Page 1
General Description
The MAX6674 cold-junction-compensation thermocouple-to-digital converter performs cold-junction compensation and digitizes the signal from a type-K
thermocouple. The data is output in a 10-bit resolution,
SPI™-compatible, read-only format.
This converter resolves temperatures to 0.125°C, allows
readings as high as +128°C, and exhibits thermocouple
accuracy of ±2°C for temperatures ranging from 0°C to
+125°C.
The MAX6674 is available in a small, 8-pin SO package.
Applications
Industrial
Appliances
HVAC
Automotive
Features
♦ Cold-Junction Compensation
♦ Simple SPI-Compatible Serial Interface
♦ 10 Bit, 0.125°C
♦ Open Thermocouple Detection
MAX6674
Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocouple-
to-Digital Converter (0°C to +128°C)
________________________________________________________________ Maxim Integrated Products 1
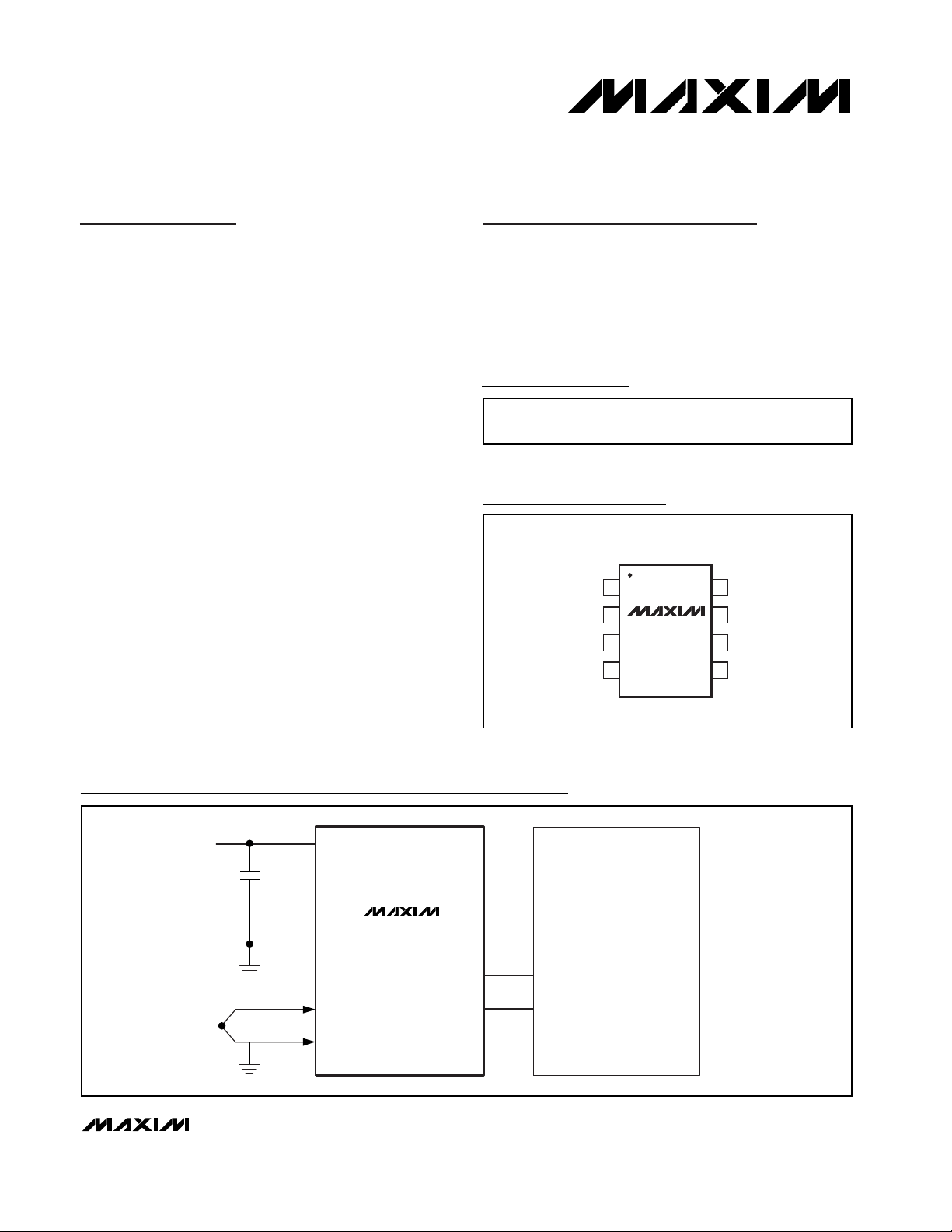
Pin Configuration
Vcc
GND
T+
T-
SO
SCK
CS
MICROCONTROLLER
68HC11A8
MISO
SCK
SSB
0.1µF
MAX6674
Typical Application Circuit
19-2241; Rev 1; 8/02
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim/Dallas Direct! at
1-888-629-4642, or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
Ordering Information
SPI is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
MAX6674ISA -20°C to +85°C 8 SO
TOP VIEW
GND
1
2
MAX6674
3
T+
4
CC
87N.C.
SOT-
CS
6
SCKV
5
SO
Page 2
MAX6674
Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocoupleto-Digital Converter (0°C to +128°C)
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VCC= +3.0V to +5.5V, TA= -20°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values specified at +25°C.) (Note 1)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Supply Voltage (VCCto GND) ................................. -0.3V to +6V
SO, SCK, CS, T-, T+ to GND .......................-0.3V to V
CC
+ 0.3V
SO Current .........................................................................50mA
ESD Protection (Human Body Model) ........................... ±2000V
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +70°C)
8-Pin SO (derate 5.88mW/°C above +70°C)................471mW
Operating Temperature Range ...........................-20°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature......................................................+150°C
SO Package
Vapor Phase (60s) ......................................................+215°C
Infrared (15s) ..............................................................+220°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) ................................ +300°C
Temperature Error
Temperature Conversion
Constant
Cold-Junction Compensation
Resolution 0.125 °C
Thermocouple Input Impedance 20 kΩ
Supply Voltage V
Supply Current I
Power-On Reset Threshold VCC rising 1 2 2.5 V
Power-On Reset Hysteresis 50 mV
Conversion Time (Note 2) 0.15 0.18 s
SERIAL INTERFACE
Input Low Voltage V
Input High Voltage V
Input Leakage Current I
Input Capacitance C
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
T
THERMOCOUPLE
+100°C, T
(Note 2)
T
THERMOCOUPLE
0°C to +125°C, T
+25°C (Note 2)
= +25°C
A
=
VCC = +3.3V -1 +1
V
= +5V -1.5 +1.5
CC
=
VCC = +3.3V -2 +2
=
A
V
= +5V -3 +3
CC
5.125 µv/LSB
CC
CC
IL
IH
LEAK
IN
TA = +25°CV
= -20°C to +85°C
T
A
(Note 2)
VIN = GND or V
CC
= +3.3V -1 +1
CC
= +3.3V and +5V -3 +3
V
CC
3.0 5.5 V
12mA
0.7 x
V
CC
-5 5 µA
5pF
0.3 x
V
CC
°C
°C
V
V
Page 3
MAX6674
Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocouple-
to-Digital Converter (0°C to +128°C)
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
Typical Operating Characteristics
(VCC= +3.3V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VCC= +3.0V to +5.5V, TA= -20°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values specified at +25°C.) (Note 1)
Note 1: All specifications are 100% tested at T
A
= +25°C. Specification limits over temperature (TA= -20°C to +85°C) are guaran-
teed by design and characterization, not production tested.
Note 2: Guaranteed by design. Not production tested.
Output High Voltage V
Output Low Voltage V
TIMING
Serial Clock Frequency f
SCK Pulse High Width t
SCK Pulse Low Width t
CSB Fall to SCK Rise t
CSB Fall to Output Enable t
CSB Rise to Output Disable t
SCK Fall to Output Data Valid t
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
V
-
OH
OL
SCL
CH
CL
CSS
DV
TR
DO
I
I
= 1.6mA
SOURCE
= 1.6mA 0.4 V
SINK
CL = 10pF 100 ns
CL = 10pF 100 ns
CL = 10pF 100 ns
CL = 10pF 100 ns
CC
0.4
100 ns
100 ns
V
4.3 MHz
OUTPUT CODE ERROR
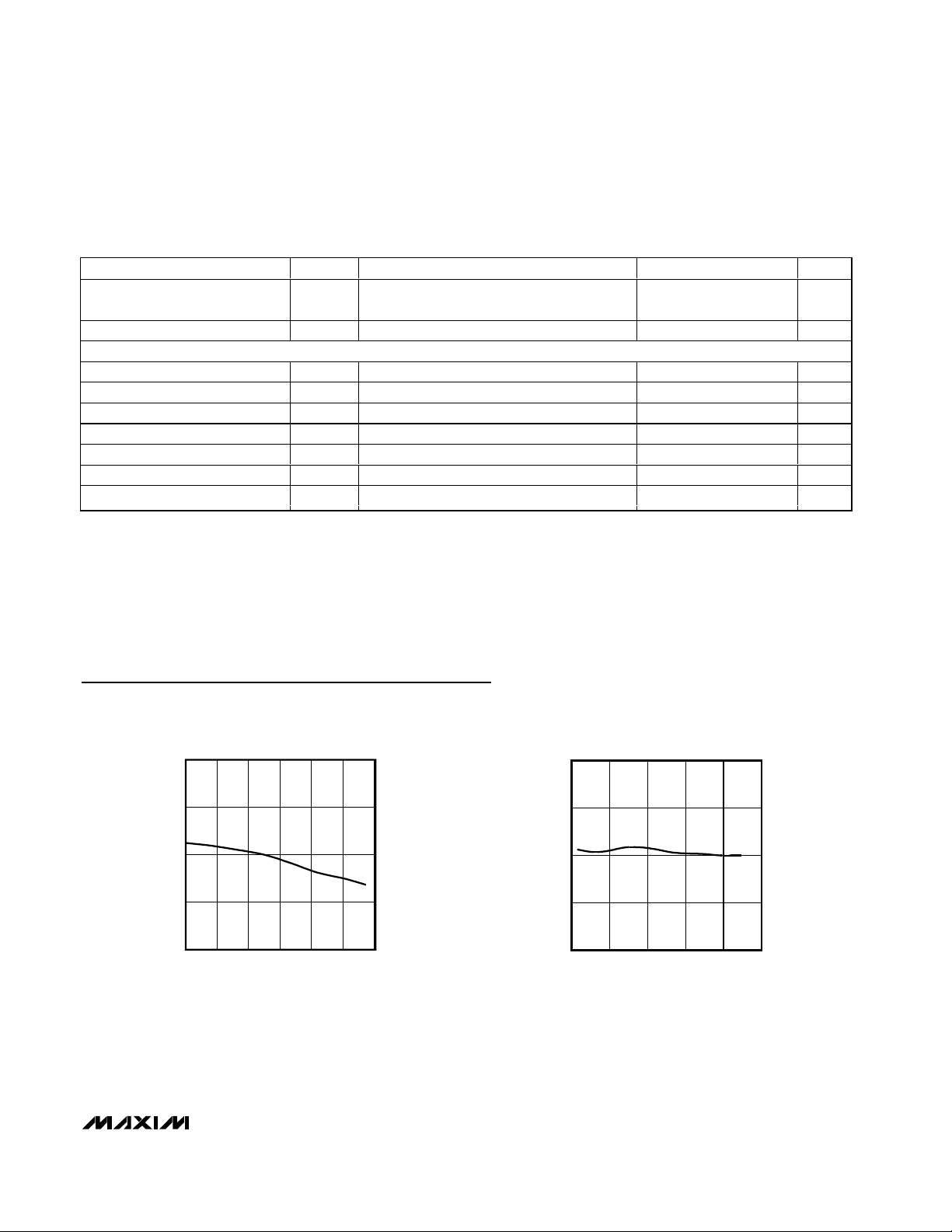
vs. TEMPERATURE
2
1
0
OUTPUT CODE ERROR (°C)
-1
-2
04515 30 60 75 90
TEMPERATURE (°C)
MAX6674 toc01
OUTPUT CODE ERROR
vs. VOLTAGE DIFFERENTIAL
2
1
0
OUTPUT CODE ERROR (°C)
-1
-2
-1200 12000 2400 3600 4800
VOLTAGE DIFFERENTIAL (µV)
MAX6674 toc02
Page 4

MAX6674
Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocoupleto-Digital Converter (0°C to +128°C)
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Detailed Description
The MAX6674 is a sophisticated thermocouple-to-digital converter with a built-in 10-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The device also contains cold-junction
compensation sensing and correction, a digital controller, an SPI-compatible interface, and associated
control logic.
The MAX6674 is designed to work in conjunction with
an external microcontroller (µC) or other intelligence in
thermostatic, process-control, or monitoring applications. The µC is typically a power-management or keyboard controller, generating SPI serial commands by
“bit-banging” general-purpose input-output (GPIO) pins
or through a dedicated SPI interface block.
Temperature Conversion
The MAX6674 includes signal conditioning hardware to
convert the thermocouple’s signal into a voltage that is
compatible with the input channels of the ADC. The T+
and T-inputs connect to internal circuitry that reduces the
introduction of noise errors from the thermocouple wires.
Before converting the thermoelectric voltages into
equivalent temperature values, it is necessary to compensate for the difference between the thermocouple
cold-junction side (MAX6674 ambient temperature) and
a 0°C virtual reference.
For a type-K thermocouple, the voltage changes by
41µV/°C, which approximates the thermocouple characteristic with the following linear equation:
V
OUT
= (41µV/°C) ✕(TR- T
AMB
)
where:
V
OUT
is the thermocouple output voltage (µV).
TRis the temperature of the remote point (°C).
T
AMB
is the ambient temperature (°C).
Cold-Junction Compensation
The function of the thermocouple is to sense a difference in temperature between two ends. The thermocouple’s hot junction can be read from 0°C to
+127.875°C. The cold end (ambient temperature of the
board on which the MAX6674 is mounted) can only
range from -20°C to +85°C. While the temperature at
the cold end fluctuates, the MAX6674 continues to
accurately sense the temperature difference at the
opposite end.
The MAX6674 senses and corrects for the changes in
the ambient temperature with cold-junction compensation. The device converts the ambient temperature
reading into a voltage using a temperature-sensing
diode. To make the actual thermocouple temperature
measurement, the MAX6674 measures the voltage from
the thermocouple’s output and from the sensing diode.
The device’s internal circuitry passes the diode’s voltage (sensing ambient temperature) and thermocouple
voltage (sensing remote temperature minus ambient
temperature) to the conversion function stored in the
ADC to calculate the thermocouple’s hot-junction temperature.
Optimal performance from the MAX6674 is achieved
when the thermocouple cold junction and the device
are at the same temperature. Avoid placing heat-generating devices or components near the MAX6674
because this may produce cold-junction-related errors.
Digitization
The ADC adds the cold-junction diode measurement
with the amplified thermocouple voltage and reads out
the 10-bit sequence onto the S0 pin. A sequence of all
zeros means the thermocouple reading is 0°C. A
sequence of all ones means the thermocouple reading
is +127.875°C.
Pin Description
PIN NAME FUNCTION
1 GND Ground
Alumel Lead of Type-K Thermocouple.
2T-
3 T+ Chromel Lead of Type-K Thermocouple
4V
5 SCK Serial Clock Input
6 CS
7 S0 Serial Data Output
8 N.C. No Connection
Should be connected to ground
externally.
Positive Supply. Bypass with a 0.1µF
CC
capacitor to GND.
Chip Select. Set CS low to enable the
serial interface.
Page 5

MAX6674
Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocouple-
to-Digital Converter (0°C to +128°C)
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
Applications Information
Serial Interface
The Typical Application Circuit shows the MAX6674
interfaced with a microcontroller. In this example, the
MAX6674 processes the reading from the thermocouple and transmits the data through a serial interface.
Force CS low and apply a clock signal at SCK to read
the results at S0. Forcing CS low immediately stops any
conversion process. Initiate a new conversion process
by forcing CS high.
Force CS low to output the first bit on the S0 pin. A
complete serial interface read requires 16 clock cycles.
Read the 16 output bits on the falling edge of the clock.
The first bit, D15, is a dummy sign bit and always zero.
Bits D14–D5 contain the converted temperature in the
order of MSB to LSB. Bit D4 reads a high value when
any of the thermocouple inputs are open. Bit D3 is
always low to provide a device ID for the MAX6674.
Bits D2–D0 are in three-state when CS is high.
Figure 1a is the serial interface protocol and Figure 1b
shows the serial interface timing. Figure 2 is the S0 output.
Open Thermocouple
Bit D4 is normally low and goes high if the thermocouple input is open. The open thermocouple detection circuit is implemented completely into the MAX6674. In
order to allow the operation of the open thermocouple
detector, T- must be grounded. Make the ground connection as close to the GND pin as possible.
Noise Considerations
The accuracy of the MAX6674 is susceptible to powersupply coupled noise. The effects of power-supply
noise can be minimized by placing a 0.1µF ceramic
bypass capacitor close to the supply pin of the device.
Thermal Considerations
Self-heating degrades the temperature measurement
accuracy of the MAX6674 in some applications. The
magnitude of the temperature errors depends on the
thermal conductivity of the MAX6674 package, the
mounting technique, and the effects of airflow. Use a
large ground plane to improve the temperature measurement accuracy.
The accuracy of a thermocouple system can also be
improved by following these precautions:
• Use the largest wire possible that does not shunt
heat away from the measurement area.
• If small wire is required, use it only in the region of
the measurement and use extension wire for the
region with no temperature gradient.
• Avoid mechanical stress and vibration that could
strain the wires.
• When using long thermocouple wires, use a twisted-pair extension wire.
• Avoid steep temperature gradients.
• Try to use the thermocouple wire well within its tem-
perature rating.
• Use the proper sheathing material in hostile environments to protect the thermocouple wire.
• Use extension wire only at low temperatures and
only in regions of small gradients.
• Keep an event log and a continuous record of thermocouple resistance.
Reducing Effects of Pick-Up Noise
The input amplifier (A1) is a low-noise amplifier
designed to enable high-precision input sensing. Keep
the thermocouple and connecting wires away from
electrical noise sources.
Page 6

MAX6674
Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocoupleto-Digital Converter (0°C to +128°C)
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Figure 1a. Serial Interface Protocol
Figure 1b. Serial Interface Timing
Figure 2. S0 Output
CS
SCK
SO
D15
D14
D13 D12
t
CSS
CS
SCK
t
DV
SO
D15 D0D1D2D3
D11
t
CH
t
D10
DO
D9
t
D7 D6
D8
CL
D5
D4 D3
D2 D1 D0
t
TR
DUMMY
BIT
SIGN BIT
Bit 15 14
13
TEMPERATURE READING
12 11
10-BIT
10 9
THERMOCOUPLE
DEVICE
INPUT
8765 4 3 210
0 MSB LSB 0 Three-state
ID
STATE
Page 7

Chip Information
TRANSISTOR COUNT: 6460
PROCESS: BiCMOS
MAX6674
Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocouple-
to-Digital Converter (0°C to +128°C)
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
Block Diagram
V
CC
0.1µF
4
COLD-JUNCTION
COMPENSATION
DIODE
300kΩ
S3
T+
3
T-
2
10kΩ
S2
10kΩ
S1
A1
1MΩ
A2
20pF
S5
S4
DIGITAL
CONTROLLER
ADC
5
SCK
7
SO
6
CS
300kΩ
MAX6674
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
1
GND
Page 8

MAX6674
Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocoupleto-Digital Converter (0°C to +128°C)
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
8 _____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 2002 Maxim Integrated Products Printed USA is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products.
Package Information
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages.)
SOICN.EPS
 Loading...
Loading...