General Description
The MAX13170E is a three-driver/three-receiver multiprotocol transceiver that operates from a +5V single supply.
The MAX13170E, along with the MAX13172E and the
MAX13174E, form a complete software-selectable data
terminal equipment (DTE) or data communication equipment (DCE) interface port that supports the V.28 (RS-232),
V.10/V.11 (RS-449/V.36, EIA-530, EIA-530A, X.21), and
V.35 protocols. The MAX13170E transceivers carry the
high-speed clock and data signals, while the MAX13172E
carry the control signals. The MAX13170E can be terminated by the MAX13174E software-selectable resistor
termination network or by discrete termination networks.
The MAX13170E has an internal charge pump and a
proprietary low-dropout transmitter output stage that
allows V.11-, V.28-, and V.35-compliant operation from
a +5V single supply. The MAX13170E features a nocable mode that reduces supply current to 0.5µA, and
disables all (high-impedance) transmitter and receiver
outputs. Short-circuit current limiting and thermal shutdown circuitry protect the receiver and transmitter outputs against excessive power dissipation. The
MAX13170E has extended ESD protection for all the
transmitter outputs and receivers inputs.
The MAX13170E is available in a 5.3mm x 10.2mm,
28-pin SSOP package and operates over the 0°C to
+70°C commercial temperature range.
Applications
Features
o The MAX13170E/MAX13172E/MAX13174E Chipset
is a Pin-for-Pin Upgrade to the MXL1544/MAX3175/
MXL1543/MXL1543B Chipset
o Supports RS-232, RS-449, EIA-530, EIA-530A,
V.35, V.36, and X.21
o Software-Selectable Cable Termination Using the
MAX13174E
o Complete DTE or DCE Port with the
MAX13172E/MAX13174E
o Fail-Safe Receivers
o +5V Single-Supply Operation
o 0.5µA No-Cable Mode
o TUV-Certified NET1/NET2 and TBR1/TBR2-
Compliant (Pending)
o Extended ESD Protection for All the Transmitter
Outputs and Receivers Inputs to GND
±13kV Using the Human Body Model
±8kV Using the Contact Method Specified in
IEC 61000-4-2
±5kV Using the Air-Gap Discharge Method
Specified in IEC 61000-4-2
MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software-
Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver
________________________________________________________________
Maxim Integrated Products
1
Ordering Information
19-3800; Rev 0; 05/08
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
M AX13170E C AI+ 0°C to + 70°C 28 SSOP
Data Networking
CSU and DSU
Data Routers
PCI Cards
Telecommunications
Equipment
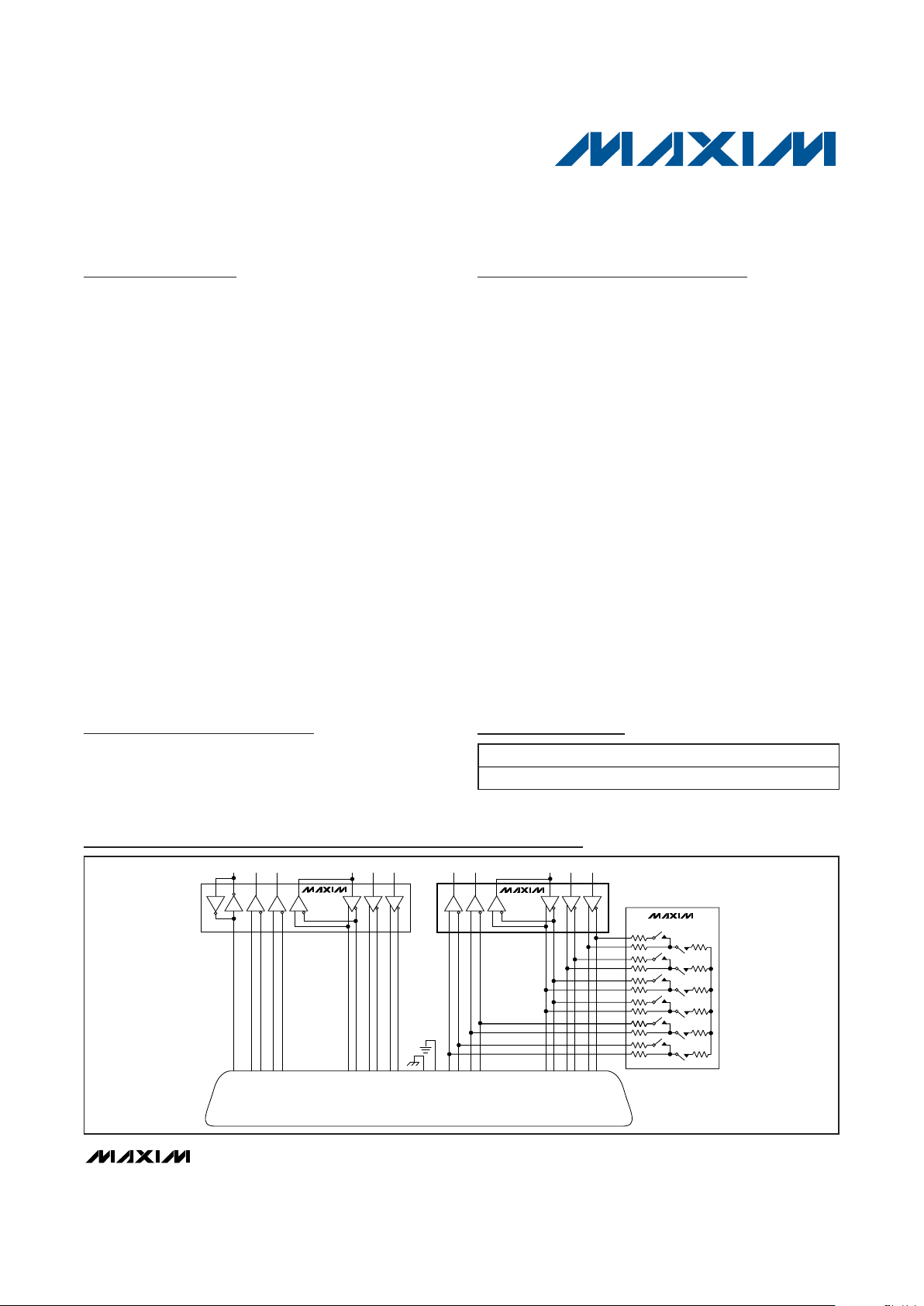
Typical Operating Circuit
T1T2
T3
T4
R1
R2R3
MAX13170E
RXD RXC TXDTXC SCTE
T1T2
T3
R1
R2R3
MAX13172E
CTS DSR RTSDTRDCD
RXC B
RXD A (104)
RXD B
SG (102)
SHIELD (101)
RTS A (105)
RTS B
DTR A (108)
DTR B
DCD A (107)
DCD B
DSR A (109)
CTS A (106)
DSR B
CTS B
LL A (141)
TXD B
SCTE A (113)
SCTE B
TXC A (114)
TXC B
TXD A (103)
DB-25 CONNECTOR
13
R4
LL
RXC A (115)
18 5 10 8 22 6 23 20 19 4 1 7 16 3 9 17 12 15 11 24 14 2
MAX13174E
+
Denotes a lead-free package.
Pin Configuration appears at end of data sheet.
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim Direct at 1-888-629-4642,
or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, SoftwareSelectable Clock/Data Transceiver
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VCC= 4.5V to 5.5V, C3= C4= C5= 4.7µF, C1= C2= 1uF, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
. Typical values are at V
CC
= 5V, and TA= +25°C.)
(Note 2)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(All voltages referenced to GND, unless otherwise noted.)
Supply Voltages
V
CC
.......................................................................-0.3V to +6V
Charge-Pump Output Voltages
V
DD
....................................................................-0.3V to +7.1V
V
EE
.....................................................................+0.3V to -7.1V
V
DD
to VCC.............................................................-0.6 to +6V
Logic Input Voltages
M0, M1, M2, DCE/DTE, T_IN ................................-0.3V to +6V
Logic Output Voltages
R_OUT....................................................-0.3V to (V
CC
+ 0.3V)
Transmitter Outputs
T_OUT_, T3OUT_/R1IN_ (No Cable Mode
or V.28) ..........................................................-15V to +15V
Short-Circuit Duration to GND...............................Continuous
Receiver Inputs
R_IN_T3OUT_/R1IN_ ..........................................-15V to +15V
R_INA to R_INB, T3OUT/R1INA to
T3OUT/R1INB................................................-15V to +15V
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +70°C)
28-Pin SSOP (derate 9.5mW/°C above +70°C) ...........762mW
Junction-to-Case Thermal Resistance (θ
JC
) (Note 1)
28-Pin SSOP ................................................................25°C/W
Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance (θ
JA
) (Note 1)
28-Pin SSOP ................................................................67°C/W
Operating Temperature Range ................................0°C to 70°C
Junction Temperature .......................................................150°C
Storage Temperature Range ............................-65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) ................................+300°C
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
VCC Operating Range V
CC
4.5 5.5 V
V.11 mode, no load 15 28
V.11 mode, full load 133 180
V.35 mode, no load 21 38
V.35 mode, full load 153 195
V.28 mode, no load 16 30
V.28 mode, full load 29 40
mA
VCC Supply Current (DCE Mode)
(Digital Inputs = GND or V
CC
)
(Transmitter Outputs Static)
I
CC
No cable mode 0.5 10 µA
V.11 mode, full load 200
V.35 mode, full load 750
Internal Power Dissipation
(DCE Mode)
P
D
V.28 mode, full load 100
mW
V.28, V.35 modes, no load 6.5 6.9 7.1
V.28, V.35 modes, with load, IDD = 10mA 5.6 6.9
V.11 mode 5.15 5.3 5.7
Positive Charge-Pump Output
Voltage (Note 3)
V
DD
V .11 m od e, V
D D
var i ati on, I
D D
= 0m A to 25m A 0.01
V
V.28, V.35 modes, no load -6.9
V.28, V.35 modes, with load, IEE = 10mA
(Note 3)
-6.7 -5.4
V.11 mode (Note 3) -4.84 -4.5 -4.16
Negative Charge-Pump Output
Voltage
V
EE
V .11 m od e, V
E E
var i ati on, I
E E
= 0m A to 25m A 0.01
V
Charge-Pump Enable Time
Time it takes for both V
DD
and VEE to reach
specified range
<1 ms
Thermal Shutdown Protection THSD 145 °C
Note 1: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JESD51-7, using a 4-layer board. For detailed
information on package thermal considerations, refer to www.maxim-ic.com/thermal-tutorial
.
MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software-
Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VCC= 4.5V to 5.5V, C3= C4= C5= 4.7µF, C1= C2= 1uF, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
. Typical values are at V
CC
= 5V, and TA= +25°C.)
(Note 2)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
LOGIC INPUTS (M0, M1, M2, DCE/DTE, T1IN, T2IN, T3IN)
Input High Voltage V
IH
0.66 x V
C C
V
Input Low Voltage V
IL
0.33 x V
C C
V
Logic-Input Current I
IN
T1IN, T2IN, T3IN -1 +1 µA
Pullup Resistor R
PUIN
M0, M1, M2, DCE/DTE to V
CC
50 100 170 kΩ
LOGIC OUTPUTS (R1OUT, R2OUT, R3OUT)
Output High Voltage V
OH
I
SOURCE
= 4mA 0.66 x V
C C
V
Output Low Voltage V
OL
I
SINK
= 4mA 0.33 x V
C C
V
Output Pullup Resistor R
PUY
No-cable mode (to VCC) 71.4 kΩ
Transmitter Output Leakage
Current
I
Z
-0.25V < V
OUT
< +0.25V, VCC = 0
or no-cable mode
+5 0.2 µA
V.11 TRANSMITTER
Open-Circuit Differential Output
Voltage
V
ODO
Open circuit, R = 1.95kΩ, Figure 1 -V
CC
+V
CC
V
R = 50Ω, Figure 1 0.5 x V
OD O
Loaded Differential Output
Voltage (Note 4)
V
ODL
R = 50Ω, Figure 1 |2|
V
Change in Magnitude of Output
Differential Voltage
ΔV
OD
R = 50Ω, Figure 1 0.2 V
Common-Mode Output Voltage V
OC
R = 50Ω, Figure 1 3.0 V
C hang e i n M ag ni tud e of
C om m on- M od e O utp ut V ol tag e
ΔV
OC
R = 50Ω, Figure 1 0.2 V
Short-Circuit Current I
SC
V
OUT
= GND 150 mA
Rise Time t
R
Figures 2, 6 4.5 10 ns
Fall Time t
F
Figures 2, 6 6.5 10 ns
Transmitter Input-to-Output Prop
Delay
t
PHL
, t
PLH
Figures 2, 6 16 22 ns
Data Skew |t
PHL-tPLH
| Figures 2, 6 (Note 3) 3 ns
Output-to-Output Skew t
SKEWT
Figures 2, 6 (Notes 3, 5) 2.5 ns
V.11 RECEIVER
Differential Threshold Voltage V
TH
-7V ≤ VCM ≤ +7V -200 -50 mV
Input Hysteresis ΔV
TH
-7V ≤ VCM ≤ +7V 13 mV
Receiver Input Current I
IN
-10V ≤ V
A,B
≤ +10V -0.66 +0.66 mA
Receiver Input Resistance R
IN
-10V ≤ V
A,B
≤ +10V 15 30 kΩ
Rise or Fall Time tR, t
F
Figures 2, 7 3 ns
Receiver Input-to-Output Delay t
PHL
, t
PLH
Figures 2, 7 23 ns
Data Skew |t
PHL-tPLH
| Figures 2, 7 ( Note 3) 3 ns
Output-to-Output Skew t
SKEWR
(Notes 3, 5) 2.5 ns
MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, SoftwareSelectable Clock/Data Transceiver
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VCC= 4.5V to 5.5V, C3= C4= C5= 4.7µF, C1= C2= 1uF, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
. Typical values are at V
CC
= 5V, and TA= +25°C.)
(Note 2)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
V.35 TRANSMITTER
Differential Output Voltage V
OD
With load, -4V < VCM < +4V, Figure 3 ±0.44 ±0.55 ±0.66 V
Output High Current I
OH
V
A,B
= 0 -13 -11 -9 mA
Output Low Current I
OL
V
A,B
= 0 9 11 13 mA
Rise or Fall Time tR, t
F
Figures 3, 6 5 ns
Transmitter Input-to-Output Delay t
PLH, tPHL
Figures 3, 6 19 35 ns
Data Skew |t
PLH - tPHL
| Figures 3, 6, (Note 3) 3 ns
Output-to-Output Skew t
SKEWT
Figures 3, 6, (Notes 3, 5) 3 ns
V.35 RECEIVER
Differential Threshold Voltage V
TH
-2V ≤ VCM ≤ +2V -200 -50 mV
Input Hysteresis ΔV
TH
-2V ≤ VCM ≤ +2V 15 mV
Receiver Input Current I
IN
-10V ≤ V
A,B
≤ +10V -0.66 +0.66 mA
Receiver Input Resistance R
IN
-10V ≤ V
A,B
≤ +10V 15 30 kΩ
Rise or Fall Time tR, t
F
Figures 3, 7 3 ns
Receiver Input-to-Output Delay t
PHL
, t
PLH
Figures 3, 7 (Note 3) 23 ns
Data Skew |t
PHL-tPLH
| Figures 3, 7 (Note 3) 3 ns
Output-to-Output Skew t
SKEWR
(Notes 3, 5) 2.5 ns
V.28 TRANSMITTER
Open circuit (output high) V
DD
Open circuit (output low) V
EE
Output high 5 6.8
Output Voltage Swing V
OD
RL = 3kΩ
Output low -6.8 -5
V
Short-Circuit Current |ISC| 85 mA
Output Slew Rate SR
R/F
RL = 3kΩ, CL = 2500pF, Figures 4, 8 4 30 V/µs
Transmitter Input-to-Output Delay
from Low to High
t
PHL
RL = 3kΩ, CL = 2500pF, Figures 4, 8 1 2 µs
Transmitter Input-to-Output Delay
from High to Low
t
PLH
RL = 3kΩ, CL = 2500pF, Figures 4, 8 1 2 µs
V.28 RECEIVER
Input Threshold Low V
IL
0.8 V
Input Threshold High V
IH
2V
Input Hysteresis V
HYST
0.25 V
Input Resistance R
IN
-15V ≤ VIN ≤ +15V 3 5 7 kΩ
Rise or Fall Time tR, t
F
Figures 5, 9 3 ns
Receiver Input-to-Output Delay t
PHL, tPLH
Figures 5, 9 150 ns
MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software-
Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(VCC= 4.5V to 5.5V, C3= C4= C5= 4.7µF, C1= C2= 1uF, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
. Typical values are at V
CC
= 5V, and TA= +25°C.)
(Note 2)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
ESD PROTECTION (T_OUT_, T_OUT_/R_OUT_, R_IN_ to GND)
Contact Discharge IEC61000-4-2 + 8
Air-Gap Discharge IEC61000-4-2 ±5ESD Protection
Human Body Model ±13
kV
Note 2: All devices are 100% production tested at TA= +70°C and are guaranteed by design for TA= 0°C to +70°C as specified.
Note 3: Guaranteed by design, not production tested.
Note 4: V
ODL
is guaranteed at both 0.5 x V
ODO
and |2V|.
Note 5: Ouput-to-output skews are evaluated as a difference of propagation delays between different channels in the same condtion
and for the same polarity (LH or HL).
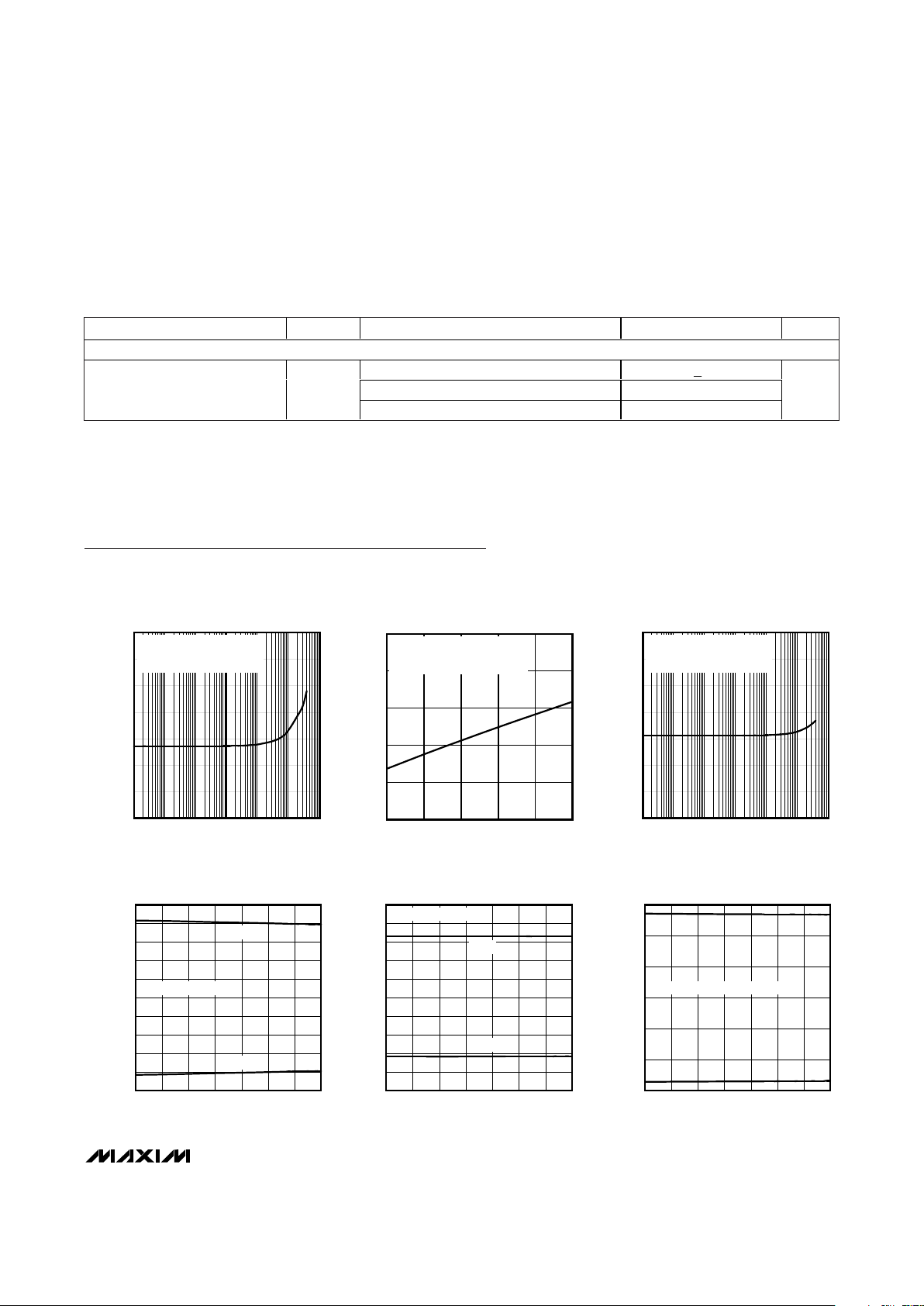
V.11 SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. DATA RATE
DATA RATE (kbps)
0.1 100 1,000 10,0001 10 100,000
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
350
0
50
100
150
200
300
250
MAX13170E toc01
DCE MODE, R = 50Ω,
ALL TRANSMITTERS OPERATING
AT THE SPECIFIED DATA RATE
0
20
60
40
80
100
0 10050 150 200 250
V.28 SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. DATA RATE
MAX13170E toc02
DATA RATE (kbps)
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
DCE MODE, ALL TRANSMITTERS
OPERATING AT THE SPECIFIED
DATA RATE, R
L
= 3kΩ, CL = 2500pF
V.35 SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. DATA RATE
DATA RATE (kbps)
0.1 100 1,000 10,0001 10 100,000
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
350
0
50
100
150
200
300
250
MAX13170E toc03
DCE MODE, FULLY LOADED,
ALL TRANSMITTERS OPERATING
AT THE SPECIFIED DATA RATE
-5
-2
-3
-4
0
-1
4
3
2
1
5
0 10203040506070
V.11 DRIVER DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX13170E toc04
TEMPERATURE (°C)
DRIVER DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
DCE MODE, R = 50
Ω
V
OUT+
V
OUT-
-10
-4
-6
-8
0
-2
8
6
4
2
10
0 10203040506070
V.28 OUTPUT VOLTAGE
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX13170E toc05
TEMPERATURE (°C)
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
DCE MODE, RL = 3k
Ω
V
OUT+
V
OUT-
-600
-200
-400
200
0
400
600
0304010 20 50 60 70
V.35 OUTPUT VOLTAGE
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX13170E toc06
TEMPERATURE (°C)
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (mV)
DCE MODE, VCM = 0, FULL LOAD
VOH
VOL
Typical Operating Characteristics
(VCC= +5.0V, C1 = C2 =1µF, C3 = C4 = C5 = 4.7µF, (Figure 10), TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, SoftwareSelectable Clock/Data Transceiver
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
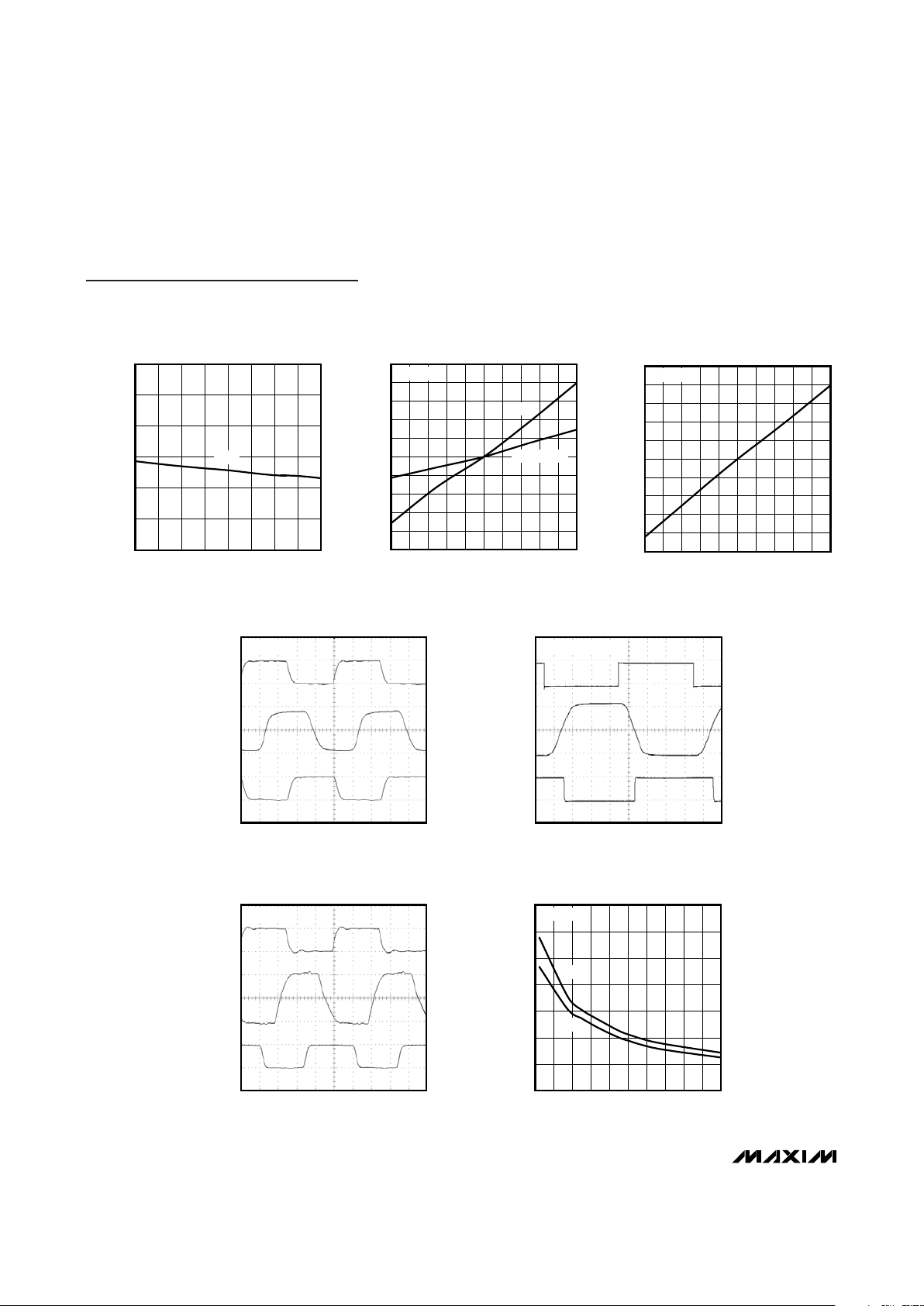
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(VCC= +5.0V, C1= C2 = C4 =1µF, C3 = C5 = 4.7µF (Figure 10), TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
530
535
540
545
550
555
560
-4 -2-3 -101234
V.35 LOADED DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
vs. COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE
MAX13170E toc07
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE (V)
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE (mV)
|
V
OD
|
-500
-300
-400
-100
-200
100
0
200
400
300
500
-10 -6 -4 -2-8 024 8610
V.11/V.35 RECEIVER INPUT CURRENT
vs. INPUT VOLTAGE
MAX13170E toc08
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
INPUT CURRENT (μA)
DTE MODE
R1IN_
R2IN_, R3IN_
-2.5
-1.5
-2.0
-0.5
-1.0
0.5
0
1.0
2.0
1.5
2.5
-10 -6-4-2-8 024 8610
V.28 RECEIVER INPUT CURRENT
vs. INPUT VOLTAGE
MAX13170E toc09
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
INPUT CURRENT (mA)
DTE MODE
V.11 LOOPBACK OPERATION
MAX13170E toc10
10ns/div
R
OUT
T
OUT/RIN
T
IN
5V/div
5V/div
5V/div
R = 50
Ω
V.28 LOOPBACK OPERATION
MAX13170E toc11
1μs/div
R
OUT
T
OUT/RIN
T
IN
5V/div
5V/div
5V/div
RL = 3kΩ,CL = 2500pF
V.35 LOOPBACK OPERATION
MAX13170E toc12
10ns/div
R
OUT
T
OUT/RIN
T
IN
5V/div
5V/div
5V/div
FULL LOAD
0
10
5
20
15
30
25
35
02K1K 3K 4K 5K
V.28 SLEW RATE
vs. LOAD CAPACITANCE
MAX13170E toc13
500 2.5K1.5K 3.5K 4.5K
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
SLEW RATE (V/μs)
RL = 3k
Ω
SRF
SRR
MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software-
Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
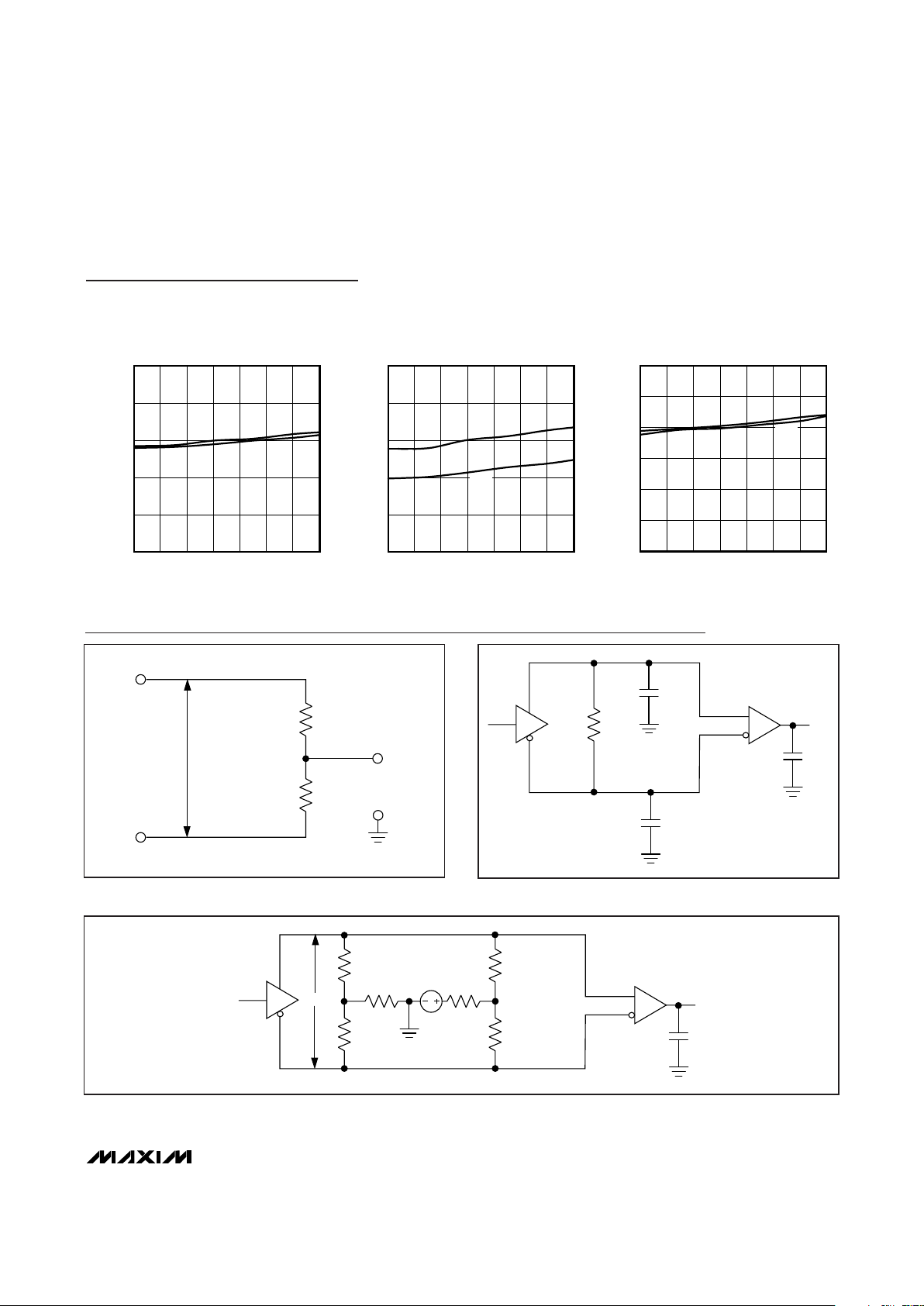
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(VCC= +5.0V, C1= C2 = C4 =1µF, C3 = C5 = 4.7µF (Figure 10), TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
V
OC
R
R
V
OD
Figure 1. V.11 DC Test Circuit
100pF
15pF
100pF
100
Ω
R
B
A
B
A
T
Figure 2. V.11 AC Test Circuit
V
CM
15pF
50
Ω
50
Ω
125
Ω
125
Ω
50
Ω
50
Ω
R
B
A
B
A
T
V
OD
Figure 3. V.35 Transmitter/Receiver Test Circuit
Test Circuits
0
4
12
8
16
20
02010 30 40 50 60 70
V.11 TRANSMITTER PROPAGATION DELAY
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX13170E toc14
TEMPERATURE (°C)
PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
t
PHL
t
PLH
0
2
6
4
8
10
02010 30 40 50 60 70
V.11/V.35 RECEIVER PROPAGATION DELAY
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX13170E toc15
TEMPERATURE (°C)
PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
t
PHL
t
PLH
0
10
5
20
15
25
30
0304010 20 50 60 70
V.35 TRANSMITTER PROPAGATION DELAY
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX13170E toc16
TEMPERATURE (°C)
PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
t
PHL
t
PLH

MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, SoftwareSelectable Clock/Data Transceiver
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
VCC/2
90%
10%
50%
t
PLH
V
CC
0
V
0
-V
0
TIN_
A - B
t
R
VCC/2
t
PHL
90%
10%
50%
t
F
f = 1MHz: tR, tF ≤ 1ns
Figure 6. V.11, V.35 Transmitter Propagation Delays
+1V
-1V
V
0H
V
0L
A -B
R
0
INPUT
OUTPUT
0
t
PLH
t
PHL
f = 1MHz: tR, tF ≤ 1ns
V
CC
/2
V
CC
/2
90%
10%
t
R
90%
10%
t
F
Figure 7. V.11, V.35 Receiver Propagation Delays
0
t
PHL
0
V
0
-V
0
TIN_
A
-3V
3V
t
F
0
t
PLH
3V
-3V
t
R
SRF = 6/t
F
SRF = 6/t
F
tR, tF ≤ 10ns
V
CC
/2 VCC/2
V
CC
Figure 8. V.28 Transmitter Propagation Delays
Timing Diagrams
C
L
R
L
V
O
A
T
Figure 4. V.28 Transmitter Test Circuit
T
A
R
15pF
Figure 5. V.28 Receiver Test Circuit
Test Circuits (continued)
V
IH
V
IL
V
0H
V
0L
A
R
1.3V
t
PHL
1.7V
t
PLH
tR, tF ≤ 10ns
V
CC
/2
V
CC
/2
90%
10%
t
F
90%
10%
t
R
Figure 9. V.28 Receiver Propagation Delays

MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software-
Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
Pin Description
PIN NAME FUNCTION
1 C1-
V
DD
Charge-Pump Flying-Capacitor Negative Terminal. Connect a 1µF ceramic capacitor between
C1+ and C1- as close as possible to the device.
2 C1+
V
DD
Charge-Pump Flying-Capacitor Positive Terminal. Connect a 1µF ceramic capacitor between
C1+ and C1- as close as possible to the device.
3V
DD
Charge-Pump Positive-Supply Output. Connect a 4.7µF ceramic capacitor from VDD to ground as
close as possible to the device.
4V
CC
Device Supply Voltage. Bypass VCC with a 4.7µF capacitor to ground as close as possible to the
device.
5 T1IN Transmitter 1 Logic Input
6 T2IN Transmitter 2 Logic Input
7 T3IN Transmitter 3 Logic Input
8 R1OUT Receiver 1 Logic Output. Internally pull up to VCC.
9 R2OUT Receiver 2 Logic Output. Internally pull up to VCC.
10 R3OUT Receiver 3 Logic Output. Internally pull up to VCC.
11 M0 Mode Select 0 Input. Internally pull up to VCC.
12 M1 Mode Select 1 Input. Internally pull up to VCC.
13 M2 Mode Select 2 Input. Internally pull up to VCC.
14
DCE/DTE
DCE/DTE Mode-Select Input. Internally pull up to VCC.
15 R3INB Receiver 3 Noninverting Input
16 R3INA Receiver 3 Inverting Input
17 R2INB Receiver 2 Noninverting Input
18 R2INA Receiver 2 Inverting Input
19
T3OUTB/
R1INB
Transmitter 3 Noninverting Output/Receiver 1 Noninverting Input
20
T3OUTA/
R1INA
Transmitter 3 Inverting Output/Receiver 1 Inverting Input
21 T2OUTB Transmitter 2 Noninverting Output
22 T2OUTA Transmitter 2 Inverting Output
23 T1OUTB Transmitter 1 Noninverting Output
24 T1OUTA Transmitter 1 Inverting Output
25 GND Ground
26 V
EE
Charge-Pump Negative Supply Output. Connect a 4.7µF ceramic capacitor from VEE to ground as
close as possible to the device.
27 C2-
V
EE
Charge-Pump Flying-Capacitor Negative Terminal. Connect a 1µF ceramic capacitor between
C2+ and C2- as close as possible to the device.
28 C2+
V
EE
Charge-Pump Flying-Capacitor Positive Terminal. Connect a 1µF ceramic capacitor between
C2+ and C2- as close as possible to the device.

MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, SoftwareSelectable Clock/Data Transceiver
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Detailed Description
The MAX13170E is a three-driver/three-receiver, multiprotocol transceiver that operates from a single +5V
supply. The MAX13170E, along with the MAX13172E
and MAX13174E, form a complete software-selectable
DTE or DCE interface port that supports the V.28 (RS-
232), V.10/V.11 (RS-449/V.36, EIA-530, EIA-530A,
X.21), and V.35 protocols. The MAX13170E transceivers carry the high-speed clock and data signals,
while the MAX13172E transceivers carry serial-interface
control signaling. The MAX13170E can be terminated
by the MAX13174E software-selectable resistor termination network or by a discrete termination network.
The MAX13170E features a 0.5µA no-cable mode, failsafe operation, and thermal shutdown circuitry. Thermal
shutdown protects the drivers against excessive power
dissipation. When activated, the thermal shutdown circuitry places the receiver and transmitter outputs into a
high-impedance state.
Mode Selection
The state of the mode-select inputs M0, M1, and M2
determines which serial interface protocol is selected
(Table 1). The state of the DCE/DTE input determines
whether the transceiver is configured as a DTE or DCE
serial port. When the DCE/DTE input is logic-high, driver T3 is activated and receiver R1 is disabled. When
the DCE/DTE input is logic-low, driver T3 is disabled
and receiver R1 is activated (Table 1). M0, M1, M2, and
DCE/DTE are internally pulled up to V
CC
to ensure a
logic-high if left unconnected.
No-Cable Mode
The MAX13170E enters no-cable mode when the
mode-select inputs are left unconnected or connected
high (M0 = M1 = M2 = 1). In this mode, the multiprotocol drivers and receivers are disabled and the supply
current drops to 0.5µA. The receivers’ outputs enter a
high-impedance state in no-cable mode, allowing these
output lines to be shared with other receivers’ outputs,
(the receivers’ outputs have internal pullup resistors to
pull the outputs high if not driven). Also, in no-cable
mode, the transmitter outputs enter a high-impedance
state so that these output lines can be shared with
other devices.
Dual Charge-Pump Voltage Converter
The MAX13170E internal power supply consists of a regulated dual charge pump that provides positive and
negative output voltages from a +5V supply. The charge
pump operates in discontinuous mode. If the output voltage is less than the regulated voltage, the charge pump
is enabled. If the output voltage exceeds the regulated
voltage, the charge pump is disabled. Each charge
pump requires a flying capacitor (C1, C2) and a reservoir capacitor (C3, C5) to generate the V
DD
and V
EE
supplies. Figure 10 shows charge-pump connections.
MAX13170E
MODE NAME
M2 M1 M0
DCE/
DTE
T1 T2 T3 R1 R2 R3
Not Used (Default V.11
)
0 0 0 0 V.11 V.11 Z V.11 V.11 V.11
RS-530A 0 0 1 0 V.11 V.11 Z V.11 V.11 V.11
RS-530 0 1 0 0 V.11 V.11 Z V.11 V.11 V.11
X.21 0 1 1 0 V.11 V.11 Z V.11 V.11 V.11
V.35 1 0 0 0 V.35 V.35 Z V.35 V.35 V.35
RS-449/V.36 1 0 1 0 V.11 V.11 Z V.11 V.11 V.11
V.28/RS-232 1 1 0 0 V.28 V.28 Z V.28 V.28 V.28
No Cable 1110ZZZZZZ
Not Used (Default V.11
)
0 0 0 1 V.11 V.11 V.11 Z V.11 V.11
RS-530A 0 0 1 1 V.11 V.11 V.11 Z V.11 V.11
RS-530 0 1 0 1 V.11 V.11 V.11 Z V.11 V.11
X.21 0 1 1 1 V.11 V.11 V.11 Z V.11 V.11
V.35 1 0 0 1 V.35 V.35 V.35 Z V.35 V.35
RS-449/V.36 1 0 1 1 V.11 V.11 V.11 Z V.11 V.11
V.28/RS-232 1 1 0 1 V.28 V.28 V.28 Z V.28 V.28
No Cable 1111ZZZZZZ
Table 1. Mode Selection

MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software-
Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver
______________________________________________________________________________________ 11
Fail-Safe Receivers
The MAX13170E guarantees a logic-high receiver output when the receiver inputs are shorted, or when they
are connected to a terminated transmission line with all
the drivers disabled. This is done by setting the
receivers’ threshold between -50mV and -200mV in the
V.11 and V.35 modes. If the differential receiver input
voltage (B - A) is ≥ -50mV, R_OUT is logic-high. If (B - A)
is ≤ -200mV, R_OUT is logic-low. In the case of a terminated bus with all transmitters disabled, the receiver’s
differential input voltage is pulled to zero by the termination. With the receiver thresholds of the MAX13170E, this
results in a logic-high with a 50mV minimum noise margin.
ESD Protection
As with all Maxim devices, a minimum of ±2kV-to-GND
ESD-protection structures are incorporated on all pins
to protect against electrostatic discharges encountered
during handling and assembly. The driver outputs and
receiver inputs of the MAX13170E have extra protection
against static electricity. Maxim’s engineers have developed state-of-the-art structures to protect these pins
against ESD of ±13kV without damage (HBM). The ESD
structures withstand high ESD in all states: normal
operation, shutdown, and powered down. After an ESD
event, the MAX13170E keeps working without latchup
or damage. ESD protection can be tested in various
ways. The transmitter outputs and receiver inputs of the
MAX13170E are characterized for protection to the following limits:
• ±13kV using the Human Body Model
• ±8kV using the Contact Method specified in IEC
61000-4-2
• ±5kV using the Air-Gap Discharge Method specified in IEC 61000-4-2
ESD Test Conditions
ESD performance depends on a variety of conditions.
Contact Maxim for a reliability report that documents
test setup, test methodology, and test results.
Human Body Model
Figure 11a shows the Human Body Model, and Figure
11b shows the current waveform it generates when discharged into a low impedance. This model consists of a
100pF capacitor charged to the ESD voltage of interest,
which is then discharged into the test device through a
1.5kΩ resistor.
C2-
V
EE
C2+
MAX13170E
GND
C1-
5V
V
CC
V
DD
C1+
C1
1μF
C5
4.7μF
C2
1μF
C3
4.7μF
C4
4.7μF
Figure 10. Charge Pump
CHARGE-CURRENT
LIMIT RESISTOR
DISCHARGE
RESISTANCE
STORAGE
CAPACITOR
C
s
100pF
R
C
1M
Ω
R
D
1500
Ω
HIGH-
VOLTAGE
DC
SOURCE
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
Figure 11a. Human Body ESD Test Model
IP 100%
90%
36.8%
t
RL
TIME
t
DL
CURRENT WAVEFORM
PEAK-TO-PEAK RINGING
(NOT DRAWN TO SCALE)
I
R
10%
0
0
AMPS
Figure 11b. Human Body Current Waveform

IEC 61000-4-2
The IEC 61000-4-2 standard covers ESD testing and
performance of finished equipment. However, it does
not specifically refer to integrated circuits. The
MAX13170E help equipment designs to meet IEC
61000-4-2, without the need for additional ESD-protection components.
The major difference between tests done using the
Human Body Model and IEC 61000-4-2 is higher peak
current in IEC 61000-4-2 because series resistance is
lower in the IEC 61000-4-2 model. Hence, the ESD
withstand voltage measured to IEC 61000-4-2 is generally lower than that measured using the Human Body
Model. Figure 11c shows the IEC 61000-4-2 model,
and Figure 11d shows the current waveform for the IEC
61000-4-2 ESD Contact Discharge test.
MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, SoftwareSelectable Clock/Data Transceiver
12 ______________________________________________________________________________________
CHARGE-CURRENT
LIMIT RESISTOR
DISCHARGE
RESISTANCE
STORAGE
CAPACITOR
C
s
150pF
R
C
50MΩ TO 100M
Ω
R
D
330
Ω
HIGH-
VOLTAGE
DC
SOURCE
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
Figure 11c. IEC 61000-4-2 ESD Test Model
tR = 0.7ns TO 1ns
30ns
60ns
t
100%
90%
10%
I
PEAK
I
Figure 11d. IEC 61000-4-2 ESD Generator Current Waveform

MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software-
Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver
______________________________________________________________________________________ 13
CTS A
4
25
21
18
2
14
24
11
15
12
17
9
3
16
7
19
20
23
8
10
6
22
5
13
CTS B
DSR A
DSR B
DCD A
DCD B
DTR A
DTR B
RTS A
RTS B
RXD A
RXD B
RXC A
RXC B
TXC A
TXC B
SCTE A
SCTE B
TXD A
TXD B
CHARGE
PUMP
DTE
DCE
RTS A
RTS B
DTR A
DTR B
DCD A
DCD B
DSR A
DSR B
CTS A
CTS B
TXD A
TXD B
SCTE A
SCTE B
TXC A
TXC B
RXC A
RXC B
RXD A
RXD B
SG
M2
C12
1μF
C13
1μF
C5
4.7μF
C2
1μF
C1
1μF
C4
4.7μF
C3
4.7μF
2
21
T1
T2
T3
R1
R2
R3
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
3
V
CC
5V
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
14
3
4 6 7 9 10 16 15 18 17 19 20 22 23 24 15
8111213
C6
100pFC7100pFC8100pF
M1
M0
DCE/DTE
M1
M2
DCE/DTE
M0
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
EE
V
EE
V
CC
V
DD
GND
LATCH
MAX13174E
MAX13170E
T1
T2
T3
T4
R1
R2
R3
26
27
28
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
5
6
7
8
9
4
3
1
2
R4
16
15
10
11
12
13
NC
NC
14
M1
M2
DCE/DTE INVERT
M0
DB-25
CONNECTOR
MAX13172E
C11
1μF
C10
1μF
C9
1μF
1
SHIELD
DTE_TXD/DCE_RXD
DTE_SCTE/DCE_RXC
DTE_TXC/DCE_TXC
DTE_RXC/DCE_SCTE
DTE_RXD/DCE_TXD
DTE_RTS/DCE_CTS
DTE_DTR/DCE_DSR
DTE_DCD/DCE_DCD
DTE_DSR/DCE_DTR
DTE_CTS/DCE_RTS
M1
DCE/DTE
M0
Figure 12. Cable-Selectable Multiprotocol DTE/DCE Port

MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, SoftwareSelectable Clock/Data Transceiver
14 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Applications Information
Capacitor Selection
The capacitors used for the charge pumps, as well as
for supply bypassing, should have a low equivalent
series resistance (ESR) and low temperature coefficient. Multilayer ceramic capacitors with an X7R dielectric offer the best combination of performance, size,
and cost. The flying capacitors (C1, C2) should have a
value of 1µF, while the reservoir capacitors (C3, C5)
and the bypass capacitor (C4) should have a minimum
value of 4.7µF (Figure 10). To reduce the ripple present
on the transmitter outputs, capacitors C3, C4, and C5
can be increased. The values of C1 and C2 should not
be increased.
Bypassing
For best performance of the charge pumps, connect
C3, C4, and C5 closer the device than C1 and C2.
Cable Termination
The MAX13174E software-selectable resistor network is
designed to be used with the MAX13170E. The
MAX13174E multiprotocol termination network provides
V.11- and V.35-compliant termination, while V.28 receiver termination is internal to the MAX13170E. These
cable termination networks provide compatibility with
V.11, V.28, and V.35 protocols. Using the MAX13174E
termination networks provide the advantage of not having to build expensive termination networks out of resistors and relays, manually changing termination
modules, or building custom termination networks.
Cable-Selectable Mode
A cable-selectable multiprotocol interface is shown in
Figure 12. The mode control lines M0, M1, and
DCE/DTE are wired to the DB-25 connector. To select
the serial interface mode, the appropriate combination
of M0, M1, and DCE/DTE are grounded within the cable
wiring. The control lines that are not grounded are
pulled high by the internal pullups on the MAX13170E.
The serial interface protocol of the MAX13170E,
MAX13172E, and MAX13174E is selected based on the
cable that is connected to the DB-25 interface.
V.11 Interface
As shown in Figure 13, the V.11 protocol is a fully balanced differential interface. The V.11 driver generates
a minimum of ±2V between nodes A and B when a
100Ω (min) resistance is presented at the load. The
V.11 receiver is sensitive to ±200mV differential signals
at receiver inputs A’ and B’. The V.11 receiver rejects
common-mode signals developed across the cable
(referenced from C to C’) of up to ±7V, allowing for
error-free reception in noisy environments. The receiver inputs must comply with the impedance curve
shown in Figure 14.
For high-speed data transmission, the V.11 specification recommends terminating the cable at the receiver
with a 100Ω resistor. This resistor, although not
required, prevents reflections from corrupting transmitted data. In Figure 15, the MAX13174E is used to terminate the V.11 receiver. Internal to the MAX13174E, S1
is closed and S2 is open to present a 100Ω minimum
differential resistance. The MAX13170E’s internal V.28
termination is disabled by opening S3.
V.35 Interface
Figure 16 shows a fully-balanced, differential standard
V.35 interface. The generator and the load must both
present a 100Ω ±10Ω differential impedance and a
150Ω ±15Ω common-mode impedance as shown by
the resistive T networks in Figure 15. The V.35 driver
generates a current output (±11mA, typ) that develops
an output voltage of ±550mV across the generator and
load termination networks. The V.35 receiver is sensitive to ±200mV differential signals at receiver inputs A’
and B’. The V.35 receiver rejects common-mode signals developed across the cable (referenced from C to
C’) of up to ±4V, allowing for error-free reception in
noisy environments.
100
Ω
MIN
A
′
B
′
C
′
A
B
C
GND GND
GENERATOR
BALANCED
INTERCONNECTING
CABLE
CABLE
TERMINATION
RECEIVER
LOAD
Figure 13. Typical V.11 Interface
-3.25mA
3.25mA
-10V
+10V
-3V
+3V
V
Z
I
Z
Figure 14. Receiver Input Impedance

MAX13170E
R6
11kΩ
R8
5kΩ
R3
124Ω
R2
52Ω
R1
52Ω
A′
B′
C′
A
B
GND
R5
55kΩ
1.4V
R7
11kΩ
R4
55kΩ
MAX13174E
MAX13170E
S3
S1
RECEIVER
S2
S1
+
-
S2
Figure 17. V.35 Termination and Internal Resistance Networks
R6
11kΩ
R8
5kΩ
R3
124Ω
R2
52Ω
R1
52Ω
A′
B′
C′
A
B
GND
R5
55kΩ
1.4V
R7
11kΩ
R4
55kΩ
MAX13174E
MAX13170E
S3
S1
RECEIVER
S2
S2
+
-
S1
Figure 15. V.11 Termination and Internal Resistance Networks
50Ω
50Ω
125Ω
50Ω
50Ω
125Ω
A′
B′
C′
A
B
C
GND GND
GENERATOR
BALANCED
INTERCONNECTING
CABLE
CABLE
TERMINATION
RECEIVER
LOAD
Figure 16. Typical V.35 Interface
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software-
Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver
______________________________________________________________________________________ 15

MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, SoftwareSelectable Clock/Data Transceiver
16 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Figure 18. Typical V.28 Interface
A
′
C
′
A
C
GND GND
GENERATOR
UNBALANCED
INTERCONNECTING
CABLE
CABLE
TERMINATION
RECEIVER
LOAD
R6
11kΩ
R8
5kΩ
R3
124Ω
R2
52Ω
R1
52Ω
A′
B′
C′
A
B
GND
R5
55kΩ
1.4V
R7
11kΩ
R4
55kΩ
MAX13174E
MAX13170E
S3
S1
RECEIVER
S2
S1
+
-
S2
Figure 19. V.28 Termination and Internal Resistance Networks
In Figure 17, the MAX13174E is used to implement the
resistive T network that is needed to properly terminate
the V.35 driver and receiver. Internal to the MAX13174E,
S1 and S2 are closed to connect the T-network resistors
to the circuit. The V.28 termination resistor (internal
to the MAX13170E) is disabled by opening S3 to
avoid interference with the T-network impedance.
V.28 Interface
The V.28 interface is an unbalanced single-ended interface (Figure 18). The V.28 driver generates a minimum
of ±5V across a 3kΩ load impedance between A’ and
C’. The V.28 receiver has a single-ended input. To aid
in rejecting system noise, the MAX13170E’s V.28
receiver has a typical hysteresis of 0.05V.
Figure 19 shows the MAX13174E’s termination
network disabled by opening S1 and S2. The
MAX13170E’s internal 5kΩ V.28 termination is enabled
by closing S3.
DTE vs. DCE Operation
Figure 20 shows a DCE or DTE controller-selectable
interface. DCE/DTE (pin 14) switches the port’s mode
of operation. See Table 1.
This application requires only one DB-25 connector,
but separate cables for DCE or DTE signal routing.
See Figure 20 for complete signal routing in DCE and
DTE modes.

MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software-
Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver
______________________________________________________________________________________ 17
CTS A
4
2
14
24
11
15
12
17
9
3
16
7
19
20
23
8
10
6
22
5
13
18
CTS B
DSR A
DSR B
DCD A
DCD B
DTR A
DTR B
RTS A
RTS B
RXD A
RXD B
RXC A
RXC B
TXC A
TXC B
SCTE A
SCTE B
TXD A
TXD B
CHARGE
PUMP
DTE
DCE
RTS A
RTS B
DTR A
DTR B
DCD A
DCD B
DSR A
DSR B
CTS A
CTS B
LLA
LLA
TXD A
TXD B
SCTE A
SCTE B
TXC A
TXC B
RXC A
RXC B
RXD A
RXD B
SG
M2
C12
1μF
C13
1μF
C5
4.7μF
C2
1μF
C1
1μF
C4
4.7μF
C3
4.7μF
2
21
T1
T2
T3
R1
R2
R3
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
3
V
CC
5V
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
14
3
4 6 7 9 10 16 15 18 17 19 20 22 23 24 15
8111213
C6
100pFC7100pFC8100pF
M1
M0
DCE/DTE
M1
M2
DCE/DTE
M0
V
CC
V
CC
V
EE
V
EE
V
CC
V
DD
GND
LATCH
MAX13174E
MAX13170E
T1
T2
T3
T4
R1
R2
R3
26
27
28
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
5
6
7
8
9
4
3
1
2
R4
16
15
10
11
12
13
14
M1
M2
DCE/DTE
INVERT
M0
M1
M2
DCE/DTE
M0
DB-25
CONNECTOR
MAX13172E
C11
1μF
C10
1μF
C9
1μF
1
SHIELD
DTE_TXD/DCE_RXD
DTE_SCTE/DCE_RXC
DTE_TXC/DCE_TXC
DTE_RXC/DCE_SCTE
DTE_RXD/DCE_TXD
DTE_RTS/DCE_CTS
DTE_DTR/DCE_DSR
DTE_DCD/DCE_DCD
DTE_DSR/DCE_DTR
DTE_CTS/DCE_RTS
DTE_LL/DCE_LL
Figure 20. Multiprotocol DCE/DTE Port

MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, SoftwareSelectable Clock/Data Transceiver
18 ______________________________________________________________________________________
T1
T2
T3
R3
R2
R1
T1
T2
T3
D4
TXD
SCTE
TXC
RXC
RXD
LL
T4
R4
T4
R3
R2
R1
104Ω
104Ω
104Ω
104Ω
104Ω
MAX13170EMAX13174E
MAX13174EMAX13170E
T1
T2
T3
R3
R2
R1
T3
T2
T1
RTS
DTR
DCD
DSR
CTS
R1
R2
R3
MAX13172E
MAX13172E
SERIAL
CONTROLLER
TXD
SCTE
TXC
RXC
RXD
RTS
DTR
DCD
DSR
CTS
LL
SERIAL
CONTROLLER
TXD
SCTE
TXC
RXC
RXD
RTS
DTR
DCD
DSR
CTS
LL
DCE
DTE
Figure 21. DCE-to-DTE X.21 Interface
Complete Multiprotocol X.21 Interface
A complete DTE-to-DCE interface operating in X.21
mode is shown in Figure 21. The MAX13170E is used
to generate the clock and data signals, and the
MAX13172E generates the control signals and local
loopback (LL). The MAX13174E is used to terminate
the clock and data signals to support the V.11 protocol
for cable termination. The control signals do not need
external termination.
Compliance Testing
A European Standard EN 45001 test report is pending
for the MAX13170E/MAX13172E/MAX13174E chipset.
A copy of the test report will be available from Maxim
upon completion.

MAX13170E
+5V Multiprotocol, 3Tx/3Rx, Software-
Selectable Clock/Data Transceiver
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600 ____________________
19
© 2008 Maxim Integrated Products is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
C2+
C2-
V
EE
GND
T1OUTA
T1OUTB
R3INB
T2OUTA
T2OUTB
T3OUTA/R1INA
T3OUTB/R1INB
R2INA
R2INB
R3INA
DCE/DTE
M2
M1
M0
R3OUT
R2OUT
R1OUT
T3IN
T2IN
T1IN
V
CC
V
DD
C1+
C1-
SSOP
TOP VIEW
MAX13170E
Pin Configuration
Package Information
For the latest package outline information, go to
www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.
PACKAGE TYPE PACKAGE CODE DOCUMENT NO.
28 SSOP A28-2
21-0056
Chip Information
TRANSISTOR COUNT: 2619
PROCESS: BiCMOS
 Loading...
Loading...