Page 1

For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim Direct at 1-888-629-4642,
or visit Maxim's website at www.maxim-ic.com.
General Description
The MAX5590–MAX5595 octal, 12/10/8-bit, voltage-output digital-to-analog converters (DACs) offer buffered
outputs and a 3µs maximum settling time at the 12-bit
level. The DACs operate from a +2.7V to +5.25V analog
supply and a separate +1.8V to +5.25V digital supply.
The 20MHz 3-wire serial interface is compatible with
SPI™, QSPI™, MICROWIRE™, and digital signal
processor (DSP) protocol applications. Multiple devices
can share a common serial interface in direct-access or
daisy-chained configuration. The MAX5590–MAX5595
provide two multifunction, user-programmable, digital
I/O ports. The externally selectable power-up states of
the DAC outputs are either zero scale, midscale, or full
scale. Software-selectable FAST and SLOW settling
modes decrease settling time in FAST mode, or reduce
supply current in SLOW mode.
The MAX5590/MAX5591 are 12-bit DACs, the MAX5592/
MAX5593 are 10-bit DACs, and the MAX5594/
MAX5595 are 8-bit DACs. The MAX5590/MAX5592/
MAX5594 provide unity-gain-configured output buffers,
while the MAX5591/MAX5593/MAX5595 provide forcesense-configured output buffers. The MAX5590–
MAX5595 are specified over the extended -40°C to
+85°C temperature range, and are available in spacesaving 24-pin and 28-pin TSSOP packages.
Applications
Portable Instrumentation
Automatic Test Equipment (ATE)
Digital Offset and Gain Adjustment
Automatic Tuning
Programmable Voltage and Current Sources
Programmable Attenuators
Industrial Process Controls
Motion Control
Microprocessor (µP)-Controlled Systems
Power Amplifier Control
Fast Parallel-DAC to Serial-DAC Upgrades
Features
o Octal, 12/10/8-Bit Serial DACs in TSSOP Packages
o 3µs (max) 12-Bit Settling Time to 1/2 LSB
o Integral Nonlinearity:
1 LSB (max) MAX5590/MAX5591 A-Grade (12-Bit)
1 LSB (max) MAX5592/MAX5593 (10-Bit)
1/2 LSB (max) MAX5594/MAX5595 (8-Bit)
o Guaranteed Monotonic, ±1 LSB (max) DNL
o Two User-Programmable Digital I/O Ports
o Single +2.7V to +5.25V Analog Supply
o +1.8V to AV
DD
Digital Supply
o 20MHz, 3-Wire, SPI-/QSPI-/MICROWIRE-/DSP-
Compatible Serial Interface
o Glitch-Free Outputs Power Up to Zero Scale,
Midscale, or Full Scale Controlled by PU Pin
o Unity-Gain or Force-Sense-Configured Output
Buffers
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
________________________________________________________________
Maxim Integrated Products
1
Ordering Information
19-2983; Rev 3; 1/10
*
Future product—contact factory for availability. Specifications
are preliminary.
+Denotes a lead(Pb)-free/RoHS-compliant package.
Selector Guide and Pin Configurations appear at end of data
sheet.
EVALUATION KIT
AVAILABLE
SPI/QSPI are trademarks of Motorola, Inc.
MICROWIRE is a trademark of National Semiconductor Corp.
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
MAX5590AEUG+* -40°C to +85°C 24 TSSOP
MAX5590BEUG+ -40°C to +85°C 24 TSSOP
MAX5591AEUI+* -40°C to +85°C 28 TSSOP
MAX5591BEUI+ -40°C to +85°C 28 TSSOP
MAX5592EUG+ -40°C to +85°C 24 TSSOP
MAX5593EUI+ -40°C to +85°C 28 TSSOP
MAX5594EUG+ -40°C to +85°C 24 TSSOP
MAX5595EUI+ -40°C to +85°C 28 TSSOP
Page 2
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
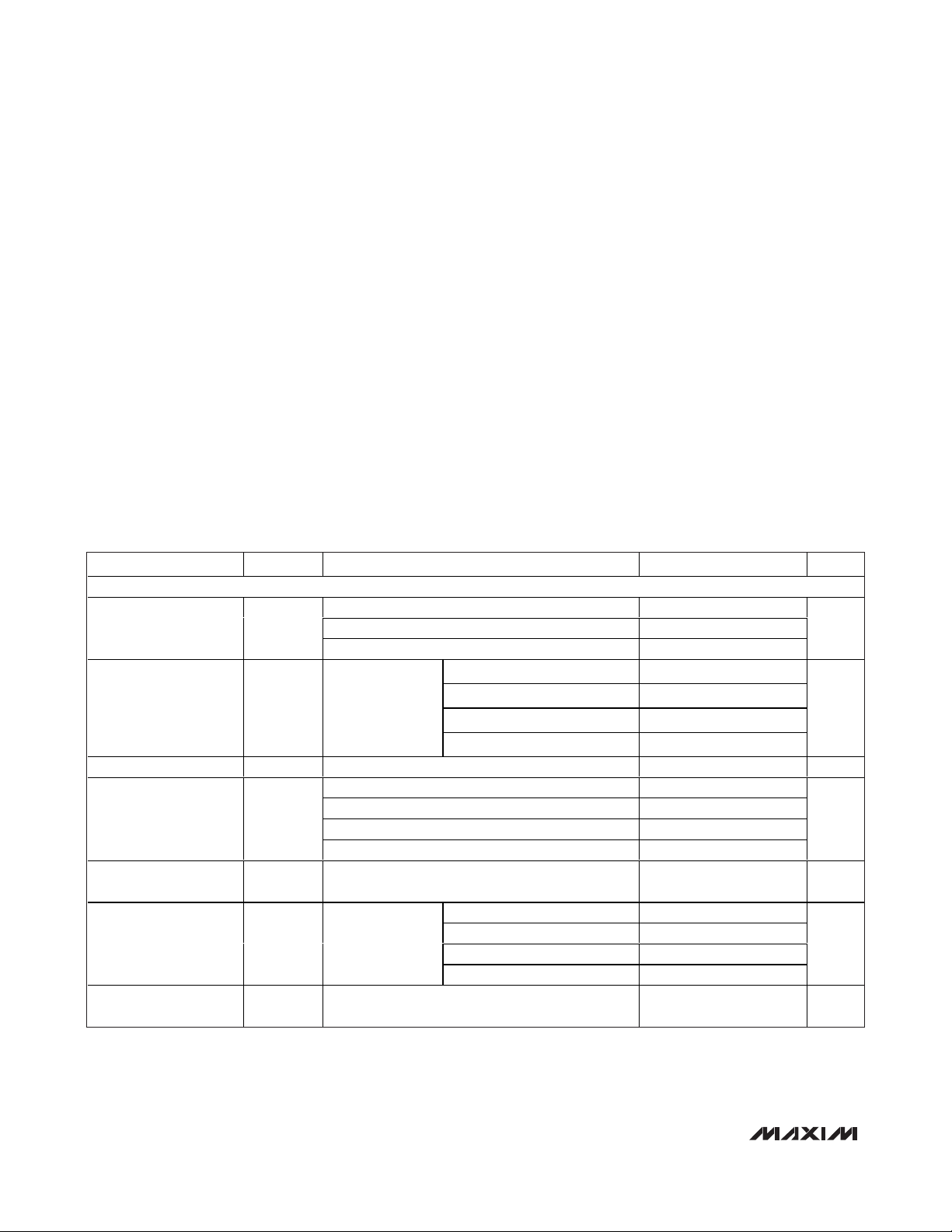
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(AVDD= 2.7V to 5.25V, DVDD= 1.8V to AVDD, V
AGND
= 0V, V
DGND
= 0V, V
REF
= 2.5V (for AVDD= 2.7V to 5.25V), V
REF
= 4.096V (for
AV
DD
= 4.5V to 5.25V), RL= 10kΩ, CL= 100pF, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
(Note 1)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
AVDDto DVDD........................................................................±6V
AGND to DGND ..................................................................±0.3V
AV
DD
to AGND, DGND.............................................-0.3V to +6V
DV
DD
to AGND, DGND ............................................-0.3V to +6V
FB_, OUT_,
REF to AGND........-0.3V to the lower of (AV
DD
+ 0.3V) or +6V
SCLK, DIN, CS, PU,
DSP to DGND .......-0.3V to the lower of (DV
DD
+ 0.3V) or +6V
UPIO1, UPIO2
to DGND ...............-0.3V to the lower of (DV
DD
+ 0.3V) or +6V
Maximum Current into Any Pin .........................................±50mA
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +70°C)
24-Pin TSSOP (derate 13.9mW/°C above +70°C) .....1111mW
28-Pin TSSOP (derate 14mW/°C above +70°C) ........1117mW
Operating Temperature Range ...........................-40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature .....................................+150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C
Soldering Temperature (reflow) .......................................+260°C
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
STATIC ACCURACY
MAX5590/MAX5591 12
MAX5592/MAX5593 10Resolution N
MAX5594/MAX5595 8
V
REF
AV
Integral Nonlinearity INL
Differential Nonlinearity DNL Guaranteed monotonic (Note 2) ±1 LSB
Offset Error V
Offset-Error Drift 5
Gain Error GE Full-scale output
Gain-Error Drift 1
OS
DD
V
REF
AV
DD
(Note 2)
M AX 5590A/M AX 5591A ( 12- b i t) , d eci m al cod e = 40 ±5
M AX 5590B/M AX 5591B ( 12- b i t) , d eci m al cod e = 40 ±5 ±25
MAX5592/MAX5593 (10-bit), decimal code = 10 ±5 ±25
MAX5594/MAX5595 (8-bit), decimal code = 3 ±5 ±25
= 2.5V at
= 2.7V and
= 4.096V at
= 5.25V
MAX5590A/MAX5591A (12-bit) ±1
MAX5590B/MAX5591B (12-bit) ±2 ±4
MAX5592/MAX5593 (10-bit) ±0.5 ±1
MAX5594/MAX5595 (8-bit) ±0.125 ±0.5
MAX5590A/MAX5591A (12-bit) ±4
MAX5590B/MAX5590B (12-bit) ±20 ±40
MAX5592/MAX5593 (10-bit) ±5 ±10
MAX5594/MAX5595 (8-bit) ±2 ±3
Bits
LSB
mV
ppm of
FS/°C
LSB
ppm of
FS/°C
Page 3
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(AVDD= 2.7V to 5.25V, DVDD= 1.8V to AVDD, V
AGND
= 0V, V
DGND
= 0V, V
REF
= 2.5V (for AVDD= 2.7V to 5.25V), V
REF
= 4.096V (for
AV
DD
= 4.5V to 5.25V), RL= 10kΩ, CL= 100pF, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
(Note 1)
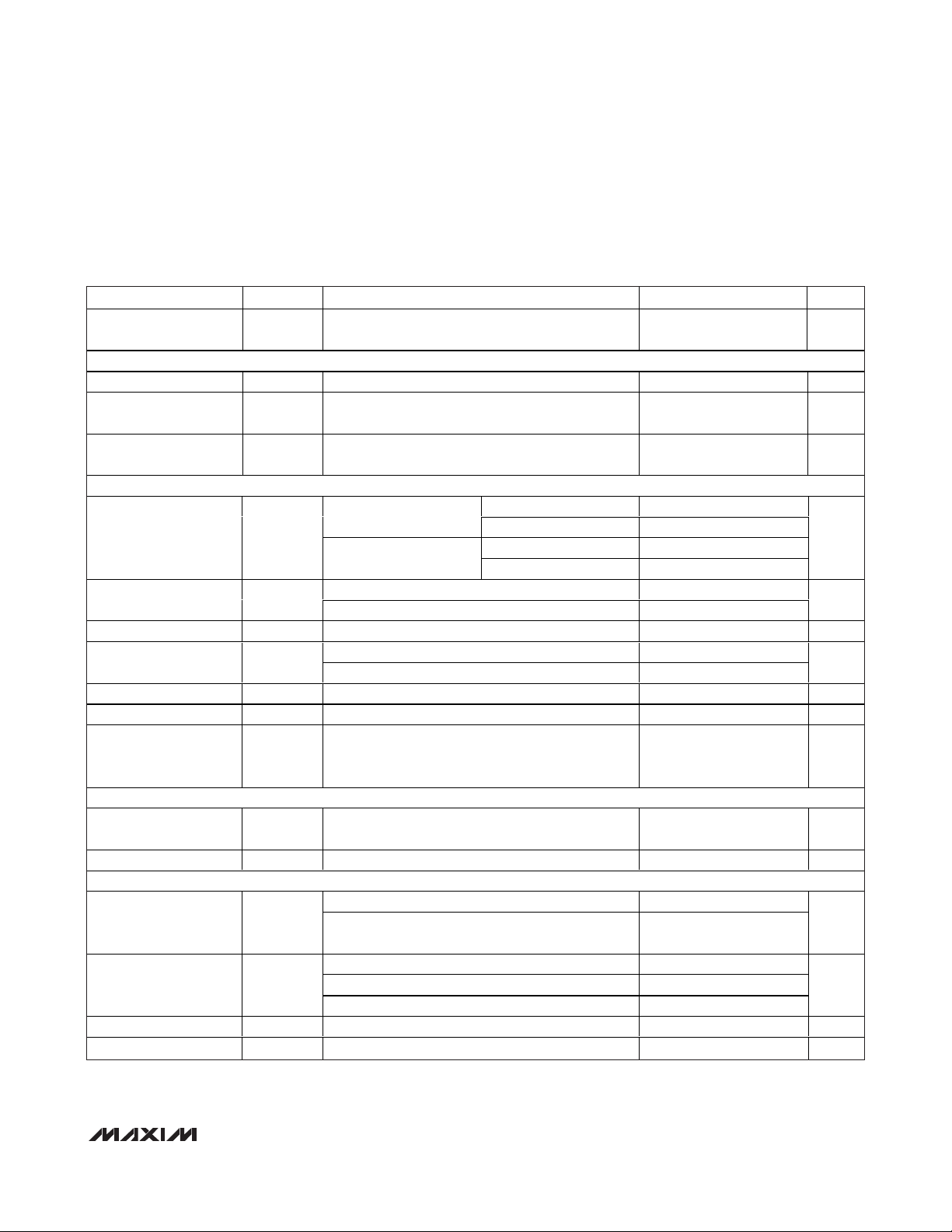
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Power-Supply Rejection
Ratio
REFERENCE INPUT
Reference Input Range V
Reference Input
Resistance
Reference Leakage
Current
DAC OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Noise
Output Voltage Range
(Note 3)
DC Output Impedance 38 Ω
Short-Circuit Current
Power-Up Time From VDD applied until interface is functional 30 60 µs
Wake-Up Time Coming out of shutdown, outputs settled 40 µs
Output OUT_ and FB_
Open-Circuit Leakage
Current
DIGITAL OUTPUTS (UPIO_)
Output High Voltage V
Output Low Voltage V
DIGITAL INPUTS (SCLK, CS, DIN, DSP, UPIO_)
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Leakage Current I
Input Capacitance C
PSRR Full-scale output, AV
REF
R
REF
OH
OL
IH
IL
IN
IN
Normal operation (no code dependence) 145 200 kΩ
Shutdown mode 0.5 1 µA
SLOW mode, full scale
FAST mode, full scale
Unity-gain output 0 AV
Force-sense output 0 AV
AVDD = 5V, OUT_ to AGND, full scale, FAST mode 57
AV
DD
Programmed in shutdown mode, force-sense
outputs only
I
SOURCE
I
SINK
DVDD ≥ 2.7V 2.4
DV
DD
DV
DD
2.7V ≤ DV
DV
DD
= 3V, OUT_ to AGND, full scale, FAST mode 45
= 2mA 0.4 V
< 2.7V
> 3.6V 0.8
< 2.7V 0.2
= 2mA
≤ 3.6V 0.6
DD
= 2.7V to 5.25V 200 µV/V
DD
Unity gain 85
Force sense 67
Unity gain 140
Force sense 110
0.25 AV
-
DV
DD
0.5
0.7 x
DV
DD
DD
DD
/ 2
DD
0.01 µA
±0.1 ±1 µA
10 pF
µV
V
RMS
V
mA
V
V
V
Page 4
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(AVDD= 2.7V to 5.25V, DVDD= 1.8V to AVDD, V
AGND
= 0V, V
DGND
= 0V, V
REF
= 2.5V (for AVDD= 2.7V to 5.25V), V
REF
= 4.096V (for
AV
DD
= 4.5V to 5.25V), RL= 10kΩ, CL= 100pF, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
(Note 1)
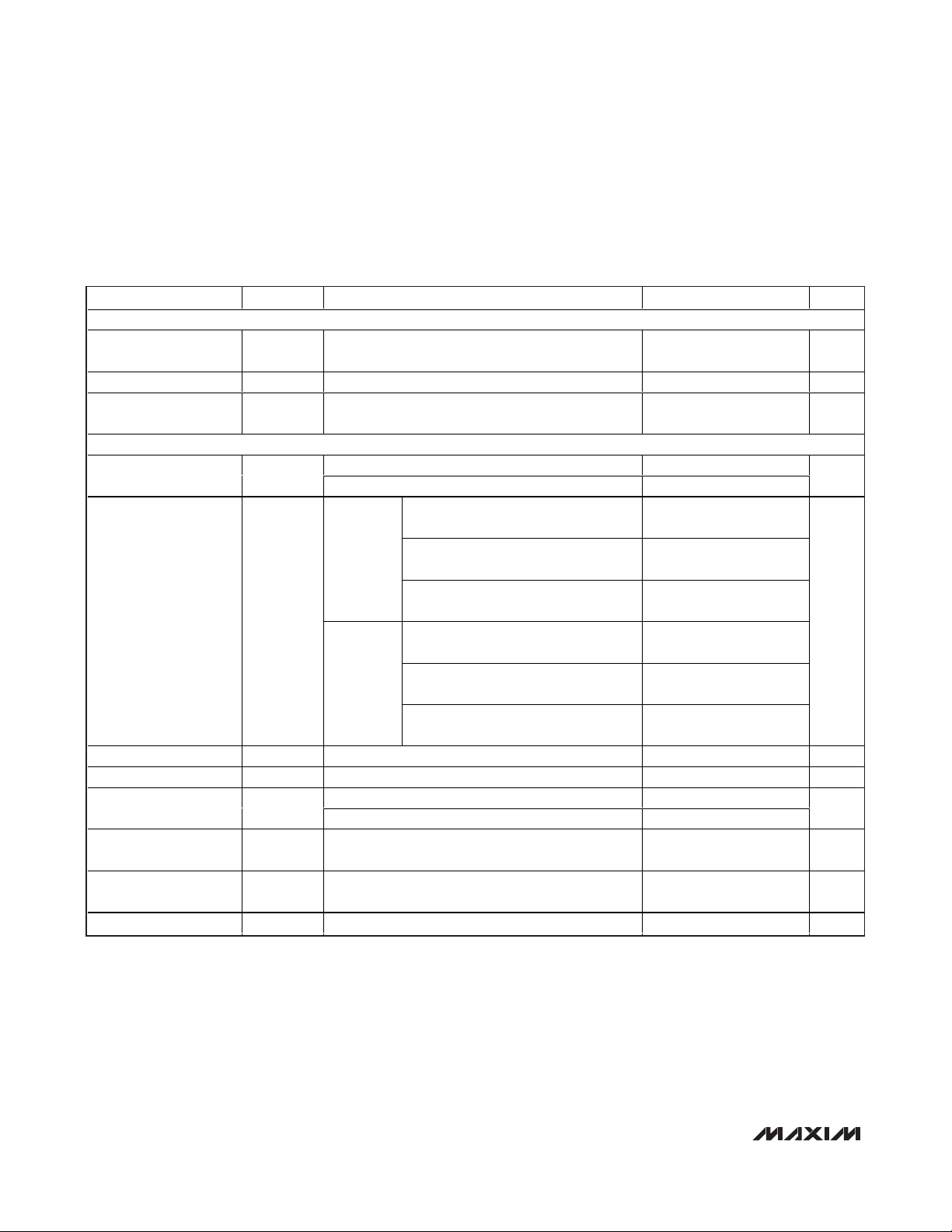
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
PU INPUT
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Leakage Current I
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Voltage-Output Slew
Rate
Voltage-Output Settling
Time (Note 5)
FB_ Input Voltage 0V
FB_ Input Current 0.1 µA
Reference -3dB
Bandwidth (Note 6)
Digital Feedthrough
Digital-to-Analog Glitch
Impulse
DAC-to-DAC Crosstalk (Note 4) 15 nV-s
IH-PU
IL-PU
IN-PU
SR
PU still considered unconnected when connected to
a tri-state bus
FAST mode 3.6
SLOW mode 1.6
FAST
mode
SLOW
mode
Unity gain 200
Force sense 150
CS = DV
from 0 to DV
Major carry transition 2 nV-s
DD
M AX 5590/M AX 5591 fr om cod e 322 to
cod e 4095 to 1/2 LS B
M AX 5592/M AX 5593 fr om cod e 10 to
cod e 1023 to 1/2 LS B
MAX5594/MAX5595 fr om cod e 3 to
code 255 to 1/2 LSB
M AX 5590/M AX 5591 fr om cod e 322 to
cod e 4095 to 1/2 LS B
MAX5592/MAX5593 fr om cod e 10 to
code 1023 1/2 LSB
MAX5594/MAX5595 fr om cod e 3 to
code 255 to 1/2 LSB
, code = zero scale, any digital input
and DVDD to 0, f = 100kHz
DD
DV
-
DD
200mV
23
1.5 3
12
36
2.5 6
24
0.1 nV-s
V
200 mV
±200 nA
V/µs
µs
/ 2 V
REF
kHz
Page 5
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(AVDD= 2.7V to 5.25V, DVDD= 1.8V to AVDD, V
AGND
= 0V, V
DGND
= 0V, V
REF
= 2.5V (for AVDD= 2.7V to 5.25V), V
REF
= 4.096V (for
AV
DD
= 4.5V to 5.25V), RL= 10kΩ, CL= 100pF, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
(Note 1)
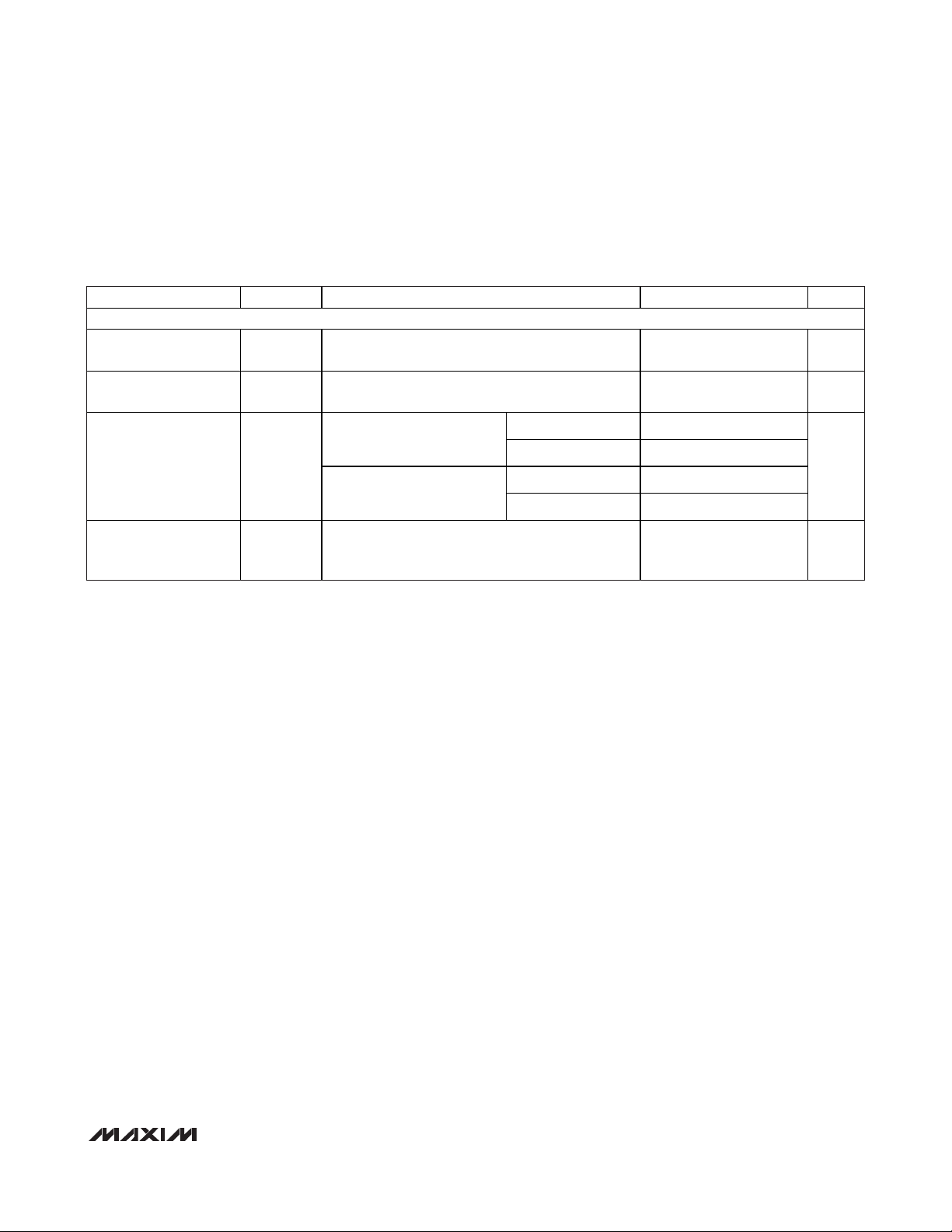
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
UNITS
POWER REQUIREMENTS
Analog Supply Voltage
Range
AV
DD
V
Digital Supply Voltage
Range
DV
DD
1.8
V
Unity gain 1.5 3.2
SLOW mode, all digital inputs
at DGND or DV
DD
, no load,
V
REF
= 4.096V
Force sense 2.4 4.8
Unity gain 2.5 8
Operating Supply
Current
I
AVDD
+
I
DVDD
FAST mode, all digital inputs
at DGND or DV
DD
, no load,
V
REF
= 4.096V
Force sense 3.4 8
mA
Shutdown Supply
Current
I
AV D D ( S H D N )
+
No clocks, all digital inputs at DGND or DVDD, all
DACs in shutdown mode
0.5 1 µA
Note 1: For the force-sense versions, FB_ is connected to its respective OUT_. V
OUT
(max) = V
REF
/ 2, unless otherwise noted.
Note 2: Linearity guaranteed from decimal code 40 to code 4095 for the MAX5590B/MAX5591B (12-bit, B-grade), code 10 to code
1023 for the MAX5592/MAX5593 (10-bit), and code 3 to code 255 for the MAX5594/MAX5595 (8-bit).
Note 3: Represents the functional range. The linearity is guaranteed at V
REF
= 2.5V (for AVDDfrom 2.7V to 5.25V), and V
REF
=
4.096V (for AVDD= 4.5V to 5.25V). See the
Typical Operating Characteristics
section for linearity at other voltages.
Note 4: DC crosstalk is measured as follows: outputs of DACA–DACH are set to full scale and the output of DACH is measured.
While keeping DACH unchanged, the outputs of DACA–DACG are transitioned to zero scale and the ∆V
OUT
of DACH is
measured.
Note 5: Guaranteed by design.
Note 6: The reference -3dB bandwidth is measured with a 0.1V
P-P
sine wave on V
REF
and with full-scale input code.
SYMBOL
I
D V D D ( S H D N )
MIN TYP MAX
2.70 5.25
AV
DD
Page 6
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
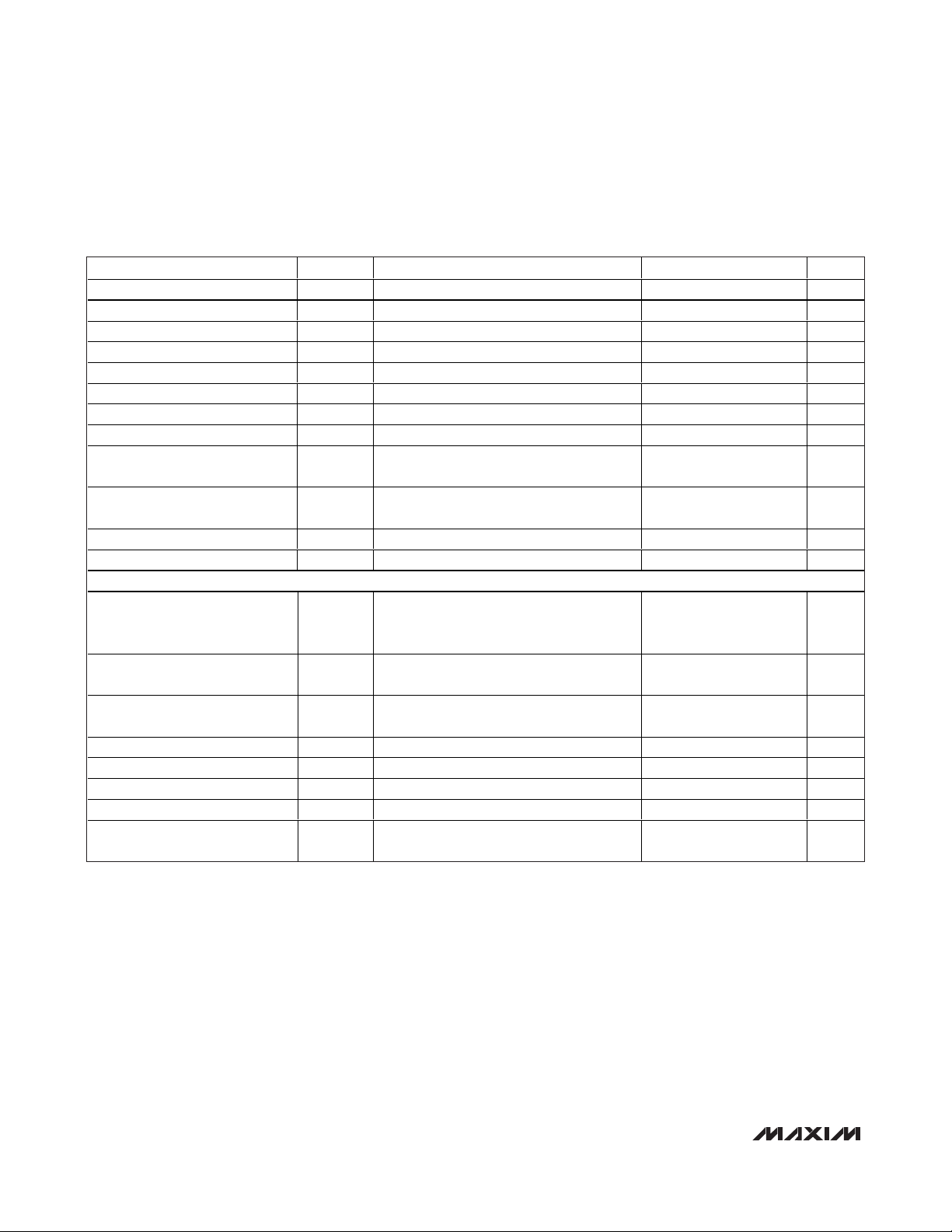
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS—DSP Mode Disabled (3V, 3.3V, 5V Logic) (Figure 1)
(DVDD= 2.7V to 5.25V, V
AGND
= 0V, V
DGND
= 0V, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted.)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
SCLK Frequency f
SCLK Pulse-Width High t
SCLK Pulse-Width Low t
CS Fall to SCLK Rise Setup Time t
SCLK Rise to CS Rise Hold Time t
SCLK Rise to CS Fall Setup t
DIN to SCLK Rise Setup Time t
DIN to SCLK Rise Hold Time t
SCLK Rise to DOUTDC1 Valid
Propagation Delay
SCLK Fall to DOUT_ Valid
Propagation Delay
CS Rise to SCLK Rise Hold Time t
CS Pulse-Width High t
UPIO_ TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
DOUT Tri-State Time when Exiting
DOUTDC0, DOUTDC1, and UPIO
Modes
SCLK
CSS
CSH
CS0
t
DO1
t
DO2
CS1
CSW
t
DOZ
CH
DH
CL
DS
2.7V < DVDD < 5.25V 20 MHz
(Note 7) 20 ns
(Note 7) 20 ns
CL = 20pF, UPIO_ = DOUTDC1 mode 30 ns
CL = 20pF, UPIO_ = DOUTDC0 or DOUTRB
mode
MICROWIRE and SPI modes 0 and 3 10 ns
CL = 20pF, from end of write cycle to UPIO_
in high impedance
10 ns
5ns
10 ns
12 ns
5ns
45 ns
30 ns
100 ns
DOUTRB Tri-State Time from CS
Rise
DOUTRB Tri-State Enable Time
from 8th SCLK Rise
LDAC Pulse-Width Low t
LDAC Effective Delay t
CLR, MID, SET Pulse-Width Low t
GPO Output Settling Time t
GPO Output High-Impedance
Time
t
DRBZ
t
ZEN
LDL
LDS
CMS
GP
t
GPZ
CL = 20pF, from rising edge of CS to UPIO_
in high impedance
CL = 20pF, from 8th rising edge of SCLK to
UPIO_ driven out of tri-state
Figure 5 20 ns
Figure 6 100 ns
Figure 5 20 ns
Figure 6 100 ns
0ns
20 ns
100 ns
Page 7
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
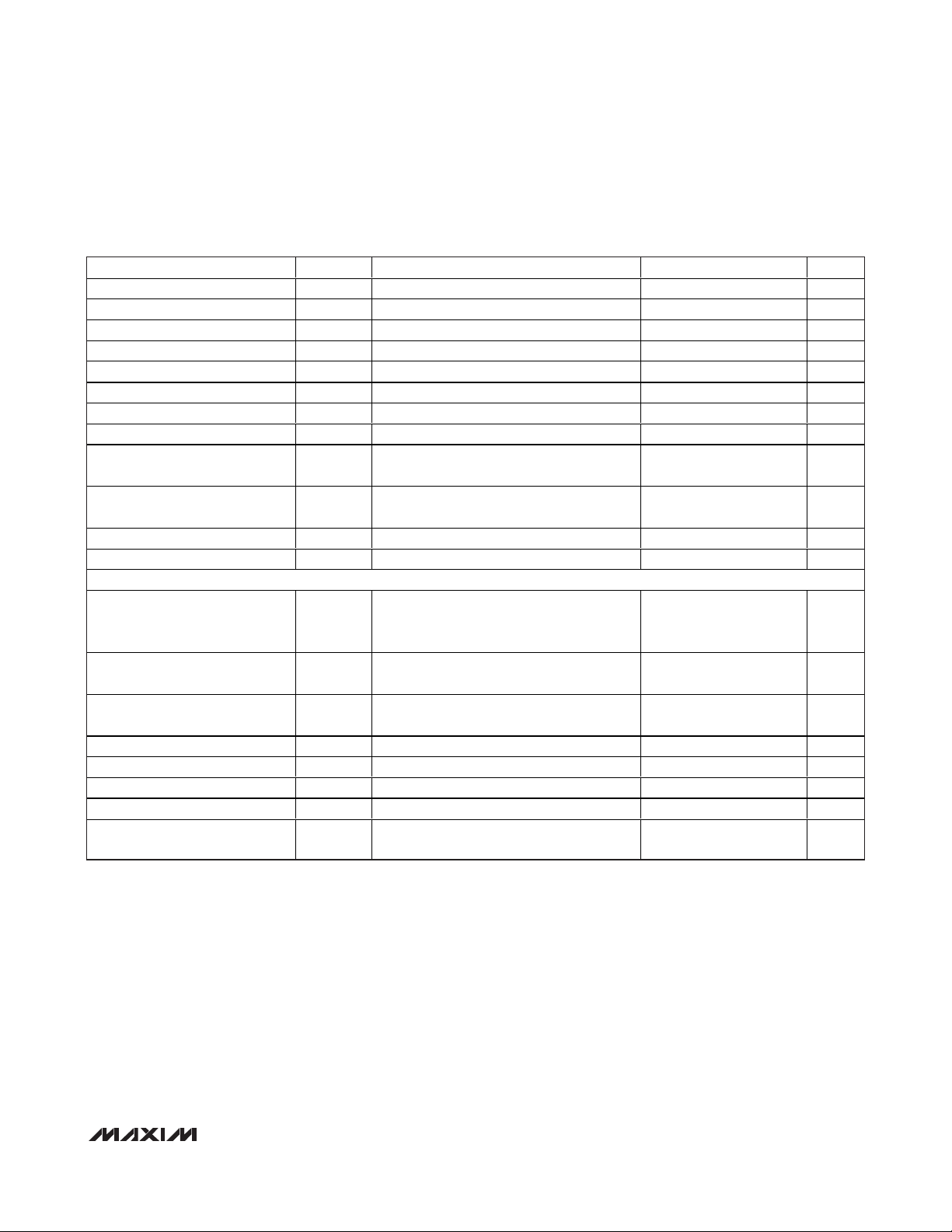
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS—DSP Mode Disabled (1.8V Logic) (Figure 1)
(DVDD= 1.8V to 5.25V, V
AGND
= 0V, V
DGND
= 0V, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted.)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
SCLK Frequency f
SCLK Pulse-Width High t
SCLK Pulse-Width Low t
CS Fall to SCLK Rise Setup Time t
SCLK Rise to CS Rise Hold Time t
SCLK Rise to CS Fall Setup t
DIN to SCLK Rise Setup Time t
DIN to SCLK Rise Hold Time t
SCLK Rise to DOUTDC1 Valid
Propagation Delay
SCLK Fall to DOUT_ Valid
Propagation Delay
CS Rise to SCLK Rise Hold Time t
CS Pulse-Width High t
UPIO_ TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
DOUT Tri-State Time when
Exiting DOUTDC0, DOUTDC1,
and UPIO Modes
DOUTRB Tri-State Time from CS
Rise
DOUTRB Tri-State Enable Time
from 8th SCLK Rise
LDAC Pulse-Width Low t
LDAC Effective Delay t
CLR, MID, SET Pulse-Width Low t
GPO Output Settling Time t
GPO Output High-Impedance
Time
SCLK
CSS
CSH
CS0
t
DO1
t
DO2
CS1
CSW
t
DOZ
t
DRBZ
t
ZEN
LDL
LDS
CMS
t
GPZ
CH
CL
DS
DH
GP
1.8V < DVDD < 5.25V 10 MHz
(Note 7) 40 ns
(Note 7) 40 ns
CL = 20pF, UPIO_ = DOUTDC1 mode 60 ns
CL = 20pF, UPIO_ = DOUTDC0 or DOUTRB
mode
MICROWIRE and SPI modes 0 and 3 20 ns
CL = 20pF, from end of write cycle to UPIO_
in high impedance
CL = 20pF, from rising edge of CS to UPIO_
in high impedance
CL = 20pF, from 8th rising edge of SCLK to
UPIO_ driven out of tri-state
Figure 5 40 ns
Figure 6 200 ns
Figure 5 40 ns
Figure 6 200 ns
20 ns
0ns
10 ns
20 ns
5ns
90 ns
0ns
60 ns
200 ns
40 ns
200 ns
Page 8
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
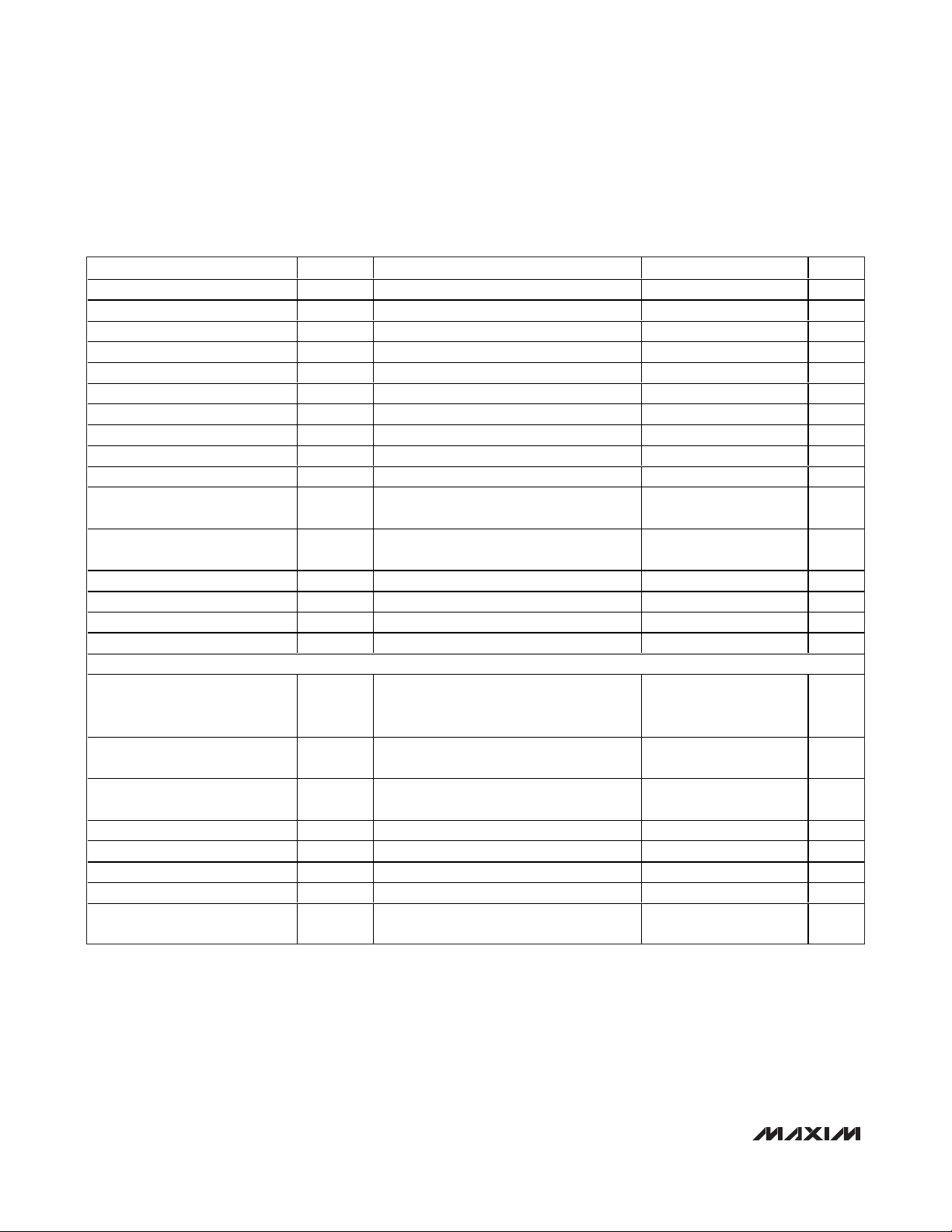
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS—DSP Mode Enabled (3V, 3.3V, 5V Logic) (Figure 2)
(DVDD= 2.7V to 5.25V, V
AGND
= 0V, V
DGND
= 0V, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted.)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
SCLK Frequency f
SCLK Pulse-Width High t
SCLK Pulse-Width Low t
CS Fall to SCLK Fall Setup Time t
DSP Fall to SCLK Fall Setup Time t
SCLK Fall to CS Rise Hold Time t
SCLK Fall to CS Fall Delay t
SCLK Fall to DSP Fall Delay t
DIN to SCLK Fall Setup Time t
DIN to SCLK Fall Hold Time t
SCLK Rise to DOUT_ Valid
Propagation Delay
SCLK Fall to DOUT_ Valid
Propagation Delay
CS Rise to SCLK Fall Hold Time t
CS Pulse-Width High t
DSP Pulse-Width High t
DSP Pulse-Width Low t
UPIO_ TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
DOUT Tri-State Time when
Exiting DOUTDC0, DOUTDC1,
and UPIO Modes
SCLK
CSS
DSS
CSH
CS0
DS0
t
DO1
t
DO2
CS1
CSW
DSW
DSPWL
t
DOZ
CH
DH
CL
DS
2.7V < DVDD < 5.25V 20 MHz
(Note 7) 20 ns
(Note 7) 20 ns
CL = 20pF, UPIO_ = DOUTDC1 or DOUTRB
mode
CL = 20pF, UPIO_ = DOUTDC0 mode 30 ns
MICROWIRE and SPI modes 0 and 3 10 ns
(Note 8) 20 ns
CL = 20pF, from end of write cycle to UPIO_
in high impedance
10 ns
10 ns
5ns
10 ns
10 ns
12 ns
5ns
45 ns
20 ns
30 ns
100 ns
DOUTRB Tri-State Time from CS
Rise
DOUTRB Tri-State Enable Time
from 8th SCLK Fall
LDAC Pulse-Width Low t
LDAC Effective Delay t
CLR, MID, SET Pulse-Width Low t
GPO Output Settling Time t
GPO Output High-Impedance
Time
t
DRBZ
t
ZEN
LDL
LDS
CMS
GP
t
GPZ
CL = 20pF, from rising edge of CS to UPIO_
in high impedance
CL = 20pF, from 8th falling edge of SCLK to
UPIO_ driven out of tri-state
Figure 5 20 ns
Figure 6 100 ns
Figure 5 20 ns
Figure 6 100 ns
0ns
20 ns
100 ns
Page 9
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
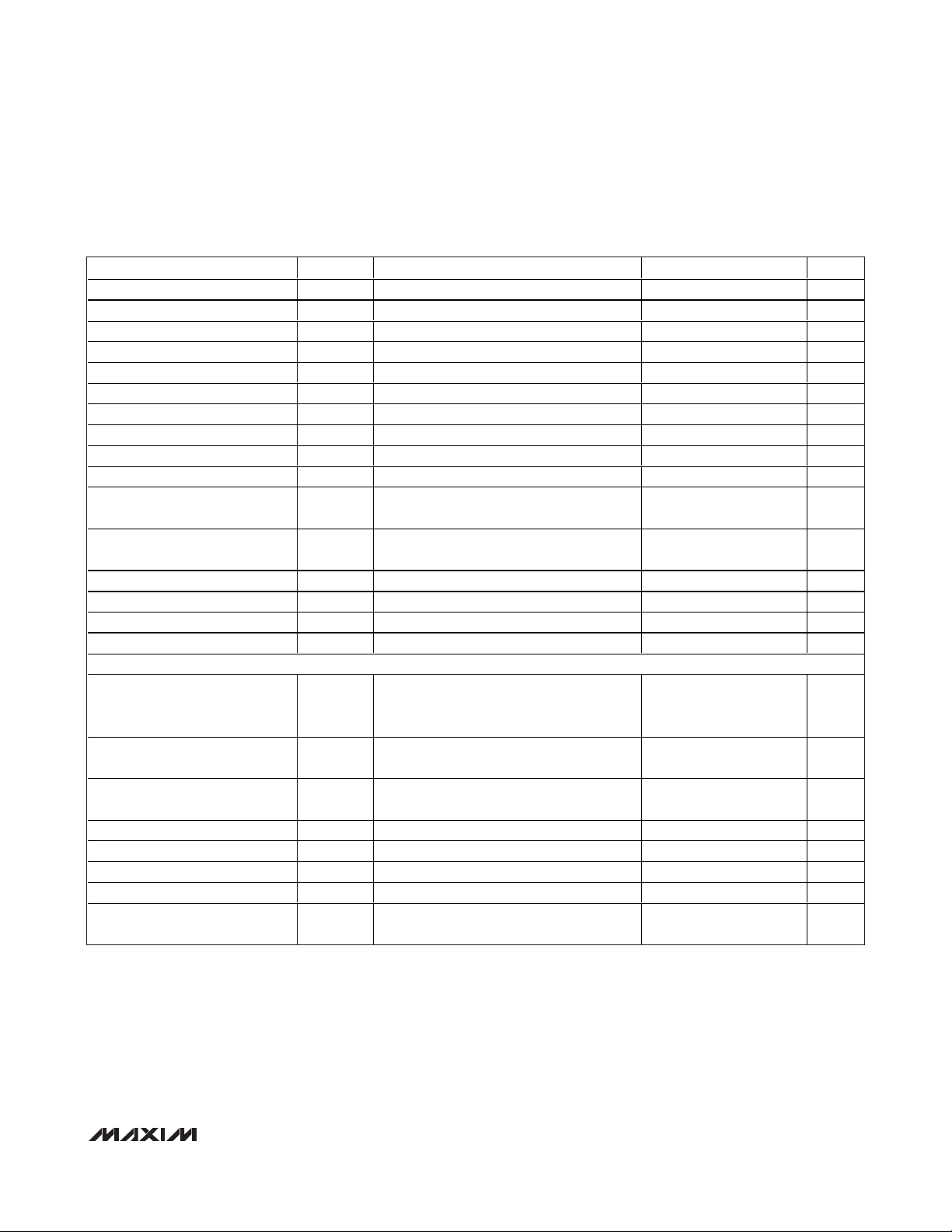
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS—DSP Mode Enabled (1.8V Logic) (Figure 2)
(DVDD= 1.8V to 5.25V, V
AGND
= 0V, V
DGND
= 0V, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted.)
Note 7: In some daisy-chain modes, data is required to be clocked in on one clock edge and the shifted data clocked out on the fol-
lowing edge. In the case of a 1/2 clock-period delay, it is necessary to increase the minimum high/low clock times to 25ns
(2.7V) or 50ns (1.8V).
Note 8: The falling edge of DSP starts a DSP-type bus cycle, provided that CS is also active low to select the device. DSP active low
and CS active low must overlap by a minimum of 10ns (2.7V) or 20ns (1.8V). CS can be permanently low in this mode of
operation.
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
SCLK Frequency f
SCLK Pulse-Width High t
SCLK Pulse-Width Low t
CS Fall to SCLK Fall Setup Time t
DSP Fall to SCLK Fall Setup Time t
SCLK Fall to CS Rise Hold Time t
SCLK Fall to CS Fall Delay t
SCLK Fall to DSP Fall Delay t
DIN to SCLK Fall Setup Time t
DIN to SCLK Fall Hold Time t
SCLK Rise to DOUT_ Valid
Propagation Delay
SCLK Fall to DOUT_ Valid
Propagation Delay
CS Rise to SCLK Fall Hold Time t
CS Pulse-Width High t
DSP Pulse-Width High t
DSP Pulse-Width Low t
UPIO_ TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
DOUT Tri-State Time when
Exiting DOUTDC0, DOUTDC1,
and UPIO Modes
SCLK
CSS
DSS
CSH
CS0
DS0
t
DO1
t
DO2
CS1
CSW
DSW
DSPWL
t
DOZ
CH
DH
CL
DS
1.8V < DVDD < 5.25V 10 MHz
(Note 7) 40 ns
(Note 7) 40 ns
CL = 20pF, UPIO_ = DOUTDC1 or DOUTRB
mode
CL = 20pF, UPIO_ = DOUTDC0 mode 60 ns
MICROWIRE and SPI modes 0 and 3 20 ns
(Note 8) 40 ns
CL = 20pF, from end of write cycle to UPIO_
in high impedance
20 ns
20 ns
0ns
10 ns
15 ns
20 ns
5ns
90 ns
40 ns
60 ns
200 ns
DOUTRB Tri-State Time from CS
Rise
DOUTRB Tri-State Enable Time
from 8th SCLK Fall
LDAC Pulse-Width Low t
LDAC Effective Delay t
CLR, MID, SET Pulse-Width Low t
GPO Output Settling Time t
GPO Output High-Impedance
Time
t
DRBZ
t
ZEN
LDL
LDS
CMS
GP
t
GPZ
CL = 20pF, from rising edge of CS to UPIO_
in high impedance
CL = 20pF, from 8th falling edge of SCLK to
UPIO_ driven out of tri-state
Figure 5 40 ns
Figure 6 200 ns
Figure 5 40 ns
Figure 6 200 ns
0ns
40 ns
200 ns
Page 10
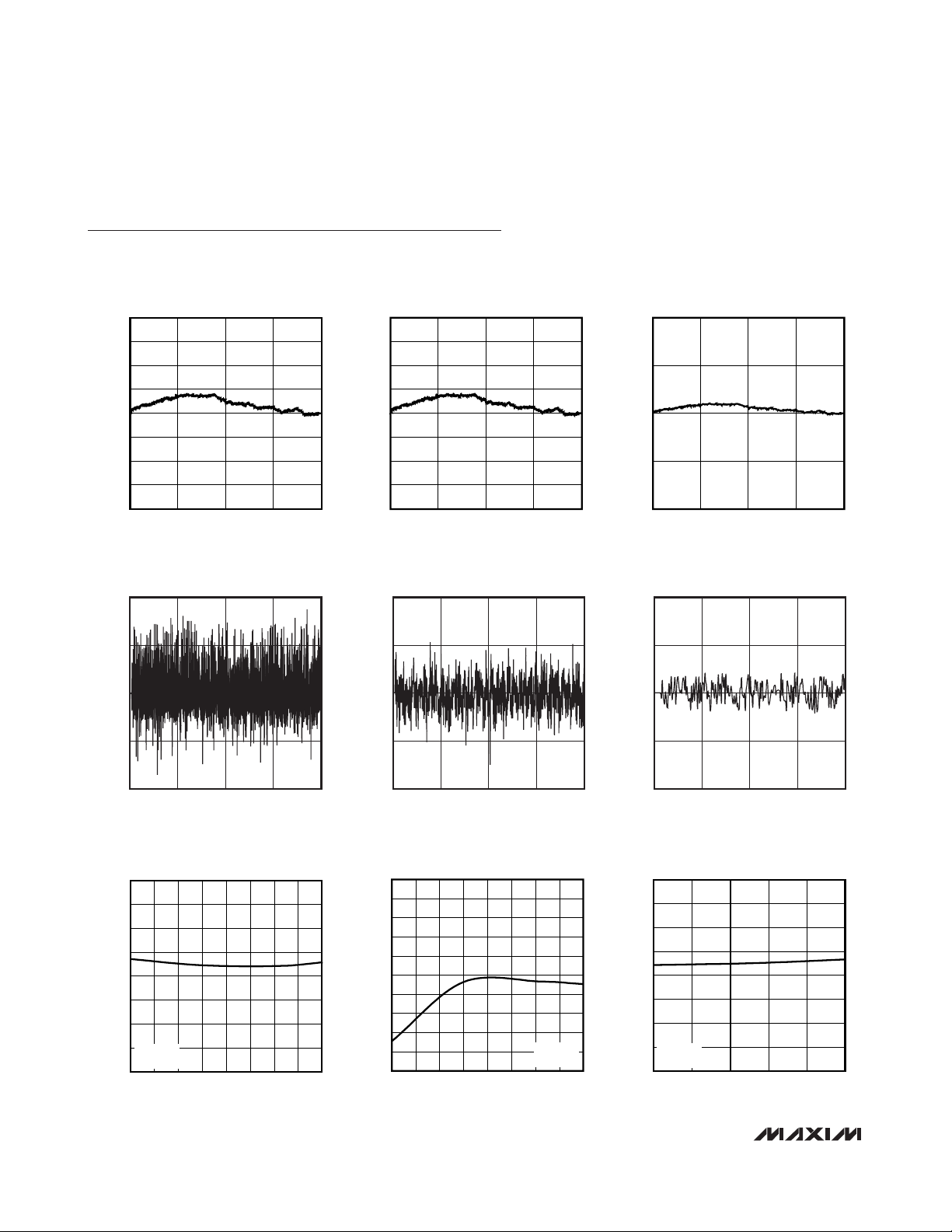
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Typical Operating Characteristics
(AVDD= DVDD= 5V, V
REF
= 4.096V, RL= 10kΩ, CL= 100pF, speed mode = FAST, PU = unconnected, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise
noted.)
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY
vs. DIGITAL INPUT CODE (12-BIT)
4
3
2
1
0
INL (LSB)
-1
-2
-3
B-GRADE
-4
0 1024 2048 3072 4095
DIGITAL INPUT CODE
DIFFERENTIAL NONLINEARITY
vs. DIGITAL INPUT CODE (12-BIT)
0.50
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY
vs. DIGITAL INPUT CODE (8-BIT)
0
0 64 128 192 255
DIFFERENTIAL NONLINEARITY
vs. DIGITAL INPUT CODE (8-BIT)
MAX5590-95 toc01
INL (LSB)
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY
vs. DIGITAL INPUT CODE (10-BIT)
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0
-0.25
-0.50
-0.75
-1.00
0 256 512 768 1023
DIGITAL INPUT CODE
DIFFERENTIAL NONLINEARITY
vs. DIGITAL INPUT CODE (10-BIT)
0.2
MAX5590-95 toc02
0.50
0.25
INL (LSB)
-0.25
-0.50
0.050
MAX5590-95 toc03
DIGITAL INPUT CODE
0.25
0
DNL (LSB)
-0.25
-0.50
0 1024 2048 3072 4095
DIGITAL INPUT CODE
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY
vs. REFERENCE VOLTAGE (12-BIT)
4
3
2
1
0
INL (LSB)
-1
-2
-3
B-GRADE
MIDSCALE
-4
1.0 2.0 2.51.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
V
(V)
REF
B-GRADE
MAX5590-95 toc04
DNL (LSB)
MAX5590-95 toc07
0.1
0
-0.1
-0.2
0 256 512 768 1023
DIGITAL INPUT CODE
DIFFERENTIAL NONLINEARITY
vs. REFERENCE VOLTAGE (12-BIT)
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
DNL (LSB)
-0.1
-0.2
-0.3
-0.4
-0.5
1.0 20 2.51.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
V
(V)
REF
B-GRADE
MIDSCALE
MAX5590-95 toc05
-0.025
-0.050
MAX5590-95 toc08
0.025
0
DNL (LSB)
0 64 128 192 255
DIGITAL INPUT CODE
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY
vs. TEMPERATURE (12-BIT)
4
3
2
1
0
INL (LSB)
-1
-2
-3
B-GRADE
MIDSCALE
-4
-40 10-15 35 60 85
TEMPERATURE (°C)
MAX5590-95 toc06
MAX5590-95 toc09
Page 11

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________
11
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(AVDD= DVDD= 5V, V
REF
= 4.096V, RL= 10kΩ, CL= 100pF, speed mode = FAST, PU = unconnected, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise
noted.)
DIFFERENTIAL NONLINEARITY
vs. TEMPERATURE (12-BIT)
0.2
0.1
0
DNL (LSB)
-0.1
B-GRADE
MIDSCALE
-0.2
-40 10-15 35 60 85
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE (FORCE-SENSE)
4
FAST MODE
3
SLOW MODE
2
SUPPLY CURRENT
12-BIT
NO LOAD
DIGITAL INPUT CODE
SHUTDOWN SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
FORCE SENSE
UNITY GAIN
MAX5590-95 toc10
MAX5590-95 toc13
vs. DIGITAL INPUT CODE (FORCE-SENSE)
SUPPLY CURRENT
5
4
3
2
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
1
12-BIT
NO LOAD
0
0 1024 2048 3072 4095
DIGITAL INPUT CODE
SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE (UNITY GAIN)
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
FAST MODE
SLOW MODE
3
MAX5590-95 toc11
2
1
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
0
60
50
MAX5590-95 toc14
40
30
vs. DIGITAL INPUT CODE (UNITY GAIN)
0 1024 2048 3072 4095
MAX5590-95 toc12
MAX5590-95 toc15
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
1
AV
= DV
DD
DD
NO LOAD
0
2.70 3.40 4.10 4.80 5.25
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
OFFSET ERROR vs. TEMPERATURE
7
CODE = 40
UNITY GAIN: 1 LSB = 1mV
6
FORCE SENSE: 1 LSB = 0.5mV
5
4
3
OFFSET ERROR (LSB)
2
1
0
-40 10-15 35 60 85
TEMPERATURE (°C)
FORCE SENSE
UNITY GAIN
MAX5590-95 toc16
1.0
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
0.5
AV
= DV
DD
DD
NO LOAD
0
2.70 3.40 4.10 4.80 5.25
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
GAIN ERROR vs. TEMPERATURE
0
-2
-4
FORCE SENSE
-6
GAIN ERROR (LSB)
-8
UNITY GAIN: 1 LSB = 1mV
FORCE SENSE: 1 LSB = 0.5mV
-10
-40 10-15 35 60 85
TEMPERATURE (°C)
UNITY GAIN
20
10
SHUTDOWN SUPPLY CURRENT (nA)
NO LOAD
0
2.70 4.103.40 4.80 5.25
vs. OUTPUT SOURCE/SINK CURRENT
2.5
2.0
MAX5590-95 toc17
1.5
1.0
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.5
0
-15 -5-10 0 5 10 15
MIDSCALE
UNITY GAIN
= 4.096V
V
REF
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
I
(mA)
OUT
MAX5590-95 toc18
Page 12

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
12 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(AVDD= DVDD= 5V, V
REF
= 4.096V, RL= 10kΩ, CL= 100pF, speed mode = FAST, PU = unconnected, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise
noted.)
1µs/div
DIGITAL FEEDTHROUGH
OUT_
(AC-COUPLED)
2mV/div
SCLK
2V/div
MAX5590-95 toc25
400µs/div
POWER-UP GLITCH
OUT_
2V/div
AV
DD
2V/div
MAX5590-95 toc26
PU = DV
DD
10µs/div
EXITING SHUTDOWN TO MIDSCALE
OUT_
2V/div
CS
2V/div
MAX5590-95 toc27
MAJOR-CARRY TRANSITION GLITCH
MAX5590-95 toc19
CS
5V/div
OUT_
2mV/div
SETTLING TIME POSITIVE
MAX5590-95 toc20
CS
5V/div
SETTLING TIME NEGATIVE
MAX5590-95 toc21
FULL-SCALE
TRANSITION
CS
5V/div
250ns/div
REFERENCE INPUT BANDWIDTH
5
0
-5
-10
GAIN (dB)
-15
-20
V
= 0.1V
REF
UNITY GAIN
-25
1 100 100010 10,000
AT 4.096V
P-P
FREQUENCY (kHz)
DC
MAX5590-95 toc22
-22
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
SIGNAL AMPLITUDE (dB)
-110
-120
-130
-142
FULL-SCALE
TRANSITION
400ns/div
REFERENCE FEEDTHROUGH AT 1kHz
0.5 5.5
FREQUENCY (kHz)
5.04.53.5 4.01.5 2.0 2.5 3.01.0
OUT_
2V/div
MAX5590-95 toc23
400ns/div
DAC-TO-DAC CROSSTALK
200
µs/div
MAX5590-95 toc24
OUT_
2V/div
OUTA–OUTG
2V/div
OUTH
1mV/div
Page 13

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 13
Pin Description
PIN
MAX5590
MAX5592
MAX5594
11AV
2 2 AGND Analog Ground
3 3 OUTA DACA Output
4, 8, 17, 21 — N.C. No Connection. Not internally connected.
5 6 OUTB DACB Output
6 7 OUTC DACC Output
7 10 OUTD DACD Output
911CS Active-Low Chip-Select Input
10 12 SCLK Serial Clock Input
11 13 DIN Serial Data Input
12 14 DSP
13 15 DV
14 16 DGND Digital Ground
15 17 UPIO1 User-Programmable Input/Output 1
16 18 UPIO2 User-Programmable Input/Output 2
18 19 OUTE DACE Output
19 22 OUTF DACF Output
20 23 OUTG DACG Output
22 26 OUTH DACH Output
23 27 PU
24 28 REF Reference Input
— 4 FBA Feedback for DACA
— 5 FBB Feedback for DACB
— 8 FBC Feedback for DACC
— 9 FBD Feedback for DACD
— 20 FBE Feedback for DACE
— 21 FBF Feedback for DACF
— 24 FBG Feedback for DACG
— 25 FBH Feedback for DACH
MAX5591
MAX5593
MAX5595
NAME FUNCTION
Analog Supply
DD
Clock Enable. Connect DSP to DV
of SCLK. Connect DSP to GND to transfer data on the falling edge of SCLK.
Connect DSP to DGND at power-up to transfer data on the falling edge of SCLK.
Digital Supply
DD
Power-Up State Select Input. Connect PU to DV
upon power-up. Connect PU to DGND to set OUTA–OUTH to zero upon power-up.
Leave PU unconnected at power-up to set OUTA–OUTH to midscale.
at power-up to transfer data on the rising edge
DD
to set OUTA–OUTH to full scale
DD
Page 14
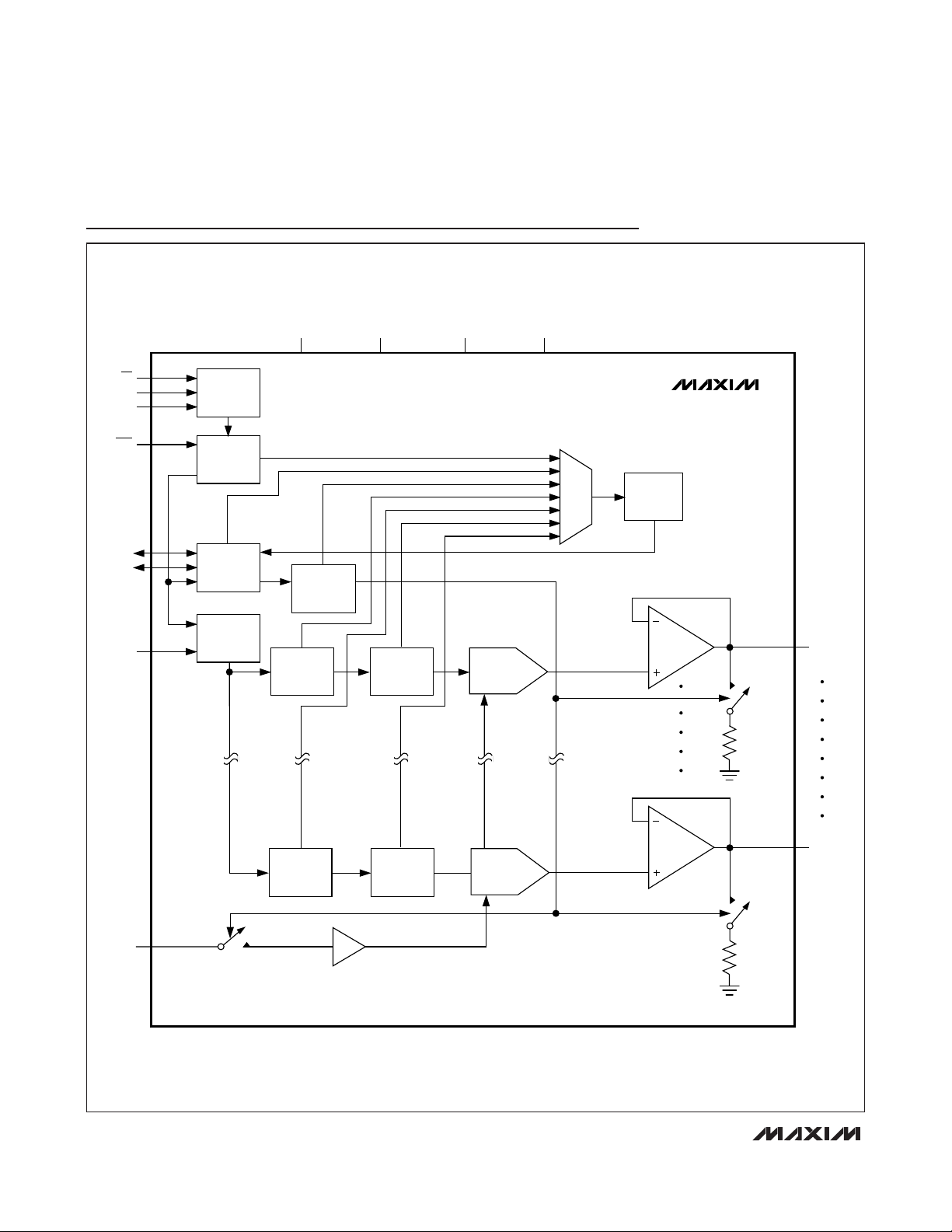
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
14 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Functional Diagrams
AV
DD
CS
SCLK
DIN
DSP
UPIO1
UPIO2
PU
SERIAL
INTERFACE
CONTROL
16-BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
UPIO1 AND
UPIO2
LOGIC
DECODE
CONTROL
POWER-DOWN
LOGIC AND
REGISTER
INPUT
REGISTER
A
DV
DD
DAC
REGISTER
A
AGND DGND
DACA
MUX
DOUT
REGISTER
MAX5590
MAX5592
MAX5594
OUTA
REF
INPUT
REGISTER
H
DAC
REGISTER
H
DACH
OUTH
Page 15

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 15
Functional Diagrams (continued)
SCLK
DSP
UPIO1
UPIO2
DIN
AV
DD
CS
SERIAL
INTERFACE
CONTROL
DV
DD
AGND DGND
MAX5591
MAX5593
MAX5595
16-BIT SHIFT
REGISTER
MUX
UPIO1 AND
UPIO2
LOGIC
DECODE
PU
CONTROL
POWER-DOWN
LOGIC AND
REGISTER
INPUT
REGISTER
A
DAC
REGISTER
A
DACA
DOUT
REGISTER
FBA
OUTA
REF
INPUT
REGISTER
H
DAC
REGISTER
H
DACH
FBH
OUTH
Page 16

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
16 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Detailed Description
The MAX5590–MAX5595 octal, 12/10/8-bit, voltage-output DACs offer buffered outputs and a 3µs maximum
settling time at the 12-bit level. The DACs operate from a
single 2.7V to 5.25V analog supply and a separate 1.8V
to AVDDdigital supply. The MAX5590–MAX5595 include
an input register and DAC register for each channel and
a 16-bit data-in/data-out shift register. The 3-wire serial
interface is compatible with SPI, QSPI, MICROWIRE, and
DSP applications. The MAX5590– MAX5595 provide two
user-programmable digital I/O ports, which are programmed through the serial interface. The externally
selectable power-up states of the DAC outputs are either
zero scale, midscale, or full scale.
Reference Input
The reference input, REF, accepts both AC and DC values with a voltage range extending from analog ground
(AGND) to AV
DD
. The voltage at REF sets the full-scale
output of the DACs. Determine the output voltage using
the following equations:
Unity-gain versions:
V
OUT_
= (V
REF
x CODE) / 2
N
Force-sense versions (FB_ connected to OUT_):
V
OUT
= 0.5 x (V
REF
x CODE) / 2
N
where CODE is the numeric value of the DAC’s binary
input code and N is the bits of resolution. For the
MAX5590/MAX5591, N = 12 and CODE ranges from 0
to 4095. For the MAX5592/MAX5593, N = 10 and
CODE ranges from 0 to 1023. For the MAX5594/
MAX5595, N = 8 and CODE ranges from 0 to 255.
Output Buffers
The DACA and DACH output-buffer amplifiers of the
MAX5590–MAX5595 are unity-gain stable with rail-torail output voltage swings and a typical slew rate
of 3.6V/µs (FAST mode). The MAX5590/MAX5592/
MAX5594 provide unity-gain outputs, while the
MAX5591/MAX5593/MAX5595 provide force-sense outputs. For the MAX5591/MAX5593/MAX5595, access to
the output amplifier’s inverting input provides flexibility
in output gain setting and signal conditioning (see the
Applications Information
section).
The MAX5590–MAX5595 offer FAST and SLOW settlingtime modes. In the SLOW mode, the settling time is 6µs
(max), and the supply current is 3.2mA (max). In the
FAST mode, the settling time is 3µs (max), and the supply current is 8mA (max). See the
Digital Interface
section
for settling-time mode programming details.
Use the serial interface to set the shutdown output
impedance of the amplifiers to 1kΩ or 100kΩ for the
MAX5590/MAX5592/MAX5594 and 1kΩ or high impedance for the MAX5591/MAX5593/MAX5595. The DAC
outputs can drive a 10kΩ (typ) load and are stable with
up to 500pF (typ) of capacitive load.
Power-On Reset
At power-up, all DAC outputs power up to full scale,
midscale, or zero scale, depending on the configuration
of the PU input. Connect PU to DVDDto set OUT_ to full
scale upon power-up. Connect PU to digital ground
(DGND) at power-up to set OUT_ to zero scale. Leave
PU unconnected to set OUT_ to midscale.
Digital Interface
The MAX5590–MAX5595 use a 3-wire serial interface
that is compatible with SPI, QSPI, MICROWIRE, and DSP
protocol applications (Figures 1 and 2). Connect DSP to
DVDDbefore power-up to clock data in on the rising
edge of SCLK. Connect DSP to DGND before power-up
to clock data in on the falling edge of SCLK. After powerup, the device enters DSP frame-sync mode on the first
rising edge of DSP. Refer to the
MAX5590–MAX5595
Programmer’s Handbook
for details.
The MAX5590–MAX5595 include a 16-bit input shift
register. The data is loaded into the input shift register
through the serial interface. The 16 bits can be sent in
two serial 8-bit packets or one 16-bit word (CS must
remain low until all 16 bits are transferred). The data is
loaded MSB first. For the MAX5590/MAX5591, the 16
bits consist of 4 control bits (C3–C0) and 12 data bits
(D11–D0) (see Table 1). For the 10-bit MAX5592/
MAX5593 devices, D11–D2 are the data bits and D1
and D0 are sub-bits. For the 8-bit MAX5594/
MAX5595 devices, D11–D4 are the data bits and
D3–D0 are sub-bits. Set all sub-bits to zero for optimum
performance.
Each DAC channel includes two registers: an input register and the DAC register. At power-up, the DAC output is set according to the state of PU. The DACs are
double-buffered, which allows any of the following for
each channel:
• Loading the input register without updating the DAC
register
• Updating the DAC register from the input register
• Updating the input and DAC registers simultaneously
Page 17

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 17
Table 1. Serial Write Data Format
MSB 16 BITS OF SERIAL DATA
LSB
CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
C3
D9 D8 D7 D6
D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 1. Serial-Interface Timing Diagram (DSP Mode Disabled)
Figure 2. Serial-Interface Timing Diagram (DSP Mode Enabled)
C2 C1 C0 D11 D10
SCLK
DIN
t
CS0
t
CS
DOUTDC1*
DOUTDC0
OR
DOUTRB*
*UPIO1/UPIO2 CONFIGURED AS DOUTDC_ (DAISY-CHAIN DATA OUTPUT, MODE 0 OR 1) OR DOUTRB (READ-BACK DATA OUTPUT).
SEE THE DATA OUTPUT (DOUTRB, DOUTDC0, DOUTDC1) SECTION FOR DETAILS.
t
CSW
CSS
D5
t
CH
t
t
DO1
DOUT VALID
CL
C1 D0C2C3
DOUT VALID
t
CSH
t
CS1
t
DS
t
DH
t
DO2
SCLK
t
DS
DIN
CS
DSP
DOUTDC0*
DOUTDC1
OR
DOUTRB*
*UPIO1/UPIO2 CONFIGURED AS DOUTDC_ (DAISY-CHAIN DATA OUTPUT, MODE 0 OR 1) OR DOUTRB (READ-BACK DATA OUTPUT).
SEE THE DATA OUTPUT (DOUTRB, DOUTDC0, DOUTDC1) SECTION FOR DETAILS.
t
CSW
t
CS0
t
DSWtDSPWL
C3 C2 C1 D0
t
DH
t
CCS
t
DSS
t
DS0
t
D01
t
CL
t
D02
DOUT VALID
t
CH
DOUT VALID
t
CSH
t
CS1
Page 18

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
18 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Figure 3. MICROWIRE and SPI Single DAC Writes (CPOL = 0, CPHA = 0 or CPOL = 1, CPHA = 1)
Figure 4. DSP and SPI Single DAC Writes (CPOL = 0, CPHA = 1 or CPOL = 1, CPHA = 0)
Serial-Interface Programming Commands
Tables 2a, 2b, and 2c provide all of the serial-interface
programming commands for the MAX5590–MAX5595.
Table 2a shows the basic DAC programming commands, Table 2b gives the advanced-feature programming commands, and Table 2c provides the 24-bit
read commands. Figures 3 and 4 provide the serialinterface diagrams for read and write operations.
Loading Input and DAC Registers
The MAX5590–MAX5595 contain a 16-bit shift register
that is followed by a 12-bit input register and a 12-bit
DAC register for each channel (see the
Functional
Diagrams
). Tables 3, 4, and 5 highlight a few of the
commands that handle the loading of the input and
DAC registers. See Table 2a for all DAC programming
commands.
V
MICROWIRE
MICROWIRE OR SPI (CPOL = 0, CPHA = 0) 8-BIT CONTROL DATA OR 12-BIT DAC DATA WRITE:
CS
SCLK
DIN
SPI (CPOL = 1, CPHA = 1) 8-BIT CONTROL DATA OR 12-BIT DAC DATA WRITE:
CS
SCLK
DIN
C3 C2 C1 C0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
C3 C2 C1 C0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DD
MAX5590–
V
DD
SK
SO
I/O
DV
MAX5595
DD
SCLK
DIN
CS
CS MUST REMAIN LOW BETWEEN BYTES ON A 16-BIT WRITE OPERATION
CS MUST REMAIN LOW BETWEEN BYTES ON A 16-BIT WRITE OPERATION
V
SPI OR QSPI
SS OR I/O
DD
V
DD
SCK
MOSI
COMMAND TAKES EFFECT HERE
ONLY IF SCLK COUNT = N
COMMAND TAKES EFFECT HERE
ONLY IF SCLK COUNT = N
DV
DSPDSP
SCLK
DIN
CS
MAX5590–
DD
MAX5595
✕
16
✕
16
DSP
MAX5590–
V
SS
TCLK, SCLK, OR CLKX
DT OR DX
TFS OR FSX
DSP OR SPI (CPOL = 0, CPHA = 1) 8-BIT CONTROL DATA OR 12-BIT DAC DATA WRITE:
CS
SCLK
DIN
DSP OR SPI (CPOL = 1, CPHA = 0) 8-BIT CONTROL DATA OR 12-BIT DAC DATA WRITE:
CS
SCLK
DIN
C3 C2 C1 C0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
C3 C2 C1 C0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DGND
MAX5595
SCLK
DIN
CS
CS MUST REMAIN LOW BETWEEN BYTES ON A 16-BIT WRITE OPERATION
CS MUST REMAIN LOW BETWEEN BYTES ON A 16-BIT WRITE OPERATION
SPI OR QSPI
V
SS
SCK
MOSI
SS OR I/O
COMMAND TAKES EFFECT HERE
ONLY IF SCLK COUNT = N
COMMAND TAKES EFFECT HERE
ONLY IF SCLK COUNT = N
DGND
DSPDSP
SCLK
DIN
CS
MAX5590–
MAX5595
✕
✕
16
16
Page 19

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 19
Table 2a. DAC Programming Commands
*
For the MAX5592/MAX5593 (10-bit version), D11–D2 are the significant bits and D1 and D0 are sub-bits. For the MAX5594/MAX5595 (8-bit version),
D11–D4 are the significant bits and D3–D0 are sub-bits. Set all sub-bits to zero during the write commands.
FUNCTION
Load input register A from shift register; DAC
registers are unchanged. DAC outputs are
unchanged.*
Load input register B from shift register; DAC
registers are unchanged. DAC outputs are
unchanged.*
Load input register C from shift register; DAC
registers are unchanged. DAC outputs are
unchanged.*
Load input register D from shift register; DAC
registers are unchanged. DAC outputs are
unchanged.*
Load input register E from shift register; DAC
registers are unchanged. DAC outputs are
unchanged.*
Load input register F from shift register; DAC
registers are unchanged. DAC outputs are
unchanged.*
Load input register G from shift register; DAC
registers are unchanged. DAC outputs are
unchanged.*
Load input register H from shift register; DAC
registers are unchanged. DAC outputs are
unchanged.*
CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
C3 C2 C1 C0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DIN 0 0 0 0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D 3/0 D 2/0 D 1/0 D 0/0
INPUT REGISTERS (A–H)
D A T A
DIN 0 0 0 1 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D 3/0 D 2/0 D 1/0 D 0/0
DIN 0 0 1 0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D 3/0 D 2/0 D 1/0 D 0/0
DIN 0 0 1 1 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D 3/0 D 2/0 D 1/0 D 0/0
DIN 0 1 0 0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D 3/0 D 2/0 D 1/0 D 0/0
DIN 0 1 0 1 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D 3/0 D 2/0 D 1/0 D 0/0
DIN 0 1 1 0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D 3/0 D 2/0 D 1/0 D 0/0
DIN 0 1 1 1 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D 3/0 D 2/0 D 1/0 D 0/0
Page 20

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
20 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Table 2b. Advanced-Feature Programming Commands
X = Don’t care.
*
For the MAX5592/MAX5593 (10-bit version), D11–D2 are the significant bits and D1 and D0 are sub-bits. For the MAX5594/MAX5595 (8-bit version),
D11–D4 are the significant bits and D3–D0 are sub-bits. Set all sub-bits to zero during the write commands.
FUNCTION
Read-back DACA–DACD
Load D AC r eg i ster “_”
fr om i np ut r eg i ster “_”
w hen M _ = 1. D AC r eg i ster
“_” i s unchang ed i f M _ = 0.
Load all input registers
A–H from shift register;
DAC registers are
unchanged. DAC outputs
are unchanged.*
Load all input and DAC
registers A–H from shift
register. DAC outputs
updated.
Write DACA–DACD
shutdown-mode bits.
shutdown-mode bits.
See Table 8.
Write DACE–DACH
Read-back DACE–DACH
shutdown-mode bits.
shutdown-mode bits.
See Table 8.
Read-back DAC
Write DAC shutdown-
shutdown-control settings.
control bits.
CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
C3 C2 C1 C0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DATA
SELECT BITS
DIN 1000XXXXMHMGMFMEMDMCMBMA
LOADING INPUT AND DAC REGISTERS (A–H)
DIN 1001D11D10D9D8D7D6D5D4D3/0 D2/0 D1/0 D0/0
DIN 1010D11D10D9D8D7D6D5D4D3/0 D2/0 D1/0 D0/0
DIN 10110000PDD1 PDD0 PDC1 PDC0 PDB1 PDB0 PDA1 PDA0
SHUTDOWN BITS
DIN 10110001XXXXXXXX
DOUTRB XXXXXXXXPDD1 PDD0 PDC1 PDC0 PDB1 PDB0 PDA1 PDA0
DIN 10110010PDH1 PDH0 PDG1 PDG0 PDF1 PDF0 PDE1 PDE0
DIN 10110011XXXXXXXX
DOUTRB XXXXXXXXPDH1 PDH0 PDG1 PDG0 PDF1 PDF0 PDE1 PDE0
DIN 10110100PDCHPDCG PDCF PDCE PDCD PDCC PDCB PDCA
DIN 10110101XXXXXXXX
DOUTRB XXXXXXXXPDCHPDCG PDCF PDCE PDCD PDCC PDCB PDCA
Page 21

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 21
Table 2b. Advanced-Feature Programming Commands (continued)
X = Don’t care.
FUNCTION
b i ts. S ee Tab l es 19 and 22.
Read - b ack U P IO
Wr i te U P IO confi g ur ati on
confi g ur ati on b i ts functi on.
Wr i te settl i ng - ti m e b i ts for
D AC A–D AC H ( 0 = S LOW
[ d efaul t, 6µs] , 1 = FAS T
Read - b ack D AC settl i ng -
ti m e b i ts.
[ 3µs] ) .
Read U P IO _ i np uts ( val i d
p ur p ose i np ut.) S ee the
onl y w hen U P IO1 or U P IO2
GP I, GP OL, GP OH secti on.
i s confi g ur ed as a g ener al -
Wr i te C P O L, C P H A contr ol
b i ts. S ee Tab l e 15.
b i ts.
Read C P OL, C P H A contr ol
CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
C3 C2 C1 C0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DIN 10110110U P S L2 U P S L1 U P 3U P 2U P 1U P 0X X
DATA
UPIO CONFIGURATION BITS
DIN 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 X X X X X X X X
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X U P 3- 2U P 2- 2U P 1- 2U P 0- 2U P 3- 1U P 2- 1U P 1- 1U P 0- 1
SETTLING-TIME-MODE BITS
DIN 10111000S P D H S P D GS P D FS P D E S P D D S P D C S P D BS P D A
DIN 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 X X X X X X X X
DIN 1011101XXXXXXXXX
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X S P D H S P D GS P D FS P D E S P D D S P D C S P D BS P D A
UPIO_ AS GPI (GENERAL-PURPOSE INPUT)
DOUTRB X X X XXXXXXXRTP2 LF2 LR2 RTP1 LF1 LR1
DIN 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 X X X X X X C P O LC P H A
CPOL AND CPHA CONTROL BITS
DIN 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 X X X X X X X X
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X X X X X X X C P O LC P H A
Page 22

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
22 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Table 2c. 24-Bit Read Commands
X = Don’t care.
**
D23–D12 represent the 12-bit data from the corresponding DAC register. D11–D0 represent the 12-bit data from the corresponding input register. For
the MAX5592/MAX5593, bits D13, D12, D1, and D0 are zero bits. For the MAX5594/MAX5595, bits D15–D12 and D3–D0 are zero bits.
†
During readback, all ones (code FF) must be clocked into DIN for all 24 bits. No command can be issued before all 24 bits have been clocked out.
CS must be kept low while all 24 bits are being clocked out.
†
FUNCTION
Read input
register A and
DAC register A
(all 24 bits).**
IDA_0
IDA_1
IDA_2
IDA_3
IDA_4
IDA_5
IDA_6
IDA_7
IDA_8
IDA_9
IDA_10
IDA_11
DDA_0
DDA_1
DDA_2
DDA_3
DDA_4
DDA_5
DDA_6
DDA_7
DDA_8
DDA_9
DDA_10
Read input
register B and
DAC register B
†
(all 24 bits).**
IDB_0
IDB_1
IDB_2
IDB_3
IDB_4
IDB_5
IDB_6
IDB_7
IDB_8
IDB_9
IDB_10
IDB_11
DDB_0
DDB_1
DDB_2
DDB_3
DDB_4
DDB_5
DDB_6
DDB_7
DDB_8
DDB_9
DDB_10
Read input
register C and
DAC register C
†
(all 24 bits).**
IDC_0
IDC_1
IDC_2
IDC_3
IDC_4
IDC_5
IDC_6
IDC_7
IDC_8
IDC_9
IDC_10
IDC_11
DDC_0
DDC_1
DDC_2
DDC_3
DDC_4
DDC_5
DDC_6
DDC_7
DDC_8
DDC_9
DDC_10
†
Read input
register D and
DAC register D
(all 24 bits).**
IDD_0
IDD_1
IDD_2
IDD_3
IDD_4
IDD_5
IDD_6
IDD_7
IDD_8
IDD_9
IDD_10
IDD_11
DDD_0
DDD_1
DDD_2
DDD_3
DDD_4
DDD_5
DDD_6
DDD_7
DDD_8
DDD_9
DDD_10
Read input
register E and
DAC register E
†
(all 24 bits).**
IDE_0
IDE_1
IDE_2
IDE_3
IDE_4
IDE_5
IDE_6
IDE_7
IDE_8
IDE_9
IDE_10
IDE_11
DDE_0
DDE_1
DDE_2
DDE_3
DDE_4
DDE_5
DDE_6
DDE_7
DDE_8
DDE_9
DDE_10
Read input
register F and
DAC register F
†
(all 24 bits).**
IDF_0
IDF_1
IDF_2
IDF_3
IDF_4
IDF_5
IDF_6
IDF_7
IDF_8
IDF_9
IDF_10
IDF_11
DDF_0
DDF_1
DDF_2
DDF_3
DDF_4
DDF_5
DDF_6
DDF_7
DDF_8
DDF_9
DDF_10
†
Read input
register G and
DAC register G
(all 24 bits).**
IDG_0
IDG_1
IDG_2
IDG_3
IDG_4
IDG_5
IDG_6
IDG_7
IDG_8
IDG_9
IDG_10
IDG_11
DDG_0
DDG_1
DDG_2
DDG_3
DDG_4
DDG_5
DDG_6
DDG_7
DDG_8
DDG_9
DDG_10
Read input
register H and
DAC register H
†
(all 24 bits).**
IDH_0
IDH_1
IDH_2
IDH_3
IDH_4
IDH_5
IDH_6
IDH_7
IDH_8
IDH_9
IDH_10
IDH_11
DDH_0
DDH_1
DDH_2
DDH_3
DDH_4
DDH_5
DDH_6
DDH_7
DDH_8
DDH_9
DDH_10
DDA_11
CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
C3 C2 C1 C0 D27 D26 D25 D24 D23 D22 D21 D20 D19 D18 D17 D16 D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DIN 1101000X 1 11 1 11111 111 1 111XX XXXXXX
DATA
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X
READ INPUT AND DAC REGISTERS A–H
DIN 1101001X 1 11 1 11111 111 1 111XX XXXXXX
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X
DDB_11
DIN 1101010X 1 11 1 11111 111 1 111XX XXXXXX
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X
DDC_11
DIN 1101011X 1 11 1 11111 111 1 111XX XXXXXX
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X
DDD_11
DIN 1101100X 1 11 1 11111 111 1 111XX XXXXXX
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X
DDE_11
DIN 1101101X 1 11 1 11111 111 1 111XX XXXXXX
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X
DDF_11
DIN 1101110X 1 11 1 11111 111 1 111XX XXXXXX
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X
DDG_11
DIN 1101111X 1 11 1 11111 111 1 111XX XXXXXX
DDH_11
DOUTRB X X X X X X X X
Page 23

MAX5590–MAX5595
DAC Programming Examples:
To load input register A from the shift register, leaving
DAC register A unchanged (DAC output unchanged),
use the command in Table 3.
The MAX5590–MAX5595 can load all of the input registers (A–H) simultaneously from the shift register, leaving
the DAC registers unchanged (DAC output unchanged),
by using the command in Table 4.
To load all of the input registers (A–H) and all of the DAC
registers (A–H) simultaneously, use the command in
Table 5.
For the 10-bit and 8-bit versions, set sub-bits = 0 for
best performance.
Advanced-Feature
Programming Commands
Select Bits (M_)
The select bits allow synchronous updating of any combination of channels. The select bits command the
loading of the DAC register from the input register of
each channel. Set the select bit M_ = 1 to load the DAC
register “_” with data from the input register “_”, where
“_” is replaced with A, B, or C and so on through H,
depending on the selected channel. Setting the select
bit M_ = 0 results in no action for that channel (Table 6).
Select Bits Programming Example:
To load DAC register B from input register B while
keeping other channels (A, C–H) unchanged, set MB =
1 and M_ = 0 (Table 7).
Table 3. Load Input Register A from Shift Register
Table 4. Load Input Registers (A–H) from Shift Register
Table 5. Load Input Registers (A–H) and DAC Registers (A–H) from Shift Register
Table 6. Select Bits (M_)
Table 7. Select Bits Programming Example
X = Don’t care.
X = Don’t care.
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 23
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN 0 0 0 0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3/0 D2/0 D1/0 D0/0
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN 1 0 0 1 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3/0 D2/0 D1/0 D0/0
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN 1 0 1 0 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3/0 D2/0 D1/0 D0/0
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN1000XXXXMHMGMFMEMDMCMBMA
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN1000XX0000000010
Page 24

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
24 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Table 9. Shutdown-Mode Write Command (DACA–DACD)
Table 10. Shutdown-Mode Write Command (DACE–DACH)
Table 11. Shutdown-Control-Bits Write Command
X = Don’t care.
X = Don’t care.
Table 12. Settling-Time-Mode Write Command
X = Don’t care.
Shutdown-Mode Bits (PD_0, PD_1)
Use the shutdown-mode bits and control bits to
shut down each DAC independently. The shutdownmode bits determine the output state of the selected
channels. The shutdown-control bits put the selected
channels into shutdown-mode. To select the shutdown
mode for DACA–DACH, set PD_0 and PD_1 according
to Table 8 (where “_” is replaced with one of the selected channels (A–H)). The three possible states for unitygain versions are 1) normal operation, 2) shutdown with
1kΩ output impedance, and 3) shutdown with 100kΩ
output impedance. The three possible states for forcesense versions are 1) normal operation, 2) shutdown
with 1kΩ output impedance, and 3) shutdown with the
output in a high-impedance state. Tables 9 and 10
show the commands for writing to the shutdown-mode
bits. Table 11 shows the commands for writing the
shutdown-control bits. This command is required to put
the selected channels into shutdown.
Always write the shutdown-mode-bits command first
and then write the shutdown-control-bits command to
properly shut down the selected channels. The shutdown-control-bits command can be written at any time
after the shutdown-mode-bits command. It does not
have to immediately follow the shutdown-mode-bits
command.
Settling-Time-Mode Bits (SPD_)
The settling-time-mode bits select the settling time (FAST
mode or SLOW mode) of the MAX5590–MAX5595.
Set SPD_ = 1 to select FAST mode or set SPD_ = 0 to
select SLOW mode, where “_” is replaced by A, B, or C
and so on through H, depending on the selected channel (Table 12). FAST mode provides a 3µs maximum settling time, and SLOW mode provides a 6µs maximum
settling time.
Table 8. Shutdown-Mode Bits
PD_1 PD_0 DESCRIPTIONS
00
01
1 0 Ignored.
11
Shutdown with 1kΩ termination to ground
on DAC_ output.
Shutdown with 100kΩ termination to
ground on DAC_ output for unity-gain
versions. Shutdown with high-impedance
output for force-sense versions.
DAC_ is powered up in its normal
operating mode.
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN10110000P D D 1P D D 0P D C 1P D C 0P D B1 P D B0 P D A1 P D A0
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN10110010P D H 1P D H 0P D G 1P D G 0P D F1 P D F0 P D E 1P D E 0
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN10110100P D C H P D C GP D C FP D C E P D C D P D C C P D C BP D C A
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN10111000S P D H S P D GS P D FS P D E S P D D S P D C S P D BS P D A
Page 25

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 25
Settling-Time-Mode Write Example:
To configure DACA and DACD into FAST mode and
DACB and DACC into SLOW mode, use the command
in Table 13.
To read back the settling-time-mode bits, use the command in Table 14.
CPOL and CPHA Control Bits
The CPOL and CPHA control bits of the
MAX5590–MAX5595 are defined the same as the CPOL
and CPHA bits in the SPI standard. Set the DAC’s
CPOL and CPHA bits to CPOL = 0 and CPHA = 0 or
CPOL = 1 and CPHA = 1 for MICROWIRE and SPI
applications requiring the clocking of data in on the ris-
ing edge of SCLK. Set the DAC’s CPOL and CPHA bits
to CPOL = 0 and CPHA = 1 or CPOL = 1 and CPHA =
0 for DSP and SPI applications, requiring the clocking
of data in on the falling edge of SCLK (refer to the
Programmer’s Handbook
and see Table 15 for details).
At power-up, if DSP = DV
DD
, the default value of CPHA
is zero and if DSP = DGND, the default value of CPHA
is one. The default value of CPOL is zero at power-up.
To write to the CPOL and CPHA bits, use the command
in Table 16.
To read back the device’s CPOL and CPHA bits, use
the command in Table 17.
Table 13. Settling-Time-Mode Write Example
X = Don’t care.
Table 14. Settling-Time-Mode Read Command
Table 17. CPOL and CPHA Read Command
Table 15. CPOL and CPHA Bits
Table 16. CPOL and CPHA Write Command
X = Don’t care.
X = Don’t care.
X = Don’t care.
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN10111000XXXX1001
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN10111001XXXXXXXX
D OU TRBXXXXXXXXS P D H S P D GS P D FS P D E S P D D S P D C S P D BS P D A
CPOL CPHA DESCRIPTION
00
01
1 0 Data is clocked in on the falling edge of SCLK.
1 1 Data is clocked in on the rising edge of SCLK.
Default values at power-up when DSP is connected to DV
of SCLK.
Default values at power-up when DSP is connected to DGND. Data is clocked in on the falling edge
of SCLK.
. Data is clocked in on the rising edge
DD
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN11000000XXXXXXC P O LC P H A
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 X X X X X X X X
D OU TRBXXX X XXX XX XXXXXC P O LC P H A
Page 26

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
26 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Table 20. UPIO Programming Example
X = Don’t care.
Table 21. UPIO Read Command
X = Don’t care.
UPIO Bits (UPSL1, UPSL2, UP0–UP3)
The MAX5590–MAX5595 provide two user-programmable input/output (UPIO) ports: UPIO1 and UPIO2. These
ports have 15 possible configurations, as shown in
Table 22. UPIO1 and UPIO2 can be programmed independently or simultaneously by writing to the UPSL1,
UPSL2, and UP0–UP3 bits (Table 18).
Table 19 shows how UPIO1 and UPIO2 are selected for
configuration. The UP0–UP3 bits select the desired
functions for UPIO1 and/or UPIO2 (Table 22).
UPIO Programming Example:
To set only UPIO1 as LDAC and leave UPIO2
unchanged, use the command in Table 20.
The UPIO selection and configuration bits can be read
back from the MAX5590–MAX5595 when UPIO1 or
UPIO2 is configured as a DOUTRB output. Table 21
shows the read-back data format for the UPIO bits.
Writing the command in Table 21 initiates a read operation of the UPIO bits. The data is clocked out starting on
the ninth clock cycle of the sequence. Bits UP3-2
through UP0-2 provide the UP3–UP0 configuration bits
for UPIO2 (Table 22), and bits UP3-1 through UP0-1
provide the UP3–UP0 configuration bits for UPIO1.
Table 18. UPIO Write Command
X = Don’t care.
Table 19. UPIO Selection Bits (UPSL1 and UPSL2)
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN10110110U P S L2 U P S L1 UP3 UP2 UP1 UP0 X X
UPSL2 UPSL1 UPIO PORT SELECTED
0 0 None selected
0 1 UPIO1 selected
1 0 UPIO2 selected
1 1 Both UPIO1 and UPIO2 selected
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN10110110010000XX
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN10110111XXXXXXXX
DOUTRB X X XXXXXXU P 3- 2U P 2- 2U P 1- 2U P 0- 2U P 3- 1U P 2- 1U P 1- 1U P 0- 1
Page 27

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 27
UPIO Configuration
Table 22 lists the possible configurations for UPIO1 and
UPIO2. UPIO1 and UPIO2 use the selected function
when configured by the UP3–UP0 configuration bits.
LDAC
LDAC controls the loading of the DAC registers. When
LDAC is high, the DAC registers are latched, and any
change in the input registers does not affect the contents of the DAC registers or the DAC outputs. When
LDAC is low, the DAC registers are transparent, and the
values stored in the input registers are fed directly to the
DAC registers, and the DAC outputs are updated.
Drive LDAC low to asynchronously load the DAC registers from their corresponding input registers (DACs that
are in shutdown remain shut down). The LDAC input
does not require any activity on CS, SCLK, or DIN to
take effect. If LDAC is brought low coincident with a rising edge of CS (which executes a serial command
modifying the value of either DAC input register), then
LDAC must remain asserted for at least 120ns following
the CS rising edge. This requirement applies only for
serial commands that modify the value of the DAC input
registers. See Figures 5 and 6 for timing details.
Table 22. UPIO Configuration Register Bits (UP3–UP0)
UPIO CONFIGURATION BITS
UP3 UP2 UP1 UP0
0000 LDAC
0001 SET Active-Low Input. Drive low to set all input and DAC registers to full scale.
0010 MID Active-Low Input. Drive low to set all input and DAC registers to midscale.
0011 CLR Active-Low Input. Drive low to set all input and DAC registers to zero scale.
0100 PDL Active-Low Power-Down Lockout Input. Drive low to disable software shutdown.
0101Reserved This mode is reserved. Do not use.
0110SHDN1K
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
Active-Low Load DAC Input. Drive low to asynchronously load all DAC registers
with data from input registers.
Active-Low 1kΩ Shutdown Input. Overrides PD_1 and PD_0 settings. For the
MAX5590/MAX5592/MAX5594, drive SHDN1K low to pull OUTA–OUTH to AGND
with 1kΩ. For the MAX5591/MAX5593/MAX5595, drive SHDN1K low to leave
OUTA–OUTH high impedance.
Active-Low 100kΩ Shutdown Input. Overrides PD_1 and PD_0 settings. For the
0111SHDN100K
1000DOUTRB Data Read-Back Output
1001DOUTDC0
1010DOUTDC1 Mode 1 Daisy-Chain Data Output. Data is clocked out on the rising edge of SCLK.
1011 GPIGeneral-Purpose Logic Input
1100 GPOLGeneral-Purpose Logic-Low Output
1101GPOH General-Purpose Logic-High Output
1110TOGG
1111 FAST
MAX5590/MAX5592/MAX5594, drive SHDN100K low to pull OUTA–OUTH to
AGND with 100kΩ. For the MAX5591/MAX5593/MAX5595, drive low to leave
OUTA–OUTH high impedance.
Mode 0 Daisy-Chain Data Output. Data is clocked out on the falling edge of
Toggle Input. Toggles DAC outputs between data in input registers and data in
DAC registers. Drive low to set all DAC outputs to values stored in input registers.
Drive high to set all DAC outputs to values stored in DAC registers.
Fast/Slow Settling-Time-Mode Input. Drive low to select FAST (3µs) mode or drive
high to select SLOW (6µs) settling mode. Overrides the SPDA–SPDH settings.
Page 28

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
28 ______________________________________________________________________________________
SET, MID, CLR
The SET, MID, and CLR signals force the DAC outputs
to full scale, midscale, or zero scale (Figure 5). These
signals cannot be active at the same time.
The active-low SET input forces the DAC outputs to full
scale when SET is low. When SET is high, the DAC outputs follow the data in the DAC registers.
The active-low MID input forces the DAC outputs to
midscale when MID is low. When MID is high, the DAC
outputs follow the data in the DAC registers.
The active-low CLR input forces the DAC outputs to
zero scale when CLR is low. When CLR is high, the
DAC outputs follow the data in the DAC registers.
If CLR, MID, or SET signals go low during a write command, reload the data to ensure accurate results.
Power-Down Lockout (PDL)
The PDL active-low, software-shutdown lockout input
overrides (not overwrites) the PD_0 and PD_1 shutdownmode bits. PDL cannot be active at the same time as
SHDN1K or SHDN100K (see the
Shutdown Mode
(SHDN1K, SHDN100K)
section).
If the PD_0 and PD_1 bits command the DAC to
shut down prior to PDL going low, the DAC returns to
shutdown mode immediately after PDL goes high,
unless the PD_0 and PD_1 bits were modified through
the serial interface in the meantime.
Shutdown Mode (
SSHHDDNN11KK, SSHHDDNN110000KK
)
The SHDN1K and SHDN100K are active-low signals
that override (not overwrite) the PD_1 and PD_0 bit settings. For the MAX5590/MAX5592/MAX5594, drive
SHDN1K low to select shutdown mode with OUTA–
OUTH internally terminated with 1kΩ to ground, or drive
SHDN100K low to select shutdown with an internal
100kΩ termination. For the MAX5591/MAX5593/
MAX5595, drive SHDN1K low for shutdown with 1kΩ
output termination, or drive SHDN100K low for shutdown with high-impedance outputs.
For proper shutdown, first select a shutdown mode
(Table 8), then use the shutdown-control bits as listed
in Table 2b.
Data Output (DOUTRB, DOUTDC0, DOUTDC1)
UPIO1 and UPIO2 can be configured as serial data outputs, DOUTRB (data out for read back), DOUTDC0
(data out for daisy-chaining, mode 0), and DOUTDC1
(data out for daisy-chaining, mode 1). The differences
between DOUTRB and DOUTDC0 (or DOUTDC1) are
as follows:
• The source of read-back data on DOUTRB is the
DOUT register. Daisy-chain DOUTDC_ data comes
directly from the shift register.
• Read-back data on DOUTRB is only present after a
DAC read command. Daisy-chain data is present on
DOUTDC_ for any DAC write after the first 16 bits
are written.
• The DOUTRB idle state (CS = high) for read back is
high impedance. Daisy-chain DOUTDC_ idles high
when inactive to avoid floating the data input in the
next device in the daisy-chain.
See Figures 1 and 2 for timing details.
Figure 5. Asynchronous Signal Timing
Figure 6. GPO_ and LDAC Signal Timing
t
LDL
LDAC
TOGG
PDL
t
CLR,
MID, OR
SET
V
OUT_
PDL AFFECTS DAC OUPTUTS (V
CMS
t
S
) ONLY IF DACS WERE PREVIOUSLY SHUT DOWN.
OUT_
±0.5 LSB
END OF
CYCLE*
GPO_
LDAC
* END-OF-CYCLE REPRESENTS THE RISING EDGE OF CS OR THE 16TH
ACTIVE CLOCK EDGE, DEPENDING ON THE MODE OF OPERATION.
t
GP
t
LDS
Page 29
MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 29
GPI, GPOL, GPOH
UPIO1 and UPIO2 can each be configured as a general-purpose input (GPI), a general-purpose output low
(GPOL), or a general-purpose output high (GPOH).
The GPI can serve to detect interrupts from µPs or microcontrollers. The GPI has three functions:
1) Sample the signal at GPI at the time of the read
(RTP1 and RTP2).
2) Detect whether or not a falling edge has occurred
since the last read or reset (LF1 and LF2).
3) Detect whether or not a rising edge has occurred
since the last read or reset (LR1 and LR2).
RTP1, LF1, and LR1 represent the data read from
UPIO1; RTP2, LF2, and LR2 represent the data read
from UPIO2.
To issue a read command for the UPIO configured as
GPI, use the command in Table 23.
Once the command is issued, RTP1 and RTP2 provide
the real-time status (0 or 1) of the inputs at UPIO1 or
UPIO2, respectively, at the time of the read. If LF2 or
LF1 is one, then a falling edge has occurred on the
respective UPIO1 or UPIO2 input since the last read or
reset. If LR2 or LR1 is one, then a rising edge has
occurred since the last read or reset.
GPOL outputs a constant low, and GPOH outputs a
constant high. See Figure 6.
TOGG
Use the TOGG input to toggle the DAC outputs
between the values in the input registers and DAC registers. A delay of greater than 100ns from the end of the
previous write command is required before the TOGG
signal can be correctly switched between the new
value and the previously stored value. When TOGG =
0, the output follows the information in the input registers. When TOGG = 1, the output follows the information in the DAC register (Figure 5).
FAST
The MAX5590–MAX5595 have two settling-time-mode
options: FAST (3µs max) and SLOW (6µs max). To
select the FAST mode, drive FAST low, and to select
SLOW mode, drive FAST high. This overrides (not overwrites) the SPDA–SPDH bit settings.
Table 23. GPI Read Command
Table 24. Unipolar Code Table (Gain = +1)
Figure 7. Unipolar Output Circuit
X = Don’t care.
DATA CONTROL BITS DATA BITS
DIN1011101XXXXXXXXX
DOUTRB X X XXXXXXXXRTP2 LF2 LR2 RTP1 LF1 LR1
DAC CONTENTS
MSB LSB
1111 1111 1111 +V
1000 0000 0001 +V
1000 0000 0000 +V
0111 1111 1111 +V
0000 0000 0001 +V
0000 0000 0000 0
ANALOG OUTPUT
(4095 / 4096)
REF
(2049 / 4096)
REF
(2048 / 4096) = V
REF
(2047 / 4096)
REF
(1 / 4096)
REF
REF
/ 2
REF_
DAC_
MAX5590
OUT_
V
= V
OUT_
CODE IS THE DAC_ INPUT
CODE (0 TO 4095 DECIMAL).
x CODE / 4096
REF_
Page 30

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
30 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Applications Information
Unipolar Output
Figure 7 shows the unity-gain MAX5590 in a unipolar
output configuration. Table 24 lists the unipolar output codes.
Bipolar Output
The MAX5590 outputs can be configured for bipolar
operation, as shown in Figure 8. The output voltage is
given by the following equation:
V
OUT_
= V
REF
x (CODE - 2048) / 2048
where CODE represents the numeric value of the
DAC’s binary input code (0 to 4095 decimal). Table 25
shows digital codes and the corresponding output voltage for the Figure 8 circuit.
Configurable Output Gain
The MAX5591/MAX5593/MAX5595 have force-sense
outputs, which provide a direct connection to the inverting terminal of the output op amp, yielding the most
flexibility. The force-sense output has the advantage
that specific gains can be set externally for a given
application. The gain error for the MAX5591/MAX5593/
MAX5595 is specified in a unity-gain configuration (opamp output and inverting terminals connected), and
additional gain error results from external resistor
tolerances. The force-sense DACs allow many useful
circuits to be created with only a few simple external
components.
An example of a custom, fixed gain using the
MAX5591’s force-sense output is shown in Figure 9. In
this example, the external reference is set to 1.25V, and
the gain is set to +1.1V/V with external discrete resistors to provide an approximate 0 to 1.375V DAC output
voltage range.
V
OUT
= [(0.5 x V
REF_
x CODE) / 4096] x [1 + (R2 / R1)]
where CODE represents the numeric value of the
DAC’s binary input code (0 to 4095 decimal).
In this example, R2 = 12kΩ and R1 = 10kΩ to set the
gain = 1.1V/V.
V
OUT
= [(0.5 x 1.25V x CODE) / 4096] x 2.2
Table 25. Bipolar Code Table (Gain = +1)
Figure 8. Bipolar Output Circuit
Figure 9. Configurable Output Gain
10kΩ 10kΩ
V+
V
R2 = 12kΩ
0.1%
25ppm
R1 = 10kΩ
0.1%
25ppm
REF
DAC_
MAX5590
DAC_
MAX5591
REF
OUT_
V-
OUT_
FB_
DAC CONTENTS
MSB LSB
1111 1111 1111 +V
1000 0000 0001 +V
1000 0000 0000 0
0111 1111 1111 -V
0000 0000 0001 -V
0000 0000 0000 -V
ANALOG OUTPUT
(2047 / 2048)
REF
(1 / 2048)
REF
(1 / 2048)
REF
(2047 / 2048)
REF
(2048 / 2048) = -V
REF
REF
OUT
Page 31

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
______________________________________________________________________________________ 31
Power-Supply and Layout Considerations
Bypass the analog and digital power supplies by using a
10µF capacitor in parallel with a 0.1µF capacitor to AGND
and DGND (Figure 10). Minimize lead lengths to reduce
lead inductance. Use shielding and/or ferrite beads to further increase isolation.
Digital and AC transient signals coupling to AGND can
create noise at the output. Connect AGND to the highest quality ground available. Use proper grounding
techniques, such as a multilayer board with a low-
inductance ground plane. Wire-wrapped boards and
sockets are not recommended. For optimum system
performance, use PC boards with separate analog and
digital ground planes. Connect the two ground planes
together at the low-impedance power-supply source.
Using separate power supplies for AV
DD
and DV
DD
improves noise immunity. Connect AGND and DGND at
the low-impedance power-supply sources (Figure 11).
Figure 10. Bypassing Power Supplies AVDD, DVDD, and REF
Figure 11. Separate Analog and Digital Power Supplies
V
REF
10µF*
0.1µF*
SCLK
DIN
DSP
UPIO1
UPIO2
AV
DD
AV
DD
REF
CS
PU
MAX5590–MAX5595
AGND** DGND**
DV
DV
DD
MAX5591
MAX5593
MAX5595
DD
ONLY
10µF0.1µF10µF0.1µF
OUTA
OUTH
FBA
FBH
ANALOG SUPPLY DIGITAL SUPPLY
AV
DD
10µF
0.1µF
AV
DD
MAX5590–MAX5595
AGND
AGND
DV
DV
DGND
DD
10µF
0.1µF
DGND
DD
DV
DD
DIGITAL
CIRCUITRY
DGND
*REMOVE BYPASS CAPACITORS ON REF FOR AC-REFERENCE INPUTS.
**CONNECT ANALOG AND DIGITAL GROUND PLANES AT THE
LOW-IMPEDANCE POWER-SUPPLY SOURCE.
Page 32

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
32 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Chip Information
PROCESS: BiCMOS
Pin Configurations
Selector Guide
Package Information
For the latest package outline information and land patterns, go
to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
. Note that a “+”, “#”, or “-” in
the package code indicates RoHS status only. Package drawings may show a different suffix character, but the drawing pertains to the package regardless of RoHS status.
PACKAGE TYPE PACKAGE CODE DOCUMENT NO.
24 TSSOP U24+1
21-0066
28 TSSOP U28+2
21-0066
TOP VIEW
DIN
+
1
DD
2
3
4
MAX5590
5
MAX5592
6
MAX5594
7
8
9
CS
10
11
12
AV
AGND
OUTA
OUTB
OUTC
OUTD
SCLK
DSP
REF
24
PU
23
OUTH
22
N.C.N.C.
21
20
OUTG
19
OUTF
18
OUTE
17
N.C.N.C.
16
UPIO2
15
UPIO1
14
DGND
13
DV
TSSOP
OUTPUT
PART
BUFFER
CO NFIGUR ATION
MAX5590AEUG+
Unity Gain 12 ±1
MAX5590BEUG+ Unity Gain 12 ±4
MAX5591AEUI+ Force Sense 12 ±1
MAX5591BEUI+ Force Sense 12 ±4
MAX5592EUG+ Unity Gain 10 ±1
MAX5593EUI+ Force Sense 10 ±1
MAX5594EUG+ Unity Gain 8 ±0.5
MAX5595EUI+ Force Sense 8 ±0.5
R ESO L U TIO N
( B IT S)
+
1
AV
DD
2
AGND
3
OUTA
4
FBA
5
FBB
OUTB
OUTC
FBC
FBD
OUTD
CS
SCLK
DD
DIN
DSP
MAX5591
6
MAX5593
MAX5595
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28
REF
27
PU
26
OUTH
25
FBH
24
FBG
23
OUTG
22
OUTF
21
FBF
20
FBE
19
OUTE
18
UPIO2
17
UPIO1
16
DGND
15
DV
DD
TSSOP
INL
(LSBs
MAX)
Page 33

MAX5590–MAX5595
Buffered, Fast-Settling, Octal, 12/10/8-Bit,
Voltage-Output DACs
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600 ____________________
33
© 2010 Maxim Integrated Products Maxim is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Revision History
REVISION
NUMBER
2 7/07 Updated EC table specifications 1, 6–9, 33
3 1/10 Added lead-free information and amended data sheet
REVISION
DATE
DESCRIPTION
PAGES
CHANGED
1–13, 16, 20,
32, 33
 Loading...
Loading...