
General Description
The MAX1444 10-bit, 3V analog-to-digital converter
(ADC) features a pipelined 10-stage ADC architecture
with fully differential wideband track-and-hold (T/H)
input and digital error correction incorporating a fully
differential signal path. This ADC is optimized for lowpower, high dynamic performance applications in
imaging and digital communications. The MAX1444
operates from a single 2.7V to 3.6V supply, consuming
only 57mW while delivering a 59.5dB signal-to-noise
ratio (SNR) at a 20MHz input frequency. The fully differential input stage has a 400MHz -3dB bandwidth and
may be operated with single-ended inputs. In addition
to low operating power, the MAX1444 features a 5µA
power-down mode for idle periods.
An internal 2.048V precision bandgap reference is
used to set the ADC full-scale range. A flexible reference structure allows the user to supply a buffered,
direct, or externally derived reference for applications
requiring increased accuracy or a different input voltage range.
Higher speed, pin-compatible versions of the MAX1444
are also available. Please refer to the MAX1446 data
sheet (60Msps) and the MAX1448 data sheet
(80Msps).
The MAX1444 has parallel, offset binary, CMOS-compatible three-state outputs that can be operated from
1.7V to 3.6V to allow flexible interfacing. The device is
available in a 5x5mm 32-pin TQFP package and is
specified over the extended industrial (-40°C to +85°C)
temperature range.
________________________Applications
Ultrasound Imaging
CCD Imaging
Baseband and IF Digitization
Digital Set-Top Boxes
Video Digitizing Applications
Features
o Single 3.0V Operation
o Excellent Dynamic Performance
59.5dB SNR at f
IN
= 20MHz
74dBc SFDR at f
IN
= 20MHz
o Low Power
19mA (Normal Operation)
5μA (Shutdown Mode)
o Fully Differential Analog Input
o Wide 2V
p-p Differential Input Voltage Range
o 400MHz -3dB Input Bandwidth
o On-Chip 2.048V Precision Bandgap Reference
o CMOS-Compatible Three-State Outputs
o 32-Pin TQFP Package
o Evaluation Kit Available
MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
________________________________________________________________
Maxim Integrated Products
1
Pin Configuration
19-1745; Rev 3; 8/10
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim Direct at 1-888-629-4642,
or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
EVALUATION KIT
AVAILABLE
Ordering Information
Functional Diagram appears at end of data sheet.
/V Denotes an automotive qualified part.
+
Denotes a lead(Pb)-free/RoHS-compliant package.
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
MAX1444EHJ -40°C to +85°C 32 TQFP
MAX1444EHJ/V+ -40°C to +85°C 32 TQFP
TOP VIEW
REFIN
GND
REFOUT
REFN
COM
V
GND
GND
IN+
REFP
32 28
1
2
3
DD
4
5
6
7
IN-
8GND
10
9
DD
DD
V
V
293031
MAX1444
CLK
GND
D0
D1
D2
D3
25
27
26
24 D4
OGND
23
T.P.
22
OV
21
DD
D5
20
D6
19
D7
18
17
D8
14
13
15
1611 12
D9
OE
PD
GND
TQFP
MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VDD= 3V; OVDD= 2.7V; 0.1µF and 1µF capacitors from REFP, REFN, and COM to GND; V
REFIN
= 2.048V; REFOUT connected to
REFIN through a 10kΩ resistor; V
IN
= 2V
P-P
(differential with respect to COM); CL= 10pF at digital outputs; f
CLK
= 40MHz; TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. ≥ +25°C guaranteed by production test, < +25°C guaranteed by design and characterization; typi-
cal values are at T
A
= +25°C.)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
VDD, OVDDto GND ...............................................-0.3V to +3.6V
OGND to GND.......................................................-0.3V to +0.3V
IN+, IN- to GND........................................................-0.3V to V
DD
REFIN, REFOUT, REFP,
REFN, and COM to GND........................-0.3V to (V
DD
+ 0.3V)
OE, PD, CLK to GND..................................-0.3V to (V
DD
+ 0.3V)
D9–D0 to GND.........................................-0.3V to (OV
DD
+ 0.3V)
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +70°C)
32-Pin TQFP (derate 18.7mW/°C above +70°C).....1495.3mW
Operating Temperature Range ...........................-40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range .............................-60°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C
Soldering Temperature (reflow) .......................................+260°C
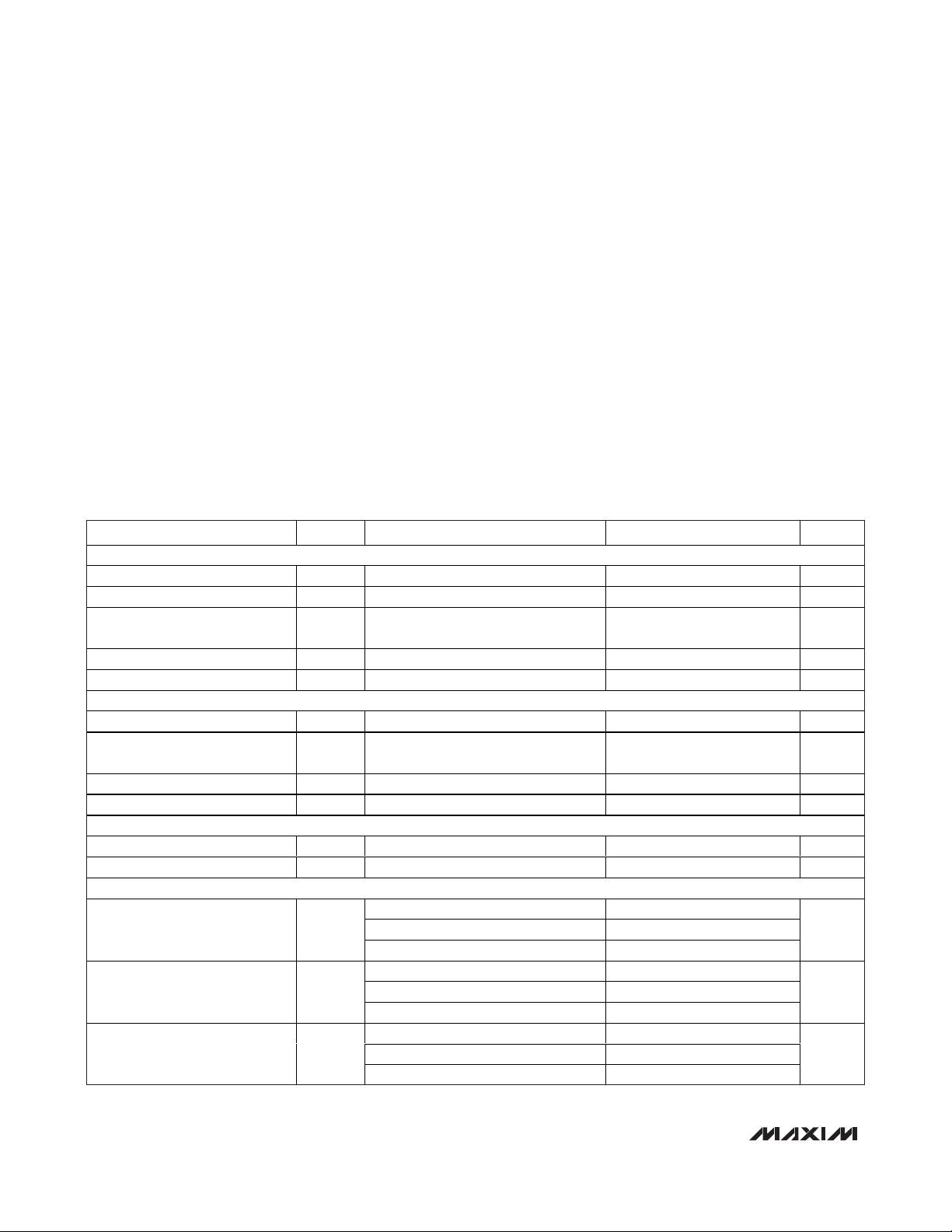
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DC ACCURACY
Resolution 10 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity INL fIN = 7.51MHz, TA ≥ +25°C ±0.6 ±1.9 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity DNL
Offset Error <±0.1 ±1.7 % FS
Gain Error TA ≥ +25°C 0 ±2% FS
ANALOG INPUT
Input Differential Range V
Common-Mode
Voltage Range
Input Resistance R
Input Capacitance C
CONVERSION RATE
Maximum Clock Frequency f
Data Latency 5.5 Cycles
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS (f
Signal-to-Noise Ratio SNR
Signal-to-Noise + Distortion
(Up to 5th harmonic)
f
IN
guaranteed
DIFF
V
COM
CLK
= 40MHz, 4096-point FFT)
CLK
SINAD
Differential or single-ended inputs ±1.0 V
Switched capacitor load 50 kΩ
IN
IN
fIN = 7.51MHz 57.5 59.5
fIN = 19.91MHz 56.3 59.5
f
IN
fIN = 7.51MHz 57 59.4
fIN = 19.91MHz 56.1 59
f
IN
fIN = 7.51MHz 67 75
fIN = 19.91MHz 66 74Spurious-Free Dynamic Range SFDR
f
IN
= 7.51MHz, no missing codes
= 39.9MHz (Note 1) 58.5
= 39.9MHz (Note 1) 58.3
= 39.9 MHz (Note 1) 72.5
40 MHz
±0.4 ±1.0 LSB
VDD/2
±0.5
5pF
V
dB
dB
dBc
MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VDD= 3V; OVDD= 2.7V; 0.1µF and 1µF capacitors from REFP, REFN, and COM to GND; V
REFIN
= 2.048V; REFOUT connected to
REFIN through a 10kΩ resistor; V
IN
= 2V
P-P
(differential with respect to COM); CL= 10pF at digital outputs; f
CLK
= 40MHz; TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. ≥ +25°C guaranteed by production test, < +25°C guaranteed by design and characterization; typi-
cal values are at T
A
= +25°C.)
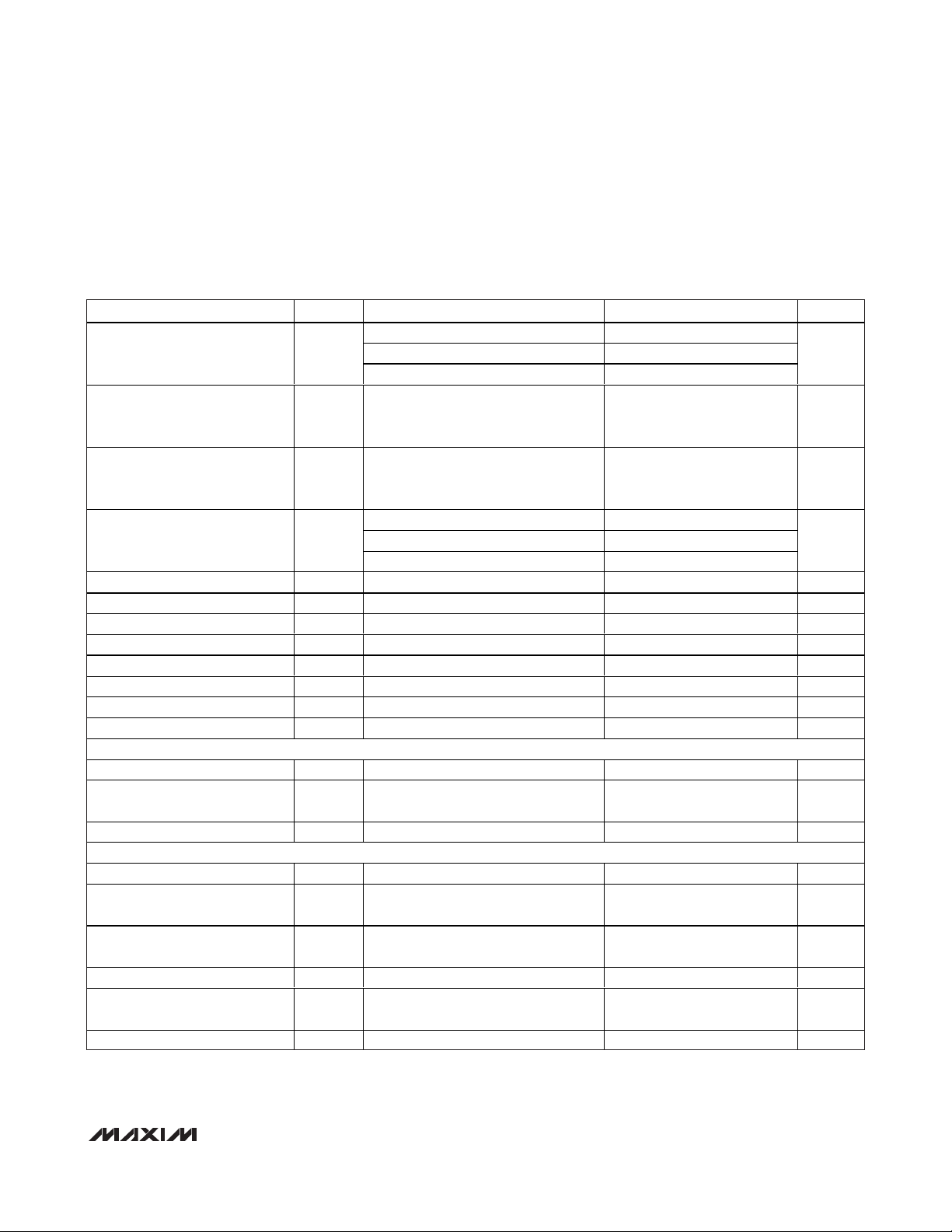
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX
UNITS
fIN = 7.51MHz -75
fIN = 19.91MHz -74
Third-Harmonic Distortion HD3
f
IN
= 39.9MHz (Note 1) -72.5
dBc
Two-Tone Intermodulation
Distortion
IMD
f
1
= 11.5MHz at -6.5dBFS
f
2
= 13.5MHz at -6.5dBFS
(Note 2)
-76 dBc
Third-Order Intermodulation
Distortion
IM3
f
1
= 11.5MHz at -6.5dBFS
f
2
= 13.5MHz at -6.5dBFS
(Note 2)
-76 dBc
fIN = 7.51MHz -73.8 -65
fIN = 19.91MHz -72.2 -65
Total Harmonic Distortion
(First 4 Harmonics)
THD
f
IN
= 39.9MHz (Note 1) -70
dBc
Small-Signal Bandwidth Input at -20dBFS, differential inputs 500 MHz
Full-Power Bandwidth FPBW Input at -0.5dBFS, differential inputs 400 MHz
Aperture Delay t
AD
1ns
Aperture Jitter t
AJ
2
ps
RMS
Overdrive Recovery Time For 1.5 × full-scale input 2 ns
Differential Gain ±1%
Differential Phase
Degrees
Output Noise IN+ = IN- = COM 0.2
LS B
RM S
INTERNAL REFERENCE
Reference Output Voltage
2.048 ±1% V
Reference Temperature
Coefficient
60
p p m/°C
Load Regulation 1.25
mV/mA
BUFFERED EXTERNAL REFERENCE (V
REFIN
= 2.048V)
REFIN Input Voltage
V
Positive Reference Output
Voltage
V
REFP
V
Negative Reference Output
Voltage
V
Common-Mode Level V
COM
V
Differential Reference Output
Voltage Range
ΔV
REF
= V
REFP
- V
REFN
, TA ≥ +25°C 0.98
1.07 V
REFIN Resistance
>50 MΩ
REFOUT
TC
REF
V
REFIN
V
REFN
ΔV
REF
R
REFIN
±0.25
2.048
2.012
0.988
VDD / 2
1.024
MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VDD= 3V; OVDD= 2.7V; 0.1µF and 1µF capacitors from REFP, REFN, and COM to GND; V
REFIN
= 2.048V; REFOUT connected to
REFIN through a 10kΩ resistor; V
IN
= 2V
P-P
(differential with respect to COM); CL= 10pF at digital outputs; f
CLK
= 40MHz; TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. ≥ +25°C guaranteed by production test, < +25°C guaranteed by design and characterization; typi-
cal values are at T
A
= +25°C.)
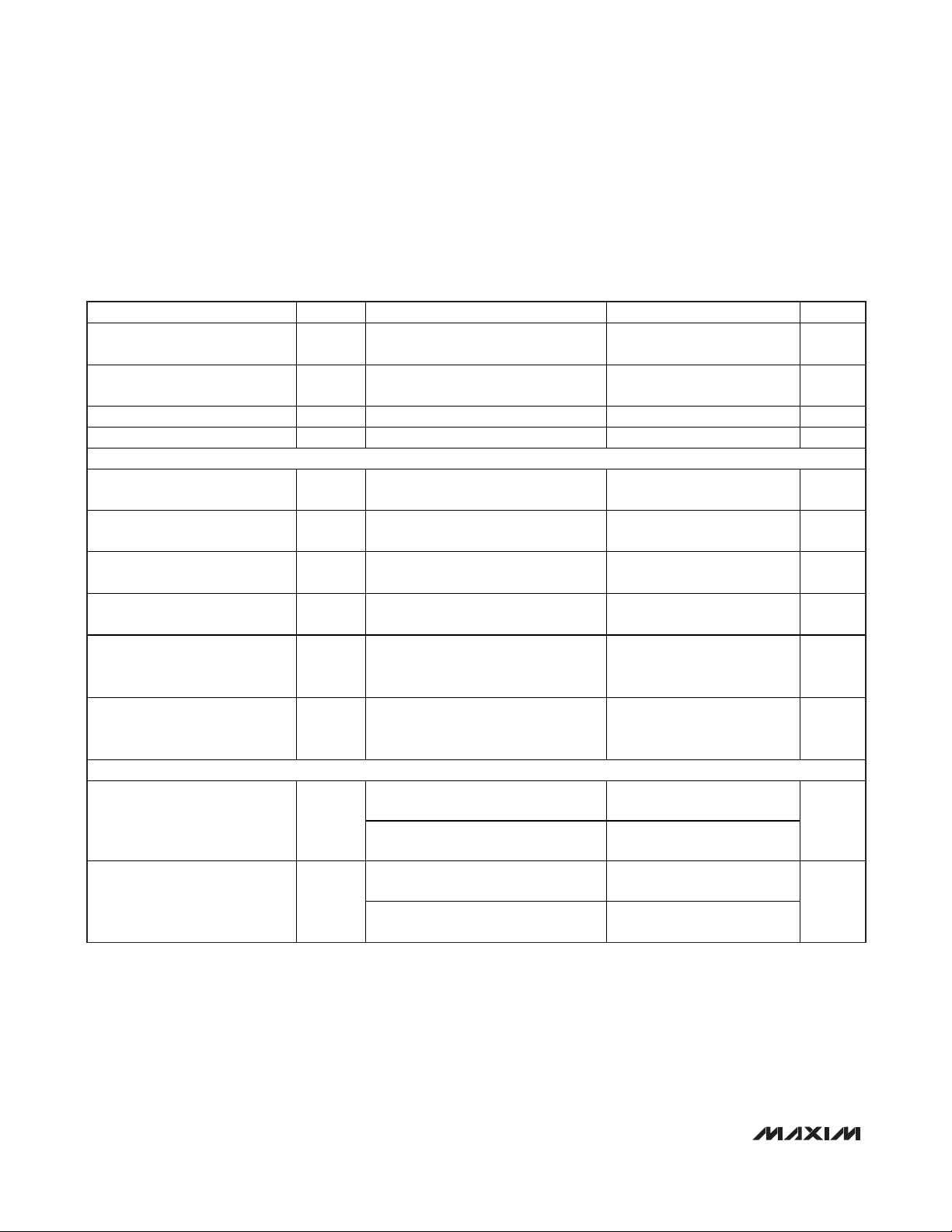
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Maximum REFP, COM Source
Current
Maximum REFP, COM Sink
Current
Maximum REFN Source Current I
Maximum REFN Sink Current I
UNBUFFERED EXTERNAL REFERENCE (V
REFP, REFN Input Resistance
REFP, REFN, COM Input
Capacitance
Differential Reference Input
Voltage Range
COM Input Voltage Range V
I
S OU RC E
I
SINK
S OU RC E
SINK
= AGND, reference voltage applied to REFP, REFN, and COM)
REFIN
,
R
R
ΔV
REFP
REFN
C
REF
COM
Measured between REFP and COM
and REFN and COM
IN
ΔV
REF
= V
REFP
- V
REFN
-250 µA
1.024
±10%
VDD / 2
±10%
5mA
250 µA
-5 mA
4kΩ
15 pF
V
V
REFP Input Voltage V
REFN Input Voltage V
DIGITAL INPUTS (CLK, PD, OE)
Input High Threshold V
Input Low Threshold V
REFP
REFN
IH
IL
CLK
PD, OE
CLK
PD, OE
0.8 ×
V
DD
0.8 ×
OV
DD
V
C OM
ΔV
V
COM
ΔV
RE F
2
REF
2
+
/
-
/
0.2 ×
V
DD
0.2 ×
OV
DD
V
V
V
V
MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VDD= 3V; OVDD= 2.7V; 0.1µF and 1µF capacitors from REFP, REFN, and COM to GND; V
REFIN
= 2.048V; REFOUT connected to
REFIN through a 10kΩ resistor; V
IN
= 2V
P-P
(differential with respect to COM); CL= 10pF at digital outputs; f
CLK
= 40MHz; TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, unless otherwise noted. ≥ +25°C guaranteed by production test, < +25°C guaranteed by design and characterization; typi-
cal values are at T
A
= +25°C.)
Note 1: SNR, SINAD, THD, SFDR, and HD3 are based on an analog input voltage of -0.5dBFS referenced to a 1.024V full-scale
input voltage range.
Note 2: Intermodulation distortion is the total power of the intermodulation products relative to the individual carrier. This number is
6dB better if referenced to the two-tone envelope.
Note 3: Digital outputs settle to V
IH
, VIL.
Note 4: REFIN is driven externally. REFP, COM, and REFN are left open while powered down.
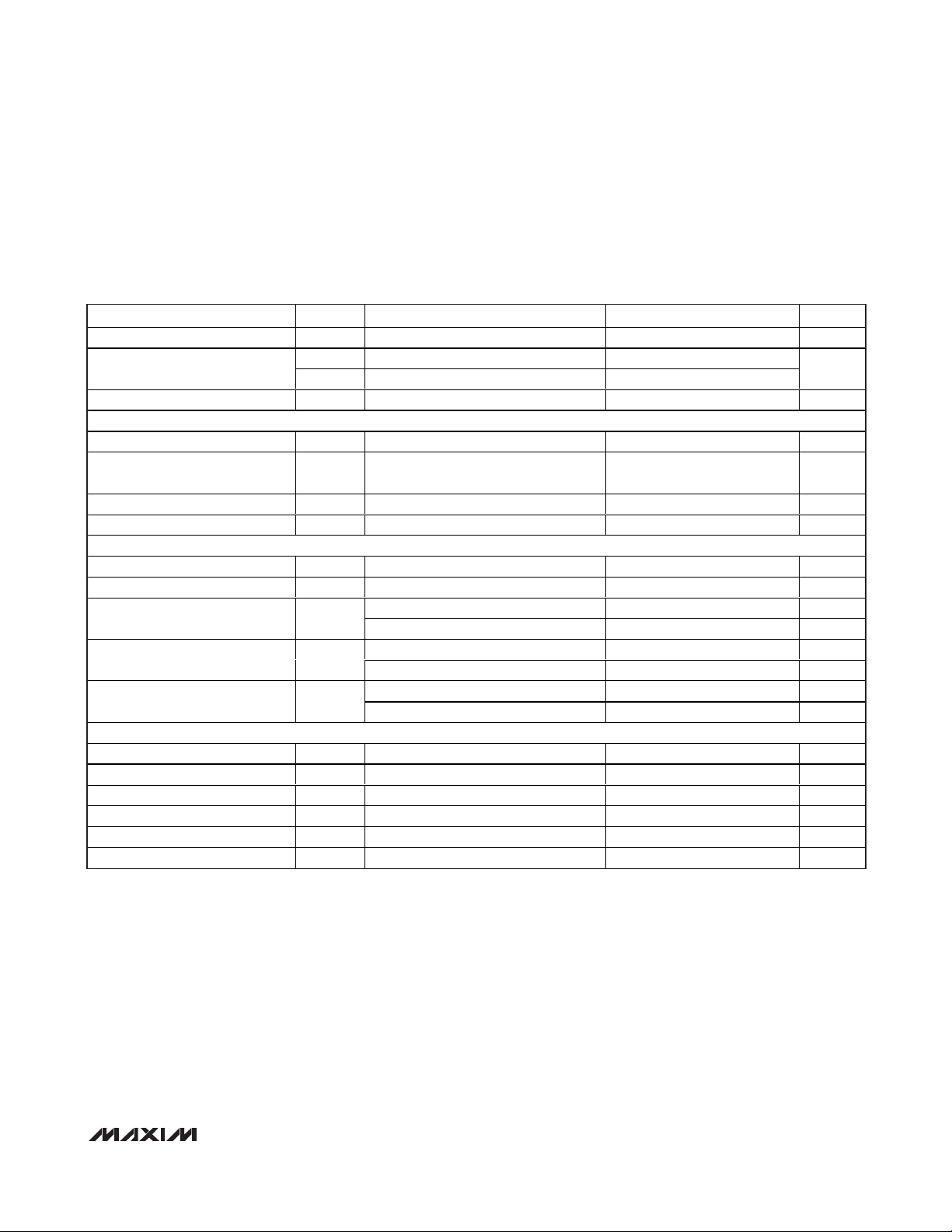
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Input Hysteresis V
Input Leakage
Input Capacitance C
HYST
I
IH
I
IL
IN
VIH = VDD = OV
DD
VIL = 0V ±5
DIGITAL OUTPUTS (D9–D0)
Output Voltage Low V
Output Voltage High V
Three-State Leakage Current I
Three-State Output Capacitance C
LEAK
OUT
OL
OH
I
= 200μA 0.2 V
SINK
I
SOURCE
OE = OV
OE = OV
= 200μA
DD
DD
OV
POWER REQUIREMENTS
Analog Supply Voltage V
Output Supply Voltage OV
Analog Supply Current I
Output Supply Current I
Power-Supply Rejection PSRR
DD
DD
VDD
OVDD
O p er ati ng , f
S hutd ow n, cl ock i d l e, P D = O E = OV
O p er ati ng , f
S hutd ow n, cl ock i d l e, P D = O E = OV
= 19.91M H z at - 0.5d BFS 19 27 mA
I N
D D
= 19.91M H z at - 0.5d BFS 4.5 mA
I N
D D
Offset ±0.1 mV/V
Gain ±0.1 %/V
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
CLK Rise to Output Data Valid t
OE Fall to Output Enable t
OE Rise to Output Disable t
ENABLE
DISABLE
CLK Pulse Width High t
CLK Pulse Width Low t
Wake-up Time t
DO
CH
CL
WAKE
Figure 6 (Note 3) 5 8 ns
Figure 5 10 ns
Figure 5 15 ns
Figure 6, clock period 25ns 12.5 ±3.8 ns
Figure 6, clock period 25ns 12.5 ±3.8 ns
(Note 4) 1.7 µs
0.1 V
5pF
-
DD
0.2
±10 µA
5pF
2.7 3.0 3.6 V
1.7 3.0 3.6 V
415µA
120µA
±5
µA
V
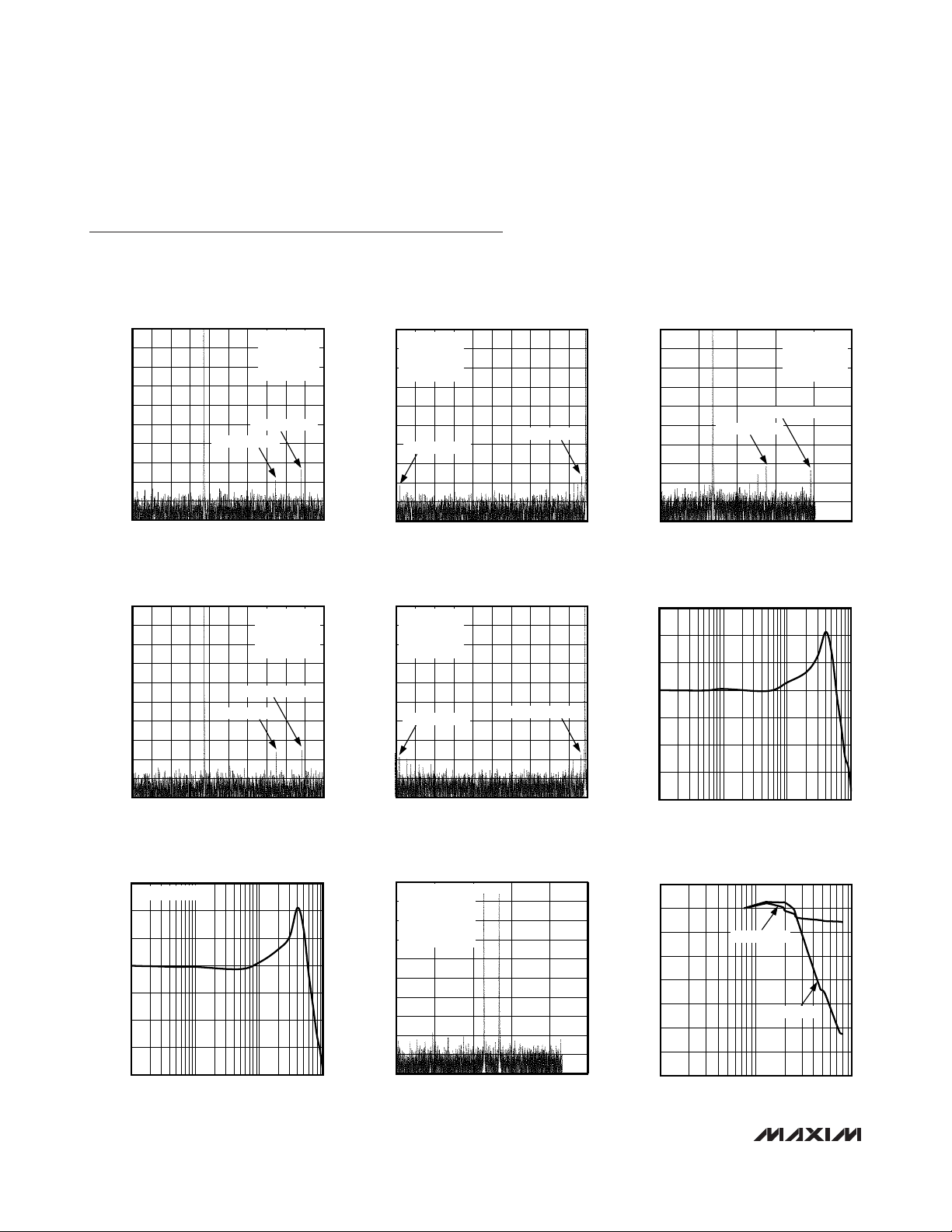
MAX1444-01
-100
-70
-80
-90
-50
-60
-10
-20
-30
-40
0
0 2 4 6 8101214161820
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
AMPLITUDE (dB)
SINAD = 59dB
SNR = 59.3dB
THD = -71.6dBc
SFDR = 73dBc
FFT PLOT (fIN = 7.51MHz,
8192-POINT FFT, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT)
3RD HARMONIC
2ND HARMONIC
MAX1444-02
-100
-70
-80
-90
-50
-60
-10
-20
-30
-40
0
0 2 4 6 8101214161820
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
AMPLITUDE (dB)
SINAD = 58.9dB
SNR = 59.1dB
THD = -72.8dBc
SFDR = 75.2dBc
FFT PLOT (fIN = 19.91MHz,
8192-POINT FFT, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT)
3RD HARMONIC
2ND HARMONIC
MAX1444-03
-100
-70
-80
-90
-50
-60
-10
-20
-30
-40
0
0 5 10 15 20 25
FFT PLOT (fIN = 47MHz,
8192-POINT FFT, DIFFERENTIAL INPUT)
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
AMPLITUDE (dB)
SINAD = 58.1dB
SNR = 58.4dB
THD = -69.7dBc
SFDR = 72.4dBc
3RD HARMONIC
2ND HARMONIC
MAX1444-04
-100
-70
-80
-90
-50
-60
-10
-20
-30
-40
0
0 2 4 6 8101214161820
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
AMPLITUDE (dB)
SINAD = 59.7dB
SNR = 60dB
THD = -71.8dBc
SFDR = 75dBc
FFT PLOT (fIN = 7.51MHz,
8192-POINT FFT, SINGLE-ENDED INPUT)
3RD HARMONIC
2ND HARMONIC
MAX1444-05
-100
-70
-80
-90
-50
-60
-10
-20
-30
-40
0
0 2 4 6 8101214161820
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
AMPLITUDE (dB)
SINAD = 59.1dB
SNR = 59.2dB
THD = -74.6dBc
SFDR = 77.6dBc
FFT PLOT (fIN = 19.91MHz,
8192-POINT FFT, SINGLE-ENDED INPUT)
3RD HARMONIC
2ND HARMONIC
6
1 100 1000
FULL-POWER INPUT BANDWIDTH
vs. ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (SINGLE ENDED)
-6
-8
-4
-2
0
2
4
MAX1444-06
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
GAIN (dB)
10
6
1 100 1000
SMALL-SIGNAL INPUT BANDWIDTH
vs. ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (SINGLE ENDED)
-6
-8
-4
-2
0
2
4
MAX1444-07
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
GAIN (dB)
10
VIN = 100mVp-p
MAX1444-08
-100
-70
-80
-90
-50
-60
-10
-20
-30
-40
0
0 5 10 15 20 25
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
AMPLITUDE (dB)
TWO-TONE INTERMODULATION
8192-POINT IMD (DIFFERENTIAL INPUT)
f1 = 11.5MHz AT
-6.5dB FS
f
2
= 13.5MHz AT
-6.5dB FS
IMD = -76dBc
80
40
110100
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE
vs. ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY
50
45
MAX1444-09
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
SFDR (dBc)
60
55
65
70
75
SINGLE ENDED
DIFFERENTIAL
MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Typical Operating Characteristics
(VDD= 3.0V, OVDD= 2.7V, internal reference, differential input at -0.5dB FS, f
CLK
= 40MHz, CL≈ 10pF, TA= +25°C, unless other-
wise noted.)

62
54
1 10 100
56
55
MAX1444-10
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
SNR (dB)
58
57
59
60
61
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO
vs. ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY
SINGLE ENDED
DIFFERENTIAL
-45
-75
1 10 100
-70
MAX1444-11
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
THD (dBc)
-60
-65
-55
-50
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY
SINGLE ENDED
DIFFERENTIAL
65
45
1 10 100
49
MAX1444-12
ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
SINAD (dB)
53
57
61
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE + DISTORTION
vs. ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY
SINGLE ENDED
DIFFERENTIAL
50
60
55
70
65
75
80
-15 -9-12 -6 -3 0
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE
vs. ANALOG INPUT POWER
MAX1444-13
ANALOG INPUT POWER (dB FS)
SFDR (dBc)
fIN = 19.91MHz
40
50
45
55
60
65
-15 -9-12 -6 -3 0
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO
vs. ANALOG INPUT POWER
MAX1444-14
ANALOG INPUT POWER (dB FS)
SNR (dB)
fIN = 19.91MHz
-80
-70
-75
-60
-65
-55
-50
-15 -9-12 -6 -3 0
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. ANALOG INPUT POWER
MAX1444-15
ANALOG INPUT POWER (dB FS)
THD (dBc)
fIN = 19.91MHz
40
50
45
55
60
65
-15 -9-12 -6 -3 0
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE + DISTORTION
vs. ANALOG INPUT POWER
MAX1444-16
ANALOG INPUT POWER (dB FS)
SINAD (dB)
fIN = 19.91MHz
68
64
76
72
80
84
-40 10-15 356085
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX1444-17
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SFDR (dBc)
fIN = 19.91MHz
54
50
62
58
66
70
-40 10-15 356085
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX1444-18
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SNR (dB)
fIN = 19.91MHz
MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
_______________________________________________________________________________________
7
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(VDD= 3.0V, OVDD= 2.7V, internal reference, differential input at -0.5dB FS, f
CLK
= 40MHz, CL≈ 10pF, TA= +25°C, unless other-
wise noted.)

-76
-80
-68
-72
-64
-60
-40 10-15 356085
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX1444-19
TEMPERATURE (°C)
THD (dBc)
fIN = 19.91MHz
54
50
62
58
66
70
-40 10-15 35 60 85
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE + DISTORTION
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX1444-20
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SINAD (dB)
fIN = 19.91MHz
-0.4
-0.3
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0 400200 600 800 1000 1200
INTEGRAL NONLINEARITY vs.
DIGITAL OUTPUT CODE (BEST STRAIGHT LINE)
MAX1444-21
DIGITAL OUTPUT CODE
INL (LSB)
0 400200 600 800 1000 1200
MAX1444-22
DIGITAL OUTPUT CODE
DNL (LSB)
DIFFERENTIAL NONLINEARITY
vs. DIGITAL OUTPUT CODE
-0.4
-0.3
-0.2
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
-0.03
-0.04
-0.05
0.01
0
-0.01
-0.02
0.03
0.02
0.05
0.04
-40 10-15 35 60 85
MAX1444-23
TEMPERATURE (°C)
GAIN ERROR (LSB)
GAIN ERROR vs. TEMPERATURE,
EXTERNAL REFERENCE (V
REFIN
= 2.048V)
2
0
6
4
8
10
-40 10-15 35 60 85
MAX1444-24
TEMPERATURE (°C)
OFFSET ERROR (LSB)
OFFSET ERROR vs. TEMPERATURE,
EXTERNAL REFERENCE (V
REFIN
= 2.048V)
16
14
20
18
22
24
-40 10-15 356085
MAX1444-26
TEMPERATURE (°C)
I
VDD
(mA)
ANALOG SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. TEMPERATURE
1
0
3
2
5
4
6
1.6 2.42.0 2.8 3.2 3.6
MAX1444-27
OVDD (V)
I
OVDD
(mA)
DIGITAL SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. DIGITAL SUPPLY VOLTAGE
fIN = 7.51MHz
16
14
20
18
22
24
2.70 3.002.85 3.15 3.30 3.45 3.60
ANALOG SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. ANALOG SUPPLY VOLTAGE
MAX1444-25
V
(V)
I
VDD
(mA)
MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(VDD= 3.0V, OVDD= 2.7V, internal reference, differential input at -0.5dB FS, f
CLK
= 40MHz, CL≈ 10pF, TA= +25°C, unless other-
wise noted.)

1
0
3
2
4
5
-40 10-15 356085
MAX1444-28
TEMPERATURE (°C)
I
OVDD
(mA)
DIGITAL SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. TEMPERATURE
fIN = 7.51MHz
3.0
2.5
2.0
4.0
3.5
4.5
5.0
2.70 3.002.85 3.15 3.30 3.45 3.60
ANALOG POWER-DOWN CURRENT
vs. ANALOG POWER SUPPLY
MAX1444-29
VDD (V)
I
VDD
(μA)
OE = OVDD,
PD = V
DD
2
0
6
4
8
10
1.2 1.8 2.4 3.0 3.6
DIGITAL POWER-DOWN CURRENT
vs. DIGITAL POWER SUPPLY
MAX1444-30
OVDD (V)
I
OVDD
(μA)
PD = VDD,
OE = OV
DD
55
50
65
60
75
70
80
30 3834 42 46 50
MAX1444-31
f
CLK
(MHz)
SNR/SINAD, THD/SFDR (dB, dBc)
SNR/SINAD, THD/SFDR
vs. CLOCK FREQUENCY (OVER-CLOCKING)
fIN = 13.24MHz
THD
SFDR
SNR
SINAD
2.02
2.00
2.06
2.04
2.08
2.10
2.70 2.85 3.00 3.15 3.30 3.45 3.60
INTERNAL REFERENCE VOLTAGE
vs. ANALOG SUPPLY VOLTAGE
MAX1444-32
VDD (V)
V
REFOUT
(V)
2.02
2.00
2.06
2.04
2.08
2.10
-40 10-15 356085
MAX1444-33
TEMPERATURE (°C)
V
REFOUT
(V)
INTERNAL REFERENCE VOLTAGE
vs. TEMPERATURE
0
7000
21000
14000
28000
35000
42000
56000
49000
63000
70000
N-2 N-1 N N+1 N+2
0 869
64515
152 0
OUTPUT NOISE HISTOGRAM (DC INPUT)
MAX1444-34
DIGITAL OUTPUT CODE
COUNTS
MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
_______________________________________________________________________________________
9
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(VDD= 3.0V, OVDD= 2.7V, internal reference, differential input at -0.5dB FS, f
CLK
= 40MHz, CL≈ 10pF, TA= +25°C, unless other-
wise noted.)

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Pin Description
PIN NAME FUNCTION
1 REFN
2 COM Common-Mode Voltage Output. Bypass to GND with a >0.1μF capacitor.
3, 9, 10 V
4, 5, 8, 11, 14, 30 GND Analog Ground
6 IN+ Positive Analog Input. For single-ended operation, connect signal source to IN+.
7 IN- Negative Analog Input. For single-ended operation, connect IN- to COM.
12 CLK Conversion Clock Input
13 PD Power Down Input. High: Power-down mode. Low: Normal operation.
15 OE Output Enable Input. High: Digital outputs disabled. Low: Digital outputs enabled.
16–20 D9–D5 Three-State Digital Outputs D9–D5. D9 is the MSB.
21 OV
22 T.P. Test Point. Do not connect.
DD
DD
Lower Reference. Conversion range is ±(V
Bypass to GND with a > 0.1μF capacitor.
Analog Supply Voltage. Bypass to GND with a capacitor combination of 2.2μF in parallel
with 0.1μF.
Output Driver Supply Voltage. Bypass to GND with a capacitor combination of 2.2μF in
parallel with 0.1μF.
REFP
- V
REFN
).
23 OGND Output Driver Ground
24–28 D4–D0 Three-State Digital Outputs D4–D0. D0 is the LSB.
29 REFOUT
31 REFIN Reference Input. V
32 REFP
Internal Reference Voltage Output. May be connected to REFIN through a resistor or a
resistor-divider.
= 2 × (V
REFIN
Upper Reference. Conversion range is ±(V
capacitor.
REFP
- V
). Bypass to GND with a >0.1μF capacitor.
REFN
- V
REFP
). Bypass to GND with a >0.1μF
REFN

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
______________________________________________________________________________________ 11
Detailed Description
The MAX1444 uses a 10-stage, fully differential,
pipelined architecture (Figure 1) that allows for highspeed conversion while minimizing power consumption. Each sample moves through a pipeline stage
every half-clock cycle. Counting the delay through the
output latch, the clock-cycle latency is 5.5.
A 1.5-bit (2-comparator) flash ADC converts the held
input voltage into a digital code. The following digitalto-analog converter (DAC) converts the digitized result
back into an analog voltage, which is then subtracted
from the original held input signal. The resulting error
signal is then multiplied by two, and the product is
passed along to the next pipeline stage where the
process is repeated until the signal has been
processed by all 10 stages. Each stage provides a
1-bit resolution.
Input Track-and-Hold Circuit
Figure 2 displays a simplified functional diagram of the
input track-and-hold (T/H) circuit in both track and hold
mode. In track mode, switches S1, S2a, S2b, S4a, S4b,
S5a, and S5b are closed. The fully differential circuit
samples the input signal onto the two capacitors (C2a
and C2b). Switches S2a and S2b set the common
mode for the amplifier input. The resulting differential
voltage is held on C2a and C2b. Switches S4a, S4b,
S5a, S5b, S1, S2a, and S2b are then opened before
S3a, S3b, and S4c are closed, connecting capacitors
C1a and C1b to the amplifier output. This charges C1a
and C1b to the same values originally held on C2a and
C2b. This value is then presented to the first-stage
quantizer and isolates the pipeline from the fast-changing input. The wide-input-bandwidth T/H amplifier
allows the MAX1444 to track and sample/hold analog
inputs of high frequencies beyond Nyquist. The analog
inputs (IN+ and IN-) can be driven either differentially
or single-ended. It is recommended to match the
impedance of IN+ and IN- and set the common-mode
voltage to midsupply (V
DD
/2) for optimum performance.
Analog Input and Reference Configuration
The MAX1444 full-scale range is determined by the
internally generated voltage difference between REFP
(VDD/2 + V
REFIN
/4) and REFN (VDD/2 - V
REFIN
/4). The
ADC’s full-scale range is user-adjustable through the
REFIN pin, which provides a high input impedance for
this purpose. REFOUT, REFP, COM (VDD/2), and REFN
are internally buffered, low-impedance outputs.
Figure 1. Pipelined Architecture—Stage Blocks
Figure 2. Internal T/H Circuit
MDAC
V
IN
FLASH
ADC
T/H
Σ
DAC
V
OUT
x2
IN+
INTERNAL
BIAS
S2a
S4a
C2a
S4c
S1
C1a
COM
S5a
S3a
OUT
1.5 BITS
V
IN
STAGE 1 STAGE 2
DIGITAL ALIGNMENT LOGIC
10
V
= INPUT VOLTAGE BETWEEN
IN
IN+ AND IN- (DIFFERENTIAL OR SINGLE-ENDED)
D9–D0
STAGE 10
IN-
S4b
TRACK
HOLD HOLD
TRACK
C2b
INTERNAL
BIAS
CLK
C1b
S2b
INTERNAL
NON-OVERLAPPING
CLOCK SIGNALS
OUT
S3b
S5b
COM

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
12 ______________________________________________________________________________________
The MAX1444 provides three modes of reference operation:
• Internal reference mode
• Buffered external reference mode
• Unbuffered external reference mode
In internal reference mode, the internal reference output (REFOUT) can be connected to the REFIN pin
through a resistor (e.g., 10kΩ) or resistor-divider if an
application requires a reduced full-scale range. For stability purposes, it is recommended to bypass REFIN
with a >10nF capacitor to GND.
In buffered external reference mode, the reference voltage levels can be adjusted externally by applying a
stable and accurate voltage at REFIN. In this mode,
REFOUT may be left open or connected to REFIN
through a >10kΩ resistor.
In unbuffered external reference mode, REFIN is connected to GND, thereby deactivating the on-chip
buffers of REFP, COM, and REFN. With their buffers
shut down, these pins become high impedance inputs
and can be driven by external reference sources.
Clock Input (CLK)
The MAX1444 CLK input accepts CMOS-compatible
clock signals. Since the interstage conversion of the
device depends on the repeatability of the rising and
falling edges of the external clock, use a clock with low
jitter and fast rise and fall times (<2ns). In particular,
sampling occurs on the falling edge of the clock signal,
mandating this edge to provide lowest possible jitter.
Any significant aperture jitter would limit the SNR performance of the ADC as follows:
SNR = 20log (1 / 2πfINtAJ)
where fINrepresents the analog input frequency, and
tAJis the time of the aperture jitter.
Clock jitter is especially critical for undersampling
applications. The clock input should always be considered as an analog input and routed away from any analog input or other digital signal lines.
The MAX1444 clock input operates with a voltage
threshold set to VDD/2. Clock inputs with a duty cycle
other than 50% must meet the specifications for high
and low periods as stated in the
Electrical Character-
istics
. See Figures 3a, 3b, 4a, and 4b for the relationship between spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR),
signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), total harmonic distortion
(THD), or signal-to-noise plus distortion (SINAD) versus
clock duty cycle.
Output Enable (OE), Power Down (PD),
and Output Data (D0–D9)
All data outputs, D0 (LSB) through D9 (MSB), are
TTL/CMOS-logic compatible. There is a 5.5 clock-cycle
latency between any particular sample and its valid
output data. The output coding is straight offset binary
(Table 1). With OE and PD (power down) high, the digital output enters a high-impedance state. If OE is held
low with PD high, the outputs are latched at the last
value prior to the power down.
The capacitive load on the digital outputs D0–D9
should be kept as low as possible (<15pF) to avoid
large digital currents that could feed back into the analog portion of the MAX1444, thus degrading its dynamic performance. The use of buffers on the ADC’s digital
outputs can further isolate the digital outputs from
heavy capacitive loads.
Figure 5 displays the timing relationship between output enable and data output valid as well as powerdown/wake-up and data output valid.
Table 1. MAX1444 Output Code for Differential Inputs
*
V
REF
= V
REFP
- V
REFN
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT VOLTAGE* DIFFERENTIAL INPUT STRAIGHT OFFSET BINARY
V
× 511/512 +Full Scale -1LSB 11 1111 1111
REF
V
× 510/512 +Full Scale -2LSB 11 1111 1110
REF
V
× 1/512 +1LSB 10 0000 0001
REF
0 Bipolar Zero 10 0000 0000
- V
× 1/512 -1LSB 01 1111 1111
REF
- V
× 511/512 Negative Full Scale + 1LSB 00 0000 0001
REF
- V
× 512/512 Negative Full Scale 00 0000 0000
REF

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
______________________________________________________________________________________ 13
Figure 3a. Spurious-Free Dynamic Range vs. Clock Duty Cycle
(Differential Input)
Figure 3b. Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs. Clock Duty Cycle
(Differential Input)
Figure 4a. Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Clock Duty Cycle
(Differential Input)
Figure 4b. Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion vs. Clock Duty Cycle
(Differential Input)
Figure 5. Output Enable Timing
90
fIN = 13.24MHz AT-0.5dB FS
85
80
75
SFDR (dBc)
70
65
60
20 4030 50 60 70
CLOCK DUTY CYCLE (%)
61
fIN = 13.24MHz AT-0.5dB FS
60
59
SNR (dB)
58
-60
fIN = 13.24MHz AT-0.5dB FS
-64
-68
THD (dBc)
-72
-76
-80
20 4030 50 60 70
CLOCK DUTY CYCLE (%)
61
fIN = 13.24MHz AT-0.5dB FS
60
59
SINAD (dB)
57
56
20 4030 50 60 70
CLOCK DUTY CYCLE (%)
OE
OUTPUT
DATA D9–D0
t
ENABLE
58
57
20 4030 50 60 70
CLOCK DUTY CYCLE (%)
t
DISABLE
VALID DATA
HIGH-ZHIGH-Z

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
14 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Figure 6. System and Output Timing Diagram
System Timing Requirements
Figure 6 shows the relationship between the clock
input, analog input, and data output. The MAX1444
samples at the falling edge of the input clock. Output
data is valid on the rising edge of the input clock. The
output data has an internal latency of 5.5 clock cycles.
Figure 5 shows the relationship between the input clock
parameters and the valid output data.
__________Applications Information
Figure 7 shows a typical application circuit containing a
single-ended to differential converter. The internal reference provides a V
DD
/2 output voltage for level shifting
purposes. The input is buffered and then split to a voltage follower and inverter. A lowpass filter follows the op
amps to suppress some of the wideband noise associated with high-speed op amps. The user may select the
R
ISO
and CINvalues to optimize the filter performance
to suit a particular application. For the application in
Figure 7, an R
ISO
of 50Ω is placed before the capaci-
tive load to prevent ringing and oscillation. The 22pF
CINcapacitor acts as a small bypassing capacitor.
Using Transformer Coupling
An RF transformer (Figure 8) provides an excellent
solution for converting a single-ended source signal to
a fully differential signal, required by the MAX1444 for
optimum performance. Connecting the transformer’s
center tap to COM provides a VDD/2 DC level shift to
the input. Although a 1:1 transformer is shown, a stepup transformer may be selected to reduce the drive
requirements. A reduced signal swing from the input
driver, such as an op amp, may also improve the overall distortion.
In general, the MAX1444 provides better SFDR and
THD with fully differential input signals than singleended drive, especially for very high input frequencies.
In differential input mode, even-order harmonics are
lower since both inputs (IN+, IN-) are balanced, and
each of the inputs only requires half the signal swing
compared to single-ended mode.
Single-Ended AC-Coupled Input Signal
Figure 9 shows an AC-coupled, single-ended application. The MAX4108 op amp provides high speed, high
bandwidth, low noise, and low distortion to maintain the
integrity of the input signal.
5.5 CLOCK-CYCLE LATENCY
N
ANALOG INPUT
CLOCK INPUT
DATA OUTPUT
t
AD
t
DO
N - 6
N - 5
N + 1
N - 4
N + 2
N + 3
N - 3
t
CLtCH
N - 2
N + 4
N + 5
N - 1
N
N + 6
N + 7
N + 1

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
______________________________________________________________________________________ 15
Figure 8. Using a Transformer for AC Coupling
Figure 9. Single-Ended AC-Coupled Input
Figure 7. Typical Application Circuit for Single-Ended to Differential Conversion
INPUT
5V
MAX4108
-5V
0.1μF
0.1μF
300Ω
300Ω
300Ω
300Ω
0.1μF
600Ω
0.1μF
600Ω
5V
MAX4108
-5V
5V
MAX4108
-5V
600Ω
0.1μF
0.1μF
0.1μF
0.1μF
LOWPASS FILTER
R
ISO
50Ω
LOWPASS FILTER
R
ISO
50Ω
C
IN
22pF
C
IN
22pF
IN+
MAX1444
COM
IN-
300Ω
300Ω
600Ω
25Ω
0.1μF
V
IN
N.C.
MINI-CIRCUITS
3
T1
5
ADT1–1WT
4
2
61
2.2μF
10pF
0.1μF
25Ω
10pF
IN+
COM
IN-
MAX1444
V
IN
MAX4108
= 50Ω
R
ISO
C
= 22pF
IN
100
100Ω
REFP
1k
REFN
1k
Ω
R
ISO
Ω
0.1μF
IN+
C
IN
MAX1444
COM
R
ISO
IN-
C
IN
0.1μF
Ω

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
16 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Buffered External Reference Drives
Multiple ADCs
Multiple-converter systems based on the MAX1195 are
well suited for use with a common reference voltage.
The REFIN pin of those converters can be connected
directly to an external reference source. A precision
bandgap reference like the MAX6062 generates an
external DC level of 2.048V (Figure 10), and exhibits a
noise voltage density of 150nV/√Hz. Its output passes
through a one-pole lowpass filter (with 10Hz cutoff fre-
quency) to the MAX4250, which buffers the reference
before its output is applied to a second 10Hz lowpass
filter. The MAX4250 provides a low offset voltage (for
high gain accuracy) and a low noise level. The passive
10Hz filter following the buffer attenuates noise produced in the voltage reference and buffer stages. This
filtered noise density, which decreases for higher frequencies, meets the noise levels specified for precision
ADC operation.
Figure 10. Buffered External Reference Drives Up to 1000 ADCs
3.3V
0.1μF
1
MAX6062
3
0.1μF
16.2k
Ω
2
1μF
10Hz LOWPASS
FILTER 10Hz LOWPASS
3
MAX4250
4
5
3.3V
N.C.
29
0.1μF
0.1μF
31
32
29
31
32
1
2
1
2
REFOUT
REFIN
REFP
REFN
COM
REFOUT
REFIN
REFP
REFN
COM
MAX1444
N = 1
MAX1444
N = 1000
0.1μF
2.2μF
10V
2.048V
0.1μF
162
Ω
1
0.1μF
100μF2
FILTER
0.1μF
0.1μF
0.1μF
N.C.
0.1μF
NOTE: ONE FRONT-END REFERENCE CIRCUIT DESIGN MAY BE USED WITH UP TO 1000 ADCs.

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
______________________________________________________________________________________ 17
Unbuffered External Reference Drives
Multiple ADCs
Connecting each REFIN to analog ground disables the
internal reference of each device, allowing the internal
reference ladders to be driven directly by a set of external reference sources. Followed by a 10Hz lowpass filter and precision voltage-divider (Figure 11), the
MAX6066 generates a DC level of 2.500V. The buffered
outputs of this divider are set to 2.0V, 1.5V, and 1.0V,
with an accuracy that depends on the tolerance of the
divider resistors. The three voltages are buffered by the
MAX4252, which provides low noise and low DC offset.
The individual voltage followers are connected to 10Hz
lowpass filters, which filter both the reference voltage
and amplifier noise to a level of 3nV/√Hz. The 2.0V and
1.0V reference voltages set the differential full-scale
range of the associated ADCs at 2V
P-P
. The 2.0V and
1.0V buffers drive the ADC’s internal ladder resistances
between them. Note that the common power supply for
all active components removes any concern regarding
Figure 11. Unbuffered External Reference Drives Up to 32 ADCs
3.3V
0.1μF
1
21.5k
2
MAX6066
3
3.3V
0.1μF
MAX4254 POWER-SUPPLY BYPASSING.
PLACE CAPACITOR AS CLOSE AS
POSSIBLE TO THE OP AMP.
1μF
N.C.
29
REFOUT
31
REFIN
21.5k
21.5k
21.5k
21.5k
2.0V
3
4
1/4 MAX4252
2
Ω
1.5V
Ω
1.0V
10
Ω
Ω
5
1/4 MAX4252
6
1/4 MAX4252
9
11
4
11
4
11
Ω
3.3V
2.0V AT 8mA
47
Ω
1
10μF
6V
1.47k
3.3V
7
10μF
6V
1.47k
3.3V
8
10μF
6V
1.47k
Ω
1.5V AT 0mA
47
Ω
Ω
1.0V AT -8mA
47
Ω
Ω
330μF
6V
330μF
330μF
0.1μF
0.1μF
6V
N.C.
6V
0.1μF
0.1μF
0.1μF
0.1μF
32
29
31
32
1
2
1
2
REFP
REFN
COM
REFOUT
REFIN
REFP
REFN
COM
MAX1444
N = 1
MAX1444
N = 32
0.1μF
2.2μF
10V
NOTE: ONE FRONT-END REFERENCE CIRCUIT DESIGN MAY BE USED WITH UP TO 32 ADCs.

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
18 ______________________________________________________________________________________
power-supply sequencing when powering up or down.
With the outputs of the MAX4252 matching better than
0.1%, the buffers and subsequent lowpass filters can
be replicated to support as many as 32 ADCs. For
applications that require more than 32 matched ADCs,
a voltage reference and divider string common to all
converters is highly recommended.
Grounding, Bypassing,
and Board Layout
The MAX1444 requires high-speed board layout design
techniques. Locate all bypass capacitors as close to
the device as possible, preferably on the same side as
the ADC, using surface-mount devices for minimum
inductance. Bypass VDD, REFP, REFN, and COM with
two parallel 0.1µF ceramic capacitors and a 2.2µF
bipolar capacitor to GND. Follow the same rules to
bypass the digital supply (OVDD) to OGND. Multilayer
boards with separated ground and power planes produce the highest level of signal integrity. Consider
using a split ground plane arranged to match the physical location of the analog ground (GND) and the digital
output driver ground (OGND) on the ADC's package.
The two ground planes should be joined at a single
point so that the noisy digital ground currents do not
interfere with the analog ground plane. The ideal location of this connection can be determined experimentally at a point along the gap between the two ground
planes that produces optimum results. Make this connection with a low-value, surface-mount resistor (1Ω to
5Ω), a ferrite bead, or a direct short. Alternatively, all
ground pins could share the same ground plane if the
ground plane is sufficiently isolated from any noisy, digital systems ground plane (e.g., downstream output
buffer or DSP ground plane). Route high-speed digital
signal traces away from sensitive analog traces. Keep
all signal lines short and free of 90° turns.
Static Parameter Definitions
Integral Nonlinearity
Integral nonlinearity (INL) is the deviation of the values
on an actual transfer function from a straight line. This
straight line can be either a best straight-line fit or a line
drawn between the endpoints of the transfer function
once offset and gain errors have been nullified. The
MAX1444’s static linearity parameters are measured
using the best straight-line fit method.
Differential Nonlinearity
Differential nonlinearity (DNL) is the difference between
an actual step width and the ideal value of 1LSB. A
DNL error specification of less than 1LSB guarantees
no missing codes and a monotonic transfer function.
Dynamic Parameter Definitions
Aperture Jitter
Figure 12 depicts the aperture jitter (tAJ), which is the
sample-to-sample variation in the aperture delay.
Aperture Delay
Aperture delay (tAD) is the time defined between the
falling edge of the sampling clock and the instant when
an actual sample is taken (Figure 12).
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
For a waveform perfectly reconstructed from digital
samples, the theoretical maximum SNR is the ratio of
the full-scale analog input (RMS value) to the RMS
quantization error (residual error). The ideal, theoretical
minimum A/D noise is caused by quantization error only
and results directly from the ADC’s resolution (N bits):
SNR
(MAX)
= (6.02 x N + 1.76)dB
In reality, there are other noise sources besides quantization noise: thermal noise, reference noise, clock jitter,
etc. SNR is computed by taking the ratio of the RMS
signal to the RMS noise, which includes all spectral
components minus the fundamental, the first five harmonics, and the DC offset.
Figure 12. T/H Aperture Timing
CLK
ANALOG
INPUT
SAMPLED
DATA (T/H)
T/H
t
AD
TRACK TRACK
t
AJ
HOLD

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
______________________________________________________________________________________ 19
Functional Diagram
Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion (SINAD)
SINAD is computed by taking the ratio of the RMS signal to all spectral components minus the fundamental
and the DC offset.
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
ENOB specifies the dynamic performance of an ADC at
a specific input frequency and sampling rate. An ideal
ADC’s error consists of quantization noise only. ENOB
is computed from:
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
THD is typically the ratio of the RMS sum of the input
signal’s first four harmonics to the fundamental itself.
This is expressed as:
where V
1
is the fundamental amplitude, and V2through
V
5
are the amplitudes of the 2nd- through 5th-order
harmonics.
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
SFDR is the ratio expressed in decibels of the RMS
amplitude of the fundamental (maximum signal component) to the RMS value of the next largest spurious
component, excluding DC offset.
Intermodulation Distortion (IMD)
The two-tone IMD is the ratio expressed in decibels of
either input tone to the worst 3rd-order (or higher) intermodulation products. The individual input tone levels
are at -6.5dB full scale.
Chip Information
PROCESS: CMOS
Package Information
For the latest package outline information and land patterns, go
to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
. Note that a “+”, “#”, or “-” in
the package code indicates RoHS status only. Package drawings may show a different suffix character, but the drawing pertains to the package regardless of RoHS status.
PACKAGE
TYPE
PACKAGE
CODE
OUTLINE
NO.
LAND
PATTERN NO.
32 TQFP H32+2F
21-0110 90-0149
ENOB
()
SINAD
=
−
176
602..
2
⎞
⎟
⎟
⎠
THD
20
=×
log
⎛
VVVV
+++
2232425
⎜
⎜
⎝
V
1
CLK
IN+
MAX1444
CONTROL
10
D
T/H
IN-
ADC
E
C
OUTPUT
DRIVERS
V
DD
GND
D9–D0
OV
PD
REF
REF SYSTEM +
BIAS
REFINREFOUT REFP COM REFN
OE
DD
OGND

MAX1444
10-Bit, 40Msps, 3.0V, Low-Power
ADC with Internal Reference
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
20
____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 2010 Maxim Integrated Products Maxim is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Revision History
REVISION
NUMBER
3 8/10 Added MAX1444EHJ/V+ to Ordering Information 1
REVISION
DATE
DESCRIPTION
PAGES
CHANGED
 Loading...
Loading...