Page 1

ADOBE® BRIDGE
February 2013
Help and tutorials
Page 2

Contents
Adobe Bridge 1.................................................................................................................................................
What's new in CS6 2..................................................................................................................................................................
About Adobe Bridge 3.................................................................................................................................................................
The Adobe Bridge workspace 4..................................................................................................................................................
View and manage files in Adobe Bridge 8..................................................................................................................................
Work with metadata in Adobe Bridge 13....................................................................................................................................
Create web galleries and PDFs with Adobe Output Module 18..................................................................................................
Adjust Adobe Bridge Content panel display 20..........................................................................................................................
Adobe Bridge keyboard shortcuts 22..........................................................................................................................................
Automate tasks in Adobe Bridge 24...........................................................................................................................................
Export photos from Adobe Bridge to the web 26........................................................................................................................
Get photos from a digital camera or card reader into Adobe Bridge 28.....................................................................................
Preview and compare images in Adobe Bridge 30.....................................................................................................................
Preview dynamic media files in Adobe Bridge 33.......................................................................................................................
Stack files in Adobe Bridge 34....................................................................................................................................................
Start Adobe Bridge 36................................................................................................................................................................
Use collections in Adobe Bridge 38............................................................................................................................................
Use keywords in Adobe Bridge 40..............................................................................................................................................
Work with the Adobe Bridge cache 42........................................................................................................................................
Mini Bridge 43...................................................................................................................................................
Mini Bridge 44.............................................................................................................................................................................
Camera Raw 46................................................................................................................................................
Introduction to Camera Raw 47..................................................................................................................................................
Navigate, open, and save images in Camera Raw 51................................................................................................................
Make color and tonal adjustments in Camera Raw 54...............................................................................................................
Sharpening and noise reduction in Camera Raw 59..................................................................................................................
Process versions in Camera Raw 61..........................................................................................................................................
Make local adjustments in Camera Raw 62...............................................................................................................................
Page 3

Adobe Bridge
1
Page 4

What's new in CS6
2
Print a contact sheet
Filmstrip view in Mini Bridge
Camera Raw processing improvements
Print a contact sheet
Contact sheets let you easily preview groups of images by displaying a series of thumbnails on a single page. You can automatically create and
place thumbnails on a page using the Contact Sheet II command.
In Adobe Bridge, choose Tools > Photoshop > Contact Sheet II to open the Contact Sheet II plug-in in Photoshop CS6.
Filmstrip view in Mini Bridge
The redesigned Mini Bridge panel in Photoshop® CS6 and InDesign® CS6 provides a filmstrip view of your photos for easy scrolling and
browsing.
Mini Bridge appears as a docked panel at the bottom of the Photoshop window or as a regular panel in InDesign.
For more information, see Mini Bridge.
Camera Raw processing improvements
Simplified Basic tab sliders improve highlight and shadow rendering. Additional local corrections are available for white balance, highlights,
shadows, noise reduction, and moiré.
See the new Basic sliders and local adjustment options with new images or with previously processed images that you convert to Process Version
2012 (PV2012). To convert an image, click the exclamation-point icon in the lower-right corner of the image preview area.
For more information, see Make color and tonal adjustments in Camera Raw, Make local adjustments in Camera Raw, and Process Versions in
Camera Raw.
To the top
To the top
To the top
Video tutorials
What's New in Adobe Bridge CS6
What is Bridge?
Twitter™ and Facebook posts are not covered under the terms of Creative Commons.
Legal Notices | Online Privacy Policy
Page 5

About Adobe Bridge
3
Adobe® Bridge, provided with Adobe Creative Suite® 6 and CS5 components, lets you organize the assets you use to create content for print,
web, and video. Adobe Bridge keeps native Adobe files (such as PSD and PDF) as well as non-Adobe files available for easy access. You can
drag assets into your layouts, projects, and compositions as needed, preview files, and even add metadata (file information), making the files
easier to locate.
File browsing
You can use Adobe Bridge to rename, move, and delete files; edit metadata; rotate images; and run batch commands. You can also view files and
data imported from your digital still or video camera. See View and manage files.
Mini Bridge
communicates with Adobe Bridge to create thumbnails and keep files up- to-date. Mini Bridge lets you work with files more easily within the host
application. See Mini Bridge.
Camera raw
in Photoshop. You can edit the images directly in the Camera Raw dialog box without starting Photoshop, and copy settings from one image to
another. If you don’t have Photoshop installed, you can still preview the camera raw files in Adobe Bridge. See Work with Camera Raw.
Color management
color-managed Adobe Creative Suite components. This synchronization ensures that colors look the same in all Adobe Creative Suite
components. See Manage color.
Legal Notices | Online Privacy Policy
From Adobe Bridge you can view, search, sort, filter, manage, and process image, page layout, PDF, and dynamic media files.
Browse and manage assets using the Mini Bridge panel in Adobe Photoshop®, Adobe InDesign®, and Adobe InCopy®. Mini Bridge
If you have Adobe Photoshop, or Adobe Creative Suite installed, you can open camera raw files from Adobe Bridge and save them
If you have an edition of Adobe Creative Suite 6 or CS5, you can use Adobe Bridge to synchronize color settings across
Twitter™ and Facebook posts are not covered under the terms of Creative Commons.
Page 6
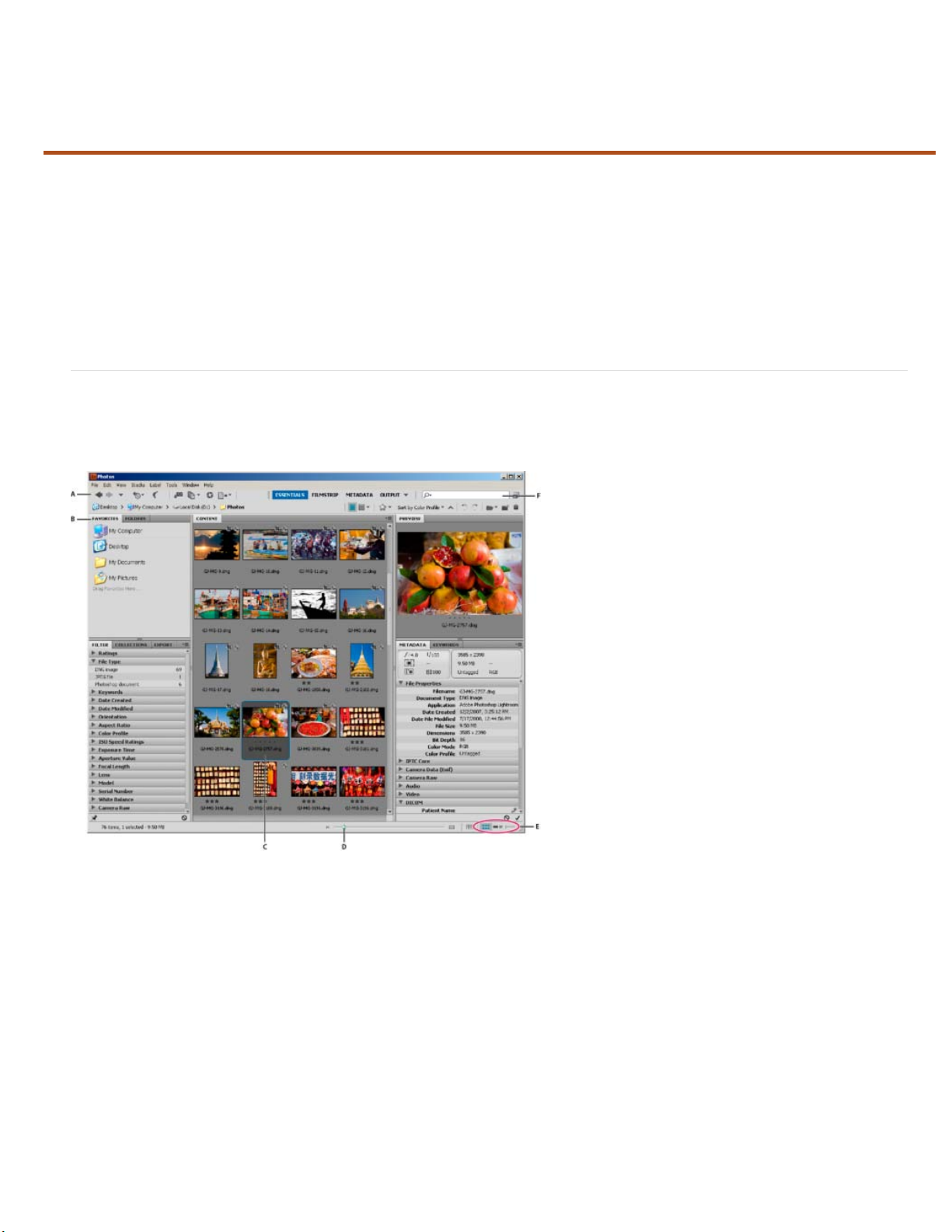
The Adobe Bridge workspace
4
Workspace overview
Adjust panels
Work with Favorites
Select and manage workspaces
Adjust brightness and colors
Work in Compact mode
Manage color
Change language settings
Enable startup scripts
Restore preferences
Workspace overview
The Adobe® Bridge workspace consists of three columns, or panes, that contain various panels. You can adjust the Adobe Bridge workspace by
moving or resizing panels. You can create custom workspaces or select from several preconfigured Adobe Bridge workspaces.
To the top
Adobe Bridge workspace
A. Application bar B. Panels C. Selected item D. Thumbnail slider E. View buttons F. Search
The following are the main components of the Adobe Bridge workspace:
Application bar
Path bar
Favorites panel
Folders panel
Filter panel
Collections panel
Content panel
Export panel
Provides buttons for essential tasks, such as navigating the folder hierarchy, switching workspaces, and searching for files.
Shows the path for the folder you’re viewing and allows you to navigate the directory.
Gives you quick access to frequently browsed folders.
Shows the folder hierarchy. Use it to navigate folders.
Lets you sort and filter files that appear in the Content panel.
Lets you create, locate, and open collections and smart collections.
Displays files specified by the navigational menu buttons, Path bar, Favorites panel, Folders panel, or Collections panel.
Save photos as JPEG for web uploads.
Page 7

Preview panel
Displays a preview of the selected file or files. Previews are separate from, and typically larger than, the thumbnail image
displayed in the Content panel. You can reduce or enlarge the preview by resizing the panel.
5
Metadata panel
and exposure setting) is listed.
Keywords panel
Output panel
Adjust panels
You can adjust the Adobe Bridge window by moving and resizing its panels. However, you can’t move panels outside the Adobe Bridge window.
Work with Favorites
Do any of the following:
Drag a panel by its tab into another panel.
Drag the horizontal divider bar between panels to make them larger or smaller.
Drag the vertical divider bar between the panels and the Content panel to resize the panels or Content panel.
Press Tab to show or hide all panels except the center panel (the center panel varies depending on the workspace you’ve
chosen).
Choose Window, followed by the name of the panel you want to display or hide.
Right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) a panel tab and choose the name of the panel you want to display.
To specify Favorites preferences, choose Edit > Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS6 > Preferences (Mac OS). Click
General, and select desired options in the Favorite Items area of the Preferences dialog box.
To add items to Favorites, do one of the following:
Drag a file or folder to the Favorites panel from Windows Explorer (Windows), the Finder (Mac OS), or the Content or
Folders panel of Adobe Bridge.
Select a file, folder, or collection in Adobe Bridge and choose File > Add To Favorites.
To remove an item from the Favorites panel, select it and choose File > Remove From Favorite. Or right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac
OS) the item and choose Remove From Favorites from the context menu.
Contains metadata information for the selected file. If multiple files are selected, shared data (such as keywords, date created,
Helps you organize your images by attaching keywords to them.
Contains options for creating PDF documents and HTML or Flash® web galleries. Appears when the Output workspace is selected.
To the top
To the top
Select and manage workspaces
An Adobe Bridge workspace is a certain configuration or layout of panels. You can select either a preconfigured workspace or a custom
workspace that you have previously saved.
By saving various Adobe Bridge workspaces, you can work in (and quickly switch between) different layouts. For instance, use one workspace to
sort new photos and another to work with footage files from an After Effects composition.
Adobe Bridge provides the following preconfigured workspaces:
Output
script is selected in Adobe Bridge Preferences.
Metadata
Essentials
Filmstrip
Preview panel). Also displays the Favorites, Folders, Filter, Collections, and Export panels.
Keywords
Note:
by using the keyboard shortcut, first disable the VoiceOver shortcut in Mac OS Keyboard Shortcuts preferences. For instructions, see Mac OS
Help.
Preview
Export panels.
Displays the Favorites, Folders, Content, Preview, and Output panels. This workspace is available when the Adobe Output Module startup
Displays the Content panel in List view, along with the Favorites, Metadata, Filter, and Export panels.
Displays the Favorites, Folders, Filter, Collections, Export, Content, Preview, Metadata, and Keywords panels.
Displays thumbnails in a scrolling horizontal row (in the Content panel) along with a preview of the currently selected item (in the
Displays the Content panel in Details view, along with the Favorites, Keywords, Filter, and Export panels.
In Mac OS, pressing Command+F5 to load the Keywords workspace starts Mac OS VoiceOver by default. To load the Preview workspace
Displays a large Preview panel; a narrow, vertical Content panel in Thumbnails view; and the Favorites, Folders, Filter, Collections, and
To the top
Page 8
Light Table
Displays only the Content panel. Files are displayed in Thumbnails view.
6
Folders
Workspace buttons and pop -up menu
Displays the Content panel in Thumbnails view, along with the Favorites, Folders, and Export panels.
To select a workspace, choose Window > Workspace, and then choose the desired workspace. Or, click one of the workspace
buttons in the Adobe Bridge application bar.
Drag the vertical bar to the left of the workspace buttons to show more or fewer buttons. Drag the buttons to rearrange their order.
To save the current layout as a workspace, choose Window > Workspace > New Workspace. In the New Workspace dialog
box, enter a name for the workspace, specify options, and then click Save.
To delete or restore a custom workspace, choose Window > Workspace, and then choose one of the following commands:
Delete Workspace
click Delete.
Reset Workspace
Reset Standard Workspace
Adjust brightness and colors
Brighten or darken the Adobe Bridge background and specify accent colors in General preferences. To open preferences, choose Edit >
Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS6 > Preferences (Mac OS).
To brighten or darken the background, go to the General panel of the Preferences dialog box and do the following:
Drag the User Interface Brightness slider to make the Adobe Bridge background darker or lighter.
Drag the Image Backdrop slider to make the background of slide shows and of the Content and Preview panels darker or
lighter.
To specify accent colors, go to the General panel of the Preferences dialog box and choose a color from the Accent Color
menu.
Work in Compact mode
Switch to Compact mode when you want to shrink the Adobe Bridge window. In Compact mode, the panels are hidden and the Content panel is
simplified. A subset of common Adobe Bridge commands remains available from the pop-up menu in the upper-right corner of the window.
By default, the Compact mode Adobe Bridge window floats on top of all windows. (In Full mode, the Adobe Bridge window can move behind other
windows.) This floating window is useful because it is always available as you work in different applications. For instance, use Compact mode after
you select the files you plan to use, and then drag them into the application as you need them.
Deselect Compact Window Always On Top from the Adobe Bridge window menu to prevent the Compact mode Adobe Bridge window from
floating on top of all windows.
Deletes the saved workspace. Choose the workspace from the Workspace menu in the Delete Workspace dialog box, and
Restores the currently selected saved workspace to its default settings.
Restores the default settings for the Adobe pre -defined workspaces (Essentials, Output, etc.)
To the top
To the top
1. Click the Switch To Compact Mode button
2. Do any of the following:
Choose commands from the menu at the upper-right corner of the Adobe Bridge window.
(CS5 only) Click the Switch To Ultra Compact Mode button to hide the Content panel, further minimizing the Adobe
Bridge window. You can click the button again to return to Compact mode.
.
Page 9
Click the Switch To Full Mode button to return to Full mode, displaying the panels, and letting Adobe Bridge move
7
behind the current window.
Manage color
In Adobe Bridge, the thumbnail quality determines whether color profile settings are used. High-quality thumbnails use color-profile settings, while
quick thumbnails do not. In CS5 only, use the Advanced Preferences and the Options For Thumbnail Quality and Preview Generation button in the
application bar to determine thumbnail quality.
If you own Adobe Creative Suite, you can use Adobe Bridge to synchronize color settings across all color-managed Creative Suite components.
When you specify Creative Suite color settings using the Edit > Creative Suite Color Settings command in Adobe Bridge, color settings are
automatically synchronized. Synchronizing color settings ensures that colors look the same in all color-managed Adobe Creative Suite
components.
See Synchronize color settings across Adobe applications.
Change language settings
Adobe Bridge can display menus, options, and tool tips in multiple languages. You can also specify that Adobe Bridge use a specific language for
keyboard shortcuts.
1. Choose Edit > Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS6 > Preferences (Mac OS), and click Advanced.
2. Do either or both of the following:
Choose a language from the Language menu to display menus, options, and tool tips in that language.
Choose a language from the Keyboard menu to use that language keyboard configuration for keyboard shortcuts.
3. Click OK, and restart Adobe Bridge.
The new language takes effect the next time you start Adobe Bridge.
To the top
To the top
Enable startup scripts
You can enable or disable startup scripts in Adobe Bridge preferences. Scripts listed vary depending on the Creative Suite® components you’ve
installed. Disable startup scripts to improve performance or to resolve incompatibilities between scripts.
1. Choose Edit > Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS6 > Preferences (Mac OS), and click Startup Scripts.
2. Do any of the following:
Select or deselect the desired scripts.
To enable or disable all scripts, click Enable Allor Disable All.
Click Reveal My Startup Scripts to go to Adobe Bridge Startup Scripts folder on your hard drive.
Restore preferences
Numerous program settings are stored in the Adobe Bridge preferences file, including display, Adobe Photo Downloader, performance, and filehandling options.
Restoring preferences returns settings to their defaults and can often correct unusual application behavior.
1. Press and hold the Ctrl key (Windows) or the Option key (Mac OS) while starting Adobe Bridge.
2. In the Reset Settings dialog box, select one or more of the following options:
Reset Preferences
a new preferences file when it starts.
Purge Entire Thumbnail Cache
Adobe Bridge re-creates the thumbnail cache when it starts.
Returns preferences to their factory defaults. Some labels and ratings may be lost. Adobe Bridge creates
Purging the thumbnail cache can help if Adobe Bridge is not displaying thumbnails properly.
To the top
To the top
Reset Standard Workspaces
3. Click OK, or click Cancel to open Adobe Bridge without resetting preferences.
Returns Adobe predefined workspaces to their factory default configurations.
Page 10

View and manage files in Adobe Bridge
8
Navigate files and folders
Show subfolder contents
Open files in Adobe Bridge
Change file type associations
Place files into another application
Search for files and folders with Adobe Bridge
Perform a Quick Search
Label and rate files
Sort files
Filter files
Copy, move, and delete files and folders
Rotate images
Work with Camera Raw
Use Adobe Device Central with Adobe Bridge
Navigate files and folders
Do any of the following:
Select a folder in the Folders panel. Press the Down Arrow and Up Arrow keys in the Folders panel to navigate the
directory. Press the Right Arrow key to expand a folder. Press the Left Arrow key to collapse a folder.
Select an item in the Favorites panel.
Click the Go To Parent Or Favorites button orReveal Recent button in the application bar and choose an item.
To reveal a file in the operating system, select it and choose File > Reveal In Explorer (Windows) or File > Reveal In
Finder (Mac OS).
Click the Go Back button orGo Forward button in the application bar to navigate between recently visited folders.
Double-click a folder in the Content panel to open it.
Ctrl-double click (Windows) or Command-double click (Mac OS) a folder in the Content panel to open that folder in a
new window.
Drag a folder from Windows Explorer (Windows) or the Finder (Mac OS) to the path bar to go to that location in
Adobe Bridge.
Drag a folder from Windows Explorer (Windows) or the Finder (Mac OS) to the Preview panel to open it. In Mac OS, you
can
also drag a folder from the Finder to the Adobe Bridge icon to open it.
Use the path bar to navigate:
Click an item in the path bar to go to it.
Right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) an item in the path bar to turn on folder “cruising.” Folder cruising allows
you to see and go to the subfolders of the selected item. You can also click a right-pointing arrow
cruise the subfolders of the preceding item.
Drag an item from the Content panel to the path bar to go to that location.
Click the last item in the path bar to edit the path. Press Esc to return to the icon mode.
Note: Show or hide the path bar by choosing Window >Path Bar.
in the path bar to
To the top
Show subfolder contents
You can specify that Adobe Bridge display folders and subfolders in one continuous, “flat” view. Flat view displays the entire contents of a folder,
including its subfolders, so you don’t have to navigate the subfolders.
To display the contents of folders in flat view, choose View > Show Items From Subfolders.
Open files in Adobe Bridge
To the top
To the top
Page 11

You can open files from Adobe Bridge, even files that were not made with Adobe software. When you use Adobe Bridge to open a file, the file
currently selected folder or in My Computer (Windows) and Computer (Mac OS).
9
opens in its native application or the application you specify. You can also use Adobe Bridge to place files in an open document in an Adobe
application.
Select a file and do any of the following:
Choose File > Open.
Press Enter (Windows) or Return (Mac OS).
Press Ctrl+Down Arrow key (Windows) or Command+Down Arrow key (Mac OS).
Double-click the file in the Content panel.
Choose File > Open With, followed by the name of the application with which to open the file.
Drag the file onto an application icon.
Choose File > Open In Camera Raw to edit the camera raw settings for the file.
To open photos from a digital camera into Adobe Bridge, use the Adobe Photo Downloader. See Get photos from a digital
camera or card reader into Adobe Bridge.
Change file type associations
Selecting the application to open a specific file type affects only those files that you open using Adobe Bridge and overrides operating system
settings.
1. Choose Edit > Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS5.1 > Preferences (Mac OS), and click File Type Associations.
2. Click the name of the application (or None) and click Browse to locate the application to use.
3. To reset the file type associations to their default settings, click Reset To Default Associations.
4. To hide any file types that don’t have associated applications, select Hide Undefined File Associations.
Place files into another application
Select the file in Adobe Bridge and choose File > Place, followed by the name of the application. For instance, you can use this
command to place a JPEG image into Adobe Illustrator.
Drag a file from Adobe Bridge into the desired application. Depending on the file, the document into which you want to place
the file may need to be opened first.
Search for files and folders with Adobe Bridge
You can search for files and folders with Adobe Bridge by using multiple combinations of search criteria. You can save search criteria as a smart
collection, which is a collection that stays up to date with files that meet your criteria.
1. Choose Edit > Find.
2. Choose a folder in which to search.
3. Choose search criteria by selecting options and limiters from the Criteria menus. Enter search text in the box on the right.
4. To add search criteria, click the plus sign (+). To remove search criteria, click the minus sign (-).
5. Choose an option from the Match menu to specify whether any or all criteria must be met.
6. (Optional) Select Include All Subfolders to expand the search to any subfolders in the source folder.
7. (Optional) Select Include Non-Indexed Files to specify that Adobe Bridge search uncached as well as cached files. Searching
uncached files (in folders that you have not previously browsed in Adobe Bridge) is slower than searching just cached files.
8. Click Find.
9. (Optional) To save the search criteria, click the New Smart Collection button
displays your search results. The Smart Collection dialog box automatically includes the criteria of your search. Refine the
criteria if desired, and then click Save. Type a name for the smart collection in the Collections panel, and then press Enter
(Windows) or Return (Mac OS). See Create a smart collection.
in the Collections panel when Adobe Bridge
To the top
To the top
To the top
Perform a Quick Search
Use the Quick Search field in the application bar to find files and folders in Adobe Bridge. Quick Searchlets you search using either the
Adobe Bridge search engine or Windows Desktop Search (Windows) or Spotlight (Mac OS). The Adobe Bridge engine searches filenames and
keywords. Operating system engines look for filenames, folder names, and image keywords. Adobe Bridge search looks within the currently
selected folder and all subfolders, including My Computer (Windows) and Computer (Mac OS). Operating system search engines look in the
To the top
Page 12
1. Click the magnifying glass icon in the Quick Search field and choose Adobe Bridge, Windows Desktop Search (Windows),
10
or Spotlight (Mac OS) as your search engine.
2. Enter a search criteria.
3. Press Enter (Windows) or Return (Mac OS).
Note: Windows Desktop Search is installed by default for Vista. Windows XP users can download and install it from the Microsoft website. Adobe
Bridge detects if Windows Desktop Searchis installed and enables the functionality accordingly. The defaultWindows Desktop Search only indexes
to the Documents and Settings directory. To include additional locations, modify your options in the Windows Desktop Search Options dialog box.
Label and rate files
Labeling files with a certain color or assigning ratings of zero (0) to five stars lets you mark a large number of files quickly. You can then sort files
according to their color label or rating.
For example, suppose you’re viewing a large number of imported images in Adobe Bridge. As you review each new image, you can label the
images you want to keep. After this initial pass, you can use the Sort command to display and work on files that you’ve labeled with a particular
color.
You can label and rate folders as well as files.
You can assign names to labels in Labels preferences. The name is then added to the file’s metadata when you apply the label. When you change
names of labels in preferences, any files with the older label appear with white labels in the Content panel.
Note: When you view folders, Adobe Bridge shows both labeled and unlabeled files until you choose another option.
1. To label files, select one or more files and choose a label from the Label menu. To remove labels from files, choose Label >
No Label.
2. To rate files, select one or more file and do any of the following:
In the Content panel, click the dot representing the number of stars you want to give the file. (In Thumbnail view, a
thumbnail must be selected for the dots to appear. Also, dots do not appear in very small thumbnail views. If necessary,
scale the thumbnails until the dots appear. In List view, make sure that the Ratings column is visible.)
Choose a rating from the Label menu.
To add or remove one star, choose Label >Increase Rating or Label > Decrease Rating.
To remove all stars, choose Label >No Rating .
To add a Reject rating, choose Label > Reject or press Alt+Delete (Windows) or Option+Delete (Mac OS).
Note: To hide rejected files in Adobe Bridge, choose View > Show Reject Files.
To the top
Sort files
By default, Adobe Bridge sorts files that appear in the Content panel by filename. You can sort files differently by using the Sort command or Sort
By application bar button.
Choose an option from the View > Sort menu, or click the Sort button in the application bar to sort files by listed criteria.
Choose Manually to sort by the last order in which you dragged the files. If the Content panel displays search results, a
collection, or flat view, the Sort button contains a By Folder option that lets you sort files by the folder where they’re located.
In List view, click any column header to sort by that criteria.
Filter files
Control which files appear in the Content panel by selecting criteria in the Filter panel. The Filter panel displays the number of items in the current
set that have a specific value, regardless of whether they are visible. For example, by glancing at the Filter panel, you can quickly see how many
files have a specific rating or keyword.
Criteria that appear in the Filter panel are dynamically generated depending on the files that appear in the Content panel and their associated
metadata or location. For example, if the Content panel contains audio files, the Filter panel contains artist, album, genre, key, tempo, and loop
criteria. If the Content panel contains images, the Filter panel contains such criteria as dimensions, orientation, and camera data such as exposure
time and aperture value. If the Content panel displays search results or a collection with files from multiple folders, or if the Content panel displays
flat view, the Filter panel contains a Parent Folder that lets you filter the files by the folder where they’re located.
Specify that Adobe Bridge show or hide folders, rejected files, and hidden files (such as cache files) in the Content panel by choosing options
from the View menu.
To filter files, select one or more criteria in the Filter panel:
Select criteria in the same category (for example, file types) to display files that meet any of the criteria. For example, to
display both GIF and JPEG files, select GIF Imageand JPEG File beneath File Type.
To the top
To the top
Page 13

Select criteria across categories (for example, file types and ratings) to display files that meet all of the criteria. For
example, to display GIF and JPEG files that have two stars, select GIF Image and JPEG File beneath File Type and two
11
stars beneath Ratings.
Shift-click rating criteria to select that rating or higher. For example, Shift-click two stars to display all files that have two
or more stars.
Select categories from the Filter panel menu.
Select Expand All or Collapse All from the Filter panel menu to open or close all filter categories.
Alt-click (Windows) or Option-click (Mac OS) to inverse selected criteria. For example, if you’ve selected GIF Image
beneath File Type, Alt-click GIF Image to deselect it and select all the other file types listed.
Note: If you filter a closed stack, Adobe Bridge displays the stack only if the top (thumbnail) item meets the filter criteria. If
you filter an expanded stack, Adobe Bridge displays all files in the stack that meet the filter criteria of the top file.
at the bottom of the Filter panel.
To prevent filter criteria from clearing when you navigate to another location in Adobe Bridge, click the Keep Filter When
Browsing button
at the bottom of the Filter panel.
Copy, move, and delete files and folders
To copy files or folders, do any of the following:
Select the files or folders and choose Edit > Copy.
Right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) the files or folders, choose Copy To, and select a location from the list (to
specify a different location, select Choose Folder).
Ctrl-drag (Windows) or Option-drag (Mac OS) the files or folders to a different folder.
To move files to another folder, do one of the following:
Right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) the files, choose Move To, and select a location from the list (to specify a
different location, select Choose Folder).
Drag the files to a different folder in the Adobe Bridge window or in Windows Explorer (Windows) or the Finder (Mac OS).
Note: If the file you’re dragging is in a different mounted volume than Adobe Bridge, the file is copied, not moved. To
move a file to a different mounted volume, Shift-drag (Windows) or Command-drag (Mac OS) the file.
To delete files or folders, do any of the following:
Select the files or folders and click the Delete Item button .
Select the files or folders and press Ctrl+Delete (Windows) or Command+Delete (Mac OS).
Select the files or folders and press Delete, and then click Delete in the dialog box.
Rotate images
You can rotate the view of JPEG, PSD, TIFF, and camera raw images in Adobe Bridge. Rotating does not affect the image data; however, rotating
an image in Adobe Bridge may rotate the image view in the native application as well.
1. Select one or more images in the content area.
2. Do one of the following:
Choose Edit > Rotate 90° Clockwise, Rotate 90° Counterclockwise, or Rotate 180°.
Click the Rotate 90° Clockwise or Rotate 90° Counterclockwise button in the application bar.
To the top
To the top
Work with Camera Raw
Camera raw files contain unprocessed picture data from a camera’s image sensor. Adobe Photoshop Camera Raw software, available in Adobe
Bridge if you have Adobe Photoshop or Adobe AfterEffects installed, processes camera raw files. You can also process JPEG (.JPG) or TIFF files
by opening them in Camera Raw from Adobe Bridge.
Use Adobe Bridge to copy and paste settings from one file to another, to batch process files, or to apply settings to files without opening the
Camera Raw dialog box.
To open JPEG or TIFF files in Camera Raw from Adobe Bridge, specify those options in Camera Raw preferences. Choose
Edit > Camera Raw Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS5.1 > Camera Raw Preferences (Mac OS). Under JPEG And
TIFF Handling, choose JPEG > Automatically Open All Supported JPEGs and/or choose TIFF > Automatically Open All
Supported TIFFs. Then, double- click a JPEG or TIFF file to open it in Camera Raw. To open JPEG and TIFF files in
To the top
Page 14

Photoshop, choose Automatically Open [JPEGs or TIFFs] With Settings.
12
To open raw files in Camera Raw from Adobe Bridge, specify that option in Adobe Bridge preferences. Choose Edit >
Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS5.1 > Preferences (Mac OS). In the Behavior area of the General tab, select
Double-Click Edits Camera Raw Settings In Bridge. If this preference is not selected, double-clicking raw files opens them in
Photoshop.
See also Open images.
Use Adobe Device Central with Adobe Bridge
To the top
Adobe Device Central enables creative professionals and developers that use Adobe Bridge to preview how different types of files, such as
Photoshop, Flash, and Illustrator files, will look on a variety of mobile devices. This ability can streamline the testing workflows for a variety of file
types. Adobe Bridge also provides direct access to Adobe Device Central without having to open a Creative Suite component such as Photoshop
or Flash Professional first.
For example, a designer who uses several Creative Suite components may use a folder in Adobe Bridge to organize a variety of files used in the
same project. The designer can navigate to that folder in Adobe Bridge and, in turn, view how a Photoshop image, a Flash file, and an Illustrator
file will look on a mobile device.
Previewing content from Adobe Bridge is also useful if you are reusing existing content. For example, you may have some wallpaper files you
created some time ago for a certain group of devices. Now, you may want to test the wallpaper files on the newest mobile devices. Simply update
the profile list in Adobe Device Central and test the old wallpaper files on the new devices directly from Adobe Bridge.
Note: Using Adobe Device Central with Adobe Bridge is not supported in Photoshop Elements 8 for Mac®.
1. To access Adobe Device Central from Adobe Bridge, select an individual file. The supported formats are: SWF, JPG, JPEG,
PNG, GIF, WBM, MOV, 3GP, M4V, MP4, MPG, MPEG, AVI, HTM, HTML, XHTML, CHTML, URL, and WEBLOC.
2. Do one of the following:
Choose File > Test In Device Central.
Right-click and choose Test In Device Central.
The file is displayed in the Adobe Device CentralEmulator tab. To continue testing, double-click the name of a different device
in the Device Sets or Available Devices lists.
Note: To browse device profiles or to create mobile documents, select Tools > Device Central. Adobe Device Central opens
with the Device Library tab shown. For more help with Adobe Device Central, see Create and preview mobile content with
other Adobe software.
|
Page 15
Work with metadata in Adobe Bridge
13
About metadata
The Metadata panel
The metadata placard
View metadata
Edit metadata in the Metadata panel
View Camera Raw and Lightroom metadata in Adobe Bridge
View linked InDesign files
View colors (Illustrator and InDesign) or fonts (InDesign)
Add metadata using the File Info dialog box
Work with metadata templates
Import metadata into a document
About metadata
Metadata is a set of standardized information about a file, such as author name, resolution, color space, copyright, and keywords applied to it. For
example, most digital cameras attach some basic information to an image file, such as height, width, file format, and time the image was taken.
You can use metadata to streamline your workflow and organize your files.
About the XMP standard
Metadata information is stored using the Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) standard, on which Adobe® Bridge, Adobe Illustrator®, Adobe
InDesign®, and Adobe Photoshop are built. Adjustments made to images with Photoshop® Camera Raw are stored as XMP metadata. XMP is
built on XML, and in most cases the metadata is stored in the file. If it isn’t possible to store the information in the file, metadata is stored in a
separate file called a sidecar file. XMP facilitates the exchange of metadata between Adobe applications and across publishing workflows. For
example, you can save metadata from one file as a template, and then import the metadata into other files.
Metadata that is stored in other formats, such as Exif, IPTC (IIM), GPS, and TIFF, is synchronized and described with XMP so that it can be more
easily viewed and managed. Other applications and features (for example, Adobe Drive) also use XMP to communicate and store information such
as version comments, which you can search using Adobe Bridge.
In most cases, the metadata remains with the file even when the file format changes (for example, from PSD to JPG). Metadata also remains when
files are placed in an Adobe document or project.
If you’re a C++ or Java developer, use the XMP Toolkit SDK to customize the processing and exchange of metadata. If you’re an Adobe
Flash® or Flex developer, use the XMP File Info SDK to customize the File Info dialog box. For more information, visit the Adobe website.
Working with metadata in Adobe Bridge and Adobe Creative Suite components
Many of the powerful Adobe Bridge features that allow you to organize, search, and keep track of your files and versions depend on XMP
metadata in your files. Adobe Bridge provides two ways of working with metadata: through the Metadata panel and through the File Info dialog
box.
In some cases, multiple views exist for the same metadata property. For example, a property may be labeled Author in one view and Creator in
another, but both refer to the same underlying property. Even if you customize these views for specific workflows, they remain standardized
through XMP.
To the top
The Metadata panel
A file’s metadata contains information about the contents, copyright status, origin, and history of the file. In the Metadata panel, you can view and
edit the metadata for selected files, use metadata to search for files, and use templates to append and replace metadata.
Depending on the selected file, the following types of metadata may appear:
File Properties
IPTC (IIM, Legacy)
IPTC Core supersedes it. However, you can display IPTC (IIM, legacy) metadata by selecting it from the Metadata options in the Preferences
dialog box.
IPTC Core
Council (IPTC) for professional photography, especially news and stock photos.
Describes the characteristics of the file, including the size, creation date, and modification date.
Displays editable metadata such as a description and copyright information. This set of metadata is hidden by default because
Displays editable metadata about the file. The IPTC Core specification was developed by the International Press Telecommunications
To the top
Page 16

IPTC Extension
Fonts
Includes additional identifying information about photo content, including rights-related details.
14
Lists the fonts used in Adobe InDesign files.
Linked Files
Plates
Document Swatches
Camera Data (Exif)
GPS
don’t have GPS metadata.
Camera Raw
Audio
Video
Edit History
Note: The History Log preference must be turned on in Photoshop for the log to be saved with the file’s metadata.
DICOM
Mobile SWF
1. To specify the metadata that appears in the Metadata panel, do one of the following:
2. Select the metadata fields that you want to display in the Metadata panel.
Lists files that are linked to an Adobe InDesign document.
Lists CMYK plates specified for printing in Adobe Illustrator files.
List the swatches used in Adobe InDesign and Adobe Illustrator files.
Displays information assigned by digital cameras, including the camera settings used when the image was taken.
Displays navigational information from a global positioning system (GPS) available in some digital cameras. Photos without GPS information
Displays settings applied by the Camera Raw plug-in.
Displays metadata for audio files, including artist, album, track number, and genre.
Displays metadata for video files, including pixel aspect ratio, scene, and shot.
Keeps a log of changes made to images with Photoshop.
Displays information about images saved in the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) format.
Lists information about SWF files, including title, author, description, and copyright.
Choose Preferences from the Metadata panel menu.
Choose Edit > Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS6 > Preferences (Mac OS), and then select Metadata from the
list on the left.
3. Select the Hide Empty Fields option to hide fields with no information in them.
4. Click OK.
The metadata placard
The metadata placard uses common icons for digital camera commands and functions.
Metadata placard key
A. Aperture B. Metering mode C. White balance D. Image dimensions E. Image size F. Color profile or filename extension G. Shutter speed H.
Exposure compensation I. ISO
Metering mode icons that appear in the metadata placard:
Average or centerweighted
average
Spot Multispot
Matrix or pattern Partial
Centerweighted average or
center weight
Digital ESP
Evaluative
Other or unknown
To the top
Note:
See the documentation that came with your camera for more information on its metering mode icons.
White balance icons that appear in the metadata placard:
Page 17

As shot Tungsten
15
Auto Fluorescent
Daylight Flash
Cloudy Custom
Shade
To show or hide the metadata placard, do one of the following:
Select or deselect Show Metadata Placard from the Metadata panel menu.
Select or deselect Show Metadata Placard in Metadata preferences.
View metadata
Do any of the following:
Select one or more files and view the information in the Metadata panel. If you select multiple files, only metadata that is
common to the files appears. Use the scroll bars to view hidden categories. Click the triangle to display everything within a
category.
You can change the typeface size in the panel by choosing Increase Font Size or Decrease Font Size from the panel menu.
Select one or more files and choose File >File Info. Then, select any of the categories listed at the top of the dialog box.
Use the left and right arrows to scroll categories, or click the down arrow and select a category from the list.
Choose View > As Details to display the metadata next to the thumbnails in the Content panel.
Choose View > As List to display the metadata in columns in the Content panel.
Position the pointer over a thumbnail in the content area. (Metadata appears in a tool tip only if Show Tooltips is selected in
Thumbnails preferences.)
Edit metadata in the Metadata panel
1. Click the Pencil icon to the far right of the metadata field you want to edit.
2. Type in the box to edit or add metadata.
3. Press Tab to move through metadata fields.
4. When you have finished editing the metadata, click the Apply button
changes you’ve made, click the Cancel button
at the bottom of the panel.
at the bottom of the Metadata panel. To cancel any
To the top
To the top
View Camera Raw and Lightroom metadata in Adobe Bridge
Because Adobe Bridge, Camera Raw, and Lightroom all use the XMP standard for storing metadata, each application can read metadata changes
made in the others. If you add a star rating or IPTC information to a photo in Adobe Bridge, for example, Lightroom can display that metadata in
the Library module. Similarly, adjustments or other metadata changes that you make to a photo in Camera Raw or Lightroom appear in
Adobe Bridge. Metadata changes made in Lightroom must be saved to XMP in Lightroom in order for Adobe Bridge to recognize them.
While browsing files, Adobe Bridge rereads metadata, detects changes, and updates previews automatically. When Adobe Bridge detects
metadata changes have been made to a photo, it displays a Has Settings badge
Note:
If you switch between Lightroom and Adobe Bridge rapidly, you may notice a delay in the update appearing in the Content and Preview
panels. If, after waiting a few seconds, Adobe Bridge does not automatically display metadata changes from Lightroom or Camera Raw, choose
View > Refresh, or press F5.
in the photo thumbnail in the Content panel.
View linked InDesign files
Adobe InDesign CS5 and CS6 documents that contain linked files display a link badge in the upper- right corner of the thumbnail in the Content
panel. The metadata for the linked files is available in Adobe Bridge.
1. Select an Adobe InDesign document with linked files in the Content panel of the Adobe Bridge window.
2. In the Metadata panel, expand the Linked Files section to view the names and paths of the linked files.
3. Right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) the .indd file and choose Show Linked Files to see the linked files in the
Contents panel.
To the top
To the top
Page 18
View colors (Illustrator and InDesign) or fonts (InDesign)
16
When you select an InDesign document, the Metadata panel displays fonts and color swatches used in the document. When you select an
Illustrator document, the Metadata panel displays plates and color swatches used in the document.
1. Select an InDesign or Illustrator document in the Content panel of the Adobe Bridge window.
2. In the Metadata panel, expand the Fonts (InDesign only), Plates (Illustrator only), or Document Swatches sections.
To the top
Add metadata using the File Info dialog box
The File Info dialog box displays camera data, file properties, an edit history, copyright, and author information. The File Info dialog box also
displays custom metadata panels. You can add metadata directly in the File Info dialog box. If you select multiple files, the dialog box shows
where different values exist for a text field. Any information you enter in a field overrides existing metadata and applies the new value to all
selected files.
Note:
You can also view metadata in the Metadata panel, in certain views in the Content panel, and by placing the pointer over the thumbnail in
the Content panel.
1. Select one or more files.
2. Choose File > File Info .
3. Select any of the following from the tabs at the top of the dialog box:
Use the Right Arrow and Left Arrow keys to scroll the tabs, or click the down-pointing arrow and choose a category from
the list.
Description
that can be used to search for the document. To specify copyright information, select Copyrighted from the Copyright Status
pop-up menu. Then enter the copyright owner, notice text, and the URL of the person or company holding the copyright.
IPTC Core
the photographer. Image lists descriptive information for the image. Status lists workflow and copyright information.
IPTC Extension
Camera Data
model, shutter speed, and f-stop. On the right, lists read-only file information about the image file, including pixel dimensions
and resolution.
Lets you enter document information about the file, such as document title, author, description, and keywords
Includes four areas: Content describes the visual content of the image. Contact lists the contact information for
Includes additional identifying information about photo content, including rights-related details.
On the left, lists read- only information about the camera and settings used to take the photo, such as make,
To the top
GPS
Displays navigational information from a global positioning system (GPS) available in some digital cameras. Photos
without GPS information don't have GPS metadata.
Video Data
as tape name and scene name.
Audio Data
Mobile SWF
Categories
Origin
transmission information, special instructions, and headline information.
DICOM
History
if Adobe Photoshop is installed.
Advanced
Raw Data
4. Type the information to add in any displayed field.
5. (Optional) Click Preferences at the bottom of the File Info dialog box for options to speed metadata editing: enable auto -
Lists information about the video file, including video frame width and height, and lets you enter information such
Lets you enter information about the audio file, such as title and artist.
Lists information about mobile media files, including title, author, description, and content type.
Lets you enter information based on Associated Press categories.
Lets you enter file information that is useful for news outlets, including when and where the file was created,
Lists patient, study, series, and equipment information for DICOM images.
Displays Adobe Photoshop history log information for images saved with Photoshop. The History option appears only
Displays metadata properties as they are stored within their namespace structures.
Displays XMP text information about the file.
Page 19
completion, reset XMP changes, or restore the default dialog box.
6. Click OK to apply the changes.
17
Work with metadata templates
You can create new metadata templates in Adobe Bridge by using the Create Metadata Template command. You can also modify the metadata in
the File Info dialog box and save it as a text file with a .xmp filename extension. You share XMP files with other users or apply them to other files.
You can save metadata in a template that can be used to populate metadata in InDesign documents and other documents created with
XMP-enabled software. Templates you create are stored in a shared location that all XMP-enabled software can access.
To create a metadata template, choose Tools > Create Metadata Template. Enter a Template Name, and select the metadata
values
that you want to include. Then click Save.
Note:
If you select a metadata option and leave the corresponding box empty, Adobe Bridge clears existing metadata when you apply the
template.
To go to a saved metadata template in Explorer (Windows) or the Finder (Mac OS), choose Tools > Create Metadata
Template. Click the pop-up menu in the upper-right corner of the Create Metadata template dialog box and choose Show
Templates Folder.
To delete a metadata template, select it in the Explorer (Windows) or Finder (Mac OS) and press Delete, or drag it to the
Recycle Bin (Windows) or the Trash (Mac OS).
To apply metadata templates to files in Adobe Bridge, select one or more files and then choose a command from the Metadata
panel menu:
Append Metadata > [template name]
Replace Metadata > [template name]
Applies the template metadata where no metadata value or property currently exists in the file.
Completely replaces any existing metadata in the file with the metadata in the template.
To the top
To edit a metadata template, choose Tools > Edit Metadata Template > [template name]. Enter different values for the included
metadata and click Save.
To save a file’s metadata as an XMP file, choose File >File Info. Click the pop-up menu at the bottom of the dialog box, next
to the Preferences button, and chose Export. Type a filename, specify a location, and click Save.
Note:
You can only export metadata from one file at a time. If multiple files are selected, the Export option is not available.
Import metadata into a document
1. Select one or more files.
2. Choose File > File Info .
3. Choose Import from the pop-up menu at the bottom of the dialog box.
Note:
You must save a metadata template before you can import metadata from a template.
4. Specify how you want to import the data:
Clear Existing Properties And Replace With Template Properties
the XMP file.
Keep Original Metadata, But Replace Matching Properties From Template
properties in the template.
Keep Original Metadata, But Append Matching Properties From Template
where no metadata value or property currently exists in the file.
Replaces all metadata in the file with the metadata in
Replaces only metadata that has different
(Default) Applies the template metadata only
To the top
5. Click OK.
6. Navigate to the XMP text file and click Open.
Twitter™ and Facebook posts are not covered under the terms of Creative Commons.
Legal Notices | Online Privacy Policy
Page 20
Create web galleries and PDFs with Adobe Output Module
18
Create a web photo gallery
Video tutorial: Creating image galleries with Adobe Bridge
Create a PDF contact sheet
Adobe Output Module preferences
The Adobe® Output Module is a script that comes with Adobe Bridge CS5 and later. You can use it to create HTML and Flash® web galleries that
you upload to a web server. You can also create PDF contact sheets and presentations with the Adobe Output Module.
The Adobe Output Module is available through the Output workspace.
Create a web photo gallery
A web photo gallery is a website that features a home page with thumbnail images that link to gallery pages that display full- size images. Adobe
Output Module provides various gallery templates, which you can select and customize using the Output panel.
1. Select the images you want to include in the gallery and choose Window > Workspace > Output. Then, click the Web Gallery
button at the top of the Output panel.
If the Output space is not listed, open Adobe Bridge Preferences (Ctrl + K on Windows or Command + K on Mac OS),
select the Startup Scripts panel, and select Adobe Output Module.
2. Choose a gallery from the Template menu and specify a thumbnail size from the Style menu. Then, customize the appearance
of the gallery using the options in the following drawers:
Site Info
e-mail address.
Color Palette
header text, background, and borders.
Appearance
JPEG images, transition effects, layouts, and whether to include filenames on HTML gallery images.
Image Info
Output Settings
Specify information that appears on every page of the gallery, including a title, a description, and contact name and
Options vary depending on selected template. Choose colors for different elements of the gallery, such as text,
Options vary depending on selected template. Specify the size of images and thumbnails, the quality of the
(Airtight galleries only) Include a caption, based on image metadata, on gallery images.
(Airtight galleries only) Specify the size and quality of JPEG gallery images.
To the top
3. (CS5 only) Click Refresh Preview to view the gallery in the Output Preview panel in Adobe Bridge. Click Preview In Browser to
preview the gallery in your default web browser.
Gallery previews display up to 20 files, but the complete gallery is saved and uploaded.
Note:
4. (Optional) Save custom settings for reuse by clicking the Save Style button
5. To upload your gallery via FTP, open the Create Gallery drawer. Enter an FTP Server address, User Name, Password, and
Folder destination. Then, click Upload.
When typing the server path, use slashes for designating directories. Check with your web hosting provider to verify the
Note:
path for accessing your public folder on the web server.
Adobe Bridge adds characters to the text you enter in the Password field after you click or press Tab to go to another
Note:
field. Adobe Bridge adds these characters for security reasons.
6. To save your gallery on your hard drive, open the Create Gallery drawer and specify a Save Location. Then, click Save.
Create a PDF contact sheet
Using the Adobe Output Module, you can create PDF contact sheets of one or more images. For contact sheets of multiple images, all images in
the layout are a uniform size. By specifying playback options, you can also create a PDF to use as a full -screen or slideshow presentation.
.
To the top
Page 21

Note:
You can also use the Contact Sheet II plug-in. In Adobe Bridge, choose Tools > Photoshop > Contact Sheet II. For more information, see
Print photos in a picture package layout in Photoshop Community Help.
19
1. Select the images you want to include in the PDF file and choose Window > Workspace > Output. Then, click the PDF button
at the top of the Output panel.
If the Output space is not listed, open Adobe Bridge Preferences (Ctrl + K on Windows or Command + K on Mac OS),
select the Startup Scripts panel, and select Adobe Output Module.
2. Choose an option from the Template menu. Then, customize the PDF using the options in the following drawers:
Document
Specify page size, orientation, output quality (in ppi); JPEG image compression quality; background color; and
optional permissions.
Layout
Overlays
Header, Footer
Playback
Watermark
Image-placement and image -spacing options.
Print the filename under each image and page numbers in a header or footer.
Enable headers and footers and specify their positioning and type.
Options for how the PDF plays onscreen in Adobe Acrobat® or Adobe Reader®.
Add a text or graphical watermark to each page or each image. Customize the text font, size, and color.
Customize the text or graphic’s scale, opacity, offset, and rotation.
3. Click Refresh Preview to preview the PDF in the Output Preview panel.
4. (Optional) Save custom settings for reuse by clicking the Save Template button
The Output Preview panel displays only the first page of the PDF.
Note:
.
5. To automatically open the PDF in Acrobat or Reader after you save it, select View PDF After Save at the bottom of the Output
panel. Otherwise, click Save.
Adobe Output Module preferences
1. In the Startup Scripts pane of Adobe Bridge preferences, select Adobe Output Module to enable the Output panel.
2. In the Output pane of Adobe Bridge preferences, specify the following:
Use Solo Mode For Output Panel Behavior
Allows only one drawer of options in the Output panel to be open at a time.
To the top
Convert Multi-Byte Filenames To Full ASCII
Removes multibyte characters from filenames when generating a gallery. Use
if your FTP server doesn’t accept multibyte characters.
Preserve Embedded Color Profile
Preserves a color profile that is embedded in the image, if possible. If the profile is not
supported in JPEG, Adobe Output Module converts the profile to sRGB.
Twitter™ and Facebook posts are not covered under the terms of Creative Commons.
Legal Notices | Online Privacy Policy
Page 22

Adjust Adobe Bridge Content panel display
20
Choose a view mode
Adjust the size of thumbnails
Lock the grid
Show additional metadata for thumbnails
Limit file size for thumbnails
Specify monitor-size previews
Specify thumbnail quality
Customize the List view
The Content panel displays thumbnails, detailed thumbnails, or a list of the files and folders in the selected folder. By default, Adobe Bridge
generates color-managed thumbnails and displays them in the Content panel with file or folder names as well as ratings and labels.
You can customize the view in the Content panel by displaying detailed text information with thumbnails or viewing thumbnails as a list. You can
also resize thumbnails and specify thumbnail quality. Choose Horizontal Layout or Vertical Layoutfrom the Content panel menu to position scroll
bars. Choosing Auto Layoutensures that Adobe Bridge switches between a horizontal and vertical layout as needed.
Choose a view mode
Choose one of the following from the View menu:
As Thumbnails to display files and folders as thumbnails with file or folder names as well as ratings and labels.
As Details to display thumbnails with additional text information.
As List to display files and folders as a list of filenames with associated metadata in a column format.
Show Thumbnail Only to display thumbnails without any text information, labels, or ratings.
Click the buttons in the lower-right corner of the Adobe Bridge window to View Content As Thumbnails, View Content As
Details, or View Content As List.
Adjust the size of thumbnails
Make thumbnails smaller so you can see more of them at once, or enlarge them to see thumbnail details.
Drag the Thumbnail slider at the bottom of the Adobe Bridge window.
Note: When you resize the Adobe Bridge window in Auto Layoutmode, thumbnails in the Content panel also resize. To avoid
this behavior, choose Horizontal Layout or Vertical Layout from the Content panel menu.
If you don’t see the filename or other metadata with an image thumbnail in the Content panel, drag the slider to the right to
make the thumbnails larger.
Click the Smaller Thumbnail Size button at the far left of the Thumbnail slider to reduce the number of columns in the Content
panel by one. Click the Larger Thumbnail Size button at the far right of the Thumbnail slider to increase the number of columns
in the Content panel by one. Adobe Bridge automatically maximizes the size of the thumbnails for the number of columns
displayed.
To the top
To the top
Lock the grid
Lock the grid so that Adobe Bridge always displays complete thumbnails in the Content panel. When the grid is locked, thumbnails keep their
configuration if the window is resized or panels opened or closed.
Choose View > Grid Lock, or click the Grid Lock button next to the Thumbnail slider at the bottom of the Adobe Bridge window.
Show additional metadata for thumbnails
The Additional Lines Of Thumbnail Metadata preference specifies whether to show additional metadata information with thumbnails in the Content
panel.
1. Choose Edit > Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS5.1 > Preferences (Mac OS), and click Thumbnails.
2. In the Additional Lines Of Thumbnail Metadata area, choose the type of metadata to display. You can display up to four extra
lines of information.
To the top
To the top
Page 23

Limit file size for thumbnails
21
You can limit the file size for which Adobe Bridge creates thumbnails (displaying large files can slow performance). If Adobe Bridge can’t create
thumbnails, it displays the icon associated with that particular file type. Adobe Bridge disregards this setting when displaying thumbnails for video
files.
1. Choose Edit > Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS5.1 > Preferences (Mac OS), and click Thumbnails.
2. Enter a number in the Do Not Process Files Larger Than box.
To the top
Specify monitor-size previews
Monitor-size previews display the highest quality preview possible based on the resolution of your monitor. With monitor -size previews enabled,
images appear sharp in full -screen mode.
1. Choose Edit > Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS5.1 > Preferences (Mac OS), and click Advanced.
2. Select Generate Monitor-Size Previews.
Specify thumbnail quality
You can specify that Adobe Bridge display embedded, high -quality, or 1:1 previews of image thumbnails for individual folders of images.
For faster browsing, choose a folder and then select the Browse Quickly By Preferring Embedded Imagesbutton in the
Adobe Bridge application bar.
To display higher -quality thumbnail previews, click theOptions For Thumbnail Quality And Preview Generation button in the
Adobe Bridge application bar and choose one of the following:
Prefer Embedded (Faster) to use the low-resolution thumbnails embedded in the source file. These thumbnails aren’t color
managed. This option is equivalent to choosing Browse Quickly By Preferring Embedded Images.
High Quality On Demand to use embedded thumbnails until you preview an image, at which time Adobe Bridge creates
color-managed thumbnails generated from the source files.
Always High Quality to always display color-managed thumbnails for all images. Always High Quality is the default quality
setting.
Generate 100% Previews to create 100% previews of images in the background for Loupe and Slideshow views. This
option speeds loupe and slide show operations but uses more disk space and slows initial browsing. See Use the Loupe
tool and View images as a slide show.
To the top
To the top
Customize the List view
You can customize the List view by sorting and resizing the columns, and by choosing which metadata categories to display.
1. Choose View > As List.
2. Do any of the following:
Click any column header to change the direction of the sort order.
Right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) any column header to choose a different metadata category, close the
column, insert a new column, resize the column, or return to the default configuration.
Note: The Name column is always the leftmost column.
Drag the vertical divider bar between two columns to make them wider or narrower.
Double-click between two column headers to automatically resize the column to the left.
|
To the top
Page 24

Adobe Bridge keyboard shortcuts
22
Keyboard shortcuts let you quickly select tools and execute commands without using a menu. When available, the keyboard shortcut appears to
the right of the command name in the menu.
In addition to using keyboard shortcuts, you can access many commands using context-sensitive menus. Context-sensitive menus display
commands that are relevant to the active tool, selection, or panel. To display a context -sensitive menu, right-click (Windows) or Ctrl-click
(Mac OS) an area.
This is not a complete list of keyboard shortcuts. This table primarily lists only those shortcuts that aren’t displayed in menu commands or tool tips.
Result Windows Mac OS
Go to next view Ctrl+\ Command+\
Go to previous view Ctrl+Shift+\ Command+Shift+\
Show/hide panels Tab Tab
Switch between 0- and 1-star rating Ctrl+‘ Command+‘
Increase thumbnail size Ctrl+plus sign (+) Command+plus sign (+)
Decrease thumbnail size Ctrl+minus sign (-) Command+minus sign (-)
Step thumbnail size up Ctrl+Shift+plus sign (+) Command+Shift+plus sign (+)
Step thumbnail size down Ctrl+Shift+minus sign ( -) Command+Shift+minus sign (-)
Move up a folder (in Folders panel or a
row)
Move down a folder (in Folders panel or a
row)
Move up a level (in Folders panel) Ctrl+Up Arrow Command+Up Arrow
Move left one item Left Arrow Left Arrow
Move right one item Right Arrow Right Arrow
Move to the first item Home Home
Move to the last item End End
Add to selection (discontiguous) Ctrl-click Command-click
Refresh Contents panels F5 F5
Add an item to the selection Shift + Right Arrow, Left Arrow, Up Arrow,
Display Help F1 Command+/
Rename next (with filename selected in
Content panel)
Up Arrow Up Arrow
Down Arrow Down Arrow
or Down Arrow
Tab Tab
Shift + Right Arrow, Left Arrow, Up Arrow,
or Down Arrow
Rename previous (with filename selected
in Content panel)
Show items with star rating of 1-5 or
higher in Filter panel
Show items with selected star rating in
Filter panel
Shift+Tab Shift+Tab
Ctrl+Alt+1 through 5 Command+Option+1 through 5
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+1 through 5 Command+Option+Shift+1 through 5
Page 25

Show items with labels 1 -4 in Filter panel Ctrl+Alt+6 through 9 Command+Option+6 through 9
23
Show all items with selected rating or
Shift-click Shift-click
higher in Filter panel
Clear filters Ctrl+Alt+A Command+Option+A
Select inverse in Filter panel Alt-click Option-click
Display Loupe tool in Preview panel or
Click Click
Review mode
Move Loupe tool Click or drag Click or drag
Display additional Loupes in Preview panel
Click Click
(multiple selection)
Move multiple Loupe tools simultaneously Ctrl-click or Ctrl-drag Command-click or Command-drag
Zoom in with Loupe tool + +
Zoom out with Loupe tool - -
Zoom in with Loupe tool (multiple
Ctrl+plus sign (+) Command+plus sign (+)
selection)
Zoom out with Loupe tool (multiple
Ctrl+minus sign (-) Command+minus sign (-)
selection)
Select all items in a stack Alt-click Option-click
Apply or remove current keyword and all
parent keywords in Keywords panel
Forcibly remove current keyword in
Keywords panel
Open disclosure triangle in Keywords
panel
Close disclosure triangle in Keywords
panel
|
Shift-click Shift-click
Alt-click Option-click
Ctrl+Right Arrow Command+Right Arrow
Ctrl+Left Arrow Command+Left Arrow
Page 26

Automate tasks in Adobe Bridge
24
Run tasks from the Tools menu
Batch rename files
Automatically stack HDR and panoramic images
Run tasks from the Tools menu
The Tools menu contains submenus for various commands available in different Adobe Creative Suite components. For example, if you have
Adobe Photoshop installed, you can use the commands under the Tools > Photoshop submenu to process photos that you select in Adobe Bridge.
Running these tasks from Adobe Bridge saves time because you don’t have to open each file individually.
Note: Third parties can also create and add their own items to the Tools menu for added functionality in Adobe Bridge. For information about
creating scripts, visit the Bridge Developer Center.
Adobe Bridge also includes useful automation scripts. The Adobe Output Module script, for example, lets you create web photo galleries and
generate Adobe PDF contact sheets and full -screen presentations. The Auto Collection CS5 script stacks sets of photos for processing into
panoramas or HDR images in Photoshop.
1. Select the files or folders you want to use. If you select a folder, the command is applied where possible to all files in the
folder.
2. Choose Tools > [Component], followed by the command you want. (If your component doesn’t have any automated tasks
available, it doesn’t appear in the Tools menu.)
For information about a particular command, see or search the documentation for that component.
Batch rename files
You can rename files in a group, or batch. When you batch rename files, you can choose the same settings for all the selected files. For other
batch-processing tasks, you can use scripts to run automated tasks.
1. Select the files that you want to rename.
2. Choose Tools > Batch Rename.
3. Set the following options:
Destination Folder Place the renamed files in the same folder, move them to another folder, or place copies in another
folder. If you choose to put the renamed files in a different folder, click Browse to select the folder.
New Filenames Choose elements from the menus and enter text as appropriate to create new filenames. Click the Plus
button (+) or Minus button (-) to add or delete elements.
String Substitution Allows you to change all or part of a filename to custom text. First, choose what you want to
replace: Original Filename replaces the string from the original filename. Intermediate Filename replaces a string that
is defined by preceding options in the New Filenamespop-up menus. Use Regular Expression allows you to use
regular expressions to find strings based on patterns in filenames. Replace All replaces all substrings that match the
pattern in the source string.
Options Select Preserve Current Filename In XMP Metadata to retain the original filename in the metadata. For Compatibility,
select the operating systems with which you want renamed files to be compatible. The current operating system is selected by
default, and cannot be deselected.
Preview One current and new filename appear in the Preview area at the bottom of the Batch Rename dialog box. To see
how all selected files will be renamed, click the Preview button.
4. (Optional) Select a preset from the Presets menu to renaming with frequently used naming schemes. To save batch rename
settings for reuse, click Save.
For more information on batch- renaming files, see any of the following tutorials:
Stacking and renaming files,
Batch-renaming, by Deke McClelland
Changing obscure camera filenames with the Batch Rename command, by Michael Ninness
by Conrad Chavez
To the top
To the top
To the top
Page 27

Automatically stack HDR and panoramic images
The Auto Collection CS5 script in Adobe Bridge assembles sets of images into stacks for processing as high dynamic range (HDR) or panoramic
25
composites in Photoshop CS5. The script collects images into stacks based on capture time, exposure settings, and image alignment. Timestamps
must be within 18 seconds for the Auto Collection script to process the photos. If exposure settings vary across the photos and content overlaps
by more than 80%, the script interprets the photos as an HDR set. If exposure is constant and content overlaps by less than 80%, the script
interprets the photos as being part of a panorama.
Note: You must have Adobe Bridge with Photoshop CS5 or later for Auto Collection CS5 to be available.
1. To enable the Auto Collection CS5 script, choose Edit > Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS5.1 > Preferences
(Mac OS).
2. In the Startup Scripts panel, select Auto Collection CS5, and then click OK.
3. Select a folder with the HDR or panoramic shots, and choose Stacks > Auto-Stack Panorama/HDR.
4. Choose Tools > Photoshop > Process Collections In Photoshop to automatically merge them and see the result in Adobe
Bridge.
Note: For more information about panoramas and HDR in Photoshop, see the Photoshop Community Help topics Create
panoramic images with Photomerge and High dynamic range images.
|
Page 28

Export photos from Adobe Bridge to the web
26
Manage Export modules
Use Export queues
Export photos
Export photos using presets
The Export panel in Adobe Bridge CS5 provides a streamlined way to save photos as JPEG and easily upload them to photo-sharing websites,
including Facebook, Flickr, and Photoshop.com.
Note: Exporting to Facebook, Flickr, and Photoshop.com is available only in North America.
For more information about using the Export panel in Adobe Bridge, see Exporting from Bridge CS5 to social media sites by Michael Hoffman.
Important: When using the Export panel, make sure you have installed the latest Adobe Bridge update. Download updates from the Adobe
product updates page.
Manage Export modules
Adobe Bridge uses modules for exporting photos. Each module holds photos in a queue until you export them. Each module allows you to specify
image size and other options.
Save To Hard Drive
Facebook Uploads photos to a Facebook account. You can upload to an existing album or a new album.
Flickr Uploads photos to a Flickr account. You can specify privacy settings before you upload.
Photoshop.com
To enable or disable export modules, click the Export panel menu button and choose Manage Modules.
To view your export history, click the Export panel menu button and choose Export Progress.
Saves JPEG photos to a location on your hard drive .
Uploads photos to a Photoshop.com account, incluing to a specific gallery or collection.
Use Export queues
To add photos to a queue, drag them from the Content panel to a module in the Export panel.
Hide/show the contents of a queue by clicking the triangle to the left of the module name.
To remove a photo from a queue, select the photo and click the Remove Photo button .
To empty an entire queue, click the Clear Job button .
Click the Reveal In Bridge button to go to a queued photo in the Content panel.
Export photos
1. Double-click a queue or click the Export Job button .
2. Specify options in the Destination tab of the Export dialog box:
(Photo-sharing modules) Sign in to the website.
Choose a location for the exported files, such as a Flickr set, a Photoshop.com gallery, or a folder on your hard drive.
(Flickr) Specify privacy settings for the photos you upload.
(Save To Hard Drive) Specify how to resolve naming conflicts. You can rename the files, overwrite existing files with the
same name, or skip the file when you export.
3. Specify options in the Image Options tab of the Export dialog box:
Image Size And Quality If you choose Manual Size instead of Don’t Resize, specify the following:
Constrain To Fit Specify, in pixels, the maximum length of the longer side of the image. Adobe Bridge preserves the
aspect ratio of the exported image.
Resample Method Bilinear provides medium-quality results. Bicubic is slower than bilinear but produces smoother
tonal gradations. Bicubic Sharper applies sharpening, making it good for preserving detail in resampled images.
Always Render From Fullsize Image Creates the JPEG from the full-size image, not from a lower-quality preview.
Image Quality Higher numbers preserve greater image quality and apply less compression.
To the top
To the top
To the top
Page 29

Metadata Specify what metadata and keywords to include with the exported image:
Include Original Metadata Include all metadata, just the copyright, the copyright and contact information, or all
27
metadata except camera and Camera Raw metadata.
Apply Metadata Template See Work with metadata templates.
Additional Keywords Enter any additional keywords you want to apply to the photo.
4. Click Export.
Export photos using presets
To the top
Presets appear as queues in the Export panel. When you export a job using a preset, Adobe Bridge bypasses the Export dialog box and starts the
export directly.
To reuse settings, specify options in the Export dialog box, then enter a name in the Preset Name field and click Save.
|
Page 30

Get photos from a digital camera or card reader into Adobe Bridge
28
Adobe Bridge Photo Downloader
A. Name of connected device B. Options for saving files C. Options for renaming files D. Options for converting and copying files E. Get
Photos button
1. Connect your camera or card reader to the computer (see the documentation for the device, if necessary).
2. Do one of the following:
(Windows) Click Download Images - Use Adobe Bridge CS5 in the Autoplay window, or choose File > Get Photos From
Camera
.
(Mac OS) In Adobe Bridge, choose File > Get Photos From Camera.
(Mac OS) You can configure Adobe Bridge to automatically open Photo Downloader when a camera is connected to the
computer. Choose Adobe Bridge CS5.1 > Preferences. In the Behavior area of the General panel, select When A Camera
Is Connected, Launch Adobe Photo Downloader. Then, click OK.
3. In the Adobe Bridge CS5.1 Photo Downloader window, choose the name of the camera or card reader from the Get Photos
From menu.
If you click Advanced Dialog, thumbnail images of every photo on your camera’s memory card appear.
4. To remove a photo from the import batch, click Advanced Dialog, and click the box below the photo thumbnail to deselect it.
5. To change the default folder location, click the Browse button (Windows) or the Choose button (Mac OS) next to Location, and
specify a new location.
6. To store the photos in their own folder, select Create Subfolder(s), and then select one of the following:
Today’s Date creates a subfolder named with the current date.
Shot Date creates a subfolder named with the date and time you shot the photo.
Custom Name creates a subfolder using the name you type.
7. To rename the files as you import them, choose an option from the Rename Files menu. All the photos in the import batch
share the same name, and each photo has a unique number attached at the end. To preserve the camera’s original filename
in XMP metadata for later reference, check Preserve Current Filename In XMP.
8. To open Adobe Bridge after you import photos, select Open Adobe Bridge.
9. To convert Camera Raw files to DNG as you import them, select Convert To DNG.
10. To delete the original photos from your camera or card reader after they’re downloaded, select Delete Original Files.
11. To save copies of photos as you import them, select Save Copies To and specify a location.
Page 31

12. (Optional) To apply metadata, click the Advanced Dialogbutton. Then, type information in the Creator and Copyright text
29
boxes, or choose a metadata template from the Template To Use menu.
13. Click Get Photos. The photos appear in Adobe Bridge.
|
Page 32

Preview and compare images in Adobe Bridge
30
View images as a slide show
Preview images using the Preview panel
Preview images using the Full Screen Preview
Evaluate and select images using Review mode
Use the Loupe tool
Use software rendering for previews
You can preview images in Adobe Bridge in the Preview panel, in Full Screen Preview, and in Review mode. The Preview panel displays up to
nine thumbnail images for quick comparisons.Full Screen Preview displays images full screen. Review mode displays images in a full-screen view
that lets you navigate the images; refine your selection; label, rate, and rotate images; and open images in Camera Raw.
View images as a slide show
The Slideshow command lets you view thumbnails as a slide show that takes over the entire screen. This is an easy way to work with large
versions of all the graphics files in a folder. You can pan and zoom images during a slide show, and set options that control slide show display,
including transitions and captions.
To view a slide show, open a folder of images, or select the images you want to view in the slide show, and choose View >
Slideshow.
To display commands for working with slide shows, press H while in Slideshow view.
To specify slide show options, press L while in Slideshow view or choose View > Slideshow Options.
Display options Choose to black out additional monitors, repeat the slide show, or zoom back and forth.
Slide options Specify slide duration, captions, and slide scaling.
Transition options Specify transition styles and speed.
Preview images using the Preview panel
Select up to nine images from the Content panel and (if necessary) choose Window > Preview Panel.
Preview images using the Full Screen Preview
Select one or more images and choose View > Full Screen Preview, or press the spacebar.
Press the plus sign (+) or minus sign (-) key to zoom in or out of the image, or click the image to zoom to that point. You can
also use a mouse scroll wheel to increase and decrease magnification.
To pan the image, zoom in and then drag.
Press the Right Arrow and Left Arrow keys to go to the next and previous image in the folder.
Note: If you select multiple images before entering Full Screen Preview, pressing the Right Arrow and Left Arrow keys cycles
through the selected images.
Press the spacebar or Esc to exit Full Screen Preview.
To the top
To the top
To the top
Evaluate and select images using Review mode
Review mode is a dedicated full-screen view for browsing a selection of photos, refining the selection, and performing basic editing. Review mode
displays the images in a rotating “carousel” that you can navigate interactively.
To the top
Page 33

Review mode
31
For a video on using Review mode in Adobe Bridge CS4 and Adobe Bridge CS5, see www.adobe.com/go/lrvid4012_bri.
1. Open a folder of images or select the images you want to review and choose View > Review Mode.
2. Do any of the following:
Click the Left or Right Arrow buttons in the lower- left corner of the screen, or press the Left Arrow or Right Arrow key on
keyboard, to go to the previous or next image.
your
Drag the foreground image right or left to bring the previous or next image forward.
Click any image in the background to bring it to the front.
Drag any image off the bottom of the screen to remove it from the selection. Or click the Down Arrow button in the lower-
left corner of the screen.
Right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) any image to rate it, apply a label, rotate it, or open it.
Press ] to rotate the foreground image 90° clockwise. Press [ to rotate the image 90° counterclockwise.
Press Esc or click the X button in the lower-right corner of the screen to exit Review mode.
Click the New Collection button in the lower-right corner of the screen to create a collection from the selected images and
exit Review mode.
Press H while in Review mode to display keyboard shortcuts for working in Review mode.
Use the Loupe tool
The Loupe tool lets you magnify a portion of an image. The Loupe tool is available in the Preview panel and on the frontmost or selected image in
Review mode. By default, if the image is displayed at less than 100%, the Loupe tool magnifies to 100%. You can display one Loupe tool per
image.
To magnify an image with the Loupe tool, click it in the Preview panel or in Review mode. In Review mode, you can also click
the Loupe tool button in the lower-right corner of the screen.
To hide the Loupe tool, click the X in the lower- right corner of the tool, or click inside the magnified area of the tool. In Review
mode, you can also click the Loupe tool button in the lower-right corner of the screen.
Drag the Loupe tool in the image, or click a different area of the image, to change the magnified area.
To zoom in and out with the Loupe tool, use the mouse scroll wheel, or press the plus sign (+) or minus sign ( -) key.
To display multiple Loupe tools in multiple images in the Preview panel, click the individual images.
To synchronize multiple Loupe tools in the Preview panel, Ctrl-click or Ctrl-drag (Windows) or Command-click or Command-
drag (Mac OS) one of the images.
Use software rendering for previews
To the top
To the top
Page 34

Select this option if slide shows or images in the Preview panel, Full Screen Preview, or Review mode don’t display correctly. Using software
rendering for previews displays previews correctly, but the display speed may become slow and there may be other limitations.
32
1. In Advanced preferences, select Use Software Rendering.
2. Restart Adobe Bridge.
Note: Software rendering is automatically enabled on computers with less than 64 MB of VRAM and on dual- monitor systems with less than
128 MB of VRAM.
|
Page 35

Preview dynamic media files in Adobe Bridge
33
Preview media files in the Preview panel
Play full-screen previews of dynamic media files
Set playback preferences
You can preview most video, audio, and 3D files in Adobe Bridge. You can preview SWF, FLV, and F4V files as well as most files supported by
the version of QuickTime you have installed on your computer. Use Playback preferences to control how media files are played.
Preview media files in the Preview panel
1. Select the file to preview in the Content panel.
2. In the Preview panel, click the Play button
button
to turn continuous loop on or off, or click the Volume button to adjust loudness.
You can brighten or darken the Adobe Bridge interface to better preview dynamic media files. See Adjust brightness and
colors.
to start the video, click the Pause button to pause playback, click the Loop
Play full-screen previews of dynamic media files
1. Select the file to preview in the Content panel.
2. Choose View > Full Screen Preview .
3. Click the Pause button
continuous loop on or off, or click the Volume button
to pause playback, click the Play button to resume playback, click the Loop button to turn
To the top
To the top
To the top
|
Page 36

Stack files in Adobe Bridge
34
Create a file stack
Manage stacks
Preview images in stacks
Stacks let you group files together under a single thumbnail. You can stack any type of file. For example, use stacks to organize image sequences,
which often comprise many image files.
Note: Adobe Bridge stacks are different from Photoshop image stacks, which convert groups of images to layers and store them in a Smart
Object.
Commands that apply to a single file also apply to stacks. For example, you can label a stack just as you would a single file. Commands you apply
to expanded stacks apply to all files in the stack. Commands you apply to collapsed stacks apply only to the top file in the stack (if you’ve selected
only the top file in the stack) or to all files in the stack (if you’ve selected all files in the stack by clicking the stack border).
The default sort order in a stack is based on the sort order for the folder that contains the stack.
An Adobe Bridge stack in the Content panel (collapsed)
An expanded stack
For a tutorial on stacking files, see Stacking and renaming files by Conrad Chavez.
Create a file stack
Select the files you want to include in the stack, and choose Stacks > Group As Stack. The first file you select becomes the stack thumbnail.
The number on the stack indicates how many files are in the stack.
Manage stacks
To expand a collapsed stack, click the stack number or choose Stacks > Open Stack. To expand all stacks, choose Stacks >
Expand All Stacks.
To collapse an expanded stack, click the stack number or choose Stacks > Close Stack. To collapse all stacks, choose
Stacks > Collapse All Stacks.
To add files to a stack, drag the files you want to add to the stack.
Note: While you can add a stack to another stack, you cannot nest stacks. Files in the added stack are grouped with the
existing stack files.
To remove files from a stack, expand the stack and then drag the files out of the stack. To remove all files from a stack, select
the collapsed stack and choose Stacks > Ungroup From Stack.
To select all files in a collapsed stack, click the border of the stack. Alternatively, Alt-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS)
the stack thumbnail.
To the top
To the top
Page 37

Preview images in stacks
35
To the top
In stacks that contain 10 or more images, you can preview (scrub) the images at a specified frame rate and enable onion skinning, which allows
you to see preceding and succeeding frames as semitransparent overlays on the current frame.
To preview a stack, hold the mouse over the stack in the Content panel until the slider appears, and then click Play, or drag
the slider. If you don’t see the Play button or slider, increase the thumbnail size by dragging the Thumbnail slider at the bottom
of the Adobe Bridge window.
To set the playback frame rate, right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) the stack and choose a frame rate from the
Stacks > Frame Rate menu.
To set the default stack playback frame rate, choose a frame rate from the Stack Playback Frame Rate menu in Playback
preferences.
To enable onion skinning, right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) the stack and choose Stack > Enable Onion Skin.
|
Page 38

Start Adobe Bridge
36
Start Adobe Bridge from an Adobe Creative Suite 5 component
Return to the last open Adobe Creative Suite 5 component from Adobe Bridge
Switch to Adobe Bridge from Mini Bridge
Start Adobe Bridge directly
Start Adobe Bridge automatically
Hide or show Adobe Bridge
You can start Adobe Bridge directly or start it from the any of following Adobe Creative Suite 5 or CS5.5 components: After Effects, Captivate®,
Encore®, Flash® Professional, InCopy, InDesign, Illustrator®, Photoshop, and Premiere® Pro.
Start Adobe Bridge from an Adobe Creative Suite 5 component
Do either of the following:
Click the Adobe Bridge button in the application bar.
Return to the last open Adobe Creative Suite 5 component from Adobe Bridge
Choose File > Return To [Component] or click the Return To [Component] button in the application bar.
Switch to Adobe Bridge from Mini Bridge
(Photoshop, InDesign, InCopy) Click the Open Bridge button at the top of the Mini Bridge panel.
Start Adobe Bridge directly
(Windows) Choose Adobe Bridge CS5.1 from the Start > Programs menu.
(Mac OS) Double-click the Adobe Bridge CS5.1 icon located in the Applications/Adobe Bridge CS5.1 folder.
To the top
To the top
To the top
To the top
Start Adobe Bridge automatically
You can configure Adobe Bridge to run automatically in the background every time you log in. Running Adobe Bridge in the background consumes
fewer system resources until you are ready to use it.
To configure Adobe Bridge to open automatically in the background at login, do one of the following:
The first time you launch Adobe Bridge, click Yes when asked if you want to launch Adobe Bridge automatically at login.
In the Advanced panel of the Adobe Bridge Preferences dialog box, choose Start Bridge At Login.
(Windows) When Adobe Bridge is open, right-click the Adobe Bridge system tray icon and choose Start Bridge At Login.
Important: When Adobe Bridge is running in the background, it may interfere with the installation of other Adobe applications and plug-ins. If this
happens, quit Adobe Bridge. See go.adobe.com/kb/ts_cpsid_50680_en-us.
Hide or show Adobe Bridge
(Windows) To switch between operational modes, do any of the following:
Right-click the Adobe Bridge icon in the system tray and choose Show Bridge to open the application.
Choose File > Hide to run Adobe Bridge in the background.
To the top
To the top
Page 39

Right-click the Adobe Bridge icon in the system tray and choose Hide Bridge to run Adobe Bridge in the background.
(Mac OS) To switch between operational modes, do any of the following:
37
Click the Adobe Bridge CS5.1 icon in the Dock and choose Show or Hide.
In Adobe Bridge, choose Adobe Bridge CS5.1 >Hide Adobe Bridge CS5.1 to run Adobe Bridge in the background.
|
Page 40

Use collections in Adobe Bridge
38
Create a collection
Create a smart collection
Edit a smart collection
Rename a collection
Delete a collection
Add files to a collection
Remove files from a collection
Copy files between collections
Locate missing files
Collections are a way to group photos in one place for easy viewing, even if they’re located in different folders or on different hard drives. Smart
collections are a type of collection generated from a saved search. The Collections panel allows you to create, locate, and open collections, as
well as create and edit smart collections.
Create a collection
Do any of the following:
Click the New Collection button at the bottom of the Collections panel to create a new, empty collection.
Select one or more files in the Content panel and then click the New Collection button in the Collections panel. Click Yes when
asked if you want to include the selected files in the new collection.
By default, if you select a file in a collection, the file is listed as being located in the collection folder. To navigate to the folder in which the file is
physically located, select the file and then choose File > Reveal In Bridge.
Create a smart collection
Click the New Smart Collection button at the bottom of the Collections panel.
To add or remove a smart collection from the Favorites panel, right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) the smart collection in the
Collections panel and choose Add To Favorites or Remove From Favorites.
Edit a smart collection
1. Select a smart collection in the Collections panel.
2. Click the Edit Smart Collection button
3. Specify new criteria for the smart collection, and then click Save.
Important: Remove photos from a smart collection by editing the criteria. Deleting a photo while viewing a smart collection
moves the photo to the Recycle Bin (Windows) or Trash (Mac OS).
.
To the top
To the top
To the top
Rename a collection
Do any of the following:
Right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) the collection name and choose Rename from the menu. Then overwrite the
name of the collection.
Delete a collection
When you delete a collection, you simply remove it from the collections list in Adobe Bridge. No files are deleted from your hard disk.
To delete a collection, do any of the following:
In the Collections panel, select a collection name, and then click the trash icon.
Right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) a collection name, and then choose Delete from the menu.
To the top
To the top
Page 41

Add files to a collection
39
To add files to a collection, do any of the following:
Drag the files from the Content panel, the Explorer (Windows), or the Finder (Mac OS) to the collection name in the Collections
panel.
Copy and paste files from the Content panel onto a collection name in the Collections panel.
To the top
Remove files from a collection
To remove files from a collection, select the collection in the Collections panel and do any of the following:
Select a file in the Content panel and click Remove From Collection, or right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) and
choose Remove From Collection.
Select a file in the Content panel and press Delete. Click Reject to mark the file as rejected, Delete to move it to the Recycle
Bin (Windows) or the Trash (Mac OS), or Cancel to keep the file.
Copy files between collections
1. Select a collection in the Collections panel.
2. Drag a file from the Content panel to the collection in the Collections panel that you want to copy it to.
Locate missing files
Adobe Bridge tracks the locations of the files in collections. If a file is moved in Adobe Bridge, the file remains in the collection. If a collection
includes files that have been moved or renamed in the Explorer (Windows) or the Finder (Mac OS), or if the files are on a removable hard drive
that is not connected when you view the collection, Adobe Bridge displays an alert at the top of the Content panel indicating that the files are
missing.
1. Click Fix to locate the missing files.
2. In the Find Missing Files dialog box, select the missing files and do any of the following:
Click Browse to navigate to the new location of the files.
Click Skip to ignore the missing files.
Click Remove to remove the missing files from the collection.
To the top
To the top
To the top
|
Page 42

Use keywords in Adobe Bridge
40
Create new keywords or subkeywords
Add keywords to files
Remove keywords from a file
Manage keywords
Find keywords
Import or export keywords
The Keywords panel lets you create and apply Adobe Bridge keywords to files. Keywords can be organized into hierarchical categories consisting
of parent keywords and child keywords (called subkeywords). Using keywords, you identify files based on their content. For example, you can use
the Filter panel to view all files in a folder that share keywords, and you can use the Find command to locate files that contain the specified
keyword.
For more information, see Nested, hierarchal keywording | Adobe Bridge.
Create new keywords or subkeywords
1. In the Keywords panel, select a keyword.
For example, if Names is selected, adding a new keyword creates a keyword on the same level as Names, such as Sports;
and adding a new subkeyword lets you create a keyword under Names, such as Juanita.
2. Click the New Keyword button
the panel menu.
3. Type the keyword name and press Enter (Windows) or Return (Mac OS).
If you want a parent keyword to be used for structural purposes only, place the keyword in brackets, such as [Names]. Keywords in brackets
cannot be added to files.
You can also add keywords by using the Find box at the bottom of the Keywords panel. Use commas to indicate subkeywords and semicolons
to indicate separate entries. For example, to add “Los Angeles” to the Places category, select the “Places” keyword, type Los Angeles, and
then click the New Sub Keyword button.
orNew Sub Keyword button or choose either New Keyword or New Sub Keyword from
Add keywords to files
1. Select the file or files to add keywords to.
2. In the Keywords panel, select the box next to the name of the keyword or subkeyword. Shift-click the box to select all parent
keywords.
A check mark appears in the box next to the keyword when it’s added to a selected file. If you select multiple files, but the keyword was added to
only some of them, a hyphen (-) appears in the keyword box.
Note: If you Shift-click a subkeyword, the parent keywords are also added to the file. To change the behavior so that clicking a subkeyword
automatically adds the parent keywords (and Shift -clicking adds only the subkeyword), select Automatically Apply Parent Keywords in Keywords
preferences.
To the top
To the top
Remove keywords from a file
To remove the check mark, select the file, and then click the box next to the name of the keyword or keyword set. To remove
the check mark from all parent keywords as well, Shift-click the keyword box.
To remove a check mark forcibly, Alt-click (Windows) or Option-click (Mac OS) the keyword box. This method is especially
useful when you select multiple files to which the keyword was applied only to some, causing a hyphen to appear in the
keyword box. To forcibly remove a check mark from a keyword and its parents, press Alt+Shift (Windows) or Option+Shift
(Mac OS) and click the keyword box.
Select the file, and then choose Remove Keywords from the Keywords panel menu. To remove all keywords from the file, click
Yes.
To lock a file so that keywords can’t accidentally be removed, right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) the file in the
Content panel and choose Lock Item. When an item is locked, you cannot add or remove keywords, edit metadata, or
apply labels or ratings.
To the top
Page 43

Manage keywords
41
Do any of the following:
To rename a keyword, select the keyword or keyword set and choose Rename from the panel menu. Then, type over the
name in the panel and press Enter (Windows) or Return (Mac OS).
Note: When you rename a keyword, the name changes only for the selected files. The original keyword name stays in all
other files to which the keyword was previously added.
To change a subkeyword to a keyword, drag the subkeyword below the list of keywords, to the bottom of the Keywords panel.
To delete a keyword, select the keyword by clicking its name, and then click the Delete Keyword button at the bottom of the
panel or choose Delete from the panel menu.
Note: Temporary keywords, such as keywords that you get from other users, appear in italics in the Keywords panel. To
make temporary keywords permanent in Adobe Bridge, right-click (Windows) or Ctrl-click (Mac OS) the keyword and choose
Make Persistent from the context menu.
To expand or collapse keyword categories, click the arrow next to the category, or choose Expand All or Collapse All from the
panel menu.
To search for files using keywords, choose Find from the Keywords panel menu. (See Search for files and folders with
Adobe Bridge.)
To the top
Find keywords
In the box at the bottom of the Keywords panel, type the name of the keyword you’re looking for.
By default, all keywords containing the characters you type are highlighted. The first occurrence is highlighted in green; all subsequent
occurrences are highlighted in yellow. Click Find Next Keyword or Find Previous Keyword to select a different highlighted keyword.
To highlight only keywords that begin with the characters you type, click the magnifying glass icon in the search box and choose Starts With as
the search method. For example, if Contains is selected, typing “in” highlights both “Indiana” and “Maine”; if Starts With is selected, only
“Indiana” is highlighted.
Import or export keywords
You can import tab -indented text files exported from other applications, such as Adobe Photoshop Lightroom. You can also export Adobe Bridge
keywords as text files. These files are encoded as UTF-8 or ASCII, which is a subset of UTF-8.
To import a keyword file into Adobe Bridge without removing existing keywords, choose Import from the Keywords panel menu,
and then double -click the file to import.
To import a keyword file into Adobe Bridge and remove existing keywords, choose Clear And Import from the Keywords panel
menu, and then double-click the file to import.
To export a keyword file, choose Export from the Keywords panel menu, specify a filename, and click Save.
|
To the top
To the top
Page 44

Work with the Adobe Bridge cache
42
Build and manage the cache
Set cache preferences
The cache stores thumbnail and metadata information (as well as metadata that can’t be stored in the file, such as labels and ratings) to improve
performance when you view thumbnails or search for files. However, storing the cache takes up disk space. When you build a cache, you can opt
to export it for sharing or archiving, and you can choose to generate 100% previews. You can manage the cache by purging it and by setting
preferences to control its size and location.
More information on the Bridge cache is available in the article Manage the cache | Adobe Bridge CS4, CS5.
Build and manage the cache
Choose either of the following commands from the Tools > Cache menu:
Build And Export Cache Builds, as a background process, a cache for the selected folder and all the folders within it (except aliases or shortcuts
to other folders). This command reduces the time spent waiting for thumbnails and file information to be displayed as you browse in subfolders.
You can also generate 100% previews in cache to help improve performance when viewing images at 100% in slide shows and full-screen
previews, or using the Loupe tool.
The Export Cache To Folders option in the Build Cache dialog box creates a local cache for sharing or archiving to disc. When this option is
selected, Adobe Bridge creates cache files for the selected folder and its subfolders. When a folder is copied to an external disc, such as a CD or
DVD for archiving, the cache files are copied, too. When you navigate to a previously unviewed folder in Adobe Bridge, such as a folder on the
archived CD, Adobe Bridge uses the exported cache to display thumbnails faster. The exported cache is based on the central cache and includes
duplicate information.
Note: Exported cache files are hidden files. To view them in Adobe Bridge, choose View >Show Hidden Files.
Purge Cache For Folder [Selected Folder] Clears the cache for the selected folder. This command is useful if you suspect that the cache for a
folder is old and must be regenerated. (If, for example, thumbnails and metadata are not being updated.)
Set cache preferences
1. Choose Edit > Preferences (Windows) or Adobe Bridge CS5.1 > Preferences (Mac OS).
2. Click Cache.
3. Do any of the following:
Keep 100% Previews In Cache Keeps 100% previews of images in the cache to speed zoom operations in a slide show or
in full-screen preview, and when using the Loupe tool. Keeping 100% previews in cache, however, can use significant disk
space.
Automatically Export Caches To Folders When Possible Creates exported cache files in the viewed folder, if possible. For
example, you cannot place cache files in a folder on a read-only disc. Exporting cache files is useful when, for example, you
share images, because the images can display faster when viewed in Adobe Bridge on a different computer.
Location Specify a new location for the cache. The new location takes effect the next time you start Adobe Bridge.
Cache Size Drag the slider to specify a larger or smaller cache size. If the cache is near the defined limit (500,000 records) or
the volume that contains the cache is too full, older cached items are removed when you exit Adobe Bridge.
Compact Cache Optimize cache by removing obsolete records to reduce the total number of records.
Purge Cache Delete the entire cache, freeing room on the hard drive.
To the top
To the top
|
Page 45

Mini Bridge
43
Page 46

Mini Bridge
44
Open Mini Bridge
Browse files in Mini Bridge
Open or place files using Mini Bridge
Preview files in Mini Bridge
Rename files in Mini Bridge
Favorites and collections in Mini Bridge
Mini Bridge CS5 tutorials
Mini Bridge is an extension that lets you work with assets in a panel in Adobe® Photoshop®, Adobe InDesign®, and Adobe InCopy®. It is a useful
way to access many Adobe Bridge features when you work those applications. Mini Bridge communicates with Adobe Bridge to create thumbnails,
keep files synchronized, and perform other tasks.
Open Mini Bridge
Open the Mini Bridge panel by doing any of the following:
(Photoshop) Choose File > Browse In Mini Bridge.
(Photoshop) Choose Window > Extensions > Mini Bridge.
(InDesign, InCopy) Choose Window > Mini Bridge.
If the Mini Bridge panel displays the message, "Bridge must be running to browse files," click the Launch Bridge button.
Browse files in Mini Bridge
Navigate to files by clicking the Favorites pop-up menu on the left side of the panel. You can also view a folder by clicking the
folder name or arrow in the path bar.
Use the Search button to find files based on criteria you specify.
Specify what you want to see in the preview area using the following buttons:
Sort
Filter
Note:
To display rejected files, click the View button and choose Show Rejected Files.
Drag the edge of the Mini Bridge panel and resize it to make thumbnails bigger or smaller.
Sort by filename, file type, creation date, and other metadata criteria.
Filter by star ratings or labels.
To the top
To the top
Open or place files using Mini Bridge
To open or place a file, select its thumbnail in the Mini Bridge panel and do any of the following:
Drag it into the host application or onto the host application icon.
Double-click it to open it in its preferred application.
(InDesign) Drag a snippet from the Mini Bridge panel into a document. Position the loaded cursor where you want the upperleft corner of the snippet to be. Snippet files have the file extension .IDMS or .INDS.
To run an automated task, select one or more thumbnails, right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) and choose [Host
Application] > [Automated Task]. For information about a particular command, see or search Photoshop Help or InDesign Help,
as necessary.
To open a file in Adobe Bridge, select it and click the Adobe Bridge button at the top of the Mini Bridge panel. Or, right-click
(Windows) or Control -click (Mac OS) a thumbnail and choose Reveal In Bridge.
Preview files in Mini Bridge
To the top
To the top
Page 47

View menu button
45
Choose Slideshow to open a slideshow of the selected images in Adobe Bridge.
Choose Review Mode to open the selected images in Review Mode in Adobe Bridge.
Choose Full Screen Preview to open a full-screen preview in Adobe Bridge.
lets you preview images in the Mini Bridge panel. Click it and choose any of the following:
Rename files in Mini Bridge
Click a filename in the Mini Bridge panel and type to rename it. Or, right-click (Windows) or Control-click (Mac OS) a thumbnail
and choose Rename.
Favorites and collections in Mini Bridge
Adobe Bridge Favorites and collections appear in the Mini Bridge panel.
To add an item to Favorites or to a collection, drag its thumbnail to the folder or collection in the navigation area of the panel.
Mini Bridge CS5 tutorials
To learn more about using Mini Bridge in CS5, read or watch any of these tutorials:
Adobe Mini Bridge panel and InDesign CS5 (02:00)
Using Mini Bridge with Photoshop CS5
Mini Bridge in Photoshop CS5
Use Mini Bridge in CS5 applications (06:09)
New features in Bridge and Mini Bridge (10:17)
Using Mini Bridge in Adobe Photoshop CS5
To the top
To the top
To the top
Twitter™ and Facebook posts are not covered under the terms of Creative Commons.
Legal Notices | Online Privacy Policy
Page 48

Camera Raw
46
Page 49

Introduction to Camera Raw
47
About camera raw files
About Camera Raw
About the Digital Negative (DNG) format
Processing images with Camera Raw
Camera Raw dialog box overview
Work with the Camera Raw cache in Adobe Bridge
Work with Camera Raw and Lightroom
About camera raw files
A camera raw file contains unprocessed, uncompressed grayscale picture data from a digital camera’s image sensor, along with information about
how the image was captured (metadata). Photoshop® Camera Raw software interprets the camera raw file, using information about the camera
and the image’s metadata to construct and process a color image.
Think of a camera raw file as your photo negative. You can reprocess the file at any time, achieving the results that you want by making
adjustments for white balance, tonal range, contrast, color saturation, and sharpening. When you adjust a camera raw image, the original camera
raw data is preserved. Adjustments are stored as metadata in an accompanying sidecar file, in a database, or in the file itself (in the case of DNG
format).
When you shoot JPEG files with your camera, the camera automatically processes the JPEG file to enhance and compress the image. You
generally have little control over how this processing occurs. Shooting camera raw images with your camera gives you greater control than
shooting JPEG images, because camera raw does not lock you into processing done by your camera. You can still edit JPEG and TIFF images in
Camera Raw, but you will be editing pixels that were already processed by the camera. Camera raw files always contain the original, unprocessed
pixels from the camera.
To shoot camera raw images, you must set your camera to save files in its own camera raw file format.
Note: The Photoshop Raw format (.raw) is a file format for transferring images between applications and computer platforms. Don’t confuse
Photoshop raw with camera raw file formats. File extensions for camera raw files vary depending on the camera manufacturer.
Digital cameras capture and store camera raw data with a linear tone response curve (gamma 1.0). Both film and the human eye have a nonlinear,
logarithmic response to light (gamma greater than 2). An unprocessed camera raw image viewed as a grayscale image would seem very dark,
because what appears twice as bright to the photosensor and computer seems less than twice as bright to the human eye.
For a list of supported cameras and for more information about Camera Raw, see Digital camera raw file support.
To see a list of cameras and which version of Camera Raw each camera requires, see Camera Raw plug-in | Supported cameras.
To the top
About Camera Raw
Camera Raw software is included as a plug-in with Adobe After Effects® and Adobe Photoshop, and also adds functionality to Adobe Bridge.
Camera Raw gives each of these applications the ability to import and work with camera raw files. You can also use Camera Raw to work with
JPEG and TIFF files.
Note: Camera Raw supports images up to 65,000 pixels long or wide and up to 512 megapixels. Camera Raw converts CMYK images to RGB
upon opening. For a list of supported cameras, see Digital camera raw file support.
You must have Photoshop or After Effects installed to open files in the Camera Raw dialog box from Adobe Bridge. However, if Photoshop or After
Effects is not installed, you can still preview the images and see their metadata in Adobe Bridge. If another application is associated with the
image file type, it’s possible to open the file in that application from Adobe Bridge.
Using Adobe Bridge, you can apply, copy, and clear image settings, and you can see previews and metadata for camera raw files without opening
them in the Camera Raw dialog box. The preview in Adobe Bridge is a JPEG image generated using the current image settings; the preview is
not the raw camera data itself, which would appear as a very dark grayscale image.
Note: A caution icon
camera raw image.
You can modify the default settings that Camera Raw uses for a particular model of camera. For each camera model, you can also modify the
defaults for a particular ISO setting or a particular camera (by serial number). You can modify and save image settings as presets for use with
other images.
When you use Camera Raw to make adjustments (including straightening and cropping) to a camera raw image, the image’s original camera raw
data is preserved. The adjustments are stored in either the Camera Raw database, as metadata embedded in the image file, or in a sidecar XMP
file (a metadata file that accompanies a camera raw file). For more information, see Specify where Camera Raw settings are stored.
appears in the thumbnails and preview image in the Camera Raw dialog box while the preview is generated from the
To the top
Page 50

After you process and edit a camera raw file using the Camera Raw plug-in, an icon appears in the image thumbnail in Adobe Bridge.
48
If you open a camera raw file in Photoshop, you can save the image in other image formats, such as PSD, JPEG, Large Document Format (PSB),
TIFF, Cineon, Photoshop Raw, PNG, or PBM. From the Camera Raw dialog box in Photoshop, you can save the processed files in Digital
Negative (DNG), JPEG, TIFF, or Photoshop (PSD) formats. Although Photoshop Camera Raw software can open and edit a camera raw image
file, it cannot save an image in a camera raw format.
As new versions of Camera Raw become available, you can update this software by installing a new version of the plug-in. You can check for
updates to Adobe software by choosing Help > Updates.
Different camera models save camera raw images in many different formats, and the data must be interpreted differently for these formats.
Camera Raw includes support for many camera models, and it can interpret many camera raw formats.
If you have trouble opening Camera Raw files, see Why doesn't my version of Photoshop or Lightroom support my camera?
About the Digital Negative (DNG) format
The Digital Negative (DNG) format is a non- proprietary, publicly documented, and widely supported format for storing raw camera data. Hardware
and software developers use DNG because it results in a flexible workflow for processing and archiving camera raw data. You may also use DNG
as an intermediate format for storing images that were originally captured using a proprietary camera raw format.
Because DNG metadata is publicly documented, software readers such as Camera Raw do not need camera-specific knowledge to decode and
process files created by a camera that supports DNG. If support for a proprietary format is discontinued, users may not be able to access images
stored in that format, and the images may be lost forever. Because DNG is publicly documented, it is far more likely that raw images stored as
DNG files will be readable by software in the distant future, making DNG a safer choice for archival storage.
Metadata for adjustments made to images stored as DNG files can be embedded in the DNG file itself instead of in a sidecar XMP file or in the
Camera Raw database.
You can convert camera raw files to the DNG format by using the Adobe DNG Converter or the Camera Raw dialog box. For more information on
the DNG format and DNG Converter, see the Digital Negative (DNG) product page. To download the latest DNG Converter, go to the Adobe
downloads page.
Processing images with Camera Raw
1. Copy camera raw files to your hard disk, organize them, and (optionally) convert them to DNG.
Before you do any work on the images that your camera raw files represent, transfer them from the camera’s memory card, organize them, give
them useful names, and otherwise prepare them for use. Use the Get Photos From Camera command in Adobe Bridge to accomplish these tasks
automatically.
2. Open the image files in Camera Raw.
You can open camera raw files in Camera Raw from Adobe Bridge, After Effects, or Photoshop. You can also open JPEG and TIFF files in
Camera Raw from Adobe Bridge. (See Open images.)
For a video tutorial on importing raw images from a digital camera into Adobe Bridge CS4 or CS5 using Adobe Photo Downloader, watch
Download photos from a camera into Adobe Bridge by Lynda.com.
To the top
To the top
3. Adjust color.
Color adjustments include white balance, tone, and saturation. You can make most adjustments on the Basic tab, and then use controls on the
other tabs to fine-tune the results. If you want Camera Raw to analyze your image and apply approximate tonal adjustments, click Auto on the
Basic tab.
To apply the settings used for the previous image, or to apply the default settings for the camera model, camera, or ISO settings, choose the
appropriate command from the Camera Raw Settings menu
For a video tutorial on making nondestructive color adjustments to photos in Camera Raw, watch Recovering detail in raw images by Richard
Harrington or Adobe Camera Raw workflow by Russell Brown.
4. Make other adjustments and image corrections.
Use other tools and controls in the Camera Raw dialog box to perform such tasks as sharpening the image, reducing noise, correcting for lens
defects, and retouching.
5. (Optional) Save image settings as a preset or as default image settings.
To apply the same adjustments to other images later, save the settings as a preset. To save the adjustments as the defaults to be applied to all
images from a specific camera model, a specific camera, or a specific ISO setting, save the image settings as the new Camera Raw defaults. (See
Save, reset, and load Camera Raw settings.)
6. Set workflow options for Photoshop.
Set options to specify how images are saved from Camera Raw and how Photoshop should open them. You can access the Workflow Options
. (See Apply saved Camera Raw settings.)
Page 51

settings by clicking the link beneath the image preview in the Camera Raw dialog box.
7. Save the image, or open it in Photoshop or After Effects.
49
When you finish adjusting the image in Camera Raw, you can apply the adjustments to the camera raw file, open the adjusted image in Photoshop
or After Effects, save the adjusted image to another format, or cancel and discard adjustments. If you open the Camera Raw dialog box from After
Effects, the Save Image and Done buttons are unavailable.
Save Image Applies the Camera Raw settings to the images and saves copies of them in JPEG, PSD, TIFF, or DNG format. Press Alt (Windows)
or Option (Mac OS) to suppress the Camera Raw Save Optionsdialog box and save the files using the last set of save options. (See Save a
camera raw image in another format.)
Open Image or OK Opens copies of the camera raw image files (with the Camera Raw settings applied) in Photoshop or After Effects. The
original camera raw image file remains unaltered. Press Shift while clicking Open Image to open the raw file in Photoshop as a Smart Object. At
any time, you can double-click the Smart Object layer that contains the raw file to adjust the Camera Raw settings.
Done Closes the Camera Raw dialog box and stores file settings either in the camera raw database file, in the sidecar XMP file, or in the DNG
file.
Cancel Cancels the adjustments specified in the Camera Raw dialog box.
Camera Raw dialog box overview
To the top
Camera Raw dialog box
A. Filmstrip B. Toggle Filmstrip C. Camera name or file format D. Toggle full -screen mode E. Image adjustment tabs F. Histogram G.
Camera Raw Settings menu H. Zoom levels I. Workflow options J. Navigation arrows K. Adjustment sliders
Note: Some controls, such as the Workflow Options link, that are available when you open the Camera Raw dialog box from Adobe Bridge or
Photoshop are not available when you open the Camera Raw dialog box from After Effects.
To open the Camera Raw Settings menu, click the button in the upper-right corner of any of the image adjustment tabs.
Several of the commands in this menu are also available from the Edit >Develop Settings menu in Adobe Bridge.
The Camera Raw zoom controls are:
Zoom tool
or Option-click (Mac OS) to use the next lower zoom value. Drag the Zoom tool in the preview image to zoom in on a selected
area. To return to 100%, double-click the Zoom tool.
Hand tool
down the spacebar to temporarily activate the Hand tool while using another tool. Double-click the Hand tool to fit the preview
image to the window.
Select Zoom Level Choose a magnification setting from the menu or click theSelect Zoom Level buttons.
Preview Displays a preview of the image adjustments made in the current tab, combined with the settings in the other tabs.
Deselect to show the image with the original settings of the current tab combined with the settings in the other tabs.
RGB Shows the red, green, and blue values of the pixel under the pointer in the preview image.
Sets the preview zoom to the next higher preset value when you click the preview image. Alt-click (Windows)
Moves the image in the preview window if the preview image is set at a zoom level higher than 100%. Hold
Page 52

Shadows and Highlights Displays shadow and highlight clipping using the buttons at the top of the Histogram. Clipped
50
shadows appear in blue, and clipped highlights appear in red. Highlight clipping is shown if any one of the three RGB channels
is clipped (fully saturated with no detail). Shadow clipping is shown if all three RGB channels are clipped (black with no detail).
The Camera Raw image adjustment tabs are:
Basic
Tone Curve
Detail
HSL / Grayscale
Adjust white balance, color saturation, and tonality.
Fine-tune tonality using a Parametric curve and a Point curve.
Sharpen images or reduce noise.
Fine-tune colors using Hue, Saturation, and Luminance adjustments.
Split Toning Color monochrome images or create special effects with color images.
Lens Corrections
Effects
Simulate film grain or apply a postcrop vignette.
Camera Calibration
Compensate for chromatic aberration, geometric distortions, and vignetting caused by the camera lens.
Apply camera profiles to raw images to correct color casts and adjust non-neutral colors to
compensate for the behavior of a camera’s image sensor.
Presets Save and apply sets of image adjustments as presets.
Snapshots
Work with the Camera Raw cache in Adobe Bridge
Create versions of a photo that record its state at any point during the editing process.
To the top
When you view camera raw files in Adobe Bridge, the thumbnails and previews use either the default settings or your adjusted settings. The
Adobe Bridge cache stores data for the file thumbnails, metadata, and file information. Caching this data shortens the loading time when you
return to a previously viewed folder in Adobe Bridge. The Camera Raw cache speeds the opening of images in Camera Raw and rebuilds of
previews in Adobe Bridge when image settings change in Camera Raw.
Because caches can become very large, you may want to purge the Camera Raw cache or limit its size. You can also purge and regenerate the
cache if you suspect that it is corrupted or old.
Note: The Camera Raw cache holds data for about 200 images for each gigabyte of disk storage allocated to it. By default, the Camera Raw
cache is set to a maximum size of 1 GB. You can increase its limit in the Camera Raw preferences.
1. In Adobe Bridge, choose Edit >Camera Raw Preferences (Windows) or Bridge > Camera Raw Preferences (Mac OS). Or,
with the Camera Raw dialog box open, click the Open Preferences Dialog button
.
2. Do any of the following:
To change the cache size, enter a Maximum Size value.
To purge the camera raw cache, click the Purge Cachebutton.
To the top
.
2. Choose Save Image Settings In > Sidecar “.XMP” Files, and deselect Ignore Sidecar “.XMP” Files.
3. After applying adjustments to a photo in Camera Raw, save them by clicking Done or Open Image.
Note: Camera Raw reads only the current settings for the primary image in the Lightroom catalog. Adjustments made to virtual copies are not
displayed or available in Camera Raw.
|
Page 53

Navigate, open, and save images in Camera Raw
51
Process, compare, and rate multiple images
Automating image processing
Open images
Save a camera raw image in another format
Process, compare, and rate multiple images
The most convenient way to work with multiple camera raw images is to use the Filmstrip view in Camera Raw. Filmstrip view opens by default
when you open multiple images in Camera Raw from Adobe Bridge.
Note: The Filmstrip view is not available when importing multiple images into After Effects.
Images can have three states in Filmstrip pane: deselected, selected (but not active), and active (also selected). In general, adjustments are
applied to all selected images.
You can also synchronize settings to apply settings from the active image to all selected images. You can quickly apply a set of adjustments to an
entire set of images—such as all shots taken under the same conditions—and then fine-tune the individual shots later, after you’ve determined
which you’ll use for your final output. You can synchronize both global and local adjustment settings.
To select an image, click its thumbnail. To select a range of images, Shift-click two thumbnails. To add an image to a
selection, Ctrl-click (Windows) or Command-click (Mac OS) its thumbnail.
To change which image is active without changing which images are selected, click a navigation arrow at the bottom of the
preview pane.
To apply settings from the active image to all selected images, click the Synchronize button at the top of the Filmstrip pane
and choose which settings to synchronize.
To apply a star rating, click a rating under the image thumbnail.
To mark selected images for deletion, click Mark For Deletion .
A red X appears in the thumbnail of an image marked for deletion. The file is sent to the Recycle Bin (Windows) or Trash
(Mac OS) when you close the Camera Raw dialog box. (If you decide to keep an image that you marked for deletion, select it
in the Filmstrip pane and click Mark For Deletion again, before you close the Camera Raw dialog box.)
For a tutorial on synchronizing edits across multiple Camera Raw photos, see Synchronizing edits in Adobe Camera Raw byDan Moughamian.
To the top
Automating image processing
You can create an action to automate the processing of image files with Camera Raw. You can automate the editing process, and the process of
saving the files in formats such as PSD, DNG, JPEG, Large Document Format (PSB), TIFF, and PDF. In Photoshop, you can also use the Batch
command, the Image Processor, or the Create Droplet command to process one or more image files. The Image Processoris especially useful for
saving image files in different file formats during the same processing session.
Here are some tips for automating the processing of camera raw image files:
When you record an action, first select Image Settings from the Camera Raw Settings menu
If you plan to use the action with the Batch command, you may want to use the Save As command and choose the file format
when saving the camera raw image.
When you use an action to open a camera raw file, the Camera Raw dialog box reflects the settings that were in effect when
the action was recorded. You may want to create different actions for opening camera raw image files with different settings.
When using the Batch command, select Override Action “Open” Commands. Any Open commands in the action will then
operate on the batched files rather than the files specified by name in the action.Deselect Override Action “Open” Commands
only if you want the action to operate on open files or if the action uses the Open command to retrieve needed information.
When using the Batch command, select Suppress File Open Options Dialogs to prevent the display of the Camera Raw dialog
box as each camera raw image is processed.
When using the Batch command, select Override Action “Save As” Commands if you want to use the Save As instructions from
the Batch command instead of the Save As instructions in the action. If you select this option, the action must contain a Save
As command, because the Batch command does not automatically save the source files. Deselect Override Action “Save As”
To the top
Page 54

Commands to save the files processed by the Batch command in the location specified in the Batch dialog box.
When creating a droplet, select Suppress File Open Options Dialogs in the Play area of the Create Droplet dialog box. This
the preview size. If you embed JPEG previews, other applications can view the contents of the DNG file without
52
prevents the display of the Camera Raw dialog box as each camera raw image is processed.
Open images
To process raw images in Camera Raw, select one or more camera raw files in Adobe Bridge, and then choose File > Open In
Camera Raw or press Ctrl+R (Windows) or Command+R (Mac OS). When you finish making adjustments in the Camera Raw
dialog box, click Done to accept changes and close the dialog box. You can also click Open Image to open a copy of the
adjusted image in Photoshop.
To process JPEG or TIFF images in Camera Raw, select one or more JPEG or TIFF files in Adobe Bridge, and then choose
File > Open In Camera Raw or press Ctrl+R (Windows) or Command+R (Mac OS). When you finish making adjustments in the
Camera Raw dialog box, click Done to accept changes and close the dialog box. You can specify whether JPEG or TIFF
images with Camera Raw settings are automatically opened in Camera Raw in the JPEG and TIFF Handling section of the
Camera Raw preferences.
To import camera raw images in Photoshop, select one or more camera raw files in Adobe Bridge, and then choose File >
Open With > Adobe Photoshop CS5. (You can also choose the File > Open command in Photoshop, and browse to select
camera raw files.) When you finish making adjustments in the Camera Raw dialog box, click Open Image to accept changes
and open the adjusted image in Photoshop. Press Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac OS) to open a copy of the adjusted image
and not save the adjustments to the original image’s metadata. Press Shift while clicking Open Image to open the image as a
Smart Object in Photoshop. At any time, you can double-click the Smart Object layer that contains the raw file to adjust the
Camera Raw settings.
Shift-double-click a thumbnail in Adobe Bridge to open a camera raw image in Photoshop without opening the Camera Raw
dialog box. Hold down Shift while choosing File > Open to open multiple selected images.
To import camera raw images in After Effects using Adobe Bridge, select one or more camera raw files in Adobe Bridge, and
then choose File > Open With > Adobe After Effects CS5. (You can also choose a File > Import command in After Effects and
browse to select camera raw files.) When you finish making adjustments in the Camera Raw dialog box, click OK to accept
changes.
To import TIFF and JPEG files into After Effects using Camera Raw, select the File > Import command in After Effects, and
then select All Files from the Enable menu (Mac OS) or Files Of Type menu (Windows) in the After Effects Import File dialog
box. Select the file to import, select Camera Raw from the Format menu, and click Open.
To import Camera Raw images into After Effects as a sequence, choose File > Import in After Effects. Select the images,
check the Camera Raw Sequence box, and click Open. Camera Raw settings applied to the first camera raw file upon import
are applied to the remaining files in the sequence unless an XMP sidecar file is present for any subsequent file in the
sequence. In that case, the settings in the XMP file or in the DNG file are applied to that specific frame in the sequence. All
other frames use the settings that the first file in the sequence specifies.
If you have trouble opening Camera Raw files, see Why doesn't my version of Photoshop or Lightroom support my camera?
Save a camera raw image in another format
You can save camera raw files from the Camera Raw dialog box in PSD, TIFF, JPEG, or DNG format.
When you use the Save Image command in the Camera Raw dialog box, files are placed in a queue to be processed and saved. This is useful if
you are processing several files in the Camera Raw dialog box and saving them in the same format.
1. In the Camera Raw dialog box, click the Save Image button in the lower-left corner of the dialog box.
Alt-click (Windows) or Option-click (Mac OS) Save to suppress the Camera Raw Save Options dialog box when saving a
file.
2. In the Save Options dialog box, specify the following options:
Destination Specifies where to save the file. If necessary, click the Select Folder button and navigate to the location.
File Naming Specifies the filename using a naming convention that includes elements such as date and camera serial
number. Using informative filenames based on a naming convention helps you keep image files organized.
3. Choose a file format from the Format menu.
Digital Negative Saves a copy of the camera raw file in the DNG file format.
Compatibility Specifies the versions of Camera Raw and Lightroom that can read the file.
If you choose Custom, specify whether you want compatibility with DNG 1.1 or DNG 1.3. By default, the conversion
uses lossless compression, which means no information is lost while reducing file size. Choosing Linear (Demosaiced)
stores the image data in an interpolated format. That means other software can read the file even if that software does
not have a profile for the digital camera that captured the image.
JPEG Preview Embeds a JPEG preview in the DNG file. If you decide to embed a JPEG preview, you can choose
Page 55

parsing the camera raw data.
53
Embed Original Raw File Stores all of the original camera raw image data in the DNG file.
JPEG Saves copies of the camera raw files in JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) format. To specify the amount of
compression, enter a value from 0 to 12 or choose from the menu. Entering a higher value, or choosing High or Maximum,
applies less compression and increases file size and image quality. JPEG format is commonly used to display photographs
and other continuous-tone images in web photo galleries, slide shows, presentations, and other online services.
TIFF Saves copies of the camera raw files as TIFF (Tagged-ImageFile Format) files. Specify whether to apply no
compression, or LZW or ZIP file compression. TIFF is a flexible bitmap image format supported by virtually all paint, imageediting, and page -layout applications. TIFF provides greater compression and compatibility with other applications than does
PSD format.
Photoshop Saves copies of the camera raw files in the PSD file format. You can specify whether to preserve cropped pixel
data in the PSD file.
4. Click Save.
|
Page 56

Make color and tonal adjustments in Camera Raw
54
Histogram and RGB levels
Preview highlight and shadow clipping
White balance controls
Adjust tone
Fine-tune tone curves
Clarity, Vibrance, and Saturation controls
HSL / Grayscale controls
Adjust color or tone using the Targeted Adjustment tool
Tone a grayscale image
Editing HDR images in Camera Raw
Histogram and RGB levels
A histogram is a representation of the number of pixels at each luminance value in an image. A histogram that has nonzero values for each
luminance value indicates an image that takes advantage of the full tonal scale. A histogram that doesn’t use the full tonal range corresponds to a
dull image that lacks contrast. A histogram with a spike at the left side indicates shadow clipping; a histogram with a spike on the right side
indicates highlight clipping.
Select Shadows or Highlights to see in the preview image which pixels are being clipped. For more information, see Preview highlight and
shadow clipping in Camera Raw.
One common task for adjusting an image is to spread out the pixel values more evenly from left to right on the histogram, instead of having them
bunched up at one end or the other.
A histogram is made up of three layers of color that represent the red, green, and blue color channels. White appears when all three channels
overlap. Yellow, magenta, and cyan appear when two of the RGB channels overlap (yellow equals the red + green channels, magenta equals the
red + blue channels, and cyan equals the green + blue channels).
The histogram changes automatically as you adjust the settings in the Camera Raw dialog box.
The RGB values of the pixel under the pointer (in the preview image) appear below the histogram.
Note:
You can also use the Color Sampler tool to place up to nine color samplers in the preview image. The RGB values appear above the
image. To remove a color sampler, Alt-click (Windows) or Option-click (Mac OS) it. To clear the color samplers, click Clear Samplers.
preview
To the top
The Camera Raw dialog box displays the RGB values of the pixel under the pointer.
Preview highlight and shadow clipping
Clipping occurs when the color values of a pixel are higher than the highest value or lower than the lowest value that can be represented in the
image. Over bright values are clipped to output white, and over dark values are clipped to output black. The result is a loss of image detail.
To see which pixels are being clipped with the rest of the preview image, select Shadows or Highlights options at the top of the
histogram. Or press U to see shadow clipping, O to see highlight clipping.
To see only the pixels that are being clipped, press Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac OS) while dragging the Exposure, Recovery,
or Blacks sliders.
For the Exposure and Recovery sliders, the image turns black, and clipped areas appear white. For the Blacks slider, the image turns white and
clipped areas appear black. Colored areas indicate clipping in one color channel (red, green, blue) or two color channels (cyan, magenta, yellow).
In some cases, clipping occurs because the color space that you are working in has a gamut that is too small. If your colors are being
Note:
clipped, consider working in a color space with a large gamut, such as ProPhoto RGB.
To the top
Page 57

White balance controls
To adjust the white balance, identify which objects in the image you want to be neutral -colored (white or gray), and then adjust the colors to make
those objects neutral. A white or gray object in a scene takes on the color cast by the ambient light or flash used to shoot the picture. When you
use the White Balance tool
scene was shot and then adjust for scene lighting automatically.
Color temperature (in Kelvins) is used as a measure of scene lighting. Natural and incandescent light sources give off light in a predictable
distribution according to their temperature.
A digital camera records the white balance at the time of exposure as a metadata entry. The Camera Raw plug -in reads this value and makes it
the initial setting when you open the file in the Camera Raw dialog box. This setting usually yields the correct color temperature, or nearly so. You
can adjust the white balance if it is not right.
Note:
Not all color casts are a result of incorrect white balance. Use the DNG Profile Editor to correct a color cast that remains after the white
balance is adjusted. See Adjust color rendering for your camera in Camera Raw.
The Basic tab in the Camera Raw dialog box has three controls for correcting a color cast in an image:
to specify an object that you want white or gray, Camera Raw can determine the color of the light in which the
To the top
White Balance
Use these controls to fine-tune the color balance.
As Shot
Auto
Camera raw and DNG files also have the following white balance settings: Daylight, Cloudy, Shade, Tungsten, Fluorescent, and Flash.
Note:
If Camera Raw doesn’t recognize the white balance setting of a camera, choosing As Shot is the same as choosing Auto.
Temperature
temperature of light; the Camera Raw plug-in makes the image colors bluer to compensate for the lower color temperature (yellowish) of the
ambient light. Conversely, increase Temperature to correct a photo taken with a higher color temperature of light; the image colors become warmer
(yellowish) to compensate for the higher color temperature (bluish) of the ambient light.
Note:
The range and units for the Temperature and Tint controls are different when you are adjusting a TIFF or JPEG image. For example,
Camera Raw provides a true-temperature adjustment slider for raw files from 2,000 Kelvin to 50,000 Kelvin. For JPEG or TIFF files, Camera Raw
attempts to approximate a different color temperature or white balance. Because the original value was already used to alter the pixel data in the
file, Camera Raw does not provide the true Kelvin temperature scale. In these instances, an approximate scale of - 100 to 100 is used in place of
the temperature scale.
Camera Raw applies the white balance setting and changes the Temperature and Tint properties in the Basic tab accordingly.
Uses the camera’s white balance settings, if they are available.
Calculates the white balance based on the image data.
Sets the white balance to a custom color temperature. Decrease Temperature to correct a photo taken with a lower color
Correcting the white balance
A. Moving the Temperature slider to the right corrects a photo taken with a higher color temperature of light B. Moving the Temperature slider to
the left corrects a photo taken with a lower color temperature of light C. Photo after color temperature adjustment
Tint
Sets the white balance to compensate for a green or magenta tint. Decrease Tint to add green to the image; increase Tint to add magenta.
To adjust the white balance quickly, select the White Balance tool and then click an area in the image that you want to be a neutral gray. The
Temperature and Tint properties adjust to make the selected color exactly neutral (if possible). If you’re clicking whites, choose a highlight area
that contains significant white detail rather than a specular highlight. You can double -click theWhite Balance tool to reset White Balance to As
Shot.
Page 58

Adjust tone
56
You adjust the image tonal scale using the tone controls in the Basic tab.
When you click Auto at the top of the tone controls section of the Basic tab, Camera Raw analyzes the image and makes automatic adjustments
to the tone controls.
You can also apply automatic settings separately for individual tone controls. To apply an automatic adjustment to an individual tone control, such
as Exposure or Contrast, press Shift and double-click the slider. To return an individual tone control to its original value, double-click its slider.
When you adjust tone automatically, Camera Raw ignores any adjustments previously made in other tabs (such as fine-tuning of tone in the Tone
Curves tab). For this reason, apply automatic tone adjustments first—if at all—to get an initial approximation of the best settings for your image. If
you are careful during shooting and have deliberately shot with different exposures, you probably don’t want to undo that work by applying
automatic tone adjustments. On the other hand, you can always try clicking Auto and then undo the adjustments if you don’t like them.
Previews in Adobe® Bridge use the default image settings. If you want the default image settings to include automatic tone adjustments, select
Apply Auto Tone Adjustments in the Default Image settings section of the Camera Raw preferences.
Note:
If you are comparing images based on their previews in Adobe Bridge, leave the Apply Auto Tone Adjustments preference deselected,
which is the default. Otherwise, you’ll be comparing images that have already been adjusted.
As you make adjustments, keep an eye on the end points of the histogram, or use the shadow and highlight clipping previews.
While moving the tone controls sliders, hold down Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac OS) to preview where highlights or shadows are clipped.
Move the slider until clipping begins, and then reverse the adjustment slightly. (For more information, see Preview highlight and shadow
clipping in Camera Raw.)
To manually adjust a tone control, drag the slider, type a number in the box, or select the value in the box and press the Up or
Down arrow key.
To reset a value to its default, double-click the slider control.
Note:
The tone controls that appear in the Basic panel depend on whether you are working in Process Version PV2012, PV2010, or PV2003, as
noted.
To the top
Exposure (All)
Exposure values are in increments equivalent to aperture values (f-stops) on a camera. An adjustment of +1.00 is similar to opening the aperture 1
stop. Similarly, an adjustment of -1.00 is like closing the aperture 1 stop.
Contrast (All)
become darker, and the middle-to-light image areas become lighter. The image tones are inversely affected as you decrease contrast.
Highlights (PV2012)
brighten highlights while minimizing clipping.
Shadows (PV2012)
and recover shadow details.
Whites (PV2012)
clipping may be desirable for specular highlights, such as metallic surfaces.)
Blacks (PV2012)
shadow clipping.
Blacks (PV2010 and PV2003)
sometimes creating the impression of increased image contrast. The greatest effect is in the shadows, with much less change in the midtones and
highlights.
Recovery (PV2010 and PV2003)
or two color channels are clipped to white.
Fill Light (PV2010 and PV2003)
from areas in which one or two color channels are clipped to black. Using Fill Light is like using the shadows portion of the Photoshop®
Shadow/Highlight filter or the After Effects® Shadow/Highlight effect.
Adjusts the overall image brightness. Adjust the slider until the photo looks good and the image is the desired brightness.
Increases or decreases image contrast, mainly affecting midtones. When you increase contrast, the middle-to-dark image areas
Adjusts bright image areas. Drag to the left to darken highlights and recover “blown out” highlight details. Drag to the right to
Adjusts dark image areas. Drag to the left to darken shadows while minimizing clipping. Drag to the right to brighten shadows
Adjusts white clipping. Drag to the left to reduce clipping in highlights. Drag to the right to increase highlight clipping. (Increased
Adjusts black clipping. Drag to the left to increase black clipping (map more shadows to pure black). Drag to the right to reduce
Specifies which image values map to black. Moving the slider to the right increases the areas that become black,
Attempts to recover details from highlights. Camera Raw can reconstruct some details from areas in which one
Attempts to recover details from shadows, without brightening blacks. Camera Raw can reconstruct some details
Brightness (PV2010 and PV2003)
clipping the image in the highlights or shadows, Brightness compresses the highlights and expands the shadows when you move the slider to the
right. Often, the best way to use this control is to set the overall tonal scale by first setting Exposure, Recovery, and Blacks; then set Brightness.
Large Brightness adjustments can affect shadow or highlight clipping, so you may want to readjust the Exposure, Recovery, or Blacks property
after adjusting Brightness.
Learn More: Watch the video tutorial What's New in Camera Raw by Matt Kloskowski.
Adjusts the brightness or darkness of the image, much as the Exposure property does. However, instead of
Page 59

Fine-tune tone curves
57
Use the controls in the Tone Curve tab to fine-tune images after you’ve made tone adjustments in the Basic tab. The tone curves represent
changes made to the tonal scale of an image. The horizontal axis represents the original tone values of the image (input values), with black on the
left and progressively lighter values toward the right. The vertical axis represents the changed tone values (output values), with black on the
bottom and progressing to white at the top.
If a point on the curve moves up, the output is a lighter tone; if it moves down, the output is a darker tone. A straight, 45-degree line indicates no
changes to the tone response curve: the original input values exactly match the output values.
Use the tone curve in the nested Parametric tab to adjust the values in specific tonal ranges in the image. The areas of the curve affected by the
region properties ( Highlights, Lights, Darks, or Shadows) depend on where you set the split controls at the bottom of the graph. The middle region
properties (Darks and Lights) mostly affect the middle region of the curve. The Highlight and Shadows properties mostly affect the ends of the
tonal range.
To adjust tone curves, do any of the following:
Drag the Highlights, Lights, Darks, or Shadows slider in the nested Parametric tab. You can expand or contract the curve
regions that the sliders affect by dragging the region divider controls along the horizontal axis of the graph.
Drag a point on the curve in the nested Point tab. As you drag the point, the Input and Output tonal values are displayed
beneath the tone curve.
Select the Parametric Curve Targeted Adjustment tool in the toolbar and drag in the image. The Parametric Curve
Targeted Adjustment tool adjusts the Highlights, Lights, Darks, or Shadows curve region based on the values in the image
where you click.
The Targeted Adjustment tool does not affect point curves.
Note:
To the top
Clarity, Vibrance, and Saturation controls
You can change the color saturation of all colors by adjusting the Clarity, Vibrance, and Saturation controls on the Basic tab. (To adjust saturation
for a specific range of colors, use the controls on the HSL / Grayscale tab.)
Clarity
When using this setting, it is best to zoom in to 100% or greater. To maximize the effect, increase the setting until you see halos near the edge
details of the image and then reduce the setting slightly.
Vibrance
saturated colors with less effect on the higher-saturated colors. Vibrance also prevents skin tones from becoming oversaturated.
Saturation
Adds depth to an image by increasing local contrast, with greatest effect on the midtones. This setting is like a large-radius unsharp mask.
Adjusts the saturation so that clipping is minimized as colors approach full saturation. This setting changes the saturation of all lower-
Adjusts the saturation of all image colors equally from -100 (monochrome) to +100 (double the saturation).
HSL / Grayscale controls
You can use the controls in the HSL / Grayscale tab to adjust individual color ranges. For example, if a red object looks too vivid and distracting,
you can decrease the Reds values in the nested Saturation tab.
The following nested tabs contain controls for adjusting a color component for a specific color range:
Hue
Changes the color. For example, you can change a blue sky (and all other blue objects) from cyan to purple.
Saturation
Luminance
If you select Convert To Grayscale, you see only one nested tab:
Changes how vivid or pure the color. For example, you can change a blue sky from gray to highly saturated blue.
Changes the brightness of the color range.
To the top
To the top
Grayscale Mix
Adjust color or tone using the Targeted Adjustment tool
The Targeted Adjustment tool allows you to make tonal and color corrections by dragging directly on a photo. Using the Targeted Adjustment tool,
you can drag down on a blue sky to desaturate it, for example, or drag up on a red jacket to intensify its hue.
1. To make color adjustments with the Targeted Adjustment tool
want to make: Hue, Saturation, Luminance, or Grayscale Mix. Then, drag in the image.
Use controls in this tab to specify the contribution of each color range to the grayscale version of the image.
To the top
, click it in the toolbar and choose the type of correction you
Page 60

Dragging up or right increases values; dragging down or left decreases values. Sliders for more than one color may be
58
affected when you drag with the Targeted Adjustment tool. Selecting the Grayscale Mix Targeted Adjustment tool converts the
image to grayscale.
2. To make tone curve adjustments using the Targeted Adjustmenttool
, click it in the toolbar and choose Parametric Curve.
Then, drag in the image.
The Parametric Curve Targeted Adjustment tool adjusts the Highlights, Lights, Darks, or Shadows curve region based on the
values in the image where you click.
The keyboard shortcut T toggles the last Targeted Adjustment tool you used.
Tone a grayscale image
To the top
Use the controls in the Split Toning tab to color a grayscale image. You can add one color throughout the tonal range, such as a sepia
appearance, or create a split tone result, in which a different color is applied to the shadows and the highlights. The extreme shadows and
highlights remain black and white.
You can also apply special treatments, such as a cross-processed look, to a color image.
1. Select a grayscale image. (It can be an image that you converted to grayscale by selecting Convert To Grayscale in the HSL /
Grayscale tab.)
2. In the Split Toning tab, adjust the Hue and Saturation properties for the highlights and shadows. Hue sets the color of the
tone; Saturation sets the magnitude of the result.
3. Adjust the Balance control to balance the influence between the Highlight and Shadow controls. Positive values increase the
influence of the Highlight controls; negative values increase the influence of the Shadow controls.
Editing HDR images in Camera Raw
To the top
In Camera Raw 7.1 or later, you can work with 16-, 24-, and 32-bit floating point images--often referred to as HDR (high dynamic range images).
Camera Raw opens TIFF and DNG format HDR images. Make sure that the images are in process version 2012. (See Process Versions.)
You can use the Basic tab controls to edit HDR images. The Basic tab Exposure control has an expanded range when working with HDR images
(+10 to - 10).
When you are done editing, click Done or Open Image to open the image in Photoshop. The image opens as a 16-bit or 8-bit image, depending
on how you have the Workflow Options set.
To open an HDR image in Camera Raw:
Twitter™ and Facebook posts are not covered under the terms of Creative Commons.
Legal Notices | Online Privacy Policy
Page 61

Sharpening and noise reduction in Camera Raw
59
Sharpen photos
Reduce noise
Sharpen photos
The sharpening controls on the Detail tab adjust edge definition in the image. The Adjustment Brush tool and Graduated Filter tool use the
Radius, Detail, and Masking values when local sharpening is applied.
Use the Apply Sharpening To option in the Camera Raw preferences to specify whether sharpening is applied to all images or just to previews.
To open preferences from within Camera Raw, click the Open Preferences Dialog button in the toolbar.
1. Zoom the preview image to at least 100%.
2. In the Detail tab, adjust any of these controls:
Amount
In general, set Amount to a lower value for cleaner images. The adjustment is a variation of Unsharp Mask, which locates
pixels that differ from surrounding pixels based on the threshold you specify and increases the pixels’ contrast by the amount
you specify. When opening a camera raw image file, the Camera Raw plug-in calculates the threshold to use based on
camera model, ISO, and exposure compensation.
Radius
Photos with larger details can use a larger radius. Using too large a radius generally results in unnatural-looking results.
Detail
emphasizes edges. Lower settings primarily sharpen edges to remove blurring. Higher values are useful for making the
textures in the image more pronounced.
Masking
sharpening. With a setting of 100, sharpening is mostly restricted to those areas near the strongest edges. Press Alt
(Windows) or Option (Mac OS) while dragging this slider to see the areas to be sharpened (white) versus the areas masked
out (black).
Adjusts edge definition. Increase the Amount value to increase sharpening. A value of zero (0) turns off sharpening.
Adjusts the size of the details that sharpening is applied to. Photos with fine details generally need a lower setting.
Adjusts how much high-frequency information is sharpened in the image and how much the sharpening process
Controls an edge mask. With a setting of zero (0), everything in the image receives the same amount of
To the top
3. (Optional) To apply the newest sharpening algorithms to images, click the Update To Current Process (2012) button
lower-right corner of the image preview.
Reduce noise
The Noise Reduction section of the Detail tab has controls for reducing image noise , the extraneous visible artifacts that degrade image quality.
Image noise includes luminance (grayscale) noise, which makes an image look grainy, and chroma (color) noise, which is visible as colored
artifacts in the image. Photos taken with high ISO speeds or less-sophisticated digital cameras can have noticeable noise.
Note:
When making noise reduction adjustments, first zoom in on the preview image to at least 100% to see the noise reduction previewed.
Adjusting the Color and Color Detail sliders reduces chroma noise while preserving color detail (lower right).
in the
To the top
Page 62

If the Luminance Detail, Luminance Contrast, and Color Detail sliders are dimmed, click the Update To Current Process (2012) button
Note:
the lower-right corner of the image.
in
Luminance
Luminance Detail
Reduces luminance noise.
Controls the luminance noise threshold. Useful for noisy photos. Higher values preserve more detail but can produce noisier
results. Lower values produce cleaner results but also remove some detail.
Luminance Contrast
Controls the luminance contrast. Useful for noisy photos. Higher values preserve contrast but can produce noisy blotches or
mottling. Lower values produce smoother results but can also have less contrast.
Color
Reduces color noise.
Color Detail
Controls the color noise threshold. Higher values protect thin, detailed color edges but can result in color specking. Lower values
remove color speckles but can result in color bleeding.
For video tutorials about reducing noise in Camera Raw, see:
Better noise reduction in Photoshop® CS5 by Matt Kloskowski
Lens correction and noise reduction with Adobe® Camera Raw by Russell Brown
Photoshop CS5 - Camera Raw 6.0 by Justin Seeley
Twitter™ and Facebook posts are not covered under the terms of Creative Commons.
Legal Notices | Online Privacy Policy
Page 63

Process versions in Camera Raw
The process version is the technology that Camera Raw uses to adjust and render photos. Depending on which process version you use, different
options and settings area available to you in the Basic tab and when you make local adjustments.
Process Version 2012
tone-mapping algorithms for high-contrast images. With PV2012, you can adjust Highlights, Shadows, Whites, Blacks, Exposure, and Contrast in
the Basic panel. You can also apply local corrections for white balance (Temp and Tint), Highlights, Shadows, Noise, and Moiré.
Process Version 2010
the previous process version, PV2003.
Process Version 2003
To take advantage of the newer processing, you can update previously edited photos to the current process version.
To update a photo to the Camera Raw 7 process (PV2012), do either of the following:
Click the Update to Current Process button (the exclamation-point icon) in the lower-right corner of the image preview.
In the Camera Calibration tab, choose Process > 2012 (Current).
To apply an older process version to a photo, go to the Camera Calibration tab and choose Process > 2010 or Process > 2003.
Images edited for the first time in Camera Raw 7 use process version 2012. PV2012 offers new tone controls and new
Images edited in Camera Raw 6 used PV2010 by default. PV2010 offers improved sharpening and noise -reduction from
The original processing engine, used by Camera Raw versions 5.x and earlier.
Video tutorial
What's new in Camera Raw 7
Twitter™ and Facebook posts are not covered under the terms of Creative Commons.
Legal Notices | Online Privacy Policy
Page 64

Make local adjustments in Camera Raw
62
About local adjustments
Apply local adjustments with the Adjustment Brush tool in Camera Raw
Apply local adjustments with the Graduated Filter tool in Camera Raw
Save and apply local adjustment presets
About local adjustments
The controls in the image adjustment tabs of Camera Raw affect the color and tone of an entire photo. To adjust a specific area of a photo, like
dodging and burning, use the Adjustment Brush tool
The Adjustment Brush tool lets you selectively apply Exposure, Brightness, Clarity, and other adjustments by “painting” them onto the photo.
The Graduated Filter tool lets you apply the same types of adjustments gradually across a region of a photo. You can make the region as wide or
as narrow as you like.
You can apply both types of local adjustments to any photo. You can synchronize local adjustment settings across multiple selected images. You
can also create local adjustment presets so that you can quickly reapply an effect that you use frequently.
Getting local adjustments “right” in Camera Raw takes some experimentation. The recommended workflow is to select a tool and specify its
options, and then apply the adjustment to the photo. Then you can go back and edit that adjustment, or apply a new one.
As with all other adjustments applied in Camera Raw, local adjustments are nondestructive. They are never permanently applied to the photo.
Local adjustments are saved with an image in an XMP sidecar file or in the Camera Raw database, depending on what’s specified in Camera Raw
preferences.
and the Graduated Filter tool in Camera Raw.
Apply local adjustments with the Adjustment Brush tool in Camera Raw
1. Select the Adjustment Brush tool from the toolbar (or press K).
Camera Raw opens the Adjustment Brush tool options under the Histogram and sets the mask mode to New.
2. Choose the type of adjustment you want to make in the Adjustment Brush tool options by dragging an effects slider.
Note:
The effects that are available depend on whether you are working in Process Version 2012, 2010, or 2003, as noted.
To update a photo to PV2012, click the exclamation-point icon in the lower-right corner of the image preview.
To the top
To the top
Temp (PV2012)
temperature effect can improve images captured in mixed-lighting conditions.
Tint (PV2012)
Exposure (All)
traditional dodging and burning.
Highlights (PV2012)
Shadows (PV2012)
Brightness (PV2010 and PV2003)
Contrast (All)
Saturation (All)
Clarity (All)
Sharpness (All)
Noise Reduction (PV2012)
Adjusts the color temperature of an area of the image, making it warmer or cooler. A graduated filter
Compensates for a green or magenta color cast.
Sets the overall image brightness. Applying an Exposure local correction can achieve results similar to
Recovers detail in overexposed highlight areas of an image.
Recovers detail in underexposed shadow areas of an image.
Adjusts the image brightness, with a greater effect in the midtones.
Adjusts the image contrast, with a greater effect in the midtones.
Changes the vividness or purity of the color.
Adds depth to an image by increasing local contrast.
Enhances edge definition to bring out details in a photo. A negative value blurs details.
Reduces luminance noise, which can become apparent when shadow areas are opened.
Page 65

Moiré Reduction (PV2012)
Defringe (PV2012)
Removes moiré artifacts, or color aliasing.
63
Color (All)
Click the Plus icons (+) or the Minus icons (-) to increase or decrease the effect by a preset amount. Click multiple times to
select a stronger adjustment. Double-click the slider to reset the effect to zero.
3. Specify brush options:
Size
Applies a tint to the selected area. Select the hue by clicking the color sample box to the right of the effect name.
Specifies the diameter of the brush tip, in pixels.
Removes fringe colors along edges. See Remove local color fringes.
Feather
Flow
Density
Auto Mask
Show Mask
4. Move the Adjustment Brush tool over the image.
The cross hair indicates the application point. The solid circle indicates the brush size. The black-and-white dashed circle
indicates the feather amount.
Note:
circle may not be visible.
5. Paint with the Adjustment Brush tool in the area of the image that you want to adjust.
When you release the mouse, a pin icon
mode changes to Add.
6. (Optional) Refine the adjustment by doing any of the following:
Controls the hardness of the brush stroke.
Controls the rate of application of the adjustment.
Controls the amount of transparency in the stroke.
Confines brush strokes to areas of similar color.
Toggles visibility of the mask overlay in the image preview.
If the Feather is set to 0, the black-and-white circle indicates the brush size. With very small feather amounts, the solid
appears at the application point. In the Adjustment Brush tool options, the mask
Drag any of the effect sliders in the Adjustment Brush tool options to customize the effect in the image.
Press V to hide or show the pin icon.
To toggle visibility of the mask overlay, use the Show Mask option, press Y, or position the pointer over the pin icon.
To customize the color of the mask overlay, click the color swatch next to the Show Mask option. Then, choose a new
color from the Color Picker.
To undo part of the adjustment, click Erase in the Adjustment Brush tool options and paint over the adjustment.
To create an eraser brush that has different characteristics from the current Adjustment Brush tool, click the Local
Adjustment Settings menu button and choose Separate Eraser Size. Then, specify the Size, Feather, Flow, and Density
you want for the eraser.
Remove the adjustment completely by selecting the pin and pressing Delete.
Press Ctrl+Z (Windows) or Command+Z (Mac OS) to undo your last adjustment.
Click Clear All at the bottom of the tool options to remove all Adjustment Brush tool adjustments and set the mask mode
to New.
7. (Optional) Click New to apply an additional Adjustment Brush tool adjustment, and refine it as desired using the techniques in
step 6.
When working with multiple Adjustment Brush adjustments, make sure you’re in Add mode to switch between them.
Note:
Click a pin icon to select that adjustment and refine it.
Apply local adjustments with the Graduated Filter tool in Camera Raw
1. Select the Graduated Filter tool from the toolbar (or press G).
Camera Raw opens the Graduated Filter tool options under the Histogram and sets the mask mode to New.
2. Choose the type of adjustment you want to make in the Graduated Filter tool options by dragging the slider for any of the
following effects:
Note:
The effects that are available depend on whether you are working in Process Version 2012, 2010, or 2003, as
To the top
Page 66

Temp (PV2012)
noted. To update a photo to PV2012, click the exclamation-point icon in the lower-right corner of the image preview.
64
temperature effect can improve images captured in mixed-lighting conditions.
Adjusts the color temperature of an area of the image, making it warmer or cooler. A graduated filter
Tint (PV2012)
Exposure (All)
traditional dodging and burning.
Highlights (PV2012)
Shadows (PV2012)
Brightness (PV2010 and PV2003)
Contrast (All)
Saturation (All)
Clarity (All)
Sharpness (All)
Noise Reduction (PV2012)
Moiré Reduction (PV2012)
Defringe (PV 2012)
Color (All)
Click the Plus icon (+) or the Minus icon (-) to increase or decrease the effect by a preset amount. Double-click the slider
to reset the effect to zero.
3. Drag in the photo to apply a graduated filter across a region of the photo.
The filter starts at the red dot and red dotted line, and it continues past the green dot and green dotted line.
The mask mode switches to Edit in the Graduated Filter tool options.
4. (Optional) Refine the filter by doing any of the following:
Drag any of the effect sliders in the Graduated Filter tool options to customize the filter.
Toggle visibility of the guide overlays by selecting the Show Overlay option (or press V).
Drag the green or red dot to freely expand, contract, and rotate the effect.
Drag the black-and -white dotted line to shift the effect.
Position the pointer over the green-and-white or red-and-white dotted line, near the green or red dot, until a double-
pointing arrow appears. Then, drag to expand or contract the effect at that end of the range.
Position the pointer over the green-and-white or red-and-white dotted line, away from the green or red dot, until a curved
double-pointing arrow appears. Then, drag to rotate the effect.
Remove the filter by pressing Delete.
Press Ctrl+Z (Windows) or Command+Z (Mac OS) to undo your last adjustment.
Click Clear All at the bottom of the tool options to remove all Graduated Filter tool effects and set the mask mode to New.
5. (Optional) Click New to apply an additional Graduated Filter tool effect, and refine it as desired using the techniques in step 4.
When working with multiple Graduated Filter effects, click an overlay to select that effect and refine it.
Note:
Compensates for a green or magenta color cast.
Sets the overall image brightness. Applying an Exposure graduated filter can achieve results similar to
Recovers detail in overexposed highlight areas of an image.
Recovers detail in underexposed shadow areas of an image.
Adjusts the image brightness, with a greater effect in the midtones.
Adjusts the image contrast, with a greater effect in the midtones.
Changes the vividness or purity of the color.
Adds depth to an image by increasing local contrast.
Enhances edge definition to bring out details in the photo. A negative value blurs details.
Reduces luminance noise, which can become apparent when shadow areas are opened.
Removes moiré artifacts, or color aliasing.
Removes fringe color along edges. See Remove local color fringes.
Applies a tint to the selected area. Select the hue by clicking the color sample box to the right of the effect name.
Save and apply local adjustment presets
You can save local adjustments as presets so that you can quickly apply the effects to other images. You create, select, and manage local
adjustment presets using the Camera Raw Settings menu
presets using the Adjustment Brush tool
Note:
Local adjustments cannot be saved with Camera Raw image presets.
or the Graduated Filter tool .
in the Adjustment Brush or Graduated Filter tool options. You apply local adjustment
To the top
Page 67

In the Adjustment Brush or Graduated Filter tool options in the Camera Raw dialog box, click the Camera Raw Settings menu
65
button
. Then, choose one of the following commands:
New Local Correction Setting
Saves the current local adjustment effect settings as a preset. Type a name and click OK.
Saved presets appear in the Local Adjustment Settings menu and can be applied to any image that is opened in Camera Raw.
Delete “preset name”
Rename “preset name”
Preset name
Select a preset to apply its settings with the Adjustment Brush tool or the Graduated Filter tool.
Deletes the selected local adjustment preset.
Renames the selected local adjustment preset. Type a name and click OK.
When using local adjustment presets, keep in mind the following:
Only one local adjustment preset can be selected at a time.
When applying a local adjustment preset with the Adjustment Brush tool, you can still customize the brush options, including
Size, Feather, Flow, and Density. The preset applies the effect settings at the specified brush size.
After a local adjustment preset is applied, you can refine it as desired.
The same effect settings are available for the Adjustment Brush tool and the Graduated Filter tool. As a result, local
adjustment presets can be applied using either tool, regardless of which tool was used to create the preset.
Video turorial
What's new in Camera Raw 7
Twitter™ and Facebook posts are not covered under the terms of Creative Commons.
Legal Notices | Online Privacy Policy
 Loading...
Loading...