Page 1
Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard
Quick Start Guide
Rev 0; 2/14
Maxim Integrated cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim Integrated product. No circuit
patent licenses are implied. Maxim Integrated reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
Maxim Integrated 160 Rio Robles, San Jose, CA 95134 USA 1-408-601-1000
© 2014 Maxim Integrated Products, Inc. Maxim Integrated and the Maxim Integrated logo are trademarks of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Page 2

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
Table of Contents
1. Required Equipment ................................................................................................. 3
2. Overview ................................................................................................................... 3
3. Included Files ........................................................................................................... 5
4. Procedure ................................................................................................................. 6
5. Code Documentation .............................................................................................. 19
6. Appendix A: Project Structure and Key Filenames ................................................. 20
7. Trademarks ............................................................................................................ 20
8. Revision History ...................................................................................................... 21
2
Page 3

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
1. Required Equipment
• PC with Windows® OS with Xilinx® ISE®/SDK version 14.2 or later and two USB
ports (Refer to Xilinx AR# 51895 if you installed ISE WebPackTM design software
on your PC.)
• License for Xilinx EDK/SDK version 14.2 or later (free WebPack license is OK)
• Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) board
• ZedBoardTM development kit
• Industrial sensor or signal source
2. Overview
Below is a high-level overview of the steps required t o quickly get the Petaluma design
running by downloading and running the FPGA project. Detailed instructions for each
step are provided in the following pages. The Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#)
subsystem reference design will be referred to as Petaluma throughout this
document.
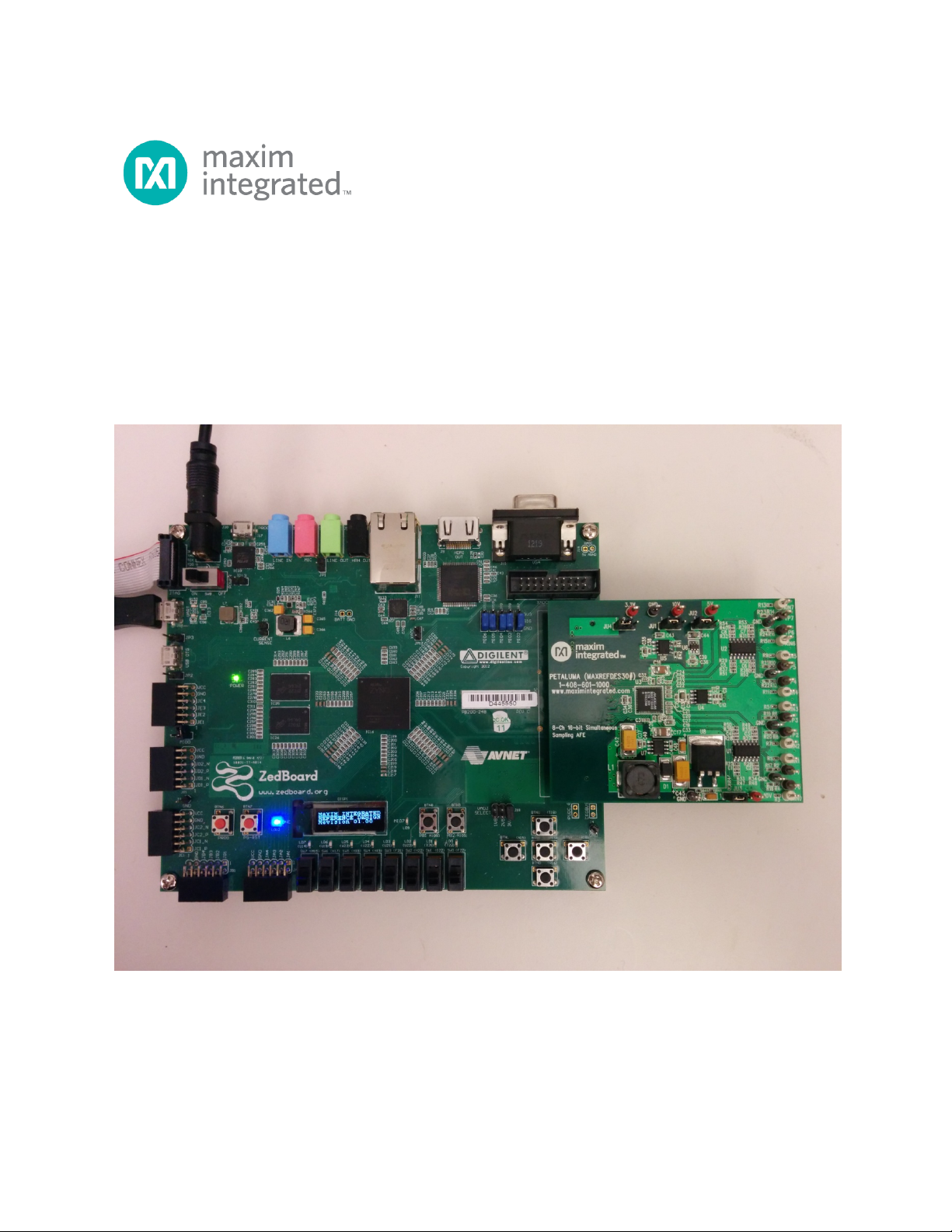
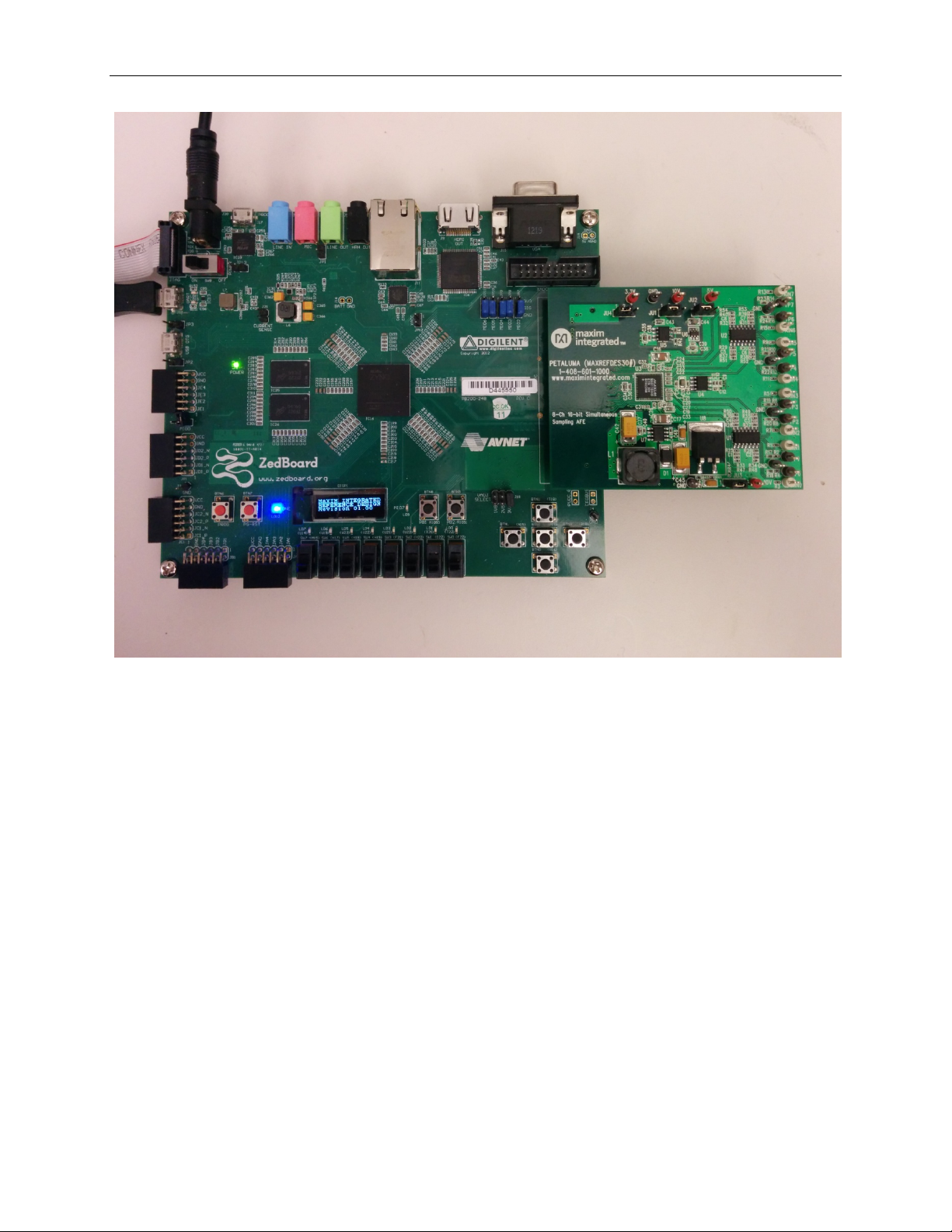
1) Connect the Petaluma board to the J1 FMC connector of a ZedBoard as shown
in Figure 1.
2) Download the latest RD30V01_00.ZIP file located at the Petaluma page.
3) Extract the RD30V01_00.ZIP file to a directory on your PC.
4) Open the Xilinx SDK.
5) Download the bitstream (.BIT) file to the board. This bitstream contains the FPGA
hardware design and software bootloader.
6) Use Xilinx SDK to download and run the executable file (.ELF) on one of the two
ARM® CortexTM-A9 processors.
3
Page 4
Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
Figure 1. Petaluma Board Connected to ZedBoard Development Kit
4
Page 5
Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
3. Included Files
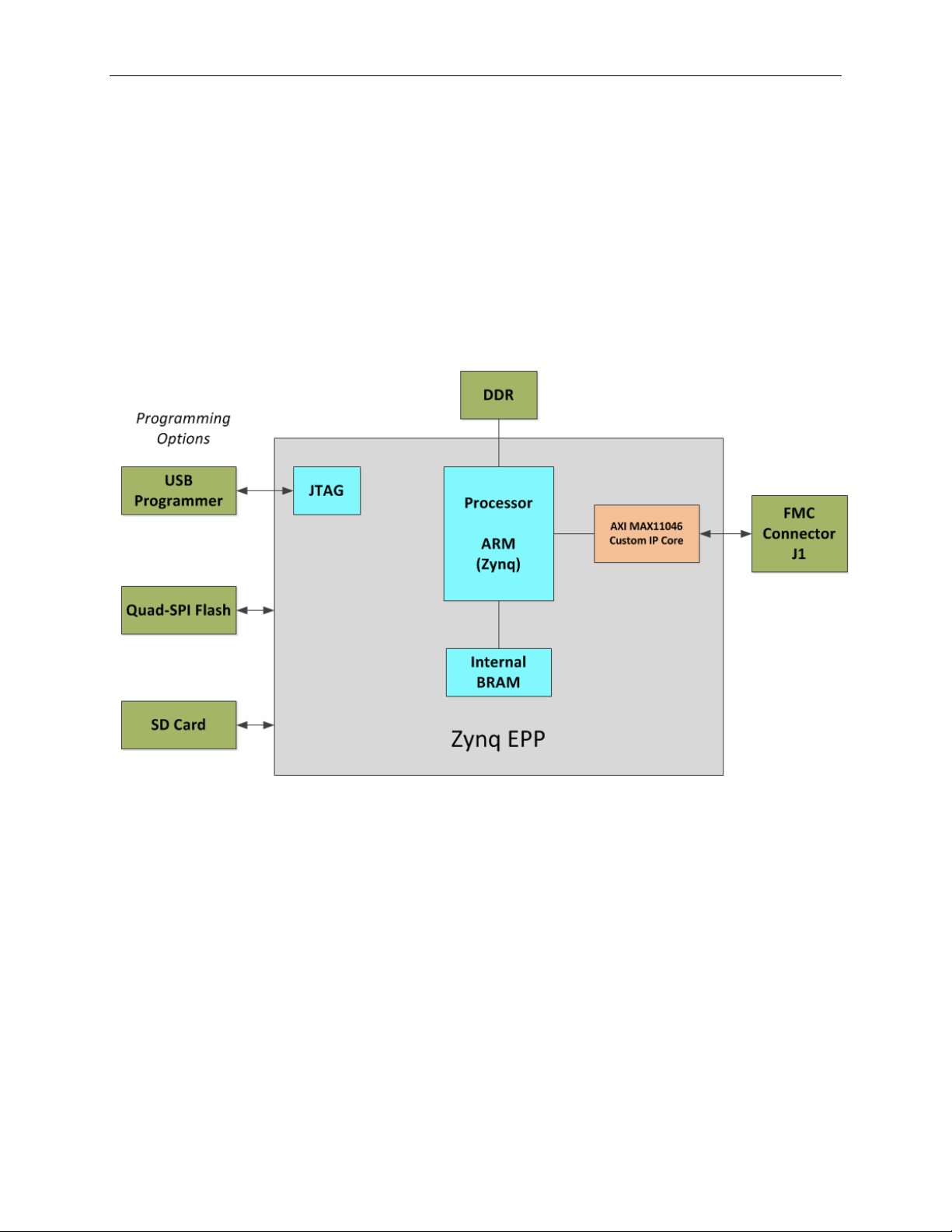
The top level of the hardware design is a Xilin x PlanAhead™ Project (.PRR) for Xilinx
PlanAhead version 14.2. The Verilog-based arm_system_stub.v module provides
FPGA/board net connectivity, and instantiates the wrapper t hat carries both the Zynq®
Processing System and AXI_MAX11046 custom IP core that interface to the FMC
connector. This is supplied as a Xilinx software development kit (SDK) project that
includes a demonstration software application to evaluate the Petaluma subsystem
reference design. The lower level c-code driver routines are portable to the user ’s own
software project.
5
Figure 2. Block Diagram of FPGA Hardware Design
Page 6

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
4. Procedure
1. Install a 2-pin h eader on the J18 connector on the ZedBoard if the 3V3 hea der is
missing.
2. Remove any shunt on 1V8 and 2V5 headers, and install a shunt on the 3V3
header.
3. Connect the Petaluma board to the J1 FMC connector of the ZedBoard as shown
in Figure 1.
4. Power up the ZedBoard by slidin g the SW8 switch on the ZedBoard to the ON
position.
5. Download the latest RD30V01_00.ZIP file at
www.maximintegrated.com/Petaluma
available at the bottom of the page.
6. Extract the RD30V01_00.ZIP file to a directory on your PC. The location is
arbitrary but the maximum path length limitation in Windows (260 characters)
should not be exceeded.
In addition, the Xilinx tools require the path to not contain any spaces.
C:\Do Not Use Spaces In The Path\RD30V01_00.ZIP
(This path has spaces.)
For the purposes of this document, it will be C:\designs\maxim\RD30V01_00\.
See Appendix A: Project Structure and Key Filenames in this document for
the project structure and key filenames.
. All files available for download are
6
Page 7
Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
7. Open the Xilinx Software Development Kit (SDK) from the Windows Start
menu.
8. SDK will prompt for a workspace directory, which is the location where the
software project is located. For this example, it is:
C:\designs\maxim\RD30V01_00\RD6_ZED_V01_00\Design_Files\top.sdk\SDK\
SDK_Export
Click OK and SDK will open. The Xilinx SDK is based on an Eclipse™-based
IDE, so it will be a familiar flow for many software developers.
7
Page 8

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
9. Review the SDK IDE. The Project Explorer in the upper left tab should have
three components as shown in the image below. If all three subfolders are
present, you can skip the next step.
8
Page 9

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
10. If the Project Explorer does not contain these three subfolders, launch the
File | Import menu, expand the General folder, and select Existing Projects
into Workspace. Click Next. Set the root directory to:
C:\designs\maxim\RD30V01_00\RD30_ZED_V01_00\Design_Files\top.sdk\SDK\
SDK_Export
and the missing projects should appear in SDK Project Explorer with their
checkboxes checked.
Click Finish to import the projects.
9
Page 10

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
11. To download the bitstream (.BIT) file to the board, click on the Program FPGA
icon (which looks like a green chain of devices).
The Program FPGA dialog box appears. From here, an FPGA bitstream (.BIT)
file is selected. Be sure to select the .BIT file by using the paths below.
Bitstream:
C:\designs\maxim\RD30V01_00\RD30_ZED_V01_00\Design_Files\top.sdk\
SDK\SDK_Export\arm_system_hw_platform
Press Program.
10
It takes approximately 10 seconds to download the FPGA, then a message box
indicating FPGA configuration complete appears.
Page 11

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
12. Set up t he terminal program to run on the PC using the following steps. Before
loading the executable firmware file on the FPGA, the terminal program on the
PC should be running. The example firmware running on the FPGA
communicates with the PC via a USB port set up to emulate a serial port (UART).
To establish this communication link, the PC must be configured with the
appropriate Windows drivers. A suitable terminal program such as Tera Term or
HyperTerminal should be invoked.
The ZedBo ard utilizes the Cypress USB-UART bridge IC. I f the Windows cannot
automatically install the driver for the Cypress USB-UART bridge IC, the dr iver is
available for download from (www.cypress.com/?rID=63794). The driver is
WHQL certified for the default Cypress VID / PID of 0x04B4 / 0x0008.
Once installed, Windows will assign a previously unused COM port. Use the
Windows Control Panel | System | Device Manager to determine the COM port
number. (It will be named Cypress Serial.) Make a n ote of which COM port this
is. That information is needed in the next step.
Next, a terminal emulation program needs to be installed and launched. For
Windows XP® and earlier systems, the HyperTerminal program is the usual
choice. However, since HyperTerminal was eliminated from Windows 7, it may
be necessary to locate an alternative. Several are available; one good choice is
called Tera Term (http://ttssh2.sourceforge.jp/). Whatever terminal program you
choose, the communication should be set up by opening the COM port number
previously described above and the port configured as:
bits per second: 460,800;
data bits: 8;
parity: none;
stop bits: 1;
flow control: none.
Note: If the terminal program does not connect correctly at the baud rate above,
drop the baud rate to 115.2kbps.
11
Page 12

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
13. Use the Xilinx SDK to download and run the executable ELF (.ELF) file on the
ARM Cortex-A9 processor using the following steps.
Right-click the mouse while the MAXREFDES30 C project is selected, c hoose
the Run As menu, and then Run Configurations… menu as shown below.
12
Page 13

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
Next, double-click the mouse on the Xilinx C/C++ ELF menu.
13
Page 14

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
Next, press the Search Project button.
14
Page 15

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
Double-click on the MAXREFDES30.elf binary.
15
Page 16

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
Verify the application is selected on the Main tab.
16
Page 17

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
On the Device Initialization tab, click Browse… button to select the right
initialization TCL file and press the Run button.
Once the Debug/MAXREFDES30 configuration is set up once, you just need to
press the Run button if you ever want to run the program again.
17
Page 18

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
At this point, the application is running on the Cortex-A9 and the terminal
program should show the menu below. Make the de sired selections by pressing
the appropriate keys on the keyboard. For example, to select continuous
sampling, press 0.
18
Page 19

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
5. Code Documentation
Code documentation can be found at:
C:\...\RD30V01_00\RD30_ZED_V01_00\Code_Documentation\
To view the code documentation in HTML format with a browser, open the
MainPage.html file.
To view the code documentation in .PDF format with a PDF reader, open the
MAXREFDES30_Code_Documentation.pdf file.
19
Page 20

Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
Top level folder contains:
• Numerous source and intermediate files (PlanAhead generated)
• top.ppr = main Xilinx PlanAhead project file.
• top.* = the Xilinx PlanAhead top level project folders
SDK Export Folder
• \MAXREFDESX = C Project Folder
\src\MAXREFDESX.c = Main example program
\src\maximDeviceSpecificUtilities.c = driver functions
\src\menu.c = menu functions
\src\utilities.c = generic system and FPGA helper functions
\src\platform.c = low-level routines, Xilinx generated
• \MAXREFDESX_bsp_0 = Board support package
• \arm_system_hw_platform = Hardware platform spcification
Driver folder for the AXI_MAX11046 custom IP core
• \axi_max11046_vX_XX_X\src\axi_max11046.c = driver functions
• \axi_max11046_vX_XX_X\src\axi_max11046.h = driver header file
Pcore folder contains:
• The HDL source files for the AXI_MAX11046 custom IP core
• \axi_max11046_vX_XX_X\hdl\verilog\axi_max11046.v = Top level
design, instantiates library components and user logic
• \axi_max11046_vX_XX_X\hdl\verilog\user_logic.v = User logic module
that implements the MAX11046 ADC SPI interface
6. Appendix A: Project Structure and Key Filenames
7. Trademarks
ARM is a registered trademark and registered service mark of ARM Ltd.
Cortex is a trademark of ARM Ltd.
Eclipse is a trademark of Eclipse Foundation, Inc.
MicroBlaze is a trademark of Xilinx, Inc.
PlanAhead is a trademark of Xilinx, Inc.
Windows is a registered trademark and registered service mark and Windows XP is a
registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Xilinx is a registered trademark and registered service mark of Xilinx, Inc.
ZedBoard is a trademark of ZedBoard.org.
Zynq is a registered trademark of Xilinx, Inc.
20
Page 21

8. Revision History
REVISION
NUMBER
REVISION
DATE
PAGES
CHANGED
0
2/14
Initial release
—
Petaluma (MAXREFDES30#) ZedBoard Quick Start Guide
DESCRIPTION
21
 Loading...
Loading...