 Conversion
Features Continued in Section 2
.
Note: Some revisions of this device may incorporate deviations from published specifications known as errata. Multiple revisions of any device
may be simultaneously available through various sales channels. For information about device errata, click here: www.maxim-ic.com/errata
1 of 310
REV: 040907
.

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. DETAILED DESCRIPTION.................................................................................................9
2. FEATURE HIGHLIGHTS..................................................................................................10
2.1 GENERAL......................................................................................................................................10
2.2 LINE INTERFACE............................................................................................................................10
2.3 CLOCK SYNTHESIZERS ..................................................................................................................10
2.4 JITTER ATTENUATOR.....................................................................................................................10
2.5 FRAMER/FORMATTER....................................................................................................................11
2.6 SYSTEM INTERFACE ......................................................................................................................11
2.7 HDCL CONTROLLERS ...................................................................................................................12
2.8 TEST AND DIAGNOSTICS................................................................................................................12
2.9 MICROCONTROLLER PARALLEL PORT.............................................................................................12
2.10 SLAVE SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI) FEATURES ............................................................12
3. APPLICATIONS ...............................................................................................................13
4. SPECIFICATIONS COMPLIANCE...................................................................................14
5. ACRONYMS AND GLOSSARY .......................................................................................16
6. MAJOR OPERATING MODES.........................................................................................17
7. BLOCK DIAGRAMS......................................................................................................... 18
8. PIN DESCRIPTIONS ........................................................................................................20
8.1 PIN FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION......................................................................................................20
9. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION .........................................................................................33
9.1 PROCESSOR INTERFACE................................................................................................................33
9.1.1 SPI Serial Port Mode............................................................................................................................ 33
9.1.2 SPI Functional Timing Diagrams ......................................................................................................... 33
9.2 CLOCK STRUCTURE.......................................................................................................................35
9.2.1 Backplane Clock Generation ............................................................................................................... 35
9.2.2 CLKO Output Clock Generation........................................................................................................... 37
9.3 RESETS AND POWER-DOWN MODES..............................................................................................38
9.4 INITIALIZATION AND CONFIGURATION..............................................................................................39
9.4.1 Example Device Initialization and Sequence.......................................................................................39
9.5 GLOBAL RESOURCES ....................................................................................................................40
9.5.1 General-Purpose I/O Pins....................................................................................................................40
9.6 PER-PORT RESOURCES ................................................................................................................40
9.7 DEVICE INTERRUPTS .....................................................................................................................41
9.8 SYSTEM BACKPLANE INTERFACE ...................................................................................................43
9.8.1 Elastic Stores....................................................................................................................................... 43
9.8.2 IBO Multiplexing................................................................................................................................... 46
9.8.3 H.100 (CT Bus) Compatibility .............................................................................................................. 55
9.8.4 Transmit and Receive Channel Blocking Registers............................................................................. 57
9.8.5 Transmit Fractional Support (Gapped Clock Mode)............................................................................ 57
9.8.6 Receive Fractional Support (Gapped Clock Mode)............................................................................. 57
9.9 FRAMERS......................................................................................................................................58
9.9.1 T1 Framing...........................................................................................................................................58
9.9.2 E1 Framing........................................................................................................................................... 61
9.9.3 T1 Transmit Synchronizer.................................................................................................................... 63
9.9.4 Signaling .............................................................................................................................................. 64
9.9.5 T1 Data Link.........................................................................................................................................69
9.9.6 E1 Data Link......................................................................................................................................... 71
2 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
9.9.7 Maintenance and Alarms..................................................................................................................... 72
9.9.8 Alarms.................................................................................................................................................. 75
9.9.9 Error Count Registers .......................................................................................................................... 77
9.9.10 DS0 Monitoring Function...................................................................................................................... 79
9.9.11 Transmit Per-Channel Idle Code Generation ...................................................................................... 80
9.9.12 Receive Per-Channel Idle Code Insertion............................................................................................ 80
9.9.13 Per-Channel Loopback ........................................................................................................................ 80
9.9.14 E1 G.706 Intermediate CRC-4 Updating (E1 Mode Only)................................................................... 80
9.9.15 T1 Programmable In-Band Loop Code Generator............................................................................... 81
9.9.16 T1 Programmable In-Band Loop Code Detection................................................................................ 82
9.9.17 Framer Payload Loopbacks................................................................................................................. 83
9.10 HDLC CONTROLLERS................................................................................................................84
9.10.1 Receive HDLC Controller.....................................................................................................................84
9.10.2 Transmit HDLC Controller.................................................................................................................... 87
9.11 POWER-SUPPLY DECOUPLING....................................................................................................89
9.12 LINE INTERFACE UNITS (LIUS)....................................................................................................90
9.12.1 LIU Operation.......................................................................................................................................92
9.12.2 Transmitter........................................................................................................................................... 93
9.12.3 Receiver............................................................................................................................................... 97
9.12.4 Hitless Protection Switching (HPS)....................................................................................................101
9.12.5 Jitter Attenuator..................................................................................................................................102
9.12.6 LIU Loopbacks................................................................................................................................... 103
9.13 BIT ERROR-RATE TEST FUNCTION (BERT)...............................................................................106
9.13.1 BERT Repetitive Pattern Set ............................................................................................................. 107
9.13.2 BERT Error Counter........................................................................................................................... 107
10. DEVICE REGISTERS.....................................................................................................108
10.1 REGISTER LISTINGS .................................................................................................................108
10.1.1 Global Register List............................................................................................................................ 109
10.1.2 Framer Register List........................................................................................................................... 110
10.1.3 LIU and BERT Register List...............................................................................................................117
10.2 REGISTER BIT MAPS ................................................................................................................118
10.2.1 Global Register Bit Map..................................................................................................................... 118
10.2.2 Framer Register Bit Map.................................................................................................................... 119
10.2.3 LIU Register Bit Map.......................................................................................................................... 128
10.2.4 BERT Register Bit Map......................................................................................................................129
10.3 GLOBAL REGISTER DEFINITIONS...............................................................................................130
10.4 FRAMER REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS...........................................................................................156
10.4.1 Receive Register Descriptions........................................................................................................... 156
10.4.2 Transmit Register Descriptions..........................................................................................................214
10.5 LIU REGISTER DEFINITIONS .....................................................................................................250
10.6 BERT REGISTER DEFINITIONS .................................................................................................260
11. FUNCTIONAL TIMING ...................................................................................................268
11.1 T1 RECEIVER FUNCTIONAL TIMING DIAGRAMS ..........................................................................268
11.2 T1 TRANSMITTER FUNCTIONAL TIMING DIAGRAMS ....................................................................273
11.3 E1 RECEIVER FUNCTIONAL TIMING DIAGRAMS..........................................................................278
11.4 E1 TRANSMITTER FUNCTIONAL TIMING DIAGRAMS ....................................................................282
12. OPERATING PARAMETERS.........................................................................................287
12.1 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS....................................................................................................288
12.2 LINE INTERFACE CHARACTERISTICS..........................................................................................288
13. AC TIMING CHARACTERISTICS..................................................................................289
13.1 MICROPROCESSOR BUS AC CHARACTERISTICS........................................................................289
13.1.1 SPI Bus Mode.................................................................................................................................... 289
13.2 JTAG INTERFACE TIMING.........................................................................................................300
3 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
13.3 SYSTEM CLOCK AC CHARACTERISTICS ....................................................................................301
14. JTAG BOUNDARY SCAN AND TEST ACCESS PORT................................................302
14.1 TAP CONTROLLER STATE MACHINE.........................................................................................303
14.1.1 Test-Logic-Reset................................................................................................................................ 303
14.1.2 Run-Test-Idle ..................................................................................................................................... 303
14.1.3 Select-DR-Scan ................................................................................................................................. 303
14.1.4 Capture-DR........................................................................................................................................ 303
14.1.5 Shift-DR.............................................................................................................................................. 303
14.1.6 Exit1-DR.............................................................................................................................................303
14.1.7 Pause-DR........................................................................................................................................... 303
14.1.8 Exit2-DR.............................................................................................................................................303
14.1.9 Update-DR......................................................................................................................................... 303
14.1.10 Select-IR-Scan ............................................................................................................................... 303
14.1.11 Capture-IR...................................................................................................................................... 304
14.1.12 Shift-IR............................................................................................................................................ 304
14.1.13 Exit1-IR...........................................................................................................................................304
14.1.14 Pause-IR......................................................................................................................................... 304
14.1.15 Exit2-IR...........................................................................................................................................304
14.1.16 Update-IR....................................................................................................................................... 304
14.2 INSTRUCTION REGISTER...........................................................................................................306
14.2.1 SAMPLE:PRELOAD .......................................................................................................................... 306
14.2.2 BYPASS.............................................................................................................................................306
14.2.3 EXTEST ............................................................................................................................................. 306
14.2.4 CLAMP...............................................................................................................................................306
14.2.5 HIGHZ................................................................................................................................................ 306
14.2.6 IDCODE............................................................................................................................................. 306
14.3 JTAG ID CODES......................................................................................................................307
14.4 TEST REGISTERS.....................................................................................................................307
14.4.1 Boundary Scan Register.................................................................................................................... 307
14.4.2 Bypass Register................................................................................................................................. 307
14.4.3 Identification Register......................................................................................................................... 307
15. PIN CONFIGURATION...................................................................................................308
15.1 PIN CONFIGURATION—484-BALL HSBGA................................................................................308
16. PACKAGE INFORMATION............................................................................................309
16.1 484-BALL HSBGA (56-G6038-002).........................................................................................309
17. DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY ................................................................................310
4 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 7-1. Block Diagram......................................................................................................................................... 18
Figure 7-2. Detailed Block Diagram........................................................................................................................... 19
Figure 9-1. SPI Serial Port Access for Read Mode, SPI_CPOL = 0, SPI_CPHA = 0............................................... 34
Figure 9-2. SPI Serial Port Access for Read Mode, SPI_CPOL = 1, SPI_CPHA = 0............................................... 34
Figure 9-3. SPI Serial Port Access for Read Mode, SPI_CPOL = 0, SPI_CPHA = 1............................................... 34
Figure 9-4. SPI Serial Port Access for Read Mode, SPI_CPOL = 1, SPI_CPHA = 1............................................... 34
Figure 9-5. SPI Serial Port Access for Write Mode, SPI_CPOL = 0, SPI_CPHA = 0 ............................................... 35
Figure 9-6. SPI Serial Port Access for Write Mode, SPI_CPOL = 1, SPI_CPHA = 0 ............................................... 35
Figure 9-7. SPI Serial Port Access for Write Mode, SPI_CPOL = 0, SPI_CPHA = 1 ............................................... 35
Figure 9-8. SPI Serial Port Access for Write Mode, SPI_CPOL = 1, SPI_CPHA = 1 ............................................... 35
Figure 9-9. Backplane Clock Generation................................................................................................................... 36
Figure 9-10. GPIO Mux Control................................................................................................................................. 40
Figure 9-11. Device Interrupt Information Flow Diagram........................................................................................... 42
Figure 9-12. IBO Multiplexer Equivalent Circuit—4.096MHz .................................................................................... 47
Figure 9-13. IBO Multiplexer Equivalent Circuit—8.192MHz .................................................................................... 48
Figure 9-14. IBO Multiplexer Equivalent Circuit—16.384MHz .................................................................................. 49
Figure 9-15. RSYNCn Input in H.100 (CT Bus) Mode...............................................................................................56
Figure 9-16. TSSYNCIOn (Input Mode) Input in H.100 (CT Bus) Mode ................................................................... 56
Figure 9-17. CRC-4 Recalculate Method .................................................................................................................. 80
Figure 9-18. HDLC Message Receive Example........................................................................................................86
Figure 9-19. HDLC Message Transmit Example.......................................................................................................88
Figure 9-20. Network Connection—Longitudinal Protection ..................................................................................... 91
Figure 9-21. T1/J1 Transmit Pulse Templates .......................................................................................................... 94
Figure 9-22. E1 Transmit Pulse Templates............................................................................................................... 95
Figure 9-23. Receive LIU Termination Options......................................................................................................... 97
Figure 9-24. Typical Monitor Application ................................................................................................................... 98
Figure 9-25. HPS Block Diagram............................................................................................................................. 101
Figure 9-26. Jitter Attenuation ................................................................................................................................. 102
Figure 9-27. Loopback Diagram.............................................................................................................................. 103
Figure 9-28. Analog Loopback................................................................................................................................. 103
Figure 9-29. Local Loopback...................................................................................................................................104
Figure 9-30. Remote Loopback 2............................................................................................................................ 104
Figure 9-31. Dual Loopback .................................................................................................................................... 105
Figure 11-1. T1 Receive-Side D4 Timing ................................................................................................................ 268
Figure 11-2. T1 Receive-Side ESF Timing..............................................................................................................268
Figure 11-3. T1 Receive-Side Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Disabled)............................................................... 269
Figure 11-4. T1 Receive-Side 1.544MHz Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Enabled)..............................................269
Figure 11-5. T1 Receive-Side 2.048MHz Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Enabled)..............................................270
Figure 11-6. T1 Receive-Side Interleave Bus Operation—BYTE Mode.................................................................. 271
Figure 11-7. T1 Receive-Side Interleave Bus Operation—FRAME Mode .............................................................. 272
Figure 11-8. T1 Receive-Side RCHCLKn Gapped Mode During F-Bit.................................................................... 272
Figure 11-9. T1 Transmit-Side D4 Timing............................................................................................................... 273
Figure 11-10. T1 Transmit-Side ESF Timing...........................................................................................................273
Figure 11-11. T1 Transmit-Side Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Disabled)............................................................274
Figure 11-12. T1 Transmit-Side 1.544MHz Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Enabled)........................................... 274
Figure 11-13. T1 Transmit-Side 2.048MHz Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Enabled)........................................... 275
Figure 11-14. T1 Transmit-Side Interleave Bus Operation—BYTE Mode............................................................... 276
Figure 11-15. T1 Transmit-Side Interleave Bus Operation—FRAME Mode ........................................................... 277
Figure 11-16. T1 Transmit-Side TCHCLKn Gapped Mode During F-Bit................................................................. 277
5 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
Figure 11-17. E1 Receive-Side Timing.................................................................................................................... 278
Figure 11-18. E1 Receive-Side Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Disabled) ............................................................ 278
Figure 11-19. E1 Receive-Side 1.544MHz Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Enabled)............................................ 279
Figure 11-20. E1 Receive-Side 2.048MHz Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Enabled)............................................ 279
Figure 11-21. E1 Receive-Side Interleave Bus Operation—BYTE Mode ............................................................... 280
Figure 11-22. E1 Receive-Side Interleave Bus Operation—FRAME Mode............................................................ 281
Figure 11-23. E1 Receive-Side RCHCLKn Gapped Mode During Channel 1 ........................................................ 281
Figure 11-24. E1 Transmit-Side Timing................................................................................................................... 282
Figure 11-25. E1 Transmit-Side Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Disabled) ........................................................... 282
Figure 11-26. E1 Transmit-Side 1.544MHz Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Enabled)........................................... 283
Figure 11-27. E1 Transmit-Side 2.048MHz Boundary Timing (Elastic Store Enabled)........................................... 283
Figure 11-28. E1 Transmit-Side Interleave Bus Operation—BYTE Mode .............................................................. 284
Figure 11-29. E1 Transmit-Side Interleave Bus Operation—FRAME Mode........................................................... 285
Figure 11-30. E1 G.802 Timing ............................................................................................................................... 286
Figure 11-31. E1 Transmit-Side TCHCLKn Gapped Mode During Channel 1........................................................286
Figure 13-1. SPI Interface Timing Diagram............................................................................................................. 290
Figure 13-2. Intel Bus Read Timing (BTS = 0) ........................................................................................................ 292
Figure 13-3. Intel Bus Write Timing (BTS = 0)......................................................................................................... 292
Figure 13-4. Motorola Bus Read Timing (BTS = 1)................................................................................................. 293
Figure 13-5 Motorola Bus Write Timing (BTS = 1) .................................................................................................. 293
Figure 13-6. Receive Framer Timing—Backplane (T1 Mode)................................................................................. 295
Figure 13-7. Receive-Side Timing—Elastic Store Enabled (T1 Mode)................................................................... 296
Figure 13-8. Receive Framer Timing—Line Side.................................................................................................... 296
Figure 13-9. Transmit Formatter Timing—Backplane ............................................................................................. 298
Figure 13-10. Transmit Formatter Timing—Elastic Store Enabled.......................................................................... 298
Figure 13-11. BPCLKn Timing.................................................................................................................................299
Figure 13-12. Transmit Formatt Timing—Line Side ................................................................................................ 299
Figure 13-13. JTAG Interface Timing Diagram........................................................................................................ 300
Figure 14-1. JTAG Functional Block Diagram......................................................................................................... 302
Figure 14-2. TAP Controller State Diagram............................................................................................................. 305
6 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
LIST OF TABLES
Table 4-1. T1-Related Telecommunications Specifications ...................................................................................... 14
Table 4-2. E1-Related Telecommunications Specifications...................................................................................... 15
Table 5-1. Time Slot Numbering Schemes................................................................................................................ 16
Table 8-1. Detailed Pin Descriptions ......................................................................................................................... 20
Table 9-1. CLKO Frequency Selection...................................................................................................................... 37
Table 9-2. Reset Functions........................................................................................................................................ 38
Table 9-3. Registers Related to the Elastic Store...................................................................................................... 43
Table 9-4. Elastic Store Delay After Initialization....................................................................................................... 44
Table 9-5. Registers Related to the IBO Multiplexer................................................................................................. 46
Table 9-6. RSERn Output Pin Definitions (GTCR1.GIBO = 0).................................................................................. 50
Table 9-7. RSIGn Output Pin Definitions (GTCR1.GIBO = 0)................................................................................... 51
Table 9-8. TSERn Input Pin Definitions (GTCR1.GIBO = 0)..................................................................................... 52
Table 9-9. TSIGn Input Pin Definitions (GTCR1.GIBO = 0)...................................................................................... 53
Table 9-10. RSYNCn Input Pin Definitions (GTCR1.GIBO = 0)................................................................................ 54
Table 9-11. D4 Framing Mode...................................................................................................................................58
Table 9-12. ESF Framing Mode ................................................................................................................................ 59
Table 9-13. SLC-96 Framing..................................................................................................................................... 59
Table 9-14. E1 FAS/NFAS Framing .......................................................................................................................... 61
Table 9-15. Registers Related to Setting Up the Framer .......................................................................................... 62
Table 9-16. Registers Related to the Transmit Synchronizer.................................................................................... 63
Table 9-17. Registers Related to Signaling............................................................................................................... 64
Table 9-18. Registers Related to SLC-96.................................................................................................................. 67
Table 9-19. Registers Related to T1 Transmit BOC..................................................................................................69
Table 9-20. Registers Related to T1 Receive BOC................................................................................................... 69
Table 9-21. Registers Related to T1 Transmit FDL...................................................................................................70
Table 9-22. Registers Related to T1 Receive FDL.................................................................................................... 70
Table 9-23. Registers Related to E1 Data Link.........................................................................................................71
Table 9-24. Registers Related to Maintenance and Alarms......................................................................................73
Table 9-25. T1 Alarm Criteria .................................................................................................................................... 75
Table 9-26. Registers Related to Transmit RAI (Yellow Alarm)................................................................................ 75
Table 9-27. Registers Related to Receive RAI (Yellow Alarm)................................................................................. 76
Table 9-28. T1 Line Code Violation Counting Options.............................................................................................. 77
Table 9-29. E1 Line Code Violation Counting Options.............................................................................................. 77
Table 9-30. T1 Path Code Violation Counting Arrangements................................................................................... 78
Table 9-31. T1 Frames Out of Sync Counting Arrangements................................................................................... 78
Table 9-32. Registers Related to DS0 Monitoring..................................................................................................... 79
Table 9-33. Registers Related to T1 In-Band Loop Code Generator........................................................................ 81
Table 9-34. Registers Related to T1 In-Band Loop Code Detection......................................................................... 82
Table 9-35. Register Related to Framer Payload Loopbacks ................................................................................... 83
Table 9-36. Registers Related to the HDLC.............................................................................................................. 84
Table 9-37. Recommended Supply Decoupling........................................................................................................ 89
Table 9-38. Registers Related to Control of the LIU.................................................................................................. 92
Table 9-39. Telecommunications Specification Compliance for DS26519 Transmitters.......................................... 93
Table 9-40. Transformer Specifications..................................................................................................................... 93
Table 9-41. Receive Impedance Control................................................................................................................... 97
Table 9-42. T1.231, G.775, and ETS 300 233 Loss Criteria Specifications............................................................ 100
Table 9-43. Jitter Attenuator Standards Compliance...............................................................................................102
Table 9-44. Registers Related to Configure, Control, and Status of BERT............................................................. 106
Table 10-1. Register Address Ranges (in Hex).......................................................................................................108
7 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
Table 10-2. Global Register Mapping...................................................................................................................... 109
Table 10-3. Global Register List.............................................................................................................................. 109
Table 10-4. Framer Register List............................................................................................................................. 110
Table 10-5. LIU Register List................................................................................................................................... 117
Table 10-6. BERT Register List............................................................................................................................... 117
Table 10-7. Global Register Bit Map........................................................................................................................ 118
Table 10-8. Framer Register Bit Map ...................................................................................................................... 119
Table 10-9. LIU Register Bit Map ............................................................................................................................ 128
Table 10-10. BERT Register Bit Map ...................................................................................................................... 129
Table 10-11. Global Register Set ............................................................................................................................ 130
Table 10-12. DS26519 GPIO Control (1 to 8) ......................................................................................................... 131
Table 10-13. DS26519 GPIO Control (9 to 16) ....................................................................................................... 132
Table 10-14. Master Clock Input Selection.............................................................................................................. 136
Table 10-15. Backplane Reference Clock Select (1 to 8)........................................................................................ 137
Table 10-16. Backplane Reference Clock Select (9 to 16) ..................................................................................... 138
Table 10-17. Device ID Codes in this Product Family............................................................................................. 142
Table 10-18. LIU Register Set.................................................................................................................................250
Table 10-19. Transmit Load Impedance Selection.................................................................................................. 252
Table 10-20. Transmit Pulse Shape Selection........................................................................................................ 252
Table 10-21. Receive Level Indication .................................................................................................................... 257
Table 10-22. Receive Impedance Selection............................................................................................................258
Table 10-23. Receiver Sensitivity Selection with Monitor Mode Disabled............................................................... 259
Table 10-24. Receiver Sensitivity Selection with Monitor Mode Enabled ............................................................... 259
Table 10-25. BERT Register Set............................................................................................................................. 260
Table 10-26. BERT Pattern Select .......................................................................................................................... 262
Table 10-27. BERT Error Insertion Rate ................................................................................................................. 263
Table 10-28. BERT Repetitive Pattern Length Select............................................................................................. 263
Table 12-1. Recommended DC Operating Conditions............................................................................................ 287
Table 12-2. Capacitance.......................................................................................................................................... 287
Table 12-3. Recommended DC Operating Conditions............................................................................................ 287
Table 12-4. Thermal Characteristics........................................................................................................................ 288
Table 12-5. Transmitter Characteristics................................................................................................................... 288
Table 12-6. Receiver Characteristics....................................................................................................................... 288
Table 13-1. SPI Bus Mode Timing........................................................................................................................... 289
Table 13-2. AC Characteristics—Microprocessor Bus Timing ................................................................................ 291
Table 13-3. Receiver AC Characteristics ................................................................................................................ 294
Table 13-4. Transmit AC Characteristics.................................................................................................................297
Table 13-5. JTAG Interface Timing.......................................................................................................................... 300
Table 13-6. System Clock AC Characteristics......................................................................................................... 301
Table 14-1. Instruction Codes for IEEE 1149.1 Architecture................................................................................... 306
Table 14-2. ID Code Structure.................................................................................................................................307
8 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
1. DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The DS26519 is an 16-port monolithic device featuring independent transceivers that can be software configured
for T1, E1, or J1 operation. Each transceiver is composed of a line interface unit, framer, HDLC controller, elastic
store, and a TDM backplane interface. The DS26519 is controlled via an 8-bit parallel port or the SPI port. Internal
impedance matching and termination is provided for both transmit and receive paths, reducing external component
count.
The LIU is composed of a transmit interface, receive interface, and a jitter attenuator. The transmit interface is
responsible for generating the necessary waveshapes for driving the network and providing the correct source
impedance depending on the type of media used. T1 waveform generation includes DSX-1 line build-outs as well
as CSU line build-outs of 0dB, -7.5dB, -15dB, and -22.5dB. E1 waveform generation includes G.703 waveshapes
for both 75Ω coax and 120Ω twisted cables. The receive interface provides network termination and recovers clock
and data from the network. The receive sensitivity adjusts automatically to the incoming signal level and can be
programmed for 0dB to -43dB or 0dB to -12dB for E1 applications and 0dB to -15dB or 0dB to -36dB for T1
applications. The jitter attenuator removes phase jitter from the transmitted or received signal. The crystal-less jitter
attenuator requires only a T1 or E1 clock rate, or multiple thereof, for both E1 and T1 applications, and can be
placed in either transmit or receive data paths.
On the transmit side, clock, data, and frame-sync signals are provided to the framer by the backplane interface
section. The framer inserts the appropriate synchronization framing patterns, alarm information, calculates and
inserts the CRC codes, and provides the B8ZS/HDB3 (zero code suppression) and AMI line coding. The receiveside framer decodes AMI, B8ZS, and HDB3 line coding, synchronizes to the data stream, reports alarm
information, counts framing/coding/CRC errors, and provides clock, data, and frame-sync signals to the backplane
interface section.
Both transmit and receive paths have access to an HDLC controller. The HDLC controller transmits and receives
data via the framer block. The HDLC controller can be assigned to any time slot, a portion of a time slot or to FDL
(T1) or Sa bits (E1). Each controller has 64-byte FIFOs, reducing the amount of processor overhead required to
manage the flow of data.
The backplane interface provides a versatile method of sending and receiving data from the host system. Elastic
stores provide a method for interfacing to asynchronous systems, converting from a T1/E1 network to a 2.048MHz,
4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, 16.384MHz, or N x 64kHz system backplane. The elastic stores also manage slip conditions
(asynchronous interface). An interleave bus option (IBO) is provided to allow up to eight transceivers (single
DS26519) to share a high-speed backplane. The DS26519 also contains an internal clock adapter useful for the
creation of a synchronous, high-frequency backplane timing source.
The microprocessor port provides access for configuration and status of all the DS26519’s features. Diagnostic
capabilities include loopbacks, PRBS pattern generation/detection, and 16-bit loop-up and loop-down code
generation and detection.
9 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
2. FEATURE HIGHLIGHTS
2.1 General
23mm x 23mm, 484-pin HSBGA (1.00mm pitch)
3.3V and 1.8V supply with 5V tolerant inputs and outputs
IEEE 1149.1 JTAG boundary scan
Development support includes evaluation kit, driver source code, and reference designs
2.2 Line Interface
Requires a single master clock (MCLK) for both E1 and T1 operation. Master clock can be 1.544MHz,
2.048MHz, 3.088MHz, 4.096MHz, 6.276MHz, 8.192MHz, 12.552MHz, or 16.384MHz.
Fully software configurable
Short- and long-haul applications
Ranges include 0dB to -43dB, 0dB to -30dB, 0dB to 20dB, and 0dB to -12dB for E1; 0dB to -36dB, 0dB to
30dB, 0dB to 20dB, and 0dB to -15dB for T1
Receiver signal level indication from -2.5dB to -36dB in T1 mode and -2.5dB to -44dB in E1 mode in 2.5dB
increments
Software-selectable receive termination for 75Ω, 100Ω, 110Ω, and 120Ω lines
Hitless protection switching
Monitor application gain settings of 14dB, 20dB, 26dB, and 32dB
G.703 receive synchronization signal mode
Flexible transmit waveform generation
T1 DSX-1 line build-outs
T1 CSU line build-outs of 0dB, -7.5dB, -15dB, and -22.5dB
E1 waveforms include G.703 waveshapes for both 75Ω coax and 120Ω twisted cables
Analog loss-of-signal detection
AIS generation independent of loopbacks
Alternating ones and zeros generation
Receiver power-down
Transmitter power-down
Transmit outputs and receive inputs present a high impedance to the line when no power is applied,
supporting redundancy applications
Transmitter short-circuit limiter with current-limit-exceeded indication
Transmit open-circuit-detected indication
2.3 Clock Synthesizers
Backplane clocks output frequencies include 2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, and 16.384MHz
− Derived from user-selected recovered receive clock or REFCLKIO
CLKO output clock selectable from a wide range of frequencies referenced to MCLK
2.4 Jitter Attenuator
32-bit or 128-bit crystal-less jitter attenuator
Requires only a 1.544MHz or 2.048MHz master clock or multiple thereof, for both E1 and T1 operation
Can be placed in either the receive or transmit path or disabled
Limit trip indication
10 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
2.5 Framer/Formatter
Fully independent transmit and receive functionality
Full receive and transmit path transparency
T1 framing formats D4 and ESF per T1.403 and expanded SLC-96 support (TR-TSY-008)
E1 FAS framing and CRC-4 multiframe per G.704/G.706, and G.732 CAS multiframe
Transmit-side synchronizer
Transmit midpath CRC recalculate (E1)
Detailed alarm and status reporting with optional interrupt support
Large path and line error counters
− T1: BPV, CV, CRC-6, and framing bit errors
− E1: BPV, CV, CRC-4, E-bit, and frame alignment errors
− Timed or manual update modes
DS1 Idle Code Generation on a per-channel basis in both transmit and receive paths
− User defined
− Digital Milliwatt
ANSI T1.403-1999 support
G.965 V5.2 link detect
Ability to monitor one DS0 channel in both the transmit and receive paths
In-band repeating pattern generators and detectors
− Three independent generators an d detectors
− Patterns from 1 to 8 bits or 16 bits in length
Bit oriented code (BOC) support
Flexible signaling support
− Software or hardware based
− Interrupt generated on change of signaling data
− Optional receive signaling freeze on loss of frame, loss of signal, or frame slip
− Hardware pins provided to indicate loss of frame (LOF), loss of signal (LOS), loss of transmit clock
(LOTC), or signaling freeze condition
Automatic RAI generation to ETS 300 011 specifications
RAI-CI and AIS-CI support
Expanded access to Sa and Si bits
Option to extend carrier loss criteria to a 1ms period as per ETS 300 233
Japanese J1 support
Ability to calculate and check CRC-6 according to the Japanese standard
Ability to generate Yellow Alarm according to the Japanese standard
T1-to-E1 conversion
2.6 System Interface
Independent two-frame receive and transmit elastic stores
Independent control and clocking
Controlled slip capability with status
Minimum delay mode supported
Flexible TDM backplane supports bus rates from 1.544MHz to 16.384MHz
Supports T1 to CEPT (E1) conversion
Programmable output clocks for fractional T1, E1, H0, and H12 applications
Interleaving PCM bus operation
Hardware signaling capability
Receive signaling reinsertion to a backplane multiframe sync
Availability of signaling in a separate PCM data stream
11 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
Signaling freezing
Ability to pass the T1 F-bit position through the elastic stores in the 2.048MHz backplane mode
User-selectable synthesized clock output
2.7 HDCL Controllers
One HDLC controller engine for each T1/E1 port
Independent 64-byte Rx and Tx buffers with interrupt support
Access FDL, Sa, or single DS0 channel
Compatible with polled or interrupt driven environments
2.8 Test and Diagnostics
IEEE 1149.1 support
Per-channel programmable on-chip bit error-rate testing (BERT)
Pseudorandom patterns including QRSS
User-defined repetitive patterns
Daly pattern
Error insertion single and continuous
Total-bit and errored-bit counts
Payload error insertion
Error insertion in the payload portion of the T1 frame in the transmit path
Errors can be inserted over the entire frame or selected channels
Insertion options include continuous and absolute number with selectable insertion rates
F-bit corruption for line testing
Loopbacks (remote, local, analog, and per-channel loopback)
2.9 Microcontroller Parallel Port
8-bit parallel control port
Intel or Motorola nonmultiplexed support
Flexible status registers support polled, interrupt, or hybrid program environments
Software reset supported
Hardware reset pin
Software access to device ID and silicon revision
2.10 Slave Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Features
Software access to device ID and silicon revision
Three-wire synchronous serial data link operating in full-duplex slave mode up to 5Mbp s
Glueless connection and fully compliant to Motorola popular communication processors such as MPC8260
and microcontrollers such as M68HC11
Software provision ability for active phase of the serial clock (i.e., rising edge vs. falling edge), bit ordering
of the serial data (most significant first vs. least significant bit first)
Flexible status registers support polled, interrupt, or hybrid program environments
12 of 310

3. APPLICATIONS
The DS26519 is useful in applications such as:
Routers
Channel Service Units (CSUs)
Data Service Units (DSUs)
Muxes
Switches
Channel Banks
T1/E1 Test Equipment
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
13 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
4. SPECIFICATIONS COMPLIANCE
The DS26519 meets all the latest relevant telecommunications specifications. Table 4-1 provides the T1
specifications and
DS26519.
Table 4-1. T1-Related Telecommunications Specifications
ANSI T1.102: Digital Hierarchy Electrical Interface
AMI Coding
B8ZS Substitution Definition
DS1 Electrical Interface. Line rate ±32ppm; Pulse Amplitude between 2.4V to 3.6V peak; power level between
12.6dBm to 17.9dBm. The T1 pulse mask is provided that we comply. DSX-1 for cross connects the return loss is
greater than -26dB. The DSX-1 cable is restricted up to 655 feet.
This specification also provides cable characteristics of DSX-Cross Connect cable—22 AVG cables of 1000 feet.
ANSI T1.231: Digital Hierarchy—Layer 1 in Service Performance Monitoring
BPV Error Definition; Excessive Zero Definition; LOS description; AIS definition.
ANSI T1.403: Network and Customer Installation Interface—DS1 Electrical Interface
Description of the Measurement of the T1 Characteristics—100Ω. Pulse shape and template compliance
according to T1.102; power level 12.4dBm to 19.7dBm when all ones are transmitted.
LBO for the Customer Interface (CI) is specified as 0dB, -7.5dB, and -15dB. Line rate is ±32ppm. Pulse Amplitude
is 2.4V to 3.6V.
AIS generation as unframed all ones is defined.
The total cable attenuation is defined as 22dB. The DS26519 functions with up to -36dB cable loss.
Note that the pulse template defined by T1.403 and T1.102 are different, specifically at Times 0.61, -0.27, -34, and
0.77. The DS26519 is compliant to both templates.
Pub 62411
This specification has tighter jitter tolerance and transfer characteristics than other sp ecifications.
The jitter transfer characteristics are tighter than G.736 and jitter tolerance is tighter the G.823.
(ANSI) “Digital Hierarchy—Electrical Interfaces”
(ANSI) “Digital Hierarchy—Formats Specification”
(ANSI) “Digital Hierarchy—Layer 1 In-Service Digital Transmission Performance Monitoring”
(ANSI) “Network and Customer Installation Interfaces—DS1 Electrical Interface”
(AT&T) “Requirements for Interfacing Digital Terminal Equipment to Services Employing the Extended Super
Frame Format”
(AT&T) “High Capacity Digital Service Channel Interface Specification”
(TTC) “Frame Structures on Primary and Secondary Hierarchical Digital Interfaces”
(TTC) “ISDN Primary Rate User-Network Interface Layer 1 Specification”
Table 4-2 provides the E1 specifications and relevant sections that are applicable to the
14 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
Table 4-2. E1-Related Telecommunications Specifications
ITU-T G.703 Physical/Electrical Characteristics of G.703 Hierarchical Digital Interfaces
Defines the 2048kbps bit rate—2048 ±50ppm; the transmission media are 75Ω coax or 120Ω twiste d pair; peak-to-
peak space voltage is ±0.237V; nominal pulse width is 244ns.
Return loss 51Hz to 102Hz is 6dB, 102Hz to 3072Hz is 8dB, 2048Hz to 3072Hz is 14dB.
Nominal peak voltage is 2.37V for coax and 3V for twisted pair.
The pulse template for E1 is defined in G.703.
ITU-T G.736 Characteristics of Synchronous Digital Multiplex Equipment Operating at 2048kbps
The peak-to-peak jitter at 2048kbps must be less than 0.05UI at 20Hz to 100Hz.
Jitter transfer between 2.048 synchronization signal and 2.048 transmission signal is provided.
ITU-T G.742 Second-Order Digital Multiplex Equipment Operating at 8448kbps
The DS26519 jitter attenuator is complaint with jitter transfer curve for sinusoidal jitter input.
ITU-T G.772
This specification provides the method for using receiver for transceiver 0 as a mo nitor for the remaining seven
transmitter/receiver combinations.
ITU-T G.775
An LOS detection criterion is defined.
ITU-T G.823 The control of jitter and wander within digital networks that are based on 2.048kbps hierarchy.
G.823 Provides the jitter amplitude tolerance at different frequencies, specifically 20Hz, 2.4kHz, 18kHz, and 100 kHz.
ETS 300 233
This specification provides LOS and AIS signal criteria for E1 mode.
Pub 62411
This specification has tighter jitter tolerance and transfer characteristics than other sp ecifications.
The jitter transfer characteristics are tighter than G.736 and jitter tolerance is tighter than G.823.
(ITU-T) “Synchronous Frame Structures used at 1544, 6312, 2048, 8488, and 44736kbps Hierarchical Levels”
(ITU-T) “Frame Alignment and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) Procedures Relating to Basic Frame Structures
Defined in Recommendation G.704”
(ITU-T) “Characteristics of Primary PCM Multiplex Equipment Operating at 2048kbps”
(ITU-T) Characteristics of a Synchronous Digital Multiplex Equipment Operating at 2048kbps”
(ITU-T) “Loss Of Signal (LOS) and Alarm Indication Signal (AIS) Defect Detection and Clearance Criteria”
(ITU-T) “The Control of Jitter and Wander Within Digital Networks Which are Based on the 2048kbps Hierarchy”
(ITU-T) “Primary Rate User-Network Interface—Layer 1 Specification”
(ITU-T) “Error Performance Measuring Equipment Operating at the Primary Rate and Above”
(ITU-T) “In-Service Code Violation Monitors for Digital Systems”
(ETS) “Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN); Primary Rate User-Network Interface (UNI); Part 1/Layer 1
Specification”
(ETS) “Transmission and Multiplexing; Physical/Electrical Characteristics of Hierarchical Digital Interfaces for
Equipment Using the 2048kbps-Based Plesiochronous or Synchronous Digital Hierarchies”
(ETS) “Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN); Access Digital Section for ISDN Primary Rate”
(ETS) “Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN); Attachment Requirements for Terminal Equipment to Connect to
an ISDN Using ISDN Primary Rate Access”
(ETS) “Business Telecommunications (BT); Open Network Provision (ONP) Technical Requirements; 2048kbps
Digital Unstructured Leased Lines (D2048U) Attachment Requirements for Terminal Equipment Interface”
(ETS) “Business Telecommunications (BTC); 2048kbps Digital Structured Leased Lines (D2048S); Attachment
Requirements for Terminal Equipment Interface”
(ITU-T) “Synchronous Frame Structures Used at 1544, 6312, 2048, 8488, and 44736kbps Hierarchical Levels”
(ITU-T) “Frame Alignment and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) Procedures Relating to Basic Frame Structures
Defined in Recommendation G.704”
15 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
5. ACRONYMS AND GLOSSARY
This data sheet assumes a particular nomenclature of the T1 and E1 operating environment. In each 125μs T1
frame, there are 24 8-bit channels plus a framing bit. It is assumed that the framing bit is sent first followed by
channel 1. For T1 and E1 each channel is made up of 8 bits, which are numbered 1 to 8. Bit 1, the MSB, is
transmitted first. Bit 8, the LSB, is transmitted last.
Locked refers to two clock signals that are phase- or frequency-locked or derived from a common clock (i.e., a
1.544MHz clock can be locked to a 2.048MHz clock if they share the same 8kHz component).
Table 5-1. Time Slot Numbering Schemes
TS
Channel
Phone
Channel
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
16 of 310

DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
6. MAJOR OPERATING MODES
The DS26519 has two major modes of operation: T1 mode and E1 mode. The mode of operation for each LIU is
configured in the
operation is a special case of T1 operating mode.
LTRCR register. The mode of operation for each framer is configured in the TMMR register. J1
17 of 310
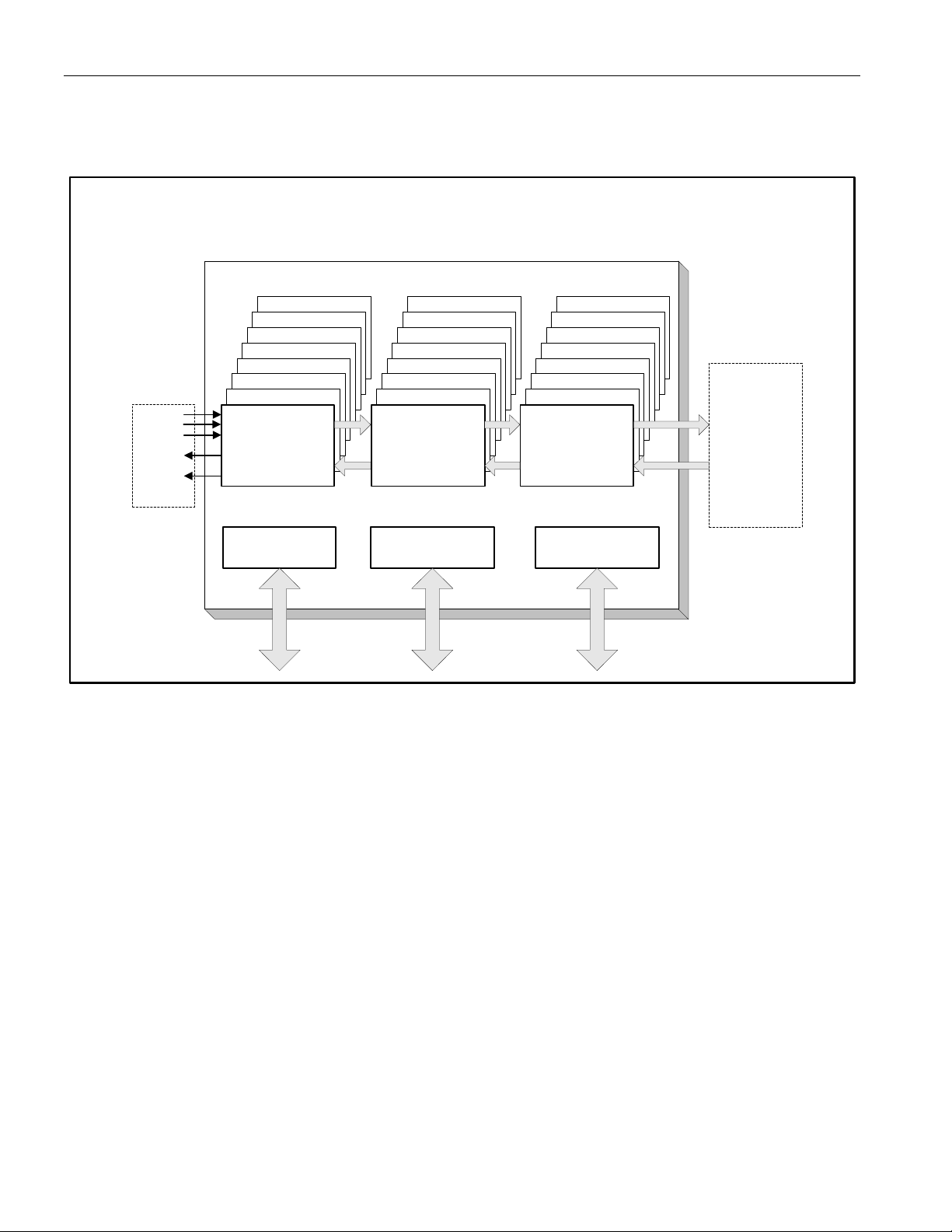
7. BLOCK DIAGRAMS
Figure 7-1. Block Diagram
DS26519
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
RTIP
RTIPE
RRING
TTIP
TRING
x16
LIU #16
LIU #15
LIU #14
...
LIU #4
LIU #3
LIU #2
LINE
INTERFACE
UNIT
MICRO PROCESSOR
INTERFACE
CONTROLLER
PORT
FRAMER #16
FRAMER #15
FRAMER #14
...
FRAMER #4
FRAMER #3
FRAMER #2
T1/E1 FRAMER
HDLC
BERT
JTAG PORT
TEST
PORT
INTERFACE #16
INTERFACE #15
INTERFACE #14
...
INTERFACE #4
INTERFACE #3
INTERFACE #2
BACKPLANE
INTERFACE
ELASTIC
STORES
CLOCK
GENERATION
CLOCK
ADAPTER
RECEIVE
BACKPLANE
SIGNALS
TRANSMIT
BACKPLANE
SIGNALS
HARDWARE
ALARM
INDICATORS
x16
18 of 310
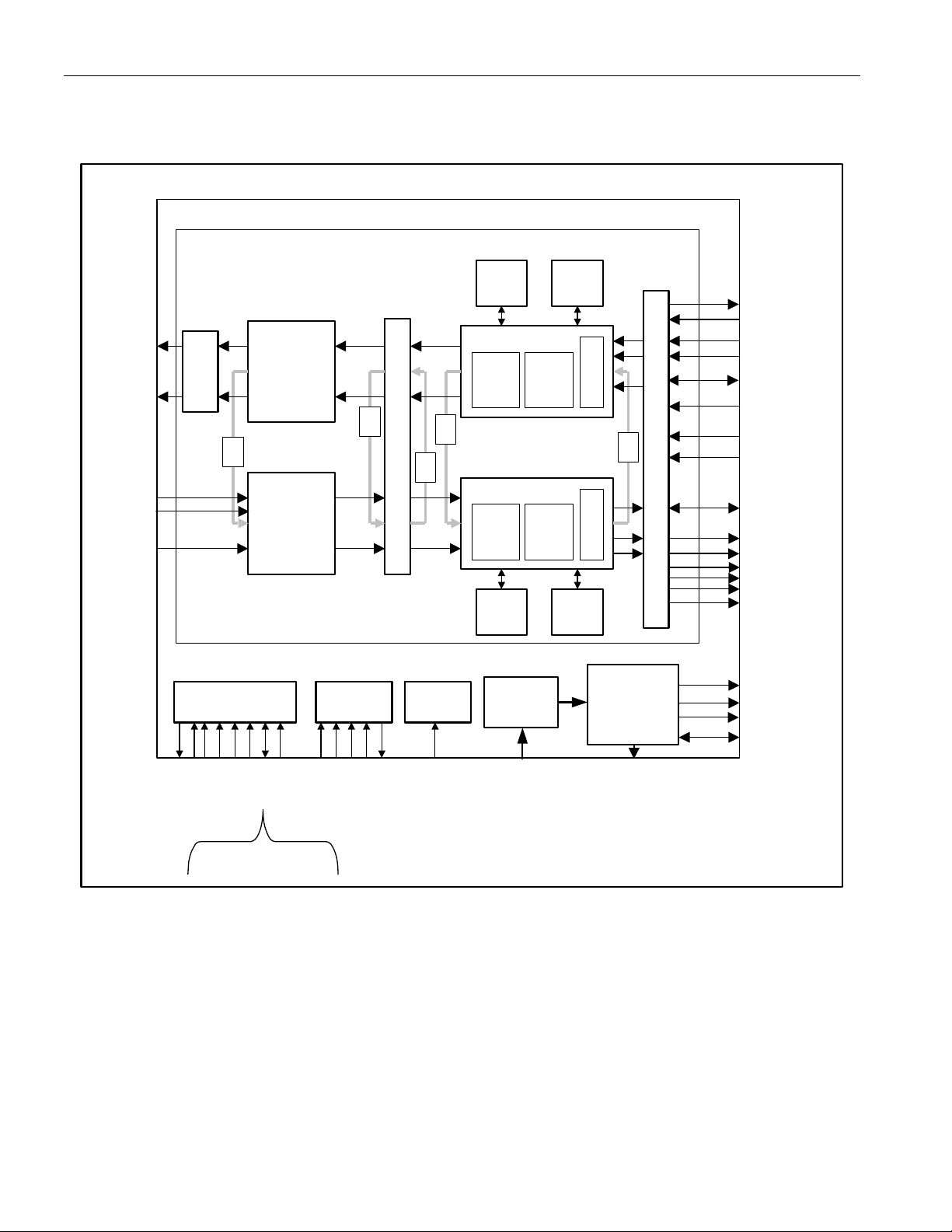
Figure 7-2. Detailed Block Diagram
TRANSCEIVER 1 OF 16
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
DS26519
TTIPn
TRINGn
RTIPn
RTIPEn
RRINGn
TRANSMIT
ENABLE
TRANSMIT
Waveform
Shaper/Line
ALB
RECEIVE
Clock/Data
Recovery
MICROPROCESSOR
INTERFACE
D[7:0]
CSB
RDB/DSB
WRB/RWB
BTS
INTB
SPI_SEL
LIU
Driver
LIU
A[13:0]
JTRST
JTAG
PORT
JTMS
JTCLK
JTDI
LLB
Tx
BERT
Tx FRAMER:
FLB
B8ZS/
HDB3
Encode
JITTER ATTENUATOR
RLB
Rx FRAMER:
B8ZS/
HDB3
Decode
Rx
BERT
RESET
BLOCK
JTDO
RESETB
PRE-SCALER
PLL
MCLK
Elastic
Store
Elastic
Store
Tx
HDLC
Rx
HDLC
System IF
PLB
System IF
CLOCK
SYNTHESIZ-
ER
CLKO
BACKPLANE INTERFACE
TCHBLK/CLKn
TSIGn
TCLKn
TSERn
TSYNCn
TSSYNCIO
(Input Mode)
TSYSCLKn
RSYSCLKn
RSYNCn
RSERn
RCLKn
RCHBLK/CLKn
RSIGn
RM/RFSYNCn
GPIOn
TSSYNCIO
(Output Mode)
BPCLK1
BPCLK2
REFCLKIO
Serial Interface Mode:
(SCLK, CPOL, CPHA,
SPI
SWAP, MOSI, and MISO)
19 of 310
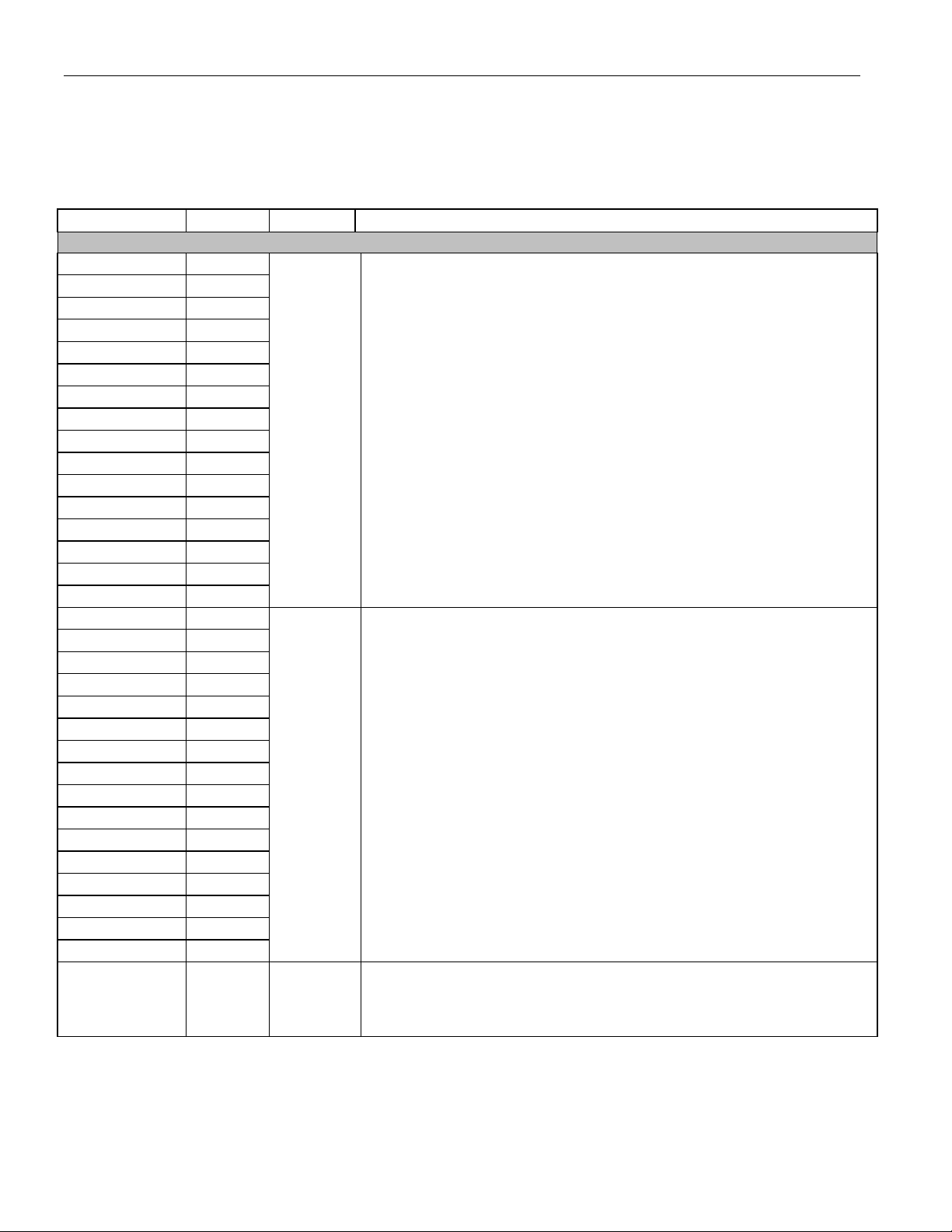
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
8. PIN DESCRIPTIONS
8.1 Pin Functional Description Table 8-1. Detailed Pin Descriptions
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
ANALOG TRANSMIT
TTIP1 C5, D5
TTIP2 N4, N5
TTIP3 T4, T5
TTIP4 V3, V4
TTIP5 W18, Y18
TTIP6 K18, K19
TTIP7 G18, G19
TTIP8 F18, F19
TTIP9 V12, W12
TTIP10 V13, W13
TTIP11 V16, W16
TTIP12 L18, L19
TTIP13 D11, E11
TTIP14 D10, E10
TTIP15 D7, E7
TTIP16 M4, M5
TRING1 D6, E6
TRING2 P4, P5
TRING3 R4, R5
TRING4 U4, U5
TRING5 V17, W17
TRING6 J18, J19
TRING7 H18, H19
TRING8 E19, E20
TRING9 Y11, Y12
TRING10 V14, W14
TRING11 V15, W15
TRING12 L20, M20
TRING13 C11, C12
TRING14 D9, E9
TRING15 D8, E8
TRING16 L3, M3
TXENABLE U16 Input
Analog
Output,
High
Impedance
Analog
Output,
High
Impedance
Transmit Bipolar Tip for Transceiver 1 to 16. These pins are diff erential line
driver tip outputs. These pins can be high impedance if:
If TXENABLE is low, TTIPn/TRINGn will be high impedance. Note that if
TXENABLE is low, the register settings for control of TTIPn/TRINGn are ignored
and output is high impedance.
The differential outputs of TTIPn and TRINGn can provide internal matched
impedance for E1 75
internal termination.
Note: The two pins shown for each transmit bipolar tip (e.g., pins C5 and D5 for
TTIP1) should be tied together.
Transmit Bipolar Ring for Transceiver 1 to 16. These pins are differenti al line
driver ring outputs. These pins can be high impedance if :
If TXENABLE is low, TTIPn/TRINGn will be high impedance. Note that if
TXENABLE is low, the register settings for control of TTIPn/TRINGn are ignored
and output is high impedance.
The differential outputs of TTIPn and TRINGn can provide internal matched
impedance for E1 75
internal termination.
Note: The two pins shown for each transmit bipolar ring (e.g., pins D6 and E6
for TRING1) should be tied together.
Transmit Enable. If this pin is pulled low, all transmitter outputs (TTIPn and
TRINGn) are high impedance. The register settings for tri-stat e control of
TTIPn/TRINGn are ignored if TXENABLE is low. If TXENABLE is high, the
particular driver can be tri-stated by the register settings.
Ω, E1 120Ω, T1 100Ω, or J1 110Ω. The user can turn off
Ω, E1 120Ω, T1 100Ω, or J1 110Ω. The user can turn off
20 of 310
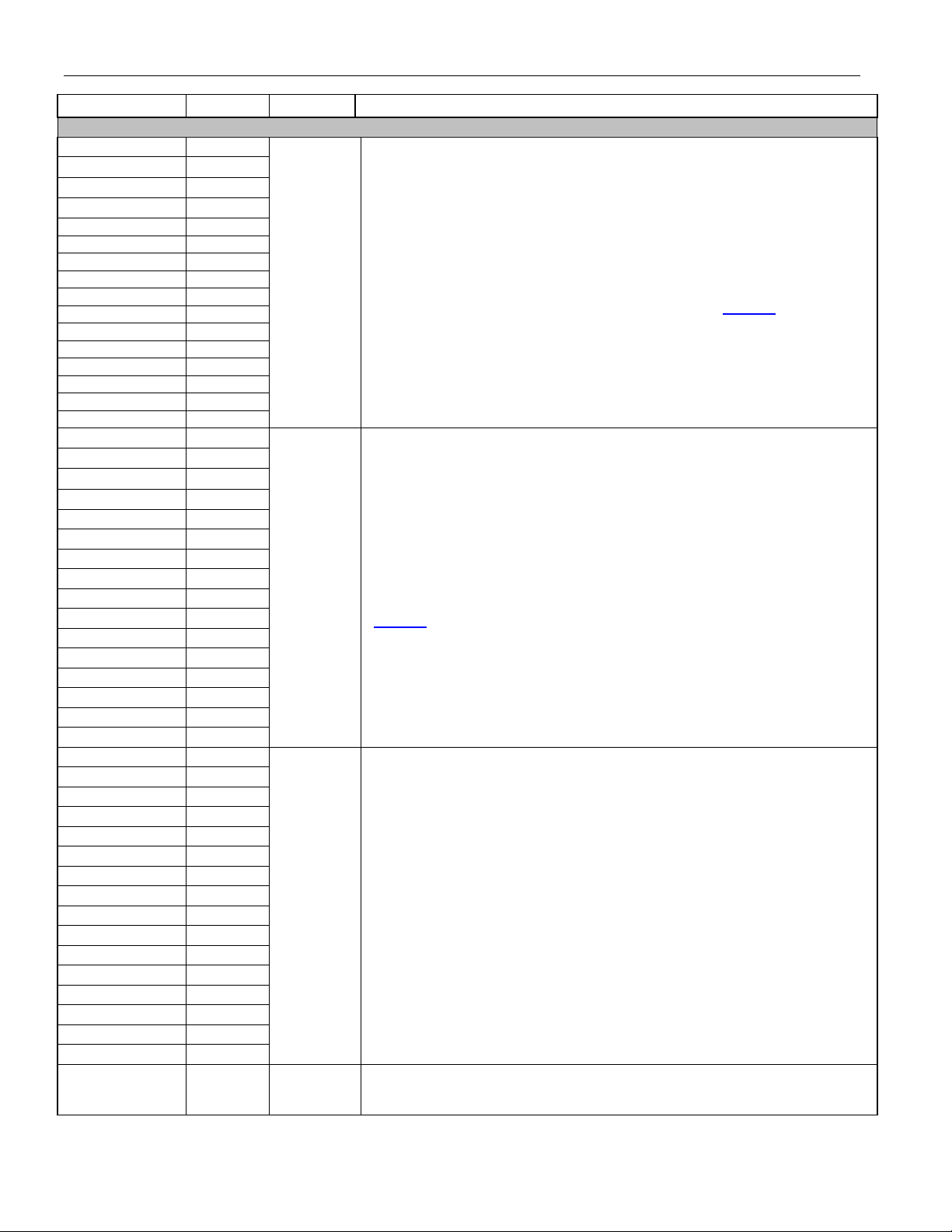
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
ANALOG RECEIVE
RTIP1 B4
RTIP2 T2
RTIP3 U1
RTIP4 Y2
RTIP5 AA20
RTIP6 J21
RTIP7 G21
RTIP8 C21
RTIP9 AB13
Analog
Input
RTIP10 AB15
RTIP11 AB17
RTIP12 M22
RTIP13 A11
RTIP14 A9
RTIP15 B6
RTIP16 N1
RRING1 A4
RRING2 R2
RRING3 V2
RRING4 Y1
RRING5 AB20
RRING6 H22
RRING7 F21
RRING8 D22
RRING9 AB12
Analog
Input
RRING10 AA15
RRING11 AA18
RRING12 N22
RRING13 A12
RRING14 B9
RRING15 A6
RRING16 N2
RTIPE1 A3
RTIPE2 R1
RTIPE3 V1
RTIPE4 AA1
RTIPE5 AB21
RTIPE6 J22
RTIPE7 F22
RTIPE8 C22
RTIPE9 AA13
Analog
Input
RTIPE10 AA16
RTIPE11 AB18
RTIPE12 L22
RTIPE13 A13
RTIPE14 B8
RTIPE15 A7
RTIPE16 M1
RESREF E5 Input
Receive Bipolar Tip for Transceiver 1 to 16. The differential inputs of RTIPn
and RRINGn can provide partially internal impedance matching for E1 75
120
Ω, T1 100Ω, or J1 110Ω. The user can turn off internal termination via the
LIU Receive Impedance and Sensitivity Monitor register (
Receive Bipolar Ring for Transceiver 1 to 16. The differential inputs of RTIPn
and RRINGn can provide partially internal impedance matching for E1 75
120
Ω, T1 100Ω, or J1 110Ω. The user has the option of turning off internal
termination via the LIU Receive Impedance and Sensit ivity Monitor register
LRISMR).
(
Receive Tip External Termination 1 to 16. These pins are used with RTIPn to
provide the ability to switch out the external termination resistor, thereby
providing high impedance to the line. Useful for redundancy applications.
Resistor Reference. This pin is used to calibrate the internal impedance match
resistors of the receive LIUs. This pin should be tied to V
resistor.
Ω, E1
LRISMR).
Ω, E1
through a 10kΩ ±1%
SS
21 of 310
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
TRANSMIT FRAMER
TSER1 B15
TSER2 D14
TSER3 T8
TSER4 R12
TSER5 T10
TSER6 U11
TSER7 C17
TSER8 E17
TSER9 U21
TSER10 R20
TSER11 W6
TSER12 C1
TSER13 E1
TSER14 H1
TSER15 H15
TSER16 F17
TCLK1 F7
TCLK2 G10
TCLK3 R8
TCLK4 AB4
TCLK5 AB6
TCLK6 AB8
TCLK7 B21
TCLK8 D18
TCLK9 K14
TCLK10 P16
TCLK11 W5
TCLK12 M18
TCLK13 N8
TCLK14 N7
TCLK15 P21
TCLK16 D17
TSYSCLK1 W11
TSYSCLK2 A16
TSYSCLK3 K8
TSYSCLK4 U7
TSYSCLK5 V10
TSYSCLK6 U14
TSYSCLK7 C18
TSYSCLK8 Y21
TSYSCLK9 L4
TSYSCLK10 R19
TSYSCLK11 E2
TSYSCLK12 AA3
TSYSCLK13 J1
TSYSCLK14 J2
TSYSCLK15 E16
TSYSCLK16 M17
Input
Input
Input
Transmit NRZ Serial Data. These pins are sampled on the falling edge of
TCLKn when the transmit-side elastic store is disabled. These pins are sampled
on the falling edge of TSYSCLKn when the transmit-side elastic store is enabled.
In IBO mode, data for multiple framers can be used in high-spee d multiplexed
scheme. This is described in Section
combination of framer data for each of the streams.
TSYSCLKn is used as a reference when IBO is invoked. See
Transmit Clock 1 to 16. A 1.544MHz or a 2.048MHz primary clock. Used to
clock data through the transmit side of the transceiver. T S ERn data is sampled
on the falling edge of TCLKn. TCLKn is used to sample TSERn when the elastic
store is not enabled or IBO is not used.
Transmit System Clock 1 to 16. 1.544MHz, 2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz,
or 16.384MHz clock. Only used when the transmit-side elastic store funct ion is
enabled. Should be tied low in applications t hat do not use the transmit-side
elastic store. The clock can be 4.096MHz, 8.912MHz, or 16.384MHz when IBO
mode is used.
9.8.2. The table there presents the
Table 9-8.
22 of 310
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
TSYNC1/
TSSYNCIO1
TSYNC2/
TSSYNCIO2
TSYNC3/
TSSYNCIO3
TSYNC4/
TSSYNCIO4
TSYNC5/
TSSYNCIO5
TSYNC6/
TSSYNCIO6
TSYNC7/
TSSYNCIO7
TSYNC8/
TSSYNCIO8
TSYNC9/
TSSYNCIO9
TSYNC10/
TSSYNCIO10
TSYNC11/
TSSYNCIO11
TSYNC12/
TSSYNCIO12
TSYNC13/
TSSYNCIO13
TSYNC14/
TSSYNCIO14
TSYNC15/
TSSYNCIO15
TSYNC16/
TSSYNCIO16
TSIG1 B14
TSIG2 C14
TSIG3 P9
TSIG4 R11
TSIG5 T12
TSIG6 U12
TSIG7 B17
TSIG8 F14
TSIG9 U22
TSIG10 V21
TSIG11 U6
TSIG12 A1
TSIG13 F1
TSIG14 H2
TSIG15 G14
TSIG16 G17
F8
D13
R9
AB3
AA7
AA9
D20
H16
K15
N16
Y6
M8
M7
K5
D19
G16
Input/
Output
Input
Transmit Synchronization 1 to 16. A pulse at these pins establishes either
frame or multiframe boundaries for the transmit side. These signals can also be
programmed to output either a frame or multiframe pulse. If these pins are set to
output pulses at frame boundaries, they can also be set t o output double-wide
pulses at signaling frames in T1 mode. The operat ion of these signals is
synchronous with TCLK[1:16] These pins are selected when the transmit elastic
store is disabled.
Transmit System Synchronization In. These pins are selected when the
transmit-side elastic store is enabled. A pulse at these pi ns establishes either
frame or multiframe boundaries for the transmit side. Note that if the elastic store
is enabled, frame or multiframe boundary is established f or t he transmitters.
Should be tied low in applications that do not use the transmit-side elastic store.
The operation of this signal is synchronous with TSYSCLK[1:16].
Transmit System Synchronization Out. If configured as an output and the
transmit elastic store is enabled, an 8kHz pulse synchronou s to BPCLK1 for
TSSYNCIO[1:8] BPCLK2 for TSSYNCIO[9:16] will be generat ed. This pulse in
combination with BPCLK[1:2] can be used as an IBO master. TSSYNCIOn can
be used as a source to RSYNCn and TSSYNCIOn of another DS26519 o r
RSYNC and TSSYNC of other Dallas Semiconductor parts.
Transmit Signaling 1 to 16. When enabled, this input samples signaling bits for
insertion into outgoing PCM data stream. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLKn
when the transmit-side elastic store is disabled. Sampled on the falling edge of
TSYSCLKn when the transmit-side elastic store is enabled. In IBO mode, the
TSIGn streams can run up to 16.384MHz. See
Table 9-9.
23 of 310
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
TCHBLK1/
TCHCLK1
TCHBLK2/
TCHCLK2
TCHBLK3/
TCHCLK3
TCHBLK4/
TCHCLK4
TCHBLK5/
TCHCLK5
TCHBLK6/
TCHCLK6
TCHBLK7/
TCHCLK7
TCHBLK8/
TCHCLK8
TCHBLK9/
TCHCLK9
TCHBLK10/
TCHCLK10
TCHBLK11/
TCHCLK11
TCHBLK12/
TCHCLK12
TCHBLK13/
TCHCLK13
TCHBLK14/
TCHCLK14
TCHBLK15/
TCHCLK15
TCHBLK16/
TCHCLK16
A15
A17
N9
V8
V9
W10
E14
H12
N20
W22
Y5
K6
D1
G2
Y22
F16
Output
Transmit Channel Block/Transmit Channel Block Clock. A dual function pin.
TCHBLK[1:16]. TCHBLKn is a user-programmable output that can be forced
high or low during any of the channels. It is synchronous with TCLKn when the
transmit-side elastic store is disabled. It is synchronous with TSYSCLKn when
the transmit-side elastic store is enabled. It is useful for blocking clocks to a serial
UART or LAPD controller in applications where not all channe ls are used such as
Fractional T1, Fractional E1, 384kbps (H0), 768kbps, or ISDN-PRI. Also useful
for locating individual channels in drop-and-insert applications, for external perchannel loopback, and for per-channel conditioning.
TCHCLK[1:16]. TCHCLKn is a 192kHz (T1) or 256kHz (E1) clock that pulses
high during the LSB of each channel. It can also be programmed to out put a
gated transmit bit clock controlled by TCHBLKn. It is synchr onous with TCLKn
when the transmit-side elastic store is disabled. It is synchronous with
TSYSCLKn when the transmit-side elastic store is enabled. Useful for parallel-toserial conversion of channel data.
24 of 310
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
RECEIVE FRAMER
RSER1 D12
RSER2 E12
RSER3 J5
RSER4 AA4
RSER5 Y10
RSER6 AA10
RSER7 B18
RSER8 T20
RSER9 L17
RSER10 L16
RSER11 B1
RSER12 K7
RSER13 J4
RSER14 P7
RSER15 H13
RSER16 M16
RCLK1 J9
RCLK2 H7
RCLK3 J8
RCLK4 H6
RCLK5 T15
RCLK6 U19
RCLK7 V20
RCLK8 W20
RCLK9 D3
RCLK10 C2
RCLK11 H3
RCLK12 G3
RCLK13 T17
RCLK14 R15
RCLK15 T18
RCLK16 N15
RSYSCLK1 U18
RSYSCLK2 G9
RSYSCLK3 J6
RSYSCLK4 W7
RSYSCLK5 AB7
RSYSCLK6 AB10
RSYSCLK7 C19
RSYSCLK8 AA22
RSYSCLK9 G6
RSYSCLK10 P18
RSYSCLK11 F2
RSYSCLK12 AB2
RSYSCLK13 P8
RSYSCLK14 R7
RSYSCLK15 G15
RSYSCLK16 T19
Output
Ouput
Input
Received Serial Data 1 to 16. Received NRZ serial data. Updated on rising
edges of RCLKn when the receive-side elastic store is disabled. Updated on the
rising edges of RSYSCLKn when the receive-side elastic store is enabled.
When IBO mode is used, the RSERn pins can output data for multiple framers.
The RSERn data is synchronous to RSYSCLKn. See Section
.
9-6
Receive Clock. A 1.544MHz (T1) or 2.048MHz (E1) clock that is used to clock
data through the receive-side framer. This clock is recovered from the signal at
RTIPn and RRINGn. RSERn data is output on the rising edge of RCLKn. RCLKn
is used to output RSERn when the elastic store is not enabled or IBO is not used.
When the elastic store is enabled or IBO is used, the RSERn is clocked by
RSYSCLKn.
Receive System Clock 1 to 16. 1.544MHz, 2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, or
16.384MHz receive backplane clock. Only used when the receive-side elastic
store function is enabled. Should be tied lo w in applications that do not use the
receive-side elastic store. Multiple of 2.048MHz is expected when the IBO mode
is used.
9.8.2 and Table
25 of 310
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
RSYNC1 F9
RSYNC2 E13
RSYNC2 T7
RSYNC2 W3
RSYNC5 W9
RSYNC6 AB9
RSYNC7 A19
RSYNC8 Y19
RSYNC9 N19
RSYNC10 P17
RSYNC11 V5
RSYNC12 L7
RSYNC13 L6
RSYNC14 L5
RSYNC15 E15
RSYNC16 R18
RMSYNC1/
RFSYNC1
RMSYNC2/
RFSYNC2
RMSYNC3/
RFSYNC3
RMSYNC4/
RFSYNC4
RMSYNC5/
RFSYNC5
RMSYNC6/
RFSYNC6
RMSYNC7/
RFSYNC7
RMSYNC8/
RFSYNC8
RMSYNC9/
RFSYNC9
RMSYNC10/
RFSYNC10
RMSYNC11/
RFSYNC11
RMSYNC12/
RFSYNC12
RMSYNC13/
RFSYNC13
RMSYNC14/
RFSYNC14
RMSYNC15/
RFSYNC15
RMSYNC16/
RFSYNC16
C13
C15
V7
T9
T13
U13
D16
W21
T21
V22
V6
H4
G1
K4
F15
N17
Input/
Output
Output
Receive Synchronization. If the receive-side elastic store is enabled, this signal
is used to input a frame or multiframe boundary pulse. If set to output frame
boundaries, RSYNCn can be programmed to output double-wide pulses on
signaling frames in T1 mode. In E1 mode, RSYNCn out can be used to indicate
CAS and CRC-4 multiframe. The DS26519 can accept an H.100-compatible
synchronization signal. The default directio n of this pin at power-up is input, as
determined by the RSIO control bit in the
Receive Multiframe/Frame Synchronization 1 to 16. A dual function pin to
indicate frame or multiframe synchronization. RF SYNCn is an extracted 8kHz
pulse, one RCLKn wide that identifies frame boundaries. RMSYNCn is an
extracted pulse, one RCLKn wide (elastic store disa bled) or one RSYSCLKn wide
(elastic store enabled), that identifies multiframe boundaries. When the receive
elastic store is enabled, the RMSYNCn signal indicates the multiframe sync on
the system (backplane) side of the elastic store. In E1 mode, this pin can indicate
either the CRC-4 or CAS multiframe as determined by the RSMS2 control bit in
the Receive I/O Configuration register (
RIOCR.2 register.
RIOCR.1).
26 of 310
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
RSIG1 D4
RSIG2 B16
RSIG3 J7
RSIG4 R10
RSIG5 U10
RSIG6 V11
RSIG7 H17
RSIG8 V19
RSIG9 F6
RSIG10 P20
RSIG11 D2
RSIG12 Y4
RSIG13 J3
RSIG14 K3
RSIG15 J14
RSIG16 P15
GPIO1 P22
GPIO2 J17
GPIO3 N21
GPIO4 B13
GPIO5 F10
GPIO6 W19
GPIO7 P19
GPIO8 N18
GPIO9 T22
GPIO10 K17
GPIO11 M19
GPIO12 K16
GPIO13 R21
GPIO14 J15
GPIO15 R22
GPIO16 J16
Ouptut
Output
Receive Signaling. Outputs signaling bits in a PCM format. Updated on rising
edges of RCLKn when the receive-side elastic store is disabled. Updated on the
rising edges of RSYSCLKn when the receive-side elastic store is enabled. See
Table 9-7.
General-Purpose I/O 1 to 16. These pins can be used as an input or a
programmable output, or be used to output the following signals: analog loss,
receive signaling freeze, framer LOS, receive loss of frame, or loss of transmit
clock. These pins are controlled by
These pins are controlled on a per-8 basis (GPIO[8:1] and GPIO[ 16:9]).
GTCR1.GPSEL[3:0] and GTCR2. GPSEL[3:0].
27 of 310
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
RCHBLK1/
RCHCLK1
RCHBLK2/
RCHCLK2
RCHBLK3/
RCHCLK3
RCHBLK4/
RCHCLK4
RCHBLK5/
RCHCLK5
RCHBLK6/
RCHCLK6
RCHBLK7/
RCHCLK7
RCHBLK8/
RCHCLK8
RCHBLK9/
RCHCLK9
RCHBLK10/
RCHCLK10
RCHBLK11/
RCHCLK11
RCHBLK12/
RCHCLK12
RCHBLK13/
RCHCLK13
RCHBLK14/
RCHCLK14
RCHBLK15/
RCHCLK15
RCHBLK16/
RCHCLK16
BPCLK1 H8
BPCLK2 R17
CLKO C3 Output
F3
G8
H5
Y7
AA8
AA11
E18
U20
G7
L15
B2
W4
M6
U17
H14
R16
Output
Output
Receive Channel Block/Receive Channel Block Clock. This pin can be
configured to output either RCHBLK or RCHCLK.
RCHBLK[1:16]. RCHBLKn is a user-programmable output that can be forced
high or low during any of the 24 T1 or 32 E1 channels. It is synchro nous with
RCLKn when the receive-side elastic store is disabled. It is synchronous with
RSYSCLKn when the receive-side elastic store is enabled. This pin is useful for
blocking clocks to a serial UART or LAPD controller in applications where not all
channels are used such as fractional service, 384kbps service, 768kbps, or
ISDN-PRI. Also useful for locating individual channels in drop-and-insert
applications, for external per-channel loo pback, and for per-channel conditioning.
RCHCLK[1:16]. RCHCLKn is a 192kHz (T1) or 256kHz (E1) clock that pulses
high during the LSB of each channel. It is synchronous with RCLKn when the
receive-side elastic store is disabled. It is synchronous with RSYSCLKn when the
receive-side elastic store is enabled. It is useful for parallel-to-serial conversion of
channel data.
Backplane Clock [1:2]. Programmable clock outputs that can be set to
2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, or 16.384MHz. The reference to these clocks
can be RCLK[8:1] for BPCLK1 and RCLK[9:16] for BPCLK2, a 1.544MHz or
2.048MHz clock frequency derived from MCLK, or an external reference clock
(REFCLKIO). This allows system clocks to be referenced from external sources,
the T1J1E1 recovered clocks, or the MCLK oscillator.
Clock Out. Clock output pin that can be programmed to output numero us
frequencies referenced to MCLK. Frequencies available: 1.544MHz, 2.048MHz,
4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, 12.288MHz, 16.384MHz, 256kHz, and 64kHz.
GTCCR3.CLKOSEL[3:0] selects the frequency.
28 of 310
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE
A13 C16
A12 F12
A11 A20
A10 G11
A9 H9
A8 A21
A7 F13
A6 A22
A5 H10
A4 B19
A3 H11
A2 D15
A1 G13
A0 B20
D[7]/
SPI_CPOL
D[6]/
SPI_CPHA
D[5]/
SPI_SWAP
D[4] T14 Input
D[3] AB5 Input
D[2]/
SPI_SCLK
D[1]/
SPI_MOSI
D[0]/
SPI_MISO
CSB
RDB/
DSB
Y9 Input
U8 Input
AA6 Input
R14 Input
AA5 Input
P14 Input
W8 I
Y8 I
Input
Address [13:0]. This bus selects a specific register in the DS26519 during
read/write access. A13 is the MSB and A0 is the LSB.
Data [7]/SPI Interface Clock Polarity
D[7]:
Bit 7 of the 16-bit or 8-bit data bus used to input data during register writes
and data outputs during register reads. Not driven when
SPI_CPOL: This signal selects the clock polarity when SPI_SEL = 1. See Section
9.1.2 for detailed timing and functionality information. Default setting is low.
Data [6]/SPI Interface Clock Phase
Bit 6 of the 16-bit or 8-bit data bus used to input data during register writes
D[6]:
and data outputs during register reads. Not driven when
SPI_CPHA: This signal selects the clock phase when SPI_SEL = 1. See Section
9.1.2 for detailed timing and functionality information. Default setting is low.
Data [5]/SPI Bit Order Swap
Bit 5 of the 16-bit or 8-bit data bus used to input data during register writes
D[5]:
and data outputs during register reads. Not driven when
SPI_SWAP: This signal is active when SPI_SEL = 1. The address and data bit
order is swapped when SPI_SWAP is high. The R/W and B bit positions are
never changed in the control word.
0 = LSB is transmitted and received first.
1 = MSB is transmitted and received first.
Data [4]. Bit 4 of the 8-bit data bus used to input data during register writes and
data outputs during register reads. Not driven when
Data [3]. Bit 3 of the 8-bit data bus used to input data during register writes and
data outputs during register reads. Not driven when
Data [2]/SPI Serial Interface Clock
D[2]: Bit 2 of the 8-bit data bus used to input data durin g register writes and data
outputs during register reads. Not driven when
SPI_SCLK: SPI Serial Clock Input when SPI_SEL = 1.
Data [1]/SPI Serial Interface Data Master Out-Slave In
D[1]
: Bit 1 of the 8-bit data bus used to input data during register writes, and data
outputs during register reads. Not driven when
SPI_MOSI: SPI Serial Data Input (Master Out-Slave In) when SPI_SEL = 1.
Data [0]/SPI Serial Interface Data Master In-Slave Out
Bit 0 of the 8-bit data bus used to input data during register writes and data
D[0]:
outputs during register reads. Not driven when
SPI_MISO: SPI Serial Data Output (Master In-Slave Out) when SPI_SEL = 1.
Chip-Select Bar. This active-low signal is used to qualify register read/write
accesses. The
Read-Data Bar/Data-Strobe Bar. This active-low signal along with CSB qualifies
read access to one of the DS26519 registers. The DS26519 drives the data bus
with the contents of the addressed register while
RDB/DSB and WRB signals are qualified with CSB.
CSB = 1.
CSB = 1.
CSB = 1.
RDB and CSB are low.
CSB = 1.
CSB = 1.
CSB = 1.
CSB = 1.
CSB = 1.
29 of 310
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
NAME PIN TYPE FUNCTION
WRB/
RWB
R13 Input
Output/
INTB
U9
Tri-
Stateable
SPI_SEL F5 Input
BTS U15 Input
Write-Read Bar/Read-Write Bar. This active-low signal along with CSB qualifies
write access to one of the DS26519 registers. Data at D[7: 0] is written into the
addressed register at the rising edge of
Interrupt Bar. This active-low output is asserted when an unmasked interrupt
event is detected.
INTB will be deasserted (and tri-stated) when all interrupts
WRB while CSB is low.
have been acknowledged and serviced. Extensive mask bits are provided at the
global level, framer, LIU, and BERT level.
SPI Serial Bus Mode Select
0 = Parallel Bus Mode
1 = SPI Serial Bus Mode
Bus Type Select. Set high to select Motorola bus timing, low to select Intel bus
timing. This pin controls the function of the
mode is selected by the SPI_SEL pin, this pin must be tied low.
SYSTEM INTERFACE
Master Clock. This is an independent free-running clock whose input can be a
RDB/DSB and WRB pins. Note: If SPI
multiple of 2.048MHz ±50ppm or 1.544MHz ±50ppm. The clock selection is
MCLK F11 Input
available by bits MPS0 and MPS1 and FREQSEL. Multiple of 2.048MHz can be
internally adapted to 1.544MHz. Multiple of 1.544MHz can be adapted to
2.048MHz. Note that TCLKn must be 2.048MHz for E1 and 1.544M Hz for T1/J1
Table 10-14.
RESETB
operation. See
T16 Input
Reset Bar. Active-low reset. This input forces the complete DS26519 reset. This
includes reset of the registers, framers, and LIUs.
Reference Clock Input/Output
Input:
A 2.048MHz or 1.544MHz clock input. This clock can be used to generate
the backplane clock. This allows for the users to synchronize the system
backplane with the reference clock. The other options for the backplane clock
REFCLKIO A18
Input/
Output
reference are LIU-received clocks or MCLK.
Output: This signal can also be used to output a 1.544MHz or 2.048MHz
reference clock. This allows for multiple DS26519s to share the same ref erence
for generation of the backplane clock. Hence, in a system c onsisting of multiple
DS26519s, one can be a master and others a slave using the same reference
clock.
TEST
Digital Enable. When this pin and JTRST are pulled low, all digital I/O pins are
placed in a high-impedance state. If this pin is high t he digital I/O pins operate
normally. This pin must be connected to V
JTAG Reset. JTRST is used to asynchronously reset the test access port
controller. After power-up,
JTRST must be toggled from low to high. This action
for normal operation.
DD
sets the device into the JTAG DEVICE ID mode. Pulling
normal device operation.
JTRST is pulled high internally via a 10kΩ resistor
DIGIOEN A14
JTRST
F4
Input,
Pullup
Input,
Pullup
operation. If boundary scan is not used, this p in should be held low.
JTMS G4
Input,
Pullup
JTCLK E3 Input
JTDI G5
Input,
Pullup
Output,
JTDO E4
High
Impedance
SCANEN N6 Input
SCANMODE V18 Input
JTAG Mode Select. This pin is sampled on the rising edge of JTCLK and is used
to place the test access port into the various defined IEEE 1149.1 states. This pin
has a 10k
JTAG Clock. This signal is used to shift data into JTDI on the rising edge and out
Ω pullup resistor.
of JTDO on the falling edge.
JTAG Data In. Test instructions and data are clocked into this pin on the rising
edge of JTCLK. This pin has a 10k
JTAG Data Out. Test instructions and data are clocked out of this pin on the
Ω pullup resistor.
falling edge of JTCLK. If not used, this pin should be left unconnected.
Scan Enable. When low, the device is in normal operation. User should tie low.
Scan Mode. When low, normal operational clocks are used to clock the flip flops.
User should tie low.
TST_TA1 T6
TST_TB1 K1
TST_TC1 R6
TST_RA1 K2
Output
LIU Test Points. Test signals from LIU 1. User should leave unconnected.
TST_RB1 P6
TST_RC1 L2
30 of 310
JTRST low restores
 Loading...
Loading...