Page 1
General Description
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 are programmable
RS-232/RS-485/422 multiprotocol transceivers. The
MAX3160/MAX3161 are pin programmable as a 2TX/2RX
RS-232 interface or a single RS-485/422 transceiver. The
MAX3162 is configured as a 2TX/2RX RS-232 interface
and a single RS-485/422 transceiver simultaneously.
All devices incorporate a proprietary low-dropout transmitter output stage and an on-board dual charge pump
to allow RS-232 and RS-485/422 compliant performance from a +3V to +5.5V supply. The receivers
feature true fail-safe circuitry that guarantees a logichigh receiver output when the receiver inputs are open
or shorted. These devices also feature pin-selectable
transmitter slew rates for both RS-232 and RS-485/422
modes. Slew-rate limiting minimizes EMI and reduces
reflections caused by improperly terminated cables,
allowing error-free data transmission up to 250kbps.
Disabling slew-rate limiting allows these devices to
transmit at data rates up to 10Mbps in RS-485/422
mode and up to 1Mbps in RS-232 mode. The
MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 feature a 1µA shutdown
mode, and short-circuit limiting and thermal shutdown
circuitry to protect against excessive power dissipation.
The MAX3160/MAX3162 offer a flow-through pinout that
facilitates board layout. The MAX3160/MAX3161/
MAX3162 are available in tiny SSOP packages and
operate over the commercial and extended temperature ranges.
________________________Applications
Point-of-Sales Equipment Peripherals
Industrial Controls Networking
RS-232 to RS-485
Interface Converters
Features
♦ Single-Supply Operation from +3V to +5.5V
♦ Pin-Programmable as 2TX/2RX RS-232 or Single
RS-485/422 (MAX3160/MAX3161)
♦ 2TX/2RX RS-232 and Single RS-485/422
(MAX3162)
♦ Pin-Programmable RS-232/RS-485 Transmitter
Slew Rates Reduce EMI
♦ 10Mbps RS-485 and 1Mbps RS-232 Data Rates
♦ Pin-Programmable Half-Duplex or Full-Duplex
RS-485/422 Operation (MAX3160/MAX3161)
♦ RS-485/422 True Fail-Safe Receivers
♦ Transmitters and Receivers Protected Against
Wiring Faults
♦ 1µA Shutdown Supply Current
♦ 1/8-Unit Load Allows up to 256 Transceivers on
the Bus
MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
________________________________________________________________
Maxim Integrated Products
1
19-1722; Rev 2; 12/09
EVALUATION KIT
AVAILABLE
Ordering Information
Typical Operating Circuit
Pin Configurations appear at end of data sheet.
Selector Guide appears at end of data sheet.
For price, delivery, and to place orders, please contact Maxim Distribution at 1-888-629-4642,
or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
+
Denotes a lead(Pb)-free/RoHS-compliant package.
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
MAX3160CAP+ 0°C to +70°C 20 SSOP
MAX3160EAP+ -40°C to +85°C 20 SSOP
MAX3161CAG+ 0°C to +70°C 24 SSOP
MAX3161EAG+ -40°C to +85°C 24 SSOP
MAX3162CAI+ 0°C to +70°C 28 SSOP
MAX3162EAI+ -40°C to +85°C 28 SSOP
+3V TO +5.5V
MAX3100
SPI
μP
13
11
12
10
TX
RTS
RX
CTS
SHDN
DI/T1IN
DE/T2IN
RO/R2OUT
R1OUT
16
15
8
7
1
V
CC
RS485/RS232
MAX3160
GND FAST HDPLX SHDN
4
12
11
5
13
14
910
Z(B)/T1OUT
Y(A)/T2OUT
6
A/R2IN
B/R1IN
DB9
RJ45
Page 2
MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VCC= +3V to +5.5V, C1–C4 = 0.1µF when tested at +3.3V ±10%; C1 = 0.047µF and C2, C3, C4 = 0.33µF when tested at +5V
±10%; T
A
= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Note 1: V+ and V- can have maximum magnitudes of 7V, but their absolute difference cannot exceed 13V.
VCCto GND..............................................................-0.3V to +6V
V+ to GND ................................................................-0.3V to +7V
V- to GND....................................................................0.3V to -7V
V+ - V- (Note 1)....................................................................+13V
Input Voltages
T1IN, T2IN, DI, DE485, RE485, TE232, RE232, SHDN,
FAST, HDPLX, RS485/RS232 to GND. ...............-0.3V to +6V
A, B, R1IN, R2IN to GND ...............................................±25V
Output Voltages
T1OUT, T2OUT, Y, Z to GND......................................±13.2V
R2OUT, R1OUT, RO to GND................-0.3V to (V
CC
+ 0.3V)
Output Short-Circuit Duration
T1OUT, T2OUT, Y, Z ............................................Continuous
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +70°C)
20-Pin SSOP (derate 11.9W/°C above +70°C) ..........952mW
24-Pin SSOP (derate 14.9W/°C above +70°C) ........1195mW
28-Pin SSOP (derate 15W/°C above +70°C) ...........1201mW
Operating Temperature Ranges
MAX316_CA_....................................................0°C to +70°C
MAX316_EA_ .................................................-40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature......................................................+150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C
DC CHARACTERISTICS
VCC Standby Current I
VCC Shutdown Current I
TRANSMITTER AND LOGIC INPUTS (DI, T1IN, T2IN, DE485, RRRREEEE444488885555, TE232, RRRREEEE222233332222, FAST, HDPLX, SHDN, RS485/RRRRSSSS222233332222)
Logic Input Low V
Logic Input High V
Logic Input Leakage Current I
Transmitter Logic Hysteresis V
RS-232 AND RS-485/422 RECEIVER OUTPUTS (R1OUT, R2OUT, RO)
Receiver Output Voltage Low V
Receiver Output Voltage High V
Receiver Output Short Circuit
Current
Receiver Output Leakage
Current
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
MAX3160/MAX3161, no load,
RS485/ RS232 = GND
CC
CC
INL
HYS
I
OSR
I
OZR
OL
OH
MAX3160/MAX3161, no load,
RS485/ RS232 = V
MAX3162 No Load 3.0 6
SHDN = GND, receiver inputs open or
grounded
IL
VCC = +3.3V 2.0
IH
VCC = +5V 2.4
I
= 2.5mA 0.4 V
OUT
I
= -1.5mA V
OUT
0 < VO < V
Receivers disabled ±0.05 ±1µA
CC
CC
1.2 2.5
2.5 5.5
110µA
0.8 V
±0.01 ±1µA
0.5 V
- 0.6 V
CC
±20 ±60 mA
mA
V
Page 3
MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VCC= +3V to +5.5V, C1–C4 = 0.1µF when tested at +3.3V ±10%; C1 = 0.047µF and C2, C3, C4 = 0.33µF when tested at +5V
±10%; T
A
= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
RS-232 RECEIVER INPUTS (R1IN, R2IN)
Input Voltage Range -25 25 V
Input Threshold Low
Input Threshold High
Input Hysteresis 0.5 V
Input Resistance 357kΩ
RS-485/422 RECEIVER INPUTS (NOTE 2)
Input Resistance R
Input Current I
Input Differential Threshold V
Input Hysteresis ΔV
RS-232 TRANSMITTER OUTPUTS (T1OUT, T2OUT)
Output Voltage Swing
Output Resistance V
Output Short-Circuit Current T_OUT = GND ±30 ±60 mA
Output Leakage Current
RS-485/422 TRANSMITTER OUTPUTS (Y, Z)
Differential Output Voltage V
Change in Magnitude of
Differential Output Voltage for
Complementary Output States
Common Mode Output Voltage V
Change in Magnitude of
Common Mode Output Voltage
for Complementary Output
States
VCC = +3.3V 0.6
V
= +5V 0.8
CC
V
=+3.3V 2.0
CC
V
= +5V 2.4
CC
-7V < VCM < +12V
IN
MAX3160
IN
MAX3161/MAX3162
TH
TH
Both transmitter outputs loaded with 3kΩ
to GND
= V + = V - = 0V , V
ΔV
Δ V
OD
OD
OC
C C
V
= ±12V
OUT
TE232 = GND or SHDN =
GND
Figure 1
R = 27Ω or 50Ω, Figure 1 -0.2 0.2 V
R = 27Ω or 50Ω, Figure 1 3 V
R = 27Ω or 50Ω, Figure 1 0.2 V
OC
T 1OU T
MAX3160 48
MAX3161/
MAX3162
VCM = +12V 0.25
= -7V -0.15
V
CM
VCM = +12V 0.125
= -7V -0.075
V
CM
= V
= + 2V 300 10M Ω
T 2OU T
MAX3160/
MAX3161
MAX3162 ±25
R = 27Ω
(RS-485)
R = 50Ω
(RS-422)
96
-200 -50 mV
30 mV
±5 ±5.4 V
1.5
2
±125
V
V
kΩ
mA
µA
V
Page 4
MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VCC= +3V to +5.5V, C1–C4 = 0.1µF when tested at +3.3V ±10%; C1 = 0.047µF and C2, C3, C4 = 0.33µF when tested at +5V
±10%; T
A
= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
Output Short-Circuit Current I
Output Leakage Current
RS-232 TIMING CHARACTERISTICS (FAST = GND, 250kbps, ONE TRANSMITTER SWITCHING)
Maximum Data Rate RL = 3kΩ, CL = 1000pF 250 kbps
Receiver Propagation Delay R_IN to R_OUT, CL = 150pF 0.15 µs
Receiver Output Enable Time 200 ns
Receiver Output Disable Time 200 ns
Transmitter Skew |t
Receiver Skew |t
Transition-Region Slew Rate
RS-232 TIMING CHARACTERISTICS (FAST = VCC, 1Mbps, ONE TRANSMITTER SWITCHING)
Maximum Data Rate
Receiver Propagation Delay R_IN to R_OUT, CL = 150pF 0.15 µs
Receiver Output Enable Time 200 ns
Receiver Output Disable Time 200 ns
Transmitter Skew |t
Receiver Skew |t
Transition-Region Slew Rate
RS-485/422 TIMING CHARACTERISTICS (FAST = GND) 250kbps
Driver Propagation Delay
Driver Rise and Fall Time
Driver Propagation Delay Skew t
Driver Output Enable Time t
Driver Output Disable Time t
Receiver Propagation Delay
Receiver Propagation Delay
Skew
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
SC
I
O
VY or VZ = +12V to –7V ±250 mA
VY or VZ = +12V,
DE485 = GND or SHDN =
GND
- t
PHL
PLH
V
CC
=3kΩ to 7kΩ, measured
R
L
| 100 ns
PLH
- t
|50ns
PHL
= +3.3V, TA = +25°C,
from +3.0V or –3.0V to
+3.0V
MAX3160/
MAX3161
±125
MAX3162 ±25
CL = 150pF
to 1000pF
= 150pF
C
L
to 2500pF
630
430
VCC = +3V to +4.5V, RL = 3kΩ, CL = 250pF 1
= +4.5V to +5.5V, RL = 3kΩ,
V
CC
= 1000pF
C
L
- t
PHL
PLH
V
CC
= 150pF to 1000pF, measured from
C
L
|25ns
PLH
- t
|50ns
PHL
= +3.3V, TA = +25°C, RL =3kΩ to 7kΩ,
1
24 150 V/μs
+3.0V or –3.0V to +3.0V
t
,
DPHL
t
DPLH
t
DPHL
t
DPLH
DSKEW
DZH
DLZ
t
RPLH,
t
RPHL
t
RSKEW
, t
, t
R
= 54Ω, CL = 50pF, Figures 3, 5 200 400 800 ns
DIFF
,
R
= 54Ω, CL = 50pF, Figures 3, 5 200 400 800 ns
DIFF
R
= 54Ω, CL = 50pF, Figure 3, 5 200 ns
DIFF
RZLRDIFF
DHZRDIFF
= 54Ω, CL = 50pF, Figures 4, 6 400 800 ns
= 54Ω, CL = 50pF, Figure 4, 6 200 400 ns
CL = 15pF, Figures 7, 9 25 80 150 ns
CL = 50pF, Figures 7, 9 10 ns
µA
V/µs
Mbps
Page 5
MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VCC= +3V to +5.5V, C1–C4 = 0.1µF when tested at +3.3V ±10%; C1 = 0.047µF and C2, C3, C4 = 0.33µF when tested at +5V
±10%; T
A
= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
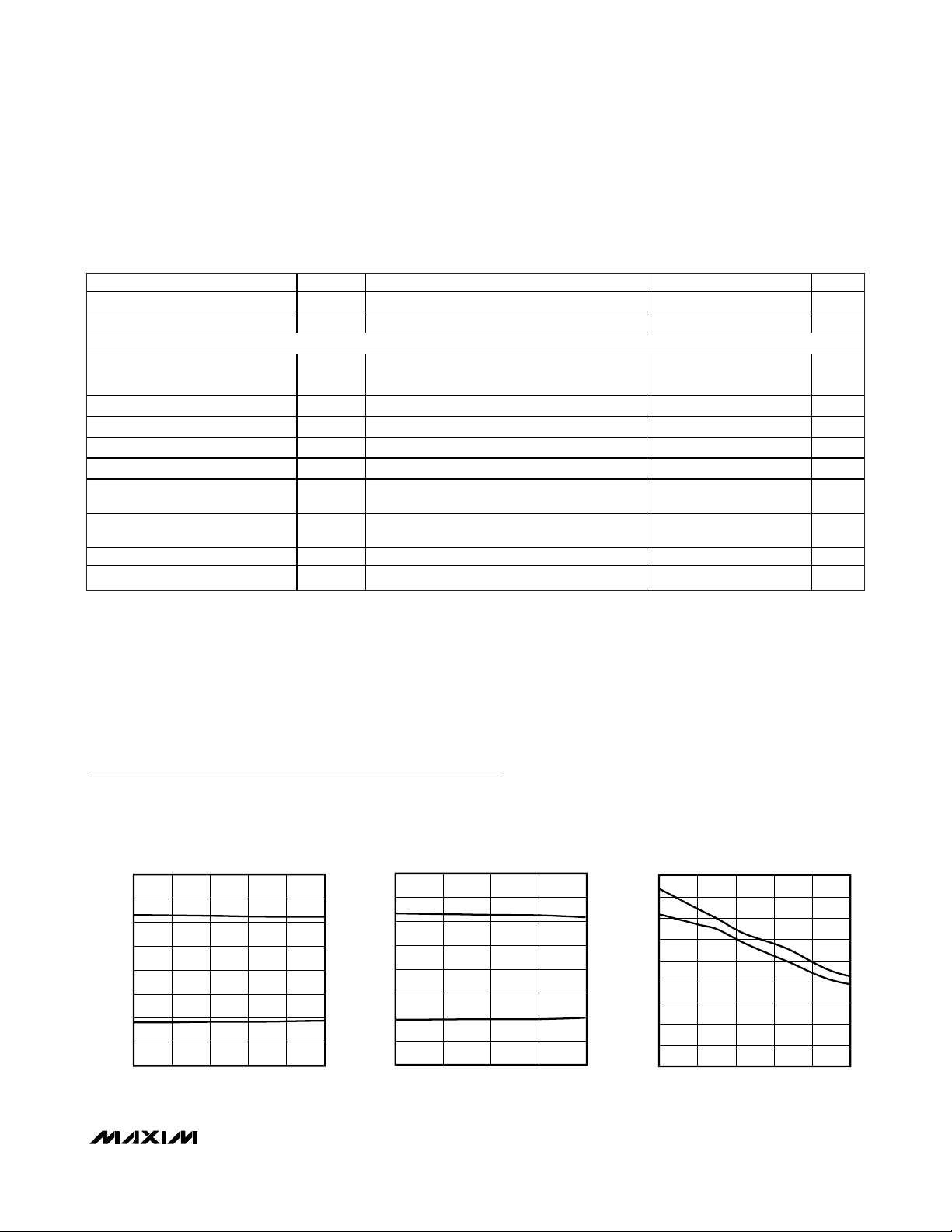
Typical Operating Characteristics
(VCC= +3.3V, 250kbps data rate, 0.1µF capacitors, all RS-232 transmitters (RS-232 mode) loaded with 3kΩ to ground, TA= +25°C,
unless otherwise noted.)
-10.0
-7.5
-5.0
-2.5
0
2.5
5.0
7.5
10.0
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000
RS-232 TRANSMITTER OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs.
LOAD CAPACITANCE (FAST = GND)
MAX3160/2 TOC1
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
TRANSMITTER OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
-10.0
-7.5
-5.0
-2.5
0
2.5
5.0
7.5
10.0
0 500 1000 1500 2000
RS-232 TRANSMITTER OUTPUT VOLTAGE
vs. LOAD CAPACITANCE (FAST =
VCC)
MAX3160/2 TOC2
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
TRANSMITTER OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0
4
2
10
8
6
16
14
12
18
0 20001000 3000 4000 5000
RS-232 TRANSMITTER SLEW RATE vs.
LOAD CAPACITANCE (FAST = GND)
MAX3160/2 TOC3
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
SLEW RATE (V/μs)
Note 2: Applies to A, B for MAX3162 and MAX3160/MAX3161 with HDPLX = GND, or Y, Z for MAX3160/MAX3161 with HDPLX = V
CC.
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Receiver Output Enable Time t
Receiver Output Disable Time t
RZL
RLZ
, t
RZHCL
, t
RHZCL
= 50pF, Figures 2, 8 100 ns
= 50pF, Figures 2, 8 100 ns
RS-485/RS-422 TIMING CHARACTERISTICS (FAST = VCC, 10Mbps)
t
Driver Propagation Delay
Driver Rise And Fall Times tDR, t
Driver Propagation Delay Skew t
Driver Output Enable Time
Driver Output Disable Time t
Receiver Propagation Delay
Receiver Propagation Delay
Skew
Receiver Output Enable Time t
Receiver Output Disable Time t
DPHL,
t
DPLH
DSKEW
t
DLZ
t
RPLH
t
RPHL
t
RSKEW
RZL
RLZ
DZL
, t
, t
, t
R
= 54Ω, CL = 50pF, Figures 3, 5 60 120 ns
DIFF
DFRDIFF
DHZRDIFF
,
= 54Ω, CL = 50pF, Figures 3, 5 10 25 ns
R
= 54Ω, CL = 50pF, Figures 3, 5 10 ns
DIFF
R
= 54Ω, CL = 50pF, Figures 4, 6 400 800 ns
DIFF
= 54Ω, CL = 50pF, Figures 4, 6 200 400 ns
CL = 15pF, Figures 7, 9 80 150 ns
CL = 50pF, Figures 7, 9 10 ns
RZHCL
RHZ
= 50pF, Figures 2, 8 100 ns
CL = 15pF, Figures 2, 8 100 ns
Page 6
MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
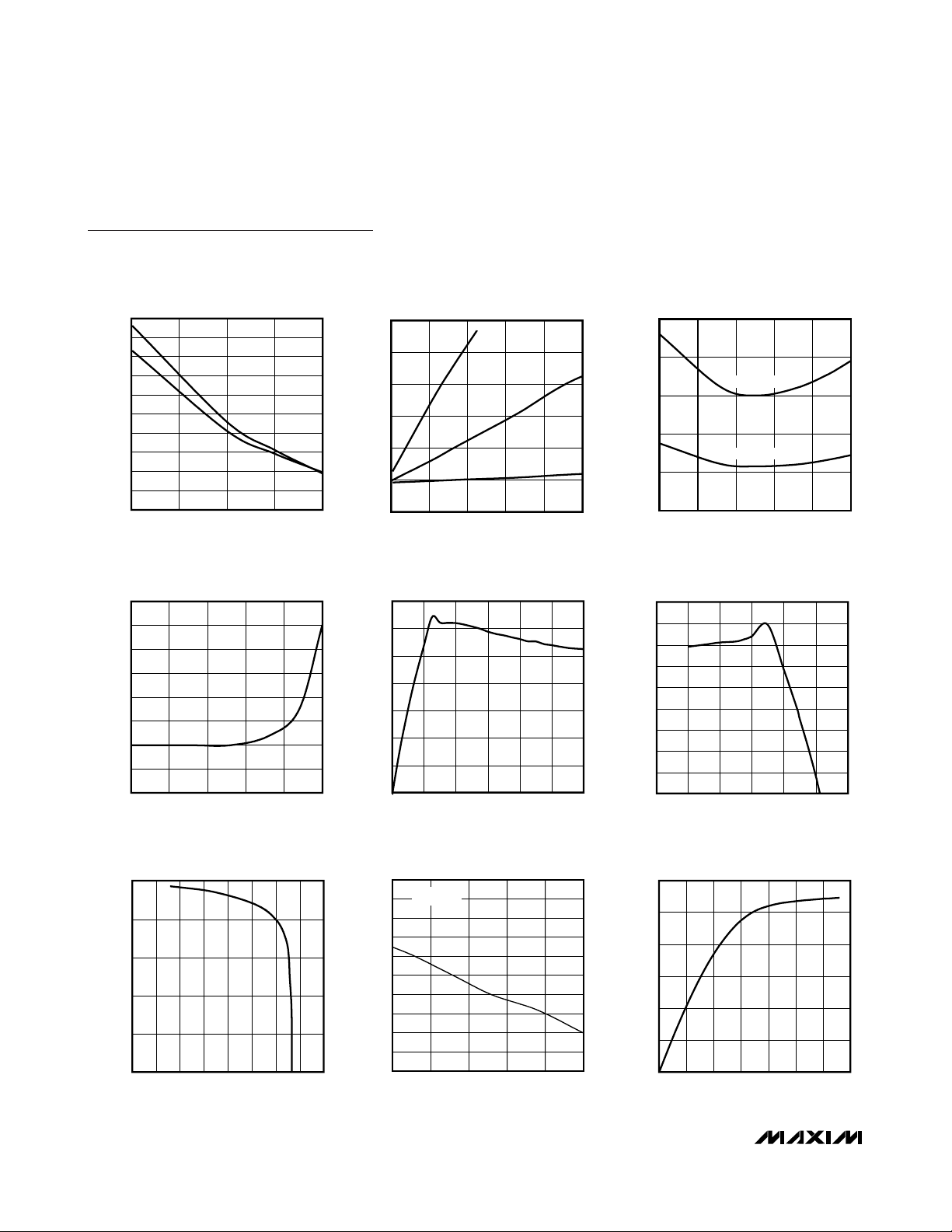
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(VCC= +3.3V, 250kbps data rate, 0.1µF capacitors, all RS-232 transmitters (RS-232 mode) loaded with 3kΩ to ground, TA= +25°C,
unless otherwise noted.)
0
30
20
10
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0 500 1000 1500 2000
RS-232 TRANSMITTER SLEW RATE
vs. LOAD CAPACITANCE (FAST = V
CC
)
MAX3160/2 TOC4
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
SLEW RATE (V/μs)
0
20
10
40
30
50
60
0 20001000 3000 4000 5000
OPERATING SUPPLY CURRENT vs.
LOAD CAPACITANCE WHEN
TRANSMITTING DATA (RS-232 MODE)
MAX3160/2 TOC5
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
1Mbps
250kbps
20kbps
0
1.0
2.0
1.5
2.5
3.0
-40 10-15 35 60 85
MAX3160/MAX3161
NO-LOAD SUPPLY CURRENT vs.
TEMPERATURE
MAX3160/2 TOC6
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
RS-485 MODE
RS-232 MODE
SHUTDOWN CURRENT vs. TEMPERATURE
160
140
120
100
80
60
SHUTDOWN CURRENT (nA)
40
20
0
-40 -15 10 35 60 85
TEMPERATURE (°C)
140
120
MAX3160/2 TOC7
100
80
60
OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
40
20
RS-485/422 DRIVER OUTPUT CURRENT vs.
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
100
10
1
0.1
OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
0.01
0.001
0 1.0 1.50.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
3.5
3.4
3.3
MAX3160/2 TOC10
3.2
3.1
3.0
2.9
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
2.8
2.7
2.6
2.5
DRIVER OUTPUT VOLTAGE
0
0462 8 10 12
OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE (V)
RS-485/422 DRIVER DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT
vs. TEMPERATURE
R = 50Ω
-40 10-15 35 60 85
TEMPERATURE (°C)
RS-485/422 OUTPUT CURRENT vs.
180
160
MAX3160/2 TOC8
140
120
100
OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
MAX3160/2 TOC11
OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
RS-485/422 OUTPUT CURRENT vs.
DRIVER OUTPUT HIGH VOLTAGE
80
60
40
20
0
-7 -3-5 -1 1 3 5
OUTPUT HIGH VOLTAGE (V)
OUTPUT CURRENT vs. RECEIVER
OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0 1.5 2.00.5 1.0 2.5 3.0 3.5
OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE (V)
MAX3160/2 TOC9
MAX3160/2 TOC12
Page 7
MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
0
40
20
80
60
100
120
-40 10-15 35 60 85
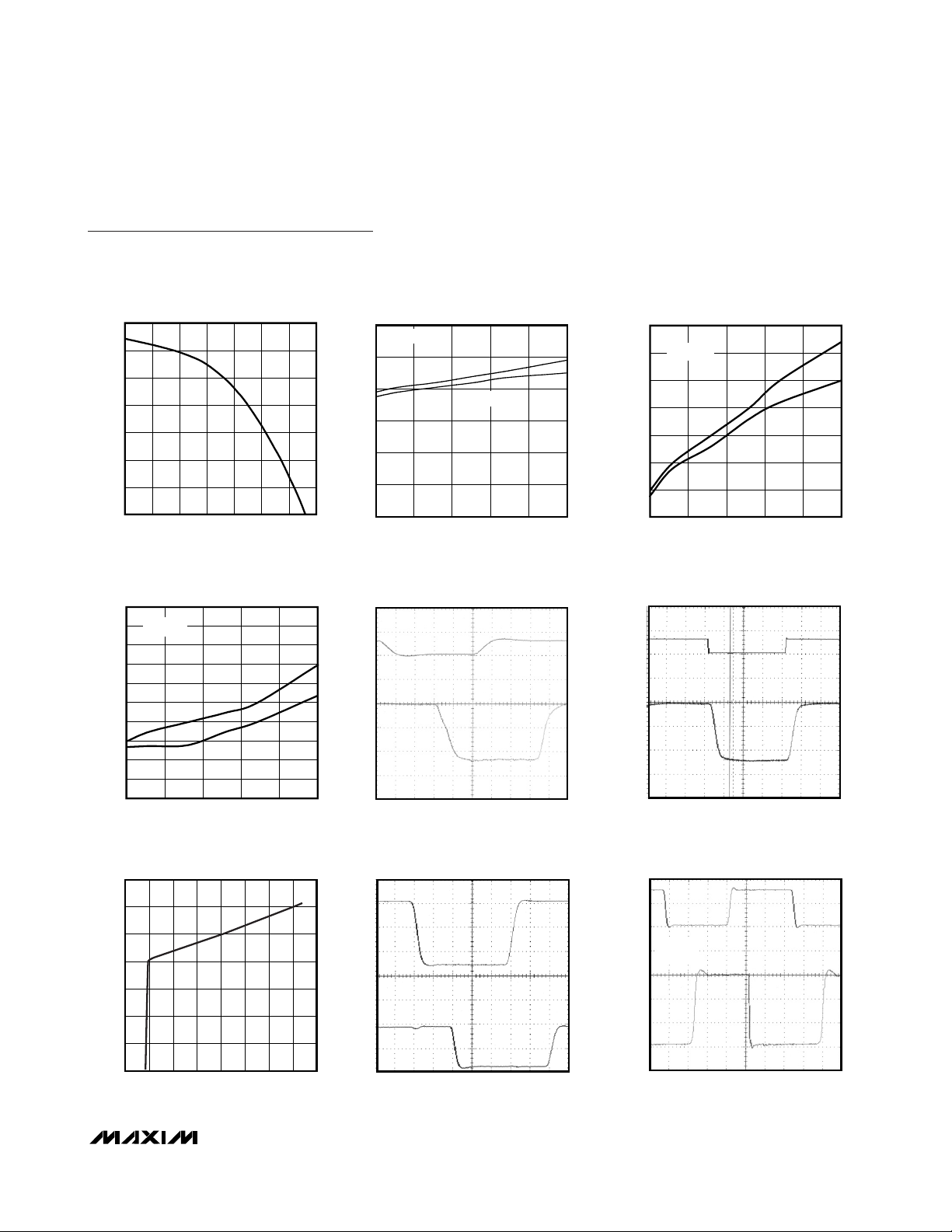
RS-485/422 RECEIVER PROPAGATION DELAY
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX3160/2 TOC16
TEMPERATURE (°C)
PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
CL = 50pF
RISING
FALLING
50
60
55
70
65
80
75
85
-40 10-15 35 60 85
RS-485/422 DRIVER PROPAGATION DELAY
vs.TEMPERATURE (FAST)
MAX3160/2 TOC18
TEMPERATURE (°C)
R = 50
Ω
TIME (ns)
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
_______________________________________________________________________________________
7
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(VCC= +3.3V, 250kbps data rate, 0.1µF capacitors, all RS-232 transmitters (RS-232 mode) loaded with 3kΩ to ground, TA= +25°C,
unless otherwise noted.)
-1000
-800
-400
-600
0
200
-200
400
-20 -10 -5-15 0 5 10 15 20
I-V OUTPUT IMPEDANCE CURVE
IN RS-232 SHUTDOWN MODE
MAX3160-A
VOLTS (V)
CURRENT (μA)
OUTPUT CURRENT vs. RECEIVER
14
12
10
8
6
OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
4
2
0
500
480
460
440
420
400
TIME (ns)
380
360
340
320
300
OUTPUT HIGH VOLTAGE
0 1.0 1.50.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5
OUTPUT HIGH VOLTAGE (V)
RS-485/422 DRIVER PROPAGATION DELAY
vs. TEMPERATURE (SLOW)
R = 50Ω
-40 10-15 35 60 85
TEMPERATURE (°C)
MAX3160/2 TOC13
MAX3160/2 TOC19
RS-485/422
RS-485/422
DRIVER PROPAGATION
(FAST, 10Mbps)
20ns/div
MAX3160/2 TOC20
RECEIVER PROPAGATION
(FAST, 5Mbps)
MAX3160/2 TOC22
DI
5V/div
V
Y-VZ
2V/div
RS-485/422 DRIVER PROPAGATION
(SLOW, 250kbps)
RS-485/422
TO DRIVER OUTPUT
1.0μs/div
DRIVER DISABLE/ENABLE
MAX3160/2 TOC21
MAX3160/2 TOC24
DI
5V/div
VY-V
Z
2V/div
C
L
= 50pF
40ns/div
VY-V
2V/div
RO
2V/div
Z
R = 50Ω
= 82pF
C
L
100ns/div
DE485
2V/div
- V
V
Y
2V/div
Z
Page 8

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Pin Description
PIN
MAX3160 MAX3161 MAX3162
1 1 1 C1+ Positive Terminal of the Positive Flying Capacitor
222V
3 3 3 C1- Negative Terminal of the Positive Flying Capacitor
4 4 4 GND Ground
— 5 5 T1OUT RS-232 Driver Output
5 — — Z(B)/T1OUT
— — 6 Z Inverting RS-485/422 Driver Output
— 6 — Z(B)
6 — — Y(A)/T2OUT
— — 7 Y Noninverting RS-485/422 Driver Output
— 7 — Y(A)
7 9 9 R1OUT RS-232 Receiver Output
— 8 8 T2OUT RS-232 Driver Output
8 10 — RO/R2OUT RS-485/422 Receiver Output/RS-232 Receiver Output
91113SHDN
— — 10 R2OUT RS-232 Driver Output
10 12 14 FAST
— — 11 RO RS-485/422 Receiver Output
11 13 — RS485/RS232
NAME FUNCTION
CC
Positive Supply Voltage
Inverting RS-485/422 Driver Output in Full-Duplex Mode
(and Inverting RS-485/422 Receiver Input in Half-Duplex
Mode)/RS-232 Driver Output
Inverting RS-485/422 Driver Output in Full-Duplex Mode
(and Inverting RS-485/422 Receiver Input in Half-Duplex
Mode)
Noninverting RS-485/422 Driver Output in Full-Duplex
Mode (and Noninverting RS-485/422 Receiver Input in
Half-Duplex Mode)/RS-232 Driver Output
Noninverting RS-485/422 Driver Output in Full-Duplex
Mode (and Noninverting RS-485/422 Receiver Input in
Half-Duplex Mode)
Active-Low Shutdown-Control Input. Drive low to shut
down transmitters and charge pump.
Select slew rate limiting for both RS-232 and RS485/422. Slew rate limits with a logic-level low.
Software-Programmable Pin Functionality. Operates as
RS-485/422 with a logic-level high; operates as RS-232
with a logic-level low.
——12RE485
12 14 — HDPLX
RS-485/422 Receiver Enable. Logic-level low enables
RS-485/422 receivers.
Software-Programmable Pin Functionality. Operates in
full-duplex mode when low; operates in half-duplex
mode when high.
Page 9

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
Pin Description (continued)
PIN
MAX3160 MAX3161 MAX3162
13 — — A/R2IN
14 — — B/R1IN
——15RE232
— 15 17 A Noninverting RS-485/422 Receiver Input
15 19 — DE485/T2IN RS-485/RS-422 Driver Enable/RS-232 Driver Input
— — 16 TE232 RS-232 Transmitter Output Enable
— 16 18 B Inverting RS-485/422 Receiver Input
16 20 — DI/T1IN RS-485/RS-422 Driver Input/RS-232 Driver Input
— 17 19 R2IN RS-232 Receiver Input
17 21 25 V- Negative Charge-Pump Rail
— 18 20 R1IN RS-232 Receiver Input
18 22 26 C2- Negative Terminal of the Negative Flying Capacitor
19 23 27 C2+ Positive Terminal of the Negative Flying Capacitor
20 24 28 V+ Positive Charge-Pump Rail
— — 21 T2IN RS-232 Driver Input
— — 22 DE485 RS-485/RS-422 Driver Enable
— — 23 DI RS-485/RS-422 Driver Input
— — 24 T1IN RS-232 Driver Input
NAME FUNCTION
Noninverting RS-485/422 Receiver Input/RS-232
Receiver Input
Inverting RS-485/422 Receiver Input/RS-232 Receiver
Input
RS-232 Receiver Enable. Logic-level low enables RS232 receivers.
Page 10

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Functional Diagrams
MAX3160
V
CC
C1
C
BYPASS
RS-232
OUTPUTS
LOGIC
OUTPUTS
RS-232 MODE
C1+
1
V
CC
2
C1-
3
GND
4
5
6
7
8
SHDN
FAST RS485/RS232
CHARGE
PUMP
T1
T2
R1
R2
C2+
C2-
HDPLX
V+
20
C3
19
C2
18
V-
17
C4
16
LOGIC
INPUTS
15
14
RS-232
INPUTS
13
129
1110
V
CC
C1
RS-485
OUTPUTS
OUTPUT
C
BYPASS
LOGIC
RS-485 MODE
C2+
C2-
D
DE
B
A
RS485/RS232
V+
20
19
18
V-
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
C3
C4
LOGIC
INPUTS
RS-485
INPUTS
HALF/FULL
DUPLEX
C2
C1+
1
V
CC
2
C1-
3
GND
4
5
6
7
R0
8
SHDN
9
10
FAST
CHARGE
PUMP
Z
Y
R
Page 11

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 11
Functional Diagrams (continued)
C1
C
BYPASS
C3
C2
C4
24
23
22
21
20
19
16
15
1
2
3
4
RS-485
OUTPUTS
LOGIC
INPUTS
LOGIC
OUTPUT
RS-485
INPUTS
SHDN
FAST RS485/RS232
5
6
9
10
18
17
7
8
V+
C2+
C2-
V-
C1-
GND
V
CC
V
CC
C1+
14
13
11
12
CHARGE
PUMP
Z
Y
B
DE
A
RS-485 MODE
D
HALF/FULL
DUPLEX
R
R0
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
1
2
3
4
RS-232
OUTPUT
RS-232
OUTPUT
LOGIC
INPUTS
LOGIC
OUTPUTS
RS-232
INPUTS
C1
C3
C2
C4
SHDN
HDPLX
FAST RS485/RS232
5
6
7
8
16
V+
C2+
C2-
V-
C1-
GND
V
CC
V
CC
C1+
14
13
11
12
CHARGE
PUMP
T1
T2
R1
R2
C
BYPASS
RS-232 MODE
15
9
10
MAX3161
Page 12

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
12 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Functional Diagrams (continued)
MAX3162
Figure 3. RS-485/422 Driver Timing Test Circuit
1k
C
L
V
CC
TEST POINT
RECEIVER
OUTPUT
S1
1k
S2
Figure 2. RS-485/422 Receiver Enable/Disable Timing Test Load
Figure 1. RS-485/422 Driver DC Test Load
V
OD
V
OC
R
R
Z
Y
Test Circuits
V
CC
C1
C
BYPASS
RS-232
OUTPUT
RS-485
OUTPUTS
RS-232
OUTPUT
LOGIC
OUTPUTS
C1+
1
V
CC
2
C1-
3
GND
4
5
Z
6
Y
7
8
R1
9
R2
10
11
RE485
12
CHARGE
PUMP
D
RO
R
T1
DE485
T2
V+
28
20
19
18
17
27
26
25
24
23
22
211
C3
C2
C4
LOGIC
INPUTS
RS-232
INPUTS
RS-485
INPUTS
C2+
C2-
V-
B
A
SHDN
13
14
FAST
TE232
16
15
3V
DE485
DI
C
L
Y
R
V
DIFF
OD
Z
C
L
Page 13

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 13
Test Circuits (continued)
Figure 4. RS-485/422 Driver Enable/Disable Timing Test Load
Figure 5. RS-485/422 Driver Propagation Delays
Figure 6. RS-485/422 Driver Enable and Disable Times
Figure 7. RS-485/422 Receiver Propagation Delays
Figure 9. RS-485/422 Receiver Propagation Delays Test Circuit
Figure 8. MAX3162 RS-485/422 Receiver Enable and Disable
Times
V
CC
OUTPUT
UNDER TEST
500Ω
C
L
S1
S2
3V
DE485
Y, Z
V
Y, Z
1.5V 1.5V
0
t
DZL
2.3V
OL
0
OUTPUT NORMALLY LOW
OUTPUT NORMALLY HIGH
2.3V
t
DZH
t
DLZ
V
+0.5V
OL
V
-0.5V
OH
t
DHZ
3V
DI
V
DIFF
RO
1V
-1V
1.5V
0
Z
V
O
Y
1/2 V
V
O
0
-V
O
V
OH
V
OL
A
B
O
10%
T
DR
t
DPLH
V
90%
t
DSKEW = | tDPLH
/2 VCC/2
V
CC
t
RPHL
DIFF
INPUT
= Vy - V
OUTPUT
t
DPHL
z
90%
T
DF
- t
DPHL
|
t
RPLH
1.5V
10%
1/2 V
O
3V
RE485
V
RO
RO
CC
1.5V 1.5V
0
t
RZL
1.5V
OUTPUT NORMALLY LOW
OUTPUT NORMALLY HIGH
0
1.5V
t
RZH
t
RLZ
VOL + 0.5V
V
- 0.5V
OH
t
RHZ
B
V
ID
R
A
RO
C
L
Page 14

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
Detailed Description
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 3V/5V, multiprotocol
transceivers can be pin configured in a number of RS232 and RS-485/422 interface combinations. These circuit configurations are ideal for the design of RS-232 to
RS-485 converters, multiprotocol buses, or any application that requires both RS-232 and RS-485 transceivers.
The slew rate of these devices is on-the-fly pin programmable, allowing reduced EMI data rates, or up to
10Mbps RS-485 communications. Power consumption
can be reduced to 1µA by using the shutdown function,
but the RS-232 receivers remain active allowing other
devices to query the interface controller. A flow-through
pinout and the space-saving SSOP packages (available in the commercial and extended temperature
ranges) facilitate board layout.
Device Selection
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 contain RS-232
transceivers and an RS-485/422 transceiver. The primary difference between the devices is the multiplexing
of the I/O pins.
The MAX3160 has common transmitter outputs and
receiver inputs for its RS-232 and RS-485/422 transceivers, and common digital I/O pins. The MAX3160 is
optimized for multiprotocol operation on a single interface bus and comes in a 20-pin SSOP.
The MAX3161 has separate transmitter outputs and
receiver inputs for its RS-232 and RS-485/422 transceivers, and common digital I/O pins. The MAX3161 is
optimized for multiplexing a single UART across two
interface buses and comes in a 24-pin SSOP.
The MAX3162 has separate transmitter outputs and
receiver inputs for its RS-232 and RS-485/422 transceivers, and separate digital I/O pins. The MAX3162 is
optimized for protocol translation between two interface
buses and comes in a 28-pin SSOP.
See Tables 1–12,
Functional Diagrams
, and the follow-
ing descriptions for details on each device.
MAX3160
The MAX3160 is a 2TX/2RX RS-232 transceiver in RS232 mode, capable of RS-232-compliant communication. Assertion of RS-485/RS232 converts the device to
a single RS-485 transceiver by multiplexing the RS-232
I/O pins to an RS-485 driver and receiver pair. The
logic inputs now control the driver input and the driver
enable. One logic output carries the RS-485 receiver
output, and the other is three-stated. The receiver input
impedance is dependent on the device mode and is
1/4-unit load for RS-485 operation and 5kΩ for RS-232
operation.
MAX3161
The MAX3161 is a 2TX/2RX RS-232 transceiver in RS232 mode or a single RS-485/422 transceiver in RS-485
mode. When in RS-485 mode, the unused RS-232
transmitter and receiver output pins are disabled. When
in RS-232 mode, the RS-485 transmitter outputs are
disabled and the RS-232 receiver inputs are 5kΩ to
GND. The RS-485 receiver inputs are always 1/8-unit
load. Logic lines are shared between the two protocols
and are used for signal inputs and as an RS-485 driver
enable.
MAX3162
The MAX3162 is a 2TX/2RX RS-232 transceiver and a
single RS-485/422 transceiver simultaneously. All drivers, receivers, and transmitters can be enabled or disabled by pin configuration. All outputs are high-Z when
not activated. RS-232 receiver inputs are 5kΩ when
enabled, and RS-485 receiver inputs are 1/8-unit load.
FAST Mode operation
The FAST control pin is used to select the slew-rate limiting of the RS-232 transmitters and the RS-485/422 drivers. With FAST unasserted, the RS-232 transmitters
and the RS-485/422 driver are slew-rate limited to
reduce EMI. RS-232 data rates up to 1Mbps and RS485/422 data rates up to 10Mbps are possible when
FAST is asserted. FAST can be changed during operation without interrupting data communications.
Half-Duplex RS-485/422 Operation
Asserting HDPLX places the MAX3160/MAX3161 in
half-duplex mode. The RS-485 receiver inputs are internally connected to the driver outputs. The RS-485 driver outputs can be disabled by pulling DE485 low.
HDPLX has no affect on RS-232 operation.
Low-Power Shutdown
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 have an active-low
shutdown control input, SHDN. When driven low, the
charge pump and transmitters are shut down and supply current is reduced to 1µA. The RS-232 receiver outputs remain active if in RS-232 mode. The chargepump capacitors must be recharged when coming out
of shutdown before resuming operation in either RS-232
or RS-485/422 mode (Figure 10).
Dual Charge-Pump Voltage Converter
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162s’ internal power
supply consists of a regulated dual charge pump that
provides output voltages of +5.5V (doubling charge
pump) and -5.5V (inverting charge pump) for input voltages (VCC) over the 3.0V to 5.5V range. The charge
pumps operate in a discontinuous mode: if the magnitude of either output voltage is less than 5.5V, the
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
14 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Page 15

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 15
charge pumps are enabled; if the magnitude of both
output voltages exceeds 5.5V, the charge pumps are
disabled. Each charge pump requires a flying capacitor (C1, C2) and a reservoir capacitor (C3, C4) to generate the V+ and V- supplies (see
Functional
Diagrams).
RS-485/422 Transceivers
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 RS-485/422 transceivers feature fail-safe circuitry that guarantees a
logic-high receiver output when the receiver inputs are
open or shorted, or when they are connected to a terminated transmission line with all drivers disabled (see
Fail-Safe
). The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 also feature pin-selectable reduced slew-rate drivers that minimize EMI and reduce reflections caused by improperly
terminated cables, allowing error-free data transmission
up to 250kbps (see
RS-485/422 Reduced EMI and
Reflection
s). The transmitters may operate at speeds
up to 10Mbps with the slew-rate limiting disabled.
Drivers are short-circuit current limited and thermally
limited to protect them against excessive power dissipation. Half-duplex communication is enabled by driving HDPLX high.
Fail-Safe
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 guarantee a logichigh RS-485 receiver output when the receiver inputs
are shorted or open, or when they are connected to a
terminated transmission line with all drivers disabled.
This is done by having the receiver threshold between
-50mV and -200mV. If the differential receiver input voltage (A-B) is greater than or equal to -50mV, RO is logic
high. If A-B is less than or equal to -200mV, RO is logic
low. In the case of a terminated bus with all transmitters
disabled, the receiver’s differential input voltage is
pulled to GND by the termination. This results in a logic
high with a 50mV minimum noise margin. Unlike other
fail-safe devices, the -50mV to -200mV threshold complies with the ±200mV EIA/TIA-485 standard.
RS-232 Transceivers
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 RS-232 transmitters
are inverting-level translators that convert CMOS-logic
levels to ±5.0V EIA/TIA-232-compliant levels. The transmitters are guaranteed at a 250kbps data rate in slewrate limited mode (FAST = GND) with worst-case loads
of 3kΩ in parallel with 1000pF. Data rates up to
1Mbps can be achieved by asserting FAST.
When powered down or in shutdown, the MAX3160/
MAX3161/MAX3162 outputs are high impedance and
can be driven to ±12V. The transmitter inputs do not
have pullup resistors. Connect unused inputs to ground
or VCC.
The receivers convert RS-232 signals to CMOS-logic output levels. All receivers have inverting outputs that
remain active in shutdown. The MAX3160/MAX3161/
MAX3162 permit their receiver inputs to be driven to Dia
±25V. Floating receiver input signals are pulled to
ground through internal 5kΩ resistors, forcing the outputs to a logic high. The MAX3162 has transmitter and
receiver enable pins that allow its outputs to be threestated.
Applications Information
Capacitor Selection
The capacitor type used for C1–C4 is not critical for
proper operation; polarized or nonpolarized capacitors
can be used. Ceramic chip capacitors with an X7R
dielectric provide the best combination of performance,
cost, and size. The charge pump requires 0.1µF
capacitors for 3.3V operation. For other supply voltages, see Table 13 for required capacitor values. Do
not use values smaller than those listed in Table 13.
Increasing the capacitor values reduces ripple on the
transmitter outputs and slightly reduces power consumption. C2, C3, and C4 can be changed without
changing C1’s value. However, do not increase C1
without also increasing the values of C2, C3, C4,
and C
BYPASS
to maintain the proper ratios to the
other capacitors.
When using the minimum required capacitor values,
make sure the capacitance value does not degrade
excessively with temperature or voltage. This is typical
of Y5V and Z5U dielectric ceramic capacitors. If in
doubt, use capacitors with a larger nominal value. The
capacitor’s equivalent series resistance (ESR), which
usually rises at low temperatures, influences the
amount of ripple on V+ and V-.
Power-Supply Decoupling
In applications that are sensitive to power-supply noise,
decouple VCCto ground with a capacitor of the same
value as reservoir capacitors C2, C3, and C4. Connect
the bypass capacitor as close to the IC as possible.
RS-232 Transmitter Outputs
when Exiting Shutdown
Figure 10 shows two transmitter outputs when exiting
shutdown mode. As they become active, the two transmitter outputs are shown going to opposite RS-232 levels (one transmitter input is high, the other is low). Each
transmitter is loaded with 3kΩ in parallel with 1000pF.
The transmitter outputs display no ringing or undesirable transients as they come out of shutdown. Note that
the transmitters are enabled only when V- exceeds
approximately -3V.
Page 16

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
16 ______________________________________________________________________________________
High Data Rates
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 maintain the RS-232
±5.0V required minimum transmitter output voltage even
at high data rates. Figure 11 shows a transmitter loopback test circuit. Figure 12 shows a loopback test result
at 250kbps, and Figure 13 shows the same test at
1000kbps. Figure 12 demonstrates a single slew-rate
limited transmitter driven at 250kbps (FAST = GND) into
an RS-232 load in parallel with 1000pF. Figure 13 shows
a single transmitter driven at 1Mbps (FAST asserted),
loaded with an RS-232 receiver in parallel with 1000pF.
These transceivers maintain the RS-232 ±5.0V minimum
transmitter output voltage at data rates up to 1Mbps.
256 Transceivers on the Bus
The standard RS-485 receiver input impedance is 12kΩ
(one-unit load), and the standard driver can drive up to
32-unit loads. The MAX3160 has a 1/4-unit load receiver input impedance (48kΩ), allowing up to 128 trans-
Table 1. MAX3160
Table 2. MAX3161
Table 3. MAX3162
Table 4. MAX3160
Table 5. MAX3161
RS-232 Transmitters
Table 6. MAX3162
RS-232 Receivers
Truth Tables
INPUTS OUTPUTS
SHDN
0 X X 1/8 Unit Load
10 0 1
10 1 0
1 1 X RS-485 Mode
RS485
RRRRSSSS2222333322
22
DI/T1IN,
DE485/T2IN
Z(B)/T1OUT,
Y(A)/T2OUT
SHDN
X0 0 1
X0 1 0
X 0 Inputs Open 1
X1 X
INPUTS OUTPUTS
SHDN
0 X X High-Z
10 0 1
10 1 0
1 1 X High-Z
RS-485/
RS-232
DI/T1IN,
DE485/T2IN
T1OUT,
T2OUT
SHDN
X0 0 1
X0 1 0
X 0 Inputs Open 1
X1 X
INPUTS OUTPUTS
RS-485/
22
RRRRSSSS----2222333322
INPUTS OUTPUTS
RS-485/
22
RRRRSSSS----2222333322
B/R1IN,
A/R2IN
R1IN, R2IN
R1OUT,
RO/R2OUT
R1OUT
High-Z,
RO/R2OUT in
RS-485 mode
R1OUT,
RO/R2OUT
R1OUT
High-Z,
RO/R2OUT in
RS-485 mode
INPUTS OUTPUTS
SHDN TE232 T1IN,T2IN
0 X X High-Z
X 0 X High-Z
11 0 1
11 1 0
T1OUT,
T2OUT
INPUTS OUTPUTS
SHDN RE232 R1IN, R2IN
X 1 X High-Z
X0 0 1
X0 1 0
X 0 Inputs open 1
R1OUT,
R2OUT
Page 17

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 17
Table 7. MAX3160
Table 8. MAX3161
Table 9. MAX3162
Table 10. MAX3160
*
Y and Z correspond to pins Y(A)/T2OUT and Z(B)/T1OUT. A and B correspond to pins A/R2IN and B/R1IN.
Truth Tables (continued)
RS-485/422 Receivers
RS-485/422 Drivers
SHDN RS485/RRRRSSSS2222333322
0 1 X X 1/8 Unit Load 1/8 Unit Load
1 1 0 X 1/8 Unit Load 1/8 Unit Load
1110 1 0
1111 0 1
X 0 X X RS-232 Mode
SHDN RS485/RRRRSSSS2222333322
0 X X X 1/8 Unit Load 1/8 Unit Load
X 0 X X 1/8 Unit Load 1/8 Unit Load
X X 0 X 1/8 Unit Load 1/8 Unit Load
1110 1 0
1111 0 1
SHDN DE485 DI Z Y
0 X X High-Z High-Z
X 0 X High-Z High-Z
110 1 0
111 0 1
INPUTS OUTPUTS
22
INPUTS OUTPUTS
22
INPUTS OUTPUTS
DE485/T2IN DI/T1IN Z(B)/T1OUT Y(A)/T2OUT
DE485/T2IN DI/T1IN Z(B) Y(A)
INPUTS OUTPUT
RS485/RS232 SHDN HDPLX A - B* Y - Z* RO/R2OUT
1 0 X X X High-Z Up to V
110≥-50mV X 1
110≤-200mV X 0
1 1 0 Floating X 1
111X≥-50mV 1
111X≤-200mV 0
1 1 1 X Floating 1
0 X X X X RS-232 Mode
CC
Page 18

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
18 ______________________________________________________________________________________
ceivers to be connected in parallel on one communication line. The MAX3161/MAX3162 have a 1/8-unit load
receiver input impedance (96kΩ), allowing up to 256
transceivers to be connected in parallel on one communication line. Any combination of these devices
and/or other RS-485 transceivers with a total of 32-unit
loads or fewer can be connected to the line.
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 RS-485 driver outputs are 1/8-unit load when disabled This impedance
may be reduced if the D1 pin is toggled at a high frequency. With no power applied (VCC= GND), the RS485 transmitter output impedances typically go to 1/2unit load on the MAX3161/MAX3162, and to one-unit
load on the MAX3160.
Driver Output Protection
Two mechanisms prevent excessive output current and
power dissipation caused by faults or by bus contention. The first, a foldback current limit on the output
stage, provides immediate protection against short circuits over the whole common-mode voltage range (see
Typical Operating Characteristics
). The second, a thermal shutdown circuit, forces the driver outputs into a
high-impedance state if the die temperature becomes
excessive.
Protection Against Wiring Faults
EIA/TIA-485 standards require a common input voltage
range of -7V to +12V to prevent damage to the device.
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 inputs are protected
to RS-232 levels of ±25V for the receiver inputs and
±13.2V for the transmitter/driver outputs. This provides
additional protection for the RS-485 transceivers
against ground differential or faults due to miswiring.
RS-485/422 Reduced EMI and Reflections
The MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162 can be configured
for slew-rate limiting by pulling FAST low. This minimizes
EMI and reduces reflections caused by improperly terminated cables. Operation in slew-rate limited mode
reduces the amplitudes of high-frequency harmonics.
Table 13. Required Minimum Capacitance
Values
Table 11. MAX3161
Table 12. MAX3162
Truth Tables (continued)
INPUTS OUTPUT
RS485/RS232 SHDN HDPLX A - B Y(A) - Z(B) RO/R2OUT
1 0 X X X High-Z up to V
1 1 0 -50mV X 1
1 1 0 -200mV X 0
1 1 0 Floating X 1
1 1 1 X -50mV 1
1 1 1 X -200mV 0
1 1 1 X Floating 1
0 X X X X RS-232 Mode
INPUTS OUTPUT
SHDN RE485 A - B RO
0 X X High-Z
X 1 X High-Z
1 0 -50mV 1
1 0 -200mV 0
1 0 Inputs Open 1
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
+3.0 TO +3.6 0.1 0.1
+4.5 TO +5.5 0.047 0.33
+3.0 TO +5.5 0.1 0.47
(V)
C1 (µF)
C2, C3, C4, C
(µF)
CC
BYPASS
Page 19

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 19
RS-485/422 Line Length vs. Data Length
The RS-485/422 standard covers line lengths up to
4000 feet. For line lengths greater than 4000 feet, use
the repeater application shown in Figure 14.
RS-232/RS-485 Protocol Translator
Figure 15 shows the MAX3162 configured as an RS232/RS-485 protocol translator. The direction of translation is controlled through the RTS signal (R1IN). The
single-ended RS-232 receiver input signal is translated
to a differential RS-485 transmitter output. Similarly, a
differential RS-485 receiver input signal is translated to
a single-ended RS-232 transmitter output. RS-232 data
received on R2IN is transmitted as an RS-485 signal on
Z and Y. RS-485 signals received on A and B are transmitted as an RS-232 signal on T1OUT.
Multiprotocol Bus
The
Typical Operating Circuit
shows a standard application for the MAX3160. The MAX3160’s output pins
are multiplexed between RS-232 and RS-485 protocols
by a microprocessor (µP). The µP also directs the shutdown functions, enable lines, and the duplex of the
MAX3160. Data is transmitted to the MAX3100 UART
through an SPI™ port. The UART asynchronously
Figure 10. MAX3160 RS-232 Transmitter Outputs When Exiting
Shutdown
Figure 12. RS-232 Loopback Test Result at 250kbps, FAST =
Low
Figure 13. RS-232 Loopback Test Result at 1000kbps, FAST =
High
Figure 11. Loopback Test Circuit
SPI is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
MAX 3160-2 FIG10
40μs/div
SHDN
5V/division
T1OUT
2V/div
GND
T2OUT
2V/div
V
CC
C
BYPASS
V
CC
MAX3160
MAX3161
MAX3162
V+
C3
V-
C4
C1
C2
C1+
C1-
C2+
C2-
MAX 3160-2 FIG12
T
IN
T
OUT
5V/div
R
OUT
1μs/div
MAX 3160-2 FIG13
T
IN
T
OUT
5V/div
R
OUT
T_ IN
R_ OUT
V
CC
SHDN
GND
T_ OUT
R_ IN
1000pF
5k
200ns/div
Page 20

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
20 ______________________________________________________________________________________
transfers data through the MAX3160 to the pin-selected
RS-232 or RS-485 protocol; see Table 14 for commonly
used cable connections.
Multiprotocol Bus Multiplexer
The
Typical Application Circuit
shows the MAX3161 configured as a multiprotocol bus multiplexer. The MAX3161
separates the RS-232 and RS-485 lines, but shares the
logic pins between modes. This application allows the
µP to monitor a point-to-point RS-232 bus, and a multidrop RS-485 interface. The MAX3100 UART asynchronously transfers data through the MAX3161 to the
pin-selected RS-232 or RS-485 protocol.
Figure 14. RS-485 Line Repeater
Figure 15. Protocol Translator
MAX3160
MAX3161
MAX3162
A
RO
RE485
DE485
DI
NOTE: RE485 ON MAX3162 ONLY
R
D DATA OUT
120Ω
B
120Ω
Z
Y
DATA IN
RCV
RTS
27
C3
100nF
C2+
26
C2-
13
SHDN
5
T1OUT
10
R2OUT
23
DI
19
R2IN
20
R1IN
15
RE232
16
TE232
14
FAST
28
V+
C2
100nF
TX
3.3V
V
CC
MAX3162
GND
4
2
C1+
C1-
T1IN
R1OUT
RE485
DE485
C
BYPASS
100nF
1
C1
3
24
11
RO
9
12
22
17
A
18
B
6
Z
7
Y
25
V-
100nF
C4
100nF
Page 21

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 21
Typical Application Circuit
Table 14. Cable Connections Commonly Used for EIA/TIA-232 and
V.24 Asynchronous Interfaces
EIA/TIA-232
STANDARD
CONNECTOR
PIN
DCD 1 Data Carrier Detect
RD 2 R2IN 13 17 19 Received Data
TD 3 T1OUT 5 5 5 Transmitted Data
DTR 4 Data Terminal Ready
SG 5 GND 4 4 4 Signal Ground
DSR 6 Data Set Ready
RTS 7 T2OUT 6 8 8
CTS 8 R1IN 14 18 20 Clear to Send (= DCE ready)
RI 9 Ring Indicator
MAX3160
MAX3161
PIN NUMBER
MAX3162
EQUIVALENT MAX3160 MAX3161 MAX3162
FUNCTION
(as seen by DTE)
Request to Send (= DTE
ready)
+
214
V
CC
HDPLX
DB9
RS-485
RS-232
1
RJ45
MAX3100
UART
SPI
μP
TX
13
RX
12
RTS
11
CTS
10
DI/T1IN
20
RO/R2OUT
10
DE/T2IN
19
R1OUT R1IN
9
GND FAST SHDN
412
RS-485/RS-232
SHDN
MAX3161
T1OUT
5
R2IN
17
T2OUT
8
18
Y(A)
7
Z(B)
6
Page 22

MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
22 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Pin Configurations
Selector Guide Chip Information
PROCESS: BiCMOS
PACKAGE TYPE PACKAGE CODE DOCUMENT NO.
20 SSOP A20+1
21-0056
24 SSOP A24+3
21-0056
28 SSOP A28+3
21-0056
Package Information
For the latest package outline information and land patterns,
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
. Note that a “+”, “#”, or
“-” in the package code indicates RoHS status only. Package
drawings may show a different suffix character, but the drawing
pertains to the package regardless of RoHS status.
TOP VIEW
C1+
V
C1-
Z(B)/T1OUT
Y(A)/T2OUT
R1OUT
SHDN
FAST
1
2
CC
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
+
MAX3160
20-PIN SSOP
20
V+
19
C2+
18
C2-
17
V-GND
16
DI/T1IN
15
DE485/T2IN
14
B/R1IN
A/R2INRO/R2OUT
13
12
HDPLX
11
RS-485/RS-232
T1OUT
R1OUT
RO/R2OUT
SHDN
C1+
V
C1-
Z(B)
Y(A)
+
1
2
CC
3
4
MAX3161
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24-PIN SSOP
FLOW-
PART DUAL-MODE
THROUGH
PIN-OUT
MAX3160 No Yes 1/4
MAX3161 No No 1/8
MAX3162 Yes Yes 1/8
RS-485
INPUT UNIT
LOADS
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
V+
C2+
C2-
V-GND
DI/T1IN
DE485/T2IN
R1IN
R2INT2OUT
B
A
HDPLX
RS-485/RS-232FAST
+
C1+
V
C1-
GND
T1OUT
T2OUT
R1OUT
R2OUT
RE485
SHDN
FAST
1
2
CC
3
4
5
Z
Y
RO
MAX3162
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
V+
28
C2+
27
C2-
26
V-
25
T1IN
24
DI
23
DE485
22
T2IN
21
R1IN
20
R2IN
19
B
18
A
17
TE232
16
RE232
15
28-PIN SSOP
Page 23

Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600 ____________________
23
© 2009 Maxim Integrated Products Maxim is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
MAX3160/MAX3161/MAX3162
+3.0V to+5.5V, 1µA, RS-232/RS-485/422
Multiprotocol Transceivers
Revision History
REVISION
NUMBER
2 12/09
REVISION
DATE
DESCRIPTION
Corrected the “Continuous Power Dissipat ion” specif icat ions under the Absolute
Maximum Ratings.
Changed pin labels in the Functional Diagrams. 11
Deleted “TRANSISTOR COUNT: 1580” and added “PROCESS: BiCMOS” to the Chip
Informat ion.
PAGES
CHANGED
2
22
 Loading...
Loading...