
19-5547; Rev 2; 9/11
EVALUATION KIT
AVAILABLE
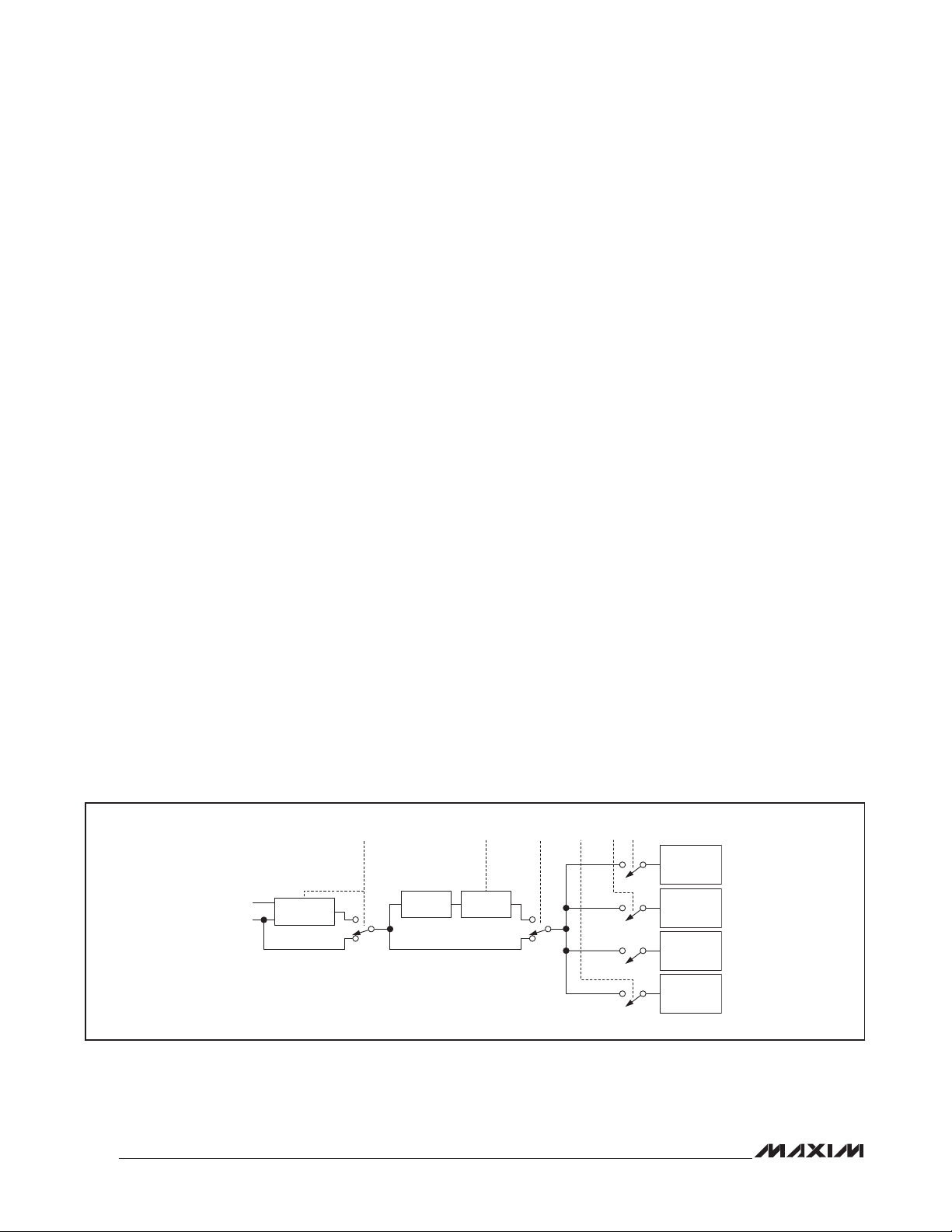
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
General Description
The MAX14830 is an advanced quad universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter (UART), each UART having 128 words of receive and transmit first-in/first-out
(FIFO) and a high-speed serial peripheral interface
(SPIK) or I
baud-rate generators allow a high degree of flexibility in
baud-rate programming and reference clock selection.
Each of the four UARTs is selected by in-band SPI/I
addressing. Logic-level translation on the transceiver
and controller interfaces allows ease of interfacing to
microcontrollers, FPGAs, and transceivers that are powered by differing supply voltages.
Extensive features simplify transceiver control in halfduplex communication applications. The MAX14830
features the ability to synchronize the start of individual
UART’s transmission by SPI-based triggering. On-board
timers allow programming of delays between transmitters as well as clock generation on GPIOs.
The 128-word FIFOs have advanced FIFO control reducing host processor data flow management.
The MAX14830 is available in a 48-pin TQFN (7mm x
7mm) package and is specified to operate over the
extended -40NC to +85NC temperature range.
Applications
2
C controller interface. A PLL and fractional
Industrial Control Systems
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)
IO-Link Master Controllers
Automotive Infotainment Systems
Medical Systems
Point-of-Sales Systems
Airplane Communication Buses
2
C
Features
S SPI Up to 26MHz Clock Rate
S Fast-Mode Plus (Fm+) I
S 128-Word Transmit and Receive FIFOs Per UART
S 6Mbaud (max) Data Rate in 16x Sampling Mode
S 12/24Mbaud (max) Data Rate in 2x/4x Rate Modes
S Fractional Baud-Rate Generators, Predivider, and
2
C Interface Up to 1MHz
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL)
S Transmitter Synchronization Through SPI
Commands
S Four Timers Routed to GPIOs
S Automatic Hardware Flow Control Using RTS_
and CTS_ Outputs and Inputs
S Automatic Software Flow Control (XON/XOFF)
S Auto Transceiver Direction Control
S Programmable Setup and Hold Times for
Transceiver Control
S Auto Transmitter Disable
S Half-Duplex Echo Suppression
S Special Character Detection
S 9-Bit Multidrop Mode Address Detection and
Filtering
S SIR- and MIR-Compliant IrDA
S 16 Flexible GPIOs with 20mA Drive Capability
S +2.35V to +3.6V Supply Range
S Logic-Level Translation Down to 1.61V on
®
Encoder/Decoders
Controller and Transceiver Interfaces
S Small TQFN (7mm x 7mm) Package
Ordering Information
MAX14830
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
Typical Operating Circuits appear at end of data sheet.
SPI is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
IrDA is a registered service mark of Infrared Data Association
Corporation.
_______________________________________________________________ Maxim Integrated Products 1
MAX14830ETM+
+Denotes a lead(Pb)-free/RoHS-compliant package.
*EP = Exposed pad.
-40NC to +85NC
48 TQFN-EP*
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim Direct at 1-888-629-4642,
or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
TABLE OF CONTENTS
General Description ............................................................................ 1
Applications .................................................................................. 1
Features ..................................................................................... 1
Ordering Information ........................................................................... 1
Functional Diagram ............................................................................ 7
Absolute Maximum Ratings ...................................................................... 8
MAX14830
Package Thermal Characteristics.................................................................. 8
DC Electrical Characteristics ..................................................................... 8
AC Electrical Characteristics .................................................................... 10
Test Circuits/Timing Diagrams ................................................................... 13
Typical Operating Characteristics ................................................................ 14
Pin Configuration ............................................................................. 15
Pin Description ............................................................................... 15
Detailed Description........................................................................... 18
Receive and Transmit FIFOs...................................................................18
Transmitter Operation ........................................................................18
Receiver Operation ..........................................................................19
Line Noise Indication.........................................................................20
Clocking and Baud-Rate Generation ............................................................20
Crystal Oscillator .........................................................................20
External Clock Source .....................................................................20
PLL and Predivider ..........................................................................20
Fractional Baud-Rate Generators ...............................................................21
2x and 4x Rate Modes .......................................................................21
Low-Frequency Timer ........................................................................22
UART Clock to GPIO.........................................................................22
Multidrop Mode .............................................................................22
Auto Data Filtering in Multidrop Mode .........................................................22
Auto Transceiver Direction Control ..............................................................22
Transmitter Triggering and Synchronization .......................................................23
Transmitter Synchronization .................................................................23
Intrachip and Interchip Synchronization........................................................23
Delayed Triggering........................................................................23
Trigger Accuracy .........................................................................24
Synchronization Accuracy ..................................................................24
Auto Transmitter Disable ......................................................................24
Echo Suppression ...........................................................................24
Auto Hardware Flow Control ...................................................................26
2

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
TABLE OF CONTENTS (continued)
AutoRTS Control..........................................................................26
AutoCTS Control..........................................................................26
FIFO Interrupt Triggering......................................................................26
Auto Software (XON/XOFF) Flow Control .........................................................26
Transmitter Flow Control....................................................................27
Receiver Overflow Control ..................................................................27
Power-Up and IRQ ..........................................................................27
Shutdown Mode ............................................................................27
Interrupt Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Interrupt Enabling.........................................................................28
Interrupt Clearing .........................................................................28
Register Map ................................................................................28
Detailed Register Description ..................................................................30
Serial Controller Interface....................................................................... 58
SPI Interface ...............................................................................58
MISO Operation ..........................................................................58
SPI Burst Access .........................................................................58
Fast Read Cycle..........................................................................59
I2C Interface ...............................................................................59
START, STOP, and Repeated START Conditions.................................................59
Slave Address ...........................................................................60
Bit Transfer ..............................................................................61
Single-Byte Write .........................................................................61
Burst Write ..............................................................................61
Single-Byte Read .........................................................................62
Burst Read ..............................................................................62
Acknowledge Bits ........................................................................63
Applications Information ........................................................................63
Startup and Initialization ......................................................................63
Low-Power Operation ........................................................................63
Interrupts and Polling ........................................................................63
Logic-Level Translation .......................................................................63
IO-Link Application ..........................................................................63
Typical Operating Circuit .......................................................................65
Chip Information .............................................................................. 67
Package Information........................................................................... 67
Revision History ..............................................................................68
MAX14830
3

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1. I2C Timing Diagram.................................................................... 13
Figure 2. SPI Timing Diagram ................................................................... 13
Figure 3. Transmit FIFO Signals .................................................................. 18
Figure 4. Receive Data Format................................................................... 19
Figure 5. Receive FIFO ........................................................................ 19
Figure 6. Midbit Sampling ...................................................................... 19
MAX14830
Figure 7. Clock Selection Diagram................................................................ 20
Figure 8. 2x and 4x Baud Rates.................................................................. 21
Figure 9. GPIO_ Clock Pulse Generator............................................................ 22
Figure 10. Auto Transceiver Direction Control .......................................................23
Figure 11. Setup and Hold times in Auto Transceiver Direction Control ...................................23
Figure 12. Single Transmitter Trigger Accuracy ...................................................... 24
Figure 13. Multiple Transmitter Synchronization Accuracy.............................................. 25
Figure 14. Echo Suppression Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 15. Half-Duplex with Echo Suppression ...................................................... 26
Figure 16. Simplified Interrupt Structure............................................................ 27
Figure 17. PLL Signal Path ...................................................................... 51
Figure 18. SPI Write Cycle ......................................................................58
Figure 19. SPI Read Cycle ...................................................................... 59
Figure 20. SPI Fast Read Cycle .................................................................. 59
Figure 21. I2C START, STOP, and Repeated START Conditions ......................................... 60
Figure 22. Write Byte Sequence.................................................................. 61
Figure 23. Burst Write Sequence ................................................................. 61
Figure 24. Read Byte Sequence ................................................................. 62
Figure 25. Burst Read Sequence................................................................. 62
Figure 26. Acknowledge Bits .................................................................... 63
Figure 27. Startup and Initialization Flow Chart ......................................................63
Figure 28. Logic-Level Translation ................................................................ 64
Figure 29. Interchip Synchronization .............................................................. 64
4

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. UART GPIO Assignments for GPIO Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 2. StopBits Truth Table .................................................................... 41
Table 3. Length_ Truth Table .................................................................... 41
Table 4. SwFlow_ Truth Table....................................................................46
Table 5. UART GPIO Assignments for GPIO Configuration ............................................. 49
Table 6. UART GPIO Assignments for GPIO Input/Output Data ......................................... 50
Table 7. PLLFactor_ Selector Guide ............................................................... 51
Table 8. GloblComnd Command Descriptions ...................................................... 54
Table 9. Extended Mode Addressing (SPI only) .....................................................54
Table 10. SPI Command Byte Configuration ........................................................58
Table 11. SPI U1, U0 UART Selection ............................................................. 58
Table 12. I2C Address Map ..................................................................... 60
MAX14830
5

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
LIST OF REGISTERS
RHR—Receive Hold Register ................................................................... 30
THR—Transmit Hold Register ................................................................... 30
IRQEn—IRQ Enable Register.................................................................... 31
ISR—Interrupt Status Register ................................................................... 32
LSRIntEn—Line Status Interrupt Enable Register .................................................... 33
LSR—Line Status Register...................................................................... 34
MAX14830
SpclChrIntEn—Special Character Interrupt Enable Register............................................ 35
SpclCharInt—Special Character Interrupt Register ................................................... 36
STSIntEn—STS Interrupt Enable Register .......................................................... 37
STSInt—Status Interrupt Register................................................................. 38
MODE1 Register.............................................................................. 39
MODE2 Register .............................................................................40
LCR—Line Control Register ..................................................................... 41
RxTimeOut—Receiver Timeout Register ...........................................................42
HDplxDelay Register ..........................................................................42
IrDA Register ................................................................................ 43
FlowLvl—Flow Level Register.................................................................... 44
FIFOTrigLvl—FIFO Interrupt Trigger Level Register ................................................... 44
TxFIFOLvl—Transmit FIFO Level Register ..........................................................45
RxFIFOLvl—Receive FIFO Level Register ..........................................................45
FlowCtrl—Flow Control Register .................................................................45
XON1 Register ............................................................................... 47
XON2 Register ............................................................................... 47
XOFF1 Register ..............................................................................48
XOFF2 Register .............................................................................. 48
GPIOConfg—GPIO Configuration Register ......................................................... 49
GPIOData—GPIO Data Register ................................................................. 50
PLLConfig—PLL Configuration Register ........................................................... 51
BRGConfig—Baud-Rate Generator Configuration Register ............................................ 52
DIVLSB—Baud-Rate Generator LSB Divisor Register................................................. 52
DIVMSB—Baud-Rate Generator MSB Divisor Register................................................ 52
CLKSource—Clock Source Register .............................................................. 53
GlobalIRQ—Global IRQ Register................................................................. 53
GloblComnd—Global Command Register.......................................................... 54
TxSynch—Transmitter Synchronization Register ..................................................... 55
SynchDelay1—Synchronization Delay Register 1 ....................................................56
SynchDelay2—Synchronization Delay Register 2 ....................................................56
TIMER1—Timer Register 1......................................................................56
TIMER2—Timer Register 2......................................................................57
RevID—Revision Identification Register............................................................ 57
6
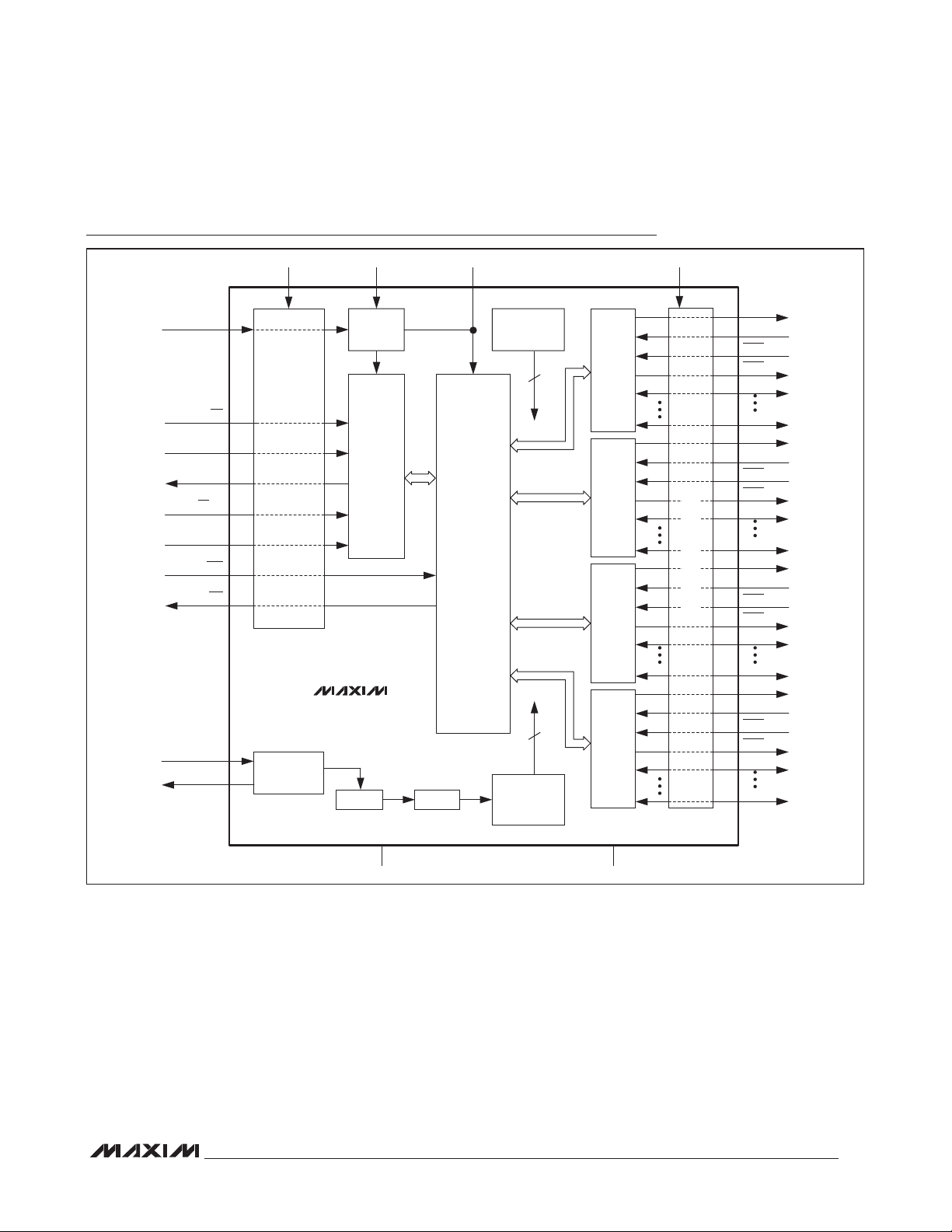
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Functional Diagram
MAX14830
LDOEN
SPI/I2C
MOSI/A1
MISO/SDA
CS/A0
SCLK/SCL
RST
IRQ
XIN
XOUT
V
L
LOGIC-LEVEL
TRANSLATION
CRYSTAL
OSCILLATOR
SPI AND
INTERFACE
MAX14830
LDO
I2C
V
EXT
TX0
RX0
CTS0
RTS0
GPIO0
GPIO3
TX1
RX1
CTS1
LOGIC-LEVEL TRANSLATION
RTS1
GPIO4
GPIO7
TX2
RX2
CTS2
RTS2
GPIO8
GPIO11
TX3
RX3
CTS3
RTS3
GPIO12
GPIO15
PLLDIVIDER
V
18
REGISTERS
AND
CONTROL
TRANSMITTER
SYNC
4
4
FRACTIONAL
BAUD-RATE
GENERATOR
UARTO
UART1
UART2
UART3
V
A
DGNDAGND
7
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(Voltages referenced to AGND.)
VL, VA, V
V18, XOUT ........... -0.3V to the lesser of (VA + 0.3V) and +2.0V
RST, IRQ, MOSI/A1, CS/A0, SCLK/SCL,
MISO/SDA, LDOEN, SPI/I2C .................. -0.3V to (VL + 0.3V)
TX0, RX0, CTS0, GPIO0, GPIO1,
GPIO2, GPIO3 ..................................... -0.3V to (V
TX1, RX1, CTS1, GPIO4, GPIO5,
GPIO6, GPIO7 ..................................... -0.3V to (V
MAX14830
TX2, RX2, CTS2, GPIO8, GPIO9,
GPIO10, GPIO11 ................................. -0.3V to (V
, XIN ................................................ -0.3V to +4.0V
EXT
EXT
EXT
EXT
+ 0.3V)
+ 0.3V)
+ 0.3V)
TX3, RX3, CTS3, GPIO12, GPIO13,
GPIO14, GPIO15 ................................. -0.3V to (V
DGND .................................................................. -0.3V to +0.3V
Continuous Power Dissipation (TA = +70NC)
TQFN (derate 38.5mW/NC above +70NC).....3076.9mW
Operating Temperature Range ........................ -40NC to +85NC
Maximum Junction Temperature ................................. +150NC
Storage Temperature Range ......................... -65NC to +150NC
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) ..................................300NC
Soldering Temperature (reflow) .....................................+260NC
EXT
+ 0.3V)
PACKAGE THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
TQFN
Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance (BJA) ...........26NC/W
Junction-to-Case Thermal Resistance (BJC) ..................1NC/W
Note 1: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JEDEC specification JESD51-7, using a four-
layer board. For detailed information on package thermal considerations, refer to www.maxim-ic.com/thermal-tutorial.
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(Note 1)
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VA = +2.35V to +3.6V, VL = +1.71V to +3.6V, V
are at VA = +2.5V, VL = +1.8V, V
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Digital Interface Supply Voltage V
Analog Supply Voltage V
UART Interface Logic Supply
Voltage
Logic Supply Voltage V
CURRENT CONSUMPTION
VA Supply Current I
VA Shutdown Supply Current I
VL Shutdown or Sleep Supply
Current
V
Shutdown Supply Current I
EXT
= +2.8V, TA = +25NC.) (Notes 2, 3)
EXT
L
A
V
EXT
18
A
ASHDN
I
L
EXT
= +1.71V to +3.6V, TA = -40NC to +85NC, unless otherwise noted. Typical values
EXT
1.71 3.6 V
2.35 3.6 V
1.71 3.6 V
1.65 1.95 V
1.8MHz crystal oscillator active, PLL disabled, SPI/I2C interface idle, UART interfaces idle, V
Baud rate = 1Mbps, 20MHz external clock,
SPI/I2C interface idle, PLL disabled, all
UARTs in loopback mode, V
Shutdown mode, V
all inputs and outputs are idle
Shutdown mode, V
all inputs and outputs are idle
Shutdown mode, V
all inputs and outputs are idle
LDOEN
= V
L
LDOEN
LDOEN
LDOEN
LDOEN
= 0V, V
= 0V, V
= 0V, V
= 0V
RST
RST
RST
= 0V,
= 0V,
= 0V,
400
0.5 mA
35
12
8
FA
FA
FA
FA
8
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VA = +2.35V to +3.6V, VL = +1.71V to +3.6V, V
are at VA = +2.5V, VL = +1.8V, V
= +2.8V, TA = +25NC.) (Notes 2, 3)
EXT
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
V18 Input Power-Supply Current
in Shutdown Mode
V18 Input Power-Supply Current I
I
18SHDN
18
SCLK/SCL, MISO/SDA
MISO/SDA Output Low Voltage
in I2C Mode
MISO/SDA Output Low Voltage
in SPI Mode
MISO/SDA Output High Voltage
in SPI Mode
Input Low Voltage V
Input High Voltage V
Input Hysteresis V
Input Leakage Current I
Input Capacitance C
V
OL,I2C
V
OL,SPIILOAD
V
OH,SPIILOAD
IL
IH
HYST
IL
IN
SPI/I2C, CS/A0, MOSI/A1 INPUTS
Input Low Voltage V
Input High Voltage V
Input Hysteresis V
Input Leakage Current I
Input Capacitance C
IL
IH
HYST
IL
IN
IRQ OUTPUT (OPEN DRAIN)
Output Low Voltage V
Output Leakage Current I
OL
LK
LDOEN AND RST INPUTS
Input Low Voltage V
Input High Voltage V
Input Hysteresis V
Input Leakage Current I
IL
IH
HYST
IN
UART INTERFACE
RTS0, RTS1, RTS2, RTS3, TX0, TX1, TX2, TX3 OUTPUTS
Output Low Voltage V
Output High Voltage V
Input Leakage Current I
Input Capacitance C
OL
OH
IN
IN
= +1.71V to +3.6V, TA = -40NC to +85NC, unless otherwise noted. Typical values
EXT
Shutdown mode, V
LDOEN
all inputs and outputs are idle
Baud rate = 1Mbps, 20MHz external clock,
PLL disabled, all UARTs in loopback mode,
V
I
I
= 0V (Note 4)
LDOEN
= -3mA, VL > 2V 0.4
LOAD
= -3mA, VL < 2V 0.2 x V
LOAD
= -2mA 0.4 V
= 2mA
SPI and I2C mode 0.3 x V
SPI and I2C mode 0.7 x V
SPI and I2C mode 0.05 x V
V
= 0 to VL, SPI and I2C mode -1 +1
IN
SPI and I2C mode 5 pF
SPI and I2C mode 0.3 x V
SPI and I2C mode 0.7 x V
SPI and I2C mode 50 mV
V
= 0 to VL, SPI and I2C mode -1 +1
IN
SPI and I2C mode 5 pF
I
= -2mA 0.4 V
LOAD
V
= 0 to VL, IRQ is not asserted
IRQ
V
= 0 to V
IN
I
LOAD
I
LOAD
L
= -2mA 0.4 V
= 2mA V
Output is three-stated, V
High-Z mode 5 pF
= 0V, V
RTS_
RST
= 0 to V
= 0V,
EXT
L
L
L
-1 +1
0.3 x V
0.7 x V
L
50 mV
-1 +1
- 0.4 V
EXT
-1 +1
200
5 mA
L
VL -
0.4
L
L
L
MAX14830
FA
V
V
V
V
V
FA
V
V
FA
FA
V
V
FA
FA
9
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VA = +2.35V to +3.6V, VL = +1.71V to +3.6V, V
are at VA = +2.5V, VL = +1.8V, V
= +2.8V, TA = +25NC.) (Notes 2, 3)
EXT
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
RX0, RX1, RX2, RX3, CTS0, CTS1, CTS2, CTS3 INPUTS
Input Low Voltage V
Input High Voltage V
Input Hysteresis V
MAX14830
CTS0, CTS1, CTS2, CTS3 Input
Leakage Current
RX0, RX1, RX2, RX3 Pullup
Current
Input Capacitance C
IL
IH
HYST
I
IN_CTS
I
IN_RX_VRX_
IN_UART
GPIO0–GPIO15 INPUTS/OUTPUTS
Output Low Voltage V
Output High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input High Voltage V
Pulldown Current I
OL
OH
IL
IH
PD
XIN
Input Low Voltage V
Input High Voltage V
Input Capacitance C
IL
IH
XIN
XOUT
Input Capacitance C
XOUT
= +1.71V to +3.6V, TA = -40NC to +85NC, unless otherwise noted. Typical values
EXT
0.7 x V
V
CTS_
= 0 to V
EXT
-1 +1
= 0V -7.5 -5.5 -3.5
I
LOAD
= -20mA, V
> 2.3V, push-pull or
EXT
open drain
I
LOAD
= -20mA, V
< 2.3V, push-pull or
EXT
open drain
I
= 5mA, push-pull V
LOAD
GPIO_ is configured as an input 0.4 V
GPIO_ is configured as an input 2/3 x V
GPIO_ = V
EXT
3.5 5.5 7.5
1.2 V
0.3 x V
EXT
50 mV
5 pF
0.45
0.55
EXT
EXT
0.2 V
16 pF
16 pF
EXT
FA
FA
- 0.4 V
FA
V
V
V
V
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VA = +2.35V to +3.6V, VL = +1.71V to +3.6V, V
are at VA = +2.8V, VL = +1.8V, V
= +2.5V, TA = +25NC.) (Notes 2, 3)
EXT
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
INTERNAL OSCILLATOR
External Crystal Frequency f
External Clock Frequency f
XOSC
CLK
External Clock Duty Cycle (Note 5) 45 55 %
Baud-Rate Generator Clock
Input
f
REF
10
= +1.71V to +3.6V, TA = -40NC to +85NC, unless otherwise noted. Typical values
EXT
1 4 MHz
0.5 35 MHz
(Note 5) 96 MHz
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VA = +2.35V to +3.6V, VL = +1.71V to +3.6V, V
are at VA = +2.8V, VL = +1.8V, V
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
I2C BUS: TIMING CHARACTERISTICS (SEE FIGURE 1)
SCL Clock Frequency f
Bus Free Time Between a STOP
and START Condition
Hold Time for START Condition
and Repeated START Condition
Low Period of the SCL Clock t
High Period of the SCL Clock t
Data Hold Time t
Data Setup Time t
Setup Time for Repeated START
Condition
Rise Time of SDA and SCL
Signals Receiving
Fall Time of SDA and SCL
Signals
Setup Time for STOP Condition t
Capacitive Load for SDA and
SCL (Note 4)
= +2.5V, TA = +25NC.) (Notes 2, 3)
EXT
SCL
t
BUF
t
HD:STA
LOW
HIGH
HD:DAT
SU:DAT
t
SU:STA
t
R
t
F
SU:STO
C
b
= +1.71V to +3.6V, TA = -40NC to +85NC, unless otherwise noted. Typical values
EXT
Standard mode 100
Fast mode plus 1000
Standard mode 4.7
Fast mode 1.3
Fast mode plus 0.5
Standard mode 4.0
Fast mode 0.6
Fast mode plus 0.26
Standard mode 4.7
Fast mode 1.3
Fast mode plus 0.5
Standard mode 4.0
Fast mode 0.6
Fast mode plus 0.26
Standard mode 0 0.9
Fast mode 0 0.9
Fast mode plus 0
Standard mode 250
Fast mode plus 50
Standard mode 4.7
Fast mode 0.6
Fast mode plus 0.26
Standard mode (0.3 x VL to 0.7 x VL)
(Note 6)
Fast mode (0.3 x VL to 0.7 x VL) (Note 6)
Fast mode plus 120
Standard mode (0.7 x VL to 0.3 x VL)
(Note 6)
Fast mode (0.7 x VL to 0.3 x VL) (Note 6)
Fast mode plus 120
Standard mode 4.7
Fast mode 0.6
Fast mode plus 0.26
Standard mode 400
Fast mode plus 550
20 +
0.1C
20 +
0.1C
20 +
0.1C
20 +
0.1C
MAX14830
kHzFast mode 400
Fs
Fs
Fs
Fs
Fs
nsFast mode 100
Fs
b
b
b
b
1000
300
300
300
ns
ns
Fs
pFFast mode 400
11
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VA = +2.35V to +3.6V, VL = +1.71V to +3.6V, V
are at VA = +2.8V, VL = +1.8V, V
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
SCL and SDA I/O Capacitance C
Pulse Width of Spike
Suppressed
SPI BUS: TIMING CHARACTERISTICS (SEE FIGURE 2)
MAX14830
SCLK Clock Period t
SCLK Pulse Width High t
SCLK Pulse Width Low t
CS Fall to SCLK Rise Time
MOSI Hold Time t
MOSI Setup Time t
Output Data Propagation Delay t
MISO Rise and Fall Times t
CS Hold Time
Note 2: All devices are production tested at TA = +25NC. Specifications over temperature are guaranteed by design.
Note 3: Currents entering the IC are negative, and currents exiting the IC are positive.
Note 4: When V18 is powered by an external voltage regulator, the external power supply must have current capability above or
equal to I18.
Note 5: Not production tested. Guaranteed by design.
Note 6: Cb is the total capacitance of either the clock or data line of the synchronous bus in pF.
= +2.5V, TA = +25NC.) (Notes 2, 3)
EXT
I/O
t
SP
CH+CL
CH
CL
t
CSS
DH
DS
DO
FT
t
CSH
= +1.71V to +3.6V, TA = -40NC to +85NC, unless otherwise noted. Typical values
EXT
(Note 5) 10 pF
50 ns
38.4 ns
16 ns
16 ns
0 ns
3 ns
5 ns
20 ns
10 ns
30 ns
12
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Test Circuits/Timing Diagrams
MAX14830
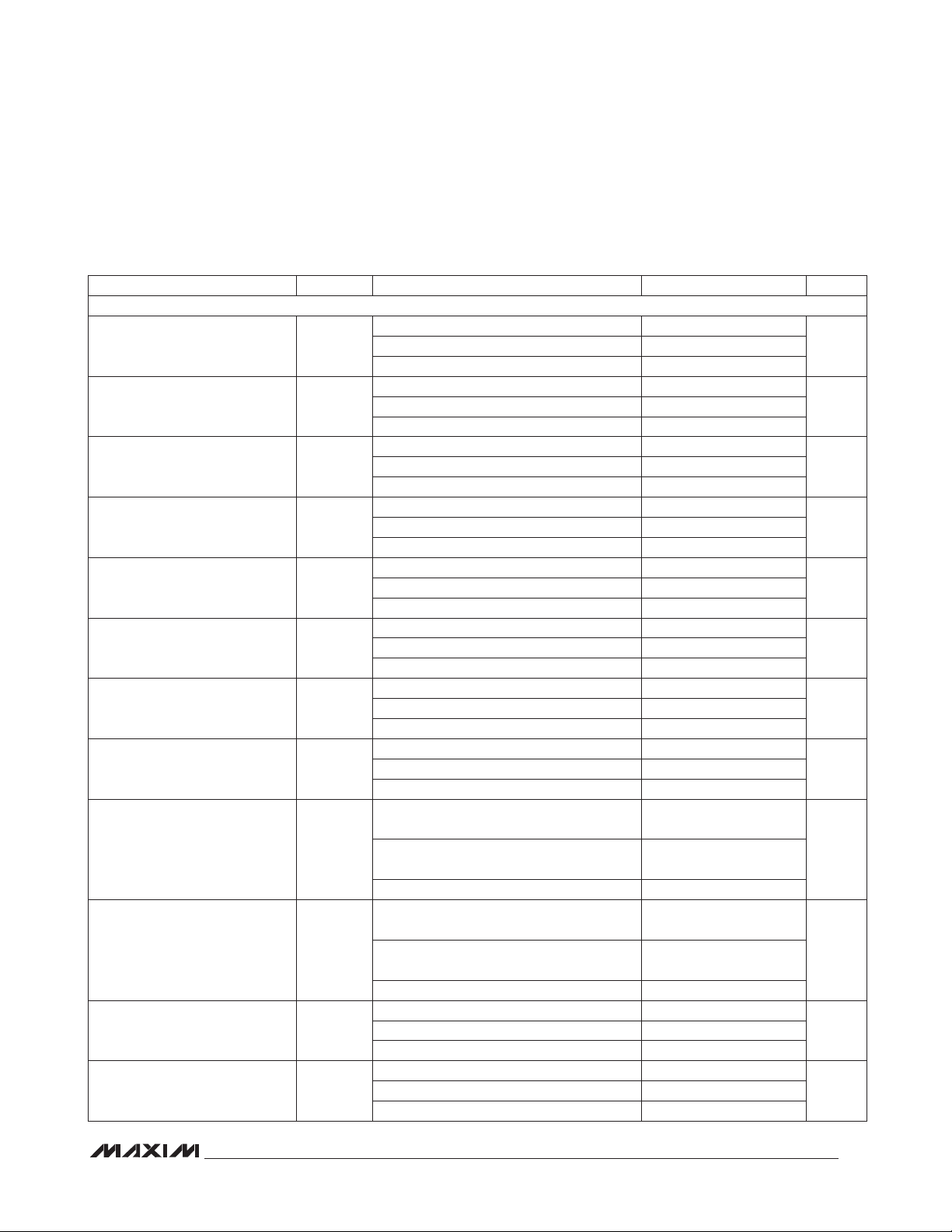
START CONDITION
(S)
SDA
t
HD:STA
SCL
Figure 1. I2C Timing Diagram
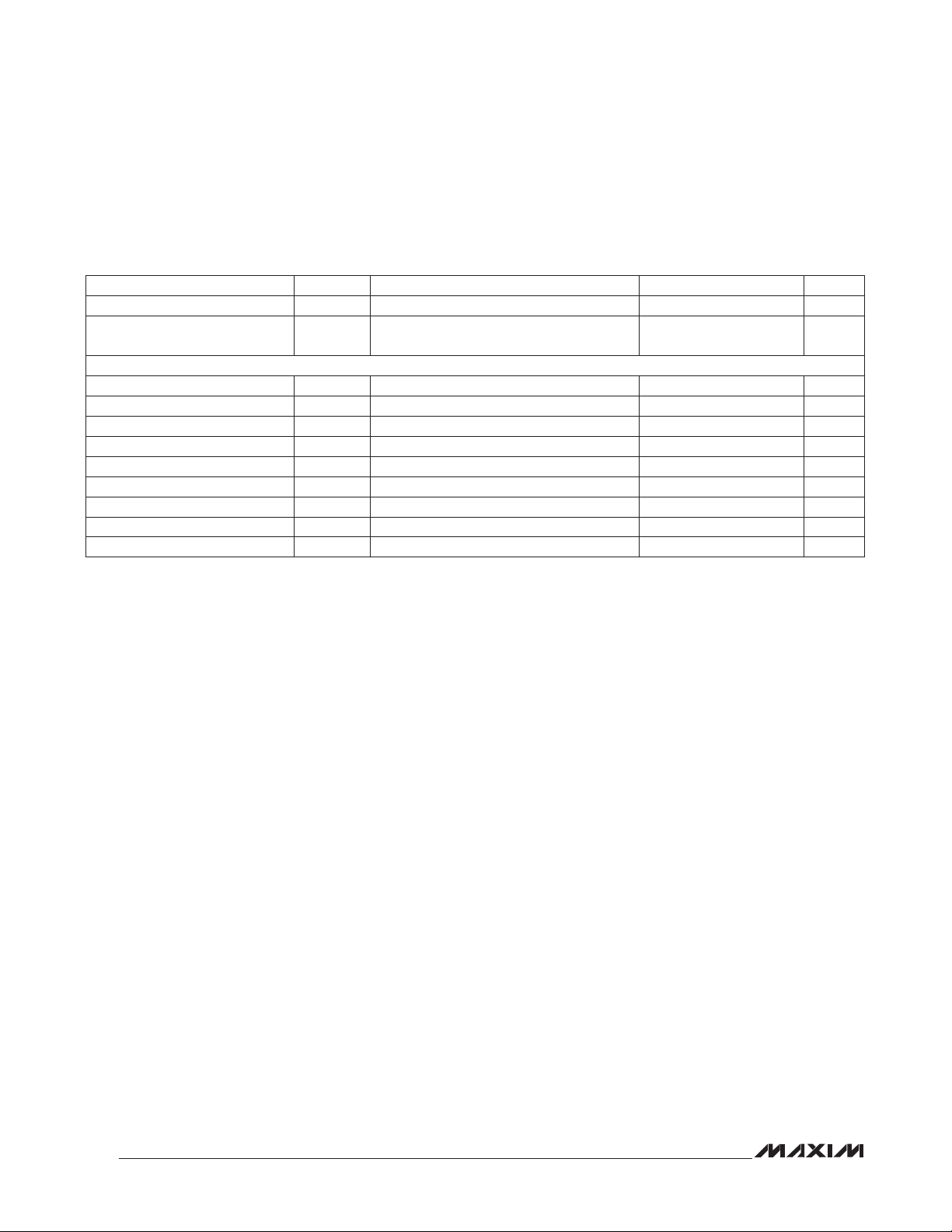
CS
SCLK
t
CSS
t
HD:DAT
t
t
DS
t
SU:DAT
HIGH
t
DH
REPEATED START CONDITION
t
SU:STA
t
R
t
CL
t
F
t
CH
(Sr)
t
t
HD:STA
t
LOW
R
t
SU:STO
t
F
STOP CONDITION
t
CSH
(P)
t
BUF
START CONDITION
(S)
MOSI
MISO
Figure 2. SPI Timing Diagram
t
DO
13
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
04
04
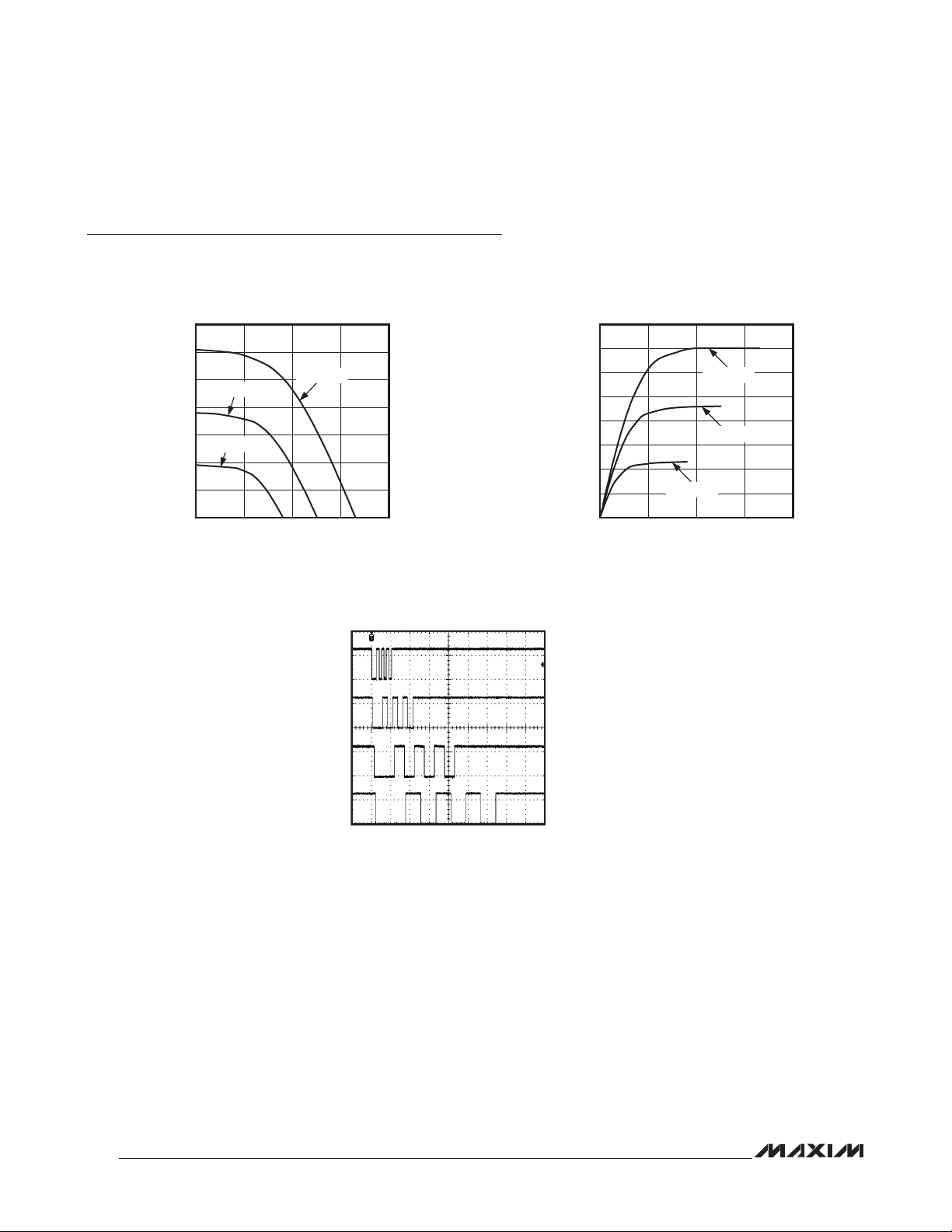
Typical Operating Characteristics
(T
= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
A
GPIO_ OUTPUT HIGH VOLTAGE
vs. SOURCE CURRENT (PUSH-PULL)
70
60
MAX14830
50
40
(mA)
30
SOURCE
I
20
10
V
EXT
V
= 1.8V
EXT
0
= 2.5V
VOH (V)
GPIO_ OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE
vs. SINK CURRENT (PUSH-PULL)
160
V
= 3.3V
EXT
321
MAX14830 toc01
TRANSMITTER SYNCHRONIZATION
200µs/div
MAX14830 toc03
140
120
100
(mA)
80
SINK
I
60
40
20
0
TX0
2V/div
138.46kbaud
TX1
2V/div
19.23kbaud
TX2
2V/div
9.615kbaud
TX3
2V/div
6.41kbaud
V
EXT
VOL (V)
= 1.8V
V
= 3.3V
EXT
V
= 2.5V
EXT
321
MAX14830 toc02
14
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
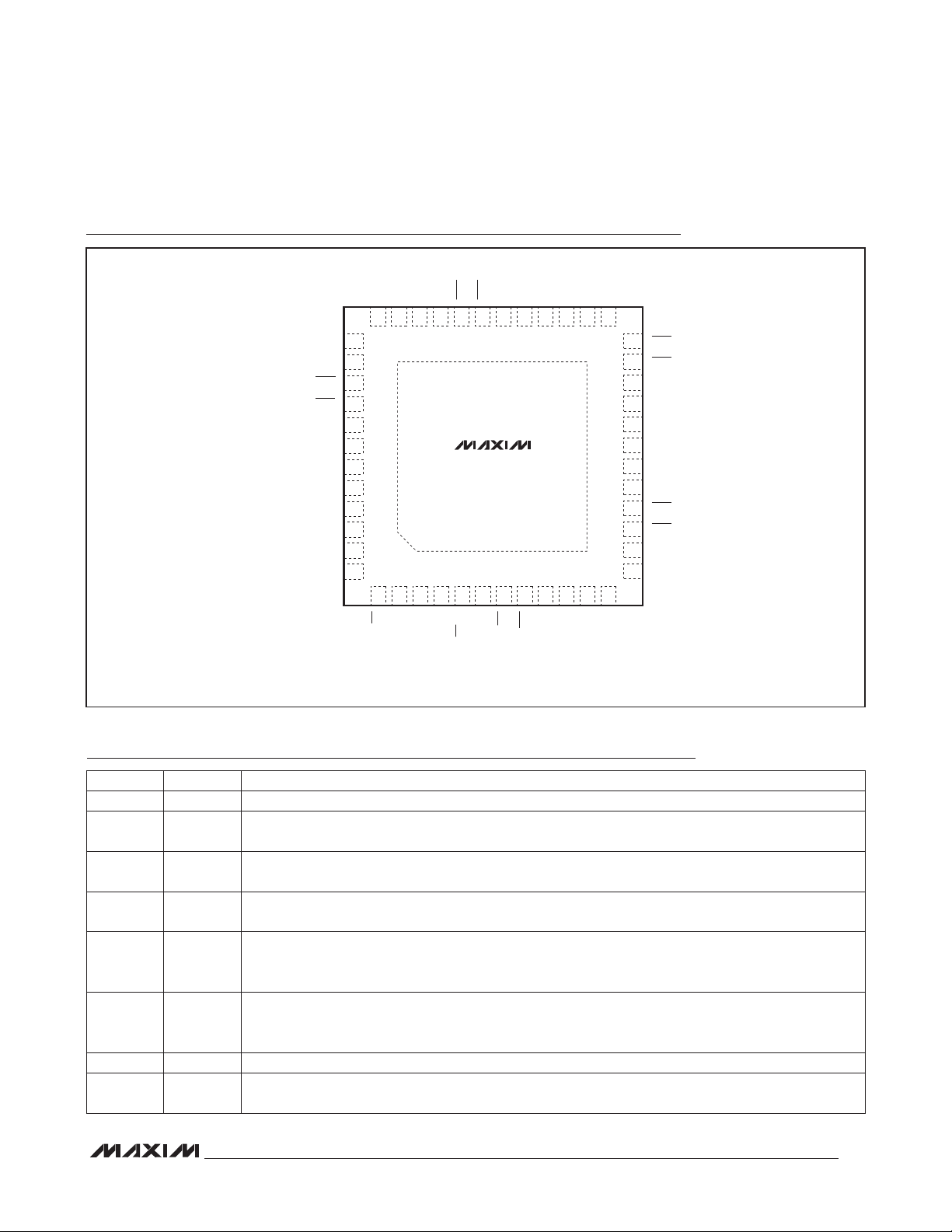
Pin Configuration
MAX14830
TOP VIEW
GPIO14
37
GPIO15
38
39
RTS3
40
CTS3
RX3
41
TX3
42
43
V
EXT
44
XOUT
45
XIN
AGND
46
V
47
A
48
V
18
*CONNECT EP TO AGND.
GPIO12
GPIO13
35
34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27
36
TX2
RX2
CTS2
MAX14830
+
2
345 678910
1
SPI/I2C
LDOEN
SCLK/SCL
MISO/SDA
CS/A0
(7mm
RTS2
MOSI/A1
TQFN
×
GPIO11
IRQ
7mm)
GPIO10
RST
GPIO9
L
V
*EP
GPIO8
26
11
DGND
TX1
25
12
GPIO0
RX1
GPIO1
24
CTS1
23
RTS1
22
GPIO7
21
GPIO6
GPIO5
20
GPIO4
19
18
TX0
17
RX0
16
CTS0
15
RTS0
GPIO3
14
13
GPIO2
Pin Description
PIN NAME FUNCTION
1
2 LDOEN
3 MISO/SDA
4 SCLK/SCL
5
6 MOSI/A1
7
8
SPI/I2C SPI or Active-Low I2C Selector Input. Drive SPI/I2C high to enable SPI. Drive SPI/I2C low to enable I2C.
LDO Enable Input. Drive LDOEN high to enable the internal 1.8V LDO. Drive LDOEN low to disable the
internal LDO. When LDOEN is low, V
can be supplied by an external voltage source.
18
Serial-Data Output. When SPI/I2C is high, MISO/SDA functions as the MISO, SPI serial-data output.
When SPI/I2C is low, MISO/SDA functions as the SDA, I2C serial-data input/output.
Serial-Clock Input. When SPI/I2C is high, SCLK/SCL functions as the SCLK, SPI serial-clock input (up
to 26MHz). When SPI/I2C is low, SCLK/SCL functions as the SCL, I2C serial-clock input (up to 1MHz).
Active-Low Chip-Select and Address 0 Input. When SPI/I2C is high, CS/A0 functions as the CS, SPI
CS/A0
active-low chip-select input. When SPI/I2C is low, CS/A0 functions as the A0, I2C device address programming input. Connect CS/A0 to SDA, SCL, DGND, or VL when SPI/I2C is low.
Serial-Data and Address 1 Input. When SPI/I2C is high, MOSI/A1 functions as the MOSI, SPI serialdata input. When SPI/I2C is low, MOSI/A1 functions as the A1, I2C device address programming input.
Connect MOSI/A1 to SDA, SCL, DGND, or VL when SPI/I2C is low.
IRQ Active-Low Interrupt Open-Drain Output. IRQ is asserted when an interrupt is pending.
RST
Active-Low Reset Input. Drive RST low to force all of the UARTs into hardware reset mode. In hardware
reset mode, the oscillator and the internal PLL are shut down and there is no clock activity.
15
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Pin Description (continued)
PIN NAME FUNCTION
Digital Interface Logic-Level Supply. VL powers the internal logic-level translators for RST, IRQ, MOSI/
9 V
10 DGND Digital Ground
MAX14830
11 GPIO0
12 GPIO1
13 GPIO2
14 GPIO3
15
16
17 RX0 Serial Receiving Data Input for UART0. RX0 has a weak pullup to V
18 TX0 Serial Transmitting Data Output for UART0
19 GPIO4
RTS0
CTS0 Active-Low Clear-to-Send Input for UART0. CTS0 is a flow control status input.
A1, CS/A0, SCLK/SCL, MISO/SDA, LDOEN, and SPI/I2C. Bypass VL with a 0.1FF ceramic capacitor to
L
DGND.
General-Purpose Input/Output 0. GPIO0 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or open
drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO0 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground. GPIO0 is the
reference clock output when bit 7 of the TxSynch register is set to 1 (see the UART Clock to GPIO section for more information).
General-Purpose Input/Output 1. GPIO1 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or open
drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO1 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground. GPIO1 is the
TIMER output when bit 7 of the TIMER2 register is set to 1.
General-Purpose Input/Output 2. GPIO2 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or open
drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO2 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground.
General-Purpose Input/Output 3. GPIO3 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or open
drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO3 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground.
Active-Low Request-to-Send Output for UART0. RTS0 can be set high or low by programming the LCR
register. RTS0 is the UART system clock/fractional divider output when bit 7 of the CLKSource register
is set to 1.
.
EXT
General-Purpose Input/Output 4. GPIO4 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or open
drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO4 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground. GPIO4 is the
reference clock output when bit 7 of the TxSynch register is set to 1 (see the UART Clock to GPIO section for more information).
General-Purpose Input/Output 5. GPIO5 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or open
20 GPIO5
21 GPIO6
22 GPIO7
23
24
25 RX1 Serial Receiving Data Input for UART1. RX1 has a weak pullup to V
26 TX1 Serial Transmitting Data Output for UART1
27 GPIO8
16
RTS1
CTS1 Active-Low Clear-to-Send Input for UART1. CTS1 is a flow control status input.
drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO5 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground. GPIO5 is the
TIMER output when bit 7 of the TIMER2 register is set to 1.
General-Purpose Input/Output 6. GPIO6 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or open
drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO6 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground.
General-Purpose Input/Output 7. GPIO7 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or open
drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO7 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground.
Active-Low Request-to-Send Output for UART1. RTS1 can be set high or low by programming the LCR
register. RTS1 is the UART system clock/fractional divider output when bit 7 of the CLKSource register
is set to 1.
General-Purpose Input/Output 8. GPIO8 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or open
drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO8 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground. GPIO8 is the
reference clock output when bit 7 of the TxSynch register is set to 1 (see the UART Clock to GPIO section for more information).
EXT
.
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Pin Description (continued)
PIN NAME FUNCTION
General-Purpose Input/Output 9. GPIO9 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or open
28 GPIO9
29 GPIO10
30 GPIO11
31
32
33 RX2 Serial Receiving Data Input for UART2. RX2 has a weak pullup to V
34 TX2 Serial Transmitting Data Output for UART2
35 GPIO12
36 GPIO13
37 GPIO14
38 GPIO15
39
40
41 RX3 Serial Receiving Data Input for UART3. RX3 has a weak pullup to V
42 TX3 Serial Transmitting Data Output for UART3
43 V
44 XOUT
45 XIN
46 AGND Analog Ground
47 V
48 V
— EP Exposed Paddle. Connect EP to AGND. Do not use EP as the main AGND connection.
RTS2
CTS2 Active-Low Clear-to-Send Input for UART2. CTS2 is a flow control status input.
RTS3
CTS3 Active-Low Clear-to-Send Input for UART3. CTS3 is a flow control status input.
EXT
drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO9 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground. GPIO9 is the
TIMER output when bit 7 of the TIMER2 register is set to 1.
General-Purpose Input/Output 10. GPIO10 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or
open drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO10 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground.
General-Purpose Input/Output 11. GPIO11 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or
open drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO11 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground.
Active-Low Request-to-Send Output for UART2. RTS2 can be set high or low by programming the LCR
register. RTS2 is the UART system clock/fractional divider output when bit 7 of the CLKSource register
is set to 1.
.
EXT
General-Purpose Input/Output 12. GPIO12 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull
or open drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO12 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground.
GPIO12 is the reference clock output when bit 7 of the TxSynch register is set to 1 (see the UART
Clock to GPIO section for more information).
General-Purpose Input/Output 13. GPIO13 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull
or open drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO13 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground.
GPIO13 is the TIMER output if bit 7 of the TIMER2 register is set to 1.
General-Purpose Input/Output 14. GPIO14 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or
open drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO14 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground.
General-Purpose Input/Output 15. GPIO15 is user-programmable as an input or output (push-pull or
open drain) or external event interrupt source. GPIO15 has a weak pulldown resistor to ground.
Active-Low Request-to-Send Output for UART3. RTS3 can be set high or low by programming the LCR
register. RTS3 is the UART system clock/fractional divider output when bit 7 of the CLKSource register
is set to 1.
.
EXT
Transceiver Interface Level Supply. V
CTS_, and GPIO_. Bypass V
Crystal Output. When using an external crystal, connect one end of the crystal to XOUT and the other
to XIN. When using an external clock source, leave XOUT unconnected.
Crystal/Clock Input. When using an external crystal, connect one end of the crystal to XIN and the
other one to XOUT. When using an external clock source, drive XIN with the external clock.
Analog Supply. VA powers the PLL, and the internal LDO. Bypass VA with a 0.1FF ceramic capacitor to
A
AGND.
Internal 1.8V LDO Output and 1.8V Logic Supply Input. Bypass V18 with a 1FF ceramic capacitor to
18
DGND.
with a 0.1FF ceramic capacitor to DGND.
EXT
powers the internal logic-level translators for RX_, TX_, RTS_,
EXT
MAX14830
17

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Detailed Description
The MAX14830 quad UART bridges an SPI/MICROWIRE™
or I2C microprocessor bus to an asynchronous interface
like RS-485, RS-232, or IrDA. The MAX14830 contains
advanced UARTs and baud-rate generators with a
synchronous serial-data interface and an interrupt generator. The MAX14830 is configured by writing an 8-bit
word to the configuration registers through either SPI or
I2C. These registers are organized by related function as
MAX14830
shown in the Register Map.
The host controller loads transmit data into the THR
register through SPI or I2C. This data is automatically
pushed into the Transmit FIFOs, formatted, and sent out
at TX_. The MAX14830 adds START and STOP and parity bits to the data and sends the data out at the selected
baud rates. The clock configuration registers determine
the baud rates, clock source selection, clock frequency
prescaling, and fractional baud-rate generators.
The MAX14830 receiver detects a START bit as a highto-low RX_ transition. An internal clock samples this data
at 16 times the data rate. The received data is automatically placed in the Receive FIFOs and can then be read
out of the RxFIFOs through the RHRs.
The MAX14830 features four identical UARTS. Text in
this data sheet references individual UART operation,
unless otherwise noted.
generates an interrupt when the Transmit FIFO level
is above the programmed trigger level. The host then
knows to throttle data writing to the Transmit FIFO.
The host can read out the number of words present in
each of the FIFOs at any time through the TxFIFOLvl and
RxFIFOLvl registers.
Transmitter Operation
Figure 3 shows the structure of the transmitter with the
TxFIFO. The Transmit FIFO can hold up to 128 words
that are written to it through the Transmit Hold Register
(THR).
The current number of words in the TxFIFO can be read
out through the TxFIFOLvl register. The Transmit FIFO
can be programmed to generate an interrupt when a
programmed number of words are present in the TxFIFO
through the FIFOTrgLvl register. The TxFIFO interrupt
trigger level is selectable through FIFOTrgLvl[3:0]. When
the Transmit FIFO fill level reaches the programmed trigger level, the ISR[4] interrupt is set.
The Transmit FIFO is empty when ISR[5]:TFifoEmptyInt
is set. ISR[5] turns high when the transmitter starts transmitting the last word in the TxFIFO. Hence the transmitter
is completely empty after ISR[5] is set with an additional delay equal to the length of a complete character
(including START, parity, and STOP bits).
Receive and Transmit FIFOs
The UART’s receiver and the transmitter each have a
128-word deep FIFO reducing the intervals that the
host processor needs to dedicate for high-speed, highvolume data transfer. As the data rates of the asynchronous RX_ and TX_ interfaces increase and get closer to
those of the host controller’s SPI/I2C data rates, UART
management and flow control can make up a significant
portion of the host’s activity. By increasing FIFO size, the
host is interrupted less often and can utilize SPI and I2C
burst data block transfers to/from the FIFOs.
FIFO trigger levels can generate interrupts to the host
controller, signaling that programmed FIFO fill levels
have been reached. The transmitter and receiver trigger levels are programmed through FIFOTrigLvl with a
resolution of eight FIFO locations. When a Receive FIFO
trigger is generated, the host knows that the Receive
FIFO has a defined number of words waiting to be read
out or that a known number of vacant FIFO locations are
available, ready to be filled. The Transmit FIFO trigger
MICROWIRE is a trademark of National Semiconductor Corp.
18
DATA FROM SPI/I2C
TRIGGER
ISR[4]
LEVEL
TxFIFOLvL
ISR[5]
Figure 3. Transmit FIFO Signals
EMPTY
CURRENT FILL LEVEL
INTERFACE
THR 128
FIFO TRGLVL[3:0]
TRANSMIT
FIFO
TRANSMIT
SHIFT-REGISTER
3
2
1
TX_
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
MAX14830
RECEIVED DATA
MID BIT
SAMPLING
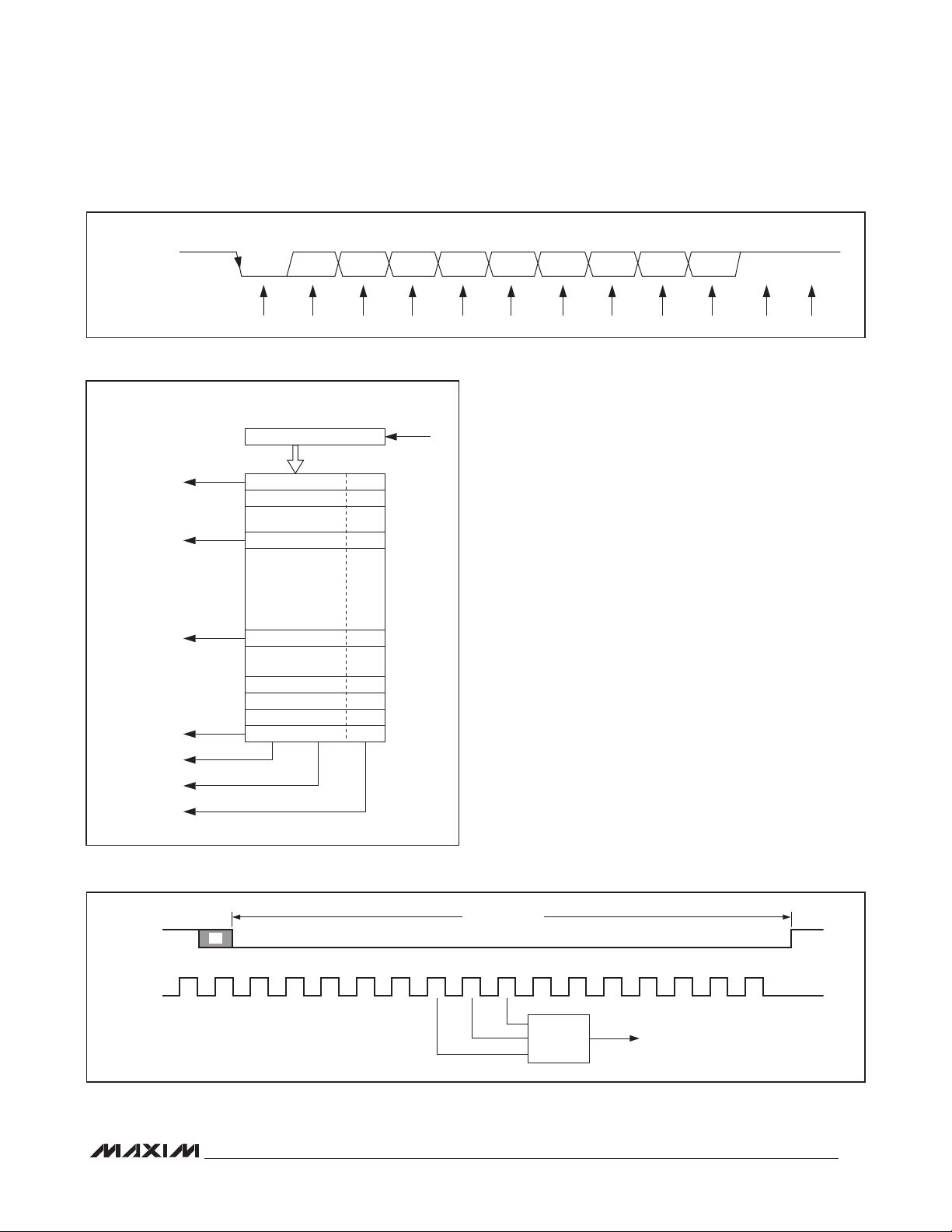
START D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 PARITY STOP STOP
Figure 4. Receive Data Format
ISR[3]
ISR[6]
OVERRUN
TRIGGER
TIMEOUT
EMPTY
ERRORS
LSR[1]
CURRENT FILL LEVEL
I2C/SPI INTERFACE
LSR[0]
LSR[5:2]
Figure 5. Receive FIFO
LSB
RECEIVER RX_
WORD ERROR 128
FIFOTrgLvl[7:4]
RECEIVE FIFO
RxFIFOLvl
RHR
RECEIVED
DATA
4
3
2
1
MSB
The contents of the TxFIFO and RxFIFOs are both
cleared through MODE2[1]: FIFORst.
To halt transmission, set MODE1[1]: TxDisabl to 1. After
MODE1[1] is set, the transmitter completes transmission
of the current character and then ceases transmission.
The TX_ output logic can be inverted through IrDA[5]:
TxInv. If not stated otherwise, all transmitter logic
described in this data sheet assumes that IrDA[5] is 0.
Receiver Operation
The receiver expects the format of the data at RX_ to be
as shown in Figure 4. The quiescent logic state is high
and the first bit (the START bit) is logic-low. The receiver
samples the data near the midbit instant (Figure 4). The
received words and their associated errors are deposited into the Receive FIFO. Errors and status information are stored for every received word (Figure 5). The
host reads the data out of the Receive FIFO through
the Receive Hold Register (RHR), oldest data first. The
status information of the most recently read word in the
RHR is located in the Line Status Register (LSR). After a
word is read out of the RHR, the LSR contains the status
information for that word.
The following three error conditions are determined for
each received word: parity error, framing error, and
noise on the line. Line noise is detected by checking the
consistency of the logic of the three samples (Figure 6).
RX_
BAUD
BLOCK
A
1
Figure 6. Midbit Sampling
ONE BIT PERIOD
23456789
10 11
MAJORITY
CENTER
SAMPLER
12 13 14 15 16
19
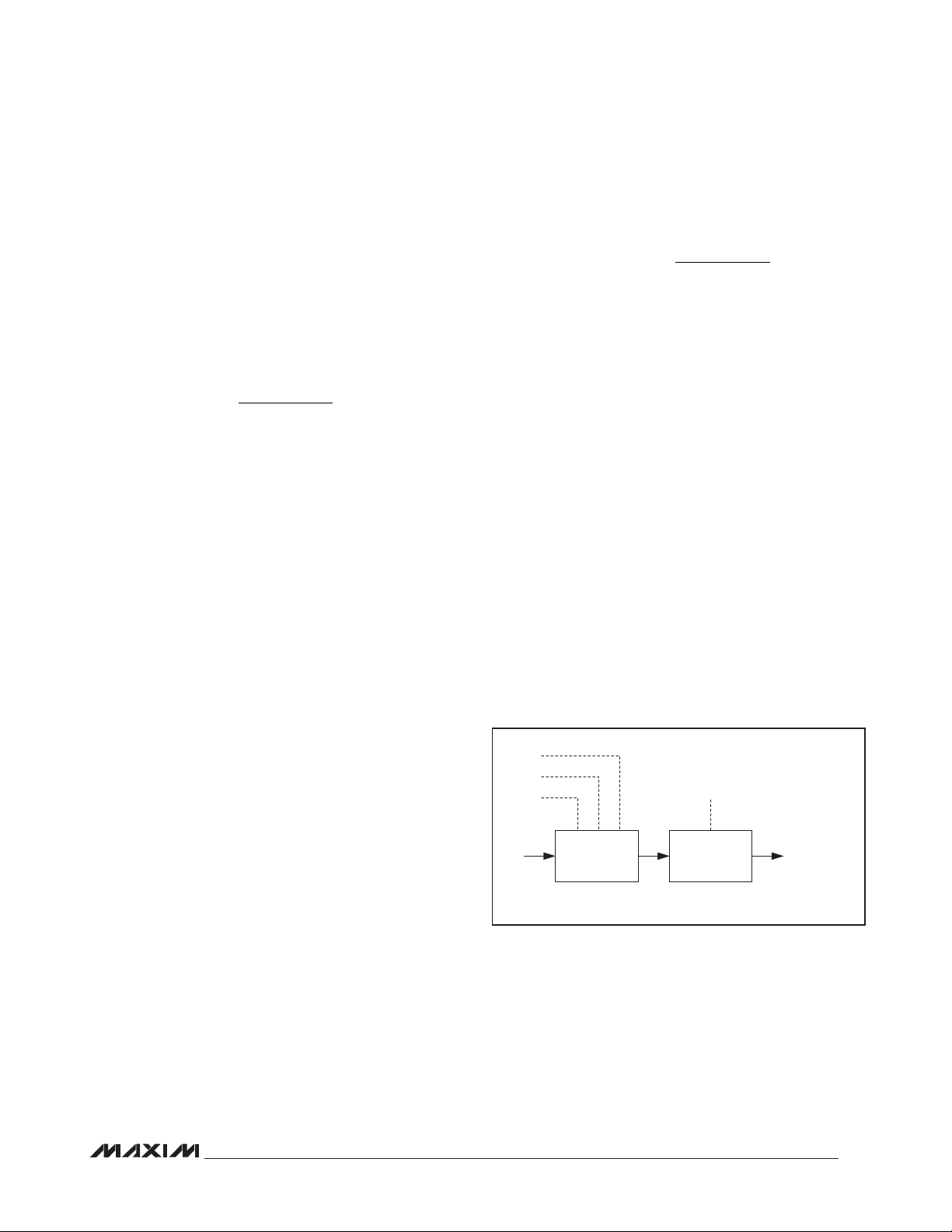
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
The receiver can be turned off through MODE1[0]:
RxDisabl. When this bit is set to 1, the MAX14830 turns
the receiver off immediately following the current word
and does not receive any further data.
The RX_ input logic can be inverted through IrDA[4]:
RxInv.
Line Noise Indication
When operating in standard or 2x (i.e. not 4x) rate mode,
the MAX14830 checks that the binary logic level of the
MAX14830
three samples per received bit are identical. If any of
the three samples have differing logic levels, then noise
on the transmission line has affected the received data
and is considered to be noisy. This noise indication is
reflected in the LSR[5]: RxNoise bit for each received
byte. Parity errors are another indication of noise, but are
not as sensitive.
Clocking and Baud-Rate Generation
The MAX14830 can be clocked by an external crystal,
or an external clock source. Figure 7 shows a simplified
diagram of the clocking circuitry. When the MAX14830
is clocked by a crystal, the STSInt[5]: ClockReady indicates when the clocks have settled and the baud-rate
generator is ready for stable operation.
Each UART baud rate can be individually programmed.
To achieve fast baud rate changes, first disable the
UART's clock by setting CLKDisabl to 1. Then change
the baud rate divisor and subsequently enable the clock
via CLKDisabl.
To check that the UART's clocking is programmed as
expected, route the baud rate clock to RTS using the
CLKtoRTS bit. The clock rate of this is 16x the baud rate
in standard operating mode and 8x the baud rate in 2x
rate mode. In 4x rate mode, the CLKOUT frequency is
4x the programmed baud rate. If the fractional portion of
the baud-rate generator is used, the clock is not regular
and exhibits jitter.
Crystal Oscillator
Set BRGConfig[6]: CLKDisabl to 0 and CLKSource[1]:
CrystalEn to 1 to enable and select the crystal oscillator. The on-chip crystal oscillator circuit has load
capacitances of 16pF (typ) integrated in both XIN and
XOUT. Connect an external crystal or ceramic oscillator
between XIN and XOUT.
External Clock Source
Connect an external clock source to XIN when not using
a crystal oscillator. Leave XOUT unconnected. Set
CLKSource[1]: CrystalEn to 0 to select external clocking.
PLL and Predivider
The internal predivider and PLL allow for a wide range of
external clock frequencies and baud rates. The PLL can
be configured to multiply the input clock rate by a factor
of 6, 48, 96, or 144 through the PLLConfig register. The
predivider, located between the input clock and the PLL,
allows division of the input clock by a factor between 1
and 63 by writing to PLLConfig[5:0]. See the PLLConfig
register description for more information.
XOUT
XIN
Figure 7. Clock Selection Diagram
20
CRYSTAL
OSCILLATOR
CrystalEn
DIVIDER
PLLEn ClkDisabl[0...3]
PLLBypass
PLL
FRACTIONAL
BAUD RATE
GENERATOR 0
FRACTIONAL
BAUD RATE
GENERATOR 1
FRACTIONAL
BAUD RATE
GENERATOR 2
FRACTIONAL
BAUD RATE
GENERATOR 3
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Fractional Baud-Rate Generators
The internal fractional baud-rate generator provides a
high degree of flexibility and high resolution in baudrate programming. The baud-rate generator has a 16-bit
integer divisor and a 4-bit word for the fractional divisor.
The fractional baud-rate generator can be used with the
external crystal or clock source.
The integer and fractional divisors are calculated through
the divisor, D:
f
D
=
where f
is the reference frequency input to the baud-
REF
rate generator and D is the ideal divisor. In 2x and 4x rate
modes, replace the divisor 16 by 8 or 4, respectively.
The integer divisor portion, DIV, of the divisor, D, is
obtained by truncating D:
DIV = TRUNC(D)
DIV can be a maximum of 16 bits wide and is programmed into the 2-byte-wide registers DIVMSB and
DIVLSB. The minimum allowed value for DIVLSB is 1.
The fractional portion of the divisor, FRACT, is a 4-bit
nibble, which is programmed into BRGConfig[3:0]. The
maximum value is 15, allowing the divisor to be programmed with a resolution of 0.0625. FRACT is calculated as:
FRACT = ROUND(16 x (D-DIV)).
The following is an example of calculating the divisor.
It is based on a required baud rate of 190kbaud and a
reference input frequency of 28.23MHz and default rate
mode.
The ideal divisor is calculated as:
D = 28,230,000 / (16 x 190,000) = 9.286
hence DIV = 9.
FRACT = ROUND(4.579) = 0x05
so that DIVMSB = 0x00, DIVLSB = 0x09, and
BRGConfig[3:0] = 0x05.
REF
16 BaudRate
×
The resulting actual baud rate can be calculated as:
f
BR
ACTUAL
For this example: D
D
ACTUAL
BR
= DIV + (FRACT/16) and
ACTUAL
= 28,230,000 / (16 x 9.3125) = 189,463.087
ACTUAL
REF
16 D=×
ACTUAL
= 9 + 5/16 = 9.313, where
baud.
Thus the baud rate is within 0.28% of the ideal rate.
2x and 4x Rate Modes
To support higher baud rates than possible with standard (16x sampling) operation, the MAX14830 offers 2x
and 4x rate modes. In this case, the reference clock rate
only needs to be either 8x or 4x of the baud rate, respectively. In 4x mode only, the bits are only sampled once,
at the midbit instant, instead of the usual three samples
to determine the logic value of the bits. This reduces the
tolerance to line noise on the received data. The 2x and
4x modes are selectable through BRGConfig[5:4]. Note
that IrDA encoding and decoding does not operate in 2x
and 4x modes.
When 2x rate mode is selected, the actual baud rate is
twice the rate programmed into the baud-rate generator. If 4x rate mode is enabled, the actual baud rate on
the line is quadruple that of the programmed baud rate
(Figure 8).
DIVLSB
DIVMSB
FRACT
f
REF
NOTE: IrDA DOES NOT WORK IN 2x AND 4x MODES.
Figure 8. 2x and 4x Baud Rates
FRACTIONAL
RATE
GENERATOR
BRGConfig[5:4]
RATE MODE
SELECTION
1 x BAUD RATE,
2 x BAUD RATE,
4 x BAUD RATE
MAX14830
21

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
UART_
f
REF
Figure 9. GPIO_ Clock Pulse Generator
MAX14830
The general-purpose timer can be used to generate a
Low-Frequency Timer
FRACTIONAL
RATE
GENERATOR
low-frequency clock at a GPIO output and can, for example, be used to drive external LEDs. The low-frequency
clock is a divided replica of a given UART baud-rate
clock. The timer is internally routed to the GPIO_ outputs
when enabled in the TIMER2 register as follows:
•UART0:GPIO1
•UART1:GPIO5
•UART2:GPIO9
•UART3:GPIO13
The clock pulses at the GPIOs are generated at a rate
defined by the baud-rate generator and the timer divider
(Figure 9). The baud-rate generator clock is divided by
(1024 x TIMERx), where TIMERx is a 15-bit integer programmed into the TIMER1 and TIMER2 registers. The
timer output is a 50% duty cycle clock.
UART Clock to GPIO
The MAX14830 reference clock can be routed to the
GPIO0, GPIO4, GPIO8, and/or GPIO12 outputs in case a
synchronous high-frequency clock is needed by another
device. Enable routing a UART clock to GPIO0, GPIO4,
GPIO8, and/or GPIO12 in the TxSynch register. This output clock could, for example, be used to clock another
UART device (Figure 29).
Multidrop Mode
In Multidrop Mode, also known as 9-bit mode, the word
length is 8 bits and a 9th bit is used for distinguishing
between an address and a data word. Multidrop mode is
enabled through MODE2[6]: MultiDrop. Parity checking
is disabled and an SpclCharInt[5]: MultiDropInt interrupt
is generated when an address (9th bit set) is received.
It is up to the host processor to filter out the data intended
for its address. Alternatively the auto data filtering mode
can be used to automatically filter out the data intended
for the station’s specific 9-bit mode address.
DIVIDE-BY-1024
TmrtoGPIO
TIMERx
GPIO_
GPIO_
Auto Data Filtering in Multidrop Mode
In multidrop mode, the MAX14830 can be configured
to automatically filter out data that is not meant for its
address. The address is user-definable either by programming a register value or a combination of a register
value and GPIO hardware inputs. Use either XOFF2 or
XOFF2[7:4] in combination with GPIO_ to define the
address.
Enable multidrop mode by setting MODE2[6]: MultiDrop
to 1 and enable auto data filtering by setting MODE2[4]:
SpecialChr to 1.
When using register bits in combination with GPIO_ to
define the address, the MSB of the address is written to
XOFF2[7:4] register bits, while the LSBs of the address
are defined through the GPIOs. To enable this mode,
set FlowCtrl[2]: GPIAddr, MODE2[4]: SpecialChr, and
MODE2[6]: MultiDrop to 1. GPIO_ are automatically read
when FlowCtrl[2]: GPIAddr is set to 1, and the address
is updated on logic changes at GPIO_.
In the auto data filtering mode, the MAX14830 automatically accepts data that is meant for its address and
places this into the Receive FIFO, while it discards data
that is not meant for its address. The received address
word is not put into the FIFO.
Auto Transceiver Direction Control
In some half-duplex communication systems the transceiver’s transmitter must be turned off when data is
being received so as not to load the bus. This is the
case in half-duplex RS-485 communication. Similarly
in full-duplex multidrop communication, like RS-485
or RS-422/V.11, only one transmitter can be enabled
at any one time and the others must be disabled. The
MAX14830 can automatically enable/disable a transceiver’s transmitter and/or receiver. This relieves the host
processor of this time-critical task.
The RTS_ output is used to control the transceivers’
transmit enable input and is automatically set high
when the MAX14830’s transmitter starts transmission.
22

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
This occurs as soon as data is present in the Transmit
FIFO. Auto transceiver direction control is enabled
through MODE1[4]: TrnscvCtrl. Figure 10 shows a typical
MAX14830 connection in a RS-485 application.
The RTS_ output can be set high in advance of TX_
transmission by a programmable time period called the
setup time (Figure 11). The setup time is programmed
through HDplxDelay[7:4]. Similarly, the RTS_ signal
can be held high for a programmable period after the
transmitter has completed transmission. The hold time is
programmed through HDplxDelay[3:0].
Transmitter Triggering and Synchronization
The MAX14830 allows synchronization of transmitters
so that selected UARTs start transmitting data when a
trigger command is received. Optional delays can also
be programmed, which delay the start of transmission
after a trigger command is received. A UART’s transmitter can be assigned one of 16 possible SPI/I2C trigger
commands. A trigger command is defined as any of 16
special values written into the GloblComnd register (see
the GloblComnd section for more information). When a
byte is written into the GloblComnd register, UART select
Tx FIFO
MAX14830
Rx FIFO
Figure 10. Auto Transceiver Direction Control
TRANSMITTER
AUTO
TRANSCEIVER
CONTROL
RECEIVER
TX_ DI
RTS_
RX_
D
DE
B
MAX14840E
RE
RO
R
A
bits (U0 and U1) are ignored by the MAX14830, and the
MAX14830
GloblComnd applies to all four UARTs. Transmission is
initiated when the MAX14830 receives the assigned SPI/
I2C trigger command if the selected transmitter is initially
disabled and data has been loaded into its TxFIFO.
Enable and configure transmitter synchronization in
the TxSynch register. Triggering and synchronization
requires that the TxFIFOs are disabled before the trigger
is received. This can be done by setting the MODE1[1]
bit to 1 or by utilizing the auto transmitter disable function
(TxSynch[4] is 1).
Transmitter Synchronization
Synchronize multiple UARTs so their transmitters start
transmission simultaneously by assigning a common
trigger command to the UARTs that should be synchronized.
Intrachip and Interchip Synchronization
Intrachip transmitter triggering occurs when any of the
four UARTs in a MAX14830 are triggered by one trigger
command. This type of synchronization is supported in
both SPI and I2C modes, as the trigger commands are
global commands that are received by all four UARTs
simultaneously.
Interchip transmitter triggering occurs when the UARTs
in different MAX14830 devices are synchronized. This
type of synchronization is achievable in SPI mode only.
Pull the CS of all the MAX14830 devices on the bus low
during the SPI master’s write trigger command so that
the commands are received by all UARTs on the shared
SPI bus.
I2C protocol does not allow simultaneous addressing of
multiple devices.
Delayed Triggering
A delay can be programmed for delaying the start of
transmission after the reception of an assigned trigger command. Set the delay by programming the
SynchDelay1 and SynchDelay2 registers.
RTS_
SETUP
TX_
FIRST CHARACTER LAST CHARACTER
Figure 11. Setup and Hold times in Auto Transceiver Direction Control
HOLD
23

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
SCLK
TX_
MAX14830
Figure 12. Single Transmitter Trigger Accuracy
Trigger Accuracy
The delay between the time when the MAX14830
receives a trigger command and the time when the
associated transmitter starts transmission is made up
of a fixed, deterministic portion and a variable, random
component. Both portions of the delay are dependent on
the UART’s clock and baud rates. When the fractional
divider is not used, the intrinsic trigger delay, t
TRIG
bounded by the following limits:
5 BR 6 BR
××
t
≤≤
16 16
TRIG
where BR is the fractional divider output clock period.
This equation is independent on the rate mode. The
reference point is the time when the trigger command is
received by the MAX14830. This occurs on the final (i.e.
the 16th) SPI clock’s low-to-high transition (Figure 12).
When the fractional baud-rate generator is used, the
random portion is larger than one UART clock period.
Synchronization Accuracy
When synchronizing multiple UART transmitters, the
accuracy of the TX_ transmitter outputs is based on the
triggering delays of each UART (Figure 13). This skew
has a baud-rate dependent component, similar to the
trigger accuracy equation for a single transmitter output.
Calculate the TX_ transmitter output skew using the following equation:
6 BR 5 BR
× −×
t max
TRIGSKEW
( )
≤
SF
16
t
TRIG_MIN
t
TRIG_MAX
, is
UNCERTAINTY
INTERVAL
where BRS is the fractional divider output clock of the
lower/slower baud-rate UART and BRF is the fractional
divider output clock of the higher/faster baud-rate UART.
Auto Transmitter Disable
The MAX14830 allows automatic disabling of the transmitter. Enable auto transmitter disabling functionality by
setting TxSynch[4] to 1. When auto transmitter disabling
is activated, the MAX14830 disables the specified
transmitter after it completes sending all the data in its
TxFIFO. New data can then be loaded into the TxFIFO. A
disabled transmitter does not send out data on the TX_
output when data is present in its TxFIFO.
To enable transmission, either clear the TxAutoDis bit
in the TxSynch register or toggle the TxDisabl bit in the
MODE1 register.
Echo Suppression
The MAX14830 can suppress echoed data, sometimes
found in half-duplex communication (e.g. RS-485 and
IrDA). If the transceiver’s receiver is not turned off while
the transceiver is transmitting, copies (echoes) are
received by the UART. The MAX14830’s receiver can
block the reception of this echoed data by enabling echo
suppression. Set MODE2[7]: EchoSuprs to 1 to enable
echo suppression.
The MAX14830 receiver can block echoes with a long
round trip delay. The transmitter can be configured to
remain enabled after the end of transmission for a programmable period of time: the hold time delay (Figure
14). The hold time delay is set by the HDplxDelay[3:0]
register. See the HDplxDelay Register section for more
information.
24

SCLK
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
MAX14830
TX0
TX1
t
TX0_MIN
t
TX0_MAX
t
TX1_MIN
t
TX1_MAX
Figure 13. Multiple Transmitter Synchronization Accuracy
TX_
DI TO RO PROPAGATION DELAY
RX_
BIT
t
TRIGSKEW
HOLD DELAYSTOP
RTS_
Figure 14. Echo Suppression Timing
25

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Echo suppression can operate simultaneously with auto
transceiver direction control (Figure 15).
Auto Hardware Flow Control
The MAX14830 is capable of automatic hardware (RTS
and CTS) flow control without the need for host processor intervention. When AutoRTS control is enabled,
the MAX14830 automatically controls the RTS handshake without the need for host processor intervention.
AutoCTS flow control separately turns the MAX14830’s
MAX14830
transmitter on and off based on the CTS_ input. AutoRTS
and AutoCTS flow control are independently enabled
through FlowCtrl[1:0].
AutoRTS Control
AutoRTS flow control ensures that the Receive FIFO does
not overflow by signaling to the far end UART to stop
data transmission. The MAX14830 does this automatically by controlling RTS_. AutoRTS flow control is enabled
through FlowCtrl[0]: AutoRTS. The HALT and RESUME
levels determine the threshold levels at which RTS_ is
asserted and deasserted. HALT and RESUME are programmed in FlowLvl. With differing HALT and RESUME
levels, hysteresis can be defined for the RTS_ transitions.
When the RxFIFO fill level reaches the HALT level
(FlowLvl[3:0]), the MAX14830 deasserts RTS_. RTS_
remains deasserted until the RxFIFO is emptied and the
number of words falls to the RESUME level.
Interrupts are not generated when the HALT and
RESUME levels are reached. This allows the host controller to be completely disengaged from RTS flow control
management.
TX
TRANSMITTER
Tx FIFO
Rx FIFO
Figure 15. Half-Duplex with Echo Suppression
LOGIC
ECHO
SUPPRESSION
RECEIVER
TX_ DI
RTS_
RX_
D
DE
MAX14840EMAX14830
RE
RO
R
AutoCTS Control
When AutoCTS flow control is enabled, the UART automatically starts transmitting data when the CTS_ input
is logic-level low and stops transmitting when CTS_ is
logic-high. This frees the host processor from managing this timing-critical flow control task. AutoCTS flow
control is enabled through FlowCtrl[1]: AutoCTS. During
AutoCTS flow control, the CTS interrupt works normally.
Set the IRQEn[7]: CTSIntEn to 0 to disable CTS interrupts
then ISR[7]: CTSInt is fixed to logic 0 and the host does
not receive interrupts from CTS_. If CTS_ is set high during transmission the MAX14830 completes transmission
of the current word and halts transmission afterwards.
Turn the transmitter off by setting MODE1[1] to 1 before
enabling AutoCTS control.
FIFO Interrupt Triggering
Receive and Transmit FIFO fill-dependent interrupts are
generated if FIFO trigger levels are defined. When the
number of words in the FIFOs reach or exceed a trigger
level, as programmed in FIFOTrgLvl, an ISR[3] or ISR[4]
interrupt is generated. There is no relationship between
the trigger levels and the HALT or RESUME levels.
The FIFO trigger level can, for example, be used for a
block data transfer, since it gives the host an indication
when a given block size of data is available for reading in
the Receive FIFO or available for transfer to the Transmit
FIFO.
Auto Software (XON/XOFF) Flow Control
When auto software flow control is enabled, the
MAX14830 recognizes and/or sends predefined XON/
XOFF characters to control the flow of data across the
asynchronous serial link. Automatic flow works autonomously and does not involve host intervention, similar
to auto hardware flow control. To reduce the chance of
receiving corrupted data that equals a single-byte XON
or XOFF character, the MAX14830 allows for double
B
wide (16-bit) XON/XOFF characters. XON and XOFF are
programmed into the XON1, XON2 and XOFF1, XOFF2
A
registers.
FlowCtrl[7:3] are used for enabling and configuring auto
software flow control. An ISR[1] interrupt is generated
when XON or XOFF are received and details are found
in SpclCharInt. The IRQ can be masked by setting
IRQEn[1]: SpclChrIEn to 0.
Software flow control consists of transmitter control and
receiver overflow control, which can operate independently of one another.
26

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Transmitter Flow Control
When auto transmitter control (FlowCtrl[5:4]) is enabled,
the receiver compares all received words with the XOFF
and XON characters. If an XOFF character is received,
the MAX14830 halts its transmitter from sending further
data. The receiver is not affected and continues reception.
Upon receiving XON, the transmitter then restarts sending
data. The received XON and XOFF characters are filtered
out and are not put into the Receive FIFO, as they do not
have significance to the higher layer protocol. An inerrupt
is not generated.
Turn the transmitter off (MODE1[1] = 1) before enabling
transmitter control.
Receiver Overflow Control
When auto receiver overflow control (FlowCtrl[7:6]) is
enabled, the MAX14830 automatically sends XOFF and
XON control characters to the far end UART to avoid
receiver overflow. XOFF1/XOFF2 is/are sent when the
Receive FIFO fill level reaches the HALT value set in the
FlowLvl register. When the host controller reads data
from the Receive FIFO to a level equal to the RESUME
level programmed into the FlowLvl register, XON1/XON2
is/are automatically sent to the far end station to signal it
to resume data transmission.
XON1/XOFF1 is transmitted before XON2/XOFF2 when
dual character (XON1 and XON2/XOFF1 and XOFF2)
flow control is enabled.
Power-Up and IRQ
IRQ has two functions. During normal operation
(MODE1[7] = 1), IRQ operates as a hardware interrupt
output, whereby the IRQ is active when an interrupt is
MAX14830
pending. An IRQ interrupt can only be produced during
normal operation if at least one of the IRQEn interrupt
enable bits are enabled.
During power-up or following a reset, IRQ has a different
function. It is held low until the MAX14830 is ready for
programming following an initialization delay. Once IRQ
goes high, the MAX14830 is ready to be programmed.
The MODE1[7]: IRQSel bit should then be set to enable
normal IRQ interrupt operation.
In polled mode, the DIVLSB register can be polled to
check whether the MAX14830 is ready for operation. If
the controller gets a valid response from DIVLSB, then
the MAX14830 is ready for operation.
Shutdown Mode
Pull RST to DGND to enter shutdown mode. Shutdown
mode is the lowest power consumption mode. In shutdown mode, all of the MAX14830 circuitry is off. This
includes the SPI/I2C interface, the registers, the FIFOs,
and clocking circuitry. The LDO is on in shutdown mode.
When the RST input is high, the MAX14830 exits shutdown mode. The chip initialization is completed when the
MAX14830 sets IRQ to logic-high.
The MAX14830 needs to be reprogrammed following a
shutdown.
Interrupt Structure
The structure of the interrupt is shown in Figure 16.
There are four interrupt source registers for each UART:
ISR, LSR, STSInt, and SpclCharInt. Read the GlobalIRQ
00 00
ISR
210
Figure 16. Simplified Interrupt Structure
ISR
210765 43
765 43
POWER-UP
COMPLETED
4
GlobalIRQ
IRQ3
8
ISR
210765 43
STSInt
[4]
[0]
IRQ1 IRQ0IRQ2
8
8
765 43
LOW-LEVEL INTERRUPTS
210
MODE1[7]:IRQSEL
8
ISR
76 5
IRQ
210765 43
8 88
SpclCharInt
43
210
TOP-LEVEL
INTERRUPTS
76543
LSR
210
27

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
register to determine which UART is the source of the
interrupt. The interrupt sources are divided into top-level
and low-level interrupts. The top-level interrupts typically
occur more often and can be read out directly through
the ISR. The low-level interrupts typically occur less often
and their specific source can be read out through the
LSR, STSInt, or SpclChar registers. The three LSBs of the
ISR point to the low-level interrupt registers that contain
the detail of the interrupt source.
MAX14830
Interrupt Enabling
Every interrupt bit of the four interrupt registers can be
enabled or masked through an associated interrupt
enable register bit. These are the IRQEn, LSRIntEn,
SpclChrIntEn, and STSIntEn registers.
Interrupt Clearing
When an ISR interrupt is pending (i.e. any bit in ISR is
set) and the ISR is subsequently read, the ISR bits and
IRQ are cleared. Both the SpclCharInt and the STSInt
registers are also clear on read (COR). The LSR bits are
only cleared when the source of the interrupt is removed,
not when LSR is read.
Reading the GlobalIRQ register does not clear the IRQ
interrupt.
Register Map
(All default reset values are 0x00, unless otherwise noted. All registers are R/W, unless otherwise noted.)
REGISTER ADDR BIT7 BIT6 BIT5 BIT4 BIT3 BIT2 BIT1 BIT0
FIFO DATA
†
RHR
†
THR
INTERRUPTS
IRQEn 0x01 CTSIEn RFifoEmtyIEn TFifoEmtyIEn TFifoTrgIEn RFifoTrgIEn STSIEn SpclChrIEn LSRErrIEn
†
ISR*
LSRIntEn 0x03 — — RxNoiseIntEn RBreakIEn FrameErrIEn ParityIEn ROverrIEn RTimoutIEn
†
LSR*
SpclChrIntEn 0x05 — — MltDrpIntEn BREAKIntEn XOFF2IntEn XOFF1IntEn XON2IntEn XON1IntEn
SpclCharInt
¥
STSIntEn
†¥
STSInt
UART MODES
MODE1 0x09 IRQSel — — TrnscvCtrl RTSHiZ TXHiZ TxDisabl RxDisabl
MODE2 0x0A EchoSuprs MultiDrop LoopBack SpecialChr RxEmtyInv RxTrgInv FIFORst RST
LCR* 0x0B
RxTimeOut 0x0C TimOut7 TimOut6 TimOut5 TimOut4 TimOut3 TimOut2 TimOut1 TimOut0
HDplxDelay 0x0D Setup3 Setup2 Setup1 Setup0 Hold3 Hold2 Hold1 Hold0
IrDA 0x0E — — TxInv RxInv MIR RTSInvert SIR IrDAEn
FIFOs CONTROL
FlowLvl 0x0F Resume3 Resume2 Resume1 Resume0 Halt3 Halt2 Halt1 Halt0
FIFOTrgLvl* 0x10 RxTrig3 RxTrig2 RxTrig1 RxTrig0 TxTrig3 TxTrig2 TxTrig1 TxTrig0
†
TxFIFOLvl
†
RxFIFOLvl
FLOW CONTROL
FlowCtrl 0x13 SwFlow3 SwFlow2 SwFlow1 SwFlow0 SwFlowEn GPIAddr AutoCTS AutoRTS
XON1 0x14 Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
XON2 0x15 Bit7 Bi6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
XOFF1 0x16 Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
XOFF2 0x17 Bit7 Bi6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0x00 RData7 RData6 RData5 RData4 RData3 RData2 RData1 RData0
0x00 TData7 TData6 TData5 TData4 TData3 TData2 TData1 TData0
0x02 CTSInt RFifoEmptyInt TFifoEmptyInt TFifoTrigInt RFifoTrigInt STSInt SpCharInt LSRErrInt
0x04 CTSbit — RxNoise RxBreak FrameErr RxParityErr RxOverrun RTimeout
†
0x06 — — MultiDropInt BREAKInt XOFF2Int XOFF1Int XON2Int XON1Int
0x07 — — ClockRdyIntEn — GPI3IntEn GPI2IntEn GPI1IntEn GPI0IntEn
0x08 — — ClockReady — GPI3Int GPI2Int GPI1Int GPI0Int
RTSbit
0x11 TxFL7 TxFL6 TxFL5 TxFL4 TxFL3 TxFL2 TxFL1 TxFL0
0x12 RxFL7 RxFL6 RxFL5 RxFL4 RxFL3 RxFL2 RxFL1 RxFL0
TxBreak ForceParity EvenParity ParityEn StopBits Length1 Length0
28

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Register Map (continued)
REGISTER ADDR BIT7 BIT6 BIT5 BIT4 BIT3 BIT2 BIT1 BIT0
GPIOs
GPIOConfg
GPIOData
CLOCK CONFIGURATION
PLLConfig*
BRGConfig 0x1B — CLKDisabl 4xMode 2xMode FRACT3 FRACT2 FRACT1 FRACT0
DIVLSB 0x1C Div7 Div6 Div5 Div4 Div3 Div2 Div1 Div0
DIVMSB 0x1D Div15 Div14 Div13 Div12 Div11 Div10 Div9 Div8
CLKSource*
GLOBAL REGISTERS
GlobalRQ 0x1F 0 0 0 0
GloblComnd 0x1F GlbCom7 GlbCom6 GlbCom5 GlbCom4 GlbCom3 GlbCom2 GlbCom1 GlbCom0
SYNCHRONIZATION REGISTERS
TxSynch
SynchDelay1
SynchDelay2
TIMER REGISTERS
TIMER1
TIMER2
REVISION
REVID*
*Denotes nonzero default reset value: ISR = 0x60, LCR = 0x05, FIFOTrgLvl = 0xFF, PLLConfig = 0x01, DIVLSB = 0x01,
CLKSource = 0x08, REVID = 0xB1.
†Denotes nonread/write value: RHR = R, THR = W, ISR = COR, SpclCharInt = COR, STSInt = R/COR,
LSR = R, TxFIFOLvl = R, RxFIFOLvl = R, REVID = R.
¥Each UART has four individually assigned GPIO outputs as follows: UART0: GPIO0–GPIO3, UART1: GPIO4–GPIO7, UART2:
GPIO8–GPIO11, UART3: GPIO12–GPIO15.
‡This register can only be programmed by accessing UART0.
#This register can only be directly addressed in I2C mode. Use extended addressing when operating in SPI mode.
¥
0x18 GP3OD GP2OD GP1OD GP0OD GP3Out GP2Out GP1Out GP0Out
¥
#
#
#
†#
0x19 GPI3Dat GPI2Dat GPI1Dat GPI0Dat GPO3Dat GPO2Dat GPO1Dat GPO0Dat
‡
0x1A PLLFactor1 PLLFactor0 PreDiv5 PreDiv4 PreDiv3 PreDiv2 PreDiv1 PreDiv0
‡
0x1E CLKtoRTS — — — PLLBypass PLLEn CystalEn —
IRQ3 IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
0x20 CLKtoGPIO TxAutoDis TrigDelay SynchEn TrigSel3 TrigSel2 TrigSel1 TrigSel0
#
0x21 SDelay7 SDelay6 SDelay5 SDelay4 SDelay3 SDelay2 SDelay1 SDelay0
#
0x22 SDelay15 SDelay14 SDelay13 SDelay12 SDelay11 SDelay10 SDelay9 SDelay8
0x23 Timer7 Timer6 Timer5 Timer4 Timer3 Timer2 Timer1 Timer0
0x24 TmrToGPIO Timer14 Timer13 Timer12 Timer11 Timer10 Timer9 Timer8
0x25 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1
MAX14830
29

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Detailed Register Description
The MAX14830 has registers that are 8 bits wide.
RHR—Receive Hold Register
ADDRESS: 0x00
MODE: R
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
MAX14830
Bits 7 –0: RData[n]
The RHR is the bottom of the Receive FIFO and is the register used for reading data out of the Receive FIFO. It contains
the oldest (first received) character in the Receive FIFO. RHR[0] is the LSB of the character received at the RX_ input.
It is the first data bit of the serial-data word received by the receiver.
THR—Transmit Hold Register
ADDRESS: 0x00
MODE: W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RData7 RData6 RData5 RData4 RData3 RData2 RData1 RData0
X X X X X X X X
TData7 TData6 TData5 TData4 TData3 TData 2 TData1 TData0
Bits 7–0: TData[n]
The THR is the register that the host controller writes data to for subsequent UART transmission. This data is deposited
in the Transmit FIFO. THR[0] is the LSB. It is the first data bit of the serial-data word that the transmitter sends out, right
after the START bit.
30

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
IRQEn—IRQ Enable Register
ADDRESS: 0x01
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The IRQEn register is used to enable the IRQ physical interrupt. Any of the eight ISR interrupt sources can be enabled
to generate an IRQ. The IRQEn bits only influence the IRQ output and do not have any effect on the ISR contents or
behavior. Every one of the IRQEn bits operates on an ISR bit.
Bit 7: CTSIEn
The CTSIEn bit enables IRQ interrupt generation when the CTSInt interrupt bit is set in the ISR. Set the CTSIEn bit low
to disable IRQ generation from CTSInt.
Bit 6: RFifoEmtyIEn
The RFifoEmtyIEn bit enables IRQ interrupt generation when the RFifoEmptyInt interrupt bit is set in the ISR. Set the
RFifoEmtyIEn bit low to disable IRQ generation from RFifoEmptyInt.
Bit 5: TFifoEmtyIEn
The TFifoEmtyIEn bit enables IRQ interrupt generation when the TFifoEmptyInt interrupt bit is set in the ISR. Set the
TFifoEmtyIEn bit low to disable IRQ generation from TFifoEmptyInt.
Bit 4: TFifoTrgIEn
The TFifoTrgIEn bit enables IRQ interrupt generation when the TFifoTrigInt interrupt bit is set in the ISR. Set TFifoTrgIEn
bit low to disable IRQ generation from TFifoTrigInt.
Bit 3: RFifoTrgIEn
The RFifoTrgIEn bit enables IRQ interrupt generation when the RFifoTrigInt interrupt bit is set in the ISR. Set the
RFifoTrgIEn bit low to disable IRQ generation from RFifoTrigInt.
Bit 2: STSIEn
The STSIEn bit enables IRQ interrupt generation when the STSInt interrupt bit is set in the ISR. Set the STSIEn bit low
to disable IRQ generation from STSInt.
Bit 1: SpclChrIEn
The SpclChrIEn bit enables IRQ interrupt generation when the SpCharInt interrupt bit is set in the ISR. Set the
SpclChrIEn bit low to disable IRQ generation from SpCharInt.
Bit 0: LSRErrIEn
The LSRErrIEn bit enables IRQ interrupt generation when the LSRErrInt interrupt bit is set in the ISR[0]. Set the
LSRErrIEn low to disable IRQ generation from LSRErrInt.
CTSIEn RFifoEmtyIEn TFifoEmtyIEn TFifoTrgIEn RFifoTrgIEn STSIEn SpclChrIEn LSRErrIEn
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAX14830
31

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
ISR—Interrupt Status Register
ADDRESS: 0x02
MODE: COR
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The Interrupt Status Register provides an overview of all interrupts generated in the MAX14830. These interrupts are
MAX14830
cleared upon reading the ISR. When the MAX14830 is operated in polled mode, the ISR can be polled to establish
the UART’s status. In interrupt-driven mode, IRQ interrupts are enabled through the appropriate IRQEn bits. The ISR
contents give direct information on the cause for the interrupt or point to other registers that contain more detailed
information.
Bit 7: CTSInt
The CTSInt is set when a logic state transition occurs at the CTS_ input. This bit is cleared after ISR is read. The current
logic state of the CTS_ input can be read out through LSR[7]: CTS bit.
Bit 6: RFifoEmptyInt
The RFifoEmptyInt is set when the Receive FIFO is empty. This bit is cleared after ISR is read. Its meaning can be
inverted by setting the MODE2[3]: RxEmtyInt bit.
Bit 5: TFifoEmptyInt
The TFifoEmptyInt bit is set when the Transmit FIFO is empty. This bit is cleared once ISR is read.
Bit 4: TFifoTrigInt
The TFifoTrigInt bit is set when the number of characters in the Transmit FIFO is equal to or greater than the Transmit
FIFO trigger level defined in FIFOTrigLvl[3:0]. TFifoTrigInt is cleared when the Transmit FIFO level falls below the trigger
level or after the ISR is read. It can be used as a warning that the Transmit FIFO is nearing overflow.
Bit 3: RFifoTrigInt
The RFifoTrigInt bit is set when the Receive FIFO fill level reaches the Receive FIFO trigger level, as defined in
FIFOTrigLvl[7:4]. This can be used as an indication that the Receive FIFO is nearing overrun. It can also be used to
report that a known number of words are available that can be read out in one block. The meaning of RFifoTrigInt can
be inverted through MODE2[2]. RFifoTrigInt is cleared when ISR is read.
Bit 2: STSInt
The STSInt bit is set high when any bit in the STSInt register that is enabled through a STSIntEn bit is high. The STSInt
bit is cleared upon reading ISR.
Bit 1: SpCharInt
The SpCharInt bit is set high when a special character is received, a line BREAK is detected or an address character is
received in multidrop mode. The cause for the SpCharInt interrupt can be read from the SpclCharInt register, if enabled
through the SpclChrIntEn bits. The SpCharInt interrupt is cleared when the ISR is read.
Bit 0: LSRErrInt
The LSRErrInt bit is set high when any LSR bits, which are enabled through the LSRIntEn, are set. This bit is cleared
after the ISR is read.
CTSInt RFifoEmptyInt TFifoEmptyInt TFifoTrigInt RFifoTrigInt STSInt SpCharInt LSRErrInt
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
32

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
LSRIntEn—Line Status Interrupt Enable Register
ADDRESS: 0x03
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The LSR Interrupt Enable register allows routing of LSR interrupt bits to the ISR[0].
Bits 7, 6: No Function
Bit 5: NoiseIntEn
Set the NoiseIntEn bit high to enable routing the RxNoise interrupt to LSR[0]. If NoiseIntEn is set low, RxNoise is not
routed to LSR[0].
Bit 4: RBreakIEn
Set the RBreakIEn bit high to enable routing the RxBreak interrupt to LSR[0]. If RBreakIEn is set low, RxBreak is not
routed to LSR[0].
Bit 3: FrameErrIEn
Set the FrameErrIEn bit high to enable routing the FrameErr interrupt to LSR[0]. If FrameErrIEn is set low, FrameErr is
not routed to LSR[0].
Bit 2: ParityIEn
Set the ParityIEn bit high to enable routing the RxParityErr interrupt to LSR[0]. If ParityIEn is set low, RxParityErr is not
routed to the LSR[0].
Bit 1: ROverrIEn
Set the ROverrIEn bit high to enable routing the RxOverrun interrupt to LSR[0]. If ROverrIEn is set low, RxOverrun is
not routed to LSR[0].
Bit 0: RTimoutIEn
Set the RTimoutIEn bit high to enable routing the RTimeout interrupt to LSR[0]. If RTimoutIEn is set low, the RTimeout
is not routed to LSR[0].
— — NoiseIntEn RBreakIEn FrameErrIEn ParityIEn ROverrIEn RTimoutIEn
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAX14830
33

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
LSR—Line Status Register
ADDRESS: 0x04
MODE: R
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The Line Status Register shows all errors related to the word in the RxFIFO most recently read out of the RHR. The LSR
MAX14830
bits are not cleared upon a read; these bits stay set until the next character without errors is read out of the RHR. The
LSR also reflects the current state of the CTS_ input.
Bit 7: CTSbit
The CTSbit reflects the current logic state of the CTS_ input. This bit is cleared when the CTS_ input is low. Following
a power-up or reset, the logic state of CTSbit depends on the input of the CTS_ input.
Bit 6: No Function
Bit 5: RxNoise
If noise is detected on the RX_ input during reception of a character, the RxNoise bit is set for that character. The
RxNoise bit indicates that there was noise on the line while the most recently read character residing in the RHR was
being received. The RxNoise flag can generate an ISR[0] interrupt, if enabled through LSRIntEn[5].
Bit 4: RxBreak
If a line BREAK (RX_ input low for a period longer than the programmed character duration) is detected, a BREAK character is put in the RxFIFO and the RxBreak bit is set for this character. A BREAK character is represented by an all-zeros
data character. The RxBreak bit distinguishes a regular character with all zeros from a BREAK character. LSR[4] corresponds to the character most recently read out of the RHR. RxBreak is cleared after the character following the BREAK
character is read out of the RHR. The RxBreak flag can generate an ISR[0] interrupt if enabled through LSRIntEn[4].
Bit 3: FrameErr
The FrameErr bit is set high when the received data frame does not match the expected frame format in length. LSR[3]
corresponds to the frame error of the character most recently read out of the RHR. A frame error is related to errors in
expected STOP bits. The FrameErr flag can generate an ISR[0] interrupt, if enabled, through LSRIntEn[3].
Bit 2: RxParityErr
If the parity computed on the character being received does not match the received character’s parity bit, the
RxParityErr bit is set for that character. LSR[2] indicates a parity error for the character most recently read out of the
RHR. In 9-bit multidrop mode (MODE2[6] = 1) the receiver does not check parity and the LSR[2] represents the 9th
(i.e. address or data) bit.
The RxParityErr flag can generate an ISR[0] interrupt, if enabled through LSRIntEn[2].
Bit 1: RxOverrun
If the Receive FIFO is full and additional data is received that does not fit into the Receive FIFO, the LSR[1] bit is set.
The Receive FIFO retains the data in it and discards all new data that does not fit into it. The RxOverrun flag can generate an ISR[0] interrupt, if enabled through LSRIntEn[1].
CTSbit
X 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
— RxNoise RxBreak FrameErr RxParityErr RxOverrun RTimeout
34

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Bit 0: RTimeout
The RTimeout bit indicates that stale data is present in the Receive FIFO. RTimeout is set when the youngest character
resides in the RxFIFO for a period longer than the time programmed into the RxTimeOut register. The timeout counter
restarts when at least one character is read out of the RxFIFO or a new character is received by the RxFIFO. If the value
in RxTimeOut is zero, LSR[0]: RTimeout is disabled. The RTimeout flag can generate an ISR[0] interrupt, if enabled
through LSRIntEn[0].
SpclChrIntEn—Special Character Interrupt Enable Register
ADDRESS: 0x05
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7, 6: No Function
Bit 5: MltDrpIntEn
The MltDrpIntEn bit enables routing the SpclCharInt[5]: MultiDropInt interrupt to ISR[1]. If MltDrpIntEn is set low
(default), the MultiDropInt is not routed to the ISR[1].
Bit 4: BREAKIntEn
The BREAKIntEn bit enables routing the SpclCharInt[4]: BREAKInt interrupt to ISR[1]. If BREAKIntEn is set low (default),
the BREAKInt is not routed to the ISR[1].
Bit 3: XOFF2IntEn
The XOFF2IntEn bit enables routing the SpclCharInt[3]: XOFF2Int interrupt to ISR[1]. If XOFF2IntEn is set low (default),
the XOFF2Int is not routed to the ISR[1].
Bit 2: XOFF1IntEn
The XOFF1IntEn bit enables routing the SpclCharInt[2]: XOFF1Int interrupt to ISR[1]. If XOFF1IntEn is set low (default),
the XOFF1Int is not routed to the ISR[1].
Bit 1: XON2IntEn
The XON2IntEn bit enables routing the SpclCharInt[1]: XON2Int interrupt to ISR[1]. If XON2IntEn is set low (default),
the XON2Int is not routed to the ISR[1].
Bit 0: XON1IntEn
The XON1IntEn bit enables routing the SpclCharInt[0]: XON1Int interrupt to ISR[1]. If XON1IntEn is set low (default),
the XON1Int is not routed to the ISR[1].
— — MltDrpIntEn BREAKIntEn XOFF2IntEn XOFF1IntEn XON2IntEn XON1IntEn
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAX14830
35

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
SpclCharInt—Special Character Interrupt Register
ADDRESS: 0x06
MODE: COR
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7, 6: No Function
MAX14830
Bit 5: MultiDropInt
The MultiDropInt interrupt is set when the MAX14830 receives an address character in 9-bit multidrop mode
(MODE2[6] = 1). This bit is cleared when SpclCharInt is read. The MultiDropInt bit can be routed to ISR[1] by enabling
SpclChrIntEn[5].
Bit 4: BREAKInt
The BreakInt interrupt is set when a line BREAK (RX_ low for longer than one character length) is detected by the
receiver. This bit is cleared after SpclCharInt is read. The BREAKInt interrupt can be routed to ISR[1] by enabling
SpclChrIntEn[4].
Bit 3: XOFF2Int
The XOFF2Int interrupt bit is set when an XOFF2 special character is received and special character detection is
enabled through MODE2[4]. This interrupt is cleared upon reading SpclCharInt. The XOFF2Int interrupt can be routed
to the ISR[1] interrupt bit, if enabled through SpclChrIntEn[3].
Bit 2: XOFF1Int
The XOFF1Int interrupt bit is set when an XOFF1 special character is received and special character detection is
enabled through MODE2[4]. This interrupt is cleared upon reading SpclCharInt. The XOFF1Int interrupt can be routed
to the ISR[1] interrupt bit, if enabled through SpclChrIntEn[2].
Bit 1: XON2Int
The XON2Int interrupt bit is set when an XON2 special character is received and special character detection is enabled
through MODE2[4]. This interrupt is cleared upon reading SpclCharInt. The XON2Int interrupt can be routed to the
ISR[1] interrupt bit, if enabled through SpclChrIntEn[1].
Bit 0: XON1Int
The XON1Int interrupt bit is set when an XON1 special character is received and special character detection is enabled
through MODE2[4]. This interrupt is cleared upon reading SpclCharInt. The XON1Int interrupt can be routed to the
ISR[1] interrupt bit, if enabled through SpclChrIntEn[0].
— —
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MultiDropInt BREAKInt XOFF2Int XOFF1Int XON2Int XON1Int
36

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
STSIntEn—STS Interrupt Enable Register
ADDRESS: 0x07
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7, 6: No Function
Bit 5: ClkRdyIntEn
Set the ClkRdyIntEn bit high to route the ClockReady status bit to the ISR[2]: STSInt bit. If set low, the STSIntEn[5]
masks the ISR[2] bit from the ClockReady status.
Bit 4: No Function
Bits 3–0: GPI[n]IntEn
Each UART has four individually assigned GPIO outputs as follows: UART0: GPIO0–GPIO3, UART1: GPIO4–GPIO7,
UART2: GPIO8–GPIO11, UART3: GPIO12–GPIO15. For example, for UART0: Bit 0 is GPI0IntEn, Bit 1 is GPI1IntEn, Bit
2 is GPI2IntEn, and Bit 3 is GPI3IntEn. See Table 1.
The GPI[n]IntEn bits that are set high route the associated STSInt[3:0]: GPI[n]Int bits to the ISR[2] interrupt. Set the
GPI[n]IntEn bits to 0 to disable the associated GPI[n]Int bits.
— — ClockRdyIntEn — GPI3IntEn GPI2IntEn GPI1IntEn GPI0IntEn
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAX14830
37

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
STSInt—Status Interrupt Register
ADDRESS: 0x08
MODE: R/COR
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7, 6: No Function
MAX14830
Bit 5: ClockReady
The ClockReady bit is set high when the clock, the divider, and PLL have settled and the MAX14830 is ready for
data communication. The ClockReady bit only works with the crystal oscillator. It does not work with external clocking
through XIN.
The ClockReady status bit is cleared when the clock is disabled and is not cleared upon read. This bit can generate
an ISR[2]: STSInt interrupt, if enabled through STSIntEn[5].
Bit 4: No Function
Bits 3–0: GPI[n]Int
Each UART has four individually assigned GPIO outputs as follows: UART0: GPIO0–GPIO3, UART1: GPIO4–GPIO7,
UART2: GPIO8–GPIO11, UART3: GPIO12–GPIO15. For example, for UART0: Bit 0 is GPI0Int, Bit 1 is GPI1Int, Bit 2 is
GPI2Int, and Bit 3 is GPI3Int. See Table 1.
The GPI[n]Int interrupts are set high when a change of logic state occurs on the associated GPIO_ input, unless
disabled by the GPI[n]IntEn bits. GPI[n]Int is cleared upon reading. These interrupts can be selectively routed to the
ISR[2] interrupt bit through the STSIntEn[3:0].
— —
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
ClockReady
—
GPI3Int GPI2Int GPI1Int GPI0Int
Table 1. UART GPIO Assignments for GPIO Interrupts
UART GPI3Int/GPI3IntEn GPI2Int/GPI2IntEn GPI1Int/GPI1IntEn GPI0Int/GPI0IntEn
UART0 GPIO3 GPIO2 GPIO1 GPIO0
UART1 GPIO7 GPIO6 GPIO5 GPIO4
UART2 GPIO11 GPIO10 GPIO9 GPIO8
UART3 GPIO15 GPIO14 GPIO13 GPIO12
38

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
MODE1 Register
ADDRESS: 0x09
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bit 7: IRQSel
Depending on the logic level of the IRQSel bit, IRQ has different meanings. After a hardware or software (MODE2[0])
reset, the IRQSel bit is set low and, after a short delay, the IRQ output signals the end of the power-up sequence. The
IRQ is low during power-up and transitions to high when the MAX14830 is ready to be programmed.
IRQSel can then be set high. In this case, IRQ becomes a regular interrupt output that signals pending interrupts, as
indicated in the ISR. Details of the IRQSel are described in the Power-up and IRQ section.
Bits 6, 5: No Function
Bit 4: TrnscvCtrl
This bit enables the automatic transceiver direction control. Set TrnscvCtrl high so that RTS_ automatically controls the
transceiver’s transmit/receive enable/disable inputs. Setting TrnscvCtrl high sets RTS_ low so that the transceiver is
in receive mode. When the TxFIFO contains data available for transmission, the auto direction control sets RTS_ high
before the transmitter sends out the data. When the transmitter is empty, RTS_ is automatically forced low again.
Setup and hold times of RTS_ with respect to the TX_ output can be defined through the HDplxDelay register. A transmitter empty interrupt ISR[5] is generated when the transmitter is empty.
Bit 3: RTSHiZ
Set the RTSHiZ bit high to three-state RTS_.
Bit 2: TxHiZ
Set the TxHiZ bit high to three-state the TX_ output.
Bit 1: TxDisabl
Set the TxDisabl bit high to disable transmission. If the TxDisabl bit is set high during transmission, the transmitter completes sending out the current character and then ceases transmission. Data still present in the Transmit FIFO remains
in the TxFIFO. The TX_ output is set to logic-high after transmission.
In auto transmitter disable mode, TxDisabl is high when the transmitter is completely empty.
Bit 0: RxDisabl
Set the RxDisabl bit high to disable the receiver of the selected UART so that the receiver stops receiving data. All data
present in the Receive FIFO remains in the RxFIFO.
IRQSel — — TrnscvCtrl RTSHiZ TxHiZ TxDisabl RxDisabl
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAX14830
39

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
MODE2 Register
ADDRESS: 0x0A
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bit 7: EchoSuprs
Set the EchoSuprs bit high so that the receiver (RX_) gates any data it receives when its transmitter is busy transmitting. In
MAX14830
half-duplex communication (like IrDA and RS-485) this allows blocking of the locally echoed data. The receiver can block
data for an extended time after the transmitter ceases transmission by programming a hold time in HDplxDelay[3:0] bits.
Bit 6: MultiDrop
Set the MultiDrop bit high to enable the 9-bit multidrop mode. If this bit is set, parity checking is not performed by the
receiver and parity generation is not done by the transmitter. The parity error bit, LSR[2], has a different meaning in
this case. The parity error bit represents the 9th bit (address/data indication) that is received with each 9-bit character.
Bit 5: Loopback
Set the Loopback bit high to enable internal local loopback mode. This internally connects TX_ to RX_ and also RTS_ to CTS_.
In local loopback mode, the TX_ output and the RX_ input are disconnected from the internal transmitter and receiver. The
TX_ output is in three-state. The RTS_ output remains connected to the internal logic and reflects the logic state programmed
in LCR[7]. The CTS_ input is disconnected from RTS_ and the internal logic. CTS_ thus remains in a high-impedance state.
Bit 4: SpecialChr
The SpecialChr bit enables special character detection. The receiver can detect up to four special characters, as
selected in FlowCtrl[5:4] and defined in the XON1, XON2, XOFF1 and/or XOFF2 registers, possibly in combination with
GPIO_ inputs, enabled through FlowCtrl[2]: GPIAddr. When a special character is received it is put into the RxFIFO
and a special character detect interrupt ISR[1] is generated.
Special character detection can be used in addition to auto XON/XOFF flow control, if enabled through FlowCtrl[3]. In
this case XON/XOFF flow control is then limited to single character XON and XOFF and only two special characters
can then be defined (in XON2 and XOFF2).
Bit 3: RxEmtyInv
The RxEmtyInv bit inverts the meaning of the receiver empty interrupt: ISR[6]: RFifoEmptyInt. If RxEmtyInv is set low
(default state), the ISR[6] interrupt is generated when the last character residing in the Receive FIFO is read out of the
RHR, and the Receive FIFO becomes empty. If the RxEmtyInv is set high, the ISR[6] interrupt is generated when the
Receive FIFO is empty, and the UART receives at least one character.
Bit 2: RxTrigInv
The RxTrigInv bit inverts the meaning of the RxFIFO triggering. When set, an ISR[3]: RFifoTrigInt is generated when
the RxFIFO is emptied to the trigger level: FIFOTrgLvl[7:4]. If the RxTrgInv bit is low (default state), the ISR[3] interrupt
is generated when the RxFIFO fill level, which starts from a level below FIFOTrgLvl[7:4], is filled up to the trigger level
programmed into FIFOTrgLvl[7:4].
Bit 1: FIFORst
Set the FIFORst bit high to clear both the Receive and Transmit FIFOs of all data contents. After the FIFO reset, the
FIFORst bit must then be set back to 0 to continue normal operation.
EchoSuprs MultiDrop Loopback SpecialChr RxEmtyInv RxTrigInv FIFORst RST
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
40

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Bit 0: RST
Set the RST bit high to reset the selected UART in the MAX14830. The SPI/I2C bus stays active during this reset and
communication with the MAX14830 is possible. All register bits in the selected UART are reset to their reset state and
the FIFOs are cleared during a reset.
The global registers are not reset when the RST bit for a given UART is set. Once set high, the RST bit must be cleared
by writing a 0 to RST.
LCR—Line Control Register
ADDRESS: 0x0B
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bit 7: RTSbit
The RTSbit provides direct control of the RTS_ output logic. If RTSbit is set to 1, then RTS_ is set to logic-high. The
RTSbit only works when CLKSource[7]: CLKtoRTS is set to 0.
Bit 6: TxBreak
Set TxBreak to 1 to generate a line break whereby the TX_ output is held low. TX_ output remains low until TxBreak is
set to 0.
Bit 5: ForceParity
The ForceParity bit enables forced parity, as used in 9-bit multidrop communication. Set both LCR[3]: ParityEn and
ForceParity to 1 to use forced parity. The parity bit is forced high by the transmitter if LCR[4]: EvenParity is low. The
parity bit is forced low if the EvenParity bit is high.
Bit 4: EvenParity
Set the EvenParity bit to 1 to generate even parity by the transmitter and parity is checked by the receiver. Odd parity
generation and checking are used if EvenParity is set low.
Bit 3: ParityEn
The ParityEn bit enables the use of a parity bit on the TX_ and RX_ interfaces. Set the ParityEn bit to 0 to disable parity usage.
When the ParityEn bit is 1, the transmitter generates the parity bit as defined in LCR[4], and the receiver checks the parity bit.
Bit 2: StopBits
This defines the number of STOP bits and depends on the length of the word programmed in LCR[1:0] (Table 2). When
LCR[2] is high and the word length is 5, the transmitter generates a word with a STOP bit length equal to 1.5. Under
these conditions, the receiver recognizes a STOP bit length greater than a 1-bit duration.
Bits 1, 0: Length[n]
The Length[n] bits configure the length of the words that the transmitter generates and the receiver checks for at the
asynchronous TX_ and RX_ interfaces (Table 3).
RTSbit
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1
TxBreak ForceParity EvenParity ParityEn StopBits Length1 Length0
MAX14830
Table 2. StopBits Truth Table Table 3. Length_ Truth Table
StopBits
BIT
0 5, 6, 7, 8 1
1 5 1–1.5
1 6, 7, 8 2
WORD LENGTH STOP BIT LENGTH
Length1 Length0 WORD LENGTH
0 0 5
0 1 6
1 0 7
1 1 8
41

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
RxTimeOut—Receiver Timeout Register
ADDRESS: 0x0C
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7–0: TimOut[n]
MAX14830
The receive data timeout bits allow programming a time delay after the last (newest) character in the Receive FIFO was
received until a receive data timeout LSR[0] interrupt is generated. The duration is measured in character intervals and
is dependent on the character length, parity, and STOP bit setting and is inversely proportional to the baud rate. If the
RxTimeOut value equals zero, a timeout interrupt is not generated.
HDplxDelay Register
ADDRESS: 0x0D
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The HDplxDelay register allows programming setup and hold times between RTS_ and the TX_ output in automatic
transceiver direction control mode (MODE1[4] = 1). The Hold[3:0] time can also be used for echo suppression in halfduplex communication. HDplxDelay also functions in the 2x and 4x rate modes.
Bits 7–4: Setup[n]
The Setup[n] bits define a setup time for RTS_ to transition high before the transmitter starts transmission of its first
character in auto transceiver direction control mode: MODE1[4]. This allows the MAX14830 to account for skew differences of the external transmitter’s enable delay and propagation delays. Setup[n] bits can also be used to fix a stable
state on the transmission line prior to start of transmission.
The unit of the HDplxDelay setup time delay is one bit interval, making this delay baud-rate dependent. The maximum
delay is 15-bit intervals.
Bits 3–0: Hold[n]
The Hold[n] bits define a hold time for RTS_ to be held stable (high) after the transmitter ends transmission of its last
character in auto transceiver direction control mode: MODE1[4]. RTS_ turns low after the last STOP bit was sent with
a Hold[n] delay. This keeps the external transmitter enabled during the Hold duration.
The second factor that the Hold[n] bits define is a delay in echo suppression mode, MODE2[7]. See the Echo
Suppression section for more information.
The unit of the HDplxDelay hold time delay is one bit interval, making the delay baud-rate dependent. The maximum
delay is 15-bit intervals.
TimOut7 TimOut6 TimOut5 TimOut4 TimOut3 TimOut2 TimOut1 TimOut0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Setup3 Setup2 Setup1 Setup0 Hold3 Hold2 Hold1 Hold0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
42

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
IrDA Register
ADDRESS: 0x0E
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The IrDA register allows selection of IrDA SIR- and MIR-compliant pulse shaping at the TX_ and RX_ interfaces. It also
allows inversion of the TX_ and RX_ logic, independently of whether IrDA is enabled or not.
Bits 7, 6: No Function
Bit 5: TxInv
Set the TxInv bit high to invert the logic at the TX_ output. This is independent of IrDA operation.
Bit 4: RxInv
Set the RxInv bit high to invert the logic state at the RX_ input. This is independent of IrDA operation.
Bit 3: MIR
Set the MIR and IrDAEn bits high to select IrDA 1.1 (MIR) with 1/4 period pulse widths.
Bit 2: RTSInvert
Set the RTSInvert bit high to invert the RTS output.
Bit 1: SIR
Set the SIR bit and the IrDAEn bits high to select IrDA 1.0 pulses (SIR) with 3/16th period pulses.
Bit 0: IrDAEn
Set the IrDAEn bit high so that IrDA compliant pulses are produced at the TX_ output and the MAX14830 receiver
expects such pulses at its Rx input. If IrDA[0] is set to low (default), normal (non-IrDA) pulses are generated and
expected at the receiver. IrDAEn must be used in conjunction with the SIR, ShortIR, or MIR select bits.
— — TxInv RxInv MIR RTSInvert SIR IrDAEn
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAX14830
43

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
FlowLvl—Flow Level Register
ADDRESS: 0x0F
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
FlowLvl is used for selecting the RxFIFO threshold levels used for software (XON/XOFF) and hardware (RTS/CTS) flow
MAX14830
control.
Bits 7–4: Resume[n]
Resume[n] bits set the Transmit FIFO threshold at which an XON is automatically sent or RTS_ is automatically set low.
This signals the far end station to start transmission. The actual threshold level is calculated as 8 x Resume[n]. The
resulting level is in the range of 0 to 120.
Bits 3–0: Halt[n]
Halt[n] bits set a Receive FIFO threshold level at which an XOFF is automatically sent or RTS_ is automatically set high,
depending on whether automatic software or hardware flow control is enabled. This signals the far end station to halt
transmission. The actual threshold level is calculated as 8 x Halt[n]. Hence the selectable threshold granularity is eight.
The resulting level is in the range of 0 to 120.
FIFOTrigLvl—FIFO Interrupt Trigger Level Register
ADDRESS: 0x10
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Resume3 Resume2 Resume1 Resume0 Halt3 Halt2 Halt1 Halt0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
RxTrig3 RxTrig2 RxTrig1 RxTrig0 TxTrig3 TxTrig2 TxTrig1 TxTrig0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Bits 7–4: RxTrig[n]
The RxTrig[n] bits allow definition of the Receive FIFO threshold level at which an ISR[3] interrupt is generated. This
can be used to signal that the Receive FIFO is nearing overflow or that a predefined number of FIFO locations are
available for being read out in one block.
The actual FIFO trigger level is 8 x RxTrig[n], hence the selectable threshold granularity is eight.
Bits 3–0: TxTrig[n]
The TxTrig[n] bits allow definition of the Transmit FIFO threshold level at which the MAX14830 generates an ISR[4]
interrupt. This can be used to manage data flow to the Transmit FIFO. For example, if the trigger level is defined near
the bottom of the TxFIFO, the host knows that a predefined number of FIFO locations are available to be written to in
one block. Alternatively, if the trigger level is set near the top of the FIFO, the host is warned when the Transmit FIFO
is nearing overflow, if written to on a word-by-word basis.
The actual FIFO trigger level is 8 x TxTrig[n], hence the selectable threshold granularity is eight.
44

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
TxFIFOLvl—Transmit FIFO Level Register
ADDRESS: 0x11
MODE: R
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7–0: TxFL[n]
The TxFIFOLvl register represents the current number of words in the Transmit FIFO.
RxFIFOLvl—Receive FIFO Level Register
ADDRESS: 0x12
MODE: R
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7–0: RxFL[n]
The RxFIFOLvl Level register represents the current number of words in the Receive FIFO.
TxFL7 TxFL6 TxFL5 TxFL4 TxFL3 TxFL2 TxFL1 TxFL0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
RxFL7 RxFL6 RxFL5 RxFL4 RxFL3 RxFL2 RxFL1 RxFL0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAX14830
FlowCtrl—Flow Control Register
ADDRESS: 0x13
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7–4: SwFlow[n]
The SwFlow[n] bits configure auto software flow control and/or special character detection in combination with the
characters defined in the XON1, XON2, XOFF1, and/or XOFF2 registers. See Table 4.
FlowCtrl[n] select which of the XON1, XON2, XOFF1, or/and XOFF2 characters are used for special character detection and/or auto flow control. If auto receiver flow control is enabled through SwFlowEn and FlowCtrl[n], the XON and
XOFF characters that the MAX14830 receives are filtered out and are not put into the RxFIFO. Set the SwFlowEn bit to
0 and set MODE2[4] to 1 to enable special character detection. Under these conditions, auto flow transmit flow control
is not used.
If both special character detection (MODE2[4]) and automatic software flow control (FlowCtrl[3]) are to be enabled,
XON1 and XOFF1 define the auto flow control characters while XON2 and XOFF2 define the special character detection characters.
Bit 3: SwFlowEn
The SwFlowEn bit enables automatic software flow control. The characters used for automatic software flow control are
selected in FlowCtrl[n]. If special character detection (MODE2[4] = 1) is used in addition to automatic software flow
control, XON1 and XOFF1 are used for flow control, while XON2 and XOFF2 define the special characters.
SwFlow3 SwFlow2 SwFlow1 SwFlow0 SwFlowEn GPIAddr AutoCTS AutoRTS
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
45

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Table 4. SwFlow_ Truth Table
SwFlow3 SwFlow2 SwFlow1 SwFlow0
TRANSMITTER FLOW
RECEIVER FLOW
CONTROL
0 0 0 0 No flow control. No character detection.
MAX14830
0 0 X X No receiver flow control.
1 0 X X Transmitter generates XON1, XOFF1.
0 1 X X Transmitter generates XON2, XOFF2.
1 1 X X Transmitter generates XON1, XON2, XOFF1, and XOFF2.
X X 0 0 No transmitter flow control.
X X 1 0
X X 0 1
X X 1 1
X = Don’t care.
CONTROL/SPECIAL
CHARACTER
DETECTION
Receiver compares XON1 and XOFF1 and controls the transmitter accordingly. XON1 and XOFF1 special character detection.
Receiver compares XON2 and XOFF2 and controls the transmitter accordingly. XON2 and XOFF2 special character detection.
Receiver compares XON1, XON2, XOFF1, and XOFF2 and controls the
transmitter accordingly. XON1, XON2, XOFF1, XOFF2 special character
detection.
DESCRIPTION
Bit 2: GPIAddr
The GPIAddr bit, when set, enables that the four GPIO_ inputs are used in conjunction with XOFF2 for the definition of
a special character. This can be used, for example, for defining the address of a RS-485 slave device through hardware. The GPIO_ input logic levels define the four LSBs of the special character, while the four MSBs are defined by
the XOFF2[7:4] bits. If GPIAddr is set, the contents of the XOFF2[3:0] bits are neglected. In this case, the XOFF2[3:0]
bits, when read, also do not reflect the logic on GPIO_.
Bit 1: AutoCTS
The AutoCTS bit enables automatic CTS flow control by which the transmitter stops and starts sending data depending on the logic state at the CTS_ input. See the Auto Hardware Flow Control section for a description of AutoCTS
flow control. Logic changes at the CTS_ input result in an ISR[7]: CTSInt interrupt. The transmitter must be turned off,
(MODE1[1] = 1), before AutoCTS is enabled.
Bit 0: AutoRTS
The AutoRTS bit enables automatic RTS flow control by which the MAX14830 sets its RTS_ output dependent on the
Receive FIFO fill level. The FIFO thresholds at which RTS_ changes state are set in FlowLvl. See the Auto Hardware
Flow Control section for more information.
46

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
XON1 Register
ADDRESS: 0x14
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The XON1 and XON2 register contents define the XON characters used for automatic XON/XOFF flow control and/or
the special characters used for special character detection. See details in the FlowCtrl register description.
Bits 7–0: Bit[n]
These bits define the XON1 character if single character XON auto software flow control is enabled in FlowCntrl[7:4]. If
double character flow control is selected in FlowCntrl[7:4], these bits constitute the LSB of the XON character. If special
character detection is enabled in MODE2[4] and auto flow control is not enabled, these bits define a special character.
If special character detection and auto software flow control are enabled, XON1 defines the XON flow control character.
XON2 Register
ADDRESS: 0x15
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAX14830
The XON1 and XON2 register contents define the XON characters for automatic XON/XOFF flow control and/or the
special characters used in special character detection. See details in the FlowCtrl register description.
Bits 7–0: Bit[n]
These bits define the XON2 character if single character auto software flow control is enabled in FlowCntrl[7:4]. If
double character flow control is selected in FlowCntrl[7:4], these bits constitute the MSB of the XON character. If
special character detection is enabled in MODE2[4] and auto software flow control is not enabled, these bits define a
special character. If both special character detection and auto flow control are enabled (MODE2[4] and FlowCntrl[3]),
these bits define a special character.
47

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
XOFF1 Register
ADDRESS: 0x16
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The XOFF1 and XOFF2 register contents define the XOFF characters for automatic XON/XOFF flow control and/or the
MAX14830
special characters used in special character detection. See details in the FlowCtrl register description.
Bits 7–0: Bit[n]
These bits define the XOFF1 character if single character XOFF auto software flow control is enabled in FlowCntrl[7:4].
If double character flow control is selected in FlowCntrl[7:4], these bits constitute the LSB of the XOFF character. If
special character detection is enabled in MODE2[4] and auto software flow control is not enabled, these bits define a
special character.
If special character detection and software flow control area both enabled, XOFF1 defines the XOFF flow control
character.
XOFF2 Register
ADDRESS: 0x17
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
The XOFF1 and XOFF2 register contents define the XOFF characters for automatic XON/XOFF flow control and/or special characters used for special character detection. See details in the FlowCtrl register description.
Bits 7–0: Bit[n]
These bits define the XOFF2 character if auto software flow control is enabled in FlowCntrl[7:4]. If double character flow
control is selected in FlowCntrl[7:4], these bits constitute the MSB of the XOFF character. If special character detection
is enabled in MODE2[4] and auto flow control is not enabled, these bits define a special character. If both special character detection and auto flow control are enabled (MODE2[4] and FlowCntrl[3]), these bits define a special character.
48

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
GPIOConfg—GPIO Configuration Register
ADDRESS: 0x18
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Each UART has four GPIOs that can be configured as inputs or outputs and can be operated in push-pull or open-drain
mode. The reference clock must be active for the GPIOs to work.
Bits 7–4: GP[n]OD
Each UART has four individually assigned GPIO outputs as follows: UART0: GPIO0–GPIO3, UART1: GPIO4–GPIO7,
UART2: GPIO8–GPIO11, UART3: GPIO12–GPIO15. For example, for UART0: Bit 4 is GP0OD, Bit 5 is GP1OD, Bit 6 is
GP2OD, and Bit 7 is GP3OD (see Table 5).
Set GP[n]OD bits to 0 to configure the GPIO_s as push-pull outputs, if configured as outputs in GPIOConfg[3:0].
Set the GP[n]OD bits to 1 to configure to open-drain output operation.
When configured as inputs in GPIOConfg[3:0], the GPIO_s are high-impedance inputs with weak pulldowns.
Bits 3–0: GP[n]Out
Each UART has four individually assigned GPIO outputs as follows: UART0: GPIO0–GPIO3, UART1: GPIO4–GPIO7,
UART2: GPIO8–GPIO11, UART3: GPIO12–GPIO15. For example, for UART0: Bit 0 is GP0Out, Bit 1 is GP1Out, Bit 2 is
GP2Out, and Bit 3 is GP3Out (see Table 5).
The GP[n]Out bits configure the GPIO_ to be inputs or outputs. Set the GP[n]Out bits to 1 to configure the associated
GPIO_s as outputs. Set the GP[n]Out bits to 0 to configure the associated GPIOs as inputs.
GP3OD GP2OD GP1OD GP0OD GP3Out GP2Out GP1Out GP0Out
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAX14830
Table 5. UART GPIO Assignments for GPIO Configuration
UART GP3OD/GP3Out GP2OD/GP2Out GP1OD/GP1Out GP0OD/GP0Out
UART0 GPIO3 GPIO2 GPIO1 GPIO0
UART1 GPIO7 GPIO6 GPIO5 GPIO4
UART2 GPIO11 GPIO10 GPIO9 GPIO8
UART3 GPIO15 GPIO14 GPIO13 GPIO12
49

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
GPIOData—GPIO Data Register
ADDRESS: 0x19
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7–4: GPI[n]Dat
MAX14830
Each UART has four individually assigned GPIO outputs as follows: UART0: GPIO0–GPIO3, UART1: GPIO4–GPIO7,
UART2: GPIO8–GPIO11, UART3: GPIO12–GPIO15. For example, for UART0: Bit 4 is GPI0Dat, Bit 5 is GPI1Dat, Bit 6 is
GPI2Dat, and Bit 7 is GPI3Dat (see Table 6).
The GPI[n]Dat bits reflect the logic on the GPIO_s.
Bits 3–0: GPO[n]Dat
Each UART has four individually assigned GPIO outputs as follows: UART0: GPIO0–GPIO3, UART1: GPIO4–GPIO7,
UART2: GPIO8–GPIO11, UART3: GPIO12–GPIO15. For example, for UART0: Bit 0 is GPO0Dat, Bit 1 is GPO1Dat, Bit
2 is GPO2Dat, and Bit 3 is GPO3Dat (see Table 6).
The GPO[n]Dat bits allow programming the logic state of the GPIO_, when configured as outputs in GPIOConfg[3:0].
For open-drain operation, pullup resistors are needed on GPIO_.
Table 6. UART GPIO Assignments for GPIO Input/Output Data
GPI3Dat GPI2Dat GPI1Dat GPI0Dat GPO3Dat GPO2Dat GPO1Dat GPO0Dat
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
UART GPI3Dat/GPO3Dat GPI2Dat/GPO2Dat GPI1Dat/GPO1Dat GPI0Dat/GPO0Dat
UART0 GPIO3 GPIO2 GPIO1 GPIO0
UART1 GPIO7 GPIO6 GPIO5 GPIO4
UART2 GPIO11 GPIO10 GPIO9 GPIO8
UART3 GPIO15 GPIO14 GPIO13 GPIO12
50

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
PLLConfig—PLL Configuration Register
ADDRESS: 0x1A
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7, 6: PLLFactor[n]
The PLLFactor[n] bits allow programming the PLL multiplication factors. The input and output frequencies of the PLL
have to be limited to the ranges shown in Table 7. Enable the PLL through CLKSource[2].
Bits 5–0: PreDiv[n]
The PreDiv[n] bits allow programming the divisor of the PLL’s predivider. The divisor must be chosen so that the output
frequency of the predivider, which equals the PLL’s input frequency, is limited to the ranges shown in Table 4. The
input frequency of XIN, is f
See Figure 17. PreDiv is an integer that must be in the range of 1 to 63.
PLLFactor1 PLLFactor0 PreDiv5 PreDiv4 PreDiv3 PreDiv2 PreDiv1 PreDiv0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
:
CLK
f
PLLIN
= f
CLK
/PreDiv
MAX14830
Figure 17. PLL Signal Path
f
CLK
PRE-DIVIDER
f
PLL IN
Table 7. PLLFactor_ Selector Guide
PLLFactor1 PLLFactor0 MULTIPLICATION FACTOR
0 0 6 500kHz 800kHz 3MHz 4.8MHz
0 1 48 850kHz 1.2MHz 40.8MHz 56MHz
1 0 96 425kHz 1MHz 40.8MHz 96MHz
1 1 144 390kHz 667kHz 56MHz 96MHz
PLL
f
REF
FRACTIONAL
BAUD-RATE
GENERATORS
f
PLLIN
MIN MAX MIN MAX
f
REF
51

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
BRGConfig—Baud-Rate Generator Configuration Register
ADDRESS: 0x1B
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bit 7: No Function
MAX14830
Bit 6: CLKDisabl
Set the CLKDisabl bit high to disable internal clocking of the UART. This is useful to achieve fast baud rate reprogramming or to reduce power dissipation when a specific UART channel is not used. Set CLKDisabl low for normal UART
operation.
Bit 5: 4xMode
When the 4xMode bit is set high, the MAX14830 baud rate is quadruple the regular (16x sampling) baud rate. The
2xMode bit should be set low if 4xMode is enabled. See the 2x and 4x Rate Modes section for more information.
Bit 4: 2xMode
When the 2xMode bit is set high, the MAX14830 baud rate is double the regular (16x sampling) baud rate. See the 2x
and 4x Rate Modes section for a detailed description.
Bits 3–0: FRACT[n]
This is the fractional portion of the baud-rate generator divisor. Set FRACT[n] to zero if not used. See the Fractional
Baud-Rate Generator section for calculations.
— CLKDisabl 4xMode 2xMode FRACT3 FRACT2 FRACT1 FRACT0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
DIVLSB—Baud-Rate Generator LSB Divisor Register
ADDRESS: 0x1C
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
DIVLSB and DIVMSB define the baud-rate generator integer divisors. The minimum value is 1. See the Fractional BaudRate Generator section for more information.
Bits 7–0: Div[n]
The DIVLSB register is the LSBs of the integer divisor portion (DIV) of the baud-rate generator.
Div7 Div6 Div5 Div4 Div3 Div2 Div1 Div0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
DIVMSB—Baud-Rate Generator MSB Divisor Register
ADDRESS: 0x1D
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7–0: Div[n]
The DIVMSB register is the MSB portion of the integer divisor (DIV).
Div15 Div14 Div13 Div12 Div11 Div10 Div9 Div8
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
52

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
CLKSource—Clock Source Register
ADDRESS: 0x1E
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bit 7: CLKtoRTS
Set the CLKtoRTS bit to 1 to route the baud-rate generator (16x baud rate) output clock to RTS_. The clock frequency
is a factor of 16x, 8x, or 4x of the baud rate, depending on the BRGConfig[5:4] settings.
Bits 6, 5: No Function
Bit 4:
Bi 4 can be programmed to logic 0 or logic 1.
Bit 3: PLLBypass
Set the PLLBypass bit to 1 to enable bypassing the internal PLL and predivider.
Bit 2: PLLEn
Set the PLLEn bit to 1 to enable the internal PLL. Set PLLEn to 0 to disable the internal PLL.
Bit 1: CrystalEn
Set the CrystalEn bit to 1 to enable the crystal oscillator. When using an external clock source at XIN, set CrystalEn to 0.
Bit 0:
Always keep Bit 0 at logic 0.
CLKtoRTS — — — PLLBypass PLLEn CrystalEn —
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
MAX14830
GlobalIRQ—Global IRQ Register
ADDRESS: 0x1F
MODE: R
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7–4: No Function
Bits 3–0: IRQ[n]
The MAX14830 has a single IRQ output. The GlobalIRQ register bits report which of the UARTs have an interrupt pending, as enabled in the ISRIntEn registers.
The GlobalIRQ register can be read in two ways: either by reading register 0x1F of any of the four UARTs or by sampling the 4 bits sent to the master on MISO during the command byte of a read cycle (full-duplex SPI) (see the Fast
Read Cycle section for more information).
IRQ[n] is set to 1 when the associated UART's internal IRQ is generated.
IRQ_ bits are cleared when the associated UART interrupt is cleared. UART interrupts are cleared by reading the UART
ISR register.
— — — —
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
IRQ3 IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
53

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
GloblComnd—Global Command Register
ADDRESS: 0x1F
MODE: W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
Bits 7–0: GlbCom[n]
The GloblComnd register is the only global write register in the MAX14830. Every byte written to GloblComnd is sent
MAX14830
simultaneously to all four UARTs. Every byte sent by the SPI/I2C master to location 0x1F is interpreted as a global command by all the four internal UARTs.
The MAX14830 logic supports the following commands (Table 8):
•GlobalTxSynchronization
•ExtendedAddressingSpaceEnable(togetaccesstoregistersbeyondaddress0x1F)
•ExtendedAddressingSpaceDisable(todisableaccesstoregistersbeyondaddress0x1F)
The last two commands (0xCE/0xCD) enable/disable the access to registers in the extended space of the register map
when MAX14830 operates in SPI mode. The SPI command byte has only 5 bits to address a given register so that the
registers beyond 0x1F could not be addressed using the standard access method.
In I2C mode, there is no need to explicitly enable and disable the extended register map access as I2C allows up to
7 bits for register addressing.
To extend the addressing capability of the SPI command byte, send a 0xCE to location 0x1F. The internal SPI address
is generated as 0010 A3A2A1A0, where A3A2A1A0 is the least significant nibble of the command byte. Bit A4 of the
command byte is disregarded when the extended space of the register map is enabled and only the least significant
nibble is used for addressing purposes (Table 9).
Bits U1 and U0 of the command byte maintain their meaning in the extended mode. See the SPI Interface section for
more information.
To return to standard addressing mode, the SPI master has to send the 0xCD command. In this case, the internal SPI
address is generated as follows (default): 000A4 A3A2A1A0
GlbCo
GlbCom6 GlbCom5 GlbCom4 GlbCom3 GlbCom2 GlbCom1 GlbCom0
m7
Table 8. GloblComnd Command Descriptions
GloblComnd[7:0] COMMAND DESCRIPTION
0xE0 Tx Command 0
0xE1 Tx Command 1
0xE2 Tx Command 2
0xE3 Tx Command 3
0xE4 Tx Command 4
0xE5 Tx Command 5
0xE6 Tx Command 6
0xE7 Tx Command 7
0xE8 Tx Command 8
0xE9 Tx Command 9
0xEA Tx Command 10
0xEB Tx Command 11
0xEC Tx Command 12
0xED Tx Command 13
0xEE Tx Command 14
54
GloblComnd[7:0] COMMAND DESCRIPTION
0xEF Tx Command 15
0xCE Enable extended register map access
0xCD Disable extended register map access
Table 9. Extended Mode Addressing
(SPI only)
REGISTER
TxSynch 0x00 0x20
SynchDelay1 0x01 0x21
SynchDelay2 0x02 0x22
TIMER1 0x03 0x23
TIMER2 0x04 0x24
RevID 0x05 0x25
SPI MODE
ADDRESS
I2C MODE
ADDRESS

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
TxSynch—Transmitter Synchronization Register
ADDRESS: 0x20
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The TxSynch register is used to configure transmitter synchronization with a global SPI or I2C command. One of 16
trigger commands (Table 5) can be selected to be the synchronization trigger source for every UART. This allows
simultaneous start of transmission of multiple UARTs that are associated with the same global trigger command. The
synchronized UARTs can be on a single MAX14830 or on multiple devices if they are controlled by a common SPI
interface.
UARTs start transmission when a global trigger command is received. Start of transmission is considered to be the
falling edge of the START bit at the TX_ output. A delay can optionally be programmed through the SynchDelay1 and
SynchDelay2 registers.
Tx synchronization is managed through software by transmitting the broadcast trigger Tx command (Table 5) to the
MAX14830 through the SPI or I2C interface. To selectively synchronize ports that are on the same MAX14830 (Intrachip
Synchronization) or on different MAX14830 (Interchip Synchronization) devices, up to 16 trigger Tx commands have
been defined (see the GloblComnd section for more information).
Bit 7: CLKtoGPIO
The CLKtoGPIO bit is used to provide a buffered replica of the UARTs system clock (i.e. the fractional divider input) to
a GPIO. The assignment is as follows: UART0’s clock is routed to GPIO0, UART1’s clock is routed to GPIO4, UART2’s
clock is routed to GPIO8, and UART3’s clock is routed to GPIO12.
Bit 6: TxAutoDis
Set the TxAutoDis bit to 1 to enable automatic transmitter disabling. When TxAutoDis is 1, the transmitter is automatically disabled when all data in the TxFIFO has been transmitted. After the transmitter is disabled, the TxFIFO can then
be filled with data that is transmitted when its assigned trigger command, defined by the TrigSelx bits, is received.
Bit 5: TrigDelay
Set TrigDelay to 1 to enable delayed start of transmission. The UART starts transmitting data following a delay programmed in SynchDelay1 and SynchDelay2 after receiving the assigned trigger command.
Bit 4: SynchEn
Set SynchEn to 1 to enable the software Tx synchronization. When SynchEn is high, the UART starts transmitting data
after receiving the expected trigger command, if the TxFIFO contains data. Setting SynchEn high forces the TxDisabl
bit (MODE1[1]) high and thereby disables the UART’s transmitter. This prevents the transmitter from sending data as
soon as the TxFIFO contains some. Once the TxFIFO has been loaded, the UART starts transmitting data only upon
receiving the assigned trigger command.
Set SynchEn to 0 to disable transmitter synchronization for that UART. When SynchEn is 0, that UART’s transmitter does
not start transmission through any trigger command.
Bits 3–0: TrigSel[n]
The TrigSel[n] bits select the trigger command for that UART’s transmitter synchronization when SynchEn is 1. For
example, set TxSynch[3:0] to 0x08 for the UART to be triggered by TX command 8 (0xE8, Table 5).
CLKtoGPIO TxAutoDis TrigDelay SynchEn TrigSel3 TrigSel2 TrigSel1 TrigSel0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
MAX14830
55

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
SynchDelay1—Synchronization Delay Register 1
ADDRESS: 0x21
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The SynchDelay1 and SynchDelay2 register contents define the time delay between when the UART receives an
MAX14830
assigned transmitter trigger command and when the UART begins transmission.
Bits 7–0: SDelay[n]
SDelay[7:0] are the 8 LSBs of the delay between when the UART receives an assigned transmitter trigger command
and when the UART begins transmission. The delay is expressed in number of UART bit intervals (1/BaudRate). The
maximum delay is 65,535-bit intervals.
For example, given a baud rate of 230.4kbps and a bit time of 4.34Fs, the maximum delay is 284ms.
SynchDelay2—Synchronization Delay Register 2
ADDRESS: 0x22
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
SDelay7 SDelay6 SDelay5 SDelay4 SDelay3 SDelay2 SDelay1 SDelay0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
SDelay15 SDelay14 SDelay13 SDelay12 SDelay11 SDelay10 SDelay9 SDelay8
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
The SynchDelay1 and SynchDelay2 register contents define the time delay between when the UART receives an
assigned transmitter trigger command and when the UART begins transmission.
Bits 7–0: SDelay[n]
SDelay[15:8] are the 8 MSBs of the delay between when the UART receives an assigned transmitter trigger command
and when the UART begins transmission. The delay is expressed in number of UART bit intervals (1/BaudRate). The
maximum delay is 65,535-bit intervals.
For example, given a baud rate of 230.4kbps and a bit time of 4.34Fs, the maximum delay is 284ms.
TIMER1—Timer Register 1
ADDRESS: 0x23
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The TIMER1 and TIMER2 register contents can be used to generate a low-frequency clock signal on a GPIO_ output.
The low-frequency clock is a divided replica of the fractional divider output.
Bits 7–0: Timer[n]
Timer[7:0] are the 8 LSBs of the 15-bit timer divisor. See the TIMER2 register description.
If TIMER1 and TIMER2 are both 0x00, the low-frequency clock is off.
Timer7 Timer6 Timer5 Timer4 Timer3 Timer2 Timer1 Timer0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
56

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
TIMER2—Timer Register 2
ADDRESS: 0x24
MODE: R/W
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
The TIMER1 and TIMER2 register contents can be used to generate a low-frequency clock signal on a GPIO_ output.
The low-frequency clock is a divided replica of the fractional divider output.
Bit 7: TmrToGPIO
Set TmrToGPIO to 1 to enable clock generation at a GPIO output. The clock signal is routed to a GPIO output as follows: UART0 clock signal to GPIO1, UART1 clock signal to GPIO5, UART2 clock signal to GPIO9, UART3 clock signal
to GPIO13. The output clock has a 50% duty cycle.
Bits 6–0: Timer[n]
Timer[14:8] are the 7 MSBs of the 15-bit timer divisor. The clock frequency is calculated using the following formula:
where UARTClk is the fractional baud-rate generator output (i.e. 16 x BaudRate). When using 2x or 4x rate modes,
UARTClk is 8 x BaudRate or 4 x BaudRate, respectively.
If TIMER1 and TIMER2 are both 0x00, the low-frequency clock is off.
TmrToGPIO Timer14 Timer13 Timer12 Timer11 Timer10 Timer9 Timer8
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
f
TIMER_CLK
= UARTClk/(1024 x Timerx)
MAX14830
RevID—Revision Identification Register
ADDRESS: 0x25
MODE: R
BIT 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NAME
RESET
Bits 7–0: Bit[n]
The RevID register indicates the revision number of the MAX14830 silicon—starting with 0xB1. This can be used during
software development as a known reference.
Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0
1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1
57

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Table 10. SPI Command Byte Configuration
SPI COMMAND BYTE
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
W/R
A[4:0] = Register Address
U1 U0 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Table 11. SPI U1, U0 UART Selection
MAX14830
U1 U0 UART SELECTED
0 0 UART0
0 1 UART1
1 0 UART2
1 1 UART3
Serial Controller Interface
The MAX14830 can be controlled through SPI or I2C as
defined by the logic on SPI/I2C. See the Pin Configuration
section for further details.
SPI Interface
The SPI interface supports both single cycle and burst
read/write access. The SPI master must generate clock
and data signals in SPI MODE0 (i.e. with clock polarity
CPOL = 0 and clock phase CPHA = 0).
Each of the four UARTs is addressed using 2 bits (U1
and U0) in the command byte (see Tables 10 and 11).
MISO Operation
Before a specific UART has been addressed, all four
UARTs can attempt to drive MISO. To avoid this contention, the MISO line is held in high impedance during a
write cycle (Figure 18).
During a read cycle, MISO is high impedance for the
first 4 clock cycles of the command byte. Once the SPI
address (U1 and U0) has been properly decoded, the
addressed SPI drives the MISO line (Figure 19).
SPI Burst Access
Burst access allows writing and reading in one block,
by only defining the initial register address in the SPI
command byte. Multiple characters can be loaded into
the TxFIFO by using the THR (0x00) as the initial burst
write address. Similarly, multiple characters can be read
out of the RxFIFO by using the RHR (0x00) as the SPI’s
burst read address. If the SPI burst address is different to 0x00, the MAX14830 automatically increments
the register address after each SPI data byte. Efficient
programming of multiple consecutive registers is thus
possible. Chip select, CS/A0, must be kept low during
the whole cycle. The SCLK/SCL clock continues clocking
throughout the burst access cycle. The burst cycle ends
when the SPI master pulls CS/A0 high.
For example, writing 128 bytes into a TxFIFO can be
achieved by a burst write access through the following
sequence:
1) Pull CS/A0 low.
2) Send SPI write command.
3) Send 128 bytes.
4) Release CS/A0.
This takes a total of (1 + 128) x 8 clock cycles.
CS
SCLK
MOSI
MISO
AX = REGISTER ADDRESS
UX = UART ADDRESS
DX = EIGHT-BIT REGISTER CONTENTS
= INSTANT AT WHICH MAX14830 SAMPLES MOSI DATA
Figure 18. SPI Write Cycle
58
WU1U0A4A3A2A1A0D7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
X X
HiZ

CS
SCLK
Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
MAX14830
MOSI
MISO
UX = UART ADDRESS
AX = REGISTER ADDRESS
DX = EIGHT-BIT REGISTER CONTENTS
= INSTANT AT WHICH MAX14830 SAMPLES MOSI DATA
= INSTANT AT WHICH MAX14830 WRITES MISO DATA
Figure 19. SPI Read Cycle
CS
SCLK
MOSI
MISO
UX = UART ADDRESS
AX = REGISTER ADDRESS
= INSTANT AT WHICH MAX14830 SAMPLES MOSI DATA
= INSTANT AT WHICH MAX14830 WRITES MISO DATA
R XU1 U0 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
RU1
HiZ
HiZ
IRQ3 IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
U0 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
IRQ3
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
IRQ2 IRQ1 IRQ0
Figure 20. SPI Fast Read Cycle
Fast Read Cycle
On the MAX14830 the four UART interrupts share the
single IRQ output. When operating in interrupt-based
mode, the microcontroller needs to locate the source of
the interrupt (i.e. which of the four UARTs generated the
interrupt) and clear the interrupt.
To locate the source of an interrupt more quickly, the
MAX14830 implements the SPI fast read cycle. This
means that the microcontroller can determine which
UART is the source of the interrupt (UART0, UART1,
UART2, or UART3) using only 8 clock cycles (Figure 20).
U1 and U0 bits are ignored during the fast read cycle.
I2C Interface
The MAX14830 contains an I2C-compatible interface
for data communication with a host processor (SCL and
SDA). The interface supports a clock frequency up to
1MHz. SCL and SDA require pullup resistors that are
connected to a positive supply.
START, STOP, and Repeated START Conditions
When writing to the MAX14830 using I2C, the master
sends a START condition (S) followed by the MAX14830
I2C address. After the address, the master sends
the register address of the register that is to be programmed. The master then ends communication by
59

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
rP
SS
SCL
MAX14830
SDA
Figure 21. I2C START, STOP, and Repeated START Conditions
Table 12. I2C Address Map
MOSI/A1
DGND DGND 0xD8 0xD9 0xB8 0xB9 0x58 0x59 0x38 0x39
DGND V
DGND SCL 0xC4 0xC5 0xA4 0xA5 0x44 0x45 0x24 0x25
DGND SDA 0xC6 0xC7 0xA6 0xA7 0x46 0x47 0x26 0x27
V
L
V
L
V
L
V
L
SCL DGND 0xD0 0xD1 0xB0 0xB1 0x50 0x51 0x30 0x31
SCL V
SCL SCL 0xD4 0xD5 0xB4 0xB5 0x54 0x55 0x34 0x35
SCL SDA 0xD6 0xD7 0xB6 0xB7 0x56 0x57 0x36 0x37
SDA DGND 0xC0 0xC1 0xA0 0xA1 0x40 0x41 0x20 0x21
SDA V
SDA SCL 0xDC 0xDD 0xBC 0xBD 0x5C 0x5D 0x3C 0x3D
SDA SDA 0xDE 0xDF 0xBE 0xBF 0x5E 0x5F 0x3E 0x3F
CS/A0
L
DGND 0xC8 0xC9 0xA8 0xA9 0x48 0x49 0x28 0x29
V
L
SCL 0xCC 0xCD 0xAC 0xAD 0x4C 0x4D 0x2C 0x2D
SDA 0xCE 0xCF 0xAE 0xAF 0x4E 0x4F 0x2E 0x2F
L
L
UART0 UART1 UART2 UART3
WRITE READ WRITE READ WRITE READ WRITE READ
0xC2 0xC3 0xA2 0xA3 0x42 0x43 0x22 0x23
0xCA 0xCB 0xAA 0xAB 0x4A 0x4B 0x2A 0x2B
0xD2 0xD3 0xB2 0xB3 0x52 0x53 0x32 0x33
0xDA 0xDB 0xBA 0xBB 0x5A 0x5B 0x3A 0x3B
issuing a STOP condition (P), to relinquish control of the
bus, or a Repeated START condition (Sr) to communicate to another I2C slave. See Figure 21.
Slave Address
The MAX14830 includes a 7-bit I2C slave address, allowing up to 16 MAX14830 devices to share the same I2C
60
bus. The address is defined by connecting the MOSI/
A1 and CS/A0 inputs to ground, VL, SDA or to SCL
(Table 12). Set the read/write bit to 1 to configure the
MAX14830 to read mode. Set the read/write bit to 0 to
configure the MAX14830 to write mode. The address is
the first byte of information sent to the MAX14830 after the
START condition.

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
WRITE SINGLE BYTE
MAX14830
S
Figure 22. Write Byte Sequence
BURST WRITE
S DEVICE SLAVE ADDRESS - W A
FROM MASTER TO STAVE FROM SLAVE TO MASTER
Figure 23. Burst Write Sequence
DEVICE SLAVE ADDRESS - W A
8 DATA BITS
FROM MASTER TO STAVE
8 DATA BITS - 1
FROM SLAVE TO MASTER
A
Bit Transfer
One data bit is transferred during each SCL clock cycle.
The data on SDA must remain stable during the high
period of the SCL clock pulse. Changes in SDA while
SCL is high and stable are considered control signals
(see the START, STOP, and Repeated START Conditions
section). Both SDA and SCL remain high when the bus
is not active.
Single-Byte Write
With this operation the master sends an address and one
or two data bytes to the slave device (Figure 22). The
write byte procedure is the following:
1) The master sends a START condition.
2) The master sends the 7-bit slave ID plus a write bit (low).
3) The addressed slave asserts an ACK on the data line.
4) The master sends the 8-bit register address.
5) The active slave asserts an ACK on the data line only
if the address is valid (NAK if not).
REGISTER ADDRESS A
A
P
REGISTER ADDRESS A
8 DATA BITS - 2 A
8 DATA BITS - N A
P
6) The master sends an 8-bit data byte.
7) The slave asserts an ACK on the data line.
8) The master generates a STOP condition.
Burst Write
With this operation the master sends an address and
multiple data bytes to the slave device (Figure 23). The
burst write procedure is as follows:
1) The master sends a START condition.
2) The master sends the 7-bit slave ID plus a write bit (low).
3) The addressed slave asserts an ACK on the data line.
4) The master sends the 8-bit register address.
5) The slave asserts an ACK on the data line only if the
address is valid (NAK if not).
6) The master sends 8 bits of data.
7) The slave asserts an ACK on the data line.
8) Repeat steps 6 and 7 as needed.
9) The master generates a STOP condition.
61

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
2A
READ SINGLE BYTE
MAX14830
Figure 24. Read Byte Sequence
Figure 25. Burst Read Sequence
S
Sr
BURST READ
S
Sr
DEVICE SLAVE ADDRESS - W A
DEVICE SLAVE ADDRESS - R
FROM MASTER TO STAVE FROM SLAVE TO MASTER
DEVICE SLAVE ADDRESS - W A
DEVICE SLAVE ADDRESS - R
FROM MASTER TO STAVE FROM SLAVE TO MASTER
A
A
A 8 DATA BITS - 38 DATA BITS -
REGISTER ADDRESS A
8 DATA BITS NA
REGISTER ADDRESS A
8 DATA BITS - 1A
8 DATA BITS - NNA
P
P
Single-Byte Read
With this operation the master sends an address and
receives 1 or 2 data bytes from the slave device
(Figure 24). The read byte procedure is as follows:
1) The master sends a START condition.
2) The master sends the 7-bit slave ID plus a write bit (low).
3) The addressed slave asserts an ACK on the data line.
4) The master sends the 8-bit register address
5) The active slave asserts an ACK on the data line only
if the address is valid (NAK if not).
6) The master sends a repeated START (Sr).
7) The master sends the 7-bit slave ID plus a read bit (high).
8) The addressed slave asserts an ACK on the data line.
9) The slave sends 8 data bits.
10) The master asserts a NACK on the data line.
11) The master generates a STOP condition.
62
Burst Read
With this operation the master sends an address and
receives multiple data bytes from the slave device
(Figure 25). The burst read procedure is as follows:
1) The master sends a START condition.
2) The master sends the 7-bit slave ID plus a write bit (low).
3) The addressed slave asserts an ACK on the data line.
4) The master sends the 8-bit register address.
5) The slave asserts an ACK on the data line only if the
address is valid (NAK if not).
6) The master sends a repeated START condition.
7) The master sends the 7-bit slave ID plus a read bit (high).
8) The slave asserts an ACK on the data line.
9) The slave sends 8 bits of data.
10) The master asserts an ACK on the data line.
11) Repeat 9 and 10 (N-2) times.
12) The slave sends the last 8 data bits.
13) The master asserts a NACK on the data line.
14) The master generates a STOP condition.

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Acknowledge Bits
Data transfers are acknowledged with an acknowledge
bit (ACK) or a not-acknowledge bit (NACK). Both the
master and the MAX14830 generate ACK bits. To generate an ACK, pull SDA low before the rising edge of the
ninth clock pulse and keep it low during the high period
of the ninth clock pulse (Figure 26). To generate a NACK,
leave SDA high before the rising edge of the ninth clock
pulse and keep it high for the duration of the ninth clock
pulse. Monitoring for NACK bits allows for detection of
unsuccessful data transfers.
S
SCL
SDA
Figure 26. Acknowledge Bits
12 89
MAX14830
NOT ACKNOWLEDGE
ACKNOWLEDGE
Applications Information
Startup and Initialization
The MAX14830 is initialized following power-up or a
hardware or software reset (Figure 27). Check that the
MAX14830 is ready for operation after a power-up or
reset by monitoring the IRQ output, if interrupt driven
operation is employed.
In polled mode, repeatedly read a known register until
the expected contents are returned.
Low-Power Operation
To reduce the power consumption during normal operation, the following techniques can be adopted:
•DonotusetheinternalPLL.Thissavesthemostpower
of the options listed here. Disable and bypass the PLL.
•WhenanyofthefourUARTsarenotbeingused,sop
clicking via CLKDisabl.
•Use an external 1.8V supply at V18. This saves the
power dissipated in the internal 1.8V linear regulator
for the 1.8V core supply. Disable the internal regulator
by connecting LDOEN to DGND.
•Keepinternalclockratesaslowaspossible.
•UsealowvoltageontheVA supply.
Interrupts and Polling
Monitor the MAX14830 by polling the ISR register or
by monitoring the IRQ output. In polled mode, the IRQ
physical interrupt output is not used and the host controller polls the ISR register at frequent intervals to establish
the state of the MAX14830.
Alternatively, the physical interrupt, IRQ, of the MAX14830
can be used to interrupt the host controller at specified
events, making polling unnecessary. The IRQ output is
an open-drain output that requires a pullup resistor to VL.
POWER-UP/
RST INPUT PULLED HIGH
IRQ IS HIGH?
OR
DIVLSB READ
SUCCESSFULLY?
YES
CONFIGURE
CLOCKING
CONFIGURE
MODES
Figure 27. Startup and Initialization Flow Chart
NO
ENABLE
INTERRUPTS
CONFIGURE
FIFO CONTROL
CONFIGURE
FLOW CONTROL
CONFIGURE
GPIOs
START
COMMUNICATION
Logic-Level Translation
The MAX14830 can be directly connected to transceivers
and controllers that have different supply voltages. The VL
input defines the logic voltage levels of the control ler interface while the V
voltage defines the logic of the trans-
EXT
ceiver interface. This ensures flexibility when selecting a
controller and transceiver. Figure 28 is an example of a
setup when the controller, transceiver, and the MAX14830
are powered by three different supplies.
IO-Link Application
The Typical Operating Circuit shows a four-part IO-link
master circuit with SPI control on the MAX14830 and the
IO-link transceivers.
63

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
MAX14830
Figure 28. Logic-Level Translation
XOUT
XIN
V
DD
MICROCONTROLLER
CrystalEn
CRYSTAL
OSCILLATOR
ClkToGPIO
2.5V
V
LVA
RST
SPI/I2C
MAX14830
IRQ
DIVIDER PLL
PLLEn
V
EXT
TX_ DI
RX_
RTS_
DGNDAGND
3.3V1.8V
RO
DE
GENERATOR _
V
CC
MAX3078
TRANSCEIVER
MAX14830
FRACTIONAL
BAUD-RATE
PHY0
PHY1
PHY2
GPIO
XOUT
XIN
XOUT
XIN
Figure 29. Interchip Synchronization
64
CrystalEn
CRYSTAL
OSCILLATOR
CrystalEn
CRYSTAL
OSCILLATOR
GPIO_
DIVIDER PLL
PLLEn
DIVIDER
PLL
PLLEn
MAX14830
FRACTIONAL
BAUD-RATE
GENERATOR _
MAX14830
FRACTIONAL
BAUD-RATE
GENERATOR _
PHY3
PHY4
PHY5
PHY6
PHY7
PHY8
PHY9
PHY10
PHY11

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Typical Operating Circuit
MISO
MOSI
CONTROLLER
SCLK
CS1
CS2
RST
MAX14830
RST CS SCLK
V
EXT
GPIO1
GPIO5
GPIO9
GPIO13
XIN XOUT
MAX14830
MOSI MISO
RTSO
RTS1
RTS2
RTS3
TX0
RX0
TX1
RX1
TX2
RX2
TX3
RX3
RX
TXC
TXEN
RX
TXC
TXEN
RX
TXC
TXEN
RX
TXC
TXEN
MAX14824
MAX14824
MAX14824
MAX14824
PORT1
ADDR1
PORT2
ADDR2
PORT3
ADDR3
PORT4
ADDR4
IO-LINK QUAD MASTER APPLICATION
65

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Typical Operating Circuits (continued)
3.3V
MAX14830
0.1µF
SPI/I2C
MOSI
MOSI
MISO
TX0
SCLK
SCLK
MICROCONTROLLER
IRQ
CS
SS
IRQ
0.1µF 0.1µF
V
A
V
EXTVL
MAX14830
V
18
TX0LDOEN
RTS0
RX0
TX1
RTS1
RX1
TX2
RTS2
RX2
1µF
MAX14840
DI
DE
RO
RE
MAX14840
DI
DE
RO
RE
MAX14840
DI
DE
RO
RE
A0
B0
A1
B1
A2
B2
66
TX3
RTS3
RX3
DGNDAGND
QUAD RS-485 INTERFACE CONTROLLED THROUGH SPI
MAX14840
DI
DE
RO
RE
A3
B3

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Chip Information
PROCESS: BiCMOS
Package Information
For the latest package outline information and land patterns
(footprints), go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages. Note that a
“+”, “#”, or “-” in the package code indicates RoHS status only.
Package drawings may show a different suffix character, but
the drawing pertains to the package regardless of RoHS status.
PACKAGE
TYPE
48 TQFN T4877+3
PACKAGE
CODE
OUTLINE
NO.
21-0144 90-0129
LAND
PATTERN NO.
MAX14830
67

Quad Serial UART with 128-Word FIFOs
Revision History
REVISION
NUMBER
0 9/10 Initial release —
1 12/10
REVISION
DATE
MAX14830
2 9/11
DESCRIPTION
Corrected specifications in the Absolute Maximum Ratings and DC Electrical
Characteristics, updated the Register Map, corrected Table 12
Removed internal oscillator description throughout data sheet; deleted TOCs 1
and 2; corrected Figure 7; changed V18 capacitor to 1FF; corrected I2C burst read
sequence; corrected ISR description; added RTSInvert bit; added CLKDisabl bit
PAGES
CHANGED
8, 9, 29, 34,
37, 38, 40,
57, 60
1, 2, 7, 8,10,
14,17,19, 20,
21, 27, 28, 29,
30, 34, 35, 40,
43, 52, 53, 57,
62, 63, 66
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are implied.
Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time. The parametric values (min and max limits) shown in the Electrical
Characteristics table are guaranteed. Other parametric values quoted in this data sheet are provided for guidance.
Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600 68
©
2011 Maxim Integrated Products Maxim is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...