Page 1

Using ColdFusion MX with Flex 2
Page 2

Trademarks
1 Step RoboPDF, ActiveEdit, ActiveTest, Authorware, Blue Sky Software, Blue Sky, Breeze, Breezo, Captivate, Central,
ColdFusion, Contribute, Database Explorer, Director, Dreamweaver, Fireworks, Flash, FlashCast, FlashHelp, Flash Lite,
FlashPaper, Flash Video Encoder, Flex, Flex Builder, Fontographer, FreeHand, Generator, HomeSite, JRun, MacRecorder, Adobe
Systems Incorporated, MXML, RoboEngine, RoboHelp, RoboInfo, RoboPDF, Roundtrip, Roundtrip HTML, Shockwave,
SoundEdit, Studio MX, UltraDev, and WebHelp are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated
and may be registered in the United States or in other jurisdictions including internationally. Other product names, logos,
designs, titles, words, or phrases mentioned within this publication may be trademarks, service marks, or trade names of Adobe
Systems Incorporated or other entities and may be registered in certain jurisdictions including internationally.
Third-Party Information
This guide contains links to third-party websites that are not under the control of Adobe Systems Incorporated, and Adobe
Systems Incorporated is not responsible for the content on any linked site. If you access a third-party website mentioned in this
guide, then you do so at your own risk. Adobe Systems Incorporated provides these links only as a convenience, and the inclusion
of the link does not imply that Adobe Systems Incorporated endorses or accepts any responsibility for the content on those thirdparty sites.
Speech compression and decompression technology licensed from Nellymoser, Inc. (www.nellymoser.com).
Sorenson™ Spark™ video compression and decompression technology licensed from
Sorenson Media, Inc.
Opera ® browser Copyright © 1995-2002 Opera Software ASA and its suppliers. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 2006 Adobe Macromedia Software LLC. All rights reserved. This manual may not be copied, photocopied,
reproduced, translated, or converted to any electronic or machine-readable form in whole or in part without written
approval from Adobe Systems Incorporated Notwithstanding the foregoing, the owner or authorized user of a valid copy
of the software with which this manual was provided may print out one copy of this manual from an electronic version of
this manual for the sole purpose of such owner or authorized user learning to use such software, provided that no part of
this manual may be printed out, reproduced, distributed, resold, or transmitted for any other purposes, including,
without limitation, commercial purposes, such as selling copies of this documentation or providing paid-for support
services.
Acknowledgments
Project Management: Randy Nielsen
Writing: Anne Sandstrom
Editing: Linda Adler
Production Management: Adam Bernett
Media Design and Production: Masayo Noda
Special thanks to Linda Adler, Randy Nielsen, Bill Sahlas, Farah Gron, Bob Powelll, Mike Nimer., Dean Harmon, and
Tom J o r dh a l
First Edition: June, 2006
Adobe Systems Incorporated
601 Townsend St.
San Francisco, CA 94103
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1: Using Flash Remoting Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
About Flash Remoting Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Using Flash Remoting Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Data translation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Chapter 2: Using the Flex Messaging Event Gateway . . . . . . . . . 13
About Flex and ColdFusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Configuring a Flex Messaging event gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Enabling communication with Flex. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Sending outgoing messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Handling incoming messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Using session and client variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Data translation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Chapter 3: Use ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter . . . . . . . . . 25
Set up your development environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Create the Flex application. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Import the required ActionScript classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Create the ColdFusion application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Test the application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Chapter 4: Using the Flex Data Service Assembler . . . . . . . . . . 35
About Flex and ColdFusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Application development and deployment process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Enabling SSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Data translation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Example application. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3
Page 4

Chapter 5: Using the ColdFusion Extensions for
Flex Builder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
About the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Installing the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Eclipse RDS Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
ActionScript to CFC wizard. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
CFC to ActionScript wizard. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
RDS CRUD wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Services Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
4Contents
Page 5

CHAPTER 1
Using Flash Remoting Update
You can use Macromedia Flash Remoting Update to create rich Internet applications in
ColdFusion MX 7.0.2.
Contents
About Flash Remoting Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Using Flash Remoting Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
About Flash Remoting Update
The Flash Remoting Update lets you create rich Internet applications (RIAs) by using Adobe
Flex Builder 2, with the advanced data retrieval features of ColdFusion, such as the c
cfldap, and cfquery tags. In addition, you can use Flash Remoting Update to create
Macromedia Flash Forms and Flash applications that contain features such as server call backs
and customized user interface.
You can use Flash Remoting Update with all configurations of ColdFusion MX 7.0.2 (server,
multiserver, and J2EE) on all the platforms that ColdFusion MX 7.0.2 supports.
To use Flash Remoting Update, you must have the following installed:
■ Flex Builder 2
■ Flash Player 9
■ ColdFusion MX 7.0.2
fpop,
1
5
Page 6

Using Flash Remoting Update
To specify a CFC to connect to, you do one of the following:
■ Specify the CFC, including the path from the web root, in the MXML.
■ Create a named resource for each CFC that you connect to. This is similar to registering a
data source.
To specify the CFC in the MXML:
■ Specify the CFC, including the path from the web root, in the MXML; for example:
<mx:RemoteObject
id="myCfc"
destination="ColdFusion"
source="myApplication.components.User"/>
The destination “ColdFusion” is preconfigured in the services-config.xml file, which is
located in the ColdFusion webroot\WEB-INF\flex directory, with the wildcard
source. To use the source attribute in MXML, you can use any destination by specifying
the
source="*". If you specify a source other than “*”, that source definition overrides
the source specified in the MXML.
To create a named resource for each CFC that you connect to:
1. Edit the services-config.xml file by adding an entry for each CFC that you connect to, for
example:
<destination id="CustomID">
<channels>
<channel ref="my-cfamf"/>
</channels>
<properties>
<source>dot_ path_to_CFC</source>
<lowercase-keys>true</lowercase-keys>
</properties>
</destination>
The source attribute specifies the dot notation to the CFC from the web root (the
classpath to the CFC).
2. Restart the ColdFusion server.
* as the
6 Using Flash Remoting Update
Page 7

To use the CFC resource in your Flex Builder 2 project:
1. For each Flex Builder 2 project, set the Flex compiler property by doing the following:
a. Select Project > Properties.
b. Select the Flex complier option.
c. Enter the following in the Additional Compiler Argument text box:
--services=C:\CFusionMX7\wwwroot\WEB-INF\flex\services-config.xml
In the mxml file, you use the <mx:RemoteObject> tag to connect to your CFC named
2.
resource. With this connection you can call any remote method on the CFC.
3. Use the destination attribute of the <mx:RemoteObbject> tag to point to the name that
you defined in the services-config.xml file; for example:
<mx:RemoteObject
id="a_named_reference_to_use_in_mxml"
destination="CustomID"
result="my_CFC_handler(event)"/>
4.
Call a CFC method, for example, as the following example shows:
<mx:Button label="reload" click="my_CFC.getUsers()"/>
In this example, when a user presses a button, the Click event calls the CFC method
getUsers.
5. Specify a handler for the return result of the CFC method call for the <mx:RemoteObject>
tag, as the following example shows.
private function my_CFC_handler( event:ResultEvent )
{
// Show alert with the value that is returned from the CFC.
mx.controls.Alert.show(ObjectUtil.toString(event.result));
}
Using Flash Remoting Update 7
Page 8
Flash Remoting Update and authentication
The Flash client passes the username and password, which are set in the Flash client, to the
CFC. To authenticate users when using Flash Remoting Update, you can then use the
cflogin tag to authenticate the user.
Flash Remoting Update supports the same authentication mechanism as any HTTP request
from the browser, including getting and setting cookies. This mechanism allws you to take
advantage of the same authentication systems you use for any normal HTTP request. To take
advantage of this functionality in a Flash application, you need to set the HTTP authorization
headers by specifying the user’s username and password with the RemoteObject
setRemoteCredentials method. When ColdFusion receives the Flash Remoting /http
request, ColdFusion populates the cflogin.name and cflogin.password variables (inside the
cflogin tag) with these values. For more information, see the documentation for the
cflogin tag.
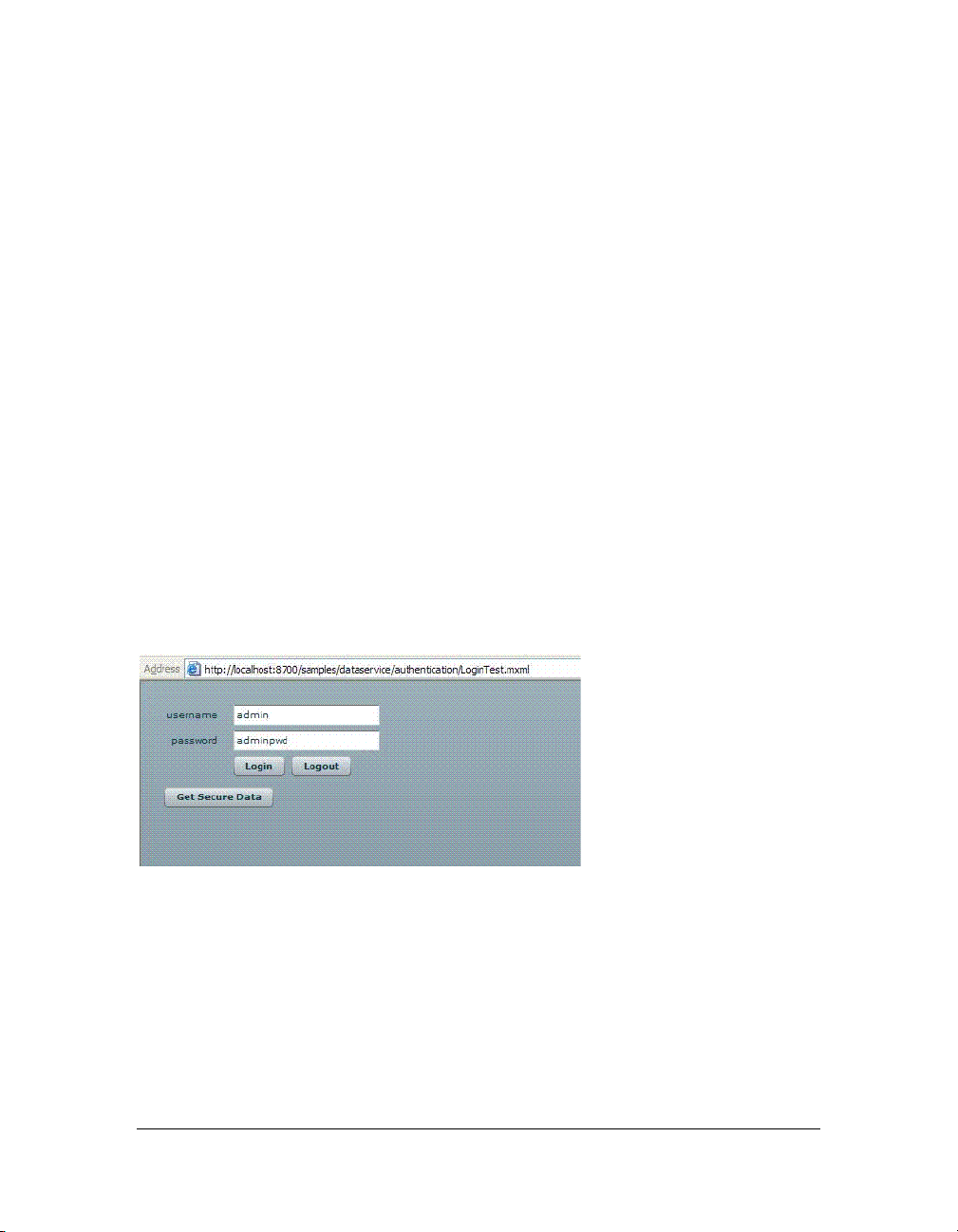
Example application
The following sample application lets you test authentication. It consists of a Flex application,
and a ColdFusion application that consists of an Application.cfm file and the ColdFusion
component that the Flex application calls.
The Flex application appears as follows:
The Flex application above lets you enter a username and password. It creates a remote object
to the CFC. Because the application creates a remote object that is managed by a CFC, you
can set a username and password for the authentication mechanism of the remote service.
When you click the Login button, the application calls the setRemoteCredentials method,
using the username and password entered in the text boxes. This sets the properties in the
mx:RemoteObject tag, which are passed in all future requests.
8 Using Flash Remoting Update
Page 9

When you click the Logout button, the application calls the setRemoteCredentials
method, which sets the username and password to null, and logs out the user on the client
side. In addition, the application calls the
logoutuser method, which handles server side
logout.
When you click the Get Secure Data button, the application calls the
MXML file, which, in turn, calls the
getData function in the CFC. The getData function in
getData method in the
the CFC returns a string for purposes of this simple test application, but could be modified to
return data such as the results of a query.
The Flex application also includes the
serverFault and serverResult methods, which
display an alert box to indicate whether the login was successful or not.
The MXML file appears as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<mx:Application xmlns:mx="http://www.adobe.com/2006/mxml" xmlns="*"
layout="absolute">
<mx:Script>
<![CDATA[
import mx.rpc.events.ResultEvent;
import mx.utils.ObjectUtil;
import mx.controls.Alert;
import mx.rpc.events.FaultEvent;
private function logIn():void{
cf.setRemoteCredentials(this.username.text, this.password.text);
}
private function logOut():void
{
cf.setRemoteCredentials(null, null);
cf.logoutuser();
}
private function getData():void
{
cf.getData();
}
private function serverFault(event:FaultEvent):void{
Alert.show( ObjectUtil.toString(event.fault) );
Alert.show( "error" );
}
private function serverResult(event:ResultEvent):void{
Alert.show( ObjectUtil.toString(event));
Alert.show( "success" );
}
]]>
</mx:Script>
Using Flash Remoting Update 9
Page 10

<mx:RemoteObject id="cf"
destination="ColdFusion"
source="CFIDE.samples.LoginTest.logintest">
<mx:method name="getData" result="serverResult(event)"
fault="serverFault(event)" />
<mx:method name="logoutuser" />
</mx:RemoteObject>
<mx:Form x="10" y="10">
<mx:FormItem label="username">
<mx:TextInput id="username" text="admin"/>
</mx:FormItem>
<mx:FormItem label="password">
<mx:TextInput id="password" text="adminpwd"/>
</mx:FormItem>
<mx:FormItem direction="horizontal">
<mx:Button label="Login" click="logIn();"/>
<mx:Button label="Logout" click="logOut()"/>
</mx:FormItem>
<mx:Button label="Get Secure Data" click="getData();"/>
</mx:Form>
</mx:Application>
The Application.cfm file authenticates the user and identifies the user with the flexadmin role.
<cfapplication name="loginTest6" sessionmanagement="true"
setclientcookies="true">
<cflogin>
<cfif isDefined("cflogin.name") or isDefined("cflogin.password")>
<cfloginuser name="#cflogin.name#" password="#cflogin.password#"
roles="flexadmin">
</cfif>
</cflogin>
10 Using Flash Remoting Update
Page 11
The CFC contains two functions: logoutuser and getData. The getData function
authenticates the user against the flexadmin role and returns a string.The logoutuser function
calls the <cflogout> tag to log the user out on the server.
<cfcomponent>
<cffunction name="logoutuser" access="remote">
<cflogout>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="getData" access="remote" roles="flexadmin">
<cfreturn "Some Secure Data!">
</cffunction>
</cfcomponent>
TIP
To make communication between the Flex application and the CFC secure, you can
specify that the AMF channel in the ColdFusion destination definiton be secure in the
WEB-INF\flex\services-config.xml file.
Data translation
The following table lists the ColdFusion data types and the corresponding ActionScript data
type:
ColdFusion data type Flash data type
String String
Array [] = Array
Struct {} = untyped Object
Query Array of untyped Objects
CFC Class = typed Object (if a matching ActionScript class
exists, otherwise the CFC becomes a generic untyped
Object (map) in ActionScript)
CFC Date ActionScript Date
CFC String ActionScript String
CFC Numeric ActionScript Numeric
ColdFusion XML Object ActionScript XML Object
Using Flash Remoting Update 11
Page 12

12 Using Flash Remoting Update
Page 13

CHAPTER 2
Using the Flex Messaging Event Gateway
You can develop an application that uses the Flex Messaging gateway type to send messages to
and receive messages from an Adobe Flex application. To do so, you configure the Flex
Messaging gateway. This document provides information about how to write and test an
application that uses the event gateway.
You should be familiar with ColdFusion event gateway in ColdFusion MX Developer’s Guide.
This document also assumes that you are familiar with Adobe Flex Data Services.
NOTE
Macromedia ColdFusion MX Standard Edition does not support event gateways.
Contents
About Flex and ColdFusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Configuring a Flex Messaging event gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Enabling communication with Flex. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Sending outgoing messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Handling incoming messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Using session and client variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Data translation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2
13
Page 14
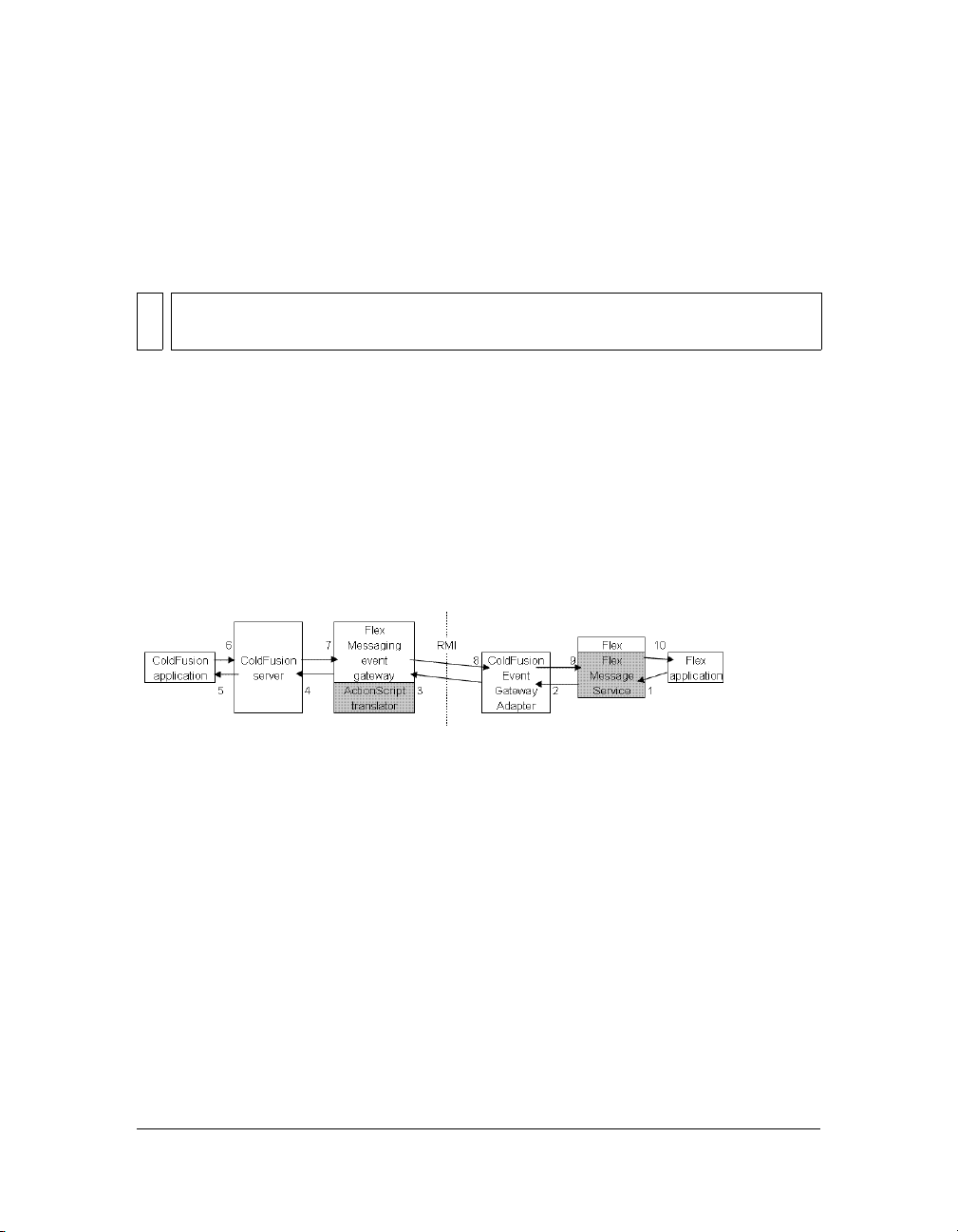
About Flex and ColdFusion
ColdFusion includes the Flex Messaging event gateway, which uses the ColdFusion Event
Gateway Adapter to send messages to and receive messages from Adobe Flex Data Services.
This means that ColdFusion applications and Flex applications can publish to and consume
events from the same event queue.
NOTE
To use the Flex Messaging event gateway to interact with a Flex application, the Flex
application must be running on Flex Data Services.
How ColdFusion and Flex interact
You can send messages from a ColdFusion application to a Flex application, through the Flex
Messaging event gateway. Conversely, you can send messages from a Flex application to a
ColdFusion application.
Either the ColdFusion application or the Flex application can initiate sending a message. The
following image shows the message handling process in which a message is sent from the Flex
application to the ColdFusion application, and then from the ColdFusion application to the
Flex application.
1. The Flex application generates a message.
2. The Flex Message Service passes the message to the ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter.
3. The ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter sends the message to the Flex Messaging event
gateway, by using Java Remote Method Invocation (Java RMI).
4. The Flex Messaging event gateway and the ActionScript translator convert ActionScript
3.0 data types to the appropriate ColdFusion values and add the message to the event
gateway queue.
5. The ColdFusion server invokes the onIncomingMessage method of the Flex Messaging
event gateway listener CFC.
6. The ColdFusion application generates a message, which it sends to the ColdFusion server.
7. The ColdFusion server sends the message to the Flex Messaging event gateway.
14 Using the Flex Messaging Event Gateway
Page 15

8. The Flex Messaging event gateway and the ActionScript translator convert ColdFusion
values to the appropriate ActionScript 3.0 data types, and then the gateway sends the
message to the ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter.
9. The ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter sends the message to the Flex Message Service.
10. The Flex Message Service passes the message to the Flex application.
NOTE
The RMI registry, which facilitates communication between the ColdFusion Event
Gateway Adapter and the Flex Messaging event gateway uses port 1099, which is the
default port for Java RMI. You cannot change this port number. To ensure that the RMI
registry provides registry service for both Flex Data Services and ColdFusion, start Flex
first, and then start ColdFusion. If you stop Flex, you must restart Flex, and then restart
the gateway.
Application development and deployment process
The following is a typical process for developing and deploying a ColdFusion application that
communicates with a Flex application through the Flex Messaging event gateway:
1. Design your application.
2. Configure a Flex Messaging Event gateway instance.
3. Write your ColdFusion CFCs, CFM pages, and any other application elements.
4. Test your application by using Flex.
5. Make the application publicly available.
Configuring a Flex Messaging event gateway
Although you can configure an instance of a Flex Messaging event gateway by creating a
configuration file, which you specify when you create the gateway instance, you can also
provide the configuration information in the message sent from the Flex application. You use
a configuration file to provide configuration information to the Flex Messaging event gateway
to do one of the following:
■ Have the Flex Messaging event gateway send messages to Flex Data Services on a different
computer
■ Use the Flex Messaging event gateway with a specific Flex destination, and ignore any
destination specified in the message
■ Specify the IP addresses from which your ColdFusion application accepts messages
Configuring a Flex Messaging event gateway 15
Page 16

The Flex Messaging event gateway configuration file is a simple Java properties file that
contains the following properties:
Property Description
destination A hard-coded destination. If you specify this value, any destination
information in the message is ignored.
host The host name or IP address of the Flex Data Services server.
allowedIPs A comma- delimited list of IP addresses from which the Flex Messaging
event gateway accepts messages. If you do not specify a list of allowed IPs,
only processes on the local computer can send messages to the gateway.
The following is an example configuration file:
#
# Flex event gateway configuration
#
# This is the destination of the messages.
destination=Gateway1
# Hostname or IP address of the Flex Enterprise Server.
host=127.0.0.1
# IP addresses from which the application will accept messages.
allowedIPs=10.60.1.1,10.60.1.2.
If you create a configuration file, save it in the {cf.rootdir}/gateway/config/ directory, with the
extension .cfg.
Enabling communication with Flex
To enable communication through the Flex Messaging event gateway, you copy and paste the
information from the sample configuration files.
To enable communization through the Flex Messaging event gateway:
1. Copy the following <adapter-definition> section from the sample messaging-config.xml
file to the web application flex-messaging-service.xml file, into the <adapter> section:
<adapter-definition id="cfgateway"
class="coldfusion.flex.CFEventGatewayAdapter"/>
The sample messaging-config.xml file is located in the C:\fds2\resources\config\flex folder
when you install Flex in the default location. The web application messaging-config.xml
file is located in the C:\fds2\jrun4\servers\default\samples\WEB-INF\flex folder when
you install Flex in the default location.
16 Using the Flex Messaging Event Gateway
Page 17

2. Copy the following <destination> section from the sample messaging-config.xml file to the
web application messaging-config.xml file:
<!-- ======================================== -->
<!-- ColdFusion Messaging Gateway -->
<!-- ======================================== -->
<destination id="ColdFusionGateway">
<adapter ref="cfgateway" />
<properties>
<!-Star ('*') means gatewayid is found in the 'gatewayid'
message header.
To restrict this destination to a specific gateway, enter its ID
here
-->
<gatewayid>*</gatewayid>
<!-If ColdFusion is running on a different host, enter that here.
Default is to look for ColdFusion on this computer.
<gatewayhost>10.1.1.1</gatewayhost>
-->
<!-List the IP addresses of CF machines allowed to send messages to
this destination
If not set, the default is to allow only this computer to connect.
Do NOT use 127.0.0.1, it must be the actual IP address
<allowedIPs>10.1.1.1,10.2.2.2</allowedIPs>
-->
<!-Credentials to pass along in the headers as CFUsername/CFPassword.
It is generally better to use setRemoteCredentials() API on client.
<remote-username></remote-username>
<remote-password></remote-password>
-->
</properties>
<!-These channels will work unless you want to pass value objects
(objects that get translated to and from CFCs) in your messages.
In that case, use the "cf-dataservice-rtmp" and "cf-polling-amf
channels".
-->
<channels>
<channel ref="my-rtmp"/>
<channel ref="my-polling-amf"/>
</channels>
</destination>
Enabling communication with Flex 17
Page 18

3. Change the ID of the destination so the destination ID for each ColdFusion destination
on that machine is unique. (For example, because ColdFusion finds the destination by
locating its name in a machine wide registry, you should not specify the same destination
ID in both the flex and the samples web application.)
4. To use the ColdFusion-specific channels (to support value objects), copy the following
channels from the sample services-config.xml file to the web application servicesconfig.xml file:
<!-- ColdFusion specific HTTP channel -->
<channel-definition id="cf-polling-amf"
class="mx.messaging.channels.AMFChannel">
<endpoint
uri="http://{server.name}:{server.port}/{context.root}/messagebroker/
cfamfpolling"
class="flex.messaging.endpoints.AMFEndpoint"/>
<properties>
<serialization>
<!-- This must be turned off for any CF channel -->
<instantiate-types>false</instantiate-types>
</serialization>
<polling-enabled>true</polling-enabled>
<polling-interval-seconds>8</polling-interval-seconds>
</properties>
</channel-definition>
The sample services-config.xml file is located in the C:\fds2\resources\config folder when
you install Flex in the default location. The web application services-config.xml file is
located in the C:\fds2\jrun4\servers\default\samples\WEB-INF\flex folder when you
install Flex in the default location.
18 Using the Flex Messaging Event Gateway
Page 19
Sending outgoing messages
Your ColdFusion application sends a message to a Flex application by doing the following
actions:
1. The ColdFusion application sends an outgoing message, in a cfreturn tag in the listener
CFC’s listener method, or by calling the ColdFusion
2. A method provided by the Flex Messaging gateway gets called when you send an outgoing
message.
In outgoing messages sent from CFML, the following structure members are translated to the
Flex message:
Name Contents
body Body of the message. This is required.
CorrelationID Correlation identifier of the message.
Destination Flex destination of the message. This is required if it is not specified in the
configuration file.
Headers If the message contains any headers, the CFML structure that contains
the header names as keys and values.
LowercaseKeys If the value is set to yes, the structure keys are converted to lowercase
during creation of ActionScript types.
TimeToLive Number of milliseconds during which this message is valid.
SendGatewayMessage function.
In addition, the Flex Messaging event gateway automatically provides values for the following
Flex message fields:
Name Contents
MessageID A UUID that identifies the message
Timestamp Time the message is sent
ClientID ID of the Flex Messaging event gateway instance
NOTE
A single instance of the Flex Messaging event gateway can send messages to any
destination that is registered with the ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter. However, if
the destination is configured in the Flex Messaging gateway configuration file, the
destination in the message is ignored.
Sending outgoing messages 19
Page 20

Sending outgoing message example
The following example from a CFM page creates a structure that contains the message. The
destination is the destination ID specified in the messaging-config.xml file for the instance
of the Flex Messaging event gateway to send the message to. The
message. The
sendGatewyMessage CFML function sends the message to the instance of the
body is the body of the
gateway.
<cfset success = StructNew()>
<cfset success.msg = "Email was sent at " & Now()>
<cfset success.Destination = "gateway1">
<cfset ret = SendGatewayMessage("Flex2CF2", success)>
Handling incoming messages
When a Flex application sends a message to a ColdFusion application, the Flex Messaging
event gateway sends a CFEvent structure to the
configured CFC, with the following information mapped to the data of the event:
Name Contents
body Body of the message.
ClientID ID of the client that sent the message.
CorrelationID Correlation identifier of the message.
Destination Flex destination of the message.
Headers If the message contains any headers, the CFML structure that contains the
header names as keys and values.
Timestamp Timestamp of the message.
onIncomingMessage function of the
The incoming message data structure also includes the values of
messageID and timeToLive
from the Flex message.
Incoming message handling example
The following example puts data that is contained in the body of the message from the Flex
application into a structure. It then uses the contents of the structure to generate an e-mail
message.
<cfcomponent displayname="SendEmail" hint="Handles incoming message from
Flex">
<cffunction name="onIncomingMessage" returntype="any">
<cfargument name="event" type="struct" required="true">
20 Using the Flex Messaging Event Gateway
Page 21

<!--- Create a structure to hold the message object sent from Flex--->
<cfset messagebody = event.data.body>
<!--- Populate the structure. --->
<cfset mailfrom="#messagebody.emailfrom#">
<cfset mailto="#messagebody.emailto#">
<cfset mailsubject="#messagebody.emailsubject#">
<cfset mailmessage ="#messagebody.emailmessage#">
<!--- Send email with values from the structure. --->
<cfmail from="#mailfrom#"
to="#mailto#"
subject="#mailsubject#">
<cfoutput>#mailmessage#</cfoutput>
</cfmail>
</cffunction>
</cfcomponent>
If the Flex application sends the message in the header instead of in the body, you create and
populate the structure, as the following example shows:
<cfset messageheader = StructNew()>
<cfset messageheader.sendto = event.data.headers.emailto>
<cfset messageheader.sentfrom = event.data.headers.emailfrom>
<cfset messageheader.subject = event.data.headers.emailsubject>
<cfset messageheader.mailmsg = event.data.headers.emailmessage>
<cfset mailfrom="#messageheader.sentfrom#">
<cfset mailto="#messageheader.sendto#">
<cfset mailsubject="#messageheader.subject#">
<cfset mailmessage ="#messageheader.mailmsg#">
Using session and client variables
The Flex Messaging event gateway supports session and client variables. In messages sent from
Flex to ColdFusion through the gateway, the clientID field of the incoming message is the key
to the session. Flex assigns the clientID to the instance of each Flex application.
Using session and client variables 21
Page 22

Authentication
Flex and ColdFusion provide the following authentication features for communicating
through the Flex Messaging event gateway:
■ Restricting IP addresses that are allowed to send a message through the Flex Messaging
event gateway
■ Specifying remote credentials in Flex, and then authenticating those credentials in
ColdFusion
Restricting IP addresses
To restrict the IP addresses from which your ColdFusion application accepts messages, you
must use a confiugration file, as specified in “Configuring a Flex Messaging event gateway”
on page 15. In addition to specifying the destination and host, you specify the comma-
delimited list of IP addresses from which your ColdFusion application accepts messages.
Also, you can specify the allowed IPs for when you send messages from Flex to ColdFusion.
You do so in the destination definition in the messaging-config.xml file on the server on
which your Flex application is running. The following example is a sample destination:
<destination id="ColdFusionGateway">
<adapter ref="cfgateway"/>
<properties>
<gatewayid>*</gatewayid>
<gatewayhost>10.60.1.7</gatewayhost>
<allowedIPs>10.60.1.7,10.60.1.8,10.60.1.9</allowedIPs>
</properties>
<channels>
<channel ref="my-rtmp"/>
<channel ref="my-polling-amf"/>
</channels>
</destination>
NOTE
The local machine is not included in the list of allowed IPs by default.
Specifying remote credentials
The Flex application passes the username and password, which are set in the Flex application,
to the CFC. To authenticate users, you can then use the
tag in an Application.cfm or Application.cfc file that executes when a method in the CFC is
called.
22 Using the Flex Messaging Event Gateway
cflogin tag. You put the cflogin
Page 23

The session ID is the client ID assigned to your Flex application. Reloading the Flex
application starts a new session with a new session ID.
To set credentials in a message in Flex, before sending the message through the gateway to the
CFC, you use the
var msg:Message = new AsyncMessage();
msg.body = input.text;
msg.headers.gatewayID = "Flex2CF";
msg.setRemoteCredentials("mycfusername", "mycfpassword");
setRemoteCredentials method, as follows:
To authenticate the credentials sent in the message, in an Application.cfm or Application.cfc
file, you use the
<cfapplication name="authenticateuser" sessionmanagement="yes">
<cflogin>
<cfif isDefined("cflogin.name") or isDefined("cflogin.password")>
<cfloginuser name="#cflogin.name#" password="#cflogin.password#"
</cfif>
</cflogin>
cflogin tag, as follows:
roles="#roles#">
Data translation
The following table lists the ColdFusion data types and the corresponding Adobe Flash or
ActionScript data type:
ColdFusion data type Flash data type
String String
Array [] = Array
Struct {} = untyped Object
Query Array of untyped Objects
CFC Class = typed Object (if a matching ActionScript class
exists, otherwise the CFC becomes a generic untyped
Object (map) in ActionScript)
CFC Date ActionScript Date
CFC String ActionScript String
CFC Numeric ActionScript Numeric
ColdFusion XML Object ActionScript XML Object
Data translation 23
Page 24

24 Using the Flex Messaging Event Gateway
Page 25

CHAPTER 3
Use ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter
This tutorial shows you how to create a Flex application to send a message to a ColdFusion
application and a ColdFusion component to send a message to a Flex application. The sample
application does not take advantage of capabilities that are unique to Adobe Flex, instead, it
describes the communication with ColdFusion applications that the ColdFusion Event
Gateway Adapter enables.
To show the capabilities of the ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter and the Flex Messaging
event gateway, the sample application lets you enter information in a form in a Flex
application. The Flex application sends the information through the ColdFusion Event
Gateway Adapter and Flex Messaging event gateway to the ColdFusion application. The
ColdFusion application then sends an e-mail message that contains the message to the
recipient specified in the Flex application. Finally, the ColdFusion component sends a
message to the Flex application, which displays the body of the message.
In this tutorial, you’ll complete the following tasks:
Set up your development environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Create the Flex application. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Create the ColdFusion application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Test the application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
3
25
Page 26
Set up your development environment
The ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter lets you create applications in which Flex Data
Services and ColdFusion MX 7.0.2 communicate. Flex Data Services includes the
ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter. ColdFusion MX 7.0.2 includes the Flex Messaging event
gateway.
To complete this tutorial, you must have the following products installed:
■ Flex Data Services
■ ColdFusion MX 7.0.2
Start Flex and ColdFusion
To set up your development environment, you must start Flex Data Services and ColdFusion.
This tutorial assumes that both Flex Data Services 2 and ColdFusion are running on localhost
(127.0.0.1) on your local computer. Because of the way in which the Remote Method
Invocation (RMI) registry is created and maintained, Adobe recommends that you start Flex
Data Services, and then start ColdFusion.
NOTE
The example ColdFusion application uses the cfmail tag. You must set up an e-mail
server in the ColdFusion MX Administrator before testing the application.
Enable the ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter
The messaging-config.xml file contains information about adapters and destinations,
including network and server properties and channels. Generally, the file contains the
following:
- service
- adapters
- adapter-definition
- destination
- properties
- network
- server
- channels
TIP
To become familiar with the messaging-config.xml file, view it in an XML editor so that
you can expand and collapse sections.
26 Use ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter
Page 27

To ensure that Flex Data Services recognizes the ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter, you edit
the messaging-config.xml file, which is located in the
C:\fds2\jrun4\servers\default\samples\WEB-INF\flex directory if you installed Flex Data
Services using the default settings.
To enable communication through the Flex Messaging event gateway:
1. Copy the <adapter-definition> section in which id=”cfgateway” from the sample
messaging-config.xml file to the <adapter> section of the web application messagingconfig.xml file.
The sample messaging-config.xml file is located in the C:\fds2\resources\config\flex
folder, and the web application messaging-config.xml file is located in the
C:\fds2\jrun4\servers\default\samples\WEB-INF\flex folder when you install Flex in the
default location.
2. Copy the <destination> section in which id=”ColdFusionGateway” from the sample
messaging-config.xml file to web application messaging-config.xml file.
3. Save the file.
Create an instance of the Flex Messaging event gateway
To be able to communicate with the ColdFusion application through the Flex Event Gateway,
you must create an instance of the gateway.
1. Create a blank file handleemail.cfc in the C:\CFusionMX7\wwwroot\flexgatewayexamples
directory. (The flexgatewayexamples directory does not already exist.)
2. Start the ColdFusion MX Administrator.
3. Select Event Gateways > Gateway Instances.
4. Enter Flex2CF2 as the Gateway ID.
5. Select Flex Messaging - Flex as the Gateway Type.
6. Specify C:\CFusionMX7\wwwroot\flexgatewayexamples\handleemail.cfc as the CFC
Path.
7. Select Automatic as the Startup Mode.
8. Click Add Gateway Instance.
Set up your development environment 27
Page 28

Create the Flex application
The Flex application in this tutorial is a simple form in which you specify the elements of an
e-mail message, including the recipient, the sender, the subject, and the message body.
Create a new MXML file
In this section, you create an MXML file in which the layout of user interface elements is
exactly as you specify them, or absolute.
1. In an MXML editor, create a file that contains the following text:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<mx:Application xmlns:mx="http://www.adobe.com/2006/mxml" xmlns="*"
layout="absolute"
creationComplete="initApp()">
</mx:Application>
2.
Save the file as flexemail2cf.mxml. in the
C:\fds2\jrun4\servers\default\samples\dataservice\myapp folder.
Create the user interface
In this section, you create the controls to enter information to send an e-mail message:
1. Add the following MXML code after the <mx:Application> tag:
<mx:Consumer id="consumer" destination="ColdFusionGateway"
message="messageHandler(event)" />
<mx:TextInput x="103" y="13" width="291" id="emailto" editable="true"/>
<mx:TextInput x="103" y="43" width="291" id="emailfrom" editable="true"/
>
<mx:TextInput x="103" y="73" width="291" id="emailsubject"
editable="true"/>
<mx:TextArea x="103" y="102" width="291" height="236" id="emailmessage"
editable="true"/>
<mx:Label x="63" y="15" text="To:" textAlign="right"/>
<mx:Label x="37" y="103" text="Message:" textAlign="right"/>
<mx:Label x="52" y="45" text="From:"/>
<mx:Label x="37" y="75" text="Subject:"/>
<mx:Button x="402" y="13" label="Send" id="emailsend"
click="sendMessage();"/>
<mx:Label id="messagestatus" x="103" y="350" width="291" text="message
not sent yet"/>
2.
Save the file.
28 Use ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter
Page 29

Import the required ActionScript classes
In this section, you create a script block and import a set of classes that you will use.
1. Create a script block for ActionScript code directly below the <mx:Application> tag:
<mx:Script>
<![CDATA[
]]>
</mx:Script>
2.
Directly below the <
Send a message to ColdFusion
In this section, you create a function to send a message through the Flex Messaging event
gateway to a ColdFusion application. You then create a structure, named msg, that contains
the gateway ID, and the information necessary to send an e-mail message. The gateway ID is
the ID you assign when you create the gateway instance in ColdFusion MX Administrator.
Finally, you send the message to ColdFusion.
1. Directly below the initApp method, add the following code:
public function sendMessage():void {
var msg:AsyncMessage = new AsyncMessage();
msg.headers.gatewayid = "Flex2CF2";
msg.body.emailto = emailto.text;
msg.body.emailfrom = emailfrom.text;
msg.body.emailsubject = emailsubject.text;
msg.body.emailmessage = emailmessage.text;
pro.send(msg);
}
2.
Save the file.
msg.body = new Object();
messagestatus.text = "Message sent to ColdFusion.";
Receive a message from ColdFusion
In this section, you display a message sent from ColdFusion.
1. Add the following function after the sendMessage function:
private function messageHandler(event:MessageEvent):void {
messagestatus.text = "Message received from ColdFusion";
}
2.
Save the file as flexemail2cf.mxml. in the
C:\fds2\jrun4\servers\default\samples\dataservice\myapp folder.
30 Use ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter
Page 31

Verify that your code is correct
Your code should match the following code example. Verify that the content is correct.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<mx:Application xmlns:mx="http://www.adobe.com/2006/mxml"
layout="absolute"
creationComplete="initApp()">
<mx:Script>
<![CDATA[
import mx.messaging.events.*;
import mx.messaging.Producer;
import mx.messaging.messages.AsyncMessage;
public var pro:mx.messaging.Producer;
public var con:mx.messaging.Consumer;
public function initApp() {
pro = new mx.messaging.Producer();
pro.destination = "ColdFusionGateway";
}
public function sendMessage():void {
var msg:AsyncMessage = new AsyncMessage();
msg.headers.gatewayid = "Flex2CF2";
msg.body.emailto = emailto.text;
msg.body.emailfrom = emailfrom.text;
msg.body.emailsubject = emailsubject.text;
msg.body.emailmessage = emailmessage.text;
pro.send(msg);
}
consumer.subscribe();
msg.body = new Object();
messagestatus.text = "Message sent to ColdFusion.";
private function messageHandler(event:MessageEvent):void {
}
]]>
</mx:Script>
<mx:Consumer id="consumer" destination="ColdFusionGateway"
message="messageHandler(event)" />
messagestatus.text = "Message received from ColdFusion.";
Create the Flex application 31
Page 32

<mx:TextInput x="103" y="13" width="291" id="emailto" editable="true"/>
<mx:TextInput x="103" y="43" width="291" id="emailfrom"
editable="true"/>
<mx:TextInput x="103" y="73" width="291" id="emailsubject"
editable="true"/>
<mx:TextArea x="103" y="102" width="291" height="236"
id="emailmessage" editable="true"/>
<mx:Label x="63" y="15" text="To:" textAlign="right"/>
<mx:Label x="37" y="103" text="Message:" textAlign="right"/>
<mx:Label x="52" y="45" text="From:"/>
<mx:Label x="37" y="75" text="Subject:"/>
<mx:Button x="402" y="13" label="Send" id="emailsend"
click="sendMessage();"/>
<mx:Label id="messagestatus" x="103" y="350" width="291" text="Message
not sent yet."/>
</mx:Application>
Create the ColdFusion application
The ColdFusion application puts the information received from the Flex application in a
structure. It then sends an e-mail message by using elements of the structure.
A ColdFusion application can handle data sent from a Flex application in either the header or
the body of the message. The sample Flex application sends the data in the body of the
message. To create the ColdFusion application, you create a ColdFusion component.
1. Create a blank file and enter the following code:
<cfcomponent
displayname="Send e-mail from Flex application"
hint="Handles incoming message from Flex">
<!--- Handle incoming message. --->
<cffunction name="onIncomingMessage" returntype="any">
<cfargument name="event" type="struct" required="true">
<!--- Create a structure to hold the message object from Flex. --->
<cfset messagebody = event.data.body>
<!--- Populate the structure. --->
<cfset mailfrom="#messagebody.emailfrom#">
<cfset mailto="#messagebody.emailto#">
<cfset mailsubject="#messagebody.emailsubject#">
<cfset mailmessage ="#messagebody.emailmessage#">
32 Use ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter
Page 33

<!--- Send the e-mail. --->
<cfmail from="#mailfrom#"
to="#mailto#"
subject="#mailsubject#">
<cfoutput>#mailmessage#</cfoutput>
</cfmail>
<!--- Create the structure to send back to Flex. --->
<cfset success = StructNew()>
<cfset success.body = "E-mail was sent at " & Now()>
<cfset success.destination = "ColdFusionGateway">
<!--- Send the structure to Flex. --->
<cfset ret = SendGatewayMessage("Flex2CF2", success)>
</cffunction>
</cfcomponent>
2.
Save the file handleemail.cfc in the C:\CFusionMX7\wwwroot\flexgatewayexamples
folder.
Test the application
To test the sample application, you must set up the testing environment, run the Flex
application, and then view your e-mail client to ensure that the application sent the e-mail
message successfully.
Set up the testing environment
Before testing the sample application, do the following:
■ Ensure that Flex Data Services 2 is running.
■ Ensure that ColdFusion is running.
TIP
To make debugging easier, you may want to start ColdFusion in a console by going to
the CFusionMX7\bin directory and entering
■ Start the Flex2CF2 Flex Event Gateway instance.
To start the Flex2CF2 Flex Event Gateway instance:
1. Start the ColdFusion MX Administrator.
2. Select Event Gateways >Gateway Instances.
3. Click the Start button next to the Flex2CF2 gateway instance.
cfstart.
Test the application 33
Page 34

Run the application
To run the Flex application, you browse to the MXML file.
1. Open the http://localhost:8700/samples/dataservice/myapp/flexemail2cf.mxml file in a
browser.
2. Enter a valid e-mail address in the To text box. Ensure that the e-mail address is one whose
incoming e-mail you can check.
3. Enter the name of the sender in the From text box.
4. Enter the subject in the Subject text box.
5. Enter the message in the Message text area.
6. Click Send.
Check e-mail messages
To ensure that the application executed successfully, check the e-mail messages of the recipient
specified in the Flex application. There should be an e-mail message sent from the sender,
with the subject and body that you specified in the Flex application.
34 Use ColdFusion Event Gateway Adapter
Page 35

CHAPTER 4
Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
This chapter describes how to develop an application that uses the Flex Data Service
assembler provided with ColdFusion MX 7.0.2. It describes how you can configure the Flex
Data Service assembler and write and test an application that uses the assembler.
This chapter assumes that you are familiar with ColdFusion components, as well as accessing
and using data in ColdFusion applications. It also assumes that you are familiar with Adobe
Flex Data Services.
Contents
About Flex and ColdFusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Application development and deployment process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Enabling SSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Data translation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Example application. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
4
35
Page 36

About Flex and ColdFusion
The Flex Data Service assembler lets ColdFusion developers use ColdFusion components
(CFCs) to provide the back-end data management for a Flex application that uses the Data
Management Service.
NOTE
To use the Flex Data Service assembler, the Flex application must be running on Flex
Data Services 2.0.
How ColdFusion and Flex interact
The Flex Data Management Service feature lets you configure a Data Management Service
destination, which is the server-side code that you connect to. To use the ColdFusion Data
Service adapter, you specify it in the destination in the Flex Data Service configuration file.
The Flex Data Management Service recognizes the methods:
which you include in your ColdFusion CFCs.
The following image shows the process that Flex and ColdFusion use when a Flex application
calls a method in a ColdFusion component.
fill, get, sync, and count,
1. A Flash client requests data that is handled by the Flex Data Management Service.
2. Flex calls a fill, sync, get, or count method in the Data Service.
3. The ColdFusion Data Service adapter sends the request to the Flex Data Service assembler
by using Java Remote Method Invocation (Java RMI).
4. The Flex Data Service assembler and the ActionScript translator convert ActionScript 3.0
data types to the appropriate ColdFusion values.
5. The ColdFusion server invokes the fill, sync, get, or count method of the assembler
CFC, which invoke the appropriate methods in the DAO CFC.
6. The ColdFusion application creates an array of Value Objects or appropriate return value,
which it sends to the ColdFusion server.
36 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 37

7. The ColdFusion server sends the results to the Flex Data Service assembler.
8. The Flex Data Service assembler and the ActionScript translator convert ColdFusion values
to the appropriate ActionScript 3.0 data types, and then the assembler sends the results to
the ColdFusion Data Service adapter.
9. The ColdFusion Data Service adapter sends the results to the Flex Data Management
Service.
10. The Flex Data Management Service passes the results to the Flash client.
NOTE
The RMI registry, which facilitates communication between the ColdFusion Data
Service assembler and the Flex Data Management Service uses port 1099, which is the
default port for Java RMI. You cannot change this port number.
Application development and deployment process
The following is a typical process for developing and deploying a Flex application that uses
the ColdFusion Data Service adapter and Flex Data Service assembler to manage back-end
database tasks:
1. Design your application.
2. Configure a destination for the ColdFusion Data Service adapter. For more information,
see “Configuring a destination for the ColdFusion Data Service Adapter” on page 38.
3. Write your ColdFusion CFCs. For more information, see “Writing the ColdFusion CFCs”
on page 42.
NOTE
To make creating the CFCs easier, ColdFusion MX 7.0.2 includes wizards that you
can use in Flex Builder. For more information, see Chapter 5, “Using the ColdFusion
Extensions for Flex Builder”.
4. Test your application using Flex.
Application development and deployment process 37
Page 38

Configuring a destination for the ColdFusion Data Service Adapter
To ensure that Flex recognizes the Flex Data Service assembler, you add the coldfusion-dao
adapter to the <adapters> section and a destination to the data-management-config.xml file
that is in the WEB-INF/flex folder of the server on which you want to run the Flex
application.
To add the coldfusion-dao adapter, copy the following adapter-definition to the <adapters>
sectoin of the data-management-config.xml file that is in the WEB-INF/flex folder of the
server on which you want to run the Flex application.
<adapter-definition id="coldfusion-dao"
class="coldfusion.flex.CFDataServicesAdapter"/>
The destination contains the following:
■ A unique ID
■ The name of the adapter to use
■ The channels to use. Flex includes a preconfigured channel, “cf-dataservice-rtmp”
■ The name or path of the assembler CFC
■ The scope, which can be “application”, “session”, or “request”. “Application” specifies that
there is only one instance; “request” specifies that there is a new CFC for each call.
ColdFusion does not support “session.” (Do not confuse this setting with ColdFuison
variable scope; they are not related.)
■ (optional) The hostname or IP address of the ColdFusion host. The default is localhost.
■ (optional) Credentials to pass to every client.
■ The access level of the CFC, which can be “public (and remote)” or “remote”
■ Whether to make property names lowercase when converting to ActionScript
■ Whether to make query column names lowercase
■ Whether to make structure keys lowercase
■ The property or list of properties that are the primary key in the database
■ (optional) Network settings
■ (optional) Fill-method settings, which specify whether to update the results of a fill
operation after a create or update operation
38 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 39

The destination can include the following:
<!-- ======================================== -->
<!-- ColdFusion Sample - Contact sample application -->
<!-- ======================================== -->
<destination id="cfcontact">
<!-Use the ColdFusion adapter for any CF specific destinations
-->
<adapter ref="coldfusion-dao"/>
<!-Use the ColdFusion configured channels which have
the instantiate-types flag set to false.
-->
<channels>
<channel ref="cf-dataservice-rtmp"/>
<channel ref="cf-polling-amf"/>
</channels>
<properties>
<!-- The component name or path on the CF server -->
<component>samples.contact.ContactAssembler</component>
<!-- Either "application" or "request" -->
<scope>request</scope>
<!-The hostname or IP address of the CF host.
Optional, default is localhost.
<hostname>localhost</hostname>
-->
<!-This is the ID of the ColdFusion Data Management server as configured
in the ColdFusion Administrator.
Only needed if you have more than one instance of CF on a machine.
<identity>default</identity>
-->
<!-Credentials to pass to the assembler CFC for all clients
Generally better to use setRemoteCredentials() API on client
<remote-username></remote-username>
<remote-password></remote-password>
-->
<!-- Define the resolution rules and access level of the cfc being
invoked -->
<access>
Application development and deployment process 39
Page 40

<!-- allow "public" (and remote) or just "remote" methods to be
invoked -->
<method-access-level>remote</method-access-level>
</access>
<!-- controls for forcing property names to lowercase when converting
to ActionScript -->
<property-case>
<!-- cfc property names -->
<force-cfc-lowercase>false</force-cfc-lowercase>
<!-- Query column names -->
<force-query-lowercase>false</force-query-lowercase>
<!-- struct keys -->
<force-struct-lowercase>false</force-struct-lowercase>
</property-case>
<metadata>
<identity property="contactId"/>
</metadata>
<network>
<!-- Add network elements here -->
</network>
<server>
<!-The method declarations are ignored for CFC Assemblers,
with the exception of the fill-method settings.
Method names are fixed: fill, sync, get, count.
No parameters are defined here, unlike Java.
Any arguments provided via the AS call are passed along to the CFC,
just use optional arguments when defining the CFC.
-->
<fill-method>
<!-Does the assembler have a "fill-contains" method?
This method is used to determine whether to refresh the fill.
If the specified method returns true the fill is re-executed
after a create or update.
Auto-refresh determines if the fill is always refreshed if not
specified.
May only be used when auto-refresh is true.
Optional. Default is false.
-->
<use-fill-contains>false</use-fill-contains>
<!-Determines whether to refresh the fill on updates or creates.
Optional. Default value is true.
40 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 41

-->
<auto-refresh>true</auto-refresh>
<!-Determines whether order is important for this filled
collection. Allows for
performance optimization when order is not important.
Optional. Default value is true.
-->
<ordered>true</ordered>
</fill-method>
</server>
</properties>
</destination>
To enable the Data Services adapter:
1. Copy the following ColdFusion-specific <channel-definiton> sections (cf-dataservice-rtmp
and cf-polling-amf) from the sample services-config.xml file to the <channels> section of
the web application flex-messaging-service.xml file:
<!-- ColdFusion specific HTTP channel -->
<channel-definition id="cf-polling-amf"
class="mx.messaging.channels.AMFChannel">
<endpoint
uri="http://{server.name}:{server.port}
/{context.root}
/messagebroker/cfamfpolling"
class="flex.messaging.endpoints.AMFEndpoint"/>
<properties>
<serialization>
<!-- This must be turned off for any CF channel -->
<instantiate-types>false</instantiate-types>
</serialization>
<polling-enabled>true</polling-enabled>
<polling-interval-seconds>8</polling-interval-seconds>
</properties>
</channel-definition>
<!-- ColdFusion specific RTMP channel -->
<channel-definition id="cf-dataservice
-rtmp"class="mx.messaging.channels.RTMPChannel">
<endpoint uri="rtmp://{server.name}:2048"
class="flex.messaging.endpoints.RTMPEndpoint"/>
<properties>
<idle-timeout-minutes>20</idle-timeout-minutes>
<serialization>
<!-- This must be turned off for any CF channel -->
<instantiate-types>false</instantiate-types>
</serialization>
</properties>
</channel-definition>
Application development and deployment process 41
Page 42

The sample services-config.xml file is located in the C:\fds2\resources\config folder, and
the web application flex-messaging-service.xml file is located in the
C:\fds2\jrun4\servers\default\samples\WEB-INF\flex folder when you install Flex in the
default location.
2. (Optional) Turn on the ColdFusion-specific debugging output in the Flex console by
adding the following <pattern> tag in the <filters> tag in the <logging> section of the web
application services-config.xml file:
<pattern>DataService.coldfusion</pattern>
3.
Add the coldfusion-dao adapter to the web application data-management-config.xml (in
the C:\fds2\jrun4\servers\default\samples\WEB-INF\flex folder when you install Flex in
the default location) by adding the following in the <adapters> section:
<adapter-definition id="coldfusion-dao"
class="coldfusion.flex.CFDataServicesAdapter"/>
For more information, see “Configuring the Data Service” in Developing Flex Applications,
which is included in the Flex documentation.
NOTE
The ColdFusion MX Administrator lets you enable or disable Flex Data Management
support. If you are running more than one instance of ColdFuison, you must use a unique
ID to specify each instance of ColdFusion for which you want to enable Flex Data
Management support. You do so by specifying the identity in the <identity> element of the
data-management-config.xml file.
Writing the ColdFusion CFCs
The Flex Data Management Service recognizes the methods: fill, get, sync, and count.
The
fill method retrieves records from a database and populates an array with the records.
The
get method retrieves a specific record. The sync method lets you keep track of
synchronization conflicts by accepting a change list, which is an array of change objects. The
count method returns a number that indicates how many records are in a result set. To
perform any of these database tasks, the Flex application calls the appropriate
sync, or count method in the assembler CFC. You can also use a fillContains method,
fill, get,
which checks whether to update the results of a fill. For more information, see “Managing
fills” on page 43.
When you create the ColdFusion CFC, you include the database manipulation in the
methods in the assembler CFC or use the Bean/DAO methodology. For more information,
see “Selecting a methodology” on page 43.
42 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 43

Selecting a methodology
When you create your ColdFusion CFCs, you can put the database manipulation
functionality directly in the methods in the assembler CFC and create a Value Object CFC,
which is a CFC that contains property definitions and related
get and set methods.
However, to separate the lower level database functionality from the high level Flex assembler
operations, you can use the Bean/DAO methodology.
The Bean/DAO methodology requires that you put the
fill, get, sync, and count methods
in the assembler CFC. Rather than performing database functions directly, such as retrieving
data, the methods in the assembler CFC call methods in the Data Access Object (DAO)
CFC, which perform the lower level database functions such as retrieving records. The DAO
CFC creates Value Objects, which are CFCs that contain the values. A Value Object is
essentially a row in the result set.
Managing fills
To determine whether to refresh a fill result after an item is created or updated, you include a
fillContains method in the assembler and set both use-fill-contains and auto-refresh to true
in the
<fill-method> section of the data-management-config.xml file. A sample <fill-
method>
<fill-method>
</fill-method>
In this example, ordered is set to false because the fill result is not sorted by any criteria.
However, if the fill result is sorted, you set ordered to true. When an item changes in a fill
result that is ordered, you must refresh the entire fill result.
The
again after an item in the fill result has changed. The
that indicates how the fill should be treated for that change. When the
method returns true, the fill is executed after a create or update operation.
The
<cffunction name="fillContains" output="no" returnType="boolean"
section appears as follows:
<use-fill-contains>true</use-fill-contains>
<auto-refresh>true</auto-refresh>
<ordered>false</ordered>
fillContains method tells the Flex application whether it is necessary to run the fill
fillCcontains method returns a value
fillContains
fillContains method signature is as follows:
access="remote">
<cfargument name="fillArgs" type="array" required="yes">
<cfargument name="item" type="[CFC type object]" required="yes">
<cfargument name="isCreate" type="boolean" required="yes">
Application development and deployment process 43
Page 44

The arguments are as follows:
■ fillArgs is a list of arguments to pass to the fill method
■ item is the record to check to determine if it is in the result set
■ isCreate indicates whether the record is new
A sample
fillContains method, which determines whether the fill arguments (part of the
first or last name) are in the Contact item passed to the function, is as follows:
<cffunction name="fillContains" output="no" returnType="boolean"
access="remote">
> <cfargument name="fillArgs" type="array" required="yes">
> <cfargument name="item" type="samples.contact.Contact" required="yes">
> <cfargument name="isCreate" type="boolean" required="yes">
>
> <cfif ArrayLen(fillArgs) EQ 0>
> <!--- This is the everything fill. --->
> <cfreturn true>
> <cfelseif ArrayLen(fillArgs) EQ 1>
> <!--- This is a search fill. --->
> <cfset search = fillArgs[1]>
> <cfset first = item.getFirstName()>
> <cfset last = item.getLastName()>
> <!--- If the first or last name contains the search string, --->
> <cfif (FindNoCase(search, first) NEQ 0) OR (FindNoCase(search, last)
> NEQ 0)>
> <!--- this record is in the fill. --->
> <cfreturn true>
> <cfelse>
> <!--- this record is NOT in the fill. --->
> <cfreturn false>
> </cfif>
> </cfif>
>
> <!--- By default, do the fill.--->
> <cfreturn true>
> </cffunction>
Authentication
To authenticate users when using the Flex Data Service Assembler, you use the Flex
setRemoteCredentials() method on the DataService object. The credentials, which are in
the FlexSession object, are passed to the ColdFusion application, where you can use the
cflogin tag to perform authentication. Alternatively, you can set credentials in the Flex
destination, although this is not the recommended way to do so.
44 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 45

You can set the cerdentials by doing either of the following:
■ Specifying credentials in ActionScript
■ Specifying credentials in the Flex destination
Specifying credentials in ActionScript
To specify credentials in ActionScript, you use the setRemoteCredentials() method, as in
the following example:
ds = new DataService(“mydest”);
ds.setRemoteCredentials(“wilsont”, “password”);
Specifying credentials in the Flex destination
To specify credentials in the Flex destination, you edit the data-management-config.xml file
that is in the WEB-INF/flex folder of the server on which you want to run the Flex
application.. In the <properties> element, you include the <remote-username> and <remotepassword> elements, as follows:
<destination id="cfcontact">
<adapter ref="coldfusion-dao" />
<channels>
<channel ref="cf-dataservice-rtmp" />
</channels>
<properties>
<source>samples.contact.ContactAssembler</source>
<scope>application</scope>
<remote-username>wilsont</remote-username>
<remote-password>password</remote-password>
...
/properties>
</destination>
Enabling SSL
You can encrypt communication between ColdFusion and Flex by enabling Secure Sockets
Layer (SSL). To use SSL, you must create a keystore file. The keystore is a self-signed
certificate. (You do not need a certificate signed by a Certificate Authority, although if you do
use one, you do not need to configure Flex as indicated in the steps below.) The information
in the keystore is encrypted and can be accessed only with the password that you specify. To
create the keystore, you use the Java keytool utility, which is included in your Java Runtime
Environment (JRE).
Enabling SSL 45
Page 46

To enable SSL, you do the following:
■ Create the keystore
■ Configure Flex
■ Enable SSL in the ColdFusion MX Administrator
To create the keystore:
1. Generate the SSL server (ColdFusion) keystore file by using the keytool utility, with a
command similar to the following:
keytool -genkey -v -alias FlexAssembler -dname "cn=FlexAssembler" -
keystore cf.keystore -keypass mypassword -storepass mypassword
The following table describes the parameters of the keytool utility that you use:
Parameter Description
-alias
-dname
-
keystore The location of the keystore file.
-keypass
-storepass
-rfc
-file
-v
The name of the keystore entry. You can use any name for this, as long
as you are consistent when referring to it.
The Distinguished Name, which contains the Common Name (cn) of
the server.
The password for your private key.
The password for the keystore. The encrypted storepass is stored in
ColdFuison configuration files.
Generates the certificate in the printable encoding format.
The name of the keystore file.
Generates detailed certificate information.
Next, you place the certificate you created in the file that the JVM uses to decide what
certificates to trust. The file in which you put the certificate, (usually named cacerts), is
located in the JRE, under the lib/security folder.
To configure Flex:
1. Export the keystore to a certificate by using the keytool utility, with a command similar to
the following:
keytool -export -v -alias FlexAssembler -keystore cf.keystore -rfc -file
cf.cer
2.
Import the certificate into the JRE cacerts file for your server by using the keytool utility,
with a command similar to the following:
keytool -import -v -alias FlexAssembler -file cf.cer -keystore
C:\fds2\UninstallerData\jre\lib\security\cacerts
46 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 47

The previous example specifies the location of the keystore for Flex Data Services with
integrated JRun, installed using the default settings. If you are using a different server,
specify the location of the cacerts file for the JRE that you are using. For example, if you
are using JBoss, you specify the keystore location as
cacerts.
To enable SSL in the ColdFusion MX Administrator:
1. In the ColdFusion MX Administrator, select Data & Services > Flex Integration, and
$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/security/
specify the keystore file in the Full Path to Keystore text box.
2. Specify the keystore password in the Keystore password text box.
3. Select the Enable RMI over SSL for Data Management option, and then click Submit
Changes.
If you specify an invalid keystore file or password, ColdFusion does not enable SSL, and
disables Flex Data Management Support.
Data translation
The following table lists the ColdFusion data types and the corresponding Adobe Flash or
ActionScript data type: [arrays become lists - which are AS arrayCollections; ask mike]
ColdFusion data type Flash data type
String String
Array [] = Array
Struct {} = untyped Object
Query Array of untyped Objects
CFC Class = typed Object (if a matching ActionScript class exists,
otherwise the CFC becomes a generic untyped Object (map) in
ActionScript)
CFC Date ActionScript Date
CFC String ActionScript String
CFC Numeric ActionScript Numeric
ColdFusion XML Object ActionScript XML Object
Data translation 47
Page 48

Example application
This section describes creating a Flex application that uses the ColdFusion Data Service
adapter and Flex Data Service assembler so that a ColdFusion component handles the backend database management.
You can download the source code for the files that are included in the Flex sample Contact
application from “Using ColdFusion with Flex – Part 1: Creating and Running a Contact
Manager Application.” In addition, you can view the code for the Flex sample Contact
appliation in “The Flex Contact Manager Application” on page 62.
To use ColdFusion instead of the Java adapter:
1. Create the assembler CFC.
2. Create the DAO CFC.
3. Create the Value Object CFC.
NOTE
To make creating the CFCs easier, ColdFusion MX 7.0.2 includes wizards that you
can use in Flex Builder. For more information, see Chapter 5, “Using the ColdFusion
Extensions for Flex Builder”.
4. Specify the destination in the data-management-config.xml file.
5. Copy the files for the Flex Contact sample application to the appropriate folders.
6. Run the application.
Creating the assembler CFC
The assembler CFC contains the fill, sync, get, and count methods.
Creating the fill method
In the Contact sample application, the fill operation has two forms: one that takes no
argument, and one that takes a string. The corresponding Java function returns a List of
Contact objects. Because a List corresponds to an array in ColdFusion, the
returns an array of Contact objects. The
<cffunction name="fill" output="no" returntype="samples.contact.Contact[]"
access="remote">
<cfargument name="param" type="string" required="no">
<cfset var ret = ArrayNew(1)>
<cftry>
<cfset dao = CreateObject("component","samples.contact.ContactDAO")>
48 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
fill method appears as follows:
fill method
Page 49

<cfif structKeyExists(arguments, "param")>
<cfreturn dao.read(param=arguments.param)>
<cfelse>
<cfreturn dao.read()>
</cfif>
<!--- If the SQL failed, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="database">
<cfset msg = "Error during fill: " & cfcatch.queryError &
". SQL was :" & cfcatch.sql>
</cfcatch>
<!--- If anything else happened, mark this change with --->
<!--- the error. --->
<cfcatch type="any">
<!--- <cfset co.fail(cfcatch.message & " " & cfcatch.detail)> --->
</cfcatch>
</cftry>
</cffunction>
Creating the sync method
The sync method has a specific signature. The sync method accepts an array as its argument
and have a return value of an array. The arrray that the sync method accepts contains Java
ChangeObjects, which Flex creates and documents. The
<cffunction name="sync" output="no" returnType="array" access="remote">
<cfargument name="changes" type="array" required="yes">
<!-- Create the array for the returned changes. -->
<cfset var newchanges=ArrayNew(1)>
sync method appears as follows:
<!-- Loop over the changes and apply them. --->
<cfloop from="1" to="#ArrayLen(changes)#" index="i" >
<cfset co = changes[i]>
<cfif co.isCreate()>
<cfset x = doCreate(co)>
<cfelseif co.isUpdate()>
<cfset x = doUpdate(co)>
<cfelseif co.isDelete()>
<cfset x = doDelete(co)>
</cfif>
<cfset ArrayAppend(newchanges, x)>
</cfloop>
<!-- Return the change objects, as this is how success or failure
is indicated. --->
<cfreturn newchanges>
</cffunction>
Example application 49
Page 50

The sync method calls the private methods doCreate, doUpdate, and doDelete. If an error
occurs, the method updates the change object with the failure to inform the Flex application
that the change was not processed. The ChangeObject has two APIs,
fail(). The fail() API takes an optional string argument, which contains the description
of what went wrong. The
<cffunction name="doCreate" access="private" output="no">
<cfargument name="co" required="yes" hint="The change object.">
<!--- The record to create. --->
<cfset var new = co.getNewVersion()>
<cftry>
<cfset dao = CreateObject("component", "samples.contact.ContactDAO")>
<!--- Create the record; create returns with the identity fields
set --->
<cfset dao.create(new)>
<!--- Set the new version in to the change object. --->
<cfset co.setNewVersion(new)>
<!--- Mark this change as processed successfully. --->
<cfset co.processed()>
<!--- If the SQL failed, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="database">
<cfset msg = "Error during create: " & cfcatch.queryError &
". SQL was :" & cfcatch.sql>
<cfset co.fail(msg)>
</cfcatch>
<!--- If anything else happened, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="any">
<cfset co.fail(cfcatch.message & " " & cfcatch.detail)>
</cfcatch>
</cftry>
doCreate, doUpdate, and doDelete methods appear as follows:
processed() and
<!--- Return the change object. --->
<cfreturn co>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="doUpdate" access="private" output="no">
<cfargument name="co" required="yes" hint="The change object.">
<!--- The record to update. --->
<cfset var new = co.getNewVersion()>
<cfset var old = co.getPreviousVersion()>
<cftry>
<cfset dao = CreateObject("component", "samples.contact.ContactDAO")>
<!--- Update the record. --->
50 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 51

<cfset new = dao.update(old, new)>
<!--- Mark this change as processed successfully. --->
<cfset co.processed()>
<!--- If the SQL failed, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="database">
<cfset msg = "Error during update: " & cfcatch.queryError &
". SQL was :" & cfcatch.sql>
<cfset co.fail(msg)>
</cfcatch>
<!--- If anything else happened, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="any">
<cfset co.fail(cfcatch.message & " " & cfcatch.detail)>
</cfcatch>
</cftry>
<!--- Return the change object. --->
<cfreturn co>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="doDelete" access="private" output="no">
<cfargument name="co" required="yes" hint="The change object.">
<!--- The record to delete. --->
<cfset var old = co.getPreviousVersion()>
<cftry>
<cfset dao = CreateObject("component", "samples.contact.ContactDAO")>
<!--- Delete the record. --->
<cfset dao.delete(old)>
<!--- Mark this change as processed successfully. --->
<cfset co.processed()>
<!--- If the SQL failed, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="database">
<cfset msg = "Error during delete: " & cfcatch.queryError &
". SQL was :" & cfcatch.sql>
<cfset co.fail(msg)>
</cfcatch>
<!--- If anything else happened, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="any">
<cfset co.fail(cfcatch.message & " " & cfcatch.detail)>
</cfcatch>
</cftry>
<!--- Return the change object. --->
<cfreturn co>
</cffunction>
Example application 51
Page 52

Creating the count method
The count method returns the number of records that would be returned by the fill method.
The return type of the
<cffunction name="count" output="no"
returntype="samples.contact.Contact[]" access="remote">
<cfargument name="param" type="string" required="no">
<cftry>
<cfset dao = CreateObject("component", "samples.contact.ContactDAO")>
<cfif structKeyExists(arguments, "param")>
<cfreturn dao.count(param=arguments.param)>
<cfelse>
<cfreturn dao.count()>
</cfif>
<!--- If the SQL failed, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="database">
<cfset msg = "Error during count: " & cfcatch.queryError &
". SQL was :" & cfcatch.sql>
<cfset co.fail(msg)>
</cfcatch>
<!--- If anything else happened, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="any">
<cfset co.fail(cfcatch.message & " " & cfcatch.detail)>
</cfcatch>
</cftry>
</cffunction>
count method is numeric. It appears as follows:
52 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 53

Creating the get method
The get method has a specific signature. It returns one record from the database, as a CFC
instance. It appears as follows:
<cffunction name="get" output="no" returnType="samples.contact.Contact"
access="remote">
<cfargument name="uid" type="struct" required="yes">
<cftry>
<!--- This is the user to look up. --->
<cfset key = uid.contactId>
<cfset dao = CreateObject("component", "samples.contact.ContactDAO")>
<cfset ret="">
<cfset ret=dao.read(id=key)>
<cfif ArrayLen(ret) EQ 1>
<cfreturn ret[1]>
<cfelseif ArrayLen(ret) GT 1>
<cfset co.fail("get returned more than one record when contactId
had a value of #key#.")>
<cfelse>
<cfset co.fail("get did not return anything when contactId had a
value of #key#.")>
</cfif>
<!--- If the SQL failed, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="database">
<cfset msg = "Error during get: " & cfcatch.queryError & ". SQL
was :" & cfcatch.sql>
<cfset co.fail(msg)>
</cfcatch>
<!--- If anything else happened, mark this change with the error. --->
<cfcatch type="any">
<cfset co.fail(cfcatch.message & " " & cfcatch.detail)>
</cfcatch>
</cftry>
</cffunction>
Example application 53
Page 54

Creating the DAO CFC
You create the DAO CFC to perform direct manipulations of the back-end database. The
DAO CFC appears as follows:
<cfcomponent output="false" >
<cffunction name="read" output="true" access="public"
returntype="samples.contact.Contact[]">
<cfargument name="id" required="false">
<cfargument name="param" required="false">
<cfset var qRead="">
<cfset var obj="">
<cfset var ret = ArrayNew(1)>
<cfquery name="qRead" datasource="contacts">
FirstName,
LastName,
Address,
City,
State,
Zip,
Phone
select contactId,
from Contacts
<cfif structKeyExists(arguments, "id")>
where contactId = <cfqueryparam cfsqltype="CF_SQL_INTEGER"
value="#arguments.id#" />
<cfelseif structKeyExists(arguments, "param")>
<!--- Adjust this WHERE clause based on how to filter. --->
<!--- For example, to filter by LastName, --->
<!--- pass in what you want to filter by in --->
<!--- the param attribute of the function --->
<!--- and change "where fieldname" to --->
<!--- "where LastName". --->
where LastName LIKE '%'&<cfqueryparam
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" value="#arguments.param#"/>&'%'
</cfif>
</cfquery>
<cfloop query="qRead">
<cfscript>
obj = createObject("component", "samples.contact.Contact").init();
obj.setcontactId(qRead.contactId);
obj.setFirstName(qRead.FirstName);
obj.setLastName(qRead.LastName);
obj.setAddress(qRead.Address);
obj.setCity(qRead.City);
obj.setState(qRead.State);
obj.setZip(qRead.Zip);
obj.setphone(qRead.phone);
54 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 55

ArrayAppend(ret, obj);
</cfscript>
</cfloop>
<cfreturn ret>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="create" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="Contacts" required="true"
type="samples.contact.Contact">
<cfset var qCreate="">
<cfset var localFirstName=arguments.Contacts.getFirstName()>
<cfset var localLastName=arguments.Contacts.getLastName()>
<cfset var localAddress=arguments.Contacts.getAddress()>
<cfset var localCity=arguments.Contacts.getCity()>
<cfset var localState=arguments.Contacts.getState()>
<cfset var localZip=arguments.Contacts.getZip()>
<cfset var localphone=arguments.Contacts.getphone()>
<cftransaction isolation="read_committed">
<cfquery name="qCreate" datasource="contacts">
insert into Contacts(FirstName, LastName, Address, City,
State, Zip, phone)
values (
<cfqueryparam value="#localFirstName#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
<cfqueryparam value="#localLastName#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
<cfqueryparam value="#localAddress#" cfsqltype=
"CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
<cfqueryparam value="#localCity#" cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
<cfqueryparam value="#localState#" cfsqltype=
"CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
<cfqueryparam value="#localZip#" cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
<cfqueryparam value="#localphone#" cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />
)
</cfquery>
<!--- If your server has a better way to get the ID --->
<!--- that is more reliable, use that instead. --->
<cfquery name="qGetID" datasource="contacts">
select contactId
from Contacts
where FirstName = <cfqueryparam value="#localFirstName#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />
and LastName = <cfqueryparam value="#localLastName#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />
and Address = <cfqueryparam value="#localAddress#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />
Example application 55
Page 56

and City = <cfqueryparam value="#localCity#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />
and State = <cfqueryparam value="#localState#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />
and Zip = <cfqueryparam value="#localZip#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />
and phone = <cfqueryparam value="#localphone#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />
order by contactId desc
</cfquery>
</cftransaction>
<cfscript>
arguments.Contacts.setcontactId(qGetID.contactId);
</cfscript>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="update" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="Contacts" required="true"
type="samples.contact.Contact">
<cfset var qUpdate="">
<cfquery name="qUpdate" datasource="contacts">
update Contacts
set FirstName = <cfqueryparam
value="#arguments.Contacts.getFirstName()#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
LastName = <cfqueryparam
value="#arguments.Contacts.getLastName()#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
Address = <cfqueryparam value="#arguments.Contacts.getAddress()#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
City = <cfqueryparam value="#arguments.Contacts.getCity()#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
State = <cfqueryparam value="#arguments.Contacts.getState()#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
Zip = <cfqueryparam value="#arguments.Contacts.getZip()#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />,
phone = <cfqueryparam value="#arguments.Contacts.getphone()#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR" />
where contactId = <cfqueryparam
value="#arguments.Contacts.getcontactId()#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_INTEGER">
</cfquery>
</cffunction>
56 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 57

<cffunction name="delete" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="Contacts" required="true"
type="samples.contact.Contact">
<cfset var qDelete="">
<cfquery name="qDelete" datasource="contacts">
delete from Contacts
where Contacts.contactId = <cfqueryparam
value="#arguments.Contacts.getcontactId()#"
cfsqltype="CF_SQL_INTEGER" />
</cfquery>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="count" output="false" access="public"
returntype="samples.contact.Contact[]">
<cfargument name="id" required="false">
<cfargument name="param" required="false">
<cfset var qRead="">
<cfquery name="qRead" datasource="contacts">
select COUNT(*) as totalRecords
from Contacts
<cfif structKeyExists(arguments, "id")>
where contactId = <cfqueryparam cfsqltype="CF_SQL_INTEGER"
value="#arguments.id#" />
<cfelseif structKeyExists(arguments, "param")>
<!--- Adjust this WHERE clause based on how to filter. --->
<!--- For example, to filter by LastName, --->
<!--- pass in what you want to filter by in --->
<!--- the param attribute of the function --->
<!--- and change "where fieldname" to --->
<!--- "where LastName". --->
where fieldname LIKE "%<cfqueryparam cfsqltype="CF_SQL_VARCHAR"
value="#arguments.param#"/>%
</cfif>
</cfquery>
<cfreturn qRead.totalRecords>
</cffunction>
</cfcomponent>
Example application 57
Page 58

Creating the Value Object CFC
To create the Value Object to return to Flex, you create a CFC by using the cfproperty tag
and including get and set methods. The Value Object CFC appears as follows:
<cfcomponent output="false" alias="samples.contact.Contact">
<!--- These are properties that are exposed by this CFC object. --->
<!--- These property definitions are used when calling this CFC --->
<!--- as a web services, passed back to a Flash application, --->
<!--- or when generating documentation. --->
<!--- NOTE: These cfproperty tags do not set any --->
<!--- default property values. --->
<cfproperty name="contactId" type="numeric" default="0">
<cfproperty name="firstName" type="string" default="">
<cfproperty name="lastName" type="string" default="">
<cfproperty name="address" type="string" default="">
<cfproperty name="city" type="string" default="">
<cfproperty name="state" type="string" default="">
<cfproperty name="zip" type="string" default="">
<cfproperty name="phone" type="string" default="">
<cfscript>
//Initialize the CFC with the default properties values.
this.contactId = 0;
this.firstName = "";
this.lastName = "";
this.address = "";
this.city = "";
this.state = "";
this.zip = "";
this.phone = "";
</cfscript>
<cffunction name="init" output="false"
returntype="samples.contact.Contact">
<cfreturn this>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="getContactId" output="false" access="public"
returntype="any">
<cfreturn this.contactId>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="setContactId" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="val" required="true">
<cfif (IsNumeric(arguments.val)) OR (arguments.val EQ "")>
<cfset this.ContactId = arguments.val>
<cfelse>
58 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 59

<cfthrow message="'#arguments.val#' is not a valid numeric"/>
</cfif>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="getfirstName" output="false" access="public"
returntype="any">
<cfreturn this.firstName>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="setfirstName" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="val" required="true">
<cfset this.firstName = arguments.val>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="getlastName" output="false" access="public"
returntype="any">
<cfreturn this.lastName>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="setlastName" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="val" required="true">
<cfset this.lastName = arguments.val>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="getaddress" output="false" access="public"
returntype="any">
<cfreturn this.address>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="setaddress" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="val" required="true">
<cfset this.address = arguments.val>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="getcity" output="false" access="public"
returntype="any">
<cfreturn this.city>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="setcity" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="val" required="true">
<cfset this.city = arguments.val>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="getstate" output="false" access="public"
returntype="any">
Example application 59
Page 60

<cfreturn this.state>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="setstate" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="val" required="true">
<cfset this.state = arguments.val>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="getzip" output="false" access="public"
returntype="any">
<cfreturn this.zip>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="setzip" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="val" required="true">
<cfset this.zip = arguments.val>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="getphone" output="false" access="public"
returntype="any">
<cfreturn this.phone>
</cffunction>
<cffunction name="setphone" output="false" access="public"
returntype="void">
<cfargument name="val" required="true">
<cfset this.phone = arguments.val>
</cffunction>
</cfcomponent>
Specifying the destination in the data-managementconfig.xml file
To ensure that Flex recognizes the Flex Data Service assembler, you add the destination to the
data-management-config.xml that is in the /WEB-INF/flex folder.
1. To ensure that you can revert any changes, make a copy of the data-management-
config.xml file.
2. To ensure that Flex recognizes the ColdFusion Data Service adapter, remove comments
from around the adapter definition, which appears as follows:
<adapter-definition id="coldfusion-dao"
class="coldfusion.flex.CFDataServicesAdapter" />
60 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 61

3. To ensure that the channel is enabled, remove comments from around the channel
definition for the cf-dataservice-rtmp channel.
4. Add the following destination to the data-management-config.xml file:
<destination id="cfcontact">
<adapter ref="coldfusion-dao"/>
<channels>
<channel ref="cf-dataservice-rtmp" />
</channels>
<properties>
<metadata>
<identity property="contactId"/>
</metadata>
<network>
<session-timeout>0</session-timeout>
<paging enabled="false" size="10"/>
<throttle-inbound policy="ERROR" max-frequency="500"/>
<throttle-outbound policy="REPLACE" max-frequency="500"/>
</network>
<server>
<assembler>
<!-- The component name or Path on the ColdFusion server-->
<component>samples.contact.ContactAssembler</component>
<!-- The hostname or IP address of the ColdFusion host. -->
<hostname>localhost</hostname>
<!-- The resolution rules and access level of the CFC. -->
<access>
<!-- Allow "public and remote" or just "remote" methods
to be invoked. -->
<method-access-level>remote</method-access-level>
</access>
<!-- Controls to force property names to be lowercase when
converting to ActionScript. -->
<property-case>
<!-- CFC property names. -->
<force-cfc-lowercase>false</force-cfc-lowercase>
<!-- Query column names. -->
<force-query-lowercase>false</force-query-lowercase>
<!-- Struct keys. -->
<force-struct-lowercase>false</force-struct-lowercase>
</property-case>
</assembler>
<!-- No parameters are defined here, unlike Java -->
<!-- Any options provided via the ActionScript call are passed
along to the CFC -->
<!-- Just use optional arguments -->
<fill-method>
<name>fill</name>
</fill-method>
Example application 61
Page 62

<sync-method>
<name>sync</name>
</sync-method>
<get-method>
<name>get</name>
</get-method>
<count-method>
<name>count</name>
</count-method>
</server>
</properties>
</destination>
5.
Save the file.
Run the application
To run the application, browse to the contactmgr.mxml file.
The Flex Contact Manager Application
TheFlex Contact Manager application includes the following files:
■ contactmgr.mxml
■ hourglass.mxml
■ mini.mxml
■ mini.mxml
■ wait.png
All of the files except contact.as should be in the dataservice folder of the Flex server on which
you want to run the Flex application. The contact.as file should be in the
dataservice\samples\contact folder.
contactmgr.mxml
The contactmgr.mxml file contains the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////
//
// Copyright (C) 2003-2006 Adobe Macromedia Software LLC and its licensors.
// All Rights Reserved.
62 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 63

// The following is Sample Code and is subject to all restrictions on such
code
// as contained in the End User License Agreement accompanying this product.
// If you have received this file from a source other than Adobe,
// then your use, modification, or distribution of it requires
// the prior written permission of Adobe.
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////
-->
<mx:Application xmlns:mx="http://www.adobe.com/2006/mxml" xmlns="*"
pageTitle="Contact Manager"
creationComplete="initApp()">
<mx:Script>
<![CDATA[
import mx.controls.*;
import mx.collections.ArrayCollection;
import mx.data.Conflict;
import mx.data.Conflicts;
import mx.data.DataService;
import mx.data.IManaged;
import mx.data.events.*;
import mx.messaging.events.*;
import mx.rpc.*;
import mx.rpc.events.*;
import samples.contact.*;
[Bindable]
public var contacts:ArrayCollection;
[Bindable]
public var contact:Contact;
private var ds:DataService;
private function initApp():void
{
contacts = new ArrayCollection();
ds = new DataService("cfcontact");
ds.addEventListener(ResultEvent.RESULT, resultHandler);
ds.addEventListener(DataServiceFaultEvent.FAULT, faultHandler);
ds.addEventListener(DataConflictEvent.CONFLICT,
conflictHandler);
ds.autoCommit = false;
var token:AsyncToken = AsyncToken(ds.fill(contacts));
token.kind = "fill";
}
Example application 63
Page 64

private function resultHandler(event:ResultEvent):void
{
Hourglass.remove();
if (event.token.kind == "create")
{
dg.selectedIndex = contacts.length - 1;
}
else if (event.token.kind == "delete" && contacts.length>0)
{
var index:int = event.token.index < contacts.length ?
event.token.index : contacts.length -1;
dg.selectedIndex = index;
contact = contacts[index];
}
else if (event.token.kind == "fill" && contacts.length>0)
{
dg.selectedIndex = 0;
contact = contacts[0];
}
}
private function faultHandler(event:DataServiceFaultEvent):void
{
Hourglass.remove();
Alert.show(event.fault.faultstring, "Error");
if (event.item != null)
{
ds.revertChanges(event.item as IManaged);
dg.selectedItem = event.item;
contact = event.item as Contact;
}
}
private function conflictHandler(event:DataConflictEvent):void
{
Hourglass.remove();
var conflicts:Conflicts = ds.conflicts;
var c:Conflict;
for (var i:int=0; i<conflicts.length; i++)
{
c = Conflict(conflicts.getItemAt(i));
Alert.show("Reverting to server value", "Conflict");
c.acceptServer();
}
ds.commit();
}
64 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 65

private function newContact():void
{
dg.selectedIndex = -1;
contact = new Contact();
}
private function updateContact():void
{
var token:AsyncToken;
if (!contacts.contains(contact))
{
Hourglass.show(this);
ds.createItem(contact);
token = ds.commit();
token.kind = "create";
}
else if (ds.commitRequired)
{
Hourglass.show(this);
token = ds.commit();
token.kind = "update";
}
}
private function deleteContact():void
{
Hourglass.show(this);
var index:int = dg.selectedIndex;
ds.deleteItem(contact);
var token:AsyncToken = ds.commit();
token.kind = "delete";
token.index = index;
}
private function searchContacts():void
{
var token:AsyncToken = AsyncToken(ds.fill(contacts,
searchText.text));
token.kind = "fill";
}
]]>
</mx:Script>
<mx:Binding source="firstName.text" destination="contact.firstName"/>
<mx:Binding source="lastName.text" destination="contact.lastName"/>
<mx:Binding source="address.text" destination="contact.address"/>
<mx:Binding source="city.text" destination="contact.city"/>
Example application 65
Page 66

<mx:Binding source="state.text" destination="contact.state"/>
<mx:Binding source="zip.text" destination="contact.zip"/>
<mx:Binding source="phone.text" destination="contact.phone"/>
<mx:HDividedBox width="100%" height="100%">
<mx:Panel title="Contact List" width="100%" height="100%">
<mx:DataGrid id="dg" dataProvider="{contacts}" width="100%"
height="100%"
change="contact=Contact(dg.selectedItem)" >
<mx:columns>
<mx:DataGridColumn dataField="contactId" headerText="Id"/
>
<mx:DataGridColumn dataField="firstName"
headerText="First Name"/>
<mx:DataGridColumn dataField="lastName" headerText="Last
Name"/>
</mx:columns>
</mx:DataGrid>
<mx:ControlBar>
<mx:TextInput id="searchText" width="100%"
enter="searchContacts()"/>
<mx:Button label="Search" click="searchContacts()"
width="60"/>
</mx:ControlBar>
</mx:Panel>
<mx:Panel title="Details [{dg.selectedIndex!=-1?contact.firstName+'
'+contact.lastName:'New Contact'}]" width="100%" height="100%">
<mx:Form width="100%" height="100%" label="General">
<mx:FormItem label="First Name" required="true">
<mx:TextInput id="firstName" width="250"
text="{contact.firstName}"/>
</mx:FormItem>
<mx:FormItem label="Last Name" required="true">
<mx:TextInput id="lastName" width="250"
text="{contact.lastName}"/>
</mx:FormItem>
<mx:FormItem label="Address">
<mx:TextInput id="address" width="250"
text="{contact.address}"/>
</mx:FormItem>
<mx:FormItem label="City">
<mx:TextInput id="city" width="250"
text="{contact.city}"/>
</mx:FormItem>
<mx:FormItem label="State">
<mx:TextInput id="state" width="250"
text="{contact.state}"/>
66 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 67

</mx:FormItem>
<mx:FormItem label="Zip">
<mx:TextInput id="zip" width="250" text="{contact.zip}"/>
</mx:FormItem>
<mx:FormItem label="Phone">
<mx:TextInput id="phone" width="250"
text="{contact.phone}"/>
</mx:FormItem>
</mx:Form>
<mx:ControlBar>
<mx:Button label="{dg.selectedIndex!=-1?'Update':'Add'}"
click="updateContact()" width="60"/>
<mx:Button label="Delete" click="deleteContact()"
visible="{dg.selectedIndex!=-1}" width="60"/>
<mx:Button label="New" click="newContact()"
visible="{dg.selectedIndex!=-1}" width="60"/>
</mx:ControlBar>
</mx:Panel>
</mx:HDividedBox>
</mx:Application>
hourglass.mxml
The hourglass.mxml file contains the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////
//
// Copyright (C) 2003-2006 Adobe Macromedia Software LLC and its licensors.
// All Rights Reserved.
// The following is Sample Code and is subject to all restrictions on such
code
// as contained in the End User License Agreement accompanying this product.
// If you have received this file from a source other than Adobe,
// then your use, modification, or distribution of it requires
// the prior written permission of Adobe.
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////
-->
<mx:VBox xmlns:mx="http://www.adobe.com/2006/mxml" width="220" height="60">
<mx:Script>
<
import mx.managers.PopUpManager;
import mx.core.IFlexDisplayObject;
private static var dialog:IFlexDisplayObject;
public static function show(parent:DisplayObject):void
{
dialog = PopUpManager.createPopUp(parent, Hourglass, true);
PopUpManager.centerPopUp(dialog);
}
public static function remove():void
{
PopUpManager.removePopUp(dialog);
}
]]>
</mx:Script>
<mx:Image source="@Embed('wait.png')"/>
</mx:VBox>
mini.mxml
The mini.mxml file contains the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////
//
// Copyright (C) 2003-2006 Adobe Macromedia Software LLC and its licensors.
// All Rights Reserved.
// The following is Sample Code and is subject to all restrictions on such
code
// as contained in the End User License Agreement accompanying this product.
// If you have received this file from a source other than Adobe,
// then your use, modification, or distribution of it requires
// the prior written permission of Adobe.
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////
-->
<mx:Application xmlns:mx="http://www.adobe.com/2006/mxml" xmlns="*"
creationComplete="dataService.fill(contacts)">
<mx:ArrayCollection id="contacts"/>
68 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 69

<mx:DataService destination="contact" id="dataService"
fault="faultHandler(event)" conflict="conflictHandler(event)"/>
<mx:Panel title="Contact List" width="100%" height="100%">
<mx:DataGrid id="dg" dataProvider="{contacts}" width="100%"
height="100%" editable="true">
<mx:columns>
<mx:DataGridColumn dataField="contactId" headerText="Id"
editable="false"/>
<mx:DataGridColumn dataField="firstName" headerText="First
Name"/>
<mx:DataGridColumn dataField="lastName" headerText="Last
Name"/>
<mx:DataGridColumn dataField="phone" headerText="Phone"/>
</mx:columns>
</mx:DataGrid>
</mx:Panel>
<mx:Script>
<![CDATA[
import mx.controls.Alert;
import mx.data.Conflict;
import mx.data.Conflicts;
import mx.data.events.DataConflictEvent;
import mx.rpc.events.FaultEvent;
import samples.contact.Contact;
private static var _link:Contact = null;
private function faultHandler(event:FaultEvent):void
{
Alert.show(event.fault.faultstring, 'Error')
}
private function conflictHandler(event:DataConflictEvent):void
{
var conflicts:Conflicts = dataService.conflicts;
var c:Conflict;
for (var i:int=0; i<conflicts.length; i++)
{
c = Conflict(conflicts.getItemAt(i));
Alert.show("Reverting to server value", "Conflict");
c.acceptServer();
}
}
]]>
</mx:Script>
</mx:Application>
Example application 69
Page 70

contact.as
The contact.as file contains the following:
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////
//
// Copyright (C) 2003-2006 Adobe Macromedia Software LLC and its licensors.
// All Rights Reserved.
// The following is Sample Code and is subject to all restrictions on such
code
// as contained in the End User License Agreement accompanying this product.
// If you have received this file from a source other than Adobe,
// then your use, modification, or distribution of it requires
// the prior written permission of Adobe.
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////
package samples.contact
{
[Managed]
[RemoteClass(alias="samples.contact.Contact")]
public class Contact
{
public function Contact() {}
public var contactId:int;
public var firstName:String = "";
public var lastName:String = "";
public var address:String = "";
public var city:String = "";
public var state:String = "";
public var zip:String = "";
public var phone:String = "";
}
}
70 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 71

wait.png
The wait.png file appears as follows:
Example application 71
Page 72

72 Using the Flex Data Service Assembler
Page 73

CHAPTER 5
Using the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
The ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder include wizards that help generate code for
common tasks and an extension that lets you connect to remote servers from Adobe Flex
Builder and Eclipse.
To use the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder, you should be familiar with ColdFusion
components, as well as accessing and using data in ColdFusion applications. You should also
be familiar with Adobe Flex Builder.
Contents
About the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Installing the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Eclipse RDS Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
ActionScript to CFC wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
CFC to ActionScript wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
RDS CRUD wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Services Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
5
73
Page 74

About the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
To make some common coding tasks easier, the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
include the following:
■ Eclipse RDS Support plug-in, which lets you access files and data sources on a ColdFusion
server.
■ ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard, which lets you create master and detail pages in an
application to create, read, update, and delete records in a database.
■ RDS CRUD wizard, which lets you dynamically create a ColdFusion component (CFC)
based on a table that is registered in the ColdFusion Administrator on a ColdFusion server
■ ActionScript to CFC wizard, which lets you create a CFC based on an ActionScript class
file
■ CFC to ActionScript wizard, which lets you create an ActionScript file based on a CFC
Value Object
■ Services Browser, which lets you browse CFCs, manage a list of web services, and generate
the CFML code to invoke a web service.
Installing the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
Before you install the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder, you must have the following
products installed:
■ Flex Builder 2
■ ColdFusion MX 7.0.2
To install the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder:
1. Select Help > Software Updates > Find and Install.
2. Select the Search For New Features To Install option, and then click Next.
3. Click New Archive Site.
4. Select the ColdFusion_FlexBuilder_Feature.zip file, and then click Open.
The file is located in the Extras folder if you installed ColdFusion MX 7.0.2 using the
default values.
5. When the Edit Local Site dialog box appears, click OK.
6. Ensure that the ColdFusion Flex Builder feature is selected, and then click Finish.
74 Using the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
Page 75

7. Select the check box next to ColdFusion_FlexBuilder_Feature.zip, and then click Next.
8. Select the I Accept The Terms In This License Agreement option, and then click Next.
9. Click Finish.
10. Click Install All.
11. When the installation is complete, click Yes to restart Flex Builder.
To uninstall the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder, you must first disable them, and
then uninstall them.
To uninstall the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder:
1. Select Help > Software Updates > Manage Configuration.
2. Select the ColdFusion Plugin feature.
3. Click Disable and then click Yes.
4. Click Yes to restart Flex Builder.
5. When Flex Builder restarts, select Software Updates > Manage Configuration.
6. Select the ColdFusion Flex Builder feature and click Uninstall.
7. Click Yes to confirm that you want to uninstall.
8. Restart Flex Builder.
Eclipse RDS Support
Remote Development Services (RDS) lets you access files and data sources registered in the
ColdFusion Administrator on a ColdFusion server. To use Eclipse RDS Support, you must
enable RDS when you install ColdFusion. With Eclipse RDS Support, you can use Flex
Builder or CFEclipse as your IDE and access ColdFusion files remotely.
Eclipse RDS Support is supported on all ColdFusion server platforms.
Before you install Eclipse RDS Support, you must have the following installed:
■ Eclipse 3.1 or Flex Builder 2
■ ColdFusion MX 7.0.1 or later
Eclipse RDS Support 75
Page 76

Configuring RDS
Before using RDS, you must configure ColdFusion servers.
To configure any ColdFusion servers that you want to connect to using RDS:
1. In Flex Builder or Eclipse, select Window > Preferences > RDS Configuration.
2. To configure the default localhost server, select localhost and specify the following:
■ Description
■ Host name (127.0.0.1)
■ Port number (8500 if you are using the built-in web server)
■ Context root, if necessary (For more information about the context root, see Installing
and Using ColdFusion MX.)
■ Password, which is the RDS password
3. To specify additional servers, click New, and specify the following:
■ Description, which can be any name you want
■ Host name (IP address or machine name)
■ Port number (8500 if you are using the built-in web server)
■ Context root, if necessary (For more information about the context root, see Installing
and Using ColdFusion MX .)
■ Password, which is the RDS password
4. To remove a server definition, select the server and click Remove.
5. To test a connection, select the server and click Test Connection.
NOTE
If you are using ColdFusion MX 7.0 or earlier, the message “The RDS server was
successfully contacted, but your security credentials were invalid,” appears. The
message indicates that the password was not validated, even if it is correct. Click OK
to close the message.
Once you have configured the RDS connection to your CF servers, you can view the files,
folders and data sources on RDS servers. Each RDS server appears as a node in the RDS
Fileview and Dataview, with the name you specified when you configured the RDS server.
To view files and folders or data sources do the following:
1. In Flex Builder, select Window > Other Views. In Eclipse, select Window > Show View >
Other.
2. Select RDS.
3. To access the file system on the RDS server, select RDS Fileview.
4. To access data sources on the RDS server, select RDS Dataview.
76 Using the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
Page 77

Using the RDS Fileview
The RDS Fileview lists all the folders and files on the RDS server. You use the navigation
buttons as indicated in the following table:
Button Action
Refresh the active RDS server.
Create a file in the currently selected folder.
Delete the currently selected file.
Create a folder in the currently selected folder.
Delete the currently selected folder.
NOTE
RDS Eclipse Support does not support file operations such as copy and paste, drag and
drop, and changing file attributes. However, delete, save, save as, and rename are
supported. In addition, on ColdFusion servers after ColdFusion 5, the date last modified
field does not appear.
To rename a folder or file, right-click the folder or filename.
Using the RDS Dataview
The RDS Dataview lists all the data sources on the RDS server. You use the buttons as
indicated in the following table:
Button Name Description
Refresh Refresh the currently selected item.
Query Viewer Opens the RDS Query Viewer.
You can build queries using either the RDS Query Viewer or the Visual Query Builder. The
RDS Visual Query Builder is similar to the ColdFusion Report Builder Query Builder and
the HomeSite Query Builder.
Eclipse RDS Support 77
Page 78

Building queries in the RDS Query Viewer
To build and execute a query using the RDS Query Viewer:
1. Click the RDS Query Viewer icon on the RDS Dataview tab.
The RDS Query Viewer opens in its own tab, which means that if you have other
documents open, the RDS Query Viewer has focus.
2. Do one of the following:
■ Enter the SQL, and double-click the field names and table names as appropriate.
■ Click the Visual Query Builder button.
For more information about using the Visual Query Builder, see the following section,
“Using Visual Query Builder” on page 79.
3. To try the query, click Execute query.
The first 50 records of the result set appear.
78 Using the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
Page 79

Using Visual Query Builder
You use the Query Builder to define a SQL statement. The following image shows the Query
Builder user interface:
To build a SQL statement using the Table pane and the Properties panel:
1. Expand a data source.
2. Double-click the columns to be named in the SELECT statement.
As you select columns, the Query Builder creates the SELECT statement in the area at the
lower edge of the pane.
3. If you select columns from more than one table, you must specify the column or columns
used to join them by dragging a column from one table to the related column in the second
table.
Eclipse RDS Support 79
Page 80

4. (Optional) Specify sort order by doing the following:
a. Locate the column in the Properties panel.
b. Click in the Sort Type cell of the column you want to sort by.
c. Specify Ascending or Descending.
d. (Optional) If you specify multiple sort columns, you specify precedence using the Sort
Order cell.
5. (Optional) Specify selection criteria by doing the following:
a. Locate the column in the Properties panel.
b. Click in the Condition cell.
c. Select WHERE.
d. Specify WHERE clause criteria in the Criteria cell.
NOTE
If you specify selection criteria, the Query Builder creates a WHERE clause. To
use an INNER JOIN or other advanced selection criteria instead, you must code
the SQL manually.
6. (Optional) To specify an aggregate function, GROUP BY, or an expression:
a. Locate the column in the Properties panel.
b. Click in the Condition cell.
c. Select Group By or the aggregate function (such as COUNT).
7. (Optional) To specify SQL manually, type the SQL statement in the SQL pane.
NOTE
You code SQL manually to use an INNER JOIN instead of a WHERE clause, use an
OUTER JOIN, or use a database stored procedure.
8. (Optional) To specify the data type of a query parameter:
a. Click the + button under Parameters.
b. Enter the name of the parameter.
c. Select the data type.
9. Review the SELECT statement that displays in the SQL pane, and use the Table and
Properties panes to make adjustments, if necessary.
10. (Optional) Click Test Query.
11. Click Save.
80 Using the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
Page 81

ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard
The ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard creates ColdFusion and Flex files for a create, read,
update, delete (CRUD) application. You specify the master, detail, and master/detail pages to
include in the application, and the relationship between the application’s pages. The wizard
lets you use Visual Query Builder to generate the SQL statements. For more information
about using Visual Query Builder, see “Using Visual Query Builder” on page 79.
Designing your application
Before starting the ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard, you should determine which pages to
include in your application, including the following:
■ Whether each page is a master, detail, or master/detail page
■ The fields to display in each page
■ The fields that connect one page to another
In the following example, you create an application for an art gallery. The first page lists all the
artists that your gallery represents. When a user selects an artist, a page that lists all the works
by that artist appears. When the user then selects a work of art, a page that contains details
about that piece of art appears. In this example, your application contains the following pages:
■ A master page that lists the artists
■ A master/detail page in which the master page lists the works of art by the artist selected
on the List of Artists master page, and a detail page that contains details about the artwork
selected on the Artwork master page.
You may find it helpful to draw a diagram of the tables and fields that you want to include in
your application, including which ones to display in your application, as the following figure
shows:
ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard 81
Page 82

Starting the ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard
To start the ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard:
1. Configure your RDS servers. For more information, see “Configuring RDS” on page 76.
2. In Flex Builder, select File > New > Other.
3. Under ColdFusion Wizards, select ColdFusion/Flex Application Wizard, and then click
Next.
4. After reading the introductory text, click Next.
5. To load the settings from an application you previously created using the ColdFusion/Flex
Appliation wizard, select the configuration file, and then click Load ColdFusion/Flex
Application Wizard Settings.
6. Click Next.
7. Select the RDS server on which you want the application to reside.
8. Specify the data source to use. The data source is configured in the ColdFusion MX
Administrator.
Although you specify one default data source at this point, you can access data from other
data sources in your application.
9. Click Next.
Specifying form layout
The Form Layout dialog box lets you specify the pages to use in your application. You can
create master, detail, or master/detail pages. In your application, you can link master, detail,
and master/detail pages as follows:
Page type Can link to
master master
master/detail
detail
master and detail
master and master/detail
master/detail master
master/detail
82 Using the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
Page 83

To create a page:
1. Click the plus sign (+).
2. In the Name: text box, enter the name for the page.
3. Select the page type (master, detail, or master/detail).
4. Click Edit Master Form or Edit Detail Form, depending on the type of form you are
creating.
The Visual Query Builder starts.
5. Use Visual Query Builder to specify the data source, tables, and fields to include in the
form, and then click Save to save the query. For more information about using Visual
Query Builder, see “Using Visual Query Builder” on page 79.
6. Repeat steps 1 through 5 for each form in your application.
7. Use the right and left arrows to specify the relationship of the forms in your application.
For example, detail forms should appear indented, directly under the related master form
in the Navigation Tree panel. You drag and drop items to move them in the tree structure.
8. Click Next.
The Project information page appears.
9. Specify the following:
■ Whether to include a login page in the application
■ The location of the services-config.xml configuration file that the project should use
■ The web root URL
■ Whether to use an existing or new Flex Builder project
■ The project name and the location of the project if it is new
10. Click Finish.
The ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard creates the ColdFusion and Flex files that comprise
your application. You can test the application by clicking the Run Main button in Flex
Builder or by browsing to the main application page, which is located at http://
<server_name>:<port_number>/<project_name>/bin/main.html . You can also manually
modify the application files as appropriate for your needs.
ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard 83
Page 84

Tips for creating applications with the ColdFusion/ Flex Application wizard
Although the ColdFusion/Flex Application wizard greatly simplifies creating CRUD
applications, you should keep the following in mind to ensure that you create the application
that you designed.
■ To adjust UI elements, open the MXML file in Flex Builder design mode.
■ When you create a project that has the same name as a project you previously created, the
wizard creates a backup folder that contains the files from the project you previously
created.
■ If you create a master page and a detail page for a table in which there is no primary key
defined, the wizard selects the first field in the database as the key value to represent the
row.
■ In master pages, link a field to the Parameters box to add type validation to the query by
using the
■ You must select a primary key column in the master form; the wizard chooses the key by
default. If you create a master page and do not link it to the id property, you cannot add it
to the site tree under another master page.
■ Deselect the Display column for fields that your application uses that you do not want to
appear in your application.
■ Specify the sort order for the field by which to sort data in the page, and specify any other
conditions as appropriate.
■ Change the labels for fields by clicking the field name in the Label column, and then
entering a new field name.
■ In a detail page, create a combo box that is populated by dynamic data. To do this, change
the value in the Input Control column for the field to use to populate the combo box to
be ComboBox, click the Input Lookup Query (sub-select) column in that field, and then
use the Visual Query Builder to specify the data to use.
■ When you create a detail page, display of the primary key is disabled automatically.
■ When you create a detail page, input controls are assigned by default. You can change
them from the default values, which appear as follows:
■ Boolean and bit values appears as a check box.
■ Memo and CLOB values appear as a text area.
■ Everything else appears as a text input control.
cfqueryparam tag. Doing this is optional.
84 Using the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
Page 85

ActionScript to CFC wizard
The ActionScript to CFC wizard lets you create a ColdFusion component (CFC) based on an
ActionScript class file.
To use the ActionScript to CFC wizard:
1. In Flex Builder, go to the Project Navigator.
2. Right-click an ActionScript class file.
3. Select ColdFusion Wizards > Create CFC.
4. Enter the location of the CFC file in the Save to Project Folder text box, or click Browse
and select the location.
5. Enter the filename of the CFC in the CFC Filename text box.
6. To replace an existing file, select Overwrite file.
7. To create get and set methods in the CFC, in addition to property definitions, select
Generate Get/Set Methods.
8. To specify the property scope, select public or private.
9. Click Finish.
CFC to ActionScript wizard
The CFC to ActionScript wizard lets you create an ActionScript file based on a ColdFusion
component (CFC) Value Object.
To use the CFC to ActionScript wizard:
1. In Flex Builder, go to the Project Navigator.
2. Right-click a CFC Value Object file.
3. Select ColdFusion Wizards > Create AS Class.
4. Enter the location of the ActionScript file in the Save to Project Folder text box, or click
Browse and select the location.
5. Enter the class package in the AS Class Package text box.
6. Enter the filename of the ActionScript class file in the AS Class Name text box.
7. To replace an existing file, select Overwrite file.
8. Enter the path to the CFC in the Path to CFC text box.
9. To create get and set methods in the ActionScript Class file, select Generate Get/Set Methods.
10. Click Finish.
CFC to ActionScript wizard 85
Page 86

RDS CRUD wizard
The Remote Development Services (RDS) CRUD Wizard lets you dynamically create a
ColdFusion component (CFC) based on a table that is registered in the ColdFusion
Administrator on a ColdFusion server. To use the RDS CRUD wizard, you must have the
Eclipse RDS Support plug-in installed. (The Eclipse RDS Support plug-in is installed when
you install the ColdFusion wizards.)
The RDS CRUD Wizard lets you create the following types of CFCs:
■ ActiveRecord style CRUD CFC, which includes all of the properties, get and set methods,
and SQL methods in one CFC. The CFC includes the following methods:
init() or init(primary key value)
load(primary key value)
save()
delete()
■ Bean/DAO style CRUD CFCs, which creates two related CFCs:
■ A Bean CFC, also called a Value Object, which contains the property definitions and
get and set methods.
■ The DAO CFC, which contains the following methods:
read(primary key value)
create(cfc instance)
update(cfc instance)
delete(cfc instance)
■ Data Service assembler CFC, which includes a Bean (also referred to as a Value Object), a
DAO CFC, and an assembler CFC. The assembler CFC is required to take advantage of
the Flex Data Services feature
To use the RDS CRUD wizard:
1. In Flex Builder, go to the RDS Dataview by doing the following:
a. Select Window > Show View > Other.
b. Select RDS.
c. Select RDS Dataview.
2. Right click a table name.
3. Select ColdFusion Wizards > Create CFC.
4. Enter the project folder where you want to save the CFC in the CFC Folder text box.
5. Enter the CFC package in the CFC Package Name text box.
86 Using the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
Page 87

6. (Optional) Select the Primary Key column if a primary key is not defined in the database.
7. (Optional) To specify the primary key column in addition to the other values specified in
the CFC, select the Primary Key is Controlled by the User option. If the primary key is
automatically generated by the database (the identity field), do not select this option.
8. To replace existing files, select the Overwrite Files If They Already Exist option.
9. Select one of the following CFC Types:
■ Active Record CFC
■ Bean CFC & DAO CFC
■ Flex Data Service Assembler CFCs
10. Enter the names of the CFCs in the appropriate text boxes.
11. To create an ActionScript Value Object:
a. Select the Create an ActionScript Value Object in Addition to the CFCs option.
b. Enter the location for the ActionScript Value Object in the AS Folder text box, or click
Browse to browse to the location.
c. To create get and set methods in the ActionScript Class file, select Generate Get/Set
Methods.
12. Click Finish.
Services Browser
The ColdFusion Services Browser lets you view all of the CFCs and web services on your
computer.
To use the Services Browser:
1. In Flex Builder, select Window > Show View > Other.
2. Select ColdFusion > Services Browser.
The Services Browser can do the following:
■ Browsing components
■ Managing web services
Services Browser 87
Page 88

Browsing components
The Service Browser lists the following components:
■ Components that the ColdFusion component browser lists
The ColdFusion component browser is located at cf_root/wwwroot/CFIDE/
componentutils/componentdoc.cfm.
■ Components that are located in any directories specified in the ColdFusion MX
Administrator Mappings page
■ Components that are located in any directories specified in the ColdFusion MX
Administrator Custom Tag paths page
You can restrict the list of CFCs according to whether the functions in a CFC are remote,
public, or private.
A sample element of the list appears as follows:
The first line of the listing contains the path. The second line includes the name of the CFC.
The next two lines contain the names of the functions in the CFC. The function name is
followed by any argument, a colon, then the type of the return value. The listing
echo(echoString):STRING indicates that the
echoString, and that it returns a string. The myCFC CFC appears as follows:
<cfcomponent>
<cffunction name="echo" output="No" returntype="string">
<cfargument name="echoString" required="Yes">
<cfreturn "echo: #arguments[1]#">
</cffunction>
echo function has an argument named
<cffunction name="getArtists" returntype="query" hint="query the database
and return the results.">
<cfquery name="artists" datasource="cfcodeexplorer">
select *
from artists
</cfquery>
<cfreturn artists>
</cffunction>
</cfcomponent>
88 Using the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
Page 89

Managing web services
The Services Browser lets you manage a list of web services by adding or deleting WSDL
URLs from a list. In addition, when you are editing a ColdFusion file, you can use the
Services Browser to generate CFML code to invoke a web service or to create a web service
object. Similarly, when you are editing an ActionScript file, you can use the Services Browser
to generate ActionScript.
To view the list of web services, click the Show Web Services button in the top right corner of
the Services Browser view.
To add a web service to the list:
1. Right-click in the Services Browser view.
2. Select Add WSDL.
3. Enter a valid WSDL URL.
4. Click OK.
To delete a web service from the list:
1. Right-click in the Services Browser view.
2. Select Delete WSDL.
To invoke a web service in ColdFusion:
1. Place your mouse pointer where you want to insert the code.
2. View the list of web services.
3. Highlight a web service or a method in a web service and right-click.
4. Select Insert CFInvoke.
The code that the Service Browser generates appears in the ColdFusion file. The following is
an example of the code that the Service Browser generates:
<cfinvoke
webservice="http://arcweb.esri.com/services/v2/MapImage.wsdl"
method="convertMapCoordToPixelCoord"
returnVariable="convertMapCoordToPixelCoord" >
<cfinvokeargument name="mapCoord" type="" />
<cfinvokeargument name="viewExtent" type="" />
<cfinvokeargument name="mapImageSize" type="" />
</cfinvoke>
Services Browser 89
Page 90

To create a web service object in ColdFusion:
1. Place your mouse pointer where you want to insert the code.
2. View the list of web services.
3. Highlight a web service or a method in a web service and right-click.
4. Select Insert CFInvoke.
The code that the Service Browser generates appears in the ColdFusion file. The following is
an example of the code that the Service Browser generates:
createObject("webservice", "http://arcweb.esri.com/services/v2/
MapImage.wsdl").convertMapCoordToPixelCoord(mapCoord, viewExtent,
mapImageSize);
90 Using the ColdFusion Extensions for Flex Builder
 Loading...
Loading...