Page 1
Important Information
Copyright
This publication, including all photographs, illustrations and software, is
protected under international copyright laws, with all rights reserved.
Neither this manual, nor any of the material contained herein, may be
reproduced without the express written consent of the manufacturer.
Disclaimer
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The
manufacturer makes no representations or warranties with respect to the
contents hereof and specifically disclaims any implied warranties of
merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Further, the
manufacturer reserves the right to revise this publication and to make
changes from time to time in the content hereof without obligation of the
manufacturer to notify any person of such revision or changes.
Trademark Recognition
Microsoft, MS-DOS and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corp.
MMX, Pentium, Pentium-II, Pentium-III, Celeron are registered
trademarks of Intel Corporation.
VGA, OS/2, PS/2 are registered trademarks of International Business
Machines.
AMD, K5, K6 are registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices Inc.
Cyrix, M1 are registered trademarks of Cyrix Corporation.
Other product names used in this manual are the properties of their
respective owners and are acknowledged.
Version 2.0
Page 2
Safety Compliance
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses,
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. However there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged
to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
q Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
q Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
q Connect the equipment onto an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
q Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Shielded interconnect cables and shielded AC power cable must be
employed with this equipment to insure compliance with the pertinent RF
emission limits governing this device. Changes or modifications not
expressly approved by the system’s manufacturer could void the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
Declaration of Conformity
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject
to the following conditions:
q This device may not cause harmful interference, and
q This device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
Canadian Department of Communications
This class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian
Interference-causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigences du
Réglement sur le matériel brouilieur du Canada.
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction........................................... 1
Welcome ..................................................................1
About the Manual...................................................... 2
Checklist.................................................................. 3
Standard Items -------------------------------------------------------3
Recommendations.................................................... 3
Features................................................................... 4
Chapter 2: Installation............................................. 8
Quick Installation Table .............................................8
Quick Jumper Setting Reference................................ 9
Before You Begin...................................................... 11
Static Electricity------------------------------------------------------11
Choosing a Case-----------------------------------------------------11
How to Set Jumpers ------------------------------------------------12
Preparing the Mainboard ...........................................13
Mainboard Guide-----------------------------------------------------13
I/O Ports Side View -------------------------------------------------15
Check the Jumper Settings --------------------------------------16
Install the Mainboard in the Case ...............................19
Connecting Power, Chassis Fans, Panel,
Auxiliary USB Ports, and Case Open Detect Circuit ---21
Install Other Hardware............................................... 23
Install the Processor ------------------------------------------------23
Installing a Slot1 Processor--------------------------------------25
Installing a Socket-370 Processor----------------------------27
Install the Memory Modules -------------------------------------29
Install a Hard Disk Drive and CD-ROM ---------------------30
Installing a Floppy Diskette Drive------------------------------33
Using the Expansion Slots---------------------------------------34
Add-in Card Options------------------------------------------------36
Install Options and Extension Brackets ---------------------37
Make the External Connections ................................. 42
External Connector Color Coding -----------------------------43
Chapter 3: Setup..................................................... 44
About the Setup Utility............................................... 44
Starting the Setup Utility------------------------------------------44
How to Flash a New BIOS ---------------------------------------46
Page 4
Standard CMOS Features Option............................... 47
Advanced BIOS Features Setup Option...................... 49
Advanced Chipset Features Option............................ 51
Integrated Peripherals Option .................................... 53
Power Management Setup Option.............................. 56
PNP/PCI Configuration Option................................... 59
PCI Health Status Option........................................... 60
Frequency / Voltage Control Option............................ 61
Load Fail-Safe Defaults Option .................................. 62
Load Optimized Defaults Option................................. 62
Set Supervisor and User Passwords .......................... 62
Save And Exit Setup Option....................................... 63
Exit Without Saving Option ........................................63
Chapter 4: Software................................................ 64
About the Software.................................................... 64
Folders for this Mainboard......................................... 64
Running the Support CD-ROM................................... 66
Utility Folder Installation Notes................................... 66
CMI8X38 Folder Installation Notes ............................. 67
Audio Software--------------------------------------------------------67
Modem Driver and Software-------------------------------------68
Intel Folder Installation Notes .....................................68
Mainboard (MS7012D) Installation Notes ....................69
Appendix 1: Quick Jumper Setting Reference ........ 70
Page 5

1
CChhaapptteerr 11:: IInnttrroodduuccttiioon
n
Welcome
Congratulations on purchasing the MS7012D mainboard. The mainboard
includes a Slot1 processor slot and a PPGA (Plastic Pin Grid Array)
Celeron Socket-370 processor socket. This feature means that you
can install the mainboard with a Pentium-iii or Pentium-II cartridge,
the SEPP (Single Edge Processor Package) Celeron cartridge, or
one of the new generation PPGA Celerons.
The MS7012D is a full-sized ATX mainboard that uses 4-layer printed
circuit board and measures 305mm x 243mm. The mainboard features
the new low-cost Intel 810 chipset which includes an accelerated
graphics adapter with digital video output for use by televisions of flatpanel displays. The MS7012D has a slot1 and a socket-370 so that it
can be installed with either a slot1 processor (SEPP Celeron or PentiumII) or a socket-370 processor (PPGA Celeron). The mainboard includes
integrated graphics system, integrated audio system, and integrated
fax/modem. A powerful internet-ready workstation can be developed with
just the addition of processor and memory. Therefore the MS7012D is
the ideal platform for the creation of a powerful value PC.
Page 6
2
This chapter contains the following information:
q About the Manual explains how the information in this manual is
organized
q Checklist comprises a list of the standard and optional components
that are shipped with this mainboard
q Recommendations lists some Do’s and Don’ts from the
manufacturer to help ensure reliability and performance from this
product
q Features highlights the functions and components that make this
one of the best value mainboards on the market
About the Manual
The manual consists of the following chapters:
Introduction
Use the Introduction Chapter to learn about the features of the
mainboard, and the checklist of items that are shipped with the package.
Installation
Use the Installation Chapter to learn how to install the mainboard and
get your system up and running.
Setup
Use the Setup Chapter to configure the mainboard for optimum
performance.
Software
Use the Software Chapter to learn how to use the software drivers and
support programs that are provided with this mainboard.
Page 7

3
Checklist
Compare the contents of your mainboard package with the standard
checklist below. If any item is missing or appears damaged, please
contact the vendor of your mainboard package.
Standard Items
ü
1 x MS7012D Mainboard
ü
1 x Cable/Bracket Pack
Diskette drive ribbon cable
IDE drive ribbon cable
ü
Serial ports extension bracket
ü
This User’s Manual
ü
Software Support CD-ROM Disc
Optional Items
ü
1 x V.90 Fax/modem Card
ü
1 x TV-out extension bracket
Recommendations
This mainboard automatically determines the CPU clock frequency and
system bus frequency for the kind of processor that you install. You may
be able to change these automatic settings by making changes to
jumpers on the mainboard, or changing the settings in the system setup
utility. We strongly recommend that you do not overclock the mainboard
to run processors or other components faster than their rated speed.
Overclocking components can adversely affect the reliability of the
system and introduce errors into your system. Overclocking can
permanently damage the mainboard by generating excess heat in
components that are run beyond the rated limits.
Components on this mainboard can be damaged by discharges of static
electricity. Handle the board carefully holding it by the edges. Don’t flex
or stress the circuit board. Keep the board in its static-proof packing until
you are ready to install it. Follow the static guidelines given at the
beginning of Chapter 2.
Page 8

4
Features
The key features of this mainboard are the wide range of processors that
can be installed, and the high level of integration which includes built-in
audio, video, and communications.
Value-class Processors
Functioning as a platform for a value PC, the MS7012D is ideally suited
for the PPGA (Plastic Pin Grid Array) Celeron processor. The PPGA
Celeron has 32k of internal cache memory, 128K of external cache
memory, and operates over a 66MHz system bus. The PPGA Celeron
ships with clock speeds running from 300 MHz through to 500 MHz. The
PPGA Celeron is the premiere choice for an entry-level PC. For slightly
better performance, the MS7012D can be installed with a slot-1
processor. The SEPP (Single Edge Processor Package) Celeron is the
least expensive Dlot-1 processor. It has 32K of internal cache memory,
128K of external cache memory (except for older versions), and
operates over a 66 MHz system bus. SEPP Celerons ship with clock
speed ranging from 266 MHz through 500 MHz.
For higher-performance business class computing, the slot-1 can be
installed with a Pentium-III or Pentium-II processor cartridge. The
Pentium cartridges have 32K of internal cache memory and 512K of
external cache memory. They operate over a 100 MHz system bus
(except for older versions). The Pentium-II ships with clock speeds
running from 233 MHz through to 450 MHz and the Pentium-III ships
with clock speeds of 450, 500, and 550 MHz
Intel’s 810 Chipset
This board features the 810 chipset from Intel. The 810 chipset is
designed to reduce the cost and improve the multimedia capability of
value PCs. The chipset features an integrated AGP (Accelerated
Graphics Port) graphics controller which is optimized to produce smooth
rendition of 2D and 3D video. Digital video output is supported so that
the system can display on a TV or a flat-panel display with digital video
input. The graphics controller improves performance and reduces cost
by dynamically allocating a segment of active memory as video memory.
The 810 I/O chip (82801 I/O Controller Hub) makes a direct connection
between the graphics system and the IDE controller and the PCI bus. It
uses Accelerated Hub Architecture to effectively double the bandwidth
between these components enabling more life like audio and video. It
includes an integrated Audio-Codec controller (AC97) that lets the
Page 9

5
processor more effectively decode sound generated by the integrated
audio system or the integrated fax/modem. Finally, the P82802 Firmware
Hub allows the system and video BIOS to be stored (eliminating the
need for non-volatile CMOS memory) for faster execution, and provides
a random number generator to enable strong encryption routines.
Inexpensive Memory
The board has two DIMM sockets for the installation of 168-pin, 3.3V
non-buffered DIMM memory modules. The DIMM memory modules must
be installed with SDRAM memory chips. The board supports a memory
bus of 66 MHz or 100 MHz, so you can choose between inexpensive 66
MHz memory modules or high-performance PC-100 memory modules.
Each installed memory module can be populated with 8 MB up to 256
MB of memory, so a maximum total of 512 MB memory can be installed.
The integrated video system uses a shared memory architecture so that
you must reserve some of the installed memory as video memory using
the system BIOS. You must install at least one memory module.
Highly Integrated Design
As well as the Intel 810 chipset, the MS7012D features other highly
integrated silicon chips. The ITE LPC I/O controller handles the
mainboard’s I/O functions. The CMI 8738/PCI C3DX is a two-chip
solution that provides an integrated audio and fax/modem system. The
Chrontel CH7007A is a single chip dedicated to converting digital PC
output to a TV format.
Built-in AGP 3D-Graphics
The Intel 810 chipset includes an integrated AGP controller that is
optimized for smooth 2D and 3D video. The graphics system shares
active memory and does not require dedicated video memory. Video is
delivered through a regular 15-pin connector, or as a low cost alternative
to a monitor, the system can display on a regular TV set by using an
optional TV-out extension bracket with an RCA video jack.
Built-in PCI 3D Sound
The PCI Audio CMI 8738 is a single chip solution for PCI-bus 3D audio.
The chip provides Sound Blaster 16-bit-compatible audio, plus support
for Microsoft’s DirectSound 3D specification and Aureal A3D interface.
The sound ports include jacks for speakers, microphone and stereo in,
and a game/MIDI port. The audio system supports full duplex operation
and drivers are available for WIN 95/98 and WIN NT 4.0. The audio
system can output sound to 4 loudspeakers and also supports SPDIF
24-bit digital sound input and output.
Page 10
6
Built-in V.90 Fax/modem
The PCI C3DX chip is a single chip solution for value PC
communications. The chip supports 56 Kbps transmission using rhe V.90
protocol. The chip is integrated with the built-in audio system to support
voice as well as data transmissions.
Up-to-date Expansion Options
This is a full-sized ATX board with a full set of current technology
expansion slots. The mainboard no longer supports the legacy ISA
(Industry Standard Architecture) 8/16-bit slots. Instead, the board
provides five 32-bit PCI (Peripheral Components Interconnect) slots, with
each slot supporting Ultra DMA 66/33 and bus mastering. In addition, the
board has an AMR slot. The AMR slot lets you install an AMR (Audio
Modem Riser) card. Because the regulations regarding the use of
modems is different from country to country , mainboard manufacturers
can simply install a standard AMR slot which can be used by third-party
Audio Modem Riser cards that have been certified for use in the local
territory.
Integrated I/O
Using the ITE LPC I/O chip and the Intel 810 chipset, the board has a
comprehensive set of integrated I/O ports. The I/O port array features
PS/2 keyboard and mouse ports, a parallel port, two USB ports, one
serial port, a monitor port, a game/MIDI port, and three audio jacks. The
mainboard has connectors for the installation of a second serial port ,
TV-out ports (supplied on optional extension brackets), an infrared port
(for IrDA or ASKIR), a fax/modem card, and two additional USB ports.
The mainboard includes connections for floppy diskette drives and two
PCI IDE channels.
Keyboard Power On Feature
Using the system BIOS setup program, you can configure the system to
turn on using a keyboard typed password. A green keyboard is not
required.
Programmable Firmware
The mainboard includes Award BIOS which allows BIOS setting of CPU
parameters. The fully programmable firmware enhances the system
features and allows users to set power management, CPU and memory
timing, LAN and modem wake-up alarms, and so on. The firmware can
also be used to set parameters for different Celeron processor clock
speeds so that you don’t need to change mainboard jumpers and
switches.
Page 11
7
Suspend to RAM Feature
This mainboard features the suspend to RAM function. In a suspend to
RAM, the system is totally powered down with the exception of the small
current required to refresh the system memory. To resume from a
suspend to RAM, press the power button (or use the hot keys or
password if you have enabled a hot-key or password power on). The
system will resume in just a few seconds, and it will appear in exactly the
same state as it was before it was suspended to RAM.
Page 12
8
CChhaapptteerr 22:: IInnssttaallllaattiioon
n
Quick Installation Table
This chapter explains how to successfully install the mainboard into a
computer case and build a working system. The installation procedure is
as follows:
Quick Jumper
Setting Reference
Before you Begin Provides advice on choosing a case,
Preparing the
Mainboard
Install Other
Hardware
Make the External
Connections
Provides a quick reference for the jumper
settings on this mainboard.
avoiding static electricity damage, and setting
jumpers.
Provides a guide to the mainboard and I/O
port locations, full details on the jumper
settings, and advice on installing the
mainboard in the system case.
Provides guidance on installing essential
hardware: processor, memory, hard disk
drive, CD-ROM, floppy disk drive, and
expansion cards.
Provides advice on using the external I/O
ports to install peripheral devices such as a
keyboard, a monitor, a mouse, a printer,
loudspeakers, and so on.
Page 13
9
Quick Jumper Setting Reference
Disable audio/modem
1
3
JP2
JP1
JP3
JP5
If you are familiar with most of the material in this chapter, you can begin
preparing the mainboard for installation by using this quick reference to
begin the setting the jumpers. A detailed description of the jumper setting
appears later in this chapter.
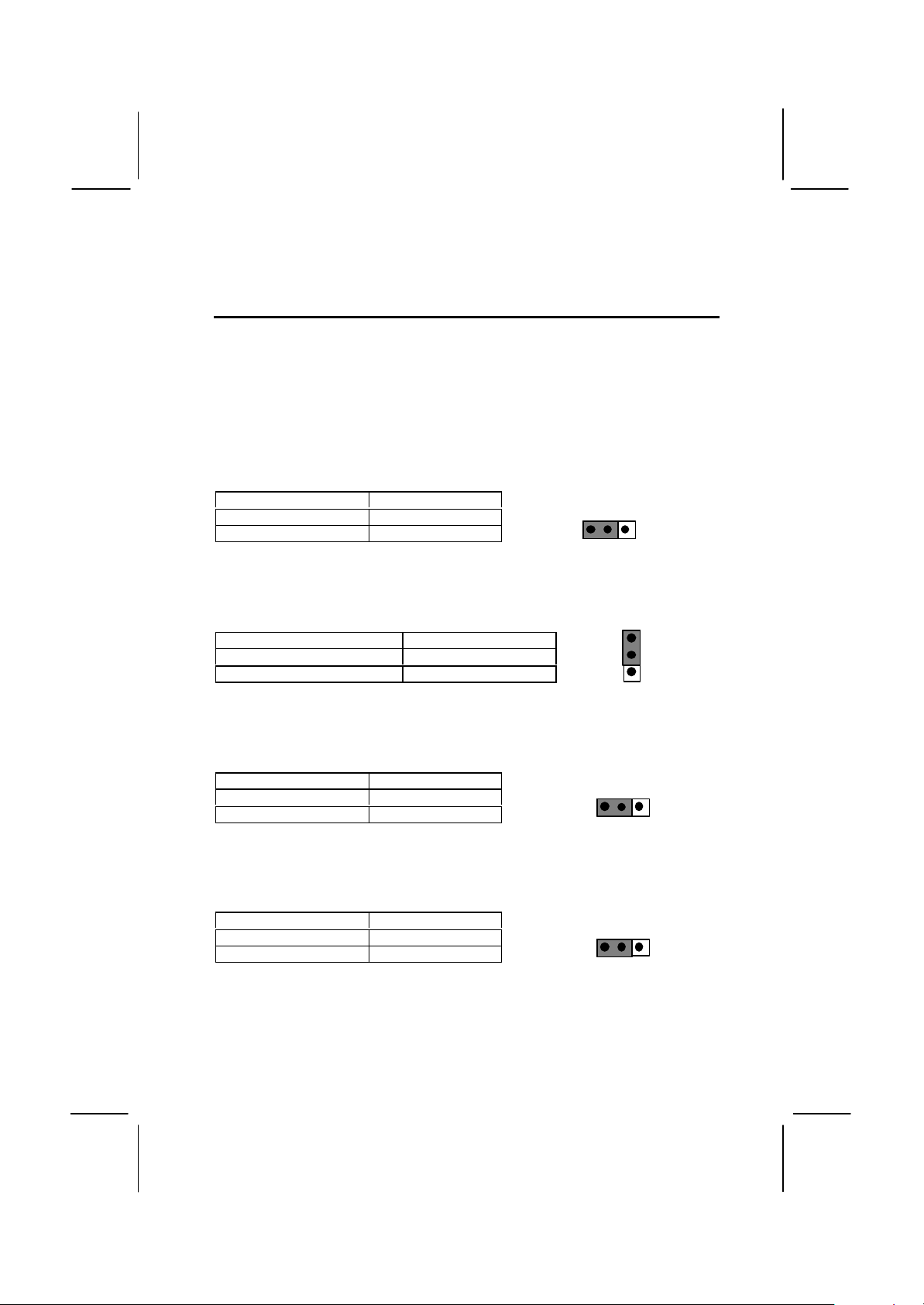
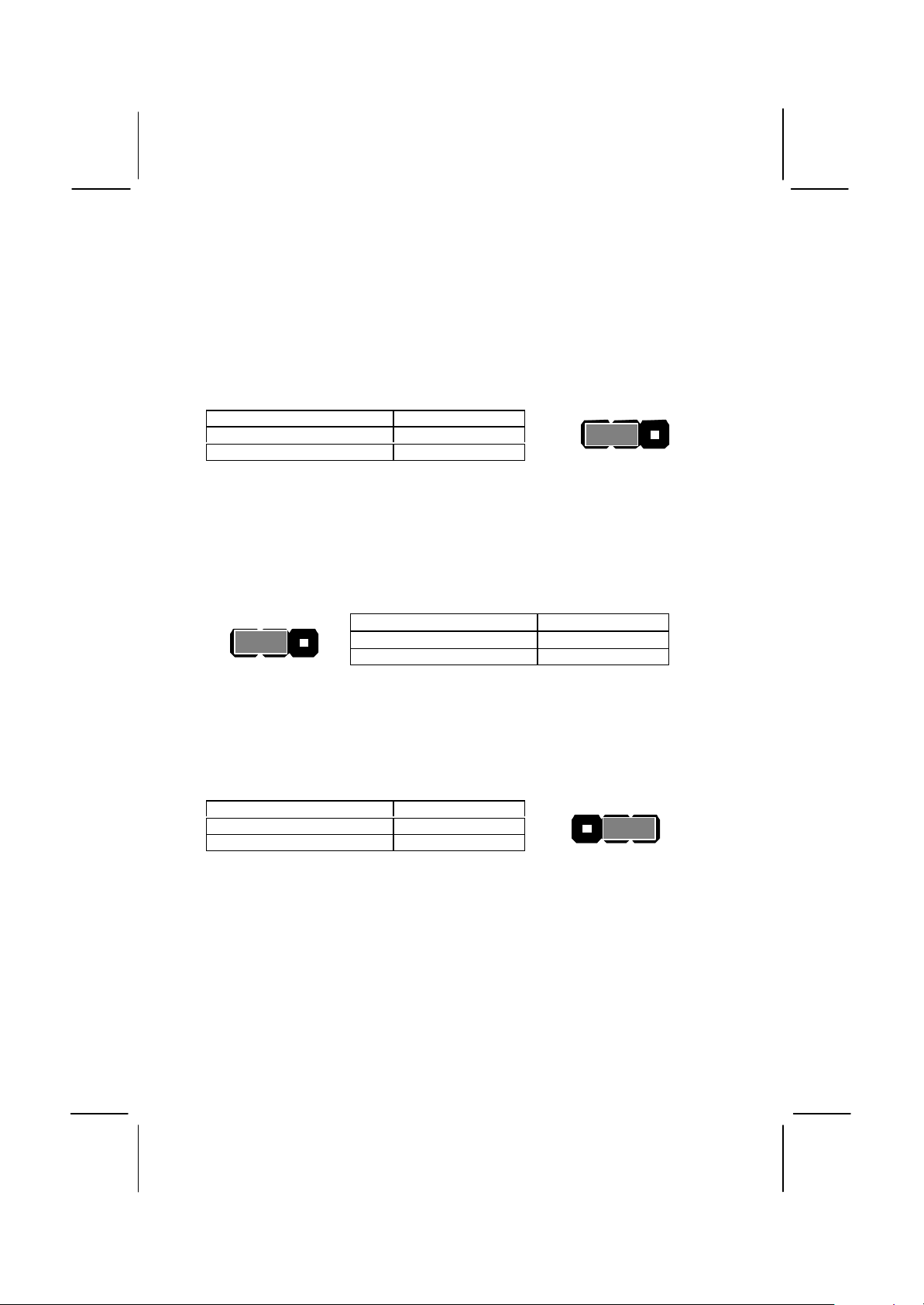
JP1: Clear CMOS memory jumper
Use this 3-pin jumper top clear all the current data stored in the CMOS
memory.
Function Jumper Cap
Normal operation Short pins 1-2
Clear CMOS Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP2: Keyboard power on jumper
Use this 3-pin jumper to enable keyboard power on with hot keys or
password.
Function Jumper Cap
Enable keyboard power on Short pins 1-2
Disable keyboard power on Short pins 2-3
2
JP3: Audio/modem enable/disable jumper
Use this jumper to enable or disable the audio system and modem
integrated on the mainboard.
Function Jumper Cap
Enable audio/modem Short Pins 1-2
Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP5: Set System bus frequency jumper (100 MHz)
Use this jumper to set the system bus frequency at auto-detect, or fixed
at 100 MHz.
Function Jumper Cap
Normal Short Pins 1-2
Force 100 MHz Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
Page 14

10
JP6: Audio codec select jumper
JP6
JP9
JP11
JP12
Use this jumper to select if the system uses the audio codec chip
integrated on the mainboard, or an audio codec chip located on an
optional AMR card.
Function Jumper Cap
Turn on onboard codec Short Pins 1-2
Turn off onboard codec Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP9: Set System bus frequency jumper (133 MHz)
Use this jumper to set the system bus frequency at auto-detect, or fixed
at 133 MHz.
Function Jumper Cap
Normal Short Pins 1-2
Force 133 MHz Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP11: Set TV-out format jumper
Use this jumper to select the format of the TV-out connector.
Function Jumper Cap
Select NTSC format Short Pins 1-2
Select PAL format Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP12: Select IDT or Intel processor jumper
Use this jumper to select if you are installing an Intel processor or an IDT
processor in the socket-370 processor socket.
Function Jumper Cap
IDT processor Short Pins 1-2
Intel processor Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
Page 15

11
Before You Begin
Before you begin to install your MS7012D mainboard, take some
precautions to ensure that you avoid the possibility of damage to the
product from static electricity. Ensure too that you are installing the
mainboard into a suitable case.
Static Electricity
In adverse conditions, static electricity can accumulate and discharge
through the integrated circuits and silicon chips on this product. These
circuits and chips are sensitive and can be permanently damaged by
static discharge.
♦ If possible wear a grounding wrist strap clipped to a safely
grounded device during the installation.
♦ If you don’t have a wrist strap, discharge any static by touching
the metal case of a safely grounded device before beginning the
installation.
♦ Leave all components inside their static-proof bags until they are
required for the installation procedure.
♦ Handle all circuit boards and electronic components carefully.
Hold boards by the edges only. Do not flex or stress circuit
boards.
Choosing a Case
This a full-sized ATX mainboard that measures 305mm x 243mm. It has
5 PCI expansion slots and an AMR slot. The mainboard will fit most ATX
cases that are designed for full-sized ATX mainboards. With a full set of
expansion slots and support for 4 IDE devices, you might like to choose
a case that has a robust power supply unit that delivers at least 250
watts.
Some features on the mainboard are implemented by cabling connectors
on the mainboard to indicators and switches on the system case. Ensure
that your case supports all the features required. The MS7012D
mainboard can support one or two floppy diskette drives and four
enhanced IDE drives. Ensure that your case has sufficient power and
space for all the drives that you intend to install.
Page 16

12
The mainboard has a set of I/O ports on the rear edge. Ensure that your
case has an I/O template that supports the I/O ports and expansion slots.
How to Set Jumpers
A jumper consists of two or more pins mounted on the mainboard. Some
jumpers might be arranged in a series with each pair of pins numbered
differently. Jumpers are used to change the electronic circuits on the
mainboard. When a jumper cap is placed on two jumper pins, the pins
are SHORT. If the jumper cap is removed (or placed on just a single pin)
the pins are OPEN.
OPEN
SHORT
This illustration shows a 3-pin jumper. The jumper cap is
placed on pins 2 and 3, so this jumper setting is SHORT
PINS 2-3.
pin numbers. When you are setting the jumpers, make sure that the
jumper caps are placed on the correct pins to select the function or
feature that you want to enable or disable.
This illustration shows a 2-pin jumper. When the
jumper cap is placed on both pins, the jumper is
SHORT. If you remove the jumper cap, or place the
jumper cap on just one pin, the jumper is OPEN.
This illustration shows the same 3-pin jumper. The jumper
cap is placed on pins 1 and 2, so this jumper setting is
SHORT PINS 1-2.
In this manual, all the jumper illustrations clearly show the
Page 17

13
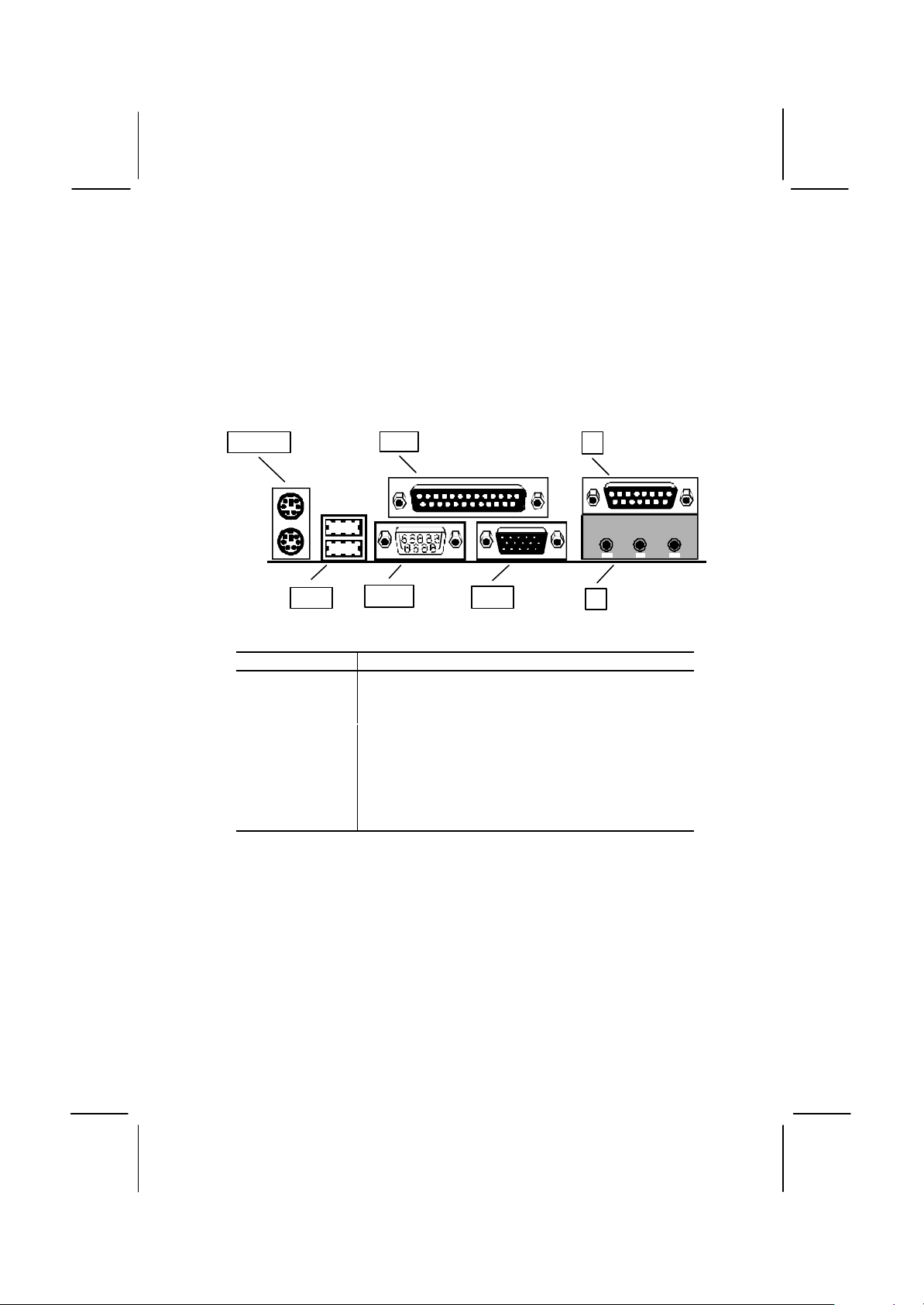
Preparing the Mainboard
JP2
CASFAN1
DIMM1
DIMM2
LED2
PANEL1
WOM1
JP1
AMR Slot
TV1J4J5
Socket-370
PCI2
PCI3
PCI4
PCI5
ATX1
COM2
LED1
J6
JP5J7JP12
JP11
Mainboard Guide
Use the following illustration and key to identify the components on your
mainboard.
JP6
CPUFAN1
PWRFAN1
JP9
FDD1
IDE2
Slot-1
IDE1
PCI1
J8
SPDIF1
SIR1
JP3
WOL1
Page 18
14
Key to Mainboard Components
Socket-370
PCI 1,2,3,4,5
AMR Slot
DIMM 1, 2
FDD1
IDE1, IDE2
ATX1
PANEL1
WOM1
WOL1
SIR1
SPDIF
TV1
COM2
CASFAN1
CPUFAN1
PWRFAN1
J6
J8
J4
J5
J7
JP1
JP2
JP3
JP5
JP6
JP9
JP11
JP12
LED1*
LED2**
Component Description
Slot-1 Slot for Slot-1 processor cartridge
Socket for PPGA Celeron Processor
Five 32-bit PCI Slots
Slot for an Audio Modem Riser card.
Two slots for 168-pin SDRAM memory module
Connector for floppy disk drives
Primary and secondary IDE channels
Connector for ATX power supply
Panel connector for switches and indicators
Connector for modem wake up
Connector for LAN wake up
Connector for infrared port
SPDIF In/out connector (24-bit digital audio interface)
Connector for optional TV-out extension bracket
Connector for serial port 2/4
Power connector for case cooling fan
Power connector for CPU cooling fan
Power connector for power supply cooling fan
Case open detect connector
Onboard modem connector
Audio connector for CD-ROM/DVD drive
Auxiliary audio connector for CD-ROM/DVD drive
Auxiliary USB Ports connector
Clear CMOS memory jumper
Keyboard power on jumper
Audio/modem enable/disable jumper
Set system bus frequency jumper (100 MHz)
Select onboard audio codec or AMR audio codec
Set system bus frequency jumper (133 MHz)
Set TV-out format jumper
Select IDT or Intel processor jumper
Suspend-to-RAM indicator
Suspension Indicator
*LED1
This red indicator turns on if your system is suspended to RAM. In a
suspend to RAM, the system turns off most of the power-consuming
components except for the 3.3V required to refresh the memory. If LED1
is turned on, it warns you that the computer is suspended to RAM and a
refresh current is passing through the memory modules. You should not
attempt to remove or install memory modules when LED1 is turned on.
Page 19
15
**LED2
PS2KBM
USB1
J3
LPT1
J3 (Upper)
J3 (Lower)
VGA1
COM1
This red indicator turns on whenever system is turned on. The LED
warns users not to work on the mainboard, for example adding
expansion cards or changing jumpers, because the system is still active.
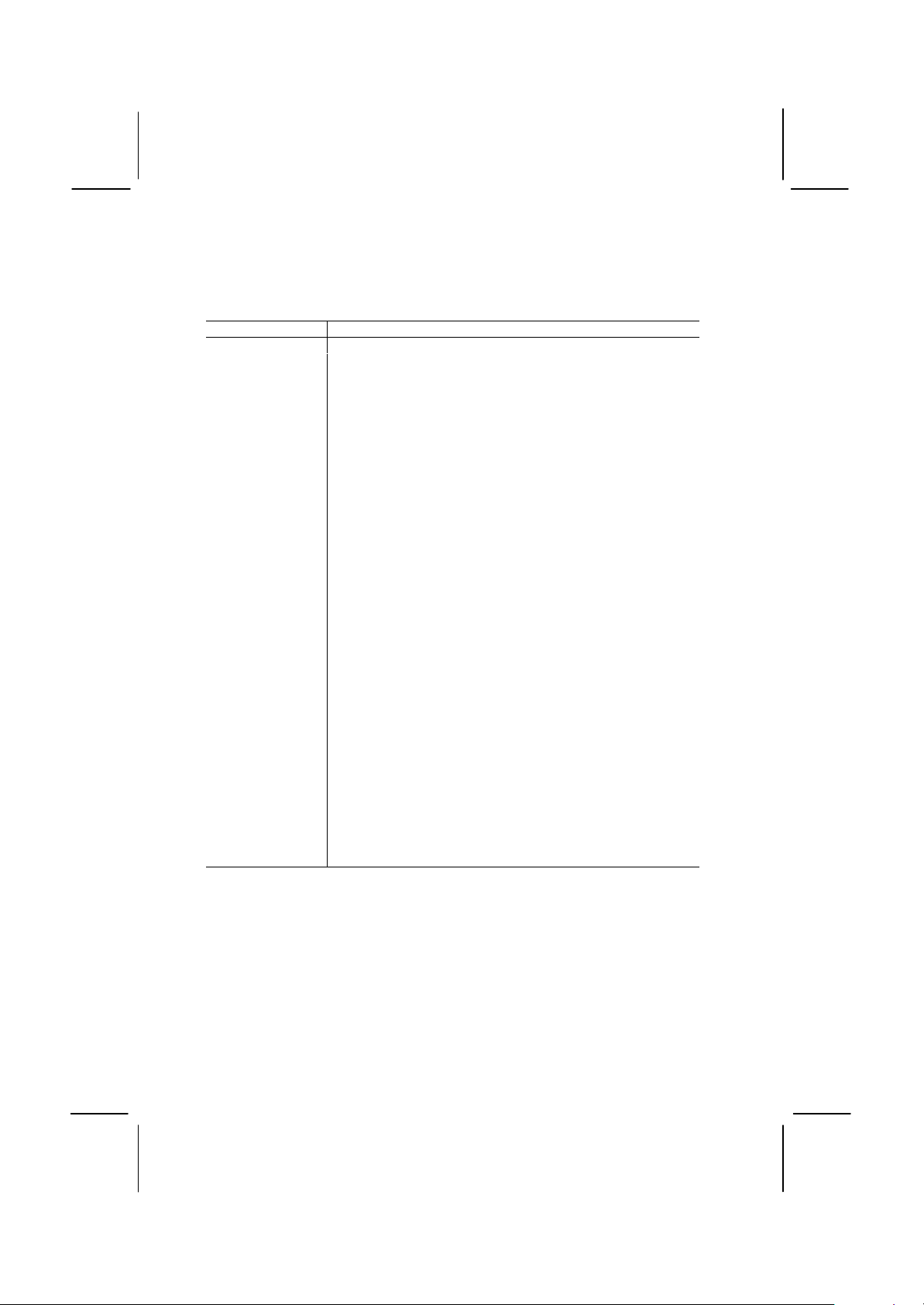
I/O Ports Side View
J3
COM1
Key to I/O Ports
Component Description
PS2KBM PS/2 port for pointing device (upper port)
PS/2 port for keyboard (lower port)
LPT1 External parallel port
External game/MIDI port
Audio jacks for (left to right) line out, line in,
microphone
External monitor port
Serial port COM1/3
USB1 Two stacked Universal Serial Bus ports
VGA1
Page 20
16
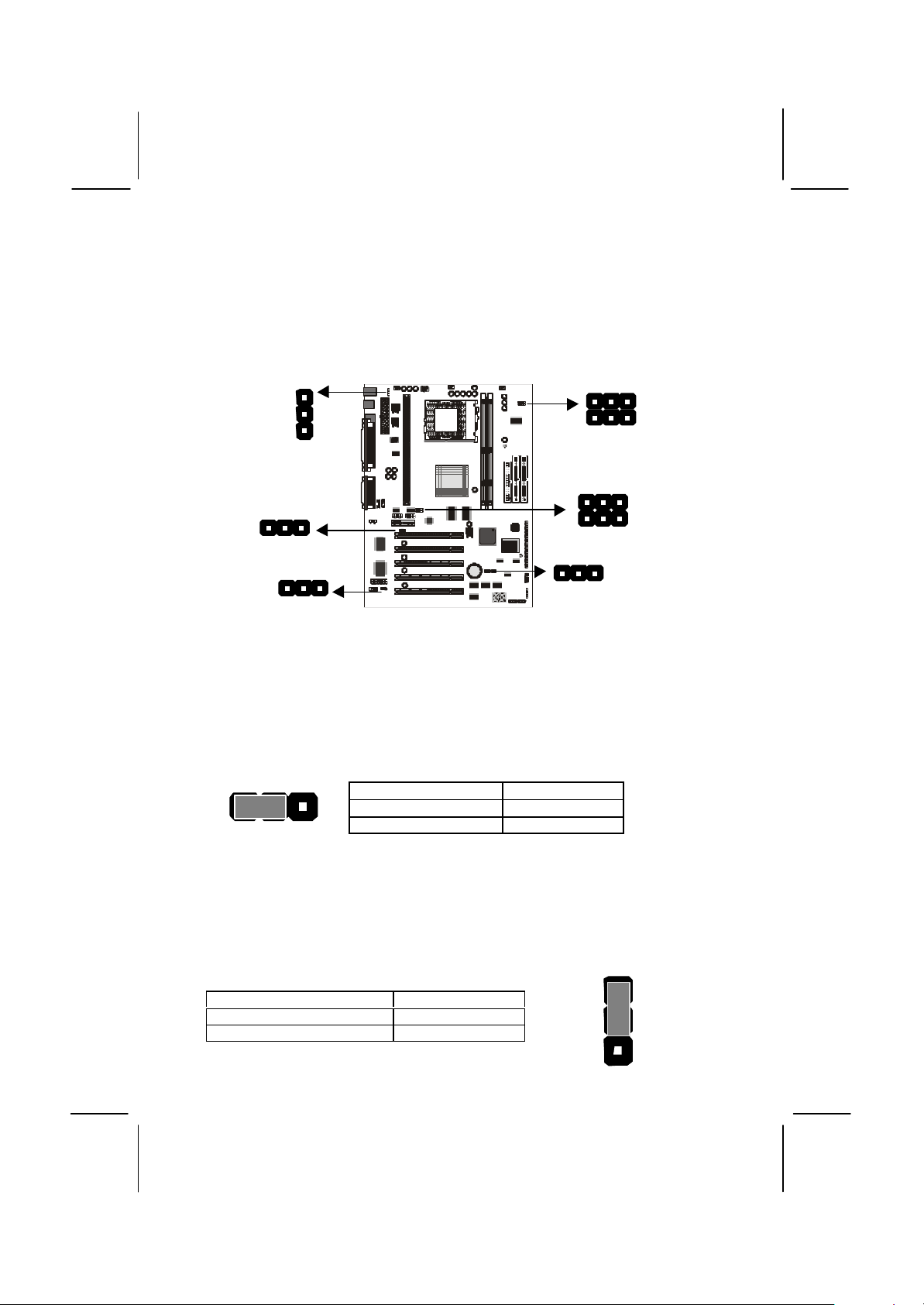
Check the Jumper Settings
Disable keyboard power on
1
JP5
Check all the mainboard jumpers to ensure that the board is configured
correctly.
JP2
JP9
JP12
JP6
JP11
JP3
JP1
JP1 Clear CMOS Memory Jumper
This jumper lets you erase the system setup settings that are stored in
CMOS memory. You might need to erase this data if incorrect settings
are preventing your system from operating. To clear the CMOS memory,
turn off the system, disconnect the power cable from the mainboard, and
short the appropriate pins for a few seconds.
JP1
1 2 3
Function Jumper Cap
Normal Operation Short pins 1-2
Clear CMOS Short pins 2-3
JP2: Keyboard Power On Jumper
This jumper lets you use a typed-in password as a power switch to turn
your system on. If you enable this property, you need to define the
password or the hot keys using the setup utility. See Chapter 3.
Function Jumper Cap
Short pins 1-2
Enable keyboard power on Short pins 2-3
JP2
2
3
Page 21
17
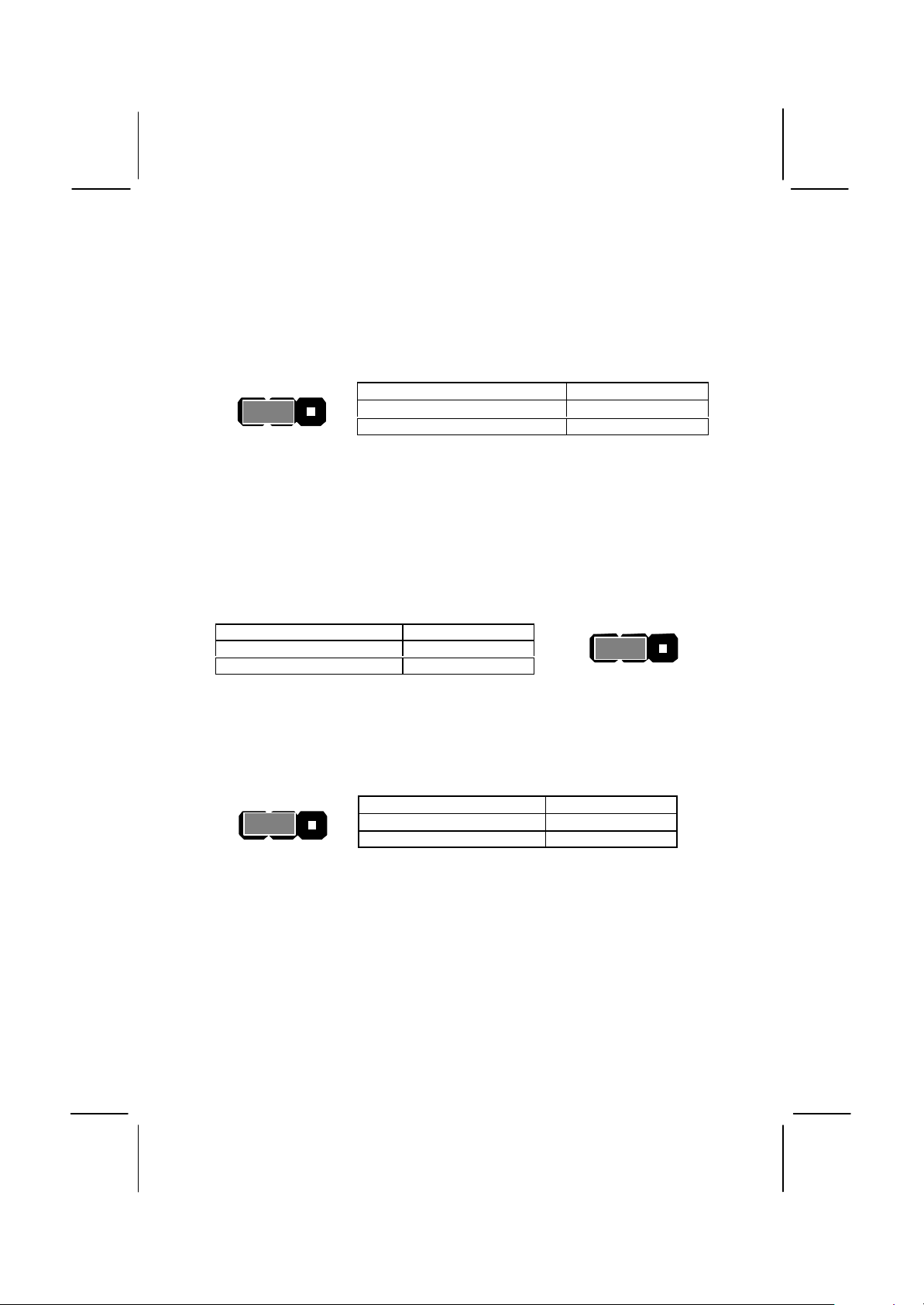
JP3: Audio/Modem System Enable/disable Jumper
This 3-pin jumper can be used to enable or disable the onboard audio
system. If you prefer to install a different audio system on a third party
expansion card, you must disable the onboard audio.
JP3
1 2 3
Function Jumper Cap
Enable audio/modem system Short pins 1-2
Disable audio/modem system Short pins 2-3
JP5: Set System Bus Frequency Jumper (100 MHz)
Use this 3-pin jumper to set the system bus frequency. In the normal
setting, the system automatically selects the correct frequency according
to the kind of processor installed. In the Force 100 MHz setting, the
system uses a 100 MHz system bus even if the processor is designed to
operate with a 66 MHz bus.
Function Jumper Cap
Auto-detect bus frequency Short pins 1-2
Force 100 MHz Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP5
JP6: Select audio codec jumper
Use this 3-pin jumper to select if the system uses the audio codec chip
installed on the mainboard, or an audio codec chip located on an
optional AMR (Audio Modem Riser) card.
JP6
1 2 3
Function Jumper Cap
Turn on onboard codec Short pins 1-2
Turn off onboard codec Short pins 2-3
Page 22
18
JP9: Set System Bus Frequency Jumper (133 MHz)
Use this 3-pin jumper to set the system bus frequency. In the normal
setting, the system automatically selects the correct frequency according
to the kind of processor installed. In the Force 133 MHz setting, the
system uses a 133 MHz system bus even if the processor is designed to
operate with a 100 MHz bus.
Function Jumper Cap
Auto-detect bus frequency Short pins 1-2
Force 133 MHz Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP9
JP11: Set the TV-out Connector Format
Use this 3-pin jumper to select if the TV-out connector TV-1 delivers an
NTSC format TV signal or a PAL format TV signal. You need to install an
optional TV-out extension bracket to use this feature.
JP11
1 2 3
Function Jumper Cap
Select NTSC format Short pins 1-2
Select PAL format Short pins 2-3
JP12: Select an Intel or an IDT Processor Jumper
Use this 3-pin jumper to select if you are going to install the the socket370 with an Intel processor or an IDT processor.
Function Jumper Cap
Select IDT processor Short pins 1-2
Select Intel processor Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP12
Page 23
19
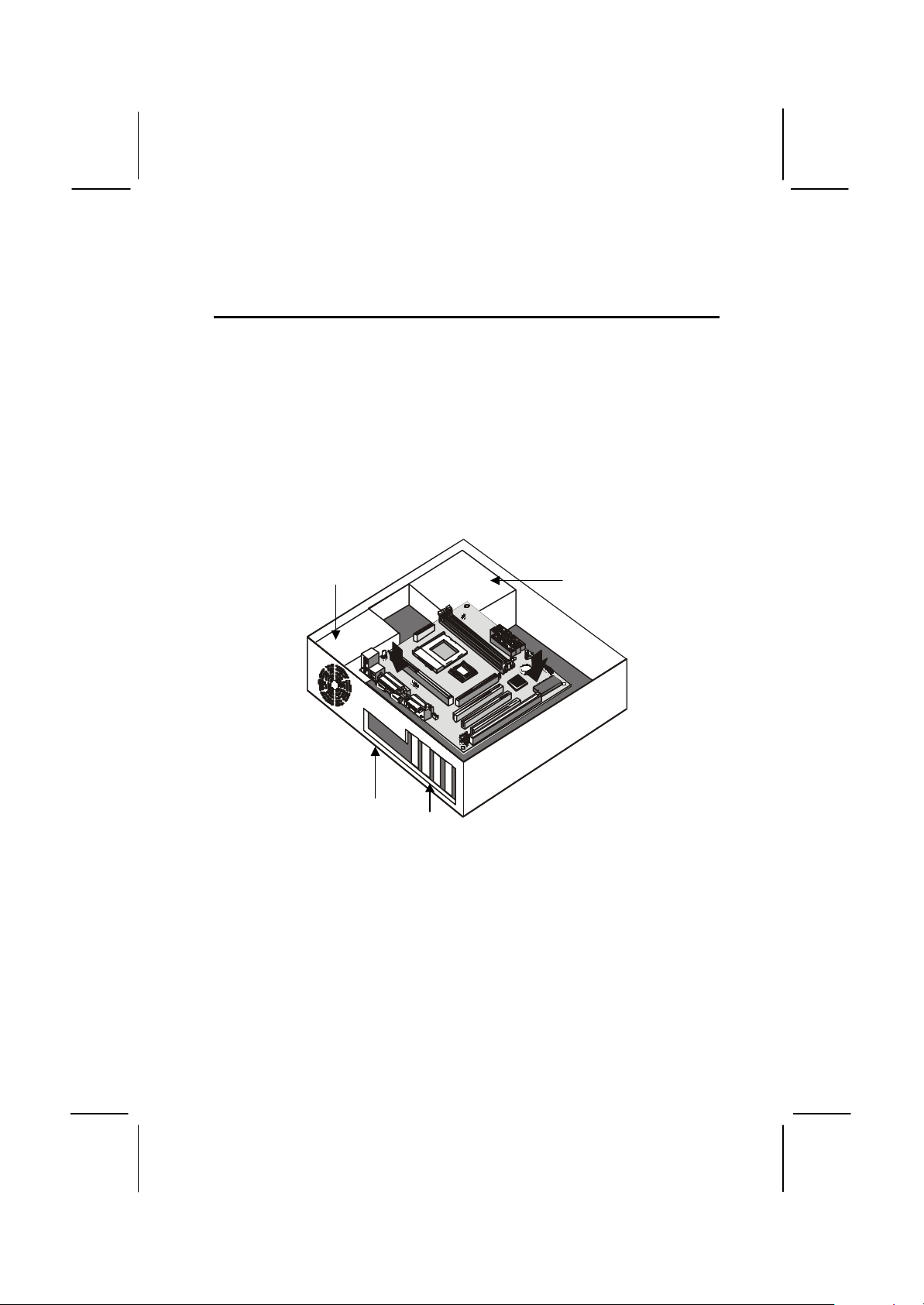
Install the Mainboard in the Case
Slots
The mainboard is drilled with a series of holes. Most system cases have
mounting brackets installed in the case which correspond to the holes in
the mainboard. You can secure the mainboard in the system case by
placing the mainboard over the mounting brackets and driving screws
through the mainboard into the mounting brackets.
Note: Do not overtighten the screws as this can stress the
mainboard.
The illustration below shows a mainboard installing in a standard
desktop case.
Power Supply
Unit
Drive
Cage
I/O
Template
Expansion
Page 24
20
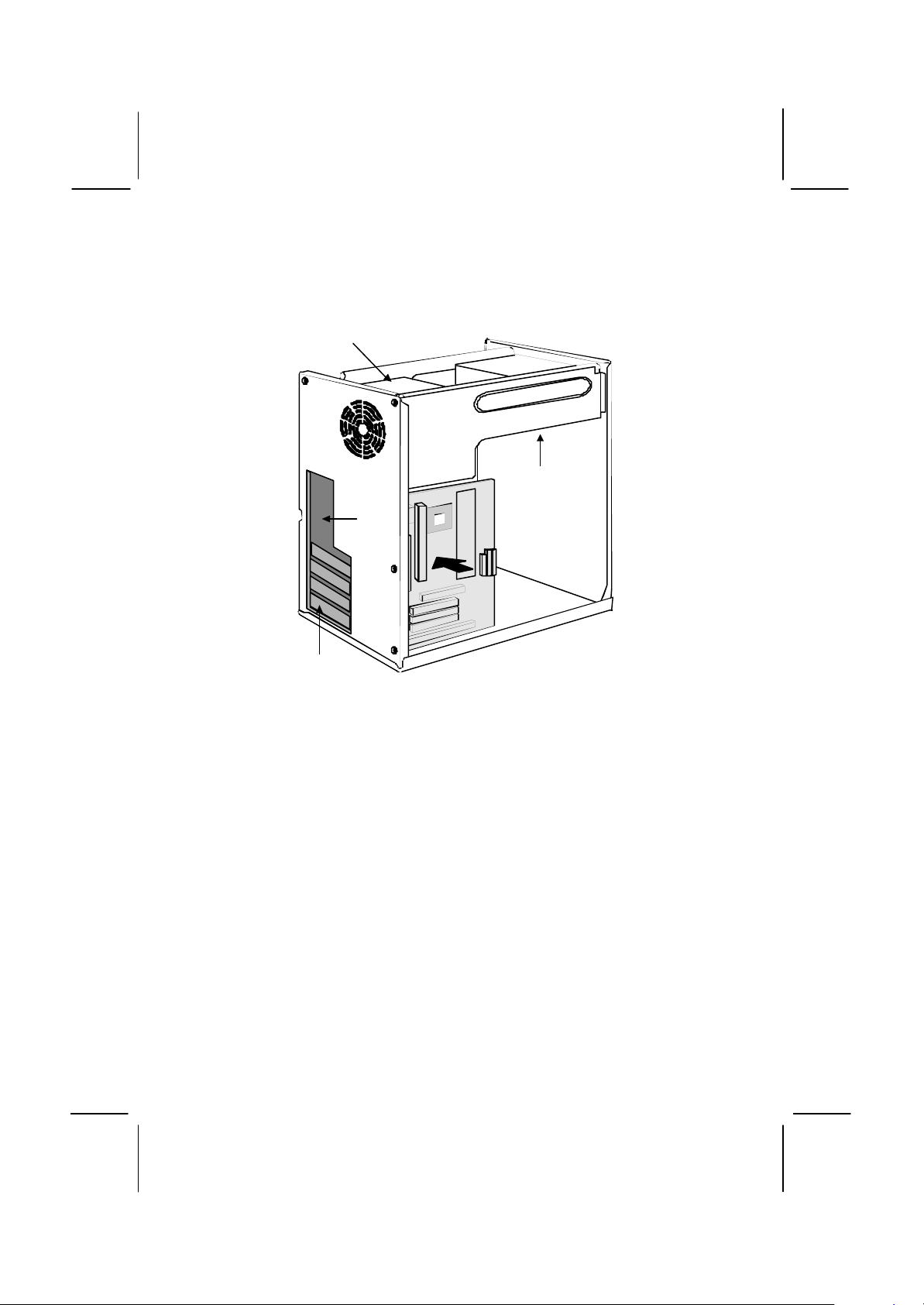
The illustration below shows the mainboard installing into a tower-type
Slots
case.
Power Supply
Unit
Drive
Cage
I/O
Template
Expansion
Page 25
21
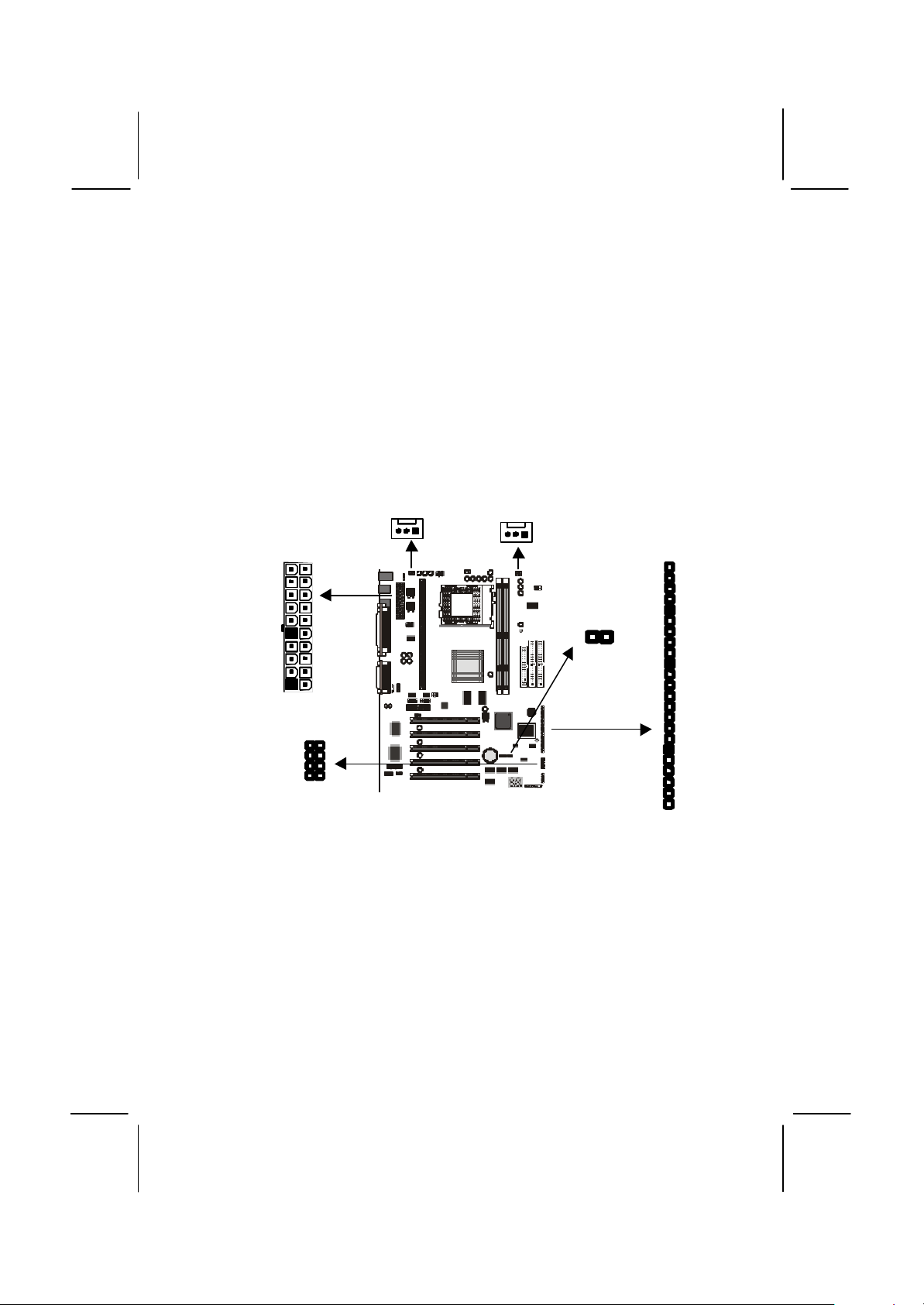
Connecting Power, Chassis Fans, Panel, Auxiliary USB
J7
J6
Ports, and Case Open Detect Circuit
After you have installed the mainboard into the system case, connect the
power cable from the case power supply unit to the mainboard power
connector ATX1. Connect the chassis/power fans (if your case has them)
to the 12V power supply connectors CASFAN1or PWRFAN1 on the
mainboard. Then connect the case switches and indicators to the
PANEL connector on the mainboard. If your case has a case open
detect circuit, you can implement the feature with the connector J6. If
your case has extra USB ports, you can connect them to J7
CASFAN1
ATX1
Power Connector
Locate the power cable from the case power supply unit and plug it into
the ATX1 power connector.
Chassis and Power Fans
If your case has a cooling fan installed in the chassis, plug the cable
from the chassis-mounted fan into the mainboard 12V power supply
connector CASFAN1. If your case has a cooling fan for the power supply
unit, plug the cable into the 12V power supply connector PWRFAN1.
PWRFAN1
PANEL1
Page 26

22
J7: Auxiliary USB Connector
PANEL1
Speaker 15-16-17-18
Power LED 1-2-3
KeyLock 10-11
Reset SW 12-13
Green LED 7-8-9
Power SW 22-23
HDD LED 20-21
Suspend SW 4-5
This mainboard has two built-in USB ports on the rear edge of the board.
Some system cases have built-in USB ports on the chassis that must be
connected to a USB connector on the mainboard. If you have this kind of
system case, connect the cable from the chassis-mounted USB ports to
the J7 connector.
J6: Case Open Detect Circuit
If your case has a case open detect circuit, connect ot to the case open
detect connector J6.
Panel Connector
The mainboard PANEL1 connector has a standard set of switch and
indicator connectors that are commonly found on ATX system cases.
Use the illustration below to make the correct connections to the case
switches and indicators.
23
Function Pins
Power Indicator 1+, 2+, 3
Suspend Switch 4, 5
Green Indicator 7+, 8+, 9
Keylock 10, 11
Reset Switch 12, 13
Speaker 15+, 16, 17, 18
HDD Indicator 20+, 21
Power Switch 22+, 23
1
Page 27

23
Install Other Hardware
Start installing the essential hardware required to get your system
started.
Install the Processor
This mainboard has a Slot1 processor slot and a Socket-370 processor
socket. You can only install one processor however, so you must choose
what kind of processor to run on this. To choose a processor, you need
to consider the performance requirements of the system and also the
price of the processor. Performance is based on the processor design,
the clock speed and system bus frequency of the processor, and the
quantity of internal cache memory and external cache memory. Higher
clock speeds and larger amounts of cache memory deliver greater
performance.
About Slot1 Processors
You can install three kinds of processor into the Slot1: Pentium-III,
Pentium-II, and SEPP Celeron.
Intel Pentium-III
The Pentium-III has the highest performance. This processor is similar to
the Pentium-II but it includes new instructions to improve the throughput
of multimedia data such as 3D audio and video, speech recognition.
MPEG2 motion picture encoding/decoding and TCP/IP internet
connections. However, only recently released software has the capability
of using these improved instructions. The Pentium-III has 32K of internal
cache memory and 512K of external cache memory. Currently PentiumIII processors are available at clock speeds up to 600 MHz and they
operate over a 100 MHz system bus. The Pentium-III is the most
expensive of the processors supported by this mainboard.
Intel Pentium-II
The Pentium– II has a wide range of performance. Pentium-II processors
have shipped with clock speeds of 233 MHz through to 450 MHz.
Currently you might find that stores only stock Pentium- IIs with clock
speeds of 350 MHz and higher. Pentium- IIs with a clock speed of 350
MHz or higher operate over a 100 MHz system bus. Pentium-IIs slower
than 350 MHz operate over a 66 MHz system bus. All Pentium- IIs have
32K of internal cache memory and 512K of external cache memory.
Pentium-IIs are the most powerful, and the most expensive, processors
that you can install on this mainboard.
Page 28

24
Intel SEPP Celeron
SEPP stands for Single Edge Processor Package. The SEPP Celeron is
similar to a Pentium-II except that it only has 128K of external cache
memory. The first generation of SEPP Celerons had no external cache
memory at all and ran at 266 MHz. These Celerons do not ship currently
but are still supported by this mainboard. SEPP Celerons are available
with clock speeds of 266 MHz through to 500 MHz. They all operate over
a 66 MHz system bus. The SEPP Celeron is less expensive than a
Pentium-II with the same clock speed.
About Socket-370 Processors
The socket-370 only supports the Intel PPGA Celeron processor.
Intel PPGA Celeron
PPGA stands for Plastic Pin Grid Array. This is a description of the
square plastic package that the processor is embedded in. The PPGA
Celeron is identical to the SEPP Celeron, except for the external
packaging. PPGA Celerons run at clock speeds from 300 MHz through
to 500 MHz. All the current PPGA Celerons operate over a 66 MHz
system bus. The PPGA Celeron is less expensive than a SEPP Celeron
with the same clock speed.
Page 29

25
Installing a Slot1 Processor
holder
This board has a SLOT1 processor cartridge slot. The slot must be
installed with a cartridge holder that supports the processor cartridge.
The cartridge holder may be already installed on your mainboard with
the support brackets folded over. In this case simply pull the support
brackets into the upright position.
Cartridge
Slot1
Folded down
cartridge holder
If the cartridge holder is not already installed, install it onto the slot1.
Some cartridge holders are in two parts, one part for each end of the
slot1. Other cartridge holders are a single assembly that sits over the
whole length of the slot1.
Some cartridge holders are secured in place with screws. If you have
this kind of cartridge holder, don’t overtighten the screws as this can
stress the mainboard. Some cartridge holders are secured in place with
plastic pins. In this case, place the mainboard on a foam plastic mat
when you push the pins into place.
Some cartridge holders also include a support bar for the processor heat
sink. This bar installs to the side of the cartridge holder. Some processor
cartridges have support struts for the heat sink which lock into the
support bar. The documentation supplied with the processor shows how
to do this.
Page 30

26
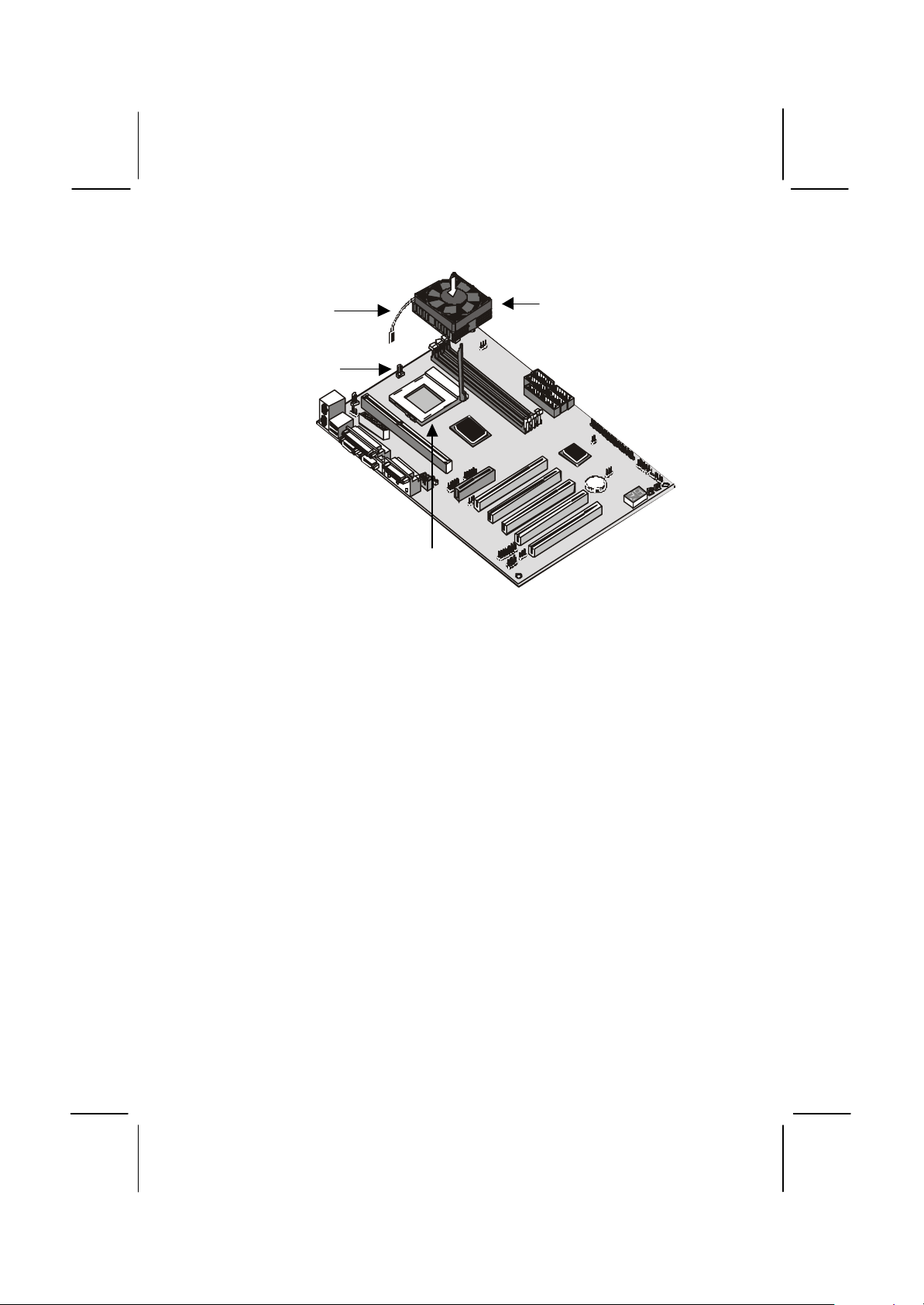
Install the Processor Cartridge
After you have installed the cartridge holder, follow the instructions
supplied with the processor cartridge to insert the cartridge into the
holder. If the processor has a cooling fan, connect the power cable of the
fan to the power supply connector on the mainboard CPUFAN1.
The mainboard must be configured to deliver the correct clock speed
and the correct system bus for the kind of processor that you have
installed. You can do this by using the system setup utility. The first time
you start the system, immediately enter the setup system and make the
appropriate settings. Usually, you can automatically configure the CPU
by using the BIOS Features page of the setup utility. See Chapter 3 for
more information.
Page 31

27
Installing a Socket-370 Processor
If you have decided to install the mainboard with a PPGA Celeron
processor, follow the steps below.
Locate the Socket-370 and CPUFAN1
CPUFAN1
Socket-370
Pin-1 corner
Locking lever
1. On the mainboard, locate the socket-370 and CPUFAN1.
2. On the socket-370, pull the locking lever away from the socket to
unhook it and then raise the locking lever to the upright position.
3. Identify the pin-1 corner on the socket-370 and the pin-1 corner on
the processor. The socket pin-1 corner is adjacent to the handle of
the locking lever. The processor pin-1 corner is beveled.
4. Matching the pin-1 corners, drop the processor into the socket. No
force is required and the processor should seat into the socket easily.
5. Swing the locking lever down and hook it under the latch on the
edge of the socket. This locks the processor in place.
6. Locate the power cable on the heatsink/cooling fan assembly that is
attached to the top of the processor.
7. Plug the power cable into the CPUFAN1 12V power supply on the
mainboard.
Page 32
28
Cooling fan
power cable
CPUFAN1 cooling
fan power supply
Socket-370 with
locking lever in
upright position
Socket-370 processor
with heatsink/cooling
fan assembly
The mainboard must be configured to deliver the correct clock speed
and the correct system bus for the kind of processor that you have
installed. You can do this by using the system setup utility. The first time
you start the system, immediately enter the setup system and make the
appropriate settings. Usually, you can automatically configure the CPU
by using the CPU & BIOS Features page of the setup utility. See
Chapter 3 for more information.
Page 33
29
Install the Memory Modules
For this mainboard, you must use 168-pin 3.3V non-buffered Dual In-line
Memory Modules (DIMMs). The memory chips must be standard or
registered SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory).
The memory bus can run at 66 MHz, 100 MHz or 133 MHz. If your
processor operates over a 100 MHz system bus, install PC100 or PC133 memory that operates over a 100 MHz or 133 MHz bus. If you install
a processor that operates over a 66 MHz bus, you can install memory
chips that operate at 66 MHz.
You must install at least one memory module. You can install the
memory module in either DIMM1 or DIMM2. Each module may be
installed with up to 256 MB of memory so the maximum capacity is 512
MB. The mainboard supports memory chips that have EC (Error
Correction) or ECC (Error Correction Code).
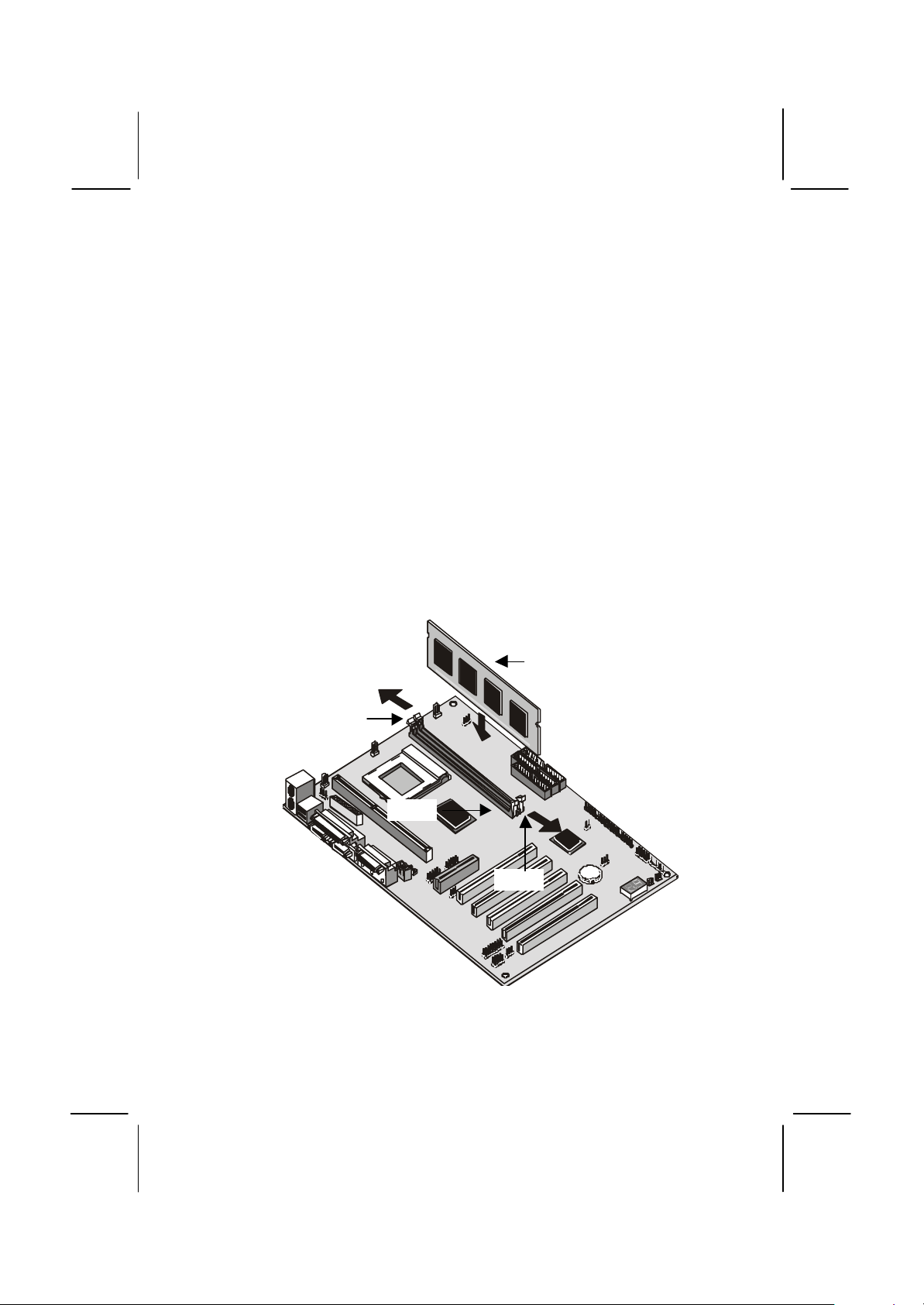
1. Locate the DIMM slots on the mainboard.
Memory module
Locking latches
DIMM1
DIMM2
Page 34
30
2. The DIMM slots are keyed with notches and the DIMMs are keyed
with cut-outs so that they can only be installed correctly. Check that
the cut-outs on the DIMM module edge connector match the notches
in the DIMM slot.
3. Push the latches on each side of the DIMM slot down.
4. Install the DIMM module into the slot and press it carefully but firmly
down so that it seats correctly. The latches at either side of the slot
will be levered upwards and latch on to the edges of the DIMM when
it is installed correctly.
Install a Hard Disk Drive and CD-ROM
This section describes how to install IDE devices such as a hard disk
drive and a CD-ROM drive.
Note: Ribbon cable connectors are usually keyed so that they can
only be installed correctly on the device connector. If the
connector is not keyed make sure that you match the pin-1 side of
the cable connector with the pin-1 side of the device connector.
Each connector has the pin-1 side clearly marked. The pin-1 side
of each ribbon cable is always marked with a colored stripe on the
cable.
About IDE Devices.
Your mainboard has a primary IDE channel interface (IDE1) and a
secondary IDE interface (IDE2). The mainboard ships with one IDE
ribbon cable which supports one or two IDE devices. All IDE devices
have jumpers or switches that can be used to set the IDE device as
MASTER or SLAVE.
If you install two IDE devices on one cable, you must make sure that one
device is set to MASTER and the other device is set to SLAVE. The
documentation of your IDE device explains how to do this.
If you want to install more than two IDE devices, obtain a second IDE
cable and you can add two more devices to the secondary IDE channel.
If there are two devices on the cable, make one MASTER and one
SLAVE.
About UDMA
This board supports UltraDMA 33/66. UDMA is a technology that speeds
the performance of devices in the IDE channel. We recommend that you
install IDE devices that support UDMA, and use IDE cables that support
UDMA.
Page 35
31
Installing a Hard Disk Drive
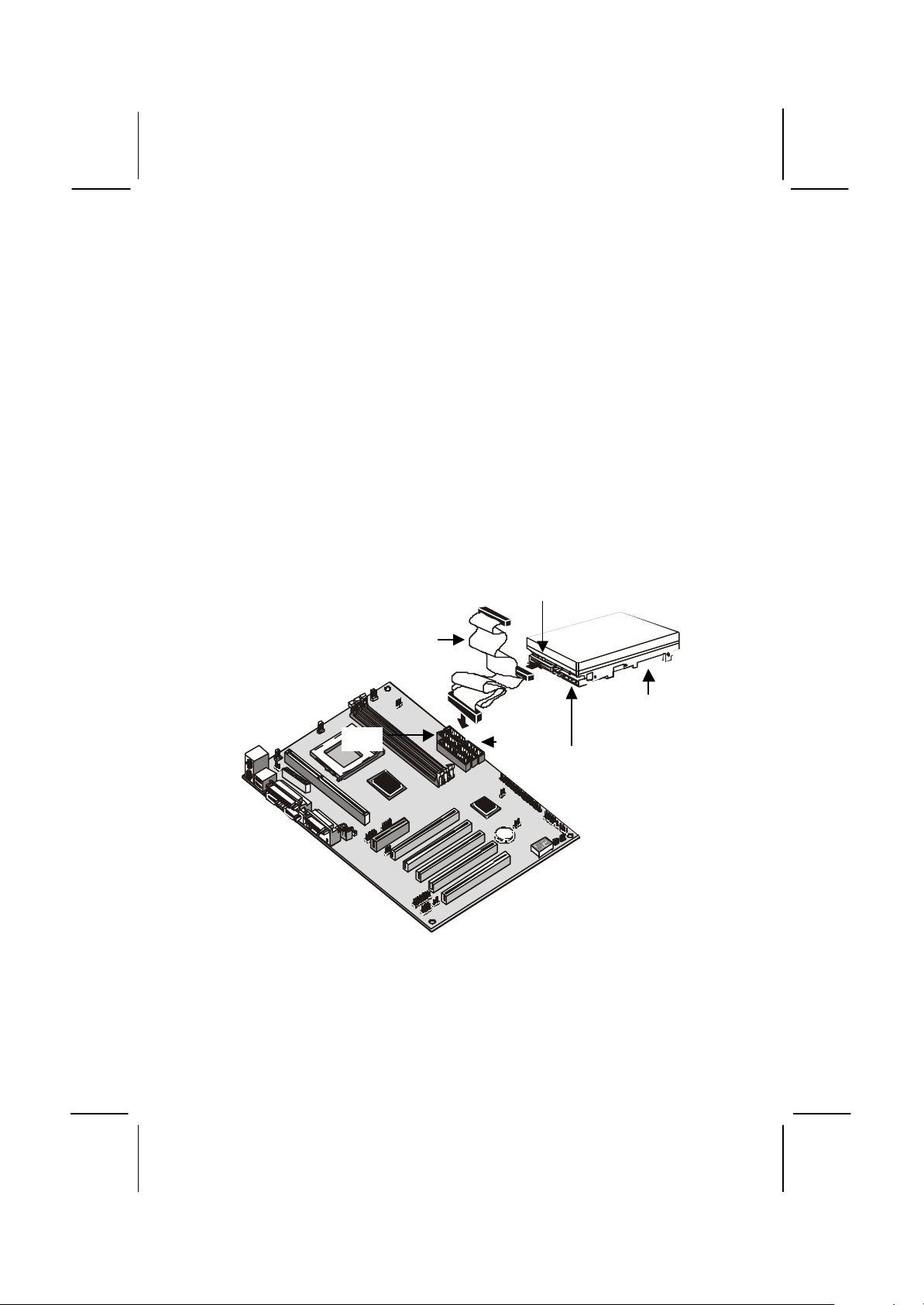
1. Install the hard disk drive into the drive cage in your system case.
2. Plug the IDE cable into the primary IDE channel on the mainboard
IDE1.
3. Plug one of the connectors on the IDE cable into the IDE connector
on the back edge of the hard disk drive. It doesn’t matter which
connector on the cable that you use. Make sure that you have the
pin-1 side of the cable matched with the pin-1 side of the connector.
4. Plug a power cable from the case power supply unit into the power
connector on the back edge of the hard disk drive.
5. When you first start up your system, go immediately to the setup
utility and use the IDE Hard Disk Auto Detect feature to configure the
IDE devices that you have installed. See Chapter 3 for more
information.
IDE connector
IDE ribbon cable
Hard disk drive
IDE2
IDE1
Power connector
Page 36
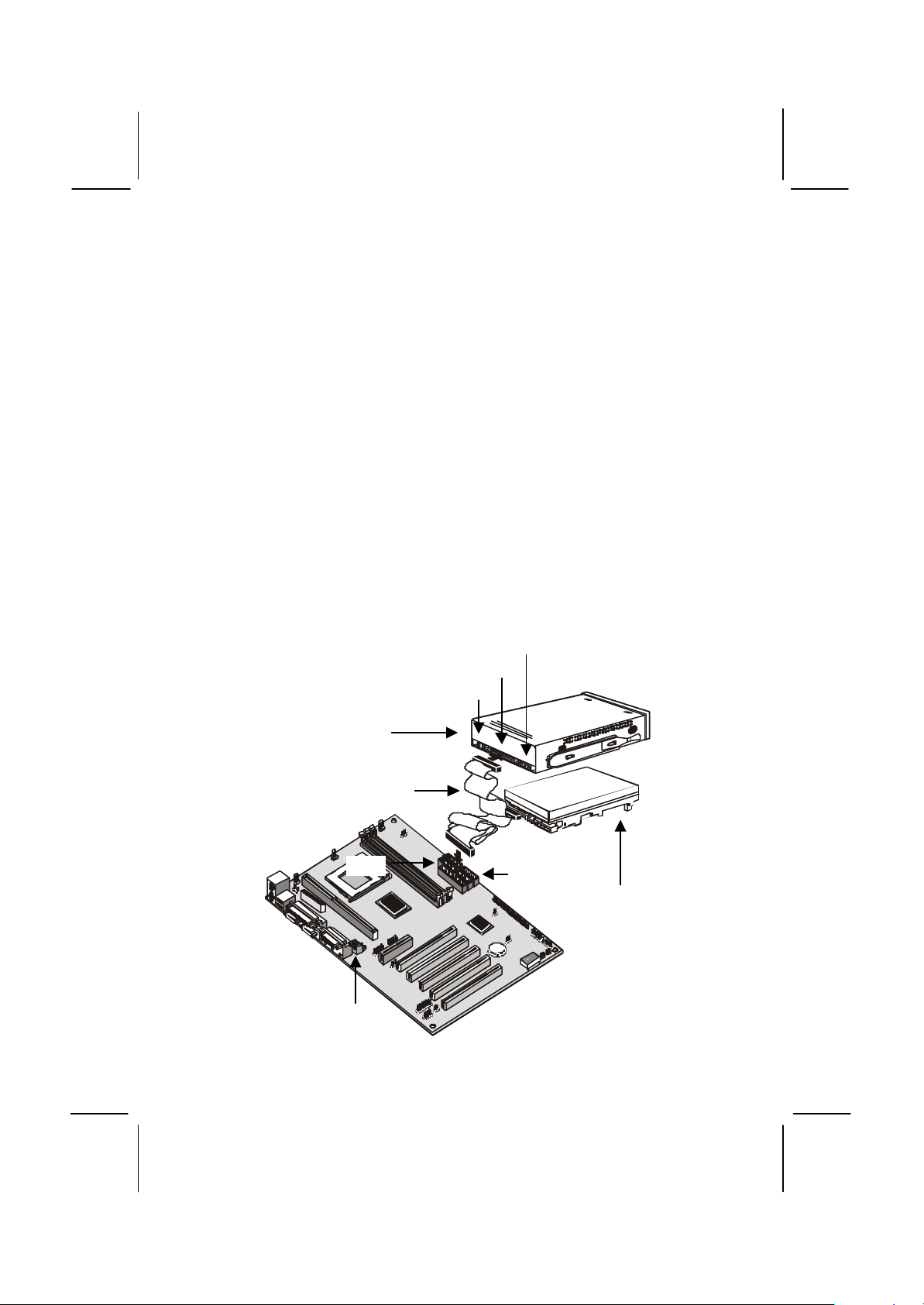
32
Installing a CD-ROM/DVD Drive
1. Install the CD-ROM/DVD drive into the drive cage in your system
case. Plug the IDE cable into the primary IDE channel on the
mainboard IDE1.
2. Plug one of the connectors on the IDE cable into the IDE connector
on the back edge of the CD-ROM/DVD drive. It doesn’t matter which
connector on the cable that you use. Make sure that you have the
pin-1 side of the cable matched with the pin-1 side of the connector.
3. Plug a power cable from the case power supply unit into the power
connector on the back edge of the CD-ROM/DVD drive.
4. Use the audio cable provided with the CD-ROM/DVD drive to
connect the audio connector on the rear edge of the CD-ROM/DVD
drive to the one of the two audio-in connectors J4 and J5 on the
mainboard.
5. When you first start up your system, go immediately to the setup
utility and use the IDE Hard Disk Auto Detect feature to configure the
IDE devices that you have installed. See Chapter 3 for more
information.
Power connector
IDE connector
Audio connector
CD-ROM/DVD drive
IDE ribbon cable
IDE2
J4 & J5
IDE1
Hard disk drive
Page 37
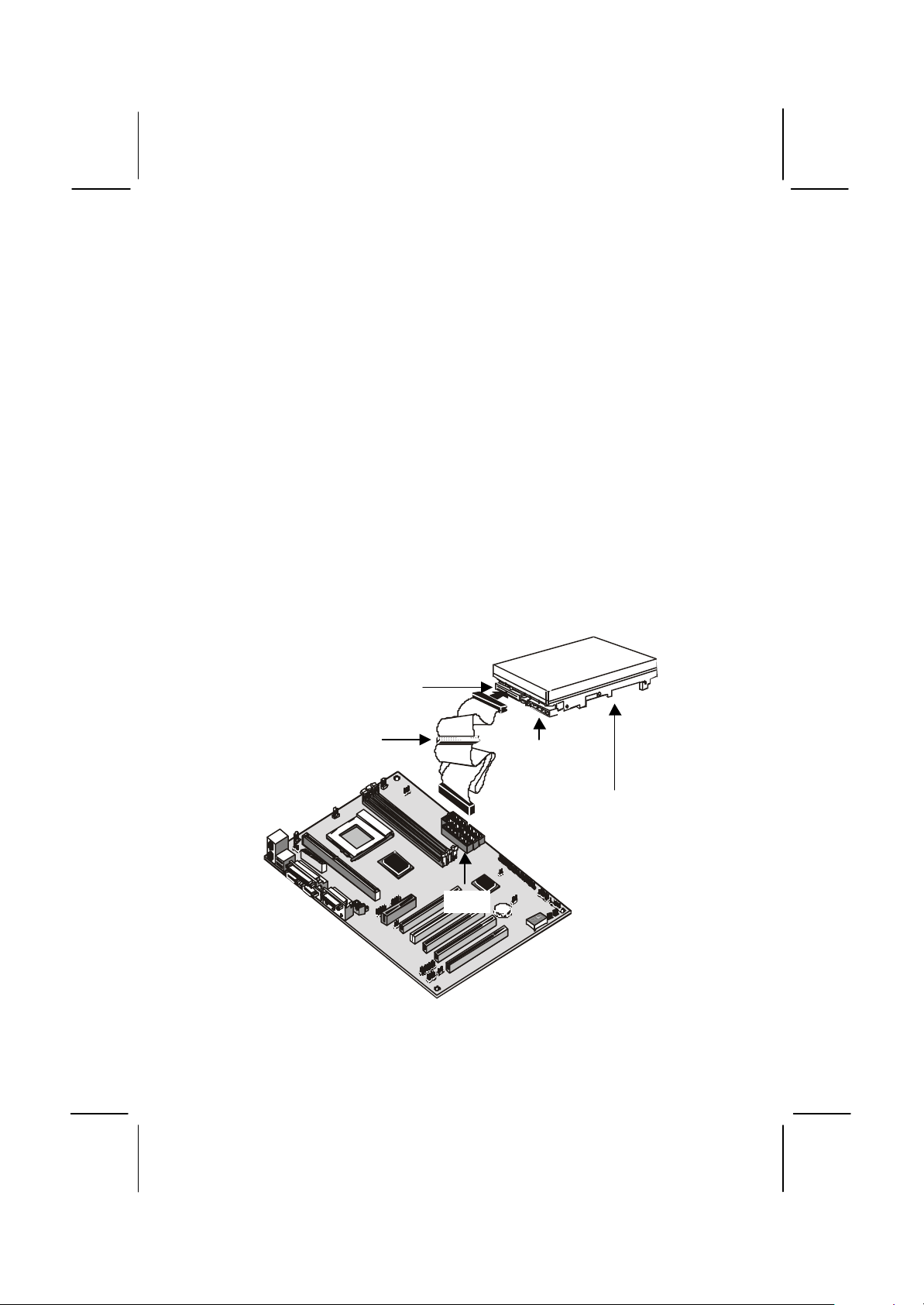
33
Installing a Floppy Diskette Drive
The mainboard has a floppy diskette drive interface and it ships with a
diskette drive ribbon cable that supports one or two floppy diskette drives.
You can install a 5.25” drive or a 3.5” drive with various capacities. The
floppy diskette drive cable has one type of connector for a 5.25” drive
and another type of connector for a 5.25” drive
1. Install the floppy diskette drive into the drive cage in your system
case. Plug the diskette drive cable into the diskette drive interface on
the mainboard FDD1.
2. Plug one of the connectors on the diskette drive cable into the data
connector on the back edge of the floppy diskette drive. Make sure
that you have the pin-1 side of the cable matched with the pin-1 side
of the connector.
3. Plug a power cable from the case power supply unit into the power
connector on the back edge of the diskette drive.
4. When you first start up your system, go immediately to the setup
utility and use the Standard page to configure the floppy diskette
drives that you have installed. See Chapter 3 for more information.
Data connector
Floppy diskette
drive cable
Power
connector
FDD1
Floppy diskette
drive
Page 38

34
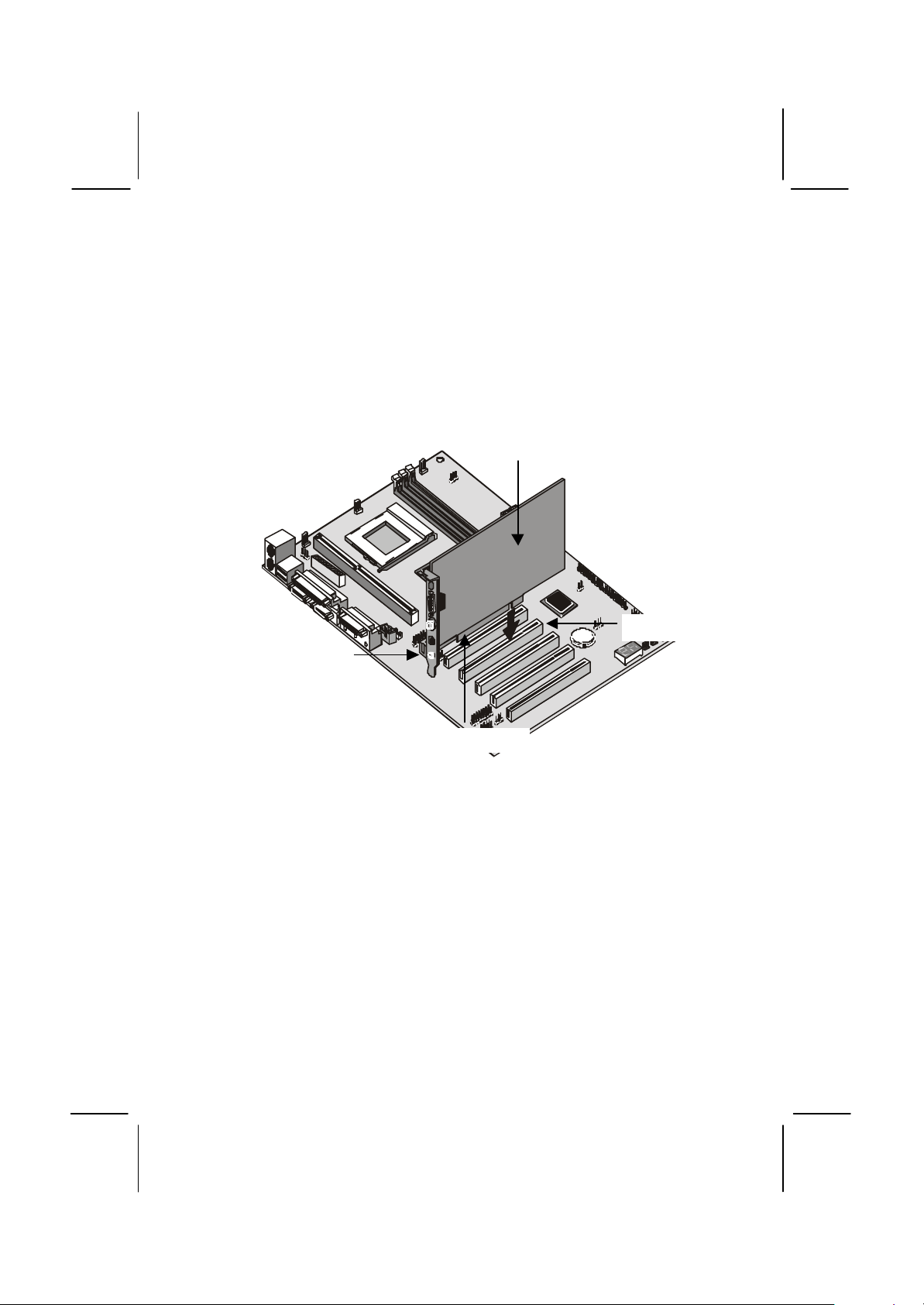
Using the Expansion Slots
This mainboard has five 32-bit PCI expansion slots and one AMR slot.
PCI Slots: The PCI slots can be used to install add-in cards that have
the 32-bit PCI (Peripheral Components Interconnect) interface.
AMR Slot: The AMR (Audio Modem Riser) slot is an industry standard
slot that allows for the installation of a special audio/modem riser card.
Different territories have different regulations regarding the specifications
of a modem card. You can purchase an AMR card that is approved in
your area and install it directly into the AMR slot.
PCI1
AMR
PCI2
PCI4
PCI3
PCI5
1. Before installing an expansion card, check the documentation for the
card carefully. If the card is not Plug and Play, you may have to
manually configure the card before installation.
2. Select which expansion slot you are going to use for your add-in
card.
3. In the system case, remove the blanking plate from the slot in the
system case that corresponds to the expansion slot that you are
going to use.
4. Position the edge connector of the add-in card over the expansion
slot. Position the metal bracket of the card in the empty slot in the
system case.
Page 39
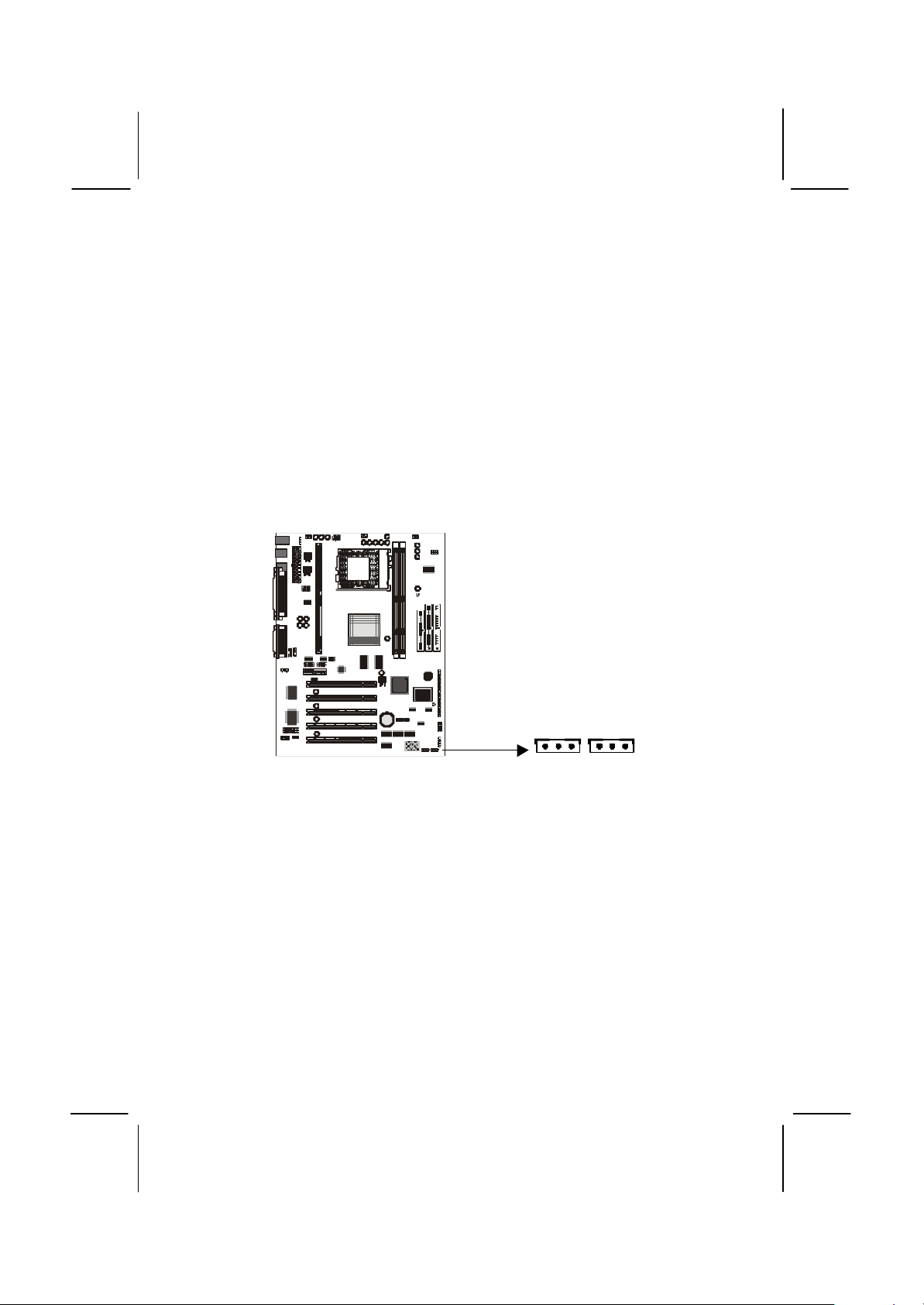
35
5. Install the edge connector of the add-in card into the expansion slot.
Press down quite firmly so that you are sure that the edge connector
is correctly seated in the slot.
6. Secure the metal bracket of the card in the empty slot in the system
case with a screw.
7. For some add-in cards, for example graphics adapters and network
adapters, you have to install drivers and software before you can
begin using the add-in card.
PCI add-in card
PCI slot
Metal bracket
Edge connector
Note: If you have installed an AMR card, you should check the
settings of jumpers JP3 (audio/modem enable/disable) and JP6
(select onboard codec or AMR codec). You should disable the
onboard audio/modem to avoid conflicts with the AMR card. You
can use the AMR codec chip (if it has one) or the onboard codec
chip.
Page 40
36
Add-in Card Options
The mainboard has two features that can be used if you have installed
either a fax/modem card or a network adapter card.
WOL1: Wake on LAN
If you have installed a network adapter (LAN adapter), you can use the
cable provided with the card to plug into the WOL1 connector on the
mainboard. This is the Wake On LAN feature. When your system is in a
power–saving mode, any traffic through the network automatically
resume the system. You must enable this item using the Power
Management page of the setup utility. See Chapter three for more
information.
WOM1WOL1
WOM1: Wake on Modem
If you have installed a fax/modem card, you can use the cable provided
with the card to plug into the WOM1 connector on the mainboard. This is
the Wake On Modem feature. When your system is in a power–saving
mode, any incoming calls to the modem automatically resume the
system. You must enable this item using the Power Management page
of the setup utility. See Chapter Three for more information.
Page 41
37
Install Options and Extension Brackets
This mainboard has a number of special connectors that allow you to
add optional features to your system. You can install any of the following
items:
♦ Fax/modem card option
♦ Infrared port
♦ Serial port extension bracket
♦ 24-bit digital audio extension bracket (SPDIF)
♦ TV-out extension bracket
Fax/modem Card
You must install the fax/modem card in order to use the built-in
fax/modem.
J8
The fax/modem card is supplied with this mainboard.
1. Locate the J8 fax/modem connector on the mainboard.
2. Remove the expansion slot blanking plate from the system chassis
that is adjacent to the fax/modem connector.
3. Install the fax/modem card on to the J8 connector as shown below.
The RJ11 Line and Telephone sockets on the bracket are positioned
in the expansion slot with the removed blanking plate.
Page 42

38
Line and Tel
RJ11 sockets
Fax/modem
J8
fax/modem
connector
card
Serial Port Extension Bracket
If you want to have a second external serial port available in your
computer case, you must install a serial port extension bracket.
COM2
1. Locate the serial port connector COM2. Remove a blanking plate
from a free expansion slot in the system chassis.
2. Plug the cable from the serial port extension bracket into the COM2
connector on the mainboard. The port connected to COM2 is
identified as COM2/4
3. Install the metal bracket into the expansion slot in the system
chassis from which you removed the blanking plate.
4. Secure the bracket by driving a screw through the slot in the top of
the metal bracket into the system chassis.
Page 43

39
Note: An IR port and a second serial port use the same resources,
and they may use some of the resources required by a fax/modem
card. If you have more than one of these items installed, you may
not be able to use them at the same time. You can use the
Peripherals page of the setup utility to switch resources between
an IR port and a second serial port. See Chapter 3 for more
information.
TV-out Extension Bracket
The TV-out extension bracket provides video out jacks (RCA and/or Svideo). You can use these jacks to connect your computer to a TV set or
digital flat panel display.
TV1
1. Locate the TV-out connector TV1. Remove a blanking plate from a
free expansion slot in the system chassis.
2. Plug the cable from the TV-out extension bracket into the TV1
connector on the mainboard.
3. Install the metal bracket into the expansion slot in the system
chassis from which you removed the blanking plate.
4. Secure the bracket by driving a screw through the slot in the top of
the metal bracket into the system chassis.
5. Use the jumper JP11 to set the video output to NTSC or PAL format
according to the format of the TV-set you are using.
Page 44

40
Infrared Port
This option can be purchased from third-party vendors.
SIR1
1. Connect the cable from the optional IR port to the SIR1 connector on
the mainboard.
2. After you have connected the cable, secure the optional IR port to
the appropriate place on your system case.
Note: An IR port and a second serial port use the same resources,
and they may use some of the resources required by a fax/modem
card. If you have more than one of these items installed, you may
not be able to use them at the same time. You can use the
Peripherals page of the setup utility to switch resources between
an IR port and a second serial port. See Chapter 3 for more
information.
Page 45

41
Digital Audio Extension Bracket
Audio Input
1
2
7
8
You can purchase an optional 24-bit digital audio extension bracket from
a third-party vendor. You can use the audio RCA jacks to connect to
digital audio devices. If your CD-ROM/DVD drive has digital audio output,
you can connect it to the input pins of the SPDIF connector.
Pins
SPDIF
On the mainboard, locate the digital audio connector SPDIF. Connect
the cable from the digital audio extension bracket to SPDIF. If you have
digital audio output from your CD-ROM/DVD drive, connect it to the
marked audio input pins.
Page 46

42
Make the External Connections
PS2KBM
USB1
J3
LPT1
After you have installed the mainboard, make the connections to the
external ports.
J3
COM1
1. PS2KBM is a stack of two PS/2 mini-DIN ports. The upper port can
be used by a PS/2 mouse or pointing device. The lower port can be
used by a PS/2 keyboard.
2. LPT1 is a parallel port that can be used by printers or other parallel
communications devices. The system identifies the parallel port as
LPT1.
3. The upper 15-pin port J3 is a game/MIDI port. You can use this port
to connect a joystick or a MIDI device to your system
4. The lower part of J3 is three audio jacks. The left side jack is for a
stereo line out signal. The middle jack is for a stereo line in signal.
The right side jack is for a microphone.
5. VGA1 is the connector for a display monitor. Plug the data cable
from the monitor into VGA1.
6. COM1 is a serial port that can be used by serial devices such as a
mouse, a fax/modem and so on. This serial port is identified by the
system as COM1/3.
7. USB1 is a stack of two Universal Serial Bus ports. Use these ports to
connect to USB devices.
VGA1
Page 47

43
External Connector Color Coding
To help identify the external connectors, many connectors now use
standard colors as shown in the table below.
Connector Color
Analog VGA Blue
Audio line in Light blue
Audio line out Lime
Digital monitor / flat panel White
IEEE 1394 Grey
Microphone Pink
MIDI/Game Gold
Parallel Burgundy
PS/2 compatible keyboard Purple
PS/2 compatible mouse Green
Serial Teal or Turquoise
Speaker out / subwoofer Orange
Right-to-left speaker Brown
USB Black
Video out Yellow
SCSI, network, telephone, modem,
and so on
None
Page 48
44
CChhaapptteerr 33:: SSeettuup
p
About the Setup Utility
This chapter explains how to use and modify the BIOS setup utility that is
stored on the mainboard. The setup utility stores data about the
mainboard components and the configuration of devices that are
connected to it. This information is used to test and initialize components
at start-up time and to make sure everything runs properly when the
system is operating.
The setup utility is installed with a set of default values. You will probably
have to make changes to the setup utility whenever you add new
components to your system such as new disk drives. You may be able to
generate increased performance by changing some of the timing values
in the setup, but this can be limited by the kind of hardware you are
using, for example the rating of your memory chips. In certain
circumstances, the system may generate an error message that asks
you to make changes to the setup utility. This happens when the system
finds an error during the POST (Power On Self Test) that it carries out at
start up.
Starting the Setup Utility
You can only start the setup utility shortly after the computer has been
turned on. A prompt appears on the computer display which says “Press
DEL to run Setup ”. When you see this prompt, press the Delete key, and
the system will start the setup utility and display the main menu of the
utility.
Using the Setup Utility
When you start setup, the main menu appears. The main menu of the
setup utility shows a list of the options that are available. A highlight
shows which option is currently selected. You can use the cursor arrow
keys to move the highlight to other options. When an option is
highlighted, you can execute the option by pressing the Enter key.
Some options lead to dialog boxes which ask you verify that that you
wish to execute that option. You usually answer these dialogs by typing
Y for yes and N for no. Some options lead to dialog boxes which ask for
more information. Setting passwords have this kind of dialog box.
Page 49
45
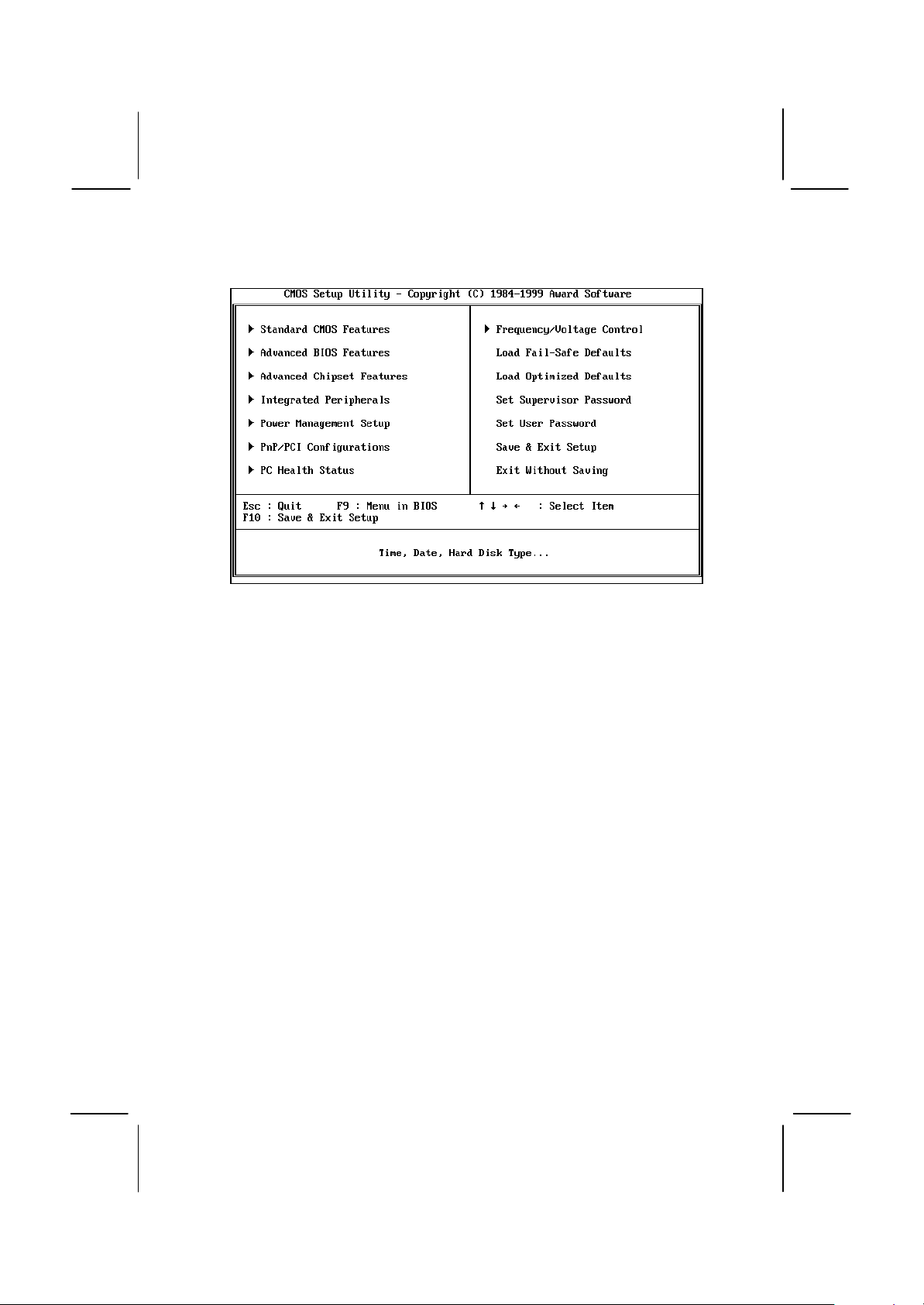
Some options (marked with a triangle) lead to tables of items that usually
have a value on the right side. The value of the first item is highlighted,
and you can use the cursor arrow keys to select any of the other values
in the table of items. When an item is highlighted, you can change the
value by pressing the PageUp or PageDown keys, or the Plus or Minus
keys. The PageUp and Plus keys cycle forward through the available
values, the PageDown and Minus keys cycle backwards through the
values.
When you are in the main menu, you can exit the utility by pressing the
Escape key. You can save the current selections and exit the utility by
pressing the F10 key. When you are in one of the options that displays a
dialog box, you can return to the main menu by pressing the Escape key.
When you are in an option that displays a table of items, you can return
to the main menu by pressing the Escape key. For some items, you can
display a help message by pressing the F2 key. You can display a
general help screen by pressing F1. Press F5 to discard any changes
you have made and return all items to the value that they held when the
setup utility was started. Press F6 to load the displayed items with a
standard list of fail-safe values. Press F7 to load the displayed items with
a high-performance list of default values.
Page 50

46
How to Flash a New BIOS
You can install an updated BIOS for this motherboard that you can
download from the manufacturer’s website. New BIOS may provide
support for new peripherals, improvements in performance or fixes to
address known bugs. Install a new BIOS as follows:
1. Some mainboards have a Flash BIOS jumper that protects the
current BIOS from being changed or overwritten. If your mainboard
has this jumper, change the setting to allow flashing a new BIOS.
2. Some Setup programs have an item called Firmware Write Protect
that prevents the BIOS from being overwritten. If your BIOS has this
item (check the Advanced BIOS Features Setup page) disable it for
the present.
3. Your computer must be running in a real-mode DOS environment,
not the DOS window of Windows NT or Windows 95/98. We
recommend that you create a new formatted DOS system floppy
diskette.
4. Locate the flash memory utility on the support CD-ROM. It ’s called
AWD712.EXE. Copy this file to the new system diskette.
5. Copy the new BIOS file that you downloaded from the
manufacturer’s website to the newly formatted system diskette.
6. Turn off your computer and insert the newly formatted DOS diskette
in your computer’s diskette drive.
7. You might need to run the setup utility and change the boot priority
items on the Advanced BIOS Features Setup page, to force your
computer to boot from the floppy diskette drive first.
8. At the A:\ prompt, after your computer has booted a clean DOS from
the diskette, type in the filename AWD712 and press Enter.
Page 51
47
9. In the opening dialog box, type in the filename of the new BIOS and
follow the onscreen directions to flash the new BIOS to the
motherboard.
10. When the installation is complete, remove the floppy diskette from
the diskette drive and restart your computer. If your mainboard has a
Flash BIOS jumper, don’t forget to reset the jumper to protect the
newly installed BIOS from being overwritten.
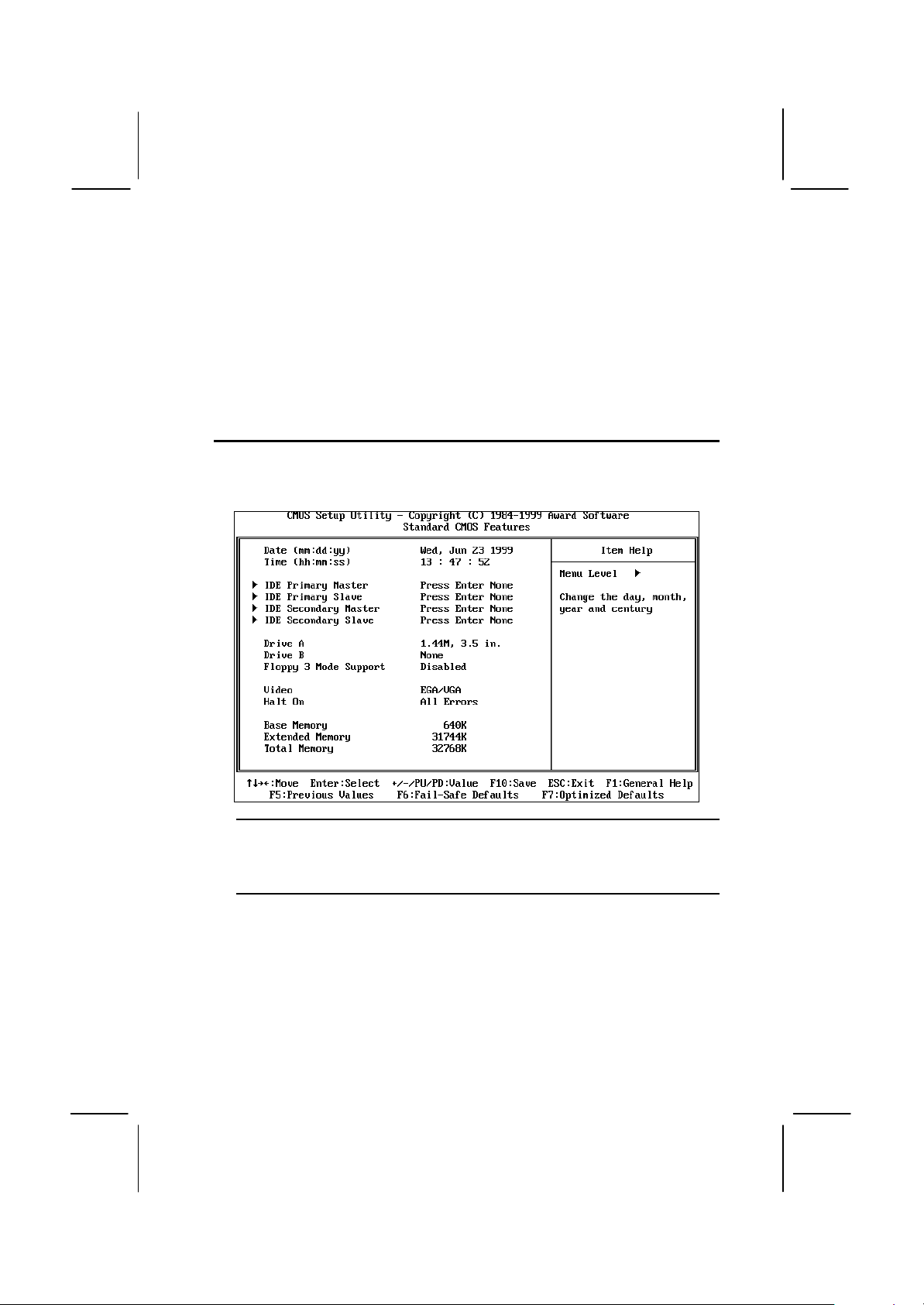
Standard CMOS Features Option
This option displays a table of items which defines basic information
about your system.
Date and Time
The Date and Time items show the current date and time held by your computer.
If you are running a Windows OS, these items are automatically updated
whenever you make changes to the Windows Date and Time Properties utility.
IDE Devices Defaults: None
Your computer has two IDE channels (Primary and Secondary) and each
channel can be installed with one or two devices (Master and Slave). Use these
items to configure each device on the IDE channel. Press Enter to display the
IDE sub-menu.
Page 52

48
IDE HDD Auto-Detection
Press Enter while this item is highlighted if you want the setup utility to
automatically detect and configure a hard disk drive on the IDE channel.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave
If you leave this item at Auto, the system will automatically detect and configure
any IDE devices it finds. If it fails to find a hard disk, change the value to Manual
and then manually configure the drive be entering the characteristics of the drive
in the items below (Capacity, Cylinder, Head, Precomp, etc.), If you have no
device installed change the value to None.
Access Mode
This items defines some special ways that can be used to access IDE hard disks
such as LBA (Large Block Addressing). Leave this value at Auto and the system
will automatically decide the fastest way to access the hard disk drive.
Press Esc to close the IDE device sub-menu and return to the Standard CMOS
Features page.
Drive A and Drive B Default: 1.44M, 3.5 in., None
These items define the characteristics of any diskette drive attached to the
system. You can connect one or two diskette drives.
Floppy 3 Mode Support Default: Disabled
Floppy 3 mode refers to a 3.5” diskette with a capacity of 1.2 MB. Floppy 3 mode
is sometimes used in Japan.
Video Default: EGA/VGA
This item defines the video mode of the system. This mainboard has a built-in
VGA graphics system so you must leave this item at the default value.
Page 53

49
Halt On Default: All Errors
This item defines the operation of the system POST (Power On Self Test) routine.
You can use this item to select which kind of errors in the POST are sufficient to
halt the system.
Base Memory, Extended Memory, Total Memory
These items are automatically detected by the system at start up time.
Advanced BIOS Features Setup Option
This option displays a table of items which defines more advanced
information about your system. You can make modifications to most of
these items without introducing fatal errors to your system. Note that the
page has a scroll-bar to scroll down to more items.
Anti-Virus Protection Default: Disabled
When this item is enabled it provides some protection against viruses which try
to write to the boot sector and partition table of your hard disk drive. This item is
Disabled as a default. You need to disable it so that you can install an operating
system. We recommend that you enable Anti-Virus Protection as soon as you
have installed your disk with an OS.
CPU Internal Cache Default: Enabled
All the processors that can be installed in this mainboard use internal (level 1)
cache memory to improve performance. Leave this item at the default value
Enabled for better performance.
Page 54

50
External Cache Default: Enabled
Most processors that can be installed in this system use external (L2) cache
memory to improve performance. The exceptions are older SEPP Celeron CPUs
running at 266 or 300 MHz. Enable this item for all but these two processors.
CPU L2 Cache ECC Checking Default: Enabled
This item enables or disables ECC (Error Correction Code) error checking on the
CPU cache memory. We recommend that you leave this item at the default value.
Processor Number Feature Default: Enabled
Each Pentium-III processor cartridge is installed with a unique processor number.
This number may be used for verification in internet transactions and ecommerce. If you prefer not to use or distribute the unique processor number,
use this item to suppress the processor number.
Quick Power On Self Test Default: Enabled
You can enable this item to shorten the power on testing and have your system
start up a little faster. You might like to enable this item after you are confident
that your system hardware is operating smoothly.
First/Second/Third Boot Device Default: Floppy/HDD-0/LS/ZIP
Use these three items to select the priority and order of the devices that your
system will search for an operating system at start-up time.
Boot Other Device Default: Enabled
If you enable this item, the system will search all other possible locations for an
operating system if it fails to find one in the devices specified under the first,
second and third boot devices.
Swap Floppy Drive Default: Disabled
If you have two floppy diskette drives in your system, this item allows you to
swap around the assigned drive letters so that drive A becomes drive B, and
drive B becomes drive A.
Boot Up Floppy Seek Default: Enabled
If this item is enabled, it checks the geometry of the floppy disk drives at start-up
time. You don’t need to enable this item unless you have a old diskette drive with
360K capacity.
Boot Up NumLock Status Default: On
This item defines if the keyboard Num Lock key is active when your system is
started.
Gate A20 Option Default: Fast
This item defines how the system handles legacy software that was written for an
earlier generation of processors. Leave this item at the default value.
Firmware Write Protect Default: Disabled
If you enable this item, it protects the firmware (BIOS) from being overwritten.
Disable this item if you plan to flash a new BIOS to the system.
Page 55

51
Chassis Open Warning Default: Disabled
Chassis has been Default: CLOSING
If you have connected a chassis open circuit to the Chassis Open detect
connector on the mainboard, use these items to enable or disable the feature
and determine the setting of the feature.
Typematic Rate Setting Default: Disabled
If this item is enabled, you can use the following two items to set the typematic
rate and the typematic delay settings for your keyboard.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) Default: 6
If the item Typematic Rate Setting is enabled, you can use this item to define
how many characters per second are generated by a held-down key.
Typematic Delay ( Msec) Default: 250
If the item Typematic Rate Setting is enabled, you can use this item to define
how many milliseconds must elapse before a held-down key begins generating
repeat characters.
Security Option Default: Setup
If you have installed password protection, this item defines if the password is
required at system start up, or if it is only required when a user tries to enter the
setup utility.
OS Select For DRAM > 64 MB Default: Non-OS2
This item is only required if you have installed more than 64 MB of memory and
you are running the OS/2 operating system. Otherwise, leave this item at the
default Non-OS2.
Report No FDD for WIN 95 Default: Yes
If you are running a system with no floppy drive and using the Windows 95 OS,
select Yes for this item to ensure compatibility with the Windows 95 logo
certification.
Advanced Chipset Features Option
This option displays a table of items that define critical timing parameters
of the mainboard components including the memory, and the system
logic. Generally, you should leave the items on this page at their default
values unless you are very familiar with the technical specifications of
your system hardware. If you change the values incorrectly you may
introduce fatal errors or recurring instability into your system. Note that
the page has a scroll-bar to scroll down to more items.
Page 56

52
SDRAM CAS latency Time Default: 3
SDRAM Cycle Time Tras/Trc Default: 6/8
SDRAM RAS-to-CAS Delay Default: 3
SDRAM RAS Precharge Time Default: 3
These four items set the timing and wait states for SDRAM memory. We
recommend that you leave these items at the default value.
System BIOS Cacheable Default: Enabled
Video BIOS Cacheable Default: Enabled
These items allow the video and/or system BIOS to be cached in memory for
faster execution. We recommend that you leave these items at the default value.
Memory Hole at 15M-16M Default: Disabled
This item can be used to reserve memory space for some ISA expansion cards
that require it.
Delayed Transaction Default: Enabled
If the chipset has an embedded 32-bit write buffer to support delay transaction
cycles, you can enable this item to provide compliance with PCI Ver. 2.1
specifications. We recommend that you leave this item at the default value.
On-Chip Video Window Size Default: 64 MB
This item defines the size of the aperture if you use an AGP graphics adapter. It
refers to a section of the PCI memory address range used for graphics memory.
We recommend that you leave this item at the default value.
Page 57

53
Local Memory Frequency Default: 100 MHz
On this mainboard, you can select a frequency for the memory bus that
is different from the frequency of the FSB (front side bus) used by the
processor. Use this item to select the frequency required by the memory
modules that you install.
* On Board Display Cache Setting *
The items under this heading are used to set the parameters for Display cache
memory which may be optionally installed on your mainboard. Igf you have
display cache memory , we recommend that you leave these items at the default
setting.
Integrated Peripherals Option
This option displays a list of items which defines the operation of some
peripheral items on the system’s input/output ports.
On-Chip Primary PCI IDE Default: Enabled
On-Chip Secondary PCI IDE Default: Enabled
Use these items to enable or disable the Primary and Secondary PCI IDE
channels that are integrated on this mainboard.
IDE Primary Master PIO Default: Auto
IDE Primary Slave PIO Default: Auto
IDE Secondary Master PIO Default: Auto
IDE Secondary Slave PIO Default: Auto
Each IDE channel supports a master device and a slave device. These four
items let you assign which kind of PIO (Programmed Input/Output) is used by
Page 58

54
IDE devices. You can choose Auto, to let the system auto detect which PIO
mode is best, or you can install a PIO mode from 0-4.
IDE Primary Master UDMA Default: Auto
IDE Primary Slave UDMA Default: Auto
IDE Secondary Master UDMA Default: Auto
IDE Secondary Slave UDMA Default: Auto
Each IDE channel supports a master device and a slave device. This
motherboard supports UltraDMA. UltraDMA technology provides faster access to
IDE devices. If you install a device which supports UltraDMA, change the
appropriate item on this list to Auto. You may have to install the UltraDMA driver
supplied with this motherboard in order to use an UltraDMA device.
USB Controller Default: Enabled
Use this item to enable the USB ports that are integrated on this mainboard.
USB Keyboard Support Default: Disabled
Enable this item if you are using a keyboard connected through the USB Port.
Init Display First Default: PCI Slot
Use this item to define if your graphics adapter is installed in one of the PCI slots
or select Onboard if you have a graphics system integrated on the mainboard.
Hardware Reset Default: Enabled
If you enable this item, you can reset the system by pressing a hardware reset
button if you have connected this function to the mainboard.
Onboard PCI Audio Default: Enabled
If your mainboard has an integrated PCI audio system, use this item to enable or
disable it.
Onboard PCI Modem Default: Disabled
If your mainboard has an integrated PCI modem, use this item to enable or
disable it.
AC97 Audio Default: Disabled
We recommend that you set this item to Enabled when you use an AMR card.
AC97 Modem Default: Disabled
We recommend that you set this item to Enabled when you use an MR/AMR
card.
IDE HDD Block Mode Default: Enabled
Block mode transfers can improve the access to IDE devices. Enable this item if
your IDE devices support block mode transfers.
Page 59

55
Power On Function Default: Hot KEY
KB Power ON Password Default: Enter
Hot Key Power ON Default: Ctrl-F12
The Power On Function item allows you to power on the system by pressing hotkeys, or typing a password. If you choose Password, you can use the item KB
Power On Password to install a power on password. Press Enter to display the
Password dialog box. If you set it to Hot Key, you can then use the item Hot Key
Power On to choose which hot keys are used to power on the system.
Onboard FDC Controller Default: Enabled
Use this item to turn on or off the floppy disk controller that is built into this
mainboard.
Onboard Serial Port 1 Default: 3F8/IRQ4
This item lets you disable the built-in serial port 1, or enable it by assigning an
I/O address and an Interrupt Request Line (IRQ).
Onboard Serial Port 2 Default: Disabled
If you have installed an optional second serial port, this item lets you disable the
built-in serial port 1, or enable it by assigning an I/O address and an Interrupt
Request Line (IRQ).
UART Mode Select Default: IrDA
UR2 Duplex Mode DefaultL Half
This item defines the operation of serial port 2. In the Normal setting, serial port 2
is assigned to the (optional) COM2 connector. If you have installed an optional
infrared port, you must change the setting of this item to one of the Infrared
settings (usually IrDA or FIR). These settings will disable the external COM2
serial port connector and assign the resources to the infrared device. If you have
selected an IR mode, use the following item UR2 Duplex Mode to define if the IR
port is full duplex or half duplex.
Onboard Parallel Port Default: 378/IRQ7
This item lets you disable the built-in parallel port, or enable it by assigning an
I/O address and an Interrupt Request Line (IRQ).
Parallel Port Mode Default: SPP
ECP Mode Use DMA Default: 3
This item defines the operation of the parallel port. As a default it is set to SPP
(standard parallel port). If you are connected to a parallel device that supports
the higher-performance EPP (enhanced parallel port) or the ECP (extended
capabilities port) make the appropriate changes to this item. If you have changed
the parallel port to ECP mode, use the following item ECP Mode Use DMA to
assign a DMA channel to the port.
PWRON After PWR-Fail Default: Off
If this item is enabled, the system will automatically resume when power is
restored after an interruption in the power supply.
Page 60

56
Game Port Address Default: 201
This item lets you disable the built-in game port, or enable it by assigning an I/O
address.
Midi Port Address Default: 330
Midi Port IRQ Default: 10
This item lets you disable the built-in MIDI port, or enable it by assigning an I/O
address. If you enable the MIDI port, use the following item Midi Port IRQ to
assign an Interrupt Request line to the port.
Power Management Setup Option
This option displays items that let you control the system power
management. Modern operating systems take care of much of the power
management. This mainboard supports ACPI (advanced configuration
and power interface). The system has various power saving modes
including powering down the hard disk, turning off the video, suspending
to RAM, and a software power down that allows the system to be
automatically resumed by certain events.
Power Management Timeouts
The power-saving modes can be controlled by timeouts. If the system is
inactive for a time, the timeouts begin counting. If the inactivity continues
so that the timeout period elapses, the system enters a power-saving
mode. If any item in the list of Reload Global Timer Events is Enabled,
then any activity on that item will reset the timeout counters to zero.
Wake Up Calls
If the system is suspended, or has been powered down by software, it
can be resumed by a wake up call that is generated by incoming traffic to
a modem, a LAN card, a PCI card, or a fixed alarm on the system
realtime clock.
Page 61

57
ACPI Function Default: Enabled
This mainboard supports ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power
management Interface). Use this item to enable or disable the ACPI feature.
ACPI Suspend Type Default: S1 (POS)
Use this item to define how your system suspends. In the default, S1(POS), the
suspend mode is equivalent to a software power down. If you select S3 (STR),
the suspend mode is a suspend to RAM – the system shuts down with the
exception of a refresh current to the system memory.
Power Management Default: User Define
This item acts like a master switch for the power-saving modes and hard disk
timeouts. If this item is set to Max Saving, power-saving modes occur after a
short timeout. If this item is set to Min Saving, power-saving modes occur after a
longer timeout. If the item is set to User Define, you can insert your own timeouts
for the power-saving modes.
Video Off Method Default: DPMS
This item defines how the video is powered down to save power. As a default,
this is set to DPMS (display power management software).
Video Off In Suspend Default: Yes
This option defines if the video is powered down when the system is put into
suspend mode.
Suspend Type Default: Stop Grant
If this item set to Default "Stop Grant", the CPU will go into the Idle Mode.
Page 62

58
Modem Use IRQ Default: 3
If you want an incoming call on a modem to automatically resume the system
from a power-saving mode, use this item to specify the interrupt request line
(IRQ) that is used by the modem. You might have to connect the fax/modem to a
mainboard Wake On Modem connector for this feature to work.
Suspend Mode Default: Disabled
If you have selected User Define for the Power Management item, you can set
this item to a timeouts from 1 Min to 1 Hour. The system will go into the power-
saving suspend mode if the timeout passes without any system activity.
HDD Power Down Default: Disabled
If you have selected User Define for the Power Management item, you can set
this item to a selection of timeouts from 1 to 15 minutes. The hard disk drive will
power down if the selected timeout passes without any activity on the hard disk.
Soft-Off by PWR-BTTN Default: Instant-Off
Under ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power management Interface) you
can create a software power down. In a software power down, the system can be
resumed by Wake Up Alarms. This item lets you install a software power down
that is controlled by the normal power button on your system. If the item is set to
Instant-Off, then the power button causes a software power down. If the item is
set to Delay 4 Sec. Then you have to hold the power button down for four
seconds to cause a software power down.
Wake Up by PCI Card Default: Disabled
If you enable this item, it allows activity on an add-in card in one of the PCI slots
to resume the system from a power-saving mode.
Power On by Ring Default: Disabled
If this item is enabled, it allows the system to resume from a software
powerdown or a power-saving mode whenever there is an incoming call to an
installed fax/modem. You might have to connect the fax/modem to a mainboard
Wake On Modem connector for this feature to work.
Wake Up On LAN Default: Enabled
If this item is enabled, it allows the system to resume from a software
powerdown or a power-saving mode whenever there is an incoming traffic to a
network (LAN) adapter. You might have to connect the LAN card to a mainboard
Wake On LAN connector for this feature to work.
Resume by Alarm Default: Disabled
If this item is Enabled, it allows you to set a date and time alarm that will
automatically resume the system from a software power down. When you enable
this feature, new setup items appear to let you set the alarm. Date (of Month)
Alarm lets you select a day from 1 to 31. Time Alarm lets you select a time for
the alarm in hours, minutes, and seconds.
Page 63

59
Primary IDE 0 Default: Disabled
Primary IDE 1 Default: Disabled
Secondary IDE 0 Default: Disabled
Secondary IDE 1 Default: Disabled
When these items are enabled, the system will restart the power-saving timeout
counters when any activity is detected on any of the drives or devices on the
primary or secondary IDE channels.
FDD,COM,LPT Port Default: Disabled
When this item is enabled, the system will restart the power-saving timeout
counters when any activity is detected on the floppy diskette drives, the serial
ports, or the parallel port.
PCI PIRQ[A-D]# Default: Disabled
When this item is enabled, the system will restart the timeout counters when any
activity is detected on the Interrupt request lines used over the PCI bus.
PNP/PCI Configuration Option
This option displays a table of items that configures how PNP (Plug and
Play) and PCI expansion cards operate in your system.
Reset Configuration Data Default: Disabled
If you enable this item and restart the system, any PNP configuration data stored
in the BIOS setup is cleared from memory. New updated data is created.
Page 64

60
Resources Controlled By Default: Auto(ESCD)
You should leave this item at the default Auto(ESCD). Under this setting, the
system dynamically allocates resources to plug and play devices as they are
required. If you cannot get a legacy ISA (Industry Standard Architecture)
expansion card to work properly, you might be able to solve the problem by
changing this item to Manual, and then opening up the IRQ Resources and
Memory Resources sub-menus.
In the IRQ Resources sub-menu, if you change any of the IRQ assignations to
Legacy ISA, then that Interrupt Request Line is reserved for a legacy ISA
expansion card. Press Esc to close the IRQ Resources sub-menu.
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop Default: Disabled
This item is designed to overcome some problems that can be caused by some
non-standard VGA cards. This board includes a built-in VGA system that does
not require palette snooping so you must leave this item disabled.
PCI Health Status Option
On mainboards which support hardware monitoring, this item lets you set
parameters for critical voltages, critical temperatures, and fan speeds.
If this option is active on your system, we recommend that you accept
the default values for these items that are installed by the manufacturer.
The system will alert you whenever the manufacturer’s safe operating
parameters are exceeded.
Page 65

61
Frequency / Voltage Control Option
This item allows you to set the clock speed and system bus for your
system. The clock speed and system bus are determined by the kind of
processor you have installed in your system.
Auto Detect DIMM/PCI Clk Default: Enabled
When this item is enabled, the BIOS will disable the clock generator signal for
unused DIMM and PCI slots.
CPU Internal Core Speed Default: 300 MHz
Use this item to automatically set up the mainboard for the kind of processor that
you have installed. Set this item to the rated internal clock speed of the installed
processor. If you set this to Manual, two new items appear: CPU Clock / Sread
Spectrum.SPECTRUM Freq. and CPU Clock Ratio
CPU Clock/Spread Spectrum
CPU Clock Ratio
These items appear if you have set the CPU Internal Core Speed to Manual. Use
the CPU Clock/Spread Spectrum to set the system bus frequency for the
installed processor (usually 100 MHz or 66 MHz). Then use CPU Clock
Frequency to set a multiple. The multiple times the system bus must equal the
core speed of the installed processor e.g. 3.5 (multiple) x 100 MHz (system
bus) = 350 MHz (installed processor clock speed).
CPU Core Voltage Default: Default
Use this item to set the core voltage of the installed CPU.
Page 66
62
Load Fail-Safe Defaults Option
This option opens a dialog box that lets you install fail-safe defaults for
all appropriate items in the whole setup utility. Press the Y key and then
Enter to install the defaults. Press the N key and then Enter to not install
the defaults. The fail-safe defaults place no great demands on the
system and are generally stable. If your system is not functioning
correctly, try installing the fail-safe defaults as a first step in getting your
system working properly again. If you only want to install a fail-safe
defaults for a specific option, select and display that option, and then
press the F6 key.
Load Optimized Defaults Option
This option opens dialog box that lets you install optimized defaults for all
appropriate items in the whole setup utility. Press the Y key and then
Enter to install the defaults. Press the N key and then Enter to not install
the defaults. The optimized defaults place demands on the system that
may be greater than the performance level of the components, such as
the CPU and the memory. You can cause fatal errors or instability if you
install the optimized defaults when your hardware does not support them.
If you only want to install setup defaults for a specific option, select and
display that option, and then press the F7 key.
Set Supervisor and User Passwords
These items can be used to install a password. A Supervisor password
takes precedence over a User password, and the Supervisor can limit
the activities of a User.To install a password, follow these steps:
1. Highlight the item Set Supervisor/User password on the main menu
and press Enter.
2. The password dialog box appears.
3. If you are installing a new password, carefully type in the password.
You cannot use more than 8 characters or numbers. The password
will differentiate between upper case and lower characters. Press
Enter after you have typed in the password. If you are deleting a
password that is already installed just press Enter when the
password dialog box appears.
4. The system will ask you to confirm the new password by asking you
to type it in a second time. Carefully type the password again and
Page 67

63
press Enter, or just press Enter if you are deleting a password that
is already installed.
5. If you typed the password correctly, the password will be installed.
Save And Exit Setup Option
Highlight this item and press Enter to save the changes that you have
made in the setup utility and exit the setup program. When the Save and
Exit dialog box appears, press Y to save and exit, or press N to return to
the setup main menu.
Exit Without Saving Option
Highlight this item and press Enter to discard any changes that you have
made in the setup utility and exit the setup program. When the Exit
Without Saving dialog box appears, press Y to discard changes and exit,
or press N to return to the setup main menu.
Page 68
64
CChhaapptteerr 44:: SSooffttwwaarre
e
About the Software
The software for this mainboard is supplied on a CD-ROM. The disk has
some folders that can be used by many different mainboards, for
example the UTILITY and PERIPHERAL folders. Some folders can only
be used by mainboards which have certain brands of chipsets, for
example the INTEL and VIA folders. In addition, software that is
specifically intended for one kind of mainboard is stored in a folder with
the name of that board. The folder for this mainboard is stored in the
MS7012D folder.
Note: Never try to install software from a folder that is not
specified for use with your mainboard.
Folders for this Mainboard
For this board, you can install software from the following folders:
Utility Folder
You can use the software in the following sub-folders:
q AWDFLASH: Software to erase and install new revisions of the
system BIOS
q DIRECTX5: Software display drivers for Microsoft’s DirectX Rev. 5
specification
q PC-CILLIN: Anti-virus software
q BITWARE: Software for the built-in fax/modem
q GAMUT: Audio rack for built-in sound system
CMI8X38 Folder
You can use the software from the following sub-folders:
q AUDIO: Drivers and software for the built-in audio system
q MODEM: Drivers and software for the built-in fax/modem
Page 69
65
Peripheral Folder
You can use the software in the following sub-folders:
q KEYBOARD, CD-ROM, MOUSE: These three folders have drivers
for accessories manufactured by BTC. Some system assemblers
ship these accessories with complete systems based on this
mainboard.
Intel Folder
q I810_ACPI: This folder has a patch program so that the suspend to
RAM feature will run under Windows 98(ACPI)
q INF: This folder has a variety of programs, all designed to improve
the operation of Intel chipsets under Windows 95/98.
q VGA: This folder has drivers and software for the graphics system
built into the Intel 810 chipset.
MS7012D Folder
You can use the software in the following sub-folders:
q MONITOR : Hardware monitoring software for Windows 95/98, and
Windows NT4.0/5.0
q ACPI, AUDIO, LAN, MODEM, VGA, WIN9x-Inf: These folders are
empty. A readme file directs you to an alternate location with the
required software.
Note: Some folders are subdivided into different operating
systems such as DOS, Windows 95, Windows NT, and so on.
Always make sure that you are installing the correct software for
the operating system on your computer. Some folders are also
subdivided into different language versions, such as English,
French, German and so on.
Note: Before installing any software, always inspect the folder for
files named README.TXT, INSTALL.TXT, or something similar.
These files may contain important information that is not included
in this manual.
Page 70
66
Running the Support CD-ROM
1. Place the disk in your CD-ROM drive. If you are running Windows
with Autoplay enabled, the opening screen of the CD appears
automatically. Click on READ ME to read the latest instructions.
2. Click on the item BROWSE THE CD TITLE. This uses Windows
Explorer to show the contents of the support CD.
3. Double click on a folder to display the sub-folders.
4. Before installing the software, look for a file named README.TXT,
or something similar. This file may contain important information to
help you install the software correctly.
5. Some software is installed in separate folders for different operating
systems, such as DOS, WIN NT, WIN95/98, and so on. Always log
on to the correct folder for the kind of OS you are using.
6. To install the software, you usually execute a file named
SETUP.EXE or INSTALL.EXE by double clicking on the filename.
Utility Folder Installation Notes
Award Flash Memory Utility
This utility lets you erase the system BIOS stored on a Flash Memory
chip on the mainboard, and lets you copy an updated BIOS to the chip.
Take care how you use this program. If you erase the current BIOS and
fail to write a new BIOS, or write a new BIOS that is incorrect, your
system will malfunction.
There are two flash memory utilities called AWD66.EXE and
AWD712.EXE. For this mainboard you must use the AWD712.EXE utility.
To use the utility, you must be in real-mode DOS (not the DOS box that
is available in Windows 95/98/NT). If you are using WINDOWS 95/98,
shut down your computer and select the option Restart in DOS in the
shut-down dialog box. If you are running Windows NT, shut down your
computer and boot from a DOS diskette temporarily in order to run the
flash memory utility.
DirectX5 Drivers
The DirectX drivers are for installation only in Windows 95/98. The
directX drivers need to be installed before you install an AGP driver. You
may be able to get more up-to-date directX drivers from the Microsoft
web site. Start the installation by clicking on the file DX5CORE.EXE.
Page 71

67
PC-Cillin Anti-Virus Utility
Anti-virus software is provided for DOS, for WIN95, and WIN 98. Log on
to the appropriate directory for your operating system. For DOS, copy all
the files in the DOS folder to your hard disk drive. For Windows 95, log
on to the Disk 1 folder and run SETUP. For Windows 98, run SETUP.
CMI8X38 Folder Installation Notes
Audio Software
This folder has software and drivers for the sound system that is
integrated on this mainboard. Drivers are provided for Windows 95/98,
Windows NT, and DOS. An MS-WORD format manual is stored in the
MANUAL folder.
DOS Installation
Log on to the DOSDRV folder and run the program INSTALL.EXE
Windows 95/98 Installation
Please specify the path to the CD-ROM\CMI8X38\AUDIO_ITE_GAME
\W95-98\DRV\ when your system detects the installed audio system. To
install the audio applications, log on to the W95-98 folder, and then log
on to the APPS folder. Run the SETUP program.
Windows NT 4.0 Installation
1. Press the "Start" button.
2. Move the highlight to "Settings" and select "Control Panel".
3. Double click on the "Multimedia" icon.
4. Select the "Devices" tab.
5. Press the "Add..." button.
6. Select item "Unlisted or Updated Driver" in the "List of Drivers" list
box.
7. Specify the path to the PCI audio NT drivers.
8. Select "C-Media CM8338 PCI Device" and press the "OK" button.
9. Choose proper I/O or the "OK" button for the default setting.
10. Restart the Windows NT system.
To install the audio applications, log on to the NT4 folder, and then log
on to the APPS folder. Run the SETUP program.
Page 72

68
Modem Driver and Software
Install the Modem driver from the sub-folders for Windows 95/98 or
Windows NT4.0.
Windows 95/98
The modem is a plug and play device so Windows 95/98 will
automatically detect the presence of your modem. When the Plug and
Play wizard begins to look for modem drivers, click on the button that
says Have Disk and then browse or type in the pathname to the
CMI8x58\modem\win9x folder.
Windows NT 4.0
Follow the instructions in the README file in the WINNT4 sub-folder.
Intel Folder Installation Notes
I810_ACPI
This folder has a patch that allows a Windows 95/98 system to carry out
a suspend to RAM. Run SETUP.EXE to install the patch.
Inf
The Intel INF Installation Utility installs to the target system the
Windows* INF files that outline to the operating system how the chipset
components shall be configured. This is needed for proper functionality
of the following features:
♦ Core PCI and ISAPNP Services
♦ AGP Support
♦ IDE/ATA33/ATA66 Storage Support
♦ USB Support
♦ Identification of Intel Chipset Components in Device Manager
To install the files, run SETUP.EXE.
VGA
This folder has the software and drivers for the graphics system built into
the 810 chipset. Select the folder for the operating system that you are
running and then begin the installation by running SETUP.EXE.
Page 73

69
Mainboard (MS7012D) Installation Notes
Most of the sub-folders in this folder are empty, with a short README
file giving directions to alternate folders for the appropriate software. One
folder contains software that you can install.
Monitor Sub-folder
The software in this folder provides a graphical interface to the hardware
monitoring feature of this mainboard. The software will run under
Windows 95/98 or Windows NT4.0. Follow the installation instructions
contained in the file INSTALL.TXT.
Page 74

70
Appendix 1: Quick Jumper Setting Reference
Enable keyboard power on
Turn off onboard codec
1
3
JP2
JP1
JP3
JP5
JP6
JP1: Clear CMOS memory jumper
Use this 3-pin jumper top clear all the current data stored in the CMOS
memory.
Function Jumper Cap
Normal operation Short pins 1-2
Clear CMOS Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP2: Keyboard power on jumper
Use this 3-pin jumper to enable keyboard power on with hot keys or
password.
Function Jumper Cap
Short pins 1-2
Disable keyboard power on Short pins 2-3
2
JP3: Audio/modem enable/disable jumper
Use this jumper to enable or disable the audio system and modem
integrated on the mainboard.
Function Jumper Cap
Enable audio/modem Short Pins 1-2
Disable audio/modem Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP5: Set System bus frequency jumper (100 MHz)
Use this jumper to set the system bus frequency at auto-detect, or fixed
at 100 MHz
Function Jumper Cap
Normal Short Pins 1-2
Force 100 MHz Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP6: Audio codec select jumper
Use this jumper to select if the system uses the audio codec chip
integrated on the mainboard, or an audio codec chip located on an
optional AMR card.
Function Jumper Cap
Turn on onboard codec Short Pins 1-2
Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
Page 75

71
JP9: Set System bus frequency jumper (133 MHz)
JP9
JP11
JP12
Use this jumper to set the system bus frequency at auto-detect, or fixed
at 133 MHz.
Function Jumper Cap
Normal Short Pins 1-2
Force 133 MHz Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP11: Set TV-out format jumper
Use this jumper to select the format of the TV-out connector.
Function Jumper Cap
Select NTSC format Short Pins 1-2
Select PAL format Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
JP12: Select IDT or Intel processor jumper
Use this jumper to select if you are installing an Intel processor or an IDT
processor in the socket-370 processor socket.
Function Jumper Cap
IDT processor Short Pins 1-2
Intel processor Short pins 2-3
1 2 3
Page 76

72
Panel Connector
PANEL1
Speaker 15-16-17-18
Power LED 1-2-3
KeyLock 10-11
Reset SW 12-13
Green LED 7-8-9
Power SW 22-23
HDD LED 20-21
Suspend SW 4-5
The mainboard PANEL1 connector has a standard set of switch and
indicator connectors that are commonly found on ATX system cases.
Use the illustration below to make the correct connections to the case
switches and indicators.
23
Function Pins
Power Indicator 1+, 2+, 3
Suspend Switch 4, 5
Green Indicator 7+, 8+, 9
Keylock 10, 11
Reset Switch 12, 13
Speaker 15+, 16, 17, 18
HDD Indicator 20+, 21
Power Switch 22+, 23
1
 Loading...
Loading...