Page 1

General Description
The MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238 deserialize three
LVDS serial-data inputs into 21 single-ended
LVCMOS/LVTTL outputs. A parallel-rate LVDS clock
received with the LVDS data streams provides timing for
deserialization. The outputs have a separate supply,
allowing 1.8V to 5V output logic levels. All these devices
are hot-swappable and allow “on-the-fly” frequency
programming.
The MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238 feature DC balance,
which allows isolation between a serializer and deserializer using AC-coupling. Each deserializer decodes
data transmitted by one of the MAX9209/MAX9211/
MAX9213/MAX9215 serializers.
The MAX9234 has a rising-edge output strobe. The
MAX9236/MAX9238 have a falling-edge output strobe.
The MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238 operate in DCbalanced mode only.
The MAX9234/MAX9236 operate with a parallel input
clock of 8MHz to 34MHz, while the MAX9238 operates
from 16MHz to 66MHz. The transition time of the singleended outputs is increased on the low-frequency version
parts (MAX9234/MAX9236) for reduced EMI. The LVDS
inputs meet ISO 10605 ESD specification, ±25kV for AirGap Discharge and ±8kV Contact Discharge.
The MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238 are available in 48-pin
TSSOP packages and operate over the -40°C to +85°C
temperature range.
Applications
Automotive Navigation Systems
Automotive DVD Entertainment Systems
Digital Copiers
Laser Printers
Features
♦ DC Balance Allows AC-Coupling for Wider Input
Common-Mode Voltage Range
♦ On-the-Fly Frequency Programming
♦ Operating Frequency Range
8MHz to 34MHz (MAX9234/MAX9236)
16MHz to 66MHz (MAX9238)
♦ Falling-Edge Output Strobe (MAX9236/MAX9238)
♦ Slower Output Transitions for Reduced EMI
(MAX9234/MAX9236)
♦ High-Impedance Outputs when PWRDWN Is Low
Allow Output Busing
♦ 5V-Tolerant PWRDWN Input
♦ PLL Requires No External Components
♦ Up to 1.386Gbps Throughput
♦ Separate Output Supply Pins Allow Interface to
1.8V, 2.5V, 3.3V, and 5V Logic
♦ LVDS Inputs Meet ISO 10605 ESD Requirements
♦ LVDS Inputs Conform to ANSI TIA/EIA-644 LVDS
Standard
♦ Low-Profile, 48-Lead TSSOP Package
♦ +3.3V Main Power Supply
♦ -40°C to +85°C Operating Temperature Range
MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
________________________________________________________________ Maxim Integrated Products 1
Ordering Information
19-3641; Rev 1; 10/07
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim Direct at 1-888-629-4642,
or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
Functional Diagram and Pin Configuration appear at end of
data sheet.
PART
TEMP RANGE
PINPACKAGE
PKG
CODE
MAX9234EUM
48 TSSOP
U48-1
MAX9236EUM
48 TSSOP
U48-1
MAX9238EUM
48 TSSOP
U48-1
-40°C to +85°C
-40°C to +85°C
-40°C to +85°C
Page 2
MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VCC= +3.0V to +3.6V, V
CCO
= +3.0V to +5.5V, PWRDWN = high, differential input voltage ⏐VID⏐ = 0.05V to 1.2V, input common-
mode voltage V
CM
= ⏐VID/2⏐ to 2.4V - ⏐VID/2⏐, TA= -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at VCC= V
CCO
=
+3.3V, ⏐V
ID
⏐ = 0.2V, VCM= 1.25V, TA= +25°C.) (Notes 1, 2)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
VCCto GND...........................................................-0.5V to +4.0V
V
CCO
to GND.........................................................-0.5V to +6.0V
RxIN_, RxCLK IN_ to GND ....................................-0.5V to +4.0V
PWRDWN to GND....................................................-0.5V to 6.0V
RxOUT_, RxCLK OUT to GND ................-0.5V to (V
CCO
+ 0.5V)
Continuous Power Dissipation (TA= +70°C)
48-Pin TSSOP (derate 16mW/°C above +70°C) ....... 1282mW
Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature......................................................+150°C
ESD Protection
Human Body Model (RD= 1.5kΩ, CS= 100pF)
All Pins to GND ..................................………………….±5kV
IEC 61000-4-2 (RD= 330Ω, CS = 150pF)
Contact Discharge (RxIN_, RxCLK IN_) to GND .........±8kV
Air-Gap Discharge (RxIN_, RxCLK IN_) to GND .......±15kV
ISO 10605 (RD= 2kΩ, CS= 330pF)
Contact Discharge (RxIN_, RxCLK IN_) to GND ........±8kV
Air Discharge (RxIN_, RxCLK IN_) to GND ...............±25kV
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
SINGLE-ENDED INPUT (PWRDWN)
High-Level Input Voltage V
IH
2.0 5.5 V
Low-Level Input Voltage V
IL
V
Input Current I
IN
VIN = high or low -70
µA
Input Clamp Voltage V
CL
ICL = -18mA
V
SINGLE-ENDED OUTPUTS (RxOUT_, RxCLK OUT)
IOH = -100µA
V
CCO
-
0.1
V
CCO
-
MAX9234/
MAX9236
RxOUT_
V
CCO
-
High-Level Output Voltage V
OH
IOH = -2mA
MAX9238
V
CCO
-
V
IOL = 100µA 0.1
RxOUT_
Low-Level Output Voltage V
OL
IOL = 2mA
MAX9238 0.2
V
High-Impedance Output Current
I
OZ
PWRDWN = low,
V
OUT_
= -0.3V to V
CCO
+ 0.3V
-20
µA
-10 -40
MAX9234/
RxOUT_ -5 -20
V
CCO
= 3.0V to
MAX9238 -10 -40
-28 -75
MAX9234/
RxOUT_ -14 -37
Output Short-Circuit Current
(Note: Short one output at a
time.)
I
OS
V
CCO
= 4.5V to
MAX9238 -28 -75
mA
3.6V, V
5.5V, V
OUT
OUT
-0.3 +0.8
+70
-1.5
RxCLK OUT
RxCLK OUT 0.2
MAX9234/
MAX9236
MAX9236
= 0
MAX9236
= 0
RxCLK OUT
RxCLK OUT
0.25
0.40
0.25
0.26
+20
Page 3
MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VCC= +3.0V to +3.6V, V
CCO
= +3.0V to +5.5V, PWRDWN = high, differential input voltage ⏐VID⏐ = 0.05V to 1.2V, input common-
mode voltage V
CM
= ⏐VID/2⏐ to 2.4V - ⏐VID/2⏐, TA= -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at VCC= V
CCO
=
+3.3V, ⏐V
ID
⏐ = 0.2V, VCM= 1.25V, TA= +25°C.) (Notes 1, 2)
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
LVDS INPUTS
Differential Input-High Threshold
V
TH
50 mV
Differential Input-Low Threshold V
TL
-50 mV
Input Current
PWRDWN = high or low -25
µA
Power-Off Input Current
VCC = V
CCO
= 0 or open,
PWRDWN = 0 or open
-40
µA
PWRDWN = high or low (Figure 1)
Input Resistor 1 R
IN1
VCC = V
CCO
= 0 or open (Figure 1)
42 78 kΩ
POWER SUPPLY
8MHz 42
16MHz 57
MAX9234/
MAX9236
34MHz 98
16MHz 63
34MHz
Worst-Case Supply Current I
CCW
CL = 8pF,
worst-case
pattern; V
CC
=
V
CCO
= 3.0V to
3.6V, Figure 2
MAX9238
66MHz
mA
Power-Down Supply Current I
CCZ
PWRDWN = low 50 µA
I
IN+, IIN-
I
INO+, IINO-
+25
+40
106
177
Page 4
MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Note 1: Current into a pin is defined as positive. Current out of a pin is defined as negative. All voltages are referenced to ground
except V
TH
and VTL.
Note 2: Maximum and minimum limits overtemperature are guaranteed by design and characterization. Devices are production
tested at T
A
= +25°C.
Note 3: AC parameters are guaranteed by design and characterization, and are not production tested. Limits are set at ±6 sigma.
Note 4: C
L
includes probe and test jig capacitance.
Note 5: RCIP is the period of RxCLK IN. RCOP is the period of RxCLK OUT. RCIP = RCOP.
Note 6: RSKM measured with
≤
150ps cycle-to-cycle jitter on RxCLK IN.
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VCC= V
CCO
= +3.0V to +3.6V, 100mV
P-P
at 200kHz supply noise, CL= 8pF, PWRDWN = high, differential input voltage ⏐VID⏐ =
0.1V to 1.2V, input common mode voltage V
CM
= ⏐VID/2⏐ to 2.4V - ⏐VID/2⏐, TA= -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical
values are at V
CC
= V
CCO
= +3.3V, ⏐VID⏐ = 0.2V, VCM= 1.25V, TA= +25°C.) (Notes 3, 4, 5)
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
RxOUT
MAX9234/
MAX9236
2.2
3.9
Output Rise Time CLHT
0.1V
CCO
to
0.9V
CCO
,
Figure 3
MAX9238 2.2
3.9
ns
RxOUT
MAX9234/
MAX9236
1.3
2.9Output Fall Time CHLT
0.9V
CCO
to
0.1V
CCO
,
Figure 3
MAX9238 1.3
2.9
ns
8MHz
16MHz
34MHz
RxIN Skew Margin RSKM
Figure 4
(Note 6)
MAX9238 66MHz
ps
RxCLK OUT High Time RCOH Figures 5a, 5b
0.35 x
ns
RxCLK OUT Low Time RCOL Figures 5a, 5b
0.35 x
ns
RxOUT Setup to RxCLK OUT RSRC Figures 5a, 5b
0.30 x
ns
RxOUT Hold from RxCLK OUT RHRC Figures 5a, 5b
0.45 x
ns
RxCLK IN to RxCLK OUT Delay RCCD Figures 6a, 6b 4.9
8.1 ns
Deserializer Phase-Locked Loop
Set
RPLLS Figure 7
32800
ns
Deserializer Power-Down Delay RPDD Figure 8
ns
3.52 5.04 6.24
RxCLK OUT
1.95 3.18 4.35
RxCLK OUT
6600 7044
2560 3137
900 1327
330 685
RCOP
RCOP
3.15
3.15
2.12
2.12
RCOP
RCOP
6.17
x RCIP
100
Page 5
MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
MAX9234/MAX9236
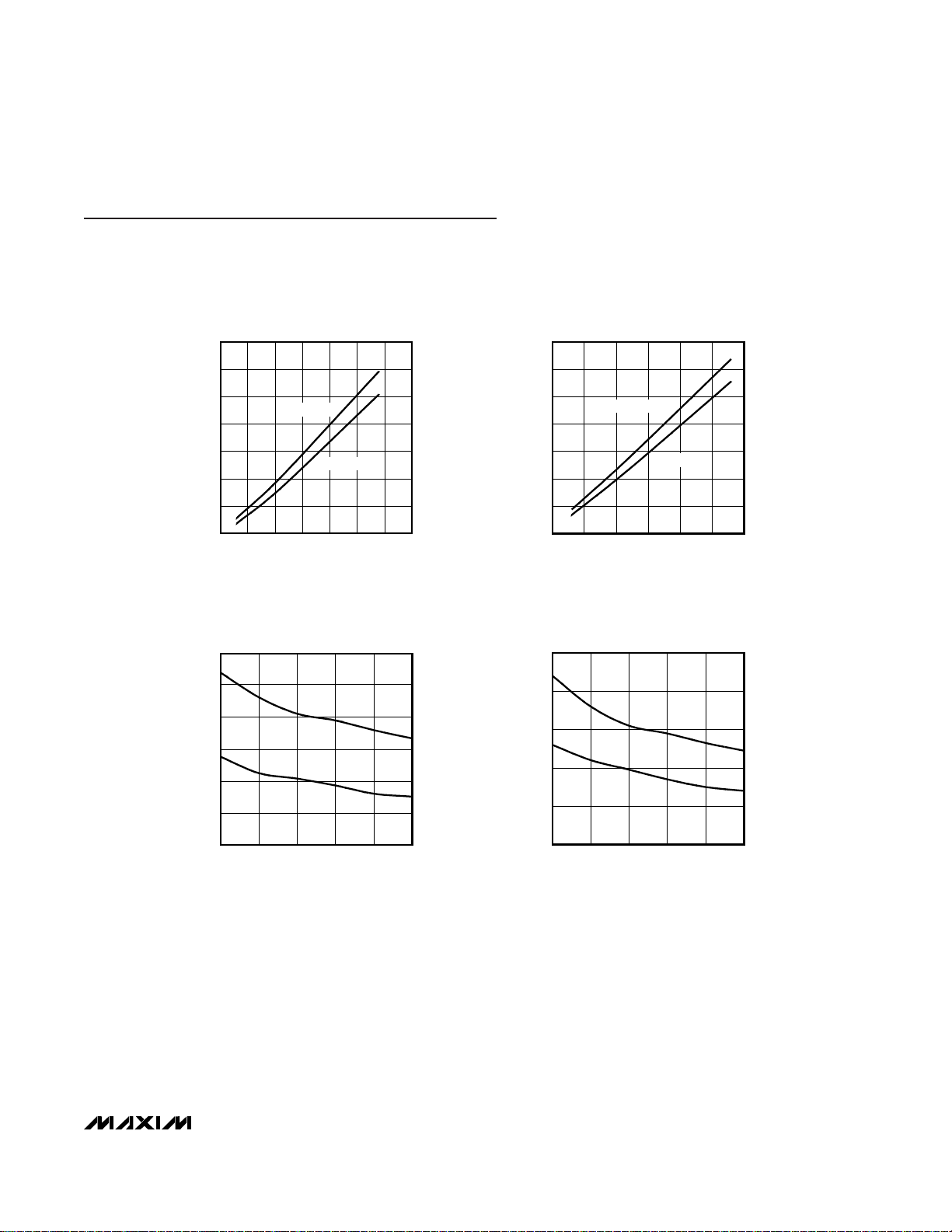
WORST-CASE PATTERN AND PRBS
SUPPLY CURRENT vs. FREQUENCY
MAX9234/6/8 toc01
FREQUENCY (MHz)
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
3025201510
40
30
50
60
70
80
90
100
54035
WORST CASE
27 - 1 PRBS
MAX9238
WORST-CASE PATTERN AND PRBS
SUPPLY CURRENT vs. FREQUENCY
MAX9234/6/8 toc02
FREQUENCY (MHz)
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
6050403020
60
40
80
100
120
140
160
180
10 70
WORST CASE
27 - 1 PRBS
MAX9234/MAX9236
RxOUT TRANSITION TIME
vs. OUTPUT SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V
CCO
)
MAX9234/6/8 toc03
OUTPUT SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
OUTPUT TRANSITION TIME (ns)
4.54.03.53.0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2.5 5.0
CLHT
CHLT
MAX9238
RxOUT TRANSITION TIME
vs. OUTPUT SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V
CCO
)
MAX9234/6/8 toc04
OUTPUT SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
OUTPUT TRANSITION TIME (ns)
4.54.03.53.0
0
1
2
3
4
5
2.5 5.0
CLHT
CHLT
Typical Operating Characteristics
(VCC= V
CCO
= +3.3V, CL= 8pF, PWRDWN = high, differential input voltage ⏐VID⏐ = 0.2V, input common-mode voltage VCM= 1.2V,
T
A
= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
Page 6

MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Pin Description
PIN NAME FUNCTION
1, 2, 4, 5, 45,
46, 47
Channel 2 Single-Ended Outputs
3, 25, 32, 38,
44
GND Ground
6 N.C. No Connection
7, 13, 18 LVDS GND LVDS Ground
8 RxIN0- Inverting Channel 0 LVDS Serial-Data Input
9 RxIN0+ Noninverting Channel 0 LVDS Serial-Data Input
10 RxIN1- Inverting Channel 1 LVDS Serial-Data Input
11 RxIN1+ Noninverting Channel 1 LVDS Serial-Data Input
12 LVDS V
CC
LVDS Supply Voltage. Bypass to LVDS GND with 0.1µF and 0.001µF capacitors in parallel as
close to LVDS V
CC
as possible, with the smallest value capacitor closest to the supply pin.
14 RxIN2- Inverting Channel 2 LVDS Serial-Data Input
15 RxIN2+ Noninverting Channel 2 LVDS Serial-Data Input
16 RxCLK IN- Inverting LVDS Parallel Rate Clock Input
17 RxCLK IN+ Noninverting LVDS Parallel Rate Clock Input
19, 21 PLL GND PLL Ground
20 PLL V
CC
PLL Supply Voltage. Bypass to PLL GND with 0.1µF and 0.001µF capacitors in parallel as
close to PLL V
CC
as possible, with the smallest value capacitor closest to the supply pin.
22 PWRDWN
5V Tolerant LVTTL/LVCMOS Power-Down Input. Internally pulled down to GND. Outputs are
high impedance when PWRDWN = low or open.
23 RxCLK OUT
Parallel Rate Clock Single-Ended Output. The MAX9234 has a rising-edge strobe. The
MAX9236/MAX9238 have a falling-edge strobe.
24, 26, 27, 29,
30, 31, 33
Channel 0 Single-Ended Outputs
28, 36, 48 V
CCO
Output Supply Voltage. Bypass to GND with 0.1µF and 0.001µF capacitors in parallel as
close to V
CCO
as possible, with the smallest value capacitor closest to the supply pin.
34, 35, 37, 39,
40, 41, 43
Channel 1 Single-Ended Outputs
42 V
CC
Digital Supply Voltage. Bypass to GND with 0.1µF and 0.001µF capacitors in parallel as close
to V
CC
as possible, with the smallest value capacitor closest to the supply pin.
RxOUT14–RxOUT20
RxOUT0–RxOUT6
RxOUT7–RxOUT13
Page 7

MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
Detailed Description
The MAX9234/MAX9236 operate at a parallel clock frequency of 8MHz to 34MHz. The MAX9238 operates at a
parallel clock frequency of 16MHz to 66MHz. The transition times of the single-ended outputs are increased
on the MAX9234/MAX9236 for reduced EMI.
DC Balance
Data coding by the MAX9209/MAX9211/MAX9213/
MAX9215 serializers (which are companion devices to
the MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238 deserializers) limits
the imbalance of ones and zeros transmitted on each
channel. If +1 is assigned to each binary 1 transmitted
and -1 is assigned to each binary 0 transmitted, the variation in the running sum of assigned values is called the
digital sum variation (DSV). The maximum DSV for the
data channels is 10. At most, 10 more zeros than ones,
or 10 more ones than zeros, are transmitted. The maximum DSV for the clock channel is five. Limiting the DSV
and choosing the correct coupling capacitors maintains
differential signal amplitude and reduces jitter due to
droop on AC-coupled links.
To obtain DC balance on the data channels, the serializer parallel data is inverted or not inverted, depending
on the sign of the digital sum at the word boundary.
Two complementary bits are appended to each group
of 7 parallel input data bits to indicate to the MAX9234/
MAX9236/MAX9238 deserializers whether the data bits
are inverted (see Figure 9). The deserializer restores
the original state of the parallel data. The LVDS clock
signal alternates duty cycles of 4/9 and 5/9, which
maintain DC balance.
AC-Coupling Benefits
Bit errors experienced with DC-coupling can be eliminated by increasing the receiver common-mode voltage
range by AC-coupling. AC-coupling increases the common-mode voltage range of an LVDS receiver to nearly
the voltage rating of the capacitor. The typical LVDS driver output is 350mV centered on an offset voltage of
1.25V, making single-ended output voltages of 1.425V
and 1.075V. An LVDS receiver accepts signals from 0 to
2.4V, allowing approximately ±1V common-mode difference between the driver and receiver on a DC-coupled
link (2.4V - 1.425V = 0.975V and 1.075V - 0V = 1.075V).
Common-mode voltage differences may be due to
ground potential variation or common-mode noise. If
there is more than ±1V of difference, the receiver is not
guaranteed to read the input signal correctly and may
cause bit errors. AC-coupling filters low-frequency
ground shifts and common-mode noise and passes
high-frequency data. A common-mode voltage difference up to the voltage rating of the coupling capacitor
(minus half the differential swing) is tolerated. DC-balanced coding of the data is required to maintain the differential signal amplitude and limit jitter on an
AC-coupled link. A capacitor in series with each output
of the LVDS driver is sufficient for AC-coupling.
However, two capacitors—one at the serializer output
and one at the deserializer input—provide protection in
case either end of the cable is shorted to a high voltage.
RIN1
RxIN_ + OR
RxCLK IN+
RxIN_ - OR
RxCLK IN-
RIN1
1.2V
Figure 1. LVDS Input Circuit
RCIP
RxCLK OUT
ODD RxOUT
EVEN RxOUT
RISING-EDGE STROBE SHOWN.
Figure 2. Worst-Case Test Pattern
Table 1. Part Equivalent Table
PART
EQUIVALENT WITH DCB/NC = HIGH OR OPEN
OPERATING
FREQUENCY (MHz)
OUTPUT STROBE
MAX9234 MAX9210 8 to 34 Rising edge
MAX9236 MAX9220 8 to 34 Falling edge
MAX9238 MAX9222 16 to 66 Falling edge
Page 8
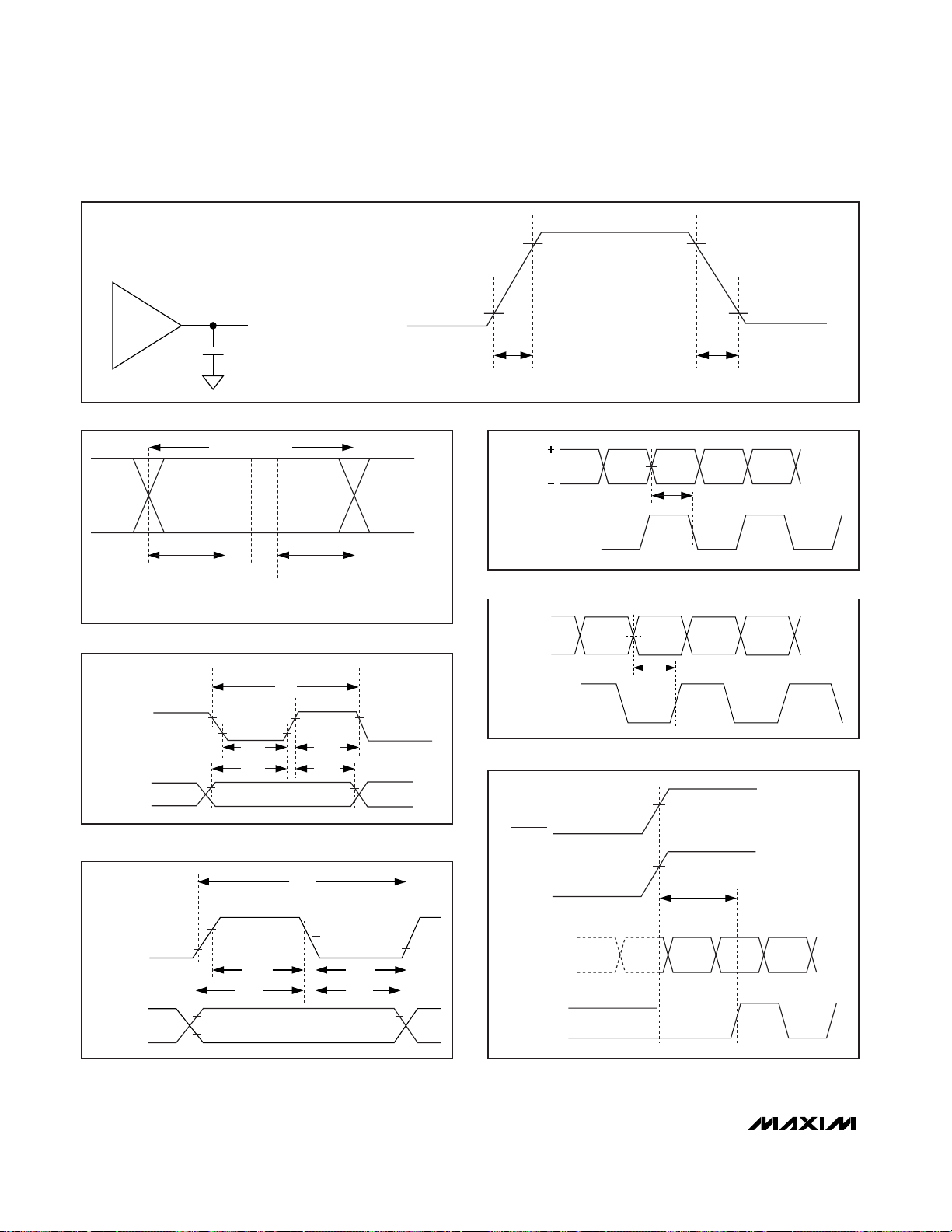
MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
IDEAL
MIN MAX
INTERNAL STROBE
IDEAL
RSKM RSKM
IDEAL SERIAL BIT TIME
1.3V
1.1V
Figure 4. LVDS Receiver Input Skew Margin
RxOUT_
RxCLK OUT
RCIP
RCOHRCOL
2.0V
0.8V
2.0V
0.8V
2.0V
2.0V
2.0V
0.8V 0.8V
RHRCRSRC
Figure 5a. MAX9234 Output Setup/Hold and High/Low Times
RxOUT_
RxCLK OUT
RCIP
RCOH RCOL
2.0V
0.8V
2.0V
0.8V
2.0V 2.0V
0.8V 0.8V 0.8V
RHRCRSRC
Figure 5b. MAX9236/MAX9238 Output Setup/Hold and High/Low
Times
VID = 0
1.5V
RCCD
RxCLK IN
RxCLK OUT
Figure 6a. MAX9234 Clock-IN to Clock-OUT Delay
RxCLK IN
RxCLK OUT
+
-
RCCD
1.5V
VID = 0
Figure 6b. MAX9236/MAX9238 Clock-IN to Clock-OUT Delay
90%90%
10%10%
CHLTCLHT
RxOUT_ OR
RxCLK OUT
RxOUT_ OR
RxCLK OUT
8pF
Figure 3. Output Load and Transition Times
PWRDWN
V
CC
RxCLK IN
RxCLK OUT
3V
2V
RPLLS
HIGH-Z
Figure 7. Phase-Locked Loop Set Time
Page 9

MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238 vs.
MAX9210/MAX9220/MAX9222
The MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238 operate in DC-balance mode only. Pinouts are the same as the
MAX9210/MAX9220/MAX9222 except that pin 6 on the
MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238 is no connect (N.C.). DC
balance allows AC-coupling with series capacitors. The
MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238 are hot-swappable and
the input frequency can be changed on the fly, but otherwise the specifications and functionality are the same
as the MAX9210/MAX9220/MAX9222 operating in DCbalance mode. See Table 1.
Applications Information
Selection of AC-Coupling Capacitors
Voltage droop and the DSV of transmitted symbols
cause signal transitions to start from different voltage
levels. Because the transition time is finite, starting the
signal transition from different voltage levels causes
timing jitter. The time constant for an AC-coupled link
needs to be chosen to reduce droop and jitter to an
acceptable level.
The RC network for an AC-coupled link consists of the
LVDS receiver termination resistor (R
T
), the LVDS driver
output resistor (RO), and the series AC-coupling capacitors (C). The RC time constant for two equal-value
series capacitors is (C x (RT + RO)) / 2 (Figure 10). The
RC time constant for four equal-value series capacitors
is (C x (RT + RO)) / 4 (Figure 11).
RTis required to match the transmission line impedance (usually 100Ω) and ROis determined by the LVDS
driver design (the minimum differential output resistance of 78Ω for the MAX9209/MAX9211/MAX9213/
MAX9215 serializers is used in the following example).
This leaves the capacitor selection to change the system time constant.
TxIN_, DCA_, AND DCB_ ARE DATA FROM THE SERIALIZER.
DCA0
DCB1DCA1
DCB2DCA2
CYCLE N + 1CYCLE NCYCLE N - 1
TxIN2TxIN6 TxIN3TxIN4TxIN5
TxIN9TxIN13 TxIN10TxIN11TxIN12
TxIN2TxIN3TxIN4DCA0 TxIN5TxIN6DCB0
TxIN9TxIN10TxIN11DCA1 TxIN12TxIN13DCB1
TxIN16TxIN17TxIN18DCA2 TxIN19TxIN20DCB2
TxIN0TxIN1
TxIN7TxIN8
TxIN14TxIN15TxIN16TxIN20 TxIN17TxIN18TxIN19
DCB0
RxCLK IN
RxIN1
RxIN0
RxIN2
TxIN1
TxIN8
TxIN15
TxIN0
TxIN7
TxIN14
+
-
Figure 9. Deserializer Serial Input
0.8V
PWRDWN
RxCLK IN
RxOUT_
RxCLK OUT
RPDD
HIGH-Z
Figure 8. Power-Down Delay
Page 10

MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
(7 + 2):1
1:(9 - 2)
7
7
100Ω
(7 + 2):1
1:(9 - 2)
7
7
100Ω
(7 + 2):1
1:(9 - 2)
7
7
100Ω
PLL
PLL
100Ω
MAX9209
MAX9211
MAX9213
MAX9215
MAX9234
MAX9236
MAX9238
TxOUT
TxCLK OUT
RxIN
RxCLK IN
21:3 SERIALIZER 3:21 DESERIALIZER
PWRDWN
RxCLK OUT
RxOUT
PWRDWN
TxCLK IN
TxIN
HIGH-FREQUENCY, CERAMIC
SURFACE-MOUNT CAPACITORS
CAN ALSO BE PLACED AT THE
SERIALIZER INSTEAD OF THE DESERIALIZER.
Figure 10. Two Capacitors per Link, AC-Coupled
(7 + 2):1
1:(9 - 2)
7
7
100Ω
(7 + 2):1
1:(9 - 2)
7
7
100Ω
(7 + 2):1
1:(9 - 2)
7
7
100Ω
PLL
PLL
100Ω
MAX9209
MAX9211
MAX9213
MAX9215
MAX9234
MAX9236
MAX9238
TxOUT
TxCLK OUT
RxIN
RxCLK IN
21:3 SERIALIZER 3:21 DESERIALIZER
PWRDWN
RxCLK OUT
RxOUT
PWRDWN
TxCLK IN
TxIN
HIGH-FREQUENCY CERAMIC
SURFACE-MOUNT CAPACITORS
Figure 11. Four Capacitors per Link, AC-Coupled
Page 11

MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 11
In the following example, the capacitor value for a
droop of 2% is calculated. Jitter due to this droop is
then calculated assuming a 1ns transition time:
C = - (2 x tBx DSV) / (ln (1 - D) x (RT+ RO)) (Eq 1)
where:
C = AC-coupling capacitor (F).
tB= bit time (s).
DSV = digital sum variation (integer).
ln = natural log.
D = droop (% of signal amplitude).
RT= termination resistor (Ω).
RO= output resistance (Ω).
Equation 1 is for two series capacitors (Figure 10). The
bit time (tB) is the period of the parallel clock divided by
9. The DSV is 10. See equation 3 for four series capacitors (Figure 11).
The capacitor for 2% maximum droop at 8MHz parallel
rate clock is:
C = - (2 x tBx DSV) / (ln (1 - D) x (RT+ RO))
C = - (2 x 13.9ns x 10) / (ln (1 - 0.02) x (100Ω + 78Ω))
C = 0.0773µF
Jitter due to droop is proportional to the droop and
transition time:
tJ= tTx D (Eq 2)
where:
tJ= jitter (s).
tT= transition time (s) (0 to 100%).
D = droop (% of signal amplitude).
Jitter due to 2% droop and assumed 1ns transition time is:
tJ= 1ns x 0.02
tJ= 20ps
The transition time in a real system depends on the frequency response of the cable driven by the serializer.
The capacitor value decreases for a higher frequency
parallel clock and for higher levels of droop and jitter.
Use high-frequency, surface-mount ceramic capacitors.
Equation 1 altered for four series capacitors (Figure 11) is:
C = - (4 x tBx DSV) / (ln (1 - D) x (RT+ RO)) (Eq 3)
Input Bias and Frequency Detection
The inverting and noninverting LVDS inputs are internally
connected to +1.2V through 42kΩ (min) to provide biasing for AC-coupling (Figure 1). A frequency-detection
circuit on the clock input detects when the input is not
switching, or is switching at low frequency. In this case,
all outputs are driven low. To prevent switching due to
noise when the clock input is not driven, bias the clock
input to differential +15mV by connecting a 10kΩ ±1%
pullup resistor between the noninverting input and V
CC
,
and a 10kΩ ±1% pulldown resistor between the inverting input and ground. These bias resistors, along with
the 100Ω ±1% tolerance termination resistor, provide
+15mV of differential input.
Unused LVDS Data Inputs
At each unused LVDS data input, pull the inverting input
up to VCCusing a 10kΩ resistor, and pull the noninverting
input down to ground using a 10kΩ resistor. Do not connect a termination resistor. The pullup and pulldown resistors drive the corresponding outputs low and prevent
switching due to noise.
PWRDWN
Driving PWRDWN low puts the outputs in high imped-
ance, stops the PLL, and reduces supply current to
50µA or less. Driving PWRDWN high drives the outputs
low until the PLL locks. The outputs of two deserializers
can be bused to form a 2:1 mux with the outputs controlled by PWRDWN. Wait 100ns between disabling one
deserializer (driving PWRDWN low) and enabling the
second one (driving PWRDWN high) to avoid contention of the bused outputs.
Input Clock and PLL Lock Time
There is no required timing sequence for the application or reapplication of the parallel rate clock (RxCLK
IN) relative to PWRDWN, or to a power-supply ramp for
proper PLL lock. The PLL lock time is set by an internal
counter. The maximum time to lock is 32,800 clock
periods. Power and clock should be stable to meet the
lock-time specification. When the PLL is locking, the
outputs are low.
Power-Supply Bypassing
There are separate on-chip power domains for digital
circuits, outputs, PLL, and LVDS inputs. Bypass each
VCC, V
CCO
, PLL VCC, and LVDS VCCpin with high-frequency, surface-mount ceramic 0.1µF and 0.001µF
capacitors in parallel as close to the device as possible, with the smallest value capacitor closest to the
supply pin.
Cables and Connectors
Interconnect for LVDS typically has a differential impedance of 100Ω. Use cables and connectors that have
matched differential impedance to minimize impedance
discontinuities.
Twisted-pair and shielded twisted-pair cables offer
superior signal quality compared to ribbon cable and
tend to generate less EMI due to magnetic field canceling effects. Balanced cables pick up noise as common
mode, which is rejected by the LVDS receiver.
Page 12

MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
12 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Board Layout
Keep the LVTTL/LVCMOS outputs and LVDS input signals separated to prevent crosstalk. A four-layer PC
board with separate layers for power, ground, LVDS
inputs, and digital signals is recommended.
ESD Protection
The MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238 ESD tolerance is
rated for IEC 61000-4-2 Human Body Model and ISO
10605 standards. IEC 61000-4-2 and ISO 10605 specifiy
ESD tolerance for electronic systems. The Human Body
Model discharge components are CS= 100pF and RD=
1.5kΩ (Figure 12). For the Human Body Model, all pins
are rated for ±5kV contact discharge. The ISO 10605 discharge components are CS= 330pF and RD= 2kΩ
(Figure 13). For ISO 10605, the LVDS outputs are rated
for ±8kV contact and ±25kV air discharge. The IEC
61000-4-2 discharge components are CS= 150pF and
RD= 330Ω (Figure 14). For IEC 61000-4-2, the LVDS
inputs are rated for ±8kV Contact Discharge and ±15kV
Air-Gap Discharge.
5V Tolerant Input
PWRDWN is 5V tolerant and is internally pulled down to
GND.
Skew Margin (RSKM)
Skew margin (RSKM) is the time allowed for degradation of the serial data sampling setup and hold times by
sources other than the deserializer. The deserializer
sampling uncertainty is accounted for and does not
need to be subtracted from RSKM. The main outside
contributors of jitter and skew that subtract from RSKM
are interconnect intersymbol interference, serializer
pulse position uncertainty, and pair-to-pair path skew.
V
CCO
Output Supply and Power Dissipation
The outputs have a separate supply (V
CCO
) for interfacing
to systems with 1.8V to 5V nominal input-logic levels. The
DC Electrical Characteristics table gives the maximum
supply current for V
CCO
= 3.6V with 8pF load at several
switching frequencies with all outputs switching in the
worst-case switching pattern. The approximate incremental supply current for V
CCO
other than 3.6V with the same
8pF load and worst-case pattern can be calculated using:
II= CTVI 0.5fCx 21 (data outputs)
+ CTVIfCx 1 (clock output)
where:
II= incremental supply current.
CT= total internal (C
INT
) and external (CL) load capacitance.
V
I
= incremental supply voltage.
f
C
= output clock-switching frequency.
The incremental current is added to (for V
CCO
> 3.6V)
or subtracted from (for V
CCO
< 3.6V) the DC Electrical
Characteristics table maximum supply current. The
internal output buffer capacitance is C
INT
= 6pF. The
worst-case pattern-switching frequency of the data outputs is half the switching frequency of the output clock.
In the following example, the incremental supply current is
calculated for V
CCO
= 5.5V, fC= 34MHz, and CL= 8pF:
V
I
= 5.5V - 3.6V = 1.9V
CT= C
INT
+ CL= 6pF + 8pF = 14pF
Figure 13. ISO 10605 Contact Discharge ESD Test Circuit
Figure 12. Human Body ESD Test Circuit
STORAGE
CAPACITOR
HIGH-
VOLTAGE
DC
SOURCE
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
CHARGE-CURRENT-
LIMIT RESISTOR
DISCHARGE
RESISTANCE
R1
1MΩ
R2
1.5kΩ
C
S
100pF
Figure 14. IEC 61000-4-2 Contact Discharge ESD Test Circuit
STORAGE
CAPACITOR
HIGH-
VOLTAGE
DC
SOURCE
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
CHARGE-CURRENT-
LIMIT RESISTOR
DISCHARGE
RESISTANCE
50Ω TO 100Ω
R
D
330Ω
C
S
150pF
R1
50Ω TO 100ΩR22kΩ
HIGH-
VOLTAGE
DC
SOURCE
CHARGE-CURRENT-
LIMIT RESISTOR
330pF
C
S
DISCHARGE
RESISTANCE
STORAGE
CAPACITOR
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
Page 13

MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 13
where:
II= CTVI 0.5FCx 21 (data outputs) + CTVIfCx 1 (clock
output).
II= (14pF x 1.9V x 0.5 x 34MHz x 21) + (14pF x 1.9V x
34MHz).
II= 9.5mA + 0.9mA = 10.4mA.
The maximum supply current in DC-balanced mode for
V
CC
= V
CCO
= 3.6V at fC= 34MHz is 106mA (from the
DC Electrical Characteristics table). Add 10.4mA to get
the total approximate maximum supply current at V
CCO
= 5.5V and VCC= 3.6V.
If the output supply voltage is less than V
CCO
= 3.6V,
the reduced supply current can be calculated using the
same formula and method.
At high switching frequency, high supply voltage, and
high capacitive loading, power dissipation can exceed
the package power-dissipation rating. Do not exceed
the maximum package power-dissipation rating. See
the Absolute Maximum Ratings for maximum package
power-dissipation capacity and temperature derating.
Rising- or Falling-Edge Output Strobe
The MAX9234 has a rising-edge output strobe, which
latches the parallel output data into the next chip on the
rising edge of RxCLK OUT. The MAX9236/MAX9238
have a falling-edge output strobe, which latches the
parallel output data into the next chip on the falling
edge of RxCLK OUT. The deserializer output strobe
polarity does not need to match the serializer input
strobe polarity. A deserializer with rising- or fallingedge output strobe can be driven by a serializer with a
rising-edge input strobe.
RxIN0+
LVDS DATA
RECEIVER 0
RxIN0-
STROBE
DATA
CHANNEL 0
RxOUT0–6
SERIAL-TO-
PARALLEL
CONVERTER
RxIN1+
LVDS DATA
RECEIVER 1
RxIN1-
STROBE
DATA
CHANNEL 1
RxOUT7–13
SERIAL-TO-
PARALLEL
CONVERTER
RxIN2+
LVDS DATA
RECEIVER 2
RxIN2-
STROBE
DATA
CHANNEL 2
RxOUT14–20
SERIAL-TO-
PARALLEL
CONVERTER
RxCLK IN+
LVDS CLOCK
RECEIVER
RxCLK IN-
9x
PLL
RxCLK OUT
REFERENCE
CLOCK
GENERATOR
PWRDWN
Functional Diagram
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
V
CCO
RxOUT16
RxOUT15
RxOUT14RxOUT19
GND
RxOUT18
RxOUT17
TOP VIEW
MAX9234
MAX9236
MAX9238
GND
RxOUT13
V
CC
RxOUT12RxIN0-
LVDS GND
N.C.
RxOUT20
RxOUT11
RxOUT10RxIN1-
RxIN0+
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
GND
RxOUT9
V
CCO
RxOUT8
RxOUT7
RxOUT6
GND
RxOUT5
RxOUT4
RxOUT3
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
RxIN2-
LVDS GND
LVDS V
CC
RxIN1+
LVDS GND
RxCLK IN+
RxCLK IN-
RxIN2+
PLL V
CC
PLL GND
20
21
PWRDWN
PLL GND
22
28
27
V
CCO
RxOUT2
TSSOP
23
RxOUT0
RxCLK OUT
24
26
25
RxOUT1
GND
Pin Configuration
Chip Information
MAX9234 TRANSISTOR COUNT: 14,104
MAX9236 TRANSISTOR COUNT: 14,104
MAX9238 TRANSISTOR COUNT: 14,104
PROCESS: CMOS
Page 14

MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
14 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Package Information
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.)
48L TSSOP.EPS
NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONS D & E ARE REFERENCE DATUMS AND DO NOT INCLUDE MOLD FLASH.
2. MOLD FLASH OR PROTRUSIONS NOT TO EXCEED 0.15MM ON D SIDE, AND 0.25MM ON E SIDE.
3. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: MILLIMETERS.
4. THIS PART IS COMPLIANT WITH JEDEC SPECIFICATION MO-153, VARIATIONS, ED (48L), EE (56L).
5. "N" REFERS TO NUMBER OF LEADS.
6. THE LEAD TIPS MUST LIE WITHIN A SPECIFIED ZONE. THIS TOLERANCE ZONE IS DEFINED BY TWO PARALLEL
PLANES. ONE PLANE IS THE SEATING PLANE, DATUM (-C-), THE OTHER PLANE IS AT THE SPECIFIED DISTANCE
FROM (-C-) IN THE DIRECTION INDICATED.
7. MARKING IS FOR PACKAGE ORIENTATION REFERENCE ONLY.
8. NUMBER OF LEADS SHOWN ARE FOR REFERENCE ONLY.
SECTION C-C
DETAIL A
N
SIDE VIEW
TOP VIEW
C
L
1
HE
e
D
b
A
A2
A1
BOTTOM VIEW
c
0.25
()
b1
b
c1
BASE METAL
c
END VIEW
SEATING
PLANE
SEE DETAIL A
PARTING
LINE
WITH PLATING
L
PACKAGE OUTLINE,
21-0155
1
1
C
48 & 56L TSSOP, 6.1mm BODY
AAA23A
MARKING
Page 15

MAX9234/MAX9236/MAX9238
Hot-Swappable, 21-Bit, DC-Balanced LVDS
Deserializers
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600 ____________________ 15
© 2007 Maxim Integrated Products is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Revision History
REVISION
REVISION
DATE
DESCRIPTION
PAGES
CHANGED
0 4/05 Initial release —
1 10/07 Added IEC 61000-4-2 ESD Performance; various style changes 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 12
NUMBER
 Loading...
Loading...