Page 1

Using
ADOBE® ROBOHELP® SERVER 9
Page 2

Copyright
© 2011 Adobe Systems Incorporated and its licensors. All rights reserved.
Using Adobe® RoboHelp® Server 9 for Windows®
This user guide is protected under copyright law, furnished for informational use only, is subject to change without notice, and should not be construed as a
commitment by Adobe Systems Incorporated. Adobe Systems Incorporated assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies that may appear
in the informational content contained in this guide.
This user guide is licensed for use under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 3.0 License. This License allows users to copy,
distribute, and transmit the user guide for noncommercial purposes only so long as (1) proper attribution to Adobe is given as the owner of the user guide; and
(2) any reuse or distribution of the user guide contains a notice that use of the user guide is governed by these terms. The best way to provide notice is to include
the following link. To view a copy of this license, visit
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/us/
Adobe, the Adobe logo, Adobe AIR, AIR, FlashHelp, and RoboHelp are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United
States and/or other countries.
Java and Oracle are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Linux is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other
countries. Macintosh is a trademark of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. Microsoft, Windows, and Windows Server are either registered
trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. Pentium is a trademark of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and
other countries. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the US and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of their respective
owners.
Updated Information/Additional Third Party Code Information available at http://www.adobe.com/go/thirdparty.
Portions include software under the following terms:
This product includes software developed by the Apache Software Foundation (http://www.apache.org/).
MPEG Layer-3 audio compression technology licensed by Fraunhofer IIS and THOMSON multimedia (http://www.iis.fhg.de/amm).
Portions utilize code licensed from Nellymoser (www.nellymoser.com)
Adobe Flash Player 10 video compression and decompression is powered by On2 TrueMotion video technology. © 1992-2005 On2 Technologies, Inc. All Rights
http://www.on2.com.
Reserved.
This product contains either BSAFE and/or TIPEM software by RSA Data Security, Inc.
Sorenson Spark™ video compression and decompression technology licensed from Sorenson Media, Inc.
Adobe Systems Incorporated, 345 Park Avenue, San Jose, California 95110, USA.
Notice to U.S. government end users. The software and documentation are ”Commercial Items,” as that term is defined at 48 C.F.R. §2.101, consisting of
”Commercial Computer Software” and ”Commercial Computer Software Documentation,” as such terms are used in 48 C.F.R. §12.212 or 48 C.F.R. §227.7202,
as applicable. Consistent with 48 C.F.R. §12.212 or 48 C.F.R. §§227.7202-1 through 227.7202-4, as applicable, the Commercial Computer Software and
Commercial Computer Software Documentation are being licensed to U.S. Government end users (a) only as Commercial items and (b) with only those rights
as are granted to all other end users pursuant to the terms and conditions herein. Unpublished rights reserved under the copyright laws of the United States. For
U.S. Government End Users, Adobe agrees to comply with all applicable equal opportunity laws including, if appropriate, the provisions of Executive Order
11246, as amended, Section 402 of the Vietnam Era Veterans Readjustment Assistance Act of 1974 (38 USC 4212), and Section 503 of the Rehabilitation Act of
1973, as amended, and the regulations at 41 CFR Parts 60-1 through 60-60, 60-250, and 60-741. The affirmative action clause and regulations contained in the
preceding sentence shall be incorporated by reference.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1: Getting started
About RoboHelp Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Activation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Help and support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Top new features/enhancements in Adobe RoboHelp Server 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
System requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Configuration Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Set up RoboHelp Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Publish from RoboHelp HTML . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Chapter 2: Administering the server
Administrator and end user tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Web Administrator tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
iii
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 4
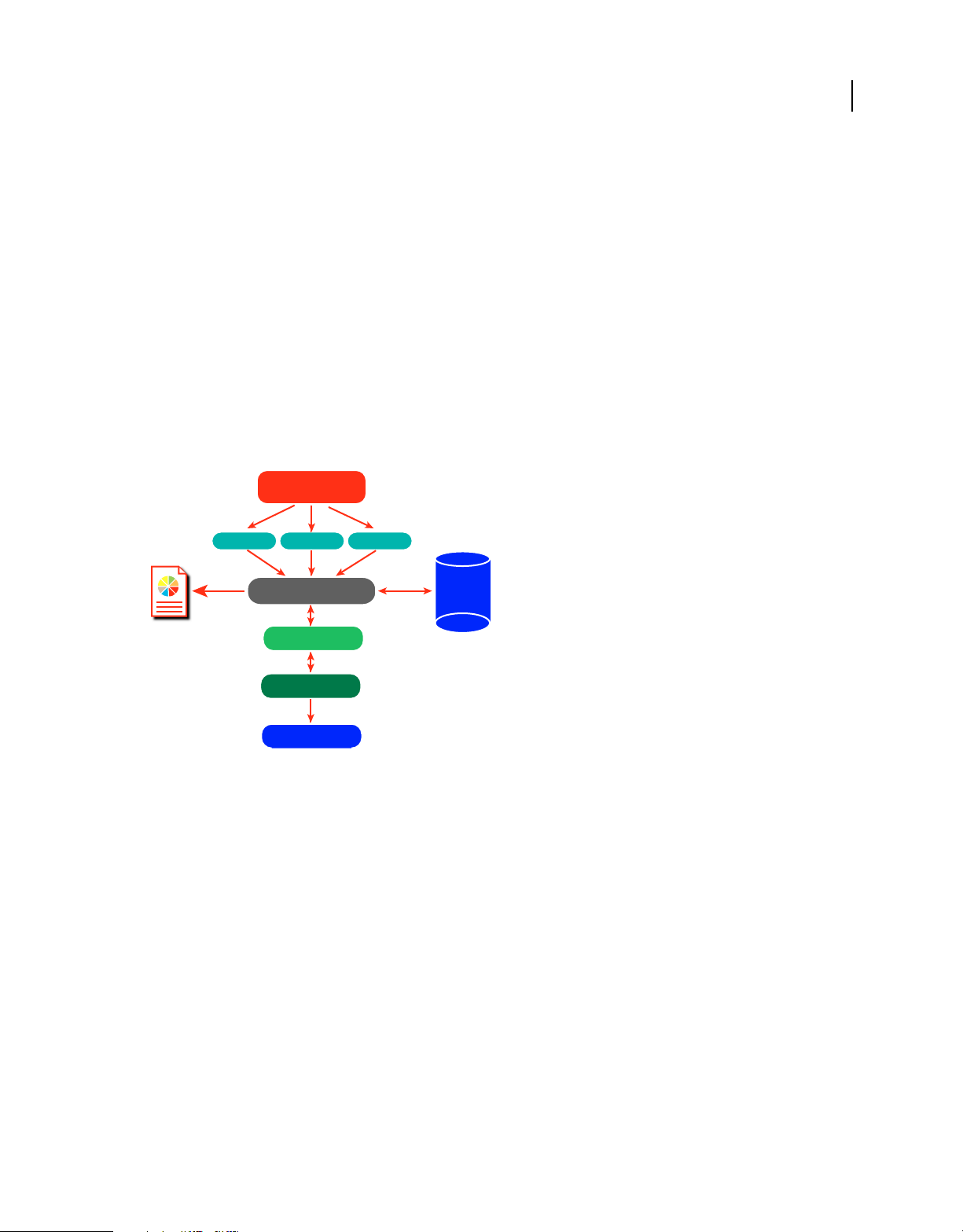
Chapter 1: Getting started
About RoboHelp Server
Adobe® RoboHelp® Server is a server-based Help solution that provides real-time end-user feedback on your Help and
knowledgebases. RoboHelp Server gathers and logs data about what questions users ask while searching content and
how users navigate through topics. Results are displayed in an easy-to-view graphical format for quick interpretation.
Your Help system resides on a server (for example, Adobe Help Resource Center), and you can make instant updates
to your Help system content.
RoboHelp Server contains the back-end processes, database functionality, and ODBC connections necessary to
integrate it. RoboHelp Server works with the authoring tool, so authors can edit content, set master project options,
maintain windows, and view reports.
Authoring Tool
RoboHelp HTML
Project A Project B Project C
1
Database
RoboHelp Server
Reports
RoboHelp Server interaction with different components
Servlet Container
Apache Tomcat
Web Server
IIS / Apache HTTP Server
Users
MS Access
Oracle
MS SQL Server
Note: With RoboHelp Server, you can install your database server on a separate machine or use any of the existing
database servers.
Tracking and reporting
Adobe RoboHelp Server provides end users with the ability to find information when they have questions. Users can
view content using any standard browser and operating system. Any number of users can access the published
documents.
Note: You can define the maximum number of database connections for Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server database
management systems through the
maxload property in the robohelp_server.properties file.
RoboHelp Server tracks the following types of data:
• Where users request assistance: Identifies the location where users make repeated requests for specific information.
• How users search: Searches that users perform repeatedly. This data can be mined to move frequently searched
information to a more prominent position in the content for easier access. You can also use this information to find
information gaps and to improve heading titles for more intuitive navigation.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 5

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
• How users navigate online content: Tracks how users seek information in online content and how frequently they
access particular information such as headings and articles. This information is available at a topic level.
• RoboHelp Server tracks all the operating system and browser details. You can use this information to improve the
content quality for browsers preferred by users.
Automatic project merging
Concurrently work on multiple projects and merge them into the project at run time.
While building an online information system, authors can develop and publish their content according to their own
schedules. RoboHelp Server provides automatic project merging, so authors can work on different parts of a project at
the same time, and publish them to the same server. When end users view the content, they see one seamless online
information system. Do not worry about sharing source or depending on a single author or project—all the separate
projects are merged when users access the content. Users can navigate across all the projects using the Index, Contents,
and Search buttons.
By default, the projects are added to the Table of Contents in the order they are published to the server. You can
customize this order in the Projects page of the Web Admin interface. When you merge projects, each project file in
the authoring tool remains intact, but the keywords from the indexes and glossary terms are combined at run time, or
when end users access the system from the server.
2
Support for languages other than English
The runtime interface (including Table of Contents, index, glossary, and search) can be automatically localized, and
authors can publish projects written in various languages to the same server. You can change the display text on the
user interface of the online system to another language, including text on the Contents, Index, and Search buttons.
In addition, end users can perform a full-text search of online content in their native language. This flexibility allows
authors to develop content in languages other than English and take advantage of server-based online information
systems.
Resources
Before you begin working with your software, take a few moments to read an overview of activation and the many
resources available to you. You have access to instructional videos, plug-ins, templates, user communities, seminars,
tutorials, RSS feeds, and much more.
Activation
To review complete system requirements and recommendations for your Adobe® RoboHelp® Server 9 software, see the
ReadMe file on the installation disc.
Help with installation
For help with installation issues, see the Installation Support Center at www.adobe.com/support/robohelp/.
Register
Register your product to receive complimentary installation support, notifications of updates, and other services.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 6

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
Note: Register only once for RoboHelp Server 9.
❖ To register, follow the onscreen instructions in the Registration dialog box, which appears after you install the
software.
ReadMe
A ReadMe file for your software is available online and on the installation disc. Open the file to read important
information about topics such as the following:
• System requirements
• Installation (including removing the software)
• Activation and registration
• Font installation
• Troubleshooting
• Customer support
• Legal notices
3
Help and support
Community Help
Community Help is an integrated environment on Adobe.com that gives you access to community-generated content
moderated by Adobe and industry experts. Comments from users help guide you to an answer. Search Community
Help to find the best content on the Web about Adobe products and technologies, including these resources:
• Videos, tutorials, tips and techniques, blogs, articles, and examples for designers and developers.
• Complete online Help, which is updated regularly and is more complete than the Help delivered with your product.
If you are connected to the Internet when you access Help, you automatically see the latest online Help rather than
the set delivered with your product.
• All other content on Adobe.com, including knowledgebase articles, downloads and updates, Adobe® Developer
Connection, and more.
Use the Help search field in your product’s user interface to access Community Help. You can search for content
within the Adobe.com site and also in websites that have useful information about your product. Moderators continue
to identify most relevant Web content for your product. You can add comments to online Help and view comments
added by other users. For a video of Community Help, see
Other resources
Online Help also includes a link to the complete, updated PDF version of Help.
Visit the Adobe Support website at www.adobe.com/support to learn about free and paid technical support options.
www.adobe.com/go/learn_community_help_en.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 7

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
Top new features/enhancements in Adobe RoboHelp Server 9
User interface enhancements
RoboHelp Server 9 features a fresh, aesthetically-appealing user interface.
Enhanced platform support
• Support for Microsoft Access 2010
• Support for Apache Tomcat 7.x. Tomcat 7.x is currently in the beta stage.
Technical enhancements
• RoboHelp Server logs are now created in a consolidated log file (robohelpserver.log) under the
<Tomcat
This new log file is generated using the Apache log4j logging framework.
Home>/logs folder. All RoboHelp Server-related exceptions and warnings are logged in this file.
If you want to tweak the size, backup limit, or format of the logs, modify the value of the relevant properties in the
<RoboHelp Server Home>/Web-INF/classes/log4j.properties file.
4
• You can now host RoboHelp Server over HTTP Secure (HTTPS) to ensure secure communications between the
server and clients.
• Authors can publish their RoboHelp HTML projects using HTTPS
• End users can view projects on the server over HTTPS
• The RoboHelp Server Web Administrator and reports can be viewed over HTTPS as well
Moderation settings for Adobe AIR Help comments
Using the Web Administrator, you can now specify the following moderation settings for comments on Adobe® AIR®
Help output:
• Allow Post Anonymous
• Mark Comments As Pending
Search-related enhancements
RoboHelp Server 9 features many search-related enhancements:
Project stop list for server-side indexing Unlike RoboHelp 8, the stop list specified in a RoboHelp HTML project is
now used for server-side indexing.
Project synonym list for server-side indexing Unlike RoboHelp 8, the synonym list specified in a RoboHelp HTML
project is now used for server-side indexing.
Synonym highlighting Synonyms for a keyword being searched for are highlighted in the search result list. This
enhancement is available only for WebHelp Pro output published using RoboHelp HTML 9.
Dynamic context in search results for server-side indexing RoboHelp Server now displays dynamic context along with
search results. Apache Lucene, the text search engine library powering search in RoboHelp Server, displays the relevant
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 8

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
words around a keyword as context in the search result list. This feature is available only for WebHelp Pro and
FlashHelp Pro projects published to RoboHelp Server with server-side indexing enabled.
• For keywords within topics, words in the immediate vicinity of the keyword in the topic are displayed as context.
• The static context of the topic is displayed for user-specified keywords. The first few words of the topic comprise
static context.
• In the case of external resources for keywords, the URL description of the external resource is displayed as the
dynamic context.
Note: For WebHelp Pro projects, dynamic context is displayed beneath a topic in the search result list, with the
relevant matched text highlighted in bold. For FlashHelp Pro projects, dynamic context is displayed as a tooltip when
the user hovers the mouse pointer over any topic in the search result list.
Reporting enhancements
RoboHelp 9 delivers several reporting improvements that will help you better optimize the value of your Help content:
• Functionality to filter reports by area
• New, intuitive names for the reports
• Improvements to the graphical representation of reports
• Functionality to export report data to the CSV format
• Flexibility to customize reports by showing/hiding columns. Column layouts can be saved across sessions.
• Fine-tuned numerical data in reports
5
Configuration Manager enhancements
You can now perform the following additional tasks using the RoboHelp Server Configuration Manager:
• Migrate context data from RoboHelp Server 8 to RoboHelp Server 9
• Deploy a context in the root context
• Delete contexts
• Set up an admin account for RoboHelp Server using LDAP authentication or database authentication
• Configure LDAP settings
• Configure search indexing settings
The little things
• The Web Administrator now provides functionalities to edit and delete users. Only RoboHelp Server
administrators are allowed to edit or delete users.
Note: These functionalities are particularly useful for setting a new password if a user has lost or forgotten the earlier
password.
• New Sign Out link in the Web Administrator
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 9

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
System requirements
Hardware requirements
• Intel Pentium 4+ or compatible processor
• 256 MB of RAM (512 MB is recommended)
• 300 MB of hard-disk space; additional free hard-disk space may be needed during installation
Note: RoboHelp Server installation is not supported on flash storage devices.
Supported operating systems
RoboHelp Server (32-bit and 64-bit) is supported on the following versions of Microsoft Windows® operating system:
• Windows Server 2003 SP2
• Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit only)
• Windows Server 2008 SP2
• Windows XP SP3
• Windows 7
6
Prerequisites for installing RoboHelp Server 9
• Java™ Development Kit (JDK) 6 or later
• Apache Tomcat 6.0.14 or later
Note: RoboHelp Server requires Apache Tomcat to run. Tomcat is a servlet container that can also work as a Web server.
Supported browsers
• For Microsoft® Windows® operating systems, the supported browsers are Microsoft Internet Explorer 6, 7, 8, and
Firefox 3.x.
• For Macintosh® operating systems, the supported browsers are Firefox 3.x and Safari 3.x.
• For Linux® or UNIX® operating systems, the supported browser is Firefox 3.x.
Supported database management systems
You can use the built-in database or select an external database (Microsoft SQL Server, SQL Server Express Edition, or
Oracle 9i or higher) to store reports and authentication information for RoboHelp Server. The following database
management systems are supported:
• Microsoft Access 2003, 2007, and 2010 (built-in)
• Oracle 9i, 10g, and 11g
• SQL Server 2005 Express Edition
• SQL Server 2005 and 2008
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 10
USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
Supported databases
RoboHelp Server connects to Microsoft Access, Oracle (9i or higher), SQL Server, or Microsoft SQL Server Express
Edition database management systems.
Microsoft Access Applications Microsoft Access seamlessly integrates with tools like Excel and Word. Microsoft
Access stores information using the Jet database server. It uses a file server model of computing in which all logic is
with the client application.
Note: You can use the Microsoft Access database for internal purposes as it does not support multi-threading.
Microsoft SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database management system capable of handling large
amounts of data and many concurrent users. When a client application requests data, the server retrieves or updates
the data. SQL Server can roll back transactions. It does not commit a partially entered record to the database.
Oracle The Oracle database management system provides for the definition, storage, and management of data in a
centralized area. It supports client-server environments, large databases, space management, concurrent database
users, high transaction-processing performance, openness, compliance with industry standards, manageable security,
portability, compatibility, and connectivity.
Microsoft SQL Server Express Edition Microsoft SQL Server Express Edition is a relational database management
system (RDBMS) produced by Microsoft. Its primary query languages are MS-SQL and T-SQL.
7
Install a database management system
To install a supported database management system, refer to the relevant documentation for your architecture (32-bit
or 64-bit):
DBMS 32-bit installation instructions 64-bit installation instructions
Oracle 9i Oracle documentation Oracle documentation
Oracle 10g Oracle documentation Oracle documentation
Oracle 11g Oracle documentation Oracle documentation
Microsoft SQL Server 2005
Edition
Express
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Microsoft documentation
Microsoft SQL Server 2008* Microsoft documentation
Microsoft Access 2003, 2007, or 2010 Built-in for RoboHelp Server
Note: The RoboHelp Server installer installs either 32-bit or 64-bit Microsoft Access runtime on your system, as
appropriate. However, if 32-bit Microsoft Office is already installed on your system, the installer does not install 64-bit
Access runtime. Therefore, if you want to install 64-bit RoboHelp Server, ensure that 32-bit Office or Access is not preinstalled on your system.
Note: If you’re installing RoboHelp Server 9 on Windows Server 2008, then you won’t be able to configure RoboHelp
Server with 64-bit SQL Server 2005 or SQL Server 2008. These combinations are unsupported due to a limitation of the
JDBC-ODBC bridge bundled with the default JDK.
Instructions and ReadMe (Microsoft)
Recommended OS/database combinations
For a table of recommended OS/database combinations on which you can install RoboHelp Server 9, refer to this
knowledgebase article.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 11

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
Supported Web servers
Optionally, you can configure Tomcat with an external Web server. Using an external Web server offers ease and
flexibility while configuring settings, such as proxy server and filtering rules.
RoboHelp Server supports the following Web servers in combination with Tomcat:
• Apache HTTP Server 2.2 or later
• Microsoft® IIS 6.0 or 7.0
Other requirements
To review the complete system requirements and recommendations for your RoboHelp Server software, see the
ReadMe file on the installation disc.
Installation
Installation overview
Installing RoboHelp Server involves the following broad steps:
8
1 Close any other Adobe applications open on your computer.
2 Install Tomcat as a Windows service.
3 You cannot install RoboHelp Server 8 and RoboHelp Server 9 together on the same system. Therefore, uninstall
RoboHelp Server 8 before installing RoboHelp Server 9. However, if you want to migrate data from RoboHelp
Server 8 to RoboHelp Server 9, ensure that you back up the following files in the
[RHS installation directory]/web-inf folder before uninstalling RoboHelp Server 8:
• robohelp_general_prop.properties
• robohelp_rh_areas.xml
• robohelp_server.properties
• robohelp_settings.properties
After RoboHelp Server 8 uninstallation is complete, copy these files to their original location.
4 (Optional) Install a supported database system.
5 Insert the installation disc into your hard drive and run the installer for your architecture (32-bit or 64-bit). Follow
the onscreen instructions.
6 If prompted, select the server.xml file for the Tomcat servlet container installed on your system.
7 Start the RoboHelp Server Configuration Manager (Start > All Programs > Adobe > Adobe RoboHelp Server 9 >
Configuration Manager) and perform the required tasks.
Note: For more information, see the ReadMe file on the installation disc.
Install Tomcat
Note: The steps in this section apply to Tomcat 6.0.14. If you want to install a later version of Tomcat, follow the
instructions at this
1 Download and install JDK 6 or later from this page.
Apache documentation page.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 12

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
2 Download the Windows service installer for Tomcat 6.0.14 (apache-tomcat-6.0.14.exe) from this page.
3 Run the Tomcat installer you downloaded.
4 If necessary, in <tomcat-install-folder>\conf\server.xml, change the port number to a desired port
number. By default, Tomcat installs on port 8080.
5 Change the minimum heap space allotted to the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) for Tomcat:
• Run the <tomcat-install-dir>/bin/tomcat6w.exe file.
• On the Java tab in the Apache Tomcat Properties dialog, specify 256 as the value for the Initial Memory Pool
and Maximum Memory Pool boxes.
6 Restart Tomcat. To do so, on the General tab in the Apache Tomcat Properties dialog, click Stop and then click
Start.
Configure Tomcat and RoboHelp Server
1 Perform one of the following tasks:
• At the Run prompt, enter services.msc. From the Windows services dialog box, you can start, stop, or restart
the Tomcat 6.0 service.
• Double-click the Apache Tomcat icon from the status bar and click Start in the Apache Tomcat Properties
dialog box. The Tomcat service starts running.
• Open the <tomcat-install-dir>/bin folder and double-click tomcat6w.exe to start Tomcat. You can start,
stop, or restart the Tomcat service from the Tomcat Configuration dialog box.
2 To verify that the Tomcat server is running, open the Tomcat home page in the browser window. To do so, enter
http://<server-name>:<port-num> in the address bar of the browser window.
Note: By default, Tomcat installs on port 8080.
9
If you see the Tomcat home page, Tomcat is running. To resolve any issues, you can view the Tomcat logs at
<tomcat-install-dir>/logs.
3 (Optional) Configure the database using the Configuration Manager, or select the option to use the built-in
database. See
4 Verify that RoboHelp Server is running by opening the admin link in the browser window. Log in to the server at
http://<servername:port>/robohelp/admin using the default user ID (admin) and password (admin).
5 Using the default user ID admin and the default password admin, publish projects to RoboHelp Server from
“Configure a database” on page 15.
RoboHelp.
Note: Using the Configuration Manager is the recommended way of changing the default user ID and password.
However, you can also change the default credentials by editing the
<server-install-folder>/WEB-INF folder. To do so, change the DefAdminUid and DefAdminPwd properties in
robohelp_server.properties file in the
this file and restart Tomcat.
As an administrator, you can create users and assign them various rights (Publishing, Report viewing, and Admin
rights) for the server.
6 To view projects, open the browser and type in the address bar:
http://<machine-name>:<portname>/robohelp/server?prj=<projectname>
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 13

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
Test the server
❖ Open http://<RoboHelp Server>:port/robohelp/admin in a Web browser and verify that you can log in using the
default user ID and password combination (
admin and admin).
(Optional) Configure Tomcat with an external Web server
Configuring Tomcat with an external Web server is optional. However, using an external Web server offers ease and
flexibility while configuring settings, such as proxy and filtering rules.
Install and configure Apache HTTP Server and Tomcat
Install Apache HTTP Server
1 Download the Windows binary distribution (.msi file) from http://www.devlib.org/apache/httpd/binaries/win32/.
2 Run the MSI file that you downloaded.
3
By default, the Apache HTTP Server is installed on port 80. If some other server is using port 80, you must change the
port on which Apache listens for requests in the
directive
4 Ensure that the Apache HTTP server is working correctly. To do so, enter the URL for the Apache server
http://<hostname>:<port-number>) in a Web browser. The server should display a page in the browser that
(
Listen in the configuration file and change the port number by changing this directive to <new-port-num>.
says, “It Works!”.
<apache httpd install>\conf\httpd.conf file. Search for the
10
Download sample workers.properties
Download sample workers.properties from this page, place it in the <apache httpd install>\conf folder. Now,
modify the following variables:
• workers.tomcat_home: Set to the Tomcat installation directory.
• workers.java_home: Set to the JDK path.
Download the mod_jk module
1 Download the mod_jk module for Apache from http://tomcat.apache.org/download-connectors.cgi. This module
exists as mod_jk-apache-2.2.4.so.
2 Place the module in the <apache httpd install>\modules\ folder.
Modify the <apache httpd install>\conf\httpd.conf file
1 Add the mod_jk module by appending the following line of text to the <apache httpd
install>\conf\httpd.conf file:
LoadModule jk_module modules/mod_jk-apache-2.2.4.so
2 Using the JkMount command, add the context names that you want to direct to Tomcat:
JkMount /robohelp/* ajp13
JkMount /robohelp ajp13
Enable Apache auto-configure
1 In the server.xml for Tomcat (<tomcat install>\conf\server.xml), enable Apache auto-configure. Tomcat
automatically generates the files required for using
mod_jk with an Apache HTTPS Web server.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 14

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
<Engine>
......
<Host>
................
</Host>
<Listener className="org.apache.jk.config.ApacheConfig"
modJk=<apache-install-folder>\modules\<mod_jk_module>
workersConfig=<apache install folder>\conf\workers.properties />
</Engine>
modJK and workersConfig must have appropriate values. For example:
<Listener className="org.apache.jk.config.ApacheConfig"
modJk="C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Apache2.2\modules\mod_jk-apache-
2.2.4.so"
workersConfig="C:\Program Files\Apache Software
Foundation\Apache2.2\conf\workers.properties" />
2 Stop the Apache HTTP Web server if it is running.
3 Restart Tomcat. The <tomcat-install-folder>\conf\auto\mod_jk.conf file is generated. This file decides
which URLs Apache passes to Tomcat.
Note: In mod_jk.conf, Tomcat creates a <VirtualHost> XML tag whose argument is the name of the <Host> tag just
before the <Listener> (for modJK) tag in server.xml of Tomcat. Change the value of the name attribute of the <Host> tag
to the server name.
11
Include the auto-generated file in Apache’s httpd.conf file
Add "Include <tomcat-install-folder>\conf\auto\mod_jk.conf" at the start of the httpd.conf file.
Restart the Apache HTTP server
If the Apache HTTP server service does not start due to some error, do the following:
1 Run the command prompt.
2 Go to <apache-install-folder>\bin.
3 Run httpd.exe to check for errors.
Enable UTF-8 encoded URLs
Modify <tomcat-install-folder>\conf\server.xml and enable UTF-8 encoded URLs in all connector tags:
..............
<Connector port="9090" protocol="HTTP/1.1" connectionTimeout="20000" redirectPort="8443"
URIEncoding="UTF-8" />
............
<Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" URIEncoding="UTF-8" />
............
Set up Tomcat for HTTPS
1 At the command prompt, change to the [JAVA_HOME]/bin directory.
Note: The JAVA_HOME environment variable usually points to the Java installation directory.
2 Run the following command:
keytool -genkeypair -alias tomcat -keyalg RSA -keystore key1 -validity 30
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 15

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
A new keystore file is created in the home directory of the user who runs the command. To specify a different
location or file name, modify the command to add the
keystore file. You will also need to specify this new path in the
-keystore parameter followed by the complete path of the
server.xml configuration file, as described in Step 6.
3 Enter the keystore password.
4 Enter the appropriate values when prompted for your personal and organization information.
5 When prompted, enter the Tomcat key password.
6 Modify the server.xml file for your Tomcat server and add the following text, replacing the bolded text with
appropriate values for your system:
<Connector port=[port number] protocol="HTTP/1.1" SSLEnabled="true"
maxThreads="150" scheme="https" secure="true"
clientAuth="false"
strategy="ms"
address="${jboss.bind.address}"
keystoreFile="${jboss.server.home.dir}/conf/THE_KEYSTORE_NAME"
keystorePass="PASSWORD_FOR_THE_KEYSTORE"
truststoreFile="${jboss.server.home.dir}/conf/THE_KEYSTORE_NAME"
truststorePass="PASSWORD_FOR_THE_KEYSTORE"
sslProtocol="TLS"/>
7 Restart Tomcat.
12
Configure Apache for IPv6
1 To enable Apache to work with IPv6 addresses, download IPv6-enabled Apache from
http://win6.jp/Apache22/index.html, unzip it, and follow the instructions in README.v6.txt.
2 Open <apache httpd install>\conf\httpd.conf,and locate the Listen directive. Add the directive to make
Apache listen on all inbound IP v6 and v4 addresses on any identified port.
Listen 80
3 Modify the VirtualHost tag in <tomcat-install-folder>\conf\auto\mod_jk.conf to enable it to accept all
IP v6 and v4 requests by specifying the following:
<VirtualHost *:port no>
....
....
</VirtualHost>
Install and configure Microsoft IIS with Tomcat
1 Download isapi_redirect.dll from http://tomcat.apache.org/download-connectors.cgi.
2 Place isapi_redirect.dll in the $<tomcat_home>\bin\win32\i386 directory.
3 Download the sample workers.properties file from this URL, set the following variables in the file, and place it
in the $<tomcat_home>\conf directory:
workers.tomcat_home Set to the Tomcat installation directory
workers.java_home Set to the JDK path (JAVA_HOME)
4 Create a text file and save it as uriworkermap.properties in the $<tomcat_home>\conf directory. In this file,
specify the URLs to map to Tomcat. The following sample file contains an entry for the default RoboHelp Server
context, robohelp:
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 16

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
# URI patterns matching the criteria on the left (of the = sign) in the lines
# below are redirected to the workers specified on the right.
/robohelp/*=ajp13
/robohelp=ajp13
Create a similar entry in the uriworkermap.properties file for every RoboHelp Server context.
5 Launch the Windows Registry Editor. To do so, type regedit at the command prompt and press Enter.
6 In the registry, create a registry key named "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Apache Software
Foundation\Jakarta Isapi Redirector\1.0".
7 Add a string value with the name extension_uri and a value of /jakarta/isapi_redirect.dll.
8 Add a string value with the name log_file and a value pointing to where you want your log file to be (for example,
$<tomcat_home>\logs\isapi.log).
9 Add a string value with the name log_level and a value for your log level (debug, info, error, or emerg).
10 Add a string value with the name worker_file and a value that is the full path to your workers.properties file (for
example,
11 Add a string value with the name worker_mount_file and a value that is the full path to your
uriworkermap.properties file (for example,
12 Using the IIS management console, add a new virtual directory to your IIS website. The name of the virtual
directory must be jakarta. Its physical path is the directory where you placed the
example,
$<tomcat_home>\conf\workers.properties).
$<tomcat_home>\conf\uriworkermap.properties).
isapi_redirect.dll file (for
<tomcat_home>\bin\win32\i386). While creating this new virtual directory, assign it with execute
access.
13 Using the IIS management console, add isapi_redirect.dll as a filter in the IIS website. The name of the filter
reflects its task (for example,
$<tomcat_home>\bin\win32\i386\isapi_redirect.dll.
14 Restart IIS. Make sure that the jakarta filter is marked with a green up arrow.
jakarta), and its executable must be
13
Configuration Manager
The RoboHelp Server Configuration Manager enables you to perform the following actions:
• Manage contexts or multiple websites
• Configure a built-in or external database
• Set up an admin account for RoboHelp Server
• Configure LDAP settings
• Configure search indexing settings
• Migrate data from RoboHelp Server 8 to RoboHelp Server 9
You can create or open existing contexts using the Configuration Manager. The default User ID and password
required to connect to the server and the database are
connect to the Microsoft Access database.
Last updated 1/17/2011
admin and admin respectively. You do not need a password to
Page 17

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
Create contexts or multiple websites
You can host different Help systems by creating multiple contexts in Tomcat. Contexts refer to websites, where a
project can be published. You can configure different instances of RoboHelp Server (on a single installation) to run on
each of these contexts. These contexts run on the same IP address and port number but with different context names.
By default, RoboHelp Server creates a single context called robohelp. You can create another context using the
Configuration Manager.
Create a context using Configuration Manager
You can create contexts to publish projects from RoboHelp HTML.
1 Select Start > All Programs > Adobe > Adobe RoboHelp Server 9 > Configuration Manager.
2 Select File > New Context.
3 Do one of the following:
• If you want to deploy the new context in the root context, select Deploy In Root Context and enter a Directory Name.
Note: The root context is a special, empty context path. If an application is deployed in the root context, it listens
for requests on the
• Specify a new Context Name and Directory Name. For example, you can have robohelp2 as the new context
name and
rh2 as the directory name.
Note: To open an existing context, you can select File > Open Context.
http://<host-name>:<port-num> URL, instead of a sub-URL.
14
4 Click OK.
Note: After creating a context, Configuration Manager automatically starts the Tomcat service.
Important: The default User ID and password required to connect to the server are admin and admin respectively.
Update uriworkermap.properties for IIS
If you have configured Tomcat to run with IIS, update uriworkermap.properties to map the new context path to
ajp connector.
the
/robohelp/*=ajp13
/robohelp=ajp13
/robohelp2/*=ajp13
/robohelp2=ajp13
Note: With Tomcat configured with Apache, if you configure Tomcat to auto-generate the mapping file, mapping for new
context is automatically added to
<tomcat-path>\conf\auto\mod_jk.conf.
More Help topics
“Web Administrator tasks” on page 19
Delete a context
• Click File > Open Context.
• In the Open Context Settings dialog, select the context that you want to delete and click OK.
• In the main Configuration Manager window, click Delete. When prompted for confirmation, click Yes.
Note: When you delete a context, all project data associated with the context is deleted. However, the database associated
with the context is deleted only if it is a Microsoft Access database. For Microsoft SQL Server/SQL Server Express Edition
and Oracle, you need to manually delete the database.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 18

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
Configure a database
You can select the Microsoft Access database (built-in) or an external Oracle or Microsoft SQL Server/SQL Server
Express Edition database to store user feedback and troubleshoot any Help content issues.
Select a database and connect to it
You can use the Configuration Manager to select and configure a database.
❖ In the Configuration Manager window, select one of the following options:
• Built-in Database
• Oracle 9i Or Higher/Microsoft SQL Server/SQL Server Express Edition
If you selected Oracle 9i Or Higher/Microsoft SQL Server/SQL Server Express Edition, follow these steps:
1 Do one the following:
• Select an existing data source name (DSN) from the pop-up menu.
• If you want to create a new DSN, click ODBC Admin. For more information about creating a DSN, click the
Help button in the ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog box.
2 Enter the database user name and password.
3 Specify the Connection Pool Size. The Connection Pool Size determines the maximum number of concurrent
connections to the database.
4 Click Test Connection.
5 If the Test Connection is successful, a message appears. Click Save.
15
Set up an admin account for RoboHelp Server
1 Do one of the following:
• If you want to use database authentication for RoboHelp Server, leave the Configure LDAP option unselected.
Now, specify the user name and password for a new Admin account for the Web Administrator.
• If you want to use LDAP authentication for RoboHelp Server, follow these steps:
• Select Configure LDAP.
• Specify the necessary LDAP settings. See “Specify LDAP settings” on page 15.
• Specify an LDAP user name in the Default Administrator section. This user will be prompted for their LDAP
password when they attempt to log in to Web Administrator.
Note: For LDAP, you don’t need to enter the fully-qualified user name.
2 Close the Configuration Manager window. RoboHelp Server automatically restarts Tomcat.
Specify LDAP settings
If you want to use LDAP authentication for RoboHelp Server, specify the following settings in Configuration Manager:
LDAP Server URL The URL of your organization’s LDAP server.
Base Node For User Search The LDAP base node within which you want to find users. For example,
dc=company,dc=com.
Base Node For Group Search The LDAP base node within which you want to find groups. For example,
dc=company,dc=com.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 19

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
User ID Attribute Name The LDAP node attribute that determines the user ID.
GroupID Attribute Name The LDAP node attribute that determines the group name.
Group Member Attribute The attribute of the LDAP group node that determines the members of the group.
Specify search settings
You can select the following search options in Configuration Manager:
Reindex Documents At Server Lucene reindexes the published projects on RoboHelp Server. The index published with
the RoboHelp HTML project is ignored.
Substring Search Is Enabled For Client Index Enables substring search for client-side indexing on RoboHelp Server.
Substring search is enabled only for client-side indexing, since it is not supported for server-side indexing. For more
information about substring search, see “RoboHelp search basics” in Using RoboHelp HTML 9.
Migrate context data
You can migrate context data from RoboHelp Server 8 to RoboHelp Server 9 for one or more contexts. The following
data is migrated:
• Published RoboHelp HTML projects
• Information about areas
• Information about users and groups
• User/group permissions on areas
• Usage data and statistics for reports
Note: Usage data for RoboHelp HTML projects is migrated only if you choose to migrate the corresponding projects.
16
Important: Oracle and SQL Server databases are not replicated during migration. Instead, the schema for these
databases is updated, such that it becomes compatible with RoboHelp Server 9. Once the database schema has been
updated, the database can no longer be used with RoboHelp Server 8.
During migration, you can choose the contexts whose data you want to migrate to RoboHelp Server 9. For example,
you can choose to migrate data for production contexts while not migrating the data for transient/test contexts.
You can migrate data for only RoboHelp Server 8 contexts to RoboHelp Server 9. Migration from earlier RoboHelp
Server versions is not supported.
Important: As part of migration planning, evaluate if you want to migrate RoboHelp HTML projects to RoboHelp Server
9 or upgrade them from RoboHelp HTML 8 to RoboHelp HTML 9. Upgrading the projects lets you benefit from the new
authoring features in RoboHelp HTML 9.
Migrate data from RoboHelp Server 8 to RoboHelp Server 9
Important: Do not install RoboHelp Server 8 and RoboHelp Server 9 on the same machine. Uninstall RoboHelp Server 8
from the machine before installing RoboHelp Server 9. However, if you want to migrate context data from RoboHelp
Server 8, ensure that you don’t manually remove data from the RoboHelp Server directory after uninstallation.
1 In Configuration Manager, select File > Migrate Legacy Data.
2 Browse and select the RoboHelp Server 8 installation path. Specify a network path if RoboHelp Server 8 is installed
on a machine different from the machine on which you’re installing RoboHelp Server 9.
3 In the Contexts area, select one or more contexts to migrate.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 20

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
Note: The existing contexts in RoboHelp Server 9 are displayed in the Existing RoboHelp Server 9 Contexts box. If you
choose to migrate a context with the same name as an existing context, all data in the existing RoboHelp Server 9
context is overwritten.
4 Specify the following migration settings:
Migrate All Projects Migrate all RoboHelp HTML projects published to the selected RoboHelp Server 8 contexts.
Migrate Usage Data Migrate project usage data and statistics along with the projects.
Migrate All Users/Groups And Their Permissions Migrate information about users/groups and their permissions
from RoboHelp Server 8 to RoboHelp Server 9.
5 Click Start Migration.
Note: If the migration of one of more contexts fails, RoboHelp Server continues migrating the other contexts that you
selected in Step 3.
6 Review the Migration Log. When migration is complete, click OK.
7 If RoboHelp Server 8 is installed on a machine different from the machine on which you’re installing RoboHelp
Server 9, recreate the system DSN for Oracle or SQL Server database management systems. Refer to step 2 in
a database and connect to it” on page 15.
8 Close the Configuration Manager window. RoboHelp Server automatically restarts Tomcat.
“Select
17
Set up RoboHelp Server
After you install RoboHelp Server and the system or network administrator completes the configuration using
Configuration Manager, you can complete the following steps in RoboHelp HTML:
1 Open a project.
2 Create or edit a single source layout (specify FlashHelp® Pro or WebHelp Pro as the output type).
3 Assign the name or address of the server.
4 Publish the content.
More Help topics
“Configure Tomcat and RoboHelp Server” on page 9
Publish from RoboHelp HTML
Publish from RoboHelp HTML 7
1 Run the latest version of RoboHelp HTML 7. If you do not have this version, apply earlier patches for RoboHelp
HTML 7. For more information on patches for RoboHelp HTML 7, see
http://www.adobe.com/go/learn_rhs_RoboHelp_7_patch.
2 Go to the server tab of the properties dialog box of the WebHelp Pro or FlashHelp® Pro layout.
3 Create a server and specify the server name as <machine-url:port>/robohelp/server.
4 Enter the default user name and password (admin, admin).
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 21

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Getting started
5 Click OK to save the settings and generate the layout to publish to the server.
RoboHelp HTML 7 projects are published to the default area of RoboHelp Server 9.
Publish from RoboHelp HTML 8 and 9
1 Do one of the following:
• Double-click the WebHelp Pro or FlashHelp Pro layout in the Single Source Layouts pod.
• Right-click the WebHelp Pro or FlashHelp Pro layout in the Single Source Layouts pod and select Properties.
2 In the WebHelp Pro Publish dialog box, click Next to go to the server selection screen. Click New to create a
RoboHelp Server destination to publish projects.
3 To publish to the default context, enter the server name in the machine-url:port format. RoboHelp HTML
appends
4 To publish to a context other than robohelp, specify a complete URL in the format <server-name>:port/<context-
name>/server. For more information on creating contexts, see
5 Click the Refresh button to refresh the list of areas from the server. If you do not select an area, the project is
published at the default area. For more information on areas, see
/robohelp/server to it.
“Create contexts or multiple websites” on page 14.
“Managing areas” on page 22.
18
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 22

Chapter 2: Administering the server
Administrator and end user tasks
The Adobe® RoboHelp® Server software uses projects created in the Adobe RoboHelp HTML application and database
information to create end-user reports. It generates reports based on how end users navigate and use online Help
systems.
You can share these reports and analyze them to optimize the value of your content. In addition, RoboHelp Server
reports help you identify the key areas of your Help content that need to be updated/enhanced on priority.
End users can view the online content using a browser.
Use the authoring tool to create content, and publish output. You can use a web browser to view the content on the
RoboHelp server.
Server administrator tasks
• Configure the server or website.
• Install software and the Help site.
• Set user permissions.
• Provide the URL and Help site port number to the documentation manager.
19
Your tasks
• Give the CD to the server administrator.
• Obtain the server’s URL.
• Connect to the server from the authoring tool project.
• Publish the project from the authoring tool.
• Create protected areas on the server.
• Manage user groups.
• Assign permissions to the relevant groups.
• Test the system on the server.
• View reports and web administration.
• Work with a developer to call context-sensitive Help (if needed).
Web Administrator tasks
About the Web Administrator
The Web Administrator is a browser-based server interface. It lets administrators or documentation managers
maintain permissions for users without going through a network administrator. It enables you to maintain databases
by letting you delete old data from the Web Admin interface.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 23

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Administering the server
The Web Administrator is an Adobe Flash-based interface. Therefore, you can press the Space key as an alternative
to the mouse click.
Open the Web Administrator interface
1 Do one of the following in your browser:
• If RoboHelp Server is not installed on the same computer, use the Web Administrator URL:
http://[IP address or server name]/robohelp/admin/
• If RoboHelp Server is installed on the same computer, use this Web Administrator URL:
http://localhost:port number/robohelp/admin/
2 Enter the user name and the password as admin and admin respectively.
3 Click Sign in.
Note: You must have the Apache Tomcat server running before starting RoboHelp Server 9.
Enable user authentication
The Web Administrator interface enables you to segregate the Help content published on the server into protected and
public areas. Only authenticated users can view the content published in protected areas, but no authentication is
required to view content published in public areas.
20
Note: You do require authentication to publish content to public or protected areas.
By default, RoboHelp Server creates a public area, general. All the RoboHelp HTML 7 projects are published to the
general area only.
Important: You cannot make this area protected and it cannot be deleted.
To make an area protected, you can select the Protected area option in the Users page of the Web Admin interface.
You can define several sets of privilege groups and assign different rights to different users. These rights include view
only, publish, admin rights, and viewing reports. You can manage the groups and their privileges from RoboHelp
Server Web Admin pages. RoboHelp Server 9 provides user authentication through both database and LDAP.
Authenticate LDAP users
Important: The recommended way of configuring LDAP settings is through the Configuration Manager. See “Specify
LDAP settings” on page 15.
You can use the <context-name>_server.properties file to authenticate an LDAP user or an administrator. Do
the following:
• Comment the authtype = db property, specify your LDAP user name in the DefaultAdminUid property, and do
not specify your LDAP password in the
DefAdminPwd property.
• Uncomment and specify your organization LDAP details:
authtype = ldap
ldapURL = ldap://ldapserver:389
usersearchbase = ou=people,o=org
rolesearchbase = ou=groups,o=org
useridkey = uid
rolename = cn
rolesearch = uniqueMember
• Restart the Tomcat service to log in as an LDAP user.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 24

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Administering the server
The following table lists the properties stored in the <context-name>_server.properties file:
Property Name Description Property Value Required (Yes/No)
21
DatabaseType Specifies the database used
(supported types are oracle/access/sql)
DSN For Oracle or SQL Server database,
specifies the dsn used to connect to
database
authtype Specifies the authentication
mechanism used.
LDAP Server URL The URL of your organization’s LDAP
server
usersearchbase The LDAP base node within which you
want to find users. For example,
dc=company,dc=com.
rolesearchbase The LDAP base node within which you
want to find groups. For example,
dc=company,dc=com.
useridkey The LDAP node attribute that
determines the user ID.
rolename The LDAP node attribute that
determines the group name.
rolesearch The attribute of the LDAP group node
that determines the members of the
group
DefAdminUID When server is started for the first time,
server is not connected to the
database. Therefore, access
permissions for a given user cannot be
verified. Provide a default user ID
which has the admin rights and can
access the web admin.
oracle/access/sql (access by default) Yes
DSN name Required for Oracle and SQL databases
db/ldap Yes
If authtype is ldap
URL of LDAP Server of the organization If authtype is ldap
If authtype is ldap
user ID key If authtype is ldap
role name key If authtype is ldap
role attribute name If authtype is ldap
User ID which has admin access to
RoboHelp Server by default.
Yes
DefAdminPwd User ID which has admin access to
RoboHelp Server by default. For LDAP
authentication, password for the
DefAdminUid is verified from the LDAP
server. For database authentication,
provide the default password for the
default user ID.
maxload Specifies maximum number of open
concurrent database connections
depending on the database used for
report logging.
ProjectsURLBase Context path of the Help projects on
the Tomcat server..
ProjectsDirBase Top-level directory of Help projects
Default Admin password if authtype is db
maximum number of open
connections database can handle.
Important: The recommended way of editing properties is through the Configuration Manager. In particular, you should
not edit the following properties manually:
ProjectDirBase.
Database Type, DSN, dsnuser, dsnpwd, ProjectURLBase, and
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 25

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Administering the server
About RoboAdmin group
By default, RoboHelp Server creates an Admin group called RoboAdmin. The RoboAdmin group has the following
permissions:
• Creation and deletion of areas.
• Publishing and viewing projects in all the areas.
• Viewing reports for all the areas.
• Creation and deletion of groups.
• Assigning and removing users from groups.
• Assigning and removing publishing or viewing access and report viewing to an area.
RoboHelp Server adds the default user specified in the configuration file as a member of RoboAdmin group. You can
use the Configuration Manager to change the default user ID and then restart the server.
On restarting the server, RoboHelp Server adds the new user ID as a member of the RoboAdmin group. But the earlier
user still exists as a member of the RoboAdmin group. If you want to remove the earlier user ID from the RoboAdmin
group, log in with the new admin ID and remove the earlier user ID from the Users page.
Managing groups
When you sign in to the Web Admin interface, the Users page opens. In this page, you can create groups and assign
users to them. You can also select existing groups and add or delete users from the group. Consider the following while
managing groups or users:
22
• A user ID or a group cannot have special characters and cannot be blank.
• As an administrator, you can remove users from a group but you cannot remove yourself from the Admin group.
• Depending on the type of authentication that is LDAP or database, enter a user name and a password.
Note: If you are logged in as an LDAP administrator, you get an additional option of adding a new LDAP user or an
existing LDAP group. For example, your LDAP group can include all the people in HR or Finance department.
• If you are logged in as a user, you cannot remove yourself from your group.
Note: Click the Users icon to access the Users page from some other page.
Managing areas
You can manage areas from the Areas page of the Web Admin interface. Click the Areas icon to create or delete
areas and assign permissions to areas.
• You can click the Add button next to the Areas list to create an area. Select the option to make the area protected
or leave it deselected to make it public.
• The request to add an area goes to the server. If the area name exists or if you have not entered any area name, an
error message appears.
Note: By default, RoboHelp Server creates a default area, general.
• You cannot delete the default area.
• You can add a user group to an area to assign it viewing, publishing, or report viewing rights.
• Public areas do not have viewing restrictions and thus, the Viewing option for the public areas is always disabled.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 26

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Administering the server
• You can select a user group from the Add new group pop-up menu and add it to a selected area. If the group is
already assigned to the selected area, a message appears.
Note: As an administrator, you can select the Protected option and change a public area to protected. Click Apply after
making the necessary changes.
Managing projects
To manage projects on a server, you can click the Projects icon in the Web Admin interface. The list of projects
listing name, type, and published dates of the projects and the name of the authors. This default project is used to
resolve name conflicts among windows, context IDs, topics, and so on. Other Help projects use the default project
settings on the server.
Areas Displays the list of areas defined on the server.
Note: The areas list shows all the areas only if you have admin rights assigned to you. If you have user rights, you can
view the areas for which you have the viewing rights.
Project List Determines the default project if you have several projects merged based on the project order. The first
project listed is the default (Master).
View Project Displays the contents of a project.
23
Delete Deletes the selected project. Error messages appear in the Adobe RoboHelp error log if other users attempt to
access a deleted project.
Note: This button is visible only if you have logged in as an administrator.
Move Up/Move Down Reorder projects.
Note: This button is visible only if you have logged in as an administrator.
Automatically Merge Projects of Same Type Merges projects of the same type (WebHelp Pro or FlashHelp Pro).
Note: Merging all projects from within RoboHelp Server ignores project merging information set in the RoboHelp HTML
application.
You can access area-specific projects using the following URL:
http://<server-name>/robohelp/server?prj=<project-name>&area=<area-name>
If you do not specify an area attribute, the default area is considered. You must have project viewing permissions to
the area.
Scheduling databases
Select the Settings icon on the Web Administrator interface to select options for data in the database and to select
options for scheduling search indexing on the server.
To make database-specific changes, select Databases in the Settings list. The Database section shows the following
options:
Delete All Data Over Select to delete user actions and server errors older than the number of days specified. Specify the
time at which the process takes place.
Delete All Data Now Select if you want to delete the data right now.
Delete All Data Over Days Now Select to delete the data, older than the specified period right away.
Keep All Data Select to keep all data.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 27

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Administering the server
Notes:
• You cannot delete user information, AIR Help comments, or statistics because they are reused and were not created
on a specific date.
• When you delete database data, the size of the database is reduced when you shrink or compress it. In Microsoft
Access, select Tools > Database Utilities > Compact and Repair Database.
Scanning documents
Regular scanning of documents updates the search index on a regular basis. You can schedule scanning of documents
at a weekly, daily, or hourly basis. With every scheduled scanning, the RoboHelp server reads all the published projects.
The server recreates indexes only if you have set the reindex property in the server.properties file to true. By default,
the reindex property is set to true. The search setting pane is not visible if the reindex property is set to false. The
indexing takes place only at scheduled intervals of rescanning and when a project is published on a server.
Specify moderation settings for Adobe AIR Help comments
1 In RoboHelp Server Web Administrator, click Settings > Moderation.
2 Select Allow Post Anonymous if you want to let users comment anonymously on Help content.
3 Select Mark New Comments As Pending if you want to display user comments on Help content only after a
moderator approves them.
4 Click Apply.
24
Troubleshooting
Click the Troubleshooting icon if you are an administrator or if you have report access to some areas. The
Troubleshooting page displays errors generated in a selected area. You can select an error and click More Info to view
detailed information on the error generated in an area. Click Delete to delete error messages generated in an area or
Delete All to delete all the error messages for the specified area.
Errors can occur due to various reasons such as absence of a default topic, missing TOC, index, or a glossary file,
missing topic, missing context ID, or missing window. The error information helps you to review the Help content
and fix issues.
Reports
About Reports
Use reports to understand user needs and then update your Help content. Reports show you where users enter the
system, what questions they ask, and which of their questions are left unanswered.
RoboHelp Server generates reports based on how end users navigate and use your Help content. You can share these
reports and analyze them to optimize the value of your content. In addition, RoboHelp Server reports help you identify
the key areas of your Help content that need to be updated/enhanced on priority.
Reports are available area wise. You can also get a consolidated report of all the areas for which you have the access
permissions.
Report data includes the following:
Where users request assistance The location where repeated requests take place.
How users search Searches that users perform repeatedly.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 28

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Administering the server
How users navigate content The user navigation and frequency.
Available reports
Search Terms with No Results Search terms that returned no results and the number of times users searched for them
Frequently Searched Terms Frequently-searched keywords and how many times users searched for them
Frequently Accessed CSH Frequently-accessed context-sensitive Help topics and how many times they are accessed.
The report is arranged by the context IDs of the CSH topics.
Frequently Viewed Topics Report on Topics that end users view most often
Usage Statistics Chronological graphical report of the number of hits to the Help system as a whole. Pages searched
for and not opened reflect in this list. The usage statistics report has three additional tabs:
• Page Views Number of pages viewed over a given window of time. The window of time is determined by the labels
along the X axis.
• Pages Per Visit Number of pages viewed per visit. Every instance when a user opens the project is considered as a
separate visit. Visits from different Web browsers are counted separately.
• Browser Comparative data about the Web browsers in which users viewed the Help content
• OS Comparative data about the operating systems on which users viewed the Help content
25
Search Trends The percentage of search terms that returned no results. The detailed view of this report gives the total
number of search terms and how many of them returned results/no results.
Help System Errors Error messages encountered by the current logged-in user
Note: You can filter any report by area or view a consolidated report for all areas.
View reports
1 In the Web Administrator, click Reports.
2 On the Reports page, select a report and click View Report.
Note: To fetch fresh report data from the server, click Reload.
Customize reports
Customizing reports facilitates easier viewing and interpretation. Some useful options that you can specify while
viewing reports are as follows:
Area Instead of viewing a consolidated report for all areas, you can filter the report by area. Viewing area-specific
reports facilitates interpretation.
CSV Click the Export To CSV icon in the bottom-right corner of the report area to export the report data as a CSV file.
Add/Remove Columns Click the Wrench icon to add/delete available columns from the data table in the bottom-half
of the report screen.
Max Results Number of results you want RoboHelp Server to display per page.
Date Range Filter the report by time window.
Update Fetch the latest report data from the RoboHelp Server.
Pie Chart View a pie chart instead of the default bar chart.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 29

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Administering the server
Access context-sensitive Help
Using context-sensitive Help, you can associate context IDs with topics. Using CSH API, you can retrieve topics
associated with a given context ID from the server. You can use the CSH API of the server to call a context-sensitive
Help topic from WebHelp Pro or FlashHelp Pro projects in RoboHelp HTML. You can access CSH for WebHelp Pro
and FlashHelp Pro projects from the CSH tool and the browser window.
Using the CSH tool, specify a URL and Map Number as follows:
• For WebHelp Pro, specify http://<server-name>/robohelp/server?project=<project
name>&area=<area-name> in the Help URL and context ID in the map number.
• For FlashHelp Pro, specify the Help URL as http://<server-
name>/robohelp/server?project=<projectname>&type=flashhelp&area=<area-name> and context ID in
the map number.
To access context-sensitive Help using the browser window:
• Specify the URL as http://<server-name>/robohelp/server?project=<project name>&ctxid=<ctx
id>&area=<area-name> for WebHelp Pro projects.
• Specify the URL as http://<server-name>/robohelp/server?project=<project name>&ctxid=<ctx
id>&type=flashhelp&area=<area-name> for FlashHelp Pro projects.
You can use CSH API to access Help using a topic name. Enter the URL http://<server-name>/<context-
name>/server?project=<project name>&tpc=<relative topic path>&area=<area-
name>[&type=flashhelp]
26
REST web services
The REST web services enable you to perform a search on the content and return results for the context-sensitive Help.
Using the REST services, you can send GET and POST requests to the RoboHelp server and get results in the XML
format. You can format the data and present it in another format in a RoboWindow. A RoboWindow is a set of
window properties that are published by RoboHelp HTML as part of FlashHelp Pro and WebHelp Pro projects.
When you install RoboHelp Server, some sample project files are stored at Program files/Adobe/Adobe RoboHelp
9/CSH API/RoboHelp.NET/[sample folder name].
RoboHelp Server provides sample files in four languages: Visual Basic, VC++, C#, and JavaScript. All the sample files
in different languages, other than JavaScript, are stored in different folders. For example, a Visual Basic folder is named
Sample_RoboHelp_CSH_VB. All the language-specific sample folders also contain solution files (.sln files) to open and
run them in Visual Studio. Using these samples, you can perform search and Robowindow service from REST services
on the projects published on the RoboHelp Server. The result of the query is responded in XML format. You can use
the results to be displayed in different formats or for scripting purposes. In the samples, the search results are displayed
in a table format. The columns display rank, title, the URL, and the summary links to the relevant topics of the specified
project.
To get a RoboWindow using the REST web services, select one of the following options:
• To get the window properties and Help URL for a context ID, use the HTTP GET method and send the query in
the following format:
URL: http://<server-name>/<context-name>/rest/robowindow?wtype=ctx&project=<projectname>&context=<context-id>&area=<area-name>[&type=flashhelp]
• To get the window properties and Help URL for a given window name, use the HTTP GET method and send your
query in the following format:
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 30

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Administering the server
URL: http://<server-name>/<context-name>/rest/robowindow?wtype=prj&project=<projectname>&wnd=<window-name>&area=<area-name>[&type=flashhelp]
Note: The method to get the Robowindow is same for both public and protected areas.
The RoboHelp Server sends the response for both public and private areas in the same format:
<Window Name="{wnd-name}" UseProp="{0/1}" URL="string"> <Style Toolbar="{0/1}"
Location="{0/1}" Status="{0/1}" Menubar="{0/1}" Resizable="{0/1}"/> <Location Left="{int}"
Top="{int}" Width="{int}" Height="{int}" LeftType="{0/1}" TopType="{0/1}" WidthType="{0/1}"
HeightType="{0/1}"/> </Window>
Send a search query to RoboHelp server
• Public area
When you send a search request to a public area, use the HTTP GET method. You can use the following format for
your search query:
URL : http://<server-name>[:port-num]/<context-name>/rest/search?project=<projectname>&area=<area-name>&quesn=<search-query>[&type=flashhelp]
The server sends the response in the following XML format:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <ftstdata> <topic name="{topic-name}" url="{url of
topic}" summary="{summary}" rank="{rank}" /> </ftstdata>
27
• Protected area
To send a query request to a protected area, use the HTTP POST method. Use the following format for your search
query:
URL : http://<server-name>[:port-num]/<context-name>/rest/search
For the query request to a protected area, enter a Request body.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <rest> <UID name="{User ID}" /> <PWD
name="{Password}" /> <PRJ name="{ProjectName}" /> <AREA name="{AreaName}" /> <QUESN
name="{Search Query}" /> [<TYPE name="flashhelp" />] </rest>
The RoboHelp server sends the response in the following format:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <ftstdata> <topic name="{topic-name}" url="{url of
topic}" summary="{summary}" rank="{rank}" /> </ftstdata>
Note: To perform a search, you must have project viewing access to that area as a user. If you specify incorrect credentials
or if you do not have access permissions, the server sends an error response in the XML format.
<error>error-message </error>
Search
1 Double-click a solution file from //Program files/Adobe/Adobe RoboHelp 9/CSH API/RoboHelp.NET/[sample
folder name].
2 Language-specific code displays in Visual Studio.
3 Run the code. A language-specific sample project executable file opens. For example, for Visual Basic code, the
CSH_VB_Sample dialog box appears.
4 To perform search, specify the URL as http://<servername>/robohelp/rest.
5 Specify the project name.
6 Enter a search keyword in the Question box.
Last updated 1/17/2011
Page 31

USING ROBOHELP SERVER 9
Administering the server
7 Specify an area, in which the project is published, general or otherwise.
Note: If you do not specify an area, the default area, general is selected.
8 Select FlashHelp Pro or WebHelp Pro (which specifies the type of project).
9 Click Search.
The search results are displayed in a table format that lists the rank, title, URL, and summary of the relevant topics of
the specified project.
Get a RoboWindow
1 Double-click a solution file from //Program files/Adobe/Adobe RoboHelp 9/CSH API/RoboHelp.NET/[sample file
folder name]. Language-specific code displays in Visual Studio.
2 Run the code. A language-specific sample project executable file opens. For example, for Visual Basic code, the
CSH_VB_Sample dialog box appears.
3 Specify the URL as http://<servername>/robohelp/rest.
4 Specify the Project Name.
5 Specify the local Help URL to display if server communication is not possible. This URL can pertain to WinHelp
(.hlp file), HTML Help (.chm file) or Web Help (.html file).
6 Specify the area in which the project is published.
7 Select FlashHelp Pro or WebHelp Pro (to indicate the type of project).
8 Select the parameter Context, TOC, index, Search, or Window.
9 Specify the parameter value, Context ID in case of context parameter, and Window name if window is selected as
parameter type.
10 Click SearchHelp.
The relevant window with the given parameter value is displayed.
28
Last updated 1/17/2011
 Loading...
Loading...