Page 1
现货库存、技术资料、百科信息、热点资讯,精彩尽在鼎好!
General Description
The MAX7324 2-wire serial-interfaced peripheral features 16 I/O ports that are divided into eight push-pull
outputs and eight inputs. Each input features selectable
internal pullups, overvoltage protection to +6V, and
transition detection with an interrupt output.
All input ports are continuously monitored for state
changes (transition detection). The interrupt is latched,
allowing detection of transient changes. Any combination of inputs can be selected using the interrupt mask
to assert the INT output. When the MAX7324 is subsequently accessed through the serial interface, any
pending interrupt is cleared.
The push-pull outputs are rated to sink 20mA and are
capable of driving LEDs. The RST input clears the serial
interface, terminating any I2C communication to or from
the MAX7324.
The MAX7324 uses two address inputs with four-level
logic to allow 16 I2C slave addresses. The slave
address also enables or disables internal 40kΩ pullups
in groups of four ports.
The MAX7324 is one device in a family of pin-compatible
port expanders with a choice of input ports, open-drain
I/O ports, and push-pull output ports (see Table 1).
The MAX7324 is available in 24-pin QSOP and TQFN
packages, and is specified over the -40°C to +125°C
automotive temperature range.
Applications
Cell Phones Notebooks
SAN/NAS Automotive
Servers Satellite Radio
Features
♦ 400kHz, +6V-Tolerant I2C Serial Interface
♦ +1.71V to 5.5V Operating Voltage
♦ Eight Push-Pull Outputs
♦ Eight Input Ports with Maskable, Latching
Transition Detection
♦ Input Ports are Overvoltage Protected to +6V
♦ Transient Changes are Latched, Allowing
Detection Between Read Operations
♦ INT Output Alerts Change on Any Selection of
Inputs
♦ AD0 and AD2 Inputs Select from 16 Slave
Addresses
♦ Low 0.6µA Standby Current
♦ -40°C to +125°C Temperature Range
MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
________________________________________________________________ Maxim Integrated Products 1
19-3785; Rev 0; 10/06
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim/Dallas Direct! at
1-888-629-4642, or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
Ordering Information
PART
TEMP RANGE
PINPACKAGE
PKG
CODE
MAX7324AEG+
24 QSOP
E24-1
MAX7324ATG+
24 TQFN-EP*
T2444-3
Typical Application Circuit and Functional Diagram appear
at end of data sheet.
Selector Guide
PART
INPUTS
INTERRUPT
MASK
OPENDRAIN
PUSH-PULL
OUTPUTS
MAX7324
8 Yes — 8
MAX7325
—
8
MAX7326
4 Yes — 12
MAX7327
—
12
Pin Configurations
TQFN (4mm x 4mm)
+
TOP VIEW
MAX7324
19
20
21
22
12 3456
18 17 16 15 14 13
23
24
12
11
10
9
8
7
SCL
V+
SDA
INT
AD2
I0
I1
I2
I3
I4
I5
AD0
O15
O13
O12
O11
RST
O10
O8
O9
GND
I6
I7
O14
EXPOSED PADDLE
+Denotes lead-free package.
*EP = Exposed paddle.
Pin Configurations continued at end of data sheet.
-40°C to +125°C
-40°C to +125°C
(4mm x 4mm)
OUTPUTS
Up to 8
Up to 4
Up to 8
Up to 4
Page 2
MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(All voltages referenced to GND.)
Supply Voltage V+....................................................-0.3V to +6V
SCL, SDA, AD0, AD2, RST, INT, I0–I7......................-0.3V to +6V
O8–O15………….…………………………..…-0.3V to (V+ + 0.3V)
O8–O15 Output Current......………………………………...±25mA
SDA Sink Current ............................................................... 10mA
INT Sink Current..................................................................10mA
Total V+ Current..................................................................50mA
Total GND Current ...........................................................100mA
Continuous Power Dissipation
24-Pin QSOP (derate 9.5mW/°C over T
A
= +70°C) ..761.9mW
24-Pin TQFN (derate 20.8mW/°C over
T
A
= +70°C) ............................................................1666.7mW
Operating Temperature Range .........................-40°C to +125°C
Junction Temperature......................................................+150°C
Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(V+ = +1.71V to +5.5V, TA= -40°C to +125°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at V+ = +3.3V, TA= +25°C.) (Note 1)
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
CONDITIONS MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
Operating Supply Voltage V+ TA = -40°C to +125°C
V
Power-On Reset Voltage V
POR
V+ falling 1.6 V
Standby Current (Interface Idle) I
STB
0.6 1.9 µA
Supply Current
(Interface Running)
I+ f
SCL
= 400kHz; other digital inputs at V+ 23 55 µA
V+ < 1.8V
Input High-Voltage
V
IH
V+ ≥ 1.8
V
V+ < 1.8V
Input Low-Voltage
V
IL
V+ ≥ 1.8
V
Input Leakage Current
IIH, I
IL
SDA, SCL, AD0, AD2, RST, I0–I7 at V+ or
GND
-0.2
µA
Input Capacitance
10 pF
V+ = +1.71V, I
SINK
= 5mA (QSOP) 90
V+ = +1.71V, I
SINK
= 5mA (TQFN) 90
V+ = +2.5V, I
SINK
= 10mA (QSOP) 110
V+ = +2.5V, I
SINK
= 10mA (TQFN) 110
V+ = +3.3V, I
SINK
= 15mA (QSOP) 130
V+ = +3.3V, I
SINK
= 15mA (TQFN) 130
V+ = +5V, I
SINK
= 20mA (QSOP) 140
Output Low Voltage
O8–O15
V
OL
V+ = +5V, I
SINK
= 20mA (TQFN) 140
mV
V+ = +1.71V, I
SOURCE
= 2mA
V+ = +2.5V, I
SOURCE
= 5mA
V+ = +3.3V, I
SOURCE
= 5mA
Output High Voltage
O8–O15
V
OH
V+ = +5V, I
SOURCE
= 10mA
mV
Output Low-Voltage SDA
I
SINK
= 6mA
mV
Output Low-Voltage INT V
OLINTISINK
= 5mA 130
mV
Port Input Pullup Resistor R
PU
25 40 55 kΩ
SCL and SDA and other digital inputs at V+
1.71 5.50
SDA, SCL, AD0, AD2, RST, I0–I7
SDA, SCL, AD0, AD2, RST, I0–I7
SDA, SCL, AD0, AD2, RST, I0–I7
SDA, SCL, AD0, AD2, RST, I0–I7
V
OLSDA
0.8 x V+
0.7 x V+
V+ - 250 V+ - 30
V+ - 360 V+ - 70
V+ - 260 V+ - 100
V+ - 360 V+ - 120
0.2 x V+
0.3 x V+
+0.2
180
230
210
260
230
280
250
300
250
250
Page 3
MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
PORT AND INTERRUPT INT TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
(V+ = +1.71V to +5.5V, TA= -40°C to +125°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at V+ = +3.3V, TA= +25°C.) (Note 1)
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
UNITS
Port-Output Data Valid t
PPV
CL ≤ 100pF 4 µs
Port-Input Setup Time t
PSU
CL ≤ 100pF 0 µs
Port-Input Hold Time t
PH
CL ≤ 100pF 4 µs
INT Input Data Valid Time t
IV
CL ≤ 100pF 4 µs
INT Reset Delay Time from STOP
t
IP
CL ≤ 100pF 4 µs
INT Reset Delay Time from
Acknowledge
t
IR
CL ≤ 100pF 4 µs
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
(V+ = +1.71V to +5.5V, TA= -40°C to +125°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at V+ = +3.3V, TA= +25°C.) (Note 1)
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
CONDITIONS MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
Serial-Clock Frequency f
SCL
400 kHz
Bus Free Time Between a STOP
and a START Condition
t
BUF
1.3 µs
Hold Time (Repeated) START
Condition
0.6 µs
Repeated START Condition
Setup Time
t
SU,STA
0.6 µs
STOP Condition Setup Time
0.6 µs
Data Hold Time
(Note 2) 0.9 µs
Data Setup Time
100 ns
SCL Clock Low Period t
LOW
1.3 µs
SCL Clock High Period t
HIGH
0.7 µs
Rise Time of Both SDA and SCL
Signals, Receiving
t
R
(Notes 3, 4)
20 +
300 ns
Fall Time of Both SDA and SCL
Signals, Receiving
t
F
(Notes 3, 4)
20 +
300 ns
Fall Time of SDA Transmitting t
F,TX
(Notes 3, 4)
20 +
250 ns
Pulse Width of Spike Suppressed
t
SP
(Note 5)
ns
Capacitive Load for Each Bus
Line
C
b
(Note 3) 400 pF
RST Pulse Width t
W
500 ns
RST Rising to START Condition
Setup Time
t
RST
1µs
Note 1: All parameters are tested at TA= +25°C. Specifications over temperature are guaranteed by design.
Note 2: A master device must provide a hold time of at least 300ns for the SDA signal (referred to V
IL
of the SCL signal) to bridge
the undefined region of SCL’s falling edge.
Note 3: Guaranteed by design.
Note 4: C
b
= total capacitance of one bus line in pF. tRand tFmeasured between 0.3 x V+ and 0.7 x V+. I
SINK
≤ 6mA.
Note 5: Input filters on the SDA and SCL inputs suppress noise spikes less than 50ns.
SYMBOL
t
HD,STA
t
SU,STO
t
HD,DAT
t
SU,DAT
MIN TYP MAX
0.1C
b
0.1C
b
0.1C
b
50
Page 4
MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
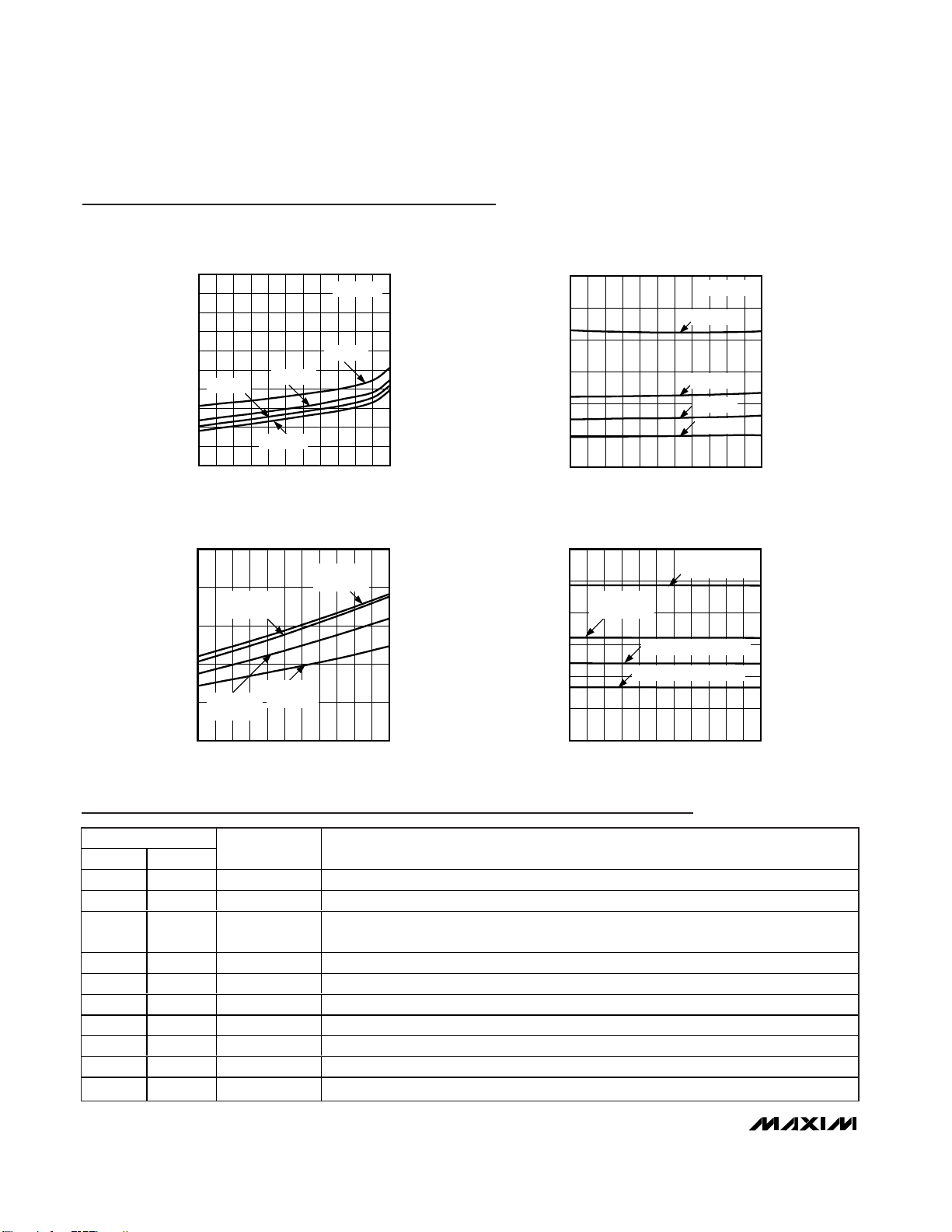
Typical Operating Characteristics
(TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
STANDBY CURRENT
vs. TEMPERATURE
TEMPERATURE (°C)
STANDBY CURRENT (µA)
MAX7324 toc01
-40 -25 -10 5 20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
V+ = +3.3V
V+ = +5.0V
V+ = +2.5V
V+ = +1.71V
f
SCL
= 0kHz
SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. TEMPERATURE
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
MAX7324 toc02
-40-25-105 203550658095110125
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
V+ = +3.3V
V+ = +5.0V
V+ = +2.5V
V+ = +1.71V
f
SCL
= 400kHz
OUTPUT-VOLTAGE LOW
vs. TEMPERATURE
TEMPERATURE (°C)
OUTPUT-VOLTAGE LOW (V)
MAX7324 toc03
-40 -25 -10 5 20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
0
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
V+ = +3.3V
I
SINK
= 15mA
V+ = +5.0V
I
SINK
= 20mA
V+ = +2.5V
I
SINK
= 10mA
V+ = +1.71V
I
SINK
= 5mA
OUTPUT-VOLTAGE HIGH
vs. TEMPERATURE
TEMPERATURE (°C)
OUTPUT-VOLTAGE HIGH (V)
MAX7324 toc04
-40 -25 -10 5 20 35 50 65 80 95 110 125
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
V+ = +3.3V
I
SOURCE
= 5mA
V+ = +5.0V
I
SOURCE
= 10mA
V+ = +2.5V I
SOURCE
= 5mA
V+ = +1.71V I
SOURCE
= 2mA
Pin Description
PIN
QSOP
TQFN
NAME FUNCTION
122 INT Active-Low Interrupt Output. INT is an open-drain output.
223 RST Active-Low Reset Input. Drive RST low to clear the 2-wire interface.
3, 21
AD2, AD0
Address Inputs. Select device slave address with AD0 and AD2. Connect AD0 and AD2
to either GND, V+, SCL, or SDA to give four logic combinations (see Tables 2 and 3).
4–11 1–8 I0–I7 Input Ports. I0 to I7 are CMOS-logic inputs.
12 9 GND Ground
13–20 10–17 08–015 Output Ports. O8–O15 are push-pull outputs rated at 20mA.
22 19 SCL I2C-Compatible Serial Clock Input
23 20 SDA I2C-Compatible Serial Data I/O
24 21 V
+
Positive Supply Voltage. Bypass V+ to GND with a ceramic capacitor of at least 0.047µF.
— EP EP Exposed Paddle. Connect exposed pad to GND.
24, 18
Page 5
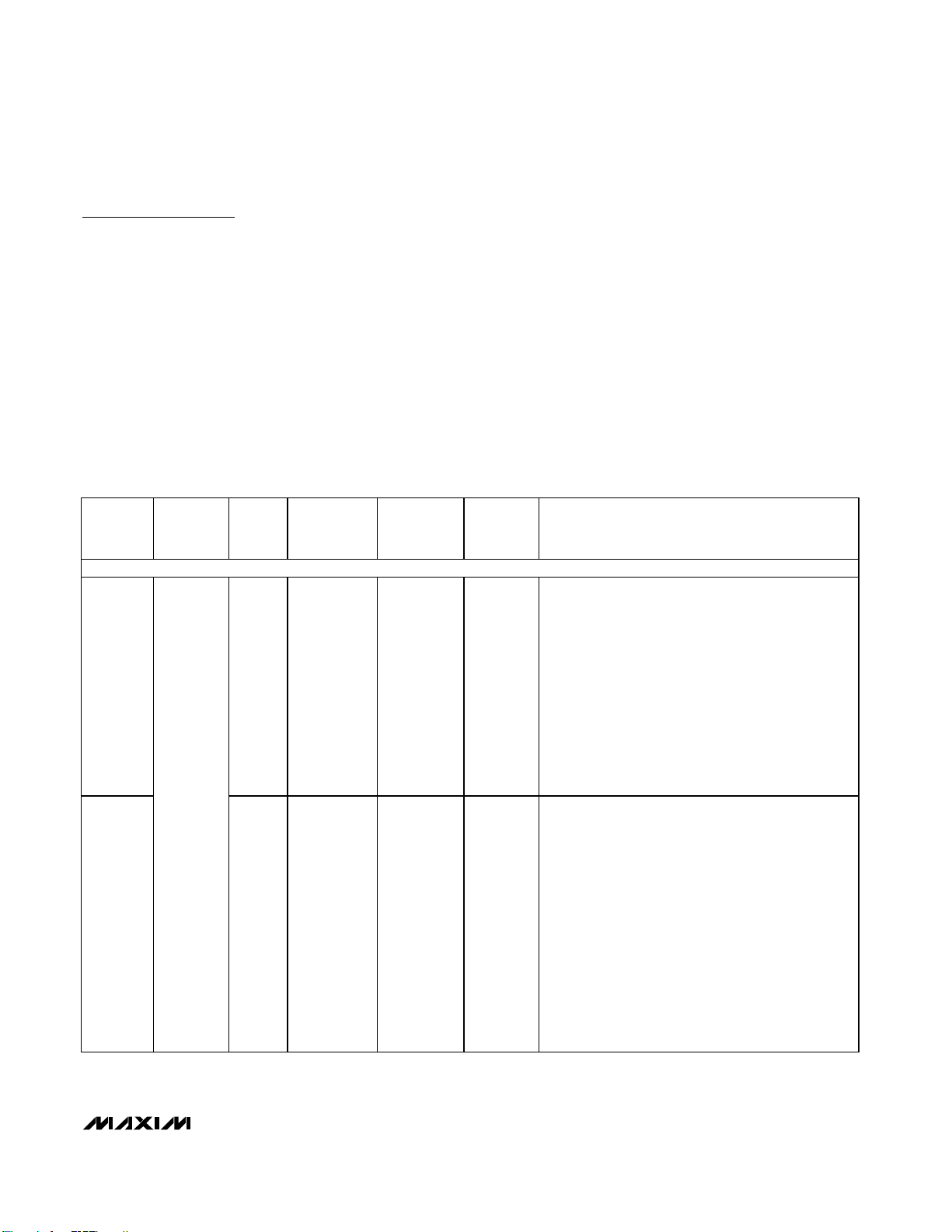
Detailed Description
MAX7324–MAX7327 Family Comparison
The MAX7324–MAX7327 family consists of four pincompatible, 16-port expanders that integrate the function of the MAX7320 and one of either the MAX7319,
MAX7321, MAX7322, or MAX7323.
Functional Overview
The MAX7324 is a general-purpose port expander
operating from a +1.71V to +5.5V supply with eight
push-pull outputs and eight CMOS input ports that are
overvoltage protected to +5.5V.
The MAX7324 is set to two of 32 I
2
C slave addresses
(see Tables 2 and 3) using address select inputs AD0
and AD2, and is accessed over an I2C serial interface
up to 400kHz. The eight outputs and eight inputs have
different slave addresses. The eight push-pull outputs
have the 101xxxx addresses and the eight inputs have
the adresses with 110xxxx. The RST input clears the
serial interface in case of a bus lockup, terminating any
serial transaction to or from the MAX7324.
The input ports offer latching transition detection feature. All input ports are continuously monitored for
changes. An input change sets 1 of 8 flag bits that
identify the changed input(s). All flags are cleared upon
a subsequent read or write transaction to the MAX7324.
MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
PART
I2C
SLAVE
INPUTS
INPUT
INTERRUPT
MASK
OPENDRAIN
PUSH-
PULL
CONFIGURATION
16-PORT EXPANDERS
MAX7324
8 Yes — 8
8 inputs and 8 push-pull outputs version:
8 input ports with programmable latching transition
detection interrupt and selectable pullups.
8 push-pull outputs with selectable default logic
levels.
Offers maximum versatility for automatic input
monitoring. An interrupt mask selects which inputs
cause an interrupt on transitions, and transition flags
identify which inputs have changed (even if only for
a transient) since the ports were last read.
MAX7325
and
— Up to 8 8
8 I/O and 8 push-pull outputs version:
8 open-drain I/O ports with latching transition
detection interrupt and selectable pullups.
8 push-pull outputs with selectable default logic
levels.
Open-drain outputs can level shift the logic-high
state to a higher or lower voltage than V+ using
external pullup resistors, but pullups draw current
when output is low. Any open-drain port can be used
as an input by setting the open-drain output to logichigh. Transition flags identify which open-drain port
inputs have changed (even if only for a transient)
since the ports were last read.
Table 1. MAX7319–MAX7329 Family Comparison
ADDRESS
OUTPUTS
OUTPUTS
101xxxx
110xxxx
Up to 8
Page 6
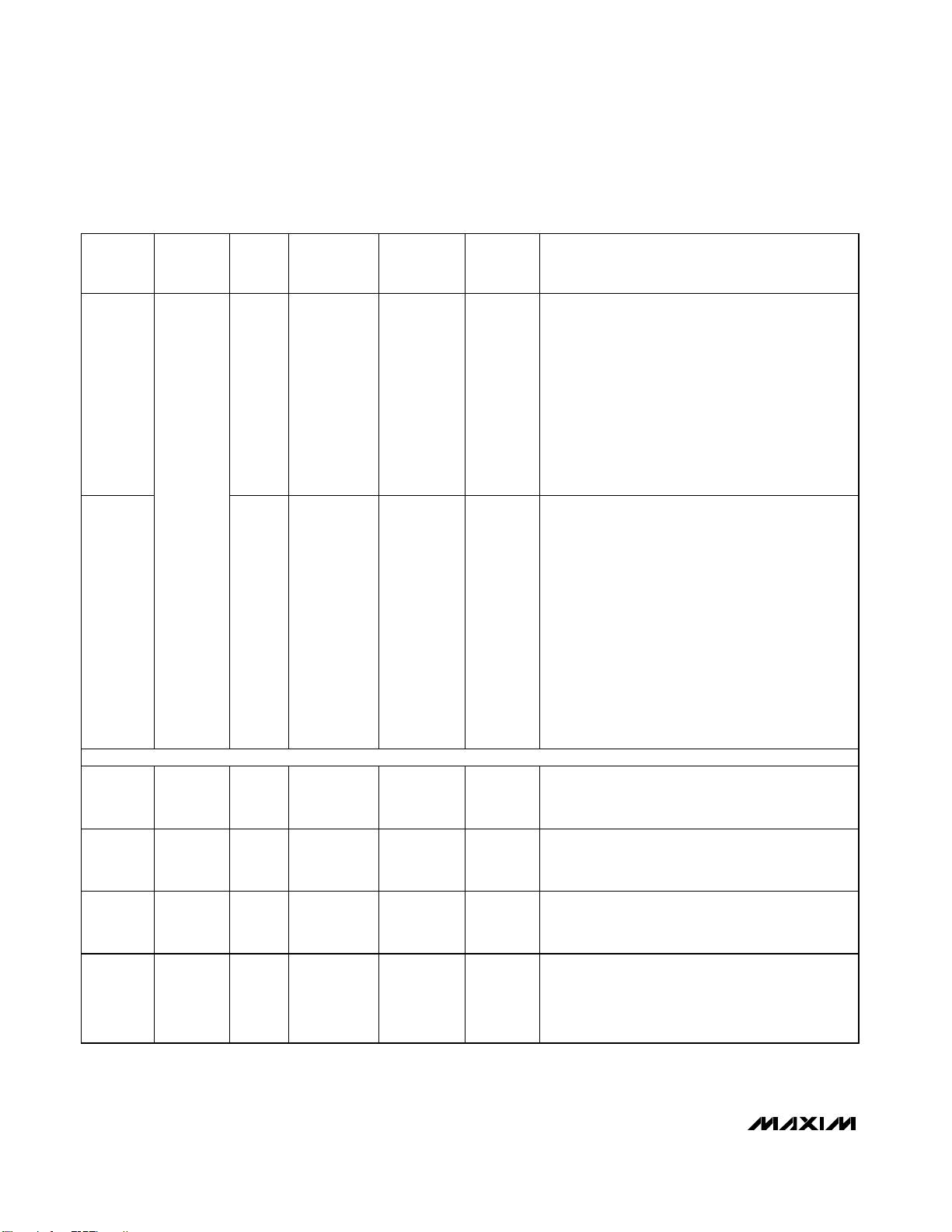
MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
PART
I2C
SLAVE
INPUTS
INPUT
INTERRUPT
MASK
OPENDRAIN
PUSH-
PULL
CONFIGURATION
MAX7326
4 Yes — 12
4 input-only, 12 push-pull output versions:
4 input ports with programmable latching transition
detection interrupt and selectable pullups.
12 push-pull outputs with selectable default logic
levels.
Offers maximum versatility for automatic input
monitoring. An interrupt mask selects which inputs
cause an interrupt on transitions, and transition flags
identify which inputs have changed (even if only for
a transient) since the ports were last read.
MAX7327
and
— Up to 4 12
4 I/O, 12 push-pull output versions:
4 open-drain I/O ports with latching transition
detection interrupt and selectable pullups.
12 push-pull outputs with selectable default logic
levels.
Open-drain outputs can level shift the logic-high
state to a higher or lower voltage than V+ using
external pullup resistors, but pullups draw current
when output is low. Any open-drain port can be used
as an input by setting the open-drain output to logichigh. Transition flags identify which open-drain port
inputs have changed (even if only for a transient)
since the ports were last read.
8-PORT EXPANDERS
MAX7319
8 Yes — —
Input-only versions:
8 input ports with programmable latching transition
detection interrupt and selectable pullups.
MAX7320
—— — 8
Output-only versions:
8 push-pull outputs with selectable power-up default
levels.
MAX7321
— Up to 8 —
I/O versions:
8 open-drain I/O ports with latching transition
detection interrupt and selectable pullups.
MAX7322
4 Yes — 4
4 input-only, 4 output-only versions:
4 input ports with programmable latching transition
detection interrupt and selectable pullups.
4 push-pull outputs with selectable power-up default
levels.
Table 1. MAX7319–MAX7329 Family Comparison (continued)
ADDRESS
101xxxx
110xxxx
Up to 4
OUTPUTS
OUTPUTS
110xxxx
101xxxx
110xxxx Up to 8
110xxxx
Page 7

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
A latching interrupt output, INT, is programmed to flag
input data changes on input ports through an interrupt
mask register. By default, data changes on any input
port force INT to a logic-low. The interrupt output INT
and all transition flags are cleared when the MAX7324
is next accessed through the serial interface.
Internal pullup resistors to V+ are selected by the
address select inputs, AD0 and AD2. Pullups are
enabled on the input ports in groups of four (see Table 2).
Initial Power-Up
On power-up, the transition detection logic is reset, and
INT is deasserted. The interrupt mask register is set to
0xFF, enabling the interrupt output for transitions on all
eight input ports. The transition flags are cleared to
indicate no data changes. The power-up default states
of the eight push-pull outputs are set according to the
I2C slave address selection inputs, AD0 and AD1 (see
Table 3).
Power-On Reset
The MAX7324 contains an integral power-on-reset
(POR) circuit that ensures all registers are reset to a
known state on power-up. When V+ rises above V
POR
(1.6V max), the POR circuit releases the registers and
2-wire interface for normal operation. When V+ drops
below V
POR
, the MAX7324 resets all register contents
to the POR defaults (Tables 2 and 3).
RST
Input
The RST input voids any I2C transaction involving the
MAX7324, forcing the MAX7324 into the I2C STOP condition. A reset does not affect the interrupt output (INT).
Standby Mode
When the serial interface is idle, the MAX7324 automatically enters standby mode, drawing minimal supply
current.
Slave Address, Power-Up Default Logic
Levels, and Input Pullup Selection
Address inputs AD0 and AD2 determine the MAX7324
slave address and select which inputs have pullup
resistors. Pullups are enabled on the input ports in
groups of four (see Table 2).
The MAX7324 slave address is determined on each I2C
transmission, regardless of whether the transmission is
actually addressing the MAX7324. The MAX7324 distinguishes whether address inputs AD0 and AD2 are connected to SDA or SCL instead of fixed logic levels V+
or GND during this transmission. This means that the
MAX7324 slave address can be configured dynamically in the application without cycling the device supply.
On initial power-up, the MAX7324 cannot decode the
address inputs AD0 and AD2 fully until the first I2C
transmission. AD0 and AD2 initially appear to be connected to V+ or GND. This is important because the
PART
I2C
SLAVE
INPUTS
INPUT
INTERRUPT
MASK
OPENDRAIN
PUSH-
PULL
CONFIGURATION
MAX7323
— Up to 4 4
4 I/O, 4 output-only versions:
4 open-drain I/O ports with latching transition
detection interrupt and selectable pullups.
4 push-pull outputs with selectable power-up default
levels.
MAX7328
MAX7329
— Up to 8 —
PCF8574-, PCF8574A-compatible versions:
8 open-drain I/O ports with nonlatching transition
detection interrupt and pullups on all ports.
Table 1. MAX7319–MAX7329 Family Comparison (continued)
ADDRESS
110xxxx Up to 4
0100xxx
0111xxx
Up to 8
OUTPUTS
OUTPUTS
Page 8

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
address selection determines which inputs have
pullups applied. However, at power-up, the I
2
C SDA
and SCL bus interface lines are high impedance at the
inputs of every device (master or slave) connected to
the bus, including the MAX7324. This is guaranteed as
part of the I
2
C specification. Therefore, address inputs
AD0 and AD2 that are connected to SDA or SCL during
power-up appear to be connected to V+. The pullup
selection logic uses AD0 to select whether pullups are
enabled for ports I0–I3, and uses AD2 to select whether
pullups are enabled for ports I4–I7. The rule is that a
logic-high SDA, or SCL connection selects the pullups,
while a logic-low deselects the pullups (Table 2). The
pullup configuration is correct on power-up for a standard I
2
C configuration, where SDA and SCL are pulled
up to V+ by the external I2C pullups.
There are circumstances where the assumption that
SDA = SCL = V+ on power-up is not true—for example,
in applications in which there is legitimate bus activity
during power-up. Also, if SDA and SCL are terminated
with pullup resistors to a different supply voltage than
the MAX7324’s supply voltage, and if that pullup supply
rises later than the MAX7324’s supply, then SDA or
SCL may appear at power-up to be connected to GND.
In such applications, use the four address combinations that are selected by connecting address inputs
AD0 and AD2 to V+ or GND (shown in bold in Tables 2
and 3). These selections are guaranteed to be correct
at power-up, independent of SDA and SCL behavior. If
one of the other 12 address combinations is used, an
unexpected combination of pullups might be asserted
until the first I2C transmission (to any device, not necessarily the MAX7324) is put on the bus.
Port Inputs
Port inputs switch at CMOS logic levels as determined
by the expander’s supply voltage, and are overvoltage
tolerant to +6V, independent of the device’s supply
voltage.
Port-Input Transition Detection
All eight input ports are monitored for changes since
the expander was last accessed through the serial
interface. The state of the input ports is stored in an
internal “snapshot” register for transition monitoring.
The snapshot is continuously compared with the actual
input conditions, and if a change is detected for any
port input, then an internal transition flag is set for that
port. The eight port inputs are sampled (internally
latched into the snapshot register) and the old transition flags cleared during the I2C acknowledge of every
MAX7324 read and write access. The previous port
transition flags are read through the serial interface as
the second byte of a 2-byte read sequence.
PIN CONNECTION
DEVICE ADDRESS
40kΩ INPUT PULLUP ENABLED
AD2 AD0
I7 I6 I5 I4 I3 I2 I1 I0
SCL GND1100000YYYY
—
SCL V+ 1100001YYYYYYYY
SCL SCL 1100010YYYYYYYY
SCL SDA 1100011YYYYYYYY
SDA GND1100100YYYY
—
SDA V+ 1100101YYYYYYYY
SDA SCL 1100110YYYYYYYY
SDA SDA 1100111YYYYYYYY
GND GND1101000
—
GND V+ 1101001
YYYY
GND SCL 1101010
YYYY
GND SDA 1101011
YYYY
V+ GND1101100YYYY
—
V+ V+ 1101101YYYYYYYY
V+ SCL 1101110YYYYYYYY
V+ SDA 1101111YYYYYYYY
Table 2. MAX7324 Address Map for Inputs I0–I7
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
———
———————
————
————
————
———
———
Page 9

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
A long read sequence (more than 2 bytes) can be used
to poll the expander continuously without the overhead
of resending the slave address. If more than 2 bytes
are read from the expander, the expander repeatedly
returns the 2 bytes of input port data followed by the
transition flags. The inputs are repeatedly resampled
and the transition flags repeatedly reset for each pair of
bytes read. All changes that occur during a long read
sequence are detected and reported.
The MAX7324 includes an 8-bit interrupt mask register
that selects which inputs generate an interrupt upon
change. Each input’s transition flag is set when its input
changes, independent of the interrupt mask register
settings. The interrupt mask register allows the processor to be interrupted for critical events, while the inputs
and the transition flags can be polled periodically to
detect less critical events.
The INT output is not reasserted during a read
sequence to avoid recursive reentry into an interrupt
service routine. Instead, if a data change occurs that
would normally cause the INT output to be set, the INT
assertion is delayed until the STOP condition. INT is not
reasserted upon a STOP condition if the changed input
data is read before the STOP occurs. The INT logic
ensures that unnecessary interrupts are not asserted,
yet data changes are detected and reported no matter
when the change occurs.
Transition-Detection Masks
The transition detection logic incorporates a transition
flag and an interrupt mask bit for each input port. The
eight transition flags can be read through the serial
interface, and the 8-bit interrupt mask is set through the
serial interface.
Each port’s transition flag is set when that port’s input
changes, and the change flag remains set even if the
input returns to its original state. The port’s interrupt
mask determines whether a change on that input port
generates an interrupt. Enable interrupts for high-priority inputs using the interrupt mask. The interrupt allows
the system to respond quickly to changes on these
inputs. Poll the MAX7324 periodically to monitor lessimportant inputs. The transition flags indicate whether a
permanent or transient change has occurred on any
input since the MAX7324 was last accessed.
PIN CONNECTION
DEVICE ADDRESS OUTPUTS POWER-UP DEFAULT
AD2 AD0
O8
SCL GND
11110000
SCL V+
11111111
SCL SCL
11111111
SCL SDA
11111111
SDA GND
11110000
SDA V+
11111111
SDA SCL
11111111
SDA SDA
11111111
GND GND
00000000
GND V+
00001111
GND SCL
00001111
GND SDA
00001111
V+ GND
11110000
V+ V+
11111111
V+
SCL
11111111
V+
SDA
11111111
Table 3. MAX7324 Address Map for Outputs O8–O15
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 O15 O14 O13 O12 O11 O10 O9
1010000
1010001
1010010
1010011
1010100
1010101
1010110
1010111
1011000
1011001
1011010
1011011
1011100
1011101
1011110
1011111
Page 10

Serial Interface
Serial Addressing
The MAX7324 operates as a slave that sends and
receives data through an I2C interface. The interface
uses a serial-data line (SDA) and a serial-clock line (SCL)
to achieve bidirectional communication between master(s) and slave(s). The master initiates all data transfers
to and from the MAX7324 and generates the SCL clock
that synchronizes the data transfer (Figure 1).
SDA operates as both an input and an open-drain output. A pullup resistor, typically 4.7kΩ, is required on
SDA. SCL operates only as an input. A pullup resistor,
typically 4.7kΩ, is required on SCL if there are multiple
masters on the 2-wire interface, or if the master in a single-master system has an open-drain SCL output.
Each transmission consists of a START condition sent
by a master, followed by the MAX7324’s 7-bit slave
address plus R/W bit, 1 or more data bytes, and finally
a STOP condition (Figure 2).
START and STOP Conditions
Both SCL and SDA remain high when the interface is
not busy. A master signals the beginning of a transmission with a START (S) condition by transitioning SDA
from high to low while SCL is high. When the master
has finished communicating with the slave, the master
issues a STOP (P) condition by transitioning SDA from
low to high while SCL is high. The bus is then free for
another transmission (Figure 2).
Bit Transfer
One data bit is transferred during each clock pulse.
The data on SDA must remain stable while SCL is high
(Figure 3).
MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
SDA
SCL
DATA LINE STABLE;
DATA VALID
CHANGE OF DATA
ALLOWED
Figure 3. Bit Transfer
SCL
SDA
t
R
t
F
t
BUF
START
CONDITION
STOP
CONDITION
REPEATED START CONDITION
START CONDITION
t
SU,STO
t
HD,STA
t
SU,STA
t
HD,DAT
t
SU,DAT
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
HD,STA
Figure 1. 2-Wire Serial-Interface Timing Details
SDA
SCL
START
CONDITION
STOP
CONDITION
SP
Figure 2. START and STOP Conditions
Page 11

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 11
Acknowledge
The acknowledge bit is a clocked 9th bit the recipient
uses to acknowledge receipt of each byte of data
(Figure 4). Each byte transferred effectively requires 9
bits. The master generates the 9th clock pulse, and the
recipient pulls down SDA during the acknowledge
clock pulse, such that the SDA line is stable low during
the high period of the clock pulse. When the master is
transmitting to the MAX7324, the MAX7324 generates
the acknowledge bit because the MAX7324 is the
recipient. When the MAX7324 is transmitting to the
master, the master generates the acknowledge bit
because the master is the recipient. The master does
not generate an acknowledge prior to issuing a stop
condition.
Slave Address
The MAX7324 has two different 7-bit slave addresses
(Tables 2 and 3). The addresses are different for communicating to either the eight push-pull outputs or the
eight inputs. The eighth bit following the 7-bit slave
address is the R/W bit. It is low for a write command
and high for a read command.
The first (A6), second (A5), and third (A4) bits of the
MAX7324 slave address are always 1, 1, and 0 (I0–I7)
or 1, 0, and 1 (O8–O15). Connect AD0 and AD2 to
GND, V+,SDA, or SCL to select the slave address bits
A3, A2, A1, and A0. The MAX7324 has 16 possible
slave address pairs (Tables 2 and 3), allowing up to 16
MAX7324 devices on an I2C bus.
Accessing the MAX7324
The MAX7324 is accessed though an I2C interface. The
MAX7324 provides two different 7-bit slave addresses
for either the eight input ports (I0–I7) or the eight pushpull ports (O8–O15). See Tables 2 and 3.
A single-byte read from the input ports of the
MAX7324 returns the status of the eight ports and
clears both the internal transition flags and the INT out-
put. A single-byte read from the output ports of the
MAX7324 returns the status of the eight output ports,
read back as inputs.
A 2-byte read from the input ports of the MAX7324
returns the status of the eight ports (as for a single-byte
read), followed by the transition flags. The internal transition flags and the INT output are cleared when the
MAX7324 acknowledges the slave address byte, but
the previous transition flag data is sent as the second
byte. A 2-byte read from the output ports of the
MAX7324 repeatedly returns the status of the eight output ports, read back as inputs.
A multibyte read (more than 2 bytes before the I2C
STOP bit) from the input ports of the MAX7324 repeatedly returns the port data, alternating with the transition
flags. As the input data is resampled for each transmission, and the transition flags are reset each time, a
multibyte read continuously returns the current data
and identifies any changing input ports.
SCL
SDA BY
TRANSMITTER
CLOCK PULSE
FOR ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
START
CONDITION
SDA BY
RECEIVER
12 89
S
Figure 4. Acknowledge
SDA
SCL
.
1A5
A3
A2 A1 A0
A4
R/W
MSB
LSB
ACK
Figure 5. Slave Address
Page 12

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
12 ______________________________________________________________________________________
If a port input data change occurs during the read
sequence, INT is reasserted during the I2C STOP bit.
The MAX7324 does not generate another interrupt during a single-byte or multibyte read.
Input-port data is sampled during the preceding I2C
acknowledge bit (the acknowledge bit for the I2C slave
address in the case of a single-byte or 2-byte read).
A multibyte read (more than 2 bytes before the I2C
STOP bit) from the output ports of the MAX7324 repeatedly returns the status of the eight output ports, read
back as inputs.
A single-byte write to the input ports of the MAX7324
sets the interrupt mask register and clears both the
internal transition flags and INT output.
A single-byte write to the output ports of the MAX7324
sets the logic state of all eight ports.
A multibyte write to the input ports of the MAX7324
sets the interrupt mask register repeatedly.
A multibyte write to the output ports of the MAX7324
repeatedly sets the logic state of all eight ports.
Reading from the MAX7324
A read from the input ports of the MAX7324 starts with
the master transmitting the input ports’ slave address
with the R/W bit set to high. The MAX7324 acknowledges the slave address and samples the ports during
the acknowledge bit. INT deasserts during the slave
address acknowledge.
Typically, the master reads 1 or 2 bytes from the
MAX7324 with each byte being acknowledged by the
master upon reception with the exception of the last
byte.
When the master reads one byte from the open-drain
ports of the MAX7324 and subsequently issues a STOP
condition (Figure 6), the MAX7324 transmits the current
port data, clears the transition flags, and resets the
transition detection. INT deasserts during the slave
acknowledge. The new snapshot data is the current
port data transmitted to the master, and therefore, port
changes occuring during the transmission are detected. INT remains high until the STOP condition.
SCL
MAX7324 SLAVE ADDRESS
SA
P
1
PORTS
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM MAX7324
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM MASTER
PORT SNAPSHOT
t
IV
t
PH
t
IR
A
I0
I1
I2I3I4I5
I6
I7
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
PORT SNAPSHOT
t
PS
t
IP
INT OUTPUT
R/W
S = START CONDITION A = ACKNOWLEDGE
P = STOP CONDITION
INT REMAINS HIGH UNTIL STOP CONDITION
Figure 6. Reading Input Ports of the MAX7324 (1 Data Byte)
Page 13

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 13
When the master reads 2 bytes from the output ports of
the MAX7324 and subsequently issues a STOP condition (Figure 7), the MAX7324 transmits the current port
data, followed by the transition flags. The transition
flags are then cleared, and transition detection is reset.
INT deasserts during the slave acknowledge. The new
snapshot data is the current port data transmitted to the
master, and therefore, port transitions occuring during
the transmission are detected. INT remains high until
the STOP condition. When the master reads more than
2 data bytes, the input port data alternates with the
transition flag.
A read from the output ports of the MAX7324 starts with
the master transmitting the ports’ slave address with
the R/W bit set high. The MAX7324 acknowledges the
slave address and samples the logic state of the output
ports during the acknowledge bit. The master can read
one or more bytes from the output ports of the
MAX7324, and then issues a STOP condition (Figure 8).
The MAX7324 transmits the current port data, read
back from the actual port outputs (not the port output
latches) during the acknowledge. If a port is forced to a
logic state other than its programmed state, the readback reflects this. If driving a capacitive load, the readback port level verification algorithms may need to take
the RC rise/fall time into account.
Typically, the master reads one byte from the ouput
ports of the MAX7324, then issues a STOP condition
(Figure 8). However, the master can read two or more
bytes from the output ports of the MAX7324, and then
issues a STOP condition. In this case, the MAX7324
resamples the port outputs during each acknowledge
and transmits the new data each time.
SCL
MAX7324 SLAVE ADDRESSSA P1
PORTS
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM MAX7324
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM MASTER
PORT SNAPSHOT
t
IV
t
PH
t
IR
A
I0
I1
I2I3I4I5
I6
I7
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
PORT SNAPSHOT
t
PS
t
IP
F0
F1
F2F3F4F5
F6
F7
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 A
PORT SNAPSHOT
FLAG
INT OUTPUT
R/W
S = START CONDITION A = ACKNOWLEDGE
P = STOP CONDITION
INT REMAINS HIGH UNTIL STOP CONDITION
Figure 7. Reading Input Ports of the MAX7324 (2 Data Bytes)
SCL
MAX7324 SLAVE ADDRESS
SA
P
1
ACKNOWLEDGE FROM MAX7324
PORT SNAPSHOT DATA
PORT SNAPSHOT TAKEN
A
P0P1P2P3
DATA 1
P4P5P6P7
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
PORT SNAPSHOT TAKEN
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM MASTER
R/W
Figure 8. Reading Output Ports of the MAX7324
Page 14

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
14 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Writing to the MAX7324
A write to the input ports of the MAX7324 starts with the
master transmitting the group’s slave address with the
R/W bit set low. The MAX7324 acknowledges the slave
address and samples the ports during the acknowledge bit. INT deasserts during the slave acknowledge.
The master can now transmit one or more bytes of
data. The MAX7324 acknowledges these subsequent
bytes of data and updates the interrupt mask register
with each new byte until the master issues a STOP condition (Figure 9).
A write to the output ports of the MAX7324 starts with
the master transmitting the group’s slave address with
the R/W bit set low. The MAX7324 acknowledges the
slave address and samples the ports during the
acknowledge bit. The master can now transmit one or
more bytes of data. The MAX7324 acknowledges these
subsequent bytes of data and updates the corresponding group’s ports with each new byte until the master
issues a STOP condition (Figure 10).
SCL
SDA
START CONDITION R/W
SLAVE ADDRESS
S0
12345678
AAA
t
PV
DATA 1 DATA 2
t
PV
DATA TO INTERRUPT MASK DATA TO INTERRUPT MASK
Figure 9. Writing to the Input Ports of the MAX7324
SCL
SDA
START CONDITION ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
SLAVE ADDRESS
S0
12345678
AAA
t
PV
DATA 1 DATA 2
DATA 2 VALIDDATA 1 VALID
WRITE
TO PORT
DATA OUT
FROM PORT
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
t
PV
DATA TO PORT DATA TO PORT
R/W
Figure 10. Writing to the Output Ports of the MAX7324
Page 15

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 15
Applications Information
Port Input and I2C Interface Level
Translation from Higher or Lower
Logic Voltages
SDA, SCL, AD0, AD2, RST, INT, and I0–I7 are overvoltage protected to +6V. This allows the MAX7324 to
operate from a lower supply voltage, such as +3.3V,
while the I2C interface and/or any of the eight input
ports are driven from a higher logic level, such as +5V.
The MAX7324 can operate from a higher supply voltage, such as +3V, while the I2C interface and/or some
of the input ports I0–I7 are driven from a lower logic
level, such as +2.5V. For V+ < 1.8V, apply a minimum
voltage of 0.8 x V+ to assert a logic-high on any input.
For V+ ≥ 1.8V, apply a voltage of 0.7 x V+ to assert a
logic-high. For example, a MAX7324 operating from a
+5V supply may not recognize a +3.3V nominal logic
high. One solution for input level translation is to drive
the MAX7324 inputs from open-drain outputs. Use a
pullup resistor to V+ or a higher supply to ensure a high
logic voltage greater than 0.7 x V+.
Port Output Signal Level Translation
RST, SCL, SDA, AD0, and AD2 remain high impedance
with up to +6V asserted on them when the MAX7324 is
powered down (V+ = 0). The MAX7324 can therefore
be used in hot-swap applications.
Each of the eight output ports has protection diodes to
V+ and GND. When a port output is driven to a voltage
higher than V+ or lower than GND, the appropriate protection diode clamps the output to a diode drop above
V+ or below GND. When the MAX7324 is powered
down (V+ = 0), every output port's protection diodes to
V+ and GND continue to appear as a diode clamp from
each output to GND (Figure 11).
Each of the input ports I0–I7 has a protection diode to
GND (Figure 12). When a port input is driven to a voltage lower than GND, the protection diode clamps the
voltage to a diode drop below GND.
Each of the eight input ports I0–I7 also has a 40kΩ (typ)
pullup resistor that can be enabled or disabled. When a
port input is driven to a voltage higher than V+,the
body diode of the pullup enable switch conducts and
the 40kΩ pullup resistor is enabled. When the
MAX7324 is powered down (V+ = 0), every input port
appears as a 40kΩ resistor in series with a diode connected to ground. Input ports are protected to +6V
under any of these circumstances.
Driving LED Loads
When driving LEDs from one of the eight output ports,
O8–O15, a resistor must be fitted in series with the LED to
limit the LED current to no more than 20mA. Connect the
LED cathode to the MAX7324 port, and the LED anode
to V+ through the series current-limiting resistor, R
LED
.
I0–I7
PULLUP
ENABLE
INPUT
40kΩ
V+
V+
MAX7324
Figure 12. MAX7324 Input Port Structure
OUTPUT
V+
GNDGND
V+
O8–O15
MAX7324
Figure 11. MAX7324 Output Port Structure
Page 16

MAX7324
Set the port output low to light the LED. Choose the
resistor value according to the following formula:
R
LED
= (V
SUPPLY
- V
LED
- VOL) / I
LED
where:
R
LED
is the resistance of the resistor in series with the
LED (Ω).
V
SUPPLY
is the supply voltage used to drive the LED
(V).
V
LED
is the forward voltage of the LED (V).
VOLis the output low voltage of the MAX7324 when
sinking I
LED
(V).
I
LED
is the desired operating current of the LED (A).
For example, to operate a 2.2V red LED at 10mA from
+5V supply:
R
LED
= (5 - 2.2 - 0.1) / 0.01 = 270Ω
Driving Load Currents Higher than 20mA
The MAX7324 can be used to drive loads such as
relays that draw more than 20mA by paralleling outputs. Use at least one output per 20mA of load current;
for example, a 5V 330mW relay draws 66mA, and
therefore, requires four paralleled outputs. Any combination of outputs can be used as part of a load-sharing
design because any combination of ports can be set or
cleared at the same time by writing to the MAX7324. Do
not exceed a total sink current of 100mA for the device.
Protect the MAX7324 from the negative voltage transient generated when switching off inductive loads
(such as relays) by connecting a reverse-biased diode
across the inductive load. Choose the peak current for
the diode to be greater than the inductive load's operating current.
Power-Supply Considerations
The MAX7324 operates with a supply voltage of
+1.71V to +5.5V over the -40°C to +125°C temperature range. Bypass the supply to GND with a ceramic
capacitor of at least 0.047µF as close as possible to
the device. For the TQFN version, additionally connect
the exposed pad to GND.
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
16 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Page 17

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 17
Pin Configurations (continued)
Chip Information
PROCESS: BiCMOS
TOP VIEW
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
V+
SDA
SCL
AD0
015
014
013
012
MAX7324
QSOP
RST
AD2
I2
I0
I1
I3
I4
16
15
9
10
011
010
I5
I6
14
13
11
12
O9
O8
I7
GND
INT
+
Functional Diagram
MAX7324
I2
I7
I6
I5
I4
O11
O10
09
08
O15
O14
013
012
V+
3.3V
µC
SCL
SCL
SDA
AD0
I1
I0
SDA
I3
GND
INPUT
INPUT
AD2
INT
INPUT
INPUT
INPUT
INPUT
INPUT
INPUT
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
RST
INT
RST
Typical Application Circuit
AD0
AD2
SCL
SDA
RST
INPUT
FILTER
POWER-
ON RESET
O15
O14
O13
O12
O11
O10
O9
I2C
CONTROL
MAX7324
I/O
PORTS
O8
I7
I6
I5
I4
I3
I2
I1
I0
N
INT
Page 18

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
18 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Package Information
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.)
24L QFN THIN.EPS
PACKAGE OUTLINE,
21-0139
2
1
E
12, 16, 20, 24, 28L THIN QFN, 4x4x0.8mm
Page 19

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 19
Package Information (continued)
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.)
PACKAGE OUTLINE,
21-0139
2
2
E
12, 16, 20, 24, 28L THIN QFN, 4x4x0.8mm
Page 20

MAX7324
I2C Port Expander with Eight Push-Pull Outputs
and Eight Inputs
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
20 ____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 2006 Maxim Integrated Products is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Package Information (continued)
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.)
QSOP.EPS
F
1
1
21-0055
PACKAGE OUTLINE, QSOP .150", .025" LEAD PITCH
Revision History
All pages changed at Rev 2.
 Loading...
Loading...