Page 1

Technician’s
Handbook
This manual is updated as new information and models are
released. Visit our website for the latest manual.
www.manitowocice.com
America’s #1 Selling Ice Machine
Manitowoc
Q210/Q270
Undercounter
Ice Machines
Part Number STH039 8/13
Page 2
Safety Notices
As you work on Manitowoc equipment, be sure to pay
close attention to the safety notices in this handbook.
Disregarding the notices may lead to serious injury
and/or damage to the equipment.
Throughout this handbook, you will see the following
types of safety notices:
!
Warning
Text in a Warning box alerts you to a potential
personal injury situation. Be sure to read the
Warning statement before proceeding, and work
carefully.
!
Caution
Text in a Caution box alerts you to a situation in
which you could damage the equ ipment. Be sure
to read the Caution statement before proceeding,
and work carefully.
Page 3
Procedural Notices
As you work on Manitowoc equipment, be sure to read
the procedural notices in this handbook. These notices
supply helpful information which may assist you as
you work.
Throughout this handbook, you will see the following
types of procedural notices:
NOTE: Text set off as a Note provides you with simple,
but useful, extra information about the procedure you
are performing.
Important
Text in an Important box provides you with
information that may help you perform a
procedure more efficiently. Disregarding this
information will not cause damage or injury, but it
may slow you down as you work.
Page 4

Read These Before Proceeding:
!
Caution
Proper installation, care and maintenance are
essential for maximum performance and troublefree operation of your equipment. Visit our
website www.manitowocfsg.com for manual
updates, translations, or contact information for
service agents in your area.
Important
Routine adjustments and maintenance
procedures outlined in this handbook are not
covered by the warranty.
! Warning
Read this manual thoroughly before operating,
installing or performing maintenance on the
equipment. Failure to follow instructions in this
manual can cause property damage, injury or
death.
! Warning
Do not use electrical appliances or accessories
other than those supplied by Manito woc for your ice
machine model.
!
Warning
Two or more people or a lifting device are
required to lift this appliance.
Page 5
! Warning
This equipment contains high voltage electricity
and refrigerant charge. Installation and repairs are
to be performed by properly trained technicians
aware of the dangers of deali ng with high voltage
electricity and refrigerant under pressure.The
technician must also be certified in proper
refrigerant handling and servicing procedures. All
lockout and tag out procedures must be followed
when working on this equipment.
! Warning
Do not damage the refrigeration circuit when
installing, maintaining or servicing the unit.
!
Warning
Do not operate equipment that has been misused,
abused, neglected, damaged, or altered/modified
from that of original manufactured specifications.
This appliance is not intended for use by persons
(including children) with reduced physical, sensory
or mental capabilities, or lack of experience and
knowledge, unless they have been given
supervision concerning use of the appliance by a
person responsible for their safety. Do not allow
children to play with this appliance.
! Warning
All covers and access panels must be in place
and properly secured, before operating this
equipment.
Page 6
!
Warning
Do not obstruct machine vents or openings.
!
Warning
Do not store gasoline or other flammable vapors
or liquids in the vicinity of this or any other
appliance.
! Warning
Do not clean with water jet.
! Warning
It is the responsibility of the equipment o wner to
perform a Personal Protective Equipment Hazard
Assessment to ensure adequate protection
during maintenance procedures.
! Warning
Two or more people are required to move this
equipment to prevent tipping.
Page 7
! Warning
When using electric appliances, basic
precautions must always be followed, including
the following:
a. Read all the instructions before using
the appliance.
b. To reduce the risk of injury, close
supervision is necessary when an
appliance is used near children.
c. Do not contact moving parts.
d. Only use attachments recommended or
sold by the manufacturer.
e. Do not use outdoors.
f. For a cord-connected appliance, the
following must be included:
• Do not unplug by pulling on cord. To
unplug, grasp the plug, not the cord.
• Unplug from outlet when not in use
and before servicing or clean i ng .
• Do not operate any appliance with a
damaged cord or plug, or after the
appliance malfunctions or is dropped
or damaged in any manner. Contact
the nearest authorized service facility
for examination, repair, or electrical
or mechanical adjustment.
g. Follow applicable lock out tag out
procedures before working on
equipment.
h. Connect to a properly grounded outlet
only.
Page 8

!
Warning
These 50 hz models contain up to 150 grams of
R290 (propane) refrigerant. R290 (propane) is
flammable in concentrations of air between
approximately 2.1% and 9.5% by volume (LEL lower
explosion limit and UEL upper explosion limit). An
ignition source at a temperature higher than 470°C
is needed for a combustion to occur. Refer to
nameplate to identify the type of refrigerant in your
equipment. Only trained and qualified personnel
aware of the dangers are allowed to work on the
equipment.
We reserve the right to make prod uct
improvements at any time. Specifications and
design are subject to change without notice.
Page 9

Part Number STH039 8/13 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
Model Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
How to Read a Model Number . . . . . . . . .6
Model/Serial Number Location . . . . . . . .7
Ice Machine Warranty Informatio n . . . . .8
Owner Warranty Registration Card . . .8
Commercial Warranty Coverage . . . . .8
Residential Warranty Coverage . . . . .10
INSTALLATION
Location of Ice Machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Ice Machine Clearance Requirements . .14
Ice Machine Heat of Rejection . . . . . . . . .14
Leveling the Ice Machin e . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Electrical Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION
MAINTENANCE
Ice Machine Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Exterior Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Cleaning the Condenser . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Air-cooled Condenser . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Interior Cleaning and Sanitizing . . . . . 24
Removal from Service/Winterization . . . 37
OPERATION
Initial Start-up or Start-up After Automatic
Shut-off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Freeze Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Harvest Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Automatic Shut-off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Energized Parts Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Operational Checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Page 10

2 Part Number STH039 8/13
TROUBLESHOOTING
Ice Machine Will Not Run . . . . . . . . . . 47
Diagnosing Ice Thickness Control Circuitry
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Ice Production Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Installation and Visual Inspection Checklist
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Water System Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Ice Formation Pattern . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Safety Limit Feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Analyzing Discharge Line Temperature 62
Analyzing Suction temperature . . . . . . 64
Hot Gas Valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Comparing Evaporator Inlet/Outlet
Temperatures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Discharge Line Temperature Analysis 74
Refrigeration Component Diagnostic Chart
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Final Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Refrigeration Component Diagnostic Chart
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Page 11

Part Number STH039 8/13 3
COMPONENT CHECK PROCEDURES
Main Fuse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Bin Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Diagnosing Start Components . . . . . . . .87
Capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Relay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
ON/OFF/WASH Toggle Switch . . . . . . . . .88
Ice Thickness Probe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
Ice Thickness Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
Compressor Electrical Diagnostics . . . .91
Fan Cycle Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
High Pressure Cutout (HPCO) Control . . 94
Liquid Line Filter-Driers . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
Refrigerant Recovery/Evacuation . . . . . .96
Recovery and Recharging Procedures 96
Q270 Condenser Fan Motor Replacement 97
COMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS
Main Fuse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
Bin Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
ON/OFF/WASH Toggle Switch . . . . . . . . .99
Fan Control Cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
High Pressure Cutout (HPCO) Control . . 100
Total System Refrigerant Charge . . . . . . 100
Page 12

4 Part Number STH039 8/13
CHARTS
Cycle Times, 24 Hr. Ice Production an d
Refrigerant Temperature Charts . . . . . . 101
Q210 Self-contained Air-cooled . . . . . 102
Q270 Self-contained Air-cooled . . . . . 103
DIAGRAMS
Wiring Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Q210 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Q270 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Electronic Control Boards . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Tubing Schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Page 13
Part Number STH039 8/13 5
General Information
Model Numbers
This manual covers the following models:
Self-contained
Air-cooled
QYP0214A
QYP0274A
!
Warning
An ice machine contains high voltage electricity
and refrigerant charge. Repairs are to be
performed by properly trained refrigeration
technicians aware of the dangers of deali ng with
high voltage electricity and refrigerant under
pressure.The technician must also be certified in
proper refrigerant handling and servicing
procedures. All lockout and tag out procedures
must be followed when working on this
equipment.
!
Warning
These 50 hz models may contain up to 150 grams of
R290 (propane) refrigerant. R290 (propane) is
flammable in concentrations of air between
approximately 2.1% and 9.5% by volume (LEL lower
explosion limit and UEL upper explosion limit). An
ignition source at a temperature higher than 470°C
is needed for a combustion to occur. Refer to
nameplate to identify the type of refrigerant in your
equipment. Only trained and qualified personnel
aware of the dangers are allowed to work on the
equipment.
Page 14
6 Part Number STH039 8/13
How to Read a Model Number
!
Caution
Use only Manitowoc approved Ice Machine
Cleaner (part number 94-0546-3 original green
ice machine cleaner or 000000084 clear metal
safe ice machine cleaner) and Sanitizer (part
number 94-0565-3). It is a violation of Federal
law to use these solutions in a manner
inconsistent with their labeling. Read and
understand all labels printed on bottles before
use.
A - Air-cooled
4 - Half-dice, Air-cooled
Series
Condenser
Type
Capacity
Q Y P 0214 A
Y - Half-dice
Cube Size
P - Propane
Page 15
Part Number STH039 8/13 7
Model/Serial Number Location
The model and serial numbers are required when
requesting information from your local Manitowoc
distributor, service representative, or Manitowoc Ice.
The model and serial number are listed on the
OWNER WARRANTY REGISTRATION CARD. They
are also listed on the MODEL/SERIAL NUMBER
DECAL affixed to the ice machine.
Model/Serial Number Location
MODEL/SERIAL
NUMBER PLATE
MODEL/SERIAL
NUMBER PLATE
SV1687G
Page 16

8 Part Number STH039 8/13
Ice Machine Warranty Information
OWNER WARRANTY REGISTRATION CARD
General
Warranty coverage begins the day the ice machine is
installed.
If the OWNER WARRANTY REGISTRATION CARD is
not returned, Manitowoc will use the date of sale to the
Manitowoc Distributor as the first day of warranty
coverage for your new ice machine.
COMMERCIAL WARRANTY COVERAGE
General
The following Warranty outline is provided for your
convenience. For a detailed explanation, read the
warranty bond shipped with each product.
Contact your local Manitowoc representative or
Manitowoc Ice, if you need further warranty
information.
Parts
1. Manitowoc warrants the ice machine against
defects in materials and workmanship, under
normal use and service for three (3) years from
the date of original installation.
2. The evaporator and compressor are covered by
an additional two (2) year (five years total)
warranty beginning on the date of the original
installation.
Labor
1. Labor required to repair or replace defective
components is covered for three (3) years from
the date of original installation.
2. The evaporator is covered by an additional two(2) year (five years total) labor warranty beginning
on the date of the original installation.
Page 17

Part Number STH039 8/13 9
Exclusions
The following items are not included in the ice
machine’s warranty coverage:
1. Normal maintenance, adjustments and cleaning
as outlined in this manual.
2. Repairs due to unauthorized modifications to the
ice machine or use of non-standard parts without
prior written approval from Manitowoc Ice.
3. Damage caused by improper installation of the ice
machine, electrical supply, water supply or
drainage, or damage caused by floods, storms, or
other acts of God.
4. Premium labor rates due to holidays, overtime,
etc.; travel time; flat rate service call charges;
mileage and miscellaneous tools and material
charges not listed on the payment schedule.
Additional labor charges resulting from the
inaccessibility of equipment are also excluded.
5. Parts or assemblies subjected to misuse, abuse,
neglect or accidents.
6. Damage or problems caused by installation,
cleaning and/or maintenance procedures
inconsistent with the technical instructions
provided in this manual.
7. This warranty is intended exclusively for
commercial application. No warranty is extended
for personal, family, or household purposes.
Authorized Warranty Service
To comply with the provisions of the warranty, a
refrigeration service company qualified and authorized
by your Manitowoc distributor, or a Contracted Service
Representative must perform the warranty repair.
Service Calls
Normal maintenance, adjustments and cleaning as
outlined in this manual are not covered by the
warranty.
Page 18
10 Part Number STH039 8/13
RESIDENTIAL WARRANTY COVERAGE
What Does this Limited Warranty Cover?
Subject to the exclusions and limitations below,
Manitowoc Ice (“Manitowoc”) warrants to the original
consumer that any new ice machine manufactured by
Manitowoc (the “Product”) shall be free of defects in
material or workmanship for the warranty period
outlined below under normal use and maintenance,
and upon proper installation and start-up in
accordance with the instruction manual supplied with
the Product.
How Long Does this Limited Warranty Last?
Who is Covered by this Limited Warranty?
This limited warranty only applies to the original
consumer of the Product and is not transferable.
What are MANITOWOC ICE’S Obligations Under
this Limited Warranty?
If a defect arises and Manitowoc receives a valid
warranty claim prior to the expiration of the warranty
period, Manitowoc shall, at its option: (1) repair the
Product at Manitowoc’s cost, including standard
straight time labor charges, (2) replace the Product
with one that is new or at least as functionally
equivalent as the original, or (3) refund the purchase
price for the Product. Replacement parts are
warranted for 90 days or the balance of the original
warranty period, whichever is longer. The foregoing
constitutes Manitowoc’s sole obligation and the
consumer’s exclusive remedy for any breach of this
limited warranty . Manitowoc’s liability under this limited
warranty is limited to the purchase price of Product.
Additional expenses including, without limitation,
service travel time, overtime or premium labor
charges, accessing or removing the Product, or
shipping are the responsibility of the consumer.
Product Covered Warranty Period
Ice Machine Twelve (12) months
from the sale date
Page 19

Part Number STH039 8/13 11
What Is Not Covered?
This limited warranty does cover, and you are solely
responsible for the costs of: (1) periodic or routine
maintenance, (2) repair or replacement of the Product
or parts due to normal wear and tear, (3) defects or
damage to the Product or parts resulting from misuse,
abuse, neglect, or accidents, (4) defects or damage to
the Product or parts resulting from improper or
unauthorized alterations, modifications, or changes;
and (5) defects or damage to any Product that has not
been installed and/or maintained in accordance with
the instruction manual or technical instructions
provided by Manitowoc. To the extent that warranty
exclusions are not permitted under some state laws,
these exclusions may not apply to you.
EXCEPT AS STATED IN THE FOLLOWING SENTENCE,
THIS LIMITED WARRANTY IS THE S OLE AND EXCLUSIVE
WARRANTY OF MANITOWOC WITH REGARD TO THE
PRODUCT. ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES ARE STRICTLY
LIMITED TO THE DURATION OF THE LIMITED
WARRANTY APPLICABLE TO THE PRODUCTS AS
STATED ABOVE, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, ANY
WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR OF FITNESS
FOR A PA RTICULAR PURPOSE.
Some states do not
allow limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts,
so the above limitation may not apply to you.
IN NO EVENT SHALL MANITOWOC OR ANY OF ITS
AFFILIATES BE LIABLE TO THE CONSUMER OR ANY
OTHER PERSON FOR ANY INCIDENTAL,
CONSEQUENTIAL OR SPECIAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND
(INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOSS OF PROFITS,
REVENUE OR BUSINESS) ARISING FROM OR IN ANY
MANNER CONNECTED WITH THE PRODUCT, ANY
BREACH OF THIS LIMITED WARRANTY, OR ANY OTHER
CAUSE WHATSOEVER, WHETHER BASED ON
CONTRACT, TORT OR ANY OTHER THEORY OF
LIABILITY.
Some states do not allo w th e excl usi o n or
limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so
the above limitation or exclusion may not apply to you.
Page 20

12 Part Number STH039 8/13
How State Law Applies
This limited warranty gives you specific legal rights,
and you may also have rights that vary from state to
state or from one jurisdiction to another.
Registration Card
To secure prompt and continuing warranty service, this
warranty registration card must be completed and sent
to Manitowoc within thirty (30) days from the sale date.
Complete the following registration card and send it to
Manitowoc at the address shown above. Retain a copy
for your records.
Page 21

Part Number STH039 8/13 13
Installation
Location of Ice Machine
The location selected for the ice machine must meet
the following criteria. If any of these criteria are not
met, select another location.
• The location must be indoors.
• The location must be free of airborne and other
contaminants.
• Air temperature must be at least 4°C but must not
exceed 43°C.
• The location must not be near heat-generating
equipment or in direct sunlight.
• The location must be capable of supporting the
weight of the ice machine and a full bin of ice.
• The location must allow enough clearance for
water , drain, and electrical connections in the rear
of the ice machine.
• The location must not obstruct airflow through or
around the ice machine (condenser airflow is in
and out the front). Refer to the chart below for
clearance requirements.
• The ice machine must be protected if it will be
subjected to temperatures below 0°C. Failure
caused by exposure to freezing temperatures is
not covered by the warranty.
Page 22
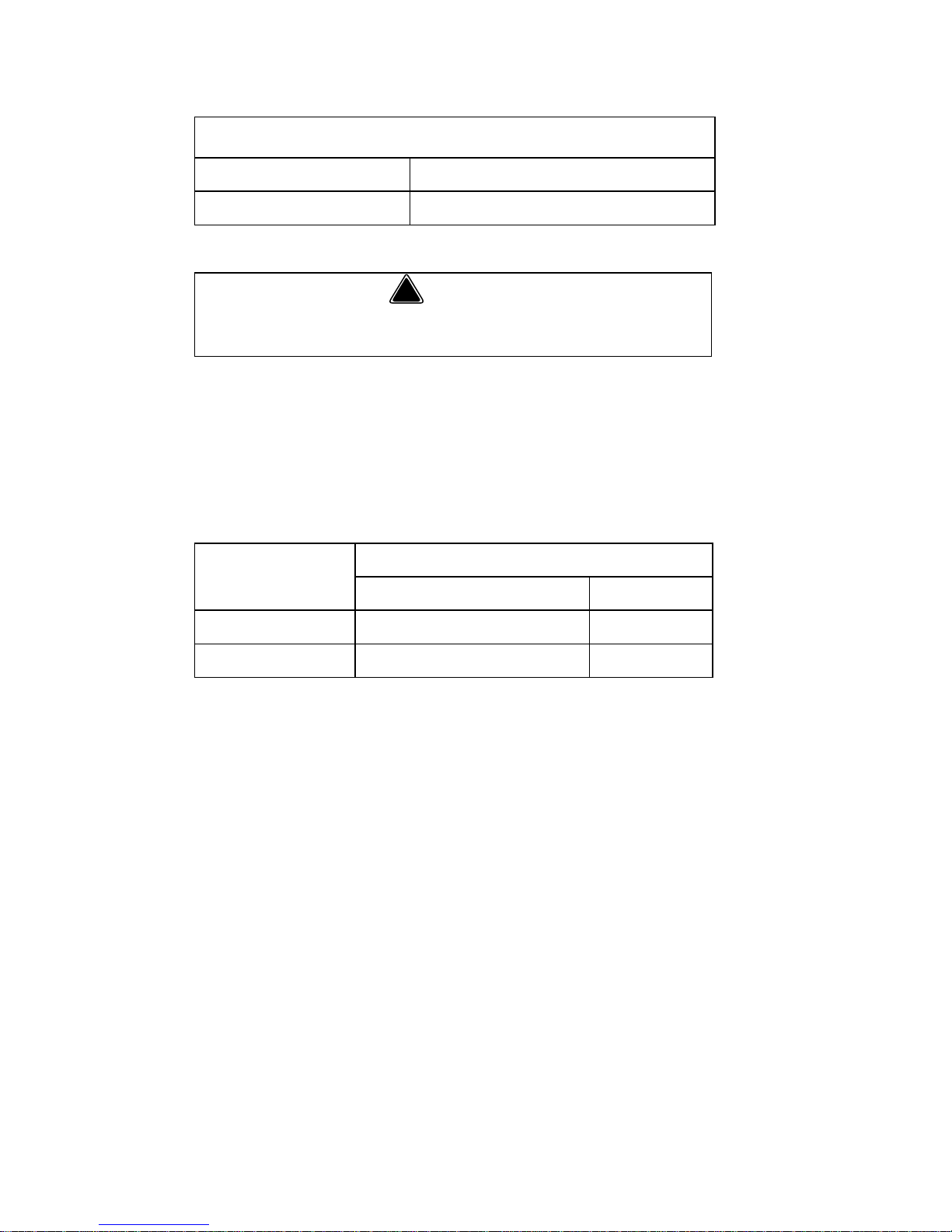
14 Part Number STH039 8/13
Ice Machine Clearance Requirements
*NOTE: The ice machine may be built into a cabinet.
There is no minimum clearance requirement for the
top or left and right sides of the ice machine. The listed
values are recommended for efficient operation and
servicing only.
Ice Machine Heat of Rejection
* B.T.U./Hour
** Because the heat of rejection varies during the ice making cycle,
the figure shown is an average.
Ice machines, like other refrigeration equipment, reject
heat through the condenser. It is helpful to know the
amount of heat rejected by the ice machine when
sizing air conditioning equipment where self-contained
air-cooled ice machines are installed.
Self-contained Air-cooled
Top/Sides 127 mm*
Back 127 mm*
!
Warning
Do not obstruct machine vents or openings.
Series
Ice Machine
Heat of Rejection*
Air Conditioning** Peak
Q210 2400 3400
Q270 3800 6000
Page 23
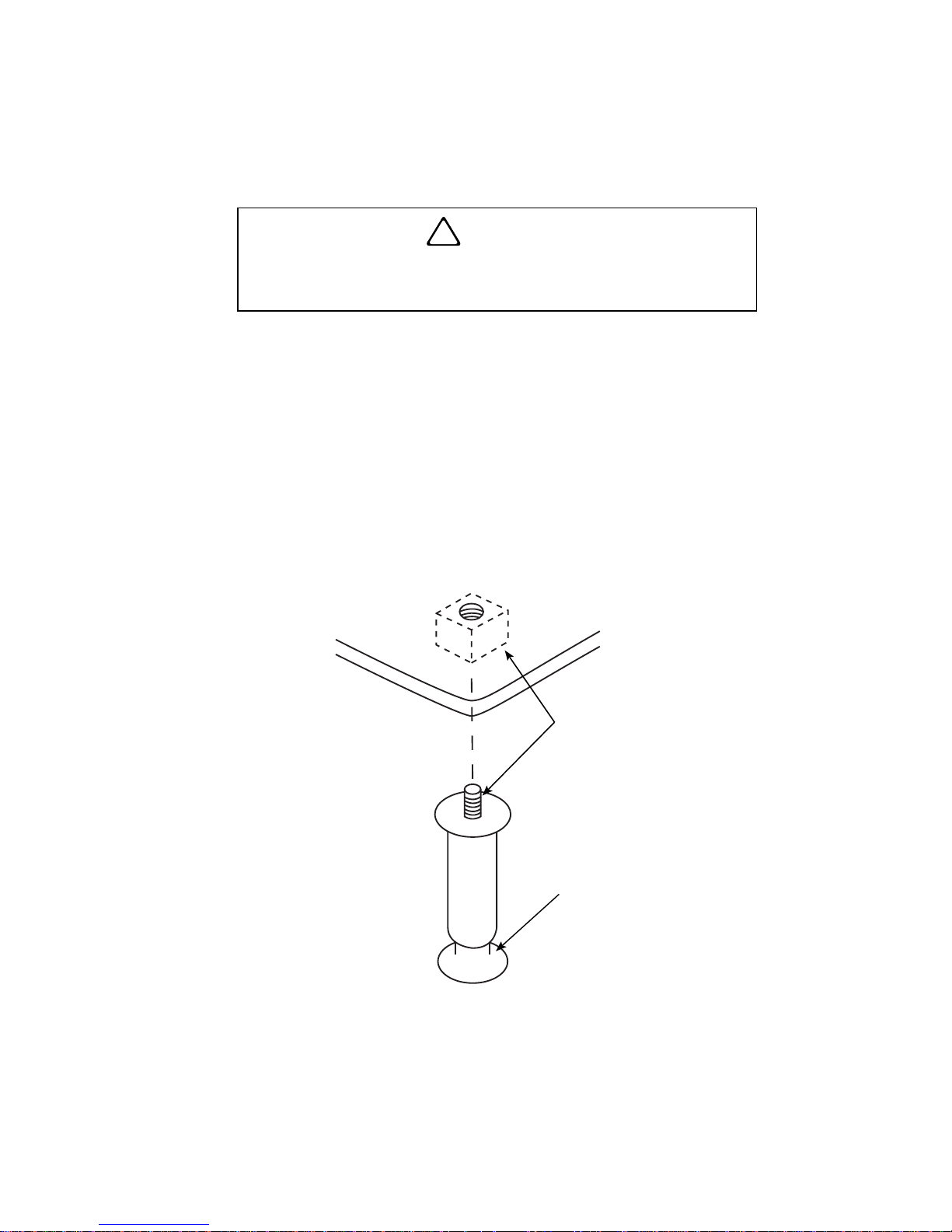
Part Number STH039 8/13 15
Leveling the Ice Machine
1. Screw the leveling legs onto the bottom of the ice
machine.
2. Screw the foot of each leg in as far as possible.
3. Move the ice machine into its final position.
4. Level the ice machine to ensure that the siphon
system functions correctly. Use a level on top of
the ice machine. Turn each foot as necessary to
level the ice machine from front to back and side
to side.
NOTE: An optional 6.35 cm caster assembly is
available for use in place of the legs. Installation
instructions are supplied with the casters.
Leg Installation
!
Caution
The legs must be screwed in tightly to prevent
them from bending.
THREAD
LEVELING LEG
INTO BASE OF
CABINET
THREAD “FOOT”
IN AS FAR AS
POSSIBLE
SV1606
Page 24
16 Part Number STH039 8/13
Electrical Requirements
Voltage
The maximum allowable voltage variation is +10/-0%
of the rated voltage on the ice machine model/serial
number plate at start-up (when the electrical load is
highest).
Fuse/Breaker
A separate fuse/circuit breaker must be provided for
each ice machine.
Total Circuit Ampacity
The total circuit ampacity is used to help select the
wire size of the electrical supply.
The wire size (or gauge) is also dependent upon
location, materials used, length of run, etc., so it must
be determined by a qualified electrician.
NOTE: This table is for reference only. Nameplate
information over rides the information in the table
below.
Electrical Specifications
Ice Machine
Voltage
Phase Cycle
Maximum.
Fuse/
Circuit
Breaker
Total
Amps
Q210 230/1/50 15 amp 3.6
Q270 230/1/50 15 amp 5.2
* Indicates Preliminary Data
! Warning
All wiring must conform to local, state and national
codes and the appliance must be grounded.
Page 25
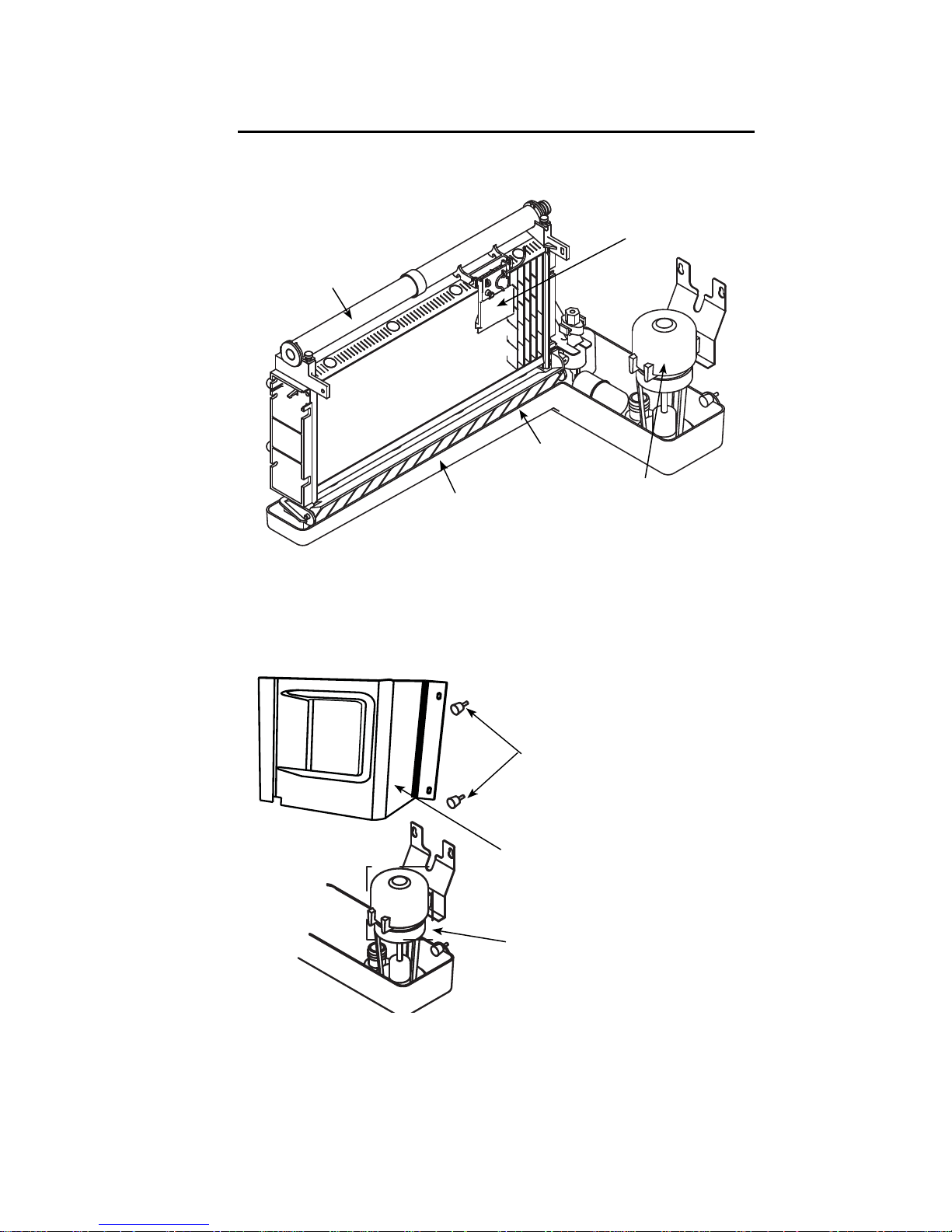
Part Number STH039 8/13 17
Component Identification
Evaporator Compartment
ICE THICKNESS
PROBE
DISTRIBUTION
TUBE
EVAPORATOR
WATER
TROUGH
ICE
DAMPER
WATER
PUMP
SV1694A
THUMBSCREWS
WATER
PUMP
COVER
WATER
PUMP
Page 26
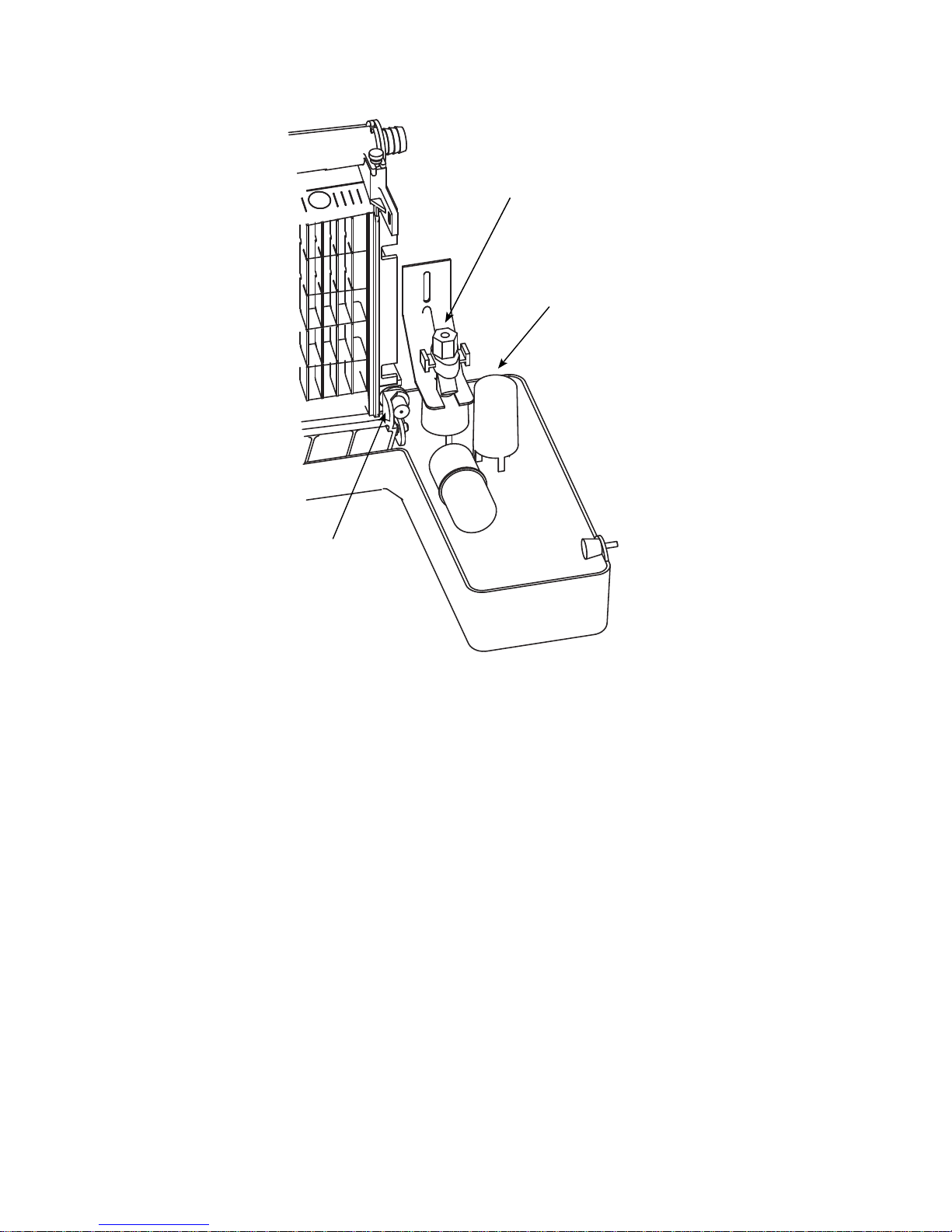
18 Part Number STH039 8/13
Evaporator Compartment
FLOAT VALVE
BIN SWITCH
MAGNET
SIPHON CAP
SV1695A
Page 27
Part Number STH039 8/13 19
Q210 Ice Machines
Q270 Ice Machines
ON/OFF/WASH
TOGGLE
SWITCH
CONDENSER AIR
FILTER
COMPRESSOR
COMPARTMENT
ACCESS SCREWS
SV1686G
CONDENSER AIR FILTER
ON/OFF/WASH
TOGGLE
SWITCH
COMPRESSOR
COMPARTMENT ACCESS
SCREWS
PT1288
Page 28

20 Part Number STH039 8/13
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
Page 29

Part Number STH039 8/13 21
Maintenance
Ice Machine Inspection
Check all water fittings and lines for leaks. Also, make
sure the refrigeration tubing is not rubbing or vibrating
against other tubing, panels, etc.
Do not put anything (boxes, etc.) in front of the ice
machine. There must be adequate airflow through and
around the ice machine to maximize ice production
and ensure long component life.
Exterior Cleaning
Clean the area around the ice machine as often as
necessary to maintain cleanliness and efficient
operation.
Sponge any dust and dirt off the outside of the ice
machine with mild soap and water. Wipe dry with a
clean, soft cloth.
A commercial grade stainless steel cleaner/polish can
be used as necessary.
clean up any spills on or around the unit.
Page 30
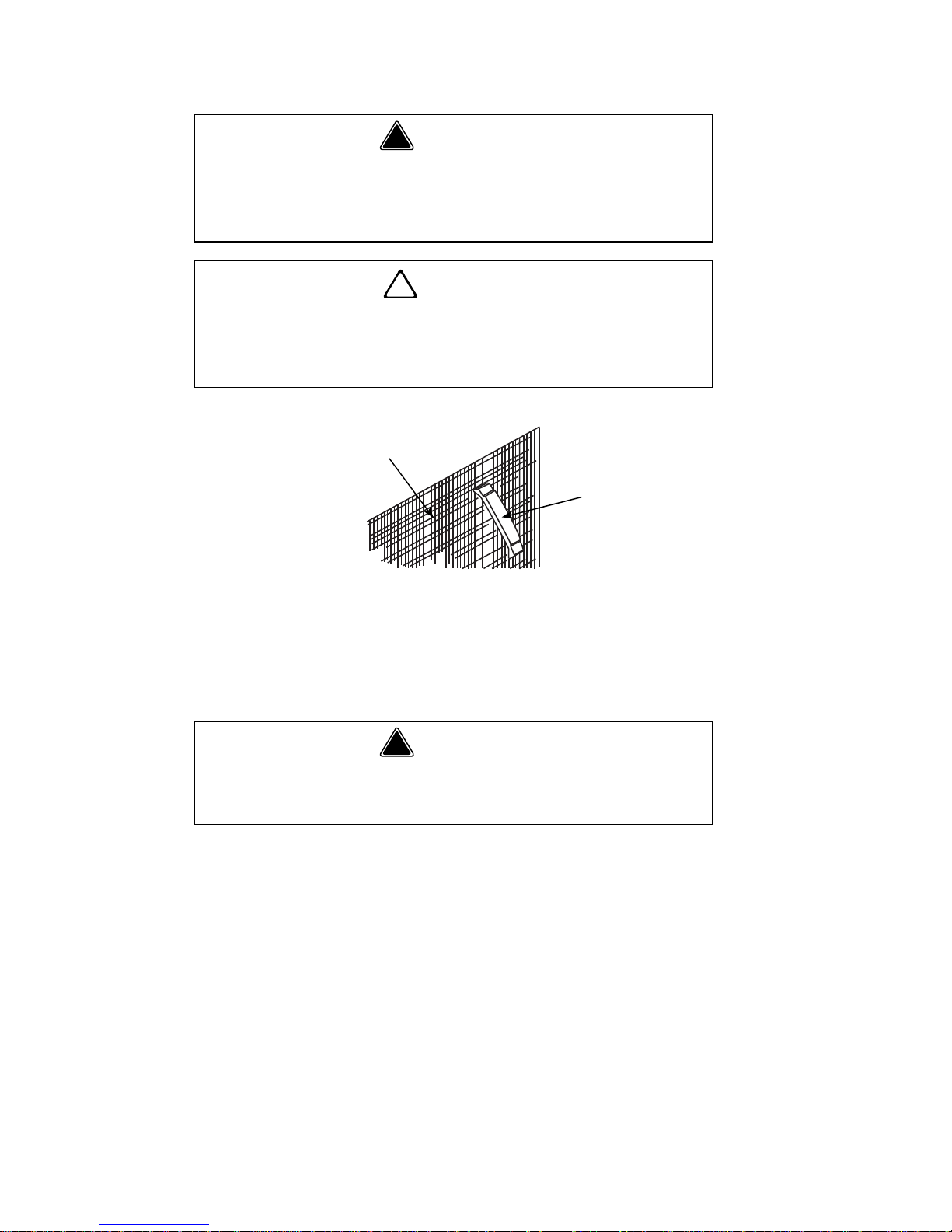
22 Part Number STH039 8/13
Cleaning the Condenser
AIR-COOLED CONDENSER
A dirty condenser restricts airflow, resulting in excessively
high operating temperatures. This reduces ice production
and shortens component life. Clean the condenser at least
every six months. Follow the steps below.
1. The washable aluminum filter on self-contained
air-cooled ice machines is designed to catch dust,
dirt, lint and grease. This helps keep the
condenser clean. Clean the filter with a mild soap
and water solution.
2. Clean the outside of the condenser with a soft
brush or a vacuum with a brush attachment.
Clean from top to bottom, not side to side. Be
careful not to bend the condenser fins.
3. Shine a flashlight through the condenser to check
for dirt between the fins. If dirt remains:
! Warning
Disconnect electric power to the ice machine at
the electric service switch and follow lockout tag
out procedures before cleaning the condenser.
!
Caution
If you are cleaning the condenser fan blades with
water, cover the fan motor to prevent water
damage.
! Warning
The condenser fins are sharp. Use care when
cleaning them.
CONDENSER
COMB
DOWN
ONLY
FIN COMB
Page 31

Part Number STH039 8/13 23
4. Blow compressed air through the condenser fins
from the inside. Be careful not to bend the fan
blades.
5. Use a commercial condenser coil cleaner. Follow
the directions and cautions supplied with the
cleaner.
6. Straighten any bent condenser fins with a fin
comb.
7. Carefully wipe off the fan blades and motor with a
soft cloth. Do not bend the fan blades. If the fan
blades are excessively dirty, wash with warm,
soapy water and rinse thoroughly.
Page 32

24 Part Number STH039 8/13
INTERIOR CLEANING AND SANITIZING
General
Clean and sanitize the ice machine every six months
for efficient operation. If the ice machine requires more
frequent cleaning and sanitizing, consult a qua lified
service company to test the water quality and
recommend appropriate water treatment.
The ice machine must be taken apart for cleaning and
sanitizing.
Cleaning and Sanitizing Procedure
Ice machine cleaner is used to remove lime scale and
mineral deposits. Ice machine sanitizer disinfects and
removes algae and slime.
!
Caution
Use only Manitowoc approved Ice Machine
Cleaner (part number 95-0546-3) and
Sanitizer (part number 94-0565-3). It is a
violation of Federal law to use these
solutions in a manner incon sistent with their
labeling. Read and understand all labels
printed on bottles before use.
!
Caution
Do not mix Ice Machine Cleaner and
Sanitizer solutions together. It is a violation of
Federal law to use these solutions in a
manner inconsistent with their labeling.
! Warning
Wear rubber gloves and safety goggles
(and/or face shield) when handling Ice
Machine Cleaner or Sanitizer.
Page 33

Part Number STH039 8/13 25
Step 1 Set the toggle switch to the OFF position after
ice falls from the evaporator at the end of a Harvest
cycle. Or, set the switch to the OFF position and allow
the ice to melt off the evaporator.
Step 2 Remove all ice from the bin.
Step 3 To start a cleaning cycle, move the toggle
switch to the WASH position.
Step 4 Add the proper amount of Manitowoc Ice
Machine Cleaner to the water trough.
Step 5 Wait until the clean cycle is complete
(approximately 22 minutes) then place the toggle
switch in the OFF position, disconnect power and
water supplies to the ice machine.
!
Caution
Never use anything to force ice from the
evaporator. Damage may result.
Model Amount of Cleaner
Q210 60 ml
Q270 60 ml
! Warning
Disconnect electric power to the ice machine
at the electric service switch and follow
lockout tag out procedures before
proceeding.
Page 34

26 Part Number STH039 8/13
Step 6 Remove parts for cleaning.
A. Remove Two Thumbscrews and Wate r
Pump Cover.
B. Remove the Vinyl Hose Connecting the
Water Pump and Water Distribution Tube
C. Remove Water Pump
• Disconnect the water pump power cord
• Loosen the screws securing the pump-
mounting bracket to the bulkhead
• Lift the pump and bracket assembly off
the mounting screws.
Water Pump Removal
DO NOT SOAK
WATER PUMP MOTOR IN
CLEANER OR SANITIZER
SOLUTIONS
REMOVE THUMBSCREWS
AND WATER PUMP COVER
Page 35

Part Number STH039 8/13 27
D. Remove the Ice Thickness Probe
• Compress the side of the ice thickness probe
near the top hinge pin and remove it from the
bracket.
Ice Thickness Probe Removal
NOTE: At this point, the ice thickness probe can easily
be cleaned. If complete removal is desired follow the
ice thickness probe wire to the bulkhead grommet (exit
point) in the back wall. Pop the bulkhead grommet out
of the back wall by inserting fingernails or a flat object
between the back wall and the grommet and prying
forward. Pull the bulkhead grommet and wire forwa r d
until the connector is accessible, then disconnect the
wire lead from the connector.
Ice Thickness Probe Cleaning
• Mix a solution of Manitowoc ice machine cleaner
and water (60 ml of cleaner to 475 ml of water) in a
container.
• Soak the ice thickness probe a minimum of 10
minutes.
Clean all ice thickness probe surfaces and verify the
ice thickness probe cavity is clean. Rinse thoroughly
with clean water, then dry completely. Incomplete
rinsing and drying of the ice thickness probe can
cause premature harvest.
SV1138A
ICE
THICKNESS
PROBE
COMPRESS SIDES OF ICE
THICKNESS PROBE
Page 36

28 Part Number STH039 8/13
E. Remove the Water Distribution Tube
Water Distribution Tube Removal
• Loosen the two thumbscrews, which secure the
distribution tube.
• Lift the right side of the distribution tube up off the
locating pin, then slide it back and to the right.
!
Caution
Do not force this removal. Be sure the
locating pin is clear of the hole be fore sliding
the distribution tube out.
SV1630
DISTRIBUTION
TUBE
THUMB
SCREW
1. LIFT UP
2. SLIDE BACK
3. SLIDE TO RIGHT
THUMB
SCREW
1
3
2
Page 37

Part Number STH039 8/13 29
Disassembly
• T wist both of the inner tube ends until the tabs line
up with the keyways.
• Pull the inner tube ends outward.
Water Distribution Tube Disassembly
SV1211
INNER
TUBE
TAB
KEYWAY
INNER
TUBE
Page 38

30 Part Number STH039 8/13
F. Remove the Float Valve
• Turn the splash shield counterclockwise one or
two turns.
Float Valve Removal
• Pull the float valve forward and off the mounting
bracket.
• Disconnect the water inlet tube from the float valve
at the compression fitting.
• Remove the cap and filter screen for cleaning.
SV1695-2
FLOAT VALVE
BRACKET
COMPRESSION
FITTING
CAP AND FILTER
SCREEN
SPLASH
SHIELD
SHUT-OFF
VALVE
FLOAT
Page 39

Part Number STH039 8/13 31
G. Remove the Water Trough
• Apply downward pressure on the siphon tube and
remove from the bottom of the water trough.
• Remove the upper thumbscrew.
• While supporting the water trough remove the two
thumbscrews from beneath the water trough.
• Remove the water trough from the bin area.
Remove Water Trough
SV1689-1
UPPER
THUMBSCREW
SV1689-2
LOWER
THUMBSCREWS
REMOVE
SIPHON
TUBE
Page 40

32 Part Number STH039 8/13
H. Remove Damper
• Gra sp ice damper and app ly pressure toward
the left hand mounting bracket.
• Apply pressure to the right hand mounting
bracket with thumb.
• Pull ice damper forward when the right hand
ice damper pin disengages.
Installation
• Place ice damper pin in left hand mounting
bracket and apply pressure toward the left
hand mounting bracket.
• Apply pressure to the right hand mounting
bracket with thumb.
• Push ice damper toward evaporator until right
hand damper pin engages.
SV1742A
STEP 2
STEP 1
STEP 3
SV1742H
STEP 2
STEP 1
STEP 3
Page 41

Part Number STH039 8/13 33
Remove the Bin Door
• Grasp the rear of the bin door and pull bin door
forward approximately 13 cm.
• Slide bin door to the rear while applying upward
pressure (The rear door pins will ride up into the
track slot and slide backward to the stop tab).
• While applying pressure against the bin door pull
down on the rear of each bin door track until the
door pins clear the stop tabs.
• Slide the rear door pins off the end and then below
the door track. Slide bin door forward allowing the
back of the door to lower into the bin. Continue
forward with the bin door until the front pins bottom
out in the track.
• Lift right side of door until the front pins clear the
track, then remove door from bin.
• Remove rollers (4) from all door pins.
STOP TAB
TRACK SLOT
SLIDE DOOR
FORWARD
Page 42

34 Part Number STH039 8/13
Step 7 Mix a solution of cleaner and warm water.
Depending on the amount of mineral buildup, a larger
quantity of solution may be required. Use the ratio in
the table below to mix enough solution to thoroughly
clean all parts.
Step 8 Use ½ of the cleaner/water solution to clean
all components. The cleaner solution will foam when it
contacts lime scale and mineral deposits; once the
foaming stops use a soft bristle brush, sponge or cloth
(not a wire brush) to carefully clean the parts. Soak the
parts for 5 minutes (15 – 20 minutes for heavily scaled
parts). Rinse all components with clean water .
Step 9 While components are soaking, use ½ of the
cleaner/water solution to clean all foodzone surfaces
of the ice machine and bin. Use a nylon brush or cloth
to thoroughly clean the following ice machine areas:
• Evaporator plastic parts – including top, bottom
and sides
• Bin bottom, sides and top
Rinse all areas thoroughly with clean water.
Step 10 Mix a solution of sanitizer and warm water.
Step 11 Use 1/2 of the sanitizer/water solution to
sanitize all removed components. Use a cloth or
sponge to liberally apply the solution to all surfaces of
the removed parts or soak the removed parts in the
sanitizer/water solution. Do not rinse parts after
sanitizing.
Solution
Type
Water Mixed with
Cleaner 4 l 500 ml cleaner
Solution
Type
Water Mixed With
Sanitizer 23 l 120 ml sanitizer
Page 43

Part Number STH039 8/13 35
Step 12 Use 1/2 of the sanitizer/water solution to
sanitize all foodzone surfaces of the ice machine and
bin. Use a cloth or sponge to liberally apply the
solution. When sanitizing, pay particular attention to
the following areas:
• Evaporator plastic parts - including top, bottom and
sides
• Bin bottom, sides and top
Do not rinse the sanitized areas.
Step 13 Replace all removed components.
Step 14 Reapply power and water to the ice machine
and place the toggle switch in the WASH position.
Add the proper amount of Manitowoc Ice Machine
Sanitizer to the water trough.
Step 15 Wait until the sanitize cycle is complete
(approximately 22 minutes) then place the toggle
switch in the OFF position, disconnect power and
water supplies to the ice machine.
Step 16 Repeat step 6 to remove parts for hand
sanitizing.
Step 17 Mix a solution of sanitizer and warm water.
Model Amount of Sanitizer
Q210 66 ml
Q270 57 ml
! Warning
Disconnect electric power to the ice machine at
the electric switch box before proceeding.
Solution
Type
Water Mixed With
Sanitizer 23 l 120 ml sanitizer
Page 44

36 Part Number STH039 8/13
Step 18 Use 1/2 of the sanitizer/water solution to
sanitize all removed components. Use a cloth or
sponge to liberally apply the solution to all surfaces of
the removed parts or soak the removed parts in the
sanitizer/water solution. Do not rinse parts after
sanitizing.
Step 19 Use 1/2 of the sanitizer/water solution to
sanitize all foodzone surfaces of the ice machine and
bin. Use a cloth or sponge to liberally apply the
solution. When sanitizing, pay particular attention to
the following areas:
• Evaporator plastic parts - including top, bottom and
sides
• Bin bottom, sides and top
Do not rinse the sanitized areas.
Step 20 Replace all removed components.
Step 21 Reapply power and water to the ice machine
and place the toggle switch in the ICE position.
Page 45

Part Number STH039 8/13 37
Removal from Service/Winterization
General
S pecial precautions must be taken if the ice machine is
to be removed from service for an extended period of
time or exposed to ambient temperatures of 0°C or
below.
Self-contained Air-cooled Ice Machines
1. Disconnect the electric power at the circuit
breaker or the electric service switch.
2. Turn of f the wat er supply.
3. Remove the water from the water trough.
4. Disconnect and drain the incoming ice-making
water line at the rear of the ice machine.
5. Blow compressed air in both the incoming water
and the drain openings in the rear of the ice
machine until no more water comes out of the
inlet water lines or the drain.
6. Make sure water is not trapped in any of the water
lines, drain lines, distribution tubes, etc.
!
Caution
If water is allowed to remain in the ice machine in
freezing temperatures, severe damage to some
components could result. Damage of this nature is
not covered by the warranty.
Page 46

38 Part Number STH039 8/13
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
Page 47

Part Number STH039 8/13 39
Operation
INITIAL START-UP OR START-UP AFTER
AUTOMATIC SHUT-OFF
1. Pressure Equalization
Before the compressor starts the hot gas valve is
energized for 15 seconds to equalize pressures during
the initial refrigeration system start-up.
2. Refrigeration System Start-up
The compressor starts after the 15-second pressure
equalization, and remains on throughout the entire
Freeze and Harvest Sequences. The hot gas valve
remains on for 5 seconds during initial compressor
start-up and then shuts off.
At the same time the compressor starts, the
condenser fan motor (air-cooled models) is supplied
with power throughout the entire Freeze and Harvest
Sequences. The fan motor is wired through a fan cycle
pressure control, therefore it may cycle on and off.
(The compressor and condenser fan motor are wired
through the relay . As a result, any time the relay coil is
energized, the compressor and fan motor are supplied
with power.)
FREEZE SEQUENCE
3. Prechill
The compressor is on for 30 seconds prior to water
flow to prechill the evaporator .
4. Freeze
The water pump starts after the 30-second prechill. An
even flow of water is directed across the evaporator
and into each cube cell, where it freezes.
When suffici ent ice has forme d, the water fl ow (not the
ice) contacts the ice thickness probe. After
approximately 7 seconds of continual water contact,
the Harvest Sequence is initiated. The ice machine
cannot initiate a Harvest Sequence until a 6-minute
freeze time has been surpassed.
Page 48

40 Part Number STH039 8/13
HARVEST SEQUENCE
5. Harvest
The water pump de-energizes stopping flow over the
evaporator. The rising level of water in the sump
trough diverts water out of the overflow tube, purging
excess minerals from the sump trough. The hot gas
valve also opens to divert hot refrigerant gas into the
evaporator.
The refrigerant gas warms the evaporator causing the
cubes to slide, as a sheet, off the evaporator and into
the storage bin. The sliding sheet of cubes contacts
the ice damper, opening the bin switch.
The momentary opening and re-closing of the bin
switch terminates the Harvest Sequence and returns
the ice machine to the Freeze Sequence (steps 3 - 4).
AUTOMATIC SHUT-OFF
6. Automatic Shut-off
When the storage bin is full at the end of a harvest
sequence, the sheet of cubes fails to clear the ice
damper and will hold it down. After the ice damper is
held open for 7 seconds, the ice machine shuts off.
The ice machine remains off for 3 minutes before it
can automatically restart.
The ice machine remains off until enough ice has been
removed from the storage bin to allow the ice to fall
clear of the damper. As the ice damper swings back to
the operating position, the bin switch re-closes and the
ice machine restarts (steps 1 - 2), provided the
3
minute delay period is complete.
Page 49

Part Number STH039 8/13 41
ENERGIZED PARTS CHART
* Condenser Fan Motor: The fan motor is wired through a fan cycle
pressure control; therefore, it may cycle on and off.
Length of
Time
15 seconds
5 seconds
30 seconds
Until 7 sec.
Water contact
w/ice
thickness
probe
Relay
3B
Compressor
Fan Motor*
off
on
on
on
3A
Compressor
off
on
on
on
Control Board Relays
3
Relay
Coil
off
on
on
on
2
Hot Gas V alve
on
on
off
off
1
Water Pump
off
off
off
on
ICE MAKING
SEQUENCE OF
OPERATION
Initial Start-up
1. Water purge
2. Refrigeration
System Start-up
Freeze Sequence
3. Pre chill
4. Freeze
Page 50

42 Part Number STH039 8/13
Length of
Time
Bin switch
activation
Until bin
switch
re-closes
Relay
3B
Condenser
Fan Motor*
on
off
3A
Compressor
on
off
Control Board Relays
3
Relay
Coil
on
off
2
Hot Gas
Valve
on
off
1
Water Pump
off
off
ICE MAKING
SEQUENCE OF
OPERAT ION
Harvest
Sequence
5. Harvest
Automatic
Shut-off
6. Auto Shut-off
Page 51

Part Number STH039 8/13 43
Operational Checks
Siphon System
To reduce mineral build-up and cleaning frequency,
the water in the sump trough must be purged during
each harvest cycle.
When the water pump de-energizes the level in the
water trough rises above the standpipe starting a
siphon action. The siphon action stops when the water
level in the sump trough drops. When the siphon
action stops, the float valve refills the water trough to
the correct level.
Follow steps 1 through 6 under water level check to
verify the siphon system functions correctly
Water Level
Check the water level while the ice machine is in the
ice mode and the water pump is running. The correct
water level is 6 mm to 10 mm below the top of the
standpipe, a line in the water trough indicates the
correct level.
SV1689-1
SET THE WATER LEVEL TO
THE LINE IN THE WATER
TROUGH
SIPHON CAP
Page 52

44 Part Number STH039 8/13
Water Level Check
The float valve is factory-set for the proper water level.
If adjustments are necessary:
1. Verify the ice machine is level.
2. Remove the siphon cap from the standpipe.
3. Place the main ON/OFF/WASH toggle switch to
the ON position, and wait until the float valve
stops adding wate r.
4. Adjust the water level 6 mm to 10mm below the
standpipe, to the line in the water trough:
A. Loosen the two screws on the float valve
bracket.
B. Raise or lower the float valve assembly as
necessary, then tighten the screws.
5. Move the main ON/OFF/WASH toggle switch to
the OFF position. The water level in the trough will
rise above the standpipe and run down the drain.
6. Replace the siphon cap on the standpipe, and
verify water level and siphon action by repeating
steps 3 through 5.
Page 53

Part Number STH039 8/13 45
Ice Thickness Check
After a harvest cycle, inspect the ice cubes in the ice
storage bin. The ice thickness probe is set to maintain
an ice bridge of 3 mm. If an adjustment is needed,
follow the steps below.
1. Turn the ice thickness probe adjustment screw
clockwise for a thicker ice bridge, or
counterclockwise for a thinner ice bridge.
Ice Thickness Adjustment
2. Make sure the ice thickness probe wire and
bracket does not restrict movement of the probe.
3 MM ICE BRIDGE
THICKNESS
ADJUSTING
SCREW
SV3114
SV3113
Page 54

46 Part Number STH039 8/13
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
Page 55

Part Number STH039 8/13 47
Troubleshooting
ICE MACHINE WILL NOT RUN
1. Verify primary voltage is supplied to ice machine
and the fuse/circuit breaker is closed.
2. Verify control board fuse is okay.
3. If the bin switch light functions, the fuse is okay.
4. Verify the bin switch functions properly. A
defective bin switch can falsely indicate a full bin
of ice.
5. Verify ON/OFF/WASH toggle switch functions
properly. A defective toggle switch may keep the
ice machine in the OFF mode.
6. V erify low DC voltage is properly grounded. Loose
DC wire connections may intermittently stop the
ice machine.
7. Replace the control board.
8. Be sure Steps 1 – 5 were followed thoroughly.
Intermittent problems are not usually related to
the control board.
! Warning
An ice machine contains high voltage electricity
and refrigerant charge. Repairs are to be
performed by properly trained refrigeration
technicians aware of the dangers of deali ng with
high voltage electricity and R290 (propane)
refrigerant under pressure.The technician must
also be certified in proper refrigerant handling and
servicing procedures. All lockout and tag out
procedures must be followed when working on
this equipment.
High (line) voltage is applied to the control board
(terminals #2 and #4) at all times. Removing
control board fuse or moving the toggle switch to
OFF will not remove the power supplied to the
control board.
Page 56

48 Part Number STH039 8/13
DIAGNOSING ICE THICKNESS CONTROL
CIRCUITRY
Ice Machine Does Not Cycle Into Harvest when
Water Contacts the Ice Thickness Control Probe
Step 1 Bypass the freeze time lock-in feature by
moving the ON/OFF/WAS H switch to OFF and back to
ON. Wait until the water starts to flow over the
evaporator.
Step 2 Clip the jumper wire to the ice thickness probe
and any cabinet ground.
Step 2 Jumper wire connected from probe to ground
Monitoring Harvest Light Correction
The harvest light comes on,
and 6-10 seconds later, ice
machine cycles from freeze
to harvest.
The ice thickness control
circuitry is functioning
properly . Do not change any
parts.
The harvest light comes on
but the ice machine stays in
the freeze sequence.
The ice control circuitry is
functioning properly . The ice
machine is in a six minute
freeze time lock-in. Verify
Step 1 of this procedure was
followed correctly.
The harvest light does not
come on.
Proceed to Step 3.
GROUND
JUMPER WIRE
ICE THICKNESS
PROBE
PROBE
CONNECTION
EVAPORATOR
BIN SWITCH
LIGHT
(GREEN)
SV1592i
HARVEST LIGHT
(RED)
Page 57

Part Number STH039 8/13 49
Step 3 Disconnect the ice thickness probe from the
control board terminal. Clip the jumper wire to the
terminal on the control board and any cabinet ground.
Monitor the harvest light.
Step 3 Jumper wire connected from control board
terminal to ground
Monitoring Harvest Light Correction
The harvest light comes on,
and 6-10 seconds later, ice
machine cycles from freeze
to harvest.
The ice thickness probe is
causing the malfunction.
The harvest light comes on
but the ice machine stays in
the freeze sequence.
The control circuitry is
functioning properly. The
ice machine is in a sixminute freeze time lock-in
(verify step 1 of this
procedure was followed
correctly).
The harvest light does not
come on.
The control board is
causing the malfunction.
GROUND
JUMPER WIRE
ICE THICKNESS
PROBE
PROBE
CONNECTION
EVAPORATOR
HARVEST LIGHT
(RED)
BIN SWITCH
LIGHT
(GREEN)
SV1592J
Page 58

50 Part Number STH039 8/13
Ice Machine Cycles Into Harvest Before Water
Contact with the Ice Thickness Probe
Step 1 Bypass the freeze time lock-in feature by
moving the ON/OFF/WAS H switch to OFF and back to
ON. Wait until the water starts to flow over the
evaporator, then monitor the harvest light.
Step 2 Disconnect the ice thickness probe from the
control board terminal.
Step 2 Disconnect probe from control board terminal.
Monitoring Harvest Light Correction
The harvest light stays off
and the ice machine remains
in the freeze sequence.
The ice thickness probe is
causing the malfunction.
Verify that the Ice
Thickness probe is
adjusted correctly.
The harvest light comes on,
and 6-10 seconds later, the
ice machine cycles from
freeze to harvest.
The control board is
causing the malfunction.
ICE THICKNESS
PROBE
DISCONNECT
PROBE WIRE
HARVEST LIGHT
(RED)
BIN SWITCH LIGHT
(GREEN)
SV1592J_2
Page 59

Part Number STH039 8/13 51
ICE PRODUCTION CHECK
The amount of ice a machine produces directly relates to the
operating water and air temperatures. This means an ice
machine with a 21°C) ambient temperature and 10°C water
produces more ice than the same ice machine with 32°C
ambient and 21°C water.
1. Determine the ice machine operating conditions:
Air temp entering condenser: ____°
Air temp around ice machine: ____°
Water temp entering sump trough: ____°
2. Refer to the appropriate 24-Hour Ice Production Chart.
Use the operating conditions determined in Step 1 to
find published 24 hr. ice production:____
Times are in minutes.
Example: 1 minute, 15 seconds converts to 1.25
minutes, (15 seconds ÷ 60 seconds = .25 minutes)
3. Perform an ice production check using the formula
below.
Weighing the ice is the only 100% accurate check. However,
if the ice pattern is normal and the 3mm thickness is
maintained, the ice slab weights listed with the 24-Hour Ice
Production Charts may be used.
4. Compare the results of step 3 with step 2. Ice production
is normal when these numbers match closely. If they
match closely, determine if:
Another larger ice machine is required.
Relocating the existing equipment to lower the load
conditions is required.
Contact the local Manitowoc distributor for information on
available options and accessories.
1. _______ + _______ = _______
Freeze Time Harvest Time Total Cycle Time
2. 1440 ÷ _______ = _______
Minutess in 24 hrs Total Cycle Time Cycles Per Day
3. _______ x _______ = _______
Weight of One Cycles Per Day Actual 24 Hr
Harvest Production
Page 60

52 Part Number STH039 8/13
INSTALLATION AND VISUAL INSPECTION
CHECKLIST
Ice machine is not level
• Level the ice machi n e
Condenser is dirty
• Clean the condenser
Water filtration is plugged (if used)
• Install a new water filter
Water drains are not run separately and/ or are not
vented
• Run and vent drains according to the Installation
Manual
Page 61

Part Number STH039 8/13 53
WATER SYSTEM CHECKLIST
A water-related problem often causes the same
symptoms as a refrigeration system component
malfunction.
Example: A water dump valve leaking during the
freeze cycle, a system low on charge, and a starving
TXV have similar symptoms.
Water system problems must be identified and
eliminated prior to replacing refrigeration components.
Water area (evaporator) is dirty
• Clean as needed
Water inlet pressure not between 1–5 bar (138–552
kPa)
• Install a water regulator valve or increase the
water pressure
Incoming water temperature is not between 4°C
and 32°C
• If too hot, check the hot water line check valves in
other store equipment
Water filtration is plugged (if used)
• Install a new water filter
Vent tube is not installed on water outlet drain
• See Installation Instructions
Hoses, fittings, etc., are leaking water
• Repair/replace as needed
Water float valve is stuck open or closed
• Clean/replace as needed
Water is spraying out of the sump trough area
• S top the water spray
Uneven water flow across the evaporator
• Clean the ice machine
Water is freezing behind the evaporator
• Correct the water flow
Plastic extrusions and gaskets are not secured to
the evaporator
• Remount/replace as needed
Page 62

54 Part Number STH039 8/13
ICE FORMATION PATTERN
Evaporator ice formation pattern analysis is helpful in
ice machine diagnostics.
Analyzing the ice formation pattern alone canno t
diagnose an ice machine malfunction. However, when
this analysis is used along with Manitowoc’s
Refrigeration System Operational Analysis Table, it
can help diagnose an ice machine malfunction.
Any number of problems can cause improper ice
formation.
Example: An ice formation that is “extremely thin at the
outlet” could be caused by a hot water supply, water
leaking out the o verflow pipe, a fault y water float valve,
a low refrigerant charge, etc.
Examples of Evaporator Tubing Routing
Normal Ice Forma t io n
Ice forms across the entire evaporator surface.
At the beginning of the Freeze cycle, it may appear
that more ice is forming on the inlet of the evaporator
than at the outlet. At the end of the Freeze cycle, ice
formation at the outlet will be close to, or just a bit
thinner than, ice formation at the inlet. The dimples in
the cubes at the outlet of the evaporator may be more
pronounced than those at the inlet. This is normal.
If ice forms uniformly across the evaporator surface,
but does not do so in the proper amount of time, this is
still considered a normal ice fill pattern.
INLET
OUTLET
Page 63

Part Number STH039 8/13 55
Extremely Thin at Evaporator Outlet
There is no ice, or a considerable lack of ice formation
on the outlet of the evaporator.
Examples: No ice at all at the outlet of the evaporator,
but ice forms at the inlet half of the evaporator. Or, the
ice at the outlet of the evaporator reaches the correct
thickness, but the outlet of the evaporator already has
12 mm to 25 mm of ice formation.
Possible cause: Water loss, low on refrigerant,
starving TXV, hot water supply, faulty float valve, etc.
Extremely Thin at Evaporator Inlet
There is no ice, or a considerable lack of ice formation
at the inlet of the evaporator. Examples: The ice at the
outlet of the evaporator reaches the correct thickness,
but there is no ice formation at all at the inlet of the
evaporator.
Possible cause: Insufficient water flow, flooding TXV,
etc.
Spotty Ice Formation
There are small sections on the evaporator where
there is no ice formation. This could be a single corner ,
or a single spot in the middle of the evaporator. This is
generally caused by loss of heat transfer from the
tubing on the backside of the evaporator.
No Ice Formation
The ice machine operates for an extended period, bu t
there is no ice formation at all on the evaporator.
Possible cause: Water float valve, water pump,
starving expansion valve, low refrigerant charge,
compressor , etc.
Page 64

56 Part Number STH039 8/13
SAFETY LIMIT FEATURE
In addition to the standard safety controls, your
Manitowoc ice machine features built-in safety limits
that will stop the ice machine if conditions arise which
could cause a major component failure.
Before calling for service, re-start the ice machine
using the following procedure:
1. Move the ON/OFF/WASH switch to OFF and then
back to ON.
2. If the safety limit feature has stopped the ice
machine, it will restart after a short delay. Proceed
to step 4.
3. If the ice machine does not restart, see “Ice
machine does not operate”.
4. Allow the ice machine to run to determine if the
condition is reoccurring.
A. If the ice machine stops again, the condition
has reoccurred. Call for service.
B. If the ice machine continues to run, the
condition has corrected itself. Allow the ice
machine to continue running.
Page 65

Part Number STH039 8/13 57
Safety Limits
In addition to standard safety controls, the control
board has two built in safety limit controls which
protect the ice machine from major component
failures.
Safety Limit #1: If the freeze time reac he s 60
minutes, the control board automatically initiates a
harvest cycle. 3 cycles outside the time limit = 1 hour
Stand-by Mode.
Safety Limit #2: If the harvest time reaches 3.5
minutes, the control board automatically returns the
ice machine to the freeze cycle. 3 cycles outside the
time limit = Safety Limit (must be MANUALLY reset).
Safety Limit Stand-by Mode: The first time a safety
limit shut down occurs, the ice machine turns off for 60
minutes (Stand-by Mode). The ice machine will then
automatically restart to see if the problem reoccurs.
During the Stand-by Mode the harvest light will be
flashing continuously and a safety limit indication can
be viewed. If the same safety limit is reached a second
time (the problem has reoccurred), the ice machine
will initiate a safety limit shut down and remain off until
it is manually restarted. During a safety limit shut down
the harvest light will be flashing continuously.
Determining Which Safety Limit Stopped
the
Ice Machine: When a safety limit condition
causes the ice machine to stop, the harvest light on
the control board continually flashes on and off. Use
the following procedures to determine which safety
limit has stopped the ice machine.
1. Move the toggle switch to OFF.
2. Move the toggle switch back to ON.
3. Watch the harvest light. It will flash one or two
times, corresponding to safety limits 1 and 2, to
indicate which safety limit stopped the ice
machine.
After safety limit indication, the ice machine will restart
and run until a safety limit is exceeded again.
Page 66

58 Part Number STH039 8/13
Safety Limit Notes
• A safety limit indication is completed before the
water pump starts. Water contacting the ice
thickness probe in the freeze cycle will cause the
harvest light to flash. Do not mistake a harvest light
flashing in the freeze cycle with a safety limit
indication.
• A continuous run of 100 harvests automatically
erases the safety limit code.
• The control board will store and indicate only one
safety limit – the last one exceeded.
• If the toggle switch is moved to the OFF position
and then back to the ON position prior to reaching
the 100-harvest point, the last safety limit
exceeded will be indicated.
• If the harvest light did not flash prior to the ice
machine restarting, then the ice machine did not
stop because it exceeded a safety limit.
Page 67

Part Number STH039 8/13 59
Safety Limit Checklist
The following checklists are designed to assist the
service technician in analysis. However, because
there are many possible external problems, do not
limit your diagnosis to only the items listed.
Safety Limit #1
Freeze time exceeds 60 minutes for 6 consecutive
freeze cycles.
Possible Cause Checklist
Improper installation
• Refer to “Installation and Visual Inspection
Checklist” on page 52
Water System
• Water Level set too high (water escaping through
over flow tube)
• Low water pressure 1.37 bar minimum
• High water pressure 5.52 bar maximum
• High water temperat ure 32° C maximu m
• Clogged water distribution tube
• Dirty/defective float valve
• Defective water pump
Page 68

60 Part Number STH039 8/13
Electrical System
• Ice thickness probe out of adjustment
• Harvest cycle not initiated electrically
• Contactor not energizing
• Compressor electrically non-operational
• Restricted condenser air flow
• High inlet air temperature 43°C maximum
• Condenser discharge air re-circulation
• Dirty condenser fins
• Defective fan cycling control
• Defective fan motor
• Low water pressure 1.37 bar minimum
• High water temperat ure 32 °C maxi mu m
• Dirty condenser
Refrigeration System
• Non-Manitowoc components
• Improper refrigerant charge
• Defective compressor
• TXV starving or flooding (check bulb mounting)
• Non-condensable in refrigeration system
• Plugged or restricted high side refrigerant lines or
component
• Defective hot gas valve
Page 69

Part Number STH039 8/13 61
Safety Limit #2
Harvest time exceeds 3.5 minutes for 6
Consecutive harvest cycles.
Possible Cause Checklist
Improper installation
• Refer to “Installation and Visual Inspection
Checklist” on page 52.
Water System
• Water area (evaporator) dirty
• Dirty/defective water dump valve
• Vent tube not installed on water outlet drain
• Water freezing behind evaporator
• Plastic extrusions and gaskets not securely
mounted to the evaporator
• Low water pressure 1.37 bar minimum
• Loss of water from sump area
• Clogged water distribution tube
• Dirty/defective float valve
• Defective water pump
Electrical system
• Ice thickness probe out of adjustment
• Ice thickness probe dirty
• Bin switch defective
• Premature harvest
Refrigeration system
• Non-Manitowoc components
• Improper refrigerant charge
• Defective hot gas valve
• TXV flooding (check bulb mounting)
• Defective fan cycling control
Page 70

62 Part Number STH039 8/13
ANALYZING DISCHARGE LINE TEMPERATURE
1. Determine the ice machine operating conditions:
Air temp. entering condenser ______
Air temp. around ice machine ______
Water temp. entering sump trough ______
2. Refer to “Cycle Times, 24 Hr. Ice Production and
Refrigerant Temperature Charts” on page 101 for
ice machine being checked.
Use the operating conditions determined in step 1 to
find the published normal discharge temperatures.
Freeze Cycle ______
Harvest Cycle ______
3. Perform an actual discharge temperature check.
4. Compare the actual discharge temperature
(step 3) with the published discharge temperature
(step 2).
The discharge temperature is normal when the actual
temperature falls within the published temperature
range for the ice machine’s operating conditions. It is
normal for the discharge temperature to be higher at
the beginning of the freeze cycle (when load is
greatest), then drop through out the freeze cycle.
Freeze
Cycle PSIG
Harvest
Cycle PSIG
Beginning of
Cycle
__________ __________
Middle of
Cycle
__________ __________
End of
Cycle
__________ __________
Page 71

Part Number STH039 8/13 63
Discharge temperature High Checklist
Improper Installation
• Refer to “Installation and Visual Inspection
Checklist” on page 52.
Restricted Condenser Air Flow
• High inlet air temperature
• Condenser discharge air re-circulation
• Dirty condenser fins
• Defective fan cycling control
• Defective fan motor
Improper Refrigerant Charge
• Overcharged
• Non-condensable in system
• Wrong type of refrigerant
Other
• Non-Manitowoc components in system
• High side refrigerant lines/component
• Restricted (before mid-condenser)
Freeze Cycle Discharge temperature Low
Checklist
Improper Installation
• Refer to “Installation and Visual Inspection
Checklist” on page 52.
Improper Refrigerant Charge
• Undercharged
• Wrong type of refrigerant
Other
• Non-Manitowoc components in system
• High side refrigerant lines/component restricted
(before mid-condenser)
• Defective fan cycle control
NOTE: Do not limit your diagnosis to only the items
listed in the checklists.
Page 72

64 Part Number STH039 8/13
ANALYZING SUCTION TEMPERATURE
The suction temperature gradually dro ps throughout
the freeze cycle. The actual suction temperature (and
drop rate) changes as the air and water temperature
entering the ice machine changes. These variables
also determine the freeze cycle times.
To analyze and identify the proper suction temperature
drop throughout the freeze cycle, compare the
published suction temperature to the published freeze
cycle time.
NOTE: Analyze discharge temperature before
analyzing suction temperature. High or low discharge
temperature may be causing high or low suction
temperature.
Page 73

Part Number STH039 8/13 65
Procedure
Step
1. Determine the ice machine operating conditions.
Example:
Air temp. entering condenser: 32°C
Air temp. around ice machine: 27°C
Water temp. entering water fill valve: 21°C
2A. Refer to “Cycle Time” and “Operating temperature”
charts for ice machine model being checked. Using
operating conditions from Step 1, determine published
freeze cycle time and published freeze cycle suction
temperature.
Example:
Published freeze cycle time: 19.5 - 21.4 minutes
Published freeze cycle suction temperature: -6 to -17
2B. Compare the published freeze cycle time and
published freeze cycle suction temperature. Develop a
chart.
Example:
Published Freeze Cycle Time (minutes)
1 2 5 10 13 17 20
|||||||
-6 -8 -10 -12 -14 -16 -17
Published Freeze Cycle Suction temperature
In the example, the proper suction temperature should
be approximately -10 degrees at 5 minutes;
-14 degrees at 13 minutes.
3. Perform an actual suction temperature check at the
beginning, middle and end of the freeze cycle. Note the
times at which the readings are taken.
Example:
Thermocouples were connected to the example ice
machine and suction temperature readings taken as
follows: ________
Beginning of Freeze cycle: -1 (at 1 minute)
Middle of freeze cycle: -6 (at 10 minutes)
End of freeze cycle: -12 (at 20 minutes)
Page 74

66 Part Number STH039 8/13
4. Compare the actual freeze cycle suction temperature
(Step 3) to the published freeze cycle time and temperature
comparison (Step 2B). Determine if the suction
temperature is high, low or acceptable.
Example:
In this example, the suction temperature is considered
high throughout the freeze cycle. It should have been:
Approximately -6 (at 1 minute) – not -1
Approximately -12 (at 10 minutes) – not -6
Approximately -17 (at 20 minutes) – not -12
Step
Page 75

Part Number STH039 8/13 67
Suction temperature High Checklist
Improper Installation
• Refer to “Installation and Visual Inspection
Checklist” on page 52.
Discharge temperature
• Discharge temper ature i s too high , and is a ffe cting
suction temperature
Improper Refrigerant Charge
• Overcharged
• Wrong type of refrigerant
• Non-condensables in system
Other
• Non-Manitowoc components in system
• Hot gas valve leaking
• TXV flooding (check bulb mounting)
• Defective compressor
Page 76

68 Part Number STH039 8/13
Suction temperature Low Checklist
Improper Installation
• Refer to “Installation and Visual Inspection
Checklist” on page 52.
Discharge temperature
• Discharge temperature is too low, and is affecting
suction temperature, refer to “Freeze Cycle
Discharge temperature Low Checklist”
Improper Refrigerant Charge
• Undercharged
• Wrong type of refrigerant
Other
• Non-Manitowoc components in system
• Improper water supply over evaporator refer to
“Water System Checklist” on page 53.
• Loss of heat transfer from tubing on back side of
evaporator
• Restricted/plugged liquid line drier
• Restricted/plugged tubing in suction side of
refrigeration system
• TXV starving
NOTE: Do not limit your diagnosis to only the items
listed in the checklists.
Page 77

Part Number STH039 8/13 69
HOT GAS VALVE
General
The hot gas valve is an electrically operated valve that
opens when energized, and closes when deenergized.
Normal Operation
The valve is de-energized (closed) during the freeze
cycle and energized (open) during the harvest cycle.
The valve is positioned between the receiver and the
evaporator and performs two functions:
1. Prevents refrigerant from entering the evaporator
during the freeze cycle.
The hot gas valve is not used during the freeze
cycle. The hot gas valve is de-energized (closed)
preventing refrigerant flow from the receiver into
the evaporator.
2. Allows refrigerant vapor to enter the evaporator in
the harvest cycle.
During the harvest cycle, the hot gas valve is
energized (open) allowing refrigerant gas from the
discharge line of the compressor to flow into the
evaporator. The heat is absorbed by the
evaporator and allows release of the ice slab.
Exact temperatures vary according to ambient
temperature and ice machine model. Harvest
temperatures can be found in the Cycle Time/24 Hour
Ice Production/ Refrigerant Temperature Charts in this
book.
Page 78

70 Part Number STH039 8/13
Hot Gas Valve Analysis
The valve can fail in two positions:
• Valve will not open in the harvest cycle.
• Valve remains open during the freeze cycle.
VALVE WILL NOT OPEN IN THE HARVEST CYCLE
Although the circuit board has initiated a harvest cycle,
the evaporator temperature remains unchanged from
the freeze cycle.
VALVE REMAINS OPEN IN THE FREEZE CYCLE:
Symptoms of a hot gas valve remaining partially open
during the freeze cycle can be similar to symptoms of
an expansion valve, float valve or compressor
problem. Symptoms are dependent on the amount of
leakage in the freeze cycle.
A small amount of leakage will cause increased freeze
times and an ice fill pattern that is “Thin at the Outlet”,
but fills in at the end of the cycle.
As the amount of leakage increases the length of the
freeze cycle increases and the amount of ice at the
outlet of the evaporator decreases.
Refer to the Parts Manual for proper valve application.
If replacement is necessary, use only “origin al”
Manitowoc replacement parts.
!
Caution
Coil must be seated 100% on solenoid to function
correctly. Install coil with a twisting motion to
properly seat.
Page 79

Part Number STH039 8/13 71
Use the following procedure and table to help
determine if a hot gas valve is remaining partially open
during the freeze cycle.
1. Wait five minutes into the freeze cycle.
2. Feel the inlet of the hot gas valve(s).
3. Feel the compressor discharge line.
4. Compare the temperature of the inlet of the hot
gas valves to the temperature of the compressor
discharge line.
Important
Feeling the hot gas valve outlet or across the hot
gas valve itself will not work for this comparison.
The hot gas valve outlet is on the suction side
(cool refrigerant). It may be cool enough to tou ch
even if the valve is leaking.
! Warning
The inlet of the hot gas valve and the compressor
discharge line could be hot enough to burn your
hand. Just touch them momentarily.
Page 80

72 Part Number STH039 8/13
5. Record your findings on the table.
Findings Comments
The inlet of the harvest
valve is cool enough to
touch and the compressor
discharge line is hot.
Cool & Hot
This is normal as the
discharge line should
always be too hot to touch
and the harvest valve inlet,
although too hot to touch
during harvest, should be
cool enough to touch after 5
minutes into the freeze
cycle.
The inlet of the harvest
valve is hot and approaches
the temperature of a hot
compressor discharge line.
Hot & Hot
This is an indication
something is wrong, as the
harvest valve inlet did not
cool down during the freeze
cycle. If the compressor
dome is also entirely hot,
the problem is not a harvest
valve leaking, but rather
something causing the
compressor (and the entire
ice machine) to get hot.
Both the inlet of the harvest
valve and the compressor
discharge line are cool
enough to touch.
Cool & Cool
This is an indication
something is wrong, causing
the compressor discharge
line to be cool to the touch.
This is not caused by a
harvest valve leaking.
Page 81

Part Number STH039 8/13 73
COMPARING EVAPORATOR INLET/OUTLET
TEMPERATURES
The temperature of the suction lines entering and
leaving the evaporator alone cannot diagno se an ice
machine. However, comparing these temperatures
during the freeze cycle, along with using Manitowoc’s
Refrigeration System Operational Analysis Table, can
help diagnose an ice machine malfunction.
The actual temperatures entering and leaving the
evaporator vary by model, and change throughout the
freeze cycle. This makes documenting the “normal”
inlet and outlet temperature readings difficult. The key
to the diagnosis lies in the difference between the two
temperatures five minutes into the freeze cycle. These
temperatures must be within 4°C of each other.
Use this procedure to document freeze cycle inlet and
outlet temperatures.
1. Use a quality temperature meter, capable of
taking temperature readings on curved copper
lines.
2. Attach the temperature meter sensing device to
the copper lines entering and leaving the
evaporator.
3. Wait five minutes into the freeze cycle.
4. Record the temperatures below and determine
the difference between them.
5. Use this with other information gathered on the
Refrigeration System Operational Analysis Table
to determine the ice machine malfunction.
Important
Do not simply insert the sensing device under the
insulation. It must be attached to and reading the
actual temperature of the copper line.
___________ ___________ ___________
Inlet
Temperature
Difference must be
within 4°C at 5
minutes
into the freeze cycle
Outlet
Temperature
Page 82

74 Part Number STH039 8/13
DISCHARGE LINE TEMPERATURE ANALYSIS
GENERAL
Knowing if the discharge line temperature is
increasing, decreasing or remaining constant can be
an important diagnostic tool. Maximum compressor
discharge line temperature on a normally operating ice
machine steadily increases throughout the freeze
cycle. Comparin g th e te mperatures over several
cycles will result in a consistent maximum discharge
line temperature.
Ambient air temperatures affect the maximum
discharge line temperature.
Higher ambient air temperatures at the condenser =
higher discharge line temperatures at the compressor.
Lower ambient air temperatures at the condenser =
lower discharge line temperatures at the compressor.
Regardless of ambient temperature, the freeze cycle
discharge line temperature will be higher than 66°C on
a normally operating ice machine.
PROCEDURE
Connect a temperature probe on the compressor
discharge line within 15 cm of the compressor.
Observe the discharge line temperature for the last
three minutes of the freeze cycle and record the
maximum discharge line temp e r at ure.
Page 83

Part Number STH039 8/13 75
Discharge Line T emperature Above 66°C at End of
Freeze Cycle:
Ice machines that are operating normally will have
consistent maximum discharge line temperatures
above 66°C.
Verify the expansion valve sensing bulb is positioned
and secured correctly.
Discharge Line Temperature Below 66°C at End of
Freeze Cycle
Ice machines that have a flooding expansion valve will
have a maximum discharge line temperature that
decreases each cycle.
Verify the expansion valve sensing bulb is 100%
insulated and sealed airtight. Condenser air contacting
an incorrectly insulated sensing bu lb will cause
overfeeding of the expansion valve.
Page 84

76 Part Number STH039 8/13
REFRIGERATION COMPONENT DIAGNOSTIC
CHART
All electrical and water related problems must be
corrected before these charts will work properly. These
tables must be used with charts, checklists and other
references to eliminate refrigeration components not
listed and external items and problems that will cause
good refrigeration components to appear defective.
The tables list four different defects that may affect the
ice machine’s operation.
NOTE: A low-on-charge ice machine and a starving
expansion valve have very similar characteristics and
are listed under the same column.
Page 85

Part Number STH039 8/13 77
PROCEDURE
Step 1 Complete each item individually in the
“Operational Analysis” column.
Enter check marks (✓) in the boxes.
Each time the actual findings of an item in the
“Operational Analysis” column matches the published
findings on the table, enter a check mark.
Example: Freeze cycle suction temperature is
determined to be low. Enter a check mark in the “low”
box.
Perform the procedures and check all information
listed. Each item in this column has supporting
reference material.
While analyzing each item separately, you may find an
“external problem” causing a good refrigerant
component to appear bad. Correct problems as they
are found. If the operational problem is found, it is
not necessary to complete the remaining
procedures.
Step 2 Add the check marks listed under each of the
four columns. Note the column number with the
highest total and proceed to “Final Analysis.”
NOTE: If two columns have matching high numbers, a
procedure was not performed properly and/or
supporting material was not analyzed correctly.
Page 86

78 Part Number STH039 8/13
FINAL ANALYSIS
The column with the highest number of check marks
identifies the refrigeration problem.
Column 1 – Hot Gas Valve Leaking
A leaking hot gas valve must be replaced.
Column 2 – Low Charge/TXV Starving
Normally, a starving expansion valve only affects the
freeze cycle temperatures, not the harvest cycle
temperatures. A low refrigerant charge normally
affects both temperatures.
Column 3 – TXV Flooding
A loose or improperly mounted expansion valve bulb
causes the expansion valve to flood. Check bulb
mounting, insulation, etc., before changing the valve.
Column 4 – Compressor
Replace the compressor and start components. To
receive warranty credit, the compressor ports must be
properly sealed by crimping and soldering them
closed. Old start components must be returned with
the faulty compressor.
Page 87

Part Number STH039 8/13 79
REFRIGERATION COMPONENT DIAGNOSTIC CHART
SINGLE EXPANSION VALVE SELF CONTAINED AIR COOLED CONDENSER
Operational Analysis 1 2 3 4
Ice Production
Air-Temperature Entering Condenser_____________
Water Temperature Entering Ice Machine_________
Published 24 hour ice production________________
Calculated (actual) ice production_______________
NOTE: The ice machine is operating properly if the ice fill patterns is normal and ice
production is within 10% of charted capacity.
Installation and Water
System
All installation and water related problems must be correcte d before proceeding with chart.
Ice Formation Pattern
Ice formation is extremely
thin on outlet of
evaporator
-or-
No ice formation on the
entire evaporator
Ice formation is
extremely thin on outlet
of evaporator
-or-
No ice formation on
entire evaporator
Ice formation normal
-or-
Ice formation is
extremely thin on inlet of
evaporator
-or-
No ice formation on
entire evaporator
Ice formation normal
-or-
No ice formation on
entire evaporator
Discharge Line
Temperature 3 minutes into
the freeze cycle
Normal or High
Normal or High Low Normal or High
Page 88

80 Part Number STH039 8/13
Suction Line Temperature
3 minutes into the freeze
cycle
Normal or High Normal or High Low Normal or High
Freeze Cycle
Suction Temperature
_______ ______ _____
1 minute Middle End
If suction temperature is High or Low refer to freeze cycle high or low suction temperature problem
checklist
page 67 to eliminate problems and/or components not listed on this table before proceeding.
Suction temperature is
High
Suction temperature is
Low or Normal
Suction temperature is
High
Suction temperature is
High
Wait 5 minutes into the
freeze cycle.
Compare temperatures of
evaporator inlet and
evaporator outlet.
Inlet _____________°C
Outlet ___________ °C
Difference________ °C
Inlet and outlet
within 4°C
of each other
Inlet and outlet
not within 4°C
of each other
-and-
Inlet is colder than
outlet
Inlet and outlet
within4°C
of each other
-or-
Inlet and outlet
not within 4°C
of each other
-and-
Inlet is warmer than
outlet
Inlet and outlet
within 4°C
of each other
SINGLE EXPANSION VALVE SELF CONTAINED AIR COOLED CONDENSER
Operational Analysis 1 2 3 4
Page 89

Part Number STH039 8/13 81
Wait 5 minutes into the
freeze cycle.
Compare temperatures of
compressor discharge line
and harvest valve inlet.
The harvest valve inlet is
Hot
-and-
approaches the
temperature of a Hot
compressor discharge
line.
The harvest valve inlet
is Cool enough to hold
hand on
-and-
the compressor
discharge line is Hot.
The harvest valve inlet
is Cool enough to hold
hand on
-and-
the compressor
discharge line is Cool
enough to hold hand on.
The harvest valve inlet
is Cool enough to hold
hand on
-and-
the compressor
discharge line is Hot.
Discharge Line
Temperature
Record freeze cycle
discharge line temperature at
the end of the freeze cycle
_________°C
Discharge line
temperature
71°C or higher
at the end of the freeze
cycle
Discharge line
temperature
71°C or higher
at the end of the freeze
cycle
Discharge line
temperature
71°C or Lower
at the end of the freeze
cycle
Discharge line
temperature
71°C or higher
at the end of the freeze
cycle
Final Analysis
Enter total number of boxes
checked in each column.
Harvest Valve
Leaking
Low On Charge
-Or-
TXV Starving
TXV Flooding Compressor
SINGLE EXPANSION VALVE SELF CONTAINED AIR COOLED CONDENSER
Operational Analysis 1 2 3 4
Page 90

82 Part Number STH039 8/13
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
Page 91

Part Number STH039 8/13 83
Component Check Procedures
Main Fuse
Function
The control board fuse stops ice machine operation if
electrical components fail causing high amp draw.
Specifications
The main fuse is 250 Volt, 10 amp.
Check Procedure
1. If the bin switch light is on with the ice damper
closed, the fuse is good.
2. Remove the fuse. Check the resistance across
the fuse with an ohmmeter.
! Warning
High (line) voltage is applied to the control board
at all times. Removing the control board fuse or
moving the toggle switch to OFF will not remove
the power supplied to the control board.
! Warning
Disconnect electrical power to the entire ice
machine before proceeding.
Reading Result
Open (OL) Replace fuse
Closed (O) Fuse is good
Page 92

84 Part Number STH039 8/13
Bin Switch
Function
Bin switch operation is controlled by the movement of
the ice damper. The bin switch has two main functions:
1. Terminating the harvest cycle and returning the
ice machine to the freeze cycle.
This occurs when the bin switch is opened and
closed again within 7 seconds of opening during
the harvest cycle.
2. Automatic ice machine shut-off.
If the storage bin is full at the end of a harvest
cycle, the sheet of cubes fails to clear the ice
damper and holds it down. After the ice damper is
held down for 7 seconds, the ice machine shuts
off.
The ice machine remains off until enough ice is
removed from the storage bin to allow the sheet of
cubes to drop clear of the ice damper. As the ice
damper swings back to the operating position, the
bin switch closes and the ice machine restarts.
Check Procedure
1. Set the toggle switch to OFF.
2. Watch the bin switch light on the control board.
3. Move the ice damper upward, toward the
evaporator. The bin switch must close. The bin
switch light “on” indicates the bin switch has
closed properly.
4. Move the ice damper away from the evaporator.
The bin switch must open. The bin switch light
“off” indicates the bin switch has opened properly.
Important
The ice damper must be up (bin switch closed) to
start ice making.
Page 93

Part Number STH039 8/13 85
Ohm Test
1. Disconnect the bin switch wires to isolate the bin
switch from the control board.
2. Connect an ohmmeter to the disconnected bin
switch wires.
3. Cycle the bin switch open and closed numerous
times by opening and closing the water curtain.
NOTE: To prevent misdiagnosis:
• Always use the water curtain magnet to cycle the
switch (a larger or smaller magnet will affect switch
operation).
• Watch for consistent readings when the bin switch
is cycled open and closed (bin switch failure could
be erratic).
Page 94

86 Part Number STH039 8/13
Bin Switch Removal
1. Disconnect power to the ice machine at service
disconnect.
2. Disconnect bin switch wires in control box.
3. Insert a small screwdriver through the hole
located in the top of the bin switch, and depress
mounting tab slightly.
4. While depressing mounting tab roll bin switch to
right to release.
5. Pull wiring into evaporator compartment.
Bin Switch Removal
SV1695B
BIN SWITCH
INSERT
SCREWDRIVER AND
DEPRESS TAB
Page 95

Part Number STH039 8/13 87
Diagnosing Start Components
If the compressor attempts to start, or hums and trips
the overload protector, check the start components
before replacing the compressor.
CAPACITOR
Visual evidence of capacitor failure can include a
bulged terminal end or a ruptured membrane. Do not
assume a capacitor is good if no visual evidence is
present. A good test is to install a known good
substitute capacitor. Use a capacitor tester when
checking a suspect capacitor. Clip the bleed resistor
off the capacitor terminals before testing.
RELAY
The relay has a set of contacts that connect and
disconnect the start capacitor from the compressor
start winding. The contacts on the relay are normally
open. The relay senses the voltage generated by the
start winding and closes and then opens the contacts
as the compressor motor starts. The contacts remain
open until the compressor is de-energized.
Page 96

88 Part Number STH039 8/13
ON/OFF/WASH Toggle Switch
Function
The switch is used to place the ice machine in ON,
OFF or WASH mode of operation.
Specifications
Single-pole, double-throw switch. The switch is
connected into a varying low D.C. voltage circuit.
Check Procedure
NOTE: Because of a wide variation in D.C. voltage, it
is not recommended that a voltmeter be used to check
toggle switch operation.
1. Inspect the toggle switch for correct wiring.
2. Isolate the toggle switch by disconnecting all
wires from the switch, or by disconnecting the
Molex connector from the control board.
3. Check across the toggle switch terminals using a
calibrated ohmmeter. Note where the wire
numbers are connected to the switch terminals, or
refer to the wiring diagram to take proper
readings.
Replace the toggle switch if ohm readings do not
match all three-switch settings.
Switch Setting Terminals Ohm Reading
ON
24-21 Open
24-20 Closed
20-21 Open
WASH
24-20 Open
24-21 Closed
20-21 Open
OFF
24-20 Open
24-21 Open
20-21 Open
Page 97

Part Number STH039 8/13 89
Ice Thickness Probe
How The Probe Works
Manitowoc’s electronic sensing circuit does not rely on
refrigerant temperature, evaporator temperature,
water levels or timers to produce consistent ice
formation.
As ice forms on the evaporator, water (not ice)
contacts the ice thickness probe. After the water
completes this circuit across the probe continuously
for 6-10 seconds, a harvest cycle is initiated.
Freeze Time Lock-In Feature
The ice machine control system incorporates a freeze
time lock-in feature. This prevents the ice machine
from short cycling in and out of harvest.
The control board locks the ice machine in the freeze
cycle for six minutes. If water contacts the ice
thickness probe during these six minutes, the harvest
light will come on (to indicate that water is in contact
with the probe), but the ice machine will stay in the
freeze cycle. After the six minutes are up, a harvest
cycle is initiated. This is important to remember when
performing diagnostic procedures on the ice thickness
control circuitry.
To allow the service technician to initiate a harvest
cycle without delay , this feature is not used on the first
cycle after moving the toggle switch OFF and back to
ON.
Maximum Freeze Time
The control system includes a built-in safety , which will
automatically cycle the ice machine into harvest after
60 minutes in the freeze cycle.
Page 98

90 Part Number STH039 8/13
ICE THICKNESS CHECK
The ice thickness probe is factory-set to maintain the
ice bridge thickness at 3 mm.
NOTE: Make sure the water curtain is in place when
performing this check. It prevents water from splashing
out of the water trough.
1. Inspect the bridge connecting the cubes. It should
be about 3 mm thick.
2. If adjustment is necessary, turn the ice thickness
probe adjustment screw clockwise to increase
bridge thickness, or counterclockwise to decrease
bridge thickness.
NOTE: Turning the adjustment 1/3 of a turn will
change the ice thickness about 1.5 mm.
Ice Thickness Check
Make sure the ice thickness probe wire and the
bracket do not restrict movement of the probe.
3MM ICE BRIDGE
THICKNESS
ADJUSTING
SCREW
SV3114
SV3113
Page 99

Part Number STH039 8/13 91
Compressor Electrical Diagnostics
The compressor does not start or will trip repeatedly
on overload.
Check Resistance (Ohm) Values
NOTE: Compressor windings can have very low ohm
values. Use a properly calibrated meter.
Perform the resistance test after the compressor
cools. The compressor dome should be cool enough
to touch (below 49°C) to ensure that the overload is
closed and the resistance readings will be accurate.
Single Phase Compressors
1. Disconnect power from the condensing unit and
remove the wires from the compressor terminals.
2. The resistance values between C and S and
between C and R, when added together should
equal the resistance value between S and R.
3. If the overload is open, there will be a resistance
reading between S and R, and open readings
between C and S and between C and R. Allow the
compressor to cool, then check the readings
again.
Page 100

92 Part Number STH039 8/13
Check Motor Windings to Ground
Check continuity between all three terminals and the
compressor shell or copper refrigeration line. Scrape
metal surface to get good contact. If continuity is
present, the compressor windings are grounded and
the compressor should be replaced.
To determine if the compressor is seized check the
amp draw while the compressor is trying to start.
Compressor Drawing Locked Rotor
The two likely causes of this are:
• Defective starting component
• Mechanically seized compressor
Compressor Drawing High Amps
The continuous amperage draw on start-up should not
be near the maximum fuse size indicated on the serial
tag.
The wiring must be correctly sized to minimize voltage
drop at compressor start-up. The voltage when the
compressor is trying to start must be within ±10% of
the nameplate voltage.
 Loading...
Loading...