
ADOBE® AFTER EFFECTS® CS6
SCRIPTING GUIDE
DRAFT

© Copyright 1992-2012 Adobe Systems Incorporated. All rights reserved.
®
Adobe
After Effects® CS6 Scripting Guide
NOTICE: All information contained herein is the property of Adobe Systems Incorporated. No part of this publication (whether in hardcopy or
electronic form) may be reproduced or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or
otherwise, without the prior written consent of Adobe Systems Incorporated. The software described in this document is furnished under
license and may only be used or copied in accordance with the terms of such license.
This publication and the information herein is furnished AS IS, is subject to change without notice, and should not be construed as a
commitment by Adobe Systems Incorporated. Adobe Systems Incorporated assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or
inaccuracies, makes no warranty of any kind (express, implied, or statutory) with respect to this publication, and expressly disclaims any and
all warranties of merchantability, fitness for particular purposes, and noninfringement of third party rights.
Any references to company names in sample templates are for demonstration purposes only and are not intended to refer to any actual
organization.
Adobe, the Adobe logo, After Effects, and Photoshop are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the
United States and/or other countries.
Apple, Mac, and Macintosh are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries. Microsoft, and
Windows are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries. JavaScript and all
Java-related marks are trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and other countries. UNIX is a
registered trademark of The Open Group. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
If this guide is distributed with software that includes an end user agreement, this guide, as well as the software described in it, is furnished
under license and may be used or copied only in accordance with the terms of such license. Except as permitted by any such license, no part
of this guide may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, recording,
or otherwise, without the prior written permission of Adobe Systems Incorporated. Please note that the content in this guide is protected
under copyright law even if it is not distributed with software that includes an end user license agreement.
The content of this guide is furnished for informational use only, is subject to change without notice, and should not be construed as a
commitment by Adobe Systems Incorporated. Adobe Systems Incorporated assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or
inaccuracies that may appear in the informational content contained in this guide.
Adobe Systems Incorporated, 345 Park Avenue, San Jose, California 95110, USA.

Overview
Introduction to scripting in After Effects
A script is a series of commands that tells an application to perform a series of operations. You can use scripts
in most Adobe applications to automate repetitive tasks, perform complex calculations, and even use some
functionality not directly exposed through the graphical user interface. For example, you can direct After
Effects to reorder the layers in a composition, find and replace source text in text layers, or send an e-mail
message when rendering is complete.
See “Examples” on page 191 for examples of what scripts can do.
Although both the After Effects expressions language and the After Effects ExtendScript scripting language are
based on JavaScript, the expressions features and scripting features of After Effects are separate and distinct.
Expressions cannot access information from scripts (such as variables and functions). Whereas a script tells an
application to do something, an expression says that a property is something. However, because the After
Effects expression language and ExtendScript are both based on JavaScript, familiarity with either one is very
helpful in understanding the other.
The heart of a scriptable application is the object model. When you use Adobe After Effects, you create projects,
compositions, and render queue items along with all of the elements that they contain: footage, images, solids,
layers, masks, effects, and properties. Each of these items, in scripting terms, is an object. This guide describes
the ExtendScript objects that have been defined for After Effects projects.
The After Effects object model is composed of a project, items, compositions, layers, and render queue items.
Each object has its own special attributes, and every object in an After Effects project has its own identity
(although not all are accessible to scripting). You should be familiar with the After Effects object model in order
to create scripts.
NOTE: JavaScript objects normally referred to as “properties” are consistently called “attributes” in this guide, to
avoid confusion with After Effects’ own definition of a property (an animatable value of an effect, mask, or
transform within an individual layer).
Nearly all of what scripting can accomplish replicates what can be done by means of the After Effects graphical
user interface. A thorough knowledge of the application itself and its graphical user interface is essential to
understanding how to use scripting in After Effects.
The ExtendScript language
After Effects scripts use the Adobe ExtendScript language, which is an extended form of JavaScript used by
several Adobe applications, including Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign. ExtendScript implements the
JavaScript language according to the ECMA-262 specification. The After Effects scripting engine supports the
3rd Edition of the ECMA-262 Standard, including its notational and lexical conventions, types, objects, expressions, and statements. ExtendScript also implements the E4X ECMA-357 specification, which defines access
to data in XML format.
ExtendScript defines a global debugging object, the dollar ($) object, and a reporting utility for ExtendScript
elements, the ExtendScript Reflection interface.
3

Overview The ExtendScript Toolkit (ESTK)
4
File and Folder Objects: Because path name syntax is very different in different operating systems, Adobe
ExtendScript defines
system.
ScriptUI User Interface Module: The ExtendScript ScriptUI module provides the ability to create and interact
with user interface elements. ScriptUI provides an object model for windows and UI control elements that you
can use to create a user interface for your scripts.
Tools and Utilities: In addition, ExtendScript provides tools and features such as a localization utility for
providing user-interface string values in different languages and global functions for displaying short
messages in dialog boxes (
External Communication: ExtendScript provides a Socket object that allows you to communicate with remote
systems from your After Effects scripts.
Interapplication Communication: ExtendScript provides a common scripting environment for all Adobe
applications, and allows interapplication communication through scripts.
File and Folder objects to provide platform-independent access to the underlying file
alert, confirm, and prompt).
The ExtendScript Toolkit (ESTK)
After Effects includes a script editor and debugger, the ExtendScript Toolkit (ESTK), which provides a convenient interface for creating and testing your own scripts.
To start the ESTK, choose File > Scripts > Open Script Editor.
If you choose to use another text editor to create, edit, and save scripts, be sure to choose an application that
does not automatically add header information when saving files and that saves with Unicode (UTF-8)
encoding. In many text editors, you can set preferences for saving with UTF-8 encoding. Some applications
(such as Microsoft Word) by default add header information to files that can cause “line 0” errors in scripts,
causing them to fail.
For detailed information on the ExtendScript Toolkit, see the JavaScript Tools Guide.
The .jsx and .jsxbin file-name extensions
ExtendScript script files are distinguished by the .jsx file-name extension, a variation on the standard .js
extension used with JavaScript files. After Effects scripts must include the
properly recognized by the application. Any UTF-8-encoded text file with the
an ExtendScript file.
You can use the ExtendScript Toolkit to export a binary version of an ExtendScript file, which has the
extension
Effects.
.jsxbin. Such a binary file may not be usable with all of the scripting integration features in After
.jsx file extension in order to be
.jsx extension is recognized as
Activating full scripting features
The default is for scripts to not be allowed to write files or send or receive communication over a network. To
allow scripts to write files and communicate over a network, choose Edit > Preferences > General (Windows)
or After Effects > Preferences > General (Mac OS), and select the Allow Scripts To Write Files And Access
Network option.
4

Overview Loading and running scripts
5
Any After Effects script that contains an error preventing it from being completed generates an error message
from the application. This error message includes information about the nature of the error and the line of the
script on which it occurred. The ExtendScript Toolkit (ESTK) debugger can open automatically when the
application encounters a script error. This feature is disabled by default so that casual users do not encounter
it. To activate this feature, choose Preferences > General, and select Enable JavaScript Debugger.
Loading and running scripts
Running scripts directly from the File > Scripts menu
When After Effects starts, it searches the Scripts folder for scripts to load. Loaded scripts are available from
the File > Scripts menu.
To run a loaded script, choose File > Scripts > [script name].
If you edit a script while After Effects is running, you must save your changes for the changes to be applied. If
you place a script in the Scripts folder while After Effects is running, you must restart After Effects for the
script to appear in the Scripts menu, though you can immediately run the new script using the Run Script File
command.
Running scripts using File > Scripts > Run Script File
To run a script that has not been loaded, choose File > Scripts > Run Script File, locate and select a script, and
click Open.
Running scripts from the command line, a batch file, or an AppleScript script
If you are familiar with how to run a script from the command line in Windows or via AppleScript, you can
send a script directly to the open After Effects application, so that the application automatically runs the script.
To run a script from the command line, call afterfx.exe from the command line. Use the -r switch and the full
path of the script to run as arguments. This command does not open a new instance of the After Effects application; it runs the script in the existing instance.
Example (for Windows):
afterfx -r c:\script_path\example_script.jsx
You can use this command-line technique—together with the software that comes with a customizable
keyboard—to bind the invocation of a script to a keyboard shortcut.
Following are examples of Windows command-line entries that will send an After Effects script to the application without using the After Effects user interface to execute the script.
In the first example, you copy and paste your After Effects script directly on the command line and then run
it. The script text appears in quotation marks following the
afterfx.exe -s "alert("You just sent an alert to After Effects")"
afterfx.exe -s command:
Alternatively, you can specify the location of the JSX file to be executed. For example:
afterfx.exe -r c:\myDocuments\Scripts\yourAEScriptHere.jsx
afterfx.exe -r "c:\myDocuments\Scripts\Script Name with Spaces.jsx"
5

Overview Loading and running scripts
6
How to include After Effects scripting in an AppleScript (Mac OS)
Following are three examples of AppleScript scripts that will send an existing JSX file containing an After
Effects script to the application without using the After Effects user interface to execute the script.
In the first example, you copy your After Effects script directly into the Script Editor and then run it. The script
text appears within quotation marks following the DoScript command, so internal quotes in the script must
be escaped using the backslash escape character, as follows:
tell application "Adobe After Effects CS6"
DoScript "alert(\"You just sent an alert to After Effects\")"
end tell
Alternatively, you could display a dialog box asking for the location of the JSX file to be executed, as follows:
set theFile to choose file
tell application "Adobe After Effects CS6"
DoScript theFile
end tell
Finally, this script is perhaps most useful when you are working directly on editing a JSX script and want to
send it to After Effects for testing or to run. To use it effectively you must enter the application that contains
the open JSX file (in this example it is TextEdit); if you do not know the proper name of the application, type
in your best guess to replace “TextEdit” and AppleScript prompts you to locate it.
Simply highlight the script text that you want to run, and then activate this AppleScript:
(*
This script sends the current selection to After Effects as a script.
*)
tell application "TextEdit"
set the_script to text of front document
end tell
tell application "Adobe After Effects CS6"
activate
DoScript the_script
end tell
Running scripts automatically during application startup or shutdown
Within the Scripts folder are two folders called Startup and Shutdown. After Effects runs scripts in these
folders automatically, in alphabetical order, on starting and quitting, respectively.
In the Startup folder you can place scripts that you wish to execute at startup of the application. They are
executed after the application is initialized and all plug-ins are loaded.
Scripting shares a global environment, so any script executed at startup can define variables and functions that
are available to all scripts. In all cases, variables and functions, once defined by running a script that contains
them, persist in subsequent scripts during a given After Effects session. Once the application is quit, all such
globally defined variables and functions are cleared. Be sure to give variables in scripts unique names, so that
a script does not inadvertently reassign global variables intended to persist throughout a session.
Attributes can also be added to existing objects such as the Application object (see “Application object” on
page 17) to extend the application for other scripts.
6

Overview Loading and running scripts
7
The Shutdown folder scripts are executed as the application quits. This occurs after the project is closed but
before any other application shutdown occurs.
Running scripts from the Window menu
Scripts in the ScriptUI Panels folder are available from the bottom of the Window menu. If a script has been
written to provide a user interface in a dockable panel, the script should be put in the ScriptUI folder. ScriptUI
panels work much the same as the default panels in the After Effects user interface.
Inste ad of creating a Window object and adding controls to it, a S criptUI Panels script uses t he
this object that
represents the panel. For example, the following code adds a button to a panel:
var myPanel = this;
myPanel.add("button", [10, 10, 100, 30], "Tool #1");
If your script creates its user interface in a function, you cannot use this as it will refer to the function itself,
not the panel. In this case, you should pass the
function createUI(thisObj) {
var myPanel = thisObj;
myPanel.add("button", [10, 10, 100, 30], "Tool #1");
return myPanel;
}
var myToolsPanel = createUI(this);
this object as an argument to your function. For example:
You cannot use the File > Scripts > Run Script File menu command to run a script that refers to this. To make
your script work with either a Window object (accessible from the File > Scripts menu) or a native panel
(accessible from the Window menu), check whether
function createUI(thisObj) {
var myPanel = (thisObj instanceof Panel) ? thisObj : new Window("palette", "My Tools",
[100, 100, 300, 300]);
myPanel.add("button", [10, 10, 100, 30], "Tool #1");
return myPanel;
}
var myToolsPanel = createUI(this);
this is a Panel object. For example:
Stopping a running script
A scr ipt can be stopped by pressing Es c or Cmd+p eriod (in Mac OS) when the Af ter Effects or the script’s user
interface has focus. However, a script that is busy processing a lot of data might not be very responsive.
7
After Effects scripting reference
This chapter lists and describes JavaScript classes, objects, methods, attributes, and global functions defined by
After Effects.
The After Effects scripting engine supports ExtendScript, Adobe’s extended version of JavaScript, which implements the 3rd Edition of the ECMA-262 Standard, including its notational and lexical conventions, types,
objects, expressions and statements. For a complete listing of the keywords and operators included with
ECMAScript, refer to
262.htm. For an overview of the most common keywords and statements available from ECMA-262, see
“JavaScript keywords and statement syntax” on page 8.
Elements of basic JavaScript relevant to After Effects scripting
JavaScript variables
Scripting shares a global environment, so any script executed at startup can define variables and functions that
are available to all scripts. In all cases, variables and functions, once defined by running a script that contains
them, persist in subsequent scripts during a given After Effects session. Once the application is quit, all such
globally defined variables and functions are cleared. Scripters should be careful about giving variables in scripts
unique names, so that a script does not inadvertently reassign global variables intended to persist throughout
a session.
ECMA-262.pdf, available at www.ecma-international.org/publications/standards/Ecma-
JavaScript keywords and statement syntax
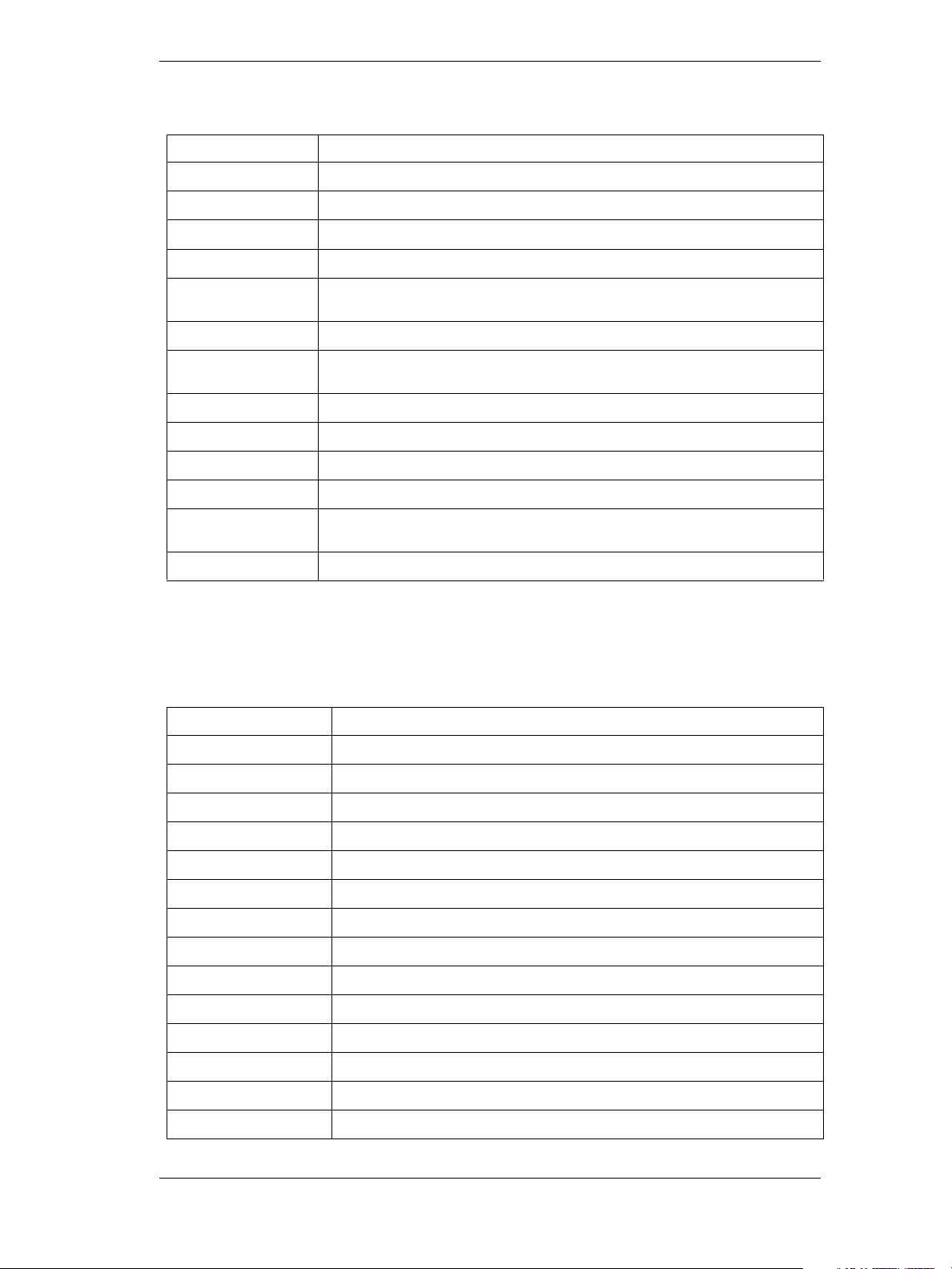
Although it is not possible to provide an exhaustive resource describing usage of JavaScript, the following tables
provide an overview of keywords, statements, operators, precedence, and associativity.
The following table lists and describes all keywords and statements recognized by the After Effects scripting
engine.
Table 1 Keywords and Statement Syntax
Keyword/Statement Description
break
continue
case
default
do...while
false
for
Standard JavaScript; exit the currently executing loop.
Standard JavaScript; cease execution of the current loop iteration.
Label used in a switch statement.
Label used in a switch statement when a case label is not found.
Standard JavaScript construct. Similar to the while loop, except loop condition evaluation occurs
at the end of the loop.
Literal representing the Boolean false value.
Standard JavaScript loop construct.
8
After Effects scripting reference Elements of basic JavaScript relevant to After Effects scripting
9
Keyword/Statement Description
for...in
function
if/if...else
new
null
return
switch
this
true
undefined
var
while
with
Standard JavaScript construct. Provides a way to easily loop through the properties of an object.
Used to define a function.
Standard JavaScript conditional constructs.
Standard JavaScript constructor statement.
Assigned to a variable, array element, or object property to indicate that it does not contain a legal
value.
Standard JavaScript way of returning a value from a function or exiting a function.
Standard JavaScript way of evaluating a JavaScript expression and attempting to match the expression’s value to a case label.
Standard JavaScript method of indicating the current object.
Literal representing the Boolean true value.
Indicates that the variable, array element, or object property has not yet been assigned a value.
Standard JavaScript syntax used to declare a local variable.
Standard JavaScript construct. Similar to the do...while loop, except loop condition evaluation
occurs at the beginning of the loop.
Standard JavaScript construct used to specify an object to use in subsequent statements.
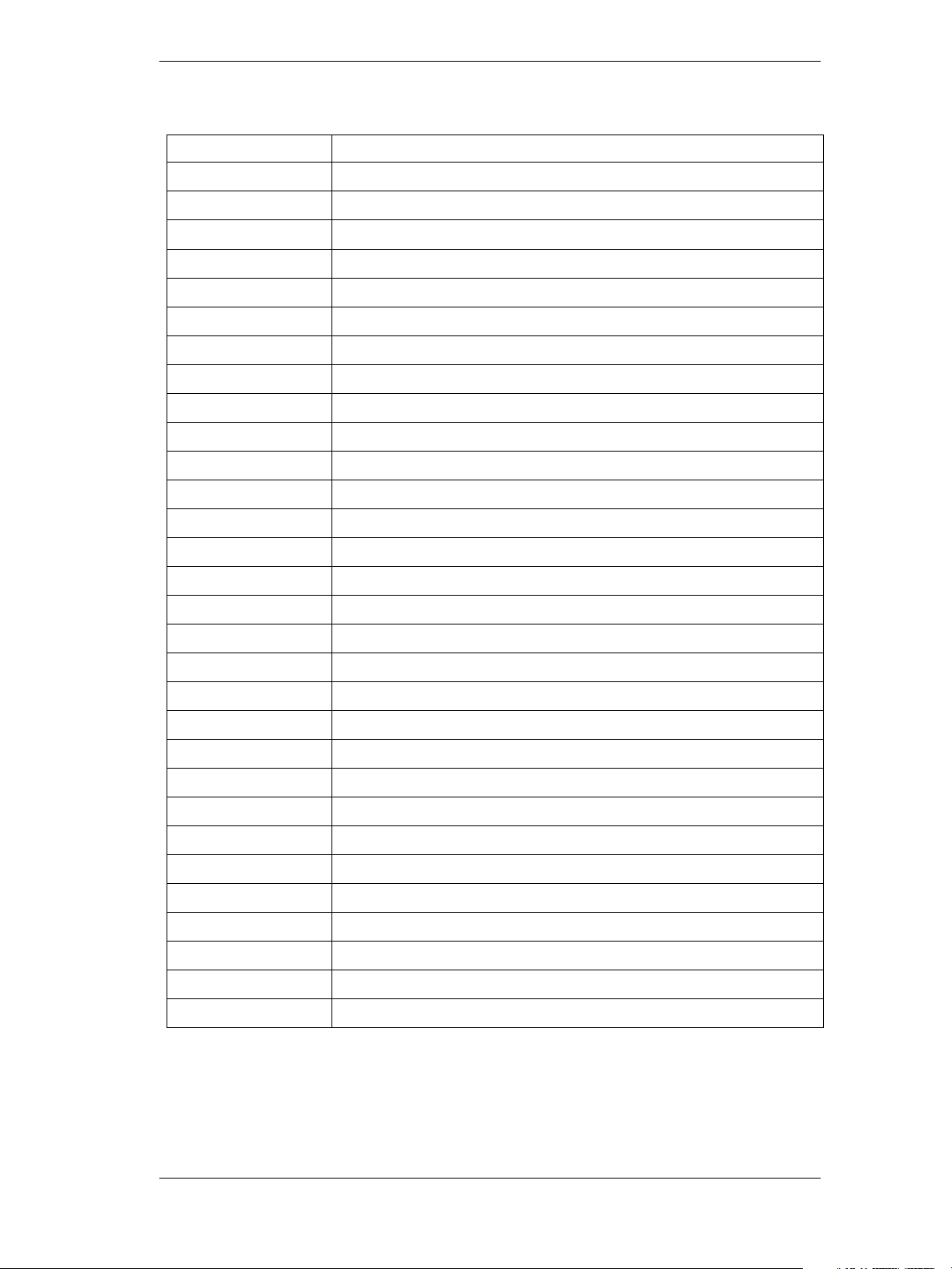
JavaScript operators
The following tables list and describe all operators recognized by the After Effects scripting engine and show
the precedence and associativity for all operators.
Table 2 Description of Operators
Operators Description
new
delete
typeof
void
.
[]
()
++
––
–
~
!
*
/
Allocate object.
Deallocate object.
Returns data type.
Returns undefined value.
Structure member.
Array element.
Function call.
Pre- or post-increment.
Pre- or post-decrement.
Unary negation or subtraction.
Bitwise NOT.
Logical NOT.
Multiply.
Divide.
9
After Effects scripting reference Elements of basic JavaScript relevant to After Effects scripting
10
Operators Description
%
+
<<
>>
>>>
<
<=
>
>=
==
!=
&
^
|
&&
||
?:
Modulo division.
Add.
Bitwise left shift.
Bitwise right shift.
Unsigned bitwise right shift.
Less than.
Less than or equal.
Greater than.
Greater than or equal.
Equal.
Not equal.
Bitwise AND.
Bitwise XOR.
Bitwise OR.
Logical AND.
Logical OR.
Conditional (ternary).
=
+=
–=
*=
/=
%=
<<=
>>=
>>>=
&=
^=
|=
,
Assignment.
Assignment with add operation.
Assignment with subtract operation.
Assignment with multiply operation.
Assignment with divide operation.
Assignment with modulo division operation.
Assignment with bitwise left shift operation.
Assignment with bitwise right shift operation.
Assignment with unsigned bitwise right shift operation.
Assignment with bitwise AND operation.
Assignment with bitwise XOR operation.
Assignment with bitwise OR operation.
Multiple evaluation.
10
After Effects scripting reference The After Effects Object Model
APPLICATION
PROJECT
SETTINGS
RENDER1UEUE ITEMS
ITEMSMAYBEANYOFTHEFOLLOWINGTYPESOFITEM
ITEMS
RENDER1UEUE)TEMS
OUTPUT-ODULES
SOCKETFILE FOLDERSYSTEM
FOLDER)TEMFOOTAGE)TEM
PROXY3OURCE PROXY3OURCEMAIN3OURCE
SOLID3OURCE
COLOR
FILE3OURCE
FILE
PLACEHOLDER3OURCE
LAYERS
PROPERTIES
COMP)TEM
/2
/2
/2
/2
MAIN3OURCEPROXY3OURCE
MAYBEANYOFTHEFOLLOWINGTYPESOFITEM
11
Table 3 Operator Precedence
Operators (highest precedence to lowest) Associativity
[], (), .
new, delete, – (unary negation), !, typeof, void, ++, ––
*, /, %
+, – (subtraction)
<<, >>, >>>
<, <=, >, >=
==, !=
&
^
|
&&
||
?:
=, /=, %=, <<=, >>=, >>>=, &=, ^=, |=, +=, –=, *=
,
left to right
right to left
left to right
left to right
left to right
left to right
left to right
left to right
left to right
left to right
left to right
left to right
right to left
right to left
left to right
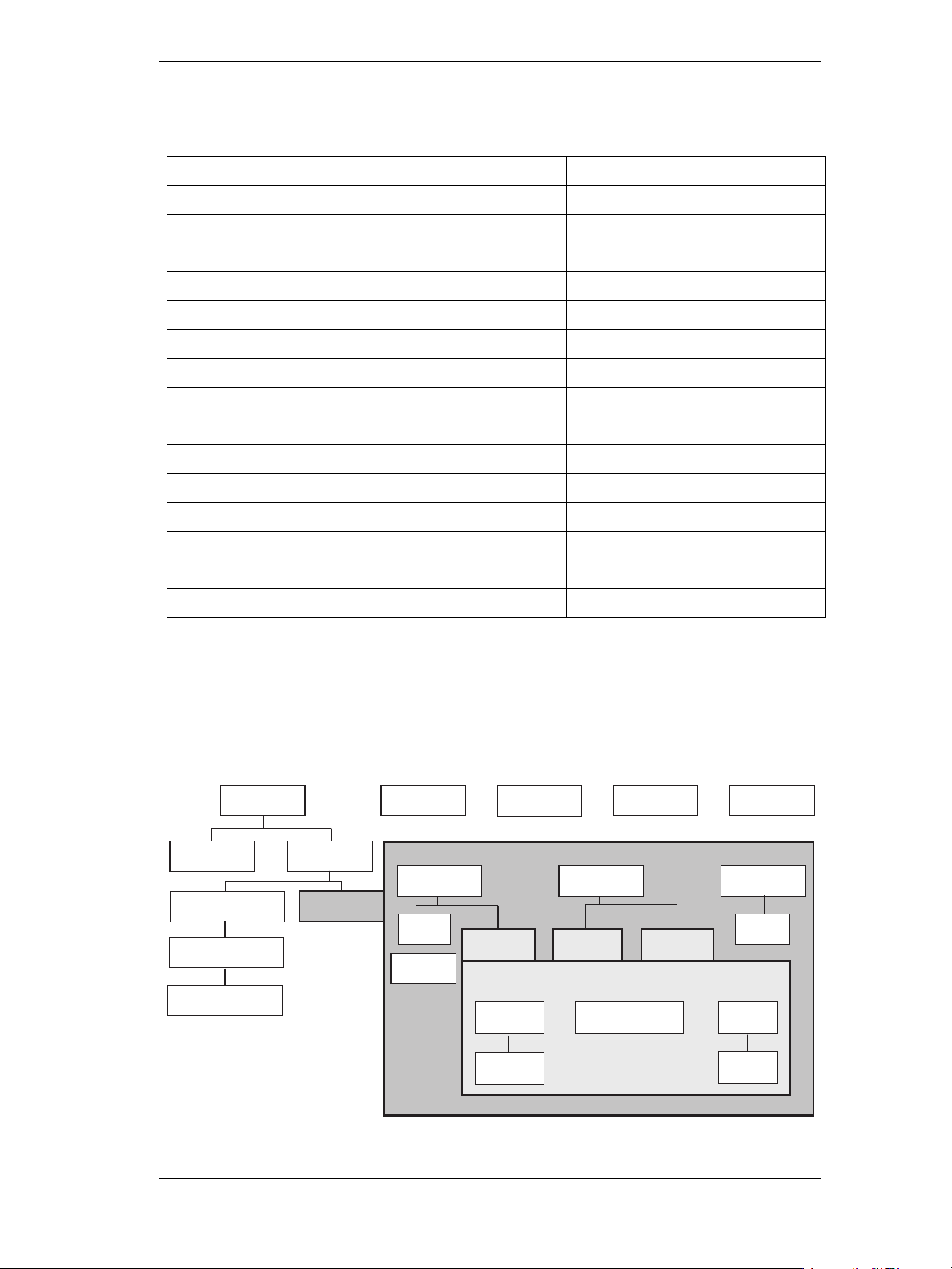
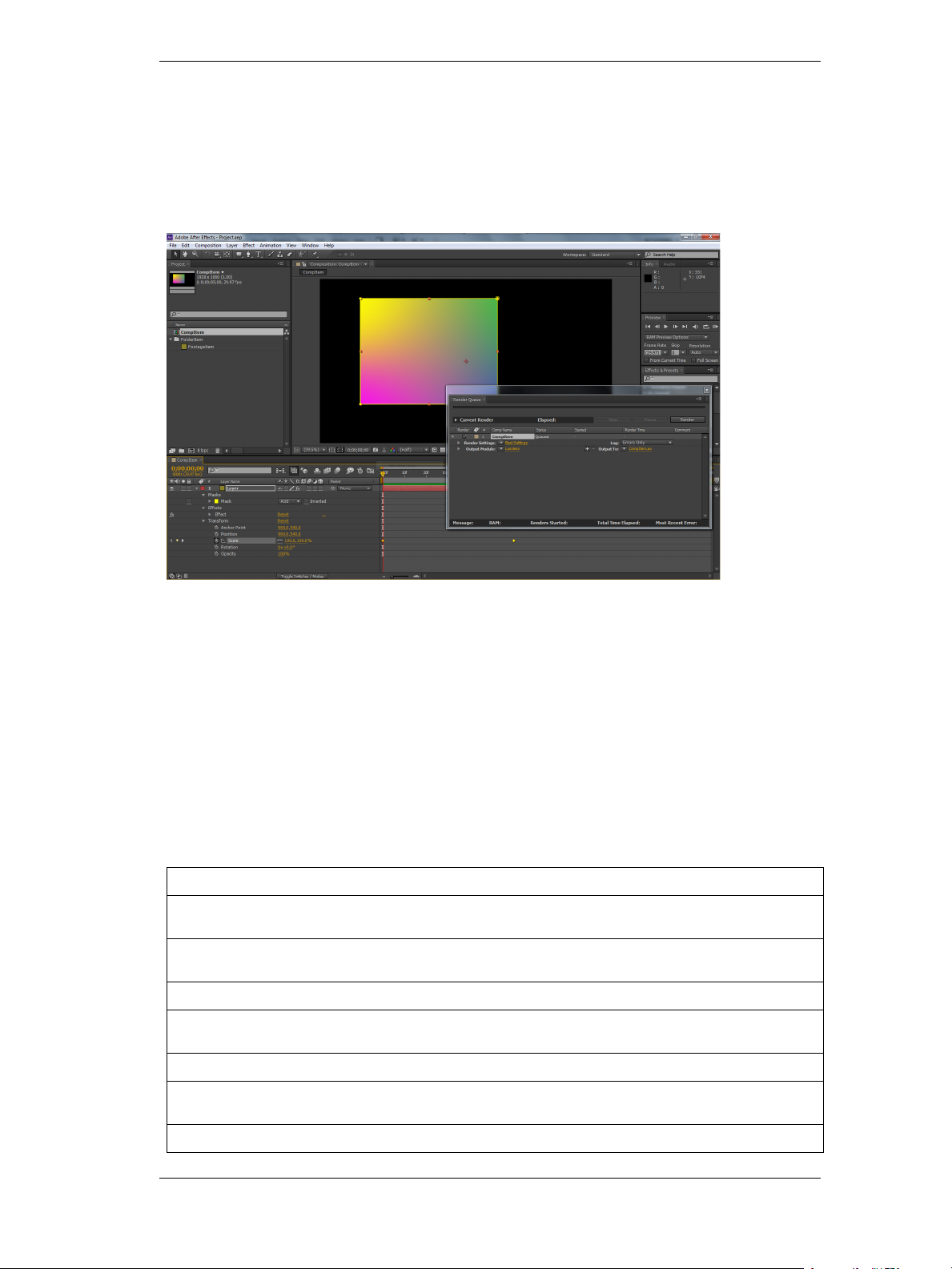
The After Effects Object Model
As you look through this reference section, which is organized alphabetically by object, you can refer to the
following diagrams for an overview of where the various objects fall within the hierarchy, and their correspondence to the user interface.
Hierarchy diagram of the main After Effects scripting objects
11
After Effects scripting reference The After Effects Object Model
12
Note that the File, Folder, and Socket objects are defined by ExtendScript, and are documented in the JavaScript Tools Guide. ExtendScript also defines the ScriptUI module, a set of window and user-interface control
objects, which are available to After Effects scripts. These are also documented in the JavaScript Tools Guide.
The hierarchy of objects in scripting corresponds to the hierarchy in the user interface.
The application contains a Project panel, which displays a project. The project contains compositions, which
contain layers. The source for a layer can be a footage file, placeholder, or solid, also listed in the Project panel.
Each layer contains settings known as properties, and these can contain markers and keyframes. The render
queue contains render-queue items as well as render settings and output modules. All of these entities are represented by objects in scripting.
NOTE: To avoid ambiguity, this manual uses the term “attribute” to refer to JavaScript object properties, and the
term “property” or “AE property” to refer to After Effects layer properties.
Object summary
The following table lists all objects alphabetically, with links to the documentation page for each.
Object Description
“Global functions” on page 14 Globally available functions that allow you to display text for script debugging purposes,
“Application object” on page 17 A single global object, available by its name (app), that provides access to objects and
“AVItem object” on page 30 Represents audio/visual files imported into After Effects.
“AVLayer object” on page 38 Represents those layers that contain AVItem objects (composition layers, footage layers,
“CameraLayer object” on page 50 Represents a camera layer within a composition.
“Collection object” on page 51 Associates a set of objects or values as a logical group and provides access to them by
and help convert time values between seconds and frames.
application settings within the After Effects application.
solid layers, text layers, and sound layers).
index.
“CompItem object” on page 52 Represents a composition, and allows you to manipulate it and get information about it.
12

After Effects scripting reference The After Effects Object Model
13
Object Description
“FileSource object” on page 61 Describes footage that comes from a file.
“FolderItem object” on page 63 Represents a folder in the Project panel.
“FootageItem object” on page 65 Represents a footage item imported into a project, which appears in the Project panel.
“FootageSource object” on page 69 Describes the file source of some footage.
“ImportOptions object” on page 75 Encapsulates options for importing files into After Effects.
“Item object” on page 78 Represents an item in a project that appears in the Project panel.
“ItemCollection object” on page 82 Collects items in a project.
“KeyframeEase object” on page 84 Encapsulates keyframe ease values in an After Effects property.
“Layer object” on page 86 A base class for layer classes.
“LayerCollection object” on page 95 Collects layers in a project.
“LightLayer object” on page 100 Represents a light layer within a composition.
“MarkerValue object” on page 102 Encapsulates marker values in an After Effects property.
“MaskPropertyGroup object” on
page 106
“OMCollection object” on page 109 Collects output modules in a render queue.
“OutputModule object” on page 110 Represents an output module for a render queue.
“PlaceholderSource object” on page 113 Describes a placeholder for footage.
“Project object” on page 114 Represents an After Effects project.
“Property object” on page 124 Represents an After Effects property.
“PropertyBase object” on page 148 A base class for After Effects property and property group classes.
“PropertyGroup object” on page 155 Represents an After Effects property group.
“RenderQueue object” on page 160 Represents the After Effects render queue.
“RenderQueueItem object” on page 163 Represents a renderable item in a render queue.
“RenderQueueItem object” on page 163 Collects render-queue items in a render queue.
“RQItemCollection object” on page 169 Provides access to application settings and preferences.
“Shape object” on page 172 Encapsulates the outline shape information for a mask.
“ShapeLayer object” on page 178 Represents a shape layer within a composition.
“SolidSource object” on page 179 Describes a solid color that is the source of some footage.
“System object” on page 180 Provides access to the operating system from the application.
“TextDocument object” on page 182 Encapsulates the text in a text layer.
Encapsulates mask attributes in a layer.
“TextLayer object” on page 188 Represents a text layer within a composition.
“Viewer object” on page 189 Represents a Composition, Layer, or Footage panel.
13
After Effects scripting reference Global functions
14
Global functions
These globally available functions that are specific to After Effects. Any JavaScript object or function can call
these functions, which allow you to display text in a small (3-line) area of the Info panel, and to convert
numeric time values to and from string values.
Global function Description
clearOutput()
currentFormatToTime()
timeToCurrentFormat()
write()
writeLn()
isValid()
Additional global functions for standard user I/O (
Clears text from the Info panel.
Converts string time value to a numeric time value.
Converts a numeric time value to a string time value.
Writes text to the Info panel, with no line break added.
Writes text to the Info panel, adding a line break at the end.
When true, the specified object exists.
alert, confirm, and prompt) and static functions for file
I/O, are defined by ExtendScript; for detailed reference information, see the JavaScript Tools Guide (available
from the ExtendScript Toolkit’s Help menu).
clearOutput() global function
clearOutput()
Description
Clears the output in the Info panel.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
currentFormatToTime() global function
currentFormatToTime(formattedTime, fps, isDuration)
Description
Converts a formatted string for a frame time value to a number of seconds, given a specified frame rate. For
example, if the formatted frame time value is 0:00:12 (the exact string format is determined by a project
setting), and the frame rate is 24 fps, the time would be 0.5 seconds (12/24). If the frame rate is 30 fps, the time
would be 0.4 seconds (12/30).
If the time is a duration, the frames are counted from 0. Otherwise, the frames are counted from the project’s
starting frame (see “Project displayStartFrame attribute” on page 117).
Parameters
formattedTime
fps
The frame time value, a string specifying a number of frames in the project’s current time display format.
The frames-per-second, a floating-point value.
14
After Effects scripting reference Global functions
15
isDuration
Returns
Optional. When true, the time is a duration (measured from frame 0). When false (the default), the time is
measured from the project’s starting frame.
Floating-point value, the number of seconds.
isValid() global function
isValid(obj)
Description
Determines if the specified After Effects object (e.g., composition, layer, mask, etc.) still exists. Some operations, such as the
objects. This function allows you to test whether those assignments are still valid before attempting to access
them.
Parameters
obj
Returns
Boolean.
Example
var layer = app.project.activeItem.layer(1); // assume layer has three masks
alert(isValid(layer)); // displays “true”
var mask1 = layer.mask(1);
var mask2 = layer.mask(2);
var mask3 = layer.mask(3);
mask3.moveTo(1); // move the third mask to the top of the mask stack
alert(isValid(mask1)); // displays “false”; mask2 and mask3 do as well
PropertyBase moveTo() method, might invalidate existing variable assignments to related
The After Effects object to check for validity.
timeToCurrentFormat() global function
timeToCurrentFormat(time, fps, isDuration)
Description
Converts a numeric time value (a number of seconds) to a frame time value; that is, a formatted string that
shows which frame corresponds to that time, at the specified rate. For example, if the time is 0.5 seconds, and
the frame rate is 24 fps, the frame would be 0:00:12 (when the project is set to display as timecode). If the frame
rate is 30 fps, the frame would be 0:00:15. The format of the timecode string is determined by a project setting.
If the time is a duration, the frames are counted from 0. Otherwise, the frames are counted from the project’s
starting frame (see “Project displayStartFrame attribute” on page 117).
Parameters
time
fps
The number of seconds, a floating-point value.
The frames-per-second, a floating-point value.
15
After Effects scripting reference Global functions
16
isDuration
Returns
Optional. When true, the time is a duration (measured from frame 0). When false (the default), the time is
measured from the project’s starting frame.
String in the project’s current time display format.
write() global function
write(text)
Description
Writes output to the Info panel, with no line break added.
Parameters
text
Returns
Nothing.
Example
write("This text appears in Info panel ");
write("with more on same line.");
The string to display. Truncated if too long for the Info panel.
writeLn() global function
writeLn(text)
Description
Writes output to the Info panel and adds a line break at the end.
Parameters
text
Returns
Nothing.
Example
writeln("This text appears on first line");
writeln("This text appears on second line");
The string to display.
16
After Effects scripting reference Application object
17
Application object
app
Description
Provides access to objects and application settings within the After Effects application. The single global object
is always available by its name,
Attributes of the Application object provide access to specific objects within After Effects. Methods of the
Application object can create a project, open an existing project, control Watch Folder mode, purge memory,
and quit the After Effects application. When the After Effects application quits, it closes the open project,
prompting the user to save or discard changes as necessary, and creates a project file as necessary.
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
app.
project
isoLanguage
version
buildName
buildNumber
isWatchFolder
isRenderEngine
settings
onError
exitCode
“Application project attribute” on
page 26 and “Project object” on
page 114
“Application isoLanguage attribute” on
page 22
“Application version attribute” on
page 29
“Application buildName attribute” on
page 19
“Application buildNumber attribute” on
page 20
“Application isWatchFolder attribute” on
page 23
“Application isRenderEngine attribute”
on page 23
“Application settings attribute” on
page 28 and “RQItemCollection object”
on page 169
“Application onError attribute” on
page 24
“Application exitCode attribute” on
page 22
The current After Effects project.
The locale (language and region) in which the application is running.
The version number of the After Effects application.
The name of this build of the application.
The number of this build of the application.
When true, the local application is running in Watch
Folder mode.
When true, the local After Effects application is running
as a render engine.
Application settings that can be set via scripting.
A callback function that is called when an error occurs
in the application.
A numeric status code used when executing a script
externally (that is, from a command line or AppleScript).
0 if no error occurred. A positive number indicates an
error that occurred while running the script.
exitAfterLaunchAndEval
saveProjectOnCrash
memoryInUse
effects
activeViewer
“Application exitAfterLaunchAndEval
attribute” on page 22
“Application saveProjectOnCrash attribute” on page 27
“Application memoryInUse attribute” on
page 23
“Application effects attribute” on
page 20
“Application activeViewer attribute” on
page 19
When true, the application remains open after running
a script from the command line on Windows.
When true, the project is saved if the application closes
unexpectedly.
Memory in use by this application.
The effects available in the application.
The currently focused or last-focused viewer panel.
17
After Effects scripting reference Application object
18
Methods
Method Reference Description
newProject()
open()
quit()
watchFolder()
pauseWatchFolder()
endWatchFolder()
purge()
beginUndoGroup()
endUndoGroup()
beginSuppressDialogs()
endSuppressDialogs()
setMemoryUsageLimits()
“Application newProject() method” on
page 24
“Application open() method” on page 24 Opens a project or an Open Project dialog box.
“Application quit() method” on page 27 Quits the application.
“Application watchFolder() method” on
page 29
“Application pauseWatchFolder() method”
on page 26
“Application endWatchFolder() method” on
page 21
“Application purge() method” on page 26 Purges a targeted type of cached information
“Application beginUndoGroup() method”
on page 19
“Application endUndoGroup() method” on
page 21
“Application beginSuppressDialogs()
method” on page 19
“Application endSuppressDialogs()
method” on page 21
“Application setMemoryUsageLimits()
method” on page 28
Creates a new project in After Effects.
Starts Watch Folder mode; does not return
until Watch Folder mode is turned off.
Pauses a current watch-folder process.
Ends a current watch-folder process.
(replicates Purge options in the Edit menu).
Groups the actions that follow it into a single
undoable step.
Ends an undo group; needed only when a
script contains more than one undo group.
Begins suppression of dialogs in the user interface.
Ends suppression of dialogs in the user interface.
Sets memory usage limits as in the Memory &
Cache preferences area.
setSavePreferencesOnQuit()
activate()
scheduleTask()
cancelTask()
parseSwatchFile()
“Application setSavePreferencesOnQuit()
method” on page 28
“Application activate() method” on page 18 Brings the After Effects main window to the
“Application scheduleTask() method” on
page 27
“Application cancelTask() method” on
page 20
“Application parseSwatchFile() method” on
page 25
Sets whether preferences are saved when the
application is quit.
front of the screen.
Schedules a JavaScript script for delayed execution.
Cancels a scheduled task.
Loads a color swatch from an Adobe Swatch
Exchange (ASE) file.
Application activate() method
app.activate()
Description
Opens the application main window if it is minimized or iconified, and brings it to the front of the desktop.
Parameters
None.
18

After Effects scripting reference Application object
19
Returns
Nothing.
Application activeViewer attribute
app.activeViewer
Description
The Viewer object for the currently focused or active-focused viewer (Composition, Layer, or Footage) panel.
Returns null if no viewers are open.
Typ e
Viewer obj e c t; rea d - only.
Application beginSuppressDialogs() method
app.beginSuppressDialogs()
Description
Begins suppression of script error dialog boxes in the user interface. Use endSuppressDialogs() to resume the
display of error dialogs. See “Application endSuppressDialogs() method” on page 21.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
Application beginUndoGroup() method
app.beginUndoGroup(undoString)
Description
Marks the beginning of an undo group, which allows a script to logically group all of its actions as a single
undoable action (for use with the Edit > Undo/Redo menu items). Use the
the end of the group. (See “Application endUndoGroup() method” on page 21.)
beginUndoGroup() and endUndoGroup() pairs can be nested. Groups within groups become part of the
larger group, and will undo correctly. In this case, the names of inner groups are ignored.
Parameters
undoString
Returns
The text that will appear for the Undo command in the Edit menu (that is, “Undo <undoString>”)
Nothing.
endUndoGroup() method to mark
Application buildName attribute
app.buildName
19
After Effects scripting reference Application object
20
Description
The name of the build of After Effects being run, used internally by Adobe for testing and troubleshooting.
Typ e
String; read-only.
Application buildNumber attribute
app.buildNumber
Description
The number of the build of After Effects being run, used internally by Adobe for testing and troubleshooting.
Typ e
Integer; read-only.
Application cancelTask() method
app.cancelTask(taskID)
Description
Removes the specified task from the queue of tasks scheduled for delayed execution.
Parameters
taskID
Returns
An integer that identifies the task, as returned by app.scheduleTask().
Nothing.
Application effects attribute
app.effects
Description
The effects available in the application.
Typ e
Array, with each element containing the following properties; read-only:
displayName
category
String representing the localized display name of the effect as seen in the Effect menu.
String representing the localized category label as seen in the Effect menu. This can be "" for synthetic
effects that aren’t normally shown to the user.
matchName
Example
var effectName = app.effects[12].displayName;
String representing the internal unique name for the effect. This name does not change between versions of After Effects. Use this value to apply the effect.
20

After Effects scripting reference Application object
21
Application endSuppressDialogs() method
app.endSuppressDialogs(alert)
Description
Ends the suppression of script error dialog boxes in the user interface. Error dialogs are displayed by default;
call this method only if
Dialogs() method” on page 19.
Parameters
beginSuppressDialogs() has previously been called. See “Application beginSuppress-
alert
Returns
Boolean; when true, errors that have occurred following the call to beginSuppressDialogs() are displayed in a
dialog box.
Nothing.
Application endUndoGroup() method
app.endUndoGroup()
Description
Marks the end of an undo group begun with the app.beginUndoGroup() method. You can use this method to
place an end to an undo group in the middle of a script, should you wish to use more than one undo group for
a single script.
If you are using only a single undo group for a given script, you do not need to use this method; in its absence
at the end of a script, the system will close the undo group automatically.
Calling this method without having set a
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
beginUndoGroup() method yields an error.
Application endWatchFolder() method
app.endWatchFolder()
Description
Ends Watch Folder mode.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
21

After Effects scripting reference Application object
22
See also
“Application watchFolder() method” on page 29
“Application parseSwatchFile() method” on page 25
“Application isWatchFolder attribute” on page 23
Application exitAfterLaunchAndEval attribute
app.exitAfterLaunchAndEval
Description
This attribute is used only when executing a script from a command line on Windows. When the application
is launched from the command line, the
(from a file or from a string, respectively).
If this attribute is set to true, After Effects will exit after the script is run; if it is false, the application will remain
open.
This attribute only has an effect when After Effects is run from the Windows command line. It has no effect
in Mac OS.
–r or –s command line flag causes the application to run a script
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
Application exitCode attribute
app.exitCode
Description
A numeric status code used when executing a script externally (that is, from a command line or AppleScript).
• In Windows, the value is returned on the command line when After Effects was launched on the command
line (using the
• in Mac OS, the value is returned as the AppleScript DoScript result for each script.
In both Mac OS and Windows, the value is set to 0 (
ation. In the event of an error while the script is running, the script can set this to a positive integer that
indicates what error occurred.
Typ e
Integer; read/write.
Example
app.exitCode = 2; //on quit, if value is 2, an error has occurred
afterfx or afterfx –m command), and a script was specified with the –r or –s option.
EXIT_SUCCESS) at the beginning of each script evalu-
Application isoLanguage attribute
app.isoLanguage
Description
A string indicating the locale (language and regional designations) After Effects is running.
$.locale returns the operating system language, not the language of the After Effects application.
NOTE:
22

After Effects scripting reference Application object
23
Typ e
String; read-only. Some common values include:
• en_US for English (United States)
• de_DE for German (Germany)
• es_ES for Spanish (Spain)
• fr_FR for French (France)
• it_IT for Italian (Italy)
• ja_JP for Japanese (Japan)
• ko_KR for Korean (Korea)
Example
var lang = app.isoLanguage;
if (lang == "en_US")
alert("After Effects is running in English.");
else if (lang == "fr_FR")
alert("After Effects is running in French.");
else
alert("After Effects is not running in English or French.");
Application isRenderEngine attribute
app.isRenderEngine
Description
True if After Effects is running as a render engine.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
Application isWatchFolder attribute
app.isWatchFolder
Description
True if the Watch Folder dialog box is currently displayed and the application is currently watching a folder
for rendering.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
Application memoryInUse attribute
app.memoryInUse
Description
The number of bytes of memory currently used by this application.
23

After Effects scripting reference Application object
24
Typ e
Number; read-only.
Application newProject() method
app.newProject()
Description
Creates a new project in After Effects, replicating the File > New > New Project menu command.
If the current project has been edited, the user is prompted to save it. If the user cancels out of the Save dialog
box, the new project is not created and the method returns null. Use
tions.DO_NOT_SAVE_CHANGES)
to close the current project before opening a new one. See “Project
close() method” on page 116.
Parameters
None.
Returns
A new Project object, or null if no new project is created.
app.project.close(CloseOp-
Example
app.project.close(CloseOptions.DO_NOT_SAVE_CHANGES);
app.newProject();
Application onError attribute
app.onError
Description
The name of a callback function that is called when an error occurs. By creating a function and assigning it to
this attribute, you can respond to errors systematically; for example, you can close and restart the application,
noting the error in a log file if it occurred during rendering. See “RenderQueue render() method” on page 161.
The callback function is passed the error string and a severity string. It should not return any value.
Typ e
A function name string, or null if no function is assigned; read/write.
Example
function err(errString) {
alert(errString);
}
app.onError = err;
Application open() method
app.open()
app.open(file)
24
After Effects scripting reference Application object
25
Description
Opens a project.
Parameters
file
Returns
Optional. An ExtendScript File object for the project file to open. If not sup plied, the method prompts the
user to select a project file.
A new Project object for the specified project, or null if the user cancels the Open dialog box.
Example
var my_file = new File("../my_folder/my_test.aep");
if (my_file.exists){
new_project = app.open(my_file);
if (new_project){
alert(new_project.file.name);
}
}
Application parseSwatchFile() method
app.parseSwatchFile(file)
Description
Loads color swatch data from an Adobe Swatch Exchange (ASE) file.
Parameters
file
Returns
The file specification, an ExtendScript File object.
The swatch data, in this format:
data.majorVersion
data.minorVersion
data.values
SwatchValue.type
SwatchValue.r
SwatchValue.g
SwatchValue.b
SwatchValue.c
SwatchValue.m
SwatchValue.y
SwatchValue.k
The ASE version number.
An array of SwatchValue.
One of "RGB", "CMYK", "LAB", "Gray"
When type = "RGB", the color values in the range [0.0..1.0].
0, 0, 0 is Black.
When type = "CMYK", the color values in the range [0.0..1.0].
0, 0, 0, 0 is White.
25
After Effects scripting reference Application object
26
SwatchValue.L
SwatchValue.a
SwatchValue.b
SwatchValue.value
When type = "LAB", the color values.
L is in the range [0.0..1.0]. a and b are in the range [-128.0..+128.0]
0, 0, 0 is Black.
When type = "Gray", the value range is [0.0..1.0].
0.0 is Black.
Application pauseWatchFolder() method
app.pauseWatchFolder(pause)
Description
Pauses or resumes the search of the target watch folder for items to render.
Parameters
pause
Returns
Nothing.
See also
“Application isWatchFolder attribute” on page 23
“Application watchFolder() method” on page 29
“Application endWatchFolder() method” on page 21
True to pause, false to resume.
Application project attribute
app.project
Description
The project that is currently loaded. See “Project object” on page 114.
Typ e
Project object; read-only.
Application purge() method
app.purge(target)
Description
Purges unused data of the specified types from memory. Replicates the Purge options in the Edit menu.
26
After Effects scripting reference Application object
27
Parameters
target
The type of elements to purge from memory; a PurgeTarget enumerated value, one of:
• PurgeTarget.ALL_CACHES: Purges all data that After Effects has cached to physical memory.
• PurgeTarget.UNDO_CACHES: Purges all data saved in the undo cache.
• PurgeTarget.SNAPSHOT_CACHES: Purges all data cached as composition/layer snapshots.
• PurgeTarget.IMAGE_CACHES: Purges all saved image data.
Returns
Nothing.
Application quit() method
app.quit()
Description
Quits the After Effects application.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
Application saveProjectOnCrash attribute
app.saveProjectOnCrash
Description
When true (the default), After Effects attempts to display a dialog box that allows you to save the current
project if an error causes the application to quit unexpectedly. Set to false to suppress this dialog box and quit
without saving.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
Application scheduleTask() method
app.scheduleTask(stringToExecute, delay, repeat)
Description
Schedules the specified JavaScript for delayed execution.
Parameters
stringToExecute
delay
A string containing JavaScript to be executed.
A number of milliseconds to wait before executing the JavaScript. A floating-point value.
27
After Effects scripting reference Application object
28
repeat
Returns
When true, execute the script repeatedly, with the specified delay between each execution. When false
the script is executed only once.
Integer, a unique identifier for this task, which can be used to cancel it with app.cancelTask().
Application setMemoryUsageLimits() method
app.setMemoryUsageLimits(imageCachePercentage, maximumMemoryPercentage)
Description
Sets memory usage limits as in the Memory & Cache preferences area. For both values, if installed RAM is less
than a given amount (n gigabytes), the value is a percentage of the installed RAM, and is otherwise a
percentage of n. The value of n is: 2 GB for 32-bit Windows, 4 GB for 64-bit Windows, 3.5 GB for Mac OS.
Parameters
imageCachePercentage
maximumMemoryPercentage
Returns
Nothing.
Floating-point value, the percentage of memory assigned to image cache.
Floating-point value, the maximum usable percentage of memory.
Application setSavePreferencesOnQuit() method
app.setSavePreferencesOnQuit(doSave)
Description
Set or clears the flag that determines whether preferences are saved when the application is closed.
Parameters
doSave
Returns
When true, preferences saved on quit, when false they are not.
Nothing.
Application settings attribute
app.settings
Description
The currently loaded settings. See “Settings object” on page 170.
Typ e
Settings object; read-only.
28
After Effects scripting reference Application object
29
Application version attribute
app.version
Description
An alphanumeric string indicating which version of After Effects is running.
Typ e
String; read-only.
Example
var ver = app.version;
alert("This machine is running version " + ver + " of After Effects.");
Application watchFolder() method
app.watchFolder(folder_object_to_watch)
Description
Starts a Watch Folder (network rendering) process pointed at a specified folder.
Parameters
folder_object_to_watch
Returns
The ExtendScript Folder object for the folder to watch.
Nothing.
Example
var theFolder = new Folder(“c:/tool”);
app.watchFolder(theFolder);
See also
“Application endWatchFolder() method” on page 21
“Application parseSwatchFile() method” on page 25
“Application isWatchFolder attribute” on page 23
29
After Effects scripting reference AVItem object
30
AVItem object
app.project.item(index)
Description
The AVItem object provides access to attributes and methods of audio/visual files imported into After Effects.
• AVItem is a subclass of Item. All methods and attributes of Item, in addition to those listed below, are
available when working with AVItem. See “Item object” on page 78.
• AVItem is the base class for both CompItem and FootageItem, so AVItem attributes and methods are also
available when working with CompItem and FootageItem objects. See “CompItem object” on page 52 and
“FootageItem object” on page 65.
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
name
width
height
pixelAspect
frameRate
frameDuration
duration
useProxy
proxySource
time
usedIn
hasVideo
hasAudio
footageMissing
Methods
“AVItem name attribute” on page 33 The name of the object as shown in the Project panel.
“AVItem width attribute” on page 37 The width of the item.
“AVItem height attribute” on page 32 The height of the item.
“AVItem pixelAspect attribute” on page 33 The pixel aspect ratio of the item.
“AVItem frameRate attribute” on page 32 The frame rate of the item.
“AVItem frameDuration attribute” on page 31 The frame duration for the item.
“AVItem duration attribute” on page 31 The total duration of the item.
“AVItem useProxy attribute” on page 36 When true, a proxy source is used for this item.
“AVItem proxySource attribute” on page 34 The FootageItem object used as proxy for the item.
“AVItem time attribute” on page 36 Current time of the item.
“AVItem usedIn attribute” on page 36 The CompItem objects that use this item.
“AVItem hasVideo attribute” on page 32 When true, the item has a video component.
“AVItem hasAudio attribute” on page 32 When true, the item has an audio component.
“AVItem footageMissing attribute” on
page 31
When true, the item cannot be found or is a placeholder.
Method Reference Description
setProxy()
setProxyWithSequence()
setProxyWithSolid()
setProxyWithPlaceholder()
setProxyToNone()
“AVItem setProxy() method” on page 34 Sets a proxy for the item.
“AVItem setProxyWithSequence() method” on
page 35
“AVItem setProxyWithSolid() method” on
page 35
“AVItem setProxyWithPlaceholder() method” on
page 35
“AVItem setProxyToNone() method” on page 34 Removes the proxy for the item.
Sets a sequence as a proxy for the item.
Sets a solid as a proxy for the item.
Sets a placeholder as a proxy for the item.
30

After Effects scripting reference AVItem object
31
AVItem duration attribute
app.project.item(index).duration
Description
Returns the duration, in seconds, of the item. Still footage items have a duration of 0.
• In a CompItem, the value is linked to the duration of the composition, and is read/write.
• In a FootageItem, the value is linked to the duration of the mainSource object, and is read-only.
Typ e
Floating-point value in the range [0.0..10800.0]; read/write for a CompItem; otherwise, read-only.
AVItem footageMissing attribute
app.project.item(index).footageMissing
Description
When true, the AVItem is a placeholder, or represents footage with a source file that cannot be found. In this
case, the path of the missing source file is in the
object. See “FootageItem mainSource attribute” on page 66 and “FileSource missingFootagePath attribute” on
page 61.
missingFootagePath attribute of the footage item’s source-file
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
AVItem frameDuration attribute
app.project.item(index).frameDuration
Description
Returns the length of a frame for this AVItem, in seconds. This is the reciprocal of frameRate. When set, the
reciprocal is automatically set as a new
This attribute returns the reciprocal of the
value is not evenly divisible into 1.0 (for example, 0.3). Due to numerical limitations, (1 / (1 / 0.3)) is close to,
but not exactly, 0.3.
If the AVItem is a FootageItem, this value is linked to the
conformFrameRate of the mainSource object. This sets both the frameRate and frameDuration of the
FootageItem.
Typ e
Floating-point value in the range [1/99.. 1.0]; read-only for a FootageItem, otherwise read/write.
frameRate value.
frameRate, which may not be identical to a value you set, if that
mainSource, and is read-only. To change it, set the
31

After Effects scripting reference AVItem object
32
AVItem frameRate attribute
app.project.item(index).frameRate
Description
The frame rate of the AVItem, in frames-per-second. This is the reciprocal of the frameDuration. When set,
the reciprocal is automatically set as a new
• In a CompItem, the value is linked to the frameRate of the composition, and is read/write.
• In a FootageItem, the value is linked to the frameRate of the mainSource obj ect , an d is re ad- onl y. To c hange
it, set the
conformFrameRate of the mainSource object. This sets both the frameRate and frameDuration
of the FootageItem.
Typ e
Floating-point value in the range [1.0..99.0]; read-only for a FootageItem, otherwise read/write.
AVItem hasAudio attribute
app.project.item(index).hasAudio
frameDuration value.
Description
When true, the AVItem has an audio component.
• In a CompItem, the value is linked to the composition.
• In a FootageItem, the value is linked to the mainSource object.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
AVItem hasVideo attribute
app.project.item(index).hasVideo
Description
When true, the AVItem has an video component.
• In a CompItem, the value is linked to the composition.
• In a FootageItem, the value is linked to the mainSource object.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
AVI tem height attribu te
app.project.item(index).height
Description
The height of the item in pixels.
• In a CompItem, the value is linked to the composition, and is read/write.
32

After Effects scripting reference AVItem object
33
• In a FootageItem, the value is linked to the mainSource object, and is read/write only if the mainSource
object is a SolidSource. Otherwise, it is read-only.
Typ e
Integer in the range [1...30000]; read/write, except as noted.
AVI tem name attr ibute
app.project.item(index).name
Description
The name of the item, as shown in the Project panel.
• In a FootageItem, the value is linked to the mainSource object. If the mainSource object is a FileSource, this
value controls the display name in the Project panel, but does not affect the file name.
Typ e
String; read/write.
AVItem pixelAspect attribute
app.project.item(index).pixelAspect
Description
The pixel aspect ratio (PAR) of the item.
• In a CompItem, the value is linked to the composition.
• In a FootageItem, the value is linked to the mainSource object.
The value you retrieve after setting may be slightly different from the value you supplied. The following table
compares the value as it appears in the UI with the more-accurate value returned by this attribute.
PAR in the After Effects UI PAR returned by the pixelAspect attribute
0.91 0.90909090909091
11
1.5 1.5
1.09 1.09401709401709
1.21 1.21212121212121
1.33 1.33333333333333
1.46 1.45868945868946
22
Typ e
Floating-point value, in the range [0.01..100.0]; read/write.
33

After Effects scripting reference AVItem object
34
AVItem proxySource attribute
app.project.item(index).proxySource
Description
The FootageSource being used as a proxy. The attribute is read-only; to change it, call any of the AVItem
methods that change the proxy source:
setProxyWithPlaceholder().
Typ e
FootageSource object; read-only.
AVI tem setProx y() method
app.project.item(index).setProxy(file)
Description
Sets a file as the proxy of this AVItem. Loads the specified file into a new FileSource object, sets this as the
value of the
eters, instead using the user preferences. If the file has an unlabeled alpha channel, and the user preference
says to ask the user what to do, the method estimates the alpha interpretation, rather than asking the user.
proxySource attribute, and sets useProxy to true. It does not preserve the interpretation param-
setProxy(), setProxyWithSequence(), setProxyWithSolid(), or
This differs from setting a FootageItem's main source, but both actions are performed as in the user interface.
Parameters
file
Returns
An ExtendScript File object for the file to be used as a proxy.
None.
AVI tem setProx yToNone () method
app.project.item(index).setProxyToNone()
Description
Removes the proxy from this AVItem, sets the value of proxySource to null, and sets the value of useProxy to
false.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
34

After Effects scripting reference AVItem object
35
AVItem setProxyWithPlaceholder() method
app.project.item(index).setProxyWithPlaceholder(name, width, height, frameRate, duration)
Description
Creates a PlaceholderSource object with specified values, sets this as the value of the proxySource attribute,
and sets
ences.
NOTE: There is no direct way to set a placeholder as a proxy in the user interface; this behavior occurs when a
proxy has been set and then moved or deleted.
Parameters
useProxy to true. It does not preserve the interpretation parameters, instead using the user prefer-
name
width, height
frameRate
duration
Returns
A string containing the name of the new object.
The pixel dimensions of the placeholder, an integer in the range [4..30000].
The frames-per-second, an integer in the range [1..99].
The total length in seconds, up to 3 hours. An integer in the range [0.0..10800.0].
Nothing.
AVItem setProxyWithSequence() method
app.project.item(index).setProxyWithSequence(file, forceAlphabetical)
Description
Sets a sequence of files as the proxy of this AVItem, with the option of forcing alphabetical order. Loads the
specified file sequence into a new FileSource object, sets this as the value of the
useProxy to true. It does not preserve the interpretation parameters, instead using the user preferences. If any
file has an unlabeled alpha channel, and the user preference says to ask the user what to do, the method
estimates the alpha interpretation, rather than asking the user.
Parameters
file
An ExtendScript File object for the first file in the sequence.
proxySource attribute, and sets
forceAlphabetical
Returns
When true, use the “Force alphabetical order” option.
Nothing.
AVItem setProxyWithSolid() method
app.project.item(index).setProxyWithSolid(color, name, width, height, pixelAspect)
Description
Creates a SolidSource object with specified values, sets this as the value of the proxySource attribute, and sets
useProxy to true. It does not preserve the interpretation parameters, instead using the user preferences.
35

After Effects scripting reference AVItem object
36
NOTE: There is no way, using the user interface, to set a solid as a proxy; this feature is available only through
scripting.
Parameters
color
name
width, height
pixelAspect
Returns
The color of the solid, an array of 3 floating-point values, [R, G, B], in the range [0.0..1.0].
A string containing the name of the new object.
The pixel dimensions of the placeholder, an integer in the range [1...30000].
The pixel aspect of the solid, a floating-point value in the range [0.01... 100.0].
Nothing.
AVItem time attribute
app.project.item(index).time
Description
The current time of the item when it is being previewed directly from the Project panel. This value is a number
of seconds. Use the global method
in terms of frames; see “timeToCurrentFormat() global function” on page 15.
It is an error to set this value for a FootageItem whose
Typ e
Floating-point value; read/write.
timeToCurrentFormat to convert it to a string value that expresses the time
mainSource is still (item.mainSource.isStill is true).
AVItem usedIn attribute
app.project.item(index).usedIn
Description
All the compositions that use this AVItem.
Note that upon retrieval, the array value is copied, so it is not automatically updated. If you get this value, then
add this item into another composition, you must retrieve the value again to get an array that includes the new
item.
Typ e
Array of CompItem objects; read-only.
AVItem useProxy attribute
app.project.item(index).useProxy
Description
When true, a proxy is used for the item. It is set to true by all the SetProxy methods, and to false by the
SetProxyToNone() method.
36

After Effects scripting reference AVItem object
37
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
AVItem width attribute
app.project.item(index).width
Description
The width of the item, in pixels.
• In a CompItem, the value is linked to the composition, and is read/write.
• In a FootageItem, the value is linked to the mainSource object, and is read/write only if the mainSource
object is a SolidSource. Otherwise, it is read-only.
Typ e
Integer in the range [1...30000]; read/write, except as noted.
37

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
38
AVLayer object
app.project.item(index).layer(index)
Description
The AVLayer object provides an interface to those layers that contain AVItem objects (composition layers,
footage layers, solid layers, text layers, and sound layers).
• AVLayer is a subclass of Layer. All methods and attributes of Layer, in addition to those listed below, are
available when working with AVLayer. See “Layer object” on page 86.
• AVLayer is a base class for TextLayer, so AVLayer attributes and methods are available when working with
TextLayer objects. See “TextLayer object” on page 188.
AE Properties
Different types of layers have different AE properties. AVLayer has the following properties and property
groups:
Marker
Time Remap
Motion Trackers
Masks
Effects
Tra n sfor m
Anchor Point
Position
Scale
Orientation
X Rotation
Y Rotation
Rotation
Opacity
Layer Styles
Geometry Options // Ray-traced 3D
Material Options
Casts Shadows
Light Transmission
Accepts Shadows
Accepts Lights
Appears in Reflections // Ray-traced 3D
Ambient
Diffuse
Specular Intensity
Specular Shininess
Metal
Reflection Intensity // Ray-traced 3D
Reflection Sharpness // Ray-traced 3D
Reflection Rolloff // Ray-traced 3D
Tra n spare n c y / / R ay-trac e d 3 D
Transparency Rolloff // Ray-traced 3D
Index of Refraction // Ray-traced 3D
Audio
Audio Levels
38

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
39
Example
If the f irst item in the project is a CompItem, and the first l ayer of that Comp Item is an AVLayer, the follow ing
sets the layer
var firstLayer = app.project.item(1).layer(1);
firstLayer.quality = LayerQuality.BEST;
firstLayer.startTime = 1;
firstLayer.inPoint = 2;
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
quality, startTime, and inPoint.
source
isNameFromSource
height
width
audioEnabled
motionBlur
effectsActive
adjustmentLayer
guideLayer
threeDLayer
threeDPerChar
environmentLayer
“AVLayer source attribute” on page 47 The source item for this layer.
“AVLayer isNameFromSource attribute”
on page 46
“AVLayer height attribute” on page 45 The height of the layer.
“AVLayer width attribute” on page 49 The width of the layer.
“AVLayer audioEnabled attribute” on
page 41
“AVLayer motionBlur attribute” on
page 46
“AVLayer effectsActive attribute” on
page 44
“AVLayer adjustmentLayer attribute” on
page 40
“AVLayer guideLayer attribute” on
page 45
“AVLayer threeDLayer attribute” on
page 48
“AVLayer threeDPerChar attribute” on
page 48
“AVLayer environmentLayer attribute”
on page 44
When true, the layer has no expressly set name,
but contains a named source.
When true, the layer's audio is enabled.
When true, the layer's motion blur is enabled.
When true, the layer's effects are active.
When true, this is an adjustment layer.
When true, this is a guide layer.
When true, this is a 3D layer.
When true, 3D is set on a per-character basis in
this text layer.
When true, this is an environment layer.
canSetCollapseTransformation
collapseTransformation
frameBlending
frameBlendingType
canSetTimeRemapEnabled
timeRemapEnabled
hasAudio
“AVLayer canSetCollapseTransformation
attribute” on page 43
“AVLayer collapseTransformation attribute” on page 44
“AVLayer frameBlending attribute” on
page 44
“AVLayer frameBlendingType attribute”
on page 44
“AVLayer canSetTimeRemapEnabled
attribute” on page 43
“AVLayer timeRemapEnabled attribute”
on page 48
“AVLayer hasAudio attribute” on
page 45
When true, it is legal to change the value of
collapseTransformation.
When true, collapse transformation is on.
When true, frame blending is enabled.
The type of frame blending for the layer.
When true, it is legal to change the value of
timeRemapEnabled.
When true, time remapping is enabled on this
layer.
When true, the layer contains an audio component.
39

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
40
Attribute Reference Description
audioActive
blendingMode
preserveTransparency
trackMatteType
isTrackMatte
hasTrackMatte
quality
autoOrient
“AVLayer audioActive attribute” on
page 40
“AVLayer blendingMode attribute” on
page 42
“AVLayer preserveTransparency attribute” on page 47
“AVLayer trackMatteType attribute” on
page 49
“AVLayer isTrackMatte attribute” on
page 46
“AVLayer hasTrackMatte attribute” on
page 45
“AVLayer quality attribute” on page 47 The layer quality setting.
“AVLayer autoOrient attribute” on
page 41
When true, the layer's audio is active at the current time.
The blending mode of the layer.
When true, preserve transparency is enabled.
if layer has a track matte, specifies the way it is
applied.
When true, this layer is being used as a track
matte for the layer below it.
When true, the layer above is being used as a
track matte on this layer.
The type of automatic orientation for the layer.
Methods
Method Reference Description
audioActiveAtTime()
calculateTransformFromPoints()
“AVLayer audioActiveAtTime() method”
on page 41
“AVLayer calculateTransformFromPoints() method” on page 43
Reports whether this layer's audio is
active at a given time.
Calculates a transformation from a set of
points in this layer.
replaceSource()
sourceRectAtTime()
openInViewer()
“AVLayer replaceSource() method” on
page 47
“AVLayer sourceRectAtTime() method”
on page 48
“AVLayer openInViewer() method” on
page 46
AVLayer adjustmentLayer attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).adjustmentLayer
Description
True if the layer is an adjustment layer.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
AVLayer audioActive attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).audioActive
Description
True if the layer's audio is active at the current time.
Changes the source item for this layer.
Retrieves the source rectangle of a layer.
Opens the layer in a Layer panel.
40

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
41
For this value to be true, audioEnabled mu st b e tr ue, no othe r laye r wit h audi o ma y be sol oing u nles s th is l ayer
is soloed too, and the time must be between the
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
AVLayer audioActiveAtTime() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).audioActiveAtTime(time)
Description
Returns true if this layer's audio will be active at the specified time.
inPoint and outPoint of this layer.
For this method to return true,
this layer is soloed too, and the time must be between the
Parameters
time
Returns
audioEnabled must be true, no other layer with audio may be soloing unless
inPoint and outPoint of this layer.
The time, in seconds. A floating-point value.
Boolean.
AVLayer audioEnabled attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).audioEnabled
Description
When true, the layer's audio is enabled. This value corresponds to the audio toggle switch in the Timeline
panel.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
AVLayer autoOrient attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).autoOrient
Description
The type of automatic orientation to perform for the layer.
Typ e
An AutoOrientType enumerated value; read/write. One of:
AutoOrientType.ALONG_PATH
AutoOrientType.CAMERA_OR_POINT_OF_INTEREST
AutoOrientType.CHARACTERS_TOWARD_CAMERA
Layer faces in the direction of the motion path.
Layer always faces the active camera or points at its
point of interest.
Each character in a per-character 3D text layer auto matically faces the active camera.
41
After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
42
AutoOrientType.NO_AUTO_ORIENT
AVL ayer blendingMode attri bute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).blendingMode
Description
The blending mode of the layer.
Typ e
A BlendingMode enumerated value; read/write. One of:
BlendingMode.ADD
BlendingMode.ALPHA_ADD
BlendingMode.CLASSIC_COLOR_BURN
BlendingMode.CLASSIC_COLOR_DODGE
BlendingMode.CLASSIC_DIFFERENCE
BlendingMode.COLOR
BlendingMode.COLOR_BURN
BlendingMode.COLOR_DODGE
BlendingMode.DANCING_DISSOLVE
BlendingMode.DARKEN
BlendingMode.DARKER_COLOR
BlendingMode.DIFFERENCE
BlendingMode.DISSOLVE
BlendingMode.EXCLUSION
BlendingMode.HARD_LIGHT
BlendingMode.HARD_MIX
BlendingMode.HUE
BlendingMode.LIGHTEN
BlendingMode.LIGHTER_COLOR
BlendingMode.LINEAR_BURN
BlendingMode.LINEAR_DODGE
BlendingMode.LINEAR_LIGHT
BlendingMode.LUMINESCENT_PREMUL
BlendingMode.LUMINOSITY
BlendingMode.MULTIPLY
BlendingMode.NORMAL
BlendingMode.OVERLAY
BlendingMode.PIN_LIGHT
Bl endi ngMo de.S AT URATION
BlendingMode.SCREEN
BlendingMode.SILHOUETE_ALPHA
BlendingMode.SILHOUETTE_LUMA
BlendingMode.SOFT_LIGHT
BlendingMode.STENCIL_ALPHA
BlendingMode.STENCIL_LUMA
BlendingMode.VIVID_LIGHT
Layer rotates freely, independent of any motion
path, point of interest, or other layers.
42

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
43
AVLayer calculateTransformFromPoints() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).calculateTransformFromPoints(pointTopLeft, pointTopRight, point-
BottomRight)
Description
Calculates a transformation from a set of points in this layer.
Parameters
pointTopLeft
pointTopRight
pointBottomRight
Returns
The top left point coordinates in the form of an array, [x, y, z].
The top right point coordinates in the form of an array, [x, y, z].
The bottom right point coordinates in the form of an array, [x, y, z].
An Object with the transformation properties set.
Example
var newLayer = comp.layers.add(newFootage);
newLayer.threeDLayer = true;
newLayer.blendingMode = BlendingMode.ALPHA_ADD;
var transform = newLayer.calculateTransformFromPoints(tl, tr, bl);
for(var sel in transform) {
newLayer.transform[sel].setValue(transform[sel]);
}
AVLayer canSetCollapseTransformation attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).canSetCollapseTransformation
Description
True if it is legal to change the value of the collapseTransformation attribute on this layer.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
AVLayer canSetTimeRemapEnabled attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).canSetTimeRemapEnabled
Description
True if it is legal to change the value of the timeRemapEnabled attribute on this layer.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
43

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
44
AVLayer collapseTransformation attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).collapseTransformation
Description
True if collapse transformation is on for this layer.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
AVLayer effectsActive attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).effectsActive
Description
True if the layer's effects are active, as indicated by the <f> icon next to it in the user interface.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
AVLayer environmentLayer attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).environmentLayer
Description
True if this is an environment layer in a Ray-traced 3D composition. Setting this attribute to true automatically
makes the layer 3D (
Typ e
threeDLayer becomes true).
Boolean; read/write.
AVLayer frameBlending attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).frameBlending
Description
True if frame blending is enabled for the layer.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
AVLayer frameBlendingType attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).frameBlendingType
Description
The type of frame blending to perform when frame blending is enabled for the layer.
44

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
45
Typ e
A FrameBlendingType enumerated value; read/write. One of:
FrameBlendingType.FRAME_MIX
FrameBlendingType.NO_FRAME_BLEND
FrameBlendingType.PIXEL_MOTION
AVLayer guideLayer attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).guideLayer
Description
True if the layer is a guide layer.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
AVLayer hasAudio attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).hasAudio
Description
True if the layer contains an audio component, regardless of whether it is audio-enabled or soloed.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
AVL ayer hasTrackM atte attrib ute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).hasTrackMatte
Description
True if the layer in front of this layer is being used as a track matte on this layer. When true, this layer's track-
MatteType
Typ e
value controls how the matte is applied.
Boolean; read-only.
AVL ayer height attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).height
Description
The height of the layer in pixels.
Typ e
Floating-point; read-only.
45

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
46
AVLayer isNameFromSource attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).isNameFromSource
Description
True if the layer has no expressly set name, but contains a named source. In this case, layer.name has the same
value as
False if the layer has an expressly set name, or if the layer does not have a source.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
AVLayer isTrackMatte attribute
app.project.item(index)layer(index).isTrackMatte
Description
True if this layer is being used as a track matte for the layer behind it.
layer.source.name.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
AVLayer motionBlur attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).motionBlur
Description
True if motion blur is enabled for the layer.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
AVLayer openInViewer() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).openInViewer()
Description
Opens the layer in a Layer panel, and moves the Layer panel to front and gives it focus.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Viewer object for the Layer panel, or null if the layer could not be opened (e.g., for text or shape layers, which
cannot be opened in the Layer panel).
46

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
47
AVLayer preserveTransparency attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).preserveTransparency
Description
True if preserve transparency is enabled for the layer.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
AVLayer quality attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).quality
Description
The quality with which this layer is displayed.
Typ e
A LayerQuality enumerated value; read/write. One of:
LayerQuality.BEST
LayerQuality.DRAFT
LayerQuality.WIREFRAME
AVLayer replaceSource() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).replaceSource (newSource, fixExpressions)
Description
Replaces the source for this layer.
Parameters
newSource
fixExpressions
Returns
The new source AVItem object.
to adjust expressions for the new source, false otherwise. Note that this feature can be
True
resource-intensive; if replacing a large amount of footage, do this only at the end of the operation.
See also “Project autoFixExpressions() method” on page 115.
Nothing.
AVLayer source attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).source
Description
The source AVItem for this layer. The value is null in a Text layer. Use AVLayer.replaceSource() to change t he
value.
Typ e
AVItem o bj e ct ; re a d- o nl y.
47

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
48
AVLayer sourceRectAtTime() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).sourceRectAtTime(timeT, extents)
Description
Retrieves the rectangle bounds of the layer at the specified time index, corrected for text or shape layer content.
Use, for example, to write text that is properly aligned to the baseline.
Parameters
timeT
extents
Returns
The time index, in seconds. A floating-point value.
to include the extents, false o therwise. Extents apply to shape layers, increasing the size of
True
the layer bounds as necessary.
A JavaScript object with four attributes, [top, left, width, height].
AVLayer threeDLayer attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).threeDLayer
Description
True if this is a 3D layer.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
AVLayer threeDPerChar attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).threeDPerChar
Description
True if this layer has the Enable Per-character 3D switch set, allowing its characters to be animated off the
plane of the text layer. Applies only to text layers.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
AVLayer timeRemapEnabled attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).timeRemapEnabled
Description
True if time remapping is enabled for this layer.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
48

After Effects scripting reference AVLayer object
49
AVLayer trackMatteType attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).trackMatteType
Description
If this layer has a track matte, specifies the way the track matte is applied.
Typ e
A TrackMatteType enumerated value; read/write. One of:
Tra c k Mat t eType.AL P HA
Tra c k Mat t eType.AL P HA_I N V E RTE D
Tra c k Mat t eType.LUMA
Tra c k Mat t eType.LUMA_I N V E RTE D
Tra c k Mat t eType.NO _ T R ACK _ M AT TE
AVLayer width attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).width
Description
The width of the layer in pixels.
Typ e
Floating-point; read-only.
49

After Effects scripting reference CameraLayer object
50
CameraLayer object
app.project.item(index).layer(index)
Description
The CameraLayer object represents a camera layer within a composition. Create it using the LayerCollection
addCamera method; see “LayerCollection addCamera() method” on page 96. It can be accessed in an
object’s
item’s layer collection either by index number or by a name string.
• CameraLayer is a subclass of Layer. All methods and attributes of Layer are available when working with
CameraLayer. See “Layer object” on page 86.
AE Properties
CameraLayer defines no additional attributes, but has different AE properties than other layer types. It has the
following properties and property groups:
Marker
Tra n sfor m
Point of Interest
Position
Scale
Orientation
X Rotation
Y Rotation
Rotation
Opacity
Camera Options
Zoom
Depth of Field
Focus Distance
Blur Level
50

After Effects scripting reference Collection object
51
Collection object
Like an array, a collection associates a set of objects or values as a logical group and provides access to them
by index. However, most collection objects are read-only. You do not assign objects to them yourself—their
contents update automatically as objects are created or deleted.
The index numbering of a collection starts with 1, not 0.
Objects
Object Reference Description
ItemCollection
LayerCollection
OMCollection
RQItemCollection
Attributes
length
Methods
[]
“ItemCollection object ” on page 82 All of the items (imported files, folders, solids, and so on) found in
“LayerCollection object” on
page 95
“OMCollection object” on page 109 All of the Output Module items in the project.
“RenderQueueItem object” on
page 163
The number of objects in the collection.
Retrieves an object in the collection by its index number. The first object is at index 1.
the Project panel.
All of the layers in a composition.
All of the render-queue items in the project.
51

After Effects scripting reference CompItem object
52
CompItem object
app.project.item(index)
app.project.items[index]
Description
The CompItem object represents a composition, and allows you to manipulate and get information about it.
Access the objects by position index number in a project’s
• CompItem is a subclass of AVItem, which is a subclass of Item. All methods and attributes of AVItem and
Item, in addition to those listed below, are available when working with CompItem. See “AVItem object” on
page 30 and “Item object” on page 78.
Example
Given that the first item in the project is a CompItem, the following code displays two alerts. The first shows
the number of layers in the CompItem, and the second shows the name of the last layer in the CompItem.
var firstComp = app.project.item(1);
alert("number of layers is " + firstComp.numLayers);
alert("name of last layer is " + firstComp.layer(firstComp.numLayers).name);
item collection.
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
frameDuration
dropFrame
workAreaStart
workAreaDuration
numLayers
hideShyLayers
motionBlur
draft3d
frameBlending
preserveNestedFrameRate
“CompItem frameDuration attribute” on
page 55
“CompItem dropFrame attribute” on
page 54
“CompItem workAreaStart attribute” on
page 60
“CompItem workAreaDuration attribute” on
page 59
“CompItem numLayers attribute” on page 57 The number of layers in the composi-
“CompItem hideShyLayers attribute” on
page 55
“CompItem motionBlur attribute” on
page 56
“CompItem draft3d attribute” on page 54 When true, Draft 3D mode is enabled
“CompItem frameBlending attribute” on
page 55
“CompItem preserveNestedFrameRate attribute” on page 57
The duration of a single frame.
When true, indicates that the composition uses drop-frame timecode.
The work area start time.
The work area duration.
tion.
When true, shy layers are visible in the
Timeline panel.
When true, motion blur is enabled for
this composition.
for the Composition panel.
When true, time filtering is enabled for
this composition.
When true, the frame rate of nested
compositions is preserved.
preserveNestedResolution
bgColor
activeCamera
“CompItem preserveNestedResolution attribute” on page 58
“CompItem bgColor attribute” on page 54 The background color of the composi-
“CompItem activeCamera attribute” on
page 53
When true, the resolution of nested
compositions is preserved.
tion.
The current active camera layer.
52

After Effects scripting reference CompItem object
53
Attribute Reference Description
displayStartTime
resolutionFactor
shutterAngle
shutterPhase
motionBlurSamplesPerFrame
motionBlurAdaptiveSampleLimit
layers
selectedLayers
selectedProperties
renderer
renderers
“CompItem displayStartTime attribute” on
page 54
“CompItem resolutionFactor attribute” on
page 58
“CompItem shutterAngle attribute” on
page 59
“CompItem shutterPhase attribute” on
page 59
“CompItem motionBlurSamplesPerFrame
attribute” on page 57
“CompItem motionBlurAdaptiveSampleLimit attribute” on page 56
“CompItem layers attribute” on page 56
“LayerCollection object” on page 95
“CompItem selectedLayers attribute” on
page 59
“CompItem selectedProperties attribute” on
page 59
“CompItem renderer attribute” on page 58 The rendering plug-in module to be
“CompItem renderers attribute” on page 58 The set of available rendering plug-in
Changes the display of the start time in
the Timeline panel.
The factor by which the x and y resolu-
tion of the Composition panel is
downsampled.
The camera shutter angle.
The camera shutter phase.
The minimum number of motion blur
samples per frame for Classic 3D layers,
shape layers, and certain effects.
The maximum number of motion blur
samples of 2D layer motion.
The layers of the composition.
The selected layers of the composition.
The selected properties of the composition.
used to render this composition.
modules.
Methods
Method Reference Description
duplicate()
layer()
openInViewer()
“CompItem duplicate() method” on page 54 Creates and returns a duplicate of this composition.
“CompItem layer() method” on page 55 Gets a layer from this composition.
“CompItem openInViewer() method” on
page 57
Opens the composition in a Composition panel.
CompItem activeCamera attribute
app.project.item(index).activeCamera
Description
The active camera, which is the front-most camera layer that is enabled. The value is null if the composition
contains no enabled camera layers.
Typ e
CameraLayer object; read-only.
53

After Effects scripting reference CompItem object
54
CompItem bgColor attribute
app.project.item(index).bgColor
Description
The background color of the composition. The three array values specify the red, green, and blue components
of the color.
Typ e
An array containing three floating-point values, [R, G, B], in the range [0.0..1.0]; read/write.
CompItem displayStartTime attribute
app.project.item(index).displayStartTime
Description
The time set as the beginning of the composition, in seconds. This is the equivalent of the Start Timecode or
Start Frame setting in the Composition Settings dialog box.
Typ e
Floating-point value in the range [0.0...86339.0] (1 second less than 25 hours); read/write.
CompItem draft3d attribute
app.project.item(index).draft3d
Description
When true, Draft 3D mode is enabled for the Composition panel. This corresponds to the value of the Draft
3D button in the Composition panel.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
CompItem dropFrame attribute
app.project.item(index).dropFrame
Description
When true, indicates that the composition uses drop-frame timecode. When false, indicates non-drop-frame
timecode. This corresponds to the setting in the Composition Settings dialog box.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
CompItem duplicate() method
app.project.item(index).duplicate()
Description
Creates and returns a duplicate of this composition, which contains the same layers as the original.
54

After Effects scripting reference CompItem object
55
Parameters
None.
Returns
CompItem object.
CompItem frameBlending attribute
app.project.item(index).frameBlending
Description
When true, frame blending is enabled for this Composition. Corresponds to the value of the Frame Blending
button in the Composition panel.
Typ e
Boolean; if true, frame blending is enabled; read/write.
CompItem frameDuration attribute
app.project.item(index).frameDuration
Description
The duration of a frame, in seconds. This is the inverse of the frameRate value (frames-per-second).
Typ e
Floating-point; read/write.
CompItem hideShyLayers attribute
app.project.item(index).hideShyLayers
Description
When true, only layers with shy set to false are shown in the Timeline panel. When false, all layers are visible,
including those whose
shy value is true. Corresponds to the value of the Hide All Shy Layers button in the
Composition panel.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
CompItem layer() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index)
app.project.item(index).layer(otherLayer, relIndex)
app.project.item(index).layer(name)
Description
Returns a Layer object, which can be specified by name, an index position in this layer, or an index position
relative to another layer.
55

After Effects scripting reference CompItem object
56
Parameters
index
The index number of the desired layer in this composition. An integer in the range [1...numLayers], where numLayers is the number of layers in the composition.
—or—
otherLayer
relIndex
A Layer object in this composition. The relIndex value is added to the index value of this
layer to find the position of the desired layer.
The position of the desired layer, relative to otherLayer. An integer in the range [1–other-
Layer.index...
layers in the composition.
This value is added to the otherLayer value to derive the absolute index of the layer to
return.
numLayers–otherLayer.index], where numLayers is the number of
—or—
name
Returns
The string containing the name of the desired layer.
Layer object.
CompItem layers attribute
app.project.item(index).layers
Description
A LayerCollection object that contains all the Layer objects for layers in this composition. See “LayerCollection object” on page 95.
Typ e
LayerCollection object; read-only.
CompItem motionBlur attribute
app.project.item(index).motionBlur
Description
When true, motion blur is enabled for the composition. Corresponds to the value of the Motion Blur button
in the Composition panel.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
CompItem motionBlurAdaptiveSampleLimit attribute
app.project.item(index).motionBlurAdaptiveSampleLimit
Description
The maximum number of motion blur samples of 2D layer motion. This corresponds to the Adaptive Sample
Limit setting in the Advanced tab of the Composition Settings dialog box.
56

After Effects scripting reference CompItem object
57
Typ e
Integer (between 16 and 256); read/write.
CompItem motionBlurSamplesPerFrame attribute
app.project.item(index).motionBlurSamplesPerFrame
Description
The minimum number of motion blur samples per frame for Classic 3D layers, shape layers, and certain
effects. This corresponds to the Samples Per Frame setting in the Advanced tab of the Composition Settings
dialog box.
Typ e
Integer (between 2 and 64); read/write.
CompItem numLayers attribute
app.project.item(index).numLayers
Description
The number of layers in the composition.
Typ e
Integer; read-only.
CompItem openInViewer() method
app.project.item(index).openInViewer()
Description
Opens the composition in a Composition panel, and moves the Composition panel to front and gives it focus.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Viewer object for the Composition panel, or null if the composition could not be opened.
CompItem preserveNestedFrameRate attribute
app.project.item(index).preserveNestedFrameRate
Description
When true, the frame rate of nested compositions is preserved in the current composition. Corresponds to the
value of the “Preserve frame rate when nested or in render queue” option in the Advanced tab of the Composition Settings dialog box.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
57

After Effects scripting reference CompItem object
58
CompItem preserveNestedResolution attribute
app.project.item(index).preserveNestedResolution
Description
When true, the resolution of nested compositions is preserved in the current composition. Corresponds to the
value of the “Preserve Resolution When Nested” option in the Advanced tab of the Composition Settings
dialog box.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
CompItem renderer attribute
app.project.item(index).renderer
Description
The current rendering plug-in module to be used to render this composition, as set in the Advanced tab of the
Composition Settings dialog box. Allowed values are the members of
compItem.renderers.
Typ e
String; read/write.
CompItem renderers attribute
app.project.item(index).renderers
Description
The available rendering plug-in modules. Member strings reflect installed modules, as seen in the Advanced
tab of the Composition Settings dialog box.
Typ e
Array of strings; read-only.
CompItem resolutionFactor attribute
app.project.item(index).resolutionFactor
Description
The x and y downsample resolution factors for rendering the composition.
The two values in the array specify how many pixels to skip when sampling; the first number controls
horizontal sampling, the second controls vertical sampling. Full resolution is [1,1], half resolution is [2,2], and
quarter resolution is [4,4]. The default is [1,1].
Typ e
Array of two integers in the range [1..99]; read/write.
58

After Effects scripting reference CompItem object
59
CompItem selectedLayers attribute
app.project.item(index).selectedLayers
Description
All of the selected layers in this composition. This is a 0-based array (the first object is at index 0).
Typ e
Array of Layer objects; read-only.
CompItem selectedProperties attribute
app.project.item(index).selectedProperties
Description
All of the selected properties (Property and PropertyGroup objects) in this composition. The first property is
at index position 0.
Typ e
Array of Property and PropertyGroup objects; read-only.
CompItem shutterAngle attribute
app.project.item(index).shutterAngle
Description
The shutter angle setting for the composition. This corresponds to the Shutter Angle setting in the Advanced
tab of the Composition Settings dialog box.
Typ e
Integer in the range [0...720]; read/write.
CompItem shutterPhase attribute
app.project.item(index).shutterPhase
Description
The shutter phase setting for the composition. This corresponds to the Shutter Phase setting in the Advanced
tab of the Composition Settings dialog box.
Typ e
Integer in the range [–360...360]; read/write.
CompItem workAreaDuration attribute
app.project.item(index).workAreaDuration
Description
The duration of the work area in seconds. This is the difference of the start-point and end-point times of the
Composition work area.
59

After Effects scripting reference CompItem object
60
Typ e
Floating-point; read/write.
CompItem workAreaStart attribute
app.project.item(index).workAreaStart
Description
The time when the Composition work area begins, in seconds.
Typ e
Floating-point; read/write.
60

After Effects scripting reference FileSource object
61
FileSource object
app.project.item(index).mainSource
app.project.item(index).proxySource
Description
The FileSource object describes footage that comes from a file.
• FileSource is a subclass of FootageSource. All methods and attributes of FootageSource, in addition to those
listed below, are available when working with FileSource. See “FootageSource object” on page 69.
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
file
missingFootagePath
Methods
Method Reference Description
reload()
“FileSource file attribute” on page 61 The file that defines this asset.
“FileSource missingFootagePath attribute”
on page 61
“FileSource reload() method” on page 62 Reloads the asset from the file, if it is a mainSource of
The file that contains footage missing from this asset.
a FootageItem.
FileSource file attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.file
app.project.item(index).proxySource.file
Description
The ExtendScript File object for the file that defines this asset. To change the value:
• If this FileSource is a proxySource of an AVItem, call setProxy() or setProxyWithSequence().
• If this FileSource is a mainSource of a FootageItem, call replace() or replaceWithSequence().
Typ e
File object; read-only.
FileSource missingFootagePath attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.file.missingFootagePath
app.project.item(index).proxySource.file.missingFootagePath
Description
The path and filename of footage that is missing from this asset. See also “AVItem footageMissing attribute”
on page 31.
Typ e
String; read-only.
61

After Effects scripting reference FileSource object
62
FileSource reload() method
app.project.item(index).mainSource.file.mainSource.reload()
Description
Reloads the asset from the file. This method can be called only on a mainSource, not a proxySource.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
62

After Effects scripting reference FolderItem object
63
FolderItem object
app.project.FolderItem
Description
The FolderItem object corresponds to a folder in your Project panel. It can contain various types of items
(footage, compositions, solids) as well as other folders.
Example
Given that the second item in the project is a FolderItem, the following code puts up an alert for each top-level
item in the folder, showing that item’s name.
var secondItem = app.project.item(2);
if ( !(secondItem instanceof FolderItem) ) {
alert("problem: second item is not a folder");
} else {
for (i = 1; i <= secondItem.numItems; i++) {
alert("item number " + i + " within the folder is named "
+ secondItem.item(i).name);
}
}
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
items
numItems
Methods
Method Reference Description
item()
“FolderItem items attribute” on page 64 The contents of this folder.
“FolderItem numItems attribute” on page 64 The number of items contained in the folder.
“FolderItem item() method” on page 63 Gets an item from the folder.
FolderItem item() method
app.project.item(index).item
Description
Returns the top-level item in this folder at the specified index position. Note that “top-level” here means toplevel within the folder, not necessarily within the project.
Parameters
index
An integer, the position index of the item to retrieve. The first item is at index 1.
Returns
Item object.
63

After Effects scripting reference FolderItem object
64
FolderItem items attribute
app.project.item(index).items
Description
An ItemCollection object containing Item object that represent the top-level contents of this folder.
Unlike the ItemCollection in the Project object, this collection contains only the top-level items in the folder.
Top-level within the folder is not the same as top-level within the project. Only those items that are top-level
in the root folder are also top-level in the Project.
Typ e
ItemCollection object; read only.
FolderItem numItems attribute
app.project.item(index).numItems
Description
The number of items contained in the items collection (folderItem.items.length).
If the folder contains another folder, only the FolderItem for that folde r is count ed, not any subitems cont ain ed
in it.
Typ e
Integer; read only.
64

After Effects scripting reference FootageItem object
65
FootageItem object
app.project.item(index)
app.project.items[index]
Description
The FootageItem object represents a footage item imported into a project, which appears in the Project panel.
These are accessed by position index number in a project’s
• FootageItem is a subclass of AVItem, which is a subclass of Item. All methods and attributes of AVItem and
Item, in addition to those listed below, are available when working with FootageItem. See “AVItem object”
on page 30 and “Item object” on page 78.
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
item collection.
file
mainSource
Methods
Method Reference Description
replace()
replaceWithPlaceholder()
replaceWithSequence()
replaceWithSolid()
openInViewer()
“FootageItem file attribute” on page 65 The footage source file.
“FootageItem mainSource attribute” on page 66 All settings related to the footage item.
“FootageItem replace() method” on
page 66
“FootageItem replaceWithPlaceholder()
method” on page 67
“FootageItem replaceWithSequence()
method” on page 67
“FootageItem replaceWithSolid()
method” on page 67
“FootageItem openInViewer() method”
on page 66
Replaces a footage file with another footage file.
Replaces a footage file with a placeholder object.
Replaces a footage file with an image sequence.
Replaces a footage file with a solid.
Opens the footage in a Footage panel.
FootageItem file attribute
app.project.item(index).file
Description
The ExtendScript File object for the footage's source file.
If the FootageItem's
it is null.
Typ e
File object; read only.
mainSource is a FileSource, this is the same as FootageItem.mainSource.file. Otherwise
65

After Effects scripting reference FootageItem object
66
FootageItem mainSource attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource
Description
The footage source, an object that contains all of the settings related to that footage item, including those that
are normally accessed through the Interpret Footage dialog box. The attribute is read-only. To change its value,
call one of the FootageItem “replace” methods.
See the “FootageSource object” on page 69, and its three types:
• “SolidSource object” on page 179
• “FileSource object” on page 61
• “PlaceholderSource object” on page 113
If this is a FileSource object, and the
FileSource.missingFootagePath attribute. See “AVItem footageMissing attribute” on page 31 and “FileSource
missingFootagePath attribute” on page 61.
Typ e
FootageSource object; read-only.
footageMissing value is true, the path to the missing footage file is in the
FootageItem openInViewer() method
app.project.item(index).openInViewer()
Description
Opens the footage in a Footage panel, and moves the Footage panel to front and gives it focus.
NOTE: Missing and placeholder footage can be opened using this method, but cannot manually (via doubleclicking it).
Parameters
None.
Returns
Viewer object for the Footage panel, or null if the footage could not be opened.
FootageItem replace() method
app.project.item(index).replace(file)
Description
Changes the source of this FootageItem to the specified file. In addition to loading the file, the method creates
a new FileSource object for the file and sets
name, width, height, frameDuration, and duration attributes (see “AVItem object” on page 30) based on the
contents of the file.
mainSource to that object. In the new source object, it sets the
The method preserves interpretation parameters from the previous
mainSource object. If the specified file has
an unlabeled alpha channel, the method estimates the alpha interpretation.
66

After Effects scripting reference FootageItem object
67
Parameters
file
An ExtendScript File object for the file to be used as the footage main source.
FootageItem replaceWithPlaceholder() method
app.project.item(index).replaceWithPlaceholder(name, width, height, frameRate, duration)
Description
Changes the source of this FootageItem to the specified placeholder. Creates a new PlaceholderSource object,
sets its values from the parameters, and sets
Parameters
name
width
height
frameRate
duration
A string containing the name of the placeholder.
The width of the placeholder in pixels, an integer in the range [4..30000].
The height of the placeholder in pixels, an integer in the range [4..30000].
The frame rate of the placeholder, a floating-point value in the range [1.0..99.0]
The duration of the placeholder in seconds, a floating-point value in the range [0.0..10800.0].
mainSource to that object.
FootageItem replaceWithSequence() method
app.project.item(index).replaceWithSequence(file, forceAlphabetical)
Description
Changes the source of this FootageItem to the specified image sequence. In addition to loading the file, the
method creates a new FileSource object for the file and sets
object, it sets the
name, width, height, frameDuration, and duration attributes (see “AVItem object” on
mainSource to that object. In the new source
page 30) based on the contents of the file.
The method preserves interpretation parameters from the previous
mainSource object. If the specified file has
an unlabeled alpha channel, the method estimates the alpha interpretation.
Parameters
file
forceAlphabetical
An ExtendScript File object for the first file in the sequence to be used as the footage main source.
When true, use the “Force alphabetical order” option.
FootageItem replaceWithSolid() method
app.project.item(index).replaceWithSolid(color, name, width, height, pixelAspect)
Description
Changes the source of this FootageItem to the specified solid. Creates a new SolidSource object, sets its values
from the parameters, and sets
mainSource to that object.
67

After Effects scripting reference FootageItem object
68
Parameters
color
name
width
height
pixelAspect
The color of the solid, an array of three floating-point values, [R, G, B], in the range [0.0..1.0].
A string containing the name of the solid.
The width of the solid in pixels, an integer in the range [4..30000].
The height of the solid in pixels, an integer in the range [4..30000].
The pixel aspect ratio of the solid, a floating-point value in the range [0.01..100.0].
68
After Effects scripting reference FootageSource object
69
FootageSource object
app.project.item(index).mainSource
app.project.item(index).proxySource
Description
The FootageSource object holds information describing the source of some footage. It is used as the
mainSource of a FootageItem, or the proxySource of a CompItem or FootageItem. See “FootageItem object”
on page 65 and “CompItem object” on page 52.
• FootageSource is the base class for SolidSource, so FootageSource attributes and methods are available
when working with SolidSource objects. See “SolidSource object” on page 179.
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
hasAlpha
alphaMode
premulColor
invertAlpha
isStill
fieldSeparationType
highQualityFieldSeparation
removePulldown
loop
nativeFrameRate
displayFrameRate
“FootageSource hasAlpha attribute” on
page 72
“FootageSource alphaMode attribute”
on page 70
“FootageSource premulColor attribute”
on page 73
“FootageSource invertAlpha attribute”
on page 72
“FootageSource isStill attribute” on
page 72
“FootageSource fieldSeparationType
attribute” on page 71
“FootageSource highQualityFieldSeparation attribute” on page 72
“FootageSource removePulldown attribute” on page 73
“FootageSource loop attribute” on
page 73
“FootageSource nativeFrameRate attribute” on page 73
“FootageSource displayFrameRate
attribute” on page 70
When true, a footage clip or proxy includes an
alpha channel.
The mode of an alpha channel.
The color to be premultiplied.
When true, an alpha channel in a footage clip or
proxy should be inverted.
When true, footage is a still image.
The field separation type.
How the fields are to be separated in non-still footage.
The pulldown type for the footage.
How many times an image sequence is set to loop.
The native frame rate of the footage.
The effective frame rate as displayed and rendered
in compositions by After Effects.
conformFrameRate
“FootageSource conformFrameRate
attribute” on page 70
The rate to which footage should conform.
Methods
Method Reference Description
guessAlphaMode()
guessPulldown()
“FootageSource guessAlphaMode()
method” on page 71
“FootageSource guessPulldown()
method” on page 71
Estimates the alphaMode setting.
Estimates the pulldownType setting.
69

After Effects scripting reference FootageSource object
70
FootageSource alphaMode attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.alphaMode
app.project.item(index).proxySource.alphaMode
Description
The alphaMode attribute of footageSource defines how the alpha information in the footage is to be interpreted. If hasAlpha is false, this attribute has no relevant meaning.
Typ e
An AlphaMode enumerated value; (read/write). One of:
AlphaMode.IGNORE
AlphaMode.STRAIGHT
AlphaMode.PREMULTIPLIED
FootageSource conformFrameRate attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.conformFrameRate
app.project.item(index).proxySource.conformFrameRate
Description
A frame rate to use instead of the nativeFrameRate value. If set to 0, the nativeFrameRate is used instead.
It is an error to set this value if
Pulldown
PulldownPhase.OFF, then this is automatically set to the value of nativeFrameRate.
Typ e
is not set to PulldownPhase.OFF. If this is 0 when you set removePulldown to a value other than
FootageSource.isStill is true. It is an error to set this value to 0 if remove-
Floating-point value in the range [0.0.. 99.0]; read/write.
FootageSource displayFrameRate attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.displayFrameRate
app.project.item(index).proxySource.displayFrameRate
Description
The effective frame rate as displayed and rendered in compositions by After Effects.
removePulldown is PulldownPhase.OFF, then this is the same as the conformFrameRate (if non-zero) or
If
nativeFrameRate (if conformFrameRate is 0). If removePulldown is not PulldownPhase.OFF, this is
the
conformFrameRate * 0.8, the effective frame rate after removing 1 of every 5 frames.
Typ e
Floating-point value in the range [0.0.. 99.0]; read-only.
70

After Effects scripting reference FootageSource object
71
FootageSource fieldSeparationType attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.fieldSeparationType
app.project.item(index).proxySource.fieldSeparationType
Description
How the fields are to be separated in non-still footage.
It is an error to set this attribute if
removePulldown is not PulldownPhase.OFF.
Typ e
isStill is true. It is an error to set this value to FieldSeparationType.OFF if
A FieldSeparationType enumerated value; read/write. One of:
FieldSeparationType.OFF
FieldSeparationType.UPPER_FIELD_FIRST
FieldSeparationType.LOWER_FIELD_FIRST
FootageSource guessAlphaMode() method
app.project.item(index).mainSource.guessAlphaMode()
app.project.item(index).proxySource.guessAlphaMode()
Description
Sets alphaMode, premulColor, and invertAlpha to the best estimates for this footage source. If hasAlpha is
false, no change is made.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
FootageSource guessPulldown() method
app.project.item(index).mainSource.guessPulldown(method)
app.project.item(index).proxySource.guessPulldown(method)
Description
Sets fieldSeparationType and removePulldown to the best estimates for this footage source. If isStill is true,
no change is made.
Parameters
method
Returns
The method to use for estimation. A PulldownMethod enumerated value, one of:
PulldownMethod.PULLDOWN_3_2
PulldownMethod.ADVANCE_24P
Nothing.
71

After Effects scripting reference FootageSource object
72
FootageSource hasAlpha attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.hasAlpha
app.project.item(index).proxySource.hasAlpha
Description
When true, the footage has an alpha component. In this case, the attributes alphaMode, invertAlpha, and
premulColor have valid values. When false, those attributes have no relevant meaning for the footage.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
FootageSource highQualityFieldSeparation attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.highQualityFieldSeparation
app.project.item(index).proxySource.highQualityFieldSeparation
Description
When true, After Effects uses special algorithms to determine how to perform high-quality field separation.
It is an error to set this attribute if
Typ e
isStill is true, or if fieldSeparationType is FieldSeparationType.OFF.
Boolean; read/write.
FootageSource invertAlpha attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.invertAlpha
app.project.item(index).proxySource.invertAlpha
Description
When true, an alpha channel in a footage clip or proxy should be inverted.
This attribute is valid only if an alpha is present. If
hasAlpha is false, or if alphaMode is AlphaMode.IGNORE,
this attribute is ignored.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
FootageSource isStill attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.isStill
app.project.item(index).proxySource.isStill
Description
When true the footage is still; when false, it has a time-based component.
Examples of still footage are JPEG files, solids, and placeholders with duration of 0. Examples of non-still
footage are movie files, sound files, sequences, and placeholders of non-zero duration.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
72

After Effects scripting reference FootageSource object
73
FootageSource loop attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.loop
app.project.item(index).proxySource.loop
Description
The number of times that the footage is to be played consecutively when used in a composition.
It is an error to set this attribute if
Typ e
isStill is true.
Integer in the range [1.. 9999]; default is 1; read/write.
FootageSource nativeFrameRate attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.nativeFrameRate
app.project.item(index).proxySource.nativeFrameRate
Description
The native frame rate of the footage.
Typ e
Floating-point; read/write.
FootageSource premulColor attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.premulColor
app.project.item(index).proxySource.premulColor
Description
The color to be premultiplied. This attribute is valid only if the alphaMode is alphaMode.PREMULTIPLIED.
Typ e
Array of three floating-point values [R, G, B], in the range [0.0..1.0]; read/write.
FootageSource removePulldown attribute
app.project.item(index).mainSource.removePulldown
app.project.item(index).proxySource.removePulldown
Description
How the pulldowns are to be removed when field separation is used.
It is an error to set this attribute if
PulldownPhase.OFF in the case where fieldSeparationType is FieldSeparationType.OFF.
Typ e
A PulldownPhase enumerated value; read/write. One of:
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.OFF
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.WSSWW
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.SSWWW
isStill is true. It is an error to attempt to set this to a value other than
73

After Effects scripting reference FootageSource object
74
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.SWWWS
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.WWWSS
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.WWSSW
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.WSSWW_24P_ADVANCE
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.SSWWW_24P_ADVANCE
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.SWWWS_24P_ADVANCE
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.WWWSS_24P_ADVANCE
PulldownPhase.RemovePulldown.WWSSW_24P_ADVANCE
74

After Effects scripting reference ImportOptions object
75
ImportOptions object
new ImportOptions();
new ImportOptions(file);
Description
The ImportOptions object encapsulates the options used to import a file with the Project.importFile
methods. See “Project importFile() method” on page 118.
The constructor takes an optional parameter, an ExtendScript File object for the file. If it is not supplied, you
must explicitly set the value of the
example:
new ImportOptions().file = new File("myfile.psd");
Attributes
Attributes Reference Description
file attribute before using the object with the importFile method. For
importAs
sequence
forceAlphabetical
file
Methods
Method Reference Description
canImportAs()
“ImportOptions importAs attribute” on
page 76
“ImportOptions sequence attribute” on
page 77
“ImportOptions forceAlphabetical attribute” on page 76
“ImportOptions file attribute” on
page 76
“ImportOptions canImpor tAs() method”
on page 75
The type of file to be imported.
When true, import a sequence of files, rather than an individual file.
When true, the “Force alphabetical order” option is set.
The file to import, or the first file of the sequence to import.
Restricts input to a particular file type.
ImportOptions canImportAs() method
importOptions.canImportAs(type)
Description
Reports whether the file can be imported as the source of a particular object type. If this method returns true,
you can set the given type as the value of the
page 76.
importAs attribute. See “ImportOptions importAs attribute” on
Parameters
type
The type of file that can be imported. An ImportAsType enumerated value; one of:
ImportAsType.COMP
ImportAsType.FOOTAGE
ImportAsType.COMP_CROPPED_LAYERS
ImportAsType.PROJECT
75

After Effects scripting reference ImportOptions object
76
Returns
Boolean.
Example
var io = new ImportOptions(File(“c:\\myFile.psd”));
if io.canImportAs(ImportAsType.COMP);
io.importAs = ImportAsType.COMP;
ImportOptions file attribute
importOptions.file
Description
The file to be imported. If a file is set in the constructor, you can access it through this attribute.
Typ e
ExtendScript File object; read/write.
ImportOptions forceAlphabetical attribute
importOptions.forceAlphabetical
Description
When true, has the same effect as setting the “Force alphabetical order” option in the File > Import > File
dialog box.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
ImportOptions importAs attribute
importOptions.importAs
Description
The type of object for which the imported file is to be the source. Before setting, use canImportAs to check
that a given file can be imported as the source of the given object type. See “ImportOptions canImportAs()
method” on page 75.
Typ e
An ImportAsType enumerated value; read/write. One of:
ImportAsType.COMP_CROPPED_LAYERS
ImportAsType.FOOTAGE
ImportAsType.COMP
ImportAsType.PROJECT
76

After Effects scripting reference ImportOptions object
77
ImportOptions sequence attribute
importOptions.sequence
Description
When true, a sequence is imported; otherwise, an individual file is imported.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
77

After Effects scripting reference Item object
78
Item object
app.project.item(index)
app.project.items[index]
Description
The Item object represents an item that can appear in the Project panel.
The first item is at index 1.
• Item is the base class for AVItem and for FolderItem, which are in turn the base classes for various other
item types, so Item attributes and methods are available when working with all of these item types. See
“AVItem object” on page 30 and “FolderItem object” on page 63.
Attributes
Attributes Reference Description
name
comment
id
parentFolder
selected
typeName
label
Methods
Method Reference Description
remove()
Example
“Item name attribute” on page 79 The name of the object as shown in the Project panel.
“Item comment attribute” on page 79 A descriptive string.
“Item id attribute” on page 79 A unique identifier for this item.
“Item parentFolder attribute” on page 80 The parent folder of this item.
“Item selected attribute” on page 80 When true, this item is currently selected.
“Item typeName attribute” on page 81 The type of item.
“Item label attribute” on page 79 The label color for the item.
“Item remove() method” on page 80 Deletes the item from the project.
This example gets the second item from the project and checks that it is a folder. It then removes from the
folder any top-level item that is not currently selected. It also checks to make sure that, for each item in the
folder, the parent is properly set to the correct folder.
var myFolder = app.project.item(2);
if (myFolder.typeName != "Folder") {
alert("error: second item is not a folder");
}
else {
var numInFolder = myFolder.numItems;
// Always run loops backwards when deleting things:
for(i = numInFolder; i >= 1; i--) {
var curItem = myFolder.item(i);
if ( curItem.parentFolder != myFolder) {
alert("error within AE: the parentFolder is not set correctly");
}
else {
if ( !curItem.selected && curItem.typeName == "Footage") {
78

After Effects scripting reference Item object
79
//found an unselected solid.
curItem.remove();
}
}
}
}
Item comment attribute
app.project.item(index).comment
Description
A string that holds a comment, up to 15,999 bytes in length after any encoding conversion. The comment is
for the user's purpose only; it has no effect on the item's appearance or behavior.
Typ e
String; read/write.
Item id attribute
app.project.item(index).id
Description
A unique and persistent identification number used internally to identify an item between sessions. The value
of the ID remains the same when the project is saved to a file and later reloaded. However, when you import
this project into another project, new IDs are assigned to all items in the imported project. The ID is not
displayed anywhere in the user interface.
Typ e
Integer; read-only.
Item label attribute
app.project.item(index).label
Description
The label color for the item. Colors are represented by their number (0 for None, or 1 to 16 for one of the preset
colors in the Labels preferences).
Custom label colors cannot be set programmatically.
Typ e
Integer (0 to 16); read/write.
Item name attribute
app.project.item(index).name
Description
The name of the item as displayed in the Project panel.
79

After Effects scripting reference Item object
80
Typ e
String; read/write.
Item parentFolder attribute
app.project.item(index).parentFolder
Description
The FolderItem object for the folder that contains this item. If this item is at the top level of the project, this is
the project's root folder (
a new folder, and set this value to put items in the new folder. See “ItemCollection addFolder() method” on
page 82.
Typ e
FolderItem object; read/write.
Example
This script creates a new FolderItem in the Project panel and moves compositions into it.
app.project.rootFolder). You can use the ItemCollection’s addFolder method to add
// create a new FolderItem in project, with name “comps”
var compFolder = app.project.items.addFolder(“comps”);
// move all compositions into new folder by setting
// compItem’s parentFolder to “comps” folder
for(var i = 1; i <= app.project.numItems; i++) {
if(app.project.item(i) instanceof CompItem)
app.project.item(i).parentFolder = compFolder;
}
Item remove() method
app.project.item(index).remove()
Description
Deletes this item from the project and from the Project panel. If the item is a FolderItem, all the items
contained in the folder are also removed from the project. No files or folders are removed from disk.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
Item selected attribute
app.project.item(index).selected
Description
When true, this item is selected. Multiple items can be selected at the same time. Set to true to select the item
programmatically, or to false to deselect it.
80

After Effects scripting reference Item object
81
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
Item typeName attribute
app.project.item(index).typeName
Description
A user-readable name for the item type; for example, “Folder”, “Footage”, or “Composition”.
Typ e
String; read-only.
81

After Effects scripting reference ItemCollection object
82
ItemCollection object
app.project.items
Description
The ItemCollection object represents a collection of items. The ItemCollection belonging to a Project object
contains all the Item objects for items in the project. The ItemCollection belonging to a FolderItem object
contains all the Item objects for items in that folder.
• ItemCollection is a subclass of Collection. All methods and attributes of Collection, in addition to those
listed below, are available when working with ItemCollection. See “Collection object” on page 51.
Methods
Method Reference Description
addComp()
addFolder()
“ItemCollection addComp() method” on
page 82
“ItemCollection addFolder() method” on
page 82
Creates a new CompItem object and adds it to the collection.
Creates a new FolderItem object and adds it to the collection.
ItemCollection addComp() method
app.project.items.addComp(name, width, height, pixelAspect, duration, frameRate)
Description
Creates a new composition. Creates and returns a new CompItem object and adds it to this collection.
If the ItemCollection belongs to the project or the root folder, then the new item’s
folder. If the ItemCollection belongs to any other folder, the new item’s
Parameters
name
width
height
pixelAspect
duration
A string containing the name of the composition.
The width of the composition in pixels, an integer in the range [4..30000].
The height of the composition in pixels, an integer in the range [4..30000].
The pixel aspect ratio of the composition, a floating-point value in the range [0.01..100.0].
The duration of the composition in seconds, a floating-point value in the range [0.0..10800.0].
parentFolder is that FolderItem.
parentFolder is the root
frameRate
Returns
The frame rate of the composition, a floating-point value in the range [1.0..99.0]
CompItem object.
ItemCollection addFolder() method
app.project.items.addFolder(name)
Description
Creates a new folder. Creates and returns a new FolderItem object and adds it to this collection.
82

After Effects scripting reference ItemCollection object
83
If the ItemCollection belongs to the project or the root folder, then the new folder’s parentFolder is the root
folder. If the ItemCollection belongs to any other folder, the new folder’s
parentFolder is that FolderItem.
To put items in the folder, set the item object’s
parentFolder attribute; see “Item parentFolder attribute” on
page 80.
Parameters
name
Returns
A string containing the name of the folder.
FolderItem object.
Example
This script creates a new FolderItem in the Project panel and moves compositions into it.
// create a new FolderItem in project, with name “comps”
var compFolder = app.project.items.addFolder(“comps”);
// move all compositions into new folder by setting
// compItem’s parentFolder to “comps” folder
for(var i = 1; i <= app.project.numItems; i++) {
if(app.project.item(i) instanceof CompItem)
app.project.item(i).parentFolder = compFolder;
}
83

After Effects scripting reference KeyframeEase object
84
KeyframeEase object
myKey = new KeyframeEase(speed, influence);
Description
The KeyframeEase object encapsulates the keyframe ease settings of a layer’s AE property. Keyframe ease is
determined by the speed and influence values that you set using the property’s
method. See “Property setTemporalEaseAtKey() method” on page 144.
The constructor creates a KeyframeEase object. Both parameters are required.
• speed: A floating-point value. Sets the speed attribute.
• influence: A floating-point value in the range [0.1..100.0]. Sets the influence attribute.
Example
This example assumes that the Position, a spatial property, has more than two keyframes.
var easeIn = new KeyframeEase(0.5, 50);
var easeOut = new KeyframeEase(0.75, 85);
var myPositionProperty = app.project.item(1).layer(1).property("Position")
myPositionProperty.setTemporalEaseAtKey(2, [easeIn], [easeOut]);
setTemporalEaseAtKey
This example sets the Scale, a temporal property with either two or three dimensions. For 2D and 3D
properties you must set an
var easeIn = new KeyframeEase(0.5, 50);
var easeOut = new KeyframeEase(0.75, 85);
var myScaleProperty = app.project.item(1).layer(1).property("Scale")
myScaleProperty.setTemporalEaseAtKey(2, [easeIn, easeIn, easeIn], [easeOut, easeOut, easeOut]);
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
speed
influence
easeIn and easeOut value for each dimension:
“KeyframeEase speed attribute” on page 85 The speed setting for a keyframe.
“KeyframeEase influence attribute” on page 84 The influence setting for a keyframe.
KeyframeEase influence attribute
myKey.influence
Description
The influence value of the keyframe, as shown in the Keyframe Velocity dialog box.
Typ e
Floating-point value in the range [0.1..100.0]; read/write.
84

After Effects scripting reference KeyframeEase object
85
KeyframeEase speed attribute
myKey.speed
Description
The speed value of the keyframe. The units depend on the type of keyframe, and are displayed in the Keyframe
Velo cit y di a lo g bo x .
Typ e
Floating-point value; read/write.
85

After Effects scripting reference Layer object
86
Layer object
app.project.item(index).layer(index)
Description
The Layer object provides access to layers within compositions. It can be accessed from an item’s layer
collection either by index number or by a name string.
• Layer is the base class for CameraLayer, LightLayer, and AVLayer, so Layer attributes and methods are
available when working with all layer types. See “AVLayer object” on page 38,
“CameraLayer object” on page 50, and “LightLayer object” on page 100.
Layers contain AE properties, in addition to their JavaScript attributes and methods. For examples of how to
access properties in layers, see “PropertyBase object” on page 148.
Example
If the first item in the project is a CompItem, this example disables the first layer in that composition and
renames it. This might, for example, turn an icon off in the composition.
var firstLayer = app.project.item(1).layer(1);
firstLayer.enabled = false;
firstLayer.name = "Disabled Layer";
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
index
name
parent
time
startTime
stretch
inPoint
outPoint
enabled
solo
shy
locked
hasVideo
active
“Layer index attribute” on page 90 The index position of the layer.
“Layer name attribute” on page 92 The name of the layer.
“Layer parent attribute” on page 92 The parent of this layer.
“Layer time attribute” on page 94 The current time of the layer.
“Layer startTime attribute” on page 94 The start time of the layer.
“Layer stretch attribute” on page 94 The time stretch percentage of the layer.
“Layer inPoint attribute” on page 90 The “in” point of the layer.
“Layer outPoint attribute” on page 92 The “out” point of the layer.
“Layer enabled attribute” on page 89 When true, the layer is enabled.
“Layer solo attribute” on page 94 When true, the layer is soloed.
“Layer shy attribute” on page 93 When true, the layer is shy.
“Layer locked attribute” on page 90 When true, the layer is locked.
“Layer hasVideo attribute” on page 89 When true, the layer contains a video component.
“Layer active attribute” on page 87 When true, the layer is active at the current time.
nullLayer
selectedProperties
comment
containingComp
“Layer nullLayer attribute” on page 92 When true, this is a null layer.
“Layer selectedProperties attribute” on page 93 All selected AE properties in the layer.
“Layer comment attribute” on page 88 A descriptive comment for the layer.
“Layer containingComp attribute” on page 88 The composition that contains this layer.
86

After Effects scripting reference Layer object
87
Attribute Reference Description
isNameSet
Methods
Method Reference Description
remove()
moveToBeginning()
moveToEnd()
moveAfter()
moveBefore()
duplicate()
copyToComp()
activeAtTime()
setParentWithJump()
applyPreset()
“Layer isNameSet attribute” on page 90 When true, the layer’s name has been explicitly set.
“Layer remove() method” on page 93 Deletes the layer from the composition.
“Layer moveToBeginning() method” on
page 91
“Layer moveToEnd() method” on
page 91
“Layer moveAfter() method” on page 90 Moves the layer below another layer.
“Layer moveBefore() method” on
page 91
“Layer duplicate() method” on page 89 Duplicates the layer.
“Layer copyToComp() method” on
page 89
“Layer activeAtTime() method” on
page 87
“Layer setParentWithJump() method”
on page 93
“Layer applyPreset() method” on
page 88
Moves the layer to the top of the composit ion (makes it the
first layer).
Moves the layer to the bottom of the composition (makes it
the last layer).
Moves the layer above another layer.
Copies the layer to the top (beginning) of another composition.
Reports whether this layer will be active at a specified time.
Sets a new parent for this layer.
Applies a named collection of animation settings to the
layer.
Layer active attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).active
Description
When true, the layer's video is active at the current time.
For this to be true, the layer must be enabled, no other layer may be soloing unless this layer is soloed too, and
the time must be between the
This value is never true in an audio layer; there is a separate
Typ e
inPoint and outPoint values of this layer.
audioActive attribute in the AVLayer object.
Boolean; read-only.
Layer activeAtTime() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).activeAtTime(time)
Description
Returns true if this layer will be active at the specified time. To return true, the layer must be enabled, no other
layer may be soloing unless this layer is soloed too, and the time must be between the
values of this layer.
inPoint and outPoint
87
After Effects scripting reference Layer object
88
Parameters
time
Returns
The time in seconds, a floating-point value.
Boolean.
Layer applyPreset() method
appapp.project.item(index).layer(index).applyPreset(presetName);
Description
Applies the specified collection of animation settings (an animation preset) to the layer. Predefined animation
preset files are installed in the Presets folder, and users can create new animation presets through the user
interface.
Parameters
presetName
Returns
An ExtendScript File object for the file containing the animation preset.
Nothing.
Layer comment attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).comment
Description
A descriptive comment for the layer.
Typ e
String; read/write.
Layer containingComp attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).containingComp
Description
The composition that contains this layer.
Typ e
CompItem object; read-only.
88

After Effects scripting reference Layer object
89
Layer copyToComp() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).copyToComp(intoComp)
Description
Copies the layer into the specified composition. The original layer remains unchanged. Creates a new Layer
object with the same values as this one, and prepends the new object to the
CompItem. Retrieve the copy using
intoComp.layer(1).
Copying in a layer changes the index positions of previously existing layers in the target composition. This is
the same as copying and pasting a layer through the user interface.
Parameters
layers collection in the target
intoComp
Returns
The target composition, and CompItem object.
Nothing.
Layer duplicate() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).duplicate()
Description
Duplicates the layer. Creates a new Layer object in which all values are the same as in this one. This has the
same effect as selecting a layer in the user interface and choosing Edit > Duplicate, except the selection in the
user interface does not change when you call this method.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Layer object.
Layer enabled attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).enabled
Description
When true, the layer is enabled; otherwise false. This corresponds to the video switch state of the layer in the
Timeline panel.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
Layer hasVideo attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).hasVideo
Description
When true, the layer has a video switch (the eyeball icon) in the Timeline panel; otherwise false.
89

After Effects scripting reference Layer object
90
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
Layer index attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).index
Description
The index position of the layer.
Typ e
Integer in the range [1..numLayers]; read-only.
Layer inPoint attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).inPoint
Description
The “in” point of the layer, expressed in composition time (seconds).
Typ e
Floating-point value in the range [-10800.0..10800.0] (minus or plus three hours); read/write.
Layer isNameSet attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).isNameSet
Description
True if the value of the name attribute has been set explicitly, rather than automatically from the source.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
Layer locked attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).locked
Description
When true, the layer is locked; otherwise false. This corresponds to the lock toggle in the Layer panel.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
Layer moveAfter() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).moveAfter(layer)
Description
Moves this layer to a position immediately after (below) the specified layer.
90

After Effects scripting reference Layer object
91
Parameters
layer
Returns
The target layer, a layer object in the same composition.
Nothing.
Layer moveBefore() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).moveBefore(layer)
Description
Moves this layer to a position immediately before (above) the specified layer.
Parameters
layer
Returns
The target layer, a layer object in the same composition.
Nothing.
Layer moveToBeginning() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).moveToBeginning()
Description
Moves this layer to the topmost position of the layer stack (the first layer).
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
Layer moveToEnd() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).moveToEnd()
Description
Moves this layer to the bottom position of the layer stack (the last layer).
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
91

After Effects scripting reference Layer object
92
Layer name attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).name
Description
The name of the layer. By default, this is the same as the Source name (which cannot be changed in the Layer
panel), but you can set it to be different.
Typ e
String; read/write.
Layer nullLayer attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).nullLayer
Description
When true, the layer was created as a null object; otherwise false.
Typ e
Boolean; read-only.
Layer outPoint attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).outPoint
Description
The “out” point of the layer, expressed in composition time (seconds).
Typ e
Floating-point value in the range [-10800.0..10800.0] (minus or plus three hours); read/write.
Layer parent attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).parent
Description
The parent of this layer; can be null.
Offset values are calculated to counterbalance any transforms above this layer in the hierarchy, so that when
you set the parent there is no apparent jump in the layer's transform. For example, if the new parent has a
rotation of 30 degrees, the child layer is assigned a rotation of -30 degrees.
To set the parent without changing the child layer's transform values, use the
Typ e
Layer object or null; read/write.
setParentWithJump method.
92

After Effects scripting reference Layer object
93
Layer remove() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).remove()
Description
Deletes the specified layer from the composition.
Parameters
None.
Returns
Nothing.
Layer selectedProperties attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).selectedProperties
Description
An array containing all of the currently selected Property and PropertyGroup objects in the layer.
Typ e
Array of PropertyBase objects; read-only.
Layer setParentWithJump() method
app.project.item(index).layer(index).setParentWithJump()
app.project.item(index).layer(index).setParentWithJump(newParent)
Description
Sets the parent of this layer to the specified layer, without changing the transform values of the child layer.
There may be an apparent jump in the rotation, translation, or scale of the child layer, as this layer’s transform
values are combined with those of its ancestors.
If you do not want the child layer to jump, set the
and set in the child layer's transform fields, to prevent the jump from occurring.
Parameters
newParent
Returns
Optional, a layer object in the same composition. If not specified, it sets the parent to None.
Nothing.
parent attribute directly. In this case, an offset is calculated
Layer shy attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).shy
Description
When true, the layer is “shy,” meaning that it is hidden in the Layer panel if the composition’s “Hide all shy
layers” option is toggled on.
93

After Effects scripting reference Layer object
94
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
Layer solo attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).solo
Description
When true, the layer is soloed, otherwise false.
Typ e
Boolean; read/write.
Layer startTime attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).startTime
Description
The start time of the layer, expressed in composition time (seconds).
Typ e
Floating-point value in the range [-10800.0..10800.0] (minus or plus three hours); read/write.
Layer stretch attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).stretch
Description
The layer’s time stretch, expressed as a percentage. A value of 100 means no stretch. Values between 0 and 1
are set to 1, and values between -1 and 0 (not including 0) are set to -1.
Typ e
Floating-point value in the range [-9900.0..9900.0]; read/write.
Layer time attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).time
Description
The current time of the layer, expressed in composition time (seconds).
Typ e
Floating-point value; read-only.
94
After Effects scripting reference LayerCollection object
95
LayerCollection object
app.project.item(index).layers
Description
The LayerCollection object represents a set of layers. The LayerCollection belonging to a CompItem object
contains all the layer objects for layers in the composition. The methods of the collection object allow you to
manipulate the layer list.
• LayerCollection is a subclass of Collection. All methods and attributes of Collection, in addition to those
listed below, are available when working with LayerCollection. See “Collection object” on page 51.
Example
Given that the first item in the project is a CompItem and the second item is an AVItem, this example shows
the number of layers in the CompItem's layer collection, adds a new layer based on an AVItem in the project,
then displays the new number of layers.
var firstComp = app.project.item(1);
var layerCollection = firstComp.layers;
alert("number of layers before is " + layerCollection.length);
var anAVItem = app.project.item(2);
layerCollection.add(anAVItem);
alert("number of layers after is " + layerCollection.length);
Methods
Method Reference Description
add()
addNull()
addSolid()
addText()
addBoxText()
addCamera()
addLight()
addShape()
byName()
precompose()
“LayerCollection add() method” on
page 96
“LayerCollection addNull() method” on
page 97
“LayerCollection addSolid() method” on
page 98
“LayerCollection addText() method” on
page 98
“LayerCollection addBoxText() method”
on page 96
“LayerCollection addCamera() method”
on page 96
“LayerCollection addLight() method” on
page 97
“LayerCollection addShape() method”
on page 97
“LayerCollection byName() method” on
page 99
“LayerCollection precompose()
method” on page 99
Creates a new AVLayer and adds it to this collection.
Creates a new, null layer and adds it to this collection.
Creates a new layer, a FootageItem with a SolidSource, and adds it
to this collection.
Creates a new point text layer and adds it to this collection.
Creates a new paragraph (box) text layer and adds it to this collection.
Creates a new camera layer and adds it to this collection.
Creates a new light layer and adds it to this collection.
Creates a new shape layer and adds it to this collection.
Retrieves the layer object with a specified name.
Collects specified layers into a new composition.
95

After Effects scripting reference LayerCollection object
96
LayerCollection add() method
app.project.item(index).layers.add(item, duration)
Description
Creates a new AVLayer object containing the specified item, and adds it to this collection.
The new layer honors the Create Layers at Composition Start Time preference.
This method generates an exception if the item cannot be added as a layer to this CompItem.
Parameters
item
duration
Returns
The AVItem object for the item to be added.
Optional, the length of a still layer in seconds, a floating-point value. Used only if the item contains a piece of
still footage. Has no effect on movies, sequences or audio.
If supplied, sets the
preferences. By default, this is the same as the duration of the containing CompItem. To set another preferred
value, choose Edit > Preferences > Import ( Windows) or After Effects > Preferences > Import (Mac OS), and specify options under Still Footage.
duration value of the new layer. Otherwise, the duration value is set according to user
AVL a y er o bj e ct .
LayerCollection addBoxText() method
app.project.item(index).layers.addBoxText(sourceText)
Description
Creates a new paragraph (box) text layer and adds the new TextLayer object to this collection.
To create a point text layer, use the
method” on page 98.
Parameters
sourceText
addText() method. For more information, see “LayerCollection addText()
Optional; a string containing the source text of the new layer, or a TextDocument object containing the source text of the new layer. See “TextDocument object” on page 182.
Returns
Text La y er o bj e ct .
LayerCollection addCamera() method
app.project.item(index).layers.addCamera(name, centerPoint)
Description
Creates a new camera layer and adds the CameraLayer object to this collection.
The new layer honors the Create Layers at Composition Start Time preference.
Parameters
name
A string containing the name of the new layer.
96

After Effects scripting reference LayerCollection object
97
centerPoint
Returns
The center of the new camera, a floating-point array [x, y]. This is used to set the initial x and y values of the
new camera’s Point of Interest property. The z value is set to 0.
CameraLayer object.
LayerCollection addLight() method
app.project.item(index).layers.addLight(name, centerPoint)
Description
Creates a new light layer and adds the LightLayer object to this collection.
The new layer honors the Create Layers at Composition Start Time preference.
Parameters
name
centerPoint
Returns
LightLayer object.
A string containing the name of the new layer.
The center of the new light, a floating-point array [x, y].
LayerCollection addNull() method
app.project.item(index).layers.addNull(duration)
Description
Creates a new null layer and adds the AVLayer object to this collection. This is the same as choosing
Layer > New > Null Object.
Parameters
duration
Returns
Optional, the length of a still layer in seconds, a floating-point value.
If supplied, sets the duration value of the new layer. Otherwise, the duration value is set according to user
preferences. By default, this is the same as the duration of the containing CompItem. To set another preferred
value, choose Edit > Preferences > Import ( Windows) or After Effects > Preferences > Import (Mac OS), and specify
options under Still Footage.
AVL a y er o bj e ct .
LayerCollection addShape() method
app.project.item(index).layers.addShape()
Description
Creates a new ShapeLayer object for a new, empty Shape layer. Use the ShapeLayer object to add properties,
such as shape, fill, stroke, and path filters.
97

After Effects scripting reference LayerCollection object
98
This is the same as using a shape tool in "Tool Creates Shape" mode. Tools automatically add a vector group
that includes Fill and Stroke as specified in the tool options.
Parameters
None.
Returns
ShapeLayer object.
LayerCollection addSolid() method
app.project.item(index).layers.addSolid(color, name, width, height, pixelAspect, duration)
Description
Creates a new SolidSource object, with values set as specified; sets the new SolidSource as the mainSource
value of a new FootageItem object, and adds the FootageItem to the project. Creates a new AVLayer object,
sets the new FootageItem as its
Parameters
source, and adds the layer to this collection.
color
name
width
height
pixelAspect
duration
Returns
The color of the solid, an array of three floating-point values, [R, G, B], in the range [0.0..1.0].
A string containing the name of the solid.
The width of the solid in pixels, an integer in the range [4..30000].
The height of the solid in pixels, an integer in the range [4..30000].
The pixel aspect ratio of the solid, a floating-point value in the range [0.01..100.0].
Optional, the length of a still layer in seconds, a floating-point value.
If supplied, sets the duration value of the new layer. Otherwise, the duration value is set according to
user preferences. By default, this is the same as the duration of the containing CompItem. To set another
preferred value, choose Edit > Preferences > Import (Windows) or After Effects > Preferences > Import (Mac
OS), and specify options under Still Footage.
AVL a y er o bj e ct .
LayerCollection addText() method
app.project.item(index).layers.addText(sourceText)
Description
Creates a new point text layer and adds the new TextLayer object to this collection.
To create a paragraph (box) text layer, use the
lection addBoxText() method” on page 96.
addBoxText() method. For more information, see “LayerCol-
Parameters
sourceText
Optional; a string containing the source text of the new layer, or a TextDocument object containing the source text of the new layer. See “TextDocument object” on page 182.
98

After Effects scripting reference LayerCollection object
99
Returns
Text La y er o bj e ct .
LayerCollection byName() method
app.project.item(index).layers.byName(name)
Description
Returns the first (topmost) layer found in this collection with the specified name, or null if no layer with the
given name is found.
Parameters
name
Returns
A string containing the name.
Layer object or null.
LayerCollection precompose() method
app.project.item(index).layers.precompose(layerIndicies, name, moveAllAttributes)
Description
Creates a new CompItem object and moves the specified layers into its layer collection. It removes the
individual layers from this collection, and adds the new CompItem to this collection.
Parameters
layerIndices
name
moveAllAttributes
The position indexes of the layers to be collected. An array of integers.
The name of the new CompItem object.
Optional. When true (the default), retains all attributes in the new composition.
This is the same as selecting the “Move all attributes into the new composition”
option in the Pre-compose dialog box.
You can only set this to false if there is just one index in the
This is the same as selecting the “Leave all attributes in” option in the Pre-compose dialog box.
layerIndices array.
Returns
CompItem object.
99

After Effects scripting reference LightLayer object
100
LightLayer object
app.project.item(index).layer(index)
Description
The LightLayer object represents a light layer within a composition. Create it using the LayerCollection
addLight method; see “LayerCollection addLight() method” on page 97. It can be accessed in an item’s
object’s
layer collection either by index number or by a name string.
• LightLayer is a subclass of Layer. All methods and attributes of Layer are available when working with Light-
Layer. See “Layer object” on page 86.
AE Properties
LightLayer defines no additional attributes, but has different AE properties than other layer types. It has the
following properties and property groups:
Marker
Tra n sfor m
Point of Interest
Position
Scale
Orientation
X Rotation
Y Rotation
Rotation
Opacity
Light Options
Intensity
Color
Cone Angle
Cone Feather
Casts Shadows
Shadow Darkness
Shadow Diffusion
Attributes
Attribute Reference Description
lightType
“LightLayer lightType attribute” on page 100 For light layers, the type of light.
LightLayer lightType attribute
app.project.item(index).layer(index).lightType
Description
For a light layer, its light type.
Trying to set this attribute for a non-light layer produces an error.
100
 Loading...
Loading...