Page 1

TM
Instruction and
Installation Manual
AirScan
iR
Refrigerant Sensor for
Commercial Applications
MOUNT ENCL OSURE T HIS END UP. DO NOT B LOCK PER FORATE D VENT HOLE S.
AirScan
ha_manning@honeywell.com
405 Barclay Boulevard
Lincolnshire, Illinois 60069
www.honeywellanalytics.com
Tel: +1 847 955 8200
Toll free: +1 800 538 0363
Manning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 01/2006 REVA Copyright © 2006 Manning Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1
Fax: +1 847 955 8208
www.manningsytems.com
18908 AirScan-iR-comm 01/2014 REVC
Page 2

Contents Serial number:
Section Title Page
1 Sensor Description System Specifications and Sensor Specifications 4
2 Installation A Locating the Sensor 5
Figure 1: Mounting Dimensions for the AirScan
B Wiring 6
Figure 2: Wiring Diagram for AirScan
eration A Start-up Procedure 7
3 Op
TM
iR 6
TM
iR 5
Figure 3: Required LED Status at Start-up 7
B Pushbutton Operation, LED Indicators, Adjustment Pots and Test Points 8
Figure 4: Board Component Layout 8
Figure 5: LED Layout 8
LED Indicators and Blink Sequence 9
Figure 6: LED Blink Sequence 9
Figure 7: LED Indicator Summary 10
Normal Run Modes 10
4/20 mA Loop Test Mode 10
Calibration Mode 10
Fault Indicator Error Sequences 11
C Modes of Operation 12
Normal Run Modes 12
4/20 mA Loop Modes 13
Calibration / Programming Modes 14
D
Calibratio
n 15
Figure 8: Board Component Layout 15
4/20 mA Output Calibration 17
Zero Calibration 17
Figure 9: Board Component Layout 18
Span Calibratio
E
Diagnostic Procedures
n 18
19
Simple Zero Test 19
4/20 mA Output Loop Integrity Check 19
F
Troubleshooting
Electrical Interfer
ence 21
Figure 10: Troubleshooting the AirScan
TM
iR 21
21
Sensor On-Board Diagnostic System 21
Error on 4/20 mA Output 22
Sensor Output at 0 mA 22
Sensor Output at .5 mA 22
Gas Concentration Indicated with No Refrigerant Present 22
IR Source Failure 22
4 Maintenance 23
5 Replacement Parts 23
6 Limited Warranty 24
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 2
Ma
Page 3

Introduction
This manual has been prepared to help in the use and installation of the Manning Systems
AirScan
principles of the sensor, ensure proper installation, and demonstrate start-up and routine
maintenance procedures.
This manual must be carefully followed by all individuals who have or will have the
responsibility for using or servicing the AirScan
Manning Systems, Inc. with respect to this equipment will be voided if the equipment is
not used and serviced in accordance with the instructions in this manual. If in doubt
about a procedure, please contact Manning Systems, Inc. before proceeding.
TM
iR (Infrared Refrigerants) Sensor. This manual will convey the operating
TM
iR Sensor. Warranties made by
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm. 3
Ma
Page 4

1 Sensor Description
Gas detection by the infrared method is based on the
principle that most gases absorb infrared energy at a
characteristic frequency. In this instrument, a broad
band infrared source emits energy which is then bandpass filtered to produce a narrow range of frequencies
characteristic of the refrigerants’ (CFC/HCFC/HFC)
absorption spectra. Any refrigerant in the gas sample cell
selectively absorbs energy reaching the detector. This
reduction in energy is detected, amplified and sent to the
signal processing portion of the system.
TM
The Manning Systems AirScan
iR Sensor line is a threewire, 4/20 mA sensor for two bands of refrigerants
available in a range of 0–3,000 ppm, but can be adjusted
for lower ranges, if required. The low-band or R-404a
infrared sensor reacts to R-123, R-134a, R-404a and R-507.
The high-band or R-22 AirScan
TM
iR sensor reacts to R-22.
Its solid, high-mass metal bench provides structural and
thermal stability, greater immunity to vibration, as well as
superior EMI/RFI shielding of the detector and source.
Internal compensation for environmental changes allows
the sensor to automatically adapt to fluctuating
temperature and humidity conditions. The unit exhibits
extremely high reliability with no moving parts.
Every two seconds SensorCheckTM technology monitors
the AirScan
TM
iR source and ensures that the dual
channels are functioning properly. A notification signal
will be transmitted if any of several performance
parameters is not met.
Monitoring equipment must be configured to indicate a
fault if the signal is less than 1.5 mA. All signals over
20 mA must be considered a high gas concentration.
Manning Systems infrared sensors are normally longlived (5 years plus), unless physically damaged or wetted
with water or other liquid.
System Specifications
Electrical Power: 24 Volts DC regulated, 1.0 amp.
Output: Linear 4/20 mA output into a load resistor of
500 ohms maximum
Cable Length to Sensor: 1,000 feet maximum
Cable Recommendation: Three conductor, stranded,
shielded cable with drain wire, all enclosed in a vinyl
jacket. For cable runs up to 200 feet use, #18 AWG
(Belden #8770 or equivalent). For cable runs up to 1,000
feet, use #16 AWG (Belden #8618 or equivalent).
Unit Enclosure: NEMA 4, gasketed, molded fiberglass
reinforced polyester. Non-painted, non-rusting
construction appropriate for food areas. UL 508 listed,
CSA certified for use with industrial control equipment.
NOTE: The standard AirScan
TM
iR is for use in non-
classified areas only.
Sensor Specifications
Type: CFC/HCFC/HFC selective infrared gas sensor/
transmitter AirScan
Method of Detection: Dual channel infrared energy
absorption (N.D.I.R. Non-dispersive Infrared)
Gases Monitored: Low-Band (R-404a, R-507, R-134a,
and R-123), High-Band (R-22)
Range Available: 0–3,000 ppm (can be rescaled to
0–1,000 ppm, or 0–500 ppm if required)
SensorCheckTM Features: Dual channel functionality test,
source strength evaluation, incoming voltage monitor,
IR source integrity check, operating temperature monitor,
“zero” down drift monitor, and internal circuitry check.
Accuracy: ± 3% of full scale
Repeatability: ± 1% of full scale
Cross Sensitivity: Not affected by moisture, food odors,
floor cleaners, temperature changes, etc.
Operating Humidity: 0–100% RH (condensing)
Operating Temperatures: –20° F to +140° F
Storage Temperature: –20° F to +140° F
Gas Sampling: Diffusion method with no moving parts
Sampling Frequency: Real time continuous monitoring
of all points
Response Time: T
calibration gas @ .75 liters/min. flow rate
Weight: 4.4 lbs.
TM
iR
90
in 10 seconds with full-scale target
Dimensions: 9.59" high x 7.71" wide x 4.52" deep
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm. 4
Ma
Page 5
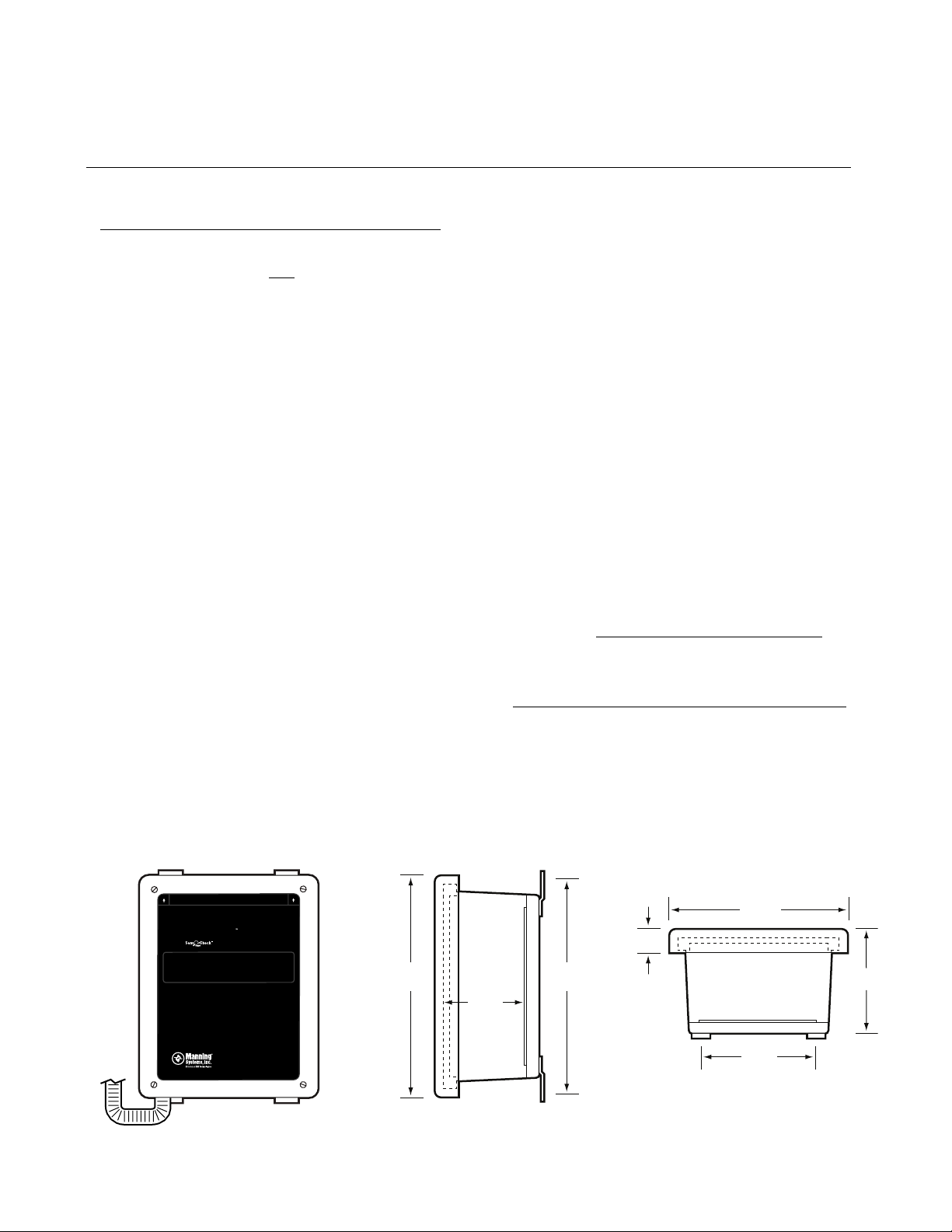
2 Installation
”
A Locating the Sensor
Because each sensor can only “report” what it is
seeing at the moment,
sensor be located where leaks are most likely to
occur.
CFC/ HCFC/HFC vapor is heavier than
ambient air, so in a room with no air movement it will
tend to settle. For quickest detection, mount the
sensor about one to two feet from the floor, close to
the potential leak source.
If the primary application is the fastest possible leak
detection, mount the sensor near the potential leak
sources. In doing this, be aware that the indicated
concentration may not be representative of personnel
exposure and easy access for the required calibration
and maintenance could be compromised.
General Mounting Considerations:
• Must be easily accessible for calibration and
maintenance.
Always mount the sensor vertically.
•
• Mount the sensor clos
sour
ce for fastest possible leak detection.
• If personnel protection is the primary
application, moun
Protect sensor from water, excessive hu
•
and
wash-dow
Take air movement and ventilation patterns into
•
account.
Figure 1: Mounting Dimensions for the AirScanTMiR Sensor
it is very important that the
e to the potential leak
t in the “breathing zone.”
midity,
n.
•
To prevent electrical interference, keep sensor
and wire runs away from mercury vapor lights
var
iable speed drives, and radio repeaters.
,
• Protect sensor from physical damage (fork lifts,
etc.).
• Do not mount the sensor over a door in a
refrigerated area.
• For highly critical locations more than one
sor should be installed in each room.
sen
Very Important:
• Sensor must be mounted vertically
Never mount sensor flat on a ceiling
•
• E
nter enclosure
bottom of
Always make a drip loop in the conduit
•
Never mount sensor on a vibrating surface.
•
only through existing hole in
enclosur
e
Mount sensor enclosures through the flange holes as
shown in Figure 1, and
Penthouses: Multi-Coil (defrost one coil at a time) –
always mount vertically.
In this case the best location is usually in the center of
the penthouse four or five feet above the grate.
Single Coil (or when all coils defrost at the same time)
In this case high moisture conditions can occur and the
sensor should be mounted one foot above the grate.
Engine Rooms: The AirScan
TM
iR sensor should be
mounted in a cool part of the room, if possible. Keep
the sensor away from hot air exhausting from electric
motors or other machinery.
–
MOUNT ENCLOSURE T HIS END UP. DO NOT BLO CK PERFOR ATED VEN T HOLES.
AirScan
9.19”9.59”
3.68”
SIDE VIEWFRONT VIEW
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 5
Ma
1”
7.71”
4.52
5.01”
TOP VIEW
Page 6
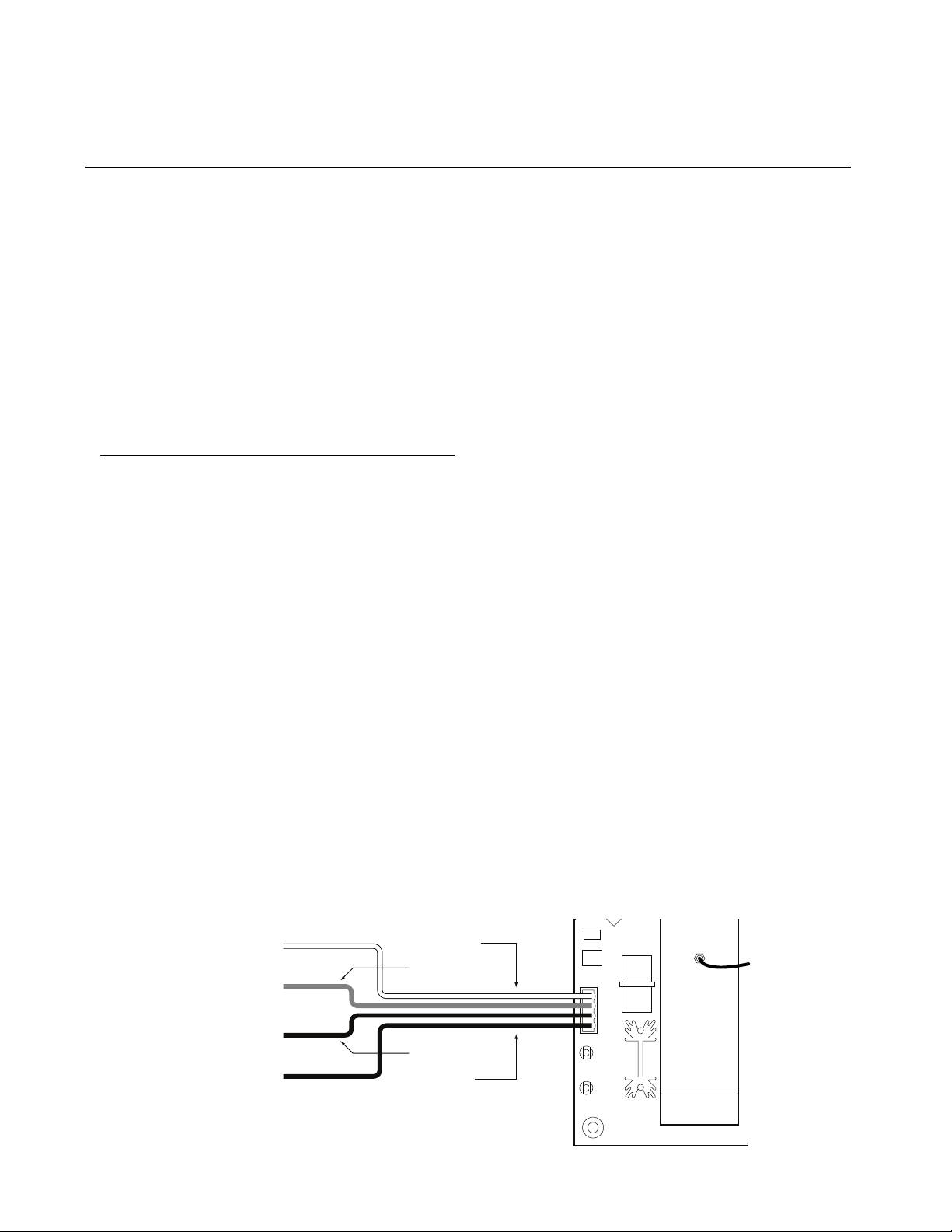
2 Installation continued
Ceiling Hung Evaporators: When mounting AirScan
TM
iR
sensors near evaporators, mount the sensor no higher
than two feet below the top of the evaporator coil.
Do not mount in high air flow (1,200 feet/minute
maximum).
Never mount the sensor on evaporators as
vibration can damage the sensor.
Other Locations: When mounting AirScan
TM
iR sensors
in locations such as roof top air units, ductwork, attic
spaces, makeup air intakes, etc., contact Manning Systems
for application assistance and recommendations.
B Wiring
Electrical wiring must comply with all applicable codes.
Plant equipment that may be involved and operating conditions should be discussed with local operating personnel
to determine if any special needs should be considered.
Nearly all start-up problems are due to improper wiring
or monitor configuration. Please follow these guidelines
carefully.
Always use three conductor, insulated, stranded,
shielded copper cable. Use
not two cables of two conductor wire (see Figure 2).
If the AirScan
TM
iR is to be used with the AirAlertTM96d,
please call Manning Systems for specific wiring instructions.
Do not pull sensor wiring with AC power cables. This will
cause electrical interference. Be sure there are no breaks
or splices in sensor wiring runs. If cable runs cannot be
made without a splice, all connections must be soldered.
Soldering should be done using a rosin flux to tie the
connecting ends of sensor wires to ensure a positive and
long-lasting contact.
only three conductor cable,
Ground the shield at the main control panel. Connect
the shield wire in the sensor terminal block labeled
shield. Tape all exposed shield wire at the sensor to
insulate it from the enclosure.
All penetrations into a refrigerated room should be
sealed to prevent condensate from forming in the
conduit and dripping into the sensor enclosure.
Make drip loops for cables going into sensor housings
(see Figure 1). Follow the special mounting instructions
on the enclosure (…This End Up).
Electrical Power: 24 VDC regulated, 1.0 amp.
Output: Circuit board mounted sensor provides a linear
4/20 mA output. Monitoring equipment may have a
maximum input impedance of 500 ohms.
Contact Manning Systems for specific wiring
instructions when using AirScanTMiR sensors with an
AirAlert
Cable Recommendation: Use #18/3 (Belden #8770)
TM
96d readout unit.
for cable runs up to 200 feet. Use #16/3 (Belden
#8618) for cable runs up to 1,000 feet. Use only the
existing punched holes for connections to the sensor.
Monitoring: The AirScan
TM
iR Refrigerant Sensor may be
monitored by any Manning Systems Readout/Alarm unit
or other appropriately configured system. Monitoring
equipment must be configured to indicate a fault if the
signal is below 1.5 mA. All signals above 20 mA must be
considered a high gas concentration. A failed sensor will
output a 0.5 mA signal.
Figure 2: Wiring Diagram for the AirScanTMiR Sensor
White connects to signal input of
monitoring equipment
Red connects to 24 VDC power supply
positive side
Black connects to 24 VDC ground side
Bare wire wrap connects to case ground
at monitoring equipment (earth ground)
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 6
Ma
Output (white)
+24 VDC (red)
DC ground (black)
Shield (bare)
JP1
TEST +
TEST -
SIG
+24
GND
SHLD
Page 7
3 Operation
TM
The AirScan
iR has several modes of operation,
including two normal run modes, two 4/20 mA loop
check modes and five calibration modes. These will be
explained in Operation, Section C, Modes of Operation.
Modes are entered by properly activating pushbuttons
located on the circuit board, shown in Figure 4.
Sensor operation status is indicated by the blink
pattern of seven LEDs located in a vertical row on the
right side of the sensor circuit board (see Figure 4).
LED status is differentiated by color and duration/
pattern of blink(s). LED Indicators and Blink
Sequences are shown in Figure 6, followed by an
explanation of blink patterns.
A Start-Up Procedure
Before applying power, make a final check of all wiring
for continuity, shorts, grounds, etc. It is usually best to
disconnect external alarms and other equipment from the
sensor until the initial start-up procedures are completed.
Check the power supply voltage to the sensor with a
digital volt meter set to VDC. Place the black lead on
sensor terminal GND and the red lead on +24 (see
Figure 4, Note 1). Voltage should be between 21 and 28
VDC. If voltage is outside this range, check power supply
and wiring.
After power-up, ensure the LEDs below are operational
as follows (see Figure 3):
TM
IMPORTANT: The AirScan
iR sensor is factory
calibrated and should require minimal adjustments after
installation.
CARB Compliance: To ensure continued compliance
with CARB performance guidelines, calibrate the unit
in the environment in which it will be used. Frequency
of calibration can improve accuracy; Honeywell
Analytics recommends calibration every 6 months.
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity,
and pressure can affect accuracy. Consider these factors
when establishing a maintenance program .
Allow the sensor to operate for 12 hours with the
enclosure sealed prior to testing the sensors. This will
give the sensor time to reach thermal equilibrium to the
external and internal temperatures while in operation.
Because sensors are normally located at a distance from
the main unit, the test time required and accuracy of the
response checks will be improved if two people perform
the start-up procedures and use radio contact.
Start-Up Test:
1)
One person exposes each sensor to a small amount
of the gas that is being monitored.
2)
The second person stays at the control unit to
determine that each sensor, when exposed to the
gas fumes, is connected to the proper input and
responds, causing appropriate alarm functions.
• Green “Power” LED continuous ON
• Both Fault LED’s are OFF
• Green “source” LED is blinking once every
2 seconds
NOTE: For cold/humid adverse environmental conditions
the “ATMOS” LED may be turning on and off periodically. In addition, the “system” LED may be blinking or
continuous ON, also described in later sections.
Manning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm
Figure 3: Required LED Status at Start-up
LED
POWER
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
G
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
WITH OUTPUT
FILTERING
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON PERIODICALLY
WITHOUT OUTPUT
FILTERING
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON PERIODICALLY
7
Page 8
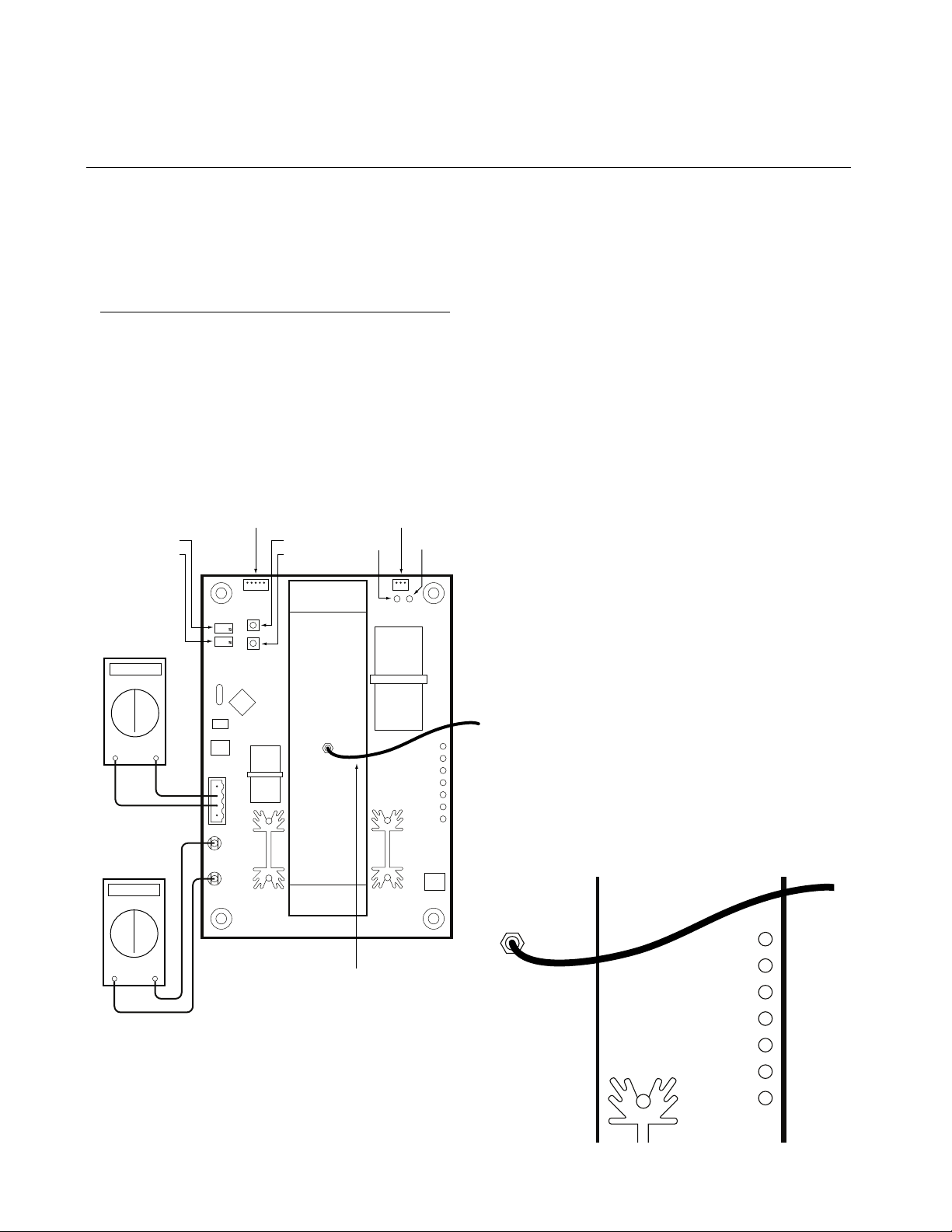
3 Operation continued
Draw
B Pushbutton Operation,
LED Indicators,
Adjustment Pots and
Test Points
The AirScanTMiR has two internal pushbuttons, and two
adjustment pots that are utilized for navigation of test
functions, calibrations, and operating modes. In addition,
a pair of test points is also provided that assist in the
connection to standard meter leads for use in the
upcoming calibration and diagnostic procedures (see
Figure 4).
Figure 4: Board Component Layout
Serial PortICSP Programming Port
Zero Adjust
Span Adjust
Note 1: Checking
voltage to sensor
at +24 and GND
24
VDC
Black-Red
Note 2: Reading
signal at TEST+
and TEST-
+
40-200
mVDC
JP1
TEST +
TEST -
ZERO
SPAN
SIG
+24
GND
SHLD
Pushbutton S2
JP3
S1
S2
Chamber
Draw
Rx LEDPushbutton S1
Tx LED
JP2
CALIBRATE
mA FAULT
IR SOURCE
POWER
SYSTEM
FAULT
ATMOS
ACTIVE
“Zero” adjustment pot – adjusts output calibration
•
of the 4 mA nominal resting point
• “Span” adjustment pot – adjusts the 20 mA
concentration level or unit span/sensitivity.
• Pushbutton S1 – used to initiate the auto-zero
f
unction, program the 4 mA output calibration,
and initiate the 4/20 mA loop test.
• Pushbutton S2 – used to program the span setting.
• Test(+) and Test(–) for connection to a DC Volt
me
ter (see Figure 4, Note 2)
IMPORTANT: The pushbutton(s) must be pressed the
correct number of times and at the correct rate.
• When a multi-press sequence must be performed,
the button must be pressed rapidly and evenly,
lifting one’s finger completely from the actuator
for each consecutive press.
• For press and hold activations, one’s finger must
always be applying a down pressure withou
ruption for the sp
dis
ecified time in order to
activate the desired mode.
•
See complete details of each operation in other
parts of the manual.
TM
The AirScan
iR also has a group of LED’s (see Figure 5)
that blink in specific sequences (see Figure 6 on next
page) to indicate sensor operation and programming
modes. A summary of sensor operation and
programming modes with corresponding LED blink
sequences is shown in Figure 7 on page 10.
Figure 5: LED Layout
.
Chamber
t
POWER
Black-Red
Ma
+
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 8
Tubing to
calibration point
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
IR SOURCE
ATMOS
ACTIVE
Page 9

3 Operation continued
LED Indicators and Blink Sequence
Figure 6: LED Blink Sequence
1 sec. 2 sec. 3 sec.SEQUENCE
SOURCE BLINK
SLOW BLINK
MEDIUM DOUBLE BLINK
FAST BLINK
CONTINUOUS ON
G
reen Power LED
• Continuous ON when power is applied
Yellow System LED
• Continuous ON during normal filtered output run
mode – “dead band” f
•
Slow blink during normal non-filtered output ru
rom 4 to 4.
mode
• Fast blink indicating unit lost calibration data
• OFF during 4/20 mA loop check
Yellow Calibrate LED
• Continuous momentary ON for auto-zero mode
activation
•
Slow blink fo
•
Medium double blink indicates 4/20 mA loop
check .
•
Fast blink fo
r 4 mA output calibration mode
(low)
5 mA
r “span” calibration mode and
4/20 mA loop check 22 mA (high)
6 mA
Red Fault LED (all scenarios produce a .5 mA output)
• Continuous ON indicates a failed source, low
si
gnal, or circuit failur
•
Slow blink indicates the power su
t voltage is
inpu
•
Medium double blink indicates sensor is ou
the oper
Fast blink indicates the si
•
ating temperature range.
and needs to be r
output r
d mA Fault LED attempts to output .5 mA fault signal
Re
un mode (no dead-band).
e
pply DC 24V
too low.
gnal drifted below 4 mA
e-calibrated, only in non-filter
tside
ed
• Fast blink indicates 4/20 mA loop failure or load
r
esistance t
Green Source LED
oo high
• One blink every 2 seconds indicates when source
is
energized and also that the source is not sh
cir
cuited.
Green ATMOS LED
ort
• Continuous ON indicates ATMOS circuitry is active
or
n
NOTES:
adjusting the enclosure’s internal enviro
co
nditions for the sensor to function reliably
nmental
.
• If the Source LED isn’t blinking, do not proceed
until the condition is corrected.
•
If a Fault LED is lighted, immediately refer to
Fault Indicator Error Sequences (page 11) to
determine potential problem. Do not attempt
calibration if
All status LED’s are subordinate to Faul
•
a Faul
t is indicated.
t
indicators.
If an LED is indicated as OFF, it must actually
•
F for proper sensor operation.
OF
be
•
If an LED status is N/A (not applicable),
dication may vary depending on other
in
that LED
operational factors.
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 9
Ma
Page 10

3 Operation continued
POWER
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
G
G
G
R
R
Y
Y
4/20 mA LOOP TEST
(22 mA HIGH)
1
4/20mA LOOP TEST
(.5 mA LOW)
1
NOTE 1: Error on output will result in fast blink on red mA FAULT LED.
LED
OFF
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
OFF
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
= Green LED
Figure 7: LED Indicator Summary
G
See LED indicators and blink sequence descriptions on page 9.
Normal Run Mode 4/20 mA Loop Test Mode
LED
POWER
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
G
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
WITH OUTPUT
FILTERING
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON PERIODICALLY
1
3
NOTE 1: Dead-band from 4 mA to 4.6 mA
NOTE 2: No dead-band from 0 to 26 mA
NOTE 3: Environmental compensation energized for cold temperatures
WITHOUT OUTPUT
FILTERING
ON PERIODICALLY
2
OFF
OFF
OFF
3
= Yellow LED
Y
= Red LED= Initiated by button press
R
Calibration Mode
ZERO FUNCTION
1
INITIATED
N/A
OFF
OFF
N/A
N/A
LED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
mA FAULT
NOTE 1: Indicates that “Zero” function is initiated and pushbutton S1 can be released. Yellow Calibrate LED will be off after pushbutton is released.
NOTE 2: Indicates unit lost the factory calibration data. Contact Manning Systems.
FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
R
R
G
G
DURING SPAN
CALIBRATION
OFF
OFF
N/A
N/A
DURING 4 mA
OUTPUT CALIBRATION
N/A
OFF
N/A
N/A
FACTORY CALIBRATION
LOST
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
2
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 10
Ma
Page 11

3 Operation continued
Figure 7: LED Indicator Summary, continued
G
Y
= Green LED
See LED indicators and blink sequence descriptions on page 9.
Fault Indicator Error Sequences
LED
POWER
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
LOST FACTORY
CALIBRATION
1
G
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
FAILED 4/20 mA
OUTPUT
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
2
NOTE 1: Indicates Normal Run Mode wthout output filtering where unit lost factory calibration data. Contact Manning Systems for technical support.
NOTE 2: Indicates failed 4/20 mA output signal. Load resistance is too high.
LOW SIGNAL OR
FAILED SOURCE OR CIRCUIT
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
POWER SUPPLY
VOLTAGE TOO LOW
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
= Yellow LED
OPERATING TEMPERATURE
R
RANGE EXCEEDED
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
= Red LED= Initiated by button press
LED
POWER
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
READING DRIFTED
BELOW 4 mA
1
G
Y
Y
N/A
N/A
R
R
G
G
N/A
N/A
N/A
SHORTED
SOURCE
N/A
N/A
N/A
OFF
N/A
NOTE 1: Indicates the gas reading drifted below 4 mA and needs to be
re-calibrated only in non-filtered output run mode (no dead-band).
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 11
Ma
Page 12

3 Operation continued
C Modes of Operation
The AirScanTMiR has various modes of operation and
calibration:
Normal run mode with output
•
•
Normal run mode without output
filtering
filtering
• 4/20 mA loop check
4/20 mA calibration to an external PLC or
•
read-out panel
Neut
•
ral gas resting point or “zero” calibration
mode
•
Span calibration modes
Normal Run Modes
Normal run mode with output filtering
This mode outputs a signal from 4 to 27 mA with a
“dead band” from 4 to 4.6 mA. This “dead band” masks
small environmental anomalies that could facilitate
output signal fluctuations or transients around the 4 mA
resting point when the unit is not sensing target gas.
Start: If the “system” LED is blinking slowly, press and
hold both S1 and S2 simultaneously for 1 second or
more until the “system” LED is continuous ON, then
release both buttons. If the “system” LED is blinking
fast, this mode cannot be engaged and the factory needs
to be contacted. See the following example.
Normal run mode without output filtering
This mode outputs a signal that nominally rests at 4 mA
and can range continuously from 0 to 27 mA. Any subtle
changes in sensor response will be sent to the mA loop
output. This mode is entered automatically when the
calibration modes are activated. Some users may wish
to see the subtle anomalies in the signal near the
nominal 4 mA rest area.
Start: If the “system” LED is continuous ON, press and
hold both S1 and S2 simultaneously for 1 second or
more until the “system” LED is blinking slowly then
release both buttons to enter this mode. If the “system”
LED is blinking fast this mode is always engaged and
can only be exited by fully calibrating the unit. See the
following example.
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
Y
R
R
G
OFF
OFF
OFF
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
mA FAULT
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 12
Ma
FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
R
R
G
G
OFF
OFF
OFF
N/A
ATMOS
G
N/A
Page 13

3 Operation continued
4/20 mA Loop Test
{22 mA full-scale and .5 mA fault check}
Start: Press S1 5 times within a two to three second
period of time. The yellow “system” LED will turn off
and the yellow “calibrate” LED will blink fast. See the
following example. Output should be 21 to 22.5 mA.
22 mA Full Scale Output Test
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
Y
Y
R
R
G
OFF
N/A
N/A
N/A
T
o proceed to the next step in the mA test, press and
hold S1 for 1 second or more until the yellow “calibrate”
LED is a medium double blink. See the following
example. The output should be between .4 and .6 mA.
.5 mA Fault Output Test
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
OFF
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
ATMOS
G
N/A
Exit: Press and hold S1 for 1 second or more until the
yellow “system” LED resumes the state before the mA
test was initiated and the yellow “calibrate” LED turns
off.
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 13
Ma
Page 14

3 Operation continued
Calibration/Programming Modes:
Refer to Calibration, Section D before proceeding.
Auto “ZERO” Program Function
Press and hold S1 for 1 second or until the yellow
Start:
“calibrate” LED turns continuous ON. Release S1 and the
yellow “calibrate” LED will turn off. This indicates the unit
“zero” is now programmed to a neutral or 4 mA resting
state for
0 ppm of target gas.
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
mA FAULT
FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
R
R
G
G
SEQUENCELED
N/A
OFF
OFF
N/A
N/A
Exit: To program the “span” setting and exit this mode,
press and hold S2 for 1 second or until the yellow
“system” LED resumes the state before the calibration
mode was initiated and the yellow “calibrate” LED turns
off.
4 mA Output Calibration/Programming Mode
Press and hold S1 for 7 seconds or until the yellow
Start:
“system” LED turns continuous ON and the yellow
“calibrate LED blinks slowly. See the following example.
Once in this mode the “zero” pot can be adjusted to
calibrate the 4 mA output to a PLC, SCADA system,
panel, etc.
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
mA FAULT
FAULT
Y
R
R
N/A
OFF
“Span” Calibration/Programming Mode
Press and hold S2 for 1 second or until the yellow
Start:
“system” LED blinks slowly and the yellow “calibrate”
SOURCE
ATMOS
G
G
N/A
N/A
LED blinks fast. Once in this mode the “span” pot can be
adjusted to determine the 20 mA full-scale concentration.
Exit: To program the 4 mA calibration point and exit
this mode, press and hold S1 for 1 second or until the
SEQUENCELED
yellow “system” LED resumes the state before the
calibration mode was initiated and the yellow “calibrate”
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
mA FAULT
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 14
Ma
FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
R
R
G
G
OFF
OFF
N/A
N/A
LED turns off.
Page 15

3 Operation continued
D Calibration
Before calibrating the unit, ensure the startup procedure
was followed and unit was powered on for a minimum
of 12 hours (with the enclosure door closed) in the
operating environment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
temperature is less than 10° F, during the calibration
procedure, the door must be closed as far as possible.
This will ensure the sensor temperature will not drop
below the minimum operating temperature which could
adversely affect the programmed calibration parameters.
There are only two adjustment pots and two pushbuttons
on the main board that are used for programming the
calibration parameters. See Section B, Pushbutton
Operation, LED Indicators, Adjustment Pots and Test
Points. Use Section B to familiarize yourself with the
pushbuttons S1, S2, adjustment pots “zero”, “span”,
Test(+), Test(–) and their locations on the main board
(see Figure 8).
Figure 8: Board Component Layout
Zero Adjust
Span Adjust
For environments where the ambient
Serial PortICSP Programming Port
Pushbutton S2
JP3
Rx LEDPushbutton S1
Tx LED
JP2
In addition, the LED indicators
and blink pattern
meanings are also summarized in this section. The
calibration procedure will require use and knowledge of
the following tools within the sensor:
• “Zero” adjustment pot – adjusts output calibration
of the 4 mA nominal resting point
• “Span” adjustment pot – adjusts the 20 mA
concentration level or unit span/sensitivity
Pushbutton S1 – used to initiate the au
•
unction and program the 4 mA output calibration
f
to-zero
• Pushbutton S2 – used to program the span setting
n addition, there are four LED’s used in the calibration
I
procedure. Yellow “system” and “calibrate”, and red
“fault” and “mA fault” LED’s located on the main board
are utilized as status indicators during the calibration
procedure and as diagnostic and trouble indicators.
Non-calibrated Sensor or Loss of Factory Calibration
IMPORTANT:
Upon power up, if the yellow “system”
LED is showing a fast blink pattern, the unit hasn’t been
calibrated yet or has lost the factory calibration and
requires a
full calibration before it can reliably read the
target gas. See the following example. Should this occur,
please contact Manning Systems for assistance!
S1
ZERO
SPAN
S2
Draw
Chamber
SIG
+24
GND
SHLD
JP1
TEST +
TEST -
Tubing to
calibration point
Ma
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm
POWER
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
IR SOURCE
ATMOS
ACTIVE
POWER
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
SEQUENCELED
G
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
15
Page 16

3 Operation continued
Before continuing with the calibration procedure,
determine which of the two Normal output modes is
best for the control scheme. Filtered output holds a
stable 4 mA signal within a dead-band range while the
non-filtered output allows the signal to be seen without
any output limitations.
After this output mode choice is made, continue
through Steps 1–3 of the Calibration Procedure. As a
first step, the 4 mA output is matched to the signal
input device being used as a control panel. After this is
accomplished, Step 2 (Zero Calibration) and Step 3
(Span Calibration) can be completed in that order.
Filtered Output Mode
Each unit is equipped with a filtered output or “dead
band” output mode which locks the output at 4 mA for
signal readings of 4 to 4.6 mA. This masks surrounding
abrupt adverse environmental transients that would
cause a small short-term anomaly on the 4 mA resting
point for a near 0 ppm reading of the target gas. In this
mode, the yellow “system” LED will be ON. See the
following example.
Non-Filtered Output Mode (no signal deadband)
Start: Press and hold both the “zero” (S1) and “span”
(S2) buttons simultaneously for one second or until the
“system” LED begins to blink slowly. See example
below.
This mode will allow any anomalies to be transmitted
from 0 to 27 mA on the output. This mode is also used
in the upcoming Simple Zero Test procedure.
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
Y
R
R
G
OFF
OFF
OFF
POWER
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
SEQUENCELED
G
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
OFF
OFF
OFF
N/A
ATMOS
G
Exit: To revert back to “dead band” mode, repeat the
same button press procedure above. This button press
sequence will toggle between modes (filtered to nonfiltered).
N/A
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 16
Ma
Page 17

3 Operation continued
STEP 1
4-20 mA Output Calibration
This procedure calibrates the 4/20 mA output to match a
PLC input converter or various devices that interpret the
4/20 mA signal output to ensure the 4 mA output rests at
a true 4 mA even with minor mismatches in load
resistance, long feed wiring, or adverse environmental
conditions.
Start: Set meter to mV DC and place meter leads on
Test(+) and Test(–) respectively (see Figure 9).
• Press and hold the “zero” button (S1) for 5 second
ntil the “calibrate” LED is blinking sl
or u
the “system” LED is continuous ON. Make sure the
“
mA Fault” LED is O
Adjust the zero potentiometer until the output
•
FF.
reads 3.99 to 4.01 mA (39.9 to 40.1 mV).
he 4 mA resting point. Make small adjustments an
t
wait for the ou
tput to change because adjust
response is delayed between source pulses.
4 mA output programming calibration mode
owly and
This sets
ment
STEP 2
Zero Calibration
This procedure sets the internal reference that is
indicative of 0 ppm of target gas.
before proceeding or every other setting will be offset
and inaccurate.
The “zero” can be initiated at any time as
long as a neutral gas is flowing through the calibration
port or the surrounding air is known to be FREE of any
target gas down to 1 ppm.
Start: Apply pure nitrogen (N
s
a rate of .6 liter/min. for at least 3 minutes (OR until output signal is within ± .02 mA of signal deviation/change).
• Press and hold the “zero” button (S1) for approxi-
mately 1 second or un
is continu
When yellow calibration LED is continuous ON
•
d
releas
tur
ous ON
.
e the “zero” bu
n off and the unit will be zeroed.
below.
“Zero” programming calibration mode
It MUST be performed
) into the calibration port at
2
til the yellow “calibrate” LED
,
tton. The “calibrate” LED will
See example
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
mA FAULT
FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
R
R
G
G
N/A
OFF
N/A
N/A
Exit: Press and hold the “zero” button (S1) for one
second or more until the “calibrate” LED turns off.
The “system” LED will resume the previous state, either
“filtered” or “non-filtered” output mode. This indicates the
parameters are now programmed into memory.
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
N/A
OFF
OFF
N/A
N/A
Exit: System will automatically resume previous mode,
either “normal” or “no dead band” mode. This indicates
the parameters are now programmed into memory.
Place multi-meter leads on Test(+) and Test(–) and
ensure the output is steadily resting between 3.9 to
4.1 mA (see Figure 9 on next page). If this isn’t the
case, initiate the auto “zero” procedure once again.
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 17
Ma
Page 18

3 Operation continued
Figure 9: Board Component Layout
Serial PortICSP Programming Port
Zero Adjust
Span Adjust
Note 1: Checking
voltage to sensor
at +24 and GND
24
VDC
Black-Red
Note 2: Reading
signal at TEST+
and TEST-
Black-Red
+
40-200
mVDC
+
JP1
TEST +
TEST -
ZERO
SPAN
SIG
+24
GND
SHLD
Pushbutton S2
JP3
S1
S2
Chamber
Draw
Tubing to
calibration point
Rx LEDPushbutton S1
Tx LED
JP2
POWER
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
IR SOURCE
ATMOS
ACTIVE
STEP 3
Span Calibration
This procedure sets the “span” or concentration level
that would depict a 20 mA reading for full-scale target
gas on the 4/20 mA output. The lower the target gas
concentration is for a span of 20 mA, the more sensitive
or responsive the unit would be to lower ppm readings.
NOTE: This procedure should only be performed if the
zero and 4/20 mA procedures are successfully completed.
Start: Set meter to mV DC, place meter leads on
Test(+) and Test(–) respectively (see Figure 9).
Apply pure nitrogen (N2) into the calibration port at
a rate of .6 Liter/min. for at least 3 minutes (OR until
output signal has stabilized to within ± .02 mA of signal
deviation/change). If N
“zero” calibration, disregard the additional flow time.
is currently flowing from previous
2
Press and hold the “span” button (S2) for 1 second or
more until the yellow “calibrate” LED blinks fast and the
yellow “system” LED is blinking slowly. See the
following example.
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
mA FAULT
FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
R
R
G
G
OFF
OFF
N/A
N/A
Ensure the output rests between 3.9 and 4.1 mA (39.0
to 41.0 mV). If this is not the case, perform the “zero”
procedure again.
Once the output is within the required range with
nitrogen flowing, apply
full-scale target gas into the
calibration port at a rate of .6 liters/min for 3 minutes
immediately following the nitrogen flow.
If the signal is 26 mA or greater, adjust the “span”
potentiometer counter-clockwise until the signal is near
Because there is a slight delay in potentiometer
20 mA.
movement, make small adjustments and wait for the
output to change because adjustment response is
delayed between source pulses.
Wait until the output signal has stabilized to within ± .02
mA of signal deviation/change. Adjust the “span”
potentiometer again until the output reads around 20 mA.
Exit: Press and hold the “span” button (S2) for one
second or more until the yellow “calibrate” LED turns
off. The yellow “system” LED will resume the previous
state, either “filtered” or “non-filtered” output mode.
This indicates the parameters are now programmed into
memory.
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 18
Ma
Page 19

3 Operation continued
E Diagnostic Procedures
Simple Zero Test
This test will ensure the unit is calibrated for a true
“zero” and duly represents an absence of target gas in
this condition.
Start: Set meter to mV DC, place meter leads on
Test(+) and Test(–) respectively (see Figure 9).
•
pply
A
pure nitrogen (N
at a rate o
f .6 Liter/min. for at least 3 minutes.
Check the status of the yellow “sys
I
f this LED is continuous ON, place the un
n-filtered output run mode by pressing bo
no
ero” (S1) and “span” (S2) buttons
“z
simultaneously for 1 second or until the “sys
LED begins to blink slowly. See example below.
•
Wait until output signal has st
± .02 mA o
Output should read between 3.9 and 4.
•
f signal deviation/change
(39.0 to 41.0 mV).
If this is not the case, proceed to the next step.
• Follow the “zero” procedure above to re-zer
un
it
• Follow the “simple zero test” procedure to ensure
the unit is resting at the optimu
) into the calibration port
2
tem” LED.
it in
th the
tem”
abilized to within
.
1 mA
o the
m 4 mA point.
Exit: Press and hold both the “zero” (S1) and “span”
(S2) buttons simultaneously for 1 second or more until
“system” LED is continuous ON. Unit should be ready
for long-term operation.
4/20 mA Output Loop Integrity Check
22 mA High Signal Test
STEP 1
Start: Set meter to mV DC, place meter leads on
Test(+) and Test(–) respectively (see Figure 9).
Press the “zero” (S1) button 5 times.
•
“calibrate” LED will blink fast and the yellow
“system” LED will turn off. The output should be
21 to 22.
5 mA (210 to 225 mV).
If a problem exists on the output signal line, or the
output load is not within the specified range, the “mA
fault” LED will blink either before or upon activation of
this test. In some cases the 22 mA high signal output
will cause incorrect output load resistance values to
surface because of the demand on high resistances to
produce high currents.
Low power supply voltages can also be something to
investigate if this error surfaces only when the 22 mA
high test is initiated.
The yellow
Simple “Zero” test – NO “Dead-band” mode 0 to 26 mA
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
mA FAULT
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 19
Ma
FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
R
R
G
G
OFF
OFF
OFF
N/A
During 4/20 mA loop test (22 mA high)
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
OFF
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Page 20

3 Operation continued
f
During 4/20 mA loop test (22 mA high) w/ Error on output
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
OFF
N/A
N/A
N/A
.5 mA Low Signal Output Test for
Fault Conditions
NOTE: The unit must be in the 4/20 mA loop (22 mA
high) test to proceed with this test.
During 4/20 mA loop test (.5 mA low)
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
OFF
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
During 4/20 mA loop test (.5 mA low) with Error
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
STEP 2
Start: Press and hold the “zero” (S1) button for at least
one second or until the yellow “calibrate” LED shows
medium double blink. The yellow “system” LED will
remain off and the output should change to .4 to .6 mA
(4 to 6 mV).
If a problem exists on the output signal line, or the
output load is not within the specified range, the “mA
fault” LED will blink either before or upon activation of
this test.
If an error surfaces during this test only, the possibility
of cross-talk can exist on the signal line. This is caused
by resistive shorts to power or other voltage sources
that can raise the .5 mA target current on the line.
Moisture in the connector can cause stray voltage to
migrate from the 24V DC pin over to the 4/20 mA signal
line. Check connectors or refer to the troubleshooting
section or error code analysis section for assistance.
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
OFF
N/A
N/A
N/A
STEP 3
Exit: Press and hold the “zero” (S1) button for at least
one second or until the yellow “calibrate LED turns off.
The yellow “system” LED will resume the previous state,
either “filtered” or “non-filtered” output mode.
NOTE: In addition to test procedures initiated manually,
every 2 seconds SensorCheck
several performance parameters of the AirScan
notification of .5 mA on the output signal is transmitted i
any of these parameters is not met.
TM
technology monitors
TM
iR. A
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 20
Ma
Page 21

3 Operation continued
F Troubleshooting
Electrical Interference
This sensor has been designed to be highly resistant to
EMI/RFI using multiple stages of filtering and
protection. However, in extreme environments, some
noise pickup can occur directly through the sensor.
Insure that the bare shield wire of the instrument cable
is properly connected at the readout unit. See Figure 10,
Note 2 for AirScan
Figure 10: Troubleshooting the AirScanTMiR
Zero Adjust
Span Adjust
Note 1: Checking
voltage to sensor
at +24 and GND
24
VDC
Black-Red
Note 2: Reading
signal at TEST+
and TEST-
+
40-200
mVDC
TM
iR meter test points.
Pushbutton S2
JP3
S1
ZERO
SPAN
S2
SIG
+24
GND
SHLD
JP1
TEST +
TEST -
Draw
Chamber
Serial PortICSP Programming Port
Rx LEDPushbutton S1
Tx LED
JP2
POWER
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
IR SOURCE
ATMOS
ACTIVE
Sensor On-board Diagnostic System
It is possible to have the mA output fail during normal
run mode. In some instances a mA output circuit that
is incorrectly setup can supply 4 mA to the load
reasonably well; however, an incorrect circuit
arrangement could not be capable of driving 20 mA to
the load when required. Therefore, the system will
place a fault condition out on the mA loop output and
flash the “mA fault” LED indicating the output wiring
is not correct or load resistance is too high.
To properly ensure the load is correct, during the 20 mA
or (high) 4/20 mA integrity test, the output circuit
dynamic range is tested to its fullest extent. If the mA
fault LED blinks during this test, the load resistance is
too high or power supply voltage is too low.
In the case of a mA Failure during Run mode, the “mA
fault” LED will blink Fast.
In the case of a mA failure during the mA output test,
the “mA fault” LED will also blink Fast. See figure at the
top of the next page.
Black-Red
Ma
+
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 21
Tubing to
calibration point
Page 22

3 Operation continued
Error on 4/20 mA output or during 4/20 mA test 20 mA high
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
CALIBRATE
FAULT
mA FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
Y
R
R
G
G
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
To resolve this issue, Place a resistor having at least 100
to 250 ohms across the signal output (SIG) and ground
(GND). The “mA fault” LED will stop blinking indicating
the load or wiring has a problem.
Sensor Output at 0 mA
Verify +24 VDC at the sensor terminal block (see Figure
10, Note 1 on previous page).
Check signal voltage between Test(+) and Test(–) (see
Figure 10, Note 2). Voltage should be in the range of 40 to
200 mV corresponding to an actual current flow of 4 to 20
mA. If this voltage is 0 mV, the signal has no path to
ground. Check monitoring equipment connections and
configuration. Input impedance must be 500 ohms or less.
IR Source Failure
If the IR source signal strength drops to the point that
the unit can no longer function satisfactorily, the “fault”
LED will remain continuous ON and the 4/20 mA
output will be set to 0.5 mA. See example below. This
condition can also occur in environments where there is
a significant amount of particulate contamination.
Usually is takes an appreciable amount of time for the
particles to pose signal degradation, however, under
long-term exposure the filter surface could be dirty
causing low thermal readings, hence marginal operation
for signal analysis.
SEQUENCELED
POWER
G
SYSTEM
Y
CALIBRATE
mA FAULT
FAULT
SOURCE
ATMOS
Y
R
R
G
G
NOTE: 4/20 mA will be set to 0.5 mA.
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Sensor Output at .5 mA
Please see Section D on page 15 for possible fault
conditions related to .5 mA output.
Gas Concentration Indicated With No Refrigerant Present
The AirScanTMiR is designed to be quite specific to
CFC/HCFC/HFC’s that are colorless, odorless gases
which can’t be sensed by humans at low levels. Always
double-check with another instrument before assuming
refrigerants are not present.
Performing a zero and a span calibration using certified
calibration gas will confirm or correct the sensor’s
reading.
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 22
Ma
Page 23

4 Maintenance
Expose each sensor to test gases monthly to verify that
the sensor has a normal response. This will also check
the alarm lights and relay action of the monitoring
equipment.
It is essential that signal voltages be taken and logged
on a consistent basis at least monthly. Periodically,
sensors should be exposed to refrigerant sample and
the results logged.
5 Replacement Parts
For replacement parts, contact Manning Systems. Be sure
to give serial number of unit and model number.
For proper operation it is essential that the test and
calibration schedule be adhered to. Manning Systems
recommends the following maintenance schedule:
Calibration shou
•
calibration gas every six months. Calibration kits
are available from Manning Systems.
• All tests and calibrations must be logged. It
ecommended that certified calibr
highly r
be used ever
ld be performed with certified
is
ation gas
y six months.
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 23
Ma
Page 24

6 Limited Warranty
1. Limited Warranty
Manning Sys
the original purchaser and/or ultimate cust
(“P
urchaser”) of Manning’s Products (“Pr
that if
material or workmanship within eighteen (18)
nths of the date of shipment by Manning or
mo
twelve (12) months from the date of first us
th
e purchaser, whichever comes first, such
defective part will be repaired or replaced, free of
charge, at Manning’s discretion if shipped prepaid
to Manning at 11511 W. 83rd Terrace, Lenexa,
Kansas 66214,
original container. The Produ
reight prepaid and repaired or replaced if
f
deter
mined by Manning that the part fa
d
efective materials or workmanship. The repair or
replacement of any such defective part
M
anning’s sole and exclusive responsibility an
liability under this limited warranty.
2. Exclusions
A. If gas sensors are part of the Product, the gas
sensor is covered by a twelve (12) month
limited warranty of the manu
B. If gas sensors are covered by this limited
warranty, the gas sensor is subject to
inspection by Manning for extended exposure
to excessive gas concentrations if a claim by
the Purchaser is made under this limited
warranty. Should such inspection indicate that
the gas sensor has been expended rather than
failed prematurely, this limited warranty shall
not apply to the Product.
C. This limited warranty does not cover
consumable items, such as batteries, or items
subject to wear or periodic replacement,
including lamps, fuses, valves, vanes, sensor
elements, cartridges, or filter elements.
tems, Inc. (“Manning”) warrants to
any part thereof proves to be defe
in a package equal to or in the
ct will be retu
facturer.
omer
oduct”)
ctive in
e by
rned
it is
iled due to
shall be
d
3. Warranty Limitation and Exclusion
Manning will have no further obligation under this
limited warranty. All warranty obligations
Manning are ex
been subject to abuse, misuse, negligence, or
accident or if the Purchaser fails to perfor
of the du
the Product has not been oper
if
accordance with instructions, or if the Product
s
erial number has been removed or altered.
4. Disclaimer of Unstated Warranties
THE WARRANTY PRINTED ABO
WARRANTY APPLICABLE TO THIS PURCHASE.
ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR
IMPL
IED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO
TH
E IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FO
PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE HEREBY
DISCLAIMED.
5. Limitation of Liability
IT IS UNDERSTOOD AND AGREED THAT
MANNING’S
CONTRACT, IN TORT, UNDER ANY WARRANTY,
IN NEGL
EXCEED TH
PRICE PAID B
PRODUCT AND UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES
SHALL MAN
INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
TH
E PRICE STATED FOR THE PROD
CO
NSIDERATION LIMITING MANNING’S
LIABILITY. NO ACTION, REGARDLESS OF
FORM, ARISING OUT OF THE TRANSACTIO
UN
DER THIS WARRANTY MAY BE
TH
E PURCHASER MORE THAN ON
AFTER THE CAUSE O
OCCURRED.
tinguishable if the Product has
ties set forth in this
LIABILITY, WHETHE
IGENCE OR OTHERWISE SHALL NO
E AMOUNT OF THE PURCH
Y THE PURCHASER FOR TH
NING BE LIABLE FOR SPECIA
limited warranty or
ated in
VE IS THE ON
F ACTION
S HAS
R IN
BROUGHT BY
E YEAR
of
m any
LY
,
R A
T
ASE
E
L,
UCT IS A
NS
nning AirScan-iR Refrigerant Sensor 18908 AirScan-iR-comm 24
Ma
 Loading...
Loading...