19-5235; Rev 1; 2/11
with FlexSound Technology
General Description
The MAX9888 is a full-featured audio CODEC whose
high performance and low power consumption make it
ideal for portable applications.
Class D speaker amplifiers provide efficient amplification
for two speakers. Low radiated emissions enable completely filterless operation. Integrated bypass switches
optionally connect an external amplifier to the transducer
when the Class D amplifiers are disabled.
®
DirectDrive
ground-referenced output, eliminating the need for
large DC-blocking capacitors. 1.8V headphone operation ensures low power consumption. The device also
includes a differential receiver amplifier.
Three differential analog microphone inputs are available
as well as support for two PDM digital microphones.
Integrated switches allow microphone signals to be
routed out to external devices. Two flexible single-ended
or differential line inputs may be connected to an FM
radio or other sources.
Integrated FlexSoundK technology improves loudspeaker performance by optimizing the signal level and
frequency response while limiting the maximum distortion and power at the output to prevent speaker damage.
Automatic gain control (AGC) and a noise gate optimize
the signal level of microphone input signals to make best
use of the ADC dynamic range.
The device is fully specified over the -40NC to +85NC
extended temperature range.
DirectDrive is a registered trademark and FlexSound is a
trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
headphone amplifiers provide a true
Stereo Audio CODEC
Features
S 100dB DR Stereo DAC (8kHz < fS < 96kHz)
91dB DR Stereo ADC (8kHz < f
S
Stereo Low EMI Class D Amplifiers
S
950mW/Channel (8I, V
Stereo DirectDrive Headphone Amplifiers
S
Differential Receiver Amplifier
S
2 Stereo Single-Ended/Mono Differential Line
S
Inputs
3 Differential Microphone Inputs
S
FlexSound Technology
S
5-Band Parametric EQ
Automatic Level Control (ALC)
Excursion Limiter
Speaker Power Limiter
Speaker Distortion Limiter
Microphone Automatic Gain Control
and Noise Gate
Dual I
S
Asynchronous Digital Mixing
S
Supports Master Clock Frequencies from 10MHz
S
2
S/PCM/TDM Digital Audio Interfaces
to 60MHz
RF Immune Analog Inputs and Outputs
S
Extensive Click-and-Pop Reduction Circuitry
S
2
I
C Control Interface
S
63 WLP Package (3.80mm x 3.30mm, 0.4mm Pitch)
S
Ordering Information
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
MAX9888EWY+
+Denotes lead(Pb)-free/RoHS-compliant package.
-40NC to +85NC
< 96kHz)
S
SPKVDD_
= 4.2V)
63 WLP
MAX9888
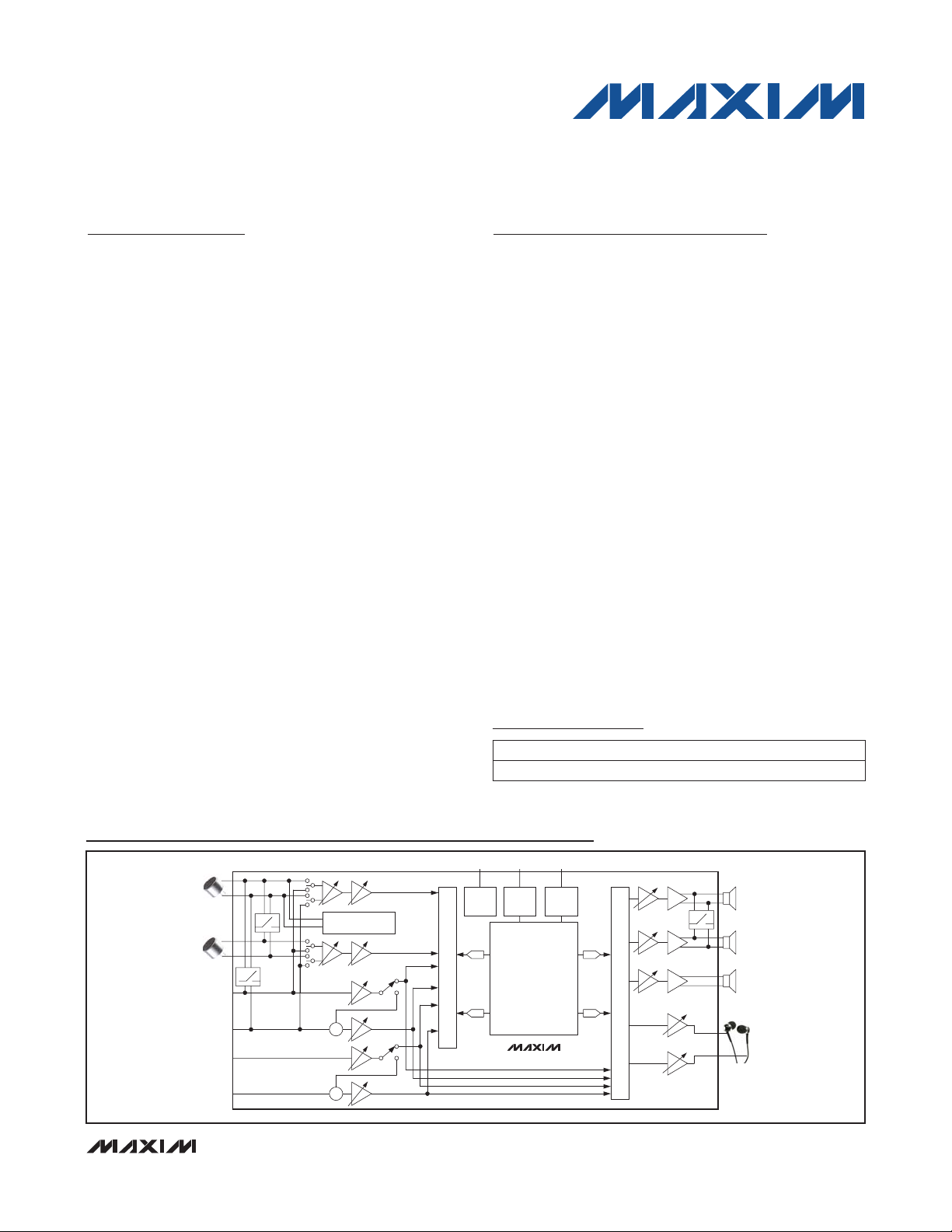
Simplified Block Diagram
2
I2C
CONTROL
DIGITAL MICROPHONE
LINEIN A1
LINEIN A2
LINEIN B1
LINEIN B2
INPUT
MIX
+
+
FlexSound TECHNOLOGY
• 5-BAND PARAMETRIC EQ
• AUTOMATIC LEVEL CONTROL
ADC
• LOUDSPEAKER PROCESSING
• EXCURSION LIMITER
• THD LIMITER
• POWER LIMITER
• MICROPHONE PROCESSING
• AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL
• NOISE GATE
ADC
• ASYNCHRONOUS DIGITAL
MIXING
_______________________________________________________________ Maxim Integrated Products 1
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim Direct at 1-888-629-4642,
or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
S/PCM
I
DIGITAL
AUDIO
INTERFACE
MAX9888
I2S/PCM
DIGITAL
AUDIO
INTERFACE
RECEIVER AMP
SPEAKER AMP
DAC
DAC
SPEAKER AMP
MIX
HEADPHONE AMP
HEADPHONE AMP

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
TABLE OF CONTENTS
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Features
Simplified Block Diagram
Ordering Information
Functional Diagram
MAX9888
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Electrical Characteristics
Digital Input/Output Characteristics
Input Clock Characteristics
Audio Interface Timing Characteristics
Digital Microphone Timing Characterstics
2
I
Power Consumption
Typical Operating Characteristics
Pin Configuration
Pin Description
Detailed Description
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
C Timing Characterstics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Microphone to ADC
Line to ADC
Digital Loopback
Analog Loopback
DAC to Receiver
Line to Receiver
DAC to Speaker
Line to Speaker
DAC to Headphone
Line to Headphone
Speaker Bypass Switch
2
C Slave Address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
I
Registers
Power Management
Microphone Inputs
Line Inputs
ADC Input Mixers
Record Path Signal Processing
Microphone AGC
Noise Gate
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
2

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
TABLE OF CONTENTS (continued)
ADC Record Level Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Sidetone
Digital Audio Interfaces
Clock Control
Passband Filtering
Playback Path Signal Processing
Playback Level Control
DAC Input Mixers
Preoutput Signal Path
Receiver Amplifier
Speaker Amplifiers
Speaker Amplifier Signal Processing
Headphone Amplifier
Output Bypass Switches
Click-and-Pop Reduction
Jack Detection
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Automatic Level Control
Parametric Equalizer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Preoutput Mixer
Preoutput PGA
Receiver Output Volume
Receiver Output Mixer
Speaker Output Volume
Speaker Output Mixers
Excursion Limiter
Power Limiter
Distortion Limiter
Headphone Output Mixers
Headphone Output Volume
Jack Insertion
Accessory Button Detection
Jack Removal
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .96
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
MAX9888
3

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
TABLE OF CONTENTS (continued)
Battery Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Device Status
Device Revision
2
C Serial Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
I
MAX9888
Bit Transfer
START and STOP Conditions
Early STOP Conditions
Slave Address
Acknowledge
Write Data Format
Read Data Format
Applications Information
Typical Operating Circuits
Analog Microphones and Bypass Switch
Digital Microphones and Receiver Amplifier
Filterless Class D Operation
RF Susceptibility
Startup/Shutdown Sequencing
Component Selection
Optional Ferrite Bead Filter
Input Capacitor
Charge-Pump Capacitor Selection
Charge-Pump Flying Capacitor
Charge-Pump Holding Capacitor
Unused Pins
Recommended PCB Routing
Supply Bypassing, Layout, and Grounding
WLP Applications Information
Package Information
Revision History
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .109
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
4
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
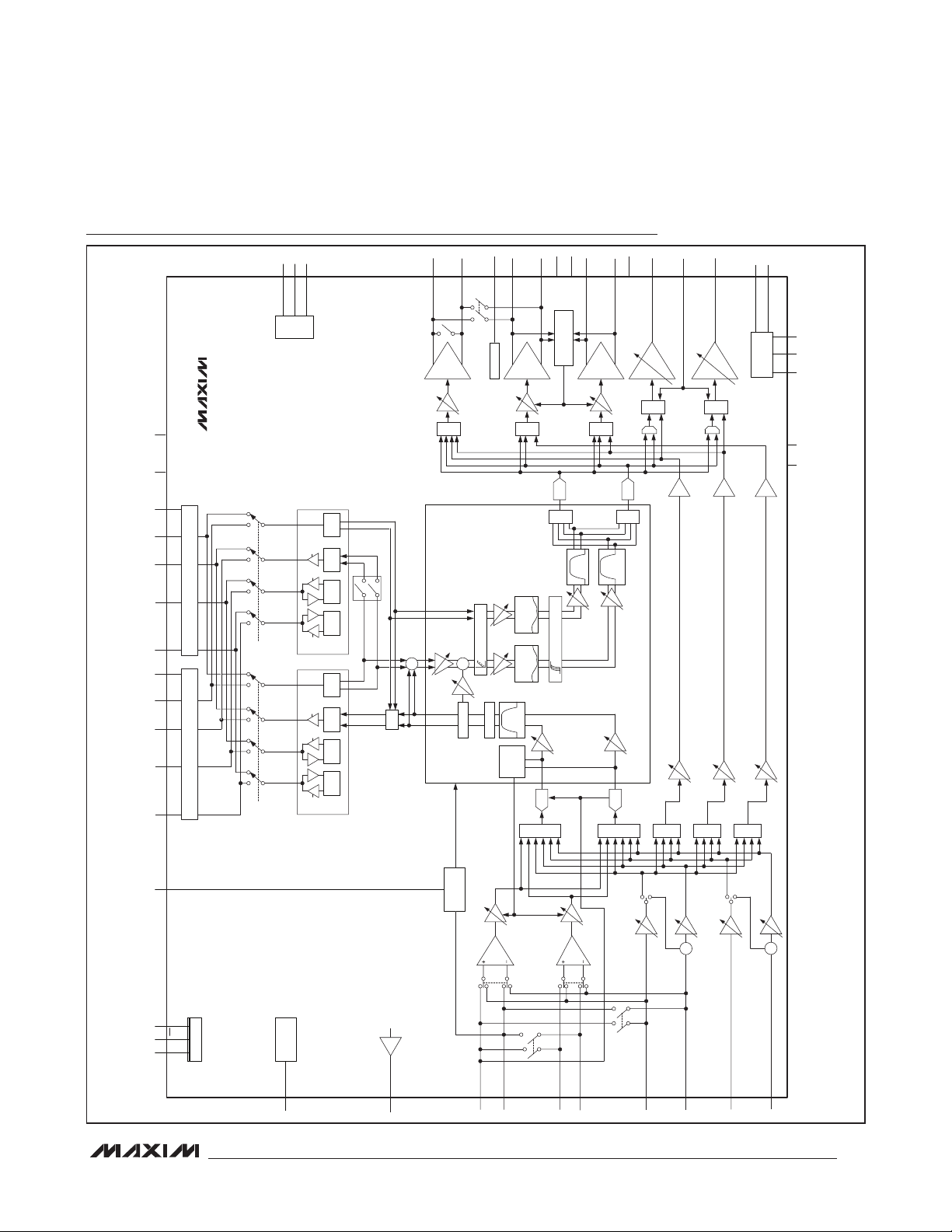
Functional Diagram
G6
F6
REF F7
REG
PREG
RECP/
A6
RXINP
RECN/
B6
RXINN
A3, B3
SPKLVDD
A4, B4
SPKLP
A5, B5
SPKLN
C4, C5
SPKLGND
SPKRVDD C3, D3
SPKRP C1, C2
SPKRN A1, B1
SPKRGND A2, B2
HPL B9
HPR C9
HPSNS C6
A8
HPVDD A7
HPGND
MAX9888
BIAS
0dB
MAX9888
G5
AVDD
G4
DVDD
SDIN2
SDOUT2
LRCLK2
LRCLKS2 SDOUTS2 SDINS2 DVDDS2
PORT S1 PORT S2
LRCLKS1 SDOUTS1 SDINS1 DVDDS1 BCLKS2
D1 D2 E4 D4 E1 F2 F3 G1 G3 G2
BCLKS1
BCLK2
SDIN1
SDOUT1
LRCLK1
BCLK1
SEL1 SEL2
DATA
INPUT
HIZOFF2
DATA
OUTPUT
MAS2
FRAME
CLOCK
BIT
CLOCK
MAS2
DAI2
DATA
INPUT
HIZOFF1
DATA
OUTPUT
MAS1
FRAME
CLOCK
BIT
CLOCK
MAS1
DAI1
LBEN1
RECVOL:
+8dB TO -62dB
MIX
FlexSound
TECHNOLOGY
DV1G:
0/6/12/18dB
+
LTEN1
DVST:
0dB TO -60dB
MUX
LBEN2
RECBYP
RECEN
MIXREC
+
MIX
SIDETONE
MULTI BAND ALC
NOISE GATE
DSTS
SPKBYP
BATTERY ADC
SPVOLL:
+8dB TO -62dB
DVEQ2:
0dB TO -15dB
DVEQ1:
0dB TO -15dB
AUDIO/
GAIN
AUTOMATIC
VOICE
+6dB
MIX
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
FILTERS
CONTROL
EQ
EQ
MODE1
ADLEN
AVFLT
MIX
POWER/
SPLEN
MIXSPL
DACL
MIX
EXCURSION LIMITER
EQ1EN EQ2EN
AVLG: 0/6/12/18dB
ADCL
DISTORTION LIMITER
DALEN
MIXDAL
AUDIO/
FILTERS
DCB2
DV2:
0dB TO -15dB
AVL: 3dB TO -12dB
MIXADL
HPVOLR:
HPLEN
MIXHPL
+9dB
PREOUT1
0dB TO -23dB
MIX
MIXOUT1
+3dB TO -67dB
MIX
PGAOUT2:
0dB TO -23dB
MIX
HPREN
MIXHPR
+9dB
PREOUT2
PGAOUT3:
MIXOUT2
HPVOLL:
+3dB TO -67dB
+6dB
SPREN
MIX
SPVOLR:
+8dB TO -62dB
MIX
MIXSPR
DACR
DAREN
MIX
MIXDAR
VOICE
AUDIO/
FILTERS
MODE1
DVFLT
DV1:
0dB TO -15dB
AVRG: 0/6/12/18dB
AVR: 3dB TO -2dB
PGAOUT1:
ADCR
ADREN
MIX
MIXADR
CHARGE
0dB TO -23dB
MIX
PUMP
+9dB
PREOUT3
MIXOUT3
B7B8A9G7F1
C1N C1P
HPVSSAGND
DGND
PSCLK
CLOCK
MCLK
E5F5F4 E2
IRQ
C
2
I
SCL
SDA
JACK
DETECTION
JACKSNS
D6
JDETEN
REG
MBEN
MICBIAS
G8
CONTROL
PGAM1:
MIC1P/
DIGMICDATA
E8
+20dB TO 0dB
MIC1N/
DIGMICCLK
F8
PA1EN:
EXTMIC
0/20/30dB
MIC2BYP
PGAM2:
+20dB TO 0dB
F9 MIC2P
G9 MIC2N
PA2EN:
EXTMIC
0/20/30dB
PGAINA:
+20dB TO -6dB
INABYP
INADIFF
INA1/EXTMICP
E9
PGAINA:
+20dB TO -6dB
INA2/EXTMICN
D9
+
PGAINB:
+20dB TO -6dB
INBDIFF
PGAINB:
+20dB TO -6dB
+
INB2
INB1
C8
D8
5
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(Voltages with respect to AGND.)
DVDD, AVDD, HPVDD
SPKLVDD, SPKRVDD, DVDDS1, DVDDS2
DGND, HPGND, SPKLGND, SPKRGND
HPVSS
............................... (HPGND - 2.2V) to (HPGND + 0.3V)
C1N
.................................... (HPVSS - 0.3V) to (HPGND + 0.3V)
C1P
.....................................(HPGND - 0.3V) to (HPVDD + 0.3V)
PREG
MAX9888
..................................................... -0.3V to (AVDD + 0.3V)
REF, MICBIAS
................................. -0.3V to (SPKLVDD + 0.3V)
.........................................-0.3V to +2.2V
..........-0.3V to +6.0V
..............-0.1V to +0.1V
MCLK, SDINS1, SDINS2, JACKSNS,
SDA, SCL, IRQ
LRCLKS1, BCLKS1, SDOUTS1
LRCLKS2, BCLKS2, SDOUTS2
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
.................................................-0.3V to +6.0V
......... -0.3V to (DVDDS1 + 0.3V)
......... -0.3V to (DVDDS2 + 0.3V)
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
= T
A
PGAIN_
MIN
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
to T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
POWER SUPPLY
Supply Voltage Range Guaranteed by PSRR
Total Supply Current (Note 2) I
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 2.2FF, C
REF
DACATTN
= 0dB, AV
REC
Full-duplex 8kHz mono,
receiver output (Note 3)
DAC playback 48kHz stereo,
headphone outputs (Note 3)
DAC playback 48kHz stereo,
VDD
speaker outputs (Note 3)
Full-duplex 48kHz stereo,
microphone inputs,
headphone outputs (Note 3)
Stereo line playback,
IN_DIF = 0, INA1 to HPL,
INA2 to HPR, V
REG, INA1, INA2, INB1, INB2, MIC1P/DIGMICDATA,
MIC1N/DIGMICCLK, MIC2P, MIC2N ...............-0.3V to +2.2V
HPSNS
............................... (HPGND - 0.3V) to (HPGND + 0.3V)
HPL, HPR
RECP, RECN
SPKLP, SPKLN
SPKRP, SPKRN
............................(HPVSS - 0.3V) to (HPVDD + 0.3V)
..............(SPKLGND - 0.3V) to (SPKLVDD + 0.3V)
...........(SPKLGND - 0.3V) to (SPKLVDD + 0.3V)
.........(SPKRGND - 0.3V) to (SPKRVDD + 0.3V)
Continuous Power Dissipation (TA = +70NC)
63-Bump WLP (derate 25.6mW/NC above +70NC)
Operating Temperature Range
Storage Temperature Range
Soldering Temperature (reflow)
SPKLVDD
= 0dB, AV
= V
SPKRVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= C
PREG
DACGAIN
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
, V
,
AVDD
,
V
SPKLVDD
V
SPKRVDD
V
DVDD
V
HPVDD
V
DVDDS1
V
DVDDS2
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
,
.......................... -40NC to +85NC
............................-65NC to +150NC
......................................+260NC
= 1FF, C
REG
ADCLVL
C1N-C1P
= 0dB, AV
ADCGAIN
2.8 5.5
1.65 1.8 2.0
1.65 3.6
Analog 6.37 10
Speaker 1.98 3.5
Digital 1.49 3
Analog 2.71 4
Speaker 1.65 2.5
Digital 2.93 4.5
Analog 1.85 3
Speaker 8.22 18
Digital 2.94 5
Analog 12.75 18
Speaker 1.7 3
Digital 3.75 5.5
Analog 5.11 7
Speaker 0.58 1
= 0V
MCLK
Digital 0.03 0.06
........2.05W
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
HPVSS
= 0dB,
V
mA
6
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
A
PGAIN_
= T
MIN
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
to T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Shutdown Supply Current
(Note 2)
REF Voltage 2.5 V
PREG Voltage 1.6 V
REG Voltage 0.7 V
Shutdown to Full Operation
MICROPHONE TO ADC PATH
Dynamic Range (Note 4) DR
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR V
Power-Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR
Path Phase Delay
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
T
A
REF
DACATTN
REC
= +25NC
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
SLEW = 0
SLEW = 1
= 8kHz, MODE = 0 (IIR voice),
f
S
THD+N
AV
MICPRE_
V
IN
f
= 8kHz, f = 1kHz
S
MICPRE_
AV
MICPRE_
= 0dB
= 0.1V
, MCLK = 12.288MHz,
P-P
= 0dB, VIN = 1V
= +30dB, VIN = 32mV
f = 1kHz
= 100mV
IN
V
= 1.65V to 2.0V, input referred, MIC
AVDD
, f = 217Hz 65 dB
P-P
inputs floating
f = 217Hz, V
RIPPLE
= 100mV
input referred
f = 1kHz, V
RIPPLE
= 100mV
input referred
f = 10kHz, V
RIPPLE
= 100mV
input referred
MODE = 0 (IIR voice)
8kHz
1kHz, 0dB input,
highpass filter
disabled measured
from analog input to
digital output
MODE = 0 (IIR voice)
16kHz
MODE = 1 (FIR audio)
8kHz
MODE = 1 (FIR audio)
48kHz
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
Analog 0.2 2
Speaker 0.1 1
Digital 1 5
30
17
75 88 dB
-77 -65
, f = 1kHz -82
P-P
,
P-P
-71
60 100
P-P
P-P
P-P
, AV
, AV
, AV
ADC
ADC
ADC
= 0dB,
= 0dB,
= 0dB,
100
91
70
2.2
1.1
4.5
0.76
HPVSS
FA
ms
dBAV
dB
ms
MAX9888
7
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
= T
A
MAX9888
MICROPHONE PREAMP
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
to T
MIN
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Full-Scale Input AV
Preamplifier Gain AV
PGA Gain AV
MIC Input Resistance R
MICROPHONE BIAS
MICBIAS Output Voltage V
Load Regulation I
Line Regulation V
Ripple Rejection
Noise Voltage
MICROPHONE BYPASS SWITCH
On-Resistance R
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
Off-Isolation
Off-Leakage Current
LINE INPUT TO ADC PATH
Dynamic Range (Note 4) DR
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
Gain Error DC accuracy 1 5 %
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
MICPRE_
REF
REC
= 0dB 1.05 V
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
PA1EN/PA2EN = 01 0
MICPRE_
(Note 5)
PA1EN/PA2EN = 11 29.4 30 30.5
MICPGA_
IN_MIC
MICBIASILOAD
(Note 5)
All gain settings, measured at MIC1P/MIC1N/
MIC2P/MIC2N
LOAD
SPKLVDD
f = 217Hz, V
f = 10kHz, V
= 1mA 2.14 2.2 2.25 V
= 1mA to 2mA 0.5 11 mV
PGAM1/PGAM2 = 0x00 19.5 20 20.5
PGAM1/PGAM2 = 0x14 0
= 2.8V to 5.5V 100
RIPPLE (SPKLVDD)
RIPPLE (SPKLVDD)
A-weighted, f = 20Hz to 20kHz 3.8
P-weighted, f = 20Hz to 4kHz 2.1
f = 1kHz 33
I
= 100mA, INABYP = MIC2BYP = 1,
ON
THD+N
MIC1_
V
MIC2_
V
IN
= V
= 2V
= (0V, V
INA_
, VCM = 0.9V, RL = 10kI,
P-P
AVDD
f = 1kHz, INABYP = MIC2BYP = 1
V
IN
= 2V
, VCM = 0.9V, RL = 10kI,
P-P
f = 1kHz
V
= (0V, V
MIC1_
V
MIC2_/VINA_
= 48kHz, MCLK = 12.288MHz, MODE = 1
f
S
= (V
AVDD
AVDD
),
, 0V)
(FIR audio)
THD+N V
IN
= 1V
, f = 1kHz -77 dB
P-P
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
30 50
= 100mV
= 100mV
)
P-P
P-P
92
83
3.5 20
-80 dB
60 dB
-2.5 +2.5
91 dB
) connected
HPVSS
= 0dB,
P-P
dBPA1EN/PA2EN = 10 19.5 20 20.5
dB
kI
FV
dB
FV
RMS
nV/√Hz
I
FA
8
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
A
PGAIN_
= T
MIN
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
to T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
LINE INPUT PREAMP
Full-Scale Input V
Level Adjust Gain AV
Input Resistance R
Feedback Resistance R
ADC LEVEL CONTROL
ADC Level Adjust Range AV
ADC Level Adjust Step Size 1 dB
ADC Gain Adjust Range AV
ADC Gain Adjust Step Size 6 dB
ADC DIGITAL FILTERS
VOICE MODE IIR LOWPASS FILTER (MODE1 = 0)
Passband Cutoff f
Passband Ripple f < f
Stopband Cutoff f
Stopband Attenuation (Note 6) f > f
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
IN
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
AV
AV
REF
DACATTN
REC
= 0dB 1
PGAIN_
= -6dB 1.4
PGAIN_
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
PGAINA/PGAINB = 0x0 19 20 21
PGAINA/PGAINB = 0x1 13 14 15
PGAINA/PGAINB = 0x2 (Note 5) 2 3 4
PGAIN_
PGAINA/PGAINB = 0x3
PGAINA/PGAINB = 0x4 -4 -3 -2
PGAINA/PGAINB = 0x5, 0x6, 0x7 -7 -6 -5
IN
IN_FB
ADCLVL
ADCGAIN
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
AV
INAEXT/INBEXT = 1
AVL/AVR = 0xF to 0x0 (Note 5) -12 +3 dB
AVLG/AVRG = 00 to 11 (Note 5) 0 18 dB
= +20dB 14.6 21 27.4
PGAIN_
= +14dB 20
PGAIN_
= +3dB 20
PGAIN_
= 0dB 7.3 10 13.7
PGAIN_
= -3dB 20
PGAIN_
= -6dB 20
PGAIN_
T
T
Ripple limit cutoff
PLP
-3dB cutoff
PLP
SLP
SLP
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
0
= +25NC
A
= T
A
MIN
= +25NC
T
A
to T
MAX
18.5 20 21.5
17.5 23
0.441
x f
s
0.449
x f
s
-0.1 +0.1 dB
0.47
x f
s
74 dB
HPVSS
V
MAX9888
P-P
dB
kI
kI
Hz
Hz
9
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
= T
A
MAX9888
VOICE MODE IIR HIGHPASS FILTER (MODE1 = 0)
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
to T
MIN
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Passband Cutoff
(-3dB from Peak)
Stopband Cutoff
(-30dB from Peak)
DC Attenuation DC
STEREO AUDIO MODE FIR LOWPASS FILTER (MODE1 = 1, DHF1 = 0, LRCLK < 50kHz)
Passband Cutoff f
Passband Ripple f < f
Stopband Cutoff f
Stopband Attenuation (Note 6) f < f
ADC STEREO AUDIO MODE FIR LOWPASS FILTER (MODE1 = 1, DHF1 = 1, LRCLK > 50kHz)
Passband Cutoff f
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
REF
DACATTN
REC
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
AVFLT = 0x1 (elliptical tuned for
f
= 16kHz + 217Hz notch)
s
AVFLT = 0x2 (500Hz Butterworth tuned for
fs = 16kHz)
f
AHPPB
AVFLT = 0x3 (elliptical tuned for
f
= 8kHz + 217Hz notch)
s
AVFLT = 0x4 (500Hz Butterworth tuned for
f
= 8kHz)
s
AVFLT = 0x5 (fs/240 Butterworth)
AVFLT = 0x1 (elliptical tuned for
f
= 16kHz + 217Hz notch)
s
AVFLT = 0x2 (500Hz Butterworth tuned for
fs = 16kHz)
f
AHPSB
AVFLT = 0x3 (elliptical tuned for
f
= 8kHz + 217Hz notch)
s
AVFLT = 0x4 (500Hz Butterworth tuned for fs =
8kHz)
AVFLT = 0x5 (fs/240 Butterworth)
ATTEN
AVFLT ≠ 000
Ripple limit cutoff
PLP
-6.02dB cutoff
PLP
SLP
SLP
Ripple limit cutoff
PLP
-3dB cutoff
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
PREG
DACGAIN
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
0.0139
x f
s
0.0156
x f
s
0.0279
x f
s
0.0312
x f
s
0.002
x f
s
90 dB
0.43
x f
s
0.48
x f
s
0.5
x f
s
-0.1 +0.1 dB
60 dB
0.208
x f
s
0.28
x f
s
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
0.0161
x f
s
0.0319
x f
s
0.0321
x f
s
0.0632
x f
s
0.0043
x f
s
0.58
x f
s
HPVSS
= 0dB,
Hz
Hz
Hz-3dB cutoff
Hz
Hz
10
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
A
PGAIN_
= T
MIN
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
to T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Passband Ripple f < f
Stopband Cutoff f
Stopband Attenuation f < f
ADC STEREO AUDIO MODE DC-BLOCKING HIGHPASS FILTER (MODE1 = 1)
Passband Cutoff
(-3dB from Peak)
DC Attenuation DC
MICROPHONE AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL
AGC Hold Duration
AGC Attack Time
AGC Release Time
AGC Threshold Level AGCTH = 0x0 to 0xF -3 +18 dB
AGC Threshold Step Size 1 dB
AGC Gain (Note 5) 0 20 dB
ADC NOISE GATE
NG Threshold Level ANTH = 0x3 to 0xF, referred to 0dBFS -64 -16 dB
NG Attenuation (Note 5) 0 12 dB
ADC-TO-DAC DIGITAL SIDETONE (MODE = 0)
Sidetone Gain Adjust Range AV
Sidetone Gain Adjust Step Size 2 dB
Sidetone Path Phase Delay
ADC-TO-DAC DIGITAL LOOP-THROUGH PATH
Dynamic Range (Note 4) DR
Total Harmonic Distortion THD
DAC LEVEL CONTROL
DAC Attenuation Range AV
DAC Attenuation Step Size
DAC Gain Adjust Range AV
DAC Gain Adjust Step Size 6 dB
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
f
AHPPB
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
SLP
Atten
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
REF
DACATTN
REC
PLP
SLP
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
AVFLT ≠ 000
AVFLT ≠ 000
AGCHLD = 01 50
AGCHLD = 11 400
AGCATK = 00 2
AGCATK = 11 123
AGCRLS = 000 0.078
AGCRLS = 111 10
STGA
DVST = 0x01 -0.5
DVST = 0x1F -60.5
1kHz, 0dB input, highpass
filter disabled
= 48kHz, MCLK = 12.288MHz, MODE = 1
f
S
(FIR audio)
f = 1kHz, f
= 48kHz, MCLK = 12.288MHz,
S
MODE = 1 (FIR audio)
DACATTN
DACGAIN
DV1DV2 = 0xF to 0x0 (Note 5) -15 0 dB
DV1G = 00 to 11 (Note 5) 0 18 dB
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
-0.1 +0.1 dB
0.417
x f
s
60 dB
0.000125
x fs
90 dB
8kHz 2.2
16kHz 1.1
89 dB
-71 -66 dB
1 dB
MAX9888
Hz
Hz
ms
ms
s
dB
ms
11
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
= T
A
MAX9888
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
to T
MIN
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DAC DIGITAL FILTERS
VOICE MODE IIR LOWPASS FILTER (MODE1 = 0)
Passband Cutoff f
Passband Ripple f < f
Stopband Cutoff f
Stopband Attenuation (Note 6) f > f
VOICE MODE IIR HIGHPASS FILTER (MODE1 = 0)
Passband Cutoff
(-3dB from Peak)
Stopband Cutoff
(-30dB from Peak)
DC Attenuation DC
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
REF
DACATTN
REC
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
Ripple limit cutoff
PLP
-3dB cutoff
PLP
SLP
SLP
DVFLT = 0x1 (elliptical tuned for
f
= 16kHz + 217Hz notch)
s
DVFLT = 0x2 (500Hz Butterworth tuned for
fs = 16kHz)
f
DHPPB
DVFLT = 0x3 (elliptical tuned for
f
= 8kHz + 217Hz notch)
s
DVFLT = 0x4 (500Hz Butterworth tuned for
f
= 8kHz)
s
DVFLT = 0x5 (fs/240 Butterworth)
DVFLT = 0x1 (elliptical tuned for
f
= 16kHz + 217Hz notch)
s
DVFLT = 0x2 (500Hz Butterworth tuned for
fs = 16kHz)
f
DHPSB
DVFLT = 0x3 (elliptical tuned for
f
= 8kHz + 217Hz notch)
s
DVFLT = 0x4 (500Hz Butterworth tuned for
f
= 8kHz)
s
DVFLT = 0x5 (fs/240 Butterworth)
ATTEN
DVFLT ≠ 000
= V
SPKRVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= C
DACGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
0.448
x f
s
0.451
x f
s
-0.1 +0.1 dB
0.476
x f
s
75 dB
0.0161
x f
s
0.0312
x f
s
0.0321
x f
s
0.0625
x f
s
0.0042
x f
s
0.0139
x f
s
0.0156
x f
s
0.0279
x f
s
0.0312
x f
s
0.002
x f
s
85 dB
HPVSS
= 0dB,
Hz
Hz
Hz
Hz
12
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
A
PGAIN_
= T
MIN
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
to T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
STEREO AUDIO MODE FIR LOWPASS FILTER (MODE1 = 1, DHF1/DHF2 = 0, LRCLK < 50kHz)
Passband Cutoff f
Passband Ripple f < f
Stopband Cutoff f
Stopband Attenuation (Note 6) f > f
STEREO AUDIO MODE FIR LOWPASS FILTER (MODE1 = 1, DHF1/DHF2 = 1 for LRCLK > 50kHz)
Passband Cutoff f
Passband Ripple f < f
Stopband Cutoff f
Stopband Attenuation (Note 6) f < f
STEREO AUDIO MODE DC-BLOCKING HIGHPASS FILTER
Passband Cutoff (-3dB from
Peak)
DC Attenuation DC
AUTOMATIC LEVEL CONTROL
Dual Band Lowpass Corner
Frequency
Dual Band Highpass Corner
Frequency
Gain Range 0 12 dB
Low Signal Threshold ALCTH = 111 to 001 -48 -12 dBFS
Release Time
PARAMETRIC EQUALIZER
Number of Bands 5 Bands
Per Band Gain Range -12 +12 dB
Preattenuator Gain Range (Note 5) -15 0 dB
Preattenuator Step Size 1
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
REF
DACATTN
REC
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
Ripple limit cutoff
PLP
-6.02dB cutoff
PLP
SLP
SLP
Ripple limit cutoff
PLP
-3dB cutoff
PLP
SLP
SLP
f
DHPPB
ATTEN
DVFLT ≠ 000 (DAI1), DCB2 = 1 (DAI2)
DVFLT ≠ 000 (DAI1), DCB2 = 1 (DAI2)
ALCMB = 1 5 kHz
ALCMB = 1 5 kHz
ALCRLS = 101 0.25
ALCRLS = 000 8
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
0.43
x f
s
0.47
x f
s
Hz-3dB cutoff
0.5
x f
s
-0.1 +0.1 dB
0.58
x f
Hz
s
60 dB
0.24
x f
0.31
x f
s
s
Hz
-0.1 +0.1 dB
0.477
x f
Hz
s
60 dB
0.000104
x f
Hz
s
90 dB
s
dB
MAX9888
13
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
= T
A
MAX9888
DAC-TO-RECEIVER AMPLIFIER PATH
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
to T
MIN
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Dynamic Range (Note 4) DR f
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
Click and Pop Level K
PREOUTPUT MIXERS
Level Adjust Gain AV
Level Adjust Step Size 2 dB
Mute Attenuation f = 1kHz 85 dB
LINE INPUT-TO-RECEIVER AMPLIFIER PATH
Dynamic Range (Note 4) DR Referenced to full-scale output level 92 dB
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
Power-Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR
Click-and-Pop Level K
RECEIVER AMPLIFIER
Output Power P
Full-Scale Output (Note 7) 1 V
Volume Control AV
Volume Control Step Size
Mute Attenuation f = 1kHz 95 dB
Output Offset Voltage V
Capacitive Drive Capability No sustained oscillations
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
THD+N
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 48kHz, MCLK = 12.288MHz, f = 1kHz 96 dB
S
f = 1kHz, P
REF
DACATTN
REC
OUT
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
= 25mW, R
MICBIAS
SPK_
Peak voltage, A-weighted, 32
samples per second, AV
CP
REC
= 0dB
PGAOUTA/PGAOUTB/
PGAOUT_
(Note 5)
PGAOUTC = 0x0
PGAOUTA/PGAOUTB/
PGAOUTC = 0xC
THD+N -70 dB
V
SPKLVDD
f = 217Hz, V
f = 1kHz, V
f = 10kHz, V
= 2.8V to 5.5V 54 89
= 100mV
RIPPLE
= 100mV
RIPPLE
= 100mV
RIPPLE
Peak voltage, A-weighted, 32
samples per second, AV
CP
REC
= 0dB
R
OUT
REC
= 32I, f = 1kHz, THD = 1%
REC
(Note 5)
+8dB to +6dB 0.5
+6dB to +0dB 1
0dB to -14dB 2
-14dB to -38dB 3
-38dB to -62dB 4
AV
OS
REC
= -62dB
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
REC
= 32I
-70 -63 dB
Into shutdown -70
Out of shutdown -73
0
-25 -23.4 -22
P-P
P-P
P-P
-63
-63
-65
Into shutdown -57
Out of shutdown -55
100 mW
RECVOL = 0x00 -65 -62 -58
RECVOL = 0x1F
T
= +25NC
A
R
= 32I
REC
= J
R
REC
+7.5 +8 +8.5
±0.13 ±1
500
100
) connected
HPVSS
= 0dB,
dBV
dB
dB
dBV
RMS
dB
dB
mV
pF
14
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
A
PGAIN_
= T
MIN
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
to T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DAC-TO-SPEAKER AMPLIFIER PATH
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
Crosstalk
Output Noise A-weighted 43
Click-and-Pop Level K
LINE INPUT-TO-SPEAKER AMPLIFIER PATH
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
Output Noise A-weighted 56
Power-Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR
Click-and-Pop Level K
SPEAKER AMPLIFIER
Output Power P
Full-Scale Output (Note 7) 2 V
Volume Control (Note 5) AV
Volume Control Step Size
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
THD+N
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
f = 1kHz, P
REF
DACATTN
REC
OUT
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
= 250mW, Z
MICBIAS
SPK_
SPKL to SPKR and SPKR to SPKL,
= 640mW, f = 1kHz
P
OUT
Peak voltage, A-weighted,
32 samples per second,
CP
AV
= 0dB
SPK_
THD+N
f = 1kHz, P
V
SPKLVDD
f = 217Hz, V
f = 1kHz, V
f = 10kHz, V
= 200mW, Z
OUT
= V
RIPPLE
RIPPLE
RIPPLE
= 2.8V to 5.5V 43 60
RIPPLE
= 100mV 75
= 100mV 73
= 100mV 50
Peak voltage, A-weighted,
32 samples per second,
CP
AV
= 0dB
SPK_
V
V
V
OUT
f = 1kHz, THD = 1%,
Z
= 8I + 68FH
SPK
V
V
V
V
V
SPK_
SPVOLL/SPVOLR = 0x00 -69 -64 -59
SPVOLL/SPVOLR = 0x1F
+8dB to +6dB 0.5
+6dB to +0dB 1
0dB to -14dB 2
-14dB to -38dB 3
-38dB to -64dB 4
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
= 8I + 68FH
SPK
-71 dB
-75
Into shutdown -65
Out of shutdown -65
= 8I + 68FH
SPK
-66 dB
Into shutdown -48
Out of shutdown -50
SPKLVDD
SPKRVDD
SPKLVDD
SPKRVDD
SPKLVDD
SPKRVDD
SPKLVDD
SPKRVDD
=
= 5.0V
=
= 4.2V
=
= 3.7V
=
= 3.2V
1370
954
733
544
+7.5 +8 +8.5
HPVSS
= 0dB,
dB
FV
RMS
dBV
FV
RMS
dB
dBV
mW
RMS
dB
dB
MAX9888
15
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
= T
A
MAX9888
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
to T
MIN
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Mute Attenuation f = 1kHz 86 dB
Output Offset Voltage V
EXCURSION LIMITER
Upper-Corner Frequency Range DHPUCF = 001 to 100 400 1000 Hz
Lower-Corner Frequency DHPLCF = 01 to 10 400 Hz
Biquad Minimum Corner
Frequency
Threshold Voltage
Release Time
POWER LIMITER
Attenuation -64 dB
Threshold
Time Constant 1 t
Time Constant 2 t
Weighting Factor k
DISTORTION LIMITER
Distortion Limit
Release Time Constant
DAC-TO-HEADPHONE AMPLIFIER PATH
Dynamic Range (Note 4) DR
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
OS
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
AV
REF
DACATTN
REC
= -64dB, TA = +25NC
SPK_
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
DHPUCF = 000 (fixed mode) 100
DHPUCF = 001 200
DHPUCF = 010 300
DHPUCF = 011 400
DHPUCF = 100 500
= 8I + 68FH,
Z
SPK
V
SPKLVDD
5.5V, AV
= V
SPK_
SPKRVDD
= +8dB
=
ALCRLS = 101 0.25
ALCRLS = 000 4
= 8I + 68FH,
Z
SPK
PWR1
PWR2
PWR
V
SPKLVDD
5.5V, AV
PWRT1 = 0x1 0.5
PWRT1 = 0xF 8.7
PWRT2 = 0x1 to 0xF 0.5
PWRT2 = 0xF 8.7
PWRK = 000 to 111 12.5 100 %
= V
SPK_
SPKRVDD
= +8dB
=
THDCLP = 0x1 < 1
THDCLP = 0xF 24
THDT1 = 000
THDT1 = 111 6.2
Master or slave mode 100
Slave mode 94
= 20mW
= 1
, RHP = 10kI
VRMS
THD+N
= 48kHz, MCLK =
f
S
12.288MHz
f
= 48kHz, MCLK = 12.288MHz,
S
f = 1kHz, P
f
= 48kHz, MCLK = 12.288MHz,
S
f = 1kHz, V
OUT
OUT
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
±0.25 ±1.25
DHPTH = 000 0.34
DHPTH = 111 4.95
PWRTH = 0x1 0.05
PWRTH = 0xF 1.80
0.76
R
R
= 16I
HP
= 32I
HP
-71 -64
-75
-79
) connected
HPVSS
= 0dB,
mV
Hz
V
P
s
W
s
min
%
s
dB
dB
16
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
A
PGAIN_
= T
MIN
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
to T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Crosstalk
Power-Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR
DAC Path Phase Delay
Gain Error 1 %
Channel Gain Mismatch 0.5 %
Click-and-Pop Level K
LINE INPUT-TO-HEADPHONE AMPLIFIER PATH
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
Dynamic Range (Note 4) DR 91 dB
Power-Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR
Click and Pop Level K
HEADPHONE AMPLIFIER
Output Power P
Full-Scale Output (Note 7) 1 V
Volume Control AV
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
REF
DACATTN
REC
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
f = 1kHz, Input = -1dBFS, R
HPL to HPR and HPR to HPL,
= 5mW, f = 1kHz, RHP = 32I
P
OUT
= V
V
AVDD
f = 217Hz, V
f = 1kHz, V
f = 10kHz, V
= 1.65V to 2.0V 60 84
HPVDD
= 100mV, AV
RIPPLE
= 100mV, AV
RIPPLE
= 100mV, AV
RIPPLE
MODE = 0 (voice) 8kHz 2.2
1kHz, 0dB input,
highpass filter
disabled measured
from digital input to
analog output
MODE = 0 (voice)
16kHz
MODE = 1 (music)
8kHz
MODE = 1 (music)
48kHz
Peak voltage, A-weighted,
32 samples per second,
CP
AV
= 0dB
HP_
THD+N
= 1V
V
IN
P-P
= V
V
AVDD
f = 217Hz, V
f = 1kHz, V
f = 10kHz, V
, f =1kHz, RHP = 32I
= 1.65V to 2.0V 42 66
HPVDD
= 100mV
RIPPLE
= 100mV
RIPPLE
= 100mV
RIPPLE
Peak voltage, A-weighted,
32 samples per second,
CP
AV
= 0dB
HP_
OUT
f = 1kHz, THD = 1%
TA = +25NC (Note 5)
HP_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
= 10kI
HP
-82 dB
-82 dB
= 0dB 92
VOL
= 0dB 91
VOL
= 0dB 57
VOL
1.1
4.5
0.76
Into shutdown -66
Out of
shutdown
-67
dBV
-70 dB
P-P
P-P
P-P
62
57
41
Into shutdown -62
dBV
mW
R
HP
R
HP
Out of
shutdown
= 32I
= 16I
-60
32
40
HPVOL_ = 0x00 -71 -67 -66
HPVOL_ = 0x1F 2.4 3 3.5
MAX9888
dB
ms
dB
RMS
dB
17
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
= T
A
MAX9888
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
to T
MIN
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Volume Control Step Size
Mute Attenuation f = 1kHz 82 dB
Output Offset Voltage V
Capacitive Drive Capability
Charge Pump Oscillator
Frequency
SPEAKER BYPASS SWITCH
On-Resistance R
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
Off-Isolation
Off-Leakage Current
RECEIVER BYPASS SWITCH
On-Resistance R
Total Harmonic Distortion +
Noise
Off-Isolation
Off-Leakage Current
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
REF
DACATTN
REC
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
+3dB to +1dB 0.5
+1dB to -5dB 1
-5dB to -19dB 2
-19dB to -43dB 3
-43dB to -67dB 4
= +25NC
T
OS
f
CP
ON
THD+N
AV
= -67dB
HP_
No sustained
oscillations
Slow mode 74
I
= 100mA, SPKBYP = 1,
SPKL_
V
= [0V, V
RXIN_
V
= 2V
IN
Z
= 8I + 68FH, f = 1kHz,
SPK
, VCM = V
P-P
SPKLVDD]
A
T
= T
A
R
HP
R
HP
SPKLVDD
SPKBYP = 1
ON
THD+N
= 2V
V
IN
Z
= 8I + 68FH, f = 1kHz
L
V
RXIN_
V
SPKL_
I
RECP
V
RECN
= 2V
V
IN
R
= 32I, f = 1kHz, RECBYP = 1
L
= 2V
V
IN
R
= 32I, f = 1kHz
L
V
RECP
V
RECN
, VCM = V
P-P
= [0V, V
= [V
SPKLVDD
SPKLVDD
SPKLVDD
, 0V]
],
= 100mA, RECBYP = 1,
= [0V, V
, VCM = V
P-P
, VCM = V
P-P
= [0V, V
= [V
SPKLVDD
SPKLVDD
SPKLVDD
]
SPKLVDD
SPKLVDD
],
, 0V]
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
±0.2 ±1
to T
MIN
= 32I
= J
MAX
±2
500
100
300 667 900
2.8 4.5
/2,
/2,
R
S
R
S
= 10I
= 0I
-77
-60
96
-1 +1
1.2 2
/2,
/2,
-66 %
80 dB
-15 +15
) connected
HPVSS
= 0dB,
dB
mV
pF
kHz
I
dB
dB
FA
I
FA
18
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
T
A
PGAIN_
= T
MIN
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
to T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
JACK DETECTION
JACKSNS High Threshold V
JACKSNS Low Threshold V
JACKSNS Sense Voltage V
JACKSNS Sense Resistance R
JACKSNS Weak Pullup Current I
JACKSNS Deglitch Period t
BATTERY ADC
Input Voltage Range 2.8 5.5 V
LSB Size 0.1 V
= V
HPVDD
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA = +25NC.) (Note 1)
MAX
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
DVDDS1
REC
MICPGA_
= 0dB, AV
= V
= J, Z
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
REF
DACATTN
REC
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
MICBIAS enabled
TH1
MICBIAS disabled
MICBIAS enabled
TH2
MICBIAS disabled
SENSE
SENSE
WPU
GLITCH
MICBIAS disabled V
MICBIAS disabled, JDWK = 0 1.7 2.4 2.9
MICBIAS disabled, JDWK = 1 2 5 9.5
JDEB = 00 25
JDEB = 11 200
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS = 1.
0.92 x
V
MICBIAS
0.92 x
V
SPKLVD
0.06 x
V
MICBIAS
0.06 x
V
SPKLVD
V
V
D
SPKLVDD
V
V
D
SPKLVDD
SPKLVDD
0.95 x
MICBIAS
0.95 x
0.10 x
MICBIAS
0.10 x
0.98 x
V
MICBIAS
0.98 x
V
SPKLVD
0.17 x
V
MICBIAS
0.17 x
V
SPKLVD
D
D
HPVSS
V
V
V
kI
FA
ms
MAX9888
DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
(V
= V
AVDD
otherwise noted. Typical values are at T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
MCLK
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Leakage Current I
Input Capacitance 10 pF
SDINS1, BCLKS1, LRCLKS1—INPUT
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Hysteresis 200 mV
Input Leakage Current I
Input Capacitance 10 pF
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= V
DVDDS1
IH
IL
, I
IH
IH
IL
, I
IH
= V
= +25NC.) (Note 1)
A
IL
IL
= 1.65V to 2.0V, V
DVDDS2
V
= 2.0V, VIN = 0V, 5.5V, TA = +25°C -1 +1 FA
DVDD
V
= 3.6V, VIN = 0V, 3.6V; TA = +25°C -1 +1 FA
DVDDS1
SPKLVDD
= V
SPKRVDD
DVDDS1
= 3.7V, TA = T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless
1.2 V
0.6 V
0.7 x
0.29 x
DVDDS1
V
V
19
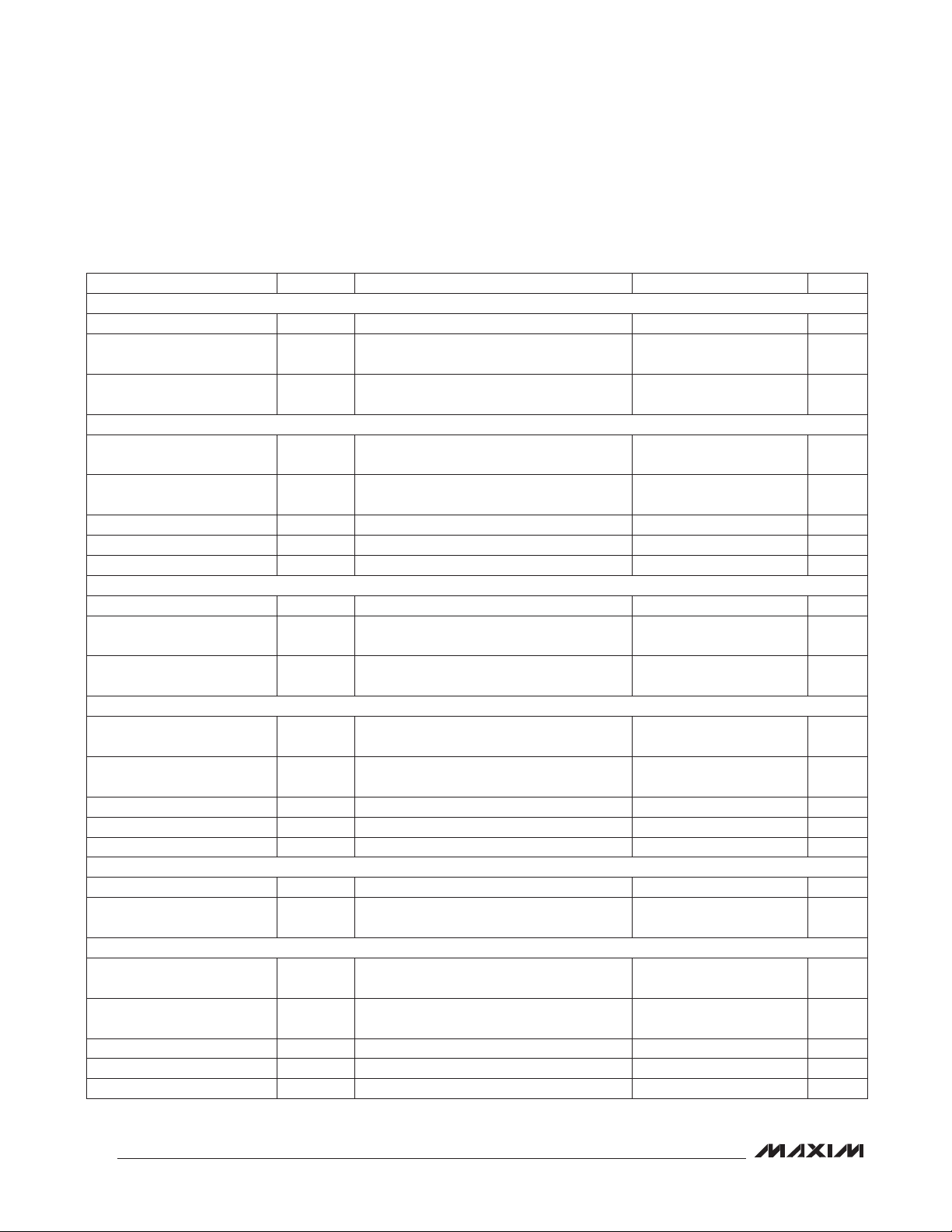
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
otherwise noted. Typical values are at T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
BCLKS1, LRCLKS1, SDOUTS1—OUTPUT
Output Low Voltage V
Output High Voltage V
MAX9888
Input Leakage Current I
SDINS2, BCLKS2, LRCLKS2—INPUT
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Hysteresis 200 mV
Input Leakage Current I
Input Capacitance 10 pF
BCLKS2, LRCLKS2, SDOUTS2—OUTPUT
Output Low Voltage V
Output High Voltage V
Input Leakage Current I
SDA, SCL—INPUT
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Hysteresis 210 mV
Input Leakage Current I
Input Capacitance 10 pF
SDA, IRQ—OUTPUT
Output High Current I
Output Low Voltage V
DIGMICDATA—INPUT
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Hysteresis 125 mV
Input Leakage Current I
Input Capacitance 10 pF
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= V
DVDDS1
OL
OH
, I
IH
IH
IL
, I
IH
OL
OH
, I
IH
IH
IL
, I
IH
OH
OL
IH
IL
, I
IH
= V
= +25NC.) (Note 1)
A
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
= 1.65V to 2.0V, V
DVDDS2
V
V
V
= 1.65V, IOL = 3mA 0.4 V
DVDDS1
= 1.65V, IOH = 3mA
DVDDS1
= 2.0V, VIN = 0V, 5.5V; TA = +25°C,
DVDD
high-impedance state
V
V
V
V
= 3.6V, VIN = 0V, 3.6V; TA = +25°C -1 +1 FA
DVDDS2
= 1.65V, IOL = 3mA 0.4 V
DVDDS2
= 1.65V, IOH = 3mA
DVDDS2
= 2.0V, VIN = 0V, 5.5V; TA = +25NC,
DVDD
high-impedance state
V
= 2.0V, VIN = 0V, 5.5V, TA = +25NC -1 +1 FA
DVDD
V
= 5.5V, TA = +25°C 1 mA
OUT
V
= 1.65V, IOL = 3mA
DVDD
V
= 2.0V, VIN = 0V, 2.0V; TA = +25°C -25 +25 FA
DVDD
SPKLVDD
= V
SPKRVDD
DVDDS1
DVDDS2
DVDDS2
= 3.7V, TA = T
MIN
to T
- 0.4
-1 +1 FA
0.7 x
0.29 x
DVDDS2
- 0.4
-1 +1 FA
0.7 x
DVDD
0.3 x
DVDD
0.2 x
DVDD
0.65 x
DVDD
0.35 x
DVDD
MAX
, unless
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
20
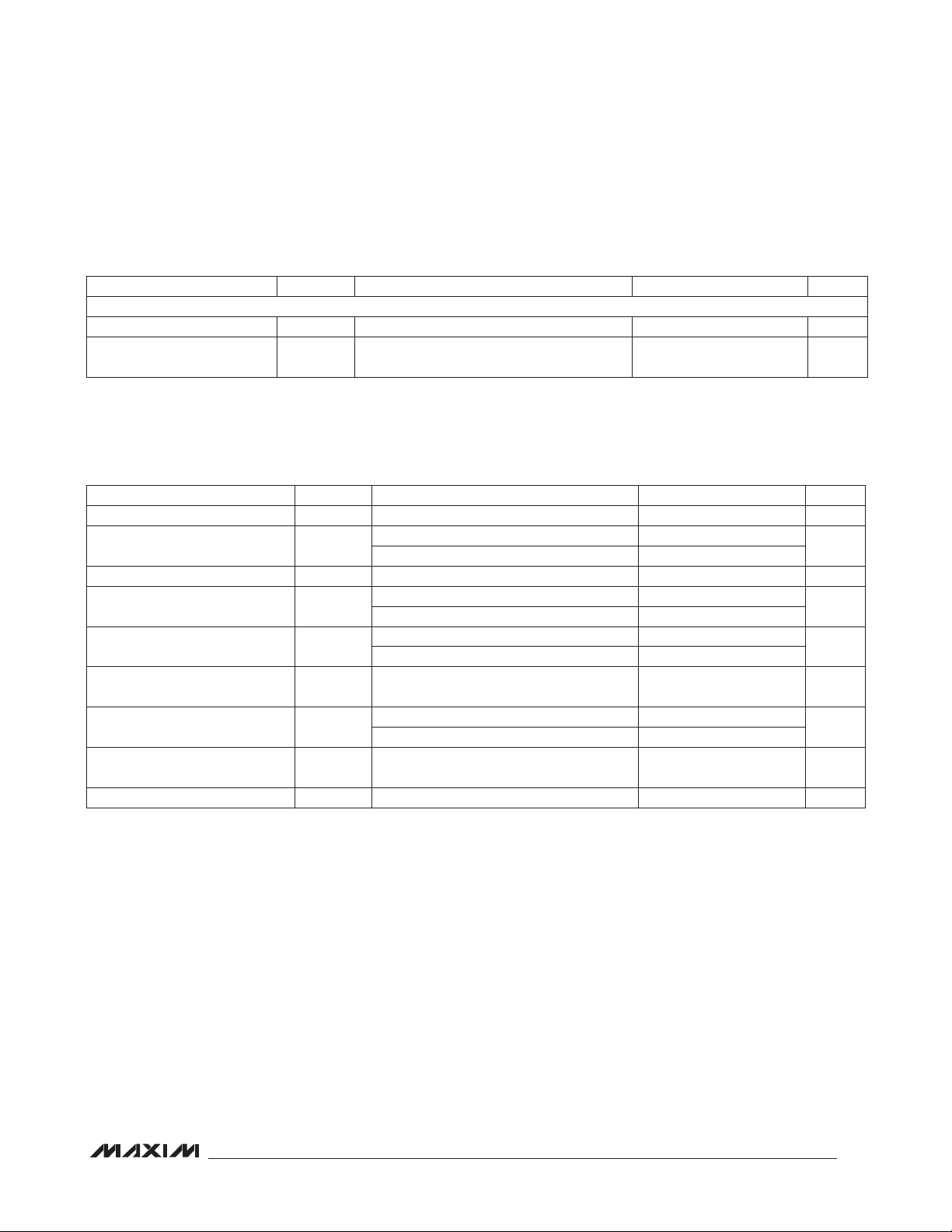
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
otherwise noted. Typical values are at T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DIGMICCLK—OUTPUT
Output Low Voltage V
Output High Voltage V
INPUT CLOCK CHARACTERISTICS
(V
= V
AVDD
noted. Typical values are at T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
MCLK Input Frequency f
MCLK Input Duty Cycle
Maximum MCLK Input Jitter 100 ps
LRCLK Sample Rate (Note 8)
DAI1 LRCLK Average Frequency
Error (Note 9)
DAI2 LRCLK Average Frequency
Error (Note 9)
PLL Lock Time
Maximum LRCLK Jitter to Maintain
PLL Lock
Soft-Start/Stop Time 10 ms
HPVDD
HPVDD
= V
= V
DVDD
DVDD
= V
DVDDS1
= V
DVDDS1
= +25NC.) (Note 1)
A
= V
= +25NC.) (Note 1)
A
OL
OH
= V
MCLK
= 1.65V to 2.0V, V
DVDDS2
V
= 1.65V, IOL = 1mA 0.4 V
DVDD
V
= 1.65V, IOH = 1mA
DVDD
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
PSCLK = 01 40 50 60
PSCLK = 10 or 11 30 70
DHF_ = 0 8 48
DHF_ = 1 48 96
FREQ1 = 0x8 to 0xF 0 0
FREQ1 = 0x0 -0.025 +0.025
Rapid lock mode 2 7
Nonrapid lock mode 12 25
SPKLVDD
SPKLVDD
= V
= V
SPKRVDD
SPKRVDD
= 3.7V, TA = T
= 3.7V, TA = T
DVDD -
0.4
10 60 MHz
-0.025 +0.025 %
MIN
to T
to T
MIN
MAX
MAX
, unless otherwise
100 ns
, unless
kHz
MAX9888
V
%
RMS
%
ms
21
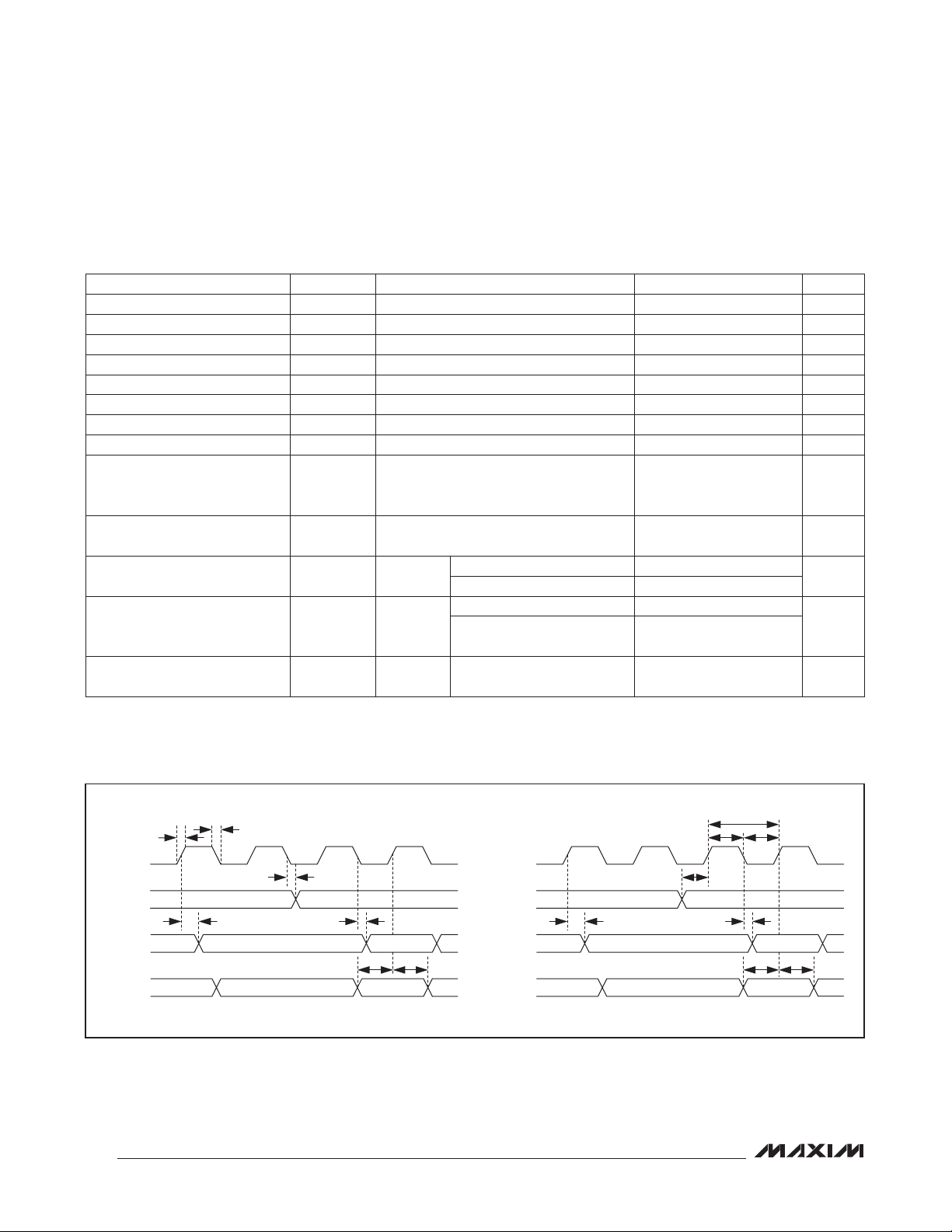
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
AUDIO INTERFACE TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
(V
= V
AVDD
noted. Typical values are at T
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
BCLK Cycle Time t
BCLK High Time t
BCLK Low Time t
MAX9888
BCLK or LRCLK Rise and Fall Time t
SDIN to BCLK Setup Time t
LRCLK to BCLK Setup Time t
SDIN to BCLK Hold Time t
LRCLK to BCLK Hold Time t
Minimum Delay Time from LSB
BCLK Falling Edge to
High-Impedance State
LRCLK Rising Edge to SDOUT
MSB Delay
BCLK to SDOUT Delay t
Delay Time from BCLK to LRCLK t
Delay Time from LRCLK to BCLK
After LSB
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= V
= +25NC.) (Note 1)
A
DVDDS1
SYNCSET
SYNCHOLD
t
HIZOUT
t
SYNCTXCL
CLKSYNC
t
ENDSYNC
= V
BCLK
BCLKH
BCLKL
, t
R
SETUP
HOLD
CLKTX
= 1.65V, V
DVDDS2
SPKLVDD
Slave mode 90 ns
Slave mode 20 ns
Slave mode 20 ns
Master mode, CL = 15pF ns
F
Slave mode 20 ns
Slave mode 20 ns
Master mode, TDM_ = 1 42 ns
= 30pF, TDM_ = 1, FSW_ = 1 50 ns
CL = 30pF
Master
mode
Master
mode
TDM_ = 1, BCLK rising edge 50
TDM_ = 0 50
TDM_ = 1 -15 +15
TDM_ = 0
TDM_ = 1, FSW_ = 1 20 ns
= V
SPKRVDD
= 2.8V, TA = T
20 ns
20 ns
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise
MAX
0.8 x
t
BCLKL
ns
ns
t
t
CLKSYNC
t
HIZOUT
F
t
CLKTX
HI-Z MSB
MASTER MODE
t
SETUPtHOLD
MSBLSB
BCLK
(OUTPUT)
LRCLK
(OUTPUT)
SDOUT
(OUTPUT)
SDIN
(INPUT)
t
R
LSB
Figure 1. Non-TDM Audio Interface Timing Diagrams (TDM_ = 0)
22
BCLK
(INPUT)
LRCLK
(INPUT)
SDOUT
(OUTPUT)
SDIN
(INPUT)
t
SYNCSET
t
HIZOUT
LSB HI-Z
LSB
SLAVE MODE
t
BCLKH
t
CLKTX
t
BCLK
t
SETUPtHOLD
MSB
t
MSB
BCLKL
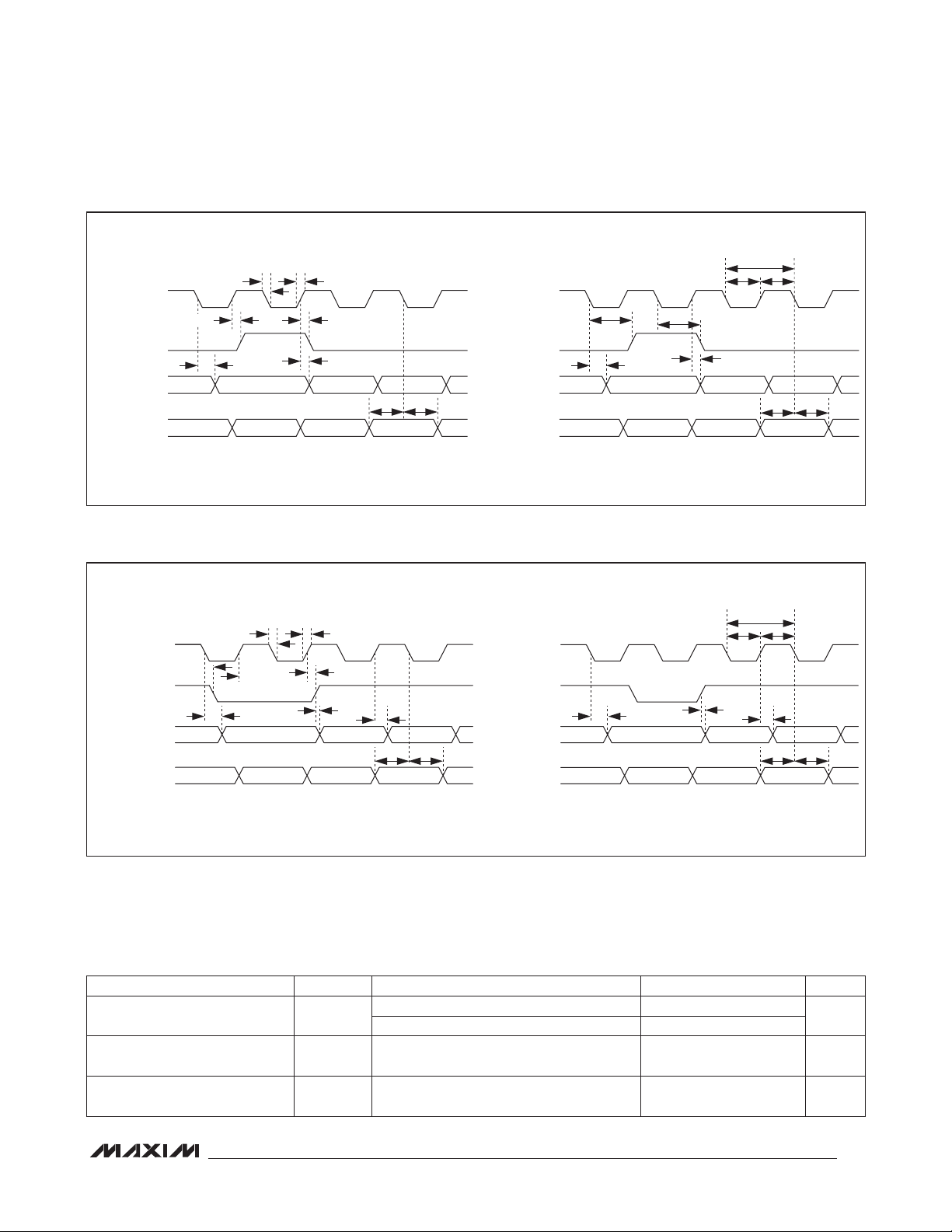
with FlexSound Technology
t
F
BCLK (OUTPUT)
t
CLKSYNC
LRCLK (OUTPUT)
t
t
SDOUT (OUTPUT)
SDIN (INPUT)
HIZOUT
LSB
CLKTX
HI-ZLSB
MASTER MODE SLAVE MODE
Figure 2. TDM Audio Interface Timing Diagram (TDM_ = 1, FSW_ = 0)
t
R
t
CLKSYNC
MSB
MSB
t
SETUP
t
HOLD
SDOUT (OUTPUT)
Stereo Audio CODEC
t
BCLK
t
BCLK (INPUT)
LRCLK (INPUT)
SDIN (INPUT)
t
SYNCSET
t
HIZOUT
LSB
t
CLKTX
HI-ZLSB
BCLKH
t
SYNCHOLD
MSB
MSB
t
SETUP
t
BCLKL
t
MAX9888
HOLD
BCLK (OUTPUT)
LRCLK (OUTPUT)
SDOUT (OUTPUT)
SDIN (INPUT)
t
F
t
ENDSY NC
t
HIZOUT
LSB MSB
t
SYNCTX
HI-ZLSB MSB
MASTER MODE
t
R
t
CLKSYNC
t
CLKTX
t
SETUP
t
HOLD
BCLK (INPUT)
LRCLK (INPUT)
SDOUT (OUTPUT)
SDIN (INPUT)
Figure 3. TDM Audio Interface Timing Diagram (TDM_ = 1, FSW_ = 1)
DIGITAL MICROPHONE TIMING CHARACTERSTICS
(V
= V
AVDD
noted. Typical values are at T
DIGMICCLK Frequency f
DIGMICDATA to DIGMICCLK
Setup Time
DIGMICDATA to DIGMICCLK
Hold Time
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= V
= +25NC.) (Note 1)
A
DVDDS1
= V
DVDDS2
= 2.0V, V
SPKLVDD
= V
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
MICCLK
t
SU,MIC
t
HD,MIC
MICCLK = 00 MCLK/8
MICCLK = 01 MCLK/6
Either clock edge 20 ns
Either clock edge 0 ns
t
HIZOUT
SPKRVDD
t
HI-ZLSB
LSB
= 2.8V, TA = T
SYNCTX
SLAVE MODE
MIN
t
BCLKH
MSB
to T
t
BCLK
t
CLKTX
MSB
t
SETUP
, unless otherwise
MAX
t
BCLKL
t
HOLD
MHz
23
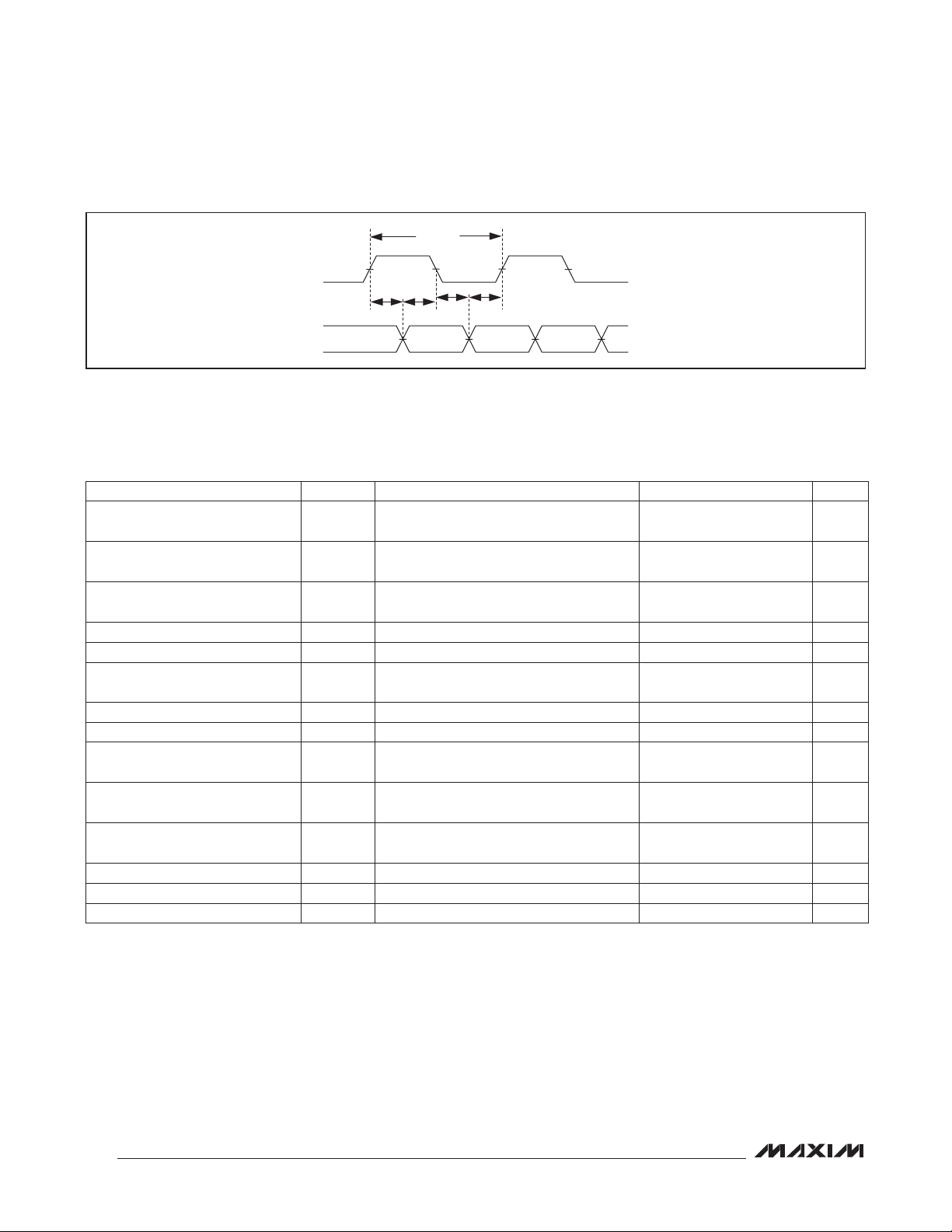
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
1/f
MICCLK
t
HD,MICtSU,MIC
t
HD,MICtSU,MIC
LEFT RIGHT LEFT RIGHT
MAX9888
Figure 4. Digital Microphone Timing Diagram
I2C TIMING CHARACTERSTICS
(V
= V
AVDD
otherwise noted. Typical values are at T
Serial-Clock Frequency f
Bus Free Time Between STOP and
START Conditions
Hold Time (Repeated) START
Condition
SCL Pulse-Width Low t
SCL Pulse-Width High t
Setup Time for a Repeated START
Condition
Data Hold Time t
Data Setup Time t
SDA and SCL Receiving Rise Time t
SDA and SCL Receiving Fall Time t
SDA Transmitting Fall Time t
Setup Time for STOP Condition t
Bus Capacitance C
Pulse Width of Suppressed Spike t
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= V
DVDDS1
= V
= +25NC.) (Note 1)
A
= 1.65V to 2.0V, V
DVDDS2
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
SCL
t
BUF
t
HD,STA
LOW
HIGH
t
SU,STA
HD,DAT
SU,DAT
SU,STO
Guaranteed by SCL pulse-width low and
high
RPU = 475I, CB = 100pF, 400pF
(Note 10)
R
(Note 10)
F
RPU = 475I, CB = 100pF, 400pF (Note 10)
F
Guaranteed by SDA transmitting fall time 400 pF
B
SP
SPKLVDD
= V
SPKRVDD
= 3.7V, TA = T
MIN
to T
MAX
0 400 kHz
1.3
0.6
1.3
0.6
0.6
0 900 ns
100 ns
20 +
0.1C
20 +
0.1C
20 +
0.05C
B
B
B
300 ns
300 ns
250 ns
0.6
0 50 ns
, unless
Fs
Fs
Fs
Fs
Fs
Fs
24
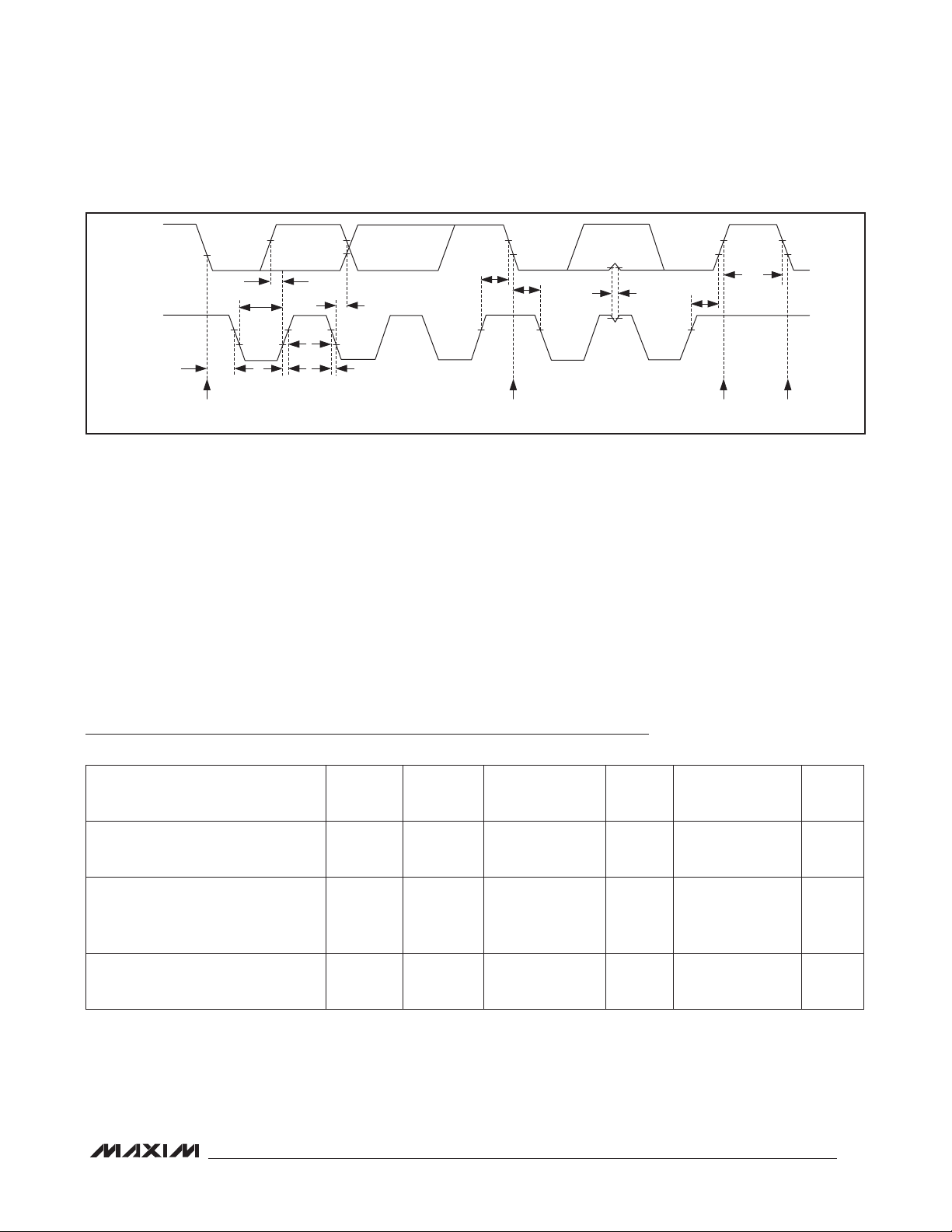
SDA
t
LOW
t
SU,DAT
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
MAX9888
t
t
t
HD,DAT
SU,STA
t
HD,STA
t
SP
t
SU,STO
BUF
t
HIGH
t
t
R
F
REPEATED START CONDITION
STOP
CONDITION
START
CONDITION
Figure 5. I
SCL
t
HD,STA
START CONDITION
2
C Interface Timing Diagram
Note 1: The IC is 100% production tested at TA = +25NC. Specifications over temperature limits are guaranteed by design.
Note 2:
Analog supply current = I
+ I
DVDDS1
+ I
DVDDS2
.
AVDD
+ I
. Speaker supply current = I
HPVDD
SPKLVDD
+ I
SPKRVDD
. Digital supply current = I
DVDD
Note 3: Clocking all zeros into the DAC. Slave mode.
Note 4: Dynamic range measured using the EIAJ method. -60dBFS, 1kHz output signal, A-weighted and normalized to 0dBFS.
f = 20Hz to 20kHz.
Note 5: Gain measured relative to the 0dB setting.
Note 6: The filter specification is accurate only for synchronous clocking modes, where NI is a multiple of 0x1000.
Note 7: 0dBFS for DAC input. 1V
for INA/INB inputs.
P-P
Note 8: LRCLK may be any rate in the indicated range. Asynchronous or noninteger MCLK/LRCLK ratios may exhibit some full-
scale performance degradation compared to synchronous integer related MCLK/LRCLK ratios.
Note 9: In master-mode operation, the accuracy of the MCLK input proportionally determines the accuracy of the sample clock rate.
Note 10: CB is in pF.
Power Consumption
(V
= V
AVDD
DAC Playback 48kHz Stereo HP
DAC à HP
24-bit, music filters
DAC Playback 48kHz Stereo HP
DAC à HP
24-bit, music filters, 0.1mW/channel,
R
= 32I
HP
DAC Playback 48kHz Stereo HP
DAC à HP
24-bit, music filters, ALC enabled
HPVDD
= V
MODE
DVDD
= V
DVDDS1
= V
DVDDS2
I
AVDD
(mA)
= +1.8V, V
I
HPVDD
(mA)
SPKLVDD
= V
SPKRVDD
I
SPKLVDD
I
SPKRVDD
(mA)
+
= 3.7V)
I
DVDD
(mA)
I
DVDDS1
+ I
(mA)
DVDDS2
1.35 1.37 1.65 2.91 0.02 16.25
1.35 4.19 1.65 3.02 0.02 21.55
1.35 1.37 1.65 2.96 0.02 16.36
POWER
(mW)
25
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Power Consumption (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
DAC Playback 48kHz Stereo HP
DAC à HP
MAX9888
24-bit, music filters, EQ enabled
DAC Playback 48kHz Stereo HP
DAC à HP
24-bit, music filters, digital mixing
DAC Playback 44.1kHz Stereo HP
DAC à HP
24-bit, music filters
DAC Playback 8kHz Stereo HP
DAC à HP
16-bit, voice filters
DAC Playback 8kHz Mono HP
DAC à HP
16-bit, voice filters
DAC Playback 48kHz Stereo SPK
DAC à SPK
24-bit, music filters
DAC Playback 48kHz Mono SPK
DAC à SPK
24-bit, music filters
Line Stereo Record 48kHz
INA à ADC
16-bit, music filters
Line Stereo Record 48kHz, Stereo HP
INA à ADC
INA à HP
16-bit, music filters
Line Stereo Record 48kHz, Stereo SPK
INA à ADC
INA à SPK
16-bit, music filters
Differential Line Record 48kHz
INA à ADCL
INB à ADCR
Differential input
Microphone Stereo Record 48kHz
MIC1/2 à ADC
16-bit, music filters
Microphone Stereo Record 8kHz
MIC1/2 à ADC
16-bit, voice filters
HPVDD
= V
MODE
DVDD
= V
DVDDS1
= V
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
I
AVDD
(mA)
1.35 1.36 1.65 3.27 0.02 16.90
1.34 1.36 1.65 2.91 0.02 16.27
1.35 1.37 1.69 2.85 0.02 16.29
1.35 1.37 1.65 1.46 0.01 13.65
1.00 0.71 1.01 1.36 0.01 9.27
1.83 0.02 8.22 2.92 0.02 39.09
1.25 0.02 4.31 2.82 0.02 23.32
9.91 0.02 0.39 1.62 0.11 22.48
10.64 2.65 0.66 1.63 0.11 29.51
10.97
10.49 0.02 0.39 1.63 0.16 23.58
10.88 0.03 0.69 1.62 0.17 25.43
10.77 0.02 0.64 1.03 0.06 23.78
SPKLVDD
I
HPVDD
(mA)
0.03 7.15 1.63 0.12 49.50
= V
SPKRVDD
I
SPKLVDD
I
SPKRVDD
(mA)
+
= 3.7V)
I
DVDD
(mA)
I
DVDDS1
+ I
(mA)
DVDDS2
POWER
(mW)
26
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Power Consumption (continued)
(V
AVDD
= V
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= V
DVDDS1
= V
DVDDS2
= +1.8V, V
SPKLVDD
= V
SPKRVDD
= 3.7V)
MAX9888
MODE
Microphone Mono Record 48kHz
MIC1/2 à ADC
16-bit, music filters
Microphone Mono Record 8kHz
MIC1/2 à ADC
16-bit, voice filters
Microphone Mono Record 8kHz
MIC1/2 à ADC
16-bit, voice filters, AGC
Microphone Mono Record 8kHz
MIC1/2 à ADC
16-bit, voice filters, AGC, noise gate
Full-Duplex 48kHz Stereo HP
MIC1/2 à ADC
DAC à HP
24-bit, music filters
Full-Duplex 8kHz Mono RCV
MIC1 à ADC
DAC à REC
16-bit, voice filters
Full-Duplex 8kHz Mono HP
MIC1 à ADC
DAC à HP
16-bit, voice filters
Full-Duplex 8kHz Stereo HP
MIC1/2 à ADC
DAC à HP
16-bit, voice filters
Line Playback Stereo HP
INA à HP
Single-ended inputs
Line Playback Stereo SPK
INA à SPK
Single-ended inputs
Line Playback Mono SPK
INA à SPK
Single-ended inputs
Differential Line Playback Stereo HP
INA à HPL
INB à HPR
Differential input
(mA)
+
I
DVDD
(mA)
I
DVDDS1
+ I
(mA)
DVDDS2
POWER
(mW)
I
I
AVDD
(mA)
6.01 0.02 0.66 1.37 0.10 15.97
5.95 0.02 0.64 0.98 0.04 14.94
5.95 0.02 0.64 0.98 0.04 15.00
5.96 0.02 0.64 0.98 0.04 14.98
11.38 1.37 1.70 3.56 0.19 36.06
6.35 0.02 1.98 1.47 0.03 21.47
6.09 0.71 1.01 1.46 0.03 18.72
10.92 1.37 1.09 1.51 0.05 28.95
1.89 2.65 0.58 0.03 0.01 10.41
2.21 0.02 7.05 0.04 0.02 30.19
1.68 0.02 3.70 0.03 0.02 16.90
2.46 2.65 0.58 0.03 0.01 11.42
I
HPVDD
(mA)
SPKLVDD
I
SPKRVDD
27
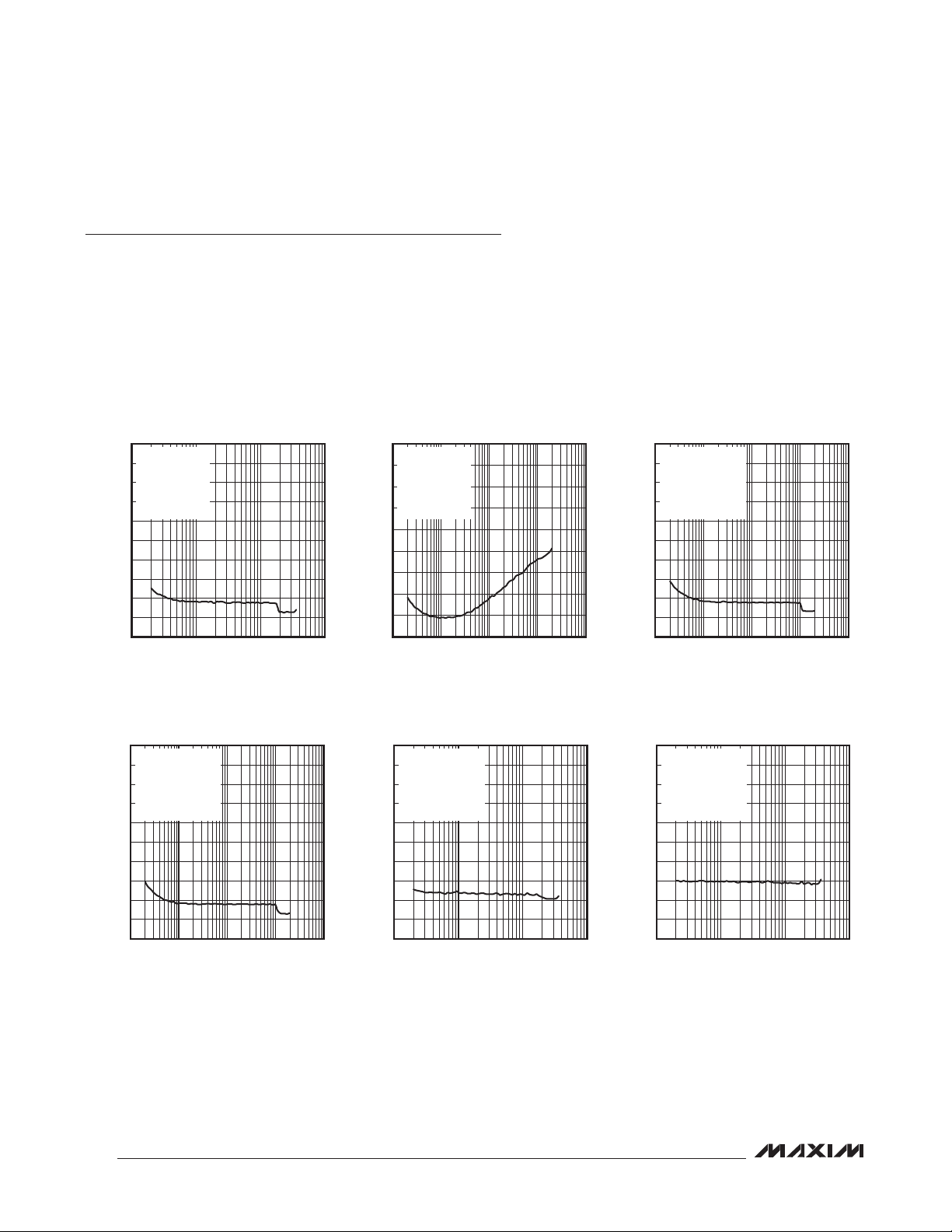
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
MAX9888
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
= V
MICBIAS
DACGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
SPK_
Microphone to ADC
SPKRVDD
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY (MIC TO ADC)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
-20
V
= 1V
IN
-30
-40
-50
-60
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-70
-80
-90
-100
P-P
AV
= 0dB
MICPRE_
10 10,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1000100
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY (MIC TO ADC)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz
-10
LRCLK = 96kHz
NI MODE
-20
V
= 1V
IN
-30
-40
-50
-60
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-70
-80
-90
-100
P-P
AV
= 0dB
MICPRE_
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
MAX9888 toc01
THD+N RATIO (dB)
MAX9888 toc04
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY (MIC TO ADC)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
-20
V
= 1V
IN
P-P
AV
MICPRE_
= 0dB
10,0001000100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
10 100,000
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY (MIC TO ADC)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
-20
V
= 0.1V
IN
AV
MICPRE_
P-P
= +20dB
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1000100
-30
-40
-50
-60
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-70
-80
-90
-100
10 10,000
MAX9888 toc02
THD+N RATIO (dB)
MAX9888 toc05
THD+N RATIO (dB)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY (MIC TO ADC)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz
-10
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
V
= 1V
IN
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
P-P
AV
= 0dB
MICPRE_
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY (MIC TO ADC)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
-20
V
= 0.032V
IN
MICPRE_
P-P
= +30dB
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1000100
-30
AV
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
10 10,000
MAX9888 toc03
MAX9888 toc06
28
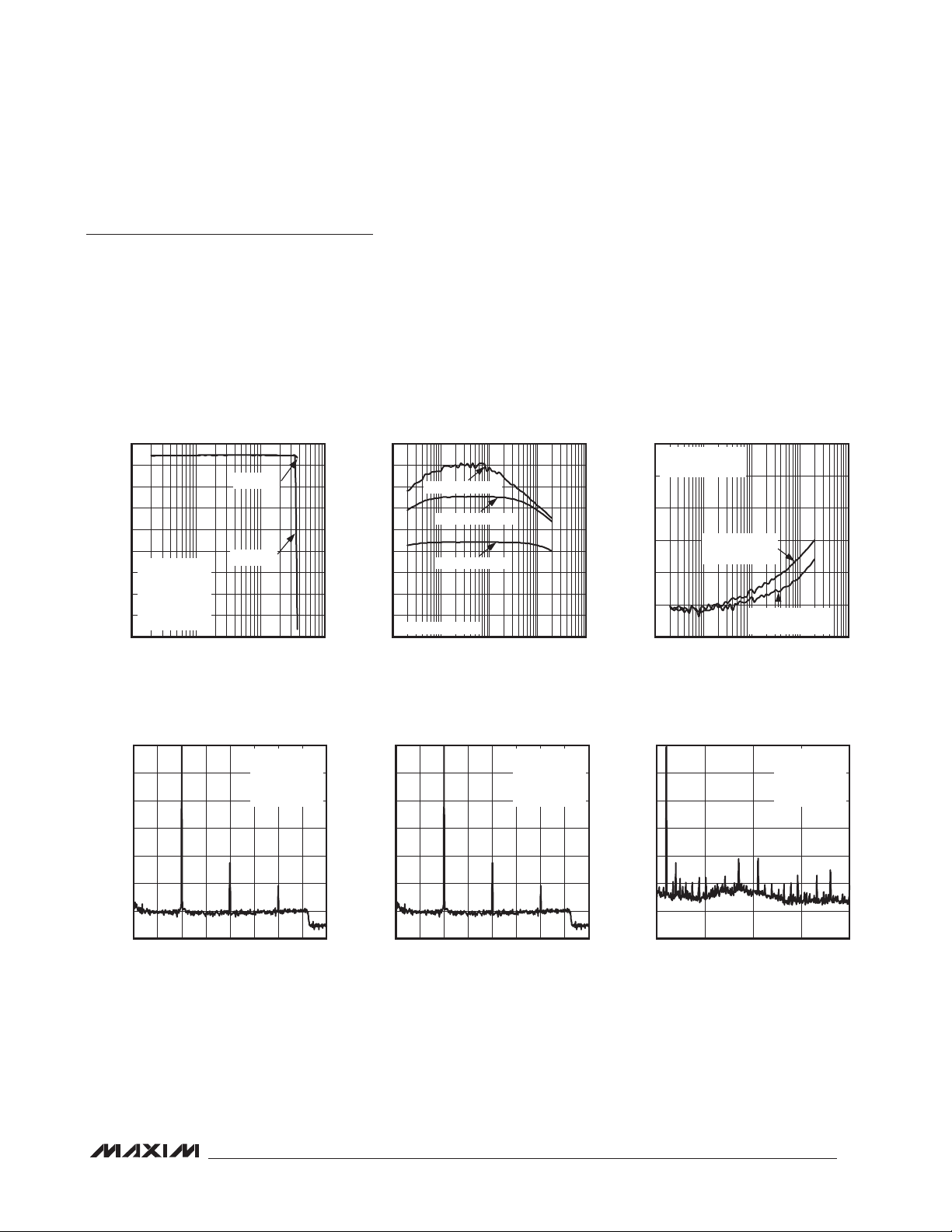
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
GAIN vs. FREQUENCY (MIC TO ADC)
5
-5
-15
-25
-35
-45
MCLK = 13MHz
-55
LRCLK = 8kHz
NORMALIZED GAIN (dB)
FREQ MODE
-65
VIN = 1V
-75
-85
P-P
AV
= 0dB
MICPRE_
10 10,000
MODE = 1
MODE = 0
1000100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
FFT, 0dBFS (MIC TO ADC)
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
AV
MICPRE_
= 0dB
MAX9888 toc07
MAX9888 toc10
COMMON-MODE REJECTION
RATIO vs. FREQUENCY (MIC TO ADC)
90
80
AV
70
60
50
40
CMRR (dB)
30
20
10
V
OUT, DIFF
0
10 100,000
= +30dB
MICPRE_
AV
MICPRE_
AV
MICPRE_
= 0dBFS
FREQUENCY (Hz)
= +20dB
= 0dB
10,0001000100
FFT, -60dBFS (MIC TO ADC)
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
AV
MICPRE_
= 0dB
MAX9888 toc08
PSRR (dB)
MAX9888 toc11
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION
RATIO vs. FREQUENCY (MIC TO ADC)
0
V
= 200mV
RIPPLE
INPUTS AC GROUNDED
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
-120
10 100,000
P-P
RIPPLE ON AVDD,
DVDD, HPVDD
RIPPLE ON
SPKLVDD, SPKRVDD
10,0001000100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
FFT, 0dBFS (MIC TO ADC)
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
AV
MICPRE_
MAX9888 toc09
MAX9888 toc12
= 0dB
-120
-140
0 4000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
-120
-140
350030002500200015001000500
0 4000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
350030002500200015001000500
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
15,00010,0005000
29
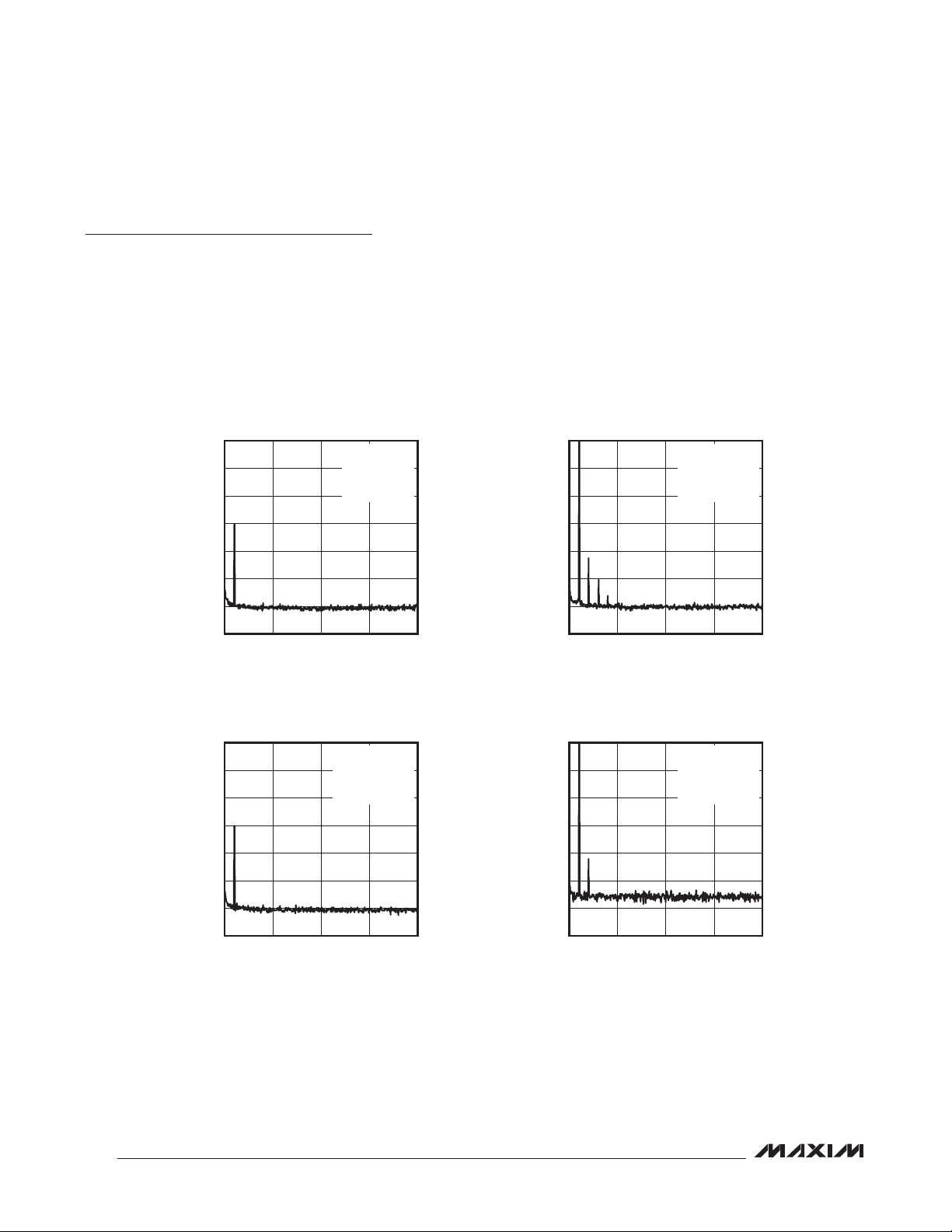
Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
HPVSS
= 0dB,
FFT, -60dBFS (MIC TO ADC)
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
AV
MICPRE_
FFT, -60dBFS (MIC TO ADC)
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
AV
MICPRE_
0
MAX9888 toc13
= 0dB
15,00010,0005000
-20
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
AV
= 0dB
MICPRE_
15,00010,0005000
MAX9888 toc14
FFT, 0dBFS (MIC TO ADC)
FFT, 0dBFS (MIC TO ADC)
= 0dB
MAX9888 toc15
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 96kHz
NI MODE
AV
= 0dB
MICPRE_
MAX9888 toc16
30
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
15,00010,0005000
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
15,00010,0005000

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
FFT, -60dBFS (MIC TO ADC)
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 96kHz
NI MODE
AV
MICPRE_
15,00010,0005000
= 0dB
SCL
2V/div
ADC
OUTPUT
0.5V/div
MAX9888 toc17
SCL
2V/div
ADC
OUTPUT
0.5V/div
SOFTWARE TURN-ON/OFF RESPONSE
(MIC TO ADC)
MAX9888 toc19
ADC ENABLE/DISABLE RESPONSE
(MIC TO ADC)
10ms/div
MAX9888 toc18
10ms/div
31

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
MAX9888
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
Line to ADC
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
HPVSS
= 0dB,
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO ADC)
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
10 100,000
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
V
IN
AV
C
IN
FREQUENCY (Hz)
= 1.4V
PGAIN_
= 1µF
10,0001000100
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO ADC)
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-70
-80
-90
-100
10 100,000
P-P
= -6dB
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MAX9888 toc20
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
V
IN
EXTERNAL GAIN MODE
RIN = 56kI, CIN = 1µF
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-70
-80
-90
-100
= 1V
RMS
10,0001000100
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO ADC)
0
10 100,000
MAX9888 toc23
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
V
IN
C
IN
AV
FREQUENCY (Hz)
= 1V
P-P
= 1µF
= 0dB
PGAIN_
10,0001000100
0
-20
-40
-60
PSRR (dB)
-80
-100
-120
10 100,000
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO ADC)
0
-10
MAX9888 toc21
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-70
-80
-90
-100
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO
vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO ADC)
V
= 200mV
INPUTS AC GROUNDED
RIPPLE ON AVDD,
DVDD, HPVDD
FREQUENCY (Hz)
RIPPLE
SPKLVDD, SPKRVDD
P-P
RIPPLE ON
10,0001000100
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
V
= 0.1V
IN
P-P
AV
= +20dB
PGAIN_
10,0001000100
MAX9888 toc24
MAX9888 toc22
32

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
= V
MICBIAS
DACGAIN
SPK_
Digital Loopback
SPKRVDD
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
(SDINS1 TO SDOUTS2 DIGITAL LOOPBACK)
FFT, 0dBFS
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
-120
-140
-160
-180
0 20,000
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
15,00010,0005000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MAX9888 toc25
(SDINS1 TO SDOUTS2 DIGITAL LOOPBACK)
FFT, -60dBFS
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
-120
-140
-160
-180
0 20,000
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
15,00010,0005000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MAX9888 toc26
33

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
MAX9888
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
= V
MICBIAS
DACGAIN
SPK_
Analog Loopback
SPKRVDD
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
HPVSS
= 0dB,
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. FREQUENCY
(LINE TO ADC TO DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
= 32I, CIN = 1µF
R
HP
P
= 0.025W
OUT
P
= 0.01W
OUT
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
FFT, -60dBFS
(LINE TO ADC TO DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
-20
-40
-60
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
= 32I
R
HP
MAX9888 toc27
THD+N RATIO (dB)
MAX9888 toc30
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
PLUS NOISE vs. FREQUENCY
(LINE TO ADC TO DAC TO HEADPHONE )
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz
-10
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
= 32I, CIN = 1µF
R
HP
P
= 0.025W
OUT
P
= 0.01W
OUT
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
FFT, 0dBFS
(LINE TO ADC TO DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
-20
-40
-60
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
= 32I
R
HP
MAX9888 toc28
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
MAX9888 toc31
(LINE TO ADC TO DAC TO HEADPHONE)
FFT, 0dBFS
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
= 32I
R
HP
15,00010,0005000
FFT, -60dBFS
(LINE TO ADC TO DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
-20
-40
-60
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
= 32I
R
HP
MAX9888 toc29
MAX9888 toc32
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
34
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
-120
15,00010,0005000
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
15,00010,0005000
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
15,00010,0005000

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
REF
DACATTN
REC
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
DACGAIN
SPK_
DAC to Receiver
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO RECEIVER)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
= 32I
R
REC
AV
= +8dB
REC
f = 3000Hz
f = 1000Hz
f = 100Hz
0 0.12
OUTPUT POWER (W)
GAIN vs. FREQUENCY
(DAC TO RECEIVER)
5
MCLK = 13MHz
4
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
3
= 32I
R
REC
2
1
0
-1
-2
NORMALIZED GAIN (dB)
-3
-4
-5
10 10,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1000100
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO RECEIVER)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
MAX9888 toc33
0.100.080.060.040.02
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
= 32I
R
REC
P
= 0.05W
OUT
P
= 0.025W
OUT
10 10,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1000100
MAX9888 toc34
POWER CONSUMPTION vs. OUTPUT
POWER (DAC TO RECEIVER)
0.25
MCLK = 13MHz
MAX9888 toc36
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
0.20
0.15
0.10
POWER CONSUMPTION (W)
0.05
= 32I
R
REC
AV
= +8dB
REC
0
0 0.12
OUTPUT POWER (W)
MAX9888 toc37
0.100.080.060.040.02
OUTPUT POWER vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(DAC TO RECEIVER)
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
OUTPUT POWER PER CHANNEL (mW)
70
60
2.5 5.5
THD+N = 10%
THD+N = 1%
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
R
REC
AV
REC
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO RECEIVER)
0
V
= 200mV
RIPPLE
ALL ZEROS AT INPUT
-20
-40
PSRR (dB)
-60
-80
-100
10 100,000
P-P
RIPPLE ON SPKLVDD,
SPKRVDD
RIPPLE ON AVDD,
DVDD, HPVDD
10,0001000100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MAX9888 toc35
= 32I
= +8dB
5.04.53.0 3.5 4.0
MAX9888 toc38
35

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
HPVSS
= 0dB,
SCL
2V/div
RECEIVER
OUTPUT
1V/div
-20
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
-120
SOFTWARE TURN-ON/OFF RESPONSE
(DAC TO RECEIVER, VSEN = 0)
10ms/div
FFT, -60dBFS (DAC TO RECEIVER)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
R
REC
MAX9888 toc39
= 32I
RECEIVER
OUTPUT
MAX9888 toc42
AMPLITUDE (dBm)
SOFTWARE TURN-ON/OFF RESPONSE
(DAC TO RECEIVER, VSEN = 1)
SCL
2V/div
1V/div
10ms/div
WIDEBAND FFT, 0dBFS
(DAC TO RECEIVER)
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
MAX9888 toc40
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 8kHz
PLL MODE
= 32I
R
REC
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
MAX9888 toc43
AMPLITUDE (dBm)
FFT, 0dBFS (DAC TO RECEIVER)
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
R
REC
15,00010,0005000
WIDEBAND FFT, -60dBFS
(DAC TO RECEIVER)
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 8kHz
PLL MODE
R
REC
= 32I
MAX9888 toc41
MAX9888 toc44
= 32I
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
36
15,00010,0005000
-120
0 10,000
FREQUENCY (kHz)
1000100101
-120
0 10,000
FREQUENCY (kHz)
1000100101

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
= V
MICBIAS
DACGAIN
SPK_
Line to Receiver
SPKRVDD
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS
NOISE vs. OUTPUT POWER
(LINE TO RECEIVER)
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
0 0.10
f = 6000Hz
f = 100Hz
OUTPUT POWER (W)
R
AV
f = 1000Hz
GAIN vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO RECEIVER)
5
R
= 32I
REC
4
= 1µF
C
IN
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
NORMALIZED GAIN (dB)
-3
-4
-5
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
REC
REC
0.080.060.02 0.04
= 32I
= +8dB
MAX9888 toc45
MAX9888 toc47
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
PLUS NOISE vs. FREQUENCY
(LINE TO RECEIVER)
0
R
= 32I
REC
-10
= 1µF
C
IN
AV
= +8dB
REC
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
10 100,000
P
= 0.05W
OUT
P
OUT
FREQUENCY (Hz)
= 0.025W
10,0001000100
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO
vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO RECEIVER)
0
V
= 200mV
RIPPLE
INPUT AC GROUNDED
-20
-40
PSRR (dB)
-60
-80
-100
RIPPLE ON SPKLVDD,
10 100,000
P-P
SPKRVDD
RIPPLE ON AVDD,
DVDD, HPVDD
10,0001000100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MAX9888 toc46
MAX9888 toc48
37

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
MAX9888
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
REF
DACATTN
REC
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
DAC to Speaker
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
HPVSS
= 0dB,
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 4.2V
SPK_VDD
-10
MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
= 8I + 68µH
Z
SPK
AV
= +8dB
SPK_
f = 6000Hz
f = 1000Hz
f = 100Hz
0 1.2
OUTPUT POWER (W)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 4.2V
SPK_VDD
-10
MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
Z
= 4I + 33µH
SPK
-30
AV
= +8dB
SPK_
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
f = 6000Hz
f = 1000Hz
f = 100Hz
OUTPUT POWER (W)
1.00.80.60.40.2
2.01.51.00.50 2.5
MAX9888 toc49
THD+N RATIO (dB)
MAX9888 toc52
THD+N RATIO (dB)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 3.7V
SPK_VDD
-10
MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
Z
= 8I + 68µH
SPK
AV
= +8dB
SPK_
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
f = 6000Hz
f = 1000Hz
f = 100Hz
0.80.60.40.20 1.0
OUTPUT POWER (W)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 3.7V
SPK_VDD
-10
MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
Z
= 4I + 33µH
SPK
-30
AV
= +8dB
SPK_
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
f = 6000Hz
f = 1000Hz
f = 100Hz
1.51.00.50 2.0
OUTPUT POWER (W)
MAX9888 toc50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
MAX9888 toc53
THD+N RATIO (dB)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 3.V
SPK_VDD
-10
MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
= 8I + 68µH
Z
SPK
AV
SPK_
f = 100Hz
= +8dB
f = 6000Hz
f = 1000Hz
0.50.40.30.20.10 0.6
OUTPUT POWER (W)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 3V
SPK_VDD
-10
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
LRCLK = 48kHz
-20
NI MODE
-30
Z
= 4I + 33µH
SPK
= +8dB
AV
SPK_
-40
f = 6000Hz
-50
-60
-70
-80
f = 100Hz
-90
0 1.4
f = 1000Hz
1.21.00.6 0.80.40.2
OUTPUT POWER (W)
MAX9888 toc51
MAX9888 toc54
38

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 4.2V
SPK_VDD
-10
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
LRCLK = 48kHz
-20
NI MODE
-30
Z
= 8I + 68µH
SPK
= +8dB
AV
SPK_
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
P
= 0.25W
OUT
-70
-80
P
= 0.55W
-90
OUT
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 3.7V
SPK_VDD
-10
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
LRCLK = 48kHz
-20
NI MODE
-30
Z
= 4I + 33µH
SPK
P
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
P
= 0.5W
OUT
10 100,000
= 1.0W
OUT
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
SPK_VDD
-10
MAX9888 toc55
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
LRCLK = 48kHz
-20
NI MODE
-30
Z
= 8I + 68µH
SPK
AV
SPK_
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
P
= 0.25W
OUT
-70
-80
P
= 0.55W
OUT
-90
10 100,000
OUTPUT POWER vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
2200
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
2000
MAX9888 toc58
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
1800
1600
1400
1200
1000
800
OUTPUT POWER PER CHANNEL (mW)
600
400
= 8I + 68µH
Z
SPK
2.5 5.5
= 3.7V
= +8dB
FREQUENCY (Hz)
(DAC TO SPEAKER)
THD+N = 10%
THD+N = 10%THD+N = 10%
THD+N = 10%
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
10,0001000100
THD+N = 1%
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 4.2V
SPK_VDD
-10
MAX9888 toc56
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
LRCLK = 48kHz
-20
NI MODE
-30
Z
= 4I + 33µH
SPK
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
P
OUT
10 100,000
= 0.5W
FREQUENCY (Hz)
P
= 1.0W
OUT
10,0001000100
MAX9888 toc57
OUTPUT POWER vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(DAC TO SPEAKER)
3500
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
3000
MAX9888 toc59
5.04.54.03.53.0
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
= 4I + 33µH
Z
2500
SPK
2000
1500
1000
OUTPUT POWER PER CHANNEL (mW)
500
0
THD+N = 10%
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
MAX9888 toc60
THD+N = 1%
5.04.54.03.53.02.5 5.5
39

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
HPVSS
= 0dB,
GAIN vs. FREQUENCY
(DAC TO SPEAKER)
5
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
4
LRCLK = 48kHz
3
NI MODE
Z
= 8I + 68µH
SPK
2
1
0
-1
-2
NORMALIZED GAIN (dB)
-3
-4
-5
FREQUENCY (Hz)
SUPPLY CURRENT vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(DAC TO SPEAKER)
30
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
LRCLK = 48kHz
25
Z
= 8I + 68µH
SPK
NI MODE
20
AV
= +8dB
SPK_
ALL ZEROS AT INPUT
15
10
10,000100010010 100,000
MAX9888 toc61
MAX9888 toc64
EFFICIENCY vs. OUTPUT POWER
(DAC TO SPEAKER)
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
Z
SPK
OUTPUT POWER PER CHANNEL (W)
Z
Z
SPK
SPK
= 8I + 68µH
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.00 2.5
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 200mV
-20
-40
PSRR (dB)
-60
RIPPLE
P-P
RIPPLE ON SPKLVDD,
SPKRVDD
= 4I + 33µH
= 4I + 33µH
V
= 4.2V
SPK_VDD
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
AV
= +8dB
SPK_
MAX9888 toc62
MAX9888 toc65
EFFICIENCY vs. OUTPUT POWER
(DAC TO SPEAKER)
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
EFFICIENCY (%)
30
20
10
0
Z
SPK
OUTPUT POWER PER CHANNEL (W)
Z
= 8I + 68µH
= 4I + 33µH
SPK
V
SPK_VDD
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
AV
= +8dB
SPK_
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO
vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
RIPPLE ON SPKLVDD, SPKRVDD
= 200mV
V
-20
-40
PSRR (dB)
-60
RIPPLE
f = 1kHz
P-P
= 3.7V
1.20.8 1.00.4 0.60.20 1.6
1.4
MAX9888 toc63
MAX9888 toc66
SPK_VDD SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
5
0
2.5 5.5
SPK_VDD SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
40
-80
5.04.54.03.53.0
-100
RIPPLE ON AVDD,
DVDD, HPVDD
10,000100010010 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
-80
-100
4.54.03.53.02.5 5.5
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
5.0

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
CROSSTALK vs. FREQUENCY
(DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
-10
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
CROSSTALK (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
= 8I + 68µH
Z
SPK
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
FFT, -60dBFS (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz,
LRCLK = 48kHz
-20
NI MODE
= 8I + 68µH
Z
SPK
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
15,00010,0005000
MAX9888 toc67
SPEAKER
OUTPUT
MAX9888 toc70
SOFTWARE TURN-ON/ OFF RESPONSE
(DAC TO SPEAKER, VSEN = 0)
SCL
2V/div
1V/div
10ms/div
FFT, -60dBFS (DAC TO SPEAKER)
0
MCLK = 13MHz,
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
-20
PLL MODE
= 8I + 68µH
Z
SPK
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dbV)
-100
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
15,00010,0005000
MAX9888 toc68
SPEAKER
OUTPUT
MAX9888 toc71
SOFTWARE TURN-ON/ OFF RESPONSE
(DAC TO SPEAKER, VSEN = 1)
SCL
2V/div
1V/div
10ms/div
WIDEBAND FFT
(DAC TO SPEAKER)
20
10
0
-10
-20
-30
AMPLITUDE (dBm)
-40
-50
-60
1 100
FREQUENCY (MHz)
MCLK = 13MHz,
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
Z
SPK
10
MAX9888 toc69
MAX9888 toc72
= 8I + 68µH
41

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
MAX9888
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
REF
DACATTN
REC
SPKLVDD
= 2.2FF, C
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
MICBIAS
SPK_
Line to Speaker
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
HPVSS
= 0dB,
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (LINE TO SPEAKER)
0
Z
= 8I + 68µH
SPK
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
AV
f = 1000Hz
0
SPK_
= +8dB
f = 6000Hz
f = 100Hz
OUTPUT POWER (W)
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO
vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO SPEAKER)
0
V
= 200mV
RIPPLE
INPUT AC GROUNDED
-20
-40
PSRR (dB)
-60
-80
-100
RIPPLE ON AVDD,
MAX9888 toc73
0.80.60.2 0.4
RMS
DVDD, HPVDD
RIPPLE ON SPKLVDD,
SPKRVDD
10,000100010010 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO SPEAKER)
0
Z
= 8I + 68µH
SPK
-10
= 1µF
C
IN
AV
= +8dB
SPK_
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
10 100,000
MAX9888 toc76
P
= 0.55W
OUT
P
= 0.25W
OUT
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
CROSSTALK (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
GAIN vs. FREQUENCY
(LINE TO SPEAKER)
5
Z
= 8I + 68µH
SPK
4
= 1µF
C
MAX9888 toc74
NORMALIZED GAIN (dB)
IN
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
FREQUENCY (Hz)
CROSSTALK vs. FREQUENCY
(LINE TO SPEAKER)
0
Z
= 8I + 68µH
SPK
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
MAX9888 toc75
10,000100010010 100,000
MAX9888 toc77
42

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
= V
MICBIAS
DACGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
SPK_
DAC to Headphone
SPKRVDD
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
MAX9888
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
R
HP
AV
HP_
f = 1000Hz
= 32I
= +3dB
f = 3000Hz
f = 100Hz
0.040.030.020.010 0.05
OUTPUT POWER (W)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz
-10
LRCLK = 96kHz
NI MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
= 32I
R
HP
AV
HP_
f = 1000Hz
= +3dB
f = 6000Hz
f = 100Hz
0.040.030.020.010 0.05
OUTPUT POWER (W)
MAX9888 toc78
THD+N RATIO (dB)
MAX9888 toc81
THD+N RATIO (dB)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
= 32I
R
HP
AV
HP_
f = 1000Hz
= +3dB
f = 6000Hz
f = 100Hz
0.040.030.020.010 0.05
OUTPUT POWER (W)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz
-10
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
= 16I
R
HP
AV
= +3dB
HP_
f = 1000Hz
f = 6000Hz
f = 100Hz
0.070.060.04 0.050.02 0.030.010 0.08
OUTPUT POWER (W)
MAX9888 toc79
THD+N RATIO (dB)
MAX9888 toc82
THD+N RATIO (dB)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz
-10
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
= 32I
R
HP
AV
HP_
f = 1000Hz
= +3dB
f = 6000Hz
f = 100Hz
0.040.030.020.010 0.05
OUTPUT POWER (W)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO SPEAKER)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
-20
RHP = 32I
AV
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
= +3dB
HP_
P
= 0.01W
OUT
P
= 0.02W
OUT
10 10,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1000100
MAX9888 toc80
MAX9888 toc83
43

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
HPVSS
= 0dB,
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 13MHz
-10
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
-20
= 32I
R
HP
-30
AV
= +3dB
HP_
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
P
= 0.025W
OUT
P
= 0.1W
OUT
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz
-10
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-20
RHP = 16I
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
10 100,000
P
= 0.01W
OUT
P
= 0.0.25W
OUT
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
0
-10
MAX9888 toc84
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-70
-80
-90
-100
10
MAX9888 toc87
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
NORMALIZED GAIN (dB)
-50
-60
-70
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
RHP = 32I
AV
= +3dB
HP_
P
= 0.025W
OUT
P
= 0.01W
OUT
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
GAIN vs. FREQUENCY
(DAC TO HEADPHONE)
MODE = 1
MODE = 0
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 8kHz
NI MODE
R
= 32I
HP
10,000100010010 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz
-10
MAX9888 toc85
LRCLK = 96kHz
-20
NI MODE
RHP = 32I
-30
AV
-40
-50
-60
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-70
-80
-90
-100
10 100,000
HPVDD INPUT CURRENT vs. OUTPUT
120
100
MAX9888 toc88
80
60
40
HPVDD INPUT CURRENT (mA)
20
0
0.01 100
= +3dB
HP_
P
= 0.025W
OUT
P
= 0.01W
OUT
10,0001000100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
POWER (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
RHP = 16I
OUTPUT POWER PER CHANNEL (mW)
MAX9888 toc86
MAX9888 toc89
RHP = 32I
1010.1
44

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
-20
-40
PSRR (dB)
-60
-80
-100
SCL
2V/div
HEADPHONE
OUTPUT
0.5V/div
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO
vs. FREQUENCY (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
V
= 200mV
RIPPLE
INPUT ALL ZEROS
P-P
RIPPLE ON SPKLVDD,
SPKRVDD
RIPPLE ON AVDD,
DVDD, HPVDD
10,000100010010 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
SOFTWARE TURN-ON/ OFF RESPONSE
(DAC TO HEADPHONE, VSEN = 1)
10ms/div
MAX9888 toc93
MAX9888 toc90
CROSSTALK vs. FREQUENCY
(DAC TO HEADPHONE)
-40
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
-50
NI MODE
= 32I
R
HP
-60
-70
CROSSTALK (dB)
-80
-90
-100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
FFT, 0dBFS (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 13MHz,
-20
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
-120
-140
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
= 32I
R
HP
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,000100010010 100,000
15,00010,0005000
MAX9888 toc91
HEADPHONE
MAX9888 toc94
SOFTWARE TURN-ON/ OFF RESPONSE
(DAC TO HEADPHONE, VSEN = 0)
SCL
2V/div
OUTPUT
0.5V/div
10ms/div
FFT, -60dBFS (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 13MHz,
-20
LRCLK = 8kHz
FREQ MODE
-40
-60
-80
-100
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-120
-140
-160
= 32I
R
HP
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MAX9888 toc92
MAX9888 toc95
15,00010,0005000
45

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
HPVSS
= 0dB,
FFT, 0dBFS (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 13MHz,
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
-20
PLL MODE
= 32I
R
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
-120
-140
HP
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
15,00010,0005000
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-100
FFT, -60dBFS (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MAX9888 toc96
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-120
-140
-160
0 20,000
FFT, 0dBFS (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
= 32I
R
HP
MCLK = 13MHz,
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
= 32I
R
HP
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MAX9888 toc98
MAX9888 toc97
15,00010,0005000
46
-120
-140
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
15,00010,0005000

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
FFT, -60dBFS (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz
-20
LRCLK = 48kHz
NI MODE
-40
-60
-80
-100
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-120
-140
-160
= 32I
R
HP
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
WIDEBAND FFT, 0dBFS
(DAC TO HEADPHONE)
20
0
-20
-40
AMPLITUDE (dBm)
-60
FFT, 0dBFS (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 12.288MHz
LRCLK = 96kHz
-20
MAX9888 toc99
AMPLITUDE (dbV)
-100
-120
-140
15,00010,0005000
NI MODE
= 32I
R
-40
-60
-80
HP
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
15,00010,0005000
MAX9888 toc100
FFT, -60dBFS (DAC TO HEADPHONE)
0
MCLK = 2.288MHz
-20
LRCLK = 96kHz
NI MODE
-40
-60
-80
-100
AMPLITUDE (dBV)
-120
-140
-160
= 32I
R
HP
0 20,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MAX9888 toc101
15,00010,0005000
WIDEBAND FFT, -60dBFS
(DAC TO HEADPHONE)
20
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
PLL MODE
= -3dB
A
VHP_
R
= 32I
HP
MAX9888 toc102
MCLK = 13MHz
LRCLK = 44.1kHz
0
PLL MODE
A
VHP_
-20
R
= 32I
HP
-40
AMPLITUDE (dBm)
-60
= -3dB
MAX9888 toc103
-80
-100
0 10,000
FREQUENCY (kHz)
-80
-100
1000100101
0 10,000
FREQUENCY (kHz)
1000100101
47

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
MAX9888
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
= 2.2FF, C
REF
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
DACATTN
SPKLVDD
= V
MICBIAS
DACGAIN
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
SPK_
Line to Headphone
SPKRVDD
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. OUTPUT POWER (LINE TO HEADPHONE)
0
RHP = 32I
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
-80
= +3dB
A
VHP_
f = 6000Hz
f = 1000Hz
f = 100Hz
0 0.05
OUTPUT POWER (W)
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO
vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO HEADPHONE)
0
V
= 200mV
-20
-40
PSRR (dB)
-60
-80
-100
RIPPLE
P-P
RIPPLE ON AVDD,
DVDD, HPVDD
RIPPLE ON SPKLVDD,
SPKRVDD
10,000100010010 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE
vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO HEADPHONE)
0
RHP = 32I
-10
= 1µF
C
MAX9888 toc104
THD+N RATIO (dB)
0.040.030.01 0.02
IN
-20
-30
-40
-50
P
-60
-70
-80
-90
10 100,000
= 0.01W
OUT
P
= 0.025W
OUT
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
5
4
MAX9888 toc105
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
NORMALIZED GAIN (dB)
-3
-4
-5
CROSSTALK vs. FREQUENCY
(LINE TO HEADPHONE)
MAX9888 toc107
0
RHP = 32I
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
CROSSTALK (dB)
-60
-70
-80
-90
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
MAX9888 toc108
70
60
50
40
30
CMRR (dB)
20
10
0
GAIN vs. FREQUENCY
(LINE TO HEADPHONE)
RHP = 32I
= 1µF
C
IN
10,000100010010 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
COMMON-MODE REJECTION RATIO
vs. FREQUENCY (LINE TO HEADPHONE)
V
= -6dBV
OUT
= 1µF
C
IN
R
= 32I
HP
AV
= 0dB
PGAIN_
AV
= 20dB
PGAIN_
10,000100010010 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
MAX9888 toc106
MAX9888 toc109
48

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V
= V
AVDD
between SPK_P and SPK_N. Receiver load (R
HPL or HPR to GND. R
= 1FF. AV
AV
1. T
MICPRE_
= 0dB, AV
PGAIN_
= +25NC, unless otherwise noted.)
A
HPVDD
= V
DVDD
= J, R
HP
= V
= +20dB, AV
PGAOUT_
= 0dB, AV
DVDDS1
= J, Z
REC
MICPGA_
= V
SPK
= 0dB, AV
= 0dB, AV
HP_
= +1.8V, V
DVDDS2
) connected between RECP and RECN. Headphone loads (RHP) connected from
REC
= J, C
= 2.2FF, C
REF
DACATTN
= 0dB, AV
REC
= 0dB, AV
Speaker Bypass Switch
SPKLVDD
MICBIAS
SPK_
= V
SPKRVDD
= C
DACGAIN
= 3.7V. Speaker loads (Z
= C
PREG
= 0dB, AV
REG
ADCLVL
= 1FF, C
= 0dB, AV
C1N-C1P
) connected
SPK
= 1FF, C
ADCGAIN
HPVSS
= 0dB,
= 0dB, MCLK = 12.288MHz, LRCLK = 48kHz, MAS =
MAX9888
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
PLUS NOISE vs. OUTPUT POWER
(SPEAKER BYPASS SWITCH)
0
RECEIVER AMPLIFIER DRIVING
-10
LOUDSPEAKER
Z
= 8I + 68µH
SPK
-20
-30
-40
-50
THD+N RATIO (dB)
-60
-70
f = 100Hz
-80
0
f = 1000Hz
OUTPUT POWER (W)
MAX9888 toc110
f = 6000Hz
0.15 0.200.100.05
OFF-ISOLATION vs. FREQUENCY
(SPEAKER BYPASS SWITCH)
0
SPEAKER AMP DRIVING LOUDSPEAKER
SPEAKER BYPASS SWITCH OPEN
-20
MEASURED AT RXIN_
-40
-60
50I LOAD ON RXIN_
ON RESISTANCE vs. V
(SPEAKER BYPASS SWITCH)
4.0
ISW = 20mA
3.5
3.0
2.5
(I)
2.0
V
= 3.0V
SPK_VDD
ON
R
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
V
= 3.7V
SPK_VDD
V
= 4.2V
SPK_VDD
V
SPK_VDD
0 6
V
(V)
COM
MAX9888 toc112
COM
MAX9888 toc111
= 5.0V
541 2 3
-80
OFF-ISOLATION (dB)
-100
-120
RECEIVER AMP DRIVING RXIN_
10 100,000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10,0001000100
49

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Pin Configuration
TOP VIEW
(BUMP SIDE DOWN)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
MAX9888
A
B
C
D
E
F
SPKRN
SPKRN
SPKRP
BCLKS1 LRCLKS1
DVDDS1 SDOUTS1
DGND
SPKRGND
MCLK IRQ
BCLKS2 LRCLKS2
SPKLVDD SPKLP
SPKLVDD SPKLPSPKRGND SPKLN
SPKRVDD
SPKRVDD SDINS1
N.C.
SPKLN
SPKLGNDSPKRP SPKLGND HPSNS
MAX9888
N.C. INB1
SCLSDA REG
RECP/
RXINP
RECN/
RXINN
JACKSNS
HPVDD HPGND
C1P C1N
N.C. INB2
N.C.
N.C.N.C.
REF
MIC1P/
DIGMICDATA
MIC1N/
DIGMICCLK
HPVSS
HPL
HPR
INA2/
EXTMICN
INA1/
EXTMICP
MIC2P
50
SDOUTS2 DVDDS2 SDINS2 MIC2N
G
AVDDDVDD PREG
AGND MICBIAS

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Pin Description
PIN NAME FUNCTION
A1, B1 SPKRN Negative Right-Channel Class D Speaker Output
A2, B2 SPKRGND Right-Speaker Ground
A3, B3 SPKLVDD
A4, B4 SPKLP Positive Left-Channel Class D Speaker Output
A5, B5 SPKLN Negative Left-Channel Class D Speaker Output
A6 RECP/RXINP
A7 HPVDD Headphone Power Supply. Bypass to HPGND with a 1FF capacitor.
A8 HPGND Headphone Ground
A9 HPVSS Inverting Charge-Pump Output. Bypass to HPGND with a 1FF ceramic capacitor.
B6 RECN/RXINN
B7 C1P
B8 C1N
B9 HPL Left-Channel Headphone Output
C1, C2 SPKRP Positive Right-Channel Class D Speaker Output
C3, D3 SPKRVDD Right-Speaker Power Supply. Bypass to SPKRGND with a 1FF capacitor.
C4, C5 SPKLGND Left-Speaker Ground
C6 HPSNS
C7, D5, D7,
E3, E6, E7
C8 INB2 Single-Ended Line Input B2. Also positive differential line input B.
C9 HPR Right-Channel Headphone Output
D1 BCLKS1
D2 LRCLKS1
D4 SDINS1 S1 Digital Audio Serial-Data DAC Input. The input voltage is referenced to DVDDS1.
D6 JACKSNS Jack Sense. Detects the insertion of a jack. See the Headset Detection section.
D8 INB1 Single-Ended Line Input B1. Also negative differential line input B.
D9
N.C. No Connection
INA2/
EXTMICN
Left-Speaker, REF, Receiver Amplifier Power Supply. Bypass to SPKLGND with a 1FF and a 10FF
capacitor.
Positive Receiver Amplifier Output. Can be positive bypass switch input when receiver amp is shut
down.
Negative Receiver Amplifier Output. Can be negative bypass switch input when receiver amp is shut
down.
Charge-Pump Flying Capacitor Positive Terminal. Connect a 1FF ceramic capacitor between C1N
and C1P.
Charge-Pump Flying Capacitor Negative Terminal. Connect a 1FF ceramic capacitor between C1N
and C1P.
Headphone Amplifier Ground Sense. Connect to the headphone jack ground terminal or connect to
ground.
S1 Digital Audio Bit Clock Input/Output. BCLKS1 is an input when the MAX9888 is in slave mode and
an output when in master mode. The input/output voltage is referenced to DVDDS1.
S1 Digital Audio Left-Right Clock Input/Output. LRCLKS1 is the audio sample rate clock and
determines whether S1 audio data is routed to the left or right channel. In TDM mode, LRCLKS1 is a
frame sync pulse. LRCLKS1 is an input when the MAX9888 is in slave mode and an output when in
master mode. The input/output voltage is referenced to DVDDS1.
Single-Ended Line Input A2. Also positive differential line input A or negative differential external
microphone input.
MAX9888
51

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Pin Description (continued)
PIN NAME FUNCTION
E1 DVDDS1 S1 Digital Audio Interface Power-Supply Input. Bypass to DGND with a 1FF capacitor.
E2 MCLK Master Clock Input. Acceptable input frequency range is 10MHz to 60MHz.
E4 SDOUTS1 S1 Digital Audio Serial-Data ADC Output. The output voltage is referenced to DVDDS1.
Hardware Interrupt Output. IRQ can be programmed to pull low when bits in status register 0x00
MAX9888
E5 IRQ
E8
E9
F1 DGND Digital Ground
F2 BCLKS2
F3 LRCLKS2
F4 SDA I
F5 SCL I
F6 REG Common-Mode Voltage Reference. Bypass to AGND with a 1FF capacitor.
F7 REF Converter Reference. Bypass to AGND with a 2.2FF capacitor.
F8
F9 MIC2P Positive Differential Microphone 2 Input. AC-couple a microphone with a series 1FF capacitor.
G1 SDOUTS2 S2 Digital Audio Serial-Data ADC Output. The output voltage is referenced to DVDDS2.
G2 DVDDS2 S2 Digital Audio Interface Power-Supply Input. Bypass to DGND with a 1FF capacitor.
G3 SDINS2 S2 Digital Audio Serial-Data DAC Input. The input voltage is referenced to DVDDS2.
G4 DVDD
G5 AVDD Analog Power Supply. Bypass to AGND with a 1FF capacitor.
G6 PREG Positive Internal Regulated Supply. Bypass to AGND with a 1FF capacitor.
G7 AGND Analog Ground
G8 MICBIAS
G9 MIC2N Negative Differential Microphone 2 Input. AC-couple a microphone with a series 1FF capacitor.
MIC1P/
DIGMICDATA
INA1/
EXTMICP
MIC1N/
DIGMICCLK
change state. Read status register 0x00 to clear IRQ once set. Repeat faults have no effect on IRQ
until it is cleared by reading the I
full output swing.
Positive Differential Microphone 1 Input. AC-couple a microphone with a series 1FF capacitor. Can
be retasked as a digital microphone data input.
Single-Ended Line Input A1. Also negative differential line input A or positive differential external
microphone input.
S2 Digital Audio Bit Clock Input/Output. BCLKS2 is an input when the IC is in slave mode and an
output when in master mode. The input/output voltage is referenced to DVDDS2.
S2 Digital Audio Left-Right Clock Input/Output. LRCLKS2 is the audio sample rate clock and
determines whether audio data on S2 is routed to the left or right channel. In TDM mode, LRCLKS2 is
a frame sync pulse. LRCLKS2 is an input when the IC is in slave mode and an output when in master
mode. The input/output voltage is referenced to DVDDS2.
2
C Serial-Data Input/Output. Connect a pullup resistor to DVDD for full output swing.
2
C Serial-Clock Input
Negative Differential Microphone 1 Input. AC-couple a microphone with a series 1FF capacitor. Can
be retasked as a digital microphone clock output.
Digital Power Supply. Supply for the digital core and I
capacitor.
Low-Noise Bias Voltage. Outputs a 2.2V microphone bias. An external resistor in the 2.2kI to 1kI
range should be used to set the microphone current.
2
C status register 0x00. Connect a 10kI pullup resistor to DVDD for
2
C interface. Bypass to DGND with a 1FF
52

with FlexSound Technology
Detailed Description
The MAX9888 is a fully integrated stereo audio codec
with FlexSound technology and integrated amplifiers.
Two differential microphone amplifiers can accept signals from three analog inputs. One input can be retasked
to support two digital microphones. Any combination of
two microphones (analog or digital) can be recorded
simultaneously. The analog signals are amplified up
to 50dB and recorded by the stereo ADC. The digital
record path supports voice filtering with selectable
preset highpass filters and high stopband attenuation
/2. An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit moni-
at f
S
tors the digitized signal and automatically adjusts the
analog microphone gain to make best use of the ADC’s
dynamic range. A noise gate attenuates signals below
the user-defined threshold to minimize the noise output
by the ADC.
The IC includes two analog line inputs. One of the line
inputs can be optionally retasked as a third analog microphone input. Both line inputs support either stereo singleended input signals or mono differential signals. The line
inputs are preamplified and then routed either to the ADC
for recording or to the output amplifiers for playback.
Integrated analog switches allow two differential microphone signals to be routed out the third microphone
input to an external device. This eliminates the need
for an external analog switch in systems that have two
devices recording signals from the same microphone.
Through two digital audio interfaces, the device can
transmit one stereo audio signal and receive two stereo
audio signals in a wide range of formats including I
PCM, and up to four mono slots in TDM. Each interface
can be connected to either of two audio ports (S1 and
S2) for communication with external devices. Both audio
interfaces support 8kHz to 96kHz sample rates. Each
input signal is independently equalized using 5-band
parametric equalizers. A multiband automatic level
control (ALC) boosts signals by up to 12dB. One signal
path additionally supports the same voiceband filtering
as the ADC path.
The IC includes a differential receiver amplifier, stereo
Class D speaker amplifiers, and DirectDrive true ground
stereo headphone amplifiers.
2
S,
Stereo Audio CODEC
When the receiver amplifier is disabled, analog switches
allow RECP/RXINP and RECN/RXINN to be reused for
signal routing. In systems where a single transducer is
used for both the loudspeaker and receiver, an external receiver amplifier can be routed to the left speaker
through RECP/RXINP and RECN/RXINN, bypassing the
Class D amplifier, to connect to the loudspeaker. If the
internal receiver amplifier is used, then leave RECP/
RXINP and RECN/RXINN unconnected. In systems
where an external amplifier drives both the receiver and
the MAX9888’s input, one of the differential signals can
be disconnected from the receiver when not needed
by passing it through the analog switch that connects
RECP/RXINP to RECN/RXINN.
The stereo Class D amplifier provides efficient amplification for two speakers. The amplifier includes active
emissions limiting to minimize the radiated emissions
(EMI) traditionally associated with Class D. In most
systems, no output filtering is required to meet standard
EMI limits.
To optimize speaker sound quality, the IC includes an
excursion limiter, a distortion limiter, and a power limiter.
The excursion limiter is a dynamic highpass filter with
variable corner frequency that increases in response
to high signal levels. Low-frequency energy typically
causes more distortion than useful sound at high signal levels, so attenuating low frequencies allows the
speaker to play louder without distortion or damage. At
lower signal levels, the filter corner frequency reduces
to pass more low frequency energy when the speaker
can handle it. The distortion limiter reduces the volume
when the output signal exceeds a preset distortion level.
This ensures that regardless of input signal and battery
voltage, excessive distortion is never heard by the user.
The power limiter monitors the continuous power into the
loudspeaker and lowers the signal level if the speaker is
at risk of overheating.
The stereo DirectDrive headphone amplifier uses an
inverting charge pump to generate a ground-referenced
output signal. This eliminates the need for DC-blocking
capacitors or a midrail bias for the headphone jack
ground return. Ground sense reduces output noise
caused by ground return current.
The IC integrates jack detection allowing the detection
of insertion and removal of accessories as well as button
presses.
MAX9888
53

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
I2C Slave Address
Configure the MAX9888 using the I2C control bus. The
IC uses a slave address of 0x20 or 00100000 for write
operations and 0x21 or 00100001 for read operations.
2
See the I
C Serial Interface section for a complete inter-
face description.
Table 1 lists all of the registers, their addresses, and
power-on-reset states. Registers 0x00 to 0x03 and 0xFF
are read-only while all of the other registers are read/
write. Write zeros to all unused bits in the register table
when updating the register, unless otherwise noted.
MAX9888
Table 1. Register Map
REGISTER B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 ADDRESS DEFAULT R/W PAGE
STATUS
Status CLD SLD ULK — — — JDET — 0x00 — R
Microphone
AGC/NG
Jack Status JKSNS — — — — — — 0x02 — R
Battery
Voltage
Interrupt
Enable
MASTER CLOCK CONTROL
Master Clock 0 0 PSCLK 0 0 0 0 0x10 0x00 R/W
DAI1 CLOCK CONTROL
Clock Mode SR1 FREQ1 0x11 0x00 R/W
Any Clock
Control
DAI1 CONFIGURATION
Format MAS1 WCI1 BCI1 DLY1 0 TDM1 FSW1 WS1 0x14 0x00 R/W
Clock OSR1 0 0 0 BSEL1 0x15 0x00 R/W
I/O
Configuration
Time-Division
Multiplex
Filters MODE1 AVFLT1 DHF1 DVFLT1 0x18 0x00 R/W
DAI2 CLOCK CONTROL
Clock Mode SR2 0 0 0 0 0x19 0x00 R/W
Any Clock
Control
DAI2 CONFIGURATION
— — — VBAT 0x03 — R/W
ICLD ISLD IULK 0 0 0 IJDET 0 0x0F 0x00 R/W
PLL1 NI1[14:8] 0x12 0x00 R/W
PLL2 NI2[14:8] 0x1A 0x00 R/W
NG AGC 0x01 — R
NI1[7:1] NI1[0] 0x13 0x00 R/W
SEL1 LTEN1 LBEN1 DMONO1 HIZOFF1 SDOEN1 SDIEN1 0x16 0x00 R/W
SLOTL1 SLOTR1 SLOTDLY1 0x17 0x00 R/W
NI2[7:1] NI2[0] 0x1B 0x00 R/W
Registers
103
65
101
102
103
76
76
77
77
71
72
72
73
79
76
77
77
Format MAS2 WCI2 BCI2 DLY2 0 TDM2 FSW2 WS2 0x1C 0x00 R/W
Clock 0 0 0 0 0 BSEL2 0x1D 0x00 R/W
I/O
Configuration
54
SEL2 0 LBEN2 DMONO2 HIZOFF2 SDOEN2 SDIEN2 0x1E 0x00 R/W
71
72
72

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 1. Register Map (continued)
REGISTER B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 ADDRESS DEFAULT R/W PAGE
Time-Division
Multiplex
Filters 0 0 0 0 DHF2 0 0 DCB2 0x20 0x00 R/W
MIXERS
DAC Mixer MIXDAL MIXDAR 0x21 0x00 R/W
Left ADC
Mixer
Right ADC
Mixer
Preoutput 1
Mixer
Preoutput 2
Mixer
Preoutput 3
Mixer
Headphone
Amplifier
Mixer
Receiver
Amplifier
Mixer
Speaker
Amplifier
Mixer
LEVEL CONTROL
Sidetone DSTS 0 DVST 0x2A 0x00 R/W
DAI1
Playback
Level
DAI1
Playback
Level
DAI2
Playback
Level
DAI2
Playback
Level
Left ADC
Level
Right ADC
Level
Microphone
1 Input Level
SLOTL2 SLOTR2 SLOTDLY2 0x1F 0x00 R/W
MIXADL 0x22 0x00 R/W
MIXADR 0x23 0x00 R/W
0 0 0 0 MIXOUT1 0x24 0x00 R/W
0 0 0 0 MIXOUT2 0x25 0x00 R/W
0 0 0 0 MIXOUT3 0x26 0x00 R/W
MIXHPL MIXHPR 0x27 0x00 R/W
0 0 0 0 MIXREC 0x28 0x00 R/W
MIXSPL MIXSPR 0x29 0x00 R/W
DV1M 0 DV1G DV1 0x2B 0x00 R/W
0 0 0
DV2M 0 0 0 DV2 0x2D 0x00 R/W
0 0 0
0 0 AVLG AVL 0x2F 0x00 R/W
0 0 AVRG AVR 0x30 0x00 R/W
0 PA1EN PGAM1 0x31 0x00 R/W
EQCLP1
EQCLP2
DVEQ1 0x2C 0x00 R/W
DVEQ2 0x2E 0x00 R/W
MAX9888
73
79
85
64
64
86
86
86
97
88
90
69
84
83
84
83
68
68
61
55

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 1. Register Map (continued)
REGISTER B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 ADDRESS DEFAULT R/W PAGE
Microphone
2 Input Level
INA Input
Level
INB Input
MAX9888
Level
Preoutput 1
Level
Preoutput 2
Level
Preoutput 3
Level
Left
Headphone
Amplifier
Volume
Control
Right
Headphone
Amplifier
Volume
Control
Receiver
Amplifier
Volume
Control
Left Speaker
Amplifier
Volume
Control
Right
Speaker
Amplifier
Volume
Control
MICROPHONE AGC
Configuration AGCSRC AGCRLS AGCATK AGCHLD 0x3D 0x00 R/W
Threshold ANTH AGCTH 0x3E 0x00 R/W
SPEAKER SIGNAL PROCESSING
Excursion
Limiter Filter
Excursion
Limiter
Threshold
ALC ALCEN ALCRLS ALCMB ALCTH 0x41 0x00 R/W
0 PA2EN PGAM2 0x32 0x00 R/W
0 INAEXT 0 0 0 PGAINA 0x33 0x00 R/W
0 INBEXT 0 0 0 PGAINB 0x34 0x00 R/W
0 0 0 0 PGAOUT1 0x35 0x00 R/W
0 0 0 0 PGAOUT2 0x36 0x00 R/W
0 0 0 0 PGAOUT3 0x37 0x00 R/W
HPLM 0 0 HPVOLL 0x38 0x00 R/W
HPRM 0 0 HPVOLR 0x39 0x00 R/W
RECM 0 0 RECVOL 0x3A 0x00 R/W
SPLM 0 0 SPVOLL 0x3B 0x00 R/W
SPRM 0 0 SPVOLR 0x3C 0x00 R/W
0 DHPUCF 0 0 DHPLCF 0x3F 0x00 R/W
0 0 0 0 0 DHPTH 0x40 0x00 R/W
61
63
63
87
87
87
97
97
88
90
90
65
66
92
92
82
56

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 1. Register Map (continued)
REGISTER B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 ADDRESS DEFAULT R/W PAGE
Power Limiter PWRTH 0 PWRK 0x42 0x00 R/W
Power Limiter PWRT2 PWRT1 0x43 0x00 R/W
Distortion
Limiter
CONFIGURATION
Audio Input INADIFF INBDIFF 0 0 0 0 0 0 0x45 0x00 R/W
Microphone MICCLK DIGMICL DIGMICR 0 0 EXTMIC 0x46 0x00 R/W
Level Control
Bypass
Switches
Jack
Detection
POWER MANAGEMENT
Input Enable INAEN INBEN 0 0 MBEN 0 ADLEN ADREN 0x4A 0x00 R/W
Output Enable HPLEN HPREN SPLEN SPREN RECEN 0 DALEN DAREN 0x4B 0x00 R/W
System
Enable
DSP COEFFICIENTS
EQ Band 1
(DAI1/DAI2)
EQ Band 2
(DAI1/DAI2)
VS2EN VSEN ZDEN
INABYP 0 0 MIC2BYP 0 0 RECBYP SPKBYP 0x48 0x00 R/W
JDETEN 0 0 0 0 0 JDEB 0x49 0x00 R/W
SHDN
THDCLP 0 THDT1 0x44 0x00 R/W
0 0 0 EQ2EN EQ1EN 0x47 0x00 R/W
VBATEN 0 0 0 0 JDWK 0 0x4C 0x00 R/W
K_1[15:8] 0x50/0x82 0xXX R/W
K_1[7:0] 0x51/0x83 0xXX R/W
K1_1[15:8] 0x52/0x84 0xXX R/W
K1_1[7:0] 0x53/0x85 0xXX R/W
K2_1[15:8] 0x54/0x86 0xXX R/W
K2_1[7:0] 0x55/0x87 0xXX R/W
c1_1[15:8] 0x56/0x88 0xXX R/W
c1_1[7:0] 0x57/0x89 0xXX R/W
c2_1[15:8] 0x58/0x8A 0xXX R/W
c2_1[7:0] 0x59/0x8B 0xXX R/W
K_2[15:8] 0x5A/0x8C 0xXX R/W
K_2[7:0] 0x5B/0x8D 0xXX R/W
K1_2[15:8] 0x5C/0x8E 0xXX R/W
K1_2[7:0] 0x5D/0x8F 0xXX R/W
K2_2[15:8] 0x5E/0x90 0xXX R/W
K2_2[7:0] 0x5F/0x91 0xXX R/W
c1_2[15:8] 0x60/0x92 0xXX R/W
c1_2[7:0] 0x61/0x93 0xXX R/W
c2_2[15:8] 0x62/0x94 0xXX R/W
c2_2[7:0] 0x63/0x95 0xXX R/W
99, 83
62, 98
MAX9888
93
94
95
63
61
101
59
59
59
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
57

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 1. Register Map (continued)
REGISTER B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 ADDRESS DEFAULT R/W PAGE
K_3[15:8] 0x64/0x96 0xXX R/W
K_3[7:0] 0x65/0x97 0xXX R/W
K1_3[15:8] 0x66/0x98 0xXX R/W
K1_3[7:0] 0x67/0x99 0xXX R/W
EQ Band 3
MAX9888
(DAI1/DAI2)
EQ Band 4
(DAI1/DAI2)
EQ Band 5
(DAI1/DAI2)
Excursion
Limiter
Biquad
(DAI1/DAI2)
REVISION ID
Rev ID REV 0xFF 0x43 R
K2_3[15:8] 0x68/0x9A 0xXX R/W
K2_3[7:0] 0x69/0x9B 0xXX R/W
c1_3[15:8] 0x6A/0x9C 0xXX R/W
c1_3[7:0] 0x6B/0x9D 0xXX R/W
c2_3[15:8] 0x6C/0x9E 0xXX R/W
c2_3[7:0] 0x6D/0x9F 0xXX R/W
K_4[15:8] 0x6E/0xA0 0xXX R/W
K_4[7:0] 0x6F/0xA1 0xXX R/W
K1_4[15:8] 0x70/0xA2 0xXX R/W
K1_4[7:0] 0x71/0xA3 0xXX R/W
K2_4[15:8] 0x72/0xA4 0xXX R/W
K2_4[7:0] 0x73/0xA5 0xXX R/W
c1_4[15:8] 0x74/0xA6 0xXX R/W
c1_4[7:0] 0x75/0xA7 0xXX R/W
c2_4[15:8] 0x76/0xA8 0xXX R/W
c2_4[7:0] 0x77/0xA9 0xXX R/W
K_5[15:8] 0x78/0xAA 0xXX R/W
K_5[7:0] 0x79/0xAB 0xXX R/W
K1_5[15:8] 0x7A/0xAC 0xXX R/W
K1_5[7:0] 0x7B/0xAD 0xXX R/W
K2_5[15:8] 0x7C/0xAE 0xXX R/W
K2_5[7:0] 0x7D/0xAF 0xXX R/W
c1_5[15:8] 0x7E/0xB0 0xXX R/W
c1_5[7:0] 0x7F/0xB1 0xXX R/W
c2_5[15:8] 0x80/0xB2 0xXX R/W
c2_5[7:0] 0x81/0xB3 0xXX R/W
a1[15:8] 0xB4/0xBE 0xXX R/W
a1[7:0] 0xB5/0xBF 0xXX R/W
a2[15:8] 0xB6/0xC0 0xXX R/W
a2[7:0] 0xB7/0xC1 0xXX R/W
b0[15:8] 0xB8/0xC2 0xXX R/W
b0[7:0] 0xB9/0xC3 0xXX R/W
b1[15:8] 0xBA/0xC4 0xXX R/W
b1[7:0] 0xBB/0xC5 0xXX R/W
b2[15:8] 0xBC/0xC6 0xXX R/W
b2[7:0] 0xBD/0xC7 0xXX R/W
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
82
91
91
91
91
91
91
91
91
91
91
104
58

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Power Management
The IC includes comprehensive power management to allow the disabling of all unused circuits, minimizing supply
current.
Table 2. Power Management Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
Global Shutdown
Disables everything except the headset detection circuitry, which is controlled
separately.
0 = Device shutdown
1 = Device enabled
Line Input A Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Line Input B Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Microphone Bias Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Left ADC Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Right ADC Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Left Headphone Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Right Headphone Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Left Speaker Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Right Speaker Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Receiver Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Left DAC Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Right DAC Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
0x4C
0x4A
0x4B
7
6 VBATEN See the Battery Measurement section.
1 JDWK See the Headset Detection section.
7 INAEN
6 INBEN
3 MBEN
1 ADLEN
0 ADREN
7 HPLEN
6 HPREN
5 SPLEN
4 SPREN
3 RECEN
1 DALEN
0 DAREN
SHDN
MAX9888
59

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Microphone Inputs
The device includes three differential microphone inputs
and a low-noise microphone bias for powering the microphones (Figure 6). One microphone input can also be configured as a digital microphone input accepting signals
from up to two digital microphones. Two microphones,
analog or digital, can be recorded simultaneously.
In the typical application, one microphone input is used
MAX9888
for the handset microphone and the other is used as an
accessory microphone. In systems using a background
noise microphone, INA can be retasked as another
microphone input.
In systems where the codec is not the only device
recording microphone signals, connect microphones to
MICBIAS
MIC1P/
DIGMICDATA
MIC1N/
DIGMICCLK
REG
MBEN
MCLK
PSCLK
CLOCK
CONTROL
MIC2P/MIC2N and EXTMICP/EXTMICN. MIC1P/MIC1N
then become outputs that route the microphone signals
to an external device as needed. Two devices can then
record microphone signals without needing external
analog switches.
Analog microphone signals are amplified by two stages
of gain and then routed to the ADCs. The first stage offers
selectable 0dB, 20dB, or 30dB settings. The second
stage is a programmable-gain amplifier (PGA) adjustable
from 0dB to 20dB in 1dB steps. To maximize the signalto-noise ratio, use the gain in the first stage whenever
possible. Zero-crossing detection is included on the PGA
to minimize zipper noise while making gain changes.
PGAM1:
+20dB TO 0dB
MIC2BYP
MIC2P
MIC2N
INABYP
INA1/EXTMICP
INA2/EXTMICN
Figure 6. Microphone Input Block Diagram
60
EXTMIC PA1EN:
0/20/30dB
EXTMIC PA2EN:
0/20/30dB
PGAINA:
+20dB TO -6dB
PGAINA:
+20dB TO -6dB
PGAM1:
+20dB TO 0dB
INADIFF
MIX
MIXADL
MIX
MIXADR
ADLEN
ADCL
ADCR
ADREN

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 3. Microphone Input Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
MIC1/MIC2 Preamplifier Gain
0x31/0x32
0x46
6
PA1EN/PA2EN
5
4
3
2
PGAM1/PGAM2
1
0
7
MICCLK
6
5 DIGMICL
4 DIGMICR
1
EXTMIC
0
Course microphone gain adjustment.
00 = Preamplifier disabled
01 = 0dB
10 = 20dB
11 = 30dB
MIC1/MIC2 PGA
Fine microphone gain adjustment.
VALUE GAIN (dB) VALUE GAIN (dB)
0x00 +20 0x0B +9
0x01 +19 0x0C +8
0x02 +18 0x0D +7
0x03 +17 0x0E +6
0x04 +16 0x0F +5
0x05 +15 0x10 +4
0x06 +14 0x11 +3
0x07 +13 0x12 +2
0x08 +12 0x13 +1
0x09 +11 0x14 to 0x1F 0
0x0A +10
Digital Microphone Clock Frequency
Select a frequency that is within the digital microphone’s clock frequency range.
Set OSR1 = 1 when using a digital microphone.
00 = PCLK/8
01 = PCLK/6
10 = 64 x LRCLK
11 = Reserved
Left Digital Microphone Enable
Set PAL1EN = 00 for proper operation.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Right Digital Microphone Enable
Set PAR1EN = 00 for proper operation.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
External Microphone Connection
Routes INA_/EXTMIC_ to the microphone preamplifiers. Set INAEN = 0 when using
INA_/EXTMIC_ as a microphone input.
00 = Disabled
01 = MIC1 input
10 = MIC2 input
11 = Reserved
MAX9888
61

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 3. Microphone Input Registers (continued)
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
INA_/EXTMIC_ to MIC1_ Bypass Switch
7 INABYP
4 MIC2BYP
MAX9888
0x48
1 RECBYP
0 SPKBYP
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
MIC1_ to MIC2_ Bypass Switch
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
See the Output Bypass Switches section.
Line Inputs
The device includes two sets of line inputs (Figure 7).
Each set can be configured as a stereo single-ended
input or as a mono differential input. Each input includes
adjustable gain to match a wide range of input signal
levels. If a custom gain is needed, the external gain
mode provides a trimmed feedback resistor. Set the gain
INABYP
PGAINA:
INA1/
EXTMICP
INA2/
EXTMICN
INB1
INB2
+20dB TO -6dB
PGAINA:
+20dB TO -6dB
PGAINB:
+20dB TO -6dB
PGAINB:
+20dB TO -6dB
INADIFF
INBDIFF
MIX
MIXOUT1
MIX
MIXOUT2
MIX
MIXOUT3
by choosing the appropriate input resistor and using the
following formula:
AV
= 20 x log (20K/RIN)
PGAIN
The external gain mode also allows summing multiple
signals into a single input, by connecting multiple input
resistors as show in Figure 8, and inputting signals larger
than 1V
P-P
LEFT
INPUT 1
LEFT
INPUT 2
RIGHT
INPUT 1
RIGHT
INPUT 2
.
20kI
INA1/EXTMICP
VCM
20kI
INA2/EXTMICN
VCM
Figure 7. Line Input Block Diagram
62
Figure 8. Summing Multiple Input Signals into INA/INB

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 4. Line Input Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
Line Input A/B External Gain
Switches out the internal input resistor and selects a trimmed 20kI feedback resistor.
Use an external input resistor to set the gain of the line input.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Line Input A/B Internal Gain Settings
000 = +20dB
001 = +14dB
010 = +3dB
011 = 0dB
100 = -3dB
101 = -6dB
110 = -6dB
111 = -6dB
Line Input A Differential Enable
0 = Stereo single-ended input
1 = Mono differential input
Line Input B Differential Enable
0 = Stereo single-ended input
1 = Mono differential input
0x33/0x34
0x45
6 INAEXT/INBEXT
2
1
PGAINA/PGAINB
0
7 INADIFF
6 INBDIFF
MAX9888
ADC Input Mixers
The device’s stereo ADC accepts input from the microphone amplifiers and line inputs. The ADC mixer routes
any combination of the six audio inputs to the left and
right ADCs (Figure 9).
PGAM1:
+20dB TO 0dB
PA1EN:
0/20/30dB
PGAM2:
+20dB TO 0dB
PA2EN:
0/20/30dB
PGAINA:
+20dB TO -6dB
INADIFF
PGAINA:
+20dB TO -6dB
+
PGAINB:
+20dB TO -6dB
INBDIFF
PGAINB:
+20dB TO -6dB
+
Figure 9. ADC Input Mixer Block Diagram
MIX
MIXADL
MIX
MIXADR
ADLEN
ADCL
ADCR
ADREN
63

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 5. ADC Input Mixer Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7
6
5
0x22/0x23
MAX9888
4
3
2
1
0
MIXADL/MIXADR
Left/Right ADC Input Mixer
Selects which analog inputs are recorded by the left/right ADC.
1xxxxxxx = MIC1
x1xxxxxx = MIC2
xx1xxxxx = Reserved
xxx1xxxx = Reserved
xxxx1xxx = INA1
xxxxx1xx = INA2 (INADIFF = 0) or INA2 - INA1 (INADIFF = 1)
xxxxxx1x = INB1
xxxxxxx1 = INB2 (INBDIFF = 0) or INB2 - INB1 (INBDIFF = 1)
Record Path Signal Processing
The device’s record signal path includes both automatic
gain control (AGC) for the microphone inputs and a digital noise gate at the output of the ADC (Figure 10).
Microphone AGC
The IC’s AGC monitors the signal level at the output of
the ADC and then adjusts the MIC1 and MIC2 analog
PGA settings automatically. When the signal level is
below the predefined threshold, the gain is increased up
to its maximum (20dB). If the signal exceeds the threshold, the gain is reduced to prevent the output signal level
exceeding the threshold. When AGC is enabled, the
microphone PGA is not user programmable. The AGC
provides a more constant signal level and improves the
available ADC dynamic range.
PGAM1:
+20dB TO -6dB
AUTOMATIC
PA1EN:
0/20/30dB
+20dB TO 0dB
PA2EN:
0/20/30dB
PGAM2:
MIX
MIXADL
MIX
MIXADR
ADLEN
ADREN
CONTROL
ADCL
ADCR
Figure 10. Record Path Signal Processing Block Diagram
GAIN
AVLG: 0/6/12/18dB
AVL: 3dB TO -12dB
AVRG: 0/6/12/18dB
AVR: 3dB TO -2dB
NOISE GATE
AUDIO/
VOICE
FILTERS
MODE1
AVFLT
Noise Gate
Since the AGC increases the levels of all signals below
a user-defined threshold, the noise floor is effectively
increased by 20dB. To counteract this, the noise gate
reduces the gain at low signal levels. Unlike typical noise
gates that completely silence the output below a defined
level, the noise gate in the IC applies downward expansion. The noise gate attenuates the output at a rate of
1dB for each 2dB the signal is below the threshold.
The noise gate can be used in conjunction with the AGC
or on its own. When the AGC is enabled, the noise gate
reduces the output level only when the AGC has set the
gain to the maximum setting. Figure 11 shows the gain
response resulting from using the AGC and noise gate.
AGC AND NOISE GATE
AMPLITUDE RESPONSE
0
-20
AGC AND NOISE GATE
-40
-60
-80
OUTPUT AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
-100
-120
-120 0
Figure 11. AGC and Noise Gate Input vs. Output Gain
AGC ONLY
AGC AND NOISE
GATE DISABLED
NOISE GATE ONLY
-20-40-60-80-100
INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBFS)
64

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 6. Record Path Signal Processing Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
Noise Gate Attenuation
Reports the current noise gate attenuation.
000 = 0dB
001 = 1dB
010 = 2dB
011 = 3dB to 5dB
100 = 6dB to 7dB
101 = 8dB to 9dB
110 = 10dB to 11dB
111 = 12dB
AGC Gain
Reports the current AGC gain setting.
VALUE GAIN (dB) VALUE GAIN (dB)
0x00 +20 0x0B +9
0x01 +19 0x0C +8
0x02 +18 0x0D +7
0x03 +17 0x0E +6
0x04 +16 0x0F +5
0x05 +15 0x10 +4
0x06 +14 0x11 +3
0x07 +13 0x12 +2
0x08 +12 0x13 +1
0x09 +11 0x14 to 0x1F 0
0x0A +10
AGC/Noise Gate Signal Source
Determines which ADC channel the AGC and noise gates analyze. Gain is adjusted on
both channels regardless of the AGCSRC setting.
0 = Left ADC output
1 = Maximum of either the left or right ADC output
AGC Release Time
Defined as the duration from start to finish of gain increase in the region shown in Figure
12. Release times are longer for low AGC threshold levels.
000 = 78ms
001 = 156ms
010 = 312ms
011 = 625ms
100 = 1.25s
101 = 2.5s
110 = 5s
111 = 10s
0x01
0x3D
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
7 AGCSRC
6
5
4
NG
AGC
AGCRLS
MAX9888
65

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 6. Record Path Signal Processing Registers (continued)
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
AGC Attack Time
3
MAX9888
0x3D
0x3E
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
AGCATK
AGCHLD
ANTH
AGCTH
Defined as the time required to reduce gain by 63% of the total gain reduction (one time
constant of the exponential response). Attack times are longer for low AGC threshold
levels. See Figure 12 for details.
00 = 2ms
01 = 7.2ms
10 = 31ms
11 = 123ms
AGC Hold Time
The delay before the AGC release begins. The hold time counter starts whenever the
signal drops below the AGC threshold and is reset by any signal that exceeds the
threshold. Set AGCHLD to enable the AGC circuit. See Figure 12 for details.
00 = AGC disabled
01 = 50ms
10 = 100ms
11 = 400ms
Noise Gate Threshold
Gain is reduced for signals below the threshold to quiet noise. The thresholds are relative
to the ADC’s full-scale output voltage.
VALUE
0x0 Noise gate disabled 0x8 -45
0x1 Reserved 0x9 -41
0x2 Reserved 0xA -38
0x3 -64 0xB -34
0x4 -62 0xC -30
0x5 -58 0xD -27
0x6 -53 0xE -22
0x7 -50 0xF -16
AGC Threshold
Gain is reduced when signals exceed the threshold to prevent clipping. The thresholds
are relative to the ADC’s full-scale voltage.
VALUE
0x0 -3 0x8 -11
0x1 -4 0x9 -12
0x2 -5 0xA -13
0x3 -6 0xB -14
0x4 -7 0xC -15
0x5 -8 0xD -16
0x6 -9 0xE -17
0x7 -10 0xF -18
THRESHOLD
(dBFS)
THRESHOLD
(dBFS)
VALUE
VALUE
THRESHOLD
(dBFS)
THRESHOLD
(dBFS)
66

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
MAX9888
ATTACK TIME
Figure 12. AGC Timing
HOLD TIME RELEASE TIME
ADC Record Level Control
The IC includes separate digital level control for the left
and right ADC outputs (Figure 13). To optimize dynamic
ADLEN
ADCL
range, use analog gain to adjust the signal level and set
the digital level control to 0dB whenever possible. Digital
level control is primarily used when adjusting the record
level for digital microphones.
NOISE GATE
AUTOMATIC
GAIN CONTROL
AVLG: 0/6/12/18dB
AVL: 3dB TO -12dB
AUDIO/
VOICE
FILTERS
MODE1
AVFLT1
ADCR
ADREN
Figure 13. ADC Record Level Control Block Diagram
AVRG: 0/6/12/18dB
AVR: 3dB TO -2dB
67

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 7. ADC Record Level Control Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
5
4
MAX9888
0x2F/0x30
3
2
1
0
AVLG/AVRG
AVL/AVR
Left/Right ADC Gain
00 = 0dB
01 = 6dB
10 = 12dB
11 = 18dB
Left/Right ADC Level
VALUE GAIN (dB) VALUE GAIN (dB)
0x0 +3 0x8 -5
0x1 +2 0x9 -6
0x2 +1 0xA -7
0x3 0 0xB -8
0x4 -1 0xC -9
0x5 -2 0xD -10
0x6 -3 0xE -11
0x7 -4 0xF -12
Sidetone
Enable sidetone during full-duplex operation to add a
low-level copy of the recorded audio signal to the playback audio signal (Figure 14). Sidetone is commonly
DVST:
0dB TO -60dB
ADLEN
ADREN
ADCL
ADCR
SIDETONE
AUTOMATIC
GAIN
CONTROL
AVLG: 0/6/12/18dB
AVL: 3dB TO -12dB
AVRG: 0/6/12/18dB
AVR: 3dB TO -2dB
DSTS
NOISE GATE
MIX
AUDIO/
VOICE
FILTERS
MODE1
AVFLT
+
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
used in telephony to allow the speaker to hear himself
speak, providing a more natural user experience. The
IC implements sidetone digitally. Doing so helps prevent
unwanted feedback into the playback signal path and
better matches the playback audio signal.
DV1G:
0/6/12/18dB
MULTIBAND ALC
DVEQ1:
0dB TO -15dB
EQ1EN EQ2EN
EXCURSION LIMITER
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
DV2:
0dB TO -15dB
DV1:
0dB TO -15dB
DVEQ2:
0dB TO -15dB
DCB2
MODE1
DVFLT
AUDIO/
FILTERS
AUDIO/
VOICE
FILTERS
MIXDAL
MIX
MIXDAR
MIX
DACL
DALEN
DACR
DAREN
Figure 14. Sidetone Block Diagram
68

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 8. Sidetone Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
Sidetone Source
Selects which ADC output is fed back as sidetone. When mixing the left and right ADC
outputs, each is attenuated by 6dB to prevent full-scale signals from clipping.
00 = Sidetone disabled
01 = Left ADC
10 = Right ADC
11 = Left + Right ADC
Sidetone Level
Adjusts the sidetone signal level. All levels are referenced to the ADC’s full-scale output.
VALUE LEVEL (dB) VALUE LEVEL (dB)
0x00 Sidetone disabled 0x10 -30.5
0x01 -0.5 0x11 -32.5
0x02 -2.5 0x12 -34.5
0x03 -4.5 0x13 -36.5
0x04 -6.5 0x14 -38.5
0x05 -8.5 0x15 -40.5
0x06 -10.5 0x16 -42.5
0x07 -12.5 0x17 -44.5
0x08 -14.5 0x18 -46.5
0x09 -16.5 0x19 -48.5
0x0A -18.5 0x1A -50.5
0x0B -20.5 0x1B -52.5
0x0C -22.5 0x1C -54.5
0x0D -24.5 0x1D -56.6
0x0E -26.5 0x1E -58.5
0x0F -28.5 0x1F -60.5
0x2A
7
DSTS
6
4
3
2
1
0
DVST
MAX9888
Digital Audio Interfaces
The IC includes two separate playback signal paths and
one record signal path. Digital audio interface 1 (DAI1)
is used to transmit the recorded stereo audio signal and
receive a stereo audio signal for playback. Digital audio
interface 2 (DAI2) is used to receive a second stereo
audio signal. Use DAI1 for all full-duplex operations and
for all voice signals. Use DAI2 for music and to mix two
playback audio signals. The digital audio interfaces are
separate from the audio ports to enable either interface
to communicate with any external device connected to
the audio ports.
Each audio interface can be configured in a variety of
2
formats including left justified, I
S, PCM, and time division multiplexed (TDM). TDM mode supports up to 4
mono audio slots in each frame. The IC can use up to
2 mono slots per interface, leaving the remaining two
slots available for another device. Table 9 shows how to
configure the device for common digital audio formats.
Figures 16 and 17 show examples of common audio
formats. By default, SDOUTS1 and SDOUTS2 are set
high impedance when the IC is not outputting data to
facilitate sharing the bus. Configure the interface in TDM
mode using only slot 1 to transmit and receive mono
PCM voice data.
The IC’s digital audio interfaces support both ADC to
DAC loop-through and digital loopback. Loop-through
allows the signal converted by the ADC to be routed
to the DAC for playback. The signal is routed from the
record path to the playback path in the digital audio
interface to allow the IC’s full complement of digital
signal processing to be used. Loopback allows digital
69

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
data input to either SDINS1 or SDINS2 to be routed
from one interface to the other for output on SDOUTS2
or SDOUTS1. Both interfaces must be configured for
the same sample rate, but the interface format need
MAX9888
BCLKS1
DAI1
LRCLKS1 SDOUTS1 SDINS1 DVDDS1 BCLKS2 LRCLKS2 SDOUTS2 SDINS2 DVDDS2
PORT S1 PORT S1
SEL1 SEL2
BCLK1
MAS1
BIT
CLOCK
LRCLK1
FRAME
CLOCK
MAS1
SDOUT1
HIZOFF1
DATA
OUTPUT
SDIN1
DATA
INPUT
not be the same. This allows the IC to route audio data
from one device to another, converting the data format
as needed. Figure 15 shows the available digital signal
routing options.
SDIN2
HIZOFF2
DATA
INPUT
DAI2
MAS2
BCLK2
BIT
CLOCK
LRCLK2
FRAME
CLOCK
SDOUT2
MAS2
DATA
OUTPUT
LBEN1
MUX
LBEN2
+
LTEN1
DAI1
RECORD PATH
Figure 15. Digital Audio Signal Routing
Table 9. Common Digital Audio Formats
MODE WCI1/WCI2 BCI1/BCI2 DLY1/DLY2 TDM1/TDM2 SLOTL1/SLOTL2 SLOTR1/SLOTR2
Left Justified Set as desired Set as desired 0 0 X X
2
S 1 0 1 0 X X
I
PCM X 1 X 1 0 0
TDM X 1 X 1 Set as desired
X = Don’t care.
70
DAI1
PLAYBACK PATH
DAI2
PLAYBACK PATH

with FlexSound Technology
Table 10. Digital Audio Interface Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
DAI1/DAI2 Master Mode
In master mode, DAI1/DAI2 outputs LRCLK and BCLK. In slave mode, DAI1/DAI2
7 MAS1/MAS2
6 WCI1/WCI2
5 BCI1/BCI2
0x14/0x1C
4 DLY1/DLY2
2 TDM1/TDM2
1 FSW1/FSW2
0 WS1/WS2
accept LRCLK and BCLK as inputs.
0 = Slave mode
1 = Master mode
DAI1/DAI2 Word Clock Invert
TDM1/TDM2 = 0:
0 = Left-channel data is transmitted while LRCLK is low.
1 = Right-channel data is transmitted while LRCLK is low.
TDM1/TDM2 = 1:
Always set WCI = 0.
DAI1/DAI2 Bit Clock Invert
BCI1/BCI2 must be set to 1 when TDM1/TDM2 = 1.
0 = SDIN is accepted on the rising edge of BCLK.
SDOUT is valid on the rising edge of BCLK.
1 = SDIN is accepted on the falling edge of BCLK.
SDOUT is valid on the falling edge of BCLK.
Master Mode:
0 = LRCLK transitions on the falling edge of BCLK.
1 = LRCLK transitions on the rising edge of BCLK.
DAI1/DAI2 Data Delay
DLY1/DLY2 has no effect when TDM1/TDM2 = 1.
0 = The most significant data bit is clocked on the first active BCLK edge after an
LRCLK transition.
1 = The most significant data bit is clocked on the second active BCLK edge after an
LRCLK transition.
DAI1/DAI2 Time-Division Multiplex Mode (TDM Mode)
Set TDM1/TDM2 when communicating with devices that use a frame synchronization
pulse on LRCLK instead of a square wave.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled (BCI1/BCI2 must be set to 1)
DAI1/DAI2 Wide Frame Sync Pulse
Increases the width of the frame sync pulse to the full data width when TDM1/TDM2 =
1. FSW1/FSW2 has no effect when TDM1/TDM2 = 0.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
DAI1/DAI2 Audio Data Bit Depth
Determines the maximum bit depth of audio being transmitted and received. Data is
always 16 bit when TDM1/TMD2 = 0.
0 = 16 bits
1 = 24 bits
Stereo Audio CODEC
MAX9888
71

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 10. Digital Audio Interface Registers (continued)
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
ADC Oversampling Ratio
Use the higher setting for maximum performance. Use the lower setting for reduced
power consumption at the expense of performance.
00 = 96x
01 = 64x
10 = Reserved
11 = Reserved
DAI1/DAI2 BCLK Output Frequency
When operating in master mode, BSEL1/BSEL2 set the frequency of BCLK. When
operating in slave mode, BSEL1/BSEL2 have no effect. Select the lowest BCLK
frequency that clocks all data input to the DAC and output by the ADC.
000 = BCLK disabled
001 = 64 x LRCLK
010 = 48 x LRCLK
011 = 128 x LRCLK (invalid for DHF1/DHF2 = 1)
100 = PCLK/2
101 = PCLK/4
110 = PCLK/8
111 = PCLK/16
DAI1/DAI2 Audio Port Selector
Selects which port is used by DAI1/DAI2.
00 = None
01 = Port S1
10 = Port S2
11 = Reserved
DAI1 Digital Loopthrough
Connects the output of the record signal path to the input of the playback path. Data
input to DAI1 from an external device is mixed with the recorded audio signal.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
DAI1/DAI2 Digital Audio Interface Loopback
LBEN1 routes the digital audio input to DAI1 back out on DAI2. LBEN2 routes the
digital audio input to DAI2 back out on DAI1. Selecting LBEN2 disables the ADC
output data.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
DAI1/DAI2 DAC Mono Mix
Mixes the left and right digital input to mono and routes the combined signal to the left
and right playback paths. The left and right input data is attenuated by 6dB prior to the
mono mix.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
MAX9888
0x15/0x1D
0x16/0x1E
7
OSR1
6
2
1
0
7
6
5 LTEN1
4
3
BSEL1/
BSEL2
SEL1/SEL2
LBEN1/
LBEN2
DMONO1/
DMONO2
72

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 10. Digital Audio Interface Registers (continued)
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
Disable DA1/DAI2 Output High-Impedance Mode
Normally SDOUT is set high impedance between data words. Set HIZOFF1/HIZOFF2 to
force a level on SDOUT at all times.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
DAI1/DAI2 Record Path Output Enable
DAI2 outputs data only if LBEN1 = 1.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
DAI1/DAI2 Playback Path Input Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
TDM Left Time Slot
Selects which of the four slots is used for left data on DAI1/DAI2. If the same slot is
selected for left and right audio, left audio is placed in the slot.
00 = Slot 1
01 = Slot 2
10 = Slot 3
11 = Slot 4
TDM Right Time Slot
Selects which of the four slots is used for right data on DAI1/DAI2. If the same slot is
selected for left and right audio, left audio is placed in the slot.
00 = Slot 1
01 = Slot 2
10 = Slot 3
11 = Slot 4
TDM Slot Delay
Adds 1 BCLK cycle delay to the data in the specified TDM slot.
1xxx = Slot 4 delayed
x1xx = Slot 3 delayed
xx1x = Slot 2 delayed
xxx1 = Slot 1 delayed
0x16/0x1E
0x17/0x1F
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
HIZOFF1/
HIZOFF2
SDOEN1/
SDOEN2
SDIEN1/
SDIEN2
SLOTL1/
SLOTL2
SLOTR1/
SLOTR2
SLOTDLY1/
SLOTDLY2
MAX9888
73

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
WCI_ = 0, BCI_ = 0, DLY_ = 0, TDM_ = 0, FSW_ = 0, WS_ = 0, HIZOFF_ = 1, SLOTL_ = 0, SLOTR_ = 0
LRCLK
SDOUT
MAX9888
BCLK
SDIN
LRCLK
SDOUT
BCLK
SDIN
LRCLK
SDOUT
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
WCI_ = 1, BCI_ = 0, DLY_ = 0, TDM_ = 0, FSW_ = 0, WS_ = 0, HIZOFF_ = 1, SLOTL_ = 0, SLOTR_ = 0
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
WCI_ = 0, BCI_ = 1, DLY_ = 0, TDM_ = 0, FSW_ = 0, WS_ = 0, HIZOFF_ = 1, SLOTL_ =
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
LEFT
LEFT
LEFT
RIGHT
RIGHT
0, SLOTR_ = 0
RIGHT
BCLK
SDIN
LRCLK
SDOUT
BCLK
SDIN
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
WCI_ = 0, BCI_ = 0, DLY_ = 1, TDM_ = 0, FSW_ = 0, WS_ = 0, HIZOFF_ = 1, SLOTL_ = 0, SLOTR_ = 0
LEFT
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 16. Non-TDM Data Format Examples
74
RIGHT

with FlexSound Technology
WCI_ = 0, BCI_ = 1, DLY_ = 0, TDM_ = 1, FSW_ = 0, WS_ = 0, HIZOFF_ = 0, SLOTL_ = 0, SLOTR_ = 1
LRCLK
Stereo Audio CODEC
MAX9888
HI-Z
SDOUT
BCLK
SDIN
LRCLK
SDOUT
BCLK
SDIN
LRCLK
SDOUT
BCLK
SDIN
L15 L14 L13 L12 L11 L10 L9 L8 L7 L6 L5 L4 L3 L2 L1 L0 R15 R14 R13 R12 R11 R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0
L15 L14 L13 L12 L11 L10 L9 L8 L7 L6 L5 L4 L3 L2 L1 L0 R15 R14 R13 R12 R11 R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0
WCI_ = 0, BCI_ = 1, DLY_ = 0, TDM_ = 1, FSW_ = 1, WS_ = 0, HIZOFF_ = 0, SLOTL_ = 0, SLOTR_ = 1
HI-Z
L15 L14 L13 L12 L11 L10 L9 L8 L7 L6 L5 L4 L3 L2 L1 L0 R15 R14 R13 R12 R11 R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0
L15 L14 L13 L12 L11 L10 L9 L8 L7 L6 L5 L4 L3 L2 L1 L0 R15 R14 R13 R12 R11 R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0
WCI_ = 0, BCI_ = 1, DLY_ = 0, TDM_ = 1, FSW_ = 0, WS_ = 0, HIZOFF_ = 1, SLOTL_ = 0, SLOTR_ = 1
L15 L14 L13 L12 L11 L10 L9 L8 L7 L6 L5 L4 L3 L2 L1 L0 R15 R14 R13 R12 R11 R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0
L15 L14 L13 L12 L11 L10 L9 L8 L7 L6 L5 L4 L3 L2 L1 L0 R15 R14 R13 R12 R11 R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0
HI-Z
HI-Z
WCI_ = 0, BCI_ = 1, DLY_ = 0, TDM_ = 1, FSW_ = 0, WS_ = 0, HIZOFF_ = 0, SLOTL_ = 2, SLOTR_ = 3
LRCLK
SDOUT
BCLK
SDIN
LRCLK
SDOUT
BCLK
SDIN
HI-Z
32 CYCLES
WCI_ = 0, BCI_ = 1, DLY_ = 0, TDM_ = 1, FSW_ = 0, WS_ = 0, HIZOFF_ = 0, SLOTL_ = 0, SLOTR_ = 1
HI-Z
L L L L L L L L R R R R R R R R
HI-Z
L L L L L L L L 1 1 1 1 R R R R
L15 L14 L13 L12 L11 L10 L9 L8 L7 L6 L5 L4 L3 L2 L1 L0 R15 R14 R13 R12 R11 R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0
L15 L14 L13 L12 L11 L10 L9 L8 L7 L6 L5 L4 L3 L2 L1 L0 R15 R14 R13 R12 R11 R10 R9 R8 R7 R6 R5 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0
16 CYCLES 16 CYCLES 16 CYCLES 16 CYCLES
Figure 17. TDM Mode Data Format Examples
HI-Z
HI-Z
75

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Clock Control
The digital signal paths in the IC require a master
clock (MCLK) between 10MHz and 60MHz to function. Internally, the MAX9888 requires a clock between
10MHz and 20MHz. A prescaler divides MCLK by 1, 2,
or 4 to create the internal clock (PCLK). PCLK is used to
clock all portions of the IC.
The MAX9888 includes two digital audio signal paths,
MAX9888
both capable of supporting any sample rate from 8kHz
to 96kHz. Each path is independently configured to allow
different sample rates. To accommodate a wide range
of system architectures, three main clocking modes are
supported:
PLL Mode: When operating in slave mode, enable
U
the PLL to lock onto any LRCLK input. This mode
requires the least configuration, but provides the
lowest performance. Use this mode to simplify initial
setup or when normal mode and exact integer mode
cannot be used.
Normal Mode: This mode uses a 15-bit clock divider
U
to set the sample rate relative to PCLK. This allows
high flexibility in both the PCLK and LRCLK frequencies and can be used in either master or slave mode.
Exact Integer Mode (DAI1 only): In both master and
U
slave modes, common MCLK frequencies (12MHz,
13MHz, 16MHz, and 19.2MHz) can be programmed
to operate in exact integer mode for both 8kHz and
16kHz sample rates. In these modes, the MCLK and
LRCLK rates are selected by using the FREQ1 bits
instead of the NI, and PLL control bits.
Table 11. Clock Control Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
MCLK Prescaler
0x10
0x11/0x19
5
PSCLK
4
7
6
SR1/SR2
5
4
Generates PCLK, which is used by all internal circuitry.
00 = PCLK disabled
01 = 10MHz P MCLK P 20MHz (PCLK = MCLK)
10 = 20MHz P MCLK P 40MHz (PCLK = MCLK/2)
11 = 40MHz P MCLK P 60MHz (PCLK = MCLK/4)
DAI1/DAI2 Sample Rate
Used by the ALC to correctly set the dual-band crossover frequency and the excursion
limiter to set the predefined corner frequencies.
VALUE
0x0 Reserved 0x8 48
0x1 8 0x9 88.2
0x2 11.025 0xA 96
0x3 16 0xB Reserved
0x4 22.05 0xC Reserved
0x5 24 0xD Reserved
0x6 32 0xE Reserved
0x7 44.1 0xF Reserved
SAMPLE RATE
(kHz)
VALUE
SAMPLE RATE
(kHz)
76

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 11. Clock Control Registers (continued)
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
Exact Integer Mode
Overrides PLL1 and NI1 and configures a specific PCLK to LRCLK ratio.
0x11
0x12/0x1A
0x13/0x1B
3
2
1
7 PLL1/PLL2
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0 NI1[0]/NI2[0]
FREQ1
NI1/
NI2
VALUE SAMPLE RATE VALUE SAMPLE RATE
0x0 Disabled 0x8
0x1 Reserved 0x9
0x2 Reserved 0xA
0x3 Reserved 0xB
0x4 Reserved 0xC
0x5 Reserved 0xD
0x6 Reserved 0xE
0x7 Reserved 0xF
PLL Mode Enable (Slave Mode Only)
PLL1/PLL2 enables a digital PLL that locks on to the externally supplied LRCLK
frequency and automatically sets the LRCLK divider (NI1/NI2).
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Normal Mode LRCLK Divider
When PLL1/PLL2 = 0, the frequency of LRCLK is determined by NI1/NI2. See Table 12
for common NI values.
SAMPLE RATE DHF1/DHF2 NI1/NI2 FORMULA
8kHz P LRCLK P 48kHz 0
48kHz < LRCLK P 96kHz 1
= LRCLK frequency
f
LRCLK
f
= Prescaled MCLK frequency (PCLK)
PCLK
Rapid Lock Mode
Program NI1/NI2 to the nearest valid ratio and set NI1[0]/NI2[0] when PLL1/PLL2 = 1
to enable rapid lock mode. Normally, the PLL automatically calculates and dynamically
adjusts NI1/NI2. When rapid lock mode is properly configured, the PLL starting point is
much closer to the correct value, thus speeding up lock time. Wait one LRCLK period
after programming NI1/NI2 before setting PLL1/PLL2 = 1.
PCLK = 12MHz,
LRCLK = 8kHz
PCLK = 12MHz,
LRCLK = 16kHz
PCLK = 13MHz,
LRCLK = 8kHz
PCLK = 13MHz,
LRCLK = 16kHz
PCLK = 16MHz,
LRCLK = 8kHz
PCLK = 16MHz,
LRCLK = 16kHz
PCLK = 19.2MHz,
LRCLK = 8kHz
PCLK = 19.2MHz,
LRCLK = 16kHz
65536 96 f
NI
=
65536 48 f
NI
=
× ×
f
PCLK
× ×
f
PCLK
MAX9888
LRCLK
LRCLK
77

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 12. Common NI1/NI2 Values
LRCLK (kHz)
PCLK (MHz)
8 11.025 12 16 22.05 24 32 44.1 48 64 88.2 96
10
11
11.2896
MAX9888
12
12.288 1000
13
16
16.9344
18.432
20
13A9 1B18 1D7E 2752 3631 3AFB 4EA5 6C61 75F7 4EA5 6C61 75F7
11E0 18A2 1ACF 23BF 3144 359F 477E 6287 6B3E 477E 6287 6B3E
116A
1800
1A1F 22D4
1062 1694 1893 20C5 2D29 3127 4189 5A51 624E 4189 5A51 624E
160D
1800 2000
0F20 14D8 16AF 1E3F 29AF 2D5F 3C7F 535F 5ABE 3C7F 535F 5ABE
0C4A 10EF 126F 1893 21DE 24DD 3127 43BD 49BA 3127 43BD 49BA
0B9C
0AAB 0EB3
1000
116A 1738
1000
09D5 0D8C 0EBF 13A9 1B18 1D7E 2752 3631 3AFB 2752 3631 3AFB
Note: Values in bold are exact integers that provide maximum full-scale performance.
DHF1/2 = 0 DHF1/2 = 1
3000
2C1A
2000
1555 1D66
343F 45A9
3000 4000
22D4 2E71
2000
2AAB 3ACD
6000
5833
4000
687D 45A9
6000 4000
45A9 2E71
4000
2AAB 3ACD
6000
5833
4000
687D
6000
45A9
4000
Passband Filtering
Each digital signal path in the IC includes options for
defining the path bandwidth (Figure 18). The playback
and record paths connected to DAI1 support both voice
and music filtering while the playback path connected to
DAI2 supports music filtering only.
The voice IIR filters provide greater than 70dB stopband
attenuation at frequencies above f
/2 to reduce aliasing.
S
Three selectable highpass filters eliminate unwanted
low-frequency signals.
DVST:
0dB TO -60d B
ADLEN
ADREN
ADCL
ADCR
SIDETONE
AUTOMATIC
GAIN
CONTROL
AVLG: 0/6/12/18dB
AVL: 3dB TO -12dB
AVRG: 0/6/12/18dB
AVR: 3dB TO -2dB
DSTS
NOISE GATE
MIX
AUDIO/
VOICE
FILTERS
MODE1
AVFLT
+
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
Use music mode when processing high-fidelity audio
content. The music FIR filters reduce power consumption and are linear phase to maintain stereo imaging.
An optional DC-blocking filter is available to eliminate
unwanted DC offset.
In music mode, a second set of FIR filters are available
to support sample rates greater than 50kHz. The filters
can be independently selected for DAI1 and DAI2 and
support both the playback and record audio paths.
DV1G:
0/6/12/18dB
MULTIBAND ALC
DVEQ1:
0dB TO -15dB
EQ1EN EQ2EN
EXCURSION LIMITER
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
DV2:
0dB TO -15dB
DV1:
0dB TO -15dB
DVEQ2:
0dB TO -15dB
DCB2
MODE1
DVFLT
AUDIO/
FILTERS
AUDIO/
VOICE
FILTERS
MIXDAL
MIX
MIXDAR
MIX
DACL
DALEN
DACR
DAREN
Figure 18. Digital Passband Filtering Block Diagram
78

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 13. Passband Filtering Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
DAI1 Passband Filtering Mode
0 = Voice filters
1 = Music filters (recommended for f
DAI1 ADC Highpass Filter Mode
MODE1 AVFLT1
0 See Table 14
1 Select a nonzero value to enable the DC-blocking filter
DAI1 High Sample Rate Mode
Selects the sample rate range.
0 = 8kHz P LRCLK P 48kHz
1 = 48kHz P LRCLK < 96kHz
> 24kHz)
S
0x18
7 MODE1
6
5
4
3 DHF1
AVFLT1
MAX9888
0x20
2
1
0
3 DHF2
0 DCB2
DVFLT1
DAI1 DAC Highpass Filter Mode
MODE1 DVFLT1
0 See Table 14
1 Select a nonzero value to enable the DC-blocking filter
DAI2 High Sample Rate Mode
Selects the sample rate range.
0 = 8kHz P LRCLK P 48kHz
1 = 48kHz < LRCLK P 96kHz
DAI2 DC Blocking Filter
Enables a DC-blocking filter on the DAI2 playback audio path.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
79

Stereo Audio CODEC
AMPLITUDE (dB)
AMPLITUDE (dB)
0
AMPLITUDE (dB)
with FlexSound Technology
Table 14. Voice Highpass Filters
AVFTL/DVFLT VALUE INTENDED SAMPLE RATE FILTER RESPONSE
000 N/A Disabled
0
-10
MAX9888
001/011 16kHz/8kHz
010/100 16kHz/8kHz
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
0 1000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
0 1000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
0
800600400200
800600400200
80
-10
-20
-30
101 8kHz to 48kHz
-40
-50
-60
0 1000
FREQUENCY (Hz)
110/111 N/A Reserved
LRCLK = 48kHz
800600400200

with FlexSound Technology
Playback Path Signal Processing
The IC playback signal path includes automatic level
control (ALC) and a 5-band parametric equalizer (EQ)
(Figure 19). The DAI1 and DAI2 playback paths include
separate ALCs controlled by a single set of registers.
Two completely separate parametric EQs are included
for the DAI1 and DAI2 playback paths.
Automatic Level Control
The automatic level control (ALC) circuit ensures maximum signal amplitude without producing audible clipping. This is accomplished by a variable gain stage that
works on a sample by sample basis to increase the gain
up to 12dB. A look-ahead circuit determines if the next
sample exceeds full scale and reduces the gain so that
the sample is exactly full scale.
A programmable low signal threshold determines the
minimum signal amplitude that is amplified. Select a
threshold that prevents the amplification of background
noise. When the signal level drops below the low signal
threshold, the ALC reduces the gain to 0dB until the signal increases above the threshold. Figure 20 shows an
example of ALC input vs. output curves.
Stereo Audio CODEC
The ALC can optionally be configured in dual-band
mode. In this mode, the input signal is filtered into two
bands with a 5kHz center frequency. Each band is
routed through independent ALCs and then summed
together. In multiband mode, both bands use the same
parameters.
OUTPUT SIGNAL
(dBFS)
0
INPUT
SIGNAL
(dBFS)
OUTPUT SIGNAL
(dBFS)
0
LOW-LEVEL
THRESHOLD
ALC W ITH ALCTH ≠ 000
-12 0
MAX9888
DV1G:
0/6/12/18dB
+
MULTIBAND ALC
DVEQ1:
0dB TO -15dB
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
EQ1EN EQ2EN
EXCURSION LIMITER
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
DV2:
0dB TO -15dB
DV1:
0dB TO -15dB
DVEQ2:
0dB TO -15dB
FILTERS
DCB2
FILTERS
MODE1
DVFLT
AUDIO/
AUDIO/
VOICE
MIXDAL
MIX
MIXDAR
MIX
DACL
DALEN
DACR
DAREN
INPUT
SIGNAL
(dBFS)
INPUT
SIGNAL
(dBFS)
OUTPUT SIGNAL
(dBFS)
0
LOW-LEVEL
THRESHOLD
ALC W ITH ALCTH = 000
LOW-LEVEL
THRESHOLD
ALC D ISABLED
-12 0
-12 0
Figure 20. ALC Input vs. Output ExamplesFigure 19. Playback Path Signal Processing Block Diagram
81

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 15. Automatic Level Control Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
ALC Enable
7 ALCEN
MAX9888
6
5
0x41
4
3 ALCMB
2
1
0
ALCRLS
ALCTH
Enables ALC on both the DAI1 and DAI2 playback paths.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
ALC and Excursion Limiter Release Time
Sets the release time for both the ALC and Excursion Limiter. See the Excursion
Limiter section for Excursion Limiter release times. ALC release time is defined as the
time required to adjust the gain from 12dB to 0dB.
VALUE ALC RELEASE TIME (s)
000 8
001 4
010 2
011 1
100 0.5
101 0.25
110 Reserved
111 Reserved
Multiband Enable
Enables dual-band processing with a 5kHz center frequency. SR1 and SR2 must be
configured properly to achieve the correct center frequency for each playback path.
0 = Single-band ALC
1 = Dual-band ALC
Low Signal Threshold
Selects the minimum signal level to be boosted by the ALC.
000 = -JdB (low-signal threshold disabled)
001 = -12dB
010 = -18dB
011 = -24dB
100 = -30dB
101 = -36dB
110 = -42dB
111 = -48dB
Parametric Equalizer
The parametric EQ contains five independent biquad
filters with programmable gain, center frequency, and
bandwidth. Each biquad filter has a gain range of Q12dB
and a center frequency range from 20Hz to 20kHz. Use a
filter Q less than that shown in Figure 21 to achieve ideal
frequency responses. Setting a higher Q results in nonideal frequency response. The biquad filters are series
connected, allowing a total gain of Q60dB.
82
1000
fs = 8kHz
100
10
1
MAXIMUM RECOMMENDED FILTER Q
0.1
100 100,000
Figure 21. Maximum Recommended Filter Q vs. Frequency
CENTER FREQUENCY (Hz)
fs = 48kHz
fs = 96kHz
10,0001000

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Use the attenuator at the EQ’s input to avoid clipping
the signal. The attenuator can be programmed for fixed
attenuation or dynamic attenuation based on signal level.
If the dynamic EQ clip detection is enabled, the signal
level from the EQ is fed back to the attenuator circuit to
determine the amount of gain reduction necessary to
avoid clipping.
Table 16. EQ Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
DAI1/DAI2 EQ Clip Detection
Automatically controls the EQ attenuator to prevent clipping in the EQ.
0 = Enabled
1 = Disabled
DAI1/DAI2 EQ Attenuator
Provides attenuation to prevent clipping in the EQ when full-scale signals are boosted. DVEQ1/DVEQ2 operates only when EQ1EN/EQ2EN = 1 and EQCLP1/EQCLP2
= 1.
VALUE GAIN (dB) VALUE GAIN (dB)
0x0 0 0x8 -8
0x1 -1 0x9 -9
0x2 -2 0xA -10
0x3 -3 0xB -11
0x4 -4 0xC -12
0x5 -5 0xD -13
0x6 -6 0xE -14
0x7 -7 0xF -15
0x2C/0x2E
4
3
2
1
0
EQCLP1/
EQCLP2
DVEQ1/DVEQ2
The MAX9888 EV kit software includes a graphic interface for generating the EQ coefficients. The coefficients
are sample rate dependent and stored in registers 0x50
through 0xB3.
MAX9888
0x47
7
6
5
1 EQ2EN
0 EQ1EN
VS2EN
VSEN
ZDEN
See the Click-and-Pop Reduction section.
DAI2 EQ Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
DAI1 EQ Enable
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
83

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Playback Level Control
The IC includes separate digital level control for the DAI1
and DAI2 playback audio paths. The DAI1 signal path
DV1G:
0/6/12/18dB
MAX9888
+
MULTIBAND ALC
DVEQ1:
0dB TO -15dB
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
EQ1EN EQ2EN
EXCURSION LIMITER
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
DV2:
0dB TO -15dB
DV1:
0dB TO -15dB
DVEQ2:
0dB TO -15dB
allows boost when MODE1 = 0 and attenuation in any
mode. The DAI2 signal path allows attenuation only.
MIXDAL
DACL
DALEN
DACR
DAREN
AUDIO/
FILTERS
DCB2
AUDIO/
FILTERS
MODE1
DVFLT
VOICE
MIX
MIXDAR
MIX
Figure 22. Playback Level Control Block Diagram
Table 17. DAC Playback Level Control Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
DAI1/DAI2 Mute
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
DAI1 Voice Mode Gain
DV1G only applies when MODE1 = 0.
00 = 0dB
01 = 6dB
10 = 12dB
11 = 18dB
DAI1/DAI2 Attenuation
VALUE GAIN (dB) VALUE GAIN (dB)
0x0 0 0x8 -8
0x1 -1 0x9 -9
0x2 -2 0xA -10
0x3 -3 0xB -11
0x4 -4 0xC -12
0x5 -5 0xD -13
0x6 -6 0xE -14
0x7 -7 0xF -15
0x2B/0x2D
7 DV1M/DV2M
5
DV1G
4
3
2
DV1/DV2
1
0
84

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
DAC Input Mixers
The IC’s stereo DAC accepts input from two digital audio paths. The DAC mixer routes any audio path to the left and
right DACs (Figure 23).
DV1G:
0/6/12/18dB
+
MULTIBAND ALC
MAX9888
DVEQ1:
0dB TO -15dB
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
EQ1EN EQ2EN
EXCURSION LIMITER
PARAMETRIC
DVEQ2:
0dB TO -15dB
5-BAND
EQ
DV2:
0dB TO -15dB
DV1:
0dB TO -15dB
AUDIO/
FILTERS
DCB2
AUDIO/
VOICE
FILTERS
MODE1
DVFLT
MIXDAL
MIX
MIXDAR
MIX
Figure 23. DAC Input Mixer Block Diagram
Table 18. DAC Input Mixer Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
0x21
7
6
5
MIXDAL
4
3
2
1
MIXDAR
0
Left DAC Input Mixer
1xxx = DAI1 left channel
x1xx = DAI1 right channel
xx1x = DAI2 left channel
xxx1 = DAI2 right channel
Right DAC Input Mixer
1xxx = DAI1 left channel
x1xx = DAI1 right channel
xx1x = DAI2 left channel
xxx1 = DAI2 right channel
DACL
DALEN
DACR
DAREN
85

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Preoutput Signal Path
The IC’s preoutput mixer stage provides mixing and level adjustment for line input signals routed to the output amplifiers. Figure 24 shows a block diagram of the preoutput signal path. 9dB is added between the line input amplifiers
and the output amplifiers to boost the 1V
maximum line input signal level to the 1V
P-P
maximum DAC signal level.
RMS
MAX9888
+
+
PGAINA:
+20dB TO -6dB
INADIFF
PGAINA:
+20dB TO -6dB
PGAINB:
+20dB TO -6dB
PGAINB:
+20dB TO -6dB
INBDIFF
MIX
MIXOUT1
MIX
MIXOUT2
MIX
MIXOUT3
PGAOUT1:
0dB TO -23d B
PGAOUT2:
0dB TO -23d B
PGAOUT3:
0dB TO -23d B
PREOUT1
PREOUT2
PREOUT3
+9dB
+9dB
+9dB
MIX
MIXREC
MIX
MIXSPL
MIX
MIXSPR
RECVOL:
+8dB TO -62dB
SPVOLL:
+8dB TO -62dB
SPVOLR:
+8dB TO -62dB
MIX
MIXHPL
MIX
MIXHPR
0dB
RECEN
BATTERY ADC
+6dB
SPLEN
DISTORTION LIMITER
+6dB
SPREN
HPVOLL:
+3dB TO -67dB
HPLEN
HPVOLR:
+3dB TO -67dB
HPREN
RECBYP
SPKBYP
POWER/
RECP/
RXINP
RECN/
RXINN
SPKLVDD
SPKLP
SPKLN
SPKLGND
SPKRVDD
SPKRP
SPKRN
SPKRPGND
HPL
HPSNS
HPR
Figure 24. Preoutput Signal Path Block Diagram
Preoutput Mixer
The IC’s output amplifiers each accept input from one of the three preoutput mixers. Configure each preoutput mixer to mix any combination of the four line input signals.
Table 19. Preoutput Mixer Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
0x24/0x25/
0x26
86
3
2
1
MIXOUT1/
MIXOUT2/
MIXOUT3
0
Preoutput Mixer 1
1xxx = INA1
x1xx = INA2 (INADIFF = 0) or INA2 - INA1 (INADIFF = 1)
xx1x = INB1
xxx1 = INB2 (INBDIFF = 0) or INB2 - INB1 (INBDIFF = 1)

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Preoutput PGA
The IC’s preoutput PGAs allow line input signals to be attenuated to match DAC output signal levels. Use the 0dB
setting for maximum performance.
Table 20. Preoutput PGA Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
3
2
0x35/0x36/
0x37
1
0
PGAOUT1/
PGAOUT2/
PGAOUT3
The IC includes a single differential receiver amplifier. The receiver amplifier is designed to drive 32I receivers. In
cases where a single transducer is used for the loudspeaker and receiver, use the SPKBYP switch to route the receiver
amplifier output to the left speaker outputs.
Preoutput PGA Level
VALUE GAIN (dB) VALUE GAIN (dB)
0x0 0 0x8 -15
0x1 -1 0x9 -17
0x2 -3 0xA -19
0x3 -5 0xB -21
0x4 -7 0xC -23
0x5 -9 0xD Mute
0x6 -11 0xE Mute
0x7 -13 0xF Mute
Receiver Amplifier
MAX9888
DACL
DALEN
DACR
DAREN
PGAOUT1:
0dB TO -23dB
PREOUT1
PGAOUT2:
0dB TO -23dB
PREOUT2
Figure 25. Receiver Amplifier Block Diagram
+9dB
+9dB
MIX
MIXREC
RECVOL:
+8dB TO -62dB
0dB
RECEN
RECP/
RXINP
RECN/
RXINN
RECBYP
SPKBYP
87

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Receiver Output Mixer
The IC’s receiver amplifier accepts input from the stereo DAC and the line inputs. Configure the mixer to mix any combination of the available sources. When more than one signal is selected, the mixed signal is attenuated by 6dB for 2 signals,
9.5dB for 3 signals, or 12dB for 4 signals.
Table 21. Receiver Output Mixer Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
MAX9888
0x28
3
2
1
0
MIXREC
Receiver Output Volume
Table 22. Receiver Output Level Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7 RECM
4
3
0x3A
2
RECVOL
1
0
Receiver Output Mixer
1xxx = Left DAC
x1xx = Right DAC
xx1x = Preoutput mixer 1
xxx1 = Preoutput mixer 2
Receiver Output Mute
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Receiver Output Volume Level
VALUE VOLUME (dB) VALUE VOLUME (dB)
0x00 -62 0x10 -10
0x01 -58 0x11 -8
0x02 -54 0x12 -6
0x03 -50 0x13 -4
0x04 -46 0x14 -2
0x05 -42 0x15 0
0x06 -38 0x16 +1
0x07 -35 0x17 +2
0x08 -32 0x18 +3
0x09 -29 0x19 +4
0x0A -26 0x1A +5
0x0B -23 0x1B +6
0x0C -20 0x1C +6.5
0x0D -17 0x1D +7
0x0E -14 0x1E +7.5
0x0F -12 0x1F +8
88

with FlexSound Technology
Speaker Amplifiers
The IC integrates a stereo filterless Class D amplifier that
offers much higher efficiency than Class AB without the
typical disadvantages.
The high efficiency of a Class D amplifier is due to the
switching operation of the output stage transistors. In a
Class D amplifier, the output transistors act as current
steering switches and consume negligible additional
power. Any power loss associated with the Class D output stage is mostly due to the I
on-resistance, and quiescent current overhead.
2
R loss of the MOSFET
Stereo Audio CODEC
MAX9888
The theoretical best efficiency of a linear amplifier is
78%, however, that efficiency is only exhibited at peak
output power. Under normal operating levels (typical
music reproduction levels), efficiency falls below 30%,
whereas the IC’s Class D amplifier still exhibits 80% efficiency under the same conditions.
Traditional Class D amplifiers require the use of external LC filters or shielding to meet EN55022B and FCC
electromagnetic-interference (EMI) regulation standards.
Maxim’s patented active emissions limiting edge-rate
control circuitry reduces EMI emissions (Figure 26).
40
30
20
10
AMPLITUDE (dBµV/m)
0
-10
30 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260 280 300
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 26. EMI with 15cm of Speaker Cable
DACL
DALEN
DACR
DAREN
MIX
MIXSPL
MIX
MIXSPR
40
30
20
10
AMPLITUDE (dBµV/m)
0
-10
300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 800 850 900 950 1000
BATTERY ADC
SPVOLL:
+8dB TO -62dB
+6dB
SPLEN
POWER/DISTORTION LIMITER
+6dB
SPVOLR:
+8dB TO -62dB
SPREN
FREQUENCY (MHz)
SPKLVDD
SPKLP
SPKLN
SPKLGND
SPKRVDD
SPKRP
SPKRN
SPKRPGND
PGAOUT2:
0dB TO -23dB
PREOUT2
+9dB
PGAOUT3:
0dB TO -23dB
PREOUT3
+9dB
Figure 27. Speaker Amplifier Path Block Diagram
89

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Speaker Output Mixers
The IC’s speaker amplifiers accept input from the stereo DAC and the line inputs. Configure the mixer to mix any combination of the available sources. When more than one signal is selected, the mixed signal is attenuated by 6dB for 2 signals,
9.5dB for 3 signals, or 12dB for four signals.
Table 23. Speaker Output Mixer Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
MAX9888
0x29
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
MIXSPL
MIXSPR
Speaker Output Volume
Table 24. Speaker Output Mixer Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7 SPLM/SPRM
4
3
0x3B/0x3C
2
SPVOLL/SPVOLR
1
0
Left Speaker Output Mixer
1xxx = Left DAC
x1xx = Right DAC
xx1x = Reserved
xxx1 = Preoutput mixer 3
Right Speaker Output Mixer
1xxx = Left DAC
x1xx = Right DAC
xx1x = Reserved
xxx1 = Preoutput mixer 2
Left/Right Speaker Output Mute
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Left/Right Speaker Output Volume Level
VALUE VOLUME (dB) VALUE VOLUME (dB)
0x00 -64 0x10 -10
0x01 -59 0x11 -8
0x02 -55 0x12 -6
0x03 -50 0x13 -4
0x04 -46 0x14 -2
0x05 -42 0x15 0
0x06 -38 0x16 +1
0x07 -35 0x17 +2
0x08 -32 0x18 +3
0x09 -29 0x19 +4
0x0A -26 0x1A +5
0x0B -23 0x1B +6
0x0C -20 0x1C +6.5
0x0D -17 0x1D +7
0x0E -14 0x1E +7.5
0x0F -12 0x1F +8
90

with FlexSound Technology
Speaker Amplifier Signal Processing
The IC includes signal processing to improve the sound
quality of the speaker output and protect transducers
from damage. An excursion limiter dynamically adjusts
the highpass corner frequency, while a power limiter and
distortion limiter prevent the amplifier from outputting too
much distortion or power. The excursion limiter is located
in the DSP while the distortion limiter and power limiter
control the analog volume control (Figure 28). All three
limiters analyze the speaker amplifier’s output signal to
determine when to take action.
Excursion Limiter
The excursion limiter is a dynamic highpass filter that
monitors the speaker outputs and increases the highpass corner frequency when the speaker amplifier’s output exceeds a predefined threshold. The filter smoothly
transitions between the high and low corner frequency to
prevent unwanted artifacts. The filter can operate in four
different modes:
Fixed Frequency Preset Mode. The highpass corner
U
frequency is fixed at the upper corner frequency and
does not change with signal level.
Fixed Frequency Programmable Mode. The high-
U
pass corner frequency is fixed to that specified by the
programmable biquad filter.
Stereo Audio CODEC
Preset Dynamic Mode. The highpass filter automati-
U
cally slides between a preset upper and lower corner
frequency based on output signal level.
User Programmable Dynamic Mode. The highpass
U
filter slides between a user-programmed biquad filter
on the low side to a predefined corner frequency on
the high side.
The transfer function for the user-programmable biquad is:
b b z b z
H(z)
0 1 2
=
1 a z a z
The coefficients b0, b1, b2, a1, and a2 are sample rate
dependent and stored in registers 0xB4 through 0xC7.
Store b
a
2
, b1, and b2 as positive numbers. Store a1 and
0
as negated two’s complement numbers. Separate fil-
ters can be stored for the DAI1 and DAI2 playback paths.
The MAX9888 EV kit software includes a graphic interface
for generating the user-programmable biquad coefficients.
Note: Only change the excursion limiter settings when
the signal path is disabled to prevent undesired artifacts.
-1 -2
+ +
-1 -2
+ +
1 2
MAX9888
DV1G:
0/6/12/18dB
+
MULTIBAND ALC
DVEQ1:
0dB TO -15dB
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
EQ1EN EQ2EN
EXCURSION LIMITER
Figure 28. Speaker Amplifier Signal Processing Block Diagram
5-BAND
PARAMETRIC
EQ
DV2:
0dB TO -15dB
DV1:
0dB TO -15dB
DVEQ2:
0dB TO -15dB
DCB2
MODE1
DVFLT
AUDIO/
FILTERS
AUDIO/
VOICE
FILTERS
MIX
MIXDAL
MIX
MIXDAR
DALEN
DAREN
DACL
DACR
MIX
MIXSPL
MIX
MIXSPR
SPVOLL:
+8dB TO -62dB
SPVOLR:
+8dB TO -62dB
BATTERY ADC
+6dB
SPLEN
DISTORTION LIMITER
+6dB
SPREN
POWER/
SPKLVDD
SPKLP
SPKLN
SPKLGND
SPKRVDD
SPKRP
SPKRN
SPKRPGND
91

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 25. Excursion Limiter Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
Excursion Limiter Corner Frequency
6
5
MAX9888
4
0x3F
1
0
6
0x41
0x40
92
5
4
3
2
1
0
DHPUCF
DHPLCF
ALCRLS
DHPTH
The excursion limiter has limited sliding range and minimum corner frequencies. Listed below
are all the valid filter combinations.
LOWER CORNER
FREQUENCY
Excursion limiter disabled — 000 00
Programmable using biquad 100Hz 000 11
200Hz 400Hz — 001 01
400Hz 600Hz — 010 10
400Hz 800Hz — 011 10
Programmable
using biquad
Programmable
using biquad
Programmable
using biquad
Programmable
using biquad
ALC and Excursion Limiter Release Time
Sets the release time for both the ALC and Excursion Limiter. See the Automatic Level Control
section for ALC release times. Excursion limiter release time is defined as the time required to
slide from the high corner frequency to the low corner frequency.
Excursion Limiter Threshold
Measured at the Class D speaker amplifier outputs. Signals above the threshold use the upper
corner frequency. Signals below the threshold use the lower corner frequency. V
correctly reflect the voltage of SPKLVDD to achieve accurate thresholds.
000 = 0.34V
001 = 0.71V
010 = 1.30V
011 = 1.77V
100 = 2.33V
101 = 3.25V
110 = 4.25V
111 = 4.95V
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
UPPER CORNER
FREQUENCY
400Hz — 001 00
600Hz — 010 00
800Hz — 011 00
1kHz — 100 00
400Hz 200Hz 001 11
600Hz 300Hz 010 11
800Hz 400Hz 011 11
1kHz 500Hz 100 11
VALUE EXCURSION LIMITER RELEASE TIME (s)
000 4
001 2
010 1
011 0.5
100 0.25
101 0.25
110 Reserved
111 Reserved
MINIMUM BIQUAD
CORNER FREQUENCY
DHPUCF DHPLCF
must
BAT

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Power Limiter
The IC’s power limiter tracks the RMS power delivered to
the loudspeaker and briefly mutes the speaker amplifier
output if the speaker is at risk of sustaining permanent
damage.
Loudspeakers are typically damaged when the voice coil
overheats due to extended operation above the rated
power. During normal operation, heat generated in the
voice coil is transferred to the speaker’s magnet, which
transfers heat to the surrounding air. For the voice coil to
overheat, both the voice coil and the magnet must overheat. The result is that a loudspeaker can operate above
its rated power for a significant time before it heats sufficiently to cause damage.
Table 26. Power Limiter Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
Power Limiter Threshold
If the RMS output power from the speaker amplifiers exceeds this threshold, the out-
7
6
PWRTH
5
0x42
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
4
2
1
0
PWRK
put is briefly muted to protect the speaker. The threshold is measured in watts assuming an 8I load. VBAT must correctly reflect the voltage of SPKLVDD/SPKRVDD to
achieve accurate thresholds.
VALUE
0x0
0x1 0.05 0x9 0.35
0x2 0.06 0xA 0.48
0x3 0.09 0xB 0.72
0x4 0.11 0xC 1.00
0x5 0.13 0xD 1.43
0x6 0.18 0xE 1.57
0x7 0.22 0xF 1.80
Power Limiter Weighting Factor
Determines the balance between time constant 1 and 2 to match the dominance of
each time constant in the loudspeaker.
VALUE T1 (%) T2 (%)
000 50 50
001 62.5 37.5
010 75 25
011 87.5 12.5
100 100 0
101 12.5 87.5
110 25 75
111 37.5 62.5
The IC’s power limiter includes user-programmable time
constants and power thresholds to match a wide range
of loudspeakers. Program the power limiter’s threshold to
match the loudspeaker’s rated power handling. This can
be determined through measurement or the loudspeaker’s specification. Program time constant 1 to match the
voice coil’s thermal time constant. Program time constant
2 to match the magnet’s thermal time constant. The time
constants can be determined by plotting the voice coil’s
resistance vs. time as power is applied to the speaker.
THRESHOLD
(W)
Power limiter
disabled
VALUE
0x8 0.27
THRESHOLD
MAX9888
(W)
93

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 26. Power Limiter Registers (continued)
7
6
MAX9888
5
4
0x43
3
2
1
0
PWRT2
PWRT1
Power Limiter Time Constant 2
Select a value that matches the thermal time constant of the loudspeaker’s magnet.
VALUE
0x0 Disabled 0x8 3.75
0x1 0.50 0x9 5.00
0x2 0.67 0xA 6.66
0x3 0.89 0xB 8.88
0x4 1.19 0xC Reserved
0x5 1.58 0xD Reserved
0x6 2.11 0xE Reserved
0x7 2.81 0xF Reserved
Power Limiter Time Constant 1
Select a value that matches the thermal time constant of the loudspeaker’s voice coil.
VALUE
0x0 Disabled 0x8 3.75
0x1 0.50 0x9 5.00
0x2 0.67 0xA 6.66
0x3 0.89 0xB 8.88
0x4 1.19 0xC Reserved
0x5 1.58 0xD Reserved
0x6 2.11 0xE Reserved
0x7 2.81 0xF Reserved
TIME CONSTANT
(min)
TIME CONSTANT
(s)
VALUE
VALUE
TIME CONSTANT
(min)
TIME CONSTANT
(s)
Distortion Limiter
The IC’s distortion limiter ensures that the speaker amplifier’s output does not exceed the programmed THD+N limit.
The distortion limiter analyzes the Class D output duty cycle to determine the percentage of the waveform that is
clipped. If the distortion exceeds the programmed threshold, the output gain is reduced.
94

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 27. Distortion Limiter Registers
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
Distortion Limit
Measured in % THD+N.
VALUE THD+N LIMIT (%) VALUE THD+N LIMIT (%)
0x0 Limiter disabled 0x8 12
0x1 < 1 0x9 14
0x2 1 0xA 16
0x3 2 0xB 18
0x4 4 0xC 20
0x5 6 0xD 21
0x6 8 0xE 22
0x7 10 0xF 24
Distortion Limiter Release Time Constant
Duration of time required for the speaker amplifier’s output gain to adjust back to the
nominal level after a large signal has passed.
000 = 6.2s
001 = 3.1s
010 = 1.6s
011 = 815ms
100 = 419ms
101 = 223ms
110 = 116ms
111 = 76ms
0x44
7
6
5
4
2
1
0
THDCLP
THDT1
MAX9888
Headphone Amplifier
The IC’s headphone amplifier integrates Maxim’s
DirectDrive architecture to eliminate the need for large
DC-blocking capacitors. Traditional single-supply headphone amplifiers have outputs biased at a nominal
DC voltage (typically half the supply). Large coupling
capacitors are needed to block this DC bias from the
headphone. Without these capacitors, a significant
amount of DC current flows to the headphone, resulting
in unnecessary power dissipation and possible damage
to both the headphone and headphone amplifier.
The DirectDrive architecture uses a charge pump to
create an internal negative supply voltage. This allows
the IC’s headphone outputs to be biased at GND while
operating from a single supply (Figure 29). Without a DC
component, there is no need for the large DC-blocking
capacitors. Instead of two large (220FF, typ) capacitors, the IC charge pump requires two small ceramic
capacitors, conserving board space, reducing cost, and
improving the frequency response of the headphone
amplifier. There is a low DC voltage on the amplifier outputs due to amplifier offset. However, the offset of the IC
is typically Q0.2mV, which, when combined with a 32I
load, results in less than 6FA of DC current flow to the
headphones.
In addition to the cost and size disadvantages of
the DC-blocking capacitors required by conventional
headphone amplifiers, these capacitors limit the amplifier’s low-frequency response and can distort the audio
signal. The DC-blocking capacitor not only blocks DC,
but also low-frequency audio. Improving the low-frequency response of a conventional headphone amplifier
requires increasing the capacitor size, further adding
to the cost and size of the solution. Due to the voltage
coefficient of the capacitors used for DC blocking, they
introduce significant distortion near the corner frequency
of the highpass filter they create. This distortion further
degrades the low-frequency audio quality.
95

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Alternative approaches to eliminating the output-coupling capacitors involve biasing the headphone return
(sleeve) to the DC bias voltage of the headphone amplifiers. This method raises some issues:
U The sleeve is typically grounded to the chassis. Using
the midrail biasing approach, the sleeve must be
isolated from system ground, complicating product
design.
MAX9888
U During an ESD strike, the amplifier’s ESD structures
are the only path to system ground. Thus, the amplifier must be able to withstand the full energy from an
ESD strike.
U When using the headphone jack as a line out to other
equipment, the bias voltage on the sleeve may conflict with the ground potential from other equipment,
resulting in possible damage to the amplifiers.
The IC features a low-noise charge pump to generate
a negative supply for the headphone amplifier. The
nominal switching frequency is well beyond the audio
range, and thus does not interfere with audio signals.
The switch drivers feature a controlled switching speed
that minimizes noise generated by turn-on and turn-off
transients. By limiting the switching speed of the charge
pump, the di/dt noise caused by the parasitic trace
inductance is minimized. The charge pump is active only
in headphone modes.
To reduce audible noise at the outputs, the IC’s headphone amplifier includes headphone ground sensing.
Connect the sense line (HPSNS) to the ground terminal
of the device’s headphone jack. Any noise present at
the headphone ground is then added to the headphone
output. The result is elimination of this noise from the
audible output. If ground sensing is not required, connect HPSNS directly to ground. Figure 30 shows a block
diagram of the headphone output section including the
headphone sense function.
Headphone Output Mixers
The IC’s headphone amplifier accepts input from the
stereo DAC and the line inputs. The output of the left and
right DAC cannot be mixed at the headphone mixer. Use
MIXDAL/MIXDAR to mix the left and right audio channels
before conversion.
V
DD
VDD/2
GND
CONVENTIONAL AMPLIFIER BIASING SCHEME
+V
DD
GND
-V
DD
DirectDrive AMPLIFIER BIASING SCHEME
Figure 29. Traditional Amplifier Output vs. DirectDrive Output
96
(VSS)
DACL
DALEN
DACR
DAREN
PGAOUT1:
0dB TO -23dB
PREOUT1
+9dB
PREOUT2
+9dB
PGAOUT2:
0dB TO -23dB
Figure 30. Headphone Amplifier Block Diagram
MIX
MIXHPL
MIX
MIXHPR
HPVOLL:
+3dB TO -67dB
HPL
HPLEN
HPSNS
HPVOLR:
+3dB TO -67dB
HPR
HPREN

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Table 28. Headphone Output Mixer Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7
6
5
4
0x27
3
2
1
0
MIXHPL
MIXHPR
Headphone Output Volume
Table 29. Headphone Output Level Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7 HPLM/HPRM
4
0x38/0x39
3
HPVOLL/HPVOLR
2
1
0
Left Headphone Output Mixer
10xx = Left DAC
01xx = Right DAC (requires DALEN = 0 for proper operation)
11xx = Left DAC
xx1x = Reserved
xxx1 = Preoutput mixer 1
Right Headphone Output Mixer
10xx = Left DAC (requires DAREN = 0 for proper operation)
01xx = Right DAC
11xx = Right DAC
xx1x = Reserved
xxx1 = Preoutput mixer 2
Headphone Output Mute
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
Left/Right Headphone Output Volume Level
VALUE VOLUME (dB) VALUE VOLUME (dB)
0x00 -67 0x10 -15
0x01 -63 0x11 -13
0x02 -59 0x12 -11
0x03 -55 0x13 -9
0x04 -51 0x14 -7
0x05 -47 0x15 -5
0x06 -43 0x16 -4
0x07 -40 0x17 -3
0x08 -37 0x18 -2
0x09 -34 0x19 -1
0x0A -31 0x1A 0
0x0B -28 0x1B +1
0x0C -25 0x1C +1.5
0x0D -22 0x1D +2
0x0E -19 0x1E +2.5
0x0F -17 0x1F +3
MAX9888
97

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Output Bypass Switches
The IC includes two output bypass switches that solve
common applications problems. When a single transducer is used for the loudspeaker and receiver, the need
exists for two amplifiers to power the same transducer.
Bypass switches connect the IC’s receiver amplifier
output to the speaker amplifier’s output, allowing either
amplifier to power the same transducer. In systems where
MAX9888
SPKLP
SPKLN
10I*
10I*
EXTERNAL
RECEIVER
AMP
0dB
RECEN
+6dB
SPLEN
POWER/DISTORTION
SPEAKER AMPLIFIER BYPASS USING THE
RECP/RXINP
0dB
RECEN
RECBYP
SPKBYP
+6dB
SPLEN
POWER/DISTORTION
LIMITER
*OPTIONAL 10I RESISTORS IMPROVE DISTORTION
THROUGH THE ANALOG SWITCH.
SPEAKER AMPLIFIER BYPASS USING AN
RECN/RXINN
SPKLVDD
SPKLGND
EXTERNAL RECEIVER AMPLIFIER
an external receiver amplifier is used, route its output to
the left speaker through RECP/RXINP and RECN/RXINN,
bypassing the Class D amplifier. In systems where an
external amplifier drives both the receiver and the IC’s
line input, one of the differential signals can be disconnected from the receiver when not needed by passing it
through the analog switch that connects RECP/RXINP to
RECN/RXINN.
RECP/RXINP
RECN/RXINN
RECBYP
SPKBYP
SPKLVDD
SPKLP
SPKLN
SPKLGND
LIMITER
INTERNAL RECEIVER AMPLIFIER
0dB
RECEN
RECBYP
SPKBYP
+6dB
SPLEN
POWER/DISTORTION
LIMITER
CONTROLLING AN EXTERNAL RECEIVE
AMPLIFIER AND SPEAKER
EXTERNAL
RECEIVER AMP
RECN/RXINN
RECN/RXINN
SPKLVDD
SPKLP
SPKLN
SPKLGND
Figure 31. Output Bypass Switch Block Diagrams
Table 30. Output Bypass Switches Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
7 INABYP
4 MIC2BYP
1 RECBYP
0x48
0 SPKBYP
98
See the Microphone Inputs section.
RXINP to RXINN Bypass Switch
Shorts RXINP to RXINN allowing a signal to pass through the MAX9888. Disable the
receiver amplifier when RECBYP = 1.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled
RXIN to SPKL Bypass Switch
Shorts RXINP/RXINN to SPKLP/SPKLN allowing either the internal or an external
receiver amplifier to power the left speaker. Disable the left speaker amplifier when
SPKBYP = 1.
0 = Disabled
1 = Enabled

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Click-and-Pop Reduction
The IC includes extensive click-and-pop reduction circuitry. The circuitry minimizes clicks and pops at turn-on,
turn-off, and during volume changes.
Zero-crossing detection is implemented on all analog
PGAs and volume controls to prevent large glitches
when volume changes are made. Instead of making a
volume change immediately, the change is made when
the audio signal crosses the midpoint. If no zero-crossing
occurs within the timeout window, the change is forced.
Volume slewing breaks up large volume changes into the
smallest available step size and the steps through each
step between the initial and final volume setting. When
Table 31. Click-and-Pop Reduction Register
REGISTER BIT NAME DESCRIPTION
Enhanced Volume Smoothing
During volume slewing, the controller waits for each step in the ramp to be applied
before sending the next step. When zero-crossing detection is enabled this prevents
7 VS2EN
6 VSEN
0x49
5 ZDEN
1 EQ2EN
0 EQ1EN
large steps in the output volume when no zero crossings are detected.
0 = Enabled
1 = Disabled
Applies to volume changes in HPVOLL, HPVOLR, RECVOL, SPVOLL, and SPVOLR.
Volume Adjustment Smoothing
Volume changes are smoothed by stepping through intermediate steps. Also ramps
the volume from minimum to the programmed value at turn-on and back to minimum at
turn-off.
0 = Enabled
1 = Disabled
Applies to volume changes in HPVOLL, HPVOLR, RECVOL, SPVOLL, and SPVOLR.
Zero-Crossing Detection
Holds volume changes until there is a zero crossing in the audio signal. This reduces
click and pop during volume changes (zipper noise). If no zero crossing is detected
within 100ms, the volume change is forced.
0 = Enabled
1 = Disabled
Applies to volume changes in PGAM1, PGAM2, PGAOUTA, PGAOUTB, PGAOUTC,
HPVOLL, HPVOLR, RECVOL, SPVOLL, and SPVOLR.
See the 5-Band Parametric EQ section.
enabled, volume slewing also occurs at device turn-on
and turn-off. During turn-on the volume is set to mute
before the output is enabled. Once the output is on, the
volume ramps to the desired level. At turn-off the volume
is ramped to mute before the outputs are disabled.
When there is no audio signal zero-crossing detection
can prevent volume slewing from occurring. Enable
enhanced volume slewing to prevent the volume controller from requesting another volume level until the previous one has been set. Each step in the volume ramp
then occurs after a zero crossing has occurred in the
audio signal or the timeout window has expired. During
turn-off, enhance volume slewing is always disabled.
MAX9888
99

Stereo Audio CODEC
with FlexSound Technology
Jack Detection
The IC features jack detection that can detect the insertion and removal of a jack as well as the load type. When
a jack is detected, an interrupt on IRQ can be triggered
to alert the microcontroller of the event. Figure 32 shows
the typical configuration for jack detection.
Jack Insertion
To detect a jack insertion, the IC must have a power
MAX9888
supply and MICBIAS should be disabled. Set JDETEN
to enable jack detection circuitry and apply a pullup current to JACKSNS. Set JDWK to minimize supply current.
Clear JDWK to differentiate between headsets with a
microphone and headphones without a microphone. The
voltage on JACKSNS is equal to SPKLVDD as long as no
Figure 32. Typical Configuration for Jack Detection
load is applied to JACKSNS. Table 32 shows the change
in JKSNS that occurs when a jack is inserted.
Accessory Button Detection
After jack insertion, the MAX9888 can detect button
presses on accessories that include a microphone and
a switch that shorts the microphone signal to ground.
Set JDETEN to enable jack detection circuitry. A pullup
current is automatically applied to JACKSNS if MICBIAS
is disabled. Clear JDWK to allow differentiation between
the microphone load and a short to ground. Button
presses can be detected both when MICBIAS is enabled
and disabled. Table 33 shows the change in JKSNS that
occurs when the accessory button is pressed.
HPL
HPR
MICBIAS
JACKSNS
MIC1P
Table 32. Change in JKSNS Upon Jack Insertion
JACK TYPE JDWK = 1 JDWK = 0
GND GND R L
MIC GND R L
JKSNS: 11 è 00 JKSNS: 11 è 00
JKSNS: 11 è 00 JKSNS: 11 è 01
Table 33. Change in JKSNS Upon Button Press
JACK TYPE MICBIAS ENABLED OR DISABLED
MIC GND R L
JKSNS: 01 è 00
100
 Loading...
Loading...