Page 1

Mini Magnum Panel (MMP)
Owner’s Manual
Page 2

Disclaimer of Liability
Since the use of this manual and the conditions or methods of installation, operation, use and
maintenance of the MMP enclosure (Mini Magnum Panel) is beyond the control of Magnum Energy,
Inc., this company does not assume responsibility and expressly disclaims liability for loss, damage
or expense, whether direct, indirect, consequential or incidental, arising out of or anyway connected
with such installation, operation, use, or maintenance.
Note as well that while every precaution has been taken to ensure the accuracy of the contents
of this manual, the specifi cations and product functionality may change without notice. Magnum
Energy, Inc. assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions.
Restrictions on Use
The MMP enclosure may only be used in life-support devices or systems with the express written
approval of Magnum Energy. Failure of the MMP enclosure can reasonably be expected to cause
failure of that life-support device or system, or to affect the safety or effectiveness of that device
or system. If the MMP fails, it is reasonable to assume the health of the user or other persons
may be endangered.
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2013 by Magnum Energy, Inc. All rights reserved. Permission to copy, distribute, and/or
modify this document is prohibited without express written permission from Magnum Energy, Inc.
Document Information
Description – Mini Magnum Panel (MMP) Owner’s Manual
Part Number and Revision – 64-0029 Rev D
Date Published – June 2013
This manual is printed without color for cost savings. However, this entire manual is available for
download under the Document Library tab at www.magnumenergy.com with many of the diagrams
available in color.
Contact Information
Magnum Energy, Inc.
2211 West Casino Rd.
Everett, WA 98204
Phone: 425-353-8833
Fax: 425-353-8390
Web: www.magnumenergy.com
Statement of Appreciation
From all of us at Magnum Energy –
Thank you for purchasing this Mini Magnum Panel (MMP).
We understand that you have many purchasing options in the marketplace, and are pleased that
you have decided on a Magnum Energy product. This MMP enclosure was proudly assembled and
tested in the United States in our Everett, Washington, facility.
At Magnum, we are committed to providing you with quality products and services, and hope that
your experience with us is pleasant and professional.
Magnum Energy® is a registered trademark of Magnum Energy, Inc.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page i
Page 3

Safety Information
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
THIS MANUAL CONTAINS IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE MMP ENCLOSURE THAT SHALL BE
FOLLOWED DURING THE INSTALLATION AND OPERATION OF THIS PRODUCT. Before using the
MMP, read all instructions and cautionary markings. Also, be sure to review the individual manuals
provided for each component of the system. The installation instructions are for use by qualifi ed
personnel only. Do not perform any installation or servicing other than that specifi ed in this owner’s
manual unless you are qualifi ed to do so. Incorrect installation or servicing may result in a risk of
electric shock, fi re, or other safety hazard.
Safety Symbols
The following safety symbols have been placed throughout this manual to indicate dangerous and
important safety instructions.
WARNING: This symbol indicates that failure to take a specifi ed action could result in
physical harm to the user.
CAUTION: This symbol indicates that failure to take a specifi ed action could result in
damage to the equipment.
Info: This symbol indicates information that emphasizes or supplements important
points of the main text.
Safety Precautions
• All electrical work must be performed in accordance with local and national electrical codes.
• This product is designed for indoor/compartment installation. It must not be exposed to rain,
snow, moisture, or liquids of any type.
• Use insulated tools to reduce the chance of electrical shock or accidental short circuits.
• There are no user-serviceable parts contained in this product.
• This unit is provided with integral protection against overloads.
• Live power may be present at more than one point since an inverter utilizes both DC (batteries,
PV, etc.,) and AC (utility or generator) power. To reduce risk of electric shock, ensure all DC
and AC wiring is disconnected prior to installing or performing maintenance on the inverter.
Turning off the inverter will not reduce this risk, the inverter must be totally disconnected from
all sources.
• Use Class 1 wiring methods for field wiring connections to terminals of a Class 2 circuit.
• Listed or labeled equipment shall be installed and used in accordance with any instructions
included in the listing or labeling.
• Always verify proper wiring prior to starting the inverter.
• Use only copper wires with a minimum temperature rating of 90°C.
• AC wiring must be no less than 10 AWG (5.3 mm²) gauge copper wire.
• Battery cables should be no less than #4/0 AWG for 12 and 24-volt systems and #2/0 AWG
gauge for 48-volt systems. Crimped and sealed copper ring terminal lugs with a 5/16 hole
should be used to connect to the DC terminals on the inverter.
• Torque all AC wiring connections and DC cable connections to the required torque values.
• Overcurrent protection of the battery cables must be provided as part of the system installation.
• Overcurrent protection of the AC output wiring must be provided as part of the system
installation.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page ii
Page 4

Safety Information
• The AC output neutral conductor and the DC negative conductors are not connected (bonded)
to the inverter chassis. Both the input and output conductors are isolated from the enclosure
and each other. System grounding, if required, is the responsibility of the system installer and
must comply with local and national electrical codes and standards. Refer to the Section 2.10
“MMP/Inverter System Grounding” for more information.
Battery Safety
• Use insulated tools and be very careful when working around batteries, they can produce
extremely high currents if short-circuited (e.g., dropping a metal tool across the battery
terminal), which could cause a fi re or explosion.
• Read and follow the battery manufacturer’s safety precautions before installing the inverter
and batteries. Always verify proper polarity and voltage before connecting the batteries
to the inverter. Once the batteries are connected to the inverter, ensure the maintenance
and charging requirements (i.e., charge voltage and charge rate) provided by the battery
manufacturer are followed to extend the life of the batteries and to prevent damage to the
batteries while charging.
• Wear eye protection such as safety glasses, and avoid touching your eyes and face when
working with batteries to keep any fl uid/corrosion on the battery from coming in contact
with eyes and skin. Have plenty of fresh water and soap nearby and thoroughly wash in case
battery acid contacts skin, clothing, or eyes. In the event of exposure to the eyes, fl ood them
for at least 15 minutes with running water and seek immediate medical attention. Baking soda
neutralizes lead acid battery electrolyte and vinegar neutralizes spilled NiCad and NiFe battery
electrolyte; depending on your battery type, keep a supply on hand near the batteries.
• Remove all jewelry such as rings, watches, bracelets, etc., when installing or performing
maintenance on the batteries and inverter. A battery can produce a short-circuit current high
enough to weld metal jewelry, causing severe burns.
• Never work alone. Always have someone within the range of your voice or close enough to
come to your aid when working around batteries.
• Use proper lifting techniques when working with batteries.
• Never use old or untested batteries. Check each battery’s label for age, type, and date code
to ensure all batteries are identical.
• Batteries are sensitive to changes in temperature. Always install batteries in a stable
environment.
• Batteries can produce explosive gasses, so install batteries in a well-ventilated area. For
compartment or enclosure installations, always vent batteries from the highest point to the
outside. Design the battery enclosure to prevent accumulation and concentration of hydrogen
gas in “pockets” at the top of the compartment.
• Provide at least one inch of air space between batteries to provide optimum cooling.
• Never smoke or allow a spark near batteries.
• To prevent a spark at the battery and reduce the chance of explosion, always connect the
cables to the batteries fi rst. Then connect the cables to the inverter.
• Never charge a frozen battery.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page iii
Page 5

Safety Information
CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ IMPORTANTES
CONSERVER CES INSTRUCTIONS
CE MANUEL CONTIENT DE IMPORTANTES POUR LA CLÔTURE DE MMP QUI DOIVENT ETRE SUIVIES
PENDANT L’INSTALLATION ET FONCTIONNEMENT DE CE PRODUIT. Avant d’utiliser la série MS, lire
toutes les instructions etles mises en garde. Aussi, n’oubliez pas depasser en revue les différents
manuels fournispour chaque composant du système. Lesinstructions d’installation sont pour une
utilisationpar du personnel qualifi é. Ne pas effectuer une installation ou d’entretien autres que
ceux spécifi és dans ce manuel, sauf si vous êtes qualifi é pour le faire. Une mauvaise installation ou
d’entretien peut entraîner un risque de choc électrique, un incendie ou autre danger pour la sécurité.
Symboles de sécurité
Les symboles de sécurité suivants ont été placéstout au long de ce manuel pour indiquer des
conditions dangereuses et les consignes de sécurité importantes.
AVERTISSEMENT: Ce symbole indique que le défaut de prendre une action spécifi ée
pourraitcauser des dommages physiques à l’utilisateur.
ATTENTION: Ce symbole indique que le défaut de prendre une action spécifi ée peut
entraîner des dommages à l’équipement.
Info: Ce symbole indique une information qui met l’accent ou des suppléments points
importants du texte principal.
Consignes de sécurité
• Tous les travaux électriques doivent être effectués en conformité avec les codes locaux et
nationaux électriques.
• Ce produit est conçu pour l’installation / du compartiment intérieur. Il ne doit pas être exposé
à la pluie, la neige, l’humidité ou des liquides de tout type.
• Utiliser des outils isolés pour réduire le risque de choc électrique ou courts-circuits accidentels.
• Il n’y a pas réparable par l’utilisateur contenues dans ce produit.
• Cet appareil est fourni avec une protection intégrale contre les surcharges.
• Puissance en direct peuvent être présents à plus d’un point depuis un onduleur utilise à la fois
DC (piles, PV, etc.,) et AC (utilitaire ou générateur) d’alimentation. Pour réduire le risque de
choc électrique, assurez-vous que tout le câblage DC et AC est débranchée avant l’installation
ou la maintenance sur le variateur. Mise hors tension de l’onduleur ne réduira pas ce risque,
l’onduleur doit être totalement déconnectée de toutes les sources.
• Utiliser des méthodes de câblage classe 1 pour les connexions de câblage sur le terrain aux
bornes d’un circuit de Classe 2.
• Coté ou étiquetés équipement doit être installé et utilisé conformément aux instructions
fi gurant dans la liste ou l’étiquetage.
• Toujours vérifi er le câblage avant de commencer l’onduleur.
• Utilisez des fi ls de cuivre seulement avec une cote de température minimale de 90° C.
• AC câblage ne doit pas être inférieure à 10 AWG (5,3 mm2) de cuivre de calibre.
• Les câbles de batterie ne doit pas être inférieur à # 4/0 AWG pour 12 et 24 volts systèmes
et # 2/0 AWG pour calibre 48-volts systèmes. Frisées et scellé cosses en cuivre anneau des
bornes avec un trou de 5/16 doit être utilisé pour se connecter à des bornes de courant
continu sur l’onduleur.
• Couple toutes les connexions de câblage ca et les connexions de câbles à courant continu à
des valeurs de couple nécessaires.
• La protection contre les surintensités des câbles de batterie doivent être fournis dans le cadre
de l’installation du système.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page iv
Page 6

Safety Information
• Le conducteur de courant alternatif de sortie neutre et les conducteurs à courant continu
négatives ne sont pas connectés (servitude) au châssis inverseur. La fois l’entrée et des
conducteurs de sortie sont isolés de l’enceinte et l’autre. La terre du système, si nécessaire,
est de la responsabilité de l’installateur du système et doit se conformer à des codes locaux
et nationaux et les normes électriques. Reportez-vous aux Section 2.10 “Au sol de système
interactif” pour plus d’informations.
Sûreté de batterie
• Utilisez les outils isolés et faites attention très en travaillant autour des batteries, ils peuvent
produire les courants extrêmement élevés si au sujet dont court-circuité (par exemple,
laissant tomber un outil en métal à travers la borne de batterie), pourrait causer un fi ou une
explosion.
• Lisez et suivez les mesures de sécurité du fabricant de batterie avant d’installer l’inverseur et
les batteries. Vérifi ez toujours la polarité et la tension appropriées avant de relier les batteries
à l’inverseur. Une fois que les batteries sont reliées à l’inverseur, assurez que l’entretien et les
conditions de remplissage (c.-à-tension de charge et taux de charge) fournis par le fabricant
de batterie sont suivis pour prolonger la vie des batteries et pour empêcher des dommages
aux batteries tout en chargeant.
• Portez la protection d’oeil telle que des verres de sûreté, et l’évitez de toucher vos yeux et
visage en travaillant avec des batteries pour garder n’importe quels fl uide/corrosion sur la
batterie des yeux et de la peau contactants. Ayez l’abondance de l’eau doux et du savon
tout près et lavez complètement au cas où l’acide de batterie entrerait en contact avec la
peau, l’habillement, ou les yeux. En cas de l’exposition aux yeux, à l’ood de fl ils pendant
au moins 15 minutes avec l’attention médicale immédiate d’eau courante et de recherche.
Le bicarbonate de soude neutralise l’électrolyte de batterie d’acide de plomb et le vinaigre
électrolyte neutralise batterie renversée de NiCad et de NiFe ; selon votre type de batterie,
gardez un approvisionnement en main près des batteries.
• Enlevez tous les bijoux tels que les anneaux, montres, bracelets, etc., en installant ou en
exécutant l’entretien sur les batteries et l’inverseur. Une batterie peut produire un courtcircuit courant assez haut aux bijoux en métal de soudage, causant les brûlures graves.
• Ne travaillez seul jamais. Toujours ayez quelqu’un dans la marge de votre voix ou clôturez
assez pour venir à votre aide en travaillant autour des batteries.
• Employez les techniques de levage appropriées en travaillant avec des batteries.
• N’utilisez jamais les vieilles ou non essayées batteries. Examinez l’étiquette de chaque batterie
pour assurer l’âge, type, et le code de date pour assurer toutes les batteries sont identique.
• Les batteries sont sensibles aux changements de la température. Installez toujours les
batteries dans un environnement stable.
• Les batteries peuvent produire les gaz explosifs, ainsi installez les batteries dans un secteur
well-ventilated. Pour des installations de compartiment ou de clôture, exhalez toujours les
batteries du point le plus élevé à l’extérieur. Concevez la clôture de batterie pour empêcher
l’accumulation et la concentration du gaz d’hydrogène dans des « poches » au dessus du
compartiment.
• Fournissez au moins un pouce d’espace aérien entre les batteries pour fournir le refroidissement
optimum.
• Ne fumez jamais ou permettez une étincelle près des batteries.
• Our empêcher une étincelle à la batterie et réduire la possibilité de l’explosion, reliez toujours
les câbles au rst de fi de batteries.
• Reliez alors les câbles à l’inverseur. Ne chargez jamais une batterie congelée.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page v
Page 7

Table of Contents
1.0 Introduction ...........................................................................................1
1.1 MMP Series Overview ................................................................................. 2
1.2 MMP External Components .......................................................................... 3
1.3 MMP Internal Components .......................................................................... 4
2.0 Installation ............................................................................................8
2.1 Preparation ............................................................................................... 8
2.1.1 Unpacking and Inspection ........................................................................... 8
2.1.2 Required Materials and Tools ....................................................................... 8
2.2 Location ..................................................................................................10
2.3 Conduit Knockouts ....................................................................................10
2.4 Mounting .................................................................................................12
2.5 Wiring the MMP Enclosure – General Requirements........................................14
2.5.1 Disconnect Switch and Overcurrent Protection ..............................................14
2.5.2 General Wiring Requirements .....................................................................14
2.5.3 Wire Routing ............................................................................................15
2.6 Torque Requirements ................................................................................15
2.7 Electrical System Wiring Diagrams ..............................................................15
2.8 DC Wiring ................................................................................................18
2.8.1 DC Wiring Guidelines .................................................................................18
2.8.2 DC Wiring Connection Points ......................................................................19
2.8.3 Inverter DC Overcurrent Protection and DC Disconnect ..................................21
2.8.4 Inverter and Battery Bank Wire Sizing .........................................................21
2.8.5 DC Hardware Connections ..........................................................................22
2.8.6 Wiring the Battery Bank ............................................................................23
2.8.7 Wiring the MMP Enclosure to the Battery Bank/Inverter .................................23
2.9 AC Wiring ................................................................................................24
2.9.1 AC Wiring Guidelines .................................................................................24
2.9.2 AC Connections ........................................................................................24
2.9.3 AC Wire Size and Overcurrent Protection ......................................................27
2.9.4 AC Conductor Wiring .................................................................................27
2.9.5 AC Wiring Confi gurations ...........................................................................28
2.10 MMP/Inverter System Grounding ................................................................33
2.10.1 Sizing the Grounding Electrode Conductors ..................................................34
2.10.2 Equipment Grounding Conductor.................................................................36
2.10.3 System Bonding Jumper ............................................................................36
2.11 Removing the AC Neutral to Ground Connection ............................................37
2.12 Removing the DC Negative to Ground Busbar ...............................................37
2.13 Wiring Accessories ....................................................................................38
2.14 Installation Checklist .................................................................................40
2.15 Functional Test .........................................................................................42
3.0 Operation .............................................................................................44
3.1 Inverter DC Disconnect Breaker ..................................................................45
3.2 AC Input Breaker ......................................................................................45
3.3 Inverter AC Output Breaker ........................................................................45
3.4 Inverter AC Bypass Switch Breaker .............................................................45
Page vi
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 8

Table of Contents (Cont.)
Appendix A – Optional Equipment and Accessories .......................................48
A1 Installing the Charge Controller Bracket .......................................................48
A2 Installing a Remote Control ........................................................................50
A3 Installing a Battery Monitor ........................................................................51
A4 Knockout Plate .........................................................................................52
A5 Inverter Hood Info ....................................................................................53
A6 Installing Optional DC Breakers ..................................................................54
A7 Installing Lightning Arrestors ......................................................................56
A8 MMP Back Panel Information ......................................................................58
Appendix B – Using the MMP in a Mobile Application .....................................59
Appendix C – Warranty and Service...............................................................60
C1 Limited Warranty ......................................................................................60
C2 How to Receive Repair Service ....................................................................60
List of Tables
Table 2-1, Torque Values for Busbars ...............................................................................15
Table 2-2, Torque Values for the DC Shunt and DC Disconnect Breaker ................................15
Table 2-3, Torque Values for the AC Terminal Blocks ..........................................................15
Table 2-4, Recommended DC Wire to MMP Enclosure .........................................................21
Table 2-5, AC Input/Output Wiring Configurations .............................................................28
Table 2-6, AC Grounding Electrode Conductor Sizing .........................................................34
Table 2-7, Equipment Grounding Conductor Sizing ............................................................36
Table A-1, Mounting Holes Used for Charge Controllers ......................................................48
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page vii
Page 9

List of Figures
Figure 1-1, MMP’s Outside Components ............................................................................ 3
Figure 1-2, MMPxxx-30D Internal Components .................................................................. 6
Figure 1-3, MMPxxx-30D AC Breakers .............................................................................. 6
Figure 1-4, MMPxxx-60S Internal Components .................................................................. 7
Figure 1-5, MMPxxx-60S AC Breakers ............................................................................... 7
Figure 2-1, MMP Series Simplified Installation Diagram ....................................................... 9
Figure 2-2, MMP Series Dimensions and Knockout Location/Sizes ........................................11
Figure 2-3, Removing Knockouts ....................................................................................12
Figure 2-4, Keyhole Locations for Mounting ......................................................................13
Figure 2-5, MMPxxx-30D System Wiring Diagram ..............................................................16
Figure 2-6, MMPxxx-60S System Wiring Diagram ..............................................................17
Figure 2-7, DC Wiring Connection Points ..........................................................................19
Figure 2-8, DC Wiring with Magnum Inverter ....................................................................20
Figure 2-9, DC Connections – with Magnum Inverter Installed ............................................22
Figure 2-10, AC Wiring Connections (MMPxxx-30D Models) ................................................25
Figure 2-11, AC Wiring Connections (MMPxxx-60S Models) ................................................26
Figure 2-12, AC Wiring for Single In – Single Out (30 A) Configurations ...............................29
Figure 2-13, AC Wiring for Single In – Single Out (60 A) Configurations ...............................30
Figure 2-14, AC Wiring for Dual In – Single Out Configurations ...........................................31
Figure 2-15, AC Wiring for Dual In – Dual Out Configurations .............................................32
Figure 2-16, Grounding System for Inverter with MMP Enclosure .........................................33
Figure 2-17, Single Connection to DC Ground Rod (Method 1) ............................................34
Figure 2-18, Multiple Connections to DC Ground Rod (Method 2) .........................................35
Figure 2-19, Multiple Connections to DC Ground Rod (Method 3) .........................................35
Figure 2-20, Removing the AC Neutral to Ground Connection .............................................37
Figure 2-21, Removing the DC Negative to Ground Busbar .................................................37
Figure 2-22, REMOTE Communication Cable (300V) ..........................................................38
Figure 2-23, NETWORK Communication Cable (300V) ........................................................ 38
Figure 2-24, Extension Cable (300V) ............................................................................... 38
Figure 2-25, Accessory Wiring using 300 Volt Communications Cables .................................39
Figure 2-26, AC Voltage Checks ......................................................................................43
Figure 3-1, MMP Functional Diagram ...............................................................................44
Figure 3-2, MMPxxx-30D Bypass Switch Operation ............................................................46
Figure 3-3, MMPxxx-60S Bypass Switch Operation ............................................................47
Figure A1-1, Charge Controller Bracket – Physical Dimensions ............................................48
Figure A1-2, Holes Used to Mount Bracket on MMP Enclosure ..............................................49
Figure A2-1, Installing a Remote Control on the MMP Enclosure ..........................................50
Figure A3-1, Mounting the Sense Module .........................................................................51
Figure A3-2, Wiring the Sense Module and DC Shunt .........................................................51
Figure A4-1, Attaching Knockout Plate .............................................................................52
Figure A4-2, Knockout Plate Dimensions and Knockouts .....................................................52
Figure A5-1, Inverter Hood Dimensions ...........................................................................53
Figure A6-1, Installing DIN Rail-Mounted DC Breakers .......................................................54
Figure A6-2, Installing Back Panel Mounted DC Breakers ....................................................55
Figure A6-3, Wiring DC Breakers ....................................................................................55
Figure A7-1, Installing Lightning Arrestor on MMP Enclosure ...............................................56
Figure A7-2, Wiring Lightning Arrestor to MMP Enclosure ...................................................57
Figure A8-1, MMP Back Panel (BP-MMP) Information .........................................................58
Page viii
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 10

Introduction
1.0 Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of the Mini Magnum Panel (MMP) enclosure, part of a new line of
panel systems from Magnum Energy. Installing an inverter system is now as simple as mounting
the MMP enclosure, installing the inverter, connecting the battery bank, and if needed, bringing in
AC power from a generator or the utility. The inverter’s required AC and DC disconnects and wire
connection points are all together, and integrated in one self-contained enclosure.
This unit has been specifi cally designed to combine all of the major components required for a
renewable energy system into a single, easy to install pre-wired enclosure. This includes: inverter/
battery disconnect, AC overcurrent protection, grounding connections, and a full system inverter
bypass switch as a convenient way to isolate the inverter for battery maintenance.
Designed for single inverter applications, this enclosure features convenient front panel operation
and the optional front panel remote allows easy Magnum inverter set up, monitoring, and operation.
In addition to saving time and money with a simple and easy inverter installation, this enclosure
ensures safety and reliability by providing a UL and CSA certifi ed, code compliant system.
What makes the MMP enclosure stand out from the competition?
• It is engineered to combine the ease and cost savings of a pre-wired, factory-integrated
system with the fl exibility of a single person, fi eld installed power system.
• The self-contained enclosure system is convenient and space-saving, reducing installation time
and cost compared to a conventional approach using multiple interconnected components.
• Multiple models are available to meet the fl exibility and power demands of your application.
• Specifi cally designed to fi t Magnum inverters, but easily adaptable to connect other inverter
systems in 12, 24, or 48 VDC standardized confi gurations.
• Includes a built-in AC bypass switch with full system current capability, and a DC disconnect
breaker for safe and easy servicing of the inverter and/or battery bank.
• Additional space to install up to eight
1” (25.4mm) wide back-mounted breakers for use as DC load breakers; or, space to install PV
disconnects or PV-Ground Fault Protection (PV-GFP).
• A full system capacity DC shunt (500 amps) installed to allow easy connection to a state-ofcharge battery monitor.
• AC/DC wiring connections and circuit breaker operations are easily accessible from the front.
½” (12.7mm) wide DIN rail-mounted breakers or four
Regulatory Compliance
The MMP has been designated as Interconnection System Equipment (ISE) and has been evaluated
by Intertek Testing Services (also known as ETL). ETL is a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory
(NRTL) and has listed the MMP enclosure to the following product safety standards and ratings:
Standards
• UL1741 Standard for Safety of Inverters, Converters, Controllers and Interconnection System
Equipment for Use with Distributed Energy Resources (Edition 2)
• CSA C22.2 No. 107.1, General Use Power Supplies – R2006 (Edition 3)
Ratings
• Maximum battery input: 160VDC
• Maximum PV input voltage (DC): 300VDC
• Maximum DC input short circuit current (DC): 10,000 AIC
• Operating voltage range (AC): 120-240VAC nominal
• Normal operation range: 5000 VA @25°C (MMP)
Info: NRTL’s are qualified organizations that meet Occupational Safety and Health
Administration (OSHA) regulations to perform independent safety testing and product
certification.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 1
Page 11

Introduction
1.1 MMP Series Overview
The MMP enclosure is available in four basic confi gurations. This section lists the four models and
the enclosure’s main components and features.
Individual Models:
• MMP175-30D (Mini Magnum Panel, 175 ADC breaker, dual 30 AAC bypass/input breakers)
• MMP175-60S (Mini Magnum Panel, 175 ADC breaker, single 60 AAC bypass/input breakers)
• MMP250-30D (Mini Magnum Panel, 250 ADC breaker, dual 30 AAC bypass/input breakers)
• MMP250-60S (Mini Magnum Panel, 250 ADC breaker, single 60 AAC bypass/input breakers)
Standard Features:
• Enclosure is steel construction with durable white powder coat fi nish
• Battery/inverter DC disconnect breaker (175 or 250 amps)
• Inverter AC input overcurrent protection breakers
• Pre-wired AC bypass switch for inverter isolation/battery maintenance
• Front mount AC and DC breakers for quick and easy operation
• AC and DC ground screw type compression terminals (no lugs required)
• 500A/50mV DC shunt installed for easy connection to battery status monitor
• Easy fi eld wiring with front-mounted AC and DC input/output terminals
• Enclosure and components are UL/CSA certifi ed and designated for indoor use
• Confi gurations available for both single 120 VAC and 120/240 VAC systems
• DC negative and ground busbars (negative can be isolated if PV-GFP device installed)
• Battery positive busbar for DC loads and PV arrays included
• Provides mounting for DIN rail or back-mounted DC load/disconnect breakers
• Integrates directly with Magnum MS, MS-PAE, and RD Series inverters
• Knockouts for inverter and battery cables, PV in/out, DC breakers
• Stud terminal available for large DC wire if used as system ground
• Data cables with 300-volt rated insulation to allow 240 VAC inverter installations
• Inverter hood to allow a Magnum inverter to be mounted vertically
Physical Features:
• MMP dimensions (H x W x D): 18” x 13” x 6.75” (45.7cm x 33cm x 17.1cm)
• MMP weight: 22.5 lbs. (10.2 kg)
• Shipping dimensions (H x W x D): 22” x 15” x 12.5” (56.9cm x 38.1cm x 31.8cm)
• Shipping weight: 31.5 lbs. (14.3 kg)
Optional Accessories/Components:
• ME-RC – Basic Remote Control with LCD display; allows inverter (or connected accessory) to be
confi gured and monitored, and maintains the critical settings in non-volatile memory.
• ME-ARC – Advanced Remote Control with LCD display; has all the features of the ME-RC
remote, but also confi gures the advanced features of the inverter (or any connected accessory).
• ME-BMK-NS – Battery Monitor; determines battery State of Charge (DC shunt not included).
• ME-AGS-N – Automatic Generator Start Controller (Network version); automatically starts/
stops generators.
• BP-MMP – Metal Backplate; for mounting the Magnum inverter and MMP enclosure, and is
UPS shippable. See Figure A8-1 in Appendix A for more specifi c information.
• DC Breakers – Space for up to four E-Frame/back-mounted (1” width) or eight Q-Frame/DIN
rail-mounted (1/2” width) DC breakers.
• MMP-KP – A top cover plate with knockouts to allow other (non-Magnum) inverter installations.
See Figure A4-1 in Appendix A for more specifi c information.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 2
Page 12
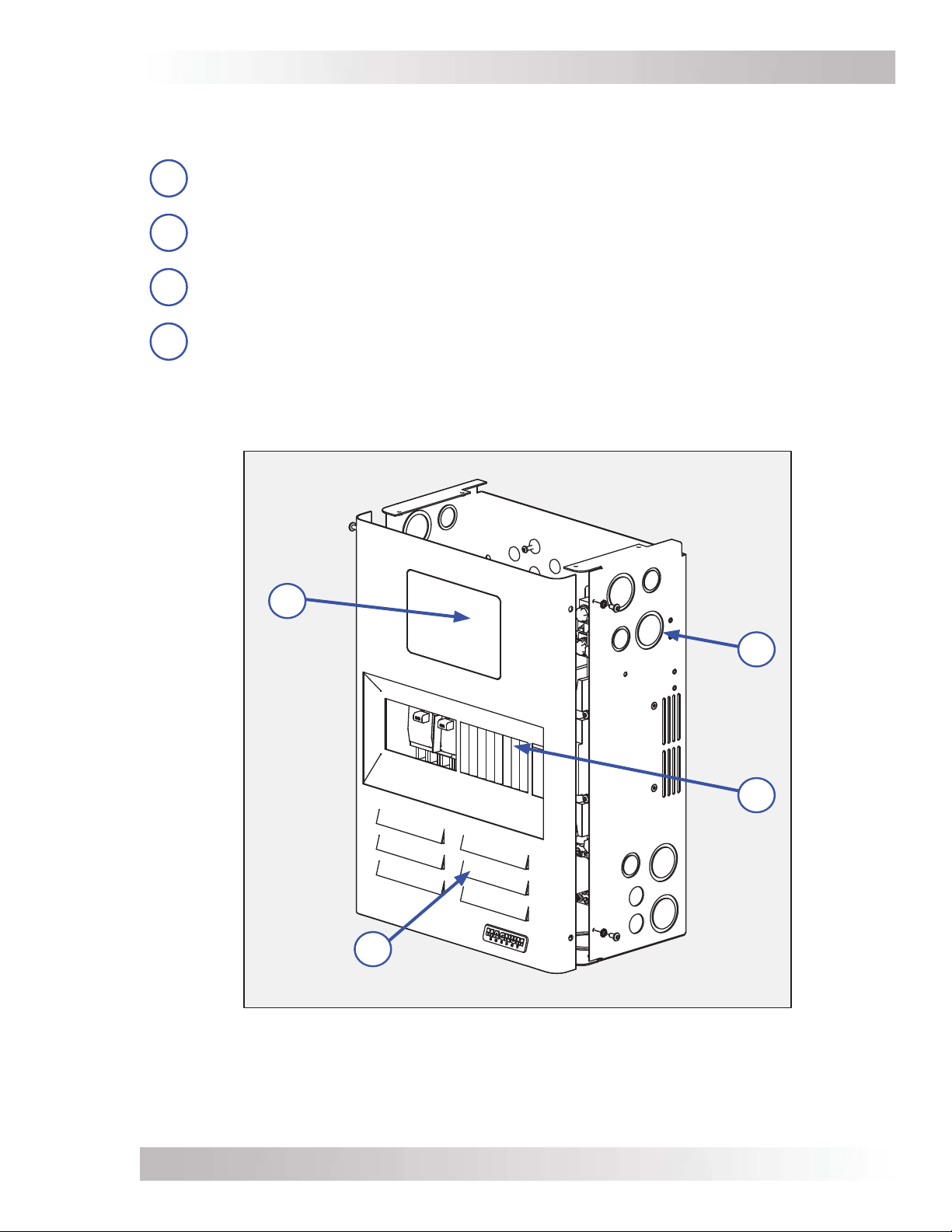
Introduction
1.2 MMP External Components
As shown in Figure 1-1, the main components found on the outside of the MMP enclosure are:
Remote Blank Plate – This plate is removed when an optional ME-RC or ME-ARC
1
remote control is installed.
Conduit Knockouts – Knockouts to allow metal and PVC conduits. For dimensions and
2
sizes see Figure 2-2.
Knockout Panels – Eight 1/2” rectangular knockout panels provided to install additional
3
DC circuit breakers.
Front Cover – The front cover is removed to allow access to the internal components.
4
Four #10 x 3/8”, T25 Torx drive screws are used to hold the front cover to the enclosure.
1
2
3
4
Figure 1-1, MMP’s Outside Components
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 3
Page 13

Introduction
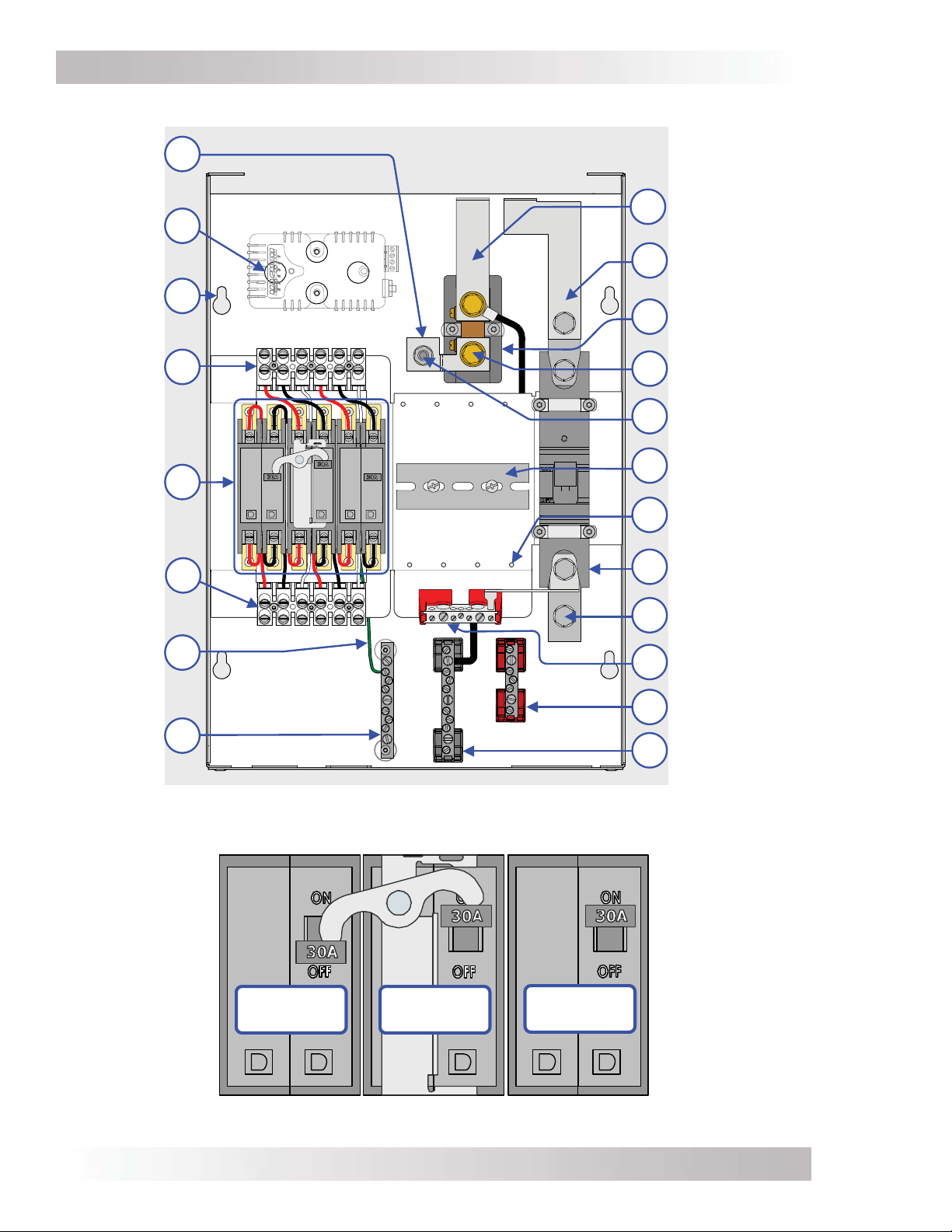
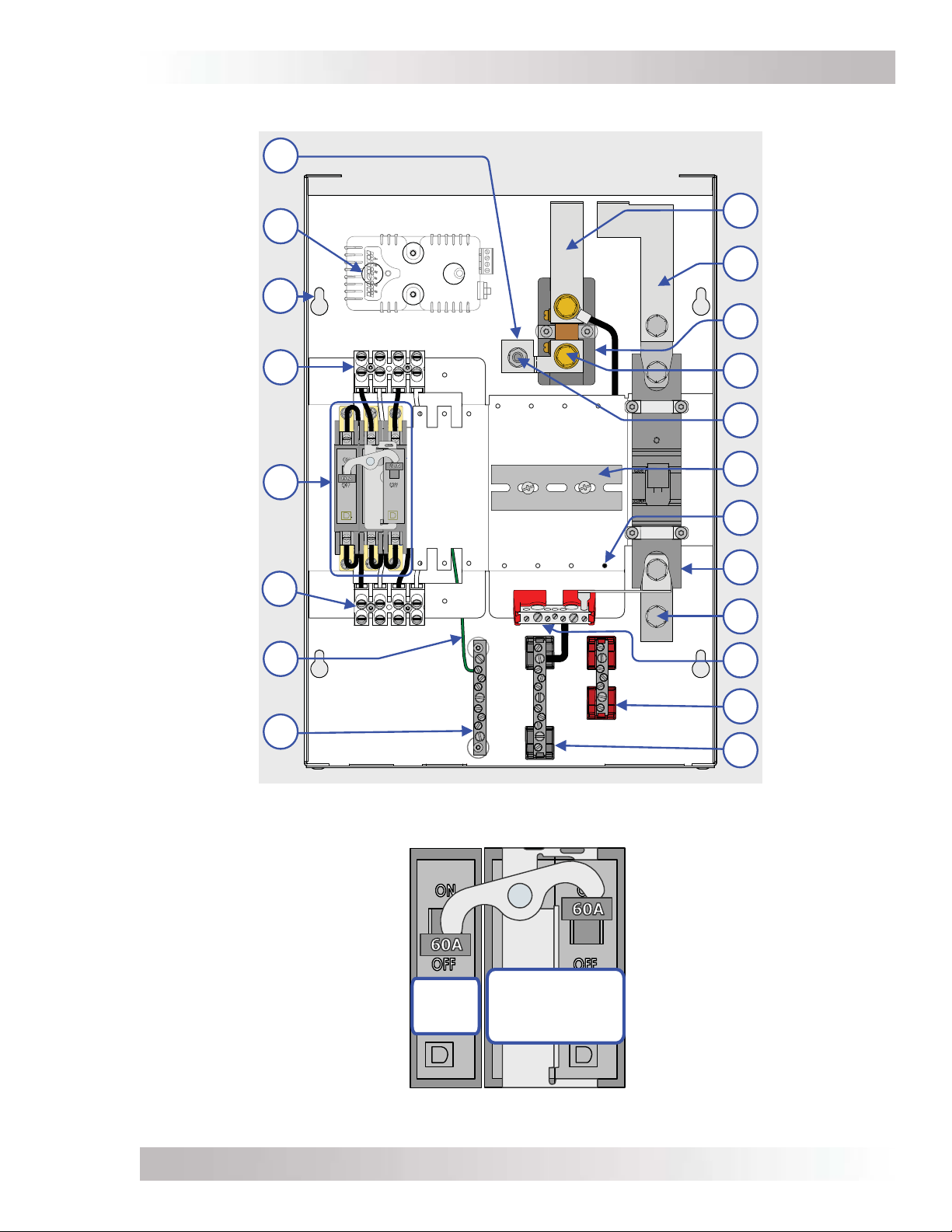
1.3 MMP Internal Components
The following components are found inside the MMP enclosure (refer to Figures 1-2 thru 1-5):
DC Negative to Ground Connection – A busbar connects the DC negative to the
1
system ground. This busbar can be removed if the primary DC negative-to-ground
connection is made elsewhere in the system (see Section 2.12).
Mounting Dimples (x4) – These dimples allow the optional ME-BMK-NS (Battery
2
Monitor Kit without DC shunt) to be installed. For more information on mounting the
battery monitor see Section A3 in Appendix A.
Mounting Keyholes (x4) – Four keyholes for mounting the enclosure. See Figure 2-4
3
for size information on these keyholes.
Inverter AC Wiring Terminal – Terminal for connecting the inverter’s AC input and
4
output wires.
AC Breakers – This AC breaker assembly is pre-wired at the factory and consists of the
5
inverter bypass switch, and the inverter input and output disconnect. These breakers
provide overcurrent protection and a way to disconnect the AC wiring inside the MMP
enclosure. These breakers can also provide overcurrent protection to the AC input source
and output load circuits if the minimum recommended AC wiring sizes are used.
External AC Wiring Terminal – Terminal for connecting the external AC source (utility/
6
generator) and the electrical panel that will be powered by the inverter.
7
8
9
10
11
12
AC Neutral to Ground Connection – A wire (green) connects the AC neutral to the
system ground. This green wire can be removed from the ground busbar if the primary
AC neutral-to-ground connection is made elsewhere in the system (see Section 2.11).
Ground Busbar – This busbar is connected to the MMP enclosure chassis and is used to
tie AC and DC equipment grounds to a common point.
This busbar has dual hole sizes—three #14 to #1/0 AWG and six #14 to #6 AWG—with
screw type compression terminals (no ring lugs required).
Inverter’s DC Negative Connection Busbar – Inverter’s DC negative terminal
connects to the top of this busbar.
Inverter’s DC Positive Connection Busbar – Inverter’s DC positive terminal connects
to the top of this busbar.
DC Shunt – A 500-amp/50 mV shunt installed in the DC negative side that is used to
measure the amperage fl owing between the battery and the inverter (and any DC loads
connected). This shunt is pre-installed so that a battery monitor may be easily connected
to display the current fl ow. See Section A3 in Appendix A for information on installing
and wiring the ME-BMK-NS battery monitor inside the MMP enclosure.
Battery Negative Connection – The bottom of the DC shunt is the connection point to
the negative terminal of the battery bank.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 4
Page 14

Introduction
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
DC Ground Stud – This 5/16” stud is connected to the MMP enclosure chassis and is
provided as a connection point to the DC grounding electrode when the conductor is
larger than #1/0 AWG.
This 5/16” stud also connects to the DC shunt through a busbar and serves as the DC
negative-to-ground connection point. If installing a PV-GFP device, this busbar must be
removed (see Section 2.12).
Note: For ground wires #1/0 AWG or smaller, use the DC negative busbar (Item 20).
DIN Rail Track – For installing up to eight 1/2” (12.7mm) wide, DIN rail-mounted,
Q-Frame type breakers. These breakers can be used for connecting DC loads or installing
a PV-GFP device.
Mounting Holes (x8) – For installing up to four 1” (25.4mm) wide, back-mounted,
E-Frame type breakers. These breakers can be used for connecting DC loads or installing
a PV-GFP device.
Inverter DC Disconnect Breaker – This disconnect is a heavy-duty high amperage circuit
breaker specifi cally designed for the MMP enclosures. It provides an easy and convenient
way to isolate the inverter from the battery, and meets the NEC/CEC requirements for DC
overcurrent protection when used in accordance with the installation instructions in this
manual. The amperage rating depends on the MMP model (175 or 250 amps).
Battery Positive Connection – The bottom of the inverter’s DC disconnect is the
connection point to the positive terminal of the battery bank. The DC disconnect has a
front connected terminal with 3/8-16 captive nuts.
Battery Positive Busbar – This busbar is connected to the battery bank positive
through the bottom of the inverter DC disconnect. This busbar is the battery positive
common point for connecting additional DC circuits, such as from the output of a charge
controller or connecting to DC load breakers.
This busbar is rated to handle 120 amps, and has dual hole sizes—two # 14 to #1/0
AWG and fi ve #14 to #6 AWG—with screw type compression terminals (no ring lugs
required).
PV Positive Busbar – This busbar provides a convenient connection point inside the
MMP for the positive output from a PV array and the positive input to the PV charge
controller.
This busbar is rated to handle 120 amps, and has dual hole sizes—two # 14 to #1/0
AWG and fi ve #14 to #6 AWG—with screw type compression terminals (no ring lugs
required).
DC Negative Busbar – This busbar is connected to the battery bank negative through
the load side of the DC shunt. This busbar is the battery negative common point for
connecting additional DC circuits, such as from the DC negative output of a charge
controller or combining the negatives of DC load circuit breakers.
This busbar is rated to handle 120 amps, and has dual hole sizes—two # 14 to #1/0
AWG and fi ve #14 to #6 AWG—with screw type compression terminals (no ring lugs
required).
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 5
Page 15
Introduction
DC NEGATIVE
TO GROUND
CONNECTION
1
MOUNTING
DIMPLES (X4) FOR
ME-BMK
(ME-BMK NOT INCLUDED)
MOUNTING
KEYHOLES (X4)
INVERTER AC
WIRING TERMINAL
(INVERTER INPUT/OUTPUT)
AC BREAKERS
(INVERTER BYPASS,
UTPUT AND INPUT)
O
EXTERNAL AC
W
IRING TERMINAL
(FOR GRID/GENERATOR
AND AC LOADS)
AC NEUTRAL
TO GROUND
CONNECTION
DC NEGATIVE
9
CONNECTION BUSBAR
2
DC POSITIVE
10
CONNECTION BUSBAR
3
11
DC SHUNT
4
5
6
7
BATTERY NEGATIVE
12
C
ONNECTION
(TO BATTERY BANK)
13
DC GROUND STUD
DIN RAIL TRACK
(FOR DIN RAIL-MOUNTED
14
BREAKERS)
DC
MOUNTING HOLES (X8)
(FOR BACK-MOUNTED
15
BREAKERS)
DC
INVERTER DC
16
DISCONNECT BREAKER
BATTERY POSITIVE
17
CONNECTION
(TO BATTERY BANK)
BATTERY POSITIVE
18
BUSBAR
GROUND
BUSBAR
8
Figure 1-2, MMPxxx-30D Internal Components
INVERTER
BYPASS
INVERTER
OUTPUT
Figure 1-3, MMPxxx-30D AC Breakers
INVERTER
INPUT
PV POSITIVE BUSBAR
19
DC NEGATIVE
20
BUSBAR
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 6
Page 16
DC NEGATIVE
TO GROUND
CONNECTION
MOUNTING DIMPLES
(X4) FOR ME-BMK
(ME-BMK NOT INCLUDED)
MOUNTING
KEYHOLES (X4)
Introduction
1
DC NEGATIVE
9
2
CONNECTION BUSBAR
DC POSITIVE
10
CONNECTION BUSBAR
3
DC SHUNT
11
INVERTER AC
WIRING TERMINAL
(INVERTER INPUT/OUTPUT)
AC BREAKERS
(INVERTER BYPASS, OUTPUT
W
(FOR GRID/GENERATOR AND
AND INPUT)
EXTERNAL AC
IRING TERMINAL
AC LOADS)
AC NEUTRAL
TO GROUND
CONNECTION
GROUND
BUSBAR
4
5
BATTERY NEGATIVE
12
C
ONNECTION
(TO BATTERY BANK)
DC GROUND STUD
13
DIN RAIL TRACK
14
(FOR DIN RAIL-MOUNTED
BREAKERS)
DC
MOUNTING HOLES (X8)
(FOR BACK-MOUNTED
15
BREAKERS)
DC
INVERTER DC
16
DISCONNECT BREAKER
6
BATTERY POSITIVE
17
C
ONNECTION
(TO BATTERY BANK)
7
BATTERY POSITIVE
18
BUSBAR
PV POSITIVE BUSBAR
19
8
DC NEGATIVE
20
BUSBAR
Figure 1-4, MMPxxx-60S Internal Components
Figure 1-5, MMPxxx-60S AC Breakers
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
INVERTER
BYPASS
INVERTER OUTPUT
(LEFT SIDE)
INVERTER INPUT
(RIGHT SIDE)
Page 7
Page 17

Installation
2.0 Installation
WARNING: Installations should be performed by qualifi ed personnel, such as a
licensed or certifi ed electrician. It is the installer’s responsibility to determine which
safety codes apply and to ensure that all applicable installation requirements are
followed. Applicable installation codes vary depending on the specifi c location and
application of the installation.
CAUTION: Review the “Important Safety Instructions” on pages ii-v before any
installation.
CAUTION: The MMP enclosure is heavy. Use proper lifting techniques during installation
to prevent personal injury.
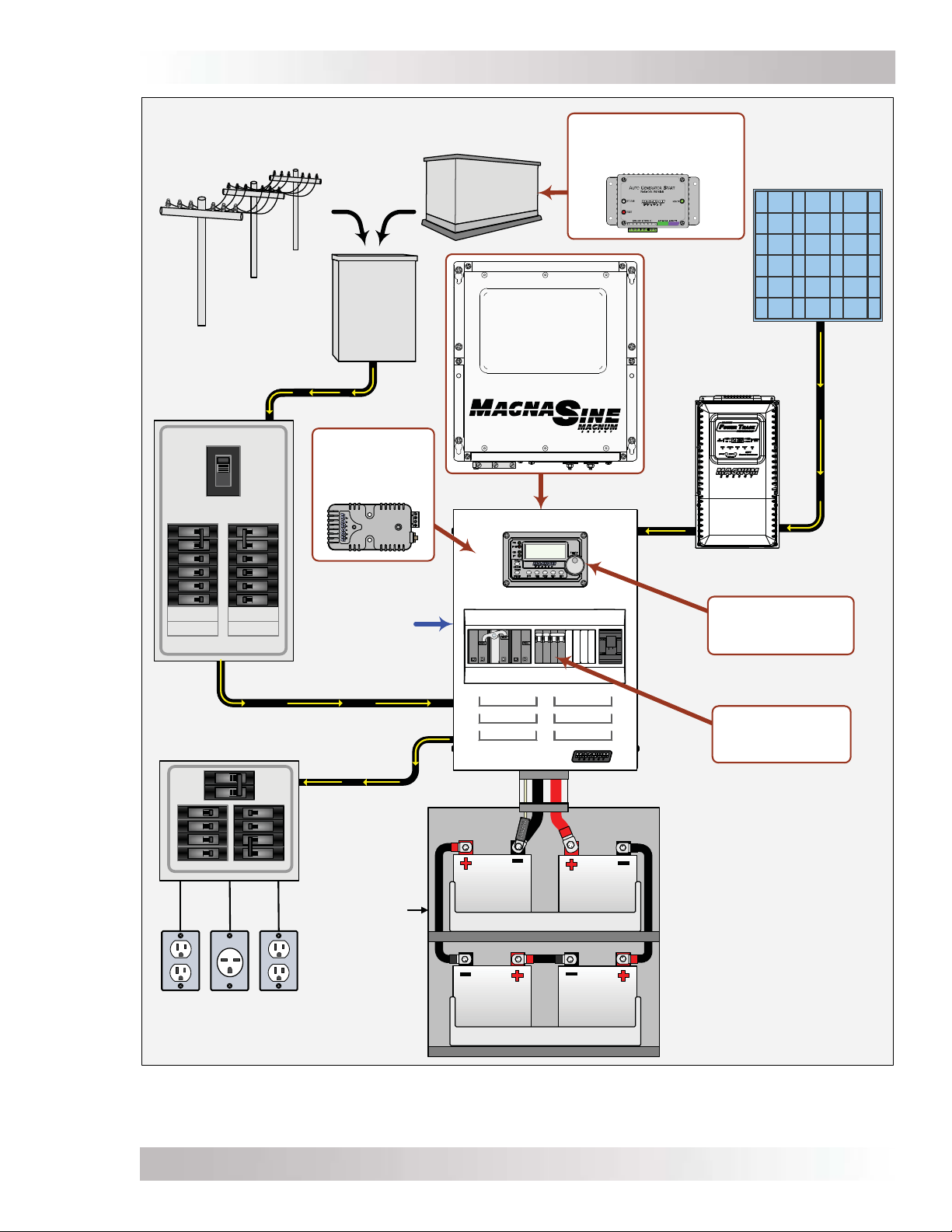
The simplifi ed system diagram shown in Figure 2-1 should be reviewed to assist you in planning
and designing your installation. This drawing is not intended to override or restrict any national
or local electrical codes, nor should it be the determining factor as to whether the installation is
compliant – that is the responsibility of the electrician and the onsite inspector.
2.1 Preparation
Before proceeding, read the entire Installation section to determine how you are going to install
your MMP enclosure. Save time and avoid common, costly mistakes by thoroughly planning before
you start.
2.1.1 Unpacking and Inspection
Carefully remove the MMP enclosure from its shipping container and inspect all contents. Verify
that the following items are included:
• MMP enclosure • RJ14 extension cable • 3/8-16 x 1” bolt
• Inverter hood • 6’ Network cable • 3/8” split lock washer
• Owner’s manual • 6’ Remote cable
• Four 8-32 x 1/2 Phillips drive, black colored screws (used to mount an optional remote control)
If items appear to be missing or damaged, contact your authorized Magnum Energy dealer or
Magnum Energy.
Save your proof-of-purchase as a record of your ownership; it will also be needed if the unit should
require in-warranty service.
2.1.2 Required Materials and Tools
The following material and tools may be required for installing this equipment:
Materials
• Conduit, strain-reliefs, and appropriate fi ttings • 1/4” mounting bolts and lock washers
• Electrical tape • Wire ties
• Conductors/cables for wiring
Tools
• Miscellaneous screwdrivers • Insulated pliers • Wire cutters/strippers
• Drill and drill bits • Pencil or marker • Multimeter
• Level • 1/2” wrench
• Torque wrenches • Ratchet drives
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 8
Page 18
Installation
UTILITY POWER
120/240VAC OUTPUT
MAIN PANEL
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
AC
T
RANSFER
SWITCH
ME-BMK-NS
Battery Monitor
(Magnum Option,
Installs inside)
MMP
NCLOSURE
E
GENERATOR POWER
120/240VAC OUTPUT
r
o
t
a
r
e
n
e
G
r
o
t
i
c
a
p
a
C
x
u
l
F
Magnum Inverter
(Attaches on
top for a
seamless look)
ON
OFF
63A
ME-AGS-N
Auto Gen Start Controller
(Magnum Option)
ON
ON
OFF
OFFONOFF
63A
63A 0.5A
PV C
HARGE
CONTROLLER
ME-RC or ME-ARC
Remote Controls
(Magnum Options)
PV PANELS
AC power to inverter
SUB-PANEL
30A
OFF
ON
OFF
30A
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
Inverter power
(or pass-thru power)
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
to Sub-panel
BATTERY
BANK
120
VAC
240
VAC
120
VAC
Figure 2-1, MMP Series Simplifi ed Installation Diagram
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Space for optional
DC circuit breakers
and PV-GFP
Page 9
Page 19

Installation
2.2 Location
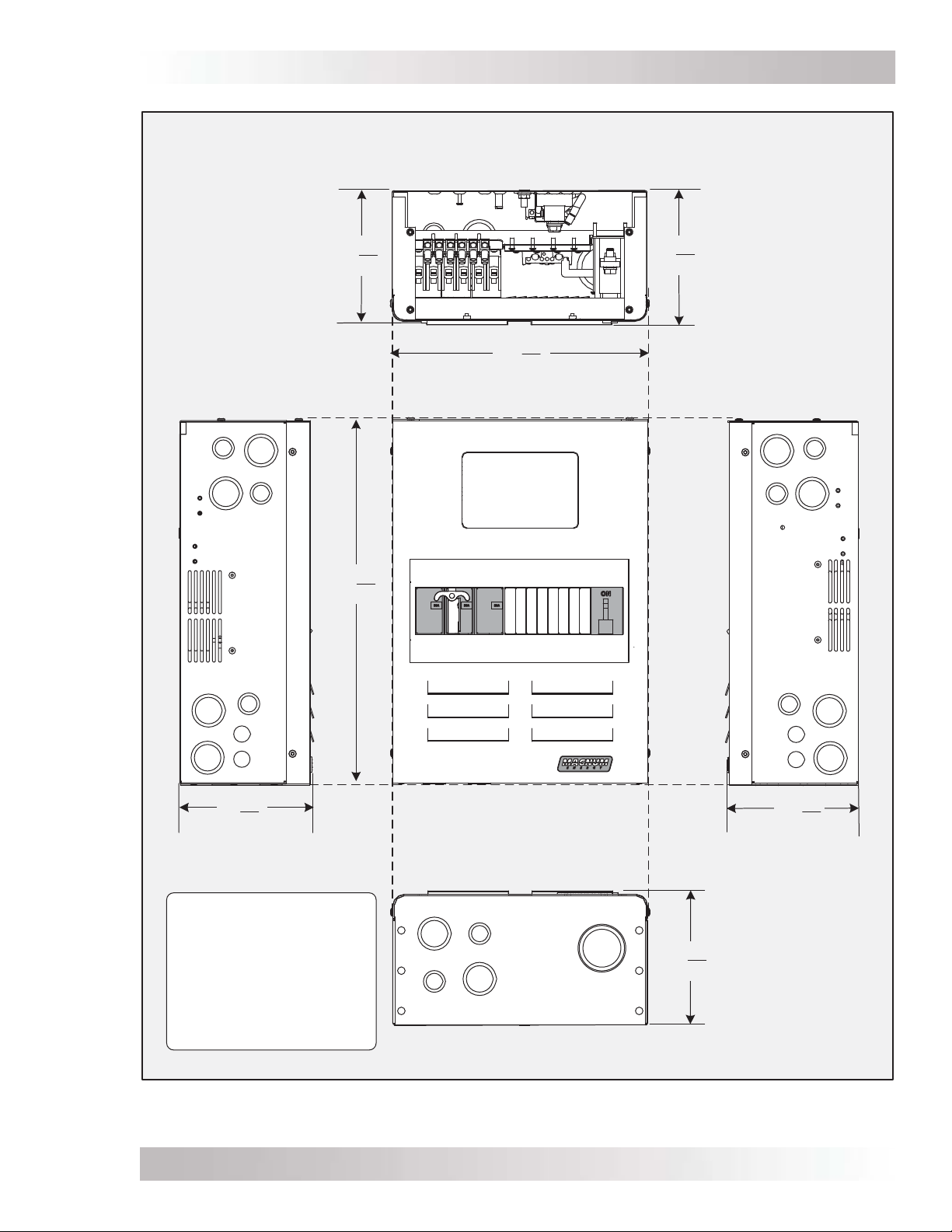
Refer to the dimensional drawing in Figure 2-2 to determine an appropriate area to install the
MMP enclosure/inverter system. Install it only in a location that meets the following requirements:
Clean and Dry – The MMP/inverter system must be mounted indoors in a relatively cool, clean,
and dry environment.
Ventilation – If a Magnum inverter is installed on the MMP enclosure, the inverter will pull in air
through the intake vents. In order for the inverter to provide full output power and avoid overtemperature fault conditions, do not cover or block the MMP enclosure ventilation openings or
install it in an area with limited airfl ow. At the minimum, allow three inches of clearance to the
left and right sides of the MMP enclosure to provide adequate ventilation.
Close to the Battery Bank – The MMP enclosure/inverter system should be located as close to the
batteries as possible. This is to ensure the battery cable length is kept as short as possible. Long DC
wires tend to lose effi ciency and reduce the overall performance of an inverter. However, the MMP
enclosure, the inverter, and any other equipment that can spark (or that corrosion could damage)
should not be installed in the same compartment/room as the batteries or mounted where it will
be exposed to gases produced by the batteries. These gases are corrosive and will damage this
equipment; also, if these gases are not ventilated and if allowed to collect, they could ignite and
cause an explosion. Consult your battery supplier for proper installation requirements.
Info: Consult your inverter owner’s manual to determine the proper sized inverterto-battery cables for the distance that is used. However, this cable must not be sized
any smaller than the minimum size requirement for the DC disconnect breaker in the
MMP enclosure. The MMP175 models require a minimum 00 (2/0) AWG cable, and the
MMP250 models require a minimum 0000 (4/0) AWG cable.
Safe – Keep any fl ammable/combustible material (e.g., paper, cloth, plastic, etc.,) that may be
ignited by heat, sparks or fl ames at a minimum distance of twelve feet away from the MMP/inverter
system. Do not install the MMP/inverter system in any area that contains extremely fl ammable
liquids like gasoline or propane, or in locations that require ignition-protected devices. Sparks
from relays, circuit breakers, etc., could ignite the fumes or spills.
Accessible – Do not block access to the front of the MMP enclosure. Maintain at least a 36”
(91 cm) clear space in front to access the AC and DC wiring terminals and connections inside the
MMP enclosure, as they will need to be checked and tightened periodically.
2.3 Conduit Knockouts
The MMP enclosure comes standard with knockouts for 1/2”, 3/4”, 1”, 1¼”, 1½”, and 2” conduits.
Figure 2-2 shows the location of these conduit knockouts. The 1/2”, 3/4”, and 1” knockouts are
for the PV array, DC loads, and other smaller input cables. Select the appropriate knockout that
is close to the terminal that the wire will connect to, or whichever one works for the way your
fi eld wiring comes in. The 1½” and 2” knockouts on the bottom of the MMP enclosure are used
to connect to the battery bank.
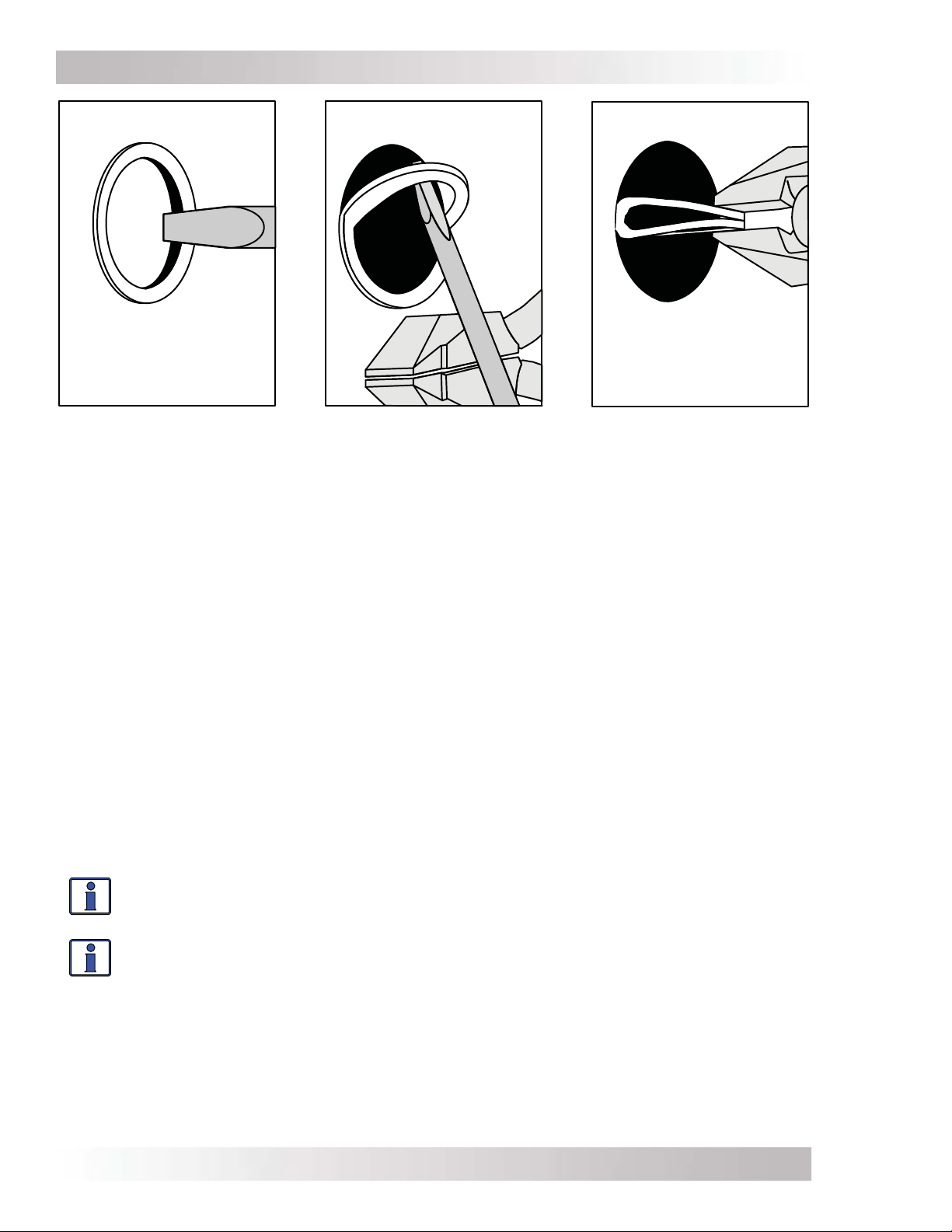
Info: The knockouts can be easily removed by tapping the edge with a straight bladed
screwdriver and a hammer, then twist out with pliers. Refer to Figure 2-3.
Before removing the appropriate knockouts and mounting the MMP enclosure, think about whether
you are going to use
• Wiring from the MMP enclosure to an AC sub-panel
• Wire runs from the utility and/or a generator to the MMP enclosure
• Battery cable wiring from the battery bank to the MMP enclosure
• Additional wiring from any external DC source (PV, wind, or hydro) to the MMP enclosure
• Small signal wiring (battery sensors, battery monitoring, auto gen starting)
• Attaching lightning arrestors
• PV charge controller wiring
cable clamps or conduit and all the different wiring required, such as:
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 10
Page 20
TOP VIEW
Installation
LEFT SIDE
VIEW
B
C
C
B
18
1
”
6
2
7
”
12
8
11
”
6
16
RIGHT SIDE
16
FRONT VIEW
1
”
V
C
B
IEW
B
C
B
C
A
C
A
11
”
6
16
CONDUIT KNOCKOUTS
(TOTAL):
A = ½” (x4)
B = ½” and ¾” (x8)
C
B
C
B
D
11
”
6
16
C = 1” and 1¼” (x10)
D = 1 ½” and 2” (x1)
BOTTOM VIEW
Figure 2-2, MMP Series Dimensions and Knockout Location/Sizes
B
C
A
C
A
11
”
6
16
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 11
Page 21
Installation
Figure 2-3, Removing Knockouts
2.4 Mounting
To meet regulatory requirements, the MMP enclosure must be mounted on a vertical surface (on
a wall) in an upright position, as shown in Figure 2-4. The DC breaker will not operate properly
unless in the vertical position.
Note the height you want to locate the MMP enclosure, and ensure you can access any controls
and wiring terminals. Refer to the physical dimensions as shown in Figure 2-2, or use the base of
the MMP as a template to mark your mounting screw locations. After marking the mounting screw
locations, fi rmly secure the MMP/inverter to the solid vertical surface using appropriate mounting
hardware.
This surface and the mounting hardware must also be capable of supporting at least three times
the combined weight of all the components (i.e., MMP enclosure, inverter, and any other accessory
mounted). When considering the strength of the support surface, remember the MMP enclosure
weighs 22.5 lbs. (10.2 kg), and the Magnum inverter can weigh up to 60 lbs. (27.2 kg).
If installing a Magnum inverter on the MMP enclosure, the inverter base can reach a temperature
up to 194°F (90°C); it is recommended that it should be mounted on a non-combustible surface*.
To meet regulatory requirements with a Magnum inverter mounted vertically, the included inverter
hood (PN: MP-HOOD) must be installed on the top to prevent the risk of fi re from objects falling
into the inverter. See Figure A5-1 in Appendix A for more information on the inverter hood.
Info: Magnum provides a steel backplate (PN: BP-MMP) that has a suitable surface and
the required support for mounting the MMP enclosure and Magnum inverter together.
For information and dimensions on this backplate, see Figure A8-1 in Appendix A.
Info: If mounting the MMP enclosure to wood (without a Magnum inverter), use at least
a #10 gauge sheet metal or wood screw. For concrete or hollow walls use a minimum
1/4 inch bolt and anchor.
* Non-combustible surface – A surface made of material that will not ignite, burn, support combustion,
or release fl ammable vapors when subjected to fi re or heat as per the ASTM E136 standard. For the most
part, these are materials that are largely comprised of inorganic materials such as stone, steel, iron, brick,
tile concrete, slate, and glass. Common building materials such as gypsum board as well as any paint, wall
coverings, and certainly wood will not pass.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 12
Page 22

INVERTER
HOOD
(INCLUDED AND
REQUIRED FOR
UL1741)
BP-MMP
ACKPLATE,
B
INI
M
16
Installation
3
”
4
”
16
1
”
13
16
MAGNUM
INVERTER
MMP
NCLOSURE
E
KEYHOLE
DETAIL (X4)
0.465"
0.409"
0.28 Ø
11
18
”
16
1
34
”
16
3
”
"
.
2
0
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
0.438"
Figure 2-4, Keyhole Locations for Mounting
3
”
11
4
5
”
12
8
KEYHOLES (X4)
WITH MOUNTING
S
CREWS
Page 13
Page 23

Installation
2.5 Wiring the MMP Enclosure – General Requirements
This section describes the requirements and recommendations for wiring to the MMP enclosure.
Read all instructions before wiring the MMP enclosure. All wiring should meet local codes and
standards and be performed by qualifi ed personnel such as a licensed electrician.
Refer to the NEC (National Electric Code, ANSI/NFPA 70) for the United States and the CEC
(Canadian Electrical Code) for Canada which provide the standards for safely wiring residential
and commercial installations.
WARNING: The AC neutral and DC negative are bonded to ground in this enclosure.
If the AC or DC circuits are already bonded to ground elsewhere in your system, you
must remove the DC and/or AC bonding inside this enclosure. Refer to Section 2.11
and 2.12 to remove the AC and/or DC ground bond connection.
WARNING: The AC neutral must be connected to safety ground (often called a “bond”)
in one, and only one, place at a time. More than one neutral to ground bond can cause
“ground loop” currents, which can trip GFCIs, cause an electrical shock hazard, and
may be the reason for other annoying side effects. In attempting to install the MMP in
a mobile application (i.e., RV, truck, or boat), refer to Appendix B for more information.
WARNING: Ensure all sources of DC power (i.e., batteries, solar, wind, or hydro) and
AC power (utility power or AC generator) are de-energized (i.e., breakers opened,
fuses removed) before proceeding—to prevent accidental shock.
2.5.1 Disconnect Switch and Overcurrent Protection
For residential and commercial electrical systems, the NEC/CEC requires a disconnect switch and
overcurrent protection for all ungrounded conductors on the AC side as well as the DC side. The
MMP enclosure provides both AC and DC circuit breakers that are used as the disconnect switch.
These circuit breakers can also be used as the overcurrent protection device when the ampacity
of the wire and its insulating material, voltage, and temperature rating are correctly sized to the
DC circuit breakers in your MMP enclosure. Refer to the appropriate installation section (AC Wiring
or DC Wiring) to determine the minimum recommended wire size required.
2.5.2 General Wiring Requirements
• The AC and DC wires into and out of the MMP enclosure must be protected as required by code.
This can be done by using jacketed wires or by feeding the wires through conduit.
Info: If the strain reliefs on the Magnum inverter are not required, they can be removed
and replaced with 3/4” grommets.
• Use proper clamps or other approved methods for securing the cable/conduit to the enclosure.
• Do not mix AC and DC wiring in the same conduit. The MMP enclosure is specifi cally approved/
designed for both AC and DC wiring. However, where DC wiring must cross AC or vice-versa,
try to make the wires at the crossing point 90° to one another.
• Use only copper wires with a minimum rating of 150V, 75°C if only 120 VAC power is being
used; or, with a minimum rating of 300V, 75°C if 120/240 VAC power is being used.
• In a system where one conductor is grounded the wire colors on the DC side and AC side are the
same. The insulation on all grounded conductors (DC negative/AC neutral) must be white, gray,
or any color except green if marked with white at each termination (marking only allowed on 6
AWG or larger conductors). The equipment grounding conductors must be bare (no insulation),
or have green or green with yellow-striped insulation or identifi cation. The hot ungrounded
conductor (DC positive/AC hot) is usually red or black.
• Terminals containing more than one conductor must be listed for multiple conductors.
• The connectors or terminals used on fl exible, fi ne-stranded conductors must be specifi cally
marked or labeled for use with fi ne-stranded conductors.
• The MMP enclosure includes wires (along with communication cables) with insulation rated for
at least 300 volts, which allows 120/240 VAC inverters to be installed. If installing a 120/240
VAC inverter, the installer must also provide wires (both power and communication) with the
insulation rated for at least 300 volts.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 14
Page 24

Installation
2.5.3 Wire Routing
Before connecting any wires, determine all wire routes to and from the MMP enclosure/inverter.
Typical routing scenarios are:
• AC input wiring from the main AC panel or from a generator to the MMP enclosure
• AC input and output from the MMP enclosure to the inverter
• DC wiring from the batteries to the MMP enclosure
• DC wiring from the inverter to the MMP enclosure
• AC output wiring from the MMP enclosure to the AC sub-panel or to dedicated circuits
• Battery Temperature Sensor cable from the inverter to the batteries
• Remote control cable to the inverter through the MMP enclosure
• Ground wiring to and from the MMP enclosure
2.6 Torque Requirements
Follow the specifi c torque recommendations below to ensure your fasteners are tightened suffi ciently.
To ensure your connections are correct, you should use an accurate, quality torque wrench. It is
highly recommended to go back over all fasteners and re-torque after fi ve days and every six months
thereafter.
CAUTION: AC and DC power/wire connections that are under-torqued could become
loose and result in a fi re hazard. On the other hand, over-tightening a bolt could cause
the fastener to be snapped off.
Table 2-1, Torque Values for Busbars
Torque values for the ground busbar, DC negative busbar, and DC positive busbar
(these busbars have different torque values for the small and large screws)
Wire Size
#14 to #10 AWG 15 in. lbs. (1.7 N-m) 35 in. lbs. (4.0 N-m)
#8 AWG 20 in. lbs. (2.3 N-m) 40 in. lbs. (4.5 N-m)
#6 AWG 25 in. lbs. (2.8 N-m) 45 in. lbs. (5.1 N-m)
#4 AWG NA 45 in. lbs. (5.1 N-m)
#3 to #1/0 AWG NA 50 in. lbs. (5.6 N-m)
10-32 (Small Screw) 5/16-24 (Large Screw)
Busbar Screw Size Torque Values
Table 2-2, Torque Values for the DC Shunt and DC Disconnect Breaker
3/8-16 Bolt Torque Value
10 to 12 ft. lbs.
(13.6 to 16.3 N-m)
Table 2-3, Torque Values for the AC Terminal Blocks
Wire Size Slotted M5 Screw Torque Values
#14 to #6 AWG
16.0 in. lbs. maximum
(2.0 N-m maximum)
2.7 Electrical System Wiring Diagrams
Diagrams of the AC and DC wiring for the MMP Series enclosure are shown in Figures 2-5 and
2-6, and are provided to assist you or your system installer. Due to the variety of applications and
differences in local and national electrical codes, these wiring diagrams should be used as general
guidelines only. They are not intended to override or restrict any national or local electrical codes;
and, the diagrams should not be the determining factor as to whether the installation is compliant,
that is the responsibility of the electrician and the on-site inspector.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 15
Page 25

Installation
MMPXXX-30D
S
YSTEM
IRING
W
S
CHEMATIC
AC
WIRING
MMP
NCLOSURE
E
INVERTER AC
INPUT / OUTPUT
TERMINAL
BLOCK
INVERTER
AC
B
YPASS
BREAKER
AND
INVERTER
AC
OUTPUT
BREAKER
MAGNUM ENERGY
INVERTER/CHARGER
H2OH1ON
Note1: Remove
the ‘N
C
the main AC
source has a
connection.
INVERTER
INPUT
BREAKER
H1
H2
O
ONNECTION’ if
neutral-to-
I
EUTRAL –
ROUND
G
ground
I
N
I
GROUND
BUSBAR
PV CHARGE
ONTROLLER
C
B
B
B
BAT + BREAKER
DC
N
EGATIVE
BUSBAR
PV
B
PV
PV + BREAKER
PV PANELS
PV
OPTIONAL
DC BREAKERS
[SPACES AVAILABLE:
DIN RAIL-MOUNT (
OR BACK-MOUNT (X4)]
DC SHUNT
INVERTER DC
DISCONNECT
PV
PV +
BUSBAR
X8)
EXTERNAL AC
INPUT / OUTPUT
TERMINAL BLOCK
HOT
120V
HOT
2
IN
IN
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
1
30A
OFF
30A
OFF
240V
GND
NEU
IN
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
120V
AC SUB-PANEL
(INVERTER LOADS)
Figure 2-5, MMPxxx-30D System Wiring Diagram
NEUTRAL -
GROUND
CONNECTION
HOT
HOT
2
OUT
OUT
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
GND
NEU
1
OUT
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
AC MAIN PANEL
(AC SOURCE)
1
< 1/0
AWG
≥ 1/0
AWG
NEGATIVE -
GROUND
ONNECTION
C
2
BATTERY +
BUSBAR
BB
.SYSTEM
G
ROUND
Note2: DC – GROUND
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
busbar shown
installed. This busbar
must be removed
when a PV-GFP
(PV Ground Fault
Protection Device)
is installed to
prevent multiple DC
to ground
connections.
BATTERY BANK
(DC SOURCE)
DC
WIRING
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 16
Page 26

Installation
MMPXXX-60S
S
YSTEM
IRING
W
S
CHEMATIC
AC
WIRING
MMP
NCLOSURE
E
INVERTER AC
NPUT / OUTPUT
I
TERMINAL BLOCK
NVERTER
I
AC BYPASS
BREAKER
AND
INVERTER
AC OUTPUT
REAKER
B
MAGNUM ENERGY
NVERTER/CHARGER
I
H2OH1ON
O
Note¹: Remove
EUTRAL –
the ‘N
ROUND
G
C
ONNECTION’ if
the main AC
source has a
neutral-to-
ground
connection.
INVERTER
INPUT
B
REAKER
H2
N
H1
I
I
I
GROUND
BUSBAR
PV CHARGE
ONTROLLER
C
BB
PV
B
B
BAT + BREAKER
DC
N
EGATIVE
BUSBAR
PV
PV + BREAKER
PV PANELS
PV
OPTIONAL
DC BREAKERS
[SPACES AVAILABLE:
DIN RAIL-MOUNT (
OR BACK-MOUNT (X4)]
INVERTER DC
DC SHUNT
D
ISCONNECT
PV +
B
USBAR
PV
X8)
EXTERNAL AC
NPUT / OUTPUT
I
TERMINAL BLOCK
HOT
1
IN
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
120V
GND
NEU
IN
60A
60A
OFF
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
120V
AC SUB-PANEL
(INVERTER LOADS)
Figure 2-6, MMPxxx-60S System Wiring Diagram
NEUTRAL -
ROUND
G
C
ONNECTION
HOT
1
OUT
AC MAIN PANEL
(AC Source)
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
NEU
OUT
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
GND
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
AC MAIN PANEL
(AC SOURCE)
1
< 1/0
AWG
≥ 1/0
AWG
NEGATIVE -
G
ROUND
ONNECTION
C
2
B
B
BATTERY +
USBAR
B
.SYSTEM
G
ROUND
Note²: DC –
ROUND busbar
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
G
shown installed.
This busbar must
be removed when a
PV-GFP
(PV Ground Fault
Protection Device)
is installed to
prevent multiple
DC to ground
connections.
BATTERY BANK
(DC SOURCE)
DC
WIRING
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 17
Page 27

Installation
2.8 DC Wiring
This section describes the DC wiring from inside the MMP enclosure to the inverter and battery bank.
Figure 2-7 shows the connection points for all battery bank and inverter (DC side) wiring inside
the MMP enclosure. If installing optional DC breakers, see Section A7 in Appendix A.
The DC wiring for the MMP enclosure is further detailed in Figure 2-9. This diagram should be
reviewed to assist in wiring the DC circuits, however, it is not intended to override or restrict any
national or local electrical codes. This drawing should not be a determining factor as to whether
the installation is compliant, that is the responsibility of the electrician and the onsite inspector.
2.8.1 DC Wiring Guidelines
WARNING: During normal operation, the terminals, busbars, and electrical components
inside the MMP enclosure may be energized – DO NOT TOUCH. Disconnect all power
sources before removing the cover.
WARNING: Even though DC voltage is “low voltage”, signifi cant hazards may be
present, particularly from short circuits of the battery system.
CAUTION: Before wiring the DC cables, review the safety information at the beginning
of this manual and the following information to ensure a safe and long-lived system.
CAUTION: If you are using fi ne-stranded DC cables, the crimp or compression lug
used must be specifi cally marked or labeled for use with fi ne-stranded conductors.
Failure to use the proper terminal may cause the connection to heat-up, and may
eventually fail or become a fi re hazard.
CAUTION: DO NOT connect the battery cables to the inverter until all wiring is
complete and the correct DC voltage and polarity have been verifi ed.
• When the inverter is installed in a Photovoltaic System, the NEC requires that the DC circuit
conductors and overcurrent devices to the inverter be sized to carry not less than 125% of
the inverter’s maximum current rating.
• The DC positive and negative cables from the battery bank should be tied together with wire
ties or electrical tape approximately every six inches. This helps improve the surge capability
and reduces the effects of inductance, which improves the inverter waveform and reduces the
wear of the inverter’s fi lter capacitors.
• Crimped and sealed copper compression lugs with a 3/8” hole should be used to connect the
battery cables to the DC disconnect breaker and the DC shunt inside the MMP enclosure.
• The battery bank voltage MUST match the DC voltage required by the inverter (i.e., 24-volt
battery bank for a 24-volt inverter), or the inverter may be damaged.
• The DC cables must be of a type listed for use in conduit (RHW or THW).
• To ensure the maximum performance from the inverter, all connections from the battery
bank to the inverter through the MMP enclosure should be minimized, the exception is the DC
circuit breaker in the positive line and the DC shunt in the negative line. Any other additional
connection will contribute to additional voltage drops and may loosen during use.
• All wiring to the inverter and battery terminals should be checked periodically (once a month)
for proper tightness. Refer to the torque requirements in Tables 2-1 to 2-3.
• After making the battery connections and ensuring they are properly tightened, cover the
outside of the connection with petroleum jelly or an antioxidant grease/spray. Do not put
jelly/anti-corrosion grease between the terminal and the battery cable.
• Ensure the color code for the DC cables/wires are correct: RED for positive (+); WHITE for
negative (–); and GREEN, GREEN/YELLOW, or bare for DC equipment grounds.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 18
Page 28

Installation
2.8.2 DC Wiring Connection Points
Figure 2-7 shows the connection points for the DC wiring inside the MMP enclosure.
Inverter DC
Negative
Connection
DC Grounding
Electrode
Connection
DC Equipment
Grounding
Connection
DC Negative
Connection
DC1
DC5A
DC5B
DC6
DC8
DC2
DC3
DC4
DC7
DC9
Inverter DC
Positive
Connection
Battery Bank
Negative
Connection
Battery Bank
Positive
Connection
PV Positive
Connection
Battery
Positive
Connection
DC1
DC2
DC3
DC4
DC5
DC6
DC7
DC8
DC9
Figure 2-7, DC Wiring Connection Points
Inverter DC Negative Connection – Top of DC negative busbar connects to Magnum
inverter’s DC negative terminal.
Inverter DC Positive Connection – Top of DC positive busbar connects to Magnum
inverter’s DC positive terminal.
Battery Bank Negative Connection – Bottom of DC shunt connects to the battery
bank’s negative terminal.
Battery Bank Positive Connection – Bottom of the inverter’s DC disconnect breaker
connects to the battery bank’s positive terminal.
DC Grounding Electrode Connection – The connection point for the MMP/inverter
system to the DC grounding electrode. Use DC5A for greater than #1/0 AWG wires and
DC5B for #6 to #1/0 AWG wires.
DC Equipment Grounding Connection – The common DC equipment ground point
for all DC equipment used in the MMP/inverter system.
PV Positive Connection – Connects the positive output of a PV array and the positive
input to the PV charge controller.
DC Negative Connection – The battery negative common point for connecting
additional DC circuits, such as from the DC negative output of a charge controller or
combining the negatives of DC load circuit breakers.
Battery Positive Connection – Serves as the battery positive connection point for
additional DC circuits (from charge controller output or connecting to DC load breakers).
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 19
Page 29

Installation
BTS
Magnum Inverter/Charger
Magnum Inverter
(front view)
BTS
Inverter’s DC Negative Busbar
Inverter’s DC Positive Busbar
Inverter’s Equipment Ground Wire
Battery Temp Sensor Cable*
* If the voltage inside the enclosure is
greater than 150 volts (i.e., 120/240
VAC source/inverter), use the provided
extension cable (with 300-volt rated
insulation) to connect the BTS cable
Battery Bank’s Equipment Ground Wire
Battery Bank’s Negative Cable
Battery Bank’s Positive Cable
DC System Grounding point
[Electrode Conductor
(i.e., ground busbar)]
Figure 2-8, DC Wiring with Magnum Inverter
Battery Bank
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 20
Page 30

Installation
2.8.3 Inverter DC Overcurrent Protection and DC Disconnect
In a battery-based inverter system, the NEC/CEC assumes that each ungrounded conductor is
connected to some source that supplies currents in excess of the ampacity rating of the conductor
and could potentially damage that conductor under fault conditions. Because of this, the NEC/
CEC requires that all ungrounded conductors in the inverter’s DC system be protected by an
overcurrent device, this can be either a circuit breaker or fuse. These breakers or fuses are not
intended to protect equipment from damage, but protect the conductor/wire from overheating
which may potentiality cause a fi re. This means the overcurrent device is required to open before
the conductor reaches its maximum current carrying capability, thereby preventing a fi re.
Info: Circuit breakers or fuses that are used on the DC side must be UL listed and DC
rated for the application.
The NEC also requires the inverter system to have a DC disconnect switch to allow the inverter
service providers to isolate the inverter from the battery. The disconnect must be either a DC
rated circuit breaker or switch.
Depending on your model, the MMP enclosure is provided with either a 175-amp or 250-amp
UL listed, high interruption capacity DC rated circuit breaker. These breakers are designed to
interrupt the tremendous amount of current a battery can deliver when short-circuited. They are
also specifi cally designed to have a long enough time delay to prevent the breaker from tripping,
as the inverter requires high current levels when powering heavy loads.
When properly located and used with the minimum DC wire size shown in Table 2-4, these circuit
breakers can provide the inverter system with both the DC overcurrent protection device and a
safety disconnect switch.
2.8.4 Inverter and Battery Bank Wire Sizing
In a low voltage/high amperage system, it is important to use the correct DC wire to achieve
maximum effi ciency from the system and reduce fi re hazards associated with overheating. Always
keep your wire runs as short as practical to help prevent low voltage shutdowns and keep the DC
breaker from nuisance tripping, because of increased current draw.
The size of the DC cables must be correctly sized according to the inverter’s DC current requirements,
DC breaker size, and the minimum voltage drop to the battery bank. If the DC circuit breaker
provided in the MMP enclosure is being used as the inverter’s DC overcurrent protection device,
the cable size must not be less than the minimum DC wire size shown in Table 2-4.
Use Table 2-4 to select the minimum DC wire size based on your MMP model. These recommendations
may not meet the inverter’s continuous current requirements1 or electrical code requirements.
Table 2-4, Recommended DC Wire to MMP Enclosure
MMP Model
DC Circuit
Breaker
Minimum DC Wire
Size (rating)
2
MMP175-30D 175 amps #2/0 AWG (195 amps) #6 AWG
MMP175-60S 175 amps #2/0 AWG (195 amps) #6 AWG
MMP250-30D 250 amps #4/0 AWG (260 amps) #4 AWG
MMP250-60S 250 amps #4/0 AWG (260 amps) #4 AWG
WARNING: If you use a battery or inverter cable smaller than the recommended
minimum DC wire size for your MMP model (as shown in Table 2-4), you must install a
fuse/circuit breaker compatible with this smaller cable to protect against a potential fi re.
DC Equipment
Grounding Wire Size
3
Note1 – Refer to your inverter’s owner’s manual to determine the minimum DC wire requirements.
2
Note
– Wire must be copper with a minimum rating of 300V, 75°C at an ambient temperature of 30°C.
3
Note
– See Section 2.10 for more information on the equipment grounding wire size.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 21
Page 31

Installation
2.8.5 DC Hardware Connections
Do not put anything between the DC cable lug and the DC terminals (i.e., on the DC circuit breaker,
DC shunt, batteries, and inverter/busbars). Ensure the hardware used to hold these connections is
stacked correctly. Incorrectly installed hardware causes a high resistance connection which could
lead to poor inverter performance, and may melt the cable and terminal connections.
Follow Figure 2-9 to connect the DC cables and stack the hardware correctly.
Info: After making the battery connections and ensuring they are properly torqued,
cover the outside of the connection with petroleum jelly or an antioxidant grease/spray.
Do not put jelly/anti-corrosion grease between the terminal and the battery cable.
INVERTER DC NEGATIVE
AND POSITIVE
CONNECTIONS
1
2
3
BATTERY NEGATIVE CONNECTION
1
5
6
4
2
3
Busbar Hardware Stack-
1 Inverter DC terminal
DC connection busbars
2
[(–) to shunt, (+) to DC
disconnect breaker]
3 5/16-18 Nut (Flange/Kep)
DO NOT place anything
between the inverter DC
terminal and the copper
Hardware Stack-up:
1 DC shunt
2 DC neg. to ground busbar
3 Neg. (–) battery cable lug
4 Brass fl at washer
5 Brass split-lock washer
6 Brass hex bolt (3/8-16)
DO NOT place anything
between the DC shunt and
the busbar or between the
busbar and the negative
battery cable lug.
up:
busbar.
Bottom of Shunt
BATTERY POSITIVE CONNECTION
Bottom of DC Breaker
1
2
4
3
Hardware Stack-up:
1 DC breaker terminal
2 Pos. (+) battery cable lug
3 Split-lock washer
4 Hex bolt (3/8-16)
DO NOT place anything
between the DC breaker
terminal and the positive
battery cable lug.
Figure 2-9, DC Connections – with Magnum Inverter Installed
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 22
Page 32

Installation
2.8.6 Wiring the Battery Bank
Depending upon the voltage of the batteries you use in the installation (6 or 12 VDC), the batteries
must be wired in series, parallel, or series-parallel to provide the correct voltage. The interconnecting
DC wires should be sized and rated exactly the same as those that are used between the battery
bank and the inverter.
Place the batteries as close as practical to the MMP enclosure/inverter system, preferably in an
insulated and ventilated enclosure. Allow adequate space above the batteries to access the terminals
and vent caps (as applicable). Also allow at least one inch of space between the batteries to provide
good air fl ow. DO NOT mount the batteries directly under the MMP enclosure/inverter system.
Info: To ensure the best performance from your MMP enclosure/inverter system, batteries
should be of the same size, type, rating, and age. Do not use old or untested batteries.
2.8.7 Wiring the MMP Enclosure to the Battery Bank/Inverter
WARNING: Ensure that all AC and DC breakers are switched OFF before connecting
or disconnecting the battery cables, and that all sources of power (both AC and DC)
are disconnected from the inverter.
WARNING: Lethal currents will be present if the positive and negative cables attached
to the battery bank touch each other. During the installation and wiring process, ensure
the cable ends are insulated or covered to prevent touching/shorting the cables.
CAUTION: DO NOT connect the DC wires to the battery bank until: 1) all DC, AC, and
accessory wiring are completed, 2) the correct DC and AC overcurrent protection have
been installed and, 3) the correct DC voltage and polarity have been verifi ed.
CAUTION: The Magnum inverter is NOT reverse polarity protected, if this happens
the inverter will be damaged and will not be covered under warranty. Before making
the fi nal DC connection from the batteries up to the inverter, verify the correct battery
voltage and polarity by using a voltmeter. If the positive (+) terminal of the battery is
connected to the negative (–) terminal of the inverter and vice versa, severe damage
will result. Ensure the cables are color-coded to avoid polarity confusion.
This section describes how to make DC connections between your Magnum inverter/charger and
the MMP enclosure, and the DC connections from the MMP enclosure to the batteries (using battery
cables provided by the installer – see Table 2-4).
1. Place the Magnum inverter onto the top of the MMP enclosure, ensuring the inverter’s DC
terminals fi t through the holes in the pre-installed DC positive and negative busbars within
the MMP enclosure.
2. Route the DC cables from the battery bank—with the cables not connected to the battery—and
connect them to the MMP enclosure; negative (–) to the bottom side of the DC shunt, positive
(+) to the bottom side of the DC breaker. Be careful to observe proper polarity.
3. Ensure the DC wire connections (on the batteries, inverter, DC circuit breaker, and DC shunt)
are fl ush on the surface of the DC terminals and the hardware used to hold these connections
are stacked correctly (see Figure 2-9); and then securely tighten these DC connections. Only
after the entire installation is complete and all connections are verifi ed should the DC circuit
breaker be closed to provide power to the inverter.
4. Route an appropriately sized DC grounding wire (green or bare wire) from the inverter’s DC
equipment ground terminal and from the battery bank enclosure to the DC ground busbar in
the MMP enclosure. Refer to Section 2.10 for grounding information and sizing the DC ground
wires.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 23
Page 33

Installation
2.9 AC Wiring
This section provides information on the AC wiring inside the MMP enclosure to/from the inverter,
from the incoming AC source, and to the outgoing AC distribution panel (i.e., inverter sub-panel).
2.9.1 AC Wiring Guidelines
CAUTION: Before installing any AC wiring, review the safety information at the
beginning of this manual and below to ensure a safe and long-lived system:
• Read all instructions and cautionary markings located at the beginning of this
manual and in the Installation section, before installing the inverter and batteries.
• AC wiring must be no less than #10 AWG (5.3 mm2) gauge copper wire and be
approved for residential wiring.
• DO NOT connect the Magnum inverter’s output to an AC power source. This could
cause severe damage to the inverter and is not covered under warranty.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of fi re, do not connect a 120 VAC only inverter to both
busbars in an AC load center (circuit breaker panel) having multi-wire branch circuits
connected. Every circuit connected to a 120 VAC panel must have its own neutral;
otherwise, currents on shared neutrals will add rather than subtract, overloading the
neutral conductor.
2.9.2 AC Connections
Use either Figure 2-10 (for MMPxxx-30D models) or Figure 2-11 (for MMPxxx-60S models) to view
the AC connection points inside the MMP enclosure.
2.9.2.1 AC Input/Output Connections
The MMP enclosure provides two AC terminal blocks that allow the AC input and output wiring to
be easily and permanently wired. These terminal blocks allow a service/distribution panel (main
panel) to be wired to the inverter’s input, and a dedicated inverter panel (sub-panel)1 to be wired
between the inverter’s output wiring and the AC loads.
Depending on your MMP model, it will either have two six-pole AC terminals (Figure 1-2, Items
4 and 6), or two four-pole AC terminals (Figure 1-4, Items 4 and 6). The six-pole terminals are
provided on the MMPxxx-30D models to allow 120/240 VAC inverters—up to 30 AC amps per leg
pass-thru capability—to be connected. The four-pole terminals are provided on the MMPxxx-60S
models to allow 120 VAC inverters—up to 60 AC amps pass-thru capability—to be connected.
The upper AC terminal block—INVERTER AC TERMINAL BLOCK—provides the connection points for
the inverter’s input and output Hot and Neutral connection points. The lower AC terminal block—
EXTERNAL AC TERMINAL BLOCK—provides the Hot and Neutral connection points for the incoming
utility/AC generator input and to the inverter AC sub-panel (if needed)1.
Info: The neutrals on the INVERTER AC TERMINAL BLOCK are NOT connected together.
You must provide both an inverter input and output neutral connection to the inverter’s AC
terminal unless the inverter has the input and output neutrals connected together.
Each connection on the AC terminal block is rated to accept one #14 to #6 AWG (2.1 to 13.3 mm2) CU
stranded wire, or, two #12 AWG (3.3 mm2) CU stranded wires. Each connection uses a M3.5 slotted
screw, and the maximum tightening torque is 16 lbf-in (1.8 N-m).
2.9.2.2 AC Ground Connections
The MMP enclosure comes with a ground busbar (Item 8, in Figure 1-2 or 1-4) to allow the AC
grounds to be connected to a common point. This busbar has three #14 to #1/0 AWG and six
#14 to #6 AWG screw type compression terminals. See Table 2-1 for torque requirements.
CAUTION: A neutral to ground connection is provided in the MMP enclosure. If this
neutral-ground connection is provided elsewhere in the AC system, this connection
must be disconnected. See Section 2.11 for information to disconnect this connection.
Note1 – MS2012/MS2000 (-15B and -20B) breaker models do not require a dedicated inverter sub-panel.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 24
Page 34

Installation
INV NEUTRAL IN
(to inverter’s AC neutral input)
INV HOT 1 IN
(to inverter’s AC Hot 1 input)
INV HOT 2 IN
(to inverter’s AC Hot 2 input)
INV NEUTRAL OUT
(from inverter’s AC
neutral output)
INV HOT 1 OUT
(from inverter’s
AC Hot 1 output)
INV HOT 2 OUT
(from inverter’s
AC Hot 2 output)
AC - GROUND CONNECTION
(remove green wire from ground
busbar if neutral is bonded to
ground from primary source)
GROUND BUSBAR (inverter’s
input and output AC ground)
AC HOT 2 OUT
(to main breaker on
L2 side in AC load panel)
AC HOT 1 OUT
(to main breaker on
L1 side in AC load panel)
AC NEUTRAL OUTPUT
(to neutral busbar in
AC load panel)
AC HOT 2 IN
(from L2 side of utility or generator)
AC HOT 1 IN
(from L1 side of utility or generator)
AC NEUTRAL IN
(from neutral of utility or generator)
Figure 2-10, AC Wiring Connections (MMPxxx-30D Models)
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
GROUND BUSBAR
(from utility/generator ground
and to AC load panel ground)
Page 25
Page 35

Installation
(to inverter’s AC neutral input)
(to inverter’s AC Hot input)
INV NEUTRAL OUT
(from inverter’s AC
INV HOT 1 OUT
(from inverter’s
INV NEUTRAL IN
neutral output)
AC Hot output)
INV HOT IN
AC - GROUND CONNECTION
(remove green wire from ground
busbar if neutral is bonded to
ground from primary source)
GROUND BUSBAR (inverter’s
input and output AC ground)
AC HOT OUT
(to main breaker
in AC load panel)
AC NEUTRAL OUTPUT
(to neutral busbar in
AC load panel)
AC HOT IN
(from hot out of utility or generator)
AC NEUTRAL IN
(from neutral of utility or generator)
Figure 2-11, AC Wiring Connections (MMPxxx-60S Models)
GROUND BUSBAR
(from utility/generator ground
and to AC load panel ground)
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 26
Page 36

Installation
2.9.3 AC Wire Size and Overcurrent Protection
The AC input and output wiring must be sized per the local electrical safety code requirements to
ensure the wire’s ability to safely handle the inverter’s maximum load current. After determining
the proper AC wire sizes, they are required to be protected from short circuits and overloads by
an overcurrent protection device, and have a means to disconnect the AC circuits.
The MMP enclosure provides AC circuit breakers for the inverter’s AC input. These breakers are
branch circuit rated and can be used as the overcurrent protection and the AC disconnect device.
This is true as long as the AC wires used are not smaller than the minimum wire size as shown
in Table 2-5 for your particular MMP model, and the ‘AC Input/Output Wiring Confi guration’ used.
If using a Magnum MS, MS-AE, MS-PAE, or RD Series inverter, the full AC continuous pass-thru
capacity of these inverters is 30 amps for each AC leg¹ (AC HOT 1 and AC HOT 2), and requires
a maximum 30-amp breaker on each AC input to protect the inverter’s inputs. This correlates
with the MMPxxx-30D models, which include a dual 30-amp input inverter breaker and requires
a minimum cable size of #10 AWG
2
in conduit.
In the MS or RD Series inverters, the AC HOT 1 and AC HOT 2 may be combined to obtain 60 amps
pass-thru capability. When tying the AC HOT 1 and HOT 2 together for a 60 amp continuous passthru capability, the AC input to the inverter requires a 60-amp breaker. This correlates with the
MMPxxx-60S models, which include a single 60-amp breaker and requires a minimum cable size
of #6 AWG2 in conduit. If you are using other circuit breakers/wire sizes, refer to the appropriate
electrical codes for proper sizing requirements.
2.9.4 AC Conductor Wiring
The following steps are basic guidelines for installing and connecting the AC wiring into and out
of the inverter. Refer to Table 2-5 to determine your AC wiring confi gurations before beginning.
WARNING: To prevent electrical shock, make sure all AC power (inverter, generator,
or utility) is off before making any AC connections inside the MMP enclosure.
Wiring External AC Source and AC Load Panel
1. Route an appropriate cable from a dedicated breaker in the main AC electrical panel through
one of the MMP enclosure’s knockouts to the EXTERNAL AC IN/OUT TERMINAL BLOCK (HOT
IN/NEUT IN side).
2. Route an appropriate cable from the EXTERNAL AC IN/OUT TERMINAL BLOCK (HOT OUT/NEUT
OUT Side) through another MMP enclosure knockout to the inverter’s AC electrical sub-panel
(or AC outlets, if using the Magnum inverter models with output breakers).
Wiring Inverter AC Input/Output
1. Route an appropriate cable from the INVERTER AC IN/OUT TERMINAL BLOCK (HOT IN/NEUT
IN side) to the inverter’s AC input terminals.
2. Route an appropriate cable from the INVERTER AC IN/OUT TERMINAL BLOCK (HOT OUT/NEUT
OUT side) to the inverter’s AC output terminals.
Wiring the AC Ground
Route the following AC ground wires; 1) the main AC panel’s ground busbar, 2) the ground wire
from the inverter’s AC sub-panel’s ground busbar (or the ground connection on the outlets, if
using the Magnum inverter with output breakers), and 3) the AC ground wire from the inverter;
and connect to the GROUND busbar in the MMP enclosure (Item 8 in Figures 1-2 and 1-4).
AC Wiring Inspection
After verifying all AC connections are correct, and all AC terminal screws are torqued correctly
(refer to Tables 2-1 to 2-3), replace the inverter’s AC wiring access cover and the covers on the
main electrical panel/sub-panel.
Note1 – On Magnum MS2012/MS2000 (-15B and -20B) breaker models, the pass-thru current is limited by
the output breaker size.
2
Note
– This wire must be copper with a minimum rating of 300V, 75°C.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 27
Page 37

Installation
2.9.5 AC Wiring Confi gurations
The following table provides the different wiring confi gurations for installing and connecting the
AC conductors into and out of the inverter (refer to Figures 2-12 to 2-15 for installation drawings
showing these confi gurations).
Table 2-5, AC Input/Output Wiring Confi gurations
AC Source1
Required
Reason to
Use
Appropriate
MMP Models
Appropriate
Magnum
Inverter
Models
AC Input
Breaker
Provided
SI/SO (30A)
[Single In/
Single Out
(30A)]
120 VAC @ < 30
amps
Have a 120 VAC
source that is
< 30 amps.
Requires a
separate inverter
sub-panel4.
MMP175-30D,
MMP250-30D
MS Series,
MS-AE Series,
MS-PAE Series,
RD Series
30A
(one pole of dual
pole breaker)
SI/SO (60A)
[Single In/
Single Out
(60A)]
120 VAC @
> 30 amps
(60 amps maximum)
Have a 120 VAC
source that is > 30
amps.
Requires a
separate inverter
sub-panel.
MMP175-60S,
MMP250-60S
MSxx12, MS4024,
MS-AE Series,
MS-PAE Series,
RD Series
60A
(single pole)
DI/SO
[Dual In/
Single Out]
120/240 VAC
(or two separate legs
of 120 VAC)
@ < 30 amps per leg
Want dedicated
charging and
dedicated pass-thru
while the AC source
is on.
Requires a
separate inverter
sub-panel.
MMP175-30D,
MMP250-30D
MSxx12,
MS4024,
RD Series
30A
(dual pole)
DI/DO
[Dual In/
Dual Out]
120/240 VAC
(or two separate legs
of 120 VAC)
@ < 30 amps per leg
May need to power
240 VAC loads when
AC source is on
(requires 120/240
VAC source).
Requires a separate
inverter sub-panel.
MMP175-30D,
MMP250-30D
MSxx12, MS4024,
MS-AE Series,
MS-PAE Series,
RD Series
30A
(dual pole)
#6 AWG
(In & Out);
Minimum AC
Wire Size
5
#10 AWG
(In & Out)
Can be split to two
#10 AWG
#10 AWG
(In & Out)
#10 AWG
(In & Out)
(for HOT 1
& HOT 2)
Maximum
Inverter
Pass-thru
3600W
(30A @ 120 VAC)
5000W
(60A @ 120 VAC)
2
Capacity
Wiring
Diagram
1
Note
– AC Source is from either the utility/grid power or an AC generator.
Figure 2-12 Figure 2-13 Figure 2-14 Figure 2-15
3600W
(30A @ 120 VAC)
5000W
(two legs of 30A
@ 120/240 VAC or
two legs of 30A @
120 VAC)
2
3
Note2 – Enclosure capacity rated for 5000 Watts maximum.
Note3 – If two legs of 30A @ 120 VAC are used, they must be from the same source.
Note4 – The MS2012 and MS2000 models with integral branch circuit rated output breakers (i.e. MS2012-
20B) allows direct wiring from the unit to the load and do not require an inverter sub-panel.
Note5 – Based on AC input breaker provided.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 28
Page 38

Installation
SINGLE IN / SINGLE OUT (30A)
AC Wiring
AC OUT
(from inverter
AC Output)
HOT 1 OUT
HOT 1 OUT
AC IN
(to inverter
AC Input)
NEUT OUT
NEUT OUT
HOT 1 IN
HOT 1 IN
NEUT IN
NEUT IN
If the main panel
has a neutral-to-
ground connection,
‘Ground to Neutral’
from the GROUND
busbar.** This will
isolate the neutral
neutral to ground
Ground to Neutral
been removed in
the inverter diagram
unscrew this
wire connection
from ground to
prevent multiple
bonds.
**Note: This
wire has already
to the right.
MMPxxx-30D Enclosure
(with Magnum Inverter)
120
VAC
GROUND
..AC OUT
(to AC loads)
OFF
AC IN
(from grid/gen)
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
.Sub-Panel and Outlets
(Inverter AC Loads)
120
VAC
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Main Panel
(Utility/Generator : 30A)
Figure 2-12, AC Wiring for Single In – Single Out (30 A) Confi gurations
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 29
Page 39

Installation
SINGLE IN / SINGLE OUT (60A)
AC Wiring
AC OUT
(from
inverter
AC Output)
HOT 1 OUT
HOT 1 OUT
AC IN
(to
inverter
AC Input)
NEUT IN
HOT 1 IN
NEUT OUT
NEUT OUT
HOT 1 IN
NEUT IN
AC GROUND
(to
inverter
AC Input)
If the main panel
ground connection,
‘Ground to Neutral’
from the GROUND
busbar.** This will
isolate the neutral
neutral to ground
Ground to Neutral
the inverter diagram
has a neutral-to-
unscrew this
wire connection
from ground to
prevent multiple
bonds.
**Note: This
wire has already
been removed in
to the right.
MMPxxx-60S Enclosure
(with Magnum Inverter)
`
`
120
VAC
.AC OUT
(to AC loads)
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
Sub-Panel and Outlets
120
VAC
(Inverter AC Loads)
AC IN
(from grid/gen)
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
GROUND
120
VAC
120
VAC
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Main Panel
(Utility/Generator 60A)
Figure 2-13, AC Wiring for Single In – Single Out (60 A) Confi gurations
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 30
Page 40

Installation
DUAL IN / SINGLE OUT
AC Wiring
AC OUT
(from inverter
AC Output)
HOT 2 OUT
HOT 2 OUT
(to inverter
NEUT OUT
HOT 2 IN
NEUT OUT
HOT 2 IN
AC IN
AC Input)
NEUT IN
HOT 1 IN
HOT 1 IN
NEUT IN
MMPxxx-30D Enclosure
(with Magnum Inverter)
If the main panel
has a neutral to
ground connection,
unscrew this
‘Ground to Neutral’
wire connection
from the GROUND
busbar.** This will
isolate the neutral
from ground to
prevent multiple
neutral to ground
bonds.
**Note: This
Ground to Neutral
wire has already
been removed in
the inverter diagram
to the right.
120
VAC
.AC OUT
(to AC loads)
OFF
AC IN
(from grid/gen)
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
Sub-Panel and Outlets
(Inverter AC Loads)
GROUND
120
VAC
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Main Panel
(Utility/Generator 30A per leg)
Figure 2-14, AC Wiring for Dual In – Single Out Confi gurations
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 31
Page 41

Installation
DUAL IN / DUAL OUT
AC Wiring
AC OUT
(from inverter
AC Output)
HOT 2 OUT
HOT 1 OUT
HOT 2 OUT
HOT 1 OUT
AC IN
(to inverter
AC Input)
NEUT OUT
HOT 2 IN
HOT 1 IN
NEUT OUT
HOT 2 IN
HOT 1 IN
NEUT IN
NEUT IN
MMPxxx-30D Enclosure
(with Magnum Inverter)
If the main panel
has a neutral-to-
ground connection,
unscrew this
‘Ground to Neutral’
wire connection
from the GROUND
busbar.** This will
isolate the neutral
from ground to
prevent multiple
neutral to ground
bonds.
**Note: This
Ground to Neutral
wire has already
been removed in
the inverter diagram
to the right.
240
VAC
.AC OUT
(to AC loads)
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
AC IN
(from grid/gen)
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Sub-Panel and Outlets
(Inverter AC Loads)
GROUND
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Main Panel
120
VAC
120
VAC
(Utility/Generator 30A per leg)
Figure 2-15, AC Wiring for Dual In – Dual Out Confi gurations
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 32
Page 42

Installation
2.10 MMP/Inverter System Grounding
The MMP/inverter system uses both AC and DC electrical systems, therefore each electrical system
is required to be properly connected to a permanent, common “ground” or “earth” reference. A
MMP/inverter system that is properly grounded limits the risk of electrical shock, reduces radio
frequency noise, and minimizes excessive surge voltages induced by lightning. To understand how
the conductors in the electrical circuit will be connected to the system ground, the following terms
should be understood (also refer to Figure 2-16):
• Grounded Conductor (GC): The wire/cable in the electrical system that normally carries current
(usually the AC neutral and/or the DC negative), and is intentionally connected or “bonded” to
the ground system. This wire or the ends of this wire must be colored white or gray.
• Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC): A wire/cable that does not normally carry current
and is used to connect the exposed metal parts of equipment—that might be accidentally
energized—to the grounding electrode system or the grounded conductor. This wire or the
ends of this wire must be green, or green with a yellow stripe; or, this wire can be bare copper.
• Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC): The wire/cable that does not normally carry current,
and connects the grounded conductor and/or the equipment grounding conductor to the
grounding electrode at the service equipment.
• Grounding Electrode (GE): A ground rod or conducting element that establishes an electrical
connection to the earth or common ground reference.
• System bonding jumper (SBJ): The connection between the grounded circuit conductor in the
electrical system and the equipment grounding conductor at a separately derived system.
There are two types of grounding – equipment grounding and system grounding.
The exposed metal parts of the equipment in the system usually don’t carry electricity. However, if
the exposed metal becomes electrifi ed by a live wire, a person touching this live part could complete
the electrical circuit and receive a shock. Equipment grounding prevents shock by connecting all
the exposed metal parts of equipment (via Equipment Grounding Conductors – EGC) together
at a common ground point (Ground BusBar – GBB). This common ground point—installed in the
service disconnect panel for each electrical system (AC and DC)—is then connected (via Grounding
Electrode Conductor – GEC) to the common ground reference, such as a ground rod (Grounding
Electrode – GE). This connection to earth is made at only one point in each electrical system;
otherwise, parallel paths will exist for the currents to fl ow. These parallel current paths would
represent a safety hazard and are not allowed in installations wired per the NEC/CEC.
System grounding takes one of the current carrying conductors (Grounded Conductor – GC) and
attaches it to the common ground point (Ground BusBar – GBB), usually by a System Bonding
Jumper (SBJ) in each electrical service disconnect panel. On the AC side, that is the neutral
conductor (GC-AC); on the DC side, it’s the negative conductor (GC-DC). The closer the grounding
connection is to the source, the better the protection from high voltage surges due to lightning.
AC Electrical
System
MAGNUM
I
NVERTER
HOT 1
HOT 2
NEUT
GND
GND
NEG
POS
DC Electrical
System
AC
S
OURCE
HOT 1
HOT 2
NEUT
GE
AC side dedicated
MAIN AC PANEL
GBB
Figure 2-16, Grounding System for Inverter with MMP Enclosure
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
SBJ
or
or
GEC-AC
or
GE
AC and DC sides shared
GBB
SBJ
MMP
ENCLOSURE
GEC-DC
or
Grounding System
S
GC-DCGC-AC
DC side dedicated
BAT
BAT
GE
DC
OURCE
Page 33
Page 43

Installation
2.10.1 Sizing the Grounding Electrode Conductors
AC Side – The size of the AC Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC–AC) depends on the size of
the largest ungrounded conductor feeding the AC load center. One #8 AWG (8.4 mm2) copper
conductor will serve as an AC Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC–AC) for AC power conductors
smaller than and including #2 AWG (33.6 mm
Table 2-6, AC Grounding Electrode Conductor Sizing
2
) copper. See Table 2-6 for additional values.
Size of Largest Ungrounded
Conductor
#2 AWG or smaller
#1 to #1/0 AWG
#2/0 or #3/0 AWG
Over #3/0 AWG
through 350 kcmil
Minimum Size of Grounding
Electrode Conductor
#8 AWG
#6 AWG
#4 AWG
#2 AWG
(8.4 mm2)
(13.3 mm2)
(21.1 mm2)
(33.6 mm2)
DC Side – To size the DC grounding electrode conductor, you must fi rst determine which one of the
following three methods will be used to connect the DC and AC grounding points in the inverter’s
two electrical systems to the common “earth” ground.
Info: There are many variables to consider when choosing the size of the DC grounding
electrode conductor. The MMP enclosure provides the means to ground both the AC and
DC to a single ground, and when feasible, the Single Connection to Ground (Method
1) is recommended. In this method, the NEC allows a #6 AWG wire which makes the
overall installation simpler and less costly.
1. Single Connection to Ground (Method 1): The AC Grounding Electrode Conductor
(GEC–AC) is bonded to the DC ground point and the DC Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC–DC)
is the only connection to the grounding electrode, which must be a rod, pipe, or plate electrode
(see Figure 2-17).
Normally the size of the DC Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC–DC) must be no less than the size
of the Battery Bank Negative Cable. However, in this method, since there is only one connection
to the ground rod, the NEC allows an exception that the DC grounding electrode conductor is
not required to be larger than #6 AWG (13 mm2) copper. The reasoning for allowing this smaller
grounding electrode conductor is that it is only required to stabilize the system voltage with respect
to earth, and the other properly sized conductors in each electrical system will safely carry any
fault currents if they occur.
AC Electrical
System
AC
OURCE
S
HOT 1
HOT 2
NEUT
MAGNUM
NVERTER
I
MAIN AC PANEL
GC-AC
GBB
SBJ
HOT 1
HOT 2
NEUT
GEC-AC
MMP
Grounding System
GND
GBB
GND
NEG
POS
SBJ
GC-DC
ENCLOSURE
GEC-DC
DC side dedicated
GE
DC Electrical
System
DC
OURCE
S
BAT
BAT
Figure 2-17, Single Connection to DC Ground Rod (Method 1)
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 34
Page 44

Installation
2. Multiple Connections to Ground – Single Electrode (Method 2): When the AC and DC
service panels are near each other, then the AC Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC–AC) and DC
Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC–DC) can be connected to a single Grounding Electrode (see
Figure 2-18). In this method—since there are multiple connections to the DC Grounding Electrode
(GEC–DC)—the size of the DC grounding electrode conductor cannot be smaller than the largest
conductor in the DC system (usually the battery-to-inverter cable).
AC Electrical
System
AC
OURCE
S
HOT 1
HOT 2
NEUT
MAGNUM
INVERTER
MAIN AC PANEL
GC-AC
SBJ
GBB
GEC-AC
HOT 1
HOT 2
GE
NEUT
GND
GBB
MMP
GND
NEG
POS
SBJ
GC-DC
ENCLOSURE
GEC-DC
Grounding System
DC Electrical
System
DC
OURCE
S
BAT
BAT
AC and DC sides shared
Figure 2-18, Multiple Connections to DC Ground Rod (Method 2)
3. Multiple Connections to Ground – Multiple Electrodes (Method 3): This method uses
a separate grounding electrode for the DC system and the AC system (see Figure 2-19). In this
method—since there are multiple connections to the DC Grounding Electrode (GEC–DC)—the size
of the DC grounding electrode conductor cannot be smaller than the largest conductor in the DC
system (usually the battery-to-inverter cable).
The DC Grounding Electrode (GE–DC) must be bonded to the AC Grounding Electrode (GE–AC)
to make a grounding electrode system; this Bonding Conductor (BC) cannot be smaller than the
largest grounding electrode conductor, either AC or DC.
AC Electrical
System
AC
OURCE
S
HOT 1
HOT 2
NEUT
GE
AC side dedicated
MAIN AC PANEL
GBB
GEC-AC
Figure 2-19, Multiple Connections to DC Ground Rod (Method 3)
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
MAGNUM
INVERTER
GC-AC
SBJ
HOT 1
HOT 2
NEUT
GND
GBB
MMP
BC
Grounding System
GND
NEG
POS
SBJ
GC-DC
ENCLOSURE
GEC-DC
DC side dedicated
DC Electrical
System
DC
OURCE
S
BAT
BAT
GE
Page 35
Page 45

Installation
2.10.2 Equipment Grounding Conductor
The MMP enclosure and all other noncurrent-carrying exposed metal surfaces in the entire electrical
system that may be accidentally energized must be grounded. The equipment-grounding conductor
must be sized to safely carry the maximum ground-fault current likely to be imposed on it from
where a ground-fault may occur.
AC Side – When the AC circuit breaker provided in the MMP enclosure is being used as the
inverter’s AC overcurrent protection device, the AC Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC–AC)
for the inverter is based on the AC breaker size provided (#10 AWG for all MMP models). Connect
the AC equipment-grounding conductor from the inverter’s AC ground connection to the Ground
Busbar (GBB) in the MMP enclosure (Item 8 in Figure 1-2 or 1-4).
DC Side – When the DC circuit breaker provided in the MMP enclosure is being used as the
inverter’s DC overcurrent protection device, the DC Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC–DC) for
the inverter is based on the DC breaker size provided (#6 AWG for MMP175 models, #4 AWG for
MMP250 models). Connect the DC equipment-grounding conductor from the inverter’s DC ground
connection to the Ground Busbar (GBB) in the MMP enclosure (Item 20 in Figure 1-2 or 1-4).
If you are using AC or DC overcurrent protection that is different than that provided in the MMP
enclosure, or installing optional DC breakers inside the MMP enclosure, in accordance with the
NEC/CEC you must determine your equipment-grounding conductors based on the ampere rating
of the overcurrent device protecting the circuit conductors. Use Table 2-7 to help determine the
equipment-grounding conductor. If the circuit conductors are oversized to compensate for voltage
drop, the equipment-grounding conductor must also be oversized proportionally.
Table 2-7, Equipment Grounding Conductor Sizing
Rating of Overcurrent
Device
15 amp #14 AWG
20 amp #12 AWG
30-60 amp #10 AWG
100 amp #8 AWG
200 amp #6 AWG
300 amp #4 AWG
400 amp #3 AWG
Minimum Size of Copper
Ground Wire
2.10.3 System Bonding Jumper
The MMP enclosure provides the single point of ground [System Bonding Jumper (SBJ)] for the
AC and DC system. If the MMP enclosure is the central connection point for all ground wiring
(usually in an off-grid system) and there is no other connection from AC neutral or DC negative
to ground in the AC or DC system, then leave the ground bond connections in place. Remove any
other neutral-ground connection in the AC system, such as in other electrical sub-panels; or, any
negative-ground connection in the DC system.
For utility connected systems where the neutral and ground are already bonded in the main utility
circuit breaker box (AC distribution panel), the GREEN GROUND/NEUTRAL bonding wire MUST BE
REMOVED from the MMP enclosure. See Section 2.11 to remove this neutral-ground connection.
Info: Inverters and portable generators that have electrical outlets usually have the
neutral and ground bonded internally. These types of devices are not recommended to
be connected to the MMP/inverter system as they would fi rst need to be modifi ed to
separate the neutral and ground bonding internally.
For systems or devices that connect the DC negative to ground independently (i.e., separate
DC main electrical distribution panel or PV-GFP device), the Negative to Ground busbar (Item 1,
Figure 1-2 or 1-4) MUST BE REMOVED inside the MMP enclosure. See Section 2.12 to remove this
negative-ground connection.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 36
Page 46

Installation
2.11 Removing the AC Neutral to Ground Connection
In installations where the MMP enclosure is powered from utility power or large permanently
installed generator systems, the AC neutral to ground connection is normally provided inside the
main AC electrical distribution panel. In these systems, the factory installed neutral to ground
connection in the MMP enclosure must be removed to prevent multiple neutral to ground bonds.
See Figure 2-20 to help remove the neutral to ground connection from the AC Ground Busbar.
Steps to remove the neutral to ground connection:
1. Inside the MMP enclosure, locate the green
wire with the NEUTRAL-GROUND CONNECTION label (Item 7, in Figure 1-2 or 1-4). This
green wire connects the neutral and ground
inside the MMP enclosure.
2. Loosen the screw and remove this green wire
from the Ground Busbar (Item 8, in Figure
1-2 or 1-4). Note: After this wire is removed,
remember to tighten the loose screw back
into the busbar to prevent it from being lost.
3. With this green wire removed, wrap electrical
tape around the bare end to insulate the wire
and prevent it from making contact with any
metal. Secure the green wire out of the way.
Neutral to
Ground
Connection
(Green Wire)
Ground
Busbar
Figure 2-20, Removing the AC Neutral
to Ground Connection
2.12 Removing the DC Negative to Ground Busbar
The MMP enclosure provides the single point of ground for the DC system by connecting the DC
shunt (battery negative connection point) to the DC Ground Stud using the DC Negative to Ground
Busbar (Item 1, in Figure 1-2 and 1-4). If the single negative-ground connection is made elsewhere
in the DC system—either at the battery terminal, inside a charge controller, or if you are installing
a PV-Ground Fault Protection (PV-GFP) device—this busbar must be removed to prevent multiple
negative-ground bonds. See Figure 2-21 to help remove the Negative to Ground Busbar.
Steps to remove the DC negative-to-ground
connection:
1. Inside the MMP enclosure, locate the Negative to Ground Busbar (Item 1, in Figure 1-2
and 1-4). This busbar connects negative and
ground inside the MMP enclosure.
2. Remove the 5/16” fl ange nut (1/2” wrench)
holding the busbar to the DC Ground Stud
(Item 13, in Figure 1-2 or 1-4), and then remove the 3/8” brass bolt and washer (9/16”
wrench) from the bottom terminal of the DC
shunt (Item 12, in Figure 1-2 or 1-4).
3. After the Negative to Ground Busbar is removed; reattach the fl ange nut on the DC
Ground Stud and the brass bolt/washer back
onto the DC shunt. Ensure the hardware
on the bottom terminal of the DC shunt is
stacked correctly. Note: Refer to Figure 2-9
to correctly stack the DC shunt hardware.
DC Ground
Stud
Bottom Terminal
(DC Shunt) Ground
Busbar
Negative to Ground
Busbar
Figure 2-21, Removing the DC
Negative to Ground Busbar
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 37
Page 47

Installation
2.13 Wiring Accessories
The NEC/CEC requires the insulation of all conductors inside the MMP enclosure to be rated for
the highest voltage present. The MMP enclosure is designed to work with 120/240 VAC inverters,
therefore, the voltage rating of the communications cables inside the MMP enclosure must be rated
for 300 volts or higher to be code compliant.
With the purchase of the MMP enclosure, Magnum has included three six-foot, yellow communication
cables with 300-volt rated insulation. These cables—shown below—are provided to make connections
between Magnum inverters and accessories easier and code compliant.
Info: These cables carry less than 30 volts and are thus considered a “limited energy
circuit”, which is normally not required to be installed in conduit.
Figure 2-22 shows the ‘REMOTE’ cable. It
allows a remote control—such as the MERC (Remote Control) or ME-ARC (Advance
Remote Control)—to be connected to the
MMP enclosure. This cable is a 6’ (1.83m),
4-conductor, telephone-type cable with a RJ14
(m) connector and a blue REMOTE label on
each end. One end of this cable is connected
to the remote, and the other end is routed
inside the MMP enclosure and then connected
to the inverter’s REMOTE port as shown in
Figure 2-25.
Figure 2-22, REMOTE Communication Cable (300V)
Figure 2-23 shows the ‘NETWORK’ cable.
It allows Magnum accessories—like the
ME-AGS (Auto Generator Start) or ME-BMK
(Battery Monitor)—to be connected to the
MMP enclosure. This cable is a 6’ (1.83m),
2-conductor, telephone-type with a RJ14 (m)
connector and a green NETWORK label on
each end. One end of this cable is connected
to the accessory, and the other end is routed
inside the MMP enclosure and then connected
to the inverter’s NETWORK port as shown in
Figure 2-25.
Figure 2-23, NETWORK Communication Cable (300V)
Figure 2-24 shows the ‘EXTENSION’ cable.
It allows the Magnum ME-BTS (Battery
Temperature Sensor) to be connected to
the MMP enclosure. This is a 6’ (1.83 m),
4-conductor, telephone-type cable with a RJ14
(m) connector on one end and a RJ14 (f) plug
on the opposite end. The female plug end
connects to the ME-BTS (Battery Temperature
Sensor). After connecting to the ME-BTS,
this extension cable is routed inside the MMP
enclosure and connects to the inverter’s BTS
port as shown in Figure 2-25.
Figure 2-24, Extension Cable (300V)
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 38
Page 48

ME-AGS-N
NETWORK Communication
Cable (300-volt rated)
REMOTE Communication
Cable (300-volt rated)
Front cover of MMP
enclosure (back side)
NETWORK
.
N
E
REMOTE
Installation
T
W
O
R
K
REMOTE
ME-RC or
ME-ARC
ME-BTS
.BTS
Extension Cable (300-volt rated)
Figure 2-25, Accessory Wiring using 300 Volt Communications Cables
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 39
Page 49

Installation
2.14 Installation Checklist
Use this checklist as a fi nal review to ensure all essential steps to install the MMP enclosure have
been completed before proceeding with the functional test.
Mounting
The MMP enclosure/inverter system is securely mounted in a clean, dry, and ventilated area.
The system is not mounted in the same enclosure as maintenance-free or vented type batteries.
The MMP enclosure is mounted in a ‘vertical only’ position.
There is adequate clearance to access the front and to view/adjust the remote (if installed).
DC Wiring (use Table 2-4 to determine the DC wire size).
Inverter Side with Magnum Inverter (see Figure 1-2, Items 9A & 10A):
The inverter is correctly placed onto the MMP enclosure with the inverter’s DC terminals attached
to the tops of the DC negative busbar and the DC positive busbar inside the MMP enclosure.
Inverter Side without Magnum Inverter (see Figure 1-2, Items 9B & 10B):
An appropriately sized DC cable is routed and attached from the inverter’s DC positive (+)
terminal to the DC positive connection at the top of the DC breaker inside the MMP enclosure.
An appropriately sized DC cable is routed and attached from the inverter’s DC negative (–)
terminal to the DC negative connection at the top of the DC shunt inside the MMP enclosure.
Battery Bank Side (see Figure 2-8):
An appropriately sized DC cable is routed and attached from the positive (+) battery terminal
to the bottom battery bank connection of the DC disconnect breaker inside the MMP enclosure.
An appropriately sized DC cable is routed and attached from the negative (–) battery terminal
to the bottom battery bank connection of the DC shunt inside the MMP enclosure.
The DC cable connections and DC hardware are stacked (Figure 2-9) and torqued (Tables 2-1
to 2-3) correctly.
AC Wiring (use Table 2-5 to determine the AC wiring confi guration and to fi nd the AC wire size).
In and Out of Inverter (see Figures 2-10 & 2-11):
The AC wires are appropriately sized and routed from the INVERTER AC TERMINAL BLOCK
(inside MMP enclosure) to the inverter’s AC input/output terminals.
To Main AC Electrical Panel (see Figures 2-12 to 2-15):
The AC wires are appropriately sized and are routed from the grid/gen side of the EXTERNAL
AC TERMINAL BLOCK (inside MMP enclosure) to the circuit breaker in the main AC electrical panel
powered by the utility or generator (i.e., main panel).
To Inverter AC Load Panel (see Figures 2-12 to 2-15):
The AC wires are appropriately sized and are routed from the AC load side of the EXTERNAL
AC TERMINAL BLOCK (inside MMP enclosure) to the main circuit breaker in the electrical panel
powered by the inverter (i.e., sub-panel).
The AC wires connected to the terminal blocks are torqued correctly (see Tables 2-1 to 2-3).
Grounding
There is only one bonding connection to ground for the DC electrical system (negative to ground)
and one bonding connection to ground for the AC electrical system (neutral to ground). These
bonding connections may be connected to the same grounding electrode system (ground rod). If
separate electrodes are used, they must be bonded together.
The exposed metal parts of equipment are properly grounded.
Equipment grounding conductors are properly sized.
Electrical Connections
Connectors are listed for the intended use and environment (inside, outside, wet, etc.,).
Pressure/screw terminals tightened to the recommended torque specifi cation.
Terminals containing more than one conductor are listed for multiple conductors.
Connectors using fl exible, fi ne-stranded conductors are listed for use with such conductors.
Re-torque electrical terminal connections in the inverter that may have loosened.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 40
Page 50

Installation
Conductors and General Wiring Methods
Conductors are rated for the application and the environment.
Standard building-wire conductors and appropriate wiring methods are used.
Note: Welding, marine, locomotive (DLO), and auto battery cables don’t meet NEC/CEC
requirements. Flexible RHW or THW cables are available, but these cables require very limited,
specially listed terminals. When the battery conductors leave the battery enclosure, the conductors
must be of a type listed for use in conduit (RHW or THW).
The DC and AC color codes for the ground conductors are the same – grounded conductors
are white and equipment-grounding conductors are green, green/yellow, or bare (no insulation).
All wiring insulation must have a minimum rating of 150V, 75°C when using only 120 VAC
power/inverter; or, with a minimum rating of 300V, 75°C when using 120/240 VAC power/inverter.
Strain reliefs/cable clamps or conduit are used on all cables and cords.
Conductors between the inverter and battery bank are required to be installed in conduit.
No multi-wire branch circuits when single, 120 VAC inverters are connected to 120/240 VAC
load centers.
Note: A multi-wire branch circuit is a three-wire circuit with a shared neutral for two, 120 VAC
branch circuits.
Overcurrent Protection
Properly sized and rated disconnects and overcurrent devices are used in the ungrounded
conductors in each circuit (AC and DC).
Overcurrent devices in the DC circuits are listed for DC operation.
DC overcurrent protection is provided at the batteries when they are located in a separate room,
or more than fi ve feet away from the MMP enclosure.
The DC overcurrent protection device and battery cables to the inverter are sized for the
inverter’s DC input current.
Note: Inverter’s DC input current is calculated using rated AC output in watts, divided by lowest
battery voltage, divided by inverter effi ciency at that power level.
When the DC disconnect inside the MMP enclosure is not used as the DC overcurrent device,
high interrupt, listed, DC-rated fuses or circuit breakers must be used in the battery cable circuits.
Batteries
Battery terminals and other live parts are guarded, and adequate working space around the
battery bank is provided.
Batteries are installed in well-vented areas (garages, outbuildings) and not in living areas.
Adhere to the “IMPORTANT BATTERY SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS” at the beginning of this manual.
Marking
Battery bank is labeled with maximum operating voltage, equalization voltage, and polarity.
Utility Back-up Systems: a visible exterior sign indicating the building contains an inverter backup system and identifi es the locations of the disconnects.
An electrical system supplied by a 120 VAC only inverter must include a label warning against
connecting multi-wire branch circuits.
All required “WARNING” and “CAUTION” signs are installed in the proper locations, as required
in the NEC/CEC.
Inspection
Electrical inspection complete and Certifi cate of Electrical Inspection issued by the local Authority
Having Jurisdiction (AHJ). The local AHJ or inspector has the fi nal say on what is or is not acceptable.
Local codes may modify the requirements of the NEC/CEC.
Part of this checklist is obtained from the Photovoltaic Electrical Power Systems Inspector/Installer Checklist
created by John Wiles, Southwest Technology Development Institute, New Mexico State University, June, 2006.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 41
Page 51

Installation
2.15 Functional Test
After all electrical connections from the MMP enclosure to the inverter, batteries, AC source, and
sub-panel
of the MMP enclosure and to verify proper operation of the BYPASS switch breakers.
1. Turn OFF all AC breakers (i.e., INV BYP, INV IN, and INV OUT) in the MMP enclosure.
have been completed, follow these steps (refer also to Figure 2-26) to test the installation
WARNING: During this functional test, the front cover is removed and exposes
personnel to potential dangerous voltages and shock hazards inside the MMP enclosure
that may cause damage, injury, or death. If you do not have experience working with AC
and DC voltage circuits, do not attempt this test—use an experienced electrical installer.
CAUTION: During this functional test, if any step cannot be verifi ed or is incorrect,
stop and recheck/correct the connections before proceeding to the next step.
CAUTION: Use a multimeter to verify the correct DC voltage for your particular inverter
model (i.e., 24-volt battery bank for a 24-volt inverter) and to ensure the polarity of
the battery voltage is correct [battery positive (+) connected to the inverter positive
terminal thru the DC circuit breaker and battery negative (–) connected to inverter
negative terminal thru the DC shunt].
CAUTION: Prior to turning on the inverter, turn OFF all inverter loads in the inverter
load panel (i.e., sub-panel).
2. After verifying that the battery bank voltage is proper for your inverter and that the battery
cable connections are the correct polarity, apply battery power to the inverter by turning the
DC disconnect breaker to the ON (up) position.
3. Turn the inverter ON.
a. Connect an AC voltmeter to the Inverter Output Terminals and verify the correct AC
output voltage of the inverter (depends on your inverter AC output voltage).
Info: If the inverter does not turn on—verify the DC connections to/from the inverter
to the battery, and/or refer to the Troubleshooting section for your particular inverter.
Info: If the inverter has a Search mode feature, the inverter’s AC full output voltage
will not be present/correct until Search is turned OFF, or by connecting a large enough
light bulb to bring the inverter out of Search. DO NOT connect anything but a light bulb
until all wiring and voltages are confi rmed to be correct.
If using a Magnum inverter, use a light bulb greater than 5 watts (5 watts is the default
setting) to bring the inverter out of Search mode; or, the Search mode can be turned
OFF with a remote control (ME-RC or ME-ARC).
1
4. Turn ON the INV OUT
breaker(s) in the MMP enclosure.
a. Ensure the inverter AC output voltage is passing thru the INV OUT (Inverter Output) breaker
by verifying the correct output voltage is present on the AC Output Terminals.
5. Turn ON the INV BYP
2
breaker(s) in the MMP enclosure.
a. Ensure the inverter AC output voltage is no longer present on the AC Output Terminals.
Note¹ – On MMPxxx-60S models, the INV OUT and INV IN breakers are physically ganged together
and turn ON and OFF as a single breaker.
2
Note
– The INV BYP and INV OUT breakers are interlocked together. Physically turning ON will turn
OFF the other, and vice-versa.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 42
Page 52

Installation
6. Apply power from an external AC source (utility or AC generator) to the AC Input Terminals.
a. Connect an AC voltmeter to the AC Input Terminals and verify that the AC voltage from
the external AC source is present. Connect the AC voltmeter to the AC Output Terminals
and check that the external AC source power is passing thru the INV BYP (Inverter Bypass)
breaker by verifying the AC source voltage present earlier is also present on the AC Output
Terminals.
7. Turn ON the INV OUT
a. Ensure the AC source power is passing thru the INV IN (Inverter Input) breaker by verifying
the AC source voltage present earlier (in Step 6) is also present on the AC Output Terminals.
8. After all the AC voltage checks pass, install the front cover and manually open and close all
circuit breakers, checking for correct alignment and free operation.
If all the steps pass, the MMP enclosure is ready for use. If the any of the steps fails, refer to
Installation section and recheck your wiring connections and/or refer to the Troubleshooting section
for your inverter.
2
and INV IN breaker(s) in the MMP enclosure.
MMP ENCLOSURE (AC SIDE)
INV
BYP
INV IN /
INV OUT
AC
BREAKERS
(-60S Models)
120V
120V
120V
INVERTER INPUT
TERMINALS
(TO INVERTER’S AC INPUT)
INVERTER OUTPUT
TERMINALS
(FROM INVERTER’S AC OUTPUT)
USE AN AC
VOLTMETER TO
READ VOLTAGE
IN
AND OUT
OF THE MMP
ENCLOSURE
AC OUTPUT TERMINALS
(TO INVERTER LOADS)
120V
240V
120V
120V
240V
120V
AC
BREAKERS
(-30D Models)
120V
240V
120V
INV
BYP
INV
OUT
INV
IN
MMPXXX-60S
ODELS
M
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
120V
AC INPUT TERMINALS
(FROM UTILITY OR GENERATOR)
120V
240V
120V
Figure 2-26, AC Voltage Checks
MMPXXX-30D
ODELS
M
Page 43
Page 53

Operation
3.0 Operation
The MMP enclosure provides you with circuit breakers/disconnects to easily operate and maintain
your inverter/battery system. These breakers
and/or overcurrent protection. Refer to Figure 3-1 (MMP Functional Diagram) to see the functional
operation of the breakers within the MMP enclosure.
Info: Figure 3-1 is for descriptive purposes only, for specifi c wiring directions please
refer to the relevant wiring diagram in the Installation section of this manual.
Info: For information on operating the inverter, refer to its owner’s manual.
If a short-circuit condition occurs, or if a load is placed on the circuit breaker that is more than its
rated capacity, the breaker will trip OFF (down). On the AC breakers, a red indicator will display
through the clear window on the circuit breaker to show a tripped condition. On the other circuit
breakers, the handle will trip all the way to the OFF position.
Before resetting the breaker, fi rst determine the cause of the overcurrent fault. Then, reset the
circuit breaker by turning it all the way OFF, and then all the way back ON. For proper maintenance
and longer life, the circuit breakers should be turned off and on several times at least once a year.
This will help to prevent the contacts inside from sticking together.
To shut the MMP/inverter system OFF completely, all of the circuit breakers in the MMP
enclosure should be switched to the OFF position.
are used as the main power disconnecting means
NEG (-)
BATTERY
BANK
(Customer
Connection)
POS (+)
AC
SOURCE
FROM MAIN
PANEL
(C
USTOMER
C
ONNECTION)
AC Side
AC INPUT
Breakers
INVERTER
(DC side)
DC
INPUT
DC NEG Busbar
DC Shunt
INV DC Breaker
DC
Breakers
(optional)
DC POS Busbar
DC Side
MMP Enclosure
EXTERNAL AC Terminal BlockAC IN AC OUT
AC BYPASS AC OUTPUT
ON
OFF
INVERTER AC Terminal BlockINV IN INV OUT
ON
OFF
DC
LOADS
(Customer
Connection)
AC
LOADS
IN SUB-
PANEL
(C
USTOMER
C
ONNECTION)
AC
INPUT
INVERTER
(AC side)
AC
OUTPUT
Figure 3-1, MMP Functional Diagram
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 44
Page 54

Operation
3.1 Inverter DC Disconnect Breaker
The Inverter DC Disconnect Breaker is used to disconnect the battery during battery maintenance.
This disconnect can also be used to protect the inverter, battery, and inverter DC cables from overloads and short circuits. The inverter DC disconnect does not, however, disconnect the battery power
from the DC positive busbar in the MMP enclosure. So, if you have installed any optional DC load
breakers, you must turn OFF all DC load breakers to disconnect battery power to all the DC loads.
Before switching the DC Inverter Disconnect OFF, turn the inverter OFF. This is to protect
the inverter and other equipment from failure, and to preserve the contacts in the breaker.
WARNING: Do not use the DC disconnect breaker to turn your inverter on and off
on a regular basis, it is there to provide safety and ease of maintenance. Turn off the
inverter at its on/off switch fi rst. However, in an emergency, the inverter DC disconnect
is provided so that you can switch it off while the inverter is operating.
Info: Always switch the DC disconnect breaker to OFF before connecting or disconnecting
the battery bank, to reduce the chance of spark and wear on the connectors.
3.2 AC Input Breaker
The AC Input Breaker when switched ON, allows the incoming AC source (utility or generator) to
be connected to the inverter’s AC input. This breaker should be switched OFF to disconnect the
AC power from the inverter AC input.
On MMPxxx-30D models, this breaker is a dual-pole 30-amp circuit breaker (see Figure 1-3). On
MMPxxx-60S models, the AC input disconnect breaker is one side of a dual 60-amp breaker; the
other side of this dual 60-amp breaker is used as the AC output breaker (see Figure 1-5).
3.3 Inverter AC Output Breaker
The Inverter AC Output Breaker when switched ON, allows the AC power out of the inverter—either
inverter power or pass-thru power (from the utility or generator)—to be connected to the AC loads.
With this breaker OFF, the connected inverter loads beyond the MMP enclosure can be serviced.
On MMPxxx-30D models, this breaker is a dual-pole 30-amp circuit breaker (see Figure 1-3). On
MMPxxx-60S models, the AC output disconnect breaker is one side of a dual 60-amp breaker; the
other side of this dual 60-amp breaker is used as the AC input breaker (see Figure 1-5).
3.4 Inverter AC Bypass Switch Breaker
The Inverter AC Bypass Switch Breaker allows the inverter loads to continue to be powered by
the incoming AC source (utility or generator) while isolating the inverter or battery system if
maintenance or repair is needed.
This switch is pre-wired in the MMP enclosure between the incoming AC source and the inverter
load panel (i.e., sub-panel). It connects the incoming AC source to the inverter’s AC loads; either
through the “inverter” or directly by “bypassing” the inverter. This bypass switch assembly uses
a mechanical interlock between two AC breakers to prevent both breakers from being ON at the
same time, but both can be OFF at the same time. This bypass switch is normally set to ‘OFF”
(inverter not bypassed), but can be easily moved to “ON” (bypass inverter) allowing the AC loads
to continue to be powered if the inverter or battery bank needs to be serviced/disconnected—
without any rewiring.
Refer to Figure 3-2 (MMPxxx-30D models) or Figure 3-3 (MMPxxx-60S models) to review the
operational modes and power fl ow of the AC bypass switch.
All AC loads should be turned off before switching the bypass switch breaker.
Info: When the bypass switch is ON the connected equipment is directly powered from
the AC source (utility or generator), and will go off if the AC source is disconnected or
turned off.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 45
Page 55

Operation
SUB-P
ANEL
OFF
OFF OFF OFF OFF
M
AIN PANEL
OFF
OFF OFF OFF OFF
OFFOFF OFFOFF
SUB-P
ANEL
OFF
OFF OFF OFF OFF
M
AIN PANEL
OFF
OFF OFF OFF OFF
OFFOFF OFFOFF
M
AGNUM
I
OFF OFF OFFOFF
B
YPASS
S
WITCH
OFF OFF OFFOFF
OFFOFFOFFOFF
NVERTER
INV BYPASS
= OFF
INV OUTPUT
= ON
INV INPUT
= ON
Normal Operation
With the AC breakers in this position, power
passes through the inverter to the connected
loads. If an AC line failure occurs, the inverter
will use DC power from the batteries to
maintain the loads in the sub-panel.
M
AGNUM
I
OFF OFF OFFOFF
B
YPASS
S
WITCH
OFF OFF OFFOFF
OFFOFFOFFOFF
NVERTER
INV BYPASS
= ON
INV OUTPUT
= OFF
INV INPUT
= ON
Inverter Bypass Operation
With the AC breakers in this position, power passes
directly to the loads in the sub-panel, bypassing the
inverter. When the Inverter Input breaker is ON,
the batteries will continue to be charged. If inverter
maintenance or service is required, the Inverter Input
breaker must be turned OFF. If AC power from the main
panel fails while the AC breakers are in this position, the
loads in the sub-panel will not be powered.
SUB-P
OFF
OFF OFF OFF OFF
M
AIN PANEL
OFF
OFF OFF OFF OFF
OFFOFF OFFOFF
ANEL
M
AGNUM
I
OFF OFF OFFOFF
B
YPASS
S
WITCH
OFF OFF OFFOFF
OFFOFFOFFOFF
NVERTER
INV BYPASS
= OFF
INV OUTPUT
= OFF
AC OFF Operation
With the AC breakers in this position, power
from both the main panel and inverter are
removed from the sub-panel. This allows
the loads in the sub-panel or any installed
equipment beyond the MMP enclosure to be
serviced. To service the inverter, the Inv Input
breaker must also be turned OFF.
Figure 3-2, MMPxxx-30D Bypass Switch Operation
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 46
INV INPUT
= ON
Page 56

SUB-P
OFF
O
O
F
N
F
O
O
F
N
F
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
M
AIN PANEL
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
SUB-P
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
M
AIN PANEL
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
ANEL
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ANEL
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
Operation
M
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
B
YPASS
S
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
WITCH
B
YPASS
S
WITCH
AGNUM
I
NVERTER
M
AGNUM
I
NVERTER
INV
BYPASS
= OFF
INV INPUT &
INV OUTPUT
= ON
Normal Operation
With the AC breakers in this position,
power passes through the inverter to
the connected loads. If an AC line failure
occurs, the inverter will use DC power from
the batteries to maintain the loads in the
sub-panel.
INV
BYPASS
= ON
INV INPUT &
INV OUTPUT
= OFF
Inverter Bypass Operation
With the AC breakers in this position, power passes
directly to the loads in the sub-panel, bypassing the
inverter. In this confi guration, the sub-panel loads will
continue to be powered if inverter maintenance or
service is required. If AC power from the main panel
fails while the AC breakers are in this position, the sub-
panel loads will not be powered.
SUB-P
ANEL
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
M
AIN PANEL
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
B
YPASS
S
WITCH
Figure 3-3, MMPxxx-60S Bypass Switch Operation
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
M
AGNUM
I
NVERTER
INV
BYPASS
= OFF
INV INPUT &
INV OUTPUT
= OFF
AC OFF Operation
With the AC breakers in this position,
power from both the main panel and
inverter are removed from the sub-panel.
This allows the inverter, the loads in the
sub-panel, or any installed equipment
beyond the MMP enclosure to be serviced.
Page 47
Page 57

Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
Appendix A – Optional Equipment and Accessories
A1 Installing the Charge Controller Bracket
A Charge Controller Bracket is provided to mount the most commonly used charge controllers to
the MMP enclosure. This bracket can be easily mounted on either the left or right side of the MMP
enclosure, and is designed to work with specifi c MidNite, MorningStar, or OutBack charge controllers.
Info: The necessary hardware is provided to secure the bracket to an enclosure and
to mount a charge controller to the bracket (see Figure A1-1).
Sizes shown in
inches (mm)
1.50
(38.1)
4
.
3
)
1.
02
.
33
(
(
118
.
65
11
)
controller. Use the supplied thread
forming screws to pre-thread the hole(s)
you will use before mounting the bracket.
Two #8-32 x 1/2”
Torx drive (T20)
screws to attach
the bracket to the
MMP enclosure.
Two #8-32 x 1/2” Torx drive (T20) screws
to attach a charge controller to the bracket.
Most controllers only use one screw.
Figure A1-1, Charge Controller Bracket – Physical Dimensions
Installation
Before proceeding, use Table A-1 to determine the following for your particular charge controller:
• which side of the enclosure (left or right) to mount the controller,
• which enclosure mounting holes (upper or lower) are used to attach the bracket,
• which bracket hole(s) (A-G) are used to attach the controller.
Holes (x8) for mounting a charge
Table A-1, Mounting Holes Used for Charge Controllers
Charge
Controller
Classic w/o Turbo (MN) (B) / [upper] (F) / [upper]
Classic w/Turbo (MN) (A) / [upper] (F) / [upper]
FlexMax 80 (OB) NA (G) and (E) / [upper]
Tristar (MS) (D) / [lower] (C) / [lower]
(MN) = MidNite, (OB) = OutBack, (MS) = MorningStar
Holes to use: (Bracket) / [Enclosure]
Left Side Install Right Side Install
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 48
Page 58

Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
Refer to Figure A1-2 to locate the holes you will use to attach the charge controller to the bracket.
Before mounting the bracket, use the provided T20 Torx drive, thread forming screws to pre-thread
your selected mounting holes. It is easier to thread the holes now rather than doing it after the
bracket and controller have been installed.
After pre-threading your particular bracket hole(s), locate the enclosure mounting holes you will
use to attach the bracket to the enclosure. Before you mount the charge controller to the attached
bracket, remove the appropriate knockout from the side of the controller and an adjacent knockout
on the side of the enclosure. This allows you to use a one inch close nipple with two locknuts to
secure the charge controller to the enclosure (in addition to the bracket), and provides a path to
run the necessary wiring between the two units. Mount the controller to the attached bracket using
the supplied hardware. Insert the close nipple through the knockouts and secure with the locknuts.
Info: It may take three locknuts on the close nipple to anchor the controller to the
enclosure. An additional locknut may be required between the enclosure and the
controller to act as a spacer. Also, a standard one inch plastic bushing should be used
on the nipple ends to protect the wire insulation as it enters/exits the nipple.
Right Side View
Upper Mounting
Holes (right side)
Lower Mounting
Holes (right side)
MMP
Left Front View
Right Front View
Charge Control Bracket
(right side)
G
Bracket to enclosure
Torx screws
MMP Enclosure
Charge Control Bracket
(left side)
F
D
C
A
B
E
Controller Mounting
Holes on Bracket
Left Side View
Upper Mounting
Holes (left side)
A
B
F
Controller Mounting
Holes on Bracket
Figure A1-2, Holes Used to Mount Bracket on MMP Enclosure
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
C
D
Bracket to enclosure
Torx screws
MMP Enclosure
G
Lower Mounting
Holes (left side)
MMP
Page 49
Page 59

Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
A2 Installing a Remote Control
Complete the steps below to install the ME-RC or ME-ARC remote control on the MMP enclosure;
refer to Figure A2-1 for assistance.
1. Unscrew the blank plate from the front cover, and remove the four 8-32 x 1/2 Phillips drive,
black colored screws taped to the back of this blank plate.
Info: The blank plate is attached to the front cover using #8-32 Hex nuts. Use a 11/32”
socket or wrench to remove/reattach these nuts.
2. Use these four screws and the four nuts that were used to hold the blank plate to attach the
remote control to the front cover.
3. Run the yellow colored remote cable that is provided between the remote and the Magnum
inverter/charger.
Info: The remote cable is a 4-wire, twisted-pair, telephony standard with 300-volt rated
insulation, and uses RJ14 (m) connectors on each end (see Figure 2-22). A standard
telephone cable would not be code compliant and should not be used.
4. Connect one end of the remote cable into the RJ14 “REMOTE” port (has blue label) on the
inverter/charger, and the other end into the RJ14 jack on the backside of the remote.
BLANK
LATE
P
FRONT COVER
(REAR VIEW)
FRONT COVER
(FRONT VIEW)
Figure A2-1, Installing a Remote Control on the MMP Enclosure
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 50
Page 60

Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
A3 Installing a Battery Monitor
Figure A3-1, Mounting the Sense Module
MOUNTING DIMPLES W/
#8 SCREW HOLES (X2)
SENSE MODULE
(PART OF ME-BMK-NS)
TWO #8 X 1/2”,
T15 TORX DRIVE SCREWS
(PROVIDED & SCREWED INTO
TWO MOUNTING DIMPLES)
THE
Negative Busbar
Positive Busbar
Communications Cable
To DC
To DC
4-Port Terminal Block
(can be removed, and
each port accepts
30 to 12 AWG wire).
red
black
orange
blue
(To Network port on
Magnum inverter)
black
red
DC Fuse (2 amps)
Twisted-pair cable
To Inverter/Loads
orange
blue
Sense Module
(from ME-BMK)
To Network Port
DC Shunt
(in MMP Enclosure)
Battery Positive
Busbar
(in MMP Enclosure)
Close-up of wiring
the ME-BMK
Figure A3-2, Wiring the Sense Module and DC Shunt
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
To Battery Bank
DC Negative Busbar
(in MMP Enclosure)
Page 51
Page 61

Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
A4 Knockout Plate
A knockout plate (PN: MMP-KP) can be purchased to facilitate running conduit from the top of
the MMP enclosure, or for use as a safety plate. If your Magnum inverter is ever removed for
service and the AC bypass breaker is used to continue to power the inverter loads, attaching
the knockout plate prevents accidental access to live electrical circuits inside the MMP enclosure
(see Figure A4-1).
WARNING: If the knockout plate is used as a safety plate, the bus bars from the
top of the DC disconnect must be prevented from touching the metal knockout plate
or a short circuit to the battery bank may occur—causing very lethal currents. Either
remove these bus bars or isolate them (i.e., using electrical tape/rubber caps), do not
rely ONLY on turning the DC disconnect switch off.
Info: Four #10-32 x 3/8” Pan head, T25 Torx drive, thread cutting screws; and four #10
lock washers are used to secure the knockout plate to the enclosure.
Info: Before removing the appropriate knockouts (Figure A4-2), think about whether
you are going to use cable clamps or conduit, and all the different wiring required.
TOP VIEW
(KNOCKOUT PLATE)
Figure A4-1, Attaching Knockout Plate
D
7
12
8
C
B
6
CONDUIT KNOCKOUTS
(TOTAL):
B = ½” and ¾” (x2)
C = 1” and 1¼” (x2)
D = 1 ½” and 2” (x1)
Figure A4-2, Knockout
Plate Dimensions and
Knockouts
B
C
1
”
2
”
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 52
Page 62

Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
A5 Inverter Hood Info
The inverter hood (PN: MP-Hood) is a powder-coated steel cover plate, designed to prevent
inverter damage from objects falling through the top vents of the inverter. The hood is required
for installations when the inverters are mounted on a vertical surface (DC side down)—such as
on the MMP enclosure.
Info:
wall.
CAUTION:
The hood does not mount to the inverter chassis, it must be mounted against the
The mounting slots on the hood will accept up to a maximum 1/4 inch screw/bolt.
The hood is not to be used as a drip shield
to prevent water drip from
entering the inverter.
Installation Guidelines:
1. The bottom edge of the hood must be mounted fl ush against the top of the Magnum inverter;
this is the optimal position for minimizing the risk of objects falling into the inverter, and at
the same time providing the clearance needed for air fl ow from the top vents of the inverter.
2. Do not place anything on top of the hood that might cause it to bend downward; or, place anything
on the sides to restrict air fl ow through the inverter.
.
8"
.
1"
.
1"
.
0.65
.
0.5
(inches)
.
1.0
.
3"
90°
90°
.
0.28
.
0.3
.
0.85
.
0.28
.
13.60"
14.45"
Figure A5-1, Inverter Hood Dimensions
.
1"
.
3"
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 53
Page 63

Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
A6 Installing Optional DC Breakers
The MMP enclosure provides the room to install additional DC circuit breakers that may be used
for charge controllers, a PV-GFP device, and other DC loads. This enclosure has been specifi cally
designed to allow both back-mounted (1” wide)¹ or DIN rail-mounted (1/2” wide)² breakers.
CAUTION: Turning the DC disconnect breaker off only removes the battery power to
the inverter, it does not interrupt power from the battery to the DC load breakers. This
must be accomplished by turning off the DC load breakers themselves. Therefore, to
shut the system off completely, all of the breakers in the MMP enclosure should be
switched to the OFF position.
To install optional DC breakers inside the MMP enclosure:
Remove the front cover to the MMP enclosure.
1.
For DIN rail-mounted breakers
2.
(refer to Figure A6-1):
a. Install the breaker(s) on the DIN rail mounting
track, and slide all the way to the left side.
b. Place the breaker(s) on the DIN rail track, and
slide a DIN rail clamp tight against the right side
of last circuit breaker; and tighten this clamp to
secure the breaker(s) on the DIN rail track.
c. For each breaker installed, remove only one
knockout (= 1/2” slot) in the front cover.
Ensure the breaker(s) align correctly into the spaces made by the knockouts removed from
3.
the front cover.
Wire the breaker(s) to the DC circuit, use Figure A6-3 to assist in wiring the breaker.
4.
Replace the MMP front cover and check that the breaker operates correctly.
5.
Note¹ – For the 1/2” wide DIN rail-mounted breakers, use Q-Frame types (QYN Series by CBI).
Note² – For the 1” back-mounted breakers, use E-Frame types (E Series by Carling Technologies,
209 Series by Airpax/Sensata Technologies or CF Series by Heinemann/Eaton).
DIN RAIL-MOUNTED DC BREAKER
(1/2” WIDTH)
For back-mounted type breakers
(refer to Figure A6-2):
a. Remove the DIN rail mounting track by
unscrewing the two #8, T15 Torx drive
screws holding this mounting track.
b. Secure the breaker(s) to the panel using
two #8 screws, minimum 1/2” length.
c. For each breaker installed, remove only
two knockouts (= 1” slot) in the front
cover.
DIN RAIL
MOUNTING TRACK
Figure A6-1, Installing DIN Rail-Mounted DC Breakers
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 54
Page 64

Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
SCREW TO BREAKER
MOUNTING PLATE
(REMOVE DIN RAIL)
TWO DC BREAKER
MOUNTING
(USE #8 X 1/2”
LENGTH MINIMUM)
BACK PANEL
MOUNTED
DC BREAKER
(1” WIDTH)
Figure A6-2, Installing Back Panel Mounted DC Breakers
SCREWS
INSIDE MMP ENCLOSURE
DC S
HUNT
GROUND TO
N
EGATIVE
CONNECTION
REMOVE THIS BUSBAR
(
WHEN PV-GFP IS
INSTALLED TO
PREVENT
MULTIPLE
CONNECTIONS)
GROUND
BUSBAR
TO PRIMARY DC
GROUND SYSTEM
B
REAKER
PV +
DC NEGATIVE
BUSBAR
TO BATTERY BANK
NEGATIVE
TERMINAL
(THROUGH DC SHUNT)
BATTERY +
B
REAKER
BATTERY +
B
USBAR
TO BATTERY BANK
POSITIVE
TERMINAL
PV +
USBAR
B
PV CHARGE CONTROLLER
(WITH INTERNAL PV-GFP
PROTECTION)
PV
PVB
B
PV
PV
P
ANELS
PV
Figure A6-3, Wiring DC Breakers
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 55
Page 65

Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
A7 Installing Lightning Arrestors
Unfortunately, in Renewable Energy (RE) systems where components are wired to outdoor electrical
systems, there is a greater chance of damage to these components from lightning strikes. Lightning
does not have to strike directly to cause damage, it can be far away and still induce power surges
or spikes in the wires of the RE system. Since the RE wires are connected to the conductors coming
into the house the inverters, charge controllers, batteries, and other components in the house or
power shed are easily susceptible to damage.
The best line of defense against these high voltage surges—caused by lightning—is to ensure you
have proper system grounding. Proper grounding attempts to divert lightning surges to earth,
instead of going through your electrical components. However, for additional protection in lightningprone areas or where good grounding is not feasible, install lightning arrestors (also known as high
voltage surge arrestors) on the DC and AC circuits of your renewable energy system. Lightning
arrestors are devices that respond to voltage variations instantaneously, effectively intercepting
potentially damaging spikes and surges and reducing them to acceptable power levels to protect
electrical equipment. Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs), Silicone Oxide Varistors (SOVs), and Zinc
Oxide Non-linear Resistors (ZNRs) are three types of lightning/surge arrestors.
The most readily available lightning arrestors in the marketplace install into 1/2’’ conduit knockouts.
Since the MMP enclosure is the central connection point for the main AC and DC electrical
components of the renewable energy system, multiple 1/2” knockouts are provided to allow these
lightning arrestors to be easily installed. The lightning arrestors should be connected as close to
the equipment you are trying to protect as possible. Review Figure A7-1 for help installing these
lightning arrestors, and use Figure A7-2 for assistance on wiring lightning arrestors on the DC and
AC circuits inside the MMP enclosure.
Info: Install additional lightning protection (secondary lightning arrestor) if equipment
is more than 60 feet away from where the primary lightning arrestor is connected.
Info: For more information on lightning protection in RE systems, review Protection
Against the Effects of Lightning on Standalone Photovoltaic Systems – Common Practices
at www.iea-pvps.org.
MMP
Enclosure
Lightning
Arrestor
½” knockout
removed
½” lock
washer
Figure A7-1, Installing Lightning Arrestor on MMP Enclosure
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 56
Page 66

NOTE: CRIMP A RING
TERMINAL WITH A 5/16"
OPENING TO THE LIGHTNING
ARRESTOR WIRES AND
CONNECT TO THE
INVERTER
OLLOW THE PROPER DC
F
HARDWARE STACK AND ENSURE
THERE IS NOTHING BETWEEN
THE
DC BUSBARS AND THE
INVERTER
TO
LIGHTNING
ARRESTOR
SERVICE
ENTRANCE
CONNECTOR
(SPLIT BOLT)
AC
TERMINAL
BLOCK
MAGNUM
DC TERMINALS.
’S DC TERMINALS.
INVERTER
AC INPUT
TO
Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
TO PROTECT
AC INPUT
INVERTER
TO
Lightning
Arrestor
(AC rated)
TO PROTECT
DC INPUT TO
INVERTER
Lightning
Arrestor
(DC rated)
SIDE VIEW
N
OTE: THE AC TERMINAL BLOCK IS NOT RATED
TO CONNECT MORE THAN ONE WIRE LARGER THAN
#12 AWG. THEREFORE, TO CONNECT A
LIGHTNING ARRESTOR, A SERVICE ENTRANCE
CONNECTOR
CONNECT BOTH THE INVERTER
AND THE LIGHTNING ARRESTOR WIRE TO THE
TERMINAL BLOCK.
NSURE THE SERVICE ENTRANCE CONNECTORS ARE
E
INSULATED FROM EACH OTHER TO PREVENT THE
AC INPUT WIRES FROM SHORTING TO EACH
OTHER
(OR SPLIT BOLT) IS REQUIRED TO
’S AC INPUT WIRE
.
AC
Figure A7-2, Wiring Lightning Arrestor to MMP Enclosure
Info: Make sure enough insulation is stripped so that the inverter’s AC input wire is
fully inserted in the AC terminal block and enough uninsulated wire is still available
to contact with the lightning arrestor wire when using the service entrance connector.
Info: Readily used service entrance connectors are available at most electrical dealers
– for example, the Type SX manufactured by Ilsco (www.ilsco.com), or the Type N
manufactured by Thomas and Betts (www.tnb.com).
TO PROTECT
INPUT TO
DC LOADS
Lightning
Arrestor
(DC rated)
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 57
Page 67

Appendix A - Optional Equipment and Accessories
A8 MMP Back Panel Information
3
16
4
3
4
15
16
5
2
2
8
1
1
3
16
3
11
4
2
1
2
3
16
3
8
3
5
8
B
B
1
1
2
15
16
5
13
8
11
16
7
16
15
16
B
B
11
1
1
16
2
16
7
32
3
8
15
1
1
16
2
11
15
16
B
3
34
8
3
3
4
8
16
9
1
16
11
3
4
B
B
B
1
15
1
2
16
5
16
1
1
9
1
16
16
3
4
11
A
B
9
1
16
7
2
16
1
3
16
9
1
16
1
3
2
4
7
4
16
7
16
5
3
16
4
B
15
5
1
16
16
14
11
3
4
7
8
1
3
4
1
3
Detail A
Notes:
1. All dimensions are in inches.
2. Material = 16 gauge steel.
3. Finish = Powder coat white.
4. Detail B (x10) = PEM Nut (1/4-20).
5. Weight: 10.5 lbs. (4.8 kg).
6. Includes ten 1/4-20 x 3/4” Hex bolts; for mounting the MMP
enclosure, a Magnum Energy inverter, and the inverter hood.
7. The outside holes on the left and right side measure 16”
center-to-center. This allows the mounting plate to be secured to
wall studs 16” apart. If the wall studs are 24” apart, a minimum
3/4” plywood board should be used to secure the backplate to
the wall studs.
Figure A8-1, MMP Back Panel (BP-MMP) Information
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.Page 58
Page 68

Appendix B - Using the MMP in a Mobile Application
Appendix B – Using the MMP in a Mobile Application
The MMP Series is designed and approved for use in residential or commercial applications. It has
been tested and listed to UL 1741, 2nd Edition (inverters, converters and controllers for use in
Independent Power Systems) for use in the US; and is also certified to CSA C22.2 No. 107.1-01
(General Use Power Supplies) for use in Canada. The AC input and output neutral connections
in the MMP are combined and are bonded to the internal ground bar. The bond from neutral to
ground can be removed as neutral is bonded to ground from the primary AC source.
In a mobile application, the standards for safely wiring RV, truck, and marine installations in the
United States requires the neutral and safety ground to be connected at the AC source; whether
it is a shorepower feed, an inverter, or a generator. This maximizes the possibility that a circuit
breaker will activate if a hotwire-to-ground fault occurs. These standards also require that the
AC neutral be connected to safety ground (often called a “bond”) in one, and only one, place at
any time. The single bond is established in order to make the electrical panel’s neutral line safe,
by connecting it to ground. Without this bond, the neutral can have up to 60 VAC with respect to
ground.
Because the neutrals are combined, if the MMP is used in a mobile application, more than one
neutral to ground bond may be established, which can cause current to circulate between the
multiple neutral to ground connections. This can cause “ground-loop” currents, which can trip
GFCI’s, cause an electrical shock hazard, and may be the reason for other annoying side effects.
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 59
Page 69

Appendix C - Warranty & Service
Appendix C – Warranty and Service
C1 Limited Warranty
Magnum Energy, Inc., warrants the MMP to be free from defects in material and workmanship that
result in product failure during normal usage, according to the following terms and conditions:
1. The limited warranty for the product extends for 36 months beginning from the product’s
original date of purchase.
Note: You can extend the normal warranties on this MMP enclosure and a Magnum
inverter or accessory to fi ve years. To be eligible for this 5-year warranty extension, a
proof-of-purchase is required at the time of repair/service showing that the Magnum
inverter/accessory and the MMP panel system were purchased at the same time.
2. The limited warranty extends to the original purchaser of the product and is not assignable or
transferable to any subsequent purchaser.
3. During the limited warranty period, Magnum Energy will repair, or replace at Magnum Energy’s
option, any defective parts, or any parts that will not properly operate for their intended use
with factory new or remanufactured replacement items if such repair or replacement is needed
because of product malfunction or failure during normal usage. The limited warranty does not
cover defects in appearance, cosmetic, decorative or structural parts or any non-operative parts.
Magnum Energy’s limit of liability under the limited warranty shall be the actual cash value of
the product at the time the original purchaser returns the product for repair, determined by the
price paid by the original purchaser. Magnum shall not be liable for any other losses or damages.
4. Upon request from Magnum Energy, the original purchaser must prove the product’s original
date of purchase by a dated bill of sale, itemized receipt.
5. The original purchaser shall return the product prepaid to Magnum Energy in Everett, WA. After
the completion of service under this limited warranty, Magnum Energy will return the product
prepaid to the original purchaser via a Magnum-selected non-expedited surface freight within
the contiguous United States and Canada; this excludes Alaska and Hawaii.
6. If Magnum repairs or replaces a product, its warranty continues for the remaining portion of
the original warranty period or 90 days from the date of the return shipment to the original
purchaser, whichever is greater. All replaced products and parts removed from repaired products
become the property of Magnum.
7. This limited warranty is voided if:
• the product has been modifi ed without authorization;
• the product label and/or serial number label has been altered, defaced or removed;
• the product has been damaged from abuse, neglect, accident, high voltage or corrosion;
• the product was not installed and operated according to the owner's manual.
C2 How to Receive Repair Service
If your product requires warranty service or repair, contact either:
1. An Authorized Service Center, which are listed on the Magnum Energy website at
www.magnumenergy.com/Service/ServiceCenters-US.htm, or
2. Magnum Energy, Inc. at: Telephone: 425-353-8833,
Fax: 425-353-8390, or
Email: warranty@magnumenergy.com
If returning the product directly to Magnum Energy for repair, you must:
• Return the unit in the original, or equivalent, shipping container.
Note: Damage from shipping is not covered under warranty, ensure the unit is properly packaged.
• Receive a Return Materials Authorization (RMA) number from the factory prior to the return
of the product to Magnum Energy for repair.
• Place RMA numbers clearly on the shipping container or on the packing slip.
BEFORE RETURNING ANY UNIT TO MAGNUM ENERGY INC.,
A RETURN MATERIAL AUTHORIZATION (RMA) NUMBER IS REQUIRED.
Page 60
© 2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Page 70

Magnum Energy, Inc.
2211 West Casino Rd.
Everett, WA 98204
Phone: 425-353-8833
Fax: 425-353-8390
Web: www.magnumenergy.com
MMP Owner’s Manual (PN: 64-0029 Rev D)
 Loading...
Loading...