Page 1

SW-A0271-HSI-002 : Rev 02
Marantz
RS232C Control Specifica tion
for
SR7300/SR7300OSE
Number of Page :19
Category
Document Version
Date
: AV. Receiver
: 2.01
: 2003/07/01
Page 2

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 2 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
Table of Contents
1.
Introduc tio n.............................................. ........ ........ ...... ......... ........ ...... ........ ......... ............................................3
1-1. Purpose.................... ...... ........ ....... ........ ........ ...... ........ ......... ...... ........ ...... ......... ........ ... .................................3
1-2. Scope................. ...... ........ ...... ......... ........ ...... ........ ......... ...... ........ ...... ........ ......... ...... .. ...... ...... ........ ......... .....3
1-3. Abbreviatio ns................. ...... ........ ......... ...... ........ ........ ....... ........ ...... ........ ......... ...... ........................... ........ ...3
1-4. References........................ ........ ......... ...... ........ ........ ....... ........ ...... ........ ........ ....... ........ .. ...... ...... ......... ........ .3
2. Global Description............................................................................................................................................ .3
2-1. Overview.............. ........ ...... ........ ......... ...... ........ ........ ....... ........ ...... ........ ........ ....... .......................... ......... .....3
2-2. Block Diagra m........................................ .......... ........ ........... .......... ........ ........... .......... ...... .... ........ ......... ...... .3
2-3. Interface connecter specification of This Product........................................................................................3
2-4. Assumptions and Dependencies.................................................................................................................3
3. Detai led De scr ipti on...................................... ............ ........... ............ ............ ........... ........... ...............................4
3-1. Connection f or mat............................ .......... .......... ......... .......... ........ .......... ........... ........ ...... ...... ......... ........ ...4
3-1-1. Ph ysi cal conn ecti on...................................... ........... ............ .......... ............. ............ .......... ...... ....... .......4
3-1-1-1. Data tra nsmi ssio n se que nce fr om Ho st to Sla ve.............. ............ ........... ............ ............. .......... .4
3-1-1-2. Data tra nsmi ssio n se que nce fr om Sl ave to Ho st.............. ............ ........... ............ ............. .......... .4
3-2. Transmi ssio n d at a f orm at......................................... ........... ........ .......... ........... ........ .......... .... ......... ........ .....5
3-2-1. Transm is sion da ta fo rma t fr om H ost to Sla ve..................... .......... ........... ........ .......... .......... ......... ..... ..5
3-2-1-1. Form1: Co mma nd............................................. ........ .......... ........ ........... .......... ........ ........... .. .......5
3-2-1-2. Form2: Sta tus req ue st....................................... ........ .......... ........ ........... .......... ........ ........... .........5
3-2-2. Transm is sion da ta fo rma t fr om S la ve to Ho st....................... ........ ........... ........ .......... .......... ......... ..... ..5
3-2-2-1. Form1: AC K/NAK.............. .......................... ............................. ........................... ..................... .....5
3-2-2-2. Form2: Sta tus an swe r................. .......... ......... .......... .......... ........ ........... ........ .......... ........... ... ........5
3-3. The transact ion seq ue nces an d th e re gu lat ion s......................... ........ ........... .......... ........ .......... .......... ........6
3-3-1. T he tra nsa ctio n se quen ces.................. .......... ............. .......... ............ ............. .......... ............ ....... ...... ...6
3-3-2. T he tra nsa ctio n reg ula tion s.......................... ............. .......... ............ ........... ............ ............ .... ............. .6
3-3-3. Ex amp le of the tr an sacti on s..................... ............ ............. .......... ............. ............ .......... ......... ........ .....6
3-3-4. Ex am pl es of t he ha nd sh aki ng fl ow ch ar t................................. ...... ......... ........ ...... ........ ........ ....... ..... ....7
3-3-4-1. Example o f su cce ss ful han dsh aki ng..................... .......... .......... ......... .......... .......... ........ ........... ...7
3-3-4-2. Example o f er ro r ha nd sha ki ng................................ ........ ...... ........ ....... ........ ........ ...... ......... ....... ..7
3-4. Command list................... ........ ........... ........ .......... .......... ......... .......... .......... ......... .......... ..............................8
3-4-1. N or mal Co mm an d li st............................. ...... ......... ...... ........ ........ ...... ......... ........ ...... ........ ..... .... ........ ...8
3-5. Statu s r eq ue st an d Stat us an sw e r li st........................ ......... ...... ........ ........ ....... ........ ...... ........ ...... ..... ...... ...13
3-5-1. N orm al Sta tu s re qu est a nd Statu s an sw er list................................ ........... ........ .......... ........... ........ ...13
3-5-2. Speci al Statu s r equ est and Statu s a nsw er list...................................... ........... ........ .......... ......... ...... .18
4. Revision h ist ory............................ ............. .......... ............ ............. ............ .......... ............. ...... ...... ......... ........ ...19
Page 3
Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 3 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
1. Introduction
1-1. Purpose
This document was written in order to clarify specification for control this product by the host controller.
1-2. Scope
This document would be using by software or h ardware engineers for prod uction of this product.
This product is [marantz SR7300/SR7300OSE]. (It’s refe r ed to a s “ Th is pr od u ct” a f ter th i s.)
1-3. Abbreviations
Abbreviation Description
1-4. References
2. Global Description
2-1. Overview
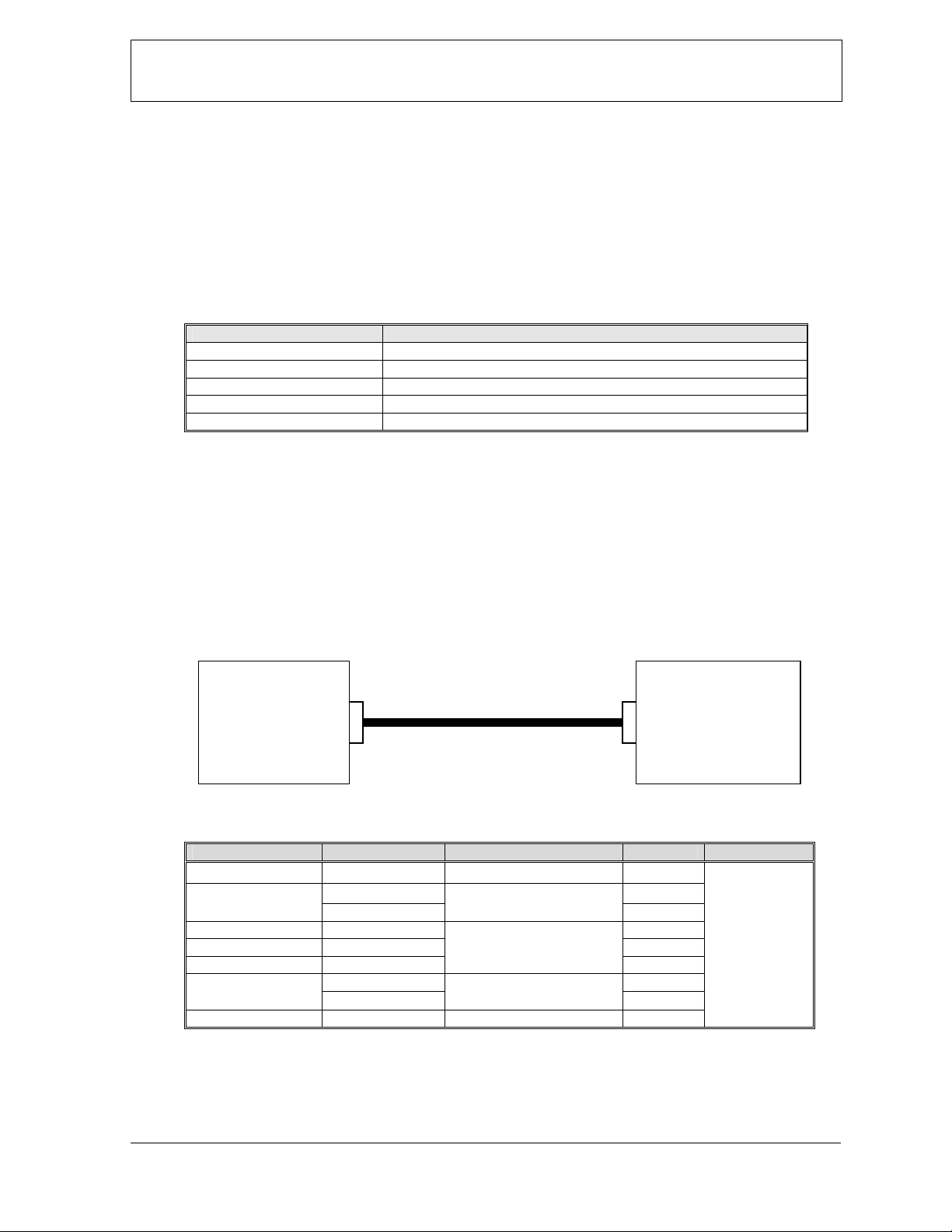
A Host controller can control or watch out this product as a Slave very easily via the communication cable.
2-2. Block Diagram
2-3. Interface connecter specification of This Product
Processor Interface Signal name Connection device D-Sub Pin Connecter
2-4. Assumptions and Dependencies
HOST
(Controller)
- N.C. - 1
TxD (output) 2 UART
RxD (input)
- N.C. 4
- GND 5
- N.C.
CTS (input) 7 GENERAL PORT
RTS (output)
- N.C. - 9
RS232C ca ble ( str aig ht)
RS232C Level shift driver
-
RS232C Level shift driver
(This product)
Connector
D-SUB (9pin, male)
3
6
8
SLAVE
RS232C
D-SUB
(9pin,male)
Page 4

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 4 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
3. Detailed Description
The interface specification between this product and a Host controller is described below.
3-1. Connection format
3-1-1. Physical connection
Host (Controller) Slave (This product)
RTS
CTS
(Serial setting <RS232C basic>)
Baud Rate : 9600bps
TxD
Data Bits : 8bit
Parity : None
RxD
Stop bit : 1bit
Handshaking : (RTS/CTS)
3-1-1-1. Data transmission sequence from Host to Slave
Host (Controller) Slave (This product)
3-1-1-2. Data transmission sequence from Slave to Host
GND
RTS → CTS
CTS ← RTS
TxD → RxD
RxD ← TxD
1. The host checks that CTS is High, then starts a data transmission from TxD.
2. The host performs the data transmission of the number of required bytes, and ends a transmission.
* The host can do RTS to Low during the transmission for disable dat a transmission from a slave.
Host (Controller) Slave (This product)
RTS → CTS
CTS ← RTS
TxD → RxD
RxD ← TxD
1. The slave checks that CTS is High, then starts a data transmission from TxD.
2. The slave performs the data transmission of the number of required bytes, and ends a transmission.
* The slave can do RTS to Low during the transmission for disable data transmission from a host.
CTS
RTS
RxD
TxD
GND
Page 5
Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 5 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
3-2. Transmission data format
3-2-1. Transmission data format from Host to Slave
There are two kinds of transmission data form from Host shown below .
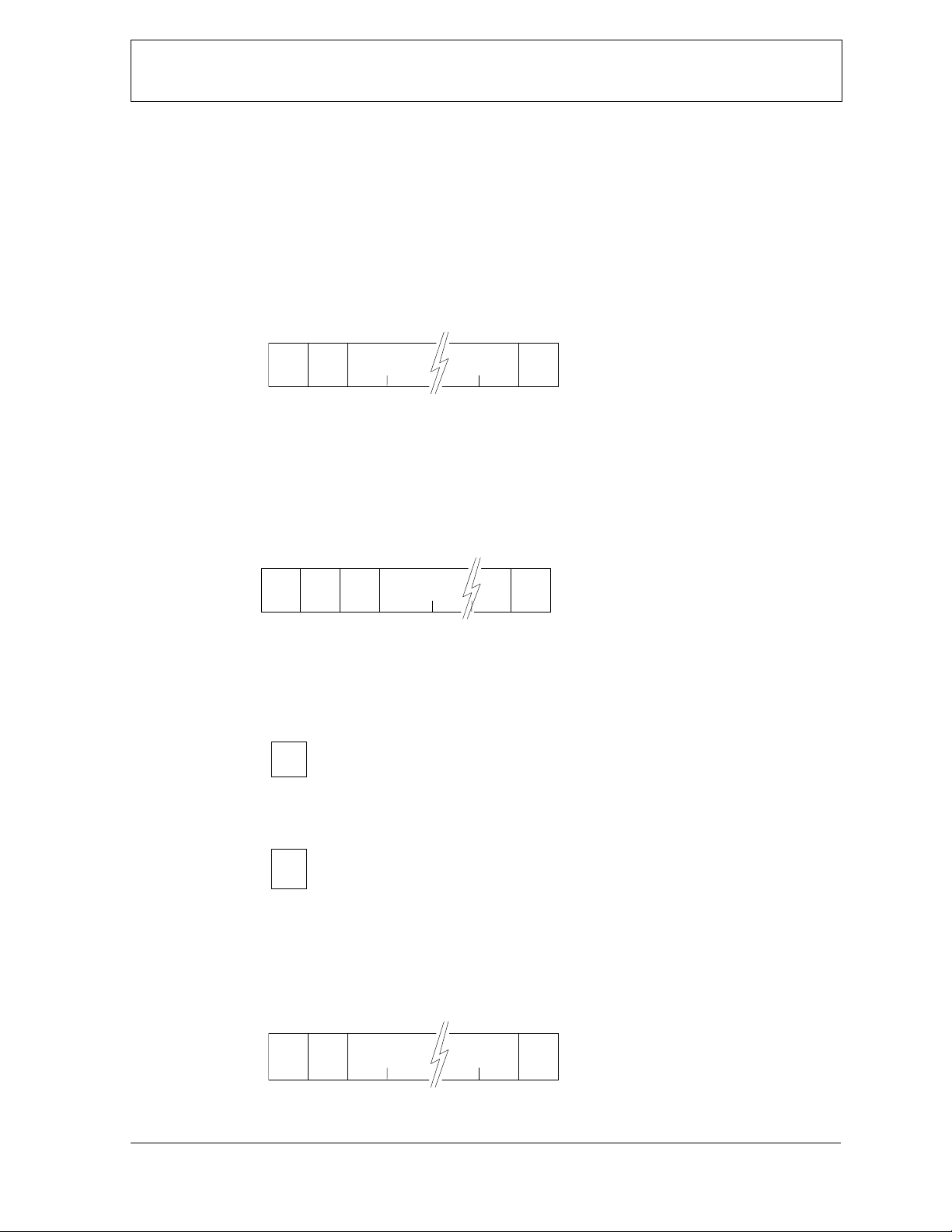
3-2-1-1. Form1: Command
Command is a data that requests some status change.
Start chara cter : ’@’
ID : ‘0’ ~ ‘9’ (A Slave has ow n ID, A Host has to set the ID.)
COMMAND : see “Command list”
End character : 0Dh
COM M ANDStart
‘@
ID
’
3-2-1-2. Form2: Status request
Status request is a data that requests a answer of some status.
Start chara cter : ’@’
ID : ‘0’ ~ ‘9’ (A Slave has ow n ID, A Host has to set the ID.)
Request character : ‘?’
Request status : see “Status request list”
End character : 0Dh
S tart
‘@ ’
ID
R equest status
‘?’
3-2-2. T ransmission dat a format from Slave to Host
There are two kinds of transmission data form from Slave shown below .
3-2-2-1. Form1: ACK/NAK
ACK is a reply data from Slave when Slave got an acceptable command data from Host.
ACK : 06h
ACK
06h
NAK is a reply data from Slave when Slave got an incorrect Command data, Status request data or
some other data from Host.
NAK : 15h
NAK
15h
3-2-2-2. Form2: Status answer
Status answers are reply dat a when Slave got an acceptable Re quest status data fro m Host.
Start chara cter : ’@’
ID : ‘0’ ~ ‘9’ (A Slave will set own ID.)
Answer cha racter : see “S t atu s an swer list”
End character : 0Dh
End
0D h
End
0D h
End
0D h
‘@ ’
Status answ erStart
ID
Page 6
Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 6 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
3-3. The transaction sequences and the regulations
3-3-1. The transaction sequences
The transactions have two kinds of sequence.
*A transaction is a Command from Host then the Sla ve will be an answer by ACK or NAK.
*A transaction is a S t atus request fro m Host then the Slave will be an an swer by Status answer.
3-3-2. The transaction regulations
The transactions have some kinds of regulation.
* A Command or a Status request transmission by the Host has to finish within one second.
* An answer (ACK , NAK or Status answer) transmitt ion by the Slave ha s to finish withi n one second
when got a Command or a Status request from the Host.
* The Host must not transmit an another Command or Status request until "it receives a answer by a
previous Command or Status request" or "it passes one second from a finishing of previous transmission
of a Command or a Sta tus request ".
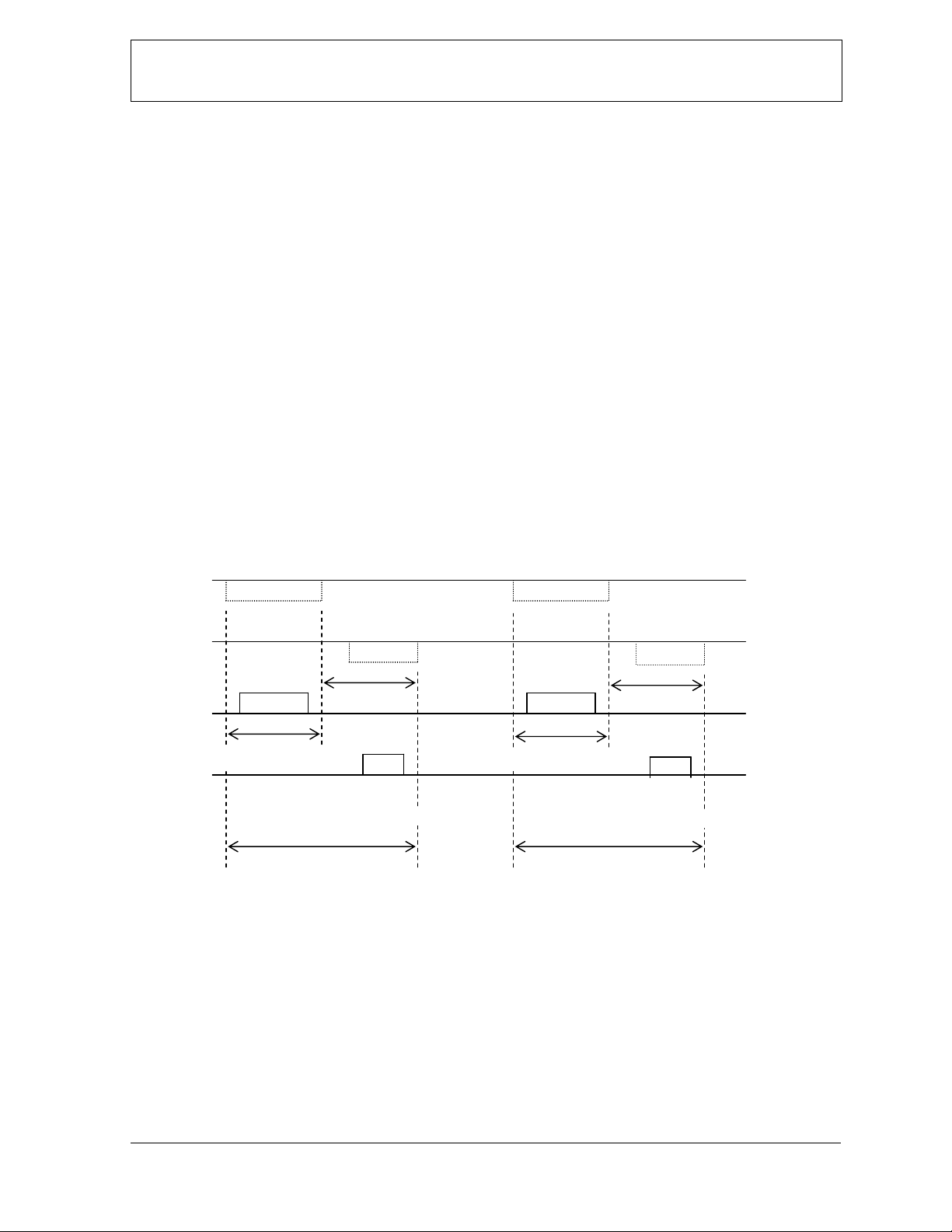
3-3-3. Example of the transactions
<Host> <Slave>
RTS CTS
CTS RTS
TxD RxD
RxD TxD
Command
max. 1sec
a transaction a transaction
max. 1sec
ACK/NAK
Example of the transactions
Status request
max. 1sec
max. 1sec
Status answer
Page 7

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 7 / 19
p
p
A
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
3-3-4. Examples of the handshaking flowchart
3-3-4-1. Example of successful handshaking
SLAVEHOST
Com mand
Status
request
3-3-4-2. Example of error handshaking
Com mand
Com mand
acce
Request
acce
SLAVEHOST
Com mand
incorrect
ta b le
CK
ta b le
Status
answer
NAK
Status
request
Request
incorrect
NAK
Page 8

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 8 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
3-4. Command list
3-4-1. Normal Command list
(Samples indicated the ID set to as ‘1’.)
Command Character Sample
POWER A0 "@1A0",0x0D
POWER
INPUT SELECT
MUL TI-CHANNEL
INPUT SIGNAL A/D
Multi Room control command as from MULTI ROOM
Command Character Sample
INPUT SELECT
INPUT SIGNAL A/D
POWER ON A1 "@1A1",0x0D
POWER OFF A2 "@1A2",0x0D
DSS B0 "@1B0",0x0D
TV B1 "@1B1",0x0D
LD B2 "@1B2",0x0D
DVD B3 "@1B3",0x0D
VCR1 B4 "@1B4",0x0D
VCR2/DVD-R
AUX1 B6 "@1B6",0x0D
AUX2 B7 "@1B7",0x0D
DVD-R B8 "@1B8",0x0D
CD B9 "@1B9",0x0D
TAPE BA "@1BA",0x0D
CD-R BB "@1BB",0x0D
FM BC "@1BC",0x0D
AM BD "@1BD”,0x0D
MW BE "@1BE”,0x0D
LW BF "@1BF",0x0D
TUNER BG "@1BG",0x0D
MULTI-CHANNEL INPUT ON
MULTI-CHANNEL INPUT OFF
DSS Ba "@1Ba",0x0D
TV Bb "@1Bb",0x0D
LD Bc "@1Bc",0x0D
DVD Bd "@1Bd",0x0D
VCR1 Be "@1Be",0x0D
VCR2/DVD-R
AUX1 Bg "@1Bg",0x0D
AUX2 Bh "@1Bh",0x0D
DVD-R Bi "@1Bi",0x 0D
CD Bj "@1Bj",0x0D
TAPE Bk "@1Bk",0x0D
CD-R Bl "@1Bl",0x0D
FM Bm "@1Bm",0x0D
AM Bn "@1Bn”,0x0D
MW Bo "@1Bo”,0x0D
LW Bp "@1Bp",0x0D
TUNER Bq "@1Bq",0x0D
B5
BH
BI
BJ
Bf
Br
"@1B5",0x0D
"@1BH",0x0D
"@1BI",0x0D
"@1BJ",0x0D
"@1Bf",0x0D
"@1Br",0x0D
Page 9

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 9 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
Command Character Sample
AUTO-TUNE C0 "@1C0",0x0D
TUNNER FREQUENCY
FREQ. UP C1 "@1C1",0x0D
FREQ. DOWN C2 "@1 C2 ",0x0 D
PRESET INFO. C3 "@1C3",0x0D
TUNNER PR ESE T
P-SCAN C4 "@1C4",0x0D
PRESET UP C5 "@1C5",0x0D
PRESET DOWN C6 "@1C6",0x0D
F-DIRECT F-DIRECT C7 "@1C7",0x0D
TUNER MODE T-MODE C8 "@1C8",0x0D
AUTO FREQ. TUNING
MEMO/CLR
AUTO UP START/STOP C9 "@1CA",0x0D
AUTO DOWN STAR T/STOP CA "@1CB",0x0D
CLR D0 "@1D0",0x0D
MEMO D1 "@1D1",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 0 E0 "@1E0",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 1 E1 "@1E1",0X0D
DIRECT KEY 2 E2 "@1E2",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 3 E3 "@1E3",0x0D
DIRECT KEY
DIRECT KEY 4 E4 "@1E4",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 5 E5 "@1E5",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 6 E6 "@1E6",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 7 E7 "@1E7”,0x0D
DIRECT KEY 8 E8 "@1E8",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 9 E9 "@1E9",0x0D
Multi Room control command as from MULTI ROOM
Command Character Sample
TUNNER FREQUENCY
FREQ. UP Ca "@1Ca",0x0D
FREQ. DOWN Cb "@1Cb",0x0D
PRESET INFO. Cc "@1Cc",0x0D
TUNNER PR ESE T
P-SCAN Cd "@1Cd",0x0D
PRESET UP Ce "@1Ce",0x0D
PRESET DOWN Cf "@1Cf",0x0D
TUNER MODE T-MODE Cg "@1Cg",0x0D
AUTO FREQ. TUNING
AUTO UP START/STOP Ch "@1Ch",0x0D
AUTO DOWN START/STOP Ci "@1Ci",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 0 Ea "@1Ea",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 1 Eb "@1Eb",0X0D
DIRECT KEY 2 Ec "@1Ec",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 3 Ed "@1Ed",0x0D
DIRECT KEY
DIRECT KEY 4 Ee "@1Ee",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 5 Ef "@1Ef",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 6 Eg "@1Eg",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 7 Eh "@1Eh”,0x0D
DIRECT KEY 8 Ei "@1Ei",0x0D
DIRECT KEY 9 Ej "@1Ej",0x0D
Page 10

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 10 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
Command Character Sample
AUTO F0 "@1F0",0x0D
THX MUSIC F1 "@1F1",0x0D
THX SURR EX F2 "@1F2",0x0D
THX CINEMA F3 "@1F3",0x0D
DTS F4 "@1F4",0x0D
DTS ES F5 "@1F5",0x0D
DOLBY F6 "@1F6",0x0D
DOLBY PROLOGIC F7 "@1F7",0x0D
DOLBY PLⅡ MOVIE F8 "@1F8",0x0D
DOLBY PLⅡ MUSIC F9 "@1F9",0x0D
VIRTUAL FA "@1FA",0x0D
S DIRECT FB "@1FB",0x0D
SURROUND MODE
MOVIE FC "@1FC",0x0D
HALL FD "@1FD",0x0D
MATRIX FE "@1FE",0x0D
Mch-STEREO FF "@1FF",0x0D
STEREO FG "@1FG",0x0D
NEO6 CINEMA FI "@1FI”,0x0D
NEO6 MUSIC FJ "@1FJ”,0x0D
THX UL TRA2 FK "@1FK”,0x0D
CSⅡ MUSIC FL "@1FL",0x0D
CSⅡ CINEMA FM "@1FM",0x0D
SURR MODE FN "@1FN",0x0D
CSⅡ MONO FO "@1FO",0x0D
SURR. MODE NEXT FX “@1FX”,0x0D
SURR. MODE PREV.
FY “@1FY”,0x0D
VOLUME UP G0 "@1G0",0x0D
VOLUME
VOLUME DOWN G1 "@1G1",0x0D
VOLMUE UP F AST G2 "@1G2",0x0D
VOLUME DOWN FAST
G3 "@1G3",0x0D
BASS UP G4 "@1G4",0x0D
TONE
BASS DOWN G5 "@1G5",0x0D
TREBLE UP G6 "@1G6",0x0D
TREBLE DOWN G7 "@1G7",0x0D
SLEEP MODE SLEEP H0 "@1H0",0x0D
MUTE
MUTE OFF H1 "@1H1",0x0D
MUTE ON H2 "@1H2" ,0x0 D
VIDEO MUTE VIDEO MUTE H3 "@1H3",0x0D
ATT ATT H4 "@1H4",0x0D
TEST TONE TEST TONE I0 "@1I0",0x0D
SPEAKER A ON SPEAKER A ON I1 "@1I1",0x0D
SPEAKER A OFF SPEAKER A OFF I2 "@1I2",0x0D
SPEAKER B ON SPEAKER B ON I3 "@1I3",0x0D
SPEAKER BOFF SPEAKER BOFF I4 "@1I4",0x0D
SPEAKER A SPEAKER A ON/OFF I5 "@1I5",0x0D
SPEAKER B SPEAKER B ON/OFF I6 "@1I6",0x0D
NIGHT NIGHT J0 "@1J0",0x0D
Page 11

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 11 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
Command Character Sample
DISP DISP J1 "@1J1",0x0D
OSD OSD J2 "@1J2",0x0D
MENU
MENU (OK) J3 "@1J3",0x0D
MENU OFF J4 "@1J4",0x0D
CURSOL UP J5 "@1J5",0x0D
CURSOL
CURSOL DOWN J6 "@1J6",0x0D
CURSOL LEFT J7 "@1J7",0x0D
CURSOL RIGHT J8 "@1J8",0x0D
RDS
RDS DISP MODE J9 "@1J9",0x0D
RDS PTY JA "@1JA",0x0D
VOLUME RESET VOL. RESET JB "@1JB",0x0D
RE-EQ RE-EQ JC "@1JC",0x0D
CHANNEL SELECT CH. SEL. JD "@1JD",0x0D
CHANNEL LEVEL
CH. LEVEL UP JE "@1JE",0x0D
CH. LEVEL DOWN JF "@1JF",0x0D
SELECT SELECT JG "@1JG",0x0D
ENTER ENTER JH "@1JH",0x0D
UP/DOWN
UP>> JI "@1JI",0x0D
DOWN<< JK "@1JK”,0x0D
FACTORY MODE into FACTORY MODE K1 "@1K1",0x0D
SERVICE MODE into SERVICE MODE K2 "@1K2”,0x0D
Multi Room control command as from MAIN ROOM
Command Character Sample
LA
LB
LC
LD
LG
LJ
LK
"@1LA",0x0D
"@1LB",0x0D
"@1LC",0x0D
"@1LD",0x0D
"@1LG",0x0D
"@1LJ",0x0D
"@1LK",0x0D
MUL TI ROOM
MUL TI ROOM MUTE
MUL TI ROOM OSD
MUL TI ROOM VOLUME
MULTI ROOM ON/OFF
MULTI R OOM ON
MULTI R OOM OFF
MULTI ROOM MUTE ON/OFF
MULTI ROOM MUTE ON LE "@1LE",0x0D
MULTI ROOM MUTE O FF
LF "@1LF",0 x0D
MULTI R OOM OSD ON/OFF
MULTI R OOM OSD ON LH "@1LH",0x0D
MULTI ROOM OSD OFF
LI "@1LI",0x0D
MUL TI VOL . UP
MUL TI VOL . DOWN
MUL TI VOL. U P FAST LL "@1LL",0x0D
MUL TI VOL. D OWN FAST LM "@1LM",0 x0 D
MULTI VOL. VALUE
MUL TI SLEEP MODE MUL TI ROOM SLEEP MODE
LN "@1LN+05",0x0D
LO
"@1LO",0x0D
MUL TI ROOM SPK O N/OFF LP "@1L P",0x0D
MUL TI SPEAKER
MUL TI ROOM SPEAKER ON LQ "@1LQ",0x0D
MUL TI ROOM SPEAKER OFF
LR "@1LR",0x0 D
Page 12

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 12 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
Multi Room control command as from MULTI ROOM
Command Character Sample
MULTI ROOM ON/OFF La "@1La",0x0D
MUL TI ROOM
MULTI R OOM ON Lb "@1Lb",0x0D
MULTI R OOM OFF Lc "@1Lc",0x0D
MULTI ROOM MUTE ON/OFF Ld "@1Ld",0x0D
MUL TI ROOM MUTE
MULTI ROOM MUTE ON Le "@1Le",0x 0D
MULTI ROOM MUTE O FF
Lf "@1Lf",0x0D
MULTI R OOM OSD ON/OFF Lg "@1Lg",0x0D
MUL TI ROOM OSD
MULTI ROOM OSD ON Lh "@1Lh",0 x0 D
MULTI ROOM OSD OFF
Li "@1LIi,0x0D
MULTI VOL. UP Lj "@1Lj",0x0D
MULTI VOL. DOWN Lk "@1Lk",0x0D
MUL TI ROOM VOLUME
MUL TI VOL. U P FAST Ll "@1Ll",0x0D
MUL TI VOL. D OWN FAST Lm "@1Lm",0 x0 D
MULTI VOL. VALUE
Ln "@1Ln+05",0x 0D
MUL TI SLEEP MODE MUL TI ROOM SLEEP MODE Lo "@1Lo",0x0D
MUL TI ROOM SPK O N/OFF Lp "@1Lp",0x0 D
MUL TI SPEAKER
MUL TI ROOM SPEAKER ON Lq "@1Lq",0x0 D
MUL TI ROOM SPEAKER OFF
Lr "@1Lr",0x0D
Page 13

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 13 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
3-5. Status request and St at us answer list
3-5-1. Normal Status request and S t atus answer list
(Samples indicated the ID set to as ‘1’.)
Request Status Char. & Sample Status answer Char. & Sample
POWER Status ‘A’ (“@1?A”,0x0D)
VIDEO INPUT ‘B’ (“@1?B”,0x0D)
AUDIO INPUT ‘C’ (“@1?C”,0x0D)
INPUT MODE ‘D’ (“@1?D”,0x0D)
‘E’ (“@1?E”,0x0D)
TUNER FFREQUENCY
TUNER PRESET ‘F’ (“@1?F”,0x0D)
TUNER MODE ‘G’ (“@1?G”,0x0D)
VOLUME Status ‘H’ (“@1?H”,0x0D)
BASS St atus ‘I’ (“@1?I” ,0x0D) BASS:xxdB(xx=-9~+9) I0xx
TREBLE St atus ‘J’ (“@1? J”,0x0D) TREBLE:xxdB(xx=-9~+9) J0xx
ATT S tatus ‘K’ (“@1?K”,0x0D)
FM:076.0-108.0
AM,MW:520-1710
L W:152-282
POWER ON A0 (“@1A0”,0x0D)
POWER OFF A1
DSS B0
TV B1
LD B2
DVD B3
VCR-1 B4
VCR-2 B5
AUX1 B6
AUX2 B7
DVD-R B8
DSS C0
TV C1
LD C2
DVD C3
VCR-1 C4
VCR-2/DVD-R C5
AUX1 C6
AUX2 C7
DVD-R C8
CD C9
TAPE CA
CD-R CB
FM (/TUNER) CC
AM CD
MW CE
LW CF
MUL TI-CHANNEL INPUT CG
TUNER
DIGIAL D0
ANALOGUE D1
TUNER FREQUENCY
E0xxxx:(Not tuned+Freq.)
E1xxxx:(Tuned+Freq.)
Frequency Scaning E2 (“@1E2”!,0x0D)
Not available E- (“@1E-“,0x0D)
Preset No (XX=01~50)
Not Preset mode (XX=00)
Not available F- (“@1F-“,0x0D)
AUTO STEREO G1
MONO G0
Not available GVOL.= XXXdB
(XXX = -90~+99)
max H1
min (-∞) H2
ATT ON K1
ATT OFF K0
CH
(FM: 87.55 = “8755”)
(FM:108.00 = “0800”)
(MW: 520=”0520”)
(L W:282=”0282”)
F0XX
H0XXX
(“@1H0-15”,0x0D)
Page 14

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 14 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
Request Status Char. & Sample Status answer Char. & Sample
AUTO L0 (“@1L0”,0x0D)
THX 5.1 L1
THX SURR EX L2
THX CINEMA L3
THX MUSIC L4
DTS MUSIC L5
DTS CINEMA L6
DTS ES L7
NEO 6 CINEMA L8
NEO 6 MUSIC L9
D DIGIT AL LA
DD PROLOGIC LB
DD PLⅡMOVIE LC
SURROUND MODE ‘L’ (“@1?L”,0x0D)
DD PLⅡMUSIC LD
CSⅡCINEMA LE
CSⅡMUSIC LF
VIRTUAL LG
S DIRECT LH
MOVIE LI
HALL LJ
MATRIX LK
Mch-STEREO LL
STEREO LM
MONO LN
THX UL TRA2 LO
CSⅡMONO LP
SLEEP TIMER Status ‘M’ (“@1?M”,0x0D)
SLEEP OFF M0
SLEEP XXX(001~120) M1XXX
DISPLAY ON N0
DISPLAY S tatus ‘N’ (“@1?N”,0x0D)
OSD Status ‘O’ (“@1?O”,0x0D)
DISPLAY OFF N1
AUTO DISPLAY OFF N2
DISPLA Y D IMMER
N3~N9 (dimmer level)
OSD ON O0
OSD OFF O1
TEST TONE OFF P0
TEST TONE L P1
TEST TONE C P2
TEST TONE R P3
TEST TONE Status ‘P’ (“@1?P”,0x0D)
TEST TONE SR P4
TEST TONE SBR P5
TEST TONE SBL P6
TEST TONE SL P7
TEST TONE SW P8
TEST TONE MODE ‘Q’ (“@1?Q”,0x0D)
NIGHT MODE ‘R’ (“@1?R”,0x0D)
MENU ‘S’ (“@1?S”,0x0D)
TEST TONE AUTO Q0
TEST TONE MANUAL Q1
NIGHT MOD E ON R0
NIGHT MOD E OFF R1
MENU ON S0
MENU OFF S1
Page 15

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 15 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
Request Status Char. & Sample Status answer Char. & Sample
F-DIRECT ON T1 (“@1T1”,0x0D)
F-DIRECT ‘T’ (“@1?T”,0x0D)
F-DIRECT OFF T0
Not available TD DIGIT AL(AC-3) U0
DD SURROUND U1
DD SURR EX U2
DTS U3
DTS ES U4
AAC U5
MPEG U6
SIGNAL FORMAT ‘U’ (“@1?U”,0x0D)
MLP U7
PCM U8
HDCD U9
DSD UA
OTHER UB
NONE_DETECTION UC
DTS ES DISCRA TE UE
DTS ES MA TRIX UF
32K V0
44.1K V1
48K V2
88.2K V3
SAMPLING FREQ. ‘V’ (“@1?V”,0x0D)
96K V4
176.4K V5
192K V6
OUT OF RANGE V7
Not available V-
CHANNEL STATUS ‘W’ (“@1?W”,0x0D)
See below W1$%
Not available W-
* Description of CHANNEL STATUS answer character . (about : $%)
(Character $ and % would be ‘0’ to ‘9’ or ‘A’ to ‘F’,it uses to as hex. bit data .)
| $ bit | % bit |
Bit 3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0
LFE
1
SR S L R C
SL
L C
R
When a bit of channel status is effective, it sets to 1.
And when it is opposite condition, it sets to 0.
ex.)
LFE
* If front L and R channel status are only effective, it will send “@1W146”,0Dh.
* If front and surr. L/R channel status are effective, it will send “@1W1B6”,0Dh.
* If all channel status are effective, it will send “@1W1FF”,0Dh.
* If all channel status are not effective, it will send “@1W180”,0Dh.
SL
S
SR
Page 16

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 16 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
Request Status Char. & Sample Status answer Char. & Sample
MUL TI ROOM ON X0 (“@1X0”,0x0D)
MULTIROOM Status ‘X’ (“@1X?”,0x0D)
MUL TI ROOM OFF X1
Not available XDSS Y0
TV Y1
LD Y2
DVD Y3
VIDEO INPUT
(Multi Room)
‘Y’ (“@1?Y”,0x0D)
VCR1 Y4
VCR2/DVD-R Y5
AUX1 Y6
AUX2 Y7
DVD-R Y8
Not available YDSS Z0
TV Z1
LD Z2
DVD Z3
VCR1 Z4
VCR2/(DVD-R) Z5
AUX1 Z6
AUX2 Z7
AUDIO INPUT
(Multi Room)
‘Z’ (“@1?Z”,0x0D)
DVD-R Z8
CD Z9
TAPE ZA
CD-R ZB
MD ZC
FM ZD
AM ZE
MW ZF
LW ZG
TUNER ZH
Not available Z-
a0XXXX
(FM:87.50 = “8750”)
(FM:108.00=”0800”)
(MW: 520=”0520”)
(MW:1710=”1710”)
TUNER FREQUENCY
(Multi Room)
‘a’ (“@1?a”,0x0D)
TUNER FREQUENCY
XXXX=076.00-108.00(FM)
=520-1710(AM,MW)
= 152-282(LW)
Not available a- (“@1a-“,0x0D)
TUNER PRESET
(Multi Room)
VOLUME Status
(Multi Room)
(Multi Room)
SLEEP TIMER S tatus
(Multi Room)
(Multi Room)
(Multi Room)
(Multi Room)
‘b’ (“@1?b”,0x0D)
‘c’ (“@1?c”,0x0D)
‘d’ (“@1?d”,0x0D)
‘e’ (“@1?e”,0x0D)
‘f’ (“@1?f”,0x0D)
‘g’ (“@1?g”,0x0D)
‘h’ (“@1?h”,0x0D)
Preset No. (XX=01~50)
Not Preset mode (XX=00)
Not available b- (“@1b-“,0x0D)
VOL .XXX(-9 0~+99) c0XXX
MAX. c1
MIN.(-∞) c2
VARIABLE d0 VOLUME SET Status
FIXED d1
SLEEP OFF e0
SLEEP XXX(1~120) e1XXX
MUL TI OSD ON f0 OSD Status
MUL TI OSD OFF f1
MUL TI SPEAKER ON g0 SPEAKER S tatu s
MUL TI SPEAKER OFF g1
MUTE ON (MR) h0 MUTE Status
MUTE OFF (MR) h1
b0XX
Page 17

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 17 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
Request Status Char. & Sample Status answer Char. & Sample
CHANNEL LEVEL
[
XX: ( 0=”10”)
(+01=”11”~+10=”20”)
(-01=”09”~ -10=”00”)
(-11=”55” ~ -15=”51”)
]
“i0” ("@1?i0", 0x0D) LEFT LEVEL i0XX (“@1i010”0x0D)
“i1” ("@1?i1", 0x0D) RIGHT LEVEL i1XX
“i2” ("@1?i2", 0x0D) CENTER LEVEL i2XX
“i3” ("@1?i3", 0x0D) SUBWF LEVEL i3XX
“i4” ("@1?i4", 0x0D) SURR L LEVEL i4XX
“i5” ("@1?i5", 0x0D) SURR R LEVEL i5XX
“i6” ("@1?i6", 0x0D) BACK L (or 1ch) LEVEL i6XX
“i7” ("@1?i7", 0x0D) BACK R LEVEL i7XX
“j0” ("@1?j0", 0x0D) LEFT DISTANCE j0XX
SPEAKER DISTANCE
[
XX: (00~30)
(1 foot = “01”)
(10 feet=”10”)
]
“j1” ("@1?j1”, 0x0D) RIGHT DIST ANCE j1XX
“j2” ("@1?j2", 0x0D) CENTER DISTANCE j2XX
“j3” ("@1?j3", 0x0D) SUBWF DISTANCE j3XX
“j4” ("@1?j4", 0x0D) SURR. L DIST ANCE j4XX
“j5” ("@1?j5", 0x0D) SURR. R DISTANCE j5XX
“j6” ("@1?j6", 0x0D) BACK L DIST ANCE j6XX
“j7” ("@1?j7", 0x0D) BACK R DISTANCE j7XX
“k0” ("@1?k0", 0x0D)
FRONT LAGE k00
FRONT SMALL k01
CENTER LAGE k10
“k1” ("@1?k1", 0x0D)
CENTER SMALL k11
CENTER OFF k12
SUBWF ON k20
SUBWF OFF k22
SPEAKER SIZE
“k2” ("@1?k2", 0x0D)
SURR. LAGE k30
“k3” ("@1?k3", 0x0D)
SURR. SMALL k31
SURR. OFF k32
BACK LAGE k40
“k4” ("@1?k4", 0x0D)
BACK SMALL k41
BACK OFF k42
BACK 1ch l0
SPEAKER BACK ‘l’ ("@1?l", 0x0D)
BACK 2ch l1
BACK NONE l2
SPEAKER A ‘o’ (“@1?o”,0x0D)
SPEAKER B ‘p’ (“@1?p”,0x0D)
SPEAKER A OFF o0
SPEAKER A ON o1
SPEAKER B OFF p0
SPEAKER B ON p1
MAIN+SUB q0
BILINGUAL ‘q’ ("@1?q",0x0D)
MAIN q1
SUB q2
AUDIO MUTE ‘r’(“@1?r”,0x0D)
VIDEO MUTE ‘s’ (“@1?s”,0x0D)
AUDIO MUTE OFF r0
AUDIO MUTE ON r1
VIDEO MUTE OFF s0
VIDEO MUTE ON s1
Page 18

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 18 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
3-5-2. Special St atus request and S tatus answer list
Request Status Char. & Sample Status answer Char. & Sample
SERIAL NUMBER ‘n’ ("@1?n", 0x0D) SERIAL NUMBER
see blow
ERROR DETECT ‘m’ ("@1?m", 0x0D)
“n0XXXXXXXXX”
("@1n0123456789",0x0D)
m0#$%&
(“@1m0#$%&”,0x0D)
No error m- (“@1m-“,0x0D)
Descriptions of ERROR DETECT status answer character. (about : #$%&)
(Character #, $, % and & would be ‘0’ to ‘9’ or ‘A’ to ‘F’, it uses to as hex. bit data.)
* # : Bit ErrorName ERROR SAFE
3 Reserved 1 1
2 Reserved 0 0
1 Reserved 0 0
0 Reserved 0 0
* $ : Bit ErrorName ERROR SAFE
3 Reserved 0 0
2 Reserved 0 0
1 PROTECT 1 0
0 DSP1 ERROR 1 0
* % : Bit ErrorName ERROR SAFE
3 Reserved 1 1
2 DSP2 ERROR 1 0
1 ADC ERROR 1 0
0 EEPROM ERROR 1 0
* & : Bit ErrorName ERROR SAFE
3 EEPROM IF ERROR 1 0
2 DSP CODE ERROR 1 0
1 RS232C ERROR 1 0
0 POWER 5V ERROR 1 0
ex.)
* If the POWER 5V ERROR only occurs that will send [“@1m080 81”,0x0D].
* If the RS232C ERROR only occurs that will send [“@1m08082”,0x0D].
* If the ADC ERROR only occurs that will send [“@1m080A0”,0x0D].
* If the DSP1 ERROR only occurs that will send [“@1m0 9080”,0x0D].
Page 19

Hardware Software Interface (HSI) Spec. Page: 19 / 19
SR7300/SR7300OSE Document Version [2.01]
4. Revision history
Rev. Date Owner Change description
2.0 ‘03-01-31 N.Sakamoto Renewal issued
2.1 ‘03-02-06 N.Sakamoto - Auto Freq. up/down command were changed to Auto Freq. up/down
Start/Stop に変更.
- Added status answers “Not tuned”, “Tuned, Scaning” for the statu request for
the tuner frequency section. (Not tuned :E0xxxx, Tuned:E1xxxx, Scaning:E2)
- Added the commands for “OSD ON/OFF”.
- Added the commands for Speaker A,B.
- modified SpeakerA ON (H1), OFF (H2), Speaker B ON (H3), OFF (H4)
commands to I1, I2, I3, I4.
 Loading...
Loading...