Page 1
General Description
The MAX9326 low-skew, 1:9 differential driver features
extremely low output-to-output skew (50ps max) and
part-to-part skew (225ps max). These features make
the device ideal for clock and data distribution across a
backplane or board. The device repeats an HSTL or
LVECL/LVPECL differential input at nine differential outputs. Outputs are compatible with LVECL and LVPECL,
and directly drive 50Ω terminated transmission lines.
The differential inputs can be configured to accept a
single-ended signal when the unused complementary
input is connected to the on-chip reference output voltage V
BB.
All inputs have internal pulldown resistors to
V
EE.
The internal pulldowns and a fail-safe circuit
ensure differential low default outputs when the inputs
are left open or at VEE.
The MAX9326 operates over a +2.375V to +3.8V supply
range for interfacing to differential HSTL and LVPECL
signals. This allows high-performance clock or data distribution in systems with a nominal +2.5V or +3.3V supply. For LVECL operation, the device operates with a
-2.375V to -3.8V supply.
The MAX9326 is offered in 28-lead PLCC and spacesaving 28-lead QFN packages. The MAX9326 is specified for operation from -40°C to +85°C.
Applications
Precision Clock Distribution
Low-Jitter Data Repeaters
Features
♦ 50ps (max) Output-to-Output Skew
♦ 1.5ps
RMS
(max) Random Jitter
♦ Guaranteed 300mV Differential Output at 1.0GHz
♦ +2.375V to +3.8V Supplies for Differential
HSTL/LVPECL
♦ -2.375V to -3.8V Supplies for Differential LVECL
♦ On-Chip Reference for Single-Ended Inputs
♦ Outputs Low for Inputs Open or at V
EE
♦ Pin Compatible with MC100LVE111
MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
________________________________________________________________ Maxim Integrated Products 1
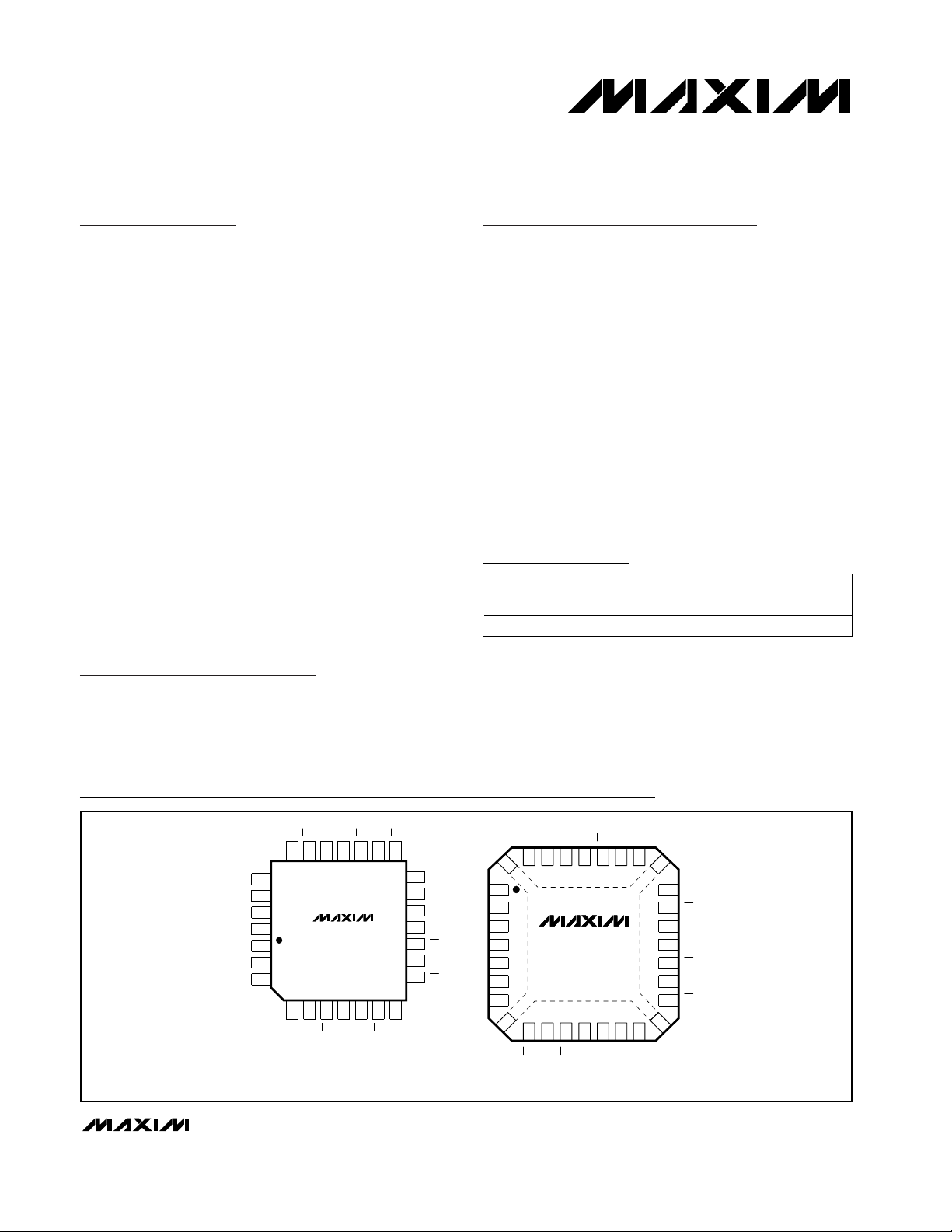
Pin Configurations
Ordering Information
19-2538; Rev 2; 10/02
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim/Dallas Direct! at
1-888-629-4642, or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
Functional Diagram appears at end of data sheet.
MAX9326EQI -40°C to +85°C 28 PLCC
MAX9326EGI -40°C to +85°C 28 QFN 5mm x 5mm
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
TOP VIEW
V
EE
N.C.
CLK
V
CC
CLK
V
BB
N.C.
Q0
Q1
Q0
26
27
28
1
2
3
4
MAX9326
567891011
Q7
Q8
Q8
PLCC
CC
V
22232425 192021
CC
V
Q2
Q2
Q1
Q3
18
Q3
17
Q4
16
V
15
CC
14
Q4
13
Q5
12
Q5
Q6
Q6
Q7
1
V
EE
2
N.C.
3
CLK
4
V
CC
5
CLK
6
V
BB
7
N.C.
*CORNER PINS AND EXPOSED PAD ARE CONNECTED TO V
Q1
Q0
28272625242322
8
Q8
VCCQ1
Q0
MAX9326
9
1011121314
CC
Q7
Q8
V
QFN*
Q7
Q2
Q2
Q3
21
Q3
20
Q4
19
18
V
CC
17
Q4
16
Q5
15
Q5
Q6
Q6
.
EE
Page 2
MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
((VCC- VEE) = 2.375V to 3.8V, RL= 50Ω±1% to V
CC
- 2V. Typical values are at (VCC- VEE) = 3.3V, VIH= (VCC- 1V), VIL= (VCC-
1.5V).) (Notes 1–4)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
VCC- VEE...............................................................-0.3V to +4.1V
Inputs (CLK, CLK) to V
EE
...........................-0.3V to (V
CC
+ 0.3V)
CLK to CLK ........................................................................±3.0V
Continuous Output Current .................................................50mA
Surge Output Current........................................................100mA
V
BB
Sink/Source Current................................................±0.65mA
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +70°C)
28-Lead PLCC (derate 10.5mW/°C above +70°C) .....842mW
θ
JA
in Still Air .............................................................+95°C/W
θ
JC
.............................................................................+25°C/W
28-Lead QFN (derate 20.8mW/°C above +70°C) .....1667mW
θ
JA
in Still Air .............................................................+48°C/W
θ
JC
...............................................................................+2°C/W
Operating Temperature Range ...........................-40°C to +85°C
Junction Temperature......................................................+150°C
Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C
ESD Protection
Human Body Model (CLK, CLK, Q_, Q_) .........................≥2kV
Soldering Temperature (10s) ...........................................+300°C
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT (CLK_, CLK_)
Single-Ended
Input High
V
Figure 1
IH
Voltage
-40°C +25°C +85°C
MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX
V
CC
- 1.165
V
V
CC
CC
- 1.165
V
CC
V
CC
- 1.165
V
CC
UNITS
V
Single-Ended
Input Low
Voltage
Differential Input
High Voltage
Differential Input
Low Voltage
Differential Input
V
Voltage
Input Current I
V
V
V
V
IHD
ILD
IHD
ILD
IN
Figure 1 V
IL
Figure 1
Figure 1 V
(V
CC
3.0V, Figure 1
-
(VCC - VEE) ≥
3.0V, Figure 1
V
IH, VIL
V
ILD
- V
, V
EE
) <
IHD
EE
V
EE
+ 1.2
EE
0.095
V
CC
- 1.475
V
CC
V
CC
- 0.095
V
CC
- V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
+ 1.2
V
EE
0.095
V
CC
- 1.475
V
CC
V
CC
- 0.095
V
CC
- V
EE
V
EE
V
EE
+ 1.2
V
EE
0.095
0.095 3.0 0.095 3.0 0.095 3.0
,
-10.0 +150.0 -10.0 +150.0 -10.0 +150.0 µA
VCC
- 1.475
V
CC
V
CC
- 0.095
V
CC
- VEE
V
V
V
V
Page 3
MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
((VCC- VEE) = 2.375V to 3.8V, RL= 50Ω±1% to V
CC
- 2V. Typical values are at (VCC- VEE) = 3.3V, VIH= (VCC- 1V), VIL= (VCC-
1.5V).) (Notes 1–4)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS
OUTPUT (Q_, QQQQ____)
Single-Ended
Output High
V
OH
Figure 2
Voltage
Single-Ended
Output Low
V
OL
Figure 2
Voltage
Differential
Output Voltage
- VOLFigure 2 535 718 595 749 595 769 mV
V
OH
REFERENCE VOLTAGE OUTPUT (VBB)
Reference
Voltage Output
V
BB
IBB = ±0.5mA
(Note 5)
SUPPLY
Supply Current I
(Note 6) 35 50 39 55 42 65 mA
EE
-40°C +25°C +85°C
MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX
V
- 1.085
V
- 1.810
V
- 1.38
CC
CC
CC
V
CC
- 0.977
V
CC
- 1.695
V
CC
- 1.318
V
CC
- 0.880
V
CC
- 1.620
V
CC
- 1.26
V
CC
- 1.025
V
CC
- 1.810
V
CC
- 1.38
V
CC
- 0.949
V
CC
- 1.697
V
CC
- 1.325
V
CC
- 0.88
V
CC
- 1.62
V
CC
- 1.26
V
CC
- 1.025
V
CC
- 1.810
V
CC
- 1.38
V
CC
- 0.929
V
CC
- 1.698
V
CC
- 1.328
V
CC
- 0.88
V
CC
- 1.62
V
CC
- 1.26
UNITS
V
V
V
Page 4
MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS–PLCC Package
((VCC- VEE) = 2.375V to 3.8V, RL= 50Ω±1% to V
CC
- 2V, fIN≤ 500MHz, input transition time = 125ps (20% to 80%). Typical values
are at (V
CC
- VEE) = 3.3V, VIH= V(VCC- 1V), VIL= (VCC- 1.5V).) (Note 7)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS
Differential
Input-to-Output
Delay
Single-Ended
Input-to-Output
Delay
t
PLHD
t
PHLD
t
PLH
t
PHL
Figure 2 365 615 375 605 383 653 ps
Figure 3 (Note 8) 350 635 360 685 360 705 ps
-40°C +25°C +85°C
MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX
UNITS
Output-toOutput Skew
Part-to-Part
Skew
Added Random
Jitter
Added
Deterministic
Jitter
Switching
Frequency
Output Rise/Fall
Time (20% to
80%)
t
SKOO
t
SKPP
t
t
f
MAX
t
R
(Note 9) 50 50 50 ps
Differential input
(Note 10)
fIN = 0.5GHz
clock pattern
RJ
(Note 11)
fIN = 1.0Gbps,
23
- 1 PRBS
2E
DJ
pattern (Note 11)
OL
≥
1.5 1.5 1.5 GHz
VOH - V
300mV clock
pattern
, tFFigure 2 140 440 140 440 140 440 ps
190 125 240 ps
1.5 1.5 1.5 ps
95 95 95 ps
RMS
P-P
Page 5

MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS–QFN Package
((VCC- VEE) = 2.375V to 3.8V, RL= 50Ω±1% to V
CC
- 2V, fIN≤ 500MHz, input transition time = 125ps (20% to 80%). Typical values
are at (V
CC
- VEE) = 3.3V, VIH= V(VCC- 1V), VIL= (VCC- 1.5V).) (Note 7)
Note 1: Measurements are made with the device in thermal equilibrium.
Note 2: Current into a pin is defined as positive. Current out of a pin is defined as negative.
Note 3: DC parameters production tested at T
A
= +25°C and guaranteed by design over the full operating temperature range.
Note 4: Single-ended input operation using V
BB
is limited to (VCC- VEE) = 3.0V to 3.8V.
Note 5: Use V
BB
only for inputs that are on the same device as the V
BB
reference.
Note 6: All pins open except V
CC
and VEE.
Note 7: Guaranteed by design and characterization. Limits are set at ±6 sigma.
Note 8: Measured from the 50% point of the input signal with the 50% point equal to V
BB
, to the 50% point of the output signal.
Note 9: Measured between outputs of the same part at the signal crossing points for a same-edge transition. Differential input signal.
Note 10: Measured between outputs of different parts under identical conditions for same-edge transition.
Note 11: Device jitter added to the input signal. Differential input signal.
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS
Differential
Input-to-Output
Delay
Single-Ended
Input-to-Output
Delay
Output-toOutput Skew
Part-to-Part
Skew
Added Random
Jitter
Added
Deterministic
Jitter
Switching
Frequency
t
PLHD
t
PHLD
t
t
t
SKOO
t
SKPP
f
MAX
Figure 2 217 541 238 448 249 486 ps
PLH
Figure 3 (Note 8) 213 558 230 506 244 503 ps
PHL
(Note 9) 50 50 50 ps
Differential input
(Note 10)
fIN = 0.5GHz
t
clock pattern
RJ
(Note 11)
fIN = 1.0Gbps,
23
- 1 PRBS
2E
t
DJ
pattern (Note 11)
OL
≥
VOH - V
300mV clock
pattern
-40°C +25°C +85°C
MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX
192 215 218 ps
1.5 1.5 1.5 ps
95 95 95 ps
1.5 1.5 1.5 GHz
UNITS
RMS
P-P
Output Rise/Fall
Time (20% to
80%)
t
, tFFigure 2 97 411 104 210 111 232 ps
R
Page 6

OUTPUT TRANSITION TIME
vs. TEMPERATURE
TRANSITION TIME (ps)
200
240
280
320
360
400
160
MAX9326 toc03
TEMPERATURE (°C)
603510-15-40 85
t
F
t
R
300
400
600
500
700
800
OUTPUT AMPLITUDE (VOH - VOL)
vs. FREQUENCY
MAX9326 toc02
FREQUENCY (MHz)
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0 500 1000 1500
SUPPLY CURRENT (IEE)
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX9326 toc01
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
603510-15
25
30
35
40
45
50
20
-40 85
MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Typical Operating Characteristics
(PLCC package, typical values are at (VCC- VEE) = 3.3V, VIH= (VCC- 1V), VIL= (VCC- 1.5V), RL= 50Ω±1% to V
CC
- 2V, fIN=
500MHz, input transition time = 125ps (20% to 80%).)
PROPAGATION DELAY
750
vs. TEMPERATURE
650
t
PHLD
550
PROPAGATION DELAY (ps)
t
PLHD
450
-40 85
TEMPERATURE (°C)
MAX9326 toc05
603510-15
Page 7

MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
Pin Description
PIN
PLCC QFN
1, 8, 15, 22 4, 11, 18, 25 V
25CLK Inverting Differential Clock Input. Internal 105kΩ pulldown to VEE.
36V
4, 27 2, 7 N.C. Not Connected
58Q8 Inverting Q8 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
6 9 Q8 Noninverting Q8 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
710Q7 Inverting Q7 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
9 12 Q7 Noninverting Q7 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
10 13 Q6 Inverting Q6 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
11 14 Q6 Noninverting Q6 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
12 15 Q5 Inverting Q5 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
13 16 Q5 Noninverting Q5 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
14 17 Q4 Inverting Q4 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
16 19 Q4 Noninverting Q4 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
17 20 Q3 Inverting Q3 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
18 21 Q3 Noninverting Q3 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
19 22 Q2 Inverting Q2 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
20 23 Q2 Noninverting Q2 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
21 24 Q1 Inverting Q1 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
23 26 Q1 Noninverting Q1 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
24 27 Q0 Inverting Q0 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
25 28 Q0 Noninverting Q0 Output. Typically terminate with 50Ω resistor to VCC - 2V.
26 1 V
28 3 CLK Noninverting Differential Clock Input. Internal 105kΩ pulldown to VEE.
—
Exposed
Pad
NAME FUNCTION
Positive Supply Voltage. Bypass each VCC to VEE with 0.1µF and 0.01µF ceramic
CC
BB
EE
— Internally Connected to V
capacitors. Place the capacitors as close to the device as possible with the smaller
value capacitor closest to the device.
Reference Output Voltage. Connect to the inverting or noninverting clock input to
provide a reference for single-ended operation. When used, bypass V
0.01µF ceramic capacitor. Otherwise leave open.
Negative Supply Voltage
EE
to VCC with a
BB
Page 8

MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Figure 1. Input Voltage Definitions
Figure 2. Differential Input (CLK,
CLK
) to Output (Q_, Q_) Delay Timing Diagram
V
CC
V
IHD
V
V
IHD
EE
- V
- V
(MAX)
V
IHD
ILD
V
(MAX)
ILD
(MIN)
V
IHD
ILD
V
(MIN)
ILD
V
CC
V
BB
V
EE
V
IH
V
IL
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT VOLTAGE DEFINITION
CLK
CLK
Q_
Q_
t
PLHD
80%
SINGLE-ENDED INPUT VOLTAGE DEFINITION
V
IHD
- V
V
IHD
ILD
V
ILD
t
PHLD
V
OH
V
- V
OH
OL
V
OL
80%
V
- V
OH
OL
0V (DIFFERENTIAL)
V
- V
OH
OL
20%
t
F
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT WAVEFORM
Q_ - Q_
20%
t
R
Page 9

MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
Detailed Description
The MAX9326 low-skew, 1:9 differential driver features
extremely low output-to-output skew (50ps max) and partto-part skew (225ps max). These features make the
device ideal for clock and data distribution across a
backplane or board. The device repeats an HSTL or
LVECL/LVPECL differential input at nine differential outputs. Outputs are compatible with LVECL and LVPECL,
and can directly drive 50Ω terminated transmission lines.
The differential inputs (CLK, CLK) can be configured to
accept a single-ended signal when the unused complementary input is connected to the on-chip reference
output voltage (VBB). A single-ended input of at least
VBB±95mV or a differential input of at least 95mV
switches the outputs to the VOHand VOLlevels specified in the DC Electrical Characteristics. The maximum
magnitude of the differential input from CLK to CLK is
±3.0V or ±(VCC- VEE), whichever is less. This limit also
applies to the difference between a single-ended input
and any reference voltage input.
All the differential inputs have 105kΩ pulldowns to VEE.
Internal pulldowns and a fail-safe circuit ensure differential low default outputs when the inputs are left open
or at VEE.
Specifications for the high and low voltages of a differential input (V
IHD
and V
ILD
) and the differential input
voltage (V
IHD
- V
ILD
) apply simultaneously.
For interfacing to differential HSTL and LVPECL signals,
these devices operate over a 2.375V to 3.8V supply
range, allowing high-performance clock or data distribution in systems with a nominal 2.5V or 3.3V supply. For
differential LVECL operation, these devices operate
from a -2.375V to -3.8V supply.
Single-Ended Operation
The differential inputs (CLK, CLK) can be configured to
accept single-ended inputs when operating at supply
voltages greater than 2.58V. The recommended supply
voltage for single-ended operation is 3.0V to 3.8V. A differential input is configured for single-ended operation
by connecting the on-chip reference voltage, VBB, to an
unused complementary input as a reference. For example, the differential CLK, CLK input is converted to a noninverting, single-ended input by connecting VBBto CLK
and connecting the single-ended input to CLK. Similarly,
an inverting input is obtained by connecting V
BB
to CLK
and connecting the single-ended input to CLK. With a
differential input configured as single ended (using VBB),
the single-ended input can be driven to VCCor VEEor
with a single-ended LVPECL/LVECL signal.
Figure 3. Single-Ended Input (CLK,
CLK
) to Output (Q_, Q_) Delay Timing Diagram
CLK WHEN CLK = V
CLK WHEN CLK = V
Q_
Q_
BB
V
BB
OR
V
BB
BB
t
PLH
V
IH
V
BB
V
IL
V
IH
V
BB
V
IL
t
PHL
V
OH
VOH - V
OL
V
OL
Page 10

MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
When configuring a differential input as a single-ended
input, a user must ensure that the supply voltage (VCCVEE) is greater than 2.58V. This is because the input high
minimum level must be at (VEE+ 1.2V) or higher for proper operation. The reference voltage VBBmust be at least
(VEE+ 1.2V) or higher for the same reason because it
becomes the high-level input when the other singleended input swings below it. The minimum VBBoutput for
the MAX9326 is (VCC- 1.38V). Substituting the minimum
VBBoutput for (VBB= VEE+ 1.2V) results in a minimum
supply (V
CC
- VEE) of 2.58V. Rounding up to standard
supplies gives the single-ended operating supply ranges
(VCC- VEE) of 3.0V to 3.8V for the MAX9326.
When using the VBBreference output, bypass it with a
0.01µF ceramic capacitor to VCC. If not used, leave it
open. The VBBreference can source or sink 0.5mA,
which is sufficient to drive two inputs.
Applications Information
Output Termination
Terminate the outputs through 50Ω to VCC- 2V or use
equivalent Thevenin terminations. Terminate each Q and
Q output with identical termination on each for the lowest
output distortion. When a single-ended signal is taken
from the differential output, terminate both Q_ and Q_.
Ensure that output currents do not exceed the current
limits as specified in the Absolute Maximum Ratings.
Under all operating conditions, the device’s total thermal limits should be observed.
Supply Bypassing
Bypass each VCCto VEEwith high-frequency surfacemount ceramic 0.1µF and 0.01µF capacitors. Place the
capacitors as close to the device as possible with the
0.01µF capacitor closest to the device pins.
Use multiple vias when connecting the bypass capacitors to ground. When using the VBBreference output,
bypass it with a 0.01µF ceramic capacitor to VCC. If the
V
BB
reference is not used, it can be left open.
Traces
Circuit board trace layout is very important to maintain
the signal integrity of high-speed differential signals.
Maintaining integrity is accomplished in part by reducing signal reflections and skew, and increasing common-mode noise immunity.
Signal reflections are caused by discontinuities in the
50Ω characteristic impedance of the traces. Avoid discontinuities by maintaining the distance between differential traces, not using sharp corners or using vias.
Maintaining distance between the traces also increases
common-mode noise immunity. Reducing signal skew
is accomplished by matching the electrical length of
the differential traces.
Exposed-Pad Package
The 28-lead QFN package (MAX9326EGI) has the
exposed paddle on the bottom of the package that provides the primary heat removal path from the IC to the
PC board, as well as excellent electrical grounding to
the PC board. The MAX9326EGI’s exposed pad is
internally connected to VEE. Do not connect the
exposed pad to a separate circuit ground plane
unless VEEand the circuit ground are the same.
Chip Information
TRANSISTOR COUNT: 1030
PROCESS: Bipolar
Q0
Q0
Q1
Q1
Q2
Q2
Q3
Q3
Q4
CLK
CLK
105kΩ
V
EE
Q4
Q5
Q5
Q6
Q6
Q7
Q7
Q8
Q8
Functional Diagram
Page 11

MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
______________________________________________________________________________________ 11
Package Information
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages.)
e
INCHES
MIN
A 0.165
A2
D3D1D
N
0.145
A3
0.020
B
0.013
B1
0.026
C
0.009
0.050
e
MAX
0.180
0.1200.090A1
0.156
---
0.021
0.032
0.011
MIN
4.20
2.29
3.69
0.51
0.33
0.66
0.23
1.27
MAX
4.57
3.04
3.96
---
0.53
0.81
0.28
D3
D1
D
A
A1
A2
B1
B
A3
D2
C
INCHES
MIN
MAX
0.385
D
D1D20.350
D
D1
D2
D3
D
D1
D2
D3
D
D1
D2
D
D1
D2 0.890 0.930
0.395
0.356
0.290
0.330
REFD3 0.200
0.495
0.485
0.456
0.450
0.430
0.390
REF
0.300
0.695
0.685
0.650
0.656
0.590
0.630
REF
0.500
0.785
0.795
0.750
0.756
0.690
0.730
0.995
0.985
0.950
0.958
REF REF
MIN
9.78
8.89
7.37
5.08
12.32
11.43
9.91
7.62
17.40
16.51
14.99
12.70
19.94
19.05
17.53
25.02
24.13
22.61
20.320.800D3
MAX
10.03
9.04
8.38
REF
12.57
11.58
10.92
REF
17.65
16.66
16.00
REF
20.19
19.20
18.54
REFREFD3 0.600 15.24
25.27
24.33
23.62
N
20
28
44
52
68
PLCC.EPS
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
NOTES:
1. D1 DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD FLASH.
2. MOLD FLASH OR PROTRUSIONS NOT TO EXCEED
.20mm (.008") PER SIDE.
3. LEADS TO BE COPLANAR WITHIN .10mm.
4. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: MILLIMETER
5. MEETS JEDEC MO047-XX AS SHOWN IN TABLE.
6. N = NUMBER OF PINS.
PROPRIETARY INFORMATION
TITLE:
FAMILY PACKAGE OUTLINE:
20L, 28L, 44L, 52L, 68L PLCC
21-0049
REV.DOCUMENT CONTROL NO.APPROVAL
1
D
1
Page 12

MAX9326
1:9 Differential LVPECL/LVECL/HSTL Clock and
Data Driver
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
12 ____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 2002 Maxim Integrated Products Printed USA is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products.
Package Information (continued)
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages.)
32L QFN.EPS
 Loading...
Loading...