Page 1

Maxim > App Notes > INTERFACE CIRCUITS
Keywords: USB, FAQ, MAX3420E, SPI, Peripheral, Controller.Interface
APPLICATION NOTE 3597
Aug 17, 2005
Frequently Asked Questions About the MAX3420E
Abstract: This application note lists Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the MAX3420E peripheral
controller with SPI interface.
1. General Questions
1. What is the MAX3420E?
2. Does the MAX3420E include a microprocessor?
3. What packages are available for the MAX3420E?
4. Are the MAX3420E packages lead-free?
2. USB Questions
1. What USB speeds does the MAX3420E support?
2. Does the MAX3420E comply with the USB spec? Which revision?
3. How many endpoints does the MAX3420E support?
4. Why doesn't the MAX3420E support isochronous transfers?
5. Can I use the MAX3420E in a self-powered peripheral?
6. Can I use the MAX3420E in a bus-powered peripheral?
7. What external circuitry do I need to connect the MAX3420E to USB?
8. Can you recommend a 3.3V regulator?
9. What does the CONNECT bit do?
3. Interface Questions
1. How does a microprocessor connect to the MAX3420E?
2. You say the SPI interface is 3, 4 or 5 wires. What does this mean?
3. What SPI clocking modes does the MAX3420E support?
4. My CPU uses a 2.5 volt supply, but the MAX3420E uses a 3.3V VCC supply. Do I need external
level translators?
5. What is the purpose of the MAX3420E INT pin?
6. Does the MAX3420E support active-low wired-OR interrupts? How about edge active interrupts?
7. How fast can I run the MAX3420E SPI interface (SCLK max frequency)?
8. Is there a low limit to the MAX3420E SCLK frequency?
9. I have an 8-pin microprocessor, and it takes 5 of its' IO pins to connect to the MAX3420E. How
do I do IO?
10. Do I need to add external pullup resistors to the GPIN pins?
11. Can I drive optocouplers from the SPI interface pins?
12. What is the purpose of the VBCOMP pin? Does it power the MAX3420E?
4. Programming Questions
1. How does my firmware talk to the MAX3420E?
2. How do I program the MAX3420E to handle USB enumeration?
3. How do I program a BULK IN transfer?
4. What if a USB IN request comes in while firmware is loading the IN FIFO?
5. How do I know when to load an IN FIFO?
6. What if there is a USB transfer error? Do I need to write code to handle the error condition?
7. How do I program a BULK OUT transfer?
8. How about INTERRUPT transfers?
Page 2

9. How do I program a SETUP transfer?
10. Do I need to program the USB data toggles?
11. The MAX3420E interrupt request bits are cleared by writing "1" to them. Is this backwards?
12. Do you have any programming tips?
5. Host Software Questions
1. How does my Windows application talk to the MAX3420E?
2. Does Maxim supply a custom Windows driver?
3. What example code does Maxim supply?
4. I want to design a MAX3420E-based device that does not conform to a standard Windows class.
What do I use for a Windows driver?
5. How does the MAX3420E compare with USB 'serial bridge' chips?
6. What are the advantages and disadvantages of the MAX3420E approach?
6. Miscellaneous Questions
1. Can my firmware determine which chip revision I have?
2. What is the current revision level of the MAX3420E?
1.
General Questions
1. What is the MAX3420E?
The MAX3420E is a USB full-speed (12Mbps) peripheral controller with a built-in transceiver and
a USB serial interface engine (SIE) that handles the low-level USB signaling details.
2. Does the MAX3420E include a microprocessor?
No. The MAX3420E is designed to interface easily to any microprocessor, DSP, or ASIC. This
makes it possible to add USB to any system without switching processors or tool sets.
3. What packages are available for the MAX3420E?
The MAX3420E is available in two packages. The 32-pin TQFP (7mm x 7mm body size) is good
for prototyping and short production runs because it has package leads. The 24-pin TQFN
package (5mm x 5mm body size, pads underneath the package) is ideal for high-volume
compact devices.
4. Are the MAX3420E packages lead-free?
Yes.
USB Questions
2.
1. What USB speeds does the MAX3420E support?
The MAX3420E supports USB full-speed (12Mbps) operation as a peripheral.
2. Does the MAX3420E comply with the USB spec? Which revision?
The MAX3420E is compliant with the USB 2.0 specification as it applies to full-speed operation.
3. How many endpoints does the MAX3420E support?
The MAX3420E contains four endpoints:
■ EP0, bidirectional CONTROL endpoint, 64 byte FIFO.
■ EP1, OUT BULK or INT endpoint, 2 x 64 byte double-buffered FIFOS
■ EP2, IN BULK or INT endpoint, 2 x 64 byte double-buffered FIFOS
■ EP3, IN BULK or INT endpoint, 64 byte FIFO
With these endpoints, it is possible to build USB peripherals that support popular USB class
drivers, such as a Human Interface Device (HID), Mass Storage, Picture Transfer Protocol (PTP),
and Printer.
4. Why does the MAX3420E not support ISOCHRONOUS transfers?
ISOCHRONOUS transfers require fast interfaces and large buffers, neither of which is consistent
with the MAX3420E design goals (a low-cost part with an SPI interface that can run at any
Page 3
speed). Most applications that seem to require ISOCHRONOUS bandwidth can actually be
handled with BULK or INTERRUPT transfers. This is because most of the ISOCHRONOUS
bandwidth available to a USB device in a system is also typically available for BULK/INT
transfers.
5. Can I use the MAX3420E in a self-powered peripheral?
Absolutely. In fact, the MAX3420E has features specifically intended to support self-powered
applications. For example, in a self-powered application the peripheral needs to know when the
device is plugged into a powered USB port. The MAX3420E's VBCOMP (V
connected to V
, and routed to an internal comparator that provides an interrupt request at
BUS
comparator) pin is
BUS
plug-in (VBUSIRQ) and another interrupt request at disconnect (NOVBUSIRQ). As another
example for the MAX3420E, a bit called VBGATE (V
disconnect the D+ pullup resistor whenever V
BUS
gate) can be set to automatically
BUS
is detected to be off. This is a required USB
specification.
6. Can I use the MAX3420E in a bus-powered peripheral?
Yes. In a bus-powered application, a 3.3V voltage regulator is connected to the USB connector's
pin. Whenever the peripheral is plugged into USB, the chip and the SPI master driving it are
V
BUS
powered. So there is no need to connect the MAX3420's VBCOMP pin to V
. In this case, the
BUS
VBCOMP input can be used as an extra general-purpose input. Care must be taken to ensure that
input signals to this pin meet the threshold requirements noted in the
MAX3420 Electrical
Characteristics table.
7. What external circuitry do I need to connect the MAX3420E to USB?
The MAX3420E requires a VCC supply of 3.3V. Bus-powered peripherals need a 3.3V regulator to
convert the power available on the V
pin (4.4V to 5.25V) to 3.3V. In addition, the MAX3420E
BUS
requires an external crystal (parallel resonant, 12MHz ±0.25%) with load capacitors from each
pin to ground, and two series resistors (33
, 1%) between the D+/D- outputs, and the USB "B"
connector.
8. Can you recommend a 3.3V regulator?
The MAX6349TL is ideal. It supplies 150mA at 3.3V, and contains a power-on-reset (POR) circuit
which can be connected directly to the MAX3420E RES# pin. A good external POR circuit is
important to have in a hot-plugged design such as a USB peripheral.
9. What does the CONNECT bit do?
The MAX3420E has a switchable internal 1500 pullup resistor between its D+ pin and VCC. The
CONNECT bit operates this switch. This switch allows a bus- powered peripheral to delay
connection to USB until it finishes initialization. It also allows a self-powered peripheral to
remove V
from the pullup resistor in the absence of V
CC
, as required by the USB
BUS
Specification.
Interface Questions
3.
1. How does a microprocessor connect to the MAX3420E?
The microprocessor connects to the MAX3420E by implementing an SPI master, using 3, 4, or 5
wires. Some microcontrollers include hardware SPI, but many do not. In this latter case, it is
easy to implement an SPI master by bit-banging general-purpose IO pins.
2. You say the SPI interface is 3, 4, or 5 wires. What does this mean?
The minimum SPI interface consists of three wires: SS# (Slave Select), SCLK (Serial Clock), and
MISO (configured for bidirectional MISO/MOSI data). Since this interface does not use the INT
pin, the controlling microprocessor would need to poll two interrupt-request registers to
determine when the MAX3420E requires service.
Page 4

By setting a control bit (FDUPSPI, full-duplex SPI), the MOSI and MISO data appear on separate
pins, providing a 4-wire interface. Finally, an INT (interrupt out) pin can be connected to a
processor's interrupt system.
3. What SPI clocking modes does the MAX3420E support?
The SPI mode is usually expressed in the form (x,y) where one variable is the clock polarity,
CPOL, and the other is the clock phase, CPHA. The MAX3420E operates in modes (0,0) or (1,1)
without requiring a mode bit. The only difference between these modes is the inactive SCLK
level: low for (0,0), high for (1,1). There are two basic requirements for running the MAX3420E
SPI interface:
■ MOSI data supplied to the MAX3420E must be valid before the first positive SCLK edge.
■ SPI input data is sampled on the positive edge of the clock, and output data changes on
the negative edge of SCLK.
Be careful with these modes—some microprocessor data sheets do not adhere to the (0,0) and
(1,1) convention. It is best to verify the above two points when setting a clock mode. Also see
the MAX3420E data sheet and MAX3420E Programming Guide for SPI example waveforms.
4. My CPU uses a 2.5V supply, but the MAX3420E uses a 3.3V V
supply. Do I need
CC
external level translators?
No. The MAX3420E contains internal level shifters. A V
pin powers the internal logic and serves
L
as the logic reference voltage for the SPI and IO pin signals. For a 2.5V interface, connect your
2.5V supply to the V
3.6V. If the controller uses 3.3V, tie V
pin. The VL pin can actually operate with a range of voltages from 1.7V to
L
to VCC.
L
5. What is the purpose of the MAX3420E INT pin?
The INT pin goes active whenever the MAX3420E requires service. During USB peripheral
operation, this includes the arrival of SETUP, IN or OUT packets, plus bus events like bus reset,
suspend, and resume. Using this pin in a system reduces the SPI traffic since the interrupt
request bits do not need to be polled over the SPI interface.
6. Does the MAX3420E support active-low wired-OR interrupts? How about edge active
interrupts?
The MAX3420E supports both interrupt types, using a control bit called INTLEVEL. Setting
INTLEVEL=1 makes the INT output pin open-drain, active-low for wired-OR applications. This
mode requires an external pullup resistor to V
. Setting INTLEVEL=0 (the default value) makes
L
the INT pin edge-active with a push-pull output driver. In edge mode, a second bit called POSINT
sets the edge polarity to positive or negative.
7. How fast can I run the MAX3420E SPI interface (SCLK max frequency)?
With V
of 2.5V or greater, the SCLK signal can be as high as 26MHz. For lower VL values, the
L
data sheet shows how much to derate the SCLK maximum frequency.
8. Is there a low limit to the MAX3420E SCLK frequency?
No. This clock can be held high or low indefinitely. Also, the MAX3420E ignores SCLK transitions
while SS# is high.
9. I have an 8-pin microprocessor, and it takes 5 of its' IO pins to connect to the
MAX3420E. How do I do IO?
The MAX3420E has four general-purpose outputs (GPOUT3-0) and four general-purpose input
pins (GPIN3-0) that are set and read using the IOPINS register, R20. This replaces the
microcontroller pins used to implement the SPI interface, and provides additional ones.
10. Do I need to add external pullup resistors to the GPIN pins?
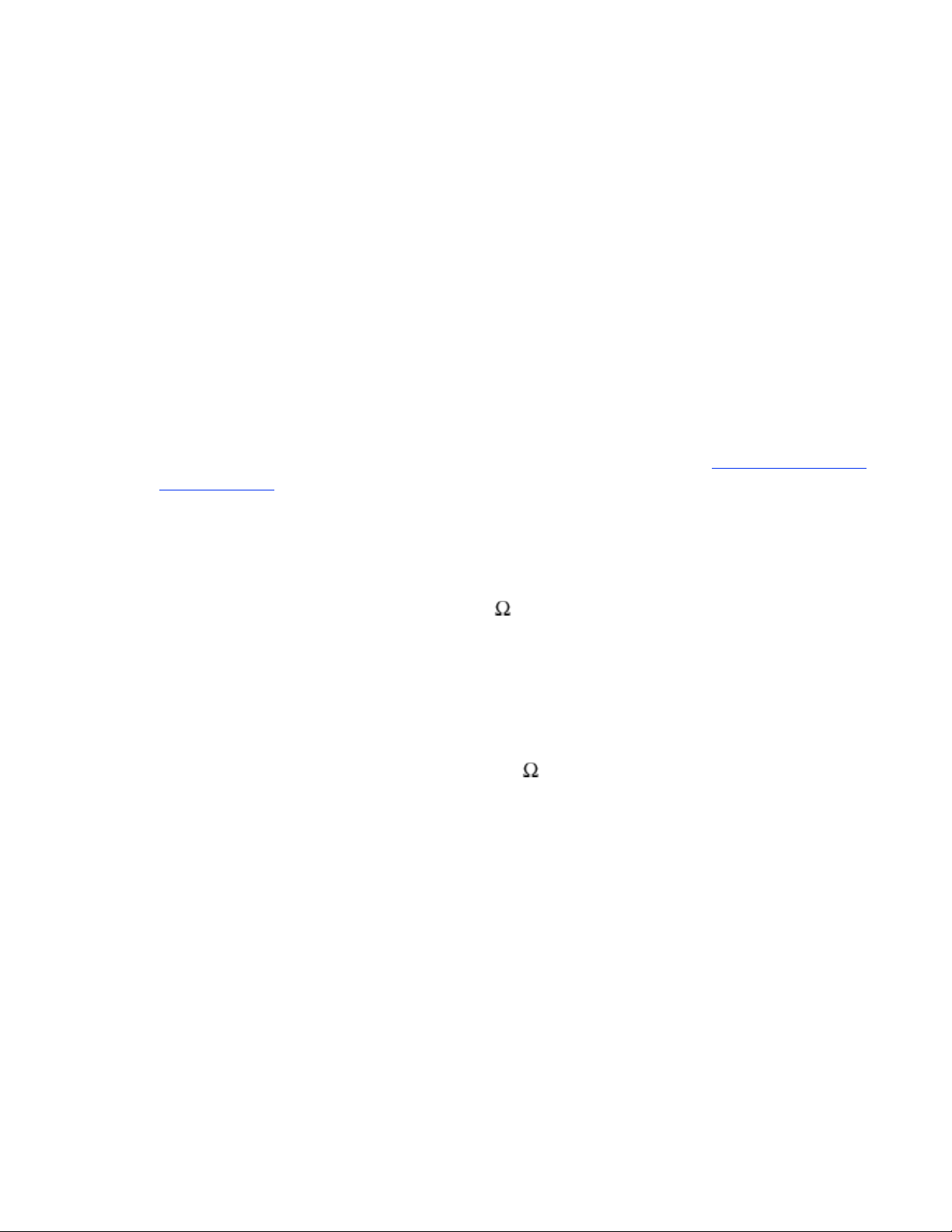
No. The GPIN pins are internally pulled up (typical value of 20k
) to VL.
11. Can I drive optocouplers from the SPI interface pins?
Yes. The MAX3420E outputs have enough drive current to drive optocoupler LEDs through series
resistors. Consult the data sheet for exact drive specs. The output buffers were designed with
opto-isolation in mind, since the MAX3420E SPI interface is uniquely suited to electrically
Page 5

isolating USB.
12. What is the purpose of the VBCOMP pin? Does it power the MAX3420E?
No. The VBCOMP pin does not power anything in the MAX3420E. It goes only to an internal
comparator to detect the presence of V
Programming Questions
4.
1. How does my firmware talk to the MAX3420E?
The MAX3420E has a set of 21 registers that are accessed by its slave SPI interface. The SPI
master first sends a command byte that sets the register address and direction, and then
transfers one or more data bytes.
2. How do I program the MAX3420E to handle USB enumeration?
As a peripheral, the MAX3420E device needs only to respond to requests from the host (usually a
PC).
3. How do I program a BULK IN transfer?
When you have data ready to send to the host, load an IN FIFO, then write the byte count
register for the particular endpoint. Since the IN FIFOs are 64 bytes in length, up to 64 bytes can
be loaded at a time. When finished loading the data, write the IN endpoint BYTECOUNT register
with the number of bytes loaded into the IN FIFO. Writing the byte count register "arms" the
endpoint for USB transfer. The MAX3420E does the rest. The next IN request to its device
address and the armed endpoint sends the FIFO data to the host.
4. What if a USB IN request comes in while firmware is loading the IN FIFO?
The MAX3420E takes care of this. It automatically answers an IN request to an "unarmed" IN
FIFO with a NAK (Negative Acknowledge) handshake. This handshake instructs the USB host that
the endpoint is busy, and that the host should try later with another IN request.
5. How do I know when to load an IN FIFO?
The MAX3420E provides interrupt request bits for the IN endpoints called IN3BAVIRQ,
IN2BAVIRQ, and IN0BAVIRQ, where "BAV" indicates "Buffer Available". The MAX3420E logic sets
an IN endpoint BAVIRQ bit after a device reset, or when IN FIFO data has been successfully
transferred and acknowledged by the host. At power-on, the BAVIRQ bits are set to indicate that
the IN FIFOS are initially available for loading. These are the only register bits that are set to 1
by a reset—all the rest are set to 0.
6. What if there is a USB transfer error? Do I need to write code to handle the error
condition?
No. The MAX3420E manages this for you. If the MAX3420E receives an error condition back from
the host, it automatically resends the same data when the host retries the IN transfer. The
MAX3420E also automatically handles other error checking such as data toggles. Some possible
USB errors (such as a user unplugging the cable in the middle of a data transfer) need to be
handled by firmware.
7. How do I program a BULK OUT transfer?
When the host sends OUT data, the MAX3420E stores the bytes in an OUT endpoint FIFO. After
the transfer is complete and verified to be error-free, the MAX3420E asserts a "DAV" (Data
Available) interrupt request bit for the particular endpoint. This alerts the SPI controller to read
the FIFO bytes. The SPI controller first reads an OUT FIFO byte-count register to determine how
many bytes in the 64 byte FIFO are valid. It then reads that number of bytes by repeated reads
to the OUTFIFO register. Finally, the SPI controller clears the OUT DAV IRQ bit (by writing 1 to it)
to "rearm" the endpoint for another OUT transfer.
8. How about INTERRUPT transfers?
Interrupt transfers are programmed identically to BULK transfers. They differ only in how they
are described in the device descriptors sent back to the host during enumeration.
BUS
.
Page 6

9. How do I program a SETUP transfer?
The USB host uses a CONTROL transfer to send a SETUP packet to the MAX3420E along with
eight bytes that serve as a USB "op-code". The MAX3420E stores these bytes in an 8-byte FIFO,
and then asserts a Setup Data Available interrupt request. The SPI master responds by reading
the eight SETUP bytes at register address R4 (SUDFIFO), interpreting the USB request from
these bytes, and taking the appropriate action. When finished servicing the request, the USPI
master sets a bit called ACKSTAT (ACK from acknowledge, STAT from STATUS stage) to tell the
MAX3420E to acknowledge the status stage of the CONTROL transfer.
10. Do I need to program the USB data toggles?
No. The MAX3420E handles these toggles automatically during USB transfers. The only time
firmware might need to intervene is when the host sets a new configuration in a
multiconfiguration design (these are rare). The MAX3420E has register bits to clear the endpoint
toggles for this purpose.
11. The MAX3420E interrupt request bits are cleared by writing "1" to them. Is this
backwards?
It may seem backwards at first, but it is the most efficient way to clear a register bit. To service
a typical interrupt request, the SPI master reads an interrupt request register (either USBIRQ or
EPIRQ), and checks using various bit masks to determine the source of the interrupt. For
example, to test for the SUDAVIRQ interrupt request, firmware would read R11 (EPIRQ) and AND
the result with 00100000 (the SUDAVIRQ bit is in the bit 5 position). Typically a program will
equate a label like bmSUDAV with 0010000. Once the IRQ bit is detected to be a 1, the firmware
can simply write the mask value back to the register (SUDAVIRQ = bmSUDAV) and only the
desired bit is cleared. IRQ bits written with a zero are unchanged.
12. Do you have any programming tips?
When using the SPI full-duplex mode, the very first register access should set the FDUPSPI bit to
1 in order to correctly set up the interface for subsequent accesses.
5.
Host Software Questions
1. How does my Windows® application talk to the MAX3420E?
A Windows® application talks to the PC's USB host controller through a driver. The driver may
be built into Windows or it may be custom. Windows includes built-in drivers for standard device
classes, such as Human Interface Devices (HID) and Mass Storage Devices. If your firmware
supports one of these standard classes, your customer does not need to load a custom driver.
If you are designing a device that does not conform to one of the built-in Windows standard
device classes, the end user must install a custom driver when your USB device is plugged in the
first time.
2. Does Maxim supply a custom Windows driver?
No.
3. What example code does Maxim supply?
You can find example C code for implementing a HID application on the Maxim website at
Enumeration Code (and More) for the MAX3420E. This example code emulates a PC keyboard,
which types a text string into any Windows application that accepts text (e.g., Notepad)
whenever a pushbutton is pressed. By conforming to the standard HID class, the application runs
without a custom Windows driver. Regardless of your target application, most of this example
code is USB 'boilerplate' that can be used as a starting point for your code.
USB
4. I want to design a MAX3420E-based device that does not conform to a standard
Windows class. What do I use for a Windows driver?
There are two alternatives:
■ Write the Windows driver yourself. This is complex and difficult, recommended for
specialists only.
Page 7

■ Purchase a general-purpose driver. These typically consist of the USB driver and a
companion library of C functions to access the driver. Drivers are matched to the VID
(Vendor ID) and PID (Product ID) in your device descriptor.
Microsoft has announced a general-purpose BULK driver for USB in the upcoming "Vista" version
of Windows.
5. How does the MAX3420E compare with USB 'serial bridge' chips?
USB serial bridge chips connect to a PC using its USB port, but appear as a virtual COM port to
the application running on the PC . A custom driver, supplied by the chip vendor, is required to
do this COM-USB transformation. A Windows application that talks to a serial (COM) port (e.g.,
HyperTerminal) can be used to talk to an USB-connected device using this method.
The advantage of this approach is that no enumeration firmware or host driver is required. The
disadvantages are in performance, flexibility, and support:
■ Performance: Because the bridge approach emulates a serial port, the maximum
achievable bandwidth is about 1 Megabit per second, well below the USB signaling rate of
12 Megabits per second.
■ Flexibility: The serial-USB bridge chips are hard-wired to emulate serial-port devices.
They are not capable of implementing standard Windows class devices (like HID) or
custom device types.
■ Support: A product you design using one of these chips will require the companion driver
to be installed by your customer. Because it is a custom driver, it is not guaranteed to
work with future versions of the operating system. If you choose this approach, try to
make sure that the vendor is committed to supporting the driver for the lifetime of your
product.
6. What are the advantages and disadvantages of the MAX3420E approach?
The disadvantages are that firmware is required for the MAX3420E controller and that Maxim
does not supply a custom Windows driver. Instead, Maxim supplies example firmware to
illustrate how to conform to a standard Windows device class (HID), and thereby to use a built-in
Windows driver.
The advantages to the MAX3420E approach are performance, flexibility and support.
■ Performance: The MAX3420E SPI port (its interface to the controller) can run up to
26MHz. If the controller supports a high SPI clock rate, the MAX3420E can support USB
transfers up to the maximum available full-speed bandwidth of 12Mbps.
■ Flexibility: The personality of a device using the MAX3420E is entirely determined by its
firmware. Therefore, it can implement any type of USB device.
■ Support: Once operating systems natively support general USB (BULK) transfers, the
need for serial-USB bridge chips will rapidly diminish.
6.
Miscellaneous Questions
1. Can my firmware determine which chip revision I have?
Yes. The read-only register R18 contains the revision number.
2. What is the current revision level of the MAX3420E?
Refer to the
MAX3420E QV for the latest data sheet and errata.
Application Note 3597: http://www.maxim-ic.com/an3597
Page 8

More Information
For technical questions and support:
For samples: http://www.maxim-ic.com/samples
Other questions and comments: http://www.maxim-ic.com/contact
Related Parts
MAX3420E:
QuickView -- Full (PDF) Data Sheet -- Free Samples
http://www.maxim-ic.com/support
AN3597, AN 3597, APP3597, Appnote3597, Appnote 3597
Copyright © by Maxim Integrated Products
Additional legal notices:
http://www.maxim-ic.com/legal
 Loading...
Loading...