Page 1
B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
mantracourt.com
B24
Bluetooth Telemetry System
Page 2

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
1
Introduction / Overview .............................................................................................................................................3
Advertising Operation ............................................................................................................................................................................... 3
Connected Operation ................................................................................................................................................................................ 3
B24 Advert Format ......................................................................................................................................................4
Local Name .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Manufacturer Specific Data .................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Format ID ................................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Status .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Units ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 5
Data Tag ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Data.............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 5
Bluetooth Connected Mode ......................................................................................................................................6
Telemetry Configuration Service .......................................................................................................................................................... 6
Data Rate ................................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Resolution ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 6
Battery Threshold ................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
View PIN ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
Serial Number .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
Data Tag ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
Battery Value ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 7
System Zero .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 7
Configuration Pin ................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Model Name ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 8
Firmware Version .................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Telemetry Data Service ............................................................................................................................................................................. 9
Status .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Data Value ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 9
Data Units .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 9
Telemetry Calibration Service ............................................................................................................................................................. 10
Sensitivity Range ................................................................................................................................................................................. 10
Coefficient (@Index)........................................................................................................................................................................... 10
Linearisation Index .............................................................................................................................................................................. 10
Linearisation Repeat ........................................................................................................................................................................... 10
Linearisation Points ............................................................................................................................................................................ 11
Base Value .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 11
Base Units ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Data Gain ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 11
Data Offset ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 11
Calibration PIN ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Calibration Units .................................................................................................................................................................................. 11
Advanced Index ................................................................................................................................................................................... 12
Advanced Data ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 12
Connection Security ................................................................................................................................................................................ 12
Operation Examples ................................................................................................................................................. 13
Decoding Data with View PIN ............................................................................................................................................................. 13
Connection ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 14
Reading Data ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 14
Examples: ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 14
Writing Data ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Examples: ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 15
Calibration .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 16
Unit Conversion ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 18
System Zero ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Appendices ................................................................................................................................................................ 19
Appendix A - Bluetooth UUID Quick Reference .......................................................................................................................... 19
Appendix B - Units .................................................................................................................................................................................. 20
Page 3

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
2
Appendix C - Advanced Parameters ................................................................................................................................................ 23
Appendix D – Filter .................................................................................................................................................................................. 25
Page 4
Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
3
Introduction / Overview
The B24 Bluetooth Telemetry range provides access to quality measurements on a mobile platform such as a
phone or tablet. The delivery mechanism is ‘Bluetooth Low Energy’ (Also known as ‘Bluetooth Smart’ or BLE)
which utilises the flexibility and availability of Bluetooth receivers while maintaining the low power requirements
of embedded systems. B24 is built upon two complimentary principles of BLE, broadcast advertising data which
enables users to deliver the same data to multiple receivers simultaneously and low power connections which can
be used in a point to point system. B24 is available in OEM bare board formats and with environmentally sealed
enclosure with integrated battery holder.
This manual provides details of data delivery and configuration mechanisms available to system developers
intending to implement their own configuration and monitoring application. There are also worked examples for
calibration, data delivery and unit conversion.
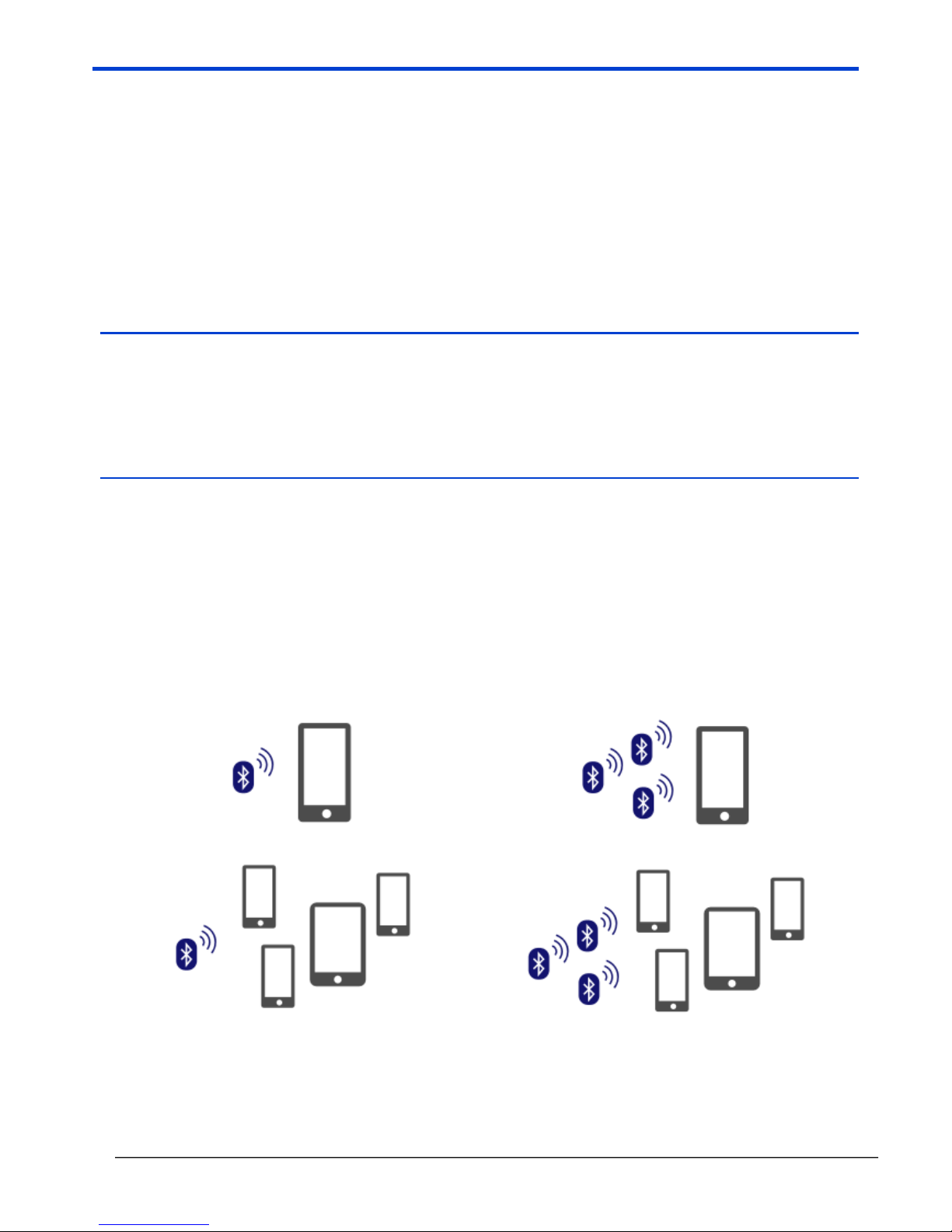
Advertising Operation
The advertising mode of operation enables B24 modules to broadcast measurement data to multiple locations
without retransmission. The advert is a new operational mode within ‘Bluetooth Low Energy’ and facilitates the
delivery of data without a connection. This mode of operation is useful in ‘many to many’ and ‘one to many’ use
cases.
Connected Operation
The connected operational mode enables Bluetooth Low Energy devices to connect directly to the B24 module. A
single mobile device can be connected to multiple B24 transmitter modules simultaneously. This mode has a dual
purpose as it may be used to monitor data and configure the device. When it is used for the delivery of data the
application can register to receive notification updates when the status and engineering unit value changes. This
mode of operation is useful in ‘one to one’ and ‘many to one’ use cases.
One to One
Many to One
One to Many
Many to Many
Page 5

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
4
B24 Advert Format
The Bluetooth advert is the primary operating role of this product. The advertising packet is broadcast
periodically at a configurable rate. The full list of configurable items will be discussed with the section on the
Bluetooth Connected Mode section.
The transmission of the advert and the corresponding data is also split into subtopics. The Bluetooth Special
Interest Group has provided specific details on the format and content of each advert type. The B24 advert is
constructed from the connection flags (advert type 0x01), manufacturer specific data (advert type 0xFF) and the
device local name (advert type 0x09).
Provision has been made for future developments and extensions of the manufacturer specific data to include
other data formats but for the moment only one will be discussed.
The basic format and structure of the B24 advert packet can be observed using a simple BLE scanner. There are
many available for android and Apple iOS (A good example is the nRF Connect app).
Local Name
The local name is part of the standard set of data defined by the Bluetooth SIG. The module name that is supplied
will depend upon the length of the name given to the product. The length of the name has an impact upon the
rest of the data packet and as such should be kept short where possible. The advert is sent with advert type 0x09
as an ASCII character array.
The local name is factory configured to the default value “B24”. The name field in the device has a maximum
length of eight characters. The advert mechanism will send the full name of the device stored in the EEPROM.
Manufacturer Specific Data
The manufacturer specific data is sent with advert type 0xFF. The current format carries data for a single sensor.
The format of this section is shown in Table 1. By default a hash is applied to the data broadcast from the unit
and this will be applied to all bytes after the first data tag pair (Shown in bold). An example decoding the advert is
provided later in this section. The measured data is a fixed length parameter in the advert of 4 bytes. This will
follow the standard Float format (IEEE 754). N.B The status byte, units, data and the terminating data tag pair are
encoded. N.B The format shown in Table 1 is indicative of the bytes transmitted. Some monitoring
applications and APIs do not present the length field to the user.
Name
Size
Description
Length field
1 byte
Part of the Spec
Advert Type
1 byte
0xFF (Manufacturer Specific Data)
Company ID
2 bytes
0x04C3
Format ID
1 byte
Data Tag
2 bytes
Module ID
Status
1 byte
Units
1 byte
Data
4 bytes
Floating point data (IEEE 754)
Data Tag
2 bytes
Used to verify decoding
Data Tag
2 bytes
Used to verify decoding
Table 1: B24 Advert Format
Format ID
The format ID uniquely identifies the format of the rest of the packet. This allows for future expansion of the
format for other purposes without impacting legacy equipment. This is currently set to 1.
Status
The status byte indicates status using the bit values and is defined in Table 2.
Page 6

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
5
Bit
Name
Description
7
Reserved
Reserved
6
Digital Input
Digital Input Active Flag
5
Batt Low
Low battery warning flag
4
Fast Mode
Unit is currently operating in “Fast” data rate mode.
3
OverRange
Input is out of sensitivity or display range
2
NotGross
A tare value has been applied.
1
Integrity
Sensor integrity Error
0
Shunt Cal
Shunt Cal active
Table 2: Status Byte format.
Units
The units for the module are sent as a single byte. The definition of these groups and values is in Appendix B -
Units. This table identifies the group within which a simple translation can be applied and the symbol that should
be displayed on the screen. It also includes the conversion factors that may be used to convert within a group.
Data Tag
The Data tag is defined as a 2 byte hexadecimal number. This number is specific to the sensor and configurable in
the unit. The default value is assigned in the factory prior to shipping and indicated on the label. The data tag is
repeated in the transmission packet in order to facilitate the extraction of the encoded data. Please refer to the
Error! Reference source not found.section.
Data
The data is a fixed length field of four bytes. All data is transmitted as a standard Float format (IEEE 754).
Page 7
Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
6
Bluetooth Connected Mode
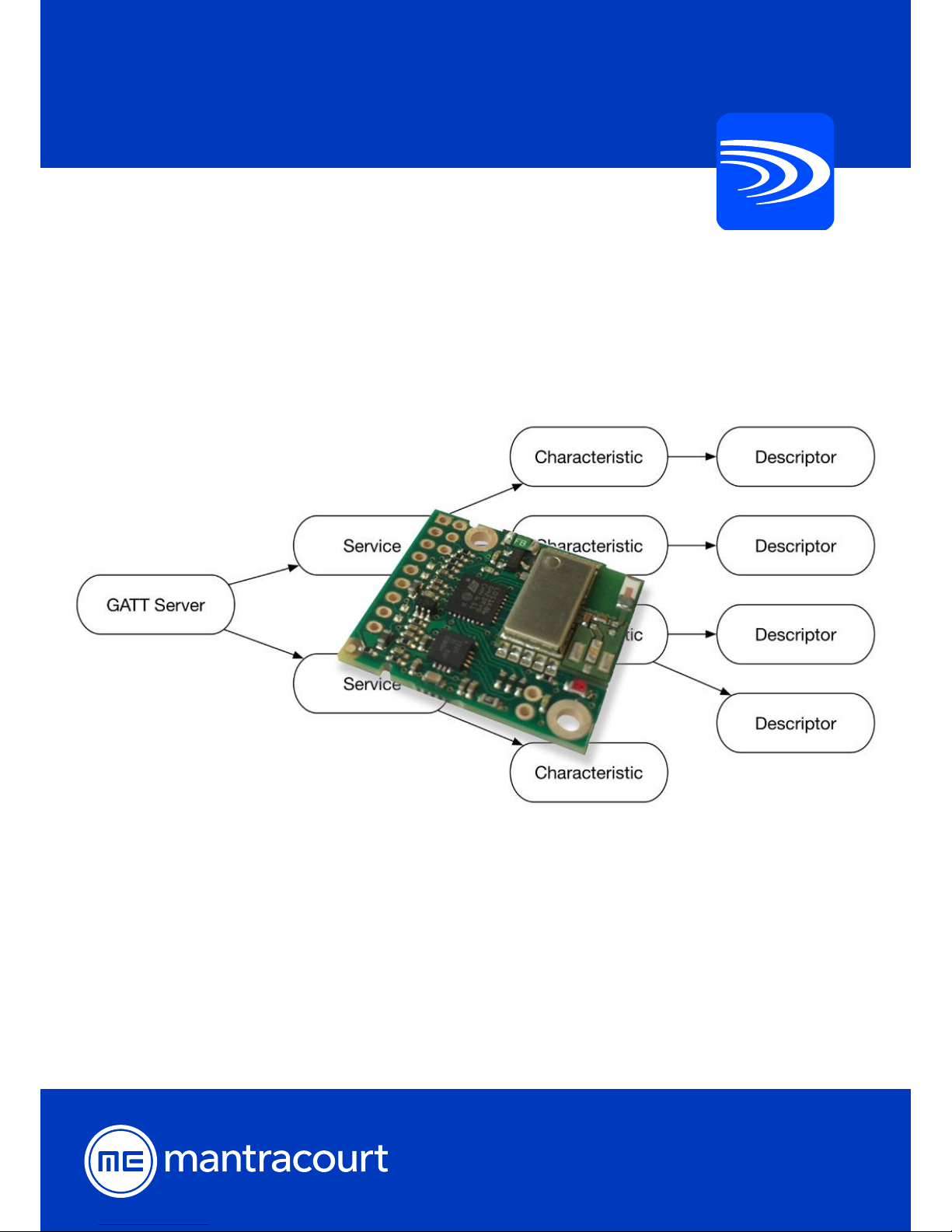
The B24 profile provides access to services and characteristics used to configure and receive measurements. They
are all custom 128-bit Unique ID’s. The only generic profiles that will be enabled in the module are the mandatory
Generic Access and Generic Attribute profiles. Please refer to documentation supplied by the Bluetooth SIG
(Special Interest Group) for a description of the characteristics provided by these services.
All the data carried over Bluetooth is received by the host application as a byte array. The data format on a read is
described in Appendix A.
It is recommended that all writes to characteristics use the Write With Response method
rather than Write With No Response. This allows time for indexed characteristics to update
internally.
Telemetry Configuration Service
The telemetry Configuration service provides access to general configuration parameters. The characteristics
within this service are likely to be required by technicians and installers.
This service is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd30-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Data Rate
The data rate defines the period between taking a measurement. The advert broadcast is also linked to this
parameter. The data rate is specified in ms as the period between measurements. The value entered may be
between 0 and 10000. N.B. Bluetooth does not allow adverts to be broadcast more often than every 80 ms. As
such, values between 1 and 79 will be accepted as a value of 80. A value of 0 will stop data acquisition. However
it will not stop the advertising profile. The adverts will be broadcast once every 5 seconds with a value of NaN and
the status byte will be set to 0xFF (255 decimal).
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd31-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Resolution
The number of samples used to produce a measurement is configurable. The resolution that can be achieved is
given in Table 3. The number of samples used to obtain a measurement will directly impact upon the battery life
of the product as it changes the time required to make a measurement. The measurement time is the time that
the Strain Bridge input is being sampled.
If the Data Rate is set to less than 200mS then the Resolution parameter is limited to a maximum of 16.
Resolution Parameter
Bits Noise Free
@ 2.5 mV/V
Measurement time
Effect on Battery Life
8 (default)
14.25
20 ms
Maximum
16
15.25
32 ms
75%
32
16
56 ms
50%
48
16.5
80 ms
37%
64
16.75
104ms
30%
Table 3: Resolution Table.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd32-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Page 8

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
7
Battery Threshold
The battery threshold value is a floating point number specified in volts. The default value (2.5 V) is designed for
use with a pair of alkaline cells. The minimum operating voltage is 2.3 V. This characteristic is identified by its
unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd33-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
View PIN
The View PIN is used to encode the broadcast data such that other users are not able to decode and read the
values. This is applied on top of the normal encoding and allows the user to hide individual systems. The View PIN
is an array of four characters. The full description of the usage of the data in this characteristic is given in the
Operation Examples section titled Decoding Data with View PIN.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd34-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Serial Number
The serial number is set in the factory and cannot be changed by the user.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd35-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Data Tag
The data tag is used to identify the transmitter. It is set in the factory and indicated on the label. The parameter is
writable and as such may be set to any 32 bit number.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd36-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Battery Value
The battery value contains the latest measurement of the battery voltage. The parameter is a read only float.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd37-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
System Zero
The system zero is a floating point value that is stored in non-volatile memory. This value is subtracted from the
final value on each measurement. It is stored as a floating point number.
This value should not be used as a live tare (i.e. for each new measurement). It is designed
such that the zero can be applied at the point of installation and stored in non-volatile
memory rather than written multiple times per day. There are 100,000 write cycles on the
non-volatile memory before it is worn out.
The system zero value will be converted automatically if a unit conversion is made to the module. This will have
no effect if the Linearisation Points is zero.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd38-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Page 9
Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
8
Configuration Pin
The Configuration PIN controls the access to the device. It must be written to as the first action after connecting
to the unit. Until it has verified the value of the Configuration PIN it will always read zero then disconnect the link.
Attempting to access any parameter prior to entering a valid Configuration PIN will result in disconnection of the
link. The Configuration PIN number is a user settable unsigned 32 bit integer. The default value is 0.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd39-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Model Name
The model name is a factory set parameter that indicates the type of acquisition module that is present. It is a
string of characters that identify the module. Currently there is only one. This is formatted as:
“B24-SSBX-A”
B24 – B24 range
SSB - Strain Sensor Bridge
X -OEM Module
A -Standard Variant
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd3a-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Firmware Version
The firmware version is a read only parameter. The value is stored as a float and updated when new firmware is
generated.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd3b-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Page 10

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
9
Telemetry Data Service
The telemetry data service is where the main measurements are exposed. The status and data values may be
enabled in notification mode. The characteristics within this profile will be used by all users planning to use the
device in a connected mode.
This service is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9712440-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Status
The status value is an unsigned integer. The format of the data is the same as in the advert. The full details of the
values are shown in Table 2. The application can register to receive notifications * from this parameter.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9712441-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Data Value
The data value is transmitted as a float in IEEE 754 format. The application can register to receive notifications *
from this parameter.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9712442-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Data Units
The data units are transmitted as an unsigned integer value. This can be decoded using the lookup table in
Appendix B - Units. The format and value is identical to the broadcast advert.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9712443-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
* When registering for notifications from the Status and Data Value characteristics be
aware that the notifications will only occur at the rate of the current Data Rate.
Page 11

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
10
Telemetry Calibration Service
The telemetry calibration profile is used by advanced users to access the linearization routines and the advanced
access to the internal memory. Access to these values is protected by the Calibration PIN.
Note that even in connected mode the measurements are still only being taken at the
Data Rate (Or Fast Rate) so time needs to be given to allow applied inputs to be
reflected in the measurements before calculating new gains and offsets.
This service is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a970fd30-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Sensitivity Range
The full Scale input sensitivity of the module is selectable. There are four sensitivity ranges available and
corresponding input sensitivity is given in Table 4.
Sensitivity Parameter
Full Scale Sensitivity
0 (default)
±6 mV/V
1
±12 mV/V
2
±24 mV/V
3
±48 mV/V
Table 4: Sensitivity ranges
If the input exceeds the full scale sensitivity + 20% then the overrange flag will be set in the Status.This
characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9717261-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Coefficient (@Index)
The coefficient parameter is used to read or write the linearization points into the unit. The value is stored as a
float. The storage method and the values that should be written to each index during calibration are described in
the Operation Examples section titled Calibration.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9717262-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Linearisation Index
The linearisation index parameter indicates the current location that will be written to by the coefficient
parameter.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9717263-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Linearisation Repeat
The linearization repeat parameter is used to set the size of the table used during calibration. The value of this
parameter is currently set to three which indicates a linear calibration. Higher order calibrations (i.e. quadratics)
are advanced and not supported or described here.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9717264-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Page 12

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
11
Linearisation Points
The linearization point’s parameter is used to set the number of calibration points used in the calibration.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9717265-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Base Value
The base value is the measurement presented in factory calibrated units (i.e. without user calibration). The value is
a read only float. Prior to running the calibration this value will match the Engineering unit value.
For the strain module this value is in mV/V terms.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9717266-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Base Units
This parameter indicates the units that the factory calibrated the unit in. The base unit will correspond to the
measurement type. The Strain module will report the base value in mV/V.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9717267-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Data Gain
The data gain value is used when applying a unit conversion to a calibration. An example of how this is applied is
in the Operation Examples section titled
Page 13

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
12
Unit Conversion.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9717268-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Data Offset
The data offset value is used when applying a unit conversion to a calibration. An example of how this is applied
is in the Operation Examples section.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a9717269-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Calibration PIN
The Calibration PIN may be used to protect the calibration of the unit. The connecting app can optionally request
a Calibration PIN from the user and access to calibration pages in the app may be restricted if the PINs do not
match. The default value is 0.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a971726a-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Calibration Units
This unit should be written with the units corresponding to the calibration. The value written to this parameter
should correspond to the unit look up table found in Appendix B - Units.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a971726b-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Page 14

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
13
Advanced Index
The advanced index is used to access the internal memory of the device. This should not normally be required.
The address locations that can be used are given in Appendix C - Advanced Parameters.
It is recommended that the Advanced Index be read back after writing to confirm that it has been changed
correctly before writing to the Advanced Data characteristic.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a971726c-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Advanced Data
The advanced data parameter is used to read and write to the internal memory of the device that is not exposed
through the other characteristics. This should not normally be required. (N.B the format of the data sent should
match the destination selected. Failure to do so may lead to unexpected behavior). The address locations that can
be used are given in Appendix C - Advanced Parameters.
This characteristic is identified by its unique 128-bit ID. This is:
a971726d-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
Connection Security
The Mantracourt product uses its own method of securing the link prior to allowing access to the data and
calibration. BLE stipulates that the initial connection request must occur without the need for security and this is
the case for this product. Once the connection is made any attempt to read data will lead to a disconnect request.
This is to avoid vanilla applications halting the delivery of data in the broadcast mode. Furthermore the correct
Configuration PIN must be set within 5 seconds of establishing the connection. Otherwise a disconnect command
will be issued.
Page 15

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
14
Operation Examples
This section looks at a few of the common operations that will need to be conducted over Bluetooth and details
the methodology involved. This encompasses both the connected and advertising mode of operation.
Decoding Data with View PIN
The encoding applied to the data in the Bluetooth advertising packet is very simple but effective. It works on the
principle of a shared ASCII View PIN. Each individual character of the View PIN is used to apply an XOR on the
corresponding data. This means that the value delivered is difficult to decipher without knowledge of the View
PIN. To decode the transmission the same process of XOR is applied. The data tag is repeated twice in an
encoded form at the end of the advert and may be used by applications to check that the decoding has been
successful.
The advert key is encoded by default with a 10 byte seed. Each byte is used in turn to encode the value that is
transmitted.
This Default Seed value is:
0x5C, 0x6F, 0x2F, 0x41, 0x21, 0x7A, 0x26, 0x45, 0x5C, 0x6F
The View PIN is repeated in the encoding table. The example below uses a View PIN of ASCII encoded 8742 (The
PIN does not need to be numeric. It is entered as a byte array of ASCII characters. 8742 is chosen over the default
of 0000 in this example to show how the PIN is repeated).
The example in Table 5 shows how the encryption array is calculated from the View PIN and the Default Seed. The
example uses a measured value of 2.54 kg and a data tag of 1234.
Description
Unencoded
Value
Encoding array
Seed PIN
▼ ▼
Encoded
Transmission
Length field – fixed at 16
0x10
0x10
Advert Type
0xFF
0xFF
Company ID – Mantracourt ID
0xC3
0xC3
0x04
0x04
Format ID
0x01
0x01
Data Tag
0x12
0x12
0x34
0x34
Status
0x00
0x5C XOR 0x38 = 0x64
0x64
Units – from look up table ‘kg’
0x2D
0x6F XOR 0x37 = 0x58
0x75
Data – MSB first
0x40
0x2F XOR 0x34 = 0x1B
0x5B
2.54 0x40228F5C
0x22
0x41 XOR 0x32 = 0x73
0x51
0x8F
0x21 XOR 0x38 = 0x19
0x96
0x5C
0x7A XOR 0x37 = 0x4D
0x11
Data Tag
0x12
0x26 XOR 0x34 = 0x12
0x00
0x34
0x45 XOR 0x32 = 0x77
0x43
Data Tag
0x12
0x5C XOR 0x38 = 0x64
0x76
0x34
0x6F XOR 0x37 = 0x58
0x6C
Table 5: Example of encoding the advert
Page 16

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
15
Connection
The device operates in a general discoverable mode. As such the device is always broadcasting its advert at the
set interval and is open to connections. A defensive connection mechanism is employed on the device. This
involves disconnecting any device that does not enter the correct value into the Configuration PIN within 5
seconds. The process flow is as follows:
Scan for devices
Select required corresponding device MAC address and connect
Send the Configuration PIN to characteristic a970fd39-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66 attributed to
service a970fd30-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66.
Read required aspects and configure as appropriate.
Disconnect to allow device to resume transmitting advertising packets.
Once connected the app can use the data profile to read data and register for notifications or configure the
device and disconnect and use the broadcast adverts.
Reading Data
When reading from the device the data will be returned in the format stored in the device.
Examples:
Reading the Status characteristic (a9712441-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66) when there are no errors (zero) will
return 1 byte as shown below.
0x00
Data Value = 0 as unsigned integer 8 bit
Reading the View PIN characteristic (a970fd34-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66) to 1234 as shown below. Note full
length of string is always returned and unused characters are padded with NULL character.
0x31
0x32
0x33
0x34
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
Data Value = 1234 as string
Reading the Configuration PIN characteristic (a970fd39-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66) of 1234 will return 4
bytes as shown below.
0x00
0x00
0x04
0xD2
Data Value = 1234
as unsigned integer 32 bit
Reading the Data Value characteristic in engineering units (a9712442-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66) when 2.54
mV/V is applied and no calibration will return 4 bytes as shown below.
0x40
0x22
0x8F
0x5C
Data Value = 2.54
as floating point
Page 17

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
16
Writing Data
When writing to the device the data must be formatted to the native characteristic format defined (See Appendix
A).
Examples:
Writing the View PIN characteristic (a970fd34-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66) to 1234 as shown below. Note
following NULL character.
0x31
0x32
0x33
0x34
0x00
Data Value = 1234 as string
Writing the View PIN characteristic (a970fd34-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66) to NULL as shown below. Note
following NULL character.
0x00
Data Value = NULL as string
Writing the Configuration PIN characteristic (a970fd39-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66) to 1234 as shown below.
0x00
0x00
0x04
0xD2
Data Value = 1234 as unsigned 32 bit
Writing the Data Gain characteristic (a9717268-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66) to 100 as shown below.
0x42
0xC8
0x00
0x00
Data Value = 100 as floating point
Page 18

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
17
Calibration
The calibration involves setting the gain and offset values in particular regions of operation of the load cell. This
can be achieved through table calibration or live calibration.
Procedure
Action
Description
1. Initialisation of parameters
Set the Linearisation Repeat
Set the Linearisation Points
Set the Sensitivity Range
Should be 3 (default)
Set to one for a two point
calibration.
Set to required range (default 0
± 6 mV/V)
2. Take readings – Live Cal
Skip this stage if
conducting the table cal.
Apply low input.
Receive input from user for the expected Low
Data Value in engineering units.
Read and store Low Base Value
Apply high input.
Read and store High Base Value
Receive input from user for the expected High
Data Value in engineering units.
3. Calculate Gain and Offset
Please see example below.
4. Program coefficients
Set the Calibration Units.
Set the Data Units.
Set the Data Gain = 1.
Set the Data Offset = 0.
Set the Linearization Index to 0.
Write the linearization table terms (values for
each cell in the table. Start from top left
progressing through each column then on to
the next row by incrementing the
Linearisation Index).
The calibration coefficients can be thought of as a table with a number of columns and rows. The number of
columns is set by the ‘Linearisation Repeat’ value and the number of rows is set by the ‘Linearisation Points’ value.
For a two point calibration the table has three columns and one row. The first column holds the base unit value
where the calculation becomes valid. The second column holds the gain and the third column holds the offset.
There is an extra row in the first column to indicate where the range ends.
This is easier to explain with an example:
Page 19

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
18
Given a table Cal (or the data gathered from a live calibration where 10 pounds weight corresponds to 2.0 mV/V
and the 0.0 pound weight gives 0.2 mV/V.
The gain and offset values are:
Gain =
HighDataValue - LowDataValue
HighBaseValue - LowBaseValue
=
10 - 0.0
2.0 - 0.2 =
5.56 Offset =
Gain x LowBaseValue - LowDataValue
=
(5.56 x 0.2) – 0.0
=
1.11
To enter this information into the linearization table the device needs to know the range within which the
calculation is valid (this is a little moot on a two point calibration but is required when extending to a multi-point
calibration). With the example given above the table becomes:
Valid from (base
units i.e. mV/V)
Gain
Offset
Valid to (base units)
-6
5.56
1.11
+6
Table 6: Example of linearization table
In this example the range of valid values has been chosen to be the full range of the load cell mV/V input with
sensitivity range set to 0 (±6 mV/V). In order to write to this table we first set the number of rows and columns
required and set the index to zero. The linearisation values in the table are then written in turn starting from the
top left and progressing through each column before proceeding to the next row.
Page 20

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
19
Unit Conversion
The unit facilitates a method of unit conversion between Calibration Units and Data Units by writing Data Gain
and Data Offset values into the device.
Following on from the calibration example which was calibrated in pounds, this section will apply a conversion to
kilograms.
Procedure
Action
Description
Prepare for conversion
Read the Calibration Units.
Calculate the conversion gain and
offset.
See below.
Write the parameters to the unit.
Write the Data Gain
Write the Data Offset
Write the Data Units
-From calculation below
-Not normally required (use zero).
-from look up table
The conversion is calculated based upon the Ratio values in the Appendix B table. The first step is to divide by the
Calibration Units Ratio and then multiply by the required Data Units Ratio.
Display Gain =
Data Units Ratio
Calibration Units Ratio
=
1
2.204585538
=
0.4536
After all the parameter values have been written, subsequent transmissions will have been converted to the new
unit range. This method may be used to convert between any of the units within the same unit group.
N.B The unit conversion values are held in non-volatile memory and will persist following a power cycle.
System Zero
The system zero may be applied at any point of the commissioning process following the calibration. The value
entered into the device incorporates any display unit conversion applied. In order to enable a simpler interface
the value read out of the device will be converted to the current Data Units value. The value written into the
system zero parameter is subtracted from any subsequent transmission.
To apply a zero to the current measurement, simply write the value of the last measurement into the system zero
parameter.
Page 21

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
20
Appendices
Appendix A - Bluetooth UUID Quick Reference
All the Mantracourt services and characteristics have a common 96 bit tail and a variable 32 bit identifier.
00000000-a0e8-11e6-bdf4-0800200c9a66
The following table shows the 32 bit identifier used to replace the 00000000 shown above to produce the full
128-bit UUID.
ID
Description
Type
Format
Min
Max
a970fd30
Configuration Profile
Service
- - -
a970fd31
Data Rate
Characteristic
Uint32
0
10000
a970fd32
Resolution
Characteristic
Uint8
0
64
a970fd33
Battery Threshold
Characteristic
Float
2.3
3.5
a970fd34
View PIN
Characteristic
String
4
4 bytes
a970fd35
Serial Number
Characteristic
Uint32
Read Only
a970fd36
Data Tag
Characteristic
Uint16
0
0xFFFF
a970fd37
Battery Value
Characteristic
Float
Read Only
a970fd38
System Zero
Characteristic
Float
-FLT_MAX
FLT_MAX1
a970fd39
Configuration PIN
Characteristic
Uint32
0
4294967295
a970fd3a
Model Name
Characteristic
String
Read Only
a970fd3b
Firmware Version
Characteristic
Float
Read Only
a9712440
Data Profile
Service
- - -
a9712441
Status
Characteristic
Uint8
Read Only
a9712442
Data Value
Characteristic
Float
Read Only
a9712443
Data Units
Characteristic
Uint8
0
255
a9717260
Calibration Profile
Service
- - -
a9717261
Sensitivity Range
Characteristic
Uint8
0 3 a9717262
Coefficient (@Index)
Characteristic
Float
-FLT_MAX
FLT_MAX
a9717263
Linearisation Index
Characteristic
Uint8
a9717264
Linearisation Repeat
Characteristic
Uint8
3
11
a9717265
Linearisation Points
Characteristic
Uint8
0
15
a9717266
Base Value
Characteristic
Float
Read Only
a9717267
Base Units
Characteristic
Uint8
Read Only
a9717268
Data Gain
Characteristic
Float
-FLT_MAX
FLT_MAX
a9717269
Data Offset
Characteristic
Float
-FLT_MAX
FLT_MAX
a971726a
Calibration PIN
Characteristic
Uint32
0
4294967295
a971726b
Calibration Units
Characteristic
Uint8
0
255
a971726c
Advanced Index
Characteristic
Uint8
0
255
a971726d
Advanced Data
Characteristic
Byte Array2
unknown
Uint8 - unsigned integer 8 bits
Uint16 - unsigned integer 16 bits
Uint32 - unsigned integer 32 bits
String - character array with length given by Max in the table
Float - float value in IEEE 754 format
1
FLT_MAX is 3.402823e+38
2
The format of the advanced data depends on the parameter that the advanced index is pointing to. The data
is transferred as a byte array and the format of the parameter being written to is applied.
Page 22

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
21
Appendix B - Units
Number
Hex
Value
Group
Unit
Symbol
Ratio
0
0x00
ratio
mV/V
mV/V
1
1
0x01
angle
radians
rad
1
2
0x02
angle
degrees
°
57.30659026
3
0x03
angle
circumference
0.159159637
4
0x04
angle
grade 63.66197711
5
0x05
angle
minutes
'
3437.607425
6
0x06
angle
seconds
“
206264.7982
7
0x07
angle
revolutions
rev
0.159159637
15
0x0F
length
meters
m
1
16
0x10
length
angstrom
Å
10000000000#
17
0x11
length
astronomical unit
AU
6.69E-12
18
0x12
length
centimeters
cm
100
19
0x13
length
chains gunters
ch
0.0497097
20
0x14
length
ell
ell
0.874890639
21
0x15
length
em
em
236.2391
22
0x16
length
fathoms
fm
0.546805453
23
0x17
length
feet
ft
3.280839895
24
0x18
length
furlongs
fur
4.97E-03
25
0x19
length
inches
in
39.37007874
26
0x1A
length
kilometers
km
0.001
27
0x1B
length
league
lea
2.07E-04
28
0x1C
length
leagues
league
0.00018
29
0x1D
length
light years
ly
1.06E-16
30
0x1E
length
lines
ln
472.4424
31
0x1F
length
microns
µ
1000000
32
0x20
length
miles nautical
mi n
5.40E-04
33
0x21
length
miles
mi
6.22E-04
34
0x22
length
millimeters
mm
1000
35
0x23
length
mils
mil
39370.07874
36
0x24
length
nanometers
nm
1000000000
37
0x25
length
parsec
pc
3.24E-17
38
0x26
length
yards
yd
1.093613298
45
0x2D
mass
kilograms
kg
1
46
0x2E
mass
drams
dr av
564.3977876
47
0x2F
mass
grains
gr
15432.7514
48
0x30
mass
grams
g
1000
Page 23

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
22
49
0x31
mass
milligrams
mg
1000000
50
0x32
mass
ounces
oz
35.27395713
51
0x33
mass
pennyweights
pwt
643.0165191
52
0x34
mass
pounds
lb
2.204585538
53
0x35
mass
kilopounds
klb
2.204585538
54
0x36
mass
scruples
s ap
771.63757
55
0x37
mass
slug
slug
6.85E-02
56
0x38
mass
tons long
ton
9.84E-04
57
0x39
mass
tons metric
T
0.001
58
0x3A
mass
tonnes
tonne
0.001
59
0x3B
mass
tons short
sh tn
1.10E-03
65
0x41
force
newtons
N
9.80665
66
0x42
force
kilonewtons
kN
0.00980665
67
0x43
force
millinewtons
mN
9806.65
68
0x44
force
meganewtons
MN
9.80665E-06
69
0x45
force
crinals
crinal
10
70
0x46
force
dynes
dyn
1000000
71
0x47
force
grams force
gf
1000
72
0x48
force
joules per cm
J/cm
0.01
73
0x49
force
kilograms force
kgf
1
74
0x4A
force
kilograms force kp
kp
1
75
0x4B
force
kilograms meter/second²
kg ms²
1
76
0x4C
force
ounces force
ozf
35.27396195
77
0x4D
force
pounds force
lbf
2.204622622
78
0x4E
force
poundals
pdl
70.93163528
79
0x4F
force
tons force long
tonfl
9.84E-04
80
0x50
force
tons force short
tonfs
0.001102311
81
0x51
force
tons force metric
tonfm
0.001
95
0x5F
pressure
bar
bar
1
96
0x60
pressure
atmosphere techn
at
1.019716213
97
0x61
pressure
atmosphere phys
atm
0.986923267
98
0x62
pressure
dyne/cm²
dyncm²
1000000
99
0x63
pressure
foot of water (39°F)
ftH2O
33.45525633
100
0x64
pressure
inch of water (39°F)
inH2O
401.463076
101
0x65
pressure
gigapascal
GPa
0.0001
102
0x66
pressure
hectopascal
hPa
1000
103
0x67
pressure
kg force / cm²
kgfcm²
1.019716213
104
0x68
pressure
kg force / m²
kgf/m²
10197.16213
105
0x69
pressure
microbar
µbar
1000000
106
0x6A
pressure
pascal
Pa
100000
107
0x6B
pressure
newton/m²
N/m²
100000
Page 24

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
23
108
0x6C
pressure
ounce(avdp)/square inch
oz/in²
3215070
109
0x6D
pressure
pounds per square foot
lb/ft²
2088.54
110
0x6E
pressure
pounds per square inch
psi
14.50377439
111
0x6F
pressure
tonne per square cm
T/cm²
0.001019716
120
0x78
speed
meter/sec
m/s
1
121
0x79
speed
centimeters/sec
cm/s
100
122
0x7A
speed
feet/min
ft/min
196.8503937
123
0x7B
speed
feet/sec
ft/s
3.280839895
124
0x7C
speed
kilometers/hr
km/h
3.599712023
125
0x7D
speed
kilometers/min
km/min
0.06
126
0x7E
speed
kilometers/sec
km/s
0.001
127
0x7F
speed
knots
kn
1.942430403
128
0x80
speed
meters/hr
m/h
3600
129
0x81
speed
meters/min
m/min
60
130
0x82
speed
miles/hr
mph
2.237136465
131
0x83
speed
miles/min
mpm
3.73E-02
132
0x84
speed
miles/sec
mps
0.000621
133
0x85
speed
nautical miles/hr
n mph
1.943846
134
0x86
speed
nautical miles/min
n mpm
0.0324
135
0x87
speed
nautical miles/sec
n mps
0.00054
150
0x96
torque
newton meter
N m
1
151
0x97
torque
meter kilogram
m kg
0.101971621
152
0x98
torque
foot pound
ft lbf
0.737562149277266
153
0x99
torque
foot poundal
ft pdl
23.7303604042319
154
0x9A
torque
inch pound
in lbf
8.85074579132716
200
0xC8
arbitrary
counts
counts
1
255
0xFF
Undefined
Undefined
Page 25

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
24
Appendix C - Advanced Parameters
Index
Access
Format
Min
Max
Parameter
5
Read
FLOAT
0 0 Peak Value – Peak Value since last power
up.
6
Read
FLOAT
0 0 Trough Value – Trough value since last
power up
26
Read and Write
FLOAT
-FLT_MAX
+FLT_MAX
Display Min – Min Value in display units.
Causes an overrange flag to be set in
status.
27
Read and Write
FLOAT
-FLT_MAX
+FLT_MAX
Display Max – Max Value in display units.
Causes an overrange flag to be set in
status.
28
Read and Write
FLOAT
-FLT_MAX
+FLT_MAX
Filter Level – See Appendix D - Filter
29
Read and Write
UINT32
0
4294967295
Filter Steps – See Appendix D - Filter
35
Read and Write
UINT8
0 1 Linearisation Direction – Set the
linearization direction as positive or
negative. Default is positive
38
Action
NONE
0 0 Calculate Coefficients – recalculate the
live coefficients. (Is automatically applied
at the end of a calibration routine)
39
Read and Write
UINT32
0 1 Digital Output Function – Set the digital
output to follow the LED with a 1.
40
Read and Write
UINT8
0 0 Fast Mode – determines how the device
can dynamically switch between the
standard Data Rate and the Fast Rate
(Below).
0 = Fast Rate disabled.
1 = On connection. Fast Mode entered
when device is connected.
2 = On Level. Fast Mode activated when
the measured value exceeds the Fast
Level.
3 = On Change. Fast Mode entered when
the rate of change between two readings
exceeds that calculated as the Fast Level
over the Data Rate.
41
Read and Write
UINT32
0 0 Fast Rate – this is the fast transmission
rate entered in milliseconds and is
equivalent to the Data Rate. Range is 80
to 10000 milliseconds.
42
Read and Write
UINT32
0 0 Fast Duration – This sets how long the
Fast Mode will be sustained. This is stated
in multiples of the Fast Rate. Example. If
Fast Rate is set to 100 (0.1S) and Fast
Duration set to 200 then the device will
remain in Fast Mode for 0.1 x 200 = 20
seconds.
Page 26

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
25
43
Read and Write
FLOAT
0 0 Fast Level – This value is entered in Data
Units and will be used depending on the
Fast Mode as follows:
When Fast Mode = 1: The Fast Rate will
return to the Data Rate after the Fast
Duration period expires from when the
device is disconnected.
When Fast Mode = 2: this value when
exceeded triggers Fast Rate returning
back to Data Rate when the level drops
below this value and after the Fast
Duration period has elapsed.
When Fast Mode = 3: this level sets the
rate of change level which triggers Fast
Rate returning back to Data Rate when
the rate of change drops below this value
and after the Fast Duration period has
elapsed.
189
Action
NONE
0 0 Restart module.
192
Action
NONE
0 0 Shunt Cal On – Apply 100 k Shunt Cal.
193
Action
NONE
0 0 Shunt Cal Off – Remove Shunt Cal
194
Action
NONE
0 0 Tare – Apply a local tare to the
measurement (N.B does not persist
through power up)
195
Action
NONE
0 0 Reset Tare – Reset Tare value to zero.
196
Action
NONE
0 0 Reset Peak and Trough
197
Action
NONE
0 0 Restore EEPROM Defaults – Restore all
default values. (Calibration would be lost.
Factory Cal remains.)
Page 27

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
26
Appendix D – Filter
The filter level and filter steps affect the frequency response of the input which is indicated at the bottom of the
page.
The Dynamic filter is basically a recursive filter and therefore behaves like an electronic ‘RC’ circuit. It has two user
settings, a level set in the calibrated engineering units and the maximum number of steps (up to 255).
This filter is very basic and operates at the mV/V level.
Instead of outputting every new value, a fraction of the difference between the new input value and the current
filtered value is added to the current filtered value to produce the filtering action.
If this difference is less than the value set in the Filter Level then the fractional amount added each time is
decremented until it reaches the minimum level set by Filter Steps i.e. Filter Steps is the limit of the divisor.
e.g. if Filter Steps = 10 the fractional part of the difference between the new value and the current filtered value
will be added to the current filtered value.
If a rapidly changing or step input occurs and the difference between the new input value and the current filtered
value is greater than the value set in Filter Level then the output of the filter will be made equal to the new input
reading i.e. the fractional amount of the new reading added to the current reading is reset to 1.
This allows the Filter to respond rapidly to fast moving input signals.
When a step change occurs which does not exceed Filter Level, the new filtered value is calculated as follows:
New Filter Output value = Current Filter Output Value + ((Input Value - Current Filter Output Value) / Filter
Steps)
The time taken to reach 63% of a step change input (which is less than Filter Level) is dependent on the
frequency at which values are passed to the dynamic filter, set in Data Rate, multiplied by Filter Steps.
The table below gives an indication of the response to a step input which is less than Filter Level.
% Of Final Value
Time To settle
63%
Data Rate * Filter Steps
99%
Data Rate * Filter Steps * 5
99.9%
Data Rate * Filter Steps * 7
For example, If Data Rate is set to 10Hz = 0.1s and Filter Steps is set to 10 then the time taken to reach a % of
step change value is as follows.
% Of Final Value
Time To settle
63%
0.1 x 10 = 1 seconds
99%
0.1 x 10 x 5 = 5 seconds
99.9%
0.1 x 10 x 7 = 7 seconds
Page 28

Mantracourt Electronics Limited B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
27
The following table shows the number of updates ‘x Filter Steps’ and the ‘% Error’ that the Filtered Output
value will differ from the constant Input Value.
x Filter Steps
% Error
1
36.78794412
2
13.53352832
3
4.97870684
4
1.83156389
5
0.67379470
6
0.24787522
7
0.09118820
8
0.03354626
9
0.01234098
10
0.00453999
x Filter Steps
% Error
11
0.00167017
12
0.00061442
13
0.00022603
14
0.00008315
15
0.00003059
16
0.00001125
17
0.00000414
18
0.00000152
19
0.00000056
20
0.00000021
Remember: if the step change in mV/V is greater than the value set in Filter Level then:
New Filter Output value = New Input Value i.e. the output jumps to the new input value and the internal
working value of Filter Steps is reset to 1. This is then incremented each update (set by Measurement Rate) until
it reaches the user set value of Filter Steps.
The filter can be disabled by entering zero for Filter Steps.
Document Title:
B24 Telemetry Technical Manual
Applies To:
B24 Product Range
Part Number:
517-944
Issue Number:
02.01
Dated:
14th March 2019
In the interests of continued product development, Mantracourt Electronics Limited
reserves the right to alter product specifications without prior notice.
www.mantracourt.com
 Loading...
Loading...