Page 1

r
DS2482-800
www.maxim-ic.com
Eight-Channel 1-Wire Maste
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The DS2482-800 is an I²C* to 1-Wireâ bridge device
that interfaces directly to standard (100kHz max) or
fast (400kHz max) I²C masters to perform bidirectional protocol conversion between the I²C
master and any downstream 1-Wire slave devices.
Relative to any attached 1-Wire slave device, the
DS2482-800 is a 1-Wire master. Internal factorytrimmed timers relieve the system host processor
from generating time-critical 1-Wire waveforms,
supporting both standard and Overdrive 1-Wire
communication speeds. To optimize 1-Wire
waveform generation, the DS2482-800 performs
slew-rate control on rising and falling 1-Wire edges
and has a programmable feature to mask the fast
presence pulse edge that some 1-Wire slave devices
can generate. Programmable strong pullup features
support 1-Wire power delivery to 1-Wire devices such
as EEPROMs and sensors. The DS2482-800
combines these features with eight independent 1Wire I/O channels. The I²C slave address assignment
is controlled by three binary address inputs, resolving
potential conflicts with other I²C slave devices in the
system.
APPLICATIONS
§ Wireless Base Stations
§ Central Office Switches
§ PBXs
§ Rack-Based Servers
§ Medical Clinical Diagnostic Equipment
TYPICAL OPERATING CIRCUIT
V
CC
R
P
SDA
(I²C port)
µC
Purchase of I2C components from Maxim Integrated Products, Inc., or one of its sublicensed Associated Companies, conveys a license under
the Philips I
defined by Philips.
1-Wire is a registered trademark of Dallas Semiconductor.
Note: Some revisions of this device may incorporate deviations from published specifications known as errata. Multiple revisions of any device
may be simultaneously available through various sales channels. For information about device errata, click here: www.maxim-ic.com/errata
2
C Patent Rights to use these components in an I2C system, provided that the system conforms to the I2C Standard Specification as
SCL
AD0
AD1
AD2
DS2482 800
IO0
IO1
IO2
IO3
IO4
IO5
IO6
IO7
1-Wire lines
R
t
1 of 22
1-Wire
Device #1
1-Wire
Device #2
FEATURES
§ I²C Host Interface, Supports 100kHz and 400kHz
I²C Communication Speeds
§ 1-Wire Master I/O with Selectable Active or
Passive 1-Wire Pullup
§ Provides Reset/Presence, 8-Bit, Single-Bit, and
Three-Bit 1-Wire I/O Sequences
§ Eight Channels of Independently Operated
1-Wire I/O
§ Standard and Overdrive 1-Wire Communication
Speeds
§ Slew Controlled 1-Wire Edges
§ Selectable 1-Wire Slave Presence Pulse Falling
Edge Masking to Control Fast Edges on the
1-Wire Line
§ Supports Low-Impedance 1-Wire Strong Pullup
for EEPROMs, Temp Sensors, or Other 1-Wire
Slaves That Have Momentary High Current
Modes
§ Three Address Inputs for I²C Address
Assignment
§ Wide Operating Range: 2.9V to 5.5V, -40°C to
+85°C
§ 16-Pin SO Package (150 mil)
ORDERING INFORMATION
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
DS2482S-800
DS2482S-800/T&R
-40 to +85°C
-40 to +85°C
16 SO (150 mil )
16 SO (150 mil )
PIN CONFIGURATION
IO3
SCL
SDA
VDD
NC
AD2
AD1
AD0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
IO2
IO1
IO0
GND
IO4
IO5
IO6
9
IO7
.
REV: 110204
Page 2
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Voltage Range on Any Pin Relative to Ground -0.5V, +6V
Maximum Current Into Any Pin
Operating Temperature Range
Junction Temperature
+150°C
Storage Temperature Range
Soldering Temperature
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only,
and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is
not implied. Exposure to the absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device.
±20mA
-40°C to +85°C
-55°C to +125°C
See IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020A
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(VCC = 2.9V to 5.5V, TA = -40°C to +85°C.)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Supply Voltage VCC
Operating Current ICC (Note 1) 0.75 mA
1-Wire Input High V
1-Wire Input Low V
1-Wire Weak Pullup Resistor R
1-Wire Output Low V
Active Pullup On Time t
Strong Pullup Voltage Drop DV
3.3V Pulldown Slew Rate
(Note 6)
5V Pulldown Slew Rate
(Note 6)
3.3V Pullup Slew Rate (Note 6) PU
5V Pullup Slew Rate (Note 6) PU
Power-On Reset Trip Point V
WPU
APUOT
STRPU
PD
PD
POR
IH1
IL1
OL1
SRC
SRC
SRC
SRC
1-Wire TIMING (Note 16) See Figures 3, 5, 6, and 7
Write 1/Read Low Time t
Read Sample Time t
1-Wire Time Slot t
W1L
MSR
slot
Fall Time High-to-Low at
Standard Speed (Note 6)
t
Fall Time High-to-Low at
F1
Overdrive Speed (Note 6)
3.3V 2.9 3.3 3.7
5V 4.5 5.0 5.5
3.3V (Notes 2, 3) 1.9
5V (Notes 2, 3) 3.4
3.3V (Notes 2, 3) 0.75
5V (Notes 2, 3) 1.0
(Note 4) 800 1675
V
V
V
W
At 4mA load 0.4 V
Standard (Notes 4, 16) 2.3 2.5 2.7
Overdrive (Notes 4, 16) 0.4 0.5 0.6
VCC ³ 3.2V, 1.5mA load
VCC ³ 5.2 V, 3mA load
Standard (3.3V ±10%)
Overdrive (3.3V ±10%)
Standard (5.0V ±10%)
Overdrive (5.0V ±10%)
Standard (3.3V ±10%)
Overdrive (3.3V ±10%)
Standard (5.0V ±10%)
Overdrive (5.0V ±10%)
0.3
0.5
1 4.2
5 22.1
2 6.5
10 40
0.8 4
2.7 20
1.3 6
3.4 31
µs
V
V/µs
V/µs
V/µs
V/µs
2.2 V
Standard 7.6 8 8.4
Overdrive 0.9 1 1.1
Standard 13.3 14 15
Overdrive 1.4 1.5 1.8
Standard 65.8 69.3 72.8
µs
µs
µs
Overdrive 9.9 10.5 11.0
3.3V to 0V (Note 5) 0.54 3.0
5.0V to 0V (Note 5) 0.55 2.2
3.3V to 0V (Note 5) 0.10 0.59
µs
5.0V to 0V (Note 5) 0.09 0.44
2 of 22
Page 3
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Write 0 Low Time t
Write 0 Recovery Time t
Reset Low Time t
Presence-Detect Sample Time t
Sampling for Short and
Interrupt
Reset High Time t
Presence Pulse Mask Start t
Presence Pulse Mask Stop t
W0L
REC0
RSTL
MSP
t
SI
RSTH
ppm1
ppm2
Standard 60 64 68
µs
Overdrive 7.1 7.5 7.9
Standard 5.0 5.3 5.6
Overdrive 2.8 3.0 3.2
Standard 570 600 630
Overdrive 68.4 72 75.6
Standard 66.5 70 73.5
Overdrive 7.1 7.5 7.9
Standard 7.6 8 8.4
Overdrive 0.7 0.75 0.8
Standard 554.8 584 613.2
Overdrive 70.3 74 77.7
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
(Note 7) 9.5 10 10.5 µs
(Note 7) 57 60 63 µs
I²C-Pins (Note 8) See Figure 10
VCC = 2.9V to 3.7V
LOW Level Input Voltage VIL
= 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC
HIGH Level Input Voltage VIH
Hysteresis of Schmitt Trigger
Inputs
LOW Level Output Voltage at
3mA Sink Current
Output Fall Time from V
V
with a Bus Capacitance
ILmax
Ihmin
to
V
hys
V
0.4 V
OL
tof 60 250 ns
-0.5
0.7 ×
V
CC
0.05 ×
V
CC
V
0.25 ×
V
CC
0.22 ×
V
CC
V
+
CC
0.5V
V
V
from 10pF to 400pF
Pulse Width of Spikes that are
Suppressed by the Input Filter
t
SDA and SCL pins only 50 ns
SP
Input Current Each I/O Pin with
an Input Voltage Between
0.1V
CCmax
and 0.9V
CCmax
(Notes 9, 10) -10 10 µA
I
i
Input Capacitance Ci (Note 9) 10 pF
SCL Clock Frequency f
0 400 kHz
SCL
Hold Time (Repeated) START
Condition. After this Period, the
t
0.6 µs
HD:STA
First Clock Pulse is Generated.
LOW Period of the SCL Clock t
HIGH Period of the SCL Clock t
Setup Time for a Repeated
START Condition
Data Hold Time t
Data Setup Time t
Setup Time for STOP Condition t
Bus Free Time Between a
STOP and START Condition
Capacitive Load for Each Bus
Line
Oscillator Warm-Up Time
1.3 µs
LOW
0.6 µs
HIGH
t
0.6 µs
SU:STA
(Notes 11, 12) 0.9 µs
HD:DAT
(Note 13) 250 ns
SU:DAT
0.6 µs
SU:STO
t
1.3 µs
BUF
C
(Note 14) 400 pF
b
t
(Note 15) 100 µs
OSCWUP
3 of 22
Page 4
Note 1:
Operating current with 1-Wire write byte sequence followed by continuous Read of Status Register at
400KHz in Overdrive.
Note 2:
With standard speed the total capacitive load of the 1-Wire bus should not exceed 1nF, otherwise the
passive pullup on threshold V
capacitive load on the 1-Wire bus must not exceed 300pF.
Note 3:
Note 4:
Note 5:
Note 6:
Active pullup guaranteed to turn on between V
Active or resistive pullup choice is configurable.
Fall time high to low (t
These values apply at full load, i. e., 1nF at standard speed and 0.3nF at Overdrive speed. For
reduced load, the pulldown slew rate is slightly faster.
Note 7:
Note 8:
Note 9:
Note 10:
Note 11:
Presence pulse masking only applies to standard speed.
All I²C timing values are referred to V
Applies to SDA, SCL, and AD0, AD1, AD2.
I/O pins of the DS2482 do not obstruct the SDA and SCL lines if V
The DS2482 provides a hold time of at least 300ns for the SDA signal (referred to the V
signal) to bridge the undefined region of the falling edge of SCL.
Note 12:
The maximum t
SCL signal.
Note 13:
A Fast-mode I²C-bus device can be used in a standard-mode I²C-bus system, but the requirement
t
³250ns must then be met. This is automatically the case if the device does not stretch the LOW
SU:DAT
period of the SCL signal. If such a device does stretch the LOW period of the SCL signal, it must
output the next data bit to the SDA line tr max + t
standard-mode I²C-bus specification) before the SCL line is released.
Note 14:
C
= total capacitance of one bus line in pF. If mixed with HS-mode devices, faster fall-times according
B
to I²C-Bus Specification v2.1 are allowed.
Note 15:
Note 16:
I²C communication should not take place for the max t
Except for t
F1
Therefore, if one of these parameters is found to be off the typical value, it is safe to assume that all of
these parameters deviate from their typical value in the same direction and by the same degree.
PIN DESCRIPTION
may not be reached in the available time. With Overdrive speed the
IL1
IL1MAX
) is derived from PD
F1
IHmin
has only to be met if the device does not stretch the LOW period (t
HD:DAT
referenced from 0.9 × VCC to 0.1 × VCC.
SRC,
and V
ILmax
, all 1-Wire timing specifications and t
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
and V
IH1MIN
.
levels.
is switched off.
CC
= 1000 + 250 = 1250ns (according to the
SU:DAT
time following a power-on reset.
OSCWUP
are derived from the same timing circuit.
APUOT
of the SCL
IHmin
) of the
LOW
PIN NAME FUNCTION
1 IO3 IO Driver for 1-Wire Line #3
2 SCL I²C Serial Clock Input; must be tied to VCC through a pullup resistor.
3 SDA I²C Serial Data Input/Output; must be tied to VCC through a pullup resistor.
4 VCC Power Supply Input
5 NC Not Connected
6 AD2
7 AD1
8 AD0
I²C Address Inputs; must be tied to VCC or GND. These inputs determine the I²C slave
address of the device, see Figure 9.
9 IO7 IO Driver for 1-Wire Line #7
10 IO6 IO Driver for 1-Wire Line #6
11 IO5 IO Driver for 1-Wire Line #5
12 IO4 IO Driver for 1-Wire Line #4
13 GND Ground Reference
14 IO0 IO Driver for 1-Wire Line #0
15 IO1 IO Driver for 1-Wire Line #1
16 IO2 IO Driver for 1-Wire Line #2
4 of 22
Page 5
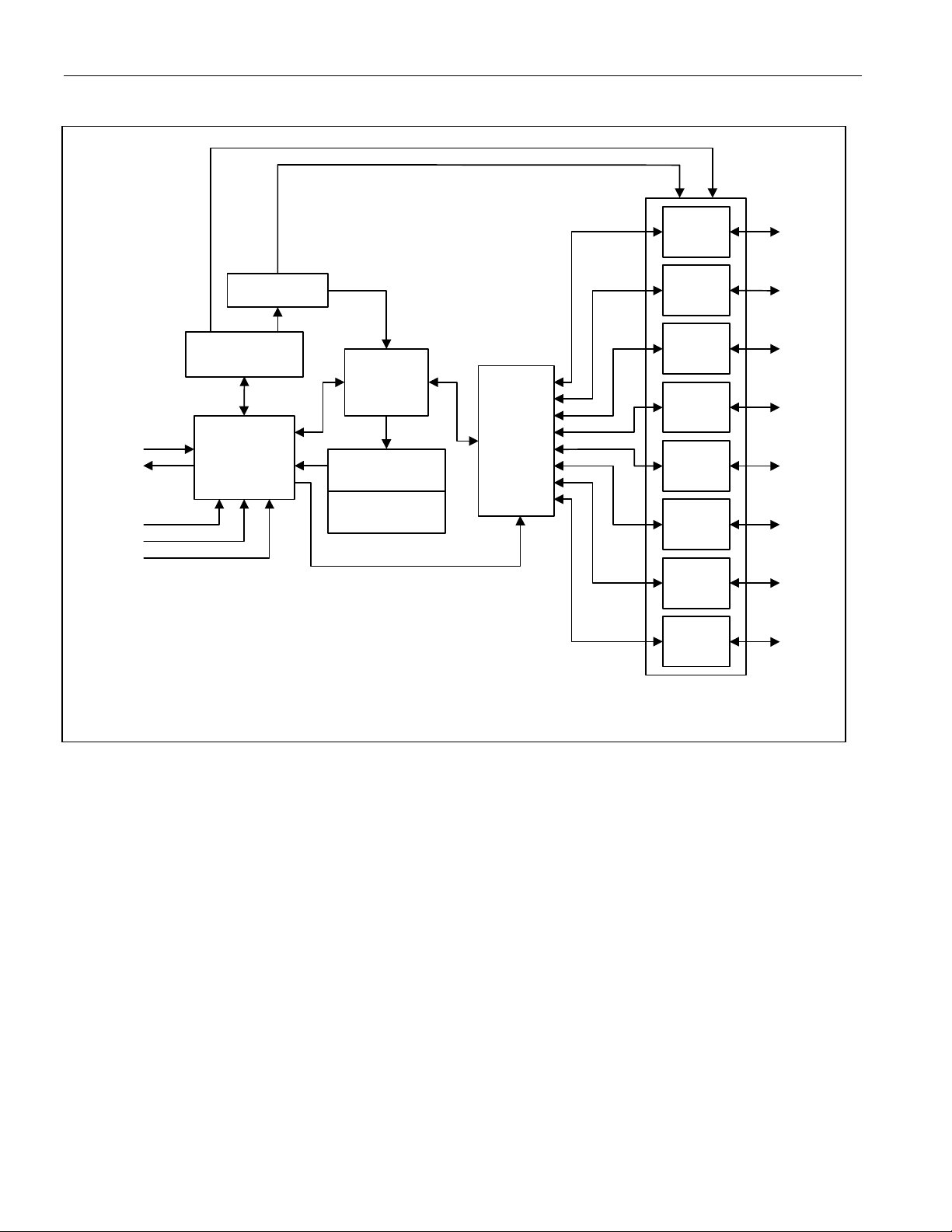
Figure 1. Block Diagram
AD0AD1A
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
SDA
SCL
D2
T-Time OSC
Config
Register
I²C
Interface
Controller
I/O
Controller
Status
Register
Read Data
Register
Channel
Select
Line
XCVR
Line
XCVR
Line
XCVR
Line
XCVR
Line
XCVR
Line
XCVR
Line
XCVR
Line
XCVR
IO0
IO1
IO2
IO3
IO4
IO5
IO6
IO7
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The DS2482-800 is a self-timed 8-channel 1-Wire master, which supports advanced 1-Wire waveform features
including standard and Overdrive speeds, active pullup, strong pullup for power delivery, and presence pulse
masking. Once supplied with command and data, the I/O controller of the DS2482 performs time-critical 1-Wire
communication functions such as reset/presence detect cycle, read-byte, write-byte, single-bit R/W and triplet for
ROM Search, without requiring interaction with the host processor. The host obtains feedback (completion of a 1Wire function, presence pulse, 1-Wire short, search direction taken) through the Status Register and data through
the Read Data register. The DS2482 communicates with a host processor through its I²C bus interface in standardmode or in fast-mode. The logic state of three address pins (2 address pins with the 1-channel version) determines
the I²C slave address of the DS2482, allowing up to 8 devices operating on the same bus segment without
requiring a hub.
DEVICE REGISTERS
The DS2482 has four registers that the I²C host can read: Channel Selection, Configuration, Status, and Read
Data. These registers are addressed by a read pointer. The position of the read pointer, i.e., the register that the
host will read in a subsequent read access, is defined by the instruction that the has DS2482 executed last. The
host has read and write access to the Channel Selection and Configuration Registers to select one of several 1Wire channels and to enable certain 1-Wire features.
5 of 22
Page 6
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
g
A
A
Channel Selection Register
The content of the Channel Selection Register specifies which of the channels is selected and will be the target of
subsequent 1-Wire communication commands. The DS2482-800 supports eight 1-Wire communication channels
IO0 to IO7. Only one of these channels can be active/selected at any time. Once selected, a 1-Wire channel
remains selected until a different channel is selected through the Channel Select command or by initiating a
device reset. After a device reset (power-up cycle or initiated by the Device Reset command) the IO0 channel is
selected.
Configuration Register
The DS2482 supports allows four 1-Wire features that are enabled or selected through the Configuration Register.
These features are:
§ Active Pullup (APU)
§ Presence Pulse Masking (PPM)
§ Strong Pullup (SPU)
§ 1-Wire Speed (1WS)
These features can be selected in any combination. They apply equally to all 1-Wire channels. While APU, PPM
and 1WS maintain their state, SPU returns to its inactive state as soon as the strong pullup has ended.
Configuration Register Bit Assignment
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
1WS SPU PPM APU 1WS SPU PPM APU
After a device reset (power-up cycle or initiated by the Device Reset command) the Configuration Register reads
00h. When writing to the Configuration Register, the new data is accepted only if the upper nibble (bits 7 to 4) is the
one's complement of the lower nibble (bits 3 to 0). When read, the upper nibble is always 0h.
Active Pullup (APU)
The APU bit controls whether an active pullup (controlled slew-rate transistor) or a passive pullup (R
resistor)
WPU
will be used to drive a 1-Wire line from low to high. When APU = 0, active pullup is disabled (resistor mode). Active
Pullup should be selected if the 1-Wire line has a substantial length (30 meters or more) or if there is a large
number (~20 or more) of devices connected to a 1-Wire line. The active pullup does not apply to the rising
edge of a presence pulse or a recovery after a short on the 1-Wire line.
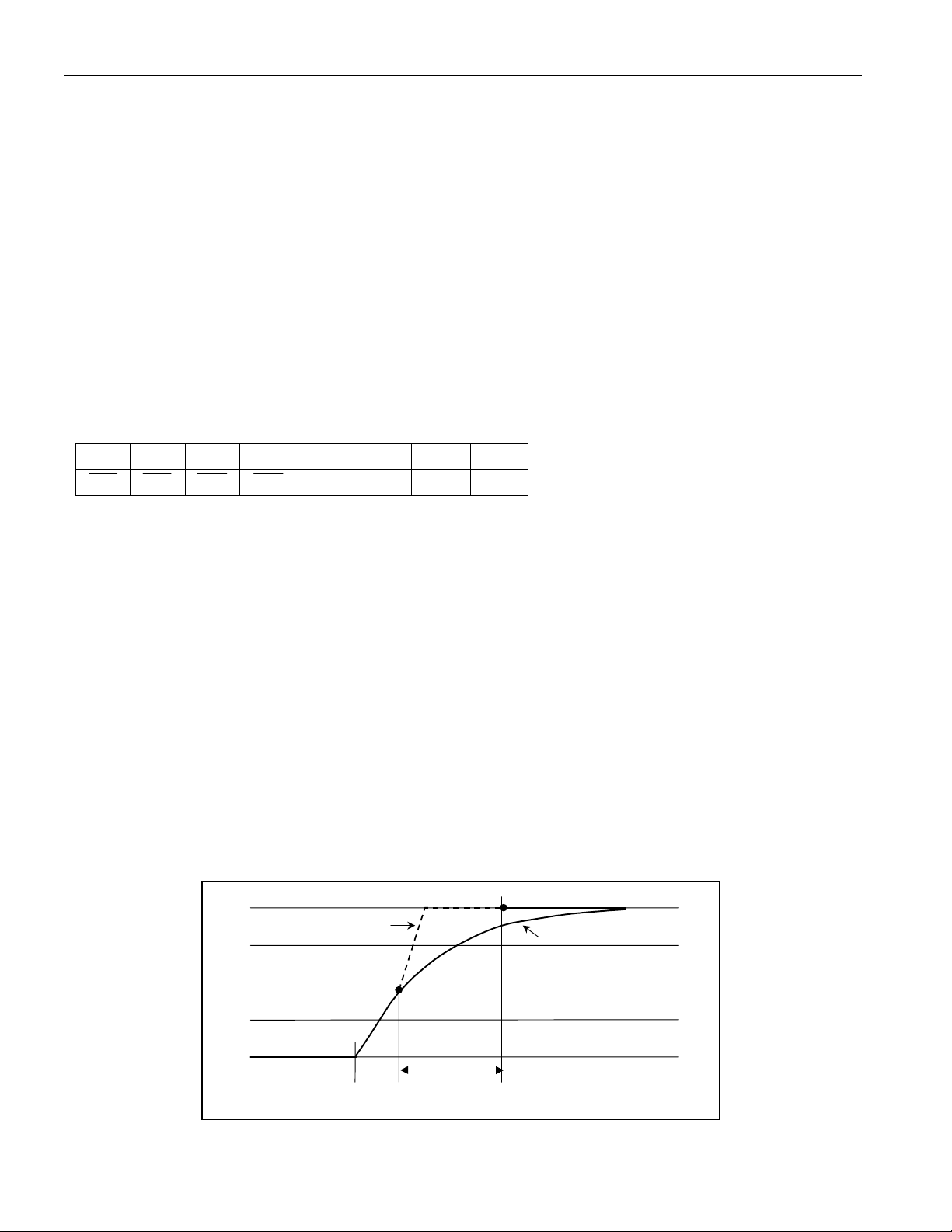
The circuit that controls rising edges (Figure 2) operates as follows: At t1 the pulldown (from DS2482 or 1-Wire
slave) ends. From this point on the 1-Wire bus is pulled high through R
internal to the DS2482. VCC and the
WPU
capacitive load of the 1-Wire line determine the slope. In case that active pullup is disabled (APU = 0), the resistive
pullup continues, as represented by the solid line. With active pullup enabled (APU = 1), when at t2 the voltage has
reached a level between V
slew rate, as represented by the dashed line. The active pullup continues until t
IL1max
and V
, the DS2482 actively pulls the 1-Wire line high applying a controlled
IH1min
is expired at t3. From that time
APUOT
on the resistive pullup will continue.
Figure 2. Rising Edge Pullup
V
CC
V
IH1MIN
V
IL1MAX
0V
1-Wire bus is
dischar
ed
PU = 1
t
1
t
APUOT
t
2
t
3
PU = 0
6 of 22
Page 7
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
Presence Pulse Masking (PPM)
The PPM bit controls whether the DS2482 will mask the leading edge (falling) of presence pulses. When PPM = 0,
masking is disabled. Presence pulse masking applies only to standard 1-Wire speed (1WS = 0); this bit has no
function if 1WS = 1 (Overdrive speed). Presence pulse masking can improve the performance of large 1-Wire
networks since it prevents the fast falling edge of a presence pulse generated by a 1-Wire slave device from
propagating through the network and getting reflected. Reflections can cause glitches in the network that in turn
may cause slave devices to lose synchronization with the 1-Wire master.
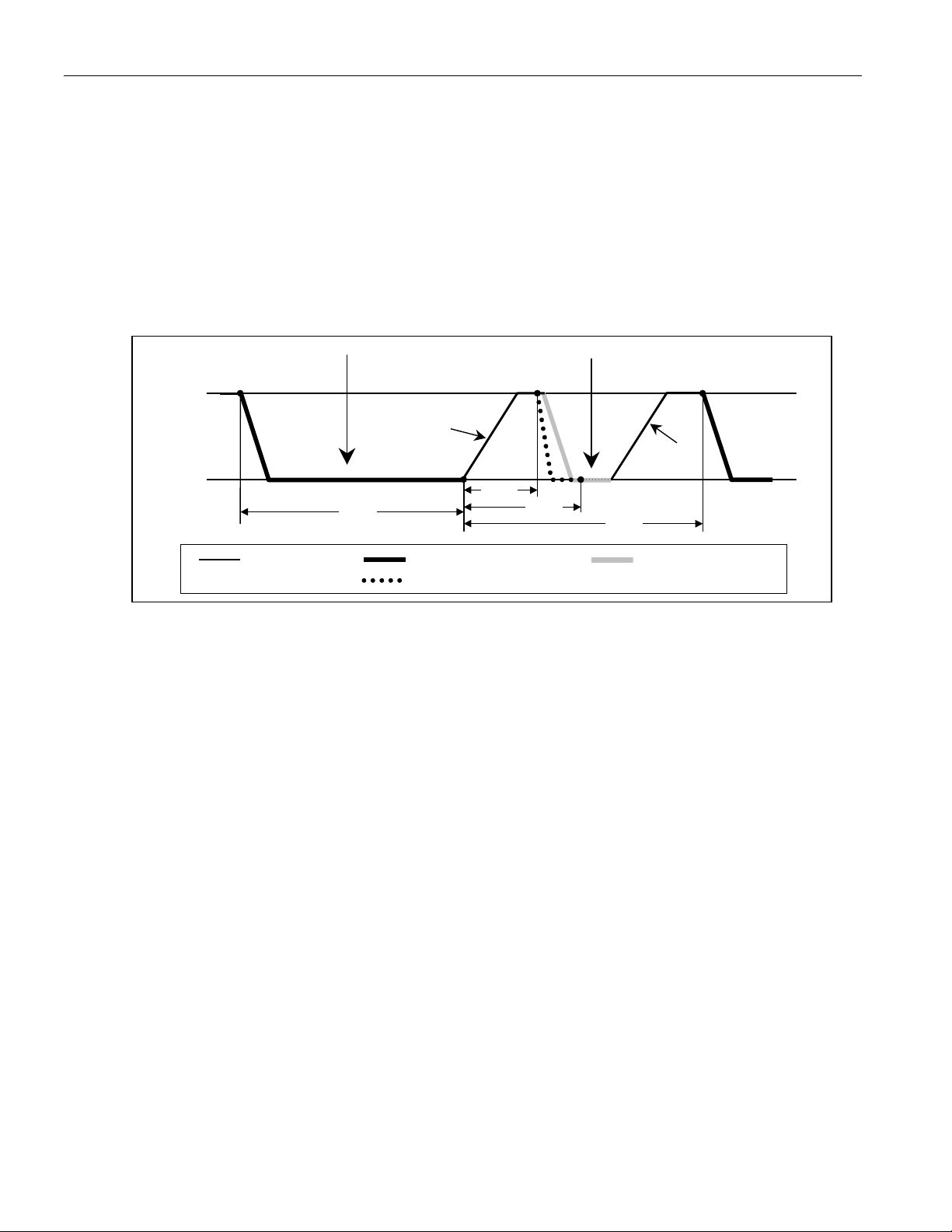
Figure 3 shows the timing references for the PPM. If enabled (PPM = 1), the DS2482 begins pulling the 1-Wire line
low at t
after the reset low time t
PPM1
is expired. The pulldown ends at t
RSTL
, at which a 1-Wire slave, if present,
PPM2
will be pulling the 1-Wire line low. The falling edge of the presence pulse mask is slew rate controlled.
Figure 3. Presence Pulse Masking
V
CC
0V
RESET PULSE PRESENCE PULSE
APU con-
t
RSTL
trolled edge
t
PPM1
t
PPM2
t
RSTH
Resistive
pull-up
Pull-up DS2482 Pull-down 1-W Slave Pull-down
DS2482 pull-down with PPM = 1; Standard speed only
Strong Pullup (SPU)
The SPU bit controls whether the DS2482 applies a low-impedance pullup to V
on the 1-Wire line after the last
CC
bit of either a 1-Wire Write Byte command or after a 1-Wire Single Bit command has completed. The strong
pullup feature is commonly used with 1-Wire EEPROM devices when copying scratchpad data to the main memory
or when performing a SHA-1 computation, and with parasitically powered temperature sensors or A-to-D
converters. The respective device data sheets specify the location in the communications protocol after which the
strong pullup should be applied. The SPU bit in the configuration register of the DS2482 must be set immediately
prior to issuing the command that puts the 1-Wire device into the state where it needs the extra power.
If SPU is 1, the DS2482 applies active pullup to the rising edge of the time slot in which the strong pullup starts,
regardless of the APU bit setting. However, in contrast to setting APU = 1 for active pullup, the low-impedance
pullup will not end after t
is expired. Instead, as shown in Figure 4, the low-impedance pullup remains active
APUOT
until: a) the next 1-Wire communication command (the typical case), b) by writing to the Configuration Register with
the SPU bit being 0 (alternative), or c) by issuing the Device Reset command. Additionally, when the pullup ends,
the SPU bit is automatically reset to 0. Using the strong pullup does not change the state of the APU bit in the
Configuration Register.
7 of 22
Page 8

DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
Figure 4. Low-Impedance Pullup Timing
V
cc
0V
1-Wire Speed (1WS)
The 1WS bit determines the timing of any 1-Wire communication generated by the DS2482. All 1-Wire slave
devices support standard speed (1WS = 0), where the transfer of a single bit (t
65µs. Many 1-Wire device can also communicate at a higher data rate, called Overdrive speed. To change from
standard to Overdrive speed, a 1-Wire device needs to receive an Overdrive Skip ROM or Overdrive Match ROM
command, as explained in the device data sheets. The change in speed occurs immediately after the 1-Wire device
has received the speed-changing command code. The DS2482 must take part in this speed change to stay
synchronized. This is accomplished by writing to the Configuration Register with the 1WS bit being 1 immediately
after the 1-Wire Byte command that changes the speed of a 1-Wire device. Writing to the Configuration Register
with the 1WS bit being 0 followed by a 1-Wire Reset command changes the DS2482 and any 1-Wire devices on
the active 1-Wire line back to standard speed.
Status Register
The read-only Status Register is the general means for the DS2482 to report bit-type data from the 1-Wire side, 1Wire busy status and its own reset status to the host processor. All 1-Wire communication commands and the
Device Reset command position the read pointer at the Status Register for the host processor to read with minimal
protocol overhead. Status information is updated during the execution of certain commands only. Details are given
in the description of the various status bits below.
Status Register Bit Assignment
Last bit of 1-Wire Write Byte or 1-Wire Single Bit Function
Write 1
Pull-up DS2482 Pull-down DS2482 Low Impedance Pull-up
Edges with
active pull-up
Write 0
t
SLOT
in Figure 4) is completed within
SLOT
Next
Time
Slot
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
DIR TSB SBR RST LL SD PPD 1WB
1-Wire Busy (1WB)
The 1WB bit reports to the host processor whether the 1-Wire line is busy. During 1-Wire communication 1WB is 1;
once the command is completed, 1WB returns to its default 0. Details on when 1WB changes state and for how
long it remains at 1 are found in the Function Commands section.
Presence Pulse Detect (PPD)
The PPD bit is updated with every 1-Wire Reset command. If the DS2482 detects a presence pulse from a 1-Wire
device at t
during the Presence Detect cycle, the PPD bit will be set to 1. This bit will return to its default 0 if
MSP
there is no presence pulse or if the 1-Wire line is shorted during a subsequent 1-Wire Reset command.
Short Detected (SD)
The SD bit is updated with every 1-Wire Reset command. If the DS2482 detects a logic 0 on the 1-Wire line at t
SI
during the Presence Detect cycle, the SD bit will be set to 1. This bit will return to its default 0 with a subsequent 1Wire Reset command provided that the short has been removed. If SD is 1, PPD will be 0. The DS2482 cannot
distinguish between a short and a DS1994 or DS2404 signaling a 1-Wire interrupt. For this reason, if a
DS2404/DS1994 is used in the application, the interrupt function must be disabled. The interrupt signaling is
explained in the respective device data sheets.
8 of 22
Page 9

DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
Logic Level (LL)
The LL bit reports the logic state of the active 1-Wire line without initiating any 1-Wire communication. The 1-Wire
line is sampled for this purpose every time the Status Register is read. The sampling and updating of the LL bit
takes place when the host processor has addressed the DS2482 in read mode (during the acknowledge cycle),
provided that the Read Pointer is positioned at the Status Register.
Device Reset (RST)
If the RST bit is 1, the DS2482 has performed an internal reset cycle, either caused by a power-on reset or from
executing the Device Reset command. The RST bit is cleared automatically when the DS2482 executes a Write
Configuration command to restore the selection of the desired 1-Wire features.
Single Bit Result (SBR)
The SBR bit reports the logic state of the active 1-Wire line sampled at t
of a 1-Wire Single Bit command or the
MSR
first bit of a 1-Wire Triplet command. The power-on default of SBR is 0. If the 1-Wire Single Bit command sends a
0-bit, SBR should be 0. With a 1-Wire Triplet command, SBR could be 0 as well as 1, depending on the response
of the 1-Wire devices connected. The same result applies to a 1-Wire Single Bit command that sends a 1-bit.
Triplet Second Bit (TSB)
The TSB bit reports the logic state of the active 1-Wire line sampled at t
of the second bit of a 1-Wire Triplet
MSR
command. The power-on default of TSB is 0. This bit is updated only with a 1-Wire Triplet command and has no
function with other commands.
Branch Direction Taken (DIR)
Whenever a 1-Write Triplet command is executed, this bit reports to the host processor the search direction that
was chosen by the 3rd bit of the triplet. The power-on default of DIR is 0. This bit is updated only with a 1-Wire
Triplet command and has no function with other commands. For additional information see the description of the 1Wire Triplet command and the Dallas Application Note 187, "1-Wire Search Algorithm".
FUNCTION COMMANDS
The DS2482 understands 9 function commands, which fall into four categories: device control, I²C communication,
1-Wire setup and 1-Wire communication. The feedback path to the host is controlled by a read pointer, which is set
automatically by each function command for the host to efficiently access relevant information. The host processor
sends these commands and applicable parameters as strings of one or two bytes using the I²C interface. The I²C
protocol requires that each byte be acknowledged by the receiving party to confirm acceptance or not be
acknowledged to indicate an error condition (invalid code or parameter) or to end the communication. Details of the
I²C protocol including acknowledge are found in the I²C interface description of this document.
Device Reset
Command Code
Command Parameter
Description
Typical Use
Restriction
Error Response
Command Duration
1-Wire Activity
Read Pointer Position
Status Bits Affected
Configuration Bits Affected
F0h
None
Performs a global reset of device state machine logic, which in turn
selects IO0 as the active 1-Wire channel.
Terminates any ongoing 1-Wire communication.
Device initialization after power-up; re-initialization (reset) as desired.
None (can be executed at any time)
None
Maximum 525ns, counted from falling SCL edge of the command code
acknowledge bit.
Ends maximum 262.5ns after the falling SCL edge of the command code
acknowledge bit.
Status Register (for busy polling)
RST set to 1,
1WB, PPD, SD, SBR, TSB, DIR set to 0
1WS, APU, PPM, SPU set to 0
9 of 22
Page 10

Set Read Pointer
Command Code
Command Parameter
Description
Typical Use
Restriction
Error Response
Command Duration
1-Wire Activity
Read Pointer Position
Status Bits Affected
Configuration Bits Affected
Valid Pointer Codes
Register Selection Code
Status Register F0h
Read Data Register E1h
Channel Selection Register D2h
Configuration Register C3h
Write Configuration
Command Code
Command Parameter
Description
Typical Use
Restriction
Error Response
Command Duration
1-Wire Activity
Read Pointer Position
Status Bits Affected
Configuration Bits Affected
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
E1h
Pointer Code
Sets the read pointer to the specified register. Overwrites the read pointer
position of any 1-Wire communication command in progress.
To prepare reading the result from a 1-Wire Byte command; random read
access of registers.
None (can be executed at any time)
If the pointer code is not valid, the pointer code will not be acknowledged
and the command will be ignored.
None; the read pointer is updated on the rising SCL edge of the pointer
code acknowledge bit.
Not Affected
As Specified by the Pointer Code
None
None
D2h
Configuration Byte
Writes a new configuration byte. The new settings take effect immediately.
NOTE: When writing to the Configuration Register, the new data is
accepted only if the upper nibble (bits 7 to 4) is the one's complement of
the lower nibble (bits 3 to 0). When read, the upper nibble is always 0h.
Defining the features for subsequent 1-Wire communication.
1-Wire activity must have ended before the DS2482 can process this
command.
Command code and parameter will not be acknowledged if 1WB = 1 at the
time the command code is received and the command will be ignored.
None; the configuration register is updated on the rising SCL edge of the
configuration byte acknowledge bit.
None
Configuration Register (to verify write)
RST set to 0
1WS, SPU, PPM, APU updated
10 of 22
Page 11

Channel Select
V
Command Code
Command Parameter
Description
Typical Use
Restriction
Error Response
Command Duration
1-Wire Activity
Read Pointer Position
Status Bits Affected
Configuration Bits Affected
Valid Channel Selection Codes
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
C3h
Selection Code
Sets the 1-Wire IO channel for subsequent 1-Wire communication
commands. NOTE: The selection code read back is different from the
code written. See the table below for the respective values.
Selecting a 1-Wire IO channel other that IO0; randomly selecting one of
the available 1-Wire IO channels.
1-Wire activity must have ended before the DS2482 can process this
command.
Command code and parameter will not be acknowledged if 1WB = 1 at the
time the command code is received and the command will be ignored.
If the selection code is not valid, the selection code will not be
acknowledged and the command will be ignored.
None; the channel selection register is updated on the rising SCL edge of
the selection code acknowledge bit.
None
Channel Selection Register (to verify write)
None
None
Channel Selection Code (to be written) Code (read back)
Channel IO0 (default) F0h B8h
Channel IO1 E1h B1h
Channel IO2 D2h AAh
Channel IO3 C3h A3h
Channel IO4 B4h 9Ch
Channel IO5 A5h 95h
Channel IO6 96h 8Eh
Channel IO7 87h 87h
Figure 5. 1-Wire Reset/Presence Detect Cycle
V
CC
V
IH1
V
IL1
0
tF1
RESET PULSE PRESENCE/SHORT DETECT
t
t
SI
t
t
RSTL
MSP
RSTH
Pullup DS2482 Pulldown 1-W Slave Pulldown
For presence-pulse masking and pullup details see Figure 3.
11 of 22
Page 12

1-Wire Reset
Command Code
Command Parameter
Description
Typical Use
Restriction
Error Response
Command Duration
1-Wire Activity
Read Pointer Position
Status Bits Affected
Configuration Bits Affected
B4h
None
Generates a 1-Wire Reset/Presence Detect cycle (Figure 5) at the
selected IO channel. The state of the 1-Wire line is sampled at t
and the result is reported to the host processor through the status register,
bits PPD and SD.
To initiate or end any 1-Wire communication sequence.
1-Wire activity must have ended before the DS2482 can process this
command.
Command code will not be acknowledged if 1WB = 1 at the time the
command code is received and the command will be ignored.
t
RSTL
+ t
+ maximum 262.5ns, counted from the falling SCL edge of the
RSTH
command code acknowledge bit.
Begins maximum 262.5ns after the falling SCL edge of the command
code acknowledge bit.
Status Register (for busy polling)
1WB (set to 1 for t
RSTL
PPD is updated at t
SD is updated at t
RSTL
1WS, PPM, APU apply
1-Wire Single Bit
Command Code
Command Parameter
Description
Typical Use
Restriction
Error Response
Command Duration
1-Wire Activity
Read Pointer Position
Status Bits Affected
Configuration Bits Affected
Bit Allocation in the Bit Byte
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
V x x x x x x x
x = don’t care
87h
Bit Byte
Generates a single 1-Wire time slot with a bit value ‘V’ as specified by the
bit byte at the selected 1-Wire IO channel. A ‘V’ value of 0b will generate a
write-zero time slot (Figure 6), a value of 1b will generate a write one slot,
which also functions as a read data time slot (Figure 7). In either case the
logic level at the 1-Wire line is tested at t
To perform single bit writes or reads on a 1-Wire IO channel when single
bit communication is necessary (the exception).
1-Wire activity must have ended before the DS2482 can process this
command.
Command code and bit byte will not be acknowledged if 1WB = 1 at the
time the command code is received and the command will be ignored.
t
+ maximum 262.5ns, counted from the falling SCL edge of the first
SLOT
bit (MS bit) of the bit byte.
Begins maximum 262.5ns after the falling SCL edge of the MS bit of the
bit byte.
Status Register (for busy polling and data reading)
1WB (set to 1 for t
SLOT
SBR is updated at t
DIR (may change its state)
1WS, APU, SPU apply
RSTL
MSR
+ t
RSTH
+ t
+ tSI
)
MSP
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
SI
),
,
and SBR is updated.
MSR
and t
MSP
12 of 22
Page 13

Figure 6. Write-0 Time Slot
V
V
V
cc
V
IH1
V
IL1
t
MSR
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
t
W0L
0
t
F1
t
SLOT
t
REC0
Pullup (see Fig. 2) DS2482 Pulldown
Figure 7. Write-1 and Read-Data Time Slot
t
V
cc
V
IH1
V
IL1
t
W1L
MSR
0
t
F1
t
SLOT
Pullup (see Fig. 2) DS2482 Pulldown 1-W Slave Pulldown
NOTE on Figure 7: Depending on its internal state, a 1-Wire slave device will transmit data to its master (e.g., the
DS2482). When responding with a 0, a 1-Wire slave will start pulling the line low during t
; its internal timing
W1L
generator determines when this pulldown ends and the voltage starts rising again. When responding with a 1, a 1Wire slave will not hold the line low at all, and the voltage starts rising as soon as t
sheets use the term t
instead of t
RL
to describe a read-data time slot. Technically, tRL and t
W1L
is over. 1-Wire device data
W1L
have identical
W1L
specifications and cannot be distinguished from each other.
1-Wire Write Byte
Command Code
Command Parameter
Description
Typical Use
Restriction
Error Response
Command Duration
1-Wire Activity
Read Pointer Position
Status Bits Affected
Configuration Bits Affected
A5h
Data Byte
Writes single data byte to selected 1-Wire IO channel.
To write commands or data to a 1-Wire IO channel; equivalent to
executing eight 1-Wire Single Bit commands, but faster due to less I²C
traffic.
1-Wire activity must have ended before the DS2482 can process this
command.
Command code and data byte will not be acknowledged if 1WB = 1 at the
time the command code is received and the command will be ignored.
8 × t
+ maximum 262.5ns, counted from falling edge of the last bit (LS
SLOT
bit) of the data byte.
Begins maximum 262.5ns after falling SCL edge of the LS bit of the data
byte (i.e., before the data byte acknowledge).
NOTE: The bit order on the I²C bus and the 1-Wire line is different.
(1-Wire: LS-bit first; I²C: MS-bit first) Therefore, 1-Wire activity cannot
begin before the DS2482 has received the full data byte.
Status Register (for busy polling)
1WB (set to 1 for 8 × t
SLOT
)
1WS, SPU, APU apply
13 of 22
Page 14

1-Wire Read Byte
Command Code
Command Parameter
Description
Typical Use
Restriction
Error Response
Command Duration
1-Wire Activity
Read Pointer Position
Status Bits Affected
Configuration Bits Affected
1-Wire Triplet
Command Code
Command Parameter
Description
Typical Use
Restriction
Error Response
Command Duration
1-Wire Activity
Read Pointer Position
Status Bits Affected
Configuration Bits Affected
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
96h
None
Generates eight read data time slots on the selected 1-Wire IO channel
and stores result in the Read Data Register.
To read data from a 1-Wire IO channel; equivalent to executing eight 1Wire Single Bit commands with V = 1 (write 1 time slot), but faster due to
less I²C traffic.
1-Wire activity must have ended before the DS2482 can process this
command.
Command code will not be acknowledged if 1WB = 1 at the time the
command code is received and the command will be ignored.
8 × t
+ maximum 262.5ns, counted from the falling SCL edge of the
SLOT
command code acknowledge bit.
Begins maximum 262.5ns after the falling SCL edge of the command
code acknowledge bit.
Status Register (for busy polling)
NOTE: To read the data byte received from the 1-Wire IO channel, issue
the Set Read Pointer command and select the Read Data Register. Then
access the DS2482 in read mode.
1WB (set to 1 for 8 × t
SLOT
)
1WS, APU apply
78h
Direction Byte
Generates three times slots, two read-time slots and one-write time slot, at
the selected 1-Wire IO channel. The type of write-time slot depends on the
result of the read-time slots and the direction byte.
The direction byte determines the type of write-time slot if both read-time
slots are 0 (a typical case). In this case the DS2482 will generate a write-1
time slot if V = 1 and a write-0 time slot if V = 0.
If the read-time slots are 0 and 1, there will follow a write 0 time slot.
If the read-time slots are 1 and 0, there will follow a write 1 time slot.
If the read-time slots are both 1 (error case), the subsequent write time
slot will be a write 1.
To perform a 1-Wire Search ROM sequence; a full sequence requires this
command to be executed 64 times to identify and address one device.
1-Wire activity must have ended before the DS2482 can process this
command.
Command code and direction byte will not be acknowledged if 1WB = 1 at
the time the command code is received and the command will be ignored.
3 × t
+ maximum 262.5ns, counted from the falling SCL edge of the
SLOT
first bit (MS bit) of the direction byte.
Begins maximum 262.5ns after the falling SCL edge of the MS bit of the
direction byte.
Status Register (for busy polling)
1WB (set to 1 for 3 × t
SBR is updated at the first t
TSB and DIR are updated at the second t
SLOT
)
MSR
(i.e., at t
MSR
SLOT
+ t
MSR
)
1WS, APU apply
14 of 22
Page 15

DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
A
r
A
Bit Allocation in the Direction Byte
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
V x x x x x x x
x = don’t care
I²C INTERFACE
General Characteristics
The I²C bus uses a data line (SDA) plus a clock signal (SCL) for communication. Both SDA and SCL are
bidirectional lines, connected to a positive supply voltage through a pullup resistor. When there is no
communication, both lines are HIGH. The output stages of devices connected to the bus must have an open-drain
or open-collector to perform the wired-AND function. Data on the I²C bus can be transferred at rates of up to
100kbps in the Standard-mode, up to 400kbps in the Fast-mode. The DS2482 works in both modes.
A device that sends data on the bus is defined as a transmitter, and a device receiving data as a receiver. The
device that controls the communication is called a “master.” The devices that are controlled by the master are
“slaves.” To be individually accessed, each device must have a slave address that does not conflict with other
devices on the bus.
Data transfers may be initiated only when the bus is not busy. The master generates the serial clock (SCL),
controls the bus access, generates the START and STOP conditions, and determines the number of data bytes
transferred between START and STOP (Figure 8). Data is transferred in bytes with the most significant bit being
transmitted first. After each byte follows an acknowledge bit to allow synchronization between master and slave.
Figure 8. I²C Protocol Overview
SDA
SCL
Idle
MS-bit
Slave Address
12 678
START
Condition
W
ACK
R/
bit
Acknowledgment
from Receive
9 912 8
CK
ACK
Repeated if more bytes
are transferred
CK
bit
STOP Condition
Repeated START
Condition
Slave Address
The slave address to which the DS2482 responds is shown in Figure 9. The logic states at the address pins AD0,
AD1 and AD2 determine the value of the address bits A0, A1, and A2. The address pins allow the device to
respond to one of eight possible slave addresses. The slave address is part of the slave-address/control byte. The
last bit of the slave-address/control byte (R/
W) defines the data direction. When set to a 0, subsequent data will
flow from master to slave (write access); when set to a 1, data will flow from slave to master (read access).
15 of 22
Page 16

Figure 9. DS2482 Slave Address
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
0 0 1 1 AD2 AD1 AD0 R/W
DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
7-Bit Slave Address
Most Significant Bit
AD2, AD1, AD0
Pin States
Determines
Read or Write
I²C Definitions
The following terminology is commonly used to describe I²C data transfers. The timing references are defined in
Figure 10.
Bus Idle or Not Busy: Both, SDA and SCL, are inactive and in their logic HIGH states.
START Condition: To initiate communication with a slave, the master has to generate a START condition. A
START condition is defined as a change in state of SDA from HIGH to LOW while SCL remains HIGH.
STOP Condition: To end communication with a slave, the master has to generate a STOP condition. A STOP
condition is defined as a change in state of SDA from LOW to HIGH while SCL remains HIGH.
Repeated START Condition: Repeated starts are commonly used for read accesses to select a specific data
source or address to read from. The master can use a repeated START condition at the end of a data transfer to
immediately initiate a new data transfer following the current one. A repeated START condition is generated the
same way as a normal START condition, but without leaving the bus idle after a STOP condition.
Data Valid: With the exception of the START and STOP condition, transitions of SDA may occur only during the
LOW state of SCL. The data on SDA must remain valid and unchanged during the entire high pulse of SCL plus
the required setup and hold time (t
after the falling edge of SCL and t
HD:DAT
before the rising edge of SCL, see
SU:DAT
Figure 10). There is one clock pulse per bit of data. Data is shifted into the receiving device during the rising edge
of the SCL.
When finished with writing, the master must release the SDA line for a sufficient amount of setup time (minimum
t
+ tR in Figure 10) before the next rising edge of SCL to start reading. The slave shifts out each data bit on
SU:DAT
SDA at the falling edge of the previous SCL pulse and the data bit is valid at the rising edge of the current SCL
pulse. The master generates all SCL clock pulses, including those needed to read from a slave.
Acknowledge: Usually, a receiving device, when addressed, is obliged to generate an acknowledge after the
receipt of each byte. The master must generate a clock pulse that is associated with this acknowledge bit. A device
that acknowledges must pull SDA LOW during the acknowledge clock pulse in such a way that SDA is stable LOW
during the HIGH period of the acknowledge-related clock pulse plus the required setup and hold time (t
the falling edge of SCL and t
before the rising edge of SCL).
SU:DAT
HD:DAT
after
Not Acknowledged by Slave: A slave device may be unable to receive or transmit data, e.g., because it is busy
performing some real-time function. In this case the slave device will not acknowledge its slave address and leave
the SDA line HIGH.
A slave device that is ready to communicate will acknowledge at least its slave address. However, some time later
the slave may refuse to accept data, e.g., because of an invalid command code or parameter. In this case the slave
device will not acknowledge any of the bytes that it refuses and will leave SDA HIGH. In either case, after a slave
has failed to acknowledge, the master first needs to generate a repeated START condition or a STOP condition
followed by a START condition to begin a new data transfer.
16 of 22
Page 17

DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
Not Acknowledged by Master: At some time when receiving data, the master must signal an end of data to the
slave device. To achieve this, the master does not acknowledge the last byte that it has received from the slave. In
response, the slave releases SDA, allowing the master to generate the STOP condition.
Figure 10. I²C Timing Diagram
SDA
t
BUF
t
LOW
SCL
STOP START
t
HD:STA
t
R
NOTE: Timing is referenced to V
ILMAX
t
HD:DAT
and V
t
t
IHMIN
F
HIGH
.
t
SU:DAT
Repeated
START
t
t
SU:STA
HD:STA
Spike
Suppression
t
SP
t
SU:STO
Writing to the DS2482
To write to the DS2482, the master must access the device in write mode, i.e., the slave address must be sent with
the direction bit set to 0. The next byte to be sent is a command code, which, depending on the command, may be
followed by a command parameter. The DS2482 will acknowledge valid command codes and expected/valid
command parameters. Additional bytes or invalid command parameters will never be acknowledged.
Reading from the DS2482
To read from the DS2482, the master must access the device in read mode, i. e., the slave address must be sent
with the direction bit set to 1. The read pointer determines the register that the master will read from. The master
may continue reading the same register over and over again, without having to re-address the device, e. g., to
watch the 1WB changing from 1 to 0. To read from a different register, the master must issue the Set Read Pointer
command and then access the DS2482 again in read mode.
I²C Communication—Legend
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
S START Condition DRST Command "Device Reset", F0h
AD,0 Select DS2482 for Write Access WCFG Command "Write Configuration", D2h
AD,1 Select DS2482 for Read Access CHSL Command "Channel Select", C3h
Sr Repeated START Condition SRP Command "Set Read Pointer", E1h
P STOP Condition 1WRS Command "1-Wire Reset", B4h
A Acknowledged 1WWB Command "1-Wire Write Byte", A5h
A\ Not Acknowledged 1WRB Command "1-Wire Read Byte", 96h
(Idle) Bus Not Busy 1WSB Command "1-Wire Single Bit", 87h
<byte> Transfer of 1 Byte 1WT Command "1-Wire Triplet", 78h
17 of 22
Page 18

DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
Data Direction Codes
Master-to-Slave Slave-to-Master
I²C Communication Examples
Device Reset, e.g., after power-up
S AD,0 A DRST A Sr AD,1 A <byte> A\ P
This example includes an optional read access to verify the success of the command.
Write Configuration, e.g., before starting 1-Wire activity power-up
Case A: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0)
S AD,0 A WCFG A <byte> A Sr AD,1 A <byte> A\ P
This example includes an optional read access to verify the success of the command.
Case B: 1-Wire busy (1WB = 1)
S AD,0 A WCFG A\ P
The master should stop and restart as soon as the DS2482 does not acknowledge the command code.
Channel Select, e.g., to select another 1-Wire channel
Case A: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0)
S AD,0 A CHSL A E1h A Sr AD,1 A <byte> A\ P
E1h is the valid channel selection code for IO1. This example includes an optional read access to verify the
success of the command.
Case B: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), invalid channel selection code
S AD,0 A CHSL A E5h A\ P
E5h is an invalid channel selection code.
Case C: 1-Wire busy (1WB = 1)
S AD,0 A CHSL A\ P
The master should stop and restart as soon as the DS2482 does not acknowledge the command code.
Set Read Pointer, e.g., to read from another register
Case A: valid read pointer code
S AD,0 A SRP A C3h A P
C3h is the valid read pointer code for the configuration register.
Case B: invalid read pointer code
S AD,0 A SRP A E5h A\ P
E5h is an invalid read pointer code.
18 of 22
Page 19

DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
1-Wire Reset, e.g., to begin or end 1-Wire communication
Case A: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), no busy polling to read the result
S AD,0 A 1WRS A P (Idle) S AD,1 A <byte> A\ P
In the first cycle, the master sends the command; then the master waits (Idle) for the 1-Wire Reset to complete. In
the second cycle the DS2482 is accessed to read the result of the 1-Wire Reset from the Status Register.
Case B: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), busy polling until the 1-Wire Command is completed, then read the result
S AD,0 A 1WRS A Sr AD,1 A <byte> A <byte> A\ P
Repeat until the 1WB bit has changed to 0
Case C: 1-Wire busy (1WB = 1)
S AD,0 A 1WRS A\ P
The master should stop and restart as soon as the DS2482 does not acknowledge the command code.
1-Wire Write Byte, e.g., to send a command code to a 1-Wire IO channel
Case A: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), no busy polling
S AD,0 A 1WWB A 33h A P (Idle)
33h is the valid 1-Wire ROM function command for Read ROM. The idle time is needed for the 1-Wire function to
complete. There is no data read back from the 1-Wire line with this command.
Case B: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), busy polling until the 1-Wire Command is completed.
S AD,0 A 1WWB A 33h A
Sr AD,1 A <byte> A <byte> A\ P
When 1WB has changed from 1 to 0, the 1-Wire Write Byte command is completed.
Case C: 1-Wire busy (1WB = 1)
S AD,0 A 1WWB A\ P
The master should stop and restart as soon as the DS2482 does not acknowledge the command code.
1-Wire Read Byte, e. g., to read a byte from a 1-Wire IO channel
Repeat until the 1WB
bit has changed to 0
Case A: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), no busy polling, set read pointer after idle time.
S AD,0 A 1WRB A P (Idle)
S AD,0 A SRP A E1h A Sr AD,1 A <byte> A\ P
The idle time is needed for the 1-Wire function to complete. Then set the read pointer to the read data register
(code E1h) and access the device again to read the data byte that was obtained from the 1-Wire IO channel.
Case B: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), no busy polling, set read pointer before idle time.
S AD,0 A 1WRB A Sr AD,0 A SRP A E1h A P
(Idle) S AD,1 A <byte> A\ P
The read pointer is set to the read data register (code E1h) while the 1-Wire Read Byte command is still in
progress. Then, after the 1-Wire function is completed, the device is accessed to read the data byte that was
obtained from the 1-Wire IO channel.
19 of 22
Page 20

DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
Case C: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), busy polling until the 1-Wire Command is completed.
S AD,0 A 1WRB A
Sr AD,1 A <byte> A <byte> A\
Sr AD,0 A SRP A E1h A Sr AD,1 A <byte> A\ P
Poll the Status Register until the 1WB bit has changed from 1 to 0. Then set the read pointer to the read data
register (code E1h) and access the device again to read the data byte that was obtained from the 1-Wire IO
channel.
Case D: 1-Wire busy (1WB = 1)
S AD,0 A 1WRB A\ P
The master should stop and restart as soon as the DS2482 does not acknowledge the command code.
1-Wire Single Bit, e. g., to generate a single time slot on a 1-Wire IO channel
Case A: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), no busy polling
S AD,0 A 1WSB A <byte> A P (Idle)
S AD,1 A <byte> A\ P
The idle time is needed for the 1-Wire function to complete. Then access the device in read mode to get the result
from the 1-Wire single-bit command.
Case B: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), busy polling until the 1-Wire Command is completed.
S AD,0 A 1WSB A <byte> A
Sr AD,1 A <byte> A <byte> A\ P
When 1WB has changed from 1 to 0, the Status Register holds the valid result of the 1-Wire Single Bit command.
Case C: 1-Wire busy (1WB = 1)
S AD,0 A 1WSB A\ P
The master should stop and restart as soon as the DS2482 does not acknowledge the command code.
1-Wire Triplet, e.g., to perform a Search ROM function on a 1-Wire IO channel
Repeat until the 1WB
bit has changed to 0
Repeat until the 1WB
bit has changed to 0
Case A: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), no busy polling
S AD,0 A 1WT A <byte> A P (Idle)
S AD,1 A <byte> A\ P
The idle time is needed for the 1-Wire function to complete. Then access the device in read mode to get the result
from the 1-Wire Triplet command.
Case B: 1-Wire idle (1WB = 0), busy polling until the 1-Wire Command is completed.
S AD,0 A 1WT A <byte> A
Sr AD,1 A <byte> A <byte> A\ P
When 1WB has changed from 1 to 0, the Status Register holds the valid result of the 1-Wire Triplet command.
Repeat until the 1WB
bit has changed to 0
20 of 22
Page 21

DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
Case C: 1-Wire busy (1WB = 1)
S AD,0 A 1WT A\ P
The master should stop and restart as soon as the DS2482 does not acknowledge the command code.
Figure 11. Application Schematic
*R
P
(I²C port)
SDA
SCL
µC
AD0
AD1
AD2
DS2482-800
SDA
SCL
V
CC
AD0
AD1
AD2
V
CC
1-Wire
1-Wire lines
*R
IO0
IO1
IO2
IO3
IO4
IO5
IO6
IO7
V
CC
IO0
IO1
IO2
IO3
IO4
IO5
IO6
IO7
t
* Rt Line termination resistor, typically 100W
I²C pull-up resistor, see
R
P
sizing.
for R
P
*R
t
Application Information
Device #1
1-Wire
Device #2
DS2482-800
Application Information
SDA and SCL Pullup Resistors
SDA is an open-drain output on the DS2482 that requires a pullup resistor to realize high logic levels. Because the
DS2482 uses SCL only as input (no clock stretching) the master can drive SCL either through an opendrain/collector output with a pullup resistor or a push-pull output.
Pullup Resistor R
According to the I²C specification, a slave device must be able to sink at least 3mA at a V
condition determines the minimum value of the pullup resistor: Rpmin = (V
voltage of 5.5V, the minimum value for the pullup resistor is 1.7kW. The "Minimum RP" line in Figure 12 shows how
the minimum pullup resistor changes with the operating voltage.
For I²C systems, the rise time and fall time are measured from 30% to 70% of the pullup voltage. The maximum
bus capacitance C
fast speed. Assuming maximum rise time, the maximum resistor value at any given capacitance C
as: Rpmaxs = 1000ns/(C
Sizing
P
of 0.4V. This DC
- 0.4V)/3mA. With an operating
CC
is 400pF. The maximum rise time at standard speed must not exceed 1000ns and 300ns at
B
*ln(7/3)) (standard speed) and Rpmaxf = 300ns/(CB*ln(7/3)) (fast speed). For a bus
B
OL
is calculated
b
21 of 22
Page 22

DS2482-800: Eight-Channel 1-Wire Master
capacitance of 400pF the maximum pullup resistor values are 2.95kW at standard speed and 885W at fast speed. A
value between of 1.7kW and 2.95kW meets all requirements at standard speed.
Since a 885W pullup resistor, as would be required to meet the rise time specification at fast speed and 400pF bus
capacitance, is lower than Rpmin at 5.5V, a different approach is necessary. The "Max. Load…" line in Figure 12 is
generated by first calculating the minimum pullup resistor at any given operating voltage ("Minimum Rp" line) and
then calculating the respective bus capacitance that yields a rise time of 300ns.
Only for pullup voltages of 3V and lower can the maximum permissible bus capacitance of 400pF be maintained. A
reduced bus capacitance of 300pF is acceptable for pullup voltages of 4V and lower. For fast speed operation at
any pullup voltage, the bus capacitance must not exceed 200pF. The corresponding pullup resistor value at the
voltage is indicated by the "Minimum Rp" line.
Figure 12. I²C Fast Speed Pullup Resistor Selection Chart
"Minimum Rp" Max. Load at Min. Rp fast mode
2000
1600
1200
800
400
Minimum Rp (Ohms)
0
12345
Pull-up Voltage
500
400
300
200
Load (pF)
100
0
PACKAGE INFORMATION
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information, go to
www.maxim-ic.com/DallasPackInfo
.)
22 of 22
 Loading...
Loading...