
g
查询DS21455供应商
www.maxim-ic.com
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The DS21455 and DS21458 are quad monolithic
devices featuring independent transceivers that
can be software configured for T1, E1, or J1
operation. Each is composed of a line interface
unit (LIU), framer, HDLC controllers, and a
TDM backplane interface, and is controlled via
an 8-bit parallel port configured for Intel or
Motorola bus operations. The DS21455* is a
direct replacement for the older DS21Q55 quad
MCM device. The DS21458, in a smaller
package (17mm CSBGA) and featuring an
improved controller interface, is software
compatible with the older DS21Q55.
*The JTAG function on the DS21455/DS21458 is a single
controller for all four transceivers, unlike the DS21Q55, which has
a JTAG controller-per-transceiver architecture.
APPLICATIONS
Routers
Channel Service Units (CSUs)
Data Service Units (DSUs)
Muxes
Switches
Channel Banks
T1/E1 Test Equipment
ORDERING INFORMATION
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
DS21455
DS21455N -40°C to +85°C
DS21458
DS21458N -40°C to +85°C
DALLAS is a registered trademark of Dallas Semiconductor Corp.
MAXIM is a re
0°C to +70°C
0°C to +70°C
istered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
256 BGA
(27mm x 27mm)
256 BGA
(27mm x 27mm)
256 CSBGA
(17mm x 17mm)
256 CSBGA
(17mm x 17mm)
DS21455/DS21458
Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
FEATURES
Four Independent Transceivers, Each Having
the Following Features:
§ Complete T1 (DS1)/ISDN-PRI/J1
Transceiver Functionality
§ Complete E1 (CEPT) PCM-30/ISDNPRI Transceiver Functionality
§ Short- and Long-Haul Line Interface for
Clock/Data Recovery and Waveshaping
§ CMI Coder/Decoder
§ Crystal-Less Jitter Attenuator
§ Fully Independent Transmit and Receive
Functionality
§ Dual HDLC Controllers
§ On-Chip Programmable BERT Generator
and Detector
§ Internal Software-Selectable Receiveand Transmit-Side Termination Resistors
for 75Ω/100Ω/120Ω T1 and E1
Interfaces
§ Dual Two-Frame Elastic-Store Slip
Buffers that can Connect to
Asynchronous Backplanes Up to
16.384MHz
§ 16.384MHz, 8.192MHz, 4.096MHz, or
2.048MHz Clock Output Synthesized to
Recovered Network Clock
§ Programmable Output Clocks for
Fractional T1, E1, H0, and H12
Applications
§ Interleaving PCM Bus Operation
§ 8-Bit Parallel Control Port, Multiplexed
or Nonmultiplexed, Intel or Motorola
§ IEEE 1149.1 JTAG-Boundary Scan
§ 3.3V Supply with 5V Tolerant Inputs and
Outputs
§ DS21455 Directly Replaces DS21Q55
§ Signaling System 7 (SS7) Support
§ RAI-CI, AIS-CI Support
Note: Some revisions of this device may incorporate deviations from published specifications known as errata. Multiple revisions of any device
may be simultaneously available through various sales channels. For information about device errata, click here: www.maxim-ic.com/errata
1 of 270
REV: 040804
.

DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY
REVISION CHANGES
040804 New Product Release.
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
2 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................................................................9
1.1 S
2. FEATURE HIGHLIGHTS ...............................................................................................................................11
2.1 G
2.2 L
2.3 C
2.4 J
2.5 F
2.6 S
2.7 HDLC C
2.8 T
2.9 E
2.10 C
3. BLOCK DIAGRAM ........................................................................................................................................15
4. DS21455/DS21458 DELTA...........................................................................................................................17
4.1 P
4.2 C
4.3 ESIB F
4.4 F
5. PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION....................................................................................................................20
5.1 T
5.2 R
5.3 P
5.4 E
5.5 JTAG T
5.6 L
5.7 S
5.8 P
5.9 P
6. PARALLEL PORT .........................................................................................................................................41
6.1 R
7. SPECIAL PER-CHANNEL REGISTER OPERATION ..................................................................................46
8. PROGRAMMING MODEL.............................................................................................................................48
8.1 P
8.2 I
8.3 S
8.4 I
8.5 I
9. CLOCK MAP .................................................................................................................................................52
10. T1 FRAMER/FORMATTER CONTROL REGISTERS .................................................................................53
10.1 T1 C
10.2 T1 T
10.3 AIS-CI
10.4 T1 R
10.5 T1 I
11. E1 FRAMER/FORMATTER CONTROL REGISTERS .................................................................................64
11.1 E1 C
11.2 A
11.3 E1 I
12. COMMON CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTERS.....................................................................................71
TANDARDS ...................................................................................................................... 10
ENERAL .......................................................................................................................... 11
INE INTERFACE ................................................................................................................ 11
LOCK SYNTHESIZER ........................................................................................................ 11
ITTER ATTENUATOR ......................................................................................................... 12
RAMER/FORMATTER ........................................................................................................ 12
YSTEM INTERFACE........................................................................................................... 13
ONTROLLERS ....................................................................................................... 13
EST AND DIAGNOSTICS .................................................................................................... 13
XTENDED SYSTEM INFORMATION BUS .............................................................................. 14
ONTROL PORT ................................................................................................................ 14
ACKAGE.......................................................................................................................... 17
ONTROLLER INTERFACE................................................................................................... 17
UNCTION................................................................................................................ 17
RAMER/LIU INTERIM SIGNALS .......................................................................................... 17
RANSMIT SIDE PINS ......................................................................................................... 20
ECEIVE SIDE PINS ........................................................................................................... 22
ARALLEL CONTROL PORT PINS ........................................................................................ 24
XTENDED SYSTEM INFORMATION BUS .............................................................................. 26
EST ACCESS PORT PINS........................................................................................ 26
INE INTERFACE PINS ........................................................................................................ 27
UPPLY PINS .................................................................................................................... 28
IN DESCRIPTIONS............................................................................................................ 29
ACKAGES........................................................................................................................ 39
EGISTER MAP ................................................................................................................. 41
OWER-UP SEQUENCE...................................................................................................... 49
8.1.1 Master Mode Register ........................................................................................................ 49
NTERRUPT HANDLING ....................................................................................................... 50
TATUS REGISTERS .......................................................................................................... 50
NFORMATION REGISTERS.................................................................................................. 51
NTERRUPT INFORMATION REGISTERS ................................................................................ 51
ONTROL REGISTERS .................................................................................................. 53
RANSMIT TRANSPARENCY........................................................................................... 58
AND RAI-CI GENERATION AND DETECTION ............................................................. 59
ECEIVE-SIDE DIGITAL-MILLIWATT CODE GENERATION ................................................. 60
NFORMATION REGISTER............................................................................................... 62
ONTROL REGISTERS .................................................................................................. 64
UTOMATIC ALARM GENERATION ....................................................................................... 68
11.2.1 Auto AIS ...........................................................................................................................68
11.2.2 Auto RAI ...........................................................................................................................68
11.2.3 Auto E-Bit .........................................................................................................................68
11.2.4 G.706 CRC-4 Interworking ............................................................................................68
NFORMATION REGISTERS ............................................................................................ 69
3 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
13. I/O PIN CONFIGURATION OPTIONS ..........................................................................................................78
14. LOOPBACK CONFIGURATIONS ................................................................................................................80
14.1 P
ER-CHANNEL PAYLOAD LOOPBACK .................................................................................. 83
15. ERROR COUNT REGISTERS ......................................................................................................................85
15.1 L
INE CODE VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER (LCVCR)............................................................ 86
15.1.1 T1 Operation....................................................................................................................86
15.1.2 E1 Operation....................................................................................................................86
15.2 P
ATH CODE VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER (PCVCR) .......................................................... 88
15.2.1 T1 Operation....................................................................................................................88
15.2.2 E1 Operation....................................................................................................................88
15.3 F
RAMES OUT OF SYNC COUNT REGISTER (FOSCR) .......................................................... 89
15.3.1 T1 Operation....................................................................................................................89
15.3.2 E1 Operation....................................................................................................................89
15.4 E-B
IT COUNTER REGISTER (EBCR)................................................................................... 90
16. DS0 MONITORING FUNCTION ...................................................................................................................91
16.1 T
16.2 R
RANSMIT DS0 MONITOR REGISTERS ................................................................................ 91
ECEIVE DS0 MONITOR REGISTERS.................................................................................. 92
17. SIGNALING OPERATION ............................................................................................................................93
17.1 R
ECEIVE SIGNALING .......................................................................................................... 93
17.1.1 Processor-Based Receive Signaling............................................................................94
17.1.2 Hardware-Based Receive Signaling ............................................................................94
17.2 T
RANSMIT SIGNALING ...................................................................................................... 100
17.2.1 Processor-Based Transmit Signaling ........................................................................100
17.2.2 Software Signaling Insertion Enable Registers, E1 CAS Mode.............................104
17.2.3 Software Signaling Insertion Enable Registers, T1 Mode ......................................106
18. PER-CHANNEL IDLE CODE GENERATION ............................................................................................108
18.1 I
DLE CODE PROGRAMMING EXAMPLES ............................................................................. 109
19. CHANNEL BLOCKING REGISTERS.........................................................................................................113
20. ELASTIC STORES OPERATION...............................................................................................................116
20.1 R
ECEIVE SIDE ................................................................................................................. 119
20.1.1 T1 Mode .........................................................................................................................119
20.1.2 E1 Mode .........................................................................................................................119
20.2 T
RANSMIT SIDE ............................................................................................................... 120
20.2.1 T1 Mode .........................................................................................................................120
20.2.2 E1 Mode .........................................................................................................................120
20.3 E
20.4 M
LASTIC STORES INITIALIZATION ...................................................................................... 120
INIMUM-DELAY MODE ................................................................................................... 121
21. G.706 INTERMEDIATE CRC-4 UPDATING (E1 MODE ONLY)................................................................122
22. T1 BIT ORIENTED CODE (BOC) CONTROLLER.....................................................................................123
22.1 T
22.2 R
RANSMIT BOC............................................................................................................... 123
ECEIVE BOC................................................................................................................. 123
23. ADDITIONAL (Sa) AND INTERNATIONAL (Si) BIT OPERATION (E1 ONLY) ........................................127
23.1 H
23.2 I
23.3 I
ARDWARE SCHEME (METHOD 1) .................................................................................... 127
NTERNAL REGISTER SCHEME BASED ON DOUBLE-FRAME (METHOD 2)............................. 127
NTERNAL REGISTER SCHEME BASED ON CRC-4 MULTIFRAME (METHOD 3)...................... 130
24. HDLC CONTROLLERS ..............................................................................................................................141
24.1 B
24.2 HDLC C
ASIC OPERATION DETAILS ............................................................................................. 141
ONFIGURATION................................................................................................... 143
24.2.1 FIFO Control ..................................................................................................................145
24.3 HDLC M
APPING.............................................................................................................. 146
24.3.1 Receive...........................................................................................................................146
24.3.2 Transmit .........................................................................................................................148
24.3.3 FIFO Information........................................................................................................... 153
24.3.4 Receive Packet Bytes Available ................................................................................. 153
24.3.5 HDLC FIFOS .................................................................................................................154
24.4 R
24.5 L
ECEIVE HDLC CODE EXAMPLE...................................................................................... 155
EGACY FDL SUPPORT (T1 MODE) ................................................................................. 155
4 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
24.5.1 Receive Section ............................................................................................................155
24.5.2 Transmit Section ...........................................................................................................157
24.6 D4/SLC–96 O
PERATION ................................................................................................. 157
25. LINE INTERFACE UNIT (LIU) ....................................................................................................................158
25.1 LIU O
25.2 LIU R
PERATION .............................................................................................................. 159
ECEIVER ................................................................................................................ 159
25.2.1 Receive Level Indicator................................................................................................160
25.2.2 Receive G.703 Section 10 Synchronization Signal .................................................160
25.2.3 Monitor Mode................................................................................................................. 160
25.3 LIU T
RANSMITTER........................................................................................................... 161
25.3.1 Transmit Short-Circuit Detector/Limiter .....................................................................161
25.3.2 Transmit Open-Circuit Detector ..................................................................................161
25.3.3 Transmit BPV Error Insertion ......................................................................................162
25.3.4 Transmit G.703 Section 10 Synchronization Signal (E1 Mode).............................162
25.4 MCLK P
25.5 J
ITTER ATTENUATOR ....................................................................................................... 162
25.6 CMI (C
25.7 LIU C
25.8 R
25.9 C
ECOMMENDED CIRCUITS................................................................................................ 173
OMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS.......................................................................................... 175
RESCALER ......................................................................................................... 162
ODE MARK INVERSION) OPTION ............................................................................ 163
ONTROL REGISTERS ............................................................................................... 164
26. PROGRAMMABLE IN-BAND LOOP CODE GENERATION AND DETECTION......................................179
27. BERT FUNCTION .......................................................................................................................................186
27.1 BERT R
27.2 BERT R
27.3 BERT B
27.4 BERT E
EGISTER DESCRIPTION ....................................................................................... 187
EPETITIVE PATTERN SET..................................................................................... 192
IT COUNTER ....................................................................................................... 193
RROR COUNTER ................................................................................................. 194
28. PAYLOAD ERROR INSERTION FUNCTION ............................................................................................195
28.1 N
UMBER OF ERROR REGISTERS ...................................................................................... 197
28.1.1 Number Of Errors Left Register ..................................................................................198
29. INTERLEAVED PCM BUS OPERATION ...................................................................................................199
29.1 C
29.2 F
HANNEL INTERLEAVE MODE ........................................................................................... 199
RAME INTERLEAVE MODE ............................................................................................... 199
30. EXTENDED SYSTEM INFORMATION BUS (ESIB) ..................................................................................202
31. PROGRAMMABLE BACKPLANE CLOCK SYNTHESIZER .....................................................................208
32. FRACTIONAL T1/E1 SUPPORT ................................................................................................................209
33. USER-PROGRAMMABLE OUTPUT PINS ................................................................................................210
34. TRANSMIT FLOW DIAGRAMS..................................................................................................................211
35. JTAG-BOUNDARY-SCAN ARCHITECTURE AND TEST-ACCESS PORT .............................................216
35.1 I
35.2 T
35.3 B
35.4 B
35.5 I
NSTRUCTION REGISTER .................................................................................................. 220
EST REGISTERS............................................................................................................. 222
OUNDARY SCAN REGISTER ............................................................................................ 222
YPASS REGISTER .......................................................................................................... 222
DENTIFICATION REGISTER ............................................................................................... 222
36. FUNCTIONAL TIMING DIAGRAMS...........................................................................................................228
36.1 T1 M
36.2 E1 M
ODE ........................................................................................................................ 228
ODE........................................................................................................................ 238
37. OPERATING PARAMETERS .....................................................................................................................251
38. AC TIMING PARAMETERS AND DIAGRAMS..........................................................................................253
38.1 M
38.2 N
38.3 R
38.4 T
ULTIPLEXED BUS AC CHARACTERISTICS........................................................................ 253
ONMULTIPLEXED BUS AC CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................. 256
ECEIVE SIDE AC CHARACTERISTICS .............................................................................. 259
RANSMIT AC CHARACTERISTICS .................................................................................... 265
39. PACKAGE INFORMATION ........................................................................................................................269
5 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 3-1. DS21458 Block Diagram ......................................................................................................................... 15
Figure 3-2. DS21455 Block Diagram ......................................................................................................................... 16
Figure 4-1. DS21455 Framer/LIU Interim Signals ..................................................................................................... 18
Figure 4-2. DS21458 Framer/LIU Interim Signals ..................................................................................................... 19
Figure 5-1. DS21455 Pin Diagram, 27mm BGA ........................................................................................................ 39
Figure 5-2. DS21458 Pin Diagram, 17mm CSBGA ................................................................................................... 40
Figure 8-1. Programming Sequence.......................................................................................................................... 48
Figure 9-1. Clock Map ............................................................................................................................................... 52
Figure 14-1. Normal Signal Flow Diagram ................................................................................................................ 80
Figure 17-1. Simplified Diagram of Receive Signaling Path...................................................................................... 93
Figure 17-2.Simplified Diagram of Transmit Signaling Path.................................................................................... 100
Figure 21-1. CRC-4 Recalculate Method ................................................................................................................ 122
Figure 25-1. Basic Balanced Network Connections ................................................................................................ 158
Figure 25-2. Basic Unbalanced Network Connections ............................................................................................ 159
Figure 25-3. Typical Monitor Application ................................................................................................................. 160
Figure 25-4. CMI Coding ......................................................................................................................................... 163
Figure 25-5. Basic Interface..................................................................................................................................... 173
Figure 25-6. Protected Interface Using Internal Receive Termination .................................................................... 174
Figure 25-7. E1 Transmit Pulse Template ............................................................................................................... 176
Figure 25-8. T1 Transmit Pulse Template ............................................................................................................... 176
Figure 25-9. Jitter Tolerance.................................................................................................................................... 177
Figure 25-10. Jitter Attenuation (T1 Mode).............................................................................................................. 177
Figure 25-11. Jitter Attenuation (E1 Mode) ............................................................................................................. 178
Figure 29-1. IBO Example ....................................................................................................................................... 201
Figure 30-1. DS21455 ESIB Group ......................................................................................................................... 203
Figure 30-2. DS21458 ESIB Group ......................................................................................................................... 204
Figure 34-1. T1 Transmit Data Flow ........................................................................................................................ 211
Figure 34-2. T1 Transmit Data Flow (continued) ..................................................................................................... 212
Figure 34-3. E1 Transmit Data Flow........................................................................................................................ 213
Figure 34-4. E1 Transmit Data Flow (continued)..................................................................................................... 214
Figure 34-5. E1 Transmit Data Flow (continued)..................................................................................................... 215
Figure 35-1. JTAG Functional Block Diagram ......................................................................................................... 216
Figure 35-2. TAP Controller State Diagram............................................................................................................. 219
Figure 36-1. Receive Side D4 Timing...................................................................................................................... 228
Figure 36-2. Receive Side ESF Timing ................................................................................................................... 229
Figure 36-3. Receive Side Boundary Timing (With Elastic Store Disabled)............................................................ 230
Figure 36-4. Receive Side 1.544MHz Boundary Timing (With Elastic Store Enabled) ........................................... 231
Figure 36-5. Receive Side 2.048MHz Boundary Timing (With Elastic Store Enabled) ........................................... 232
Figure 36-6. Transmit Side D4 Timing..................................................................................................................... 233
Figure 36-7. Transmit Side ESF Timing .................................................................................................................. 234
Figure 36-8. Transmit Side Boundary Timing (With Elastic Store Disabled) ........................................................... 235
Figure 36-9. Transmit Side 1.544MHz Boundary Timing (With Elastic Store Enabled) .......................................... 236
6 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Figure 36-10. Transmit Side 2.048MHz Boundary Timing (With Elastic Store Enabled) ........................................ 237
Figure 36-11. Receive Side Timing ......................................................................................................................... 238
Figure 36-12. Receive Side Boundary Timing (With Elastic Store Disabled) .......................................................... 239
Figure 36-13. Receive Side Boundary Timing, RSYSCLK = 1.544MHz (With Elastic Store Enabled) ................... 240
Figure 36-14. Receive Side Boundary Timing, RSYSCLK = 2.048MHz (With Elastic Store Enabled) .................. 241
Figure 36-15. Receive IBO Channel Interleave Mode Timing ................................................................................. 242
Figure 36-16. Receive IBO Frame Interleave Mode Timing.................................................................................... 243
Figure 36-17. G.802 Timing, E1 Mode Only ............................................................................................................ 244
Figure 36-18. Transmit Side Timing ........................................................................................................................ 245
Figure 36-19. Transmit Side Boundary Timing (With Elastic Store Disabled)......................................................... 246
Figure 36-20. Transmit Side Boundary Timing, TSYSCLK = 1.544MHz (With Elastic Store Enabled) ................. 247
Figure 36-21. Transmit Side Boundary Timing, TSYSCLK = 2.048MHz (With Elastic Store Enabled) .................. 248
Figure 36-22. Transmit IBO Channel Interleave Mode Timing ................................................................................ 249
Figure 36-23. Transmit IBO Frame Interleave Mode Timing................................................................................... 250
Figure 38-1. Intel Bus Read Timing (BTS = 0 / MUX = 1) ....................................................................................... 254
Figure 38-2. Intel Bus Write Timing (BTS = 0 / MUX = 1) ....................................................................................... 254
Figure 38-3. Motorola Bus Timing (BTS = 1 / MUX = 1).......................................................................................... 255
Figure 38-4. Intel Bus Read Timing (BTS = 0 / MUX = 0) ....................................................................................... 257
Figure 38-5. Intel Bus Write Timing (BTS = 0 / MUX = 0) ....................................................................................... 257
Figure 38-6. Motorola Bus Read Timing (BTS = 1 / MUX = 0)................................................................................ 258
Figure 38-7. Motorola Bus Write Timing (BTS = 1 / MUX = 0) ................................................................................ 258
Figure 38-8. Receive Side Timing, Elastic Store Disabled (T1 Mode) .................................................................... 260
Figure 38-9. Receive Side Timing, Elastic Store Disabled (E1 Mode) .................................................................... 261
Figure 38-10. Receive Side Timing, Elastic Store Enabled (T1 Mode) ................................................................... 262
Figure 38-11. Receive Side Timing, Elastic Store Enabled (E1 Mode) ................................................................... 263
Figure 38-12. Receive Line Interface Timing........................................................................................................... 264
Figure 38-13. Transmit Side Timing ........................................................................................................................ 266
Figure 38-14. Transmit Side Timing, Elastic Store Enabled.................................................................................... 267
Figure 38-15. Transmit Line Interface Timing.......................................................................................................... 268
Figure 39-1. DS21458 (17mm CSBGA) .................................................................................................................. 269
Figure 39-2. DS21455 (27mm BGA) ....................................................................................................................... 270
7 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
LIST OF TABLES
Table 5-1. DS21455 PIN DESCRIPTION .................................................................................................................. 29
Table 5-2. DS21458 PIN DESCRIPTION .................................................................................................................. 34
Table 6-1. REGISTER MAP SORTED BY ADDRESS .............................................................................................. 41
Table 10-1. T1 ALARM CRITERIA ............................................................................................................................ 63
Table 11-1. E1 SYNC/RESYNC CRITERIA .............................................................................................................. 65
Table 11-2 AUTO E-BIT CONDITIONS..................................................................................................................... 68
Table 11-3. E1 ALARM CRITERIA ............................................................................................................................ 70
Table 14-1. LIUC CONTROL..................................................................................................................................... 82
Table 15-1. T1 LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNTING OPTIONS ............................................................................. 86
Table 15-2. E1 LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNTING OPTIONS............................................................................. 86
Table 15-3. T1 PATH CODE VIOLATION COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS ............................................................. 88
Table 15-4. T1 FRAMES OUT OF SYNC COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS.............................................................. 89
Table 17-1. TIME SLOT NUMBERING SCHEMES................................................................................................. 101
Table 18-1. IDLE CODE ARRAY ADDRESS MAPPING......................................................................................... 108
Table 20-1. ELASTIC STORE DELAY AFTER INITIALIZATION ............................................................................ 120
Table 24-1. HDLC CONTROLLER REGISTERS .................................................................................................... 142
Table 25-1. TPD CONTROL.................................................................................................................................... 164
Table 25-2. E1 MODE WITH AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL MODE ENABLED (TLBC.6 = 0)............................. 165
Table 25-3. E1 MODE WITH AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL MODE DISABLED (TLBC.6 = 1)............................ 165
Table 25-4. T1 MODE WITH AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL MODE ENABLED (TLBC.6 = 0) ............................. 165
Table 25-5. T1 MODE WITH AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL MODE DISABLED (TLBC.6 = 1) ............................ 165
Table 25-6. TRANSFORMER SPECIFICATIONS................................................................................................... 175
Table 28-1. TRANSMIT ERROR INSERTION SETUP SEQUENCE ...................................................................... 195
Table 28-2. ERROR INSERTION EXAMPLES ....................................................................................................... 197
Table 35-1. INSTRUCTION CODES FOR IEEE 1149.1 ARCHITECTURE............................................................ 220
Table 35-2. ID CODE STRUCTURE ....................................................................................................................... 221
Table 35-3. DEVICE ID CODES.............................................................................................................................. 221
Table 35-4. BOUNDARY SCAN CONTROL BITS .................................................................................................. 223
8 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
1. DESCRIPTION
The DS21455 and DS21458 are quad monolithic devices featuring independent transceivers that can be
software configured for T1, E1, or J1 operation. Each is composed of a line interface unit (LIU), framer,
HDLC controllers, and a TDM backplane interface, and is controlled via an 8-bit parallel port configured
for Intel or Motorola bus operations. The DS21455* is a direct replacement for the older DS21Q55 quad
MCM device. The DS21458, which comes in a smaller package (17mm CSBGA) and features an
improved controller interface, is software compatible with the older DS21Q55.
The LIU is composed of a transmit interface, receive interface, and a jitter attenuator. The transmit
interface is responsible for generating the necessary waveshapes for driving the network and providing
the correct source impedance depending on the type of media used. T1 waveform generation includes
DSX-1 line build-outs as well as CSU line build-outs of -7.5dB, -15dB, and -22.5dB. E1 waveform
generation includes G.703 waveshapes for both 75Ω coax and 120Ω twisted cables. The receive interface
provides network termination and recovers clock and data from the network. The receive sensitivity
adjusts automatically to the incoming signal and can be programmed for 0dB to 43dB or 0dB to 12dB for
E1 applications and 0dB to 15dB or 0dB to 36dB for T1 applications. The jitter attenuator removes phase
jitter from the transmitted or received signal. The crystal-less jitter attenuator requires only a 2.048MHz
MCLK for both E1 and T1 applications (with the option of using a 1.544MHz MCLK in T1 applications)
and can be placed in either transmit or receive data paths. An additional feature of the LIU is a CMI
coder/decoder for interfacing to optical networks.
On the transmit side, clock/data, and frame-sync signals are provided to the framer by the backplane
interface section. The framer inserts the appropriate synchronization framing patterns and alarm
information, calculates and inserts the CRC codes, and provides the B8ZS/HDB3 (zero code suppression)
and AMI line coding. The receive-side framer decodes AMI, B8ZS, and HDB3 line coding, synchronizes
to the data stream, reports alarm information, counts framing/coding/CRC errors, and provides clock/data
and frame-sync signals to the backplane interface section.
Both the transmit and receive path have two HDLC controllers. The HDLC controllers transmit and
receive data via the framer block. The HDLC controllers can be assigned to any time slot, group of time
slots, portion of a time slot, or to FDL (T1) or Sa bits (E1). Each controller has 128-bit FIFOs, thus
reducing the amount of processor overhead required to manage the flow of data. In addition, built-in
support for reducing the processor time required handles SS7 applications.
The backplane interface provides a versatile method of sending and receiving data from the host system.
Elastic stores provide a method for interfacing to asynchronous systems, converting from a T1/E1
network to a 2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, or N x 64kHz system backplane. The elastic stores also
manage slip conditions (asynchronous interface). An interleave bus option (IBO) is provided to allow up
to eight transceivers (two DS21455s/DS21458s) to share a high-speed backplane.
9 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
The parallel port provides access for control and configuration of all the DS21455/DS21458’s features.
The Extended System Information Bus (ESIB) function allows up to eight transceivers, two DS21455s or
two DS21458s to be accessed via a single read for interrupt status or other user-selectable alarm status
information. Diagnostic capabilities include loopbacks, PRBS pattern generation/detection, and 16-bit
loop-up and loop-down code generation and detection.
* The JTAG function on the DS21455/DS21458 is a single controller for all four transceivers, unlike
the DS21Q55, which has a JTAG controller-per-transceiver architecture.
1.1 Standards
§ ANSI: T1.403-1995, T1.231-1993, T1.408
§ AT&T: TR54016, TR62411
§ ITU: G.703, G.704, G.706, G.736, G.775, G.823, G.932, I.431, O.151, O.161
§ ETSI: ETS 300 011, ETS 300 166, ETS 300 233, CTR4, CTR12
§ Japanese: JTG.703, JTI.431, JJ-20.11 (CMI coding only)
10 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
2. FEATURE HIGHLIGHTS
2.1 General
§ DS21455: 27mm, 1.27 pitch BGA, compatible replacement for the DS21Q55
§ DS21458: 17mm, 1.00 pitch CSBGA
§ 3.3V supply with 5V tolerant inputs and outputs
§ Evaluation kits
§ IEEE 1149.1 JTAG-boundary scan
§ Driver source code available from the factory
2.2 Line Interface
§ Requires a single master clock (MCLK) for both E1 and T1 operation. Master clock can be
2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, or 16.384MHz. Option to use 1.544MHz, 3.088MHz,
6.276MHz, or 12.552MHz for T1-only operation
§ Fully software configurable
§ Short- and long-haul applications
§ Automatic receive sensitivity adjustments
§ Ranges include 0dB to -43dB or 0dB to -12dB for E1 applications; 0dB to -36dB or 0dB to -15dB
for T1 applications
§ Receive level indication in 2.5dB steps from -42.5dB to -2.5dB
§ Internal receive termination option for 75Ω, 100Ω, and 120Ω lines
§ Monitor application gain settings of 20dB, 26dB, and 32dB
§ G.703 receive-synchronization signal-mode
§ Flexible transmit-waveform generation
§ T1 DSX-1 line build-outs
§ T1 CSU line build-outs of -7.5dB, -15dB, and -22.5dB
§ E1 waveforms include G.703 waveshapes for both 75Ω coax and 120Ω twisted cables
§ AIS generation independent of loopbacks
§ Alternating ones and zeros generation
§ Square-wave output
§ Open-drain output option
§ NRZ format option
§ Transmitter power-down
§ Transmitter 50mA short-circuit limiter with exceeded indication of current limit
§ Transmit open-circuit-detected indication
§ Line interface function can be completely decoupled from the framer/formatter
2.3 Clock Synthesizer
§ Output frequencies include 2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, and 16.384MHz
§ Derived from recovered line clock or master clock
11 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
2.4 Jitter Attenuator
§ 32-bit or 128-bit crystal-less jitter attenuator
§ Requires only a 2.048MHz master clock for both E1 and T1 operation with the option to use
1.544MHz for T1 operation
§ Can be placed in either the receive or transmit path or disabled
§ Limit trip indication
2.5 Framer/Formatter
§ Fully independent transmit and receive functionality
§ Full receive- and transmit-path transparency
§ T1 framing formats include D4, ESF, J1-D4, J1-ESF and SLC-96
§ Japanese J1 support for CRC6 and yellow alarm
§ E1 framing formats include FAS, CAS, and CRC-4
§ Detailed alarm- and status-reporting with optional interrupt support
§ Large path- and line-error counters for:
- T1 – BPV, CV, CRC6, and framing bit errors
- E1 – BPV, CV, CRC-4, E-bit, and frame alignment errors
- Timed or manual update modes
§ User-defined Idle Code Generation on a per-channel basis in both transmit and receive paths
§ Digital milliwatt code generation on the receive path
§ ANSI T1.403-1998 support
§ G.965 V5.2 link detect
§ RAI-CI detection and generation
§ AIS-CI detection and generation
§ Ability to monitor one DS0 channel in both the transmit and receive paths
§ In-band repeating-pattern generators and detectors
- Three independent generators and detectors
- Patterns from 1 bit to 8 bits or 16 bits in length
§ RCL, RLOS, RRA, and RAIS alarms interrupt on change of state
§ Flexible signaling support
- Software- or hardware-based
- Interrupt generated on change of signaling data
- Receive-signaling freeze on loss of sync, carrier loss, or frame slip
§ Hardware pins to indicate carrier loss and signaling freeze
§ Automatic RAI generation to ETS 300 011 specifications
§ Expanded access to Sa and Si bits
§ Option to extend carrier-loss criteria to a 1ms period as per ETS 300 233
12 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
2.6 System Interface
§ Dual two-frame, independent receive and transmit elastic stores
- Independent control and clocking
- Controlled-slip capability with status
- Minimum-delay mode supported
§ Supports T1 to E1 conversion
§ Ability to pass the T1 F-bit position through the elastic stores in the 2.048MHz backplane mode
§ Programmable output clocks for fractional T1, E1, H0, and H12 applications
§ Interleaving PCM bus operation with rates of 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, and 16.384MHz
§ Hardware-signaling capability
- Receive-signaling reinsertion to a backplane, multiframe sync
- Availability of signaling in a separate PCM data stream
- Signaling freezing
§ Access to the data streams in between the framer/formatter and the elastic stores (DS21455)
§ User-selectable synthesized clock output
2.7 HDLC Controllers
§ Two independent HDLC controllers
§ Fast load and unload features for FIFOs
§ SS7 support for FISU transmit and receive
§ Independent 128-byte Rx and Tx buffers with interrupt support
§ Access FDL, Sa, or single/multiple DS0 channels
§ DS0 access includes Nx64 or Nx56
§ Compatible with polled or interrupt-driven environments
§ Bit Oriented Code (BOC) support
2.8 Test and Diagnostics
§ Programmable Bit Error Rate Testing (BERT)
§ Pseudorandom patterns including QRSS
§ User-defined repetitive patterns
§ Daly pattern
§ Error insertion for single bit or continuous
§ Insertion options include continuous and absolute number with selectable insertion rates
§ Total-bit and errored-bit counters
§ Payload Error Insertion
§ Errors can be inserted over the entire frame or selected channels
§ F-bit corruption for line testing
§ Loopbacks (remote, local, analog, and per-channel payload loopback)
13 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
2.9 Extended System Information Bus
§ Host can read interrupt and alarm status on up to eight ports (two devices) with a single-bus read
2.10 Control Port
§ 8-bit parallel control port
§ Multiplexed or nonmultiplexed buses
§ Intel or Motorola formats
§ Supports polled or interrupt-driven environments
§ Software access to device ID and silicon revision
§ Software-reset supported with automatic clear on power-up
§ Hardware reset pin
Note: This data sheet assumes a particular nomenclature of the T1 and E1 operating environment. In
each 125ms T1 frame, there are 24 8-bit channels plus a framing bit. It is assumed that the framing bit is
sent first followed by channel 1. For T1 and E1 each channel is made up of 8 bits, which are numbered 1
to 8. Bit 1, the MSB, is transmitted first. Bit 8, the LSB, is transmitted last. The term “locked” is used to
refer to two clock signals that are phase- or frequency-locked or derived from a common clock (i.e., a
1.544MHz clock can be locked to a 2.048MHz clock if they share the same 8kHz component).
14 of 270
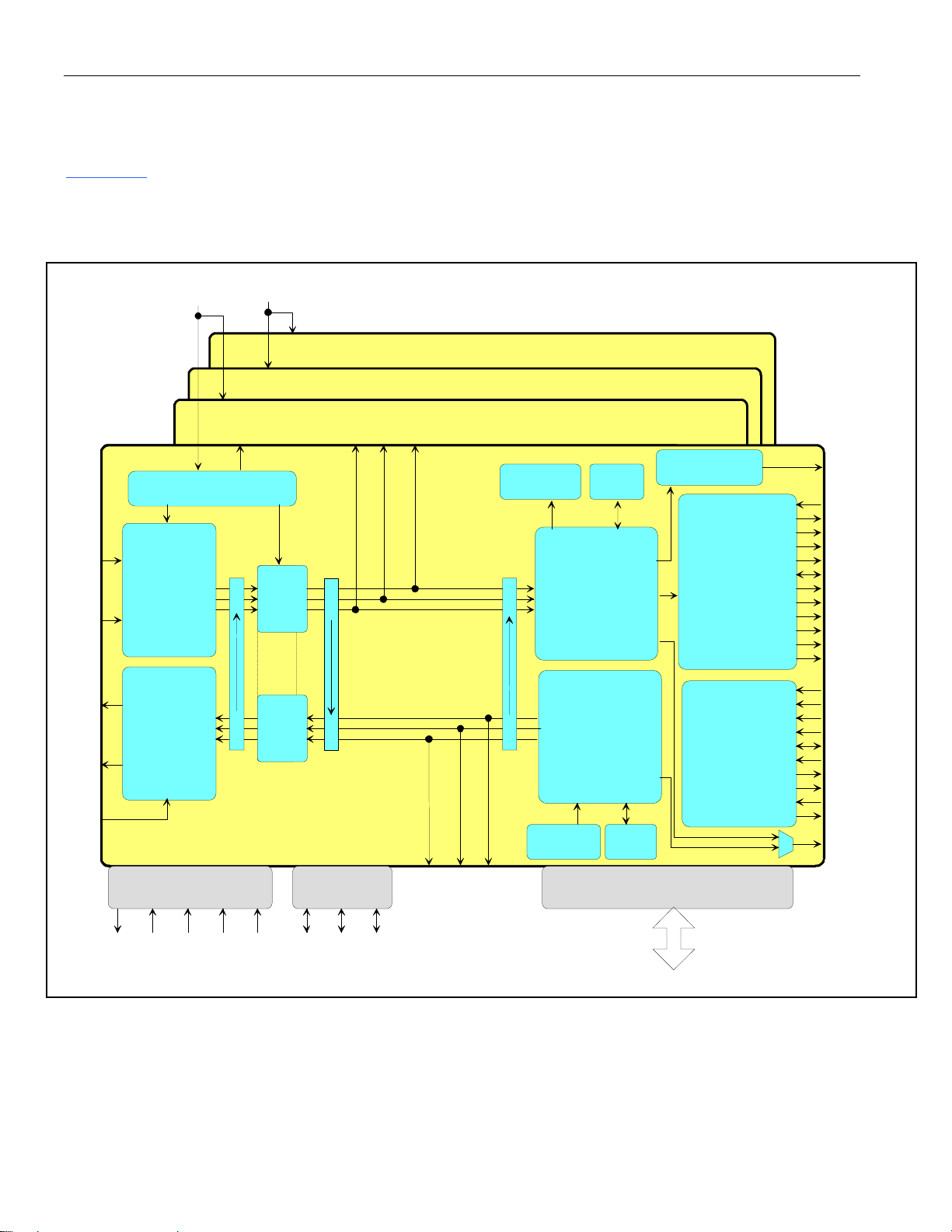
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
3. BLOCK DIAGRAM
Figure 3-1 shows a simplified block diagram highlighting the major components of the DS21458 and
DS21455.
Figure 3-1. DS21458 Block Diagram
MCLK1
MCLK2
TRANSCEIVER #4
TRANSCEIVER #3
RTIP
RRING
TTIP
TRING
TPD
8XCLK
MASTER
CLOCK
RECEIVE
LIU
CLOCK & DATA
RECOVERY
TRANSMIT
LIU
WAVESHAPE
GENERATION
DS21458
(1 OF 4 TRANSCEIVERS)
LOCAL
LOOP
BACK
JITTER
ATTEN.
TX
OR RX
PATH
JITTER
ATTEN.
REMOTE
LOOP
BACK
RNEGO
TRANSCEIVER #2
RCLKORPOSO
2 HDLCs
FRAMER
LOOP
BACK
ALARM MONITORING
SIGNALING EXTRACTION
HDB3/B8ZS DECODER
CRC RECALCULATE(E1)
SIGNALING INSERTION
2 HDLCs
BERT
RECEIVE
FRAMER
SYNCHRONIZATION
HDLC EXTRACTION
DS0 CONDITIONING
TRANSMIT
FRAMER
FRAMING
ALARM INSERTION
HDLC INSERTION
DS0 CONDITIONING
HDB3/B8ZS CODER
BERT
BACKPLANE
CLOCK
RECEIVE
BACKPLANE
INTERFACE
ELASTIC STORES
SIGNALING BUFFERS
INTERLEAVE BUS
RATE CONVERSION
PAYLOAD LOOPBACK
TRANSMIT
TRANSMIT
BACKPLANE
BACKPLANE
INTERFACE
INTERFACE
ELASTIC STORES
SIGNALING BUFFERS
INTERLEAVE BUS
RATE CONVERSION
PAYLOAD LOOPBACK
BPCLK
RSYSCLK
RCLK
RSER
RSIG
RSIGF
RSYNC
RFSYNC
RMSYNC
RCHCLK
RCHBLK
RLCLK
RLINK
TSYSCLK
TCLK
TSER
TSIG
TSYNC
TSSYNC
TCHCLK
TCHBLK
TLCLK
TLINK
RLOS/LOTC
JTDI
JTAG
JTCLK
JTRST
JTMS
ESIBS0
ESIB
ESIBRDJTDO
ESIBS1
TPOSI
TCLKO
TNEGO
CPU INTERFACE
MUX/NON-MUX, INTEL/MOTOROLA
15 of 270
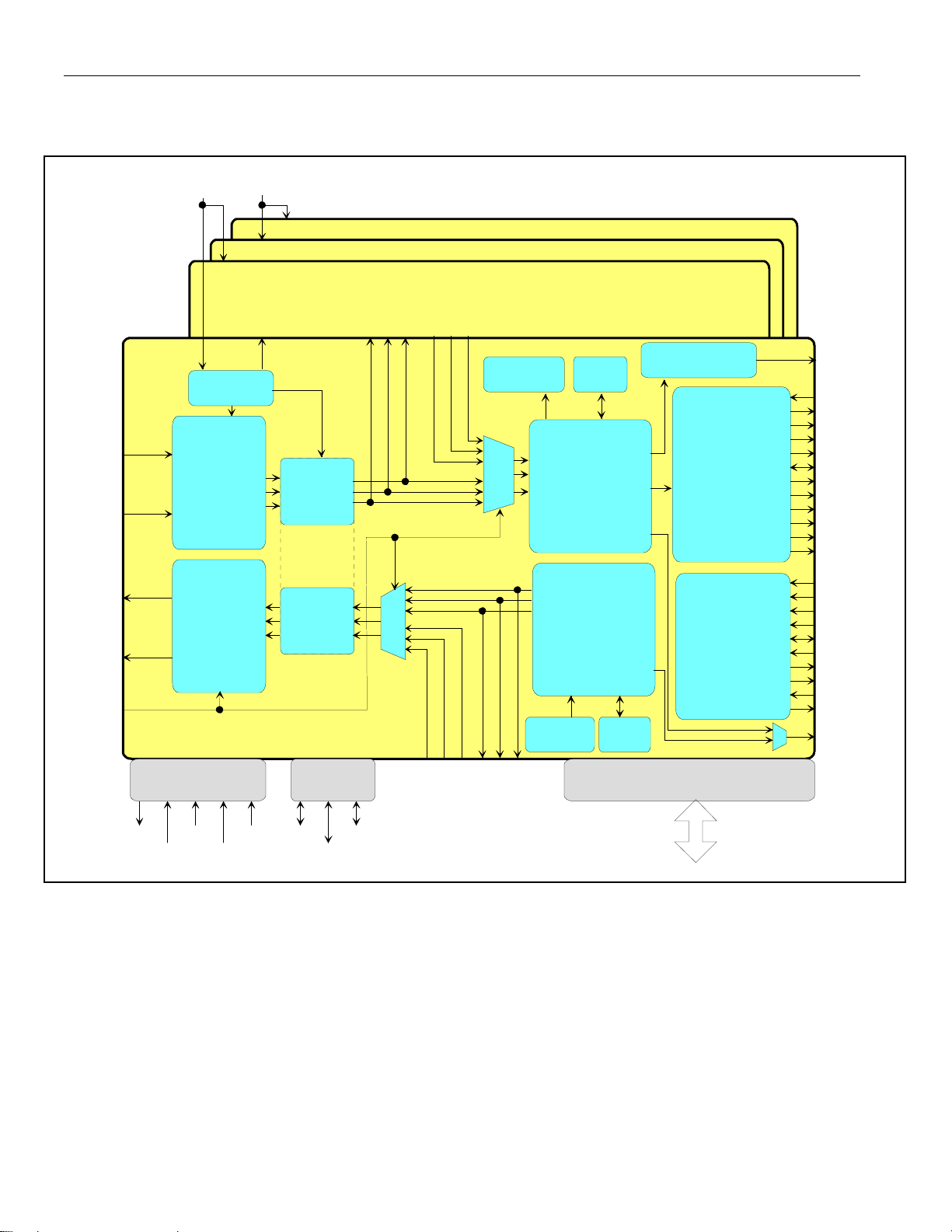
Figure 3-2. DS21455 Block Diagram
MCLK1 MCLK2
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
TRANSCEIVER #4
TRANSCEIVER #3
TRANSCEIVER #2
RTIP
RRING
TTIP
TRING
LIUC/TPD
8XCLK
MASTER
CLOCK
RECEIVE
LIU
CLOCK & DATA
RECOVERY
TRANSMIT
LIU
WAVESHAPE
GENERATION
JITTER
ATTEN.
TRANSMIT
OR RECEIVE
PATH
JITTER
ATTEN.
RPOSO
RNEGO
RCLKO
MUX
RPOSI
RNEGI
RCLKI
DS21455
2 HDLCs
MUX
ALARM MONITORING
SIGNALING EXTRACTION
HDB3/B8ZS DECODER
CRC RECALCULAION(E1)
SIGNALING INSERTION
2 HDLCs
BERT
RECEIVE
FRAMER
SYNCHRONIZATION
HDLC EXTRACTION
DS0 CONDITIONING
TRANSMIT
FRAMER
FRAMING
ALARM INSERTION
HDLC INSERTION
DS0 CONDITIONING
HDB3/B8ZS CODER
BERT
BACKPLANE
CLOCK
RECEIVE
BACKPLANE
INTERFACE
ELASTIC STORES
SIGNALING BUFFERS
INTER LEAVE BUS
RATE CONVERSION
TRANSMIT
TRANSMIT
BACKPLANE
BACKPLANE
INTERFACE
INTERFACE
ELASTIC STORES
SIGNALING BUFFERS
INTER LEAVE BUS
RATE CONVERSION
BPCLK
RSYSCLK
RCLK
RSER
RSIG
RSIGF
RSYNC
RFSYNC
RMSYNC
RCHCLK
RCHBLK
RLCLK
RLINK
TSYSCLK
TCLK
TSER
TSIG
TSYNC
TSSYNC
TCHCLK
TCHBLK
TLCLK
TLINK
RLOS/LOTC
JTAG
JTCLK
JTDI
JTRST
JTMS
ESIBS0
ESIBS1
ESIB
ESIBRDJTDO
TPOSI
TPOSI TPOSI
TNEGI
TPOSO
TCLKI
TNEGO
TCLKO
CPU INTERFACE
MUX/NON-MUX, INTEL/MOTOROLA
16 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
4. DS21455/DS21458 DELTA
This section describes the differences between the DS21455 and DS21458.
4.1 Package
DS21455: 27mm, 256-pin, 1.27 ball pitch, BGA (This package has the same footprint and pinout as the
DS21Q55.)
DS21458: 17mm, 256-pin, 1.00 ball pitch, CSBGA
4.2 Controller Interface
DS21455: The CPU interface has 8 address lines with independent chip selects (4) per transceiver.
DS21458: The CPU interface has 10 address lines with a single chip select. The upper address lines, A8
and A9, act as coded transceiver selects.
4.3 ESIB Function
The ESIB function provides a fast method of determining interrupt and alarm status when multiple ports
(up to 8) are being controlled by a single processor.
DS21455: The three ESIB signals are brought out for each transceiver. The user must externally
configure the ESIB group.
DS21458: The ESIB signals are internally bused and only a single set of signals are brought out to enable
the connection of another DS21458 into an 8-port ESIB.
4.4 Framer/LIU Interim Signals
Access to the clock and bipolar data signals between the framer and LIU function may be used for
specialized applications. An internal MUX connects the framer and LIU if these signals are unused. The
MUX is controlled via the LIUC/TPD pin and LIUC bit in the LBCR register. The unused inputs must be
connected to ground.
DS21455: The user has access to all clock and data signals between the framer and LIU on all
transceivers as shown in Figure 4-1
DS21458: The user has limited access to clock and data signals between the framer and LIU on all
transceivers as shown in Figure 4-2
.
.
17 of 270
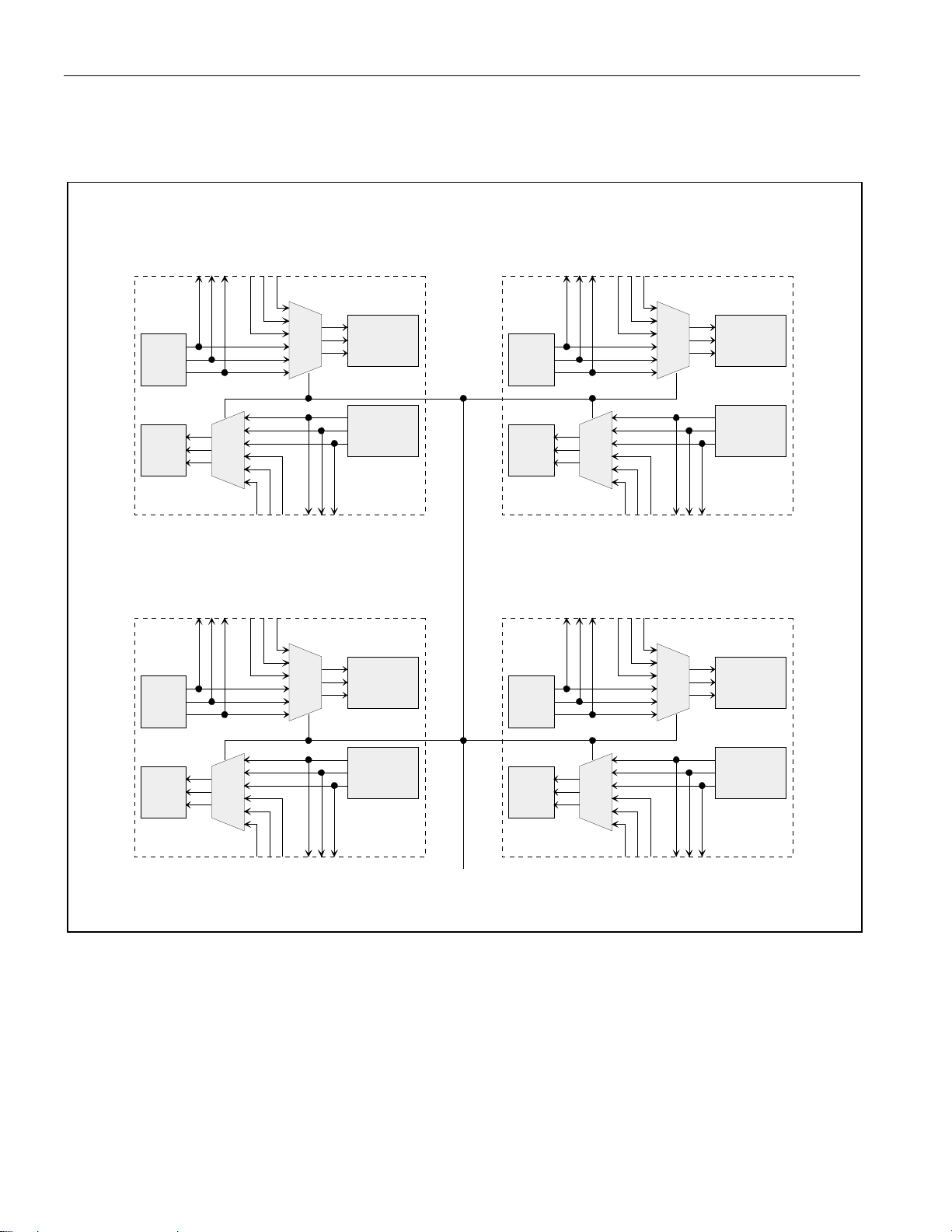
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Figure 4-1. DS21455 Framer/LIU Interim Signals
Rx
LIU
Tx
LIU
Rx
LIU
RPOSO
RNEGO
RCLKO
MUX
RPOSO
RNEGO
RCLKO
RPOSI
RNEGI
RCLKI
TPOSI
TNEGI
TCLKI
RPOSI
RNEGI
RCLKI
MUX
TPOSO
TNEGO
TCLKO
MUX
Rx
FRAMER
Tx
FRAMER
Rx
FRAMER
RPOSO
RNEGO
RCLKO
RPOSI
RNEGI
RCLKI
#1 #2
Rx
FRAMER
Rx
MUX
LIU
Tx
Tx
LIU
MUX
RPOSO
RNEGO
RCLKO
TPOSI
TNEGI
TCLKI
RPOSI
RNEGI
RCLKI
TPOSO
TNEGO
TCLKO
FRAMER
#4#3
Rx
FRAMER
Rx
MUX
LIU
Tx
LIU
MUX
TPOSI
TNEGI
TCLKI
TPOSO
TNEGO
TCLKO
Tx
FRAMER
Tx
FRAMER
LIUC
Tx
LIU
MUX
TPOSI
TNEGI
TCLKI
TPOSO
TNEGO
TCLKO
18 of 270
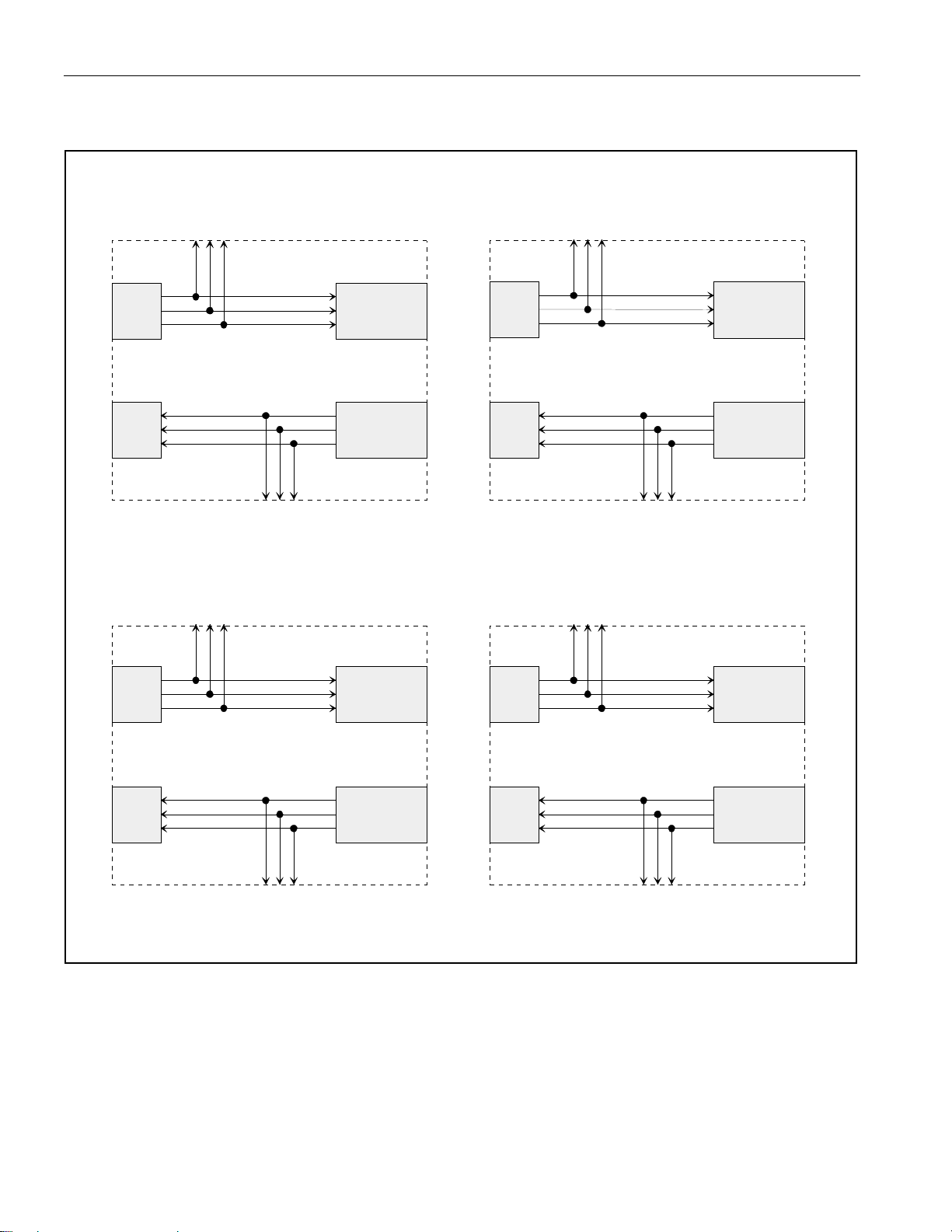
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Figure 4-2. DS21458 Framer/LIU Interim Signals
Rx
LIU
RPOSO1
RNEGO1
RCLKO1
Rx
FRAMER
#1
Rx
LIU
RPOSO2
RNEGO2
RCLKO2
#2
Rx
FRAMER
Tx
LIU
Rx
LIU
Tx
LIU
RPOSO3
RNEGO3
RCLKO3
TPOSO1
TNEGO1
TCLKO1
Tx
FRAMER
Rx
FRAMER
Tx
FRAMER
#3
Tx
LIU
Rx
LIU
Tx
LIU
Tx
FRAMER
TPOSO2
TNEGO2
TCLKO2
RPOSO4
RNEGO4
RCLKO4
#4
Rx
FRAMER
Tx
FRAMER
TPOSO3
TNEGO3
TCLKO3
TPOSO4
TNEGO4
TCLKO4
19 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
5. PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
5.1 Transmit Side Pins
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A 1.544 MHz or a 2.048MHz primary clock. Used to clock data through the transmit-side formatter.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Transmit NRZ serial data. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK when the transmit-side elastic store is disabled. Sampled on
the falling edge of TSYSCLK when the transmit-side elastic store is enabled.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A 192kHz (T1) or 256kHz (E1) clock that pulses high during the LSB of each channel. Can also be programmed to output a
gated transmit-bit clock for fractional T1/E1 applications. Synchronous with TCLK when the transmit-side elastic store is
disabled. Synchronous with TSYSCLK when the transmit-side elastic store is enabled. Useful for parallel-to-serial conversion
of channel data.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A user-programmable output that can be forced high or low during any of the channels. Synchronous with TCLK when the
transmit-side elastic store is disabled. Synchronous with TSYSCLK when the transmit-side elastic store is enabled. Useful for
locating individual channels in drop-and-insert applications, for external per-channel loopback, and for per-channel
conditioning.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
1.544MHz, 2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, or 16.384MHz clock. Only used when the transmit-side elastic-store function
is enabled. Should be tied low in applications that do not use the transmit-side elastic store. See the Interleaved PCM Bus
Operation section for details on 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, and 16.384MHz operation using the IBO.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Demand clock for the transmit link data [TLINK] input.
T1 Mode: A 4kHz or 2kHz (ZBTSI) clock.
E1 Mode: A 4kHz to 20kHz clock.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
If enabled, this pin will be sampled on the falling edge of TCLK for data insertion into either the FDL stream (ESF) or the Fsbit position (D4) or the Z-bit position (ZBTSI) or any combination of the Sa bit positions (E1).
TCLK
Transmit Clock
Input
TSER
Transmit Serial Data
Input
TCHCLK
Transmit Channel Clock
Output
TCHBLK
Transmit Channel Block
Output
TSYSCLK
Transmit System Clock
Input
TLCLK
Transmit Link Clock
Output
TLINK
Transmit Link Data
Input
20 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A pulse at this pin will establish either frame or multiframe boundaries for the transmit side. Can be programmed to output
either a frame or multiframe pulse. If this pin is set to output pulses at frame boundaries, it can also be set via IOCR1.3 to
output double-wide pulses at signaling frames in T1 mode.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Only used when the transmit-side elastic store is enabled. A pulse at this pin will establish either frame or multiframe
boundaries for the transmit side. Should be tied low in applications that do not use the transmit-side elastic store.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
When enabled, this input will sample signaling bits for insertion into outgoing PCM data stream. Sampled on the falling edge
of TCLK when the transmit-side elastic store is disabled. Sampled on the falling edge of TSYSCLK when the transmit-side
elastic store is enabled.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of TCLK with data out of the transmit-side elastic store whether the elastic store is enabled or not.
This pin is normally tied to TDATA.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK with data to be clocked through the transmit-side formatter. This pin is normally tied to
TESO.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of TCLKO with the bipolar data out of the transmit-side formatter. Can be programmed to source
NRZ data via the output-data format (IOCR1.0)-control bit. This pin is normally tied to TPOSI.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of TCLKO with the bipolar data out of the transmit-side formatter. This pin is normally tied to
TNEGI.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Buffered clock that is used to clock data through the transmit-side formatter (either TCLK or RCLKI). This pin is normally
tied to TCLKI.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Sampled on the falling edge of TCLKI for data to be transmitted out onto the T1 line. Can be internally connected to TPOSO
by tying the LIUC/TPD pin high. See the LIUC/TPD pin description for a full explanation of this function
TNEGI can be tied together in NRZ applications.
TSYNC
Transmit Sync
Input/Output
TSSYNC
Transmit System Sync
Input
TSIG
Transmit Signaling Input
Input
TESO
Transmit Elastic Store-Data Output
Output
TDATA
Transmit Data
Input
TPOSO
Transmit Positive-Data Output
Output
TNEGO
Transmit Negative-Data Output
Output
TCLKO
Transmit Clock Output
Output
TPOSI (DS21455 Only)
Transmit Positive-Data Input
Input
. TPOSI and
21 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Sampled on the falling edge of TCLKI for data to be transmitted out onto the T1 line. Can be internally connected to TNEGO
by tying the LIUC/TPD pin high. See the LIUC/TPD pin description for a full explanation of the LIUC/TPD function
and TNEGI can be tied together in NRZ applications.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Line interface transmit clock. Can be internally connected to TCLKO by tying the LIUC/TPD pin high. See the LIUC/TPD pin
description for a full explanation of the LIUC/TPD function.
TNEGI (DS21455 Only)
Transmit Negative-Data Input
Input
. TPOSI
TCLKI (DS21455 Only)
Transmit Clock Input
Input
5.2 Receive Side Pins
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
T1 Mode: Updated with either FDL data (ESF) or Fs bits (D4) or Z bits (ZBTSI) one RCLK before the start of a frame.
E1 Mode: Updated with the full E1 data stream on the rising edge of RCLK.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
T1 Mode: A 4kHz or 2kHz (ZBTSI) clock for the RLINK output.
E1 Mode: A 4kHz to 20kHz clock.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
1.544MHz (T1) or 2.048MHz (E1) clock that is used to clock data through the receive-side framer.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A 192kHz (T1) or 256kHz (E1) clock that pulses high during the LSB of each channel can also be programmed to output a
gated receive-bit clock for fractional T1/E1 applications. Synchronous with RCLK when the receive-side elastic store is
disabled. Synchronous with RSYSCLK when the receive-side elastic store is enabled. Useful for parallel-to-serial conversion
of channel data.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A user-programmable output that can be forced high or low during any of the 24 T1 or 32 E1 channels. Synchronous with
RCLK when the receive-side elastic store is disabled. Synchronous with RSYSCLK when the receive-side elastic store is
enabled. Also useful for locating individual channels in drop-and-insert applications, for external per-channel loopback, and
for per-channel conditioning. See the Channel Blocking Registers section.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Received NRZ serial data. Updated on rising edges of RCLK when the receive-side elastic store is disabled. Updated on the
rising edges of RSYSCLK when the receive-side elastic store is enabled.
RLINK
Receive Link Data
Output
RLCLK
Receive Link Clock
Output
RCLK
Receive Clock
Output
RCHCLK
Receive Channel Clock
Output
RCHBLK
Receive Channel Block
Output
RSER
Receive Serial Data
Output
22 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
An extracted pulse, one RCLK wide, is output at this pin which identifies either frame (IOCR1.5 = 0) or multiframe
(IOCR1.5 = 1) boundaries. If set to output-frame boundaries then via IOCR1.6, RSYNC can also be set to output double-wide
pulses on signaling frames in T1 mode. If the receive-side elastic store is enabled, then this pin can be enabled to be an input
via IOCR1.4 at which a frame or multiframe boundary pulse is applied.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
An extracted 8kHz pulse, one RCLK wide, is output at this pin, which identifies frame boundaries.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
An extracted pulse, one RCLK wide (elastic store disabled) or one RSYSCLK wide (elastic store enabled), is output at this pin,
which identifies multiframe boundaries.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of RCLK with the data out of the receive-side framer.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
1.544MHz, 2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, or 8.192MHz clock. Only used when the receive-side elastic-store function is enabled.
Should be tied low in applications that do not use the receive-side elastic store. See the Interleaved PCM Bus Operation
section for details on 4.096MHz and 8.192MHz operation using the IBO.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Outputs signaling bits in a PCM format. Updated on rising edges of RCLK when the receive-side elastic store is disabled.
Updated on the rising edges of RSYSCLK when the receive-side elastic store is enabled.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A dual-function output that is controlled by the CCR1.0 control bit. This pin can be programmed to either toggle high when the
synchronizer is searching for the frame and multiframe or to toggle high if the TCLK pin has not been toggled for 5ms.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Set high when the line interface detects a carrier loss.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Set high when the signaling data is frozen via either automatic or manual intervention. Used to alert downstream equipment of
the condition.
RSYNC
Receive Sync
Input/Output
RFSYNC
Receive Frame Sync
Output
RMSYNC
Receive Multiframe Sync
Output
RDATA
Receive Data
Output
RSYSCLK
Receive System Clock
Input
RSIG
Receive Signaling Output
Output
RLOS/LOTC
Receive Loss of Sync/Loss of Transmit Clock
Output
RCL
Receive Carrier Loss
Output
RSIGF
Receive Signaling Freeze
Output
23 of 270
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A user-selectable synthesized clock output that is referenced to the clock that is output at the RCLK pin.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of RCLKO with bipolar data out of the line interface. This pin is normally tied to RPOSI.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Updated on the rising edge of RCLKO with the bipolar data out of the line interface. This pin is normally tied to RNEGI.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Buffered recovered clock from the network. This pin is normally tied to RCLKI.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Sampled on the falling edge of RCLKI for data to be clocked through the receive-side framer. RPOSI and RNEGI can be tied
together for a NRZ interface. Can be internally connected to RPOSO by tying the LIUC/TPD pin high. See the LIUC/TPD pin
description for a full explanation of the LIUC/TPD function.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Sampled on the falling edge of RCLKI for data to be clocked through the receive-side framer. RPOSI and RNEGI can be tied
together for a NRZ interface. Can be internally connected to RNEGO by tying the LIUC/TPD pin high. See the LIUC/TPD pin
description for a full explanation of the LIUC/TPD function.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Clock used to clock data through the receive-side framer. This pin is normally tied to RCLKO. Can be internally connected to
RCLKO by tying the LIUC/TPD pin high. See the LIUC/TPD pin description for a full explanation of the LIUC/TPD function
BPCLK
Backplane Clock
Output
RPOSO
Receive Positive-Data Output
Output
RNEGO
Receive Negative-Data Output
Output
RCLKO
Receive Clock Output
Output
RPOSI (DS21455 Only)
Receive Positive Data Input
Input
RNEGI (DS21455 Only)
Receive Negative Data Input
Input
RCLKI (DS21455 Only)
Receive Clock Input
Input
.
5.3 Parallel Control Port Pins
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Flags host controller during events, alarms, and conditions defined in the status registers. Active-low open-drain output.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A dual-function pin. A zero-to-one transition issues a hardware reset to the DS21455/DS21458 register set. A reset clears all
configuration registers. Configuration register contents are set to zero. Leaving TSTRST high will tri-state all output and I/O
pins (including the parallel control port). Set low for normal operation. Useful in board-level testing.
INT
Interrupt
Output
TSTRST
Tri-State Control and Device Reset
Input
24 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
MUX
Bus Operation
Input
Set low to select nonmultiplexed bus operation. Set high to select multiplexed bus operation.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
AD0 to AD7
Data Bus [D0 to D7] or Address/Data Bus
Input/Output
In nonmultiplexed bus operation (MUX = 0), it serves as the data bus. In multiplexed bus operation (MUX = 1), it serves as an
8-bit, multiplexed address/data bus.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A0 to A6
Address Bus
Input
In nonmultiplexed bus operation (MUX = 0), it serves as the address bus. In multiplexed bus operation (MUX = 1), these pins
are not used and should be tied low.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A8 and A9 (DS21458 Only)
Address Bus
Input
Upper address pins for nonmultiplexed (MUX = 0), and multiplexed (MUX = 1) bus operation,.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Strap high to select Motorola bus timing; strap low to select Intel bus timing. This pin controls the function of the
ALE (AS), and
WR (R/W) pins. If BTS = 1, then these pins assume the function listed in parentheses ().
BTS
Bus Type Select
Input
RD (DS),
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
RD and DS are active-low signals. DS active HIGH when MUX = 0. See the bus timing diagrams.
RD (DS)
Read Input-Data Strobe
Input
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Must be low to read or write to Transceiver 1 of the device.
CS1 (DS21455 Only)
Chip Select for Transceiver 1
Input
CS1 is an active-low signal.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Must be low to read or write to Transceiver 2 of the device.
CS2 (DS21455 Only)
Chip Select for Transceiver 2
Input
CS2 is an active-low signal.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Must be low to read or write to Transceiver 3 of the device.
CS3 (DS21455 Only)
Chip Select for Transceiver 3
Input
CS3 is an active-low signal.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Must be low to read or write to Transceiver 4 of the device.
CS4 (DS21455 Only)
Chip Select for Transceiver 4
Input
CS4 is an active-low signal.
25 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Must be low to read or write to the device.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
In nonmultiplexed bus operation (MUX = 0), it serves as the upper address bit. In multiplexed bus operation (MUX = 1), it
serves to demultiplex the bus on a positive-going edge.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
WR is an active-low signal.
CS (DS21458 Only)
Chip Select
Input
CS is an active-low signal.
ALE (AS)/A7
Address Latch Enable (Address Strobe) or A7
Input
WR (R/W)
Write Input (Read/Write)
Input
5.4 Extended System Information Bus
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Used to group two DS21455/DS21458s into a bus-sharing mode for alarm and status reporting. See the Extended System
Information Bus (ESIB) section for more details.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Used to group two DS21455/DS21458s into a bus-sharing mode for alarm and status reporting. See the Extended System
Information Bus (ESIB) section for more details.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Used to group two DS21455/DS21458s into a bus-sharing mode for alarm and status reporting. See the Extended System
Information Bus (ESIB) section for more details.
ESIBS0
Extended System Information Bus Select 0
Input/Output
ESIBS1
Extended System Information Bus Select 1
Input/Output
ESIBRD
Extended System Information Bus Read
Input/Output
5.5 JTAG Test Access Port Pins
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
JTRST is used to asynchronously reset the test access port controller. After power-up, JTRST must be toggled from low to
high. This action will set the device into the JTAG DEVICE ID mode. Normal device operation is restored by pulling JTRST
low. JTRST is pulled HIGH internally via a 10kW resistor operation.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
This pin is sampled on the rising edge of JTCLK and is used to place the test-access port into the various defined IEEE 1149.1
states. This pin has a 10kW pullup resistor.
JTRST
IEEE 1149.1 Test Reset
Input
JTMS
IEEE 1149.1 Test Mode Select
Input
26 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
This signal is used to shift data into JTDI on the rising edge and out of JTDO on the falling edge.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Test instructions and data are clocked into this pin on the rising edge of JTCLK. This pin has a 10kW pullup resistor.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Test instructions and data are clocked out of this pin on the falling edge of JTCLK. If not used, this pin should be left
unconnected.
JTCLK
IEEE 1149.1 Test Clock Signal
Input
JTDI
IEEE 1149.1 Test Data Input
Input
JTDO
IEEE 1149.1 Test Data Output
Output
5.6 Line Interface Pins
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A (50ppm) clock source. This clock is used internally for both clock/data recovery and for the jitter attenuator for both T1 and
E1 modes. The clock rate can be 16.384MHz, 8.192MHz, 4.096MHz, or 2.048MHz. When using the DS21455/DS21458 in
T1-only operation a 1.544MHz (50ppm) clock source can be used. MCLK1 and MCLK2 can be driven from a common clock.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
A (50ppm) clock source. This clock is used internally for both clock/data recovery and for the jitter attenuator for both T1 and
E1 modes. The clock rate can be 16.384MHz, 8.192MHz, 4.096MHz, or 2.048MHz. When using the DS21455/DS21458 in
T1-only operation a 1.544MHz (50ppm) clock source can be used. MCLK1 and MCLK2 can be driven from a common clock.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
This is a dual function pin depending on the state of the LTS bit in the LBCR register (LBCR.7).
MCLK1
Master Clock Input for Transceivers 1 and 2
Input
MCLK2
Master Clock Input for Transceivers 3 and 4
Input
LIUC/TPD (DS21455), TPD (DS21458)
Line Interface Unit Connect/Transmit Power-Down
Input
LTS = 0: In this mode the LIUC/TPD pin, along with the LIUC bit of the LBCR register controls the connection between the
framer and the LIU. This function is only available on the DS21455
Table 14-1
LTS = 1: In this mode the LIUC/TPD pin along with the TPD bit in the LIC1 register (LIC1.0) controls the state of the
Transmit Power-Down function. See the TPD bit description in Section 25
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Analog inputs for clock recovery circuitry. These pins connect via a 1:1 transformer to the network. See Section 25
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
Analog line-driver outputs. These pins connect via a 1:2 step-up transformer to the network. See Section 25
.
RTIP and RRING
Receive Tip and Ring
Input
TTIP and TRING
Transmit Tip and Ring
Output
27 of 270
. See the LIUC bit description in Section 14 and
and Table 25-1.
for details.
for details.

5.7 Supply Pins
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
3.3V ±5%. Should be tied to the RVDD and TVDD pins.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
3.3V ±5%. Should be tied to the DVDD and TVDD pins.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
3.3V ±5% Should be tied to the RVDD and DVDD pins.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type: Supply
Should be tied to the RVSS and TVSS pins.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
0.0V. Should be tied to DVSS and TVSS.
Signal Name:
Signal Description:
Signal Type:
0.0V. Should be tied to DVSS and RVSS.
DVDD
Digital Positive Supply
Supply
RVDD
Receive Analog Positive Supply
Supply
TVDD
Transmit Analog Positive Supply
Supply
DVSS
Digital Signal Ground
RVSS
Receive Analog Signal Ground
Supply
TVSS
Transmit Analog Signal Ground
Supply
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
28 of 270
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
5.8 Pin Descriptions
Table 5-1. DS21455 PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NAME TYPE FUNCTION
U3 A0 I Address Bus Bit 0 (Lsb)
L17 A1 I Address Bus Bit 1
V2 A2 I Address Bus Bit 2
T4 A3 I Address Bus Bit 3
V8 A4 I Address Bus Bit 4
H4 A5 I Address Bus Bit 5
U8 A6 I Address Bus Bit 6
P4 A7/ALE (AS) I Address Bus Bit 7 (Msb)/Address Latch Enable
M1 BPCLK1 O Backplane Clock, Transceiver 1
H17 BPCLK2 O Backplane Clock, Transceiver 2
F4 BPCLK3 O Backplane Clock, Transceiver 3
V13 BPCLK4 O Backplane Clock, Transceiver 4
P2 BTS I Bus Type Select (0 = Intel/1 = Motorola)
P3
A14
B5
K17
U11 D0/AD0 I/O Data Bus Bit 0/Address/Data Bus Bit 0 (Lsb)
J19 D1/AD1 I/O Data Bus Bit 1/Address/Data Bus Bit 1
W15 D2/AD2 I/O Data Bus Bit 2/Address/Data Bus Bit 2
U7 D3/AD3 I/O Data Bus Bit 3/Address/Data Bus Bit 3
U9 D4/AD4 I/O Data Bus Bit 4/Address/Data Bus Bit 4
U5 D5/AD5 I/O Data Bus Bit 5/Address/Data Bus Bit 5
V4 D6/AD6 I/O Data Bus Bit 6/Address/Data Bus Bit 6
U4 D7/AD7 I/O Data Bus Bit 7/Address/Data Bus Bit 7 (Msb)
J3 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
N4 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
U2 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
V5 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
B12 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
C12 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
C16 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
D18 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
A9 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
B3 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
B6 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
C4 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
G20 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
M17 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
M20 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
P18 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
H3 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
U6 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
W8 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
A17 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
A20 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
B11 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
A5 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
CS1
CS2
CS3
CS4
I Chip Select for Transceiver 1
I Chip Select for Transceiver 2
I Chip Select for Transceiver 3
I Chip Select for Transceiver 4
29 of 270
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
PIN NAME TYPE FUNCTION
B7 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
B9 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
H20 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
L20 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
N17 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
J4 ESIBRD1 I/O Extended System Information Bus Read for Transceiver 1
C13 ESIBRD2 I/O Extended System Information Bus Read for Transceiver 2
C3 ESIBRD3 I/O Extended System Information Bus Read for Transceiver 3
U13 ESIBRD4 I/O Extended System Information Bus Read for Transceiver 4
W6 ESIBS0_1 I/O Extended System Information Bus 0 for Transceiver 1
F18 ESIBS0_2 I/O Extended System Information Bus 0 for Transceiver 2
D7 ESIBS0_3 I/O Extended System Information Bus 0 for Transceiver 3
T20 ESIBS0_4 I/O Extended System Information Bus 0 for Transceiver 4
V9 ESIBS1_1 I/O Extended System Information Bus 1 for Transceiver 1
B17 ESIBS1_2 I/O Extended System Information Bus 1 for Transceiver 2
A6 ESIBS1_3 I/O Extended System Information Bus 1 for Transceiver 3
J20 ESIBS1_4 I/O Extended System Information Bus 1 for Transceiver 4
U1
INT
Interrupt for All Four Transceivers
O
Y15 JTCLK I JTAG Clock
N1 JTDI I JTAG Data Input
V19 JTDO O JTAG Data Output
W13 JTMS I JTAG Test Mode Select
V18 JTRST I Jtag Reset
K2 LIUC/TPD I Line Interface Connect for All Four Transceivers or Transmit Power-Down Enable
T1 MCLK1 I Master Clock for Transceiver 1 and Transceiver 3
W20 MCLK2 I Master Clock for Transceiver 2 and Transceiver 4
U10 MUX I Mux Bus Select
M2 RCHBLK1 O Receive Channel Block for Transceiver 1
G17 RCHBLK2 O Receive Channel Block for Transceiver 2
G4 RCHBLK3 O Receive Channel Block for Transceiver 3
Y12 RCHBLK4 O Receive Channel Block for Transceiver 4
J1 RCHCLK1 O Receive Channel Clock for Transceiver 1
D14 RCHCLK2 O Receive Channel Clock for Transceiver 2
F3 RCHCLK3 O Receive Channel Clock for Transceiver 3
U14 RCHCLK4 O Receive Channel Clock for Transceiver 4
N3 RCLK1 O Receive Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 1
B13 RCLK2 O Receive Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 2
E3 RCLK3 O Receive Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 3
M18 RCLK4 O Receive Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 4
M4 RCLKI1 I Receive Clock Input for the LIU on Transceiver 1
A15 RCLKI2 I Receive Clock Input for the LIU on Transceiver 2
A4 RCLKI3 I Receive Clock Input for the LIU on Transceiver 3
R17 RCLKI4 I Receive Clock Input for the LIU on Transceiver 4
M3 RCLKO1 O Receive Clock Output from the LIU on Transceiver 1
C14 RCLKO2 O Receive Clock Output from the LIU on Transceiver 2
B4 RCLKO3 O Receive Clock Output from the LIU on Transceiver 3
T17 RCLKO4 O Receive Clock Output from the LIU On Transceiver 4
N2
RD (DS)
I Read Input (Data Strobe)
K4 RFSYNC1 O Receive Frame Sync (Before the Receive Elastic Store) for Transceiver 1
D17 RFSYNC2 O Receive Frame Sync (Before the Receive Elastic Store) for Transceiver 2
A2 RFSYNC3 O Receive Frame Sync (Before the Receive Elastic Store) for Transceiver 3
V14 RFSYNC4 O Receive Frame Sync (Before the Receive Elastic Store) for Transceiver 4
F1 RLCLK1 O Receive Link Clock for Transceiver 1
30 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
PIN NAME TYPE FUNCTION
A12 RLCLK2 O Receive Link Clock for Transceiver 2
D3 RLCLK3 O Receive Link Clock for Transceiver 3
K18 RLCLK4 O Receive Link Clock for Transceiver 4
G2 RLINK1 O Receive Link Data for Transceiver 1
A13 RLINK2 O Receive Link Data for Transceiver 2
A3 RLINK3 O Receive Link Data for Transceiver 3
U12 RLINK4 O Receive Link Data for Transceiver 4
H2 RLOS/LOTC1 O Receive Loss of Sync/Loss of Transmit Clock for Transceiver 1
E17 RLOS/LOTC2 O Receive Loss of Sync/Loss of Transmit Clock for Transceiver 2
E1 RLOS/LOTC3 O Receive Loss of Sync/Loss of Transmit Clock for Transceiver 3
V11 RLOS/LOTC4 O Receive Loss of Sync/Loss of Transmit Clock For Transceiver4
L1 RMSYNC1 O Receive Multiframe Sync for Transceiver 1
D16 RMSYNC2 O Receive Multiframe Sync for Transceiver 2
F2 RMSYNC3 O Receive Multiframe Sync for Transceiver 3
W16 RMSYNC4 O Receive Multiframe Sync for Transceiver 4
R3 RNEGI1 I Receive Negative Data for the Framer on Transceiver 1
D13 RNEGI2 I Receive Negative Data for the Framer on Transceiver 2
A1 RNEGI3 I Receive Negative Data for the Framer on Transceiver 3
P17 RNEGI4 I Receive Negative Data for the Framer on Transceiver 4
L3 RNEGO1 O Receive Negative Data from the LIU on Transceiver 1
B15 RNEGO2 O Receive Negative Data from the LIU on Transceiver 2
C2 RNEGO3 O Receive Negative Data from the LIU on Transceiver 3
U17 RNEGO4 O Receive Negative Data from the LIU on Transceiver 4
R4 RPOSI1 I Receive Positive Data for the Framer on Transceiver 1
B14 RPOSI2 I Receive Positive Data for the Framer on Transceiver 2
B2 RPOSI3 I Receive Positive Data for the Framer on Transceiver 3
V15 RPOSI4 I Receive Positive Data for the Framer on Transceiver 4
L4 RPOSO1 O Receive Positive Data from the LIU on Transceiver 1
A16 RPOSO2 O Receive Positive Data from the LIU on Transceiver 2
B1 RPOSO3 O Receive Positive Data from the LIU on Transceiver 3
U15 RPOSO4 O Receive Positive Data from the LIU on Transceiver 4
Y11 RRING1 I Receive Analog Ring Input for Transceiver 1
Y14 RRING2 I Receive Analog Ring Input For Transceiver 2
Y17 RRING3 I Receive Analog Ring Input For Transceiver 3
Y20 RRING4 I Receive Analog Ring Input For Transceiver 4
J2 RSER1 O Receive Serial Data for Transceiver 1
D15 RSER2 O Receive Serial Data for Transceiver 2
E2 RSER3 O Receive Serial Data for Transceiver 3
W17 RSER4 O Receive Serial Data for Transceiver 4
L2 RSIG1 O Receive Signaling Output for Transceiver 1
B16 RSIG2 O Receive Signaling Output for Transceiver 2
C1 RSIG3 O Receive Signaling Output for Transceiver 3
Y18 RSIG4 O Receive Signaling Output for Transceiver 4
K1 RSIGF1 O Receive Signaling Freeze Output for Transceiver 1
C15 RSIGF2 O Receive Signaling Freeze Output for Transceiver 2
D2 RSIGF3 O Receive Signaling Freeze Output for Transceiver 3
V16 RSIGF4 O Receive Signaling Freeze Output for Transceiver 4
G1 RSYNC1 I/O Receive Sync for Transceiver 1
D12 RSYNC2 I/O Receive Sync for Transceiver 2
D1 RSYNC3 I/O Receive Sync for Transceiver 3
V12 RSYNC4 I/O Receive Sync for Transceiver 4
H1 RSYSCLK1 I Receive System Clock for Transceiver 1
F17 RSYSCLK2 I Receive System Clock for Transceiver 2
31 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
PIN NAME TYPE FUNCTION
G3 RSYSCLK3 I Receive System Clock for Transceiver 3
W14 RSYSCLK4 I Receive System Clock for Transceiver 4
Y10 RTIP1 I Receive Analog Tip Input for Transceiver 1
Y13 RTIP2 I Receive Analog Tip Input for Transceiver 2
Y16 RTIP3 I Receive Analog Tip Input for Transceiver 3
Y19 RTIP4 I Receive Analog Tip Input for Transceiver 4
P1 RVDD — Receive Analog Positive Supply
J17 RVDD — Receive Analog Positive Supply
E4 RVDD — Receive Analog Positive Supply
W18 RVDD — Receive Analog Positive Supply
R2 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
T2 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
H19 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
J18 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
D4 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
D5 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
V20 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
W19 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
W1 TCHBLK1 O Transmit Channel Block for Transceiver 1
F20 TCHBLK2 O Transmit Channel Block for Transceiver 2
C11 TCHBLK3 O Transmit Channel Block for Transceiver 3
U20 TCHBLK4 O Transmit Channel Block for Transceiver 4
V10 TCHCLK1 O Transmit Channel Clock for Transceiver 1
A18 TCHCLK2 O Transmit Channel Clock for Transceiver 2
B8 TCHCLK3 O Transmit Channel Clock for Transceiver 3
L18 TCHCLK4 O Transmit Channel Clock for Transceiver 4
Y9 TCLK1 I Transmit Clock for Transceiver 1
B19 TCLK2 I Transmit Clock for Transceiver 2
B10 TCLK3 I Transmit Clock for Transceiver 3
M19 TCLK4 I Transmit Clock for Transceiver 4
V6 TCLKI1 I Transmit Clock Input for the LIU on Transceiver 1
D19 TCLKI2 I Transmit Clock Input for the LIU on Transceiver 2
C8 TCLKI3 I Transmit Clock Input for the LIU on Transceiver 3
P20 TCLKI4 I Transmit Clock Input for the LIU on Transceiver 4
W7 TCLKO1 O Transmit Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 1
E18 TCLKO2 O Transmit Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 2
A7 TCLKO3 O Transmit Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 3
P19 TCLKO4 O Transmit Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 4
V3 TLCLK1 O Transmit Link Clock for Transceiver 1
E20 TLCLK2 O Transmit Link Clock for Transceiver 2
D6 TLCLK3 O Transmit Link Clock for Transceiver 3
T18 TLCLK4 O Transmit Link Clock for Transceiver 4
W5 TLINK1 I Transmit Link Data for Transceiver 1
E19 TLINK2 I Transmit Link Data for Transceiver 2
C6 TLINK3 I Transmit Link Data for Transceiver 3
T19 TLINK4 I Transmit Link Data for Transceiver 4
R1 TNEGI1 I Transmit Negative-Data Input for the LIU on Transceiver 1
F19 TNEGI2 I Transmit Negative-Data Input for the LIU on Transceiver 2
D8 TNEGI3 I Transmit Negative-Data Input for the LIU on Transceiver 3
R20 TNEGI4 I Transmit Negative-Data Input for the LIU on Transceiver 4
T3 TNEGO1 O Transmit Negative-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 1
B20 TNEGO2 O Transmit Negative-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 2
D9 TNEGO3 O Transmit Negative-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 3
32 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
PIN NAME TYPE FUNCTION
N20 TNEGO4 O Transmit Negative-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 4
W3 TPOSI1 I Transmit Positive-Data Input for the LIU on Transceiver 1
C20 TPOSI2 I Transmit Positive-Data Input for the LIU on Transceiver 2
A8 TPOSI3 I Transmit Positive-Data Input for the LIU on Transceiver 3
R19 TPOSI4 I Transmit Positive-Data Input for the LIU on Transceiver 4
V7 TPOSO1 O Transmit Positive-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 1
C19 TPOSO2 O Transmit Positive-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 2
C9 TPOSO3 O Transmit Positive-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 3
N19 TPOSO4 O Transmit Positive-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 4
Y2 TRING1 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 1
Y4 TRING2 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 2
Y6 TRING3 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 3
Y8 TRING4 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 4
W9 TSER1 I Transmit Serial Data for Transceiver 1
C17 TSER2 I Transmit Serial Data for Transceiver 2
C10 TSER3 I Transmit Serial Data for Transceiver 3
K20 TSER4 I Transmit Serial Data for Transceiver 4
W10 TSIG1 I Transmit Signaling Input for Transceiver 1
C18 TSIG2 I Transmit Signaling Input for Transceiver 2
A10 TSIG3 I Transmit Signaling Input for Transceiver 3
L19 TSIG4 I Transmit Signaling Input for Transceiver 4
W12 TSSYNC1 I Transmit System Sync for Transceiver 1
B18 TSSYNC2 I Transmit System Sync for Transceiver 2
D10 TSSYNC3 I Transmit System Sync for Transceiver 3
K19 TSSYNC4 I Transmit System Sync for Transceiver 4
U16 TSTRST I Test/Reset
V1 TSYNC1 I/O Transmit Sync for Transceiver 1
D20 TSYNC2 I/O Transmit Sync for Transceiver 2
C7 TSYNC3 I/O Transmit Sync for Transceiver 3
R18 TSYNC4 I/O Transmit Sync for Transceiver 4
W11 TSYSCLK1 I Transmit System Clock for Transceiver 1
A19 TSYSCLK2 I Transmit System Clock for Transceiver 2
A11 TSYSCLK3 I Transmit System Clock for Transceiver 3
N18 TSYSCLK4 I Transmit System Clock for Transceiver 4
Y1 TTIP1 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 1
Y3 TTIP2 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 2
Y5 TTIP3 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 3
Y7 TTIP4 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 4
W2 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
G19 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
D11 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
U19 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
W4 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
G18 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
C5 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
U18 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
K3
WR (R/W)
I Write Input (Read/Write)
33 of 270

Table 5-2. DS21458 PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NAME TYPE FUNCTION
H2 A0 I Address Bus Bit 0 (Lsb)
E10 A1 I Address Bus Bit 1
H3 A2 I Address Bus Bit 2
G4 A3 I Address Bus Bit 3
N7 A4 I Address Bus Bit 4
B9 A5 I Address Bus Bit 5
T7 A6 I Address Bus Bit 6
G2 A7/ALE (AS) I Address Bus Bit 7 (Msb)/Address Latch Enable
H6 A8 I Address Bus Bit 8
J11 A9 I Address Bus Bit 9
J5 BPCLK1 O Backplane Clock, Transceiver 1
H13 BPCLK2 O Backplane Clock, Transceiver 2
E8 BPCLK3 O Backplane Clock, Transceiver 3
N9 BPCLK4 O Backplane Clock, Transceiver 4
B10 BTS I Bus Type Select (0 = Intel/1 = Motorola)
M8
P8 D0/AD0 I/O Data Bus Bit 0/Address/Data Bus Bit 0 (Lsb)
D10 D1/AD1 I/O Data Bus Bit 1/ Address/Data Bus Bit 1
N8 D2/AD2 I/O Data Bus Bit 2/Address/Data Bus Bit 2
P7 D3/AD3 I/O Data Bus Bit 3/Address/Data Bus Bit 3
M7 D4/AD4 I/O Data Bus Bit 4/Address/Data Bus Bit 4
R7 D5/AD5 I/O Data Bus Bit 5/Address/Data Bus Bit 5
G1 D6/AD6 I/O Data Bus Bit 6/Address/Data Bus Bit 6
G3 D7/AD7 I/O Data Bus Bit 7/Address/Data Bus Bit 7 (Msb)
P4 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
P5 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
P6 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
C11 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
C12 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
C13 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
D3 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
E3 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
F3 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
L14 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
M14 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
N14 DVDD — Digital Positive Supply
N4 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
N5 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
N6 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
D11 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
D12 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
D13 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
D4 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
E4 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
F4 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
L13 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
M13 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
N13 DVSS — Digital Signal Ground
H8 ESIBRD I/O Extended System Information Bus Read
J8 ESIBS0 I/O Extended System Information Bus 0
CS
I Chip Select
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
34 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
PIN NAME TYPE FUNCTION
J9 ESIBS1 I/O Extended System Information Bus 1
H5
INT
O
Interrupt for All Four Transceivers
K16 JTCLK I JTAG Clock
C10 JTDI I JTAG Data Input
K13 JTDO O JTAG Data Output
J15 JTMS I JTAG Test Mode Select
K14 JTRST I JTAG Reset
D9 TPD I Transmit Power-Down Enable
H4 MCLK1 I Master Clock for Transceiver 1 and Transceiver 3
J12 MCLK2 I Master Clock for Transceiver 2 and Transceiver 4
R8 MUX I Mux Bus Select
E9 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
K9 N.C. — No Connection
P3 N.C. — No Connection
K3 RCHBLK1 O Receive Channel Block for Transceiver 1
G10 RCHBLK2 O Receive Channel Block for Transceiver 2
C7 RCHBLK3 O Receive Channel Block for Transceiver 3
R11 RCHBLK4 O Receive Channel Block for Transceiver 4
L2 RCHCLK1 O Receive Channel Clock for Transceiver 1
G11 RCHCLK2 O Receive Channel Clock for Transceiver 2
D7 RCHCLK3 O Receive Channel Clock for Transceiver 3
M9 RCHCLK4 O Receive Channel Clock for Transceiver 4
K8 RCLK1 O Receive Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 1
F10 RCLK2 O Receive Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 2
G5 RCLK3 O Receive Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 3
K12 RCLK4 O Receive Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 4
H9 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
R1 RCLKO1 O Receive Clock Output from the LIU on Transceiver 1
C14 RCLKO2 O Receive Clock Output from the LIU on Transceiver 2
A2 RCLKO3 O Receive Clock Output from the LIU on Transceiver 3
P14 RCLKO4 O Receive Clock Output from the LIU on Transceiver 4
A10
RD (DS)
I Read Input (Data Strobe)
K4 RFSYNC1 O Receive Frame Sync (Before the Receive Elastic Store) for Transceiver 1
G14 RFSYNC2 O Receive Frame Sync (Before the Receive Elastic Store) for Transceiver 2
C6 RFSYNC3 O Receive Frame Sync (Before the Receive Elastic Store) for Transceiver 3
P11 RFSYNC4 O Receive Frame Sync (Before the Receive Elastic Store) for Transceiver 4
M2 RLCLK1 O Receive Link Clock for Transceiver 1
F15 RLCLK2 O Receive Link Clock for Transceiver 2
B6 RLCLK3 O Receive Link Clock for Transceiver 3
R12 RLCLK4 O Receive Link Clock for Transceiver 4
P2 RLINK1 O Receive Link Data for Transceiver 1
C15 RLINK2 O Receive Link Data for Transceiver 2
C3 RLINK3 O Receive Link Data for Transceiver 3
T15 RLINK4 O Receive Link Data for Transceiver 4
K5 RLOS/LOTC1 O Receive Loss of Sync/Loss of Transmit Clock for Transceiver 1
E15 RLOS/LOTC2 O Receive Loss of Sync/Loss of Transmit Clock for Transceiver 2
D6 RLOS/LOTC3 O Receive Loss of Sync/Loss of Transmit Clock for Transceiver 3
P12 RLOS/LOTC4 O Receive Loss of Sync/Loss of Transmit Clock for Transceiver 4
M3 RMSYNC1 O Receive Multiframe Sync for Transceiver 1
G13 RMSYNC2 O Receive Multiframe Sync for Transceiver 2
E6 RMSYNC3 O Receive Multiframe Sync for Transceiver 3
M10 RMSYNC4 O Receive Multiframe Sync for Transceiver 4
H10 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
35 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
PIN NAME TYPE FUNCTION
J2 RNEGO1 O Receive Negative Data from the LIU on Transceiver 1
H11 RNEGO2 O Receive Negative Data from the LIU on Transceiver 2
F8 RNEGO3 O Receive Negative Data from the LIU on Transceiver 3
P10 RNEGO4 O Receive Negative Data from the LIU on Transceiver 4
G8 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
J6 RPOSO1 O Receive Positive Data from the LIU on Transceiver 1
H12 RPOSO2 O Receive Positive Data from the LIU on Transceiver 2
F9 RPOSO3 O Receive Positive Data from the LIU on Transceiver 3
N10 RPOSO4 O Receive Positive Data from the LIU on Transceiver 4
L1 RRING1 I Receive Analog Ring Input for Transceiver 1
F16 RRING2 I Receive Analog Ring Input for Transceiver 2
A6 RRING3 I Receive Analog Ring Input for Transceiver 3
T11 RRING4 I Receive Analog Ring Input for Transceiver 4
J4 RSER1 O Receive Serial Data for Transceiver 1
H14 RSER2 O Receive Serial Data for Transceiver 2
C8 RSER3 O Receive Serial Data for Transceiver 3
P9 RSER4 O Receive Serial Data for Transceiver 4
K2 RSIG1 O Receive Signaling Output for Transceiver 1
G15 RSIG2 O Receive Signaling Output for Transceiver 2
B7 RSIG3 O Receive Signaling Output for Transceiver 3
R10 RSIG4 O Receive Signaling Output for Transceiver 4
L3 RSIGF1 O Receive Signaling Freeze Output for Transceiver 1
F14 RSIGF2 O Receive Signaling Freeze Output for Transceiver 2
E7 RSIGF3 O Receive Signaling Freeze Output for Transceiver 3
N11 RSIGF4 O Receive Signaling Freeze Output for Transceiver 4
K6 RSYNC1 I/O Receive Sync for Transceiver 1
E14 RSYNC2 I/O Receive Sync for Transceiver 2
B5 RSYNC3 I/O Receive Sync for Transceiver 3
N12 RSYNC4 I/O Receive Sync for Transceiver 4
J3 RSYSCLK1 I Receive System Clock for Transceiver 1
H15 RSYSCLK2 I Receive System Clock for Transceiver 2
B8 RSYSCLK3 I Receive System Clock for Transceiver 3
R9 RSYSCLK4 I Receive System Clock for Transceiver 4
K1 RTIP1 I Receive Analog Tip Input for Transceiver 1
G16 RTIP2 I Receive Analog Tip Input for Transceiver 2
A7 RTIP3 I Receive Analog Tip Input for Transceiver 3
T10 RTIP4 I Receive Analog Tip Input for Transceiver 4
H1 RVDD — Receive Analog Positive Supply
J16 RVDD — Receive Analog Positive Supply
A9 RVDD — Receive Analog Positive Supply
T8 RVDD — Receive Analog Positive Supply
N1 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
J1 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
M1 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
E16 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
H16 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
D16 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
A5 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
A8 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
A4 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
T12 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
T13 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
T9 RVSS — Receive Analog Signal Ground
36 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
PIN NAME TYPE FUNCTION
N2 TCHBLK1 O Transmit Channel Block for Transceiver 1
E13 TCHBLK2 O Transmit Channel Block for Transceiver 2
C5 TCHBLK3 O Transmit Channel Block for Transceiver 3
R13 TCHBLK4 O Transmit Channel Block for Transceiver 4
J7 TCHCLK1 O Transmit Channel Clock for Transceiver 1
D15 TCHCLK2 O Transmit Channel Clock for Transceiver 2
B4 TCHCLK3 O Transmit Channel Clock for Transceiver 3
P13 TCHCLK4 O Transmit Channel Clock for Transceiver 4
L5 TCLK1 I Transmit Clock for Transceiver 1
G12 TCLK2 I Transmit Clock for Transceiver 2
F6 TCLK3 I Transmit Clock for Transceiver 3
L9 TCLK4 I Transmit Clock for Transceiver 4
L6 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
F12 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
F7 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
L11 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
T2 TCLKO1 O Transmit Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 1
A15 TCLKO2 O Transmit Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 2
B2 TCLKO3 O Transmit Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 3
R16 TCLKO4 O Transmit Clock Output from the Framer on Transceiver 4
J14 TEST1 — Used for Factory Test – Do Not Connect
J13 TEST2 — Used for Factory Test – Do Not Connect
P1 TLCLK1 O Transmit Link Clock for Transceiver 1
C16 TLCLK2 O Transmit Link Clock for Transceiver 2
C4 TLCLK3 O Transmit Link Clock for Transceiver 3
T14 TLCLK4 O Transmit Link Clock for Transceiver 4
K7 TLINK1 I Transmit Link Data for Transceiver 1
F11 TLINK2 I Transmit Link Data for Transceiver 2
G7 TLINK3 I Transmit Link Data for Transceiver 3
L12 TLINK4 I Transmit Link Data for Transceiver 4
M5 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
E12 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
E5 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
M12 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
T1 TNEGO1 O Transmit Negative-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 1
B15 TNEGO2 O Transmit Negative-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 2
A1 TNEGO3 O Transmit Negative-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 3
T16 TNEGO4 O Transmit Negative-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 4
L4 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
F13 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
D5 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
L10 Unused I Connect to VSS for Proper Operation
R2 TPOSO1 O Transmit Positive-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 1
A16 TPOSO2 O Transmit Positive-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 2
B1 TPOSO3 O Transmit Positive-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 3
R15 TPOSO4 O Transmit Positive-Data Output from Framer on Transceiver 4
R4 TRING1 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 1
T4 TRING1 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 1
A13 TRING2 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 2
B13 TRING2 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 2
D1 TRING3 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 3
D2 TRING3 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 3
N15 TRING4 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 4
37 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
PIN NAME TYPE FUNCTION
N16 TRING4 O Transmit Analog Ring Output for Transceiver 4
M6 TSER1 I Transmit Serial Data for Transceiver 1
G9 TSER2 I Transmit Serial Data for Transceiver 2
G6 TSER3 I Transmit Serial Data for Transceiver 3
K10 TSER4 I Transmit Serial Data for Transceiver 4
L7 TSIG1 I Transmit Signaling Input for Transceiver 1
E11 TSIG2 I Transmit Signaling Input for Transceiver 2
F5 TSIG3 I Transmit Signaling Input for Transceiver 3
K11 TSIG4 I Transmit Signaling Input for Transceiver 4
M4 TSSYNC1 I Transmit System Sync for Transceiver 1
D14 TSSYNC2 I Transmit System Sync for Transceiver 2
A3 TSSYNC3 I Transmit System Sync for Transceiver 3
M11 TSSYNC4 I Transmit System Sync for Transceiver 4
K15 TSTRST I Test/Reset
N3 TSYNC1 I/O Transmit Sync for Transceiver 1
B16 TSYNC2 I/O Transmit Sync for Transceiver 2
B3 TSYNC3 I/O Transmit Sync for Transceiver 3
R14 TSYNC4 I/O Transmit Sync for Transceiver 4
H7 TSYSCLK1 I Transmit System Clock for Transceiver 1
J10 TSYSCLK2 I Transmit System Clock for Transceiver 2
D8 TSYSCLK3 I Transmit System Clock for Transceiver 3
L8 TSYSCLK4 I Transmit System Clock for Transceiver 4
R3 TTIP1 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 1
T3 TTIP1 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 1
A14 TTIP2 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 2
B14 TTIP2 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 2
C1 TTIP3 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 3
C2 TTIP3 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 3
P15 TTIP4 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 4
P16 TTIP4 O Transmit Analog Tip Output for Transceiver 4
R6 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
T6 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
A11 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
B11 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
F1 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
F2 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
L15 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
L16 TVDD — Transmit Analog Positive Supply
R5 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
T5 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
A12 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
B12 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
E1 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
E2 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
M15 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
M16 TVSS — Transmit Analog Signal Ground
C9
WR (R/W)
I Write Input (Read/Write)
38 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
5.9 Packages
The package diagrams below show the lead pattern that will be placed on the target PC board. This is the
same pattern that would be seen as viewed from the top.
Figure 5-1. DS21455 Pin Diagram, 27mm BGA
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
RNEGI3 RFSYNC3 RLINK3 RCLKI3 DVSS ESIBS13 TCLKO3 TPOSI3 DVDD TSIG3 TSYSCLK3 RLCLK2 RLINK2
A
RPOSO3 RPOSI3 DVDD RCLKO3
B
RSIG3 RNEGO3 EISBRD3 DVDD TVSS TLINK3 TSYNC3 TCLKI3 TPOSO3 TSER3 TCHBLK3 DVDD EISBRD2 RCLKO2 RSIGF2 DVDD TSER2 TSIG2 TPOSO2 TPOSI2
C
RSYNC3 RSIGF3 RLCLK3 RVSS RVSS TLCLK3 ESIBS03 TNEGI3 TNEGO3 TSSYNC3 TVDD RSYNC2 RNEGI2 RCHCLK2 RSER2 RMSYNC2 RFSYNC2 DVDD TCLKI2 TSYNC2
D
RLOS3 RSER3 RCLK3 RVDD RLOS2 TCLKO2 TLINK2 TLCLK2
E
RLCLK1 RMSYNC3 RCHCLK3 BPCLK3 RSYSCLK2 ESIBS02 TNEGI2 TCHBLK2
F
RSYNC1 RLINK1 RSYSCLK3 RCHBLK3 RCHBLK2 TVSS TVDD DVDD
G
RSYSCLK1 RLOS1 DVSS A5 BPCLK2 N.C. RVSS DVSS
H
RCHCLK1 RSER1 DVDD EISBRD1 RVDD RVSS D1/AD1 ESIBS14
J
RSIGF1 LIUC/TPD
K
RMSYNC1 RSIG1 RNEGO1 RPOSO1 A1 TCHCLK4 TSIG4 DVSS
L
BPCLK1 RCHBLK1 RCLKO1 RCLKI1 DVDD RCLK4 TCLK4 DVDD
M
JTDI
N
RVDD1 BTS
P
TNEGI1 RVSS RNEGI1 RPOSI1 RCLKI4 TSYNC4 TPOSI4 TNEGI4
R
RD
RFSYNC1
WR
RCLK1 DVDD DVSS TSYSCLK4 TPOSO4 TNEGO4
A7/ALE
CS1
(AS)
DVDD DVSS TCHCLK3 DVSS TCLK3 DVSS DVDD RCLK2 RPOSI2 RNEGO2 RSIG2 ESIBS12 TSSYNC2 TCLK2 TNEGO2
CS3
RNEGI4 DVDD TCLKO4 TCLKI4
RCLKI2 RPOSO2 DVSS TCHCLK2 TSYSCLK2 DVSS
CS2
RLCLK4 TSSYNC4 TSER4
CS4
MCLK1 RVSS TNEGO1 A3 RCLKO4 TLCLK4 TLINK4 ESIBS04
T
DVDD A0 D7/AD7 D5/AD5 DVSS D3/AD3 A6 D4/AD4 MUX D0/AD0 RLINK4 EISBRD4 RCHCLK4 RPOSO4 TSTRST RNEGO4 TVSS TVDD TCHBLK4
INT
U
TSYNC1 A2 TLCLK1 D6/AD6 DVDD TCLKI1 TPOSO1 A4 ESIBS11 TCHCLK1 RLOS4 RSYNC4 BPCLK4 RFSYNC4 RPOSI4 RSIGF4 N.C. JTRST JTDO RVSS
V
TCHBLK1 TVDD TPOSI1 TVSS TLINK1 ESIBS01 TCLKO1 DVSS TSER1 TSI G1 TSYSCLK1 TSSYNC1 JTMS RSYSCLK4 D2/AD2 RMSYNC4 RSER4 RVDD RVSS MCLK2
W
TTIP1 TRING1 TTIP2 TRING2 TTIP3 TRING3 TTIP4 TRING4 TCLK1 RTIP1 RRING1 RCHBLK4 RTIP2 RRING2 JTCLK RTIP3 RRING3 RSIG4 RTIP4 RRING4
Y
NOTE: Locations C3, C13, J4, and U13 are used for the Extended System Information Bus (ESIB). These pin locations
on the DS21Q352, DS21Q354, DS21Q552, and DS21Q554 are connected to ground. When replacing a
DS21Qx5y with a DS21455, these signals should be routed to control logic to gain access to the ESIB. If these
pins remain connected to ground, the ESIB function will be disabled. Pins labeled as “N.C.” must be
unconnected.
39 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Figure 5-2. DS21458 Pin Diagram, 17mm CSBGA
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
TNEG0 RCLKO3 TSSYNC3 RVSS RVSS RRING3 RTIP3 RVSS RVDD RD (DS) TVDD TVSS TRING2 TTIP2 TCLKO2 TPOSO2
A
TPOSO3 TCLKO3 TSYNC3 TCHCLK3 RSYNC3 RLCLK3 RSIG3 RSYSCLK3 A5 BTS TVDD TVSS TRING2 TTIP2 TNEGO2 TSYNC2
B
TTIP3 TTIP3 RLINK3 TLCLK3 TCHBLK3 RFSYNC3 RCHBLK3 RSER3 WR (R /W) JTDI DVDD DVDD DVDD RCLKO2 RLINK2 TLCLK2
C
TRING3 TRING3 DVDD DVSS UNUSED
D
TVSS TVSS DVDD DVSS UNUSED RMSYNC3 RSIGF3 BPCLK3 UNUSED A1 TS IG2 UNUSED TCHBLK2 RSYNC2
E
TVDD TVDD DVDD DVSS TSIG3 TCLK3 UNUSED RNEGO3 RPOSO3 RCLK2 TLINK3 UNUSED UNUSED RSIGF2 RLCLK2 RRING2
F
A7/ALE
D6/AD6
G
RVDD A0 A2 MCLK1 INT A8 TSYSCLK1 ESIBRD UNUSED UNUSED RNEGO2 RPOSO2 BPCLK2 RSER2 RSYSCLK2 RVSS
H
RVSS RNEGO1 RSYSCLK1 RSER1 BPCLK1 RPOSO1 TCHCLK1 ESIBS0 ESIBS1 TSYSCLK2 A9 MCLK2 TEST2 TEST1 JTMS RVDD
J
RTIP RSIG1 RCHBLK1 RFSYNC1
K
RRING1 RCHCLK1 RSIGF1 UNUSED TCLK1 UNUSED TSIG1 TSYSCLK4 TCLK4 UNUSED UNUSED TLINK4 DVSS DVDD TVDD TVDD
L
RVSS RLCLK1 RMSYNC1 TSSYNC1 UNUSED TSER1 D4/AD4 CS RCHCLK4 RMSYNC4 TSSYNC4 UNUSED DVSS DVDD TVSS TVSS
M
RVSS TCHBLK1 TSYNC1 DVSS DVSS DVSS A4 D2/AD2 BPCLK4 RPOSO4 RSIGF4 RSYNC4 DVSS DVDD TRING4 TRING4
N
TLCLK1 RLINK1 UNUSED DVDD DVDD DVDD D3/AD3 D0/AD0 RSER4 RNEGO4 RFSYNC4
P
D7/AD7 A3 RCLK3 TSER3 TLINK3 UNUSED TSER2 RCHBLK2 RCHCLK2 TCLK2 RMSYNC2 RFSYNC2 RSIG2 RTIP2
(AS)
RLOS/
RCHCLK3 TSYSCLK3 TPD D1/AD1 DVSS DVSS DVSS TSSYNC2 TCHCLK2 RVSS
LOTC3
RLOS/
RSYNC1 TLINK1 RCLK1 UNUSED TSER4 TSIG4 RCLK4 JTDO JTRST JSTRST JTCLK
LOTC1
RLOS/
TCHCLK4 RCLKO4 TTIP4 TTIP4
LOTC4
RLOS/
LOTC2
RVSS
RCLKO1 TPOSO1 TTIP1 TRING1 TVSS TVDD D5/AD5 MUX RSYSCLK4 RSIG4 RCHBLK4 RLCLK4 TCHBLK4 TSYNC4 TPOSO4 TCLKO4
R
TNEGO1 TCLKO1 TTIP1 TRING1 TVSS TVDD A6 RVDD RVSS RTIP4 RRING4 RVSS RVSS TLCLK4 RLINK4 TNEGO4
T
NOTE: Pins labeled as “UNUSED” must be connected to VSS.
40 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
6. PARALLEL PORT
The transceiver is controlled via either a nonmultiplexed (MUX = 0) or a multiplexed (MUX = 1) bus by
an external microcontroller or microprocessor. The transceiver can operate with either Intel or Motorola
bus timing configurations. If the BTS pin is tied low, Intel timing will be selected; if tied high, Motorola
timing will be selected. All Motorola bus signals are listed in parentheses (). See the timing diagrams in
the AC Electrical Characteristics for more details.
6.1 Register Map
Table 6-1. REGISTER MAP SORTED BY ADDRESS
ADDRESS REGISTER NAME
00 Master Mode Register MSTRREG 49
01 I/O Configuration Register 1 IOCR1 78
02 I/O Configuration Register 2 IOCR2 79
03 T1 Receive Control Register 1 T1RCR1 53
04 T1 Receive Control Register 2 T1RCR2 53
05 T1 Transmit Control Register 1 T1TCR1 55
06 T1 Transmit Control Register 2 T1TCR2 56
07 T1 Common Control Register 1 T1CCR1 57
08 Software Signaling Insertion Enable 1 SSIE1 104
09 Software Signaling Insertion Enable 2 SSIE2 104
0A Software Signaling Insertion Enable 3 SSIE3 105
0B Software Signaling Insertion Enable 4 SSIE4 105
0C T1 Receive Digital Milliwatt Enable Register 1 T1RDMR1 61
0D T1 Receive Digital Milliwatt Enable Register 2 T1RDMR2 61
0E T1 Receive Digital Milliwatt Enable Register 3 T1RDMR3 61
0F Device Identification Register IDR 72
10 Information Register 1 INFO1 62
11 Information Register 2 INFO2 170
12 Information Register 3 INFO3 69
13 — — —
14 Interrupt Information Register 1 IIR1 51
15 Interrupt Information Register 2 IIR2 51
16 Status Register 1 SR1 171
17 Interrupt Mask Register 1 IMR1 172
18 Status Register 2 SR2 72
19 Interrupt Mask Register 2 IMR2 73
1A Status Register 3 SR3 74
1B Interrupt Mask Register 3 IMR3 75
1C Status Register 4 SR4 76
1D Interrupt Mask Register 4 IMR4 77
1E Status Register 5 SR5 118
1F Interrupt Mask Register 5 IMR5 118
20 Status Register 6 SR6 150
21 Interrupt Mask Register 6 IMR6 151
22 Status Register 7 SR7 150
23 Interrupt Mask Register 7 IMR7 151
24 Status Register 8 SR8 125
25 Interrupt Mask Register 8 IMR8 126
26 Status Register 9 SR9 190
27 Interrupt Mask Register 9 IMR9 191
28 Per-Channel Pointer Register PCPR 46
29 Per-Channel Data Register 1 PCDR1 47
41 of 270
REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
PAGE

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
ADDRESS REGISTER NAME
2A Per-Channel Data Register 2 PCDR2 47
2B Per-Channel Data Register 3 PCDR3 47
2C Per-Channel Data Register 4 PCDR4 47
2D Information Register 4 INFO4 152
2E Information Register 5 INFO5 152
2F Information Register 6 INFO6 152
30 Information Register 7 INFO7 69
31 HDLC #1 Receive Control H1RC 144
32 HDLC #2 Receive Control H2RC 144
33 E1 Receive Control Register 1 E1RCR1 64
34 E1 Receive Control Register 2 E1RCR2 65
35 E1 Transmit Control Register 1 E1TCR1 66
36 E1 Transmit Control Register 2 E1TCR2 67
37 BOC Control Register BOCC 124
38 Receive Signaling Change Of State Information 1 RSINFO1 99
39 Receive Signaling Change Of State Information 2 RSINFO2 99
3A Receive Signaling Change Of State Information 3 RSINFO3 99
3B Receive Signaling Change Of State Information 4 RSINFO4 99
3C Receive Signaling Change Of State Interrupt Enable 1 RSCSE1 99
3D Receive Signaling Change Of State Interrupt Enable 2 RSCSE2 99
3E Receive Signaling Change Of State Interrupt Enable 3 RSCSE3 99
3F Receive Signaling Change Of State Interrupt Enable 4 RSCSE4 99
40 Signaling Control Register SIGCR 96
41 Error Count Configuration Register ERCNT 85
42 Line Code Violation Count Register 1 LCVCR1 87
43 Line Code Violation Count Register 2 LCVCR2 87
44 Path Code Violation Count Register 1 PCVCR1 88
45 Path Code Violation Count Register 2 PCVCR2 88
46 Frames Out of Sync Count Register 1 FOSCR1 90
47 Frames Out of Sync Count Register 2 FOSCR2 90
48 E-Bit Count Register 1 EBCR1 90
49 E-Bit Count Register 2 EBCR2 90
4A Loopback Control Register LBCR 80
4B Per-Channel Loopback Enable Register 1 PCLR1 83
4C Per-Channel Loopback Enable Register 2 PCLR2 83
4D Per-Channel Loopback Enable Register 3 PCLR3 84
4E Per-Channel Loopback Enable Register 4 PCLR4 84
4F Elastic Store Control Register ESCR 117
50 Transmit Signaling Register 1 TS1 102
51 Transmit Signaling Register 2 TS2 102
52 Transmit Signaling Register 3 TS3 102
53 Transmit Signaling Register 4 TS4 102
54 Transmit Signaling Register 5 TS5 102
55 Transmit Signaling Register 6 TS6 102
56 Transmit Signaling Register 7 TS7 102
57 Transmit Signaling Register 8 TS8 102
58 Transmit Signaling Register 9 TS9 102
59 Transmit Signaling Register 10 TS10 102
5A Transmit Signaling Register 11 TS11 102
5B Transmit Signaling Register 12 TS12 102
5C Transmit Signaling Register 13 TS13 102
5D Transmit Signaling Register 14 TS14 102
5E Transmit Signaling Register 15 TS15 102
REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
PAGE
42 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
ADDRESS REGISTER NAME
5F Transmit Signaling Register 16 TS16 102
60 Receive Signaling Register 1 RS1 97
61 Receive Signaling Register 2 RS2 97
62 Receive Signaling Register 3 RS3 97
63 Receive Signaling Register 4 RS4 97
64 Receive Signaling Register 5 RS5 97
65 Receive Signaling Register 6 RS6 97
66 Receive Signaling Register 7 RS7 97
67 Receive Signaling Register 8 RS8 97
68 Receive Signaling Register 9 RS9 97
69 Receive Signaling Register 10 RS10 97
6A Receive Signaling Register 11 RS11 97
6B Receive Signaling Register 12 RS12 97
6C Receive Signaling Register 13 RS13 97
6D Receive Signaling Register 14 RS14 97
6E Receive Signaling Register 15 RS15 97
6F Receive Signaling Register 16 RS16 97
70 Common Control Register 1 CCR1 71
71 Common Control Register 2 CCR2 208
72 Common Control Register 3 CCR3 209
73 Common Control Register 4 CCR4 210
74 Transmit Channel Monitor Select TDS0SEL 91
75 Transmit DS0 Monitor Register TDS0M 91
76 Receive Channel Monitor Select RDS0SEL 92
77 Receive DS0 Monitor Register RDS0M 92
78 Line Interface Control 1 LIC1 164
79 Line Interface Control 2 LIC2 167
7A Line Interface Control 3 LIC3 168
7B Line Interface Control 4 LIC4 169
7C Unused. Must be set = 00h for proper operation — —
7D Transmit Line Build-Out Control TLBC 166
7E Idle Array Address Register IAAR 110
7F Per-Channel Idle Code Value Register PCICR 110
80 Transmit Idle Code Enable Register 1 TCICE1 110
81 Transmit Idle Code Enable Register 2 TCICE2 110
82 Transmit Idle Code Enable Register 3 TCICE3 111
83 Transmit Idle Code Enable Register 4 TCICE4 111
84 Receive Idle Code Enable Register 1 RCICE1 111
85 Receive Idle Code Enable Register 2 RCICE2 111
86 Receive Idle Code Enable Register 3 RCICE3 112
87 Receive Idle Code Enable Register 4 RCICE4 112
88 Receive Channel Blocking Register 1 RCBR1 113
89 Receive Channel Blocking Register 2 RCBR2 113
8A Receive Channel Blocking Register 3 RCBR3 114
8B Receive Channel Blocking Register 4 RCBR4 114
8C Transmit Channel Blocking Register 1 TCBR1 113
8D Transmit Channel Blocking Register 2 TCBR2 114
8E Transmit Channel Blocking Register 3 TCBR3 115
8F Transmit Channel Blocking Register 4 TCBR4 115
90 HDLC #1 Transmit Control H1TC 143
91 HDLC #1 FIFO Control H1FC 145
92 HDLC #1 Receive Channel Select 1 H1RCS1 146
93 HDLC #1 Receive Channel Select 2 H1RCS2 146
REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
PAGE
43 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
ADDRESS REGISTER NAME
94 HDLC #1 Receive Channel Select 3 H1RCS3 146
95 HDLC #1 Receive Channel Select 4 H1RCS4 146
96 HDLC #1 Receive Time Slot Bits/Sa Bits Select H1RTSBS 147
97 HDLC #1 Transmit Channel Select1 H1TCS1 148
98 HDLC #1 Transmit Channel Select 2 H1TCS2 148
99 HDLC #1 Transmit Channel Select 3 H1TCS3 148
9A HDLC #1 Transmit Channel Select 4 H1TCS4 148
9B HDLC #1 Transmit Time Slot Bits/Sa Bits Select H1TTSBS 149
9C HDLC #1 Receive Packet Bytes Available H1RPBA 153
9D HDLC #1 Transmit FIFO H1TF 154
9E HDLC #1 Receive FIFO H1RF 154
9F HDLC #1 Transmit FIFO Buffer Available H1TFBA 153
A0 HDLC #2 Transmit Control H2TC 143
A1 HDLC #2 FIFO Control H2FC 145
A2 HDLC #2 Receive Channel Select 1 H2RCS1 146
A3 HDLC #2 Receive Channel Select 2 H2RCS2 146
A4 HDLC #2 Receive Channel Select 3 H2RCS3 146
A5 HDLC #2 Receive Channel Select 4 H2RCS4 146
A6 HDLC #2 Receive Time Slot Bits/Sa Bits Select H2RTSBS 147
A7 HDLC #2 Transmit Channel Select 1 H2TCS1 148
A8 HDLC #2 Transmit Channel Select 2 H2TCS2 148
A9 HDLC #2 Transmit Channel Select 3 H2TCS3 148
AA HDLC #2 Transmit Channel Select 4 H2TCS4 148
AB HDLC #2 Transmit Time Slot Bits/Sa Bits Select H2TTSBS 149
AC HDLC #2 Receive Packet Bytes Available H2RPBA 153
AD HDLC #2 Transmit FIFO H2TF 154
AE HDLC #2 Receive FIFO H2RF 154
AF HDLC #2 Transmit FIFO Buffer Available H2TFBA 153
B0 Extend System Information Bus Control Register 1 ESIBCR1 205
B1 Extend System Information Bus Control Register 2 ESIBCR2 206
B2 Extend System Information Bus Register 1 ESIB1 207
B3 Extend System Information Bus Register 2 ESIB2 207
B4 Extend System Information Bus Register 3 ESIB3 207
B5 Extend System Information Bus Register 4 ESIB4 207
B6 In-Band Code Control Register IBCC 180
B7 Transmit Code Definition Register 1 TCD1 181
B8 Transmit Code Definition Register 2 TCD2 181
B9 Receive Up Code Definition Register 1 RUPCD1 182
BA Receive Up Code Definition Register 2 RUPCD2 182
BB Receive Down Code Definition Register 1 RDNCD1 183
BC Receive Down Code Definition Register 2 RDNCD2 184
BD In-Band Receive Spare Control Register RSCC 184
BE Receive Spare Code Definition Register 1 RSCD1 185
BF Receive Spare Code Definition Register 2 RSCD2 185
C0 Receive FDL Register RFDL 156
C1 Transmit FDL Register TFDL 157
C2 Receive FDL Match Register 1 RFDLM1 156
C3 Receive FDL Match Register 2 RFDLM2 156
C4 Unused. Must be set = 00h for proper operation — —
C5 Interleave Bus Operation Control Register IBOC 200
C6 Receive Align Frame Register RAF 128
C7 Receive Nonalign Frame Register RNAF 128
C8 Receive Si Align Frame RSiAF 130
REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
PAGE
44 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
ADDRESS REGISTER NAME
C9 Receive Si Nonalign Frame RSiNAF 131
CA Receive Remote Alarm Bits RRA 131
CB Receive Sa4 Bits RSa4 132
CC Receive Sa5 Bits RSa5 137
CD Receive Sa6 Bits RSa6 133
CE Receive Sa7 Bits RSa7 133
CF Receive Sa8 Bits RSa8 134
D0 Transmit Align Frame Register TAF 129
D1 Transmit Nonalign Frame Register TNAF 129
D2 Transmit Si Align Frame TSiAF 135
D3 Transmit Si Nonalign Frame TSiNAF 136
D4 Transmit Remote Alarm Bits TRA 136
D5 Transmit Sa4 Bits TSa4 137
D6 Transmit Sa5 Bits TSa5 137
D7 Transmit Sa6 Bits TSa6 138
D8 Transmit Sa7 Bits TSa7 138
D9 Transmit Sa8 Bits TSa8 139
DA Transmit Sa Bit Control Register TSACR 140
DB BERT Alternating Word Count Rate BAWC 191
DC BERT Repetitive Pattern Set Register 1 BRP1 192
DD BERT Repetitive Pattern Set Register 2 BRP2 192
DE BERT Repetitive Pattern Set Register 3 BRP3 192
DF BERT Repetitive Pattern Set Register 4 BRP4 192
E0 BERT Control Register 1 BC1 187
E1 BERT Control Register 2 BC2 188
E2 Unused. Must be set = 00h for proper operation — —
E3 BERT Bit Count Register 1 BBC1 193
E4 BERT Bit Count Register 2 BBC2 193
E5 BERT Bit Count Register 3 BBC3 193
E6 BERT Bit Count Register 4 BBC4 193
E7 BERT Error Count Register 1 BEC1 194
E8 BERT Error Count Register 2 BEC2 194
E9 BERT Error Count Register 3 BEC3 194
EA BERT Interface Control Register BIC 189
EB Error Rate Control Register ERC 196
EC Number Of Errors 1 NOE1 197
ED Number Of Errors 2 NOE2 197
EE Number Of Errors Left 1 NOEL1 198
EF Number Of Errors Left 2 NOEL2 198
F0 Unused. Must be set = 00h for proper operation — —
F1 Pulse Shape Adjustment 1 PSA1 —
F2 Pulse Shape Adjustment 2 PSA2 —
F3–F9, FA–FF Unused. Must be set = 00h for proper operation — —
REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
PAGE
45 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
7. SPECIAL PER-CHANNEL REGISTER OPERATION
Some of the features described in the data sheet that operate on a per-channel basis use a special method
for channel selection. The registers involved are the per-channel pointer registers (PCPR) and per-channel
data registers 1 to 4 (PCDR1–4). The user selects the function(s) that are to be applied on a per-channel
basis by setting the appropriate bit(s) in the PCPR register. The user then writes to the PCDR registers to
select the channels for that function. The following is an example of mapping the transmit and receive
BERT function to channels 9, 10, 11, 12, 20, and 21:
Write 11h to PCPR
Write 00h to PCDR1
Write 0fh to PCDR2
Write 18h to PCDR3
Write 00h to PCDR4
More information about how to use these per-channel features can be found in their respective sections in
the data sheet.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RSAOICS RSRCS RFCS BRCS THSCS PEICS TFCS BTCS
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/BERT Transmit Channel Select (BTCS).
Bit 1/Transmit Fractional Channel Select (TFCS).
Bit 2/Payload Error Insert Channel Select (PEICS).
Bit 3/Transmit Hardware Signaling Channel Select (THSCS).
Bit 4/BERT Receive Channel Select (BRCS).
Bit 5/Receive Fractional Channel Select (RFCS).
Bit 6/Receive Signaling Reinsertion Channel Select (RSRCS).
Bit 7/Receive Signaling All Ones Insertion Channel Select (RSAOICS).
PCPR
Per-Channel Pointer Register
28h
46 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
Default CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
Default CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
Default CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
Default CH32 CH31 CH30 CH29 CH28 CH27 CH26 CH25
PCDR1
Per-Channel Data Register 1
29h
PCDR2
Per-Channel Data Register 2
2Ah
PCDR3
Per-Channel Data Register 3
2Bh
PCDR4
Per-Channel Data Register 4
2Ch
47 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
8. PROGRAMMING MODEL
The DS21455/DS21458 register map is divided into three groups: T1 specific features, E1 specific
features, and common features. The typical programming sequence begins with issuing a reset to the
device, selecting T1 or E1 operation in the master mode register, enabling T1 or E1 functions, and
enabling the common functions. The act of resetting the device automatically clears all configuration and
status registers. Therefore, it is not necessary to load unused registers with zeros.
Figure 8-1. Programming Sequence
SELECT T1 OR E1 OPERATION IN
MASTER MODE REGISTER
POWER-ON
ISSUE RESET
PROGRAM T1 SPECIFIC REGISTERS
PROGRAM COMMON REGISTERS
DS21455/DS21458 OPERATIONAL
PROGRAM E1 SPECIFIC REGISTERS
48 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
8.1 Power-Up Sequence
The DS21455/DS21458 contain an on-chip power-up reset function, which automatically clears the
writeable register space immediately after power is supplied to the device. The user can issue a chip reset
at any time. Issuing a reset will disrupt traffic until the device is reprogrammed. The reset can be issued
through hardware using the TSTRST pin or through software using the SFTRST function in the master
mode register. The LIRST (LIC2.6) should be toggled from zero to one to reset the line interface
circuitry. (It will take the DS21455/DS21458 about 40ms to recover from the LIRST bit being toggled.)
Finally, after the TSYSCLK and RSYSCLK inputs are stable, the receive and transmit elastic stores
should be reset (this step can be skipped if the elastic stores are disabled).
8.1.1 Master Mode Register
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — — TEST1 TEST0 T1/E1 SFTRST
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Software Issued Reset (SFTRST).
A 0 to 1 transition causes the register space to be cleared. A reset clears all configuration and status registers. The bit
automatically clears itself when the reset has completed.
Bit 1/Operating Mode (T1/E1).
Used to select the operating mode of the framer/formatter (digital) portion of the DS21455. The operating mode of the LIU
must also be programmed.
0 = T1 operation
1 = E1 operation
Bits 2, 3/Test Mode Bits (TEST0, TEST1).
Test modes are used to force the output pins of the DS21455 into known states. This can facilitate the checkout of assemblies
during the manufacturing process and also be used to isolate devices from shared buses.
TEST1 TEST0 EFFECT ON OUTPUT PINS
0 0 Operate normally
0 1 Force all output pins into tri-state (including all I/O pins and parallel port pins)
1 0 Force all output pins low (including all I/O pins except parallel port pins)
1 1 Force all output pins high (including all I/O pins except parallel port pins)
Bits 4–7/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
MSTRREG
Master Mode Register
00h
49 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
8.2 Interrupt Handling
Various alarms, conditions, and events in the DS21455/DS21458 can cause interrupts. For simplicity,
these are all referred to as events in this explanation. All STATUS registers can be programmed to
produce interrupts. Each status register has an associated interrupt mask register. For example, SR1
(Status Register 1) has an interrupt control register called IMR1 (Interrupt Mask Register 1). Status
registers are the only sources of interrupts. On power-up, all writeable registers are automatically cleared.
Since bits in the IMRx registers have to be set = 1 to allow a particular event to cause an interrupt, no
interrupts can occur until the host selects which events are to product interrupts. Since there are
potentially many sources of interrupts, several features are available to help sort out and identify which
event is causing an interrupt. When an interrupt occurs, the host should first read the IIR1, IIR2, and IIR3
registers (interrupt information registers) to identify which status register(s) is producing the interrupt.
Once that is determined, the individual status register or registers can be examined to determine the exact
source. In eight port configurations, two DS21455/DS21458s can be connected together via the 3-wire
ESIB feature. This allows all eight transceivers to be interrogated by a single CPU port read cycle. The
host can determine the synchronization status or interrupt status of eight devices with a single read. The
ESIB feature also allows the user to select from various events to be examined via this method. For more
information, see the ESIB section in this data sheet.
Once an interrupt has occurred, the interrupt handler routine should clear the IMRx registers to stop
further activity on the interrupt pin. After all interrupts have been determined and processed, the interrupt
hander routine should restore the state of the IMRx registers.
8.3 Status Registers
When a particular event or condition has occurred (or is still occurring in the case of conditions), the
appropriate bit in a status register will be set to a one. All of the status registers operate in a latched
fashion, which means that if an event or condition occurs a bit is set to a one. It will remain set until the
user reads that bit. An event bit will be cleared when it is read and it will not be set again until the event
has occurred again. Condition bits such as RBL, RLOS, etc., will remain set if the alarm is still present.
The user will always proceed a read of any of the status registers with a write. The byte written to the
register will inform the DS21455/DS21458 which bits the user wishes to read and have cleared. The user
will write a byte to one of these registers, with a one in the bit positions he or she wishes to read and a
zero in the bit positions he or she does not wish to obtain the latest information on. When a one is written
to a bit location, the read register will be updated with the latest information. When a zero is written to a
bit position, the read register will not be updated and the previous value will be held. A write to the status
registers will be immediately followed by a read of the same register. This write-read scheme allows an
external microcontroller or microprocessor to individually poll certain bits without disturbing the other
bits in the register. This operation is key in controlling the DS21455/DS21458 with higher-order
languages.
Status register bits are divided into two groups, condition bits and event bits. Condition bits are typically
network conditions such as loss of sync, or all ones detect. Event bits are typically markers such as the
one-second timer, elastic store slip, etc. Each status register bit is labeled as a condition or event bit.
Some of the status registers have bits for both the detection of a condition and the clearance of the
condition. For example, SR2 has a bit that is set when the device goes into a loss of sync state (SR2.0, a
condition bit) and a bit that is set (SR2.4, an event bit) when the loss of sync condition clears (goes in
sync). Some of the status register bits (condition bits) do not have a separate bit for the “condition clear”
event but rather the status bit can produce interrupts on both edges, setting, and clearing. These bits are
marked as “double interrupt bits.” An interrupt will be produced when the condition occurs and when it
clears.
50 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
8.4 Information Registers
Information registers operate the same as status registers except they cannot cause interrupts. They are all
latched except for INFO7 and some of the bits in INFO5 and INFO6. INFO7 register is a read only
register and it reports the status of the E1 synchronizer in real time. INFO7 and some of the bits in INFO6
and INFO5 are not latched and it is not necessary to precede a read of these bits with a write.
8.5 Interrupt Information Registers
The Interrupt Information Registers provide an indication of which Status Registers (SR1 through SR9)
are generating an interrupt. When an interrupt occurs, the host can read IIR1 and IIR2 to quickly identify
which of the 9 status registers are causing the interrupt.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name SR8 SR7 SR6 SR5 SR4 SR3 SR2 SR1
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — — — — — SR9
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
IIR1
Interrupt Information Register 1
14h
IIR2
Interrupt Information Register 2
15h
51 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
9. CLOCK MAP
Figure 9-1 shows the clock map of the DS21455/DS21458. The routing for the transmit and receive
clocks are shown for the various loopback modes and jitter attenuator positions. Although there is only
one jitter attenuator, which can be placed in the receive or transmit path, two are shown for simplification
and clarity.
Figure 9-1. Clock Map
MCLK
LLB = 0
LLB = 1
LIC4.MPS0
LIC4.MPS1
LIC2.3
JITTER ATTENUATOR
SEE LIC1 REGISTER
LTCA
JAS = 0
OR
DJA = 1
JAS = 1
AND
DJA = 0
JAS = 0
AND
DJA = 0
JAS = 1
OR
DJA = 1
LTCA
REMOTE
LOOPBACK
RLB = 1
RLB = 0
DJA = 1
DJA = 0
FRAMER
LOOPBACK
FLB = 0
FLB = 1
RECEIVE
FRAMER
TRANSMIT
FORMATTER
8 x PLL
PAYLOAD
LOOPBACK
(SEE NOTES)
PLB = 1
PLB = 0
BPCLK
SYNTH
BA
C
8XCLK
BPCLK
RCLK
TCLK
MUX
TCLK
RXCLK
TXCLK
TO
LIU
PRE-SCALER
2.048 T O 1.544
SYNTHESIZER
RCL = 1
RCL = 0
LOCAL
LOOPBAC K
The TCLK MUX is dependent on the state of the TCSS0 and TCSS1 bits in the LIC1 register and the
state of the TCLK pin.
TCSS1 TCSS0 TRANSMIT CLOCK SOURCE
0 0 The TCLK pin (C) is always the source of Transmit Clock.
0 1
1 0
Switch to the recovered clock (B) when the signal at the TCLK pin fails to
transition after 1 channel time.
Use the scaled signal (A) derived from MCLK as the Transmit Clock. The TCLK
pin is ignored.
1 1 Use the recovered clock (B) as the Transmit Clock. The TCLK pin is ignored.
52 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
10. T1 FRAMER/FORMATTER CONTROL REGISTERS
The T1 framer portion of the DS21455/DS21458 is configured via a set of nine control registers.
Typically, the control registers are only accessed when the system is first powered up. Once the device
has been initialized, the control registers will only need to be accessed when there is a change in the
system configuration. There are two receive-control registers (T1RCR1 and T1RCR2), two transmit
control registers (T1TCR1 and T1TCR2), and a common control register (T1CCR1). Each of these
registers is described in this section.
10.1 T1 Control Registers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — ARC OOF1 OOF2 SYNCC SYNCT SYNCE RESYNC
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Resynchronize (RESYNC). When toggled from low to high, a resynchronization of the receive side framer is initiated.
Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent resync.
Bit 1/Sync Enable (SYNCE).
0 = auto resync enabled
1 = auto resync disabled
Bit 2/Sync Time (SYNCT).
0 = qualify 10 bits
1 = qualify 24 bits
Bit 3/Sync Criteria (SYNCC).
In D4 Framing Mode:
0 = search for Ft pattern, then search for Fs pattern
1 = cross couple Ft and Fs pattern
In ESF Framing Mode:
0 = search for FPS pattern only
1 = search for FPS and verify with CRC6
Bits 4 to 5/Out-of-Frame Select Bits (OOF2, OOF1).
OOF2 OOF1 OUT-OF-FRAME CRITERIA
0 0 2/4 frame bits in error
0 1 2/5 frame bits in error
1 0 2/6 frame bits in error
1 1 2/6 frame bits in error
Bit 6/Auto Resync Criteria (ARC).
0 = resync on OOF or RCL event
1 = resync on OOF only
Bit 7/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
T1RCR1
T1 Receive Control Register 1
03h
53 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — RFM RB8ZS RSLC96 RZSE RZBTSI RJC RD4YM
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Receive Side D4 Yellow Alarm Select (RD4YM).
0 = zeros in bit 2 of all channels
1 = a one in the S-bit position of frame 12 (J1 Yellow Alarm Mode)
Bit 1/Receive Japanese CRC6 Enable (RJC).
0 = use ANSI/AT&T/ITU CRC6 calculation (normal operation)
1 = use Japanese standard JT–G704 CRC6 calculation
Bit 2/Receive Side ZBTSI Support Enable (RZBTSI). Allows ZBTSI information to be output on RLINK pin.
0 = ZBTSI disabled
1 = ZBTSI enabled
Bit 3/Receive FDL Zero Destuffer Enable (RZSE). Set this bit to zero if using the internal HDLC/BOC controller instead of
the legacy support for the FDL. See Legacy FDL Support (T1 Mode) for details.
0 = zero destuffer disabled
1 = zero destuffer enabled
Bit 4/Receive SLC–96 Enable (RSLC96). Only set this bit to a one in SLC-96 framing applications. See D4/SLC–96
Operation for details.
0 = SLC–96 disabled
1 = SLC–96 enabled
Bit 5/Receive B8ZS Enable (RB8ZS).
0 = B8ZS disabled
1 = B8ZS enabled
Bit 6/Receive Frame Mode Select (RFM).
0 = D4 framing mode
1 = ESF framing mode
Bit 7/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
T1RCR2
T1 Receive Control Register 2
04h
54 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TJC TFPT TCPT TSSE GB7S TFDLS TBL TYEL
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Transmit Yellow Alarm (TYEL).
0 = do not transmit yellow alarm
1 = transmit yellow alarm
Bit 1/Transmit Blue Alarm (TBL).
0 = transmit data normally
1 = transmit an unframed all one’s code at TPOS and TNEG
Bit 2/TFDL Register Select (TFDLS).
0 = source FDL or Fs bits from the internal TFDL register (legacy FDL support mode)
1 = source FDL or Fs bits from the internal HDLC controller or the TLINK pin
Bit 3/Global Bit 7 Stuffing (GB7S).
0 = allow the SSIEx registers to determine which channels containing all zeros are to be Bit 7 stuffed
1 = force Bit 7 stuffing in all zero byte channels regardless of how the SSIEx registers are programmed
Bit 4/Transmit Software Signaling Enable (TSSE).
0 = do not source signaling data from the TSx registers regardless of the SSIEx registers. The SSIEx registers still
define which channels are to have B7 stuffing preformed
1 = source signaling data as enabled by the SSIEx registers
Bit 5/Transmit CRC Pass Through (TCPT).
0 = source CRC6 bits internally
1 = CRC6 bits sampled at TSER during F-bit time
Bit 6/Transmit F-Bit Pass Through (TFPT).
0 = F bits sourced internally
1 = F bits sampled at TSER
Bit 7/Transmit Japanese CRC6 Enable (TJC).
0 = use ANSI/AT&T/ITU CRC6 calculation (normal operation)
1 = use Japanese standard JT–G704 CRC6 calculation
T1TCR1
T1 Transmit Control Register 1
05h
55 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TB8ZS TSLC96 TZSE FBCT2 FBCT1 TD4YM TZBTSI TB7ZS
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Transmit Side Bit 7 Zero Suppression Enable (TB7ZS).
0 = no stuffing occurs
1 = Bit 7 force to a one in channels with all zeros
Bit 1/Transmit Side ZBTSI Support Enable (TZBTSI). Allows ZBTSI information to be input on TLINK pin.
0 = ZBTSI disabled
1 = ZBTSI enabled
Bit 2/Transmit Side D4 Yellow Alarm Select (TD4YM).
0 = zeros in bit 2 of all channels
1 = a one in the S-bit position of frame 12
Bit 3/F-Bit Corruption Type 1. (FBCT1). A low-to-high transition of this bit causes the next three consecutive Ft (D4
framing mode) or FPS (ESF framing mode) bits to be corrupted, causing the remote end to experience a loss of
synchronization.
Bit 4/F-Bit Corruption Type 2. (FBCT2). Setting this bit high enables the corruption of one Ft (D4 framing mode) or FPS
(ESF framing mode) bit in every 128 Ft or FPS bits as long as the bit remains set.
Bit 5/Transmit FDL Zero Stuffer Enable (TZSE). Set this bit to zero if using the internal HDLC controller instead of the
legacy support for the FDL. See I/O Pin Configuration Options for details.
0 = zero stuffer disabled
1 = zero stuffer enabled
Bit 6/Transmit SLC–96/Fs-Bit Insertion Enable (TSLC96). Only set this bit to a one in D4 framing and SLC-96
applications. Must be set to one to source the Fs pattern from the TFDL register. See D4/SLC–96 Operation for details.
0 = SLC–96/Fs-bit insertion disabled
1 = SLC–96/Fs-bit insertion enabled
Bit 7/Transmit B8ZS Enable (TB8ZS).
0 = B8ZS disabled
1 = B8ZS enabled
T1TCR2
T1 Transmit Control Register 2
06h
56 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — TRAI-CI TAIS-CI TFM PDE TLOOP
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Transmit Loop Code Enable (TLOOP). See Programmable In-Band Loop Codes Generation and Detection for details.
0 = transmit data normally
1 = replace normal transmitted data with repeating code as defined in registers TCD1 and TCD2
Bit 1/Pulse Density Enforcer Enable (PDE). The framer always examines both the transmit and receive data streams for
violations of the following rules, which are required by ANSI T1.403: no more than 15 consecutive zeros and at least N ones
in each and every time window of 8 x (N +1) bits where N = 1 through 23. Violations for the transmit and receive data streams
are reported in the INFO1.6 and INFO1.7 bits respectively. When this bit is set to one, the device will force the transmitted
stream to meet this requirement no matter the content of the transmitted stream. When running B8ZS, this bit should be set to
zero since B8ZS encoded data streams cannot violate the pulse density requirements.
0 = disable transmit pulse density enforcer
1 = enable transmit pulse density enforcer
Bit 2/Transmit Frame Mode Select (TFM).
0 = D4 framing mode
1 = ESF framing mode
Bit 3/Transmit AIS-CI Enable (TAIS-CI). Setting this bit and the TBL bit (T1TCR1.1) causes the AIS-CI code to be
transmitted at TPOSO and TNEGO, as defined in ANSI T1.403.
0 = do not transmit the AIS-CI code
1 = transmit the AIS-CI code (T1TCR1.1 must also be set = 1)
Bit 4/Transmit RAI-CI Enable (TRAI-CI). Setting this bit causes the ESF RAI-CI code to be transmitted in the FDL bit
position.
0 = do not transmit the ESF RAI-CI code
1 = transmit the ESF RAI-CI code
Bit 5/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Bit 6/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Bit 7/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
T1CCR1
T1 Common Control Register 1
07h
57 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
10.2 T1 Transmit Transparency
The software-signaling insertion-enable registers, SSIE1–SSIE4, can be used to select signaling insertion
from the transmit-signaling registers, TS1–TS12, on a per-channel basis. Setting a bit in the SSIEx
register allows signaling data to be sourced from the signaling registers for that channel.
In transparent mode, bit 7 stuffing and/or robbed-bit signaling is prevented from overwriting the data in
the channels. If a DS0 is programmed to be clear, no robbed-bit signaling will be inserted nor will the
channel have bit 7 stuffing performed. However, in the D4 framing mode, bit 2 will be overwritten by a
zero when a yellow alarm is transmitted. Also, the user has the option to globally override the SSIEx
registers from determining which channels are to have bit 7 stuffing performed. If the T1TCR1.3 and
T1TCR2.0 bits are set to one, then all 24 T1 channels will have bit 7 stuffing performed on them,
regardless of how the SSIEx registers are programmed. In this manner, the SSIEx registers are only
affecting channels that are to have robbed-bit signaling inserted into them.
58 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
10.3 AIS-CI and RAI-CI Generation and Detection
The DS21455/DS21458 can transmit and detect the RAI-CI and AIS-CI codes in T1 mode. These codes
are compatible with and do not interfere with the standard RAI (Yellow) and AIS (Blue) alarms. These
codes are defined in ANSI T1.403.
The AIS-CI code (alarm indication signal-customer installation) is the same for both ESF and D4
operation. Setting the TAIS-CI bit in the T1CCR1 register and the TBL bit in the T1TCR1 register causes
the DS21455/DS21458 to transmit the AIS-CI code. The RAIS-CI status bit in the SR4 register indicates
the reception of an AIS-CI signal.
The RAI-CI (remote alarm indication-customer installation) code for T1 ESF operation is a special form
of the ESF Yellow Alarm (an unscheduled message). Setting the RAIS-CI bit in the T1CCR1 register
causes the DS21455/DS21458 to transmit the RAI-CI code. The RAI-CI code causes a standard Yellow
Alarm to be detected by the receiver. When the host processor detects a Yellow Alarm, it can then test the
alarm for the RAI-CI state by checking the BOC detector for the RAI-CI flag. That flag is a 011111 code
in the 6-bit BOC message.
The RAI-CI code for T1 D4 operation is a 10001011 flag in all 24 time slots. To transmit the RAI-CI
code the host sets all 24 channels to idle with a 10001011 idle code. Since this code meets the
requirements for a standard T1 D4 Yellow Alarm, the host can use the receive channel monitor function
to detect the 100001011 code whenever a standard Yellow Alarm is detected.
59 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
10.4 T1 Receive-Side Digital-Milliwatt Code Generation
Receive-side digital-milliwatt code generation involves using the receive digital-milliwatt registers
(T1RDMR1/2/3) to determine which of the 24 T1 channels of the T1 line going to the backplane should
be overwritten with a digital-milliwatt pattern. The digital-milliwatt code is an 8-byte repeating pattern
that represents a 1kHz sine wave (1E/0B/0B/1E/9E/8B/8B/9E). Each bit in the T1RDMRx registers
represents a particular channel. If a bit is set to a one, then the receive data in that channel will be
replaced with the digital-milliwatt code. If a bit is set to zero, no replacement occurs.
60 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Receive Digital-Milliwatt Enable for Channels 1 to 8 (CH1 to CH8).
0 = do not affect the receive data associated with this channel
1 = replace the receive data associated with this channel with digital-milliwatt code
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Receive Digital Milliwatt Enable for Channels 9 to 16 (CH9 to CH16).
0 = do not affect the receive data associated with this channel
1 = replace the receive data associated with this channel with digital-milliwatt code
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Receive Digital-Milliwatt Enable for Channels 17 to 24 (CH17 to CH24).
0 = do not affect the receive data associated with this channel
1 = replace the receive data associated with this channel with digital-milliwatt code
T1RDMR1
T1 Receive Digital-Milliwatt Enable Register 1
0Ch
T1RDMR2
T1 Receive Digital-Milliwatt Enable Register 2
0Dh
T1RDMR3
T1 Receive Digital-Milliwatt Enable Register 3
0Eh
61 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
10.5 T1 Information Register
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RPDV TPDV COFA 8ZD 16ZD SEFE B8ZS FBE
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Frame Bit Error Event (FBE). Set when a Ft (D4) or FPS (ESF) framing bit is received in error.
Bit 1/B8ZS Codeword Detect Event (B8ZS). Set when a B8ZS codeword is detected at RPOS and RNEG independent of
whether the B8ZS mode is selected or not via T1TCR2.7. Useful for automatically setting the line coding.
Bit 2/Severely Errored Framing Event (SEFE). Set when two out of six framing bits (Ft or FPS) are received in error.
Bit 3/Sixteen Zero Detect Event (16ZD). Set when a string of at least 16 consecutive zeros (regardless of the length of the
string) have been received at RPOSI and RNEGI.
Bit 4/Eight Zero Detect Event (8ZD). Set when a string of at least eight consecutive zeros (regardless of the length of the
string) have been received at RPOSI and RNEGI.
Bit 5/Change of Frame Alignment Event (COFA). Set when the last resync resulted in a change of frame or multiframe
alignment.
Bit 6/Transmit Pulse Density Violation Event (TPDV). Set when the transmit data stream does not meet the ANSI T1.403
requirements for pulse density.
Bit 7/Receive Pulse Density Violation Event (RPDV). Set when the receive data stream does not meet the ANSI T1.403
requirements for pulse density.
INFO1
Information Register 1
10h
62 of 270

Table 10-1. T1 ALARM CRITERIA
ALARM SET CRITERIA CLEAR CRITERIA
Blue Alarm (AIS) (Note 1) Over a 3ms window, five or fewer
zeros are received
Yellow Alarm (RAI)
D4 Bit-2 Mode (T1RCR2.0 = 0)
D4 12th F-bit Mode (T1RCR2.0 = 1;
this mode is also referred to as the
“Japanese Yellow Alarm”)
ESF Mode
Red Alarm (LRCL) (Also referred to
as Loss of Signal)
Note 1:
Note 2:
The definition of blue alarm (or alarm indication signal) is an unframed, all-ones signal. Blue alarm detectors should be able to
operate properly in the presence of a 10E-3 error rate, and they should not falsely trigger on a framed, all-ones signal. The blue
alarm criteria in the DS21455/DS21458 have been set to achieve this performance. It is recommended that the RBL bit be
qualified with the RLOS bit.
ANSI specifications use a different nomenclature than this data sheet does; the following terms are equivalent:
RBL = AIS
RCL = LOS
RLOS = LOF
RYEL = RAI
Bit 2 of 256 consecutive channels
is set to zero for at least 254
occurrences
12th framing bit is set to one for
two consecutive occurrences
16 consecutive patterns of 00FF
appear in the FDL
192 consecutive zeros are
received
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Over a 3ms window, six or more zeros are
received
Bit 2 of 256 consecutive channels is set to
zero for less than 254 occurrences
12th framing bit is set to zero for two
consecutive occurrences
14 or fewer patterns of 00FF hex out of 16
possible appear in the FDL
14 or more ones out of 112 possible bit
positions are received, starting with the
first one received
63 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
11. E1 FRAMER/FORMATTER CONTROL REGISTERS
The E1 framer portion of the DS21455/DS21458 is configured via a set of four control registers.
Typically, the control registers are only accessed when the system is first powered up. Once the device
has been initialized, the control registers will only need to be accessed when there is a change in the
system configuration. There are two receive control registers (E1RCR1 and E1RCR2) and two transmit
control registers (E1TCR1 and E1TCR2). There are also four status and information registers. Each of
these eight registers is described in this section.
11.1 E1 Control Registers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RSERC RSIGM RHDB3 RG802 RCRC4 FRC SYNCE RESYNC
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Resync (RESYNC). When toggled from low to high, a resync is initiated. Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent
resync.
Bit 1/Sync Enable (SYNCE).
0 = auto resync enabled
1 = auto resync disabled
Bit 2/Frame Resync Criteria (FRC).
0 = resync if FAS received in error 3 consecutive times
1 = resync if FAS or bit 2 of non-FAS is received in error three consecutive times
Bit 3/Receive CRC-4 Enable (RCRC4).
0 = CRC-4 disabled
1 = CRC-4 enabled
Bit 4/Receive G.802 Enable (RG802). See the Signaling Operation section for details.
0 = do not force RCHBLK high during bit 1 of time slot 26
1 = force RCHBLK high during bit 1 of time slot 26
Bit 5/Receive HDB3 Enable (RHDB3).
0 = HDB3 disabled
1 = HDB3 enabled
Bit 6/Receive Signaling Mode Select (RSIGM).
0 = CAS signaling mode
1 = CCS signaling mode
Bit 7/RSER Control (RSERC).
0 = allow RSER to output data as received under all conditions
1 = force RSER to one under loss-of-frame alignment conditions
E1RCR1
E1 Receive Control Register 1
33h
64 of 270

Table 11-1. E1 SYNC/RESYNC CRITERIA
FRAME OR
MULTIFRAME
LEVEL
FAS FAS present in frame N
SYNC CRITERIA RESYNC CRITERIA ITU SPEC.
Three consecutive incorrect FAS
and N + 2, and FAS not
present in frame N + 1
received
Alternate: (E1RCR1.2 = 1) The
above criteria is met or three
consecutive incorrect bit 2 of non-
FAS received.
DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
G.706
4.1.1
4.1.2
CRC-4 Two valid MF alignment
words found within 8ms
CAS Valid MF alignment word
found and previous time
915 or more CRC-4 codewords out
of 1000 received in error
Two consecutive MF alignment
words received in error
G.706
4.2 and 4.3.2
G.732 5.2
slot 16 contains code other
than all zeros
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Sa8S Sa7S Sa6S Sa5S Sa4S — — RCLA
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Receive Carrier Loss (RCL) Alternate Criteria (RCLA). Defines the criteria for a Receive Carrier Loss condition
for both the framer and Line Interface (LIU)
0 = RCL declared upon 255 consecutive zeros (125µs)
1 = RCL declared upon 2048 consecutive zeros (1ms)
Bit 1/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Bit 2/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Bit 3/Sa4-Bit Select (Sa4S). Set to one to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa4-bit position; set to zero to force RLCLK low during
Sa4-bit position. See the Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
Bit 4/Sa5-Bit Select (Sa5S). Set to one to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa5-bit position; set to zero to force RLCLK low during
Sa5-bit position. See the Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
Bit 5/Sa6-Bit Select (Sa6S). Set to one to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa6-bit position; set to zero to force RLCLK low during
Sa6-bit position. See the Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
Bit 6/Sa7-Bit Select (Sa7S). Set to one to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa7-bit position; set to zero to force RLCLK low during
Sa7-bit position. See the Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
Bit 7/Sa8-Bit Select (Sa8S). Set to one to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa8-bit position; set to zero to force RLCLK low during
Sa8-bit position. See the Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
E1RCR2
E1 Receive Control Register 2
34h
65 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TFPT T16S TUA1 TSiS TSA1 THDB3 TG802 TCRC4
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Transmit CRC-4 Enable (TCRC4).
0 = CRC-4 disabled
1 = CRC-4 enabled
Bit 1/Transmit G.802 Enable (TG802). See the Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
0 = do not force TCHBLK high during bit 1 of time slot 26
1 = force TCHBLK high during bit 1 of time slot 26
Bit 2/Transmit HDB3 Enable (THDB3).
0 = HDB3 disabled
1 = HDB3 enabled
Bit 3/Transmit Signaling All Ones (TSA1).
0 = normal operation
1 = force time slot 16 in every frame to all ones
Bit 4/Transmit International Bit Select (TSiS).
0 = sample Si bits at TSER pin
1 = source Si bits from TAF and TNAF registers (in this mode, E1TCR1.7 must be set to zero)
Bit 5/Transmit Unframed All Ones (TUA1).
0 = transmit data normally
1 = transmit an unframed all one’s code at TPOSO and TNEGO
E1TCR1
E1 Transmit Control Register 1
35h
Bit 6/Transmit Time Slot 16 Data Select (T16S). See the Transmit Signaling section for details.
0 = time slot 16 determined by the SSIEx registers and the THSCS function in the PCPR register
1 = source time slot 16 from TS1 to TS16 registers
Bit 7/Transmit Time Slot 0 Pass Through (TFPT).
0 = FAS bits/Sa bits/Remote Alarm sourced internally from the TAF and TNAF registers
1 = FAS bits/Sa bits/Remote Alarm sourced from TSER
66 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Sa8S Sa7S Sa6S Sa5S Sa4S AEBE AAIS ARA
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Automatic Remote Alarm Generation (ARA).
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Bit 1/Automatic AIS Generation (AAIS).
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Bit 2/Automatic E-Bit Enable (AEBE).
0 = E-bits not automatically set in the transmit direction
1 = E-bits automatically set in the transmit direction
Bit 3/Sa4-Bit Select (Sa4S). Set to one to source the Sa4 bit from the TLINK pin; set to zero to not source the Sa4 bit. See the
Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
Bit 4/Sa5-Bit Select (Sa5S). Set to one to source the Sa5 bit from the TLINK pin; set to zero to not source the Sa5 bit. See the
Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
Bit 5/Sa6-Bit Select (Sa6S). Set to one to source the Sa6 bit from the TLINK pin; set to zero to not source the Sa6 bit. See the
Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
Bit 6/Sa7-Bit Select (Sa7S). Set to one to source the Sa7 bit from the TLINK pin; set to zero to not source the Sa7 bit. See the
Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
Bit 7/Sa8-Bit Select (Sa8S). Set to one to source the Sa8 bit from the TLINK pin; set to zero to not source the Sa8 bit. See the
Functional Timing Diagrams section for details.
E1TCR2
E1 Transmit Control Register 2
36h
67 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
11.2 Automatic Alarm Generation
The device can be programmed to automatically transmit AIS or remote alarm.
11.2.1 Auto AIS
When automatic AIS generation is enabled (E1TCR2.1 = 1), the device monitors the receive side framer
to determine if any of the following conditions are present: loss of receive frame synchronization, AIS
alarm (all ones) reception, or loss of receive carrier (or signal). If any one (or more) of the above
conditions is present, then the framer will either force an AIS or remote alarm.
11.2.2 Auto RAI
When automatic RAI generation is enabled (E1TCR2.0 = 1), the framer monitors the receive side to
determine if any of the following conditions are present: loss of receive frame synchronization, AIS alarm
(all ones) reception, or loss of receive carrier (or signal) or if CRC-4 multiframe synchronization cannot
be found within 128ms of FAS synchronization (if CRC-4 is enabled). If any one (or more) of the above
conditions is present, then the framer will transmit a RAI alarm. RAI generation conforms to ETS 300
011 specifications and a constant remote alarm will be transmitted if the DS21455/DS21458 cannot find
CRC-4 multiframe synchronization within 400ms as per G.706.
Note: It is an illegal state to have both automatic AIS generation and automatic remote alarm
generation enabled at the same time.
11.2.3 Auto E-Bit
When automatic E-Bit generation is enabled (E1TCR2.2 = 1), and the transmitter is in CRC-4 mode, the
transmitter will automatically set the E-Bit according to the following.
Table 11-2 AUTO E-BIT CONDITIONS
CONDITION
Receive CRC-4 disabled 0
Receive CRC-4 enabled but not synchronized 0
Receive CRC-4 enabled, Synchronized, with CRC Sub Multiframe codeword error 0
Receiver synchronized in CRC-4 mode with no CRC Sub Multiframe codeword errors 1
11.2.4 G.706 CRC-4 Interworking
G.706 Specifies a method to allow automatic interworking between equipment with and without CRC-4
capability. When basic frame alignment is established the device begins searching for the CRC-4
alignment pattern. If after 8ms the CRC-4 alignment is not found, it is assumed that frame alignment was
invalid and the device returns to the basic frame alignment search to establish new frame alignment.
After the new frame alignment is established the device starts a new 8ms search period for CRC-4
alignment. If CRC-4 alignment is found, the device starts CRC-4 performance monitoring and setting of
the transmitted E-bits according to G.706. (See the Auto E-bit section.) If CRC-4 alignment is not
achieved the device continues to return to the basic frame alignment procedure followed by an 8ms
search period for CRC-4. This process continues for 400ms. At the end of this 400ms period, it is
assumed that the far end equipment is non-CRC-4, the search for CRC-4 alignment is terminated and the
E-bits transmitter toward the far end equipment are set continuously = 0. The DS21455/DS21458 provide
a flexible method for implementing this procedure. Once the device is put into the receive CRC-4 mode, a
counter begins to run. The user can access this counter via Information Register 7.
E-BIT
STATE
68 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
11.3 E1 Information Registers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — — — CRCRC FASRC CASRC
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/CAS Resync Criteria Met Event (CASRC). Set when two consecutive CAS MF alignment words are received in error.
(Note: During a CRC resync the FAS synchronizer is brought online to verify the FAS alignment. If during this process a
FAS emulator exists, the FAS synchronizer may temporarily align to the emulator. The FASRC will go active indicating a
search for a valid FAS has been activated.)
Bit 1/FAS Resync Criteria Met Event (FASRC. Set when three consecutive FAS words are received in error.
Bit 2/CRC Resync Criteria Met Event (CRCRC). Set when 915/1000 codewords are received in error.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CSC5 CSC4 CSC3 CSC2 CSC0 FASSA CASSA CRC4SA
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/CRC-4 MF Sync Active (CRC4SA). Set while the synchronizer is searching for the CRC-4 MF alignment word.
Bit 1/CAS MF Sync Active (CASSA). Set while the synchronizer is searching for the CAS MF alignment word.
Bit 2/FAS Sync Active (FASSA). Set while the synchronizer is searching for alignment at the FAS level.
Bit 3 to 7/CRC-4 Sync Counter Bits (CSC0 and CSC2 to CSC4). The CRC-4 sync counter increments each time the 8ms-
CRC-4 multiframe search times out. The counter is cleared when the framer has successfully obtained synchronization at the
CRC-4 level. The counter can also be cleared by disabling the CRC-4 mode (E1RCR1.3 = 0). This counter is useful for
determining the amount of time the framer has been searching for synchronization at the CRC-4 level. ITU G.706 suggests that
if synchronization at the CRC-4 level cannot be obtained within 400ms, then the search should be abandoned and proper action
taken. The CRC-4 sync counter will rollover. CSC0 is the LSB of the 6-bit counter. (Note: The second LSB, CSC1, is not
accessible. CSC1 is omitted to allow resolution to >400ms using 5 bits.)
INFO3
Information Register 3
12h
INFO7
Information Register 7 (Real Time)
30h
69 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Table 11-3. E1 ALARM CRITERIA
ALARM SET CRITERIA CLEAR CRITERIA
An RLOS condition exists on
power-up prior to initial
RLOS
RCL
RRA
synchronization, when a resync
criteria has been met, or when a
manual resync has been initiated
via E1RCR1.0
255 or 2048 consecutive zeros
received as determined by
E1RCR2.0
Bit 3 of non-align frame set to
one for three consecutive
occasions
In 255-bit times, at least 32 ones
are received
Bit 3 of nonalign frame set to
zero for three consecutive
occasions
ITU
SPEC.
G.775/G.962
O.162
2.1.4
RUA1
RDMA
V52LNK
Fewer than three zeros in two
frames (512 bits)
Bit 6 of time slot 16 in frame 0
has been set for two consecutive
multiframes
Two out of three Sa7 bits are
zero
More than two zeros in two
frames (512 bits)
O.162
1.6.1.2
G.965
70 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
12. COMMON CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTERS
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — CRC4R SIE ODM — TCSS1 TCSS0 RLOSF
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Function of the RLOS/LOTC Output (RLOSF).
0 = Receive Loss of Sync (RLOS)
1 = Loss of Transmit Clock (LOTC)
Bit 1/Transmit Clock Source Select Bit 0 (TCSS0).
Bit 2/Transmit Clock Source Select Bit 1 (TCSS1).
TCSS1 TCSS0 TRANSMIT CLOCK SOURCE
0 0 The TCLK pin is always the source of transmit clock.
CCR1
Common Control Register 1
70h
0 1
1 0 Use the scaled signal present at MCLK as the transmit clock. The TCLK pin is ignored.
1 1 Use the signal present at RCLK as the transmit clock. The TCLK pin is ignored.
Bit 3/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Bit 4/Output Data Mode (ODM).
0 = pulses at TPOSO and TNEGO are one full TCLKO period wide
1 = pulses at TPOSO and TNEGO are 1/2 TCLKO period wide
Bit 5/Signaling Integration Enable (SIE).
0 = signaling changes of state reported on any change in selected channels
1 = signaling must be stable for three multiframes for a change of state to be reported
Bit 6/CRC-4 Recalculate (CRC4R) (E1 Only).
0 = transmit CRC-4 generation and insertion operates in normal mode
1 = transmit CRC-4 generation operates according to G.706 Intermediate Path Recalculation method
Bit 7/ Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Switch to the clock present at RCLK when the signal at the TCLK pin fails to transition
after one channel time.
71 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name ID7 ID6 ID5 ID4 ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0
Default 1 0 1 1 X X X X
Bits 0 to 3/Chip Revision Bits (ID0 to ID3). The lower four bits of the IDR are used to display the die revision of the chip.
IDO is the LSB of a decimal code that represents the chip revision.
Bits 4 to 7/Device ID (ID4 to ID7). The upper four bits of the IDR are used to display the device ID.
IDR
Device Identification Register
0Fh
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RYELC RUA1C FRCLC RLOSC RYEL RUA1 FRCL RLOS
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Receive Loss of Sync Condition (RLOS). Set when the device is not synchronized to the received data stream.
Bit 1/Framer Receive Carrier Loss Condition (FRCL). Set when 255 (or 2048 if E1RCR2.0 = 1) E1 mode or 192 T1 mode
consecutive zeros have been detected at RPOSI and RNEGI.
Bit 2/Receive Unframed All Ones (T1, Blue Alarm, E1, AIS) Condition (RUA1). Set when an unframed all ones code is
received at RPOSI and RNEGI.
Bit 3/Receive Yellow Alarm Condition (RYEL) (T1 Only). Set when a yellow alarm is received at RPOSI and RNEGI.
Bit 4/Receive Loss of Sync Clear Event (RLOSC). Set when the framer achieves synchronization; will remain set until read.
Bit 5/Framer Receive Carrier Loss Clear Event (FRCLC). Set when carrier loss condition at RPOSI and RNEGI is no
longer detected.
Bit 6/Receive Unframed All Ones Clear Event (RUA1C). Set when the unframed all ones condition is no longer detected.
Bit 7/Receive Yellow Alarm Clear Event (RYELC) (T1 Only). Set when the yellow alarm condition is no longer detected.
SR2
Status Register 2
18h
72 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RYELC RUA1C FRCLC RLOSC RYEL RUA1 FRCL RLOS
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Receive Loss of Sync Condition (RLOS).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled–interrupts on rising edge only
Bit 1/Framer Receive Carrier Loss Condition (FRCL).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled–interrupts on rising edge only
Bit 2/Receive Unframed All Ones (Blue Alarm) Condition (RUA1).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled–interrupts on rising edge only
Bit 3/Receive Yellow Alarm Condition (RYEL).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled–interrupts on rising edge only
Bit 4/Receive Loss of Sync Clear Event (RLOSC).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 5/Framer Receive Carrier Loss Condition Clear (FRCLC).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 6/Receive Unframed All Ones Condition Clear Event (RUA1C).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 7/Receive Yellow Alarm Clear Event (RYELC).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
IMR2
Interrupt Mask Register 2
19h
73 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LSPARE LDN LUP LOTC LORC V52LNK RDMA RRA
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Receive Remote Alarm Condition (RRA) (E1 Only). Set when a remote alarm is received at RPOSI and RNEGI
Bit 1/Receive Distant MF Alarm Condition (RDMA) (E1 Only). Set when bit 6 of time slot 16 in frame 0 has been set for
two consecutive multiframes. This alarm is not disabled in the CCS signaling mode.
Bit 2/V5.2 Link Detected Condition (V52LNK) (E1 Only). Set on detection of a V5.2 link identification signal. (G.965).
Bit 3/Loss of Receive Clock Condition (LORC). Set when the RCLKI pin has not transitioned for one channel time.
Bit 4/Loss of Transmit Clock Condition (LOTC). Set when the TCLK pin has not transitioned for one channel time. Will
force the LOTC pin high if enabled via CCR1.0.
Bit 5/Loop-Up Code Detected Condition (LUP) (T1 Only). Set when the loop up code as defined in the RUPCD1/2 register
is being received. See the Programmable In-Band Loop Code Generation and Detection section for details.
Bit 6/Loop-Down Code Detected Condition (LDN). (T1 only) Set when the loop down code as defined in the RDNCD1/2
register is being received. See the Programmable In-Band Loop Code Generation and Detection section for details.
Bit 7/Spare Code Detected Condition (LSPARE). (T1 only) Set when the spare code as defined in the RSCD1/2 registers is
being received. See the Programmable In-Band Loop Code Generation and Detection section for details.
SR3
Status Register 3
1Ah
74 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LSPARE LDN LUP LOTC LORC V52LNK RDMA RRA
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Receive Remote Alarm Condition (RRA).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled—interrupts on rising and falling edges
Bit 1/Receive Distant MF Alarm Condition (RDMA).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled—interrupts on rising and falling edges
Bit 2/V5.2 Link Detected Condition (V52LNK).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled—interrupts on rising and falling edges
Bit 3/Loss of Receive Clock Condition (LORC).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled—interrupts on rising and falling edges
Bit 4/Loss of Transmit Clock Condition (LOTC).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled—interrupts on rising and falling edges
Bit 5/Loop-Up Code Detected Condition (LUP).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled—interrupts on rising and falling edges
Bit 6/Loop-Down Code Detected Condition (LDN).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled–interrupts on rising and falling edges
Bit 7/Spare Code Detected Condition (LSPARE).
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled–interrupts on rising and falling edges
IMR3
Interrupt Mask Register 3
1Bh
75 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RAIS-CI RSA1 RSA0 TMF TAF RMF RCMF RAF
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Receive Align Frame Event (RAF) (E1 Only). Set every 250ms at the beginning of align frames. Used to alert the host
that Si and Sa bits are available in the RAF and RNAF registers.
Bit 1/Receive CRC-4 Multiframe Event (RCMF) (E1 Only). Set on CRC-4 multiframe boundaries; will continue to be set
every 2ms on an arbitrary boundary if CRC-4 is disabled.
Bit 2/Receive Multiframe Event (RMF).
E1 Mode: Set every 2ms (regardless if CAS signaling is enabled or not) on receive multiframe boundaries. Used to alert the
host that signaling data is available.
T1 Mode: Set every 1.5ms on D4 MF boundaries or every 3ms on ESF MF boundaries.
Bit 3/Transmit Align Frame Event (TAF) (E1 Only). Set every 250ms at the beginning of align frames. Used to alert the
host that the TAF and TNAF registers need to be updated.
SR4
Status Register 4
1Ch
Bit 4/Transmit Multiframe Event (TMF).
E1 Mode: Set every 2ms (regardless if CRC-4 is enabled) on transmit multiframe boundaries. Used to alert the host that
signaling data needs to be updated.
T1 Mode: Set every 1.5ms on D4 MF boundaries or every 3ms on ESF MF boundaries.
Bit 5/Receive Signaling All Zeros Event (RSA0) (E1 Only). Set when over a full MF time slot 16 contains all zeros.
Bit 6/Receive Signaling All Ones Event (RSA1) (E1 Only). Set when the contents of time slot 16 contains fewer than three
zeros over 16 consecutive frames. This alarm is not disabled in the CCS signaling mode.
Bit 7/Receive AIS-CI Event (RAIS-CI) (T1 Only). Set when the receiver detects the AIS-CI pattern as defined in ANSI
T1.403.
76 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RAIS-CI RSA1 RSA0 TMF TAF RMF RCMF RAF
Default
Bit 0/Receive Align Frame Event (RAF).
Bit 1/Receive CRC-4 Multiframe Event (RCMF).
Bit 2/Receive Multiframe Event (RMF).
Bit 3/Transmit Align Frame Event (TAF).
Bit 4/Transmit Multiframe Event (TMF).
Bit 5/Receive Signaling All-Zeros Event (RSA0).
Bit 6/Receive Signaling All-Ones Event (RSA1).
Bit 7/Receive AIS-CI Event (RAIS-CI)
0
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
IMR4
Interrupt Mask Register 4
1Dh
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
77 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
13. I/O PIN CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RSMS RSMS2 RSMS1 RSIO TSDW TSM TSIO ODF
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Output Data Format (ODF).
0 = bipolar data at TPOSO and TNEGO
1 = NRZ data at TPOSO; TNEGO = 0
Bit 1/TSYNC I/O Select (TSIO).
0 = TSYNC is an input
1 = TSYNC is an output
Bit 2/TSYNC Mode Select (TSM). Selects frame or multiframe mode for the TSYNC pin.
0 = frame mode
1 = multiframe mode
Bit 3/TSYNC Double-Wide (TSDW) (T1 Only). (Note: This bit must be set to zero when IOCR1.2 = 1 or when
IOCR1.1 = 0.)
0 = do not pulse double-wide in signaling frames
1 = do pulse double-wide in signaling frames
Bit 4/RSYNC I/O Select (RSIO). (Note: this bit must be set to zero when ESCR.0 = 0.)
0 = RSYNC is an output
1 = RSYNC is an input (only valid if elastic store enabled)
Bit 5/RSYNC Mode Select 1 (RSMS1). Selects frame or multiframe pulse when RSYNC pin is in output mode. In input
mode (elastic store must be enabled) multiframe mode is only useful when receive signaling re-insertion is enabled.
0 = frame mode
1 = multiframe mode
Bit 6/RSYNC Mode Select 2 (RSMS2).
T1 Mode: RSYNC pin must be programmed in the output frame mode (IOCR1.5 = 0, IOCR1.4 = 0).
0 = do not pulse double-wide in signaling frames
1 = do pulse double-wide in signaling frames
E1 Mode: RSYNC pin must be programmed in the output multiframe mode
(IOCR1.5 = 1, IOCR1.4 = 0).
0 = RSYNC outputs CAS multiframe boundaries
1 = RSYNC outputs CRC-4 multiframe boundaries
Bit 7/RSYNC Multiframe Skip Control (RSMS). Useful in framing format conversions from D4 to ESF. This function is not
available when the receive-side elastic store is enabled. RSYNC must be set to output multiframe pulses (IOCR1.5 = 1 and
IOCR1.4 = 0).
0 = RSYNC will output a pulse at every multiframe
1 = RSYNC will output a pulse at every other multiframe
IOCR1
I/O Configuration Register 1
01h
78 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
IOCR2
I/O Configuration Register 2
02h
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
RCLKINV TCLKINV RSYNCINV TSYNCINV TSSYNCINV H100EN TSCLKM RSCLKM
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/RSYSCLK Mode Select (RSCLKM).
0 = if RSYSCLK is 1.544MHz
1 = if RSYSCLK is 2.048MHz or IBO enabled (See the Interleaved PCM Bus Operation section.)
Bit 1/TSYSCLK Mode Select (TSCLKM).
0 = if TSYSCLK is 1.544MHz
1 = if TSYSCLK is 2.048/4.096/8.192MHz or IBO enabled (See the Interleaved PCM Bus Operation section.)
Bit 2/H.100 SYNC Mode (H100EN).
0 = normal operation
1 = SYNC shift
Bit 3/TSSYNC Invert (TSSYNCINV).
0 = no inversion
1 = invert
Bit 4/TSYNC Invert (TSYNCINV).
0 = no inversion
1 = invert
Bit 5/RSYNC Invert (RSYNCINV).
0 = no inversion
1 = invert
Bit 6/TCLK Invert (TCLKINV).
0 = no inversion
1 = invert
Bit 7/RCLK Invert (RCLKINV).
0 = no inversion
1 = invert
79 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
14. LOOPBACK CONFIGURATIONS
The DS21455/DS21458 have four loopback configurations including Framer, Payload, Local, and
Remote loopback. Figure 14-1 depicts a normal signal flow without any loopbacks enabled.
Payload loopback may be done on a per-channel basis if both the transmit and receive paths are
synchronous (RCLK = TCLK and RSYNC = TSYNC). See Section 14.1.
Figure 14-1. Normal Signal Flow Diagram
RECEIVE
LIU
TRANSMIT
LIU
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LTS — — LIUC LLB RLB PLB FLB
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Framer Loopback (FLB).
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
LBCR
Loopback Control Register
4Ah
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
NORMAL MODE
RECEIVE
FRAMER
TRANSMIT
FRAMER
BACKPLANE
I/F
BACKPLANE
I/F
RECEIVE
LIU
TRANSMIT
LIU
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
FRAMER LOOPBACK
RECEIVE
FRAMER
TRANSMIT
FRAMER
80 of 270
BACKPLANE
I/F
BACKPLANE
I/F

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
This loopback is useful in testing and debugging applications. In FLB, the device will loop data from the transmit side back to
the receive side. When FLB is enabled, the following will occur:
1) T1 Mode: An unframed all ones code will be transmitted at TPOSO and TNEGO.
E1 Mode: Normal data will be transmitted at TPOSO and TNEGO.
2) Data at RPOSI and RNEGI will be ignored.
3) All receive-side signals will take on timing synchronous with TCLK instead of RCLKI.
4) Please note that it is not acceptable to have RCLK tied to TCLK during this loopback because this will cause an unstable
condition.
Bit 1/Payload Loopback (PLB).
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
When PLB is enabled, the following will occur:
1) Data will be transmitted from the TPOSO and TNEGO pins synchronous with RCLK instead of TCLK.
2) All of the receive side signals will continue to operate normally.
3) The TCHCLK and TCHBLK signals are forced low.
4) Data at the TSER, TDATA, and TSIG pins is ignored.
5) The TLCLK signal will become synchronous with RCLK instead of TCLK.
T1 Mode: Normally, this loopback is only enabled when ESF framing is being performed but can be enabled also in D4
framing applications. In a PLB situation, the device will loop the 192 bits of payload data (with BPVs corrected) from the
receive section back to the transmit section. The FPS framing pattern, CRC6 calculation, and the FDL bits are not looped back,
they are reinserted by the device.
E1 Mode: In a PLB situation, the device will loop the 248 bits of payload data (with BPVs corrected) from the receive section
back to the transmit section. The transmit section will modify the payload as if it was input at TSER. The FAS word, Si, Sa
and E bits, and CRC-4 are not looped back, they are reinserted by the device.
Bit 2/Remote Loopback (RLB). In this loopback, data input via the RPOSI and RNEGI pins will be transmitted back to the
TPOSO and TNEGO pins. Data will continue to pass through the receive side framer of the device as it would normally and
the data from the transmit side formatter will be ignored.
RECEIVE
LIU
TRANSMIT
LIU
PAYLOAD LOOPBACK (CAN BE DONE ON A PER-CHANNEL BASIS)
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
RECEIVE
LIU
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
RECEIVE
FRAMER
TRANSMIT
FRAMER
RECEIVE
FRAMER
BACKPLANE
I/F
BACKPLANE
I/F
BACKPLANE
I/F
TRANSMIT
LIU
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
REMOTE LOOPBACK
TRANSMIT
FRAMER
81 of 270
BACKPLANE
I/F

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Bit 3/Local Loopback (LLB). In this loopback, data will continue to be transmitted as normal through the transmit side of the
transceiver. Data being received at RTIP and RRING will be replaced with the data being transmitted. Data in this loopback
will pass through the jitter attenuator.
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
RECEIVE
LIU
TRANSMIT
LIU
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
RECEIVE
FRAMER
TRANSMIT
FRAMER
BACKPLANE
I/F
BACKPLANE
I/F
LOCAL LOOPBACK
Bit 4/Line Interface Unit Mux Control (LIUC). This bit along with the LIUC/TPD pin and LBCR.7 controls the connection
between the LIU and the Framer. See the LTS (LBCR.7) description below. When the LIUC/TPD pin is connected high or
LBCR.7 = 1, the LIUC bit has control. When the LIUC/TPD pin is connected low the framer and LIU are separated and the
LIUC bit has no effect. For the DS21458 this bit should always be set = 0
.
Table 14-1. LIUC CONTROL
LBCR.7
(LTS)
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 x 0
1 x 1
Bit 5/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Bit 6/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Bit 7/LIUC/TPD Pin Function Select (LTS). This bit selects the function the of the LIUC/TPD pin. On the DS21458, this
bit should always be set = 1.
LIUC/TPD
PIN
0 = LIUC/TPD pin functions as the LIUC control (This function is not available on the DS21458
1 = LIUC/TPD pin functions as the TPD control
LBCR.4
(LIUC)
FUNCTION
LIU and Framer Separated
TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins active
(This function not available on the DS21458)
LIU and Framer Separated
TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins active
(This function not available on the DS21458)
LIU and Framer Connected
TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins ignored
(This function not available on the DS21458)
LIU and Framer Separated
TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins active
(This function not available on the DS21458)
LIU and Framer Connected
TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins ignored
LIU and Framer Separated
TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins active
(This function not available on the DS21458)
)
82 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
14.1 Per-Channel Payload Loopback
The per-channel loopback registers (PCLRs) determine which channels (if any) from the backplane
should be replaced with the data from the receive side or in other words, off of the T1 or E1 line. If this
loopback is enabled, then transmit and receive clocks and frame syncs must be synchronized. One method
to accomplish this would be to tie RCLK to TCLK and RFSYNC to TSYNC. There are no restrictions on
which channels can be looped back or on how many channels can be looped back.
Each of the bit position in the PCLRs (PCLR1/PCLR2/PCLR3/PCLR4) represent a DS0 channel in the
outgoing frame. When these bits are set to a one, data from the corresponding receive channel will
replace the data from the TSER pin for that channel.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Per-Channel Loopback Enable for Channels 1 to 8 (CH1 to CH8).
0 = loopback disabled
1 = enable loopback. Source data from the corresponding receive channel
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Per-Channel Loopback Enable for Channels 9 to 16 (CH9 to CH16).
0 = loopback disabled
1 = enable loopback. Source data from the corresponding receive channel
PCLR1
Per-Channel Loopback Enable Register 1
4Bh
PCLR2
Per-Channel Loopback Enable Register 2
4Ch
83 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Per-Channel Loopback Enable for Channels 17 to 24 (CH17 to CH24).
0 = loopback disabled
1 = enable loopback. Source data from the corresponding receive channel
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CH32 CH31 CH30 CH29 CH28 CH27 CH26 CH25
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Per-Channel Loopback Enable for Channels 25 to 32 (CH25 to CH32).
0 = loopback disabled
1 = enable loopback. Source data from the corresponding receive channel
PCLR3
Per-Channel Loopback Enable Register 3
4Dh
PCLR4
Per-Channel Loopback Enable Register 4
4Eh
84 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
15. ERROR COUNT REGISTERS
The DS21455/DS21458 contain four counters that are used to accumulate line coding errors, path errors,
and synchronization errors. Counter update options include one second boundaries, 42ms (T1 mode
only), 62ms (E1 mode only) or manually. See Error Counter Configuration Register (ERCNT). When
updated automatically, the user can use the interrupt from the timer to determine when to read these
registers. All four counters will saturate at their respective maximum counts and they will not rollover
(Note: Only the line-code violation count register has the potential to overflow but the bit error would
have to exceed 10E-2 before this would occur).
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — MECU ECUS EAMS VCRFS FSBE MOSCRF LCVCRF
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/T1 Line Code Violation Count Register Function Select (LCVCRF).
0 = do not count excessive zeros
1 = count excessive zeros
Bit 1/Multiframe Out-of-Sync Count Register Function Select (MOSCRF).
0 = count errors in the framing bit position
1 = count the number of multiframes out of sync
Bit 2/PCVCR Fs-Bit Error Report Enable (FSBE).
0 = do not report bit errors in Fs-bit position; only Ft-bit position
1 = report bit errors in Fs-bit position as well as Ft-bit position
Bit 3/E1 Line Code Violation Count Register Function Select (VCRFS).
0 = count Bipolar Violations (BPVs)
1 = count Code Violations (CVs)
Bit 4/Error Accumulation Mode Select (EAMS).
0 = ERCNT.5 determines accumulation time
1 = ERCNT.6 determines accumulation time
Bit 5/Error Counter Update Select (ECUS).
T1 Mode: 0 = Update error counters once a second
1 = Update error counters every 42ms (333 frames)
E1 Mode: 0 = Update error counters once a second
1 = Update error counters every 62.5ms (500 frames)
Bit 6/Manual Error Counter Update (MECU). When enabled by ERCNT.4, the changing of this bit from a zero to a one
allows the next clock cycle to load the error counter registers with the latest counts and reset the counters. The user must wait a
minimum of 1.5 RCLK clock periods before reading the error count registers to allow for proper update.
Bit 7/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
ERCNT
Error Counter Configuration Register
41h
85 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
15.1 Line Code Violation Count Register (LCVCR)
15.1.1 T1 Operation
T1 code violations are defined as bipolar violations (BPVs) or excessive zeros. If the B8ZS mode is set
for the receive side, then B8ZS codewords are not counted. This counter is always enabled; it is not
disabled during receive loss of synchronization (RLOS = 1) conditions.
Table 15-1. T1 LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNTING OPTIONS
COUNT EXCESSIVE
ZEROS?
(ERCNT.0)
B8ZS ENABLED?
(T1RCR2.5)
WHAT IS COUNTED IN THE LCVCRs
No No BPVs
Yes No BPVs + 16 Consecutive Zeros
No Yes BPVs (B8ZS Codewords Not Counted)
Yes Yes BPVs + 8 Consecutive Zeros
15.1.2 E1 Operation
Either bipolar violations or code violations can be counted. Bipolar violations are defined as consecutive
marks of the same polarity. In this mode, if the HDB3 mode is set for the receive side, then HDB3
codewords are not counted as BPVs. If ERCNT.3 is set, then the LVC counts code violations as defined
in ITU O.161. Code violations are defined as consecutive bipolar violations of the same polarity. In most
applications, the framer should be programmed to count BPVs when receiving AMI code and to count
CVs when receiving HDB3 code. This counter increments at all times and is not disabled by loss of sync
conditions. The counter saturates at 65,535 and will not rollover. The bit error rate on an E1 line would
have to be greater than 10** -2 before the VCR would saturate.
Table 15-2. E1 LINE CODE VIOLATION COUNTING OPTIONS
E1 CODE VIOLATION SELECT
(ERCNT.3)
0 BPVs
1 CVs
WHAT IS COUNTED IN THE
LCVCRs
86 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LCVC15 LCVC14 LCVC13 LCVC12 LCVC11 LCVC10 LCVC9 LCCV8
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Line Code Violation Counter Bits 8 to 15 (LCVC8 to LCVC15). LCV15 is the MSB of the 16-bit code violation
count.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name LCVC7 LCVC6 LCVC5 LCVC4 LCVC3 LCVC2 LCVC1 LCVC0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Line Code Violation Counter Bits 0 to 7 (LCVC0 to LCVC7). LCV0 is the LSB of the 16-bit code violation
count.
LCVCR1
Line Code Violation Count Register 1
42h
LCVCR2
Line Code Violation Count Register 2
43h
87 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
15.2 Path Code Violation Count Register (PCVCR)
15.2.1 T1 Operation
The path code violation count register records either Ft, Fs, or CRC6 errors in T1 frames. When the
receive side of a framer is set to operate in the T1 ESF framing mode, PCVCR will record errors in the
CRC6 codewords. When set to operate in the T1 D4 framing mode, PCVCR will count errors in the Ft
framing bit position. Via the ERCNT.2 bit, a framer can be programmed to also report errors in the Fs
framing bit position. The PCVCR will be disabled during receive loss of synchronization (RLOS = 1)
conditions. See Table 15-3 for a detailed description of exactly what errors the PCVCR counts.
Table 15-3. T1 PATH CODE VIOLATION COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS
FRAMING MODE COUNT Fs ERRORS? WHAT IS COUNTED IN THE PCVCRs
D4 No Errors in the Ft Pattern
D4 Yes Errors in Both the Ft and Fs Patterns
ESF Don’t Care Errors in the CRC6 Codewords
15.2.2 E1 Operation
The PCVCR records CRC-4 errors. Since the maximum CRC-4 count in a one-second period is 1000, this
counter cannot saturate. The counter is disabled during loss of sync at either the FAS or CRC-4 level; it
will continue to count if loss of multiframe sync occurs at the CAS level.
The PCVCR1 is the most significant word and PCVCR2 is the least significant word of a 16-bit counter
that records path violations (PVs).
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name PCVC15 PCVC14 PCVC13 PCVC12 PCVC11 PCVC10 PCVC9 PCVC8
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Path Code Violation Counter Bits 8 to 15 (PCVC8 to PCVC15). PCVC15 is the MSB of the 16-bit path code
violation count.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name PCVC7 PCVC6 PCVC5 PCVC4 PCVC3 PCVC2 PCVC1 PCVC0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Path Code Violation Counter Bits 0 to 7 (PCVC0 to PCVC7). PCVC0 is the LSB of the 16-bit path code
violation count.
PCVCR1
Path Code Violation Count Register 1
44h
PCVCR2
Path Code Violation Count Register 2
45h
88 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
15.3 Frames Out Of Sync Count Register (FOSCR)
15.3.1 T1 Operation
The FOSCR is used to count the number of multiframes that the receive synchronizer is out of sync. This
number is useful in ESF applications needing to measure the parameters loss of frame count (LOFC) and
ESF error events as described in AT&T publication TR54016. When the FOSCR is operated in this
mode, it is not disabled during receive loss of synchronization (RLOS = 1) conditions. The FOSCR has
alternate operating mode whereby it will count either errors in the Ft framing pattern (in the D4 mode) or
errors in the FPS framing pattern (in the ESF mode). When the FOSCR is operated in this mode, it is
disabled during receive loss of synchronization (RLOS = 1) conditions. See Table 15-4 for a detailed
description of what the FOSCR is capable of counting.
Table 15-4. T1 FRAMES OUT OF SYNC COUNTING ARRANGEMENTS
FRAMING MODE
(T1RCR1.3)
COUNT MOS OR F-BIT ERRORS
(ERCNT.1)
WHAT IS COUNTED IN THE
FOSCRs
D4 MOS Number of Multiframes Out of Sync
D4 F-Bit Errors in the Ft Pattern
ESF MOS Number of Multiframes Out of Sync
ESF F-Bit Errors in the FPS Pattern
15.3.2 E1 Operation
The FOSCR counts word errors in the frame alignment signal in time slot 0. This counter is disabled
when RLOS is high. FAS errors will not be counted when the framer is searching for FAS alignment
and/or synchronization at either the CAS or CRC-4 multiframe level. Since the maximum FAS word
error count in a one-second period is 4000, this counter cannot saturate.
The FOSCR1 (FOSCR1) is the most significant word and FOSCR2 is the least significant word of a 16bit counter that records frames out of sync.
89 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name FOS15 FOS14 FOS13 FOS12 FOS11 FOS10 FOS9 FOS8
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Frames Out of Sync Counter Bits 8 to 15 (FOS8 to FOS15). FOS15 is the MSB of the 16-bit frames out of sync
count.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name FOS7 FOS6 FOS5 FOS4 FOS3 FOS2 FOS1 FOS0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Frames Out of Sync Counter Bits 0 to 7 (FOS0 to FOS7). FOS0 is the LSB of the 16-bit frames out of sync
count.
FOSCR1
Frames Out Of Sync Count Register 1
46h
FOSCR2
Frames Out Of Sync Count Register 2
47h
15.4 E-Bit Counter Register (EBCR)
This counter is only available in the E1 mode. EBCR1 (EBCR1) is the most significant word and EBCR2
is the least significant word of a 16-bit counter that records far end block errors (FEBE), as reported in
the first bit of frames 13 and 15 on E1 lines running with CRC-4 multiframe. These count registers will
increment once each time the received E-bit is set to zero. Since the maximum E-bit count in a onesecond period is 1000, this counter cannot saturate. The counter is disabled during loss of sync at either
the FAS or CRC-4 level; it will continue to count if loss of multiframe sync occurs at the CAS level.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EB15 EB14 EB13 EB12 EB11 EB10 EB9 EB8
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/E-Bit Counter Bits 8 to 15 (EB8 to EB15). EB15 is the MSB of the 16-bit E-bit count.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name EB7 EB6 EB5 EB4 EB3 EB2 EB1 EB0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/E-Bit Counter Bits 0 to 7 (EB0 to EB7). EB0 is the LSB of the 16-bit E-bit count.
EBCR1
E-Bit Count Register 1
48h
EBCR2
E-Bit Count Register 2
49h
90 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
16. DS0 MONITORING FUNCTION
The DS21455/DS21458 can monitor one DS0 64kbps channel in the transmit direction and one DS0
channel in the receive direction at the same time. In the transmit direction the user will determine which
channel is to be monitored by properly setting the TCM0 to TCM4 bits in the TDS0SEL register. In the
receive direction, the RCM0 to RCM4 bits in the RDS0SEL register need to be properly set. The DS0
channel pointed to by the TCM0 to TCM4 bits will appear in the transmit DS0 monitor (TDS0M) register
and the DS0 channel pointed to by the RCM0 to RCM4 bits will appear in the receive DS0 (RDS0M)
register. The TCM4 to TCM0 and RCM4 to RCM0 bits should be programmed with the decimal decode
of the appropriate T1 or E1 channel. T1 channels 1 through 24 map to register values 0 through 23. E1
channels 1 through 32 map to register values 0 through 31. For example, if DS0 channel 6 in the transmit
direction and DS0 channel 15 in the receive direction needed to be monitored, then the following values
would be programmed into TDS0SEL and RDS0SEL:
TCM4 = 0 RCM4 = 0
TCM3 = 0 RCM3 = 1
TCM2 = 1 RCM2 = 1
TCM1 = 0 RCM1 = 1
TCM0 = 1 RCM0 = 0
16.1 Transmit DS0 Monitor Registers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — TCM4 TCM3 TCM2 TCM1 TCM0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 4 Transmit Channel Monitor Bits (TCM0 to TCM4). TCM0 is the LSB of a 5-bit channel select that determines
which transmit channel data will appear in the TDS0M register.
Bits 5 to 7/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Transmit DS0 Channel Bits (B1 to B8). Transmit channel data that has been selected by the transmit channel
monitor select register. B8 is the LSB of the DS0 channel (last bit to be transmitted).
TDS0SEL
Transmit Channel Monitor Select
74h
TDS0M
Transmit DS0 Monitor Register
75h
91 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
16.2 Receive DS0 Monitor Registers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — RCM4 RCM3 RCM2 RCM1 RCM0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 4/Receive Channel Monitor Bits (RCM0 to RCM4). RCM0 is the LSB of a 5-bit channel-select that determines
which receive DS0 channel data will appear in the RDS0M register.
Bits 5 to 7/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 7/Receive DS0 Channel Bits (B1 to B8). Receive-channel data that has been selected by the receive-channel
monitor-select register. B8 is the LSB of the DS0 channel (last bit to be received).
RDS0SEL
Receive Channel Monitor Select
76h
RDS0M
Receive DS0 Monitor Register
77h
92 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
17. SIGNALING OPERATION
There are two methods to access receive signaling data and provide transmit signaling data: processorbased (i.e., software-based) or hardware-based. Processor-based refers to access through the transmit and
receive signaling registers, RS1–RS16 and TS1–TS16. Hardware-based refers to the TSIG and RSIG
pins. Both methods can be used simultaneously.
17.1 Receive Signaling
Figure 17-1. Simplified Diagram of Receive Signaling Path
PER-CHANNEL
CONTROL
T1/E1 DATA STREAM
SIGNALING
EXTRACTION
RECEIVE SIGNALING
REGISTERS
CHANGE OF STATE
INDICATION
REGISTERS
ALL
ONES
RE-INSERTION
CONTROL
SIGNALING
BUFFERS
RSER
RSYNC
RSIG
93 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
17.1.1 Processor-Based Receive Signaling
The robbed-bit signaling (T1) or TS16 CAS signaling (E1) is sampled in the receive data stream and
copied into the receive signaling registers, RS1 through RS16. In T1 mode, only RS1 through RS12 are
used. The signaling information in these registers is always updated on multiframe boundaries. This
function is always enabled.
17.1.1.1 Change Of State
In order to avoid constant monitoring of the receive signaling registers, the DS21455/DS21458 can be
programmed to alert the host when any specific channel or channels undergo a change of their signaling
state. RSCSE1 through RSCSE4 for E1 and RSCSE1 through RSCSE3 for T1 are used to select which
channels can cause a change of state indication. The change of state is indicated in Status Register 5
(SR1.5). If signaling integration, CCR1.5, is enabled then the new signaling state must be constant for
three multiframes before a change of state indication is indicated. The user can enable the INT pin to
toggle low upon detection of a change in signaling by setting the IMR1.5 bit. The signaling integration
mode is global and cannot be enabled on a channel-by-channel basis.
The user can identity which channels have undergone a signaling change of state by reading the
RSINFO1 through RSINFO4 registers. The information from this registers will tell the user which RSx
register to read for the new signaling data. All changes are indicated in the RSINFO1–RSINFO4 register
regardless of the RSCSE1–RSCSE4 registers.
17.1.2 Hardware-Based Receive Signaling
In hardware-based signaling the signaling data can be obtained from the RSER pin or the RSIG pin.
RSIG is a signaling PCM-stream output on a channel-by-channel basis from the signaling buffer. The
signaling data, T1 robbed bit or E1 TS16, is still present in the original data stream at RSER. The
signaling buffer provides signaling data to the RSIG pin and also allows signaling data to be reinserted
into the original data stream in a different alignment that is determined by a multiframe signal from the
RSYNC pin. In this mode, the receive elastic store can be enabled or disabled. If the receive elastic store
is enabled, then the backplane clock (RSYSCLK) can be either 1.544MHz or 2.048MHz. In the ESF
framing mode, the ABCD signaling bits are output on RSIG in the lower nibble of each channel. The
RSIG data is updated once a multiframe (3ms) unless a freeze is in effect. In the D4 framing mode, the
AB signaling bits are output twice on RSIG in the lower nibble of each channel. Hence, bits 5 and 6
contain the same data as bits 7 and 8 respectively in each channel. The RSIG data is updated once a
multiframe (1.5ms) unless a freeze is in effect. See the Functional Timing Diagrams for some examples.
17.1.2.1 Receive-Signaling Reinsertion at RSER
In this mode, the user will provide a multiframe sync at the RSYNC pin and the signaling data will be
reinserted based on this alignment. In T1 mode, this results in two copies of the signaling data in the
RSER data stream. The original signaling data based on the Fs/ESF frame positions and the realigned
data based on the user supplied multiframe sync applied at RSYNC. In voice channels this extra copy of
signaling data is of little consequence. Reinsertion can be avoided in data channels since this feature is
activated on a per-channel basis. For reinsertion, the elastic store must be enabled; however, the
backplane clock can be either 1.544MHz or 2.048MHz.
Signaling reinsertion mode is enabled, on a per-channel basis by setting the RSRCS bit high in the PCPR
register. The channels that are to have signaling reinserted are selected by writing to the PCDR1-PCDR3
registers for T1 mode and PCDR1–PCDR4 registers for E1 mode. In E1 mode, the user will generally
select all channels when doing reinsertion.
94 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
17.1.2.2 Force Receive Signaling All Ones
In T1 mode, the user can, on a per-channel basis, force the robbed-bit signaling-bit positions to a one.
This is done by using the per-channel register, which is described in the Special Per-Channel Operation
section. The user sets the BTCS bit in the PCPR register. The channels that are to be forced to one are
selected by writing to the PCDR1–PCDR3 registers.
17.1.2.3 Receive-Signaling Freeze
The signaling data in the four-multiframe signaling buffer will be frozen in a known good state upon
either a loss of synchronization (OOF event), carrier loss, or frame slip. This action meets the
requirements of BellCore TR–TSY–000170 for signaling freezing. To allow this freeze action to occur,
the RFE control bit (SIGCR.4) should be set high. The user can force a freeze by setting the RFF control
bit (SIGCR.3) high. The RSIGF output pin provides a hardware indication that a freeze is in effect. The
four multiframe buffer provides a three-multiframe delay in the signaling bits provided at the RSIG pin
(and at the RSER pin if receive signaling reinsertion is enabled). When freezing is enabled (RFE = 1), the
signaling data will be held in the last known good state until the corrupting error condition subsides.
When the error condition subsides, the signaling data will be held in the old state for at least an additional
9ms (or 4.5ms in D4 framing mode) before being allowed to be updated with new signaling data.
95 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name GRSRE — — RFE RFF RCCS TCCS FRSAO
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0/Force Receive Signaling All Ones (FRSAO). In T1 mode, this bit forces all signaling data at the RSIG and RSER pin to
all ones. This bit has no effect in E1 mode.
0 = normal signaling data at RSIG and RSER
1 = force signaling data at RSIG and RSER to all ones
Bit 1/Transmit Time Slot Control for CAS Signaling (TCCS). Controls the order that signaling is transmitted from the
transmit signaling registers. This bit should be set = 0 in T1 mode.
0 = signaling data is CAS format
1 = signaling data is CCS format
Bit 2/Receive Time Slot Control for CAS Signaling (RCCS). Controls the order that signaling is placed into the receive
signaling registers. This bit should be set = 0 in T1 mode.
0 = signaling data is CAS format
1 = signaling data is CCS format
Bit 3/Receive Force Freeze (RFF). Freezes receive-side signaling at RSIG (and RSER if receive signaling reinsertion is
enabled); will override receive-freeze enable (RFE). See the Receive Signaling Freeze section.
0 = do not force a freeze event
1 = force a freeze event
Bit 4/Receive Freeze Enable (RFE). See the Receive Signaling Freeze section.
0 = no freezing of receive signaling data will occur
1 = allow freezing of receive signaling data at RSIG (and RSER if receive signaling reinsertion is enabled).
Bit 5/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Bit 6/Unused, must be set to zero for proper operation.
Bit 7/Global Receive Signaling Reinsertion Enable (GRSRE). This bit allows the user to reinsert all signaling channels
without programming all channels through the per-channel function.
0 = do not reinsert all signaling
1 = reinsert all signaling
SIGCR
Signaling Control Register
40h
96 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
RS1 to RS12
Receive Signaling Registers (T1 Mode, ESF Format)
60h to 6Bh
(MSB)
(LSB)
CH2-A CH2-B CH2-C CH2-D CH1-A CH1-B CH1-C CH1-D RS1
CH4-A CH4-B CH4-C CH4-D CH3-A CH3-B CH3-C CH3-D RS2
CH6-A CH6-B CH6-C CH6-D CH5-A CH5-B CH5-C CH5-D RS3
CH8-A CH8-B CH8-C CH8-D CH7-A CH7-B CH7-C CH7-D RS4
CH10-A CH10-B CH10-C CH10-D CH9-A CH9-B CH9-C CH9-D RS5
CH12-A CH12-B CH12-C CH12-D CH11-A CH11-B CH11-C CH11-D RS6
CH14-A CH14-B CH14-C CH14-D CH13-A CH13-B CH13-C CH13-D RS7
CH16-A CH16-B CH16-C CH16-D CH15-A CH15-B CH15-C CH15-D RS8
CH18-A CH18-B CH18-C CH18-D CH17-A CH17-B CH17-C CH17-D RS9
CH20-A CH20-B CH20-C CH20-D CH19-A CH19-B CH19-C CH19-D RS10
CH22-A CH22-B CH22-C CH22-D CH21-A CH21-B CH21-C CH21-D RS11
CH24-A CH24-B CH24-C CH24-D CH23-A CH23-B CH23-C CH23-D RS12
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
RS1 to RS12
Receive Signaling Registers (T1 Mode, D4 Format)
60h to 6Bh
(MSB)
CH2-A CH2-B
CH4-A CH4-B
CH6-A CH6-B
CH8-A CH8-B
CH10-A CH10-B
CH12-A CH12-B
CH14-A CH14-B
CH16-A CH16-B
CH18-A CH18-B
CH20-A CH20-B
CH22-A CH22-B
CH24-A CH24-B
Note: In D4 format, TS1–TS12 contain signaling data for two frames. Bold type indicates data for second frame.
CH2-A CH2-B
CH4-A CH4-B
CH6-A CH6-B
CH8-A CH8-B
CH10-A CH10-B
CH12-A CH12-B
CH14-A CH14-B
CH16-A CH16-B
CH18-A CH18-B
CH20-A CH20-B
CH22-A CH22-B
CH24-A CH24-B
CH1-A CH1-B
CH3-A CH3-B
CH5-A CH5-B
CH7-A CH7-B
CH9-A CH9-B
CH11-A CH11-B
CH13-A CH13-B
CH15-A CH15-B
CH17-A CH17-B
CH19-A CH19-B
CH21-A CH21-B
CH23-A CH23-B
CH1-A CH1-B
CH3-A CH3-B
CH5-A CH5-B
CH7-A CH7-B
CH9-A CH9-B
CH11-A CH11-B
CH13-A CH13-B
CH15-A CH15-B
CH17-A CH17-B
CH19-A CH19-B
CH21-A CH21-B
CH23-A CH23-B
(LSB)
RS1
RS2
RS3
RS4
RS5
RS6
RS7
RS8
RS9
RS10
RS11
RS12
97 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
RS1 to RS16
Receive Signaling Registers (E1 Mode, CAS Format)
60h to 6Fh
(MSB)
(LSB)
0 0 0 0 X Y X X RS1
CH2-A CH2-B CH2-C CH2-D CH1-A CH1-B CH1-C CH1-D RS2
CH4-A CH4-B CH4-C CH4-D CH3-A CH3-B CH3-C CH3-D RS3
CH6-A CH6-B CH6-C CH6-D CH5-A CH5-B CH5-C CH5-D RS4
CH8-A CH8-B CH8-C CH8-D CH7-A CH7-B CH7-C CH7-D RS5
CH10-A CH10-B CH10-C CH10-D CH9-A CH9-B CH9-C CH9-D RS6
CH12-A CH12-B CH12-C CH12-D CH11-A CH11-B CH11-C CH11-D RS7
CH14-A CH14-B CH14-C CH14-D CH13-A CH13-B CH13-C CH13-D RS8
CH16-A CH16-B CH16-C CH16-D CH15-A CH15-B CH15-C CH15-D RS9
CH18-A CH18-B CH18-C CH18-D CH17-A CH17-B CH17-C CH17-D RS10
CH20-A CH20-B CH20-C CH20-D CH19-A CH19-B CH19-C CH19-D RS11
CH22-A CH22-B CH22-C CH22-D CH21-A CH21-B CH21-C CH21-D RS12
CH24-A CH24-B CH24-C CH24-D CH23-A CH23-B CH23-C CH23-D RS13
CH26-A CH26-B CH26-C CH26-D CH25-A CH25-B CH25-C CH25-D RS14
CH28-A CH28-B CH28-C CH28-D CH27-A CH27-B CH27-C CH27-D RS15
CH30-A CH30-B CH30-C CH30-D CH29-A CH29-B CH29-C CH29-D RS16
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
RS1 to RS16
Receive Signaling Registers (E1 Mode, CCS Format)
60h to 6Fh
(MSB)
(LSB)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 RS1
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 RS2
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 RS3
25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 RS4
33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 RS5
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 RS6
49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 RS7
57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 RS8
65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 RS9
73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 RS10
81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 RS11
89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 RS12
97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 RS13
105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 RS14
113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 RS15
121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 RS16
98 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
(MSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17
CH30 CH29 CH28 CH27 CH26 CH25
Setting any of the CH1 through CH30 bits in the RSCSE1 through RSCSE4 registers will cause an interrupt when that
channel’s signaling data changes state.
RSCSE1, RSCSE2, RSCSE3, RSCSE4
Receive Signaling Change Of State Interrupt Enable
3Ch, 3Dh, 3Eh, 3Fh
(LSB)
RSCSE1
RSCSE2
RSCSE3
RSCSE4
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
(MSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17
CH30 CH29 CH28 CH27 CH26 CH25
When a channel’s signaling data changes state, the respective bit in registers RSINFO1-4 will be set. If the channel was also
enabled as an interrupt source by setting the appropriate bit in RSCSE1–4, an interrupt is generated. The bit will remain set
until read.
RSINFO1, RSINFO2, RSINFO3, RSINFO4
Receive Signaling Change Of State Information
38h, 39h, 3Ah, 3Bh
(LSB)
RSINFO1
RSINFO2
RSINFO3
RSINFO4
99 of 270

DS21455/DS21458 Quad T1/E1/J1 Transceivers
17.2 Transmit Signaling
Figure 17-2.Simplified Diagram of Transmit Signaling Path
T1/E1 DATA
STREAM
0
1
B7
T1TCR1.4
PER-CHANNEL
CONTROL
SSIE1 - SSIE4
ONLY APPLIES TO T1 MODE
1
0
TRANSMIT
SIGNALING
REGISTERS
PER-CHANNEL
CONTROL
PCPR.3
0
1
SIGNALING
BUFFERS
TSER
TSIG
17.2.1 Processor-Based Transmit Signaling
In processor-based mode, signaling data is loaded into the transmit-signaling registers (TS1–TS16) via
the host interface. On multiframe boundaries, the contents of these registers are loaded into a shift register
for placement in the appropriate bit position in the outgoing data stream. The user can utilize the transmit
multiframe interrupt in status register 4 (SR4.4) to know when to update the signaling bits. The user need
not update any transmit signaling register for which there is no change of state for that register.
Each transmit signaling register contains the robbed-bit signaling (T1) or TS16 CAS signaling (E1) for
two time slots that will be inserted into the outgoing stream if enabled to do so via T1TCR1.4 (T1 Mode)
or E1TCR1.6 (E1 Mode). In T1 mode, only TS1 through TS12 are used.
Signaling data can be sourced from the TS registers on a per-channel basis by utilizing the softwaresignaling insertion-enable registers, SSIE1 through SSIE4.
100 of 270
 Loading...
Loading...