Page 1
General Description
The MAX3801 is a +3.3V adaptive cable equalizer
designed for coaxial and twin-axial cable point-to-point
communications applications. The equalizer includes
differential CML data inputs and outputs, a loss-of-signal (LOS) output, and a cable integrity monitor (CIM)
output.
The adaptive cable equalizer is capable of equalizing
differential or single-ended signals at data rates up to
3.2Gbps. It automatically adjusts to attenuation caused
by skin-effect losses of up to 30dB at 1.6GHz. The
equalizer effectively extends the usable length of copper cable in high-frequency interconnect applications.
The MAX3801 is available in a 24-pin QFN package
with exposed pad and consumes only 125mW at
+3.3V.
Applications
High-Speed Links in Communications
and Data Systems
Backplane and Interconnect Applications
SDH/SONET Transmission Equipment
Features
♦ Single +3.3V Operation
♦ Typical Power Dissipation = 125mW at +3.3V
♦ Data Rates Up to 3.2Gbps
♦ Equalizer Automatically Adjusts for Different
Cable Lengths
♦ 0dB to 30dB Equalization at 1.6GHz (3.2Gbps)
♦ Loss-of-Signal (LOS) Indicator
♦ Cable Integrity Monitor (CIM)
♦ On-Chip Input and Output Terminations
♦ Low External Component Count
♦ Operating Temperature Range = 0°°C to +85°°C
♦ ESD Protection on Inputs and Outputs
MAX3801
3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer
________________________________________________________________ Maxim Integrated Products 1
Ordering Information
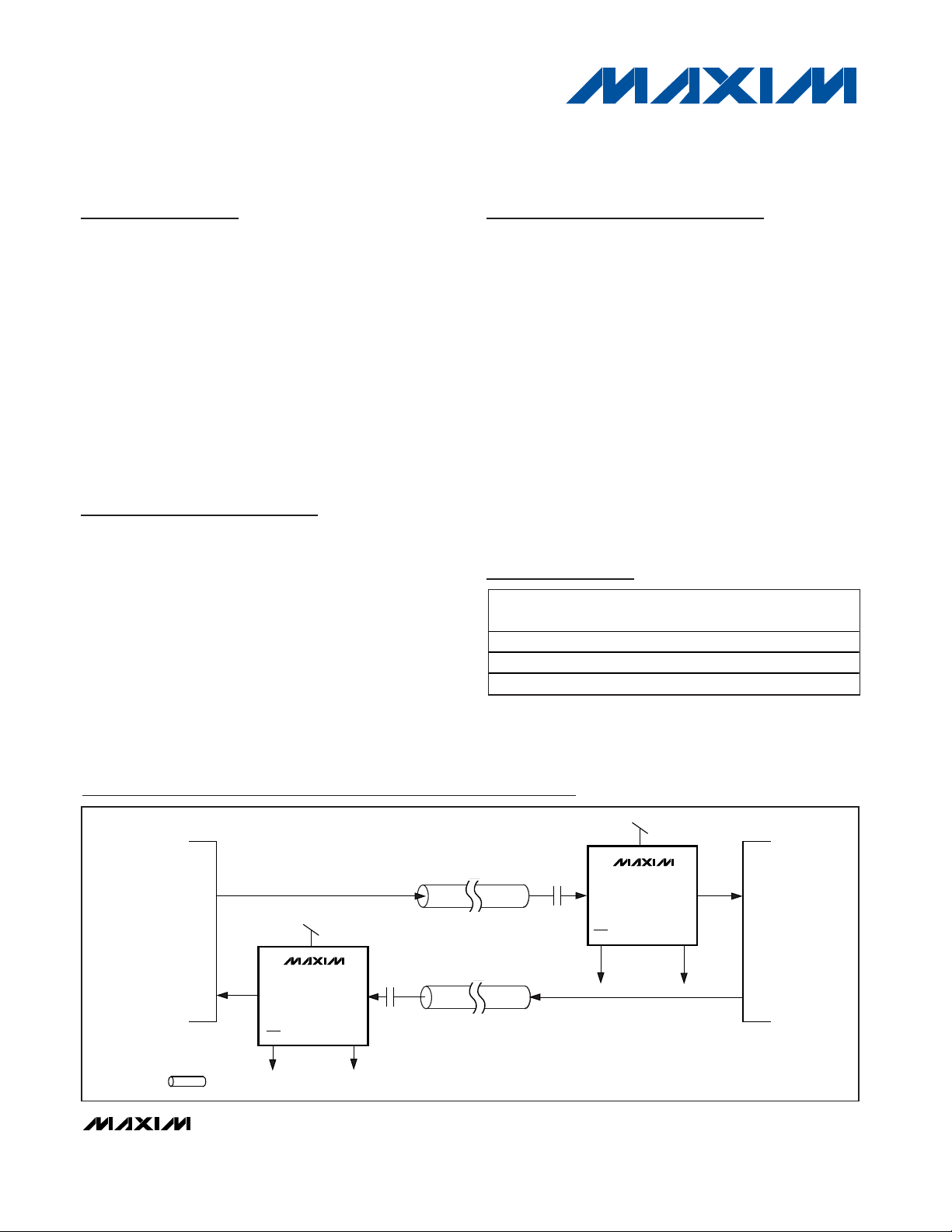
EIN EOUT
MAX3801
EIN
THIS SYMBOL INDICATES A CONTROLLED-IMPEDANCE TRANSMISSION LINE.
EOUT
CIM
MAX3801
CARD 2
CARD 1
+3.3V
+3.3V
LOS
CIM
LOS
Typical Application Circuit
19-1999; Rev 4; 7/04
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim/Dallas Direct! at
1-888-629-4642, or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
PART
TEMP
RANGE
PINPACKAGE
PACKAGE
CODE
MAX3801UGG
24 QFN
MAX3801UTG
T2444-2
MAX3801UTG+
T2444-2
Pin Configuration appears at end of data sheet.
+Denotes lead-free package.
0°C to +85°C
0°C to +85°C 24 Thin QFN
0°C to +85°C 24 Thin QFN
G2444-1
Page 2
MAX3801
3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VCC= +3.14V to +3.46V, TA= 0°C to +85°C. Typical values are at VCC= +3.3V and TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Supply Voltage, VCC..............................................-0.5V to +6.0V
Voltage at LOS, CIM+, CIM-.......................-0.5V to (V
CC
+ 0.5V)
Voltage at EIN+, EIN- .........................(V
CC
- 1V) to (VCC+ 0.5V)
Current Out of EOUT+, EOUT-............................................25mA
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +85°C)
24-Lead QFN-EP (derate 25.1mW/°C above +85°C) .1630mW
Operating Ambient Temperature Range ................0°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range .............................-55°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
Supply Current I
CC
Includes external load current 37 60 mA
INPUT SPECIFICATIONS
M i ni m um C ab l e Inp ut ( D i ffer enti al )
MV
P-P
M axi m um C ab l e Inp ut ( D i ffer enti al )
mV
P-P
Input Impedance Single-ended 40 53
Ω
OUTPUT SPECIFICATIONS
Output Voltage (Differential) (Note 2)
mV
P-P
Output Impedance Single-ended 50 65 75 Ω
V ol tag e at C IM Outp ut ( D i ffer enti al )
V
CIM
No external load, V
CIM
= (V
CIM+
) - (V
CIM-
)
V
P-P
Voltage at CIM Output
(Single-Ended)
V
CIM+,
V
CIM-
No external load 0.5
V
Output high (Note 3) 2.4
Voltage at LOS
Output low (Note 3) 0.4
V
Outp ut C om m on- M od e V ol tag e Each output DC-coupled 50Ω to V
CC
V
CC
- 0.2 V
3.2Gbps, 30dB cable loss at 1.6GHz (Note 1) 650 700
1100
500 1000
62.5
-0.5 +0.5
V
CC
- 0.5
Page 3
MAX3801
3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
Note 1: Minimum cable input for LOS to assert high.
Note 2: Input voltage within specification limits, 50Ω to V
CC
at each output.
Note 3: 100kΩ load to ground.
Note 4: AC electrical characteristics are guaranteed by design and characterization.
Note 5: Includes random jitter and deterministic jitter.
Note 6: Differential cable input voltage = 700mV
P-P
, 3.2Gbps 2
13
- 1PRBS with 100 consecutive ones and 100 consecutive zeros
substituted. Cable loss is due to skin effect only.
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VCC= +3.14V to +3.46V, TA= 0°C to +85°C. Typical values are at VCC= +3.3V and TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 4)
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
Maximum Input Data Rate 3.2
Gbps
0dB cable loss (Note 6)
24dB cable loss (Note 6)
Residual Jitter (Note 5)
30dB cable loss (Note 6)
mUI
P-P
Output Edge Speed 20% to 80% 64 90 ps
Input Return Loss (Single-Ended)
≤3.2GHz 15 dB
Outp ut Retur n Loss ( S i ng l e- E nd ed )
≤3.2GHz 15 dB
Equalization Compensation 1.6GHz (skin-effect losses only) 30 dB
Equalization Time Constant 5µs
120 240
140 240
100 200
Page 4

MAX3801
3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
0304010 20 50 60 70 80 90
SUPPLY CURRENT vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX3801 toc01
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
30
35
40
45
0.001 0.10.01 1 10 100
EQUALIZER RESIDUAL JITTER
vs. POWER-SUPPLY NOISE
(100mV
P-P
SINE WAVE)
(85FT OF GORE 89 CABLE)
MAX3801 toc02
NOISE FREQUENCY (MHz)
JITTER (ps
P-P
)
30
40
50
60
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
0400200 600 800 1000 1200
EQUALIZER RESIDUAL JITTER vs. INPUT
AMPLITUDE AT 3.2GHz (RG59 – 75Ω
COAXIAL CABLE – SINGLE-ENDED)
MAX3801 toc03
INPUT AMPLITUDE (mVp-p)
JITTER (ps
P-P
)
100FT
288FT
188FT
20
40
30
50
80
90
70
60
100
100 140 160 180 200120 220 240 260 280 300
EQUALIZER RESIDUAL JITTER
vs. CABLE LENGTH (RG59 – 75Ω COAXIAL
CABLE – SINGLE-ENDED)
INPUT LEVEL OF 500mV
P-P
MAX3801 toc04
CABLE LENGTH (ft)
JITTER (ps
P-P
)
3.2Gbps
2.5Gbps
1.2Gbps
622Mbps
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
25 35 45 55 65 75
EQUALIZER RESIDUAL JITTER
vs. CABLE LENGTH (RG179B – 75Ω
COAXIAL CABLE – SINGLE-ENDED)
INPUT LEVEL OF 700mV
P-P
MAX3801 toc05
CABLE LENGTH (ft)
JITTER (ps
P-P
)
3.2Gbps
2.5Gbps
1.2Gbps
622Mbps
0
40
20
80
60
120
100
140
180
160
200
525354515 55 65 75
95
85
EQUALIZER RESIDUAL JITTER
vs. CABLE LENGTH
(CATEGORY 5E – TWISTED PAIR)
INPUT LEVEL OF 700mV
P-P
MAX3801 toc06
CABLE LENGTH (ft)
JITTER(ps
P-P
)
3.2Gbps
2.5Gbps
1.2Gbps
622Mbps
Typical Operating Characteristics
(VCC= +3.3V, all jitter measurements done at 3.2Gbps, 700mV cable input with 2
13
- 1 PRBS pattern with 100 consecutive ones and
100 consecutive zeros substituted, T
A
= +25°C. Note: Test pattern produces near worst-case jitter results. Results vary with pattern,
unless otherwise noted.)
Page 5

MAX3801
3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
EQUALIZER OUTPUT EYE DIAGRAM
AFTER 100FT OF 75Ω RG179 CABLE
(2.5Gbps, SINGLE-ENDED, 2
7
- 1PRBS)
MAX3801 toc10
68ps/div
200ps/div
EQUALIZER OUTPUT EYE DIAGRAM
AFTER 70FT OF CATEGORY 5E CABLE
(INPUT OF 1000mV
P-P
, 1.25Gbps)
MAX3801 toc11
50ps/div
EQUALIZER OUTPUT EYE DIAGRAM
AFTER 115FT OF 50Ω GORE 89 CABLE
(INPUT OF 1000mV
P-P
, 3.2Gbps)
MAX3801 toc12
EQUALIZER INPUT RETURN LOSS (S11)
MAX3801 toc14
50
40
30
20
10
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
GAIN (dB)
0
0.4 0.8
1.2
1.6 2.0
2.4
2.8
3.2
3.6
4.0
FREQUENCY (GHz)
EQUALIZER OUTPUT RETURN LOSS (S22)
MAX3801 toc15
50
40
30
20
10
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
GAIN (dB)
0 0.4
0.8
1.2 1.6
2.0
2.4
2.8
3.2
3.6
4.0
FREQUENCY (GHz)
EQUALIZER OUTPUT EYE DIAGRAM
AFTER 288 FT OF RG59 CABLE
(INPUT OF 1000mV
P-P
, 3.2Gbps, 2
23
- 1PRBS)
MAX3801 toc09
40
60
50
80
70
100
90
110
40 50 5545 60 65 70 75 80 85 (in)
EQUALIZER RESIDUAL JITTER vs. LINE LENGTH
(FR-4 6MIL STRIPLINE – SINGLE-ENDED)
MAX3801 toc07
LINE LENGTH
JITTER (ps
p-p
)
3.2Gbps
622Mbps
2.5Gbps
1.02 1.27 1.401.14 1.52 1.65 1.77 1.90 2.03 2.16 (m)
EQUALIZER INPUT AFTER
115FT OF CABLE (TOP)
EQUALIZER OUTPUT (BOTTOM)
MAX3801 toc08
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(VCC= +3.3V, all jitter measurements done at 3.2Gbps, 700mV cable input with 2
13
- 1 PRBS pattern with 100 consecutive ones and
100 consecutive zeros substituted, T
A
= +25°C. Note: Test pattern produces near worst-case jitter results. Results vary with pattern,
unless otherwise noted.)
Page 6

Detailed Description
The adaptive cable equalizer accepts differential CML
input data at rates up to 3.2Gbps and is capable of
equalizing differential or single-ended signals. It automatically adjusts to attenuation levels of up to 30dB at
1.6GHz (because of skin-effect losses in copper cable).
The equalizer consists of a CML input buffer, a loss-ofsignal detector, a flat response amplifier, a skin-effect
compensation amplifier, a current-steering network, a
dual power-detector feedback loop, an output limiting
amplifier, and a CML output buffer (Figure 1).
General Theory of Operation
The shape of the power spectrum of a random bit
stream can be described by the square of the sinc
function, where sinc f = (sin πf) / πf. For sufficiently long
bit patterns (nonrandom bit streams), sinc2(f) is a good
approximation. From the shape of the sinc2(f) function,
we can estimate the ratio of the power densities at any
two frequencies. The MAX3801 adaptive equalizer
employs this principle by incorporating a feedback loop
that continuously monitors the power at two frequencies
and dynamically adjusts the equalizer to maintain the
correct power ratio.
CML Input and Output Buffers
The input and output buffers are implemented using
current-mode logic (CML). Equivalent circuits are
shown in Figures 2 and 3. For details on interfacing with
CML, refer to Maxim application note HFAN-1.0,
Introduction to LVDS, PECL, and CML.
Flat Response and Skin-Effect
Compensation Amplifiers
The buffered input waveform is fed equally to two
amplifiers—the flat response amplifier and the skineffect compensation amplifier. The flat response amplifier has a constant gain over the entire frequency range
of the device, and the skin-effect compensation amplifier has a gain characteristic that approximates the
inverse of the skin-effect attenuation inherent in copper
cable. The skin-effect attenuation, in dB per unit length,
is proportional to the square root of the frequency. The
output currents from the two amplifiers are supplied to
the current-steering network. Note that, when LOS
asserts low, equalization is minimized.
Current-Steering Network
The function of the current-steering network is to combine adjustable quantities of the output currents from
the flat response and skin-effect compensation ampli-
MAX3801
3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
PIN NAME FUNCTION
1, 3, 7, 12, 16, 18,
19, 24
GND Ground
2, 4, 8, 11, 17, 20,
23
V
CC
Power Supply
5 CIM- Negative Cable Integrity Monitor (CIM) Output
6 CIM+ Positive Cable Integrity Monitor (CIM) Output
9 EOUT- Negative Equalizer Output, CML
10 EOUT+ Postive Equalizer Output, CML
13, 14 N.C. No connection. Leave unconnected.
15 LOS Equalizer Loss-of-Signal Output, Active-Low
21 EIN+ Postive Equalizer Input, CML
22 EIN- Negative Equalizer Input, CML
EP Exposed Pad
Ground. The exposed pad must be soldered to the circuit board ground for proper
thermal and electrical operation.
Pin Description
Page 7

MAX3801
3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
VARIABLE
ATTENUATOR
LIMITING
AMP
FLAT
RESPONSE
AMP
Σ
f
√
MAX3801
LOOP
FILTER
|H(f)|
|H(f)|
VARIABLE
ATTENUATOR
200MHz
PWR DETECTOR
600MHz
PWR DETECTOR
CIM-
CIM+
CMLCML
EIN
EOUT
P0WER
DETECTOR
LOS
CURRENT STEERING NETWORK
SKIN
EFFECT
COMPENSATION
AMP
Figure 1. Functional Diagram
EIN-
EIN+
GND
ESD
STRUCTURES
V
CC
50
Ω
50
Ω
Figure 2. CML Input Equivalent Circuit
Figure 3. CML Output Equivalent Circuit
V
CC
Ω
62.5
GND
ESD
STRUCTURES
Ω
62.5
EOUT+
EOUT-
Page 8

MAX3801
fiers to achieve a desired current ratio. The ratio adjustment is controlled by the dual power-detector feedback
loop.
The current-steering network is implemented with two
variable attenuators that feed into a current-summing
node. The variable attenuators attenuate the output currents of the flat response and skin-effect compensation
amplifiers under control of the dual power-detector
feedback loop. The outputs of the two attenuators are
combined at the summing node and then fed to the output limiting amplifier and the feedback loop.
Dual Power-Detector Feedback Loop
The output of the current-steering network is applied to
the inputs of two frequency-specific power detectors.
One of the power detectors is tuned to 200MHz, and
the other is tuned to 600MHz. The outputs of the two
power detectors are applied to the inverting (200MHz
power detector) and noninverting (600MHz power
detector) inputs of the differential loop amplifier. The
differential outputs of the loop amplifier control the variable attenuators in the current-steering network.
Output Limiting Amplifier
The output limiting amplifier amplifies the signal from
the current-steering network to achieve the specified
output voltage swing.
Applications Information
Refer to Maxim application note HFAN-10.0, Equalizing
Gigabit Copper Cable Links with the MAX3800 (avail-
able at www.maxim-ic.com) for additional applications
information.
Cable Integrity Monitor (CIM)
The differential CIM output current is directly proportional to the output current of the loop amplifier (which
controls the current-steering network—see the Detailed
Description). This is an analog current output that indicates the amount of equalization being applied. A convenient way to monitor the CIM current is to connect a
100kΩ resistor from each of the CIM outputs to ground,
and then measure the voltage at the CIM pins.
The amount of equalization (and thus the CIM output
level) is affected by various factors, including cable
type, cable length, signal bandwidth, etc.
Loss-of-Signal (
LLOOSS
) Output
Loss-of-signal is indicated by the LOS output. A low
level on LOS indicates that the equalizer input signal
power has dropped below a threshold. The LOS output
indicates a loss of signal. When the equalizer no longer
detects a signal from the channel, the LOS output goes
low. When there is sufficient input voltage to the channel (typically greater than 650mV), LOS is high. The
LOS output is suitable for indicating problems with the
transmission link caused by, for example, a broken
cable, a defective driver, or a lost connection to the
equalizer.
Single-Ended Operation
For single-ended operation of the equalizer, connect
the unused input to ground through a series combination of a capacitor (of equal value to other AC-coupling
capacitors) and a 50Ω resistor. Note that the MAX3801
is specified for differential operation. The effective
range of equalization for single-ended use is approximately 4dB to 30dB at 1.6GHz.
Layout Considerations
The MAX3801’s performance significantly can be
affected by circuit-board layout and design. Use good
high-frequency design techniques, including minimizing ground inductance and using fixed-impedance
transmission lines for the high-frequency data signals.
Place power-supply decoupling capacitors as close as
possible to V
CC
.
3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
MAX3801*
TOP VIEW
10
13
15
14
16
11 129
EOUT+
EOUT-
2
3
4
5
6
78
CIM-
GND
GND
1
V
CC
17
18
192021222324
GND
V
CC
CIM+
N.C.
GND
GND
V
CC
LOS
N.C.
V
CC
V
CC
GND
EIN+
EIN-
GND
V
CC
V
CC
GND
*THE EXPOSED PAD MUST BE
SOLDERED TO THE SUPPLY GROUND.
QFN
Pin Configuration
Page 9

MAX3801
3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
12,16,20, 24L QFN.EPS
E
1
2
21-0106
PACKAGE OUTLINE
12,16,20,24L QFN, 4x4x0.90 MM
E
2
2
21-0106
PACKAGE OUTLINE
12,16,20,24L QFN, 4x4x0.90 MM
Package Information
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.)
Page 10

MAX3801
3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
10 ____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 2004 Maxim Integrated Products Printed USA is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products.
Package Information (continued)
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.)
24L QFN THIN.EPS
PACKAGE OUTLINE,
21-0139
2
1
E
12, 16, 20, 24, 28L THIN QFN, 4x4x0.8mm
PACKAGE OUTLINE,
21-0139
2
2
E
12, 16, 20, 24, 28L THIN QFN, 4x4x0.8mm
 Loading...
Loading...