Page 1

MS-G Series
Pure Sine Wave Inverter/Chargers
Owner’s Manual
TM
Page 2
Thank you from all of us at Sensata Technologies for purchasing this MS-G Series inverter/charger.
The MS-G Series products include the MS2000-G, MS2012-G, MS2812-G, and MS4024-G inverters;
all are under the Magnum-Dimensions brand from Sensata Technologies. We understand that you
have many purchasing options in the marketplace, and we are pleased that you have decided on
this product. This MS-G Series inverter/charger was proudly assembled and tested in the United
States at our facility in Everett, Washington.
At Sensata, we are committed to providing you with quality products and services, and hope that
your experience with us is pleasant and professional.
Disclaimer of Liability
The use of this manual and the conditions or methods of installation, operation, use, and
maintenance of the MS-G Series inverter/charger is beyond the control of Sensata Technologies.
Therefore, this company does not assume responsibility and expressly disclaims liability for loss,
damage, or expense whether direct, indirect, consequential or incidental that may arise out of or
be any way connected with such installation, operation, use, or maintenance.
Due to continuous improvements and product updates, the images shown in this manual may not
exactly match the unit purchased.
Restrictions on Use
The MS-G Series inverter/charger may only be used in life support devices and systems with
the express written approval of Sensata Technologies. Failure of this inverter can reasonably be
expected to cause failure of that life support device or system, or to affect the safety or effectiveness
of that device or system. If the MS-G Series inverter fails, it is reasonable to assume the health
of the user or other persons may be endangered.
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2015 by Sensata Technologies. All rights reserved. Permission to copy, distribute,
and/or modify this document is prohibited without express written permission from Sensata.
Document Information
Description – MS-G Series Owner’s Manual
Part Number and Revision – 64-0070 Rev A
Date Published – March 2015
This entire manual is available for download—with many of the diagrams available in color—under
the Document Library tab on our website at: www.Magnum-Dimensions.com.
Contact Information
For Magnum-Dimensions products:
Sensata Technologies
2211 West Casino Rd.
Everett, WA 98204
Phone: 425-353-8833
Fax: 425-353-8390
Web: www.Magnum-Dimensions.com
Record unit’s model & serial number in case you need to provide this information in the future.
Model: Serial Number:
MS2000-G BA
MS2012-G BB
MS2812-G AZ
MS4024-G BC
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page i
Page 3

Safety Information
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
THIS MANUAL CONTAINS IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE MS-G SERIES INVERTER/CHARGER
THAT SHALL BE FOLLOWED DURING THE INSTALLATION AND OPERATION OF THIS PRODUCT.
Before using the MS-G Series, read all instructions and cautionary markings. Also, be sure to review
the individual manuals provided for each component of the system. The installation instructions
are for use by qualified personnel only. Do not perform any installation or servicing other than
that specified in this owner’s manual unless you are qualified to do so. Incorrect installation or
servicing may result in a risk of electric shock, fire, or other safety hazard.
Safety Symbols
The following safety symbols have been placed throughout this manual to indicate dangerous and
important safety instructions.
WARNING: This symbol indicates that failure to take a specifi ed action could result in
physical harm to the user.
CAUTION: This symbol indicates that failure to take a specifi ed action could result in
damage to the equipment.
Info: This symbol indicates information that emphasizes or supplements important
points of the main text.
Safety Precautions
• All electrical work must be performed in accordance with local and national electrical codes.
• This product is designed for indoor/compartment installation. It must not be exposed to rain,
snow, moisture, or liquids of any type.
• Use insulated tools to reduce the chance of electrical shock or accidental short circuits.
• There are no user-serviceable parts contained in this product.
• This unit is provided with integral protection against overloads.
• Live power may be present at more than one point since an inverter utilizes both DC (batteries,
PV, etc.,) and AC (utility or generator) power. To reduce risk of electric shock, ensure all DC
and AC wiring is disconnected prior to installing or performing maintenance on the inverter.
Turning off the inverter will not reduce this risk, the inverter must be totally disconnected
from all sources.
• Use Class 1 wiring methods for field wiring connections to terminals of a Class 2 circuit.
• Listed or labeled equipment shall be installed and used in accordance with any instructions
included in the listing or labeling.
• Always verify proper wiring prior to starting the inverter.
• Use only copper wires with a minimum temperature rating of 90°C (194°F).
• AC wiring must be no less than 10 AWG (5.3 mm²) gauge copper wire.
• Battery cables should be no less than #4/0 AWG (107.2 mm²) for 12 and 24-volt systems.
Crimped and sealed copper ring terminal lugs with a 5/16 hole should be used to connect to
the DC terminals on the inverter.
• Torque all AC wiring connections and DC cable connections to the required torque values.
• The inverter must be properly mounted, see Section 2.2 “Mounting the Inverter” in this
manual.
• Overcurrent protection for the battery supply is not provided as an integral part of this
inverter. Overcurrent protection of the battery cables must be provided as part of the system
installation. Refer to Section 2.4 “DC Wiring” for more information.
Page ii
Page 4

Safety Information
• Overcurrent protection for the AC output wiring is not provided as an integral part of this
inverter. Overcurrent protection of the AC output wiring must be provided as part of the
system installation. Refer to Section 2.5 “AC Wiring” for more information.
• The AC output neutral conductor and the DC negative conductors are not connected (bonded)
to the inverter chassis. Both the input and output conductors are isolated from the enclosure
and each other. System grounding, if required, is the responsibility of the system installer and
must comply with local and national electrical codes and standards. Refer to the Section 2.6
“Grounding Inverters” for more information.
Battery Safety
• Use insulated tools and be very careful when working around batteries, they can produce
extremely high currents if short-circuited (e.g., dropping a metal tool across the battery
terminal), which could cause a fire or explosion.
• Read and follow the battery manufacturer’s safety precautions before installing the inverter
and batteries. Always verify proper polarity and voltage before connecting the batteries
to the inverter. Once the batteries are connected to the inverter, ensure the maintenance
and charging requirements (i.e., charge voltage and charge rate) provided by the battery
manufacturer are followed to extend the life of the batteries and to prevent damage to the
batteries while charging.
• Wear eye protection such as safety glasses, and avoid touching your eyes and face when
working with batteries to keep any fl uid/corrosion on the battery from coming in contact
with eyes and skin. Have plenty of fresh water and soap nearby and thoroughly wash in case
battery acid contacts skin, clothing, or eyes. In the event of exposure to the eyes, flood them
for at least 15 minutes with running water and seek immediate medical attention. Baking soda
neutralizes lead acid battery electrolyte and vinegar neutralizes spilled NiCad and NiFe battery
electrolyte; depending on your battery type, keep a supply on hand near the batteries.
• Remove all jewelry such as rings, watches, bracelets, etc., when installing or performing
maintenance on the batteries and inverter. A battery can produce a short-circuit current high
enough to weld metal jewelry, causing severe burns.
• Never work alone. Always have someone within the range of your voice or close enough to
come to your aid when working around batteries.
• Use proper lifting techniques when working with batteries.
• Never use old or untested batteries. Check each battery’s label for age, type, and date code
to ensure all batteries are identical.
• Batteries are sensitive to changes in temperature. Install batteries in a stable environment.
• Batteries can produce explosive gasses, so install batteries in a well-ventilated area. For
compartment or enclosure installations, always vent batteries from the highest point to the
outside. Design the battery enclosure to prevent accumulation and concentration of hydrogen
gas in “pockets” at the top of the compartment.
• Provide at least one inch (2.5 cm) of air space between batteries to provide optimum cooling.
• Never smoke or allow a spark near batteries.
• To prevent a spark at the battery and reduce the chance of explosion, always connect the
cables to the batteries first. Then connect the cables to the inverter.
• Never charge a frozen battery.
• The battery bank should be installed in a clean, dry, ventilated environment where it is
protected from high and low temperatures. If installed in a vehicle/boat, the batteries must
be mounted upright (if using liquid batteries) and securely fastened. The location must be
fully accessible and protected from exposure to heat-producing devices, and away from any
fuel tanks.
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page iii
Page 5
Safety Information
CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ IMPORTANTES
CE MANUEL CONTIENT DE IMPORTANTES POUR LA SÉRIE MS-G ONDULEUR/CHARGEUR QUI
DOIVENT ETRE SUIVIES PENDANT L’INSTALLATION ET FONCTIONNEMENT DE CE PRODUIT.
Avant d’utiliser la série MS-G, lire toutes les instructions etles mises en garde. Aussi, n’oubliez pas
depasser en revue les différents manuels fournispour chaque composant du système. Lesinstructions
d’installation sont pour une utilisationpar du personnel qualifi é. Ne pas effectuer une installation
ou d’entretien autres que ceux spécifi és dans ce manuel, sauf si vous êtes qualifi é pour le faire.
Une mauvaise installation ou d’entretien peut entraîner un risque de choc électrique, un incendie
ou autre danger pour la sécurité.
Symboles de sécurité
Les symboles de sécurité suivants ont été placéstout au long de ce manuel pour indiquer des
conditions dangereuses et les consignes de sécurité importantes.
AVERTISSEMENT: Ce symbole indique que le défaut de prendre une action spécifi ée
pourraitcauser des dommages physiques à l’utilisateur.
ATTENTION: Ce symbole indique que le défaut de prendre une action spécifi ée peut
entraîner des dommages à l’équipement.
Info: Ce symbole indique une information qui met l’accent ou des suppléments points
importants du texte principal.
Consignes de sécurité
• Tous les travaux électriques doivent être effectués en conformité avec les codes locaux et
nationaux électriques.
• Ce produit est conçu pour l’installation / du compartiment intérieur. Il ne doit pas être exposé
à la pluie, la neige, l’humidité ou des liquides de tout type.
• Utiliser des outils isolés pour réduire le risque de choc électrique ou courts-circuits accidentels.
• Il n’y a pas réparable par l’utilisateur contenues dans ce produit.
• Cet appareil est fourni avec une protection intégrale contre les surcharges.
• Puissance en direct peuvent être présents à plus d’un point depuis un onduleur utilise à la fois
DC (piles, PV, etc) et AC (utilitaire ou générateur) d’alimentation. Pour réduire le risque de
choc électrique, assurez-vous que tout le câblage DC et AC est débranchée avant l’installation
ou la maintenance sur le variateur. Mise hors tension de l’onduleur ne réduira pas ce risque,
l’onduleur doit être totalement déconnectée de toutes les sources.
• Utiliser des méthodes de câblage classe 1 pour les connexions de câblage sur le terrain aux
bornes d’un circuit de Classe 2.
• Coté ou étiquetés équipement doit être installé et utilisé conformément aux instructions
fi gurant dans la liste ou l’étiquetage.
• Toujours vérifi er le câblage avant de commencer l’onduleur.
• Utilisez des fi ls de cuivre seulement avec une cote de température minimale de 90°C.
• AC câblage ne doit pas être inférieure à 10 AWG (5.3 mm²) de cuivre de calibre.
• Les câbles de batterie ne doit pas être inférieur à #4/0 AWG (107.2 mm²) pour 12 et 24-volts
systèmes. Frisées et scellé cosses en cuivre anneau des bornes avec un trou de 5/16 doit être
utilisé pour se connecter à des bornes de courant continu sur l’onduleur.
• Couple toutes les connexions de câblage ca et les connexions de câbles à courant continu à
des valeurs de couple nécessaires.
• L’onduleur doit être correctement monté, voir le montage de la section onduleur dans le
chapitre Installation de ce manuel.
• Protection contre les surintensités pour l’alimentation de la batterie n’est pas fourni en tant
que partie intégrante de cet inverseur. La protection contre les surintensités des câbles de
batterie doivent être fournis dans le cadre de l’installation du système. Reportez-vous à la
section Câblage cc dans le chapitre d’installation pour plus d’informations.
Page iv
Page 6

Safety Information
• Protection contre les surintensités pour le câblage de sortie AC n’est pas fourni en tant que
partie intégrante de cet onduleur. Protection contre les surintensités du câblage de sortie CA
doit être fournie dans le cadre de l’installation du système. Reportez-vous à la Section 2.5
Câblage ca dans le chapitre d’installation pour plus d’informations.
• Le conducteur de sortie CA conducteurs neutre et continue négative ne sont pas connectés
(servitude) au châssis inverseur. La fois l’entrée et des conducteurs de sortie sont isolés de l’enceinte
et l’autre. La terre du système, si nécessaire, est de la responsabilité de l’installateur du système
et doit se conformer à des codes locaux et nationaux et les normes électriques. Reportez-vous à
la Section 2.6 Mise à la terre Onduleurs dans le chapitre d’installation pour plus d’informations.
Sécurité de la batterie
• Utiliser des outils isolés et être très prudent lorsque vous travaillez près des batteries, elles
peuvent produire des courants extrêmement élevés si en court-circuit (par exemple, échapper
un outil métallique à travers la borne de la batterie), ce qui pourrait provoquer un incendie
ou une explosion.
• Lisez et suivez les consignes de sécurité du fabricant de la batterie avant d’installer l’onduleur
et des batteries. Toujours vérifi er la polarité et la tension avant de brancher les batteries à
l’onduleur. Une fois que les batteries sont connectées à l’onduleur, assurer la maintenance et
les exigences de charge (c.-à-tension de charge et taux de charge) fournis par le fabricant de
la batterie sont suivies pour prolonger la vie des batteries et pour éviter d’endommager les
batteries pendant la charge.
• Porter des lunettes de protection tels que des lunettes de sécurité, et évitez de toucher vos yeux
et le visage lorsque l’on travaille avec des piles de garder tout fl uide / corrosion sur la batterie
d’entrer en contact avec les yeux et la peau. Ayez suffi samment d’eau fraîche et de savon à
proximité et se laver dans le cas d’acide contact avec la peau de la batterie, les vêtements ou les
yeux. Dans le cas d’exposition pour les yeux, les inonder pendant au moins 15 minutes à l’eau
courante et consulter immédiatement un médecin.Le bicarbonate de soude neutralise l’acide
de plomb électrolyte de la batterie et le vinaigre neutralise renversé NiCad et NiFe batterie à
électrolyte; en fonction de votre type de batterie, gardez sous la main près des batteries.
• Enlevez tous les bijoux tels que bagues, montres, bracelets, etc, lors de l’installation ou la
maintenance sur les batteries et l’onduleur. Une batterie peut produire un court-circuit assez
de courant élevé pour souder les bijoux en métal, provoquant de graves brûlures.
• Ne jamais travailler seul. Toujours avoir quelqu’un au sein de la gamme de votre voix ou
suffi samment près pour vous venir en aide lorsque vous travaillez près des batteries.
• Utiliser des techniques de levage appropriées lorsque vous travaillez avec des piles.
• Ne jamais utiliser de piles usagées ou non testés. Vérifi ez l’étiquette de chaque batterie à
l’âge, le type et le code de date afi n d’assurer toutes les batteries sont identiques.
• Piles sensibles aux changements temporaires, installer dans un environnement stable.
• Les batteries peuvent produire des gaz explosifs, etc installer les piles dans un endroit bien
ventilé. Pour les installations compartiment ou une enceinte, toujours évacuer les piles du
plus haut point à l’extérieur. Concevoir le boîtier de piles pour éviter l’accumulation et la
concentration de gaz d’hydrogène dans “poches” en haut du compartiment.
• Fournir au moins un pouce de l’espace aérien entre les batteries pour fournir un refroidissement optimal.
• Ne jamais fumer ou laisser une étincelle près des batteries.
• Pour éviter une étincelle à la batterie et de réduire le risque d’explosion, toujours connecter
les câbles aux batteries en premier. Ensuite, connectez les câbles à l’onduleur.
• Ne jamais charger une batterie gelée.
• La banque de la batterie doit être installé dans un endroit propre, sec, aéré et où ils sont
protégés contre les températures élevées et basses. S’il est installé dans un véhicule / bateau,
les batteries doivent être monté en position verticale (si vous utilisez des piles liquides) et
solidement fi xés. L’emplacement doit être pleinement accessible et protégé contre l’exposition
à la chaleur la fabrication de dispositifs, et loin de toute réservoirs de carburant.
CONSERVER CES INSTRUCTIONS
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page v
Page 7

Table of Contents
1.0 Introduction .......................................................................................... 1
1.1 How an MS-G Series Inverter/Charger Works ..................................................... 2
1.2 Advantages of a Pure Sine Wave vs a Modifi ed Sine Wave Inverter ........................ 2
1.3 Features and Benefi ts ..................................................................................... 3
2.0 Installation ............................................................................................ 6
2.1 Pre-Installation .............................................................................................. 6
2.2 Mounting the Inverter ....................................................................................10
2.3 Wiring the Inverter – General Requirements ......................................................13
2.4 DC Wiring .....................................................................................................14
2.5 AC Wiring .....................................................................................................20
2.6 Grounding Inverters ......................................................................................32
2.7 Inverter Notifi cation Requirements ...................................................................39
2.8 Final Inspection .............................................................................................39
2.9 Functional Test ..............................................................................................40
3.0 Operation ............................................................................................ 41
3.1 Inverter Mode ...............................................................................................41
3.2 Standby Mode ...............................................................................................42
3.3 Battery Charging ...........................................................................................43
3.4 Transfer Time ................................................................................................45
3.5 Battery Temperature Sensor Operation .............................................................45
3.6 Protection Circuitry Operation .........................................................................46
3.7 Inverter Startup ............................................................................................47
3.8 Factory Default Values ...................................................................................48
3.9 Using the GFCI ..............................................................................................49
3.10 Inverter Fan Operation ...................................................................................50
3.11 Using a Remote with the MS-G Series Inverter ..................................................50
4.0 Maintenance and Troubleshooting ....................................................... 51
4.1 Recommended Inverter and Battery Care .........................................................51
4.2 Storage for Mobile Installations .......................................................................51
4.3 Troubleshooting ............................................................................................52
4.4 Resetting the Inverter ....................................................................................53
Appendix A – Specifi cations and Optional Equipment ................................... 54
Appendix B – Battery Information ................................................................ 57
Appendix C – Power Consumption & Output Waveforms .............................. 62
Appendix D – Inverter/Charger Terminology ............................................... 63
Appendix E – Warranty & Service ................................................................. 65
List of Tables
Table 2-1, Recommended DC Wire/Overcurrent Device for Rated Use ................................. 16
Table 2-2, DC Wire Size For Increased Distance ............................................................... 17
Table 2-3, AC Input/Output Wiring Configurations ............................................................ 23
Table 2-4, AC Input/Output Wiring Configurations (MS2000-G models) ............................... 29
Table 2-5, AC Grounding Electrode Conductor Sizing ........................................................ 33
Table 2-6, Equipment Grounding Conductor Sizing ........................................................... 35
Table 3-1, Inverter Battery Turn On/Off Levels ................................................................. 46
Table 3-2, Inverter/Charger Default Values* .................................................................... 48
Table 3-3, Inverter Compatibility Level ........................................................................... 50
Table 4-1, Basic Troubleshooting .................................................................................... 52
Table C-1, Typical Appliance Power Consumption .............................................................. 62
Page vi
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 8

List of Figures
Figure 1-1, Power Switch, Status LED, and Accessory Connection Ports ................................ 3
Figure 1-2, Electrical Connection Points ........................................................................... 4
Figure 1-3, Left Side Features ........................................................................................ 5
Figure 2-1, Simplifi ed Installation for Permanent Installations (MS2012-G) ........................... 7
Figure 2-2, Simplifi ed Installation for Permanent Installations (MS2000-G) ........................... 8
Figure 2-3, Approved Mounting Positions ........................................................................10
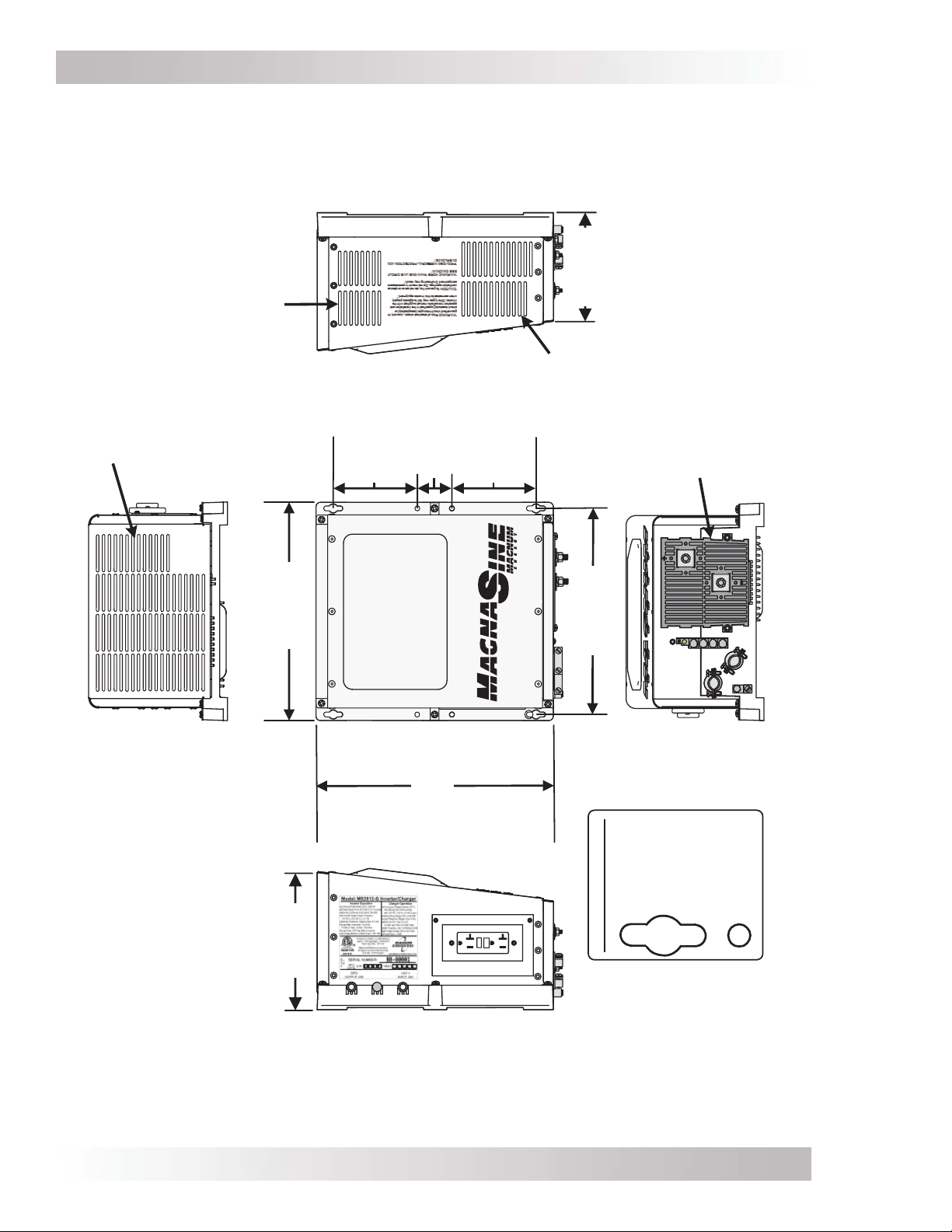
Figure 2-4, MS-G Series Dimensions (MS2012-G, MS2812-G, MS4024-G) ...........................11
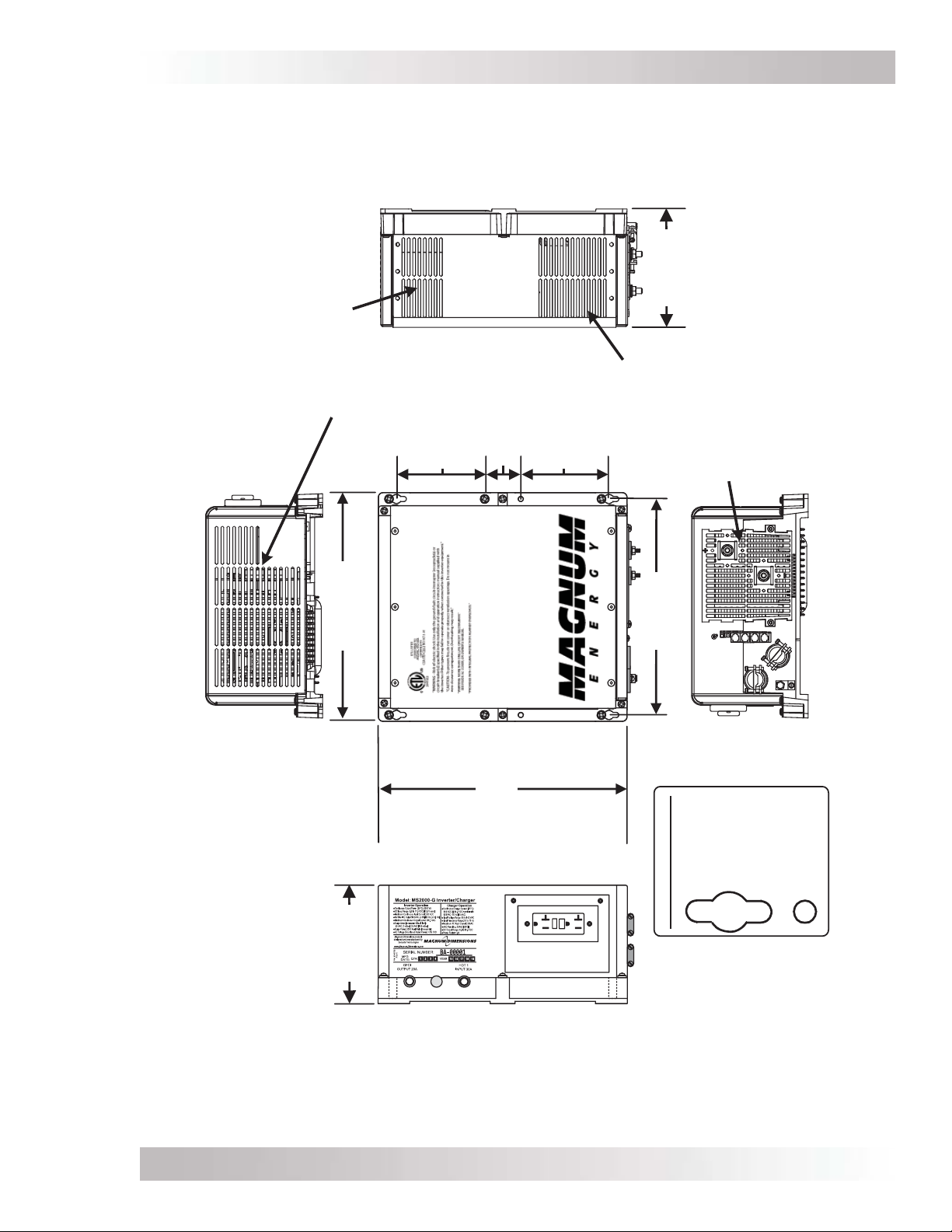
Figure 2-5, MS-G Series Dimensions (MS2000-G) ............................................................12
Figure 2-6, DC and Battery Temperature Sensor Wiring ....................................................15
Figure 2-7, Battery Hardware Installation .......................................................................17
Figure 2-8, Inverter DC Hardware Installation .................................................................17
Figure 2-9, Battery Temperature Sensor .........................................................................18
Figure 2-10, AC Terminal Block (MS2012-G/MS2812-G/MS4024-G) ....................................21
Figure 2-11, AC Wiring for a Single In Confi guration .........................................................24
Figure 2-12, AC Wiring for Single In (30A) – Single Out Confi guration ................................25
Figure 2-13, AC Wiring for Single In (50A) – Single Out Confi guration ................................26
Figure 2-14, AC Wiring for Dual In – Single Out Confi guration ...........................................27
Figure 2-15, AC Wiring for a Single In Confi guration (MS2000-G) .......................................30
Figure 2-16, AC Wiring for a Single In – Single Out Confi guration (MS2000-G) .....................31
Figure 2-17, Grounding System for MS-G Series ..............................................................32
Figure
Figure 2-19, Multiple Connections to DC Ground Rod (Method 2) ........................................34
Figure 2-20, Single Connection to DC Ground Rod (Method 3) ...........................................34
Figure 2-21, Neutral-to-Ground Connection (Inverter Mode) ..............................................37
Figure 2-22, Neutral-to-Ground Connection (Standby Mode) ..............................................37
Figure 2-23, Disconnecting the Neutral-to-Ground Connection ...........................................38
Figure 2-24, Connecting a Large DC Ground Wire ............................................................38
Figure 2-25, Warning Label ...........................................................................................39
Figure 2-26, AC Voltage Checks (MS2012-G model) .........................................................40
Figure 2-27, AC Voltage Checks (MS2000-G model) .........................................................40
Figure 3-1, Power Flow – Inverter Mode (MS2012-G/2812-G/4024-G models) .....................41
Figure 3-2, Power Flow – Inverter Mode (MS2000-G model) ..............................................42
Figure 3-3, Power Flow – Standby Mode (MS2012-G/2812-G/4024-G models) .....................42
Figure 3-4, Power Flow – Standby Mode (MS2000-G model) ..............................................43
Figure 3-5, Automatic 4-Stage Charging Graph ................................................................44
Figure 3-6, BTS Temperature to Charge Voltage Change ...................................................45
Figure 3-7, Power Switch and Status Indicator .................................................................47
Figure 3-8, Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter ....................................................................49
Figure 4-1, Performing an Inverter Reset ........................................................................53
Figure A-1, MS-G Series Effi ciency Chart .........................................................................55
Figure A-2, MS-G Series VAC Input to Charge Amps .........................................................55
Figure B-1, Series Battery Wiring ...................................................................................59
Figure B-2, Parallel Battery Wiring .................................................................................59
Figure B-3, Series-Parallel Battery Wiring .......................................................................59
Figure B-4, Battery Bank Wiring Examples (12-volt) .........................................................60
Figure B-5, Battery Bank Wiring Examples (24-volt) .........................................................61
Figure C-1, AC Waveforms ............................................................................................62
2-18, Multiple Connections to DC Ground Rod (Method 1) ........................................33
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page vii
Page 9

Introduction
1.0 Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of a MS-G Series inverter/charger from Sensata. The MS-G
Series products include the MS2000-G, MS2012-G, MS2812-G, and MS4024-G inverters; all are
under the Magnum-Dimensions brand from Sensata Technologies. The MS-G Series is a “pure”
sine wave inverter designed especially for rugged mobile applications, home backup power, and
standalone applications. Powerful, yet simple to use, this inverter/charger will provide you with
years of trouble-free performance you have come to expect from Sensata.
Installation is easy. Simply connect the inverter’s output to your distribution circuits or electrical
panel, connect your utility or AC generator power to the inverter, connect the batteries, and then
switch it on for power.
Info: This is a sizable manual and much of it is fairly technical. Terms may be used
throughout the manual that are unfamiliar to you. Refer to the Inverter/Charger
Terminology glossary in Appendix D for clarifi cation.
The MS-G Series inverter/charger includes the following:
• 2000, 2800, or 4000 watt model in a small footprint—less area needed for installation
• Pure sine wave output
• Automatic PFC (Power Factor Corrected) multi-stage battery charging
• RS485 standard communication protocol
• Factory-installed Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlet (with test and reset
capability) for AC output
• Remote and Network ports (easy connection for optional accessories)
• Inverter-mounted ON/OFF switch with LED indicator
• 30-amp per leg AC pass-thru capability
• Field serviceable for qualifi ed personnel—tested repair kits available
• Automatic battery temperature compensation (when using the Battery Temperature
Sensor) for optimum charging even during extreme temperature changes
• Overcurrent, over-temperature, and high/low battery voltage protection
Regulatory Compliance
The MS-G Series inverter/charger is designated as a standalone (non grid-interactive) power
inverter with an internal battery charger. It can be connected to the utility grid (or to a generator)
to allow the inverter batteries to be charged, and to power inverter loads while connected. The
MS-G series is not a grid-interactive (also known as utility-interactive) inverter and does not have
the capability to export (or sell) power back into the utility grid.
The MS-G Series has been tested and listed to UL 458, 5th Edition (Power Converters/Inverters
and Power Converter/Inverter Systems for Land Vehicles and Marine Crafts) and UL 1741, 2nd
Edition¹ (Inverters, Converters and Controllers for Use in Independent Power Systems) for use
in the US; and is also certifi ed to CSA C22.2 No. 107.1-01 (General Use Power Supplies) for use
in Canada. It has been tested and certified to these product safety standards by Intertek Testing
Services (known as ETL), which is a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL). NRTL’s
are qualified organizations that meet Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
regulations to perform independent safety testing and product certifi cation.
The MS-G Series also meets the KKK-A-1822E standard for use in ambulances.
Note¹ – The MS2000-G model is not listed to the UL 1741 standard.
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 1
Page 10

Introduction
1.1 How an MS-G Series Inverter/Charger Works
There are two modes of operation associated with this inverter/charger:
Inverter Mode
When the inverter is properly connected to batteries and turned on, the direct current (DC) from
the batteries is transformed into a pure sine wave alternating current (AC). This AC is similar to
the voltage provided by your utility and is used to power any electrical appliances (i.e., AC loads)
connected to the inverter’s output.
Standby Mode
When an external source of AC power (i.e., utility power or generator) is connected and
qualifi ed on the inverter’s AC input, it operates in Standby mode. In Standby mode, the unit
operates as a battery charger to convert the incoming AC power into DC power to recharge
the batteries; and at the same time, automatically closes an internal AC transfer relay to pass
the incoming AC power directly to the inverter’s output to continue powering the connected
electrical appliances.
1.1.1 Inverter Applications for Permanent Installations
An inverter can be used for backup power in a permanent location that normally uses utility power,
such as a home or offi ce. When utility power is available, the inverter keeps the batteries charged.
When the utility power fails, the inverter comes on automatically to supply AC power to your
home or offi ce during the power failure. For a home or business, reliable backup power is needed
to prevent lost computer data, maintain lights, and keep food fresh in the refrigerator/freezer.
In some areas, where utility power is not available, this inverter can be used in a standalone
renewable power system. The inverter allows AC electrical appliances to be run from the storage
battery bank. When the battery bank becomes discharged, either renewable DC sources (solar,
wind, or hydro power) can be used to recharge the batteries, or a generator can be connected to
the inverter to power the system while the batteries recharge.
1.1.2 Inverter Applications for Mobile Installations
Inverters can also be used to provide power in mobile situations, such as in an RV, truck, or boat.
In these applications, the inverter provides power to the AC loads using the energy stored in the
batteries and recharges the batteries when shorepower or an onboard generator is available.
1.2 Advantages of a Pure Sine Wave vs a Modifi ed Sine Wave Inverter
Today’s inverters come in three basic output waveforms: square wave, modifi ed sine wave (which
is actually a modifi ed square wave) and pure sine wave (see Figure C-1 in Appendix C). Modifi ed
sine wave inverters approximate a pure sine wave form and will run most appliances and electronics
without any problems. These inverters are less expensive, and therefore, offer a viable alternative
to more expensive pure sine wave inverters.
The output of the MS-G Series inverter—which is pure sine wave—is equal to, or in many cases,
better than the utility power used in your home. Virtually any electronic device will operate from
a pure sine wave inverter. Motors run cooler, microwaves usually cook faster, and clocks keep
better time just to name a few examples. Without compromising quality or performance, the
MS-G Series provides you with all the advantages of a pure sine wave inverter at a much lower
cost than many on the market.
The MS-G Series is built on the same platform as our popular ME and RD Series modifi ed sine
wave inverters—allowing for an easy upgrade to a pure sine wave inverter from the original ME
or RD Series installation. This standard platform also helps reduce cost by using standard parts/
accessories across many models. Accessories such as the Advanced Remote Control (ME-ARC),
Standard Remote Control (ME-RC), Automatic Generator Start – Networked (ME-AGS-N), and
Battery Monitor Kit (ME-BMK) can be used (see Section A-4 in Appendix A).
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 2
Page 11

Introduction
1.3 Features and Benefi ts
The MS-G Series inverter/chargers are designed to allow easy access to wiring, circuit breakers,
and controls. Their die cast baseplate with one-piece aluminum cover ensures maximum durability
with minimum weight, as well as a cooler, more effi cient operation.
Note: While not pictured, the MS2000-G inverter/charger has the same features as those listed
in this section (and as shown in Figures 1-1 through 1-3).
The front of the MS-G inverters are equipped with the following (refer to Figures 1-1 and 1-2):
Power ON/OFF Switch – a momentary pushbutton switch that alternately turns the
1
inverter on or off.
Status LED Indicator – this green LED illuminates to provide information on inverter
2
or charger operation.
Stack/Accessories Connection Port (red label) – a RJ11 port that allows series-
3
stacking, and accepts the optional RSAs (Remote Switch Adapters) for remote on/off
switch operation.
Info: The series-stacking capability—which allows two units to provide 120/240 VAC
output—is only available on the MS4024-G inverter/charger. See the ME-SSI owner’s
manual (PN: 64-0009) for additional information on series stacking.
Network Connection Port (green label) – a RJ11 port that accepts optional network
4
capable accessories (i.e., Auto Gen Start or Battery Monitor).
Remote Connection Port (blue label) – a RJ11 port that allows an optional remote
5
control to be connected.
Battery Temperature Sensor Connection Port (yellow label) – a RJ11 port that
6
accepts the remote Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS).
1
Power ON/OFF Switch
Status LED Indicator
2
(charging/inverting)
Stack/Accessories Connection Port
3
(red label – RJ11 connection)
Network Connection Port
4
(green label – RJ11 connection)
Remote Connection Port
5
(blue label – RJ11 connection)
Battery Temperature Sensor Port
6
(yellow label – RJ11 connection)
Figure 1-1, Power Switch, Status LED, and Accessory Connection Ports
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 3
Page 12
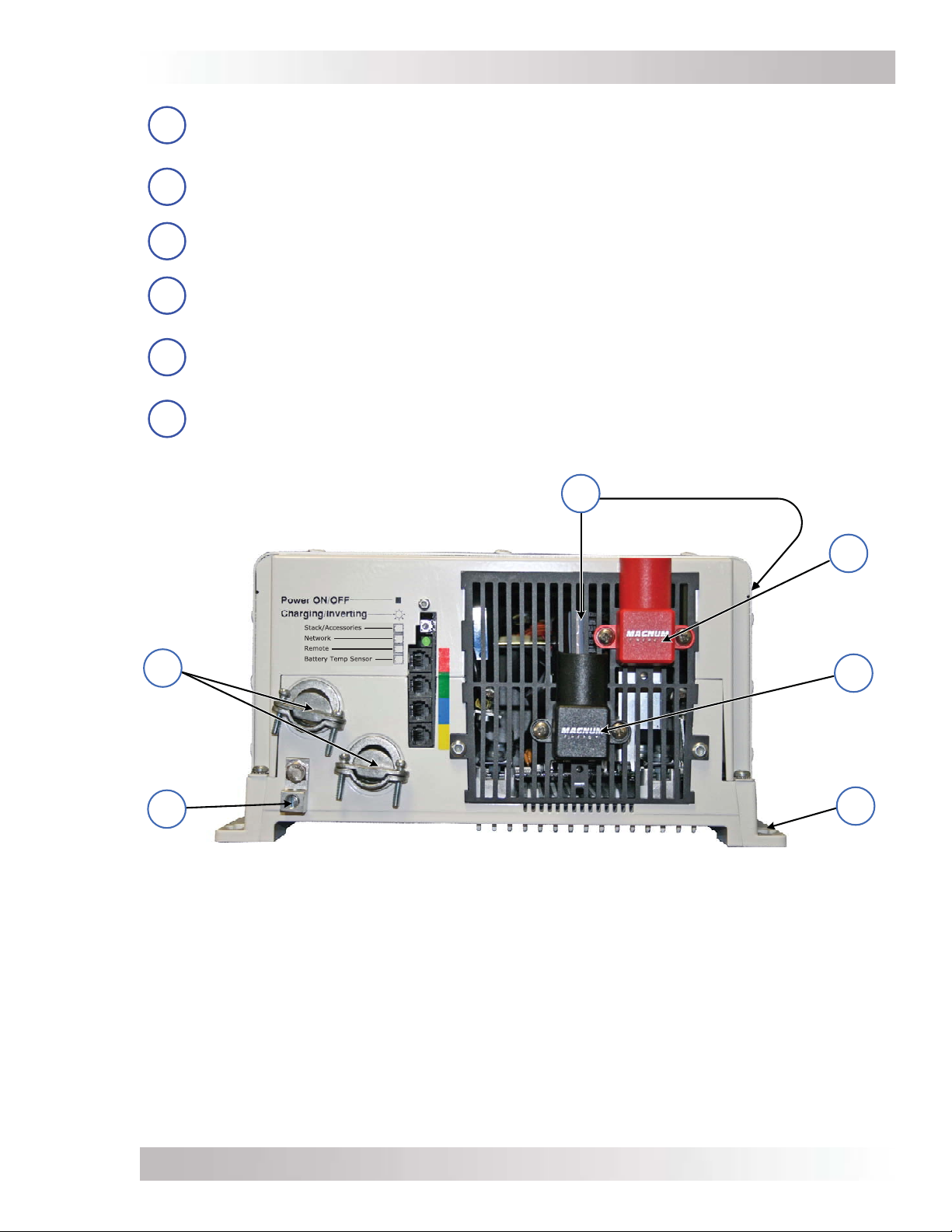
Introduction
DC Equipment Ground Terminal – this connection is used to tie the exposed chassis
7
of the inverter to the DC grounding system. This terminal accepts CU/AL conductors from
#14 to #2 AWG (2.1 to 33.6 mm2).
AC Entry/Exit Connections – two 3/4” knockouts provided with cable-clamp strain
8
reliefs to accommodate and secure the AC input and output fi eld wiring.
Intake Air Vents – ventilation openings to pull in air to keep the inverter cool for peak
9
performance.
Positive DC Terminal – provides a 360 degree connection point for the positive (+) cable
10
from the battery bank; consists of a 5/16-18 bolt with a Kep or Flange nut that holds the
battery cable to the DC terminal.
Negative DC Terminal – provides a 360 degree connection point for the negative (–)
11
cable from the battery bank; consists of a 5/16-18 bolt with a Kep or Flange nut that
holds the battery cable to the DC terminal.
Mounting Flange – used to secure the inverter to a shelf or wall.
12
8
AC Entry/
Exit
Connections
7
DC Equipment
Ground Terminal
Intake Air Vents
(and on right front side)
9
Figure 1-2, Electrical Connection Points
10
Positive (+)
DC Terminal
(under cover)
11
Negative (–)
DC Terminal
(under cover)
12
Mounting
Flange
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 4
Page 13

Introduction
The left side of MS-G Series inverters are equipped with the following features (refer to Figure 1-3):
Exhaust Air Vents – ventilation openings that allow heated air to be removed by the
13
internal cooling fan.
Model/Serial Number Label – includes model/serial number information, date of
14
manufacture, and inverter and charger specifi cations. See the MS-G Series specifi cations
in Appendix A for more information and a list of available models.
AC Access Cover – provides access to the internal AC wiring terminal block (see
15
Figure 2-10). This terminal block is used to hard wire all inverter AC input and output
wiring connections. Remove the two screws to access the AC wiring terminal block.
Note: The MS2000-G model does not have the AC wiring terminal block.
GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) – a 20-amp rated dual outlet that quickly
16
stops the flow of electricity in the event a ground fault occurs on the device that is plugged
into the inverter.
HOT 1 Input – this 30-amp circuit breaker protects the unit’s internal charger wiring
17
and pass-thru relay while in Standby mode. The circuit breaker pops out when it opens—
press in to reset. The input circuit breaker is not branch-rated, therefore branch-rated
circuit breakers must be installed in the inverter’s input wiring.
GFCI Output – this 20-amp circuit breaker is branch-rated and protects the wiring to the
18
GFCI outlet. This circuit breaker pops out when it opens—press in to reset. It can also be
manually pulled to disconnect the inverter’s loads.
CAUTION: The inverter’s internal AC transfer relay is rated for 30 amps per wired input
(not the GFCI circuit). The pass-thru current must be no greater than 30 amps per leg
or damage to the relays may occur.
AC Access Cover
15
16
GFCI
13
Exhaust
Air Vents
(back and
right side)
Model/Serial
Number Label
14
GFCI Output
Circuit Breaker
18
HOT 1 Input
17
Circuit Breaker
Figure 1-3, Left Side Features
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 5
Page 14
Installation
2.0 Installation
Info: Installations should be performed by qualifi ed personnel, such as a licensed
or certifi ed electrician. It is the installer’s responsibility to determine which safety
codes apply and to ensure that all applicable installation requirements are followed.
Applicable installation codes vary depending on the specifi c location and application of
the installation.
CAUTION: Review the “Important Product Safety Information” on pages ii-v before any
installation.
CAUTION: The inverter is heavy. Use proper lifting techniques during installation to
prevent personal injury.
The simplifi ed system diagram shown in Figure 2-1 should be reviewed to assist you in planning
and designing your installation. This drawing is not intended to override or restrict any national
or local electrical codes. This drawing should not be the determining factor as to whether the
installation is compliant, that is the responsibility of the electrician and the on-site inspector.
2.1 Pre-Installation
Before proceeding, read the entire Installation section to determine how best to install your MS-G
inverter/charger. The more thorough you plan in the beginning, the better your inverter needs
will be met.
2.1.1 Unpacking and Inspection
Carefully remove the MS-G Series inverter/charger from its shipping container and inspect all
contents. Verify the following items are included:
• The MS-G Series inverter/charger
• Red and black DC terminal covers with Phillips screws
• Two 5/16” Kep or Flange nuts (installed on the DC terminals)
• Battery Temperature Sensor
• Warning label
• MS-G Series Owner’s Manual
If items appear to be missing or damaged, contact your Magnum product authorized dealer or
Sensata. If at all possible, keep your shipping box to help protect your inverter from damage if it
ever needs to be returned for service. Save your proof-of-purchase as a record of your ownership;
it will also be needed if the unit should require in-warranty service.
Record the unit’s model and serial number in the front of this manual in case you need to provide
this information in the future. It is much easier to record this information now, instead of trying
to gather it after the unit has been installed.
2.1.2 Required Tools and Materials Hardware/Materials
• Conduit, strain-reliefs and appropriate fi ttings • Electrical tape
• 1/4” mounting bolts and lock washers (x4 min.) • Wire ties
Tools
• Miscellaneous screwdrivers • Pliers • Wire strippers
• Drill and drill bits • Pencil or marker • Multimeter
• Level • 1/2” wrench
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 6
Page 15
Installation
Utility Power
120/240VAC Output
GFCI
(inverter left side)
Main Panel
ON
OFF
120/240VAC Output
AC
Transfer
Switch
Power ON/OFF
Ch argi ng/ Inv ert ing
Stack/ Accessor ies
Net work
Rem ote
Battery Temp Se nsor
Generator Power
ME-RC50
PWR
FAULT
CHG
INV
ON/OFF
CHARGER
ON/
OFF
INVE R T E
R
Remote Controls (Magnum Accessories)
120VAC in verte r pow er
(or 120VAC pass-thru
power ) to sub-pan el
SEL ECT
AGS METER SETUPSHORE
TECH
MS-G
Series
Inverter/
Charger
ME-ARC50
Sub-Panel
OFF
ME-AGS-N
Auto Gen
Start
Controller
(Magnum
Accessory)
30A
OFF
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
AC Out
(to AC loads)
DC Shunt
DC
Overcurrent
Protection
(breaker or
fuse/switch)
120
VAC
120
VAC
120/
240VAC
power to
inverter
BTS
ME-BMK
Battery
Monitor with
shunt
(Magnum
Accessory)
ME-SBC
Smart
Battery
Combiner
(Magnum
Battery Bank
Accessory)
Figure 2-1, Simplifi ed Installation for Permanent Installations (MS2012-G)
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 7
Page 16
Introduction
Utility Power
120/240VAC Output
GFCI
(inverter left side)
Main Panel
ON
AC
Transfer
Switch
Generator Power
120/240VAC Output
Remote Controls (Magnum Accessories)
Power ON/OFF
Ch argi ng/ Inv ert ing
Stack/ Accessor ies
Net work
Rem ote
Battery Temp Se nsor
ME-RC50
PWR
FAULT
CHG
INV
ON/OFF
CHARGER
ON/
OFF
INVE R T E
AGS METER SETUPSHORE
R
MS2000-G
Inverter/
Charger
SEL ECT
TECH
Series
ME-AGS-N
Auto Gen
Start
Controller
(Magnum
Accessory)
ME-ARC50
Sub-Panel
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
AC Out
(to AC loads)
DC Shunt
120
VAC
DC Overcurrent
120VAC
power to
inverter
(breaker or fuse/switch)
Protection
BTS
ME-BMK
Battery
Monitor with
shunt
(Magnum
Accessory)
ME-SBC
Smart
Battery
Combiner
(Magnum
Accessory)
Battery Bank
Figure 2-2, Simplifi ed Installation for Permanent Installations (MS2000-G)
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 8
Page 17
Installation
2.1.3 Locating the Inverter
Only install the inverter in a location that meets the following requirements:
Clean and Dry – The inverter should not be installed in an area that allows dust, fumes, insects, or
rodents to enter or block the inverter’s ventilation openings. This area also must be free from any
risk of condensation, water, or any other liquid that can enter or fall on the inverter. The inverter
uses stainless steel fasteners and plated copper busbars, has a powder-coated aluminum base, and
the internal circuit boards are conformal coated—all to help fi ght the harmful effects of corrosive
environments. However, the inverter’s life is uncertain if used in these type of environments, and
inverter failure under these conditions is not covered under warranty.
Info: If the inverter is installed in an area where moisture may occur, we recommend
putting silicone dielectric grease compound into the electrical ports (Figure 1-1, Items
3-6). Before installing the cables, or if leaving any ports open, squirt a liberal amount
into each port. Silicone dielectric compound makes an effective moisture and corrosive
barrier to help protect and prevent corrosion to the RJ11 connections.
Cool – The inverter should be protected from direct sun exposure or equipment that produces
extreme heat. The ambient temperature around the inverter must not exceed 77°F (25°C) to
meet power specifi cations.
Ventilation – In order for the inverter to provide full output power and to avoid over-temperature
fault conditions, do not cover or block the inverter’s ventilation openings or install this inverter in
an area with limited airfl ow. The inverter uses two fans to provide forced air cooling, these fans
pull in air through the intake vents (Figure 1-2, Item 9) and blow out air through the exhaust vents
(Figure 1-3, Item 13). Allow at the minimum an airspace clearance of 6” (15.2 cm) at the intake
and exhaust vents, and 3” (7.6 cm) everywhere else to provide adequate ventilation.
If installed in an enclosure, a fresh air intake opening must be provided directly to the front side
(intake vents) of the inverter and an exhaust opening on the back side (exhaust vents) of the
inverter. This allows cool air from the outside to fl ow into the inverter, and allows interior heated
air to exit the inverter and the enclosure. When mounted in an enclosed compartment, airfl ow must
be ≥ 100 cfm in order to maintain no more than a 68°F (20°C) rise in compartment temperature.
CAUTION: Do not mount this inverter in a zero clearance compartment, nor cover or
obstruct the ventilation openings—overheating may result.
Safe – Keep any fl ammable/combustible material (i.e., paper, cloth, plastic, etc.) that may be
ignited by heat, sparks, or fl ames at a minimum distance of 2 feet (61 cm) away from the inverter.
WARNING: The MS-G Series inverter/charger is not ignition-protected. Do not install
this inverter in any area that contains extremely fl ammable liquids like gasoline or
propane.
Close to the battery bank – The inverter should be located as close to the batteries as possible.
Long DC wires tend to lose effi ciency and reduce the overall performance of an inverter. However,
the unit should not be installed in the same compartment as the batteries or mounted where it
will be exposed to gases produced by the batteries. These gases are corrosive and will damage
the inverter; also, if these gases are not ventilated and allowed to collect, they could ignite and
cause an explosion.
Accessible – Do not block access to the inverter’s remote control and accessory ports, as well
as the inverter’s on/off switch and status indicator. Allow enough room to access the AC and DC
wiring terminals and connections, as they will need to be checked and tightened periodically. See
Figures 2-4 & 2-5 for the MS-G Series inverter/charger’s dimensions.
Away from sensitive electronic equipment – High powered inverters can generate levels of RFI
(Radio Frequency Interference). Locate any electronic equipment susceptible to radio frequency
and electromagnetic interference as far away from the inverter as possible.
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 9
Page 18
Installation
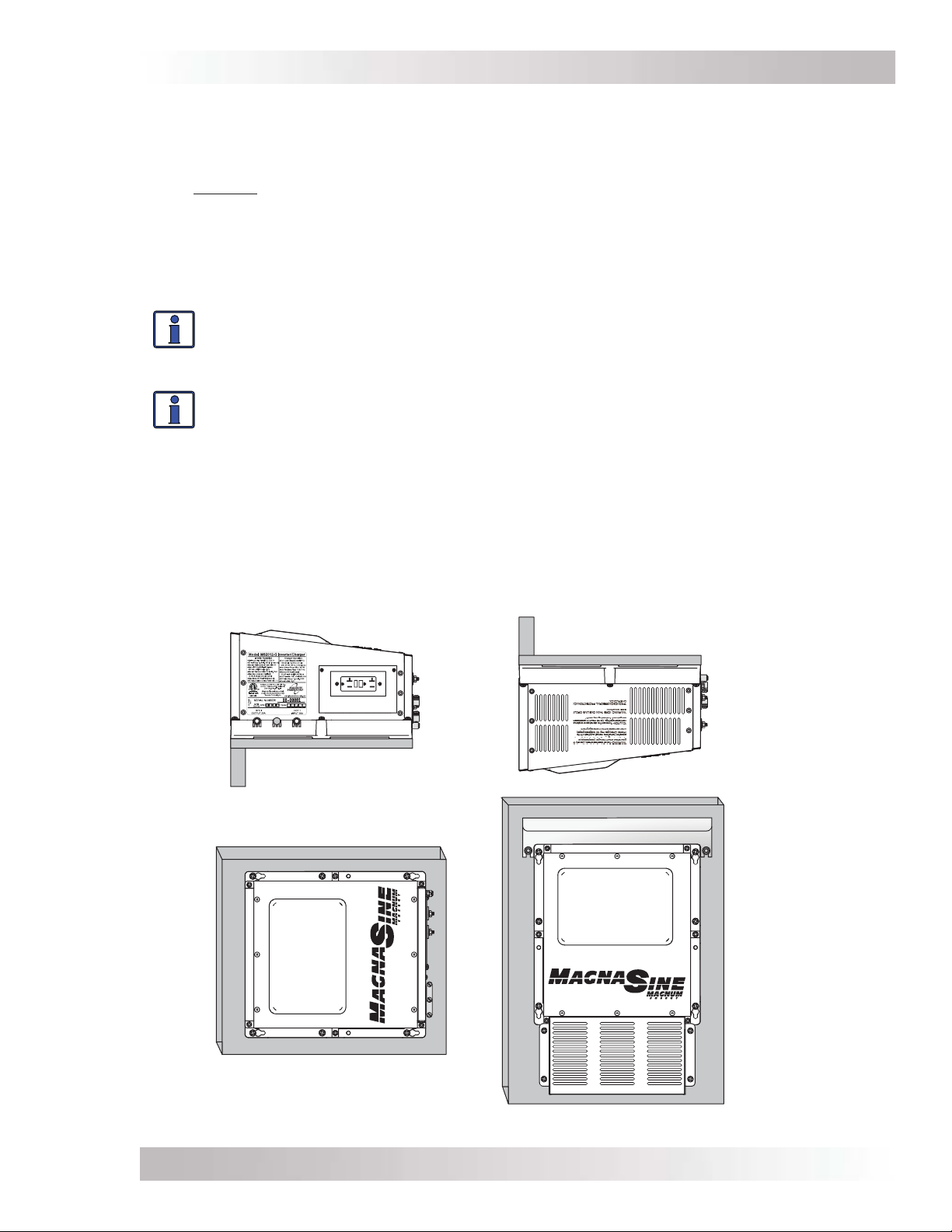
2.2 Mounting the Inverter
The inverter base can reach a temperature up to 90°C (194°F) and should be mounted on a
noncombustible surface*. This surface and the mounting hardware must also be capable of
supporting at least twice the weight of the inverter. To meet regulatory requirements, the MS-G
Series must be mounted in one of the following positions as shown in Figure 2-3:
• above or under a horizontal surface (shelf or table),
• on a vertical surface (wall) with the DC terminals to the right,
• on a vertical surface (wall) with the DC terminals toward the bottom, the MP-HOOD (inverter
hood) installed on the top, and either the ME-CB or MPX-CB (Conduit box), or the MMP series
(single inverter enclosure) installed on the inverter’s bottom.
Info: The ME-CB, MPX-CB, and MMP Series enclosures prevent material from falling
out the bottom in the event of an internal fi re, and also allow suffi cient ventilation to
prevent the inverter from overheating under normal operating conditions. The MPHOOD inverter hood prevents items from falling inside causing damage to the inverter.
Info: Sensata provides a backplate for mounting the inverter. These backplates also
provide the ability to mount the MMP Series enclosure (PN: BP-MMP).
After determining the mounting position, refer to the physical dimensions as shown in Figures
2-4 or 2-5, or use the base of the inverter as a template to mark your mounting screw locations.
After marking the mounting screw locations, mount the unit with appropriate mounting hardware.
* Noncombustible surface – A surface made of material that will not ignite, burn, support combustion, or
release fl ammable vapors when subjected to fi re or heat as per the ASTM E136 standard. For the most part,
these are materials that are largely comprised of inorganic materials such as stone, steel, iron, brick, tile,
concrete, slate, and glass. Avoid common building materials such as gypsum board as well as any paint, wall
coverings, and all types of wood.
RESET
TEST
20
30
30
SHELF OR TABLE
MOUNTED
(RIGHT SIDE UP)
WALL MOUNTED
(DC TERMINALS TO THE RIGHT)
SHELF OR TABLE MOUNTED
(UP SIDE DOWN)
WALL MOUNTED
(DC TERMINALS
DOWN*)
FACING
*WHEN THE INVERTER
IS MOUNTED ON THE
WALL IN THIS POSITION,
THE INVERTER HOOD
(MP-HOOD)
BE MOUNTED OVER THE
EXHAUST VENTS (TOP);
AND EITHER A CONDUIT
BOX (ME-CB OR
MPX-CB)
S
ERIES ENCLOSURE MUST
BE ATTACHED TO THE
INVERTER’S DC END
(
BOTTOM).
MUST
OR MMP
Figure 2-3, Approved Mounting Positions
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 10
Page 19
Installation
Exhaust Air Vents
Side
Right
6 ⅝"
(16.8 cm)
Exhaust Air Vents
Vents
4 ⅞"
2"
4 ⅞"
(12.4 cm)
(5.1 cm)
(12.4 cm)
Air Intake
Air Intake Vents
Top
12 ⅝"
(32.1 cm)
Front
12"
(30.5 cm)
Bottom
13 ¾"
(34.9 cm)
(x4)
9/32"
(7 mm)
8"
Use up to
Keyhole slots
RESE T
TEST
Mounting Holes
(20.3 cm)
20 30
30
Left
Side
screw/bolt
Mounting
Holes (x4)
Figure 2-4, MS-G Series Dimensions (MS2012-G, MS2812-G, MS4024-G)
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 11
Page 20
Installation
Side
Right
6 ⅝"
(16.8 cm)
Top
Exhaust Air Vents
4 ⅞"
(12.4 cm)
12 ⅝"
(32.1 cm)
Front
4 ⅞"
(5.1 cm)
(12.4 cm)
13 ¾"
(34.9 cm)
2"
Vents
Air Intake
Air Intake Vents
12"
(30.5 cm)
(x4)
9/32"
(7 mm)
Use up to
Keyhole slots
screw/bolt
Bottom
Mounting
Holes (x4)
6 ⅝"
Figure 2-5, MS-G Series Dimensions (MS2000-G)
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
RESE T
TEST
(16.8 cm)
20
30
Left
Side
Mounting Holes
Page 12
Page 21
Installation
2.3 Wiring the Inverter – General Requirements
This section describes the requirements and recommendations for wiring the MS-G Series inverter/
charger. Before wiring the MS-G Series inverter/charger, carefully read all instructions.
Wiring should meet all local codes and industry standards, and be performed by qualifi ed
personnel such as a licensed electrician.
The NEC (National Electric Code, ANSI/NFPA 70) for the United States and the CEC (Canadian
Electrical Code) for Canada provide the standards for safe wiring standards. The NEC/CEC lists
requirements for wire sizes, overcurrent protection, and installation methods/standards.
Inverter/charger systems involve power from multiple sources (inverter, generator, utility, batteries,
solar arrays, etc.) which make the wiring more hazardous and challenging.
The input and output AC and DC circuits are isolated from the inverter chassis. The inverter system
grounding is the responsibility of the installer in accordance with the NEC/CEC and local codes.
WARNING: Ensure all sources of DC power (i.e., batteries, solar, wind, or hydro) and
AC power (utility power or AC generator) are de-energized (i.e., breakers opened, fuses
removed) before proceeding—to prevent accidental shock.
2.3.1 Protecting Wire – Conduit Box
The AC and DC wires to and from the inverter must be protected as required by code. This can be
done by using jacketed wires or by feeding the wires through conduit. Sensata offers a DC conduit
box (ME-CB or MPX-CB) and a single inverter enclosure (MMP Series) that include the necessary AC
and DC inverter breakers that allow both the AC and DC conduit to be connected to the inverter.
Info: The strain reliefs can be removed and replaced with 3/4” grommets if you are using
either the ME-CB or MPX-CB conduit box, or the MMP enclosure, and the AC wires are
individual conductors (i.e., not jacketed).
2.3.2 Wiring Requirements
• All conductors that are at risk for physical damage must be protected by conduit, tape, or
placed in a raceway.
• Always check for existing electrical, plumbing, or other areas of potential damage prior to
making cuts in structural surfaces or walls.
• Do not mix AC and DC wiring in the same conduit or panel unless specifi cally approved/
designed for both AC and DC wiring. Where DC wiring must cross AC or vice-versa, try to
make the wires at the crossing point perpendicular (90 degrees) to one another.
• Both AC and DC overcurrent protection must be provided as part of the installation.
• The inverter requires a reliable negative and ground return path directly to the battery.
• Use only copper wires with a minimum temperature rating of 75°C (167°F).
2.3.3 Wire Routing
Before connecting any wires, determine all wire routes to and from the inverter. Conductors passing
through walls, bulkheads, or other structural members must be protected to minimize insulation
damage, such as chafi ng. During installation, always avoid placing conductors near sources of
chafi ng caused by vibration or constant rubbing. Typical routing scenarios are:
• AC input wiring from the main AC panel to the inverter
• AC input wiring from a generator (optional) to the inverter
• DC input wiring from the batteries to the inverter
• AC output wiring from the inverter to an AC sub-panel or to dedicated circuits
• Battery Temperature Sensor cable from the inverter to the batteries
• Remote control cable (optional) to the inverter
• Ground wiring to and from the inverter
2.3.4 Torque Requirements
Torque all AC wiring connections to 16 lbf-in (1.8 N-m). Torque DC cable connections from 10 to
12 lbf-ft (13.6 to 16.3 N-m).
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 13
Page 22

Installation
2.4 DC Wiring
This section describes the inverter’s required DC wire sizes, the recommended disconnect/
overcurrent protection, and how to make the DC connections to the inverter and the battery bank.
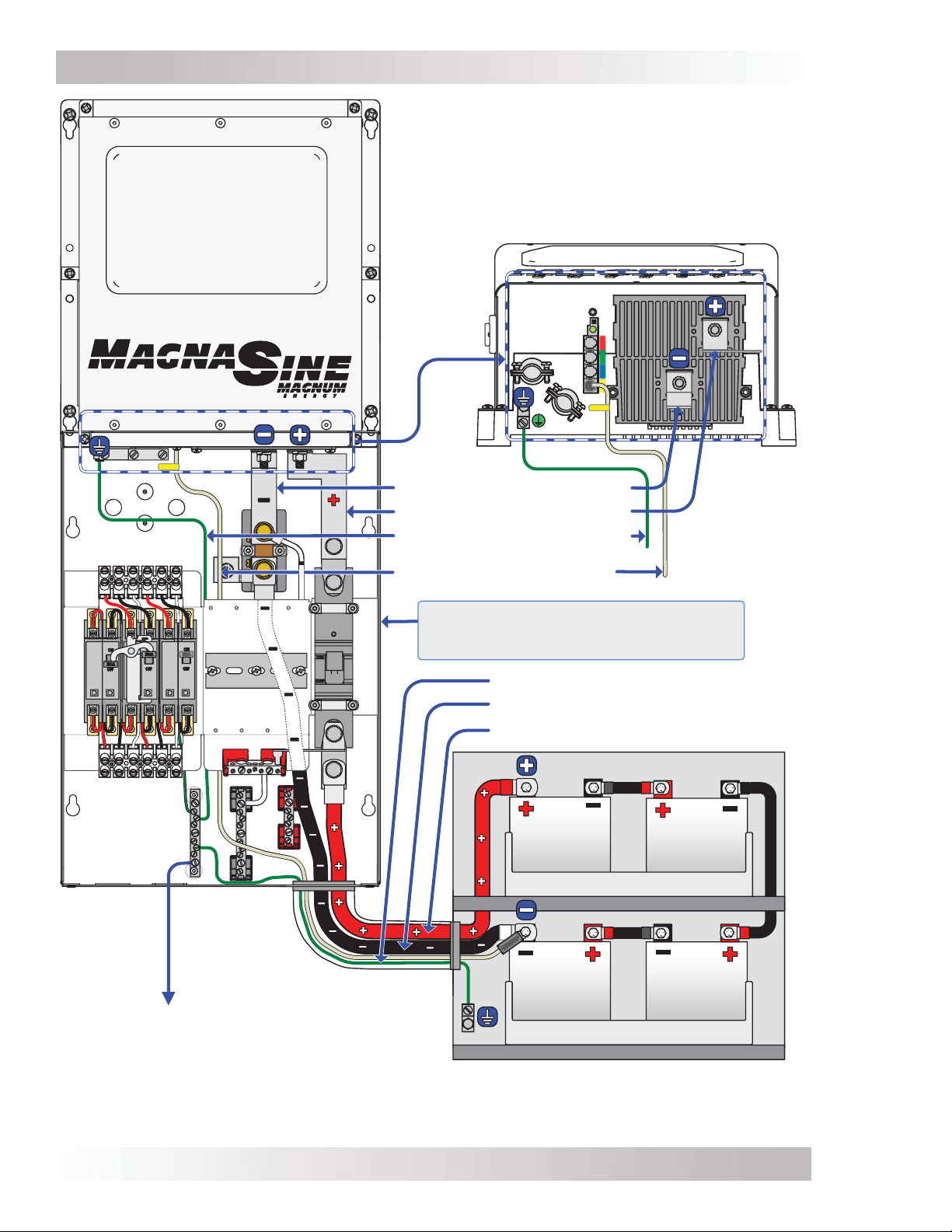
Refer to Figure 2-6 when connecting the DC wires.
Note: Figure 2-6 shows the MS-G attached to MMP enclosure.
WARNING: Even though DC voltage is “low voltage”, signifi cant hazards may be
present, particularly from short circuits of the battery system.
CAUTION: The inverter is NOT reverse polarity protected—which means that if the
negative and positive battery voltage is connected backwards to the inverter, the inverter
will likely be damaged. You should verify the correct voltage polarity using a voltmeter
BEFORE connecting the DC wires. Color code the DC cables/wires with colored tape or
heat shrink tubing: RED for positive (+); WHITE for negative (–); and GREEN (or bare
copper) for DC ground, to avoid polarity problems.
CAUTION: To remove battery power from the inverter, disconnect the battery positive
connection before the negative connection. This requirement can prevent damage to
the inverter and/or an accessory connected to the inverter.
Note: When an accessory that is not powered by the inverter (e.g., ME-AGS-N and ME-
BMK) is installed and connected to the inverter (via a network communication cable),
the battery negative connection of the inverter and each accessory must be at the same
potential (i.e., electrically common with each other) until the positive connection of
each device is removed. This prevents a high impedance path developing between the
connected devices (i.e., inverter and accessories), which can cause the network cable
to become the DC return path to the battery—possibly resulting in permanent damage
to all connected devices on the network. This can be prevented if the battery negative
connection of each device is always connected before connecting/disconnecting any
battery positive.
CAUTION: Before wiring the DC cables, review the safety information at the beginning
of this manual and the information below to ensure a safe and long-lived system.
• When the inverter is installed in a photovoltaic system, the NEC requires that the DC circuit
conductors and overcurrent devices to the inverter be sized to carry not less than 125% of
the inverter’s maximum current rating.
• The DC positive and negative cables connected to the inverter from the battery bank should
be tied together with wire ties or electrical tape approximately every 6 inches (15.2 cm). This
helps improve the surge capability and reduces the effects of inductance, which improves the
inverter waveform and reduces the wear of the inverter’s fi lter capacitors.
• Crimped and sealed copper ring terminal lugs with a 5/16” hole should be used to connect the
DC wires to the inverter’s DC terminals.
• The battery bank voltage MUST match the DC voltage required by the inverter (i.e., 24-volt
battery bank for a 24-volt inverter) or the inverter may be damaged.
• To ensure the maximum performance from the inverter, all connections from the battery bank
to the inverter should be minimized—the exception is the DC overcurrent disconnect in the
positive line and a shunt in the negative line. Any other additional connection will contribute
to additional voltage drops, and these extra connection points may loosen during use.
• Check all wiring to the battery terminals periodically (once a month) for proper tightness. The
torque requirement for the DC terminals is between 10 to 12 lbf-ft (13.6 to 16.3 N-m). Be
aware that overtightening or misthreading the nuts on the DC terminals can cause the bolts
to strip and snap/break off.
• A brief spark or arc may occur when connecting the battery cables to the inverter DC terminals;
this is normal and due to the inverter’s internal capacitors being charged.
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 14
Page 23
Installation
BTS
MS-G Series
Inverter/Charger
(front view)
BTS
Inverter’s DC Negative Busbar
Inverter’s DC Positive Busbar
Inverter’s Equipment Ground
Wire
Battery Temp Sensor Cable
DC System Grounding point
[Electrode Conductor
(i.e., ground busbar)]
MMP enclo sure – for single inverter installations
(inclu des DC disconnect breaker, DC shunt for
battery monitor, and inverter DC busbars).
Battery Bank’s Equipment Ground Wire
Battery Bank’s Negative Cable
Battery Bank’s Positive Cable
Battery Bank
Figure 2-6, DC and Battery Temperature Sensor Wiring
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 15
Page 24

Installation
2.4.1 DC Wire Sizing
It is important to use the correct sized DC wire to achieve maximum effi ciency from the system
and to reduce fi re hazards associated with overheating. Always keep your wire runs as short as
practical to prevent low voltage shutdowns and to keep the DC breaker from nuisance tripping (or
open fuses) because of increased current draw. See Table 2-1 to select the minimum DC wire size
(and corresponding overcurrent device) required based on your inverter model. The cable sizes
listed in Table 2-1 are required in order to reduce stress on the inverter, minimize voltage drops,
increase system effi ciency, and ensure the inverter’s ability to surge heavy loads.
If the distance from the inverter to the battery bank is >5 feet (1.5 m), the DC wire needs to be
increased. Longer distances cause an increase in resistance, which affects the performance of the
inverter. Use the overcurrent device previously determined from Table 2-1 and then refer to Table
2-2 to determine the minimum DC wire size needed for various distances.
2.4.2 DC Overcurrent Protection
DC overcurrent protection is not included in the inverter—for safety reasons and to comply with
electrical code regulations—it must be provided as part of the installation. The DC overcurrent
protection device must be installed in the positive DC cable line, it can be a fuse or a circuit
breaker and must be DC rated. It must be correctly sized according to the size of DC cables being
used, which means it is required to open before the cable reaches its maximum current carrying
capability, thereby preventing a fi re. In a residential or commercial electrical installation, the NEC
requires both overcurrent protection and a disconnect switch. If a circuit breaker is used as the
overcurrent protection device, it can also be used as the required DC disconnect.
If a fuse is used as an overcurrent device, a Class-T type or equivalent is recommended. This
fuse type is rated for DC operation, can handle high short-circuit currents, and has a time delay
that allows for momentary current surges from the inverter without opening the fuse. However,
because the fuse can be energized from both directions, the NEC requires that it be installed in a
manner that the power must be disconnected on both ends of the fuse before servicing.
Use Table 2-1 to select the DC overcurrent device needed based on the recommended minimum
wire size for your particular inverter model (may not meet all local code or NEC requirements).
Table 2-1, Recommended DC Wire/Overcurrent Device for Rated Use
Inverter
Model
MS2000-G 267 amps
MS2012-G 267 amps
MS2812-G 373 amps
MS4024-G 267 amps
Maximum
Continuous
Current
Minimum DC
1
(107.2 mm2)
[260 amps]
(107.2 mm
[260 amps]
(107.2 mm
[260 amps]
(107.2 mm
[260 amps]
Using Conduit In Free Air
Wire Size
(rating)
#4/0 AWG
#4/0 AWG
#4/0 AWG
#4/0 AWG
2
Recommended
DC Breaker
250 amps
2
)
2
)
2
)
250 amps
250 amps
250 amps
Size
5
5
5
5
Minimum DC
Wire Size
(rating)
#2/0 AWG
(67.4 mm2)
[300 amps]
#2/0 AWG
(67.4 mm2)
[300 amps]
#4/0 AWG
(107.2 mm2)
[405 amps]
#2/0 AWG
(67.4 mm2)
[300 amps]
Maximum DC
2
Fuse Size
300 amps with
time delay
300 amps with
time delay
400 amps with
time delay
300 amps with
time delay
3
Note1 – Maximum continuous current is based on the inverter’s continuous power rating at the lowest input
voltage with an inverter ineffi ciency factored in.
2
Note
– Copper wire rated with 90°C (194°F) insulation at an ambient temperature of 30°C (86°F), with a
multiple cable fi ll factor (0.8) de-rating (if needed).
Note3 – The next larger standard size overcurrent device may be used if the derated cable ampacity falls
between the standard overcurrent devices found in the NEC.
Note4 – Per the NEC, the DC grounding electrode conductor can be a #6 AWG conductor if that is the only
connection to the grounding electrode and that grounding electrode is a rod, pipe, or plate electrode.
Note5 – May not allow continuous operation at full rated power as defi ned by the NEC.
DC
Grounding
Electrode
Wire Size
#6 AWG
(13.3 mm2)
#6 AWG
(13.3 mm2)
#6 AWG
(13.3 mm2)
#6 AWG
(13.3 mm2)
4
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 16
Page 25

Installation
Table 2-2, DC Wire Size For Increased Distance
Inverter
Model
5 feet or less (≤1.5 m) 5 to 10 feet (1.5 to 3.1 m) 10 to 15 feet (3.1 to 4.6 m)
In Conduit In Free Air In Conduit In Free Air In Conduit In Free Air
Minimum Recommended DC Wire Size (one way)*
MS2000-G
MS2012-G
MS2812-G
MS4024-G
* Copper wire rated with 90°C (194°F) insulation at an ambient temperature of 30°C (86°F).
#4/0 AWG
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG
(107.2 mm2)
#2/0 AWG
(67.4 mm2)
#2/0 AWG
(67.4 mm2)
#4/0 AWG
(107.2 mm2)
#2/0 AWG
(67.4 mm2)
#4/0 AWG x2
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG x2
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG x2
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG x2
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG x2
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG
(107.2 mm2)
not
recommended
not
recommended
not
recommended
not
recommended
#4/0 AWG x2
(107.2 mm2)
#4/0 AWG x2
(107.2 mm2)
not
recommended
#4/0 AWG x2
(107.2 mm2)
2.4.3 DC Cable Connections
Do not put anything between the battery cable ring lug and the battery post or the fl at metal part
of the inverter’s DC terminal. When connecting the battery cable to the battery post or inverter
DC terminal, the cable should be placed directly against the inverter terminal or battery post.
Incorrectly installed hardware causes a high resistance connection which could lead to poor inverter/
charger performance, and may melt the cable and terminal connections.
Refer to Figures 2-7 and 2-8 to connect the DC cables and to stack the hardware correctly. Tighten
the terminal connections from 10 to 12 lbf-ft (13.6 to 16.3 N-m).
CAUTION: The DC terminal and Flange/Kep nuts are made of stainless steel which have
a high likelihood of seizure. To help prevent the bolt and nut from seizing—causing the
bolts to strip or snap/break off—the use of anti-seize lubricant is highly recommended.
Info: If antioxidant grease or spray is used, apply it after all the connections have been
made and are properly tightened.
Info: A 1/2-inch wrench or socket is used to tighten the 5/16 SAE Flange/Kep nuts.
CAUTION:
nut
split washer
Battery
Temperature
Sensor
Ensure nothing is
placed between the DC
terminal and ring lug.
CAUTION:
Ensure nothing is
placed between
the cable ring lug
and battery post.
battery cable
(with ring lug)
battery
post
Inverter DC terminal
(5/16–18 bolt,
5/8" usable length)
battery cable
(with ring lug)
5/16-18
Flange or
Kep nut
Figure 2-7, Battery Hardware
Installation
Figure 2-8, Inverter DC Hardware
Installation
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 17
Page 26

Installation
2.4.4 Wiring the Battery Bank
WARNING: Lethal currents will be present if the positive and negative cables attached
to the battery bank touch each other. During the installation and wiring process, ensure
the cable ends are insulated or covered to prevent touching/shorting the cables.
Info: DO NOT connect the DC wires from the battery bank to the inverter until 1) all DC
and AC wiring is complete, 2) the correct DC and AC overcurrent protection has been
installed, and 3) the correct DC voltage and polarity have been verifi ed.
Info: For the MS-G Series inverter/charger to perform optimally, a minimum battery
bank of 200 AH is recommended for moderate loads (<1000W) and greater than 400
AH for heavy loads (≥1000W).
Depending upon the voltage of the batteries you use in the installation (6 or 12 VDC), the batteries
must be wired in series, parallel, or series-parallel to provide the correct voltage (see Appendix
B – Battery Information for guidance on wiring batteries together). The interconnecting DC wires
must be sized and rated exactly the same as those used between the battery bank and the inverter.
Place the batteries as close as practical to the inverter, preferably in an insulated and ventilated
enclosure. Allow adequate space above the batteries to access the terminals and vent caps (as
applicable). Also, allow at least 1” (2.5 cm) of space between the batteries to provide good air
fl ow. DO NOT mount the batteries directly under the inverter.
CAUTION: Install batteries in a well ventilated area. Batteries can produce explosive
gasses. For compartment or enclosure installations, always vent batteries to the outside.
Info: To ensure the best performance from your inverter system, batteries should be of
the same size, type, rating, and age. Do not use old or untested batteries.
2.4.5 Battery Temperature Sensor Installation and Wiring
The Battery Temperature Sensor (Figure 2-9) provides the inverter with precise battery temperature
information to automatically adjust the ABSORB and FLOAT charge voltage set-points. This allows
the batteries to be correctly charged under extreme temperature changes.
If the temperature sensor is NOT installed and the batteries are subjected to large temperature
changes, the battery life may be shortened.
The BTS cable may be extended—using a RJ11 connector (female to female) and a standard phone
cable with RJ11 connectors—to a maximum length of 40 feet (12 m). However, your inverter to
battery cable length should not exceed the recommended distance provided in Table 2-2.
To install the BTS:
1. Attach the ring terminal end of the Battery Temperature Sensor to the negative battery terminal;
see Figure 2-7 for proper connection to the battery terminal.
2. Route the sensor’s cable to the inverter following existing wire runs.
3. Connect the RJ11 connector end of the BTS cable to the yellow-labeled BTS port on the inverter
(Figure 1-1, Item 6).
FRONT VIEW
~2"
(~5.1 cm)
Cable
~1"
(~2.54 cm)
~¾”
(~1.9 cm)
SIDE VIEW
(~1.3 cm)
~½”
0.375" diameter
Figure 2-9, Battery Temperature Sensor
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
(~.95 cm)
Page 18
Page 27

Installation
2.4.6 Wiring the Inverter to the Battery Bank
CAUTION: The inverter is NOT reverse polarity protected—if this happens the inverter
will be damaged and will not be covered under warranty.
wires from the batteries to the inverter, verify the correct battery voltage and polarity
using a voltmeter. If the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the negative
terminal of the inverter and vice versa, severe damage will result. If necessary, color
code the cables (with colored tape): RED for positive (+) and WHITE for negative (–)
to avoid polarity confusion.
Info: The DC overcurrent device (i.e., circuit breaker or fuse) must be placed in the
positive (red) DC cable line between the inverter’s positive DC terminal and the battery’s
positive terminal (red)—as close to the battery as possible.
DC Ground Wire
1. Route an appropriately sized DC grounding wire (GREEN or bare wire) from the inverter’s DC
equipment ground terminal (Figure 1-2, Item 7) to a dedicated system ground. Recommended
tightening torque is 45 lbf-in (5.1 N-m). Refer to Section 2.6 for grounding information and
sizing the DC ground wires.
DC Negative Wire
2. Route an appropriately sized DC negative wire (WHITE) from the negative terminal of the
battery bank to the inverter’s negative terminal (Figure 1-2, Item 11).
Info: If installing a battery monitor such as a ME-BMK, install a DC shunt in-line with
the negative battery cable.
Before connecting the DC
DC Positive Wire
3. Mount the circuit breaker or fuse assembly as near as practical to the batteries and leave open
(i.e., no power to inverter).
WARNING: DO NOT close the DC circuit breaker or connect the fuse to connect battery
power to the inverter at this time. This will occur in the Functional Test after the
installation is complete.
CAUTION: If connecting live battery cables to the inverter DC terminals, a brief spark
or arc may occur; this is normal and due to the inverter’s internal capacitors being
charged.
4. Route and connect an appropriately sized DC positive wire (RED) from the inverter’s positive
DC terminal (Figure 1-2, Item 10) to one end of circuit breaker (or DC fuse block).
5. Connect a short wire (same rating as the DC wires) to the other side of the DC circuit breaker
(or one end of the fuse/disconnect assembly) and the other end of the short wire to the positive
terminal of the battery bank (see Figures 2-1 or 2-2 for reference). This is essential to ensure
even charging and discharging across the entire battery bank.
6. Ensure the DC wire connections (on the batteries, inverter, and DC circuit breaker/fuse lugs)
are fl ush on the surface of the DC terminals, and the hardware (lock washer and nut) used to
hold these connections are stacked correctly (see Figures 2-7 and 2-8). Verify all DC connections
are torqued from 10 to 12 lbf-ft (13.6 to 16.3 N-m).
7. Once the DC connections are completely wired and tested, coat the terminals with an approved
anti-oxidizing spray.
8. Attach the red and black terminal covers over the inverter’s DC connectors and secure them
in place with the supplied screws.
9. If the batteries are in an enclosure, perform a fi nal check of the connections to the battery
terminals, then close and secure the battery enclosure.
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 19
Page 28

Installation
2.5 AC Wiring
This section provides information on how to make the AC connections to the MS-G inverter using
the correct AC wire size and corresponding overcurrent protection. Refer to Figures 2-11 thru 2-15
for visual overviews of the various AC wiring confi gurations.
2.5.1 Pre-AC Wiring Requirements
CAUTION: Before installing any AC wiring, review the safety information at the
beginning of this manual and the following to ensure a safe and long-lived system:
• Always use properly rated circuit breakers. If using an electrical sub-panel, circuit
breakers can be moved from the main electrical panel to the sub-panel only if the
breakers are also listed to be installed in the sub-panel.
• AC wiring must be no less than #10 AWG (5.3 mm2) gauge copper wire and be
approved for the application (i.e., residential, RV, or marine wiring).
• DO NOT connect the inverter’s output to an AC power source. This could cause
severe damage to the inverter and is not covered under warranty.
• The wire sizes recommended in this manual are based on the ampacities given in
Table 310.16 (in conduit) or Table 310.17 (in free air) of the National Electrical Code.
ANSI/NFPA 70, for 90ºC (194ºF) copper wire based on an ambient temperature of
30ºC (86ºF).
WARNING: To reduce the risk of fi re, do not connect this inverter to an AC load center
(circuit breaker panel) having multi-wire branch circuits connected.
2.5.2 AC Wire Size and Overcurrent Protection
The AC input and output wiring must be sized per the local electrical safety code requirements
to ensure the wire’s ability to safely handle the inverter’s maximum load current. The AC wiring
must be protected from short circuits and overloads by an overcurrent protection device and have
a means to disconnect the AC circuits. AC overcurrent protection is not included in the inverter
and must be provided as part of the inverter installation. The AC overcurrent protection device
must be a circuit breaker or a fuse/disconnect and be properly sized and branch circuit rated for
the wire it is protecting and the appliances being powered.
Info: When wiring the AC input and output circuits, we highly recommend a full system
Inverter Bypass Switch. This simple item provides a convenient way to isolate the
inverter for battery maintenance, and it could save you hours of downtime—if you ever
need to service your inverter—by enabling you to continue to power your AC loads
without any re-wiring. Because we think it is an essential part of an inverter system,
every Magnum panel (MMP Series) is equipped with an Inverter Bypass Switch.
When the inverter is in Standby mode, the full AC continuous pass-thru capacity of the MS-G
Series inverter/charger (when wired directly to the inverter’s input and output) is 30 amps1. For
a 30-amp continuous pass-thru capability, a 30-amp continuous duty rated breaker is required,
which corresponds to a minimum cable size of #10 AWG/5.3 mm2 (in conduit).
CAUTION: The inverter’s internal AC transfer relay contacts are rated for 30 amps
(each leg), the pass-thru current for relay contact must be no greater than 30 amps or
damage to this relay may occur.
2.5.3 Recommended GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interruption) Outlets
In compliance with UL standards, Sensata has tested the following GFCIs and fi nd that they function
properly when connected to the inverter’s AC output:
• Shock Sentry
TM
#VGF15W • Leviton Smart Lock #8899-A • Hubbel #GF520EMBKA
Note1 – The AC pass-thru capability to the GFCI is 20 amps.
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 20
Page 29

Installation
WARNING: Risk of electric shock. Use only ground-fault circuit interrupters [receptacle(s)
or circuit breaker(s)] that are compatible with your MS-G inverter. Some types may fail
to operate properly when connected to this inverter equipment.
2.5.4 AC Terminal Block Connections
The MS2012-G, MS2812-G, and MS4024-G models have a fi ve-pole AC terminal block and one
AC ground terminal to connect the inverter’s AC input and output wiring. This terminal block (see
Figure 2-10) allows a service/distribution panel (main panel) to be wired to the inverter’s input,
and also allows a dedicated panel (sub-panel) between the inverter’s output wiring and the AC
loads. To access and view the AC terminal block and ground terminal, remove the two Phillips
screws holding the AC wiring access cover plate (see Figure 1-3, Item 15).
Each connection on the AC terminal block is rated to accept one #14 to #6 AWG (2.1 to 13.3 mm2)
CU stranded wire, or two #12 AWG (3.3 mm2) CU stranded wires. Each connection uses a M3.5
slotted head screw, and the maximum tightening torque is 16 lbf-in (1.8 N-m).
Info: One of the AC wiring confi gurations [SI/SO (50A), Figure 2-13] uses a #6 AWG
(13.3 mm2) CU wire to carry 60 amps, and splits to two wires to allow 30 amps for each
leg (i.e., AC HOT 1 IN and AC HOT 2 IN). IDEAL Industries Inc. (www.idealindustries.
com) manufactures a crimp connector (PN: 412) and a separate insulator (PN: 417)
that allow up to two #8 AWG (8.4 mm2) wires, with one #6 AWG (13 mm2) wire to be
connected together.
Info: To comply with ABYC requirements for marine installations, the AC terminal has
a stainless steel wire protector to prevent wire damage from the set-screw.
Info: The inverter’s NEUT IN and NEUT OUT terminals are electrically isolated from each
other while inverting. This is related to the neutral-ground bonding requirement and
helps prevent ground-loops (see Section 2.6.5 for more information). If the installation
requires the input and output neutrals to be connected together, the inverter’s neutralto-ground connection must be disconnected (see Section 2.6.6).
The AC ground terminal can accept one #14 to #6 AWG (2.1 to 13 mm2) CU stranded wire. It uses
a slotted head screw and has a recommended maximum tightening torque of 45 lbf-in (5.1 N-m).
For multiple ground wires, use a pressure or mechanical connector to attach the single wire from
the AC ground terminal to the input and output ground connections.
HOT 2 IN
HOT 2 OUT
NEUT 2 OUT
HOT 1 IN
NEUT IN
AC GROUND
(In & Out)
Figure 2-10, AC Terminal Block (MS2012-G/MS2812-G/MS4024-G)
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 21
Page 30

Installation
2.5.5 AC Conductor Wiring (MS2012-G, MS2812-G, MS4024-G models)
The following steps are basic guidelines for installing and connecting the AC wiring to and from
all MS-G Series inverters (except a MS2000-G Series model inverter—for instructions on wiring
a MS2000-G inverter, refer to Section 2.5.7). Before proceeding, refer to Table 2-3 to determine
your AC wiring confi guration.
WARNING: Before making any AC connections, make sure the inverter is disconnected
from the battery and no AC power is connected to the inverter.
Wiring the Inverter AC Input
1. Remove the two Phillips screws on the AC wiring access cover (Figure 1-3, Item 15) to access
the internal AC terminal block (see Figure 2-10).
2. Route the wires (hot, neutral, and ground) from the AC electrical main panel through one of
the strain relief clamps on the inverter (Figure 1-2, Item 8). Tighten the strain relief clamp
securely on the wires. Always leave a little extra slack in the wiring.
3. Connect the hot wire (BLACK) from the main panel’s dedicated breaker to the inverter’s AC
HOT 1 IN terminal. Tighten the AC HOT 1 IN terminal to 16 lbf-in (1.8 N-m).
Info: You must connect to the HOT 1 IN terminal if you want to use the battery charger.
Info: Depending on the AC wiring confi guration, you may need to connect a wire to
the inverter’s AC HOT 2 IN terminal—refer to your particular confi guration drawing
(Figures 2-12 thru 2-14).
4. Connect the neutral (WHITE) from the main panel’s neutral busbar to the inverter’s AC NEUT
IN terminal. Tighten the AC NEUT IN terminal to 16 lbf-in (1.8 N-m).
Wiring the Inverter AC Output (Figures 2-12 thru 2-14)
5. Route the wires (hot, neutral, and ground) through the unused strain relief clamp on the
inverter (Figure 1-2, Item 8) to the AC electrical sub-panel. Tighten the strain relief clamp
securely on the wires.
6. Connect the hot (RED or BLACK) wire from the inverter’s AC HOT 2 OUT terminal to the subpanel‘s main breaker. Tighten the AC HOT 2 OUT terminal to 16 lbf-in (1.8 N-m).
7. Connect the neutral (WHITE) from the inverter’s AC NEUT 2 OUT terminal to the sub-panel’s
neutral busbar. Tighten the AC NEUT 2 OUT terminal to 16 lbf-in (1.8 N-m).
Wiring the Inverter AC Ground
8. Combine the ground (GREEN) wire from the main panel’s ground busbar and the ground (GREEN)
wire from the sub-panel’s ground busbar (if applicable). After these grounds are combined,
connect them to the inverter’s AC GROUND terminal. Tighten the AC GROUND terminal to
16 lbf-in (1.8 N-m).
AC Wiring Inspection
1. Verify all wire runs are secured. If installed in a mobile installation, use wire ties or other nonconductive fasteners to prevent chafi ng or damage from movement and vibration.
2. Verify strain reliefs or grommets are in place to prevent damage to the wiring or conduit where
it passes through walls/bulkheads or other openings.
3. After verifying all AC connections are correct and all inverter AC terminal screws are torqued to
16 lbf-in (1.8 N-m), replace the AC wiring access cover and the covers on the main electrical/
distribution panel.
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 22
Page 31

Installation
2.5.6 AC Wiring Confi gurations (MS2012-G, MS2812-G, MS4024-G)
The following table provides the different wiring confi gurations for installing and connecting the AC
conductors to and from the inverter (refer to Figures 2-11 to 2-14 for installation drawings showing
these confi gurations). Refer to Table 2-4 (and Figures 2-15 & 2-16) for the MS2000-G model.
Table 2-3, AC Input/Output Wiring Confi gurations
AC Input
Source
1
SI
Single In
120 VAC @ ≤30
amps
SI/SO
Single In/
Single Out
(≤ 30A output)
120 VAC @ ≤30
amps
SI/SO
Single In/
Single Out
(≤ 50A output)
120 VAC @ >30
amps
(60 amps max.)
DI/SO
Dual In/
Single Out
120/240 VAC
(or 2 separate
legs of 120 VAC)
@ ≤30 amps/leg
Reason to Use Have an 120
VAC source that
is ≤30 amps,
and using the
GFCI outlet to
connect loads.
Appropriate
Models
MS2012-G
MS2812-G
MS4024-G
Maximum
Input Breaker
30A
(single pole)
Have an 120 VAC
source that is ≤30
amps.
Requires a
separate inverter
sub-panel.
MS2012-G
MS2812-G
MS4024-G
30A
(single pole)
Have an 120 VAC
source that is
>30 amps.
Requires a
separate inverter
sub-panel.
MS2012-G
MS2812-G
MS4024-G
60A
(single pole)
Want dedicated
pass-thru while
AC source is on.
Requires a
separate inverter
sub-panel.
MS2012-G
MS2812-G
MS4024-G
30A
(dual pole)
Required
Minimum
Wire Size
(AWG)
-
#10 AWG
(In)
-
#10 AWG In
(split into two #10
AWG for HOT 1 &
HOT 2 IN)
-
#6 AWG In
(split into two
#10 AWG for
HOT 1 & HOT 2
#10 AWG
(In & Out)
IN)
#10 AWG Out
(HOT 2 OUT)
#10 AWG Out
(HOT 2 OUT)
Maximum
2400W
3600W
6000W
6000W
Inverter Pass-
thru Capacity
-
Output
Confi gurations
20A @ 120 VAC
30A @ 120 VAC =
20A @ 120 VAC =
-
3600W
(HOT 2 OUT)
or
-
30A @ 120 VAC
(HOT 2 OUT)
and
20A @ 120 VAC
(GFCI outlet)
30A @ 120 VAC
(HOT 2 OUT)
20A @ 120 VAC
(GFCI outlet)
2400W
(GFCI outlet)
Wiring
Diagram
1
Note
– AC Source is from either the utility/grid power (i.e., shorepower) or an AC generator.
2
Note
– If two legs of 30A @ 120 VAC are used, they must be from the same source (i.e., have a common
neutral). For example, 2 legs from a 3-phase source can be used.
Figure 2-11 Figure 2-12 Figure 2-13 Figure 2-14
2
-
-
and
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 23
Page 32

GFCI
Installation
AC Terminal Block
(AC input and output wiring)
SINGLE IN
(fr om mai n pan el)
(fr om mai n pan el)
AC HOT 1 IN
AC NEUT IN
AC GROUNDS
(fr om mai n
panel)
In mobile installations: neutral is typic ally not
conn ec te d to ground i n m ain pa nel.
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
30
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Main Panel
(Utility/Generator Input)
MS-G Series Inverter
..Maximum..
30- a m p break e r
(singl e pole)
required to
invert er A C inpu t
Figure 2-11, AC Wiring for a Single In Confi guration
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 24
Page 33

Installation
AC Terminal Block
(AC input and output wiring)
SI/SO wiring (≤ 30A)
(fr om mai n pan el)
(fr om mai n pan el)
AC HOT 2 OUT
AC NEUT 2
AC HOT 2 IN
OUT
(fr om mai n pan el)
AC HOT 1 IN
AC NEUT IN
GFCI
MS-G Inverter
(fr om mai n pan el,
AC GROUNDS
to outlet)
See NOTE below
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
30
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Maximum 30-amp breaker
(singl e pole) required to
invert er A C inpu t
NOTE: In mobile installations, the
OFF
OFF
ON
neutr al is typicall y not connected to
grou nd in main panel.
120
VAC
Main Panel
(Utility/Generator Input)
Direct from Inverter
(Inverter Loads)
Figure 2-12, AC Wiring for Single In (30A) – Single Out Confi guration
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 25
Page 34

AC Terminal Block
(AC input and output wiring)
Installation
SI/SO wiring (≤ 50A)
(fr om mai n pan el)
AC NEUT 2
OUT
AC HOT 2 IN
(fr om main pane l)
AC HOT 2 OUT
(fr om mai n pan el)
AC HOT 1 IN
AC NEUT IN
GFCI
MS-G Inverter
(fr om mai n pan el,
AC GROUNDS
to outlet)
See NOTE below
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
60
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Main Panel
(Utility/Generator Input)
Maximum 60-amp breaker
(single po l e) r equi r e d to
invert er A C input
NOTE: In mobile installations, the
neutr al is typically not conn ected to
grou nd in main panel.
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
120
VAC
120
VAC
Sub-Panel and Outlets
(Inverter Loads)
Figure 2-13, AC Wiring for Single In (50A) – Single Out Confi guration
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 26
Page 35

Installation
AC Terminal Block
(AC input and output wiring)
DUAL IN/SINGLE OUT wiring
(fr om mai n pan el)
AC NEUT 2
OUT
AC HOT 2 IN
(fr om mai n pan el)
AC HOT 2 OUT
(fr om mai n pan el)
AC HOT 1 IN
AC NEUT IN
(fr om mai n pan el,
AC GROUNDS
to outlet)
GFCI
MS-G Inverter
See NOTE below
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
30
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
30
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Main Panel
(Utility/Generator Input)
Figure 2-14, AC Wiring for Dual In – Single Out Confi guration
Maximum 30-amp breaker
(double pole) required to
invert er A C inpu t
NOTE: In mobile installations, the
neutral is typically not connected to
grou nd in main panel.
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
120
VAC
Sub-Panel and Outlet
(Inverter Loads)
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 27
Page 36

Installation
2.5.7 AC Conductor Wiring (MS2000-G models)
The MS2000-G offers a cost-effective alternative to the MS2012-G while still providing the same
features. This model has a slightly smaller height, but otherwise has the same footprint as the
other MS-G Series inverters. The MS2000-G uses wire leads to connect the AC wires and can be
wired in a single in (only) or single in – single out confi guration.
The following steps are basic guidelines for installing and connecting the AC wiring into and out
of the inverter. Refer to Table 2-4 to determine your AC wiring confi guration before beginning.
Refer to Figures 2-15 & 2-16 when wiring your MS2000-G inverter.
WARNING: Before making any AC connections, make sure the inverter is disconnected
from the battery and that no AC power is connected to the inverter.
Info: The MS2000-G inverter has a GFCI outlet and pigtail output wires.
Wiring the Inverter AC Input
1. Remove the two Phillips screws on the AC access cover (Figure 1-3, Item 15) to access the
internal AC wiring.
2. Route the wires (hot, neutral, and ground) from the AC electrical main panel through one of
the strain relief clamps to the AC INPUT. Tighten the strain relief clamp securely on the wires.
Always leave a little extra slack in the wiring.
3. Connect the AC hot in wire (BLACK) from the main panel’s dedicated breaker to the inverter’s
(BLACK) AC HOT IN wire using fi eld wiring leads.
4. Connect the AC neutral in wire (WHITE) from the main panel’s neutral busbar to the inverter’s
(WHITE) AC NEUT IN wire using fi eld wiring leads.
Wiring the Inverter AC Output to a Sub-panel (Figure 2-16)
5. Route the wires (hot, neutral, and ground) from the inverter’s AC OUTPUT to the AC electrical
sub-panel through the other strain relief clamp. Tighten the strain relief clamp securely on the
wires—leaving a little slack in the wiring.
6. Connect the inverter’s HOT OUT (ORANGE) wire to the sub-panel’s hot input breaker using
fi eld wiring leads.
7. Connect the inverter’s AC NEUT OUT (WHITE w/BLACK) wire to the wire from the sub-panel’s
neutral busbar using fi eld wiring leads.
Wiring the Inverter AC Ground
8. Combine the ground (GREEN) wire from the main panel’s ground busbar and the ground
(GREEN)wire from the sub-panel’s ground busbar (if applicable). After these grounds are
combined, use fi eld wiring leads to connect them to the inverter’s AC GROUND (GREEN) wire.
AC Wiring Inspection
1. Verify all wire runs are secured. If installed in a mobile installation, use wire ties or other nonconductive fasteners to prevent chafi ng or damage from movement and vibration.
2. Verify strain reliefs or grommets are in place to prevent damage to the wiring or conduit where
it passes through walls/bulkheads or other openings.
3. After verifying all AC connections are securely fastened, replace the AC wiring access cover
and the covers to the main electrical/distribution panel.
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 28
Page 37

Installation
2.5.8 AC Wiring Confi guration (MS2000-G models)
The following table provides the different wiring confi gurations for installing and connecting the
AC conductors to and from MS2000-G model inverters (see Figures 2-15 and 2-16 for installation
diagrams showing these confi gurations).
Table 2-4, AC Input/Output Wiring Confi gurations (MS2000-G models)
SI
Single In
1
AC Input Source
120 VAC @ ≤30 amps 120 VAC @ ≤30 amps
Reason to Use Have a 120 VAC source
that is ≤30 amps, and
using the GFCI outlet to
connect loads.
Appropriate
MS2000-G MS2000-G
Single In/Single Out
Have a 120 VAC source that
Requires a separate
inverter sub-panel.
SI/SO
is ≤30 amps.
Models
Maximum
Input Breaker
30A
(single pole)
30A
(single pole)
Required
-
Minimum Wire
Size
Maximum
-
#10 AWG
(In)
2400W
-
#10 AWG
(In & Out)
3600W
Inverter Pass-
thru capacity
-
Output
Confi gurations
20A @ 120 VAC
(GFCI outlet)
-
-
30A @ 120 VAC = 3600W
(HOT 1 OUT)
or
20A @ 120 VAC = 2400W
(GFCI outlet)
Wiring Diagram
1
Note
– AC Source is from either the utility/grid power (i.e., shorepower) or an AC generator.
Figure 2-15 Figure 2-16
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 29
Page 38

Installation
AC Terminal Block
(AC input and output wiring)
SINGLE IN wiring
GFCI
In mobile installations: neutral is typic a lly not
conn e cte d to gr o und in the main pane l .
AC HOT IN
BLACK
WHITE
AC NEUT IN
ORANGE
AC GROUND
GREEN
MS2000-G Inverter
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
30
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
.Maximum 30-amp
brea ke r (si ngle pole )
required to inverter
AC input.
Main Panel
(Utility/Generator Input)
Figure 2-15, AC Wiring for a Single In Confi guration (MS2000-G)
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 30
Page 39

Installation
AC Terminal Block
(AC input and output wiring)
SINGLE IN / SINGLE OUT wiring
AC HOT IN
BLACK
WHITE
AC NEUT IN
AC NEUT OUT
AC HOT OUT
AC GRNDS
MS2000-G Inverter
GFCI
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
See NOTE below
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
30
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
..Maximum..
30- a m p b r e a ker
(singl e po l e)
required to
invert e r AC inpu t
NOTE: In mobile installations, the
neutr al is typically not connected to
ground in m ain panel.
ON
120
VAC
Main Panel
(Utility/Generator Input)
Sub-Panel and Outlet
(Inverter Loads)
Figure 2-16, AC Wiring for a Single In – Single Out Confi guration (MS2000-G)
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 31
Page 40

Installation
2.6 Grounding Inverters
The inverter/charger should always be connected to a permanent, grounded wiring system.
An inverter system that is properly grounded will limit the risk of electrical shock, reduce radio
frequency noise from the inverter, and minimize excessive surge voltages induced by lightning. This
is done by ensuring there is a well-defi ned, very low-resistance path from the electrical system to
the grounding system. This low-resistance path helps stabilize the electrical system voltage with
respect to ground and carries fault currents directly to ground if the electrical system malfunctions.
To understand how the conductors in the electrical circuit will be connected to the system ground,
the following terms should be understood:
• Grounded Conductor (GC): The wire/cable in the electrical system that normally carries
current (usually AC neutral and/or the DC negative), and is intentionally connected or “bonded”
to the ground system. This wire, or the ends of this wire, should be colored white or gray.
• Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC): A wire/cable that does not normally carry current
and is used to connect the exposed metal parts of equipment—that might be accidentally
energized—to the grounding electrode system or to the grounded conductor. This wire, or the
ends of this wire, should be green or green with a yellow stripe; this wire can be bare copper.
• Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC): The wire/cable that does not normally carry
current and connects the grounded conductor and/or the equipment grounding conductor to
the grounding electrode at the service equipment.
• Grounding Electrode (GE): A ground rod or conducting element that establishes an electrical
connection to the earth.
• System bonding jumper (SBJ): The connection between the grounded circuit conductor in
the electrical system and the equipment grounding conductor at a separately derived system.
The MS-G Series inverter/charger uses both AC and DC power; however, the AC electrical system
is isolated from the DC electrical system by an internal transformer. Although this inverter/charger
has two electrical systems, each electrical system must be properly grounded and connected to
a common “earth” reference. Refer to Figure 2-17.
For proper grounding, each electrical system must connect all exposed metal parts of equipment
(via equipment grounding conductors – EGC) and one of the current-carrying conductors (grounded
conductor – GC) together at a common point (ground busbar – GBB), usually by a system bonding
jumper (SBJ) in an electrical service disconnect panel. The common point of each electrical system
is then connected (via grounding electrode conductor – GEC) to the common ground reference,
such as a ground rod (grounding electrode – GE). This connection to earth should only be made
at one point in each electrical system; otherwise, parallel paths will exist for the currents to fl ow.
These parallel current paths would represent a safety hazard and are not allowed in installations
wired per the NEC/CEC.
AC Service
Panel
Neutral
GBB GBB
SBJ
GEC-AC
or
Grounding Electrode
(AC side dedicated)
Figure 2-17, Grounding System for MS-G Series
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
GE
MS Series Inverter/Charger
Hot
AC
GC
Neu tral
AC Ground DC Ground
EGC
Grounding
System
Grounding Electrode
(AC and DC sides shared)
GE
DC Electrical SystemAC Electrical System
Positive
DC
Neg ative
GC
EGC
GEC-DC
GE
Grounding Electrode
(DC side dedicated)
DC Service
Panel
Negative
SBJ
or
Page 32
Page 41

Installation
2.6.1 Sizing the Grounding Electrode Conductors
AC Side – The size of the AC grounding electrode conductor (GEC–AC) depends on the size of
the largest ungrounded conductor feeding the AC load center. One #8 AWG (8.4 mm2) copper
conductor will serve as an AC grounding electrode conductor (GEC–AC) for AC power conductors
smaller than and including #2 AWG (33.6 mm
Table 2-5, AC Grounding Electrode Conductor Sizing
2
) copper. See Table 2-5 for additional values.
Size of Largest Ungrounded
Conductor
#2 AWG (33.6 mm
#1 to #1/0 AWG (42.4 to 53.5 mm
#2/0 or #3/0 AWG (67.4 to 85.0 mm
Over #3/0 AWG (85.0 mm
through 350 kcmil
2
) or smaller #8 AWG (8.4 mm2)
2
)
2
) #6 AWG (13.3 mm2)
2
) #4 AWG (21.1 mm2)
Minimum Size of Grounding
Electrode Conductor
#2 AWG (33.6 mm
2
)
DC Side – To size the DC grounding electrode conductor, you must fi rst determine which one
of the following three methods will be used to connect the DC and AC grounding points in the
inverter’s two electrical systems to the common “earth” ground:
Method 1 (Figure 2-18): This method uses a separate grounding electrode for the DC system
and the AC system. In this method—since there are multiple connections to the DC grounding
electrode (GEC–DC)—the size of the DC grounding electrode conductor cannot be smaller than
the largest conductor in the DC system (usually the battery-to-inverter cable).
The DC grounding electrode (GE–DC) must be bonded to the AC grounding electrode (GE–AC)
to make a grounding electrode system. This bonding conductor (BC) cannot be smaller than the
largest grounding electrode conductor—either AC or DC.
DC Electrical SystemAC Electrical System
AC Service
Panel
Neutral
GBB GBB
SBJ
GEC-AC
MS Series Inverter/Charger
Hot
AC
GC
Neu tral
AC Ground DC Ground
EGC - AC
Grounding
System
Positive
DC
Neg ative
EGC - DC
GC
DC Service
Panel
Negative
SBJ
GEC-DC
GE
Grounding Electrode
(AC side dedicated)
BC
GE
Grounding Electrode
(DC side dedicated)
Figure 2-18, Multiple Connections to DC Ground Rod (Method 1)
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 33
Page 42

Installation
Method 2 (Figure 2-19): When the AC and DC service panels are near each other, then the AC
grounding electrode conductor (GEC–AC) and DC grounding electrode conductor (GEC–DC) can be
connected to a single grounding electrode. In this method—since there are multiple connections to
the DC grounding electrode (GEC–DC)—the size of the DC grounding electrode conductor cannot
be smaller than the largest conductor in the DC system (usually the battery-to-inverter cable).
DC Electrical SystemAC Electrical System
AC Service
Panel
Neutral
GBB GBB
SBJ
MS Series Inverter/Charger
Hot
AC
GC
Neu tral
AC Ground DC Ground
EGC - AC
Grounding
Positive
DC
Neg ative
EGC - DC
GC
System
GEC-AC
GE
Grounding Electrode
(AC and DC sides shared)
DC Service
Panel
Negative
SBJ
GEC-DC
Figure 2-19, Multiple Connections to DC Ground Rod (Method 2)
Method 3 (Figure 2-20): The AC grounding electrode conductor (GEC–AC) is bonded to the DC
ground point and the DC grounding electrode conductor (GEC–DC) is the only connection to the
grounding electrode, which must be a rod, pipe, or plate electrode.
In this method, since there is only one connection to the ground rod, the DC grounding electrode
conductor is not required to be larger than #6 AWG (13 mm2) copper. The reasoning for allowing
this smaller grounding electrode conductor is that it is only required to stabilize the system voltage
with respect to earth, and the other properly-sized conductors in each electrical system will safely
carry any fault currents if they occur.
AC Service
Panel
Neutral
GBB GBB
SBJ
Figure 2-20, Single Connection to DC Ground Rod (Method 3)
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
GC
EGC - AC
GEC-AC
DC Electrical SystemAC Electrical System
MS Series Inverter/Charger
Hot
AC
Neu tral
AC Ground DC Ground
Positive
Neg ative
EGC - DC
Grounding
System
DC Service
DC
GC
Grounding Electrode
(DC side dedicated)
Negative
SBJ
GE
Panel
GEC-DC
Page 34
Page 43

Installation
2.6.2 System Bonding Jumper
The MS-G Series inverter does not include an internal bond between the grounded conductor (AC
neutral/DC negative) and the equipment grounding terminals. This bond [system bonding jumper
(SBJ)] is usually done in the main distribution panel for each electrical system.
CAUTION: There should be one and only one point in each electrical system (both
AC and DC) where the grounded conductor is attached to the grounding electrode
conductor.
AC Side – The size of the system bonding jumper (SBJ) in the AC electrical system is based on
the area of the largest AC ungrounded conductor. In accordance with the NEC, use Table 2-6 to
determine the system bonding jumper size compared to the largest AC ungrounded conductor.
DC Side – The size of the system bonding jumper (SBJ) in the DC electrical system must not be
smaller than the DC grounding electrode conductor (GEC–DC) used, which is determined from the
grounding method that will be used (see Section 2.6.1).
2.6.3 Equipment Grounding Conductor
The inverter case and all other non-current carrying exposed metal surfaces in the entire electrical
system that may be accidentally energized must be grounded. The equipment-grounding conductor
must be sized to safely carry the maximum ground-fault current likely to be imposed on it from
where a ground-fault may occur. In accordance with the NEC, use Table 2-6 to size the equipmentgrounding conductors. This table requires that the equipment-grounding conductor be sized
according to the rating of the overcurrent device protecting the circuit.
CAUTION: The connections and wiring for the equipment-grounding conductor must
be continuous to allow fault currents to properly operate overcurrent devices. Where
equipment is removed and this disconnects the bonding connection between the grounding
electrode conductor and exposed conducting surfaces, a bonding jumper must be installed
while the equipment is removed.
AC Side – Where the AC output from the inverter is connected to an AC load center, there should
be an equipment grounding conductor connected between the inverter case and the grounding
point in the AC load center. The AC equipment grounding conductor (EGC–AC) is sized per Table
2-6 and is connected to the inverter’s AC equipment grounding terminal shown in Figure 2-10 (or
a grounding wire for the MS2000-G models).
DC Side – Since the currents on the DC side are higher than the AC side (10 times at 12 volts,
5 times at 24 volts), the equipment grounding needs are different. The DC equipment grounding
conductor (EGC–DC) is sized per Table 2-6 and connected to the DC equipment grounding terminal
on the inverter as shown in Figure 1-2, Item 7.
Table 2-6, Equipment Grounding Conductor Sizing
Rating of Overcurrent
Device
15 amps
20 amps
30-60 amps
100 amps
200 amps
300 amps
400 amps
Minimum Size of Copper
Ground Wire
#14 AWG (2.1 mm
#12 AWG (3.3 mm
#10 AWG (5.3 mm
#8 AWG (8.4 mm
#6 AWG (13.3 mm
#4 AWG
#3 AWG (26.6 mm
(21.1 mm2)
2
)
2
)
2
)
2
)
2
)
2
)
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 35
Page 44

Installation
2.6.4 Grounding on Boats
When installing the MS-G Series inverter/charger on a boat, there are several considerations that
must be followed when grounding to ensure a safe installation, prevent galvanic corrosion, and
to adhere to ABYC (American Boat and Yacht Council) standards.
Ensure a Safe Ground Connection
When AC on the boat is being supplied by shorepower, the onboard neutral should be connected
to safety ground on the dock
anywhere on the boat when shorepower is present. When AC on the boat is being supplied by
the MS-G Series inverter, the inverter’s output neutral is connected to safety ground through an
internal relay, using its neutral-to-ground connection (shown in Figure 2-23).
The DC ground terminal on the MS-G Series must also be connected to the boat’s safety ground
bus. This ensures that both the inverter’s AC and DC ground terminals are connected to the boat’s
safety ground bus as a safety measure to provide protection against faults, and to provide a path
for AC fault currents while the boat is connected to shorepower.
Preventing the Risk of Corrosion
The inverter’s AC and DC ground terminals must be connected to the boat’s safety ground to
provide an important safety feature. However, this ground connection introduces the risk of galvanic
corrosion and/or electrolysis of the boat’s underwater metallic hardware.
Two possible solutions are typically used to maintain the correct onboard grounding requirements
while greatly reducing (if not eliminating) the risk of galvanic corrosion. These solutions would be
either using a galvanic isolator or an onboard isolation transformer.
Galvanic isolators allow high AC voltage faults to pass, but block low voltage corrosion/electrolysis
currents from conducting.
Marine isolation transformers allow the shorepower to be connected to one side of the transformer,
and the boat’s AC wiring system is connected to the other side. Since transformers do not allow
DC currents to pass, the problem with galvanic corrosion is eliminated.
ABYC Inverter/Charger Grounding Requirements
• DC Grounding Connections:
1) The DC grounding conductor (equipment ground) shall be:
a) connected from the metallic case or chassis of the inverter/charger to the engine negative
terminal or its bus,
b) of an ampacity equal to that of the DC positive conductor (under certain conditions, there
is an exception to allow this conductor to be one size smaller—refer to the ABYC standard).
2) The inverter/charger’s negative battery terminal and DC grounded conductor (negative
cable) shall not be connected to the inverter case or chassis at the inverter/charger itself.
• AC Grounding Connections:
1) The AC grounding conductor (green) shall be connected to the inverter/charger in a manner
so that the AC ground connection will not be disconnected in servicing. This conductor is in
addition to and independent of the DC grounding conductor.
2) The neutral for AC power sources shall be grounded only at the following points:
a) the shorepower neutral is grounded only through the shorepower cable and not grounded
on board the boat,
b) the inverter neutral shall be grounded at the inverter, and the output neutral shall be
disconnected from ground when the inverter is operating in the charger/pass-through mode,
c) on systems using an isolation transformer or a polarization transformer, the inverter
neutral (and the transformer secondary neutral) may be grounded at the AC main grounding
bus instead of at the inverter.
1
Note
– The onboard neutral is not directly connected to safety ground on the dock if an isolation
transformer is installed.
2
Note
– See the ABYC Standard for complete AC/DC grounding requirements.
1
. Consequently, neutral and safety ground should not be connected
1
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 36
Page 45

Installation
2.6.5 Neutral to Safety Ground Bonding
The standards for safely wiring residential, commercial, RV/truck, and marine installations in the
United States require the neutral and safety ground to be connected at the AC source; whether it
is the utility feed in your home, an inverter, or a generator. This is to establish a specifi cation that
maximizes the possibility that a circuit breaker will activate if a hotwire-to-ground fault occurs.
These standards also require that the AC neutral be connected to safety ground (often called a
“bond”) in one, and only one, place at any time. The single bond is established in order to make
the electrical panel’s neutral line safe, by connecting it to ground. Without this bond, the neutral
can have up to 60 VAC with respect to ground. On the other hand, if more than one bond is
established, currents can circulate between neutral and ground and cause “ground-loop” currents.
These ground-loops can trip GFCIs, cause an electric shock hazard, and may be the reason for
other annoying side effects.
In applications where you are using an inverter as one of your AC sources along with another
AC source (i.e., utility power or generator), there is the potential of having multiple connections
(bonds) between neutral and ground. Therefore, you must ensure that the inverter does not also
connect the neutral-to-ground while the other AC source is actively powering the inverter loads.
This can be prevented if your inverter is equipped with automatic neutral-to-ground switching.
WARNING: In most electrical systems, the neutral-to-ground bond is located in the
main utility service entrance panel. Remove any bond downstream from the inverter
to prevent multiple bonds. If there is an inverter sub-panel—separate from a main
electrical panel—it should have a removable wire that allows the neutral bus to be
unbonded from the ground busbar.
All MS-G Series inverter/chargers have automatic neutral-to-ground switching to specifi cally work
in multiple source or mobile (i.e., truck/RV/boat) applications. The MS-G Series inverters use an
internal relay that automatically connects the AC neutral output terminal to the vehicle/boat’s
ground while inverting (Inverter mode) to provide the neutral-to-ground bond; as shown in Figure
2-21. However, when an external AC source (i.e., shorepower or a generator) is connected, another
neutral-to-ground connection is introduced in the system. When the MS-G Series is connected to
this external AC source and goes into Standby mode, the internal relay automatically opens the
neutral-to-ground connection as shown in Figure 2-22. This design keeps two neutral-to-ground
connections from occurring at the same time, thereby preventing an electrical shock hazard
between the vehicle/boat’s neutral and the external AC source’s neutral.
Inside MS-G Series
(Inverter Mode)
NEUT IN
GROUND
Figure 2-21, Neutral-to-Ground
Connection (Inverter Mode)
* – Normally located in the AC compartment; however, on the MS2000-G model the neutral-to-ground is
located internally on the AC board and cannot be disconnected.
Neu-Gnd Relay (K1)
NEUT IN
NEUT OUT
GROUND
Neutral -to- G round Connection
(inside AC compartment)*
Figure 2-22, Neutral-to-Ground
Connection (Standby Mode)
Inside MS-G Series
(Standby Mode)
Neu-Gnd Relay (K1)
NEUT OUT
Neutral -to- G round Connection
(inside AC compartment)*
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 37
Page 46

Installation
2.6.6 Disabling the Neutral-to-Ground Connection
All MS-G Series inverter/chargers have the automatic neutral-to-ground switching feature. In some
installations/jurisdictions, this feature must be disabled by disconnecting the neutral-to-ground
connection¹. If you are not sure whether you must disable this feature, check your local code
requirements. The following steps will guide you in disabling the neutral-to-ground switching feature.
Note¹ – The neutral-to-ground switching feature cannot be disabled in MS2000-G models.
Info: The ground connection from the inverter’s AC and DC ground terminals should
still be connected to the system ground, even if ground switching has been disabled.
WARNING: Fire and Shock Hazard—disconnect all AC and DC sources before working in
the AC wiring compartment.
1. Locate and remove the AC access cover plate
(Figure 1-3, Item 15) on the side of the MS-G
Series inverter.
2. Inside the AC wiring compartment, locate
the green wire with the insulated connector;
see Figure 2-23. This insulated connector
connects the neutral and ground inside the
inverter while inverting.
3. Pull the two ends of the insulated connector
apart to separate the green wire; this will
prevent the neutral and ground from connecting inside this inverter.
4. Move the two disconnected ends away from
each other and push back out of the way. You
must ensure that the two connector ends will
not have any contact with any other wires
within the AC compartment. You may want
to use electrical tape to insulate the ends and
secure them out of the way.
Figure 2-23, Disconnecting the
Neutral-to-Ground Connection
Neutral-to-
Ground
Connection
(green wire)
2.6.7 Connecting a Large DC Ground Wire
Some marine installations require the DC ground wire to be the same size or one size smaller
than the negative cable. Use the following steps to allow a larger ground wire to be connected.
1. Locate and remove the AC access cover plate
(Figure 1-3, Item 15) on the MS-G inverter.
2. Locate the DC ground terminal (Figure 1-2,
Item 7).
3. Within the AC wiring area, locate the hex nut
on the back side of the DC ground terminal. After locating the hex nut, use a 7/16”
wrench/nut driver to remove the hex nut,
bolt, lock washer, and DC ground terminal—
remove them from the chassis.
4. Reverse the removed bolt and place it back
in the chassis hole to attach a correctly sized
ground cable with a ring terminal to the MS-G
Series chassis as shown in Figure 2-24.
Note: Ring terminal must have a hole size ≥1/4”.
5. Place the washer and nut on the bolt over the
ground cable and securely tightened the nut
[from 4 to 5 lbf-in (5.4 to 6.8 N-m)].
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Figure 2-24, Connecting a Large DC
Ground Wire
DC Ground
terminal bolt/nut,
reversed and
tightened.
Page 38
Page 47

Installation
2.7 Inverter Notifi cation Requirements
When an inverter is installed in a building, facility or structure, the NEC (National Electrical Code)
requires a label or plaque to be provided. This label/plaque is required to be easily visible and
provide information that informs personnel on the location of all electrical system disconnects.
This is to ensure all power to a building is quickly located and shut down in an emergency. There
are also specifi c requirements for this label/plaque depending on the inverter application, they
are as follows.
2.7.1 Facilities with Standalone Systems
Any building, facility, or structure with a photovoltaic power system that is not connected to a
utility service source and is a standalone system must have a permanent plaque or directory
installed on the exterior of the building or structure at a readily visible location acceptable to the
Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ). The plaque or directory must provide the location of system
disconnecting means and information regarding whether the structure contains a standalone
electrical power system.
2.7.2 Facilities with Utility Services and PV Systems
Buildings, facilities, or structures with both utility service and a photovoltaic system must have a
permanent plaque or directory providing the location of the service disconnecting means and the
photovoltaic system disconnecting means if they are not located at the same location.
2.7.3 Inverter Warning Label
A warning label as shown in Figure 2-25 is provided to inform all personnel that an inverter is
installed in your electrical system. Affi x this label in a clearly visible location at the electrical panel
that is being powered by the inverter. This is because it might be falsely assumed that the panel
is no longer “hot” after the AC power has been shut off, when power may actually still be available
due to the inverter automatically powering the panel.
This electrical system is equipped with an Automatic
Generator Starting (AGS) device and/or an inverter.
Disconnect all AC and DC power to the AGS and/
or inverter before performing any service to the
electrical system. Failure to do so can result in shock
causing serious injury or death.
PN: 62-0002 Rev A
Figure 2-25, Warning Label
2.8 Final Inspection
1. Verify all cables/conduit runs are secured with wire ties or other non-conductive fasteners to
prevent chafi ng or damage from movement and vibration.
2. Verify strain reliefs or grommets are in place to prevent damage to the wiring or conduit where
it passes through walls, bulkheads, or other openings.
3. Verify all AC connections are correct and torqued to a maximum of 16 lbf-in (1.8 N-m).
4. Replace the covers on the main electrical/distribution panel.
5. Replace the chassis access cover.
6. Verify the inverter’s front panel switch is in the “OFF” position.
Important: If required by code, have the installation inspected by an electrical inspector.
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 39
Page 48

Installation
2.9 Functional Test
After all electrical connections to the inverter, batteries, AC source and sub-panel have been
completed, follow these steps to test the installation and the inverter’s operation.
CAUTION: Use a multimeter to verify the correct DC voltage for your particular inverter
model (i.e., 24-volt battery bank for a 24-volt inverter) and to ensure the polarity of the
battery voltage is correct (battery positive connected to the inverter positive terminal
and the battery negative connected to the inverter negative terminal).
1. Apply battery power to the inverter by closing the DC circuit breaker. The inverter will remain
off, but the green status indicator on the front of the inverter will quickly blink once to indicate
that DC power has been connected and the inverter is ready to be turned on.
2. Prior to turning on the inverter, make sure all AC loads (i.e., appliances) are NOT connected
to the inverter’s output or to any AC outlets powered by the inverter.
3. Lightly press and release the inverter’s ON/OFF switch to turn the inverter on. Verify the
inverter’s status indicator is blinking—indicating the inverter is on.
4. Connect a 10-25 watt light bulb to the inverter output and verify it comes on and shines
normally. DO NOT connect anything larger than a 25-watt light bulb until all wiring and voltages
are confi rmed to be correct.
Info: The inverter’s AC output voltage will not be correct until a load greater than 5
watts (default setting) is connected to the inverter; or, Search mode is turned off with
a remote display (ME-RC, ME-ARC, or ME-RTR). A 10-25 watt light bulb is used as it is
a suffi cient load to bring the inverter out of Search mode and up to full voltage.
5. Check the AC output voltage of the inverter by connecting an AC voltmeter to the output
terminals as shown in Figures 2-26 or 2-27 (verify the correct output voltages).
6. Press and release the inverter’s ON/OFF switch to turn the inverter off. The inverter’s status
indicator and the connected load should go off.
7. Apply AC power to the inverter’s AC input. After the AC input power is qualifi ed (approximately
15 seconds), the incoming AC power will transfer through the inverter to the inverter’s AC
output and power the light bulb. Verify that the inverter’s status indicator and the light bulb
come on.
8. Even though the light bulb is on, the inverter is currently disabled (off). Press and release the
ON/OFF switch on the inverter to enable (turn on) the inverter.
9. Disconnect the incoming AC power to the inverter. Verify the light bulb remains on and is now
powered by the inverter.
If the inverter passes all the steps, the inverter is ready for use. If the inverter fails any of the
steps, refer to the Troubleshooting section in this manual.
AC Terminal Block
AC Output
120 Vac
(± 5%)
Neutral t o
Ground
< 0.5 Vac
Note: For ease of viewing,
GFCI not pictured.
Figure 2-26, AC Voltage Checks
(MS2012-G model)
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
AC Terminal Block
BLACK
WHITE
AC Output
120 Vac
(± 5%)
Note: For ease of viewing,
GFCI not pictured.
Figure 2-27, AC Voltage Checks
(MS2000-G model)
Neutral t o
Ground
< 0.5 Vac
Page 40
Page 49

Operation
3.0 Operation
The MS-G Series inverter has two normal operating routines: Inverter mode, which powers your
loads using the batteries, and Standby mode, which transfers the incoming AC current (i.e., utility
power or a generator) to power your loads and to recharge the batteries. This MS-G also includes
an extensive protection circuitry to shut down the inverter under certain fault conditions.
3.1 Inverter Mode
When the MS-G Series is fi rst powered up, it defaults to the OFF mode. The momentary ON/OFF
power switch (Figure 1-1, Item 1) must be lightly pressed to turn the inverter on. Subsequently,
pressing this switch alternately turns the inverter off and on.
Inverter OFF – When the inverter is off, no power is used from the batteries to power the AC
loads, and the status LED will be off. If AC power from an external source (utility or generator) is
connected and qualifi ed on the inverter’s AC input, this AC input power passes through the inverter
to power the AC loads. However, if this AC power is lost, the AC loads are no longer powered
because the inverter is off.
When the inverter is turned on, it operates either by “searching” or “inverting”, depending on the
connected AC loads.
Searching – When the inverter is fi rst turned on, the automatic Search feature is enabled. This
feature conserves battery power when AC power is not required. In this mode, the inverter pulses
the AC output looking for an AC load (e.g., electrical appliance). Whenever an AC load (greater
than 5 watts) is turned on, the inverter recognizes the need for power and automatically starts
inverting. When there is no load (or less than 5 watts) detected, the inverter automatically goes
back into Search mode to minimize energy consumption from the battery bank. When the inverter
is searching, the inverter’s green LED fl ashes (medium fl ash – blinks once every second).
Info: The factory default value for the Search feature is 5 watts. It can be turned off or
adjusted from 5 to 50 watts using a remote display.
Inverting – When a load greater than 5 watts is connected to the inverter output, the MS-G Series
inverts the DC power from the battery and supplies 120 VAC power to the inverter’s GFCI outlet
(and to sub-panel, if connected). The inverter’s green LED fl ashes once every second (medium
fl ash) to indicate it is inverting. The amount of time the inverter can be inverting and providing
power is directly related to the amount of AC loads that are connected, and the capacity of the
battery bank. Refer to Figures 3-1 & 3-2 to see the fl ow of power from the DC input to the AC
output while in Inverter mode.
AC
OUT
120
VAC
GFCI
120 VAC
OUTPUT
DC
IN
AC HOT 2 IN
AC HOT 1 IN
AC NEU IN
AC GROUND
DC NEGATIVE
INPUT
(30A)
AC Hot
Transfer Relay
AC HOT 2 OUT
GFCI
(20A)
AC NEU OUT
Neutral-Ground
Transfer Relay
AC
DC
DC POSITIVE
FET Bridge
Power Transform er
Figure 3-1, Power Flow – Inverter Mode (MS2012-G/2812-G/4024-G models)
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 41
Page 50

DC
IN
AC H OT 1 IN
AC NEU IN
AC GROUND
DC NEG
INPUT
(30A)
DC
AC Hot
Transfer Contact
Neutral-Ground
Transfer Contact
AC
AC HOT 1 OUT
AC NEU OUT
GFCI
(20A)
Operation
120 VAC
AC
OUT
GFCI
120 VAC
OUTPUT
DC POS
FET Brid ge
Powe r Transform er
Figure 3-2, Power Flow – Inverter Mode (MS2000-G model)
3.2 Standby Mode
The MS-G Series features an internal battery charger and an automatic transfer relay when
operating in Standby mode. Standby mode begins whenever AC power (utility or generator) is
connected to the inverter’s AC input. Once the AC voltage and frequency of the incoming AC power
is within the AC input limits, the automatic AC transfer relay is activated. This transfer relay passes
the incoming AC power through the inverter to power the AC loads on the inverter’s output. This
incoming power is also used to activate a powerful internal battery charger to keep the battery
bank charged in case of a power failure. Refer to Figures 3-3 & 3-4 to see the fl ow of power from
the AC input to the DC and AC output while in Standby mode.
AC
OUT
120
VAC
120
VAC
AC
IN
240
VAC
120
VAC
AC HOT 2 IN
AC HOT 1 IN
AC NEU IN
INPUT
(30A)
AC Hot
Transfer Relay
AC HOT 2 OUT
GFCI
(20A)
AC NEU OUT
DC
OUT
AC GROUND
DC NEGATIVE
DC POSITIVE
DC
FET Bridge
Neutral-Ground
Transfer Relay
AC
GFCI
120 VAC
OUTPUT
Power Transformer
Figure 3-3, Power Flow – Standby Mode (MS2012-G/2812-G/4024-G models)
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 42
Page 51

Operation
AC
IN
120 VAC
DC
OUT
AC H OT 1 IN
AC NEU IN
AC GROUND
DC NEG
DC POS
INPUT
(30A)
AC
DC
FET Brid ge
AC Hot
Transfer Contact
Neutral-Ground
Transfer Contact
Powe r Transform er
AC HOT 1 OUT
AC NEU OUT
GFCI
(20A)
120 VAC
AC
OUT
GFCI
120 VAC
OUTPUT
Figure 3-4, Power Flow – Standby Mode (MS2000-G model)
3.3 Battery Charging
The MS-G Series is equipped with a PFC (Power Factor Corrected) and PI (Proportional-Integral)
multi-stage battery charger. The PFC feature controls the amount of power used to charge the
batteries to obtain a power factor as close as possible to 1 (or unity). This causes the battery charger
to look like a resistor to the line (forces the charge current wave shape to mirror the voltage wave
shape). The PI feature allows the charger voltage and current to change independently. These two
features maximize the real power available from the AC power source (i.e., utility or generator),
which translates into less power wasted and increased charging capabilities.
When an AC source is connected to the AC input, the inverter begins monitoring for acceptable AC
voltage. Once the AC voltage is accepted, the AC transfer relay closes and Charge mode begins.
After Charge mode begins, the inverter’s battery voltage is monitored to determine the charging
stage. If the battery voltage is low (≤12.8 VDC/12-volt models or ≤25.6 VDC/24-volt models), the
charger begins bulk charging. If the DC voltage is high (>12.8 VDC/12-volt models or >25.6 VDC/
24-volt models), the charger will skip the Bulk and Absorb charge stages and go directly to Float
charging. However, if the incoming AC power is lost and returns within 2 minutes the charge mode
returns to the charge stage it was in prior to losing AC input—regardless of the battery voltage.
The multi-stage charger in the MS-G Series can use up to fi ve different charging stages to help
monitor and keep the batteries healthy. The fi ve stages include an automatic 4-stage charging
process (see Figure 3-5)—Bulk, Absorb, Float, and Full Charge—and a manual Equalization (EQ)
charge stage. The automatic 4-stage charge process provides complete recharging and monitoring
of the batteries without damage due to overcharging. The EQ stage (requires a remote control
display to enable) can be used to stir up stratifi ed electrolyte and to reverse any battery plate
sulfation that may have occurred—if recommended by your battery’s manufacturer.
While charging, the unit may go into charger back-off protection, which automatically reduces the
charge current to the batteries. This is caused by: 1) The internal temperature is too hot – the
charger automatically reduces the charge rate to maintain temperature; or 2) The AC input voltage
falls below 90 VAC – the charger will stop charging to help stabilize the incoming AC voltage.
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 43
Page 52

Operation
The Charge mode provides up to four separate charging stages: Bulk Charging, Absorb Charging,
Float Charging and Full Charge (Figure 3-5).
Bulk Charging: This is the initial stage of charging. While bulk charging, the charger supplies the
battery with controlled constant current. The charger remains in bulk charge until the absorption
charge voltage (determined by the Battery Type selection*) is achieved. The inverter’s green LED
stays ON (solid) to indicate bulk charging.
Absorb Charging: This is the second charging stage and begins after the absorb voltage has
been reached. Absorb charging provides the batteries with a constant voltage and reduces the DC
charging current in order to maintain the absorb voltage setting. The inverter’s green LED fl ashes
once every second (medium fl ash) to indicate absorption charging for 2 hours (determined by the
Battery AmpHrs selection*), then switches to fl oat charging.
Float Charging: The third charging stage occurs at the end of the absorb charging time. While
fl oat charging, the charge voltage is reduced to the fl oat charge voltage (determined by the
Battery Type selection*). In this stage, the batteries are kept fully charged and ready if needed by
the inverter. The inverter’s green LED fl ashes once every 8 seconds (slow fl ash) to indicate fl oat
charging. The Float Charging stage reduces battery gassing, minimizes watering requirements (for
fl ooded batteries), and ensures the batteries are maintained at optimum capacity.
Full Charge (Battery Saver™ mode): The fourth stage occurs after four hours in the Float
Charging stage. The Full Charge stage is designed to keep batteries fully charged over long periods,
and to prevent excessive loss of water in fl ooded batteries or drying out of GEL/AGM batteries.
In this stage, the charger is turned off and begins monitoring the battery voltage; if the battery
voltage drops low (12.7 VDC or less on 12-volt models or 25.4 VDC or less on 24-volt models),
the charger automatically initiates another four hours in fl oat charge.
Info: If the battery voltage falls to the re-bulk voltage (12.1 VDC on 12-volt models or
24.2 VDC on 24-volt models) or lower, the unit will begin another bulk charge.
* These settings in the MS-G Series are changeable and leave the factory with default values
(see Table 3-2, Inverter/Charger Default Values). These default values are adequate for most
installations, however, if you determine that some of the values need to be changed for your
particular system, a remote control may be purchased to adjust these settings.
Absorb
Charging
Absorb
volts
Constant
Voltage
Absorb
Time
Reduced
Current
Float
Charging
Float
volts
Reduced
Voltage
Monitored
Current
Full
Charge
Monitored
Voltage
Goes to Full
Charge after
4 hours in
Float Charge
No Current
DC
Voltage
Time
DC
Current
Bulk
Charging
Increased
Voltage
Max
Charge
Rate
Constant
Current
Figure 3-5, Automatic 4-Stage Charging Graph
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 44
Page 53

Operation
-0.75
-0.6
-0.45
-0.3
-0.15
0
0.15
0.3
0.45
0.6
0.75
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
3.4 Transfer Time
While in Standby mode, the AC input is continually monitored. Whenever AC power falls below
the VAC dropout voltage (80 VAC, default setting), the inverter automatically transfers back to
Inverter mode with minimum interruption to your appliances—as long as the inverter is turned
on. The transfer from Standby mode to Inverter mode occurs in approximately 16 milliseconds.
While the MS-G Series is not designed as a computer UPS system, this transfer time is usually
fast enough to hold them up. However, the VAC Dropout setting has an effect on the ability of the
loads to transfer without resetting. The lower this setting, the longer the effective transfer will be
and therefore, the higher the probability for the output loads to reset. This occurs because the
incoming AC voltage is allowed to fall to a level that is so low that when the transfer does occur,
the voltage on the inverter’s output has already fallen low enough to reset the loads.
The disadvantage of a higher VAC Dropout setting is that smaller generators (or large generators
with an unstable output) may nuisance transfer. This commonly happens when powering loads that
are larger than the generator can handle—causing the generator’s output voltage to constantly
fall below the inverter’s input VAC dropout threshold.
Info: When switching from Inverter mode to Standby mode, the inverter waits
approximately 15 seconds to ensure the AC source is stable before transferring.
3.5 Battery Temperature Sensor Operation
The plug-in Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) is used to determine the battery’s temperature.
This information allows the multi-stage battery charger to automatically adjust the battery charge
voltages for optimum charging performance and longer battery life.
If the temperature around an installed BTS is below 77°F (25°C), the absorb and fl oat charge
voltages increase. If the temperature around the BTS is higher than 77°F (25°C), the absorb
and fl oat charge voltages decrease. See Figure 3-6 to determine how much the charge voltage
changes (increases or decreases) depending on the temperature reading of the BTS. For example,
the nominal absorb charge voltage for a fl ooded battery at 77°F (25°C) on a 24-volt model is
29.2 VDC. If the battery temperature is 95°F (35°C), the absorb charge voltage would decrease
to 28.6 VDC (29.2 VDC – 0.6 change).
If the temperature sensor is NOT installed, the charge voltages will not be automatically adjusted
because of temperature, but will be maintained at a temperature of 77°F (25°C). The life of the
batteries may be reduced if they are subjected to large temperature changes when a BTS is not
installed.
Info: When the BTS is connected, the battery charger uses a value of -5mV/°C/Cell
from 0-50°C to change the charge voltage based on temperature.
Temperature Compensation using BTS
12VDC units
+0.75V
+0.6V
+0.45V
+0.3V
+0.15V
No Change
-0.15V
-0.3V
-0.45V
Figure 3-6, BTS Temperature to Charge Voltage Change
-0.6V
-0.75V
Change to battery charging voltage
0C
32F5C41F
10C
50F
15C
59F
20C
68F
25C
77F
30C
86F
Temperature reading from BTS
no BTS
connected
35C
95F
40C
104F
45C
113F
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 45
24VDC units
+1.5V
+1.2V
+0.9V
+0.6V
+0.3V
No Change
-0.3V
-0.6V
-0.9V
-1.2V
-1.5V
50C
122F
Page 54

Operation
3.6 Protection Circuitry Operation
The inverter is protected against fault conditions, and in normal usage it will be rare to see any.
However, if a condition occurs that is outside the inverter’s normal operating parameters, it will shut
down and attempt to protect itself, the battery bank, and your AC loads. If there is a condition that
causes the inverter to shut down, it may be one of the following [also refer to the Troubleshooting
section (Section 4.4) to help diagnose and clear the fault condition]:
• Low Battery – The inverter shuts off whenever the battery voltage falls to the LBCO (Low
Battery Cut Out) level—to protect the batteries from being over-discharged. After the inverter
has reached the LBCO level and turns off, it automatically restarts after one of the following
conditions are met:
1. AC power is applied and the inverter begins operating as a battery charger.
2. Battery voltage rises to the LBCI (Low Battery Cut In) level.
Refer to Table 3-1 to determine the LBCO and LBCI levels for your inverter model.
• High Battery – In the event the battery voltage approaches the HBCO (High Battery Cut
Out) level, the inverter automatically shuts down to prevent it from supplying unregulated
AC output voltage. The inverter’s status LED turns off when a high battery fault condition
occurs. The inverter automatically restarts when the battery falls to the HBCI (High Battery
Cut In) level. Refer to Table 3-1 to determine the HBCO and HBCI levels for your inverter
model.
Info: High battery voltage may be caused by excessive or unregulated voltage from
the solar panels or other external charging sources.
• Overload – During inverter and standby operation, the inverter monitors the DC and AC
current levels. In the event of a short-circuit or an overload condition for more than a few
seconds, the inverter shuts down. To start operating after this fault, the inverter must be
restarted (turned back on) once the inverter’s AC loads are reduced/removed.
• Over-temperature – If internal power components begin to exceed their safe operating
temperature level, the inverter shuts down to protect itself from damage. The inverter’s status
LED turns off to indicate the over-temperature fault condition. The inverter automatically
restarts after the unit cools down.
• Internal Fault – The inverter continually monitors several internal components and the
processor communications. If a condition occurs that does not allow proper internal operation,
the inverter shuts down to protect itself and the connected loads. The inverter needs to be
reset to start operating—refer to Section 4.4 for information on resetting the inverter.
Table 3-1, Inverter Battery Turn On/Off Levels
Inverter Model
Inverter battery
turn ON/OFF Levels
HBCO >16.9 VDC >16.9 VDC >33.8 VDC
HBCI 16.6 VDC 16.6 VDC 33.2 VDC
LBCI 12.5 VDC 12.5 VDC 25.0 VDC
LBCO*
(1 minute delay)
MS2000-G/
MS2012-G
10.0 VDC
(9.0 - 12.2 VDC)
MS2812-G MS4024-G
10.0 VDC
(9.0 - 12.2 VDC)
20.0 VDC
(18.0 - 24.4 VDC)
LBCO (immediate) 8.5 VDC 8.5 VDC 17.0 VDC
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
*adjustable with remote control
Page 46
Page 55

Operation
3.7 Inverter Startup
Power ON/OFF Switch – The inverter can be turned on and off by lightly pressing and releasing
the Power ON/OFF switch on the front of the inverter (see Figure 3-7). When the inverter is fi rst
connected to the batteries, or when its automatic protection circuit has turned the inverter off, the
ON/OFF switch will need to be pressed to start the unit (or reset per Section 4.4). Once the inverter
has been turned on, pressing the Power ON/OFF switch alternately turns the inverter on and off.
WARNING: The Power ON/OFF switch does not turn on or off the charger feature, or
remove pass-thru power. If AC power (utility or generator) is connected and qualifi ed on
the AC input, this AC power will also be available on the AC output and is not controlled
by the Power ON/OFF switch.
Status LED Indicator – The status indicator is a green LED (Light Emitting Diode) that provides
information on the operational mode of the inverter. Watch this indicator (Figure 3-7) for at least
10 seconds to determine the inverter’s operational condition from the information below:
• Off – Indicates the inverter is off—there is no AC power (inverter, utility, or generator)
at the inverter’s output terminals. If the LED stays off after pressing the ON/OFF switch,
there is a fault condition (such as low battery, high battery, overload, over-temperature
or an internal fault). Refer to the Troubleshooting section to help diagnose/clear any fault
condition.
• Slow Flash (blinks on for 4 seconds, then off for 4 seconds) – Indicates the batteries are
fl oat charging and the inverter is in Standby mode (any external AC power connected to
the inverter’s input is passing through the inverter and powering the inverter’s AC loads).
• Medium Flash (blinks on once every second) –
When AC power is not connected to the inverter’s input: Indicates the inverter is on and
using energy from the battery. The inverter is either: 1) Inverting – providing full power
to the connected loads; or, 2) Searching – conserving power and waiting for a load to be
turned on that meets or exceeds the Search Watts parameter (5 watts = default setting).
When AC power is connected to the inverter’s input: Indicates absorb charging, and the
inverter is in Standby mode (the external AC power that is connected to the inverter’s
input is passing through the inverter and is powering the AC loads connected to the
inverter’s output).
• Fast Flash (blinks on/off very quickly—fl utters) – Indicates the inverter is in EQ charge
mode (requires remote to enable), or the inverter is continuously in reset. If a remote was
not used to enable the equalize charge, then the inverter is likely in reset. Refer to the
Troubleshooting section to help diagnose/clear the fault condition.
• On (solid) – Indicates bulk charging, and the inverter is in Standby mode (the external
AC power that is connected to the inverter’s input is passing through the inverter and is
powering the AC loads connected to the inverter’s output).
Power ON/OFF
pushbutton switch
Charging/Inverting
Status LED indicator
Figure 3-7, Power Switch and Status Indicator
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 47
Page 56

Operation
3.8 Factory Default Values
Your MS-G Series inverter/charger uses default values for the adjustable settings (Table 3-2)
that are adequate for most installations. If the operating parameters need to be changed from
the default values, an optional remote control can be used to make those changes. To help you
determine if you need a remote, information on the inverter/charger settings that can be changed
is provided below. The settings, once programmed, are saved in the remote’s non-volatile memory
and are preserved until changed—even if DC power to the inverter is lost (as long as the remote
is connected). For information on the full range of settings for each function in your remote, refer
to its owner’s manual at www.Magnum-Dimensions.com.
• Shore Max/Input Amps: This setting ensures the inverter AC loads receive the maximum
current available from the utility or generator. When the total current used to power the
AC loads and charge the batteries begins to approach the Shore Max/Input Amps setting,
the current that was used for charging the batteries will automatically be reduced.
• Search Watts: This setting allows you to turn off the power-saving Search mode circuitry,
or to adjust the power level at which the inverter will “wake up” and start inverting.
• LowBattCutOut: This setting determines when the inverter will turn off based on low
battery voltage. The inverter turns off automatically after the battery voltage has been
below this setting for more than one minute. This protects the batteries from overdischarge and the AC loads from unregulated power (brown-outs).
• Batt AmpHrs/Absorption Time: This setting allows the user to input the battery bank
size in amp hours or to set the absorption time—which tells the charger how long to
charge the batteries in the Absorb Charge stage.
• Battery Type: Sets the type of batteries being used in the system. This information tells
the charger what voltage level to use to charge the batteries.
• Charge Rate: This setting can be used to turn off the charger, limit the amount of current
that the charger can use (leaving more current available to power loads), or to ensure
small battery banks are not overheated because of a charge rate that is too high.
• VAC Dropout: Sets the minimum AC voltage that must be present on the AC input before
the unit transfers from Standby mode to Inverter mode. This protects the AC loads from
utility outages and brown-outs.
Using a remote display also provides the following features:
• allows you control to enable an equalize charge for certain battery types
• displays inverter/charger’s operating status
• provides fault information for troubleshooting
Table 3-2, Inverter/Charger Default Values*
Adjustable Settings Default Values
Shore Max/Input Amps 30 Amps
Search Watts 5 Watts
LowBattCutOut
Batt AmpHrs/Absorption Time 600 AmpHrs (Absorb Time = 120 minutes)
Battery Type
Charge Rate 100%
VAC Dropout 80 VAC
* – These are the MS-G’s default values without a remote control connected. If a remote is
connected, the remote settings are saved in the inverter even if the remote is disconnected—
until all power to the inverter is removed.
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
12v = 10 VDC (one min. delay), 8.5 VDC (no delay)
24v = 20 VDC (one min. delay), 17.0 VDC (no delay)
Flooded – Liquid Lead Acid:
12V = Absorb 14.6 VDC, Float 13.4 VDC;
24V = Absorb 29.2 VDC, Float 26.8 VDC
Page 48
Page 57

Operation
Figure 3-8, Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter
3.9 Using the GFCI
The GFCI outlet on the left side of the MS-G inverter (Figure 1-3, Item 16) provides auxiliary
power to 120VAC devices that require 20 amps or less. If you are using both GFCI outlets at once,
the amperage cannot exceed a total of 20 amps for both devices combined. Use only a 3-prong
grounded plug when using the GFCI outlet. Refer to Figure 3-8 for this section.
IMPORTANT: Because GFCI outlets can become damaged over time, they must be tested monthly
to ensure they are providing protection. To properly test the GFCI’s operation, the inverter must
be providing ~120VAC to the GFCI outlet. If the inverter is “Searching”, the Search mode feature
must be turned off to allow the inverter to provide ~120VAC.
To test the GFCI outlet:
1. Apply DC power to the inverter, and then turn the inverter on.
2. Plug a test light (small lamp or night light) in to the GFCI outlet and turn it on. If the light
comes on, proceed to Step 3. If it does not:
a) Ensure the GFCI’s RESET button is not “tripped” (the RESET button is tripped if the button
is flush with the face of the TEST button). If fully pushing the RESET button does not cause
the light to come on, then,
b) Ensure the inverter is on and not in Search mode, or
c) Check the test light to ensure it is not faulty, or use a different test light.
3. Press the TEST button on the GFCI outlet. The RESET button immediately pops out and the
test light turns off. If this occurs, the GFCI accessory is operating correctly. However, if:
a) The RESET button does not pop out when the TEST button is pressed. The GFCI outlet is
not operating correctly.
b) The RESET button pops out, but the test light does not turn off.
This indicates you need to either:
• check the blue AC HOT 1 OUT wire and the white w/stripe AC NEUT OUT wire inside
the inverter to ensure they were not reversed during production, or
• check the HOT IN and NEUT IN wires to ensure they are not reversed from the external
AC power source.
To clear a tripped GFCI:
1. Some faults are self-clearing, try resetting the GFCI outlet by pressing the RESET button.
2. If the RESET button will not stay in, ensure the inverter is not in Search mode.
3. If the GFCI outlet continues to trip, the device is performing its intended protection function;
which means that a hazardous condition could exist. A qualifi ed electrician should be called
to evaluate the circuit.
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 49
Page 58

Operation
3.10 Inverter Fan Operation
The inverter contains two internal cooling fans that are automatically controlled. The speed of
these fans is determined either by the internal temperature of the inverter or by the load on the
inverter. The inverter’s fans will come on under the conditions listed below:
• Fans run full speed if the internal transistors (FETS) or the power transformer reaches 80°C
(176°F), or the inverter is running at 100% of its rated load.
• Fans run medium speed if the internal transistors (FETS) or the power transformer reaches
60°C (140°F), or the inverter is running at 50% of its rated load.
• Fans run low speed when the inverter is running at 25% of its rated load.
The fans shut down when none of the above conditions are met, or if the battery voltage is below
9.5V (12-volt systems)/19.0V (24-volt systems).
Whenever the inverter is fi rst connected to the battery, the fans will come on for about one
second.
Info: The inverter’s fans will not come on based on temperature sensed by the optional
Battery Temperature Sensor.
3.11 Using a Remote with the MS-G Series Inverter
The MS-G Series inverter—when connected to a remote control display (i.e., ME-RC, ME-ARC)—
has many advanced features. The inverter and remote communicate with each other to allow
these advanced features to be set up or enabled. However, the remote may have a later/newer
software revision than the inverter, so some of the features and functionality in the remote may
not be available with your inverter.
Use the steps below to determine what remote menus/features are available with your inverter:
1. Obtain your inverter’s software revision.
Note: To view the inverter’s software revision level, push the TECH button on your remote
and access the Revisions menu.
2. Use the chart below to determine the inverter’s compatibility level (L1, L2, L3 or L4) based on
your inverter’s software revision.
Table 3-3, Inverter Compatibility Level
INV/CHG
Models
MS2000-G ≥ Rev 2.6 ≥ Rev 3.6 ≥ Rev 4.2 ≥ Rev 5.4
MS2012-G ≥ Rev 2.6 ≥ Rev 3.6 ≥ Rev 4.2 ≥ Rev 5.4
MS2812-G ≥ Rev 2.6 ≥ Rev 3.6 NA ≥ Rev 5.4
MS4024-G ≥ Rev 2.6 ≥ Rev 3.6 NA ≥ Rev 5.4
3. After determining the inverter’s compatibility level, refer to the remote’s compatibility matrix
(online at: www.Magnum-Dimensions.com under the Service and Support tab) to determine
which remote features/settings you can use based on your inverter’s compatibility level.
Note: If your inverter’s compatibility level is the same or greater than the ‘Inverter Model/Level
Required’ on the remote compatibility matrix on our website, then your inverter can support
the device setting/feature you want. If your inverter does not have the required compatibility
level for a feature/setting you want, contact Sensata to determine if there is a software upgrade
option for your inverter.
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Level 1
(L1)
Level 2
(L2)
Level 3
(L3)
Level 4
(4)
Page 50
Page 59

Maintenance and Troubleshooting
4.0 Maintenance and Troubleshooting
The following information is provided to help you keep your MS-G Series inverter/charger in
optimum operational condition.
4.1 Recommended Inverter and Battery Care
The MS-G Series inverter/charger is designed to provide you with years of trouble-free service.
Even though there are no user-serviceable parts, it is recommended that every 6 months you
perform the following maintenance steps to ensure optimum performance and extend the life of
your batteries.
WARNING: Prior to performing any checks, switch OFF both the AC and DC circuits.
• Visually inspect the batteries for cracks, leaks, or swelling—replace if necessary
• Use baking soda to clean and remove any electrolyte spills or buildups
• Check and tighten all battery hold-down clamps (if applicable)
• Clean and tighten all battery terminals and connecting cables [10 to 12 lbf-ft (13.6 to 16.3
N-m)]
• Check and fi ll battery water levels (liquid lead acid batteries only)
• Check individual battery voltages (load test those that have a voltage difference of more
than 0.3 VDC from each other)—replace if necessary
• Check all cable runs for signs of chafi ng—replace if necessary
• Check the inverter’s cooling vents—clean as necessary
• Check and tighten the inverter’s internal AC terminal block connections [16 lbf-in (1.8
N-m)]
4.2 Storage for Mobile Installations
When placing the RV, boat or truck into storage, it is recommended that you perform the following
to ensure the system is properly shut down (or properly confi gured for storage). This is especially
important for maintaining the batteries.
• Perform the recommended maintenance steps listed in Section 4.1
• Fully charge the batteries
• Connect AC power (if available) and verify that the breaker to the inverter’s input is
switched ON (to allow battery charging)
• Verify the inverter is switched OFF
• Switch OFF all unnecessary AC and DC loads
• Disable the AGS (if installed) when the RV, boat, or truck is in a confi ned storage area
WARNING: If an AGS were to start and run the generator for an extended period
of time in a confi ned area, a potentially fatal level of CO (Carbon Monoxide) could
accumulate.
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 51
Page 60

Maintenance and Troubleshooting
4.3 Troubleshooting
The MS-G Series inverter/charger is a fairly simple device to troubleshoot. The following chart is
designed to help you quickly pinpoint the most common inverter failures.
Table 4-1, Basic Troubleshooting
Symptom Possible Cause Recommended Solution
No output power.
Inverter LED is OFF.
No output power.
Green LED is fl ashing.
Inverter in reset.
Low output or surge
power. Green LED is
fl ashing.
Low charging rate
when connected to AC
power.
Low charging rate when
using a generator.
Charger does not
charge.
While charging, the
DC charge voltage is
higher or lower than
expected.
Inverter is switched OFF. Switch the inverter ON.
Battery voltage is too low. The battery
voltage level has dropped below the
Low Battery Cutout (LBCO) set-point
for more than one minute.
The battery voltage is too high. The
inverter automatically resets and
resumes operation when the battery
voltage drops to the HBCI voltage or
lower.
Over-temperature condition: The
internal temperature of the inverter has
risen above acceptable limits; caused
by loads too great for the inverter to
operate continuously, or by lack of
ventilation to the inverter. When the
unit has cooled, it will automatically
reset and resume operation.
AC overload condition: The inverter
has turned off because the connected
loads are larger than the inverter’s
output capacity, or the output wires
are shorted.
Internal fault: This fault occurs when
an internal fault is detected.
Unit is in Search mode, which means
the load is too small for Search mode
circuit detection.
Loose or corroded battery cables. Clean and tighten all cables.
Low batteries. Recharge or replace batteries.
Loose AC output connections. Tighten AC output connections.
Battery cables are the wrong length
or gauge.
Charge rate set too low. Adjust charge rate or SHORE settings on remote.
Low AC voltage (< 90 VAC). Check AC input wiring.
Generator output is too low to power
both load and charger.
Loose or corroded battery cables. Clean and tighten battery cables.
Defective batteries. Replace batteries.
Wrong charger settings. Adjust the charger settings, ensure the unit is not in
Wrong AC input voltage. Verify proper AC input voltage and frequency.
If the Battery Temperature Sensor
(BTS) is installed, the DC voltage will
increase or decrease depending on the
temperature around the BTS.
Check fuses/circuit-breakers and cable connections.
Check battery voltage at the inverter’s terminals. Your
batteries may need to be charged, this fault condition
will automatically clear when the battery voltage exceeds
the LBCI voltage.
This condition usually only occurs when an additional
charging source (alternator, solar panels, or other
external charging sources) is used to charge the battery
bank. Reduce or turn off any other charger to the inverter
batteries to allow the voltage level to drop.
Reduce the number of electrical loads that you are
operating, this will avoid a repeat over-temp shutdown if
the cause was too many loads for the ambient conditions.
Check ventilation around the inverter, ensure cool air is
available to pass-thru the inverter (refer to the ventilation
requirements in Section 2.1.3).
Reduce the AC loads connected to the inverter, or remove
all AC output wiring and restart the inverter.
An inverter reset is required to clear fault. Remove
DC power to the inverter, or press and hold down the
inverter’s power switch for ~10 seconds (until green
Status LED lights). If fault does not clear, the unit needs
to be serviced.
Turn on a load greater than 5 watts to bring inverter to
full output power, or turn off Search with remote.
Verify recommended cable lengths and gauges from the
manual. Replace cables as necessary.
Reduce the load, increase the generator’s RPMs.
Check the SHORE settings (if remote connected).
charger standby.
This is normal; see Section 3.5 (Battery Temperature
Sensor Operation) for more information.
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 52
Page 61

Maintenance and Troubleshooting
4.4 Resetting the Inverter
Under some fault conditions (e.g., an internal fault), the inverter will need to be reset. Prior to
performing any reset, ensure all AC power (utility, generator, shorepower) is removed from the
inverter’s input.
CAUTION: If AC is connected while performing an inverter reset, damage may occur.
4.4.1 Performing an Inverter Reset (i.e., soft reset)
To perform an inverter reset (also known as a “soft reset”):
1. Press and hold the Power ON/OFF pushbutton (see Figure 4-1) for approximately fi fteen (15)
seconds until the Charging/Inverting Status LED comes on and fl ashes rapidly.
2. Once the rapid fl ashing has begun, release the Power ON/OFF pushbutton. The Status LED will
go off after the pushbutton is released.
3. After the inverter reset is completed, press the ON/OFF pushbutton to turn the inverter ON.
If the inverter reset fails, you will need to perform a power reset using the procedure below in
Section 4.4.2. In either case, if an internal fault does not clear, the inverter will require repair at
an Authorized Service Center (ASC).
Info: The Power ON/OFF pushbutton is a small momentary type switch which operates
by lightly pressing and releasing. Be careful not to apply too much force when pushing
or the switch might break.
1. Press and hold the Power
ON/OFF pushbutton.
2. Watch the Charging/Inverting
Status LED, after approximately
15 seconds it should come on
and fl ash rapidly to indicate the
inverter has reset. The Status LED
will go off after the pushbutton is
released.
Figure 4-1, Performing an Inverter Reset
4.4.2 Performing a Power Reset (i.e., power reset)
To perform a power reset (also known as a “hard reset”):
1. Open the inverter’s positive DC disconnect (or disconnect the positive battery cable to the
inverter).
Note: If parallel stacked with multiple inverters, open all the inverters’ DC disconnects at the
same time.
CAUTION: If removing all battery power (positive and negative) to the inverter, do
not remove the DC negative connections to the inverter or any accessory until after
all positive battery connections have been disconnected. This will prevent damage to
the inverter or to any network connected accessory.
2. Ensure the inverter and the remote are disconnected from all AC and DC power (the remote
display will be blank).
3. After the inverter has been disconnected from all power for 30 seconds, reconnect the inverter
DC disconnects (or reconnect the positive battery cable) and resume operation.
Info: If DC disconnects are not used, there may be a momentary spark when the
positive battery cable is connected to the inverter’s terminal. This is normal and
indicates that the inverter’s internal capacitors are being charged.
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 53
Page 62

Appendix A – Specifi cations
Appendix A – Specifi cations and Optional Equipment
A-1 Inverter/Charger Specifi cations
Models MS2000-G/MS2012-G MS2812-G MS4024-G
Inverter Specifi cations
Input battery voltage range 9.0 to 16.9 VDC 18.0 to 33.8 VDC
Absolute maximum DC input 25 VDC 35 VDC
AC output voltage accuracy 120 VAC ±5% (≤ continuous power)
Output frequency and accuracy 60 Hz ± 0.1 Hz
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) < 5%
Continuous power output (at 25°C) 2000 VA 2800 VA 4000 VA
Continuous AC output current 16.7 AAC 23 A 33 A
1 msec surge current (amps AC) 50 70 120
100 msec surge current (amps AC) 33 40 82
5 sec surge power (real watts) 3300 3900 5800
30 sec surge power (real watts) 3100 3800 5400
5 min surge power (real watts) 2800 3200 4900
30 min surge power (real watts) 2200 3000 4500
Maximum continuous input current 266 ADC 373 ADC 267 ADC
Inverter effi ciency (peak) 90.6% 90% 93.7%
HBCO/HBCI (High Battery Cut Out/In) 16.9 VDC/16.6 VDC 33.8 VDC/33.2 VDC
LBCO/LBCI (Low Battery Cut Out/In) 9.0 VDC (adj)/12.5 VDC 18.0 VDC (adj)/25.0 VDC
Series Stacking for 120/240 VAC No Yes, using two MS4024-G’s
AC Relay Transfer time (minimum) 16 msec
Power Consumption – searching <8 watts
Power Consumption – inverting (no load) 25 watts 30 watts 25 watts
Output Waveform Pure Sine Wave
Charger Specifi cations
Continuous charger output at 25°C 100 ADC
Input current for continuous rated output 15 AAC
Charger effi ciency 85%
AC input frequency range 50 to 70 Hz
AC input voltage range 60 to 140 VAC (120 VAC nominal)
Power factor > 0.95
General Features and Capabilities
Transfer relay capability 30 AAC max each wired input (30AAC total on MS2000-G’s, 50AAC total on other models)
Five-stage charging capability Bulk, Absorb, Float, Equalize (requires remote), and Battery Saver™
Battery temperature compensation Standard with available temp sensor connected (battery temp 0 – 50 °C)
Internal Cooling 0 to 120 cfm variable speed drive using dual 92 mm brushless DC fan
Overcurrent protection with two overlapping circuits
Over-temperature Protection on transformer, MOSFETS, and battery
Corrosion protection PCB’s conformal coated, powder coated chassis/top, and stainless steel fasteners
Safety Listings
Warranty 3 years parts and labor (extends to 5 yrs with MMP system)
ETL listed to UL/cUL 458, UL 1741, CSA C22.2 No. 107.1-01, and meets KKK-A-1822E std**
30A max wired output or 20A GFCI output
Environmental Specifi cations
Operating temperature -20°C to +60°C (-4°F to 140°F)
Non-Operating temperature -40°C to +70°C (-40°F to 158°F)
Operating humidity 0 to 95% RH non-condensing
Physical Specifi cations
Unit Dimensions (length x width x height)
Shipping Dimensions (l x w x h)
Mounting Shelf or wall (vents not to face downward unless ME-CB/MPX-CB or MMP is installed)
Unit Weight 42 lb (19.1 kg) /
Shipping Weight 50 lb (22.7 kg) / 63 lb (28.6 kg) 63 lb (28.6 kg) 63 lb (28.6 kg)
Max operating altitude 15,000’ (4570 m)
** MS2000-G models
ETL listed to UL/cUL 458, CSA C22.2 No. 107.1-01, and meet KKK-A-1822E standard.
13.75” x 12.65” x 8.0” (34.9 cm x 32.1 cm x 20.3 cm) [MS2000-G height is 7.0”/17.8 cm]
19” x 17” x 13” (48.3 cm x 43.2 cm x 33 cm)
55 lb (24.9 kg) 55 lb (24.9 kg) 55 lb (24.9 kg)
Specifi cations @ 25°C - Subject to change without notice.
125 ADC 105 ADC
18 AAC 29 AAC
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 54
Page 63

Appendix A – Specifi cations
A-2 Inverter Effi ciency
The curves in Figure A-1 are plotted to show the MS-G Series’ effi ciency over the full power range
(displayed as a percentage). This graph represents the inverter’s effi ciency while operating resistive
loads. Motors and other inductive loads run less effi ciently due to the impact of power factor losses.
95%
90%
85%
MS2000-G/MS2012-G
MS2812-G
MS4024-G
MS4024-G
80%
75%
MS2812-G
MS2000-G/
200
MS2012-G
1000
600
1400
1800
2200
2600
3000
3400
3800
4200
Efficiency
70%
65%
60%
Wattage
Figure A-1, MS-G Series Effi ciency Chart
A-3 AC Input Voltage to Output Charge Amps
The following chart shows the expected charger output capability of the MS-G Series. The maximum
charge current is dependent on the AC input voltage and the inverter battery voltage.
Note: The output charger current shown is with the inverter battery voltage at nominal (i.e., 25.2
volts for MS4024-G).
160
MS2000-G/MS2012-G
MS2812-G
MS4024-G
100
105
110
115
120
125
130
135
Peak Charge Amps
150
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
95
VAC Input
Figure A-2, MS-G Series VAC Input to Charge Amps
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 55
140
Page 64

Appendix A – Specifi cations
A-4 Optional Equipment and Accessories
The following Sensata components are available for use with the MS-G Series inverter/charger.
Some of these items are required depending upon the intended use of the inverter.
MMP Series Enclosures
The MMP enclosures have been specifi cally designed for single inverter applications. These
enclosures combine all of the major components required for a renewable energy system—inverter/
battery disconnect, AC overcurrent protection, grounding connections, and a full system inverter
bypass switch as a convenient way to isolate the inverter for battery maintenance—into a single,
easy to install pre-wired enclosure.
Remote Switch Adapters
The ME-RSA and ME-RSA-M pigtail adapters allow the inverter to be remotely switched on and
off—with or without a remote display.
Advanced Remote Control
The ME-ARC remote control panel uses an LCD screen and at-a-glance LEDs to provide operating
information and allow advanced features to be confi gured (requires a Magnum inverter with
advanced confi gurable features). This LCD remote control also provides advanced monitoring/
troubleshooting and includes a FAVS button to access your favorite features quickly.
Standard Remote Control
The ME-RC remote control panel uses an LCD screen and at-a-glance LEDs display for complete
inverter/charger status. Soft keys provide simple access to menus, and a rotary encoder knob
allows you to scroll through and select a wide range of settings such as: Inverter ON/OFF, Charger
ON/OFF, shorepower breaker setting, AGS control, METER button, SETUP and TECH menus.
Auto Generator Start Controller
The ME-AGS-N Automatic Generator Start controller (Network version) is designed to automatically
start your generator based on low battery condition or high temperature.
includes an input voltage jumper (for 12, 24, and 48-volt battery banks) and a 4-position DIP
(Dual In-line Package) switch which provides the ability to change the relay timing confi gurations
to allow compatibility with a wider range of generators. Adjustable settings when using the ME-
ARC include starting the generator based on battery voltage, time of day, battery State of Charge
(SOC), or high temperature.
Battery Monitor Kit
The ME-BMK-NS Battery Monitor Kit is a single battery bank amp-hour meter that monitors the
condition of the battery, provides information to let you know how much energy you have available,
and lets you plan your electrical usage to ensure the battery is not being over-discharged. The
–NS version does not include a DC shunt. Order PN: ME-BMK to receive the battery monitor that
includes the 500A/50mv DC shunt.
Note: The DC shunt is included with the MMP Series enclosure. Order the ME-BMK-NS version
when installed with the MMP enclosure.
ME-CB and MPX-CB Conduit Boxes
The ME-CB and MPX-CB conduit boxes are provided for installations where the electrical code
requires AC and/or DC wiring to your inverter to be enclosed and protected by conduit.
The AGS controller
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 56
Page 65

Appendix B – Battery Information
Appendix B – Battery Information
B-1 Battery Location
Periodic maintenance (i.e., checking connections, cleaning, watering) on batteries is required.
Locate the batteries in an accessible location to perform this maintenance.
Batteries must be mounted in a clean, dry, ventilated environment where they are protected
from high and low temperatures. The battery bank should be located as close to the inverter as
possible without limiting access to the inverter’s disconnects. Longer battery cable runs tend to
lose effi ciency and reduce the overall performance of an inverter.
To ensure optimum performance, a ventilated battery enclosure is recommended. Two feet of
clearance above the batteries is recommended for access to the battery terminals and removable
caps (lead acid battery types).
WARNING: Be very careful when working around batteries, they can produce extremely
high currents if they are short-circuited. Read the important safety instructions at the
beginning of this manual and the precautions from the battery supplier before installing
the inverter and batteries.
CAUTION: Do not mount the batteries beneath the inverter (or in the same
compartment). Batteries emit corrosive fumes which could damage the inverter’s
electronics. Never locate dedicated batteries near a vehicle/home fuel tank containing
gasoline or propane.
B-2 Battery Types
Batteries are available in different sizes, amp-hour ratings, voltage and chemistries. They are also
available for starting applications (such as an automobile starting battery) and deep discharge
applications. Only the deep cycle types are recommended for inverter applications; using a starting
battery in an inverter (deep cycle) application will greatly shorten their useful life. Choose the
batteries best suited for the inverter installation and cost. Use only the same battery type for all
batteries in the bank. For best performance, all batteries should be from the same lot and date.
This information is usually printed on a label located on the battery.
B-3 Battery Temperature
Battery performance of lead-acid type batteries is greatly affected by extreme temperatures. When
a lead-acid type battery is cold, its effective amp-hour capacity is reduced. When determining
the battery requirements needed for the inverter system, realize that the battery capacity will be
reduced if they will be installed in a climate where extremely cold temperatures are expected. In
this type of environment, the batteries should be located in a heated area. At the minimum, the
batteries should be installed in an insulated enclosure; which will keep the batteries warmer as
they are being charged.
The battery bank should also be protected from high temperatures, which will shorten battery
life. In high heat situations the battery room/enclosure should be ventilated to bring in cooler air
and exhaust the hotter air. The performance of the battery bank/inverter system will substantially
increase by monitoring and preventing extreme temperatures around the batteries.
B-4 Battery Bank Sizing
The size of the battery bank determines how long the inverter will power the AC loads without
recharging. The larger the battery bank, the longer the run time. Size your battery bank to the
systems AC load requirements and length of time required to run from the batteries. In general,
the battery bank should not be discharged more than 50%. Additional DC charging devices such
as solar, wind, hydro, etc., can provide longer run times by recharging the batteries in the absence
of AC utility or generator power.
Info: For the MS-G Series inverter/charger to perform optimally, a minimum battery
bank of 200 AH is recommended for moderate loads (<1000W) and greater than 400
AH for heavy loads (≥1000W).
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 57
Page 66

Appendix B – Battery Information
B-5 Battery Bank Sizing Worksheet
Complete the steps below to determine the battery bank size required to power your AC loads:
1. Determine the daily power needed for each load
a) List all AC loads required to run; and
b) List the Watt-Hours for each load (see Table C-1 for common loads/wattage); and
c) Multiply by how many hours per day (or a fraction of an hour) each load will be used; and
d) Multiply by how many days per week you will use the listed loads; and
e) Divide by seven = Average Daily Watt-Hours Per Load.
Average Daily Watt-Hours Per Load
AC load Watt-Hours (x) hours per day (x) days per week
2. Determine the total power needed each day for all the loads.
• Add the Average Daily Watt-Hours Per Load = Total Daily Watt-Hrs.
3. Determine the battery amp-hour capacity needed
(inverter battery voltage)
to run all the loads before recharging.
• Divide the Total Daily Watt-Hours by the nominal
÷ ___ =
battery voltage of the inverter (i.e., 12, 24 volts); and
Multiply this by how many days the loads will need
to run without having power to recharge the batteries
(days of storage)
x ___ =
(typically 3 to 5 days of storage) = Storage Amp-Hours.
(÷7) = total power
Total Daily Watt-Hrs
4. Determine how deeply you want to discharge your batteries.
• Divide the Storage Amp-Hours by 0.2 or 0.5 to get the Total Amp-Hours:
a) 0.2 = Discharges the batteries by 20% (80% remaining), this is
considered the optimal level for long battery life; or
b) 0.5 = Discharges the batteries by 50% (50% remaining), this is
considered a realistic trade-off between battery cost and battery life.
Total Amp-Hours
Additional compensation:
Low battery temperature: If the batteries are installed in a location that will be exposed to low
temperatures, the available output will be less. In these instances, you will need to determine
the lowest temperature the battery bank will experience and multiply the Total Amp-Hours by the
multiplier below.
Temperature 80F/27C 70F/21C 60F/15C 50F/10C 40F/4C 30F/-1C 20F/-7C
Multiplier 1.00 1.04 1.11 1.19 1.30 1.40 1.59
Inverter effi ciency: When the inverter is used in a back-up power application the inverter effi ciency
will not be a large concern; however, if the inverter is the primary AC source for the calculated load,
the Total Amp-Hours should be multiplied by 1.2 to factor in an average 80% inverter effi ciency.
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 58
Page 67

Appendix B – Battery Information
B-6 Battery Wiring Confi gurations
The battery bank must be wired to match the inverter’s DC input voltage. In addition, the batteries
can be wired to provide additional run time. The various wiring confi gurations are:
B-6.1 Series Wiring
Wiring batteries in series increases the battery bank’s output voltage. A series connection combines
each battery in a string until the total voltage matches the inverter’s DC requirement. Even though
there are multiple batteries, the capacity remains the same. In Figure B-1 below, two 6 VDC/200
AH batteries are combined into a single string resulting in a 12 VDC, 200 AH bank.
Series Battery Wiring
combines battery voltage:
6 VDC
(200 AH)
6 VDC
(200 AH)
12 VDC @
200 AH
Figure B-1, Series Battery Wiring
B-6.2 Parallel Wiring
Wiring batteries in parallel increases the battery bank’s amp-hour capacity, which allows the AC
loads to operate for a longer time. A parallel connection combines the number of batteries in the
string to increase overall battery capacity; however, the voltage remains the same. In Figure B-2
below, two 12 VDC/100 AH batteries are combined into a single 12 VDC, 200 AH battery bank.
200 AH @ 6 VDC
+ 200 AH @ 6 VDC
= 200 AH @ 12 VDC
Parallel Battery Wiring
12 VDC
(100 AH)
12 VDC
(100 AH)
12 VDC @
200 AH
combines battery capacity:
100 AH @ 12 VDC
+ 100 AH @ 12 VDC
= 200 AH @ 12 VDC
Figure B-2, Parallel Battery Wiring
B-6.3 Series-Parallel Wiring
A series/parallel confi guration increases both voltage (to match the inverter’s DC requirements)
and amp-hour capacity (to increase run-time for operating the loads) using smaller, lower-voltage
batteries. In Figure B-3 below, four 6 VDC/200 AH batteries are combined into two strings resulting
in a 12 VDC, 400 AH battery bank.
Series/Parallel Battery Wiring
combines battery voltage and capacity:
6 VDC
(200 AH)
6 VDC
(200 AH)
6 VDC
(200 AH)
6 VDC
(200 AH)
12 VDC @
400 AH
200 AH @ 6 VDC
+ 200 AH @ 6 VDC
= 200 AH @ 12 VDC
200 AH @ 6 VDC
+ 200 AH @ 6 VDC
= 200 AH @ 12 VDC
200 AH @ 12 VDC
+ 200 AH @ 12 VDC
= 400 AH @ 12 VDC
= 400 AH @ 12 VDC
add voltage
in series
add capacity
+=
in parallel
Figure B-3, Series-Parallel Battery Wiring
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 59
voltage and
capacity together
Page 68

String
(12 VDC @ 100 AH)
12-volt battery bank (one string of one 12-volt battery)
Series String
(6 VDC + 6 VDC)
12-volt battery bank (one string of two 6-volt batteries wired in series)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
Appendix B – Battery Information
overcurrent
protection
to 12 VDC
12 VDC
battery
(100 AH)
overcurrent
protection
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
inverter
(total capacity
= 100 AH)
to 12 VDC
inverter
(total capacity
= 200 AH)
Parallel String
(100 AH + 100 AH)
12-volt battery bank (parallel two 12-volt batteries)
Series String
(6 VDC + 6 VDC)
Series String
(6 VDC + 6 VDC)
overcurrent
protection
12 VDC
battery
(100 AH)
12 VDC
battery
(100 AH)
Parallel String (200 AH + 200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
to 12 VDC
inverter
(total capacity
= 200 AH)
overcurrent
protection
to 12 VDC
inverter
(total capacity
= 400AH)
(2 strings of two 6-volt batteries wired in series and connected in parallel)
Figure B-4, Battery Bank Wiring Examples (12-volt)
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
12-volt battery bank
Page 60
Page 69

Appendix B – Battery Information
Series String
(12 VDC + 12
VDC)
12 VDC
battery
(100 AH)
24-volt battery bank (one string of two 12-volt batteries wired in series)
Series String
(6 VDC + 6 VDC
+ 6 VDC + 6 VDC)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
24-volt battery bank (one string of four 6-volt batteries wired in series)
Parallel String (100 AH + 100 AH)
Series String
(12 VDC + 12
VDC)
Series String
(12 VDC + 12
VDC)
12 VDC
battery
(100 AH)
12 VDC
battery
(100 AH)
12 VDC
battery
(100 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
12 VDC
battery
(100 AH)
12 VDC
battery
(100 AH)
overcurrent
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
protection
overcurrent
protection
overcurrent
protection
to 24 VDC
inverter
(total capacity
= 100 AH)
to 24 VDC
inverter
(total capacity
= 200 AH)
to 24 VDC
inverter
(total capacity
= 200 AH)
24-volt battery bank
(two strings of two 12-volt batteries wired in series and connected in parallel)
Parallel String (200 AH + 200 AH)
overcurrent
protection
Series String
(6 VDC + 6 VDC
+ 6 VDC + 6 VDC)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
Series String
(6 VDC + 6 VDC
+ 6 VDC + 6 VDC)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
6 VDC
battery
(200 AH)
24-volt battery bank
(two strings of four 6-volt batteries wired in series and connected in parallel)
Figure B-5, Battery Bank Wiring Examples (24-volt)
to 24 VDC
inverter
(total
capacity
= 400 AH)
© 2015 Sensata TechnologiesPage 61
Page 70

Appendix C – Power Consumption & Output Waveforms
Appendix C – Power Consumption & Output Waveforms
C-1 Appliances and Run Time
The MS-G Series inverter/charger can power a wide range of household appliances including small
motors, hair dryers, clocks, and other electrical devices. As with any appliance using batteries for
power, there is a certain length of time that it can run – this is called “run time.” Actual run time
depends on several variables including the size and the type of appliance, the type of batteries
installed in your application, as well as the battery’s capacity and age. Other factors such as the
battery’s state of charge and temperature can also affect the length of time your appliances can run.
Appliances (TVs, VCRs, stereos, computers, coffee pots, incandescent lights, and toasters) can all
be successfully powered by your inverter. Larger electrical appliances, however, such as stoves,
water heaters, etc., can quickly drain your batteries and are not recommended for this application.
All electrical appliances are rated by the amount of power they consume (see Table C-1). The
rating is printed on the product’s nameplate label, usually located on its chassis near the AC
power cord. Even though it is diffi cult to calculate exactly how long an inverter will run a particular
appliance, the best advice is trial and error. Your MS-G Series inverter has a built-in safeguard
that automatically protects your batteries from over-discharge.
Info: For optimum performance, a minimum battery bank of 200 AH is recommended
for moderate loads (<1000W) and greater than 400 AH for heavy loads (≥1000W).
Table C-1, Typical Appliance Power Consumption
Device Load Device Load Device Load
Blender 400W Coffee Maker 1200W Light (Flo) 10W
Computer 300W Color TV 150W Light (Inc) 100W
Drill 500W Hair Dryer 1000W Microwave 1000W
Hot Plate 1800W Iron 1000W Refrigerator 500W
C-2 Output Waveform
The inverter’s output waveform is the shape of the wave that alternating current makes as its
voltage rises and falls with time (see Figure C-1 below). The three basic output waveforms are:
• Modifi ed Sine Wave – Also referred to
as a “quasi sine wave” or a “modifi ed
square wave”. This output looks like a
one-step staircase and the waveform
changes its width to continually
provide the correct RMS output voltage
regardless of the battery voltage. Most
loads that run from a sine wave will
also run from a modifi ed sine wave.
However, things such as clocks and
furnace controllers may have trouble.
• Sine Wave – An AC waveform that
looks like rolling waves on water. It rises
and falls smoothly with time. The grid
puts out a sine waveform. Any plug-in
AC equipment will operate from a sine
wave output inverter.
• Square Wave – The simplest AC
waveform. Some types of equipment
behave strangely when powered from a
square wave inverter.
200
160
120
80
40
0
40
VOLTAGE
80
120
160
200
TIME
Figure C-1, AC Waveforms
Square Wave
Sine Wave
Modified
Sine Wave
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 62
Page 71

Appendix D – Inverter/Charger Terminology
Appendix D – Inverter/Charger Terminology
The following is a glossary of terms with which you may not be familiar. They appear in the
various descriptions of inverter and battery charger operation.
Absorbtion Stage – In this second stage of three stage charging, the batteries are held at a
constant voltage (the absorb voltage setting) and the battery is charged to its maximum capacity.
AC (Alternating Current) – Electrical current that varies with time (i.e., utility power). The rate
at which the voltage changes polarity is the frequency in Hertz (Hz).
Ampacity – The ampacity of a wire is its current carrying capacity with reference to the crosssectional area of the conductors, the temperature rating of the insulation and the ambient
temperature.
Automatic Transfer Relay (inside the inverter) – An automatic switch that switches between
Inverter and Standby mode depending on availability of AC input power. If AC is present, the
unit will be a battery charger and pass power thru the inverter. When the AC goes away, the unit
becomes an inverter.
Bulk Charge Stage – The fi rst stage in three stage charging. In this stage, a constant current is
fed to the batteries and as they accept the current the battery voltage will rise.
CEC (Canadian Electrical Code) – The guidelines and acceptable practices for electrical
installations in Canada.
Current (Amps) – The amount of electricity fl owing through a conductor.
DC (Direct Current) – Electrical current that does not vary with time (i.e., battery voltage).
Deep Cycle – A deep cycle occurs when a battery is discharged to less than 20% of its capacity
(80% depth-of-discharge).
Deep Cycle Battery – A battery designed to be routinely discharged to 20% of its maximum
capacity without damage. This type of battery is recommended for use with an inverter system.
Derating – As an inverter (or charger) is used above its normal temperature, it’s capacity to
power loads (or charge) continuously is decreased.
Digital Volt Meter (DVM):
True RMS – A voltmeter that incorporates a RMS converter to read true RMS for any waveform
shape.
Averaging Type – A voltmeter that requires a sine wave waveform shape to provide an
accurate reading.
Effi ciency – Usually given as a percentage, effi ciency is the ratio of the output to the input. The
effi ciency changes with power output levels of any inverter.
Electrolyte – Typically a mixture of water and sulfuric acid that is used in lead-acid batteries; it
is commonly referred to as battery acid.
Equalization – Controlled “overcharging” of the battery causing it to bubble and mix. This helps
reduce stratifi cation.
Float Stage – During the third stage of three stage charging, the voltage and current are
reduced to a level that will trickle charge or maintenance charge the battery. This assures the
battery remains fully charged even while sitting.
Fuse or Disconnect – When current exceeds a preset limit the fuse or disconnect will fail before
the wiring or equipment it is protecting. Disconnects are also called circuit breakers. These are
usually reset and can act as a switch to turn off power to equipment for servicing.
Grid (The grid) – Also called the utility grid, this refers to the public power distribution system.
Impedance – Slows the electrical fl ow of Alternating Current (AC)
LED (Light Emitting Diode) – A light made up of semi-conducting material.
Line Tie – Term used when the inverter is connected to public power or the “grid” system.
Load(s) – An electrical item that draws power (i.e., lights, radio, refrigerator, etc.) to work.
Page 63
Page 72

Appendix D – Inverter/Charger Terminology
Locked Rotor Amps – The current drawn by an electric motor with the shaft or rotor stopped
and locked in position. This can be used to determine if an inverter has enough surge current to
start a motor. If the inverter is capable of producing more amperage than the locked rotor amps
rating of a motor, it will most likely start the motor easily.
NEC (National Electric Code) – The guidelines and acceptable practices for electrical
installations in the USA.
Off Grid – Not connected to public power in any way.
Pass Through Current – The amount of current the inverter can safely pass directly from the
AC input to the AC output.
Photovoltaic (PV) – Solar powered.
Resistance (Ohms) – Slows the electrical fl ow of Direct Current (DC)
RMS (Root Mean Square) – A measure of AC voltage that provides the equivalent heating
value across a resistor as would a DC source of the same voltage.
Sellback, or Selling Back To The Grid or Utility-Interactive – Some inverters have the
capability to take energy stored in batteries, or from solar panels, and put it back into the utility
grid. The local public utility company can compensate you for using this energy.
Shorepower – The process of providing shoreside electrical power to a boat while its main and
auxiliary engines are turned off. The source for shorepower may be grid power from an electric
utility company, or from an external remote generator.
Stacking:
Series – Two inverters operating together to produce twice the power and voltage of a single
inverter. Required when operating 240 VAC loads and separate 120 VAC loads from either
inverter.
Parallel – Two inverters operating together to provide twice the continuous capacity on a
single output circuit. Required when a single load is too large for one inverter.
Stratifi cation – Over time, a battery’s electrolyte (liquid) tends to separate. The electrolyte at
the top of the battery becomes watery while at the bottom it becomes more acidic. This effect is
corrosive to the plates.
Sulfating – As a battery discharges, its plates become covered with lead sulfate. During
recharging, the lead sulfate leaves the plates and recombines with the electrolyte. If the lead
sulfate remains on the plates for an extended period of time (over two months), it hardens, and
recharging will not remove it. This reduces the effective plate area and the battery’s capacity.
Temperature Compensation – Peak available battery voltage is temperature dependent. As
ambient temperatures fall, the proper voltage for each charge stage needs to be increased. A
Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) automatically re-scales charge-voltage settings to compensate
for ambient temperatures.
Voltage – The pressure that causes electrical fl ow in a circuit.
Watts – Measure of power output or utilization. Watts =Volts x Amps.
© 2015 Sensata Technologies
Page 64
Page 73

Appendix E – Warranty & Service
Appendix E – Warranty & Service
E-1 Limited Warranty
Sensata Technologies warrants the MS-G Series to be free from defects in material and workmanship
that result in product failure during normal usage, according to the following terms and conditions:
1. The limited warranty for the product extends for 36 months beginning from the product’s
original date of purchase.
Note: The normal 3-year warranty on this MS-G inverter is extended to 5 years if it was
ordered with and installed on our Magnum MMP panel system. A proof-of-purchase is required
at the time of repair/service showing that the MS-G inverter and the MMP panel system were
purchased at the same time.
2. The limited warranty extends to the original purchaser of the product and is not assignable or
transferable to any subsequent purchaser.
3. During the limited warranty period, Sensata will repair or replace at our option any defective
parts, or any parts that will not properly operate for their intended use, with factory new or
remanufactured replacement items if such repair or replacement is needed because of product
malfunction or failure during normal usage. The limited warranty does not cover defects in
appearance, cosmetic, decorative or structural parts or any non-operative parts. Sensata’s
limit of liability under this warranty shall be the actual cash value of the product at the time
the original purchaser returns the product for repair, determined by the price paid by the
original purchaser. Sensata Technologies shall not be liable for any other losses or damages.
4. Upon request from Sensata, the original purchaser must prove the product’s original date of
purchase by a dated bill of sale, itemized receipt.
5. The original purchaser shall return the product prepaid to Sensata in Everett, WA, or to one of
Sensata’s Authorized Service Centers (ASC). After the completion of service under this limited
warranty, the product will be returned prepaid to the original purchaser via a non-expedited
surface freight within the contiguous United States and Canada; this excludes Alaska and Hawaii.
6. If Sensata repairs or replaces a product, its warranty continues for the remaining portion of
the original warranty period or 90 days from the date of the return shipment to the original
purchaser, whichever is greater. All replaced products and parts removed from the repaired
products become the property of Sensata Technologies.
7. This limited warranty is voided if:
• the product has been modifi ed without authorization
• the serial number has been altered or removed
• the product has been damaged from abuse, neglect, accident, high voltage or corrosion
• the product was not installed and operated according to the owner's manual
E-2 How to Receive Repair Service
If your product requires warranty service or repair, contact either:
• An Authorized Service Center, listed at: (www.Magnum-Dimensions.com), or
• Sensata Technologies at: Telephone: 425-353-8833
Fax: 425-353-8390
Email: MagnumWarranty@Sensata.com
If returning the product directly to Sensata for repair, you must:
1. Return the unit in the original, or equivalent, shipping container.
2. Receive a Return Materials Authorization (RMA) number from the factory prior to the return
of the product to Sensata for repair.
3. Place RMA numbers clearly on the shipping container or on the packing slip.
When sending your product for service, please ensure it is properly packaged. Damage due to
inadequate packaging is not covered under warranty. We recommend sending the product
by traceable or insured service.
BEFORE RETURNING ANY UNIT,
A RETURN MATERIAL AUTHORIZATION (RMA) NUMBER IS REQUIRED
Page 65
Page 74

Magnum-Dimensions Products
Manufactured by:
Sensata Technologies
2211 West Casino Rd.
Everett, WA 98204
Phone: 425-353-8833
Fax: 425-353-8390
Web: www.Magnum-Dimensions.com
MS-G Series Owner’s Manual (PN: 64-0070 Rev A)
 Loading...
Loading...