

2
Contents
GENERAL................................................................................................................... 3
OVERALL PLAN......................................................................................................... 4
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION ...................................................................................... 5
MATERIALS................................................................................................................ 9
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS............................................................................... 10
HARNESS................................................................................................................. 10
CHECKS ON A NEW PARAGLIDER........................................................................ 11
ADJUSTING BRAKE LINES ..................................................................................... 11
FLYING THE PASHA 4............................................................................................. 12
TOWING................................................................................................................... 15
MOTORISED FLIGHT............................................................................................... 16
EXTREME FLYING MANOEUVRES ........................................................................ 16
RAPID DESCENTS................................................................................................... 20
LOOKING AFTER YOUR PARAGLIDER.................................................................. 21
TREATING NATURE WITH RESPECT.................................................................... 24
LINE PLANS ............................................................................................................. 24
Line plan Pasha 4 -39............................................................................................... 25
Line plan Pasha 4 - 42.............................................................................................. 26
FULL LINE LENGTHS .............................................................................................. 27
MANUAL FOR PARAGLIDER CHECKS................................................................... 28
CHECKS................................................................................................................... 30
TEST FLIGHT CERTIFICATE................................................................................... 31
Technical data........................................................................................................... 31

3
GENERAL
Dear MAC PARA pilot
We congratulate you on your purchase of a MAC PARA paraglider. Extensive
development work and numerous tests make the Pasha 4 a hi gh performance biplace
paraglider with maximum possible safety. The Pasha 4 is constructed for thermal and
cross-country flying, and will enable pilots to get maximum enjoyment. The Pasha 4
offers very easy inflation and simple ground-handling characteristics by take off,
excellent handling in flight and easy landing. Please read this manual carefully before
you start, this way you will g et the most out of your glider, an d enjoy many nice flights.
MAC PARA wish you many pleasant flights with your Pasha 4.
Please read this manual carefully and note following details:
Paragliding is a sport, which demands, besides the optimum equipment, a high degr ee
of attentiveness, good judgement, and theoretical knowledge. Paragliding can be a
dangerous sport, which may lead to injury and death. This paraglider meets at the time
of delivery requirements of the EN (Europea n Norm) 926 or LTF (German Certificat e of
Airworthiness). Any alternations to the paraglider will render its certification invali d! The
use of this paraglider is solely at the user's own risk! Manufacturer and distributor do n ot
accept any liability. Pilots are responsible for their own safety and their paraglider
airworthiness. The paraglider carries no warranty! The author assumes that the pilot is
in possession of a valid paragliding licence for glider's categor y, insur ance etc.
Before delivery, as well as during production, each paraglider goes through a strict
visual inspection, and is test-flown by your dealer. Stamps on the p lacard, together with
a completed test-flight certificate, confirm this. Check that the paraglider has been testflown before your first take-off. If it has not, consult your dealer.
Any inadequate use or misuse increases the risks considerably. The Pasha 4 must not
be used outside the certified weight range. The Pasha 4 must not be use d during rain or
snow-fall. The Pasha 4 must not be used in high or gusty winds. T he Pash a 4 must not
be used in cloud and fog. The Pasha 4 must not be used by pilots without sufficient
knowledge or experience.
If, after carefully reading this handbook, you still have questions, suggestions or
criticism regarding this product do not hesitate to contact your dealer or us. We will be
glad to help and advice.
MAC PARA wish you many pleasant flights with your
Pasha 4
Version 1.0 Stand 1.06.2010

4
(&(
Operating limits
The Pasha 4 has been tested by certification laboratory European Para Academy to
LTF 1-2 / EN-B category. The Pasha 4 is certified for solo flight. The Pasha 4 has been
load and shock-tested and passed with a load corresponding to 8G of the maximum
weight in flight 220 kg. Its flying tests have shown that the glider remains stable and
controllable over a wide range of normal an d abnormal flight conditions. Nevertheless,
turbulence and gusting winds can le ad to a partial or complete collapse o f the canopy.
Therefore never fly in such conditions.
Any changes made to this paraglider invalidate the certificate of air worthiness.
OVERALL PLAN
Trailing edge
Leading edge
Brake handle
Main karabineer
Rapid links
Main lines
Riser
Main brake line
Brake line
Stabilizer
Top surface
Bottom surface
Glider’s label on the
central main rib

5
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
Construction of the canopy:
The canopy of the PASHA 4 consists of 54 cells over the wingspan. The wingtips are
slightly pulled down and this produces a kind of stabiliz er. The Pasha 4 is a second rib
diagonal-construction paraglider. Every sec ond main rib is attached to the 4 or 5
suspension lines. Between these main suspension ribs, intermediate ribs are
suspended by diagonal segments. These segm ents do not lead to top surface of canopy
but are attached at 80% of rib's height. This construction ensures a smooth top surface
and precise airfoil reproduction. The intern al reinforcements maintain the precise form of
the canopy and provide stability. The cell openings on the under-surface of the profile’s
nose provide airflow into the glider. Stretch resistant flares, integrated with diagonal ribs
at the suspension points, ensure an even distribution of load throughout the canopy. A
stretch resistant Mylar strip on the top and bottom panels alongside the openings and
running the length of the trailing edge defines the wingspan, together with an optimized
sail tension; this guarantees high form stability. Large cross ports allow effective airflow
inside the canopy, providing good re-inflation without reducing the profile accuracy.
The Pasha 4 is mainly made of the proven Nylon fabrics Porcher Marine Skytex Ripstop 9092 E85A, 9017 E38A and 9017 E29A. Like any synthetic material, this can
deteriorate through excessive exposure to UV.
Rigging system:
The lines of the Pasha 4 are made of proven strong and stretch resistant Polyester HMA
Aramid/Kevlar (yellow core) lines and PES/Dynema (white core) lines. The entire rigging
system comprises individual suspension lines looped and stitched at each end. The
Aramid lines have strengths from 60 up to 340 kg. The Aramid cascade lines have
strengths from 80kg up to 160 kg. The Dynema brake lines have strengths from 80kg
up to 360 kg
The suspension lines are comprised of “cascaded top lines” (attached to the undersurface),”cascaded middle lines” (cascade 3 to top lines together on outermost main
lines), and “main lines”. Main lines lead to the “quick link” (a Maillon which conn ects
lines and risers). The “stabilizer lines” connect the upper stabilizer lines on the outer
suspension points with the quick link. The “brake lines” are not loa d carrying suspension
lines. They lead from the trailing edge of the canopy to the main brake lines and run to
the brake handles through the pulleys attached to the D-risers. A

6
(&(
mark on the main brake line indicates the position of the brake ha ndle. This adjustment,
on the one hand, allows sufficient brake to be applied during extreme flying situations
and when landing, while on the other hand, this ensures that brakes are not
permanently applied to the canopy (especially when fully accelerated). This trimming
should not be altered. For differentiation purposes the A-lines are coloured red, the
brake lines are orange, all remaining lines are yellow. Also the main suspension loop,
on the bottom of the riser, is covered red. This is where the main karabiner should be
hooked in, which then in turn connects the risers to the harness.
The Pasha 4 is equipped with 5 risers per side (A, A1, B, C, D). The two central A-lines
per side are attached to the main A-risers while the outermost A main lines are attached
to A1 risers. The 3 B-main lines and the stabilizer lines are attached to the B-riser. The
3 C-main lines to the C-riser. The 2 D-main lines to the D-riser. The main brake lines
leads through the pulleys on the D riser.
The line connections are made to triangular Maillons (quick links) fitted with a rubber ”oring” in the form of a ”figure eight” which prevents any slipping of the lines on the quick
link. See line plans for details.
Risers with trim system:
Each of the riser sets of the Pasha 4 has a lockable trimmer.
The trim system shortens and lengthens the B, C and D risers and changes the angle of
attack. In normal flight, all risers are in a "neutral position" and are of equal length (46
cm to the bottom edge of the rapid links). This position is marked with a white line on
the trimmer straps. When you pull down the straps that run through the trimmers, the Brisers are shortened up to 2 cm, C-straps up to 2.5 cm, and the D-risers up are
shortened to 5 cm. When you open the trims (push the trim buckles) , the B-risers are
extended up to 0.5 cm, C-straps up to 2.5 cm, and the D risers are extended by up to 5
cm.
Operation and handling:
Connect the risers to the spreader-bars before take off. It is important to ensure that the
hook points on each spreader bar are equal. By pulling the straps that run through the
trimmers, the B / C / D straps are shortened. This increases the angle of attack and the
glider flies slower. By opening the trimmers, the B / C / D risers are extended. This
decreases the angle of attack and therefore the glider flies faster.
Trim
The glider is delivered with a five riser system and tandem spreader-bars. Its speed
varies in the range from 36 - 44 km/h depending on the wing loading and position of the
trimmers. The brake lines should always be adjusted so that the first brake-lines just
come under tension when the brake handles have been pull ed 5 - 10 cm.
The test results relate to this brake-line adjustment. In extreme situations other settings
may lead to the glider reacting differe ntly. To be able at al l times to re act quickl y en ou gh
to possible problems; you should not let go of the brake handles

7
(&(
during the flight (it may be possible to hold both handles in one hand). Alter the line
length to bring the handles to a suitable height when using your harness.
Safety equipment
An optimal outfit should be a matter of course for every paraglider pilot. Always wear
stout footwear, a helmet, and gloves. Clothing should be warm and allow sufficient
freedom of movement. A rescue-system can be life-saving in case of an irremediable
disturbance of the canopy, collapse in the air or material failure, and is therefore
imperative.
Tandem spreader bar
The PASHA 4 tandem spreader-bar allows varied attachment possibilities, allo wing for
the difference in heights and weights of pilot and passenger. Changing the main
attachment (karabiner - min. strength 24 kN) position can allow for weight difference: the
front position (3) for heavier passengers or if their weights are the s ame and the back
position (4) for lighter passengers. The passenger weight is always compared to the
weight of the pilot!
The rescue system bridle must be connect ed to main suspensio n point on the spreaderbar (3 or 4). It is possible to use a separator karabiner (min. strength 24 kN) for the
rescue system, clipped in to the same loop as the main karabiner. The rescue system
bridle must not be connected only to the pilot's or passenger's harness or to the
spreader-bar's hang points.
WARNING: The karabiners used in position 3 or 4 must be karabiners
designed for tandem flight, which means the minimum strength must be 24 kN.
(Recommendation Austrialpin Powerfly, Austrialpin Delta). This applies also to
the karabiner used for the attachment of the rescue system in Position 3 or 4.
1. Passenger’s hang point.
2. Passenger’s hang point.

8
(&(
3. Main suspension and rescue system attachment point, when passenger is heavi er
than the pilot or when passenger is the same weight as the pilot.
4. Main suspension and rescue system attachment point, Main suspension and
rescue system attachment point, when passenger is lighter than the pilot.
5. Suspension point for the pilot.
Riser
Riser lengths Pasha 4
A A1 B C D
Trims open
460 460 465 485 510
Trims closed
460 460 440 435 410
The lengths are measured from the main attachment point to the lower edge of rapid
links.
Color
marking
Loop for main
karabineer
Trims closed Trims neutral
Trims open
Brake handle
Change of the
an
g
le of attack
A A1 B C D A A1 B C D A A1 B C D
Trim buckle
Brakeline
pulley
Magnet button
Slower
Faster

9
MATERIALS
Tissue
(PORCHER SPORT, Rue du Ruisseau B.P. 710,38290 ST. QUENTIN FALLAVIER, FRANCE)
Top Sail - Leading Edge - SKYTEX 45 E85A - 100% nylon 6.6 , 33 Dtex, 45 g/m
2
Top Sail - Trailing Edge - SKYTEX 40 E38A - 100% nylon 6.6 , 33 Dtex, 40 g/m
2
Bottom Sail - SKYTEX 40 E38A - 100% nylon 6.6 , 33 Dtex, 40 g/m
2
Main ribs, Diagonals - SKYTEX 40 E29A - 100% nylon 6.6 , 33 Dtex, 40 g/m
2
Ribs - SKYTEX 40 E38A - 100% nylon 6.6 , 33 Dtex, 40 g/m
2
Reinforcement Main Ribs - Grille Polyester 200 g/m
2
Reinforcement Ribs - W382 Polyester 180 g/m
2
Lines
(EDELMAN+RIDDER+CO. Achener Weg 66, D-88316 ISNY IM ALLGEAU, GERMANY)
Upper cascade C,D,E - Aramid/Polyester A-6843-060, Breaking Load 60 kg
Upper cascade A,B,C,D - Aramid/Polyester A-6843-080, Breaking Load 80 kg
Upper cascade A,B - Aramid/Polyester A-6843-120, Breaking Load 120 kg
Middle cascade D - Aramid/Polyester A-6843-080, Breaking Load 080 kg
Middle cascade C - Aramid/Polyester A-6843-120, Breaking Load 120 kg
Middle cascade A,B - Aramid/Polyester A-6843-160, Breaking Load 160 kg
Brake lines upper cascade wing tip - Dynema/Polyester A-7850-080, Breaking Load 80 kg
Brake lines middle cascade wing tip - Dynema/Polyester A-7850-100, Breaking Load 100 kg
Brake lines upper cascade - Dynema/Polyester A-7850-100, BBreaking Load 100 kg
Brake lines middle cascade - Dynema/Polyester A-7850-130, BBreaking Load 130 kg
Main lines C1,D2,D3 - Aramid/Polyester A-6843-200, Breaking Load 200 g
Main lines A1,B1 - Aramid/Polyester A-6843-240, Breaking Load 240 kg
Main lines A2,A3,B2,B3,C2,C3 - Aramid/Polyester A-6843-340, Breaking Load 340 kg
Stabilizer line - Aramid/Polyester A-6843-080, Breaking Load 80 kg
Main brake line - Dynema/Polyester A-7850-340, Breaking Load 340 kg
Attachment straps
(STAP a.s., 407 80 VILEMOV, CZECH REPUBLIC)
STAP-POLYESTERBRIDLE 13 mm, Breaking Load 70 kg
Risers
(MOUKA TISNOV ltd, Koráb 133, 66601 Tišnov, Czech Republic)
Polyester 367 040 025 912 25x1,5 mm Breaking Load 800 kg
Thread
(AMANN SPONIT ltd, Dobronická 635, 148 25 PRAHA 4, CZECH REPUBLIC)
Lines-SYNTON 60, Main lines-SERABOND 60, Canopy-SYNTON 40, Riser-SYNTON 30
Rapid links
(ELAIR SERVIS, CZECH REPUBLIC)
NIRO TRIANGLE 200 - Max. Load 200 kg
10
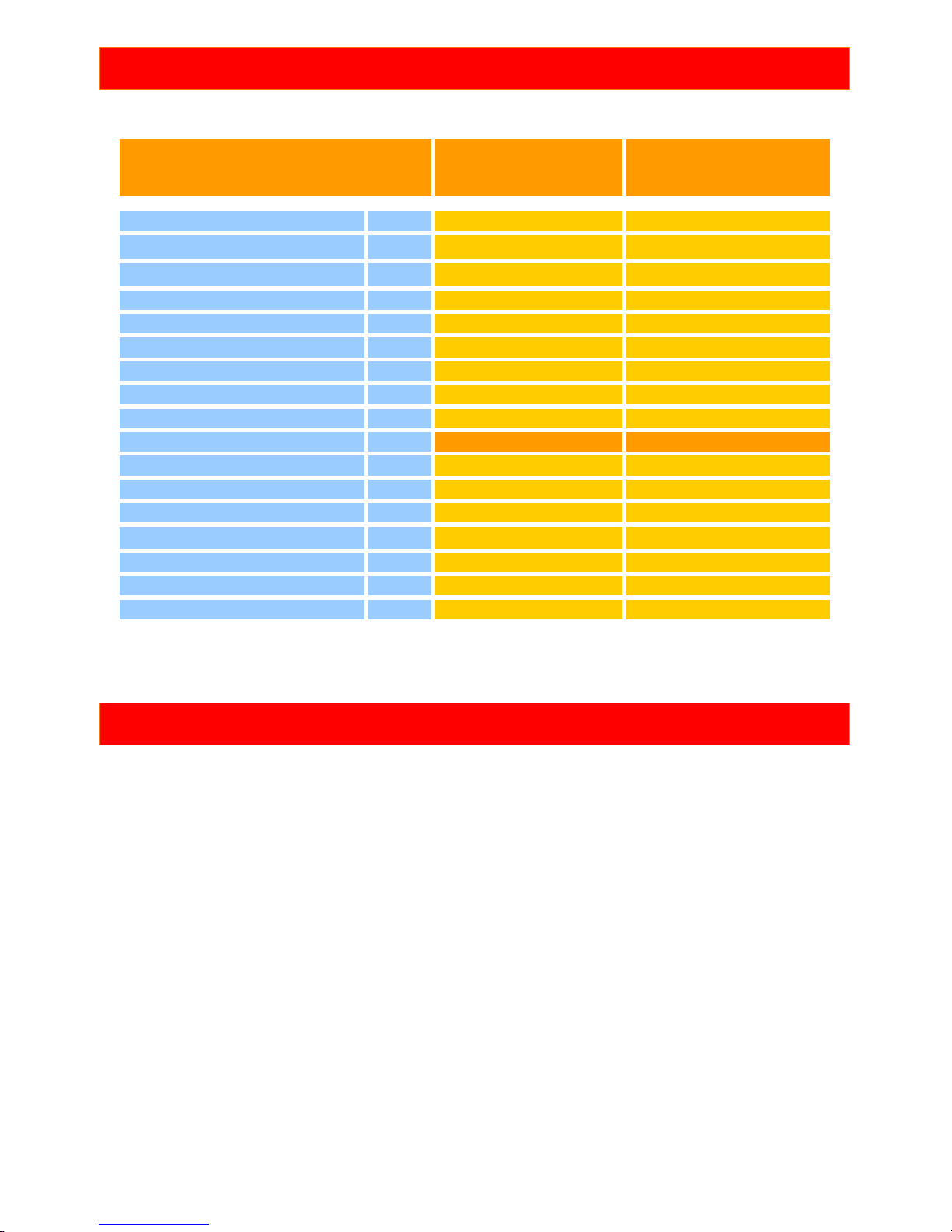
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Biplace
Pasha 4 Pasha 4
Size 39 42
Zoom flat [%] 96 100
Area flat
[m
2
]
39,31 42,65
Area projected
[m
2
]
35,46 38,48
Span flat [m] 14,56 15,17
Span projected [m] 12,31 12,82
Aspect ratio flat - 5,4 5,4
Root cord [m] 3,35 3,49
Cells - 54 54
Weight [kg] 8,6 9,0
Weight range [kg] 125-190 145-220
Min.speed [km/h] 22-24 22-24
Speed Trimmers closed [km/h] 36-38 36-38
Speed Trimmers open [km/h] 42-45 42-45
Top speed (accelerator) [km/h] - Glide ratio - 8,6 8,6
Min. Sink rate [m/s] 1,1 1,1
Cetification with trimmers - EN EN - B
HARNESS
The Pasha 4 is certified with LTF GH type certified harnesses. Nearly all harnesses
available on the market are type “GH”.
These “GH” harnesses are different to “GX“ harnesses, which hav e a lower attachment
point for the main karabiners and effective cross brac ing. The Pasha 4 was not tested
with harnesses with an effective cross bracing system.
Any certified harness with a hang point at about chest height may be used with the
Pasha 4 (37-50cm over seat plate). The distance bet ween left and right m ain karabin ers
should be between 45 and 60cm, depe nding on the size of the pilot and th e type of the
harness. Please note: the hang point position changes the position of the brakes re lative
to the pilot's body.

11
CHECKS ON A NEW PARAGLIDER
Before delivery, as well as during production, each paraglider goes through a strict
visual inspection. Additionally we recommend that you to check your new glider in
accordance with the following points. We recommend that you make this check after
flying extreme manoeuvres or after tree landings or similar.
• Inspection of the canopy for tears or damage, especially the seams which join the
ribs to the upper and lower surfaces, but also the area of the attachment tapes and
brake-line connections.
• Inspection of the lines for damage to the stitc hes. T he li ne le ngths m ust be checked
after 50 hours flying time and whenever the flight behaviour of the glider changes
• Inspection of attachment tapes for damage to the stitches. It is also important to
check the attachment tapes and brake-lines for tangles.
• Inspection of the risers for faultless condition. Rapid links must be secured.
With even slight damage the glider loses its airworthiness!
ADJUSTING BRAKE LINES
The brake lines lead from the trailing edge of the canopy to the main brake lines which
then run through pulleys on the D-risers to th e brak e han dles. A mark on t h e mai n brake
line indicates the position of the brake handle.
The glider is delivered with a standard set-up and its speed can reach 36 - 44 km/h
depending on the weight of the pilot and the passenger and position of trims. T he brakelines should always be adjusted so that the first brake-lines just come under tension
when the brake handles have been pulled 5 - 10 cm. The test results relate to this
brake-line adjustment. This adjustment, on the one hand, allows sufficient brake to be
applied during extreme flying situations and when landing, while on the other hand, it
ensures that the canopy is not permanently braked (especi ally when fully accelerated).
This trim should not be altered. In extreme situations an y other settings may lead to the
glider reacting differently to versions which have been tested.
NOTE!! If in doubt about the brake-line adjustment, it is preferable to leave them too
long, as any necessary shortening can easily be achieve d by wrapping them roun d your
hand.

12
FLYING THE PASHA 4
The following information must not under any circumstances be taken as a
manual for practising paragliding. We would like to advise you of the Pasha 4's
features and important information for your flying and security.
Preparing for take off:
As with any aircraft, a thorough pre-flight check must be made prior to each flight on the
Pasha 4!
Before every launch check lines, risers and canopy for damage! Do not launch with
even the slightest damage!
Also check the maillons connecting the lines and the risers. They have to be closed
tight.
Put on the harnesses and spreader-bars with maximum care and check the handle of
the safety system and that all the flaps of the outer conta iner are fastened securely and
correctly. The main karabiners must also be checked carefull y. Replac e it if an y dam age
is visible, or generally after 300 flying hours. Connect harne sses with the spreader-bars
and finally connect the risers to your spreader-bars with the main karabiners. Check
carefully that they are properly closed.
Attention! Never fly with an open main karabiner! Do not take off if you find any
damage to your equipment!
Having unpacked and laid out the paraglider in a slight horseshoe pattern the follo wing
checks must be made:
Checklist:
Preparing the wing:
• canopy without any damage
• risers and spreader-bars without any damage
• maillons (quick links) closed tight
• stitching of the main lines near the risers is o.k.
• all main lines run free from the riser to the canopy, brake lines are free
Putting on the harness:
• rescue handle and deployment pins secure
• buckles (leg and chest strap) closed
• main karabiners
Before takeoff:
• spreader-bars mounted and connected properly
• risers not twisted
• brake handle in hands, brake lines free
• pilot's position relative to the wing (centred: all lines same tensi on)
• wind direction
• obstacles on the ground
• free airspace

13
(&(
When laying out the glider, the wind direction should be observed. The canopy should
be deployed into the wind so both halves of it are loaded symmetrically. The paraglider
should be arranged in a semicircle into wind. This ensures that the A-lines in the centre
section of the canopy will tension before the ones at the wing tips. Thus the canopy
inflates evenly and an easy launch in the desired d irection is guaranteed.
All lines and risers should be carefully untangled an d arranged in such a way that they
do not catch on anything.
It is equally important to untangle the brake lines so that they are clear and can not
catch on any thing during launch. T he brake lines should run freely through the pulleys
to the trailing edge of the canopy.
Make sure the risers are not twisted; this can prevent the brake lines from running freel y
through their pulleys.
It can often be impossible to untangle lines during flight.
It is important that no lines are looped around the canopy. Also called a “line-over”, this
may have disastrous consequences during take off. Finally connect the risers to the
spreader-bar using the main karabiners. Check carefully that they are closed properl y.
Launch
The Pasha 4 is very easy to launch. This is possible in almo st all wind conditions e xcept
strong headwinds. The trimmers should be adjusted between closed and neutral
position according to the wind an d terrain. Generally we recommend the use of both Arisers (A and A1) for take off. Depending on the launch technique, and wind conditions
the pilot can alternatively use onl y middle A-rirers to inflate the canopy. Before take off
recheck the canopy, the direction of the wind and the air s pace around you! When the
pilot is ready to take off he/she holds all A-risers and the brake handles in each hand.
To facilitate differentiation between the risers, the A-lines, including the sleeves on the
A-risers, are coloured red. Before take-off, place yourself centrally at the gliders axis.
Let the B-, C- and D-risers fall into the crook of your arm and hold the A risers with arms
outstretched behind you. For the Pasha 4 we recommend take off from slightly
tensioned lines. The Pasha 4 is easy to l aunch. If the pilot allows too muc h slack in the
lines to the canopy the glider can get too much energy during inflation a nd the canopy
can overfly the pilot, and this may lead to a collapse. A good progressive run ensures
your Pasha 4 will inflate and come up equally and quickly. Should the canopy surge
forward, control it by braking. Now do a visual check upwards, to ensure the canopy is
completely open (otherwise, abort the take-off). Only then is the final decision to
continue the launch taken! If anything is not completely safe the launch should be
aborted! Now accelerate continuously until you lift off. It is easier to take-off in a light
headwind if after reaching minimum fl ying speed yo u apply the brakes sli ghtly. After the
take-off, gently release the brakes again.
The most important thing is the constancy of the pu ll on the A risers and n ot the power.
Since the Pasha 4 is very easy to launch, on steep take-offs or in stronger

14
(&(
winds do not forget to brake properly to contr ol the moveme nt of the canop y. As alread y
mentioned, this can be corrected by the right position of the trims.
WARNING!! Do not use the forward launch in very strong winds. Make s ure you don't
pull the risers too much towards yourself or downwards as this can result in a frontal
collapse, or in an asymmetric take-off
The Pasha 4 is easy to reverse launch. When doing a rev er s e launch or when launching
in strong winds the paraglider can possibl y surge forward more quickly or lift off sooner
than desired. To avoid this, walk uphill following the canopy during inflation. As this
launch technique can be difficult and turning the wrong way can res ult in the pilot taking
off with twisted risers. It is recommended to practice the reverse launch on a training hill
or slight slope first. When deflating the canopy in strong winds, or abortin g a launch, use
the C- or D- risers, not the brakes. Using the brakes in strong wind will cause more lift,
lifting the pilot up and dragging him/her much further back.
If you let go of the brake handles during take-off, take care that the brake line is not
twisted around the brake pulley!
Flight
The glider is delivered with a standard set-up and its speed can reach 36 - 44 km/h
depending on the weight of the pilot and trims position. Always fly with sufficient
clearance from the terrain. The Pasha 4 glides best with open brakes, descends best
with lightly applied brakes. In turbulence fly with brakes lightly applied (15-20 cm) to
avoid canopy collapse. If the canopy pendulums forward, this should be corrected by
prompt braking. A pendulum movement of the canopy backwards is corrected by
loosening the brakes in good time.
In a calm air the Pasha 4 can reach its minimum speed (depending on the wing loading)
by application of 70cm up to 75cm of the brake range.
Faster Flying:
The angle of attack is changed by the trimmers. T he speed difference bet ween "closed"
and "open" position of the trimmers is up to 4-5 km/h. The glider is less stable at higher
speed and collapses easily. Never let go of the brake handles during fast-fl ying!
Steering - turns:
The Pasha 4 is a very responsive paragl ider and re acts very dir ectly and i nstantly to any
steering input. Weight shift input quickens turns and ensures minimal height loss. Any
weight shift has a greater effect the more loosely the chest-strap is fastened. A
combined technique of weight shift and pulling on the inside brake line is the most
efficient turning method, whereby the radius of the turn is determined by the amount of
inside brake pulled and weight shift. A stalling wing tip announces itself by a gentle
surge backwards of the wingtip. If this occurs you will need to release the brakes
immediately.

15
(&(
In case it is impossible to control the Pas ha 4 with the brake lines the D-ri sers may be
used to steer and land the canopy. Attention! Pulling brake too fast or too hard can
result in the canopy entering a negative spin.
Active Flying (Thermaling and Soaring):
In turbulent conditions the glider should be flown actively with brakes lightly applied to
avoid canopy collapse. This im proves stability by increasing the angle of attack of the
canopy. The canopy should not rock back or surge forward much but should remain
above the pilot. In turbulent flight, if the canopy pendulums forward, this should be
corrected by prompt braking. A pendulum movement of the canopy backwards is
corrected by releasing the brakes in good time. This is part of basic active flying.
Approach and Landing:
To avoid excessively demanding situ ations on the appr oach to landing, it is importa nt to
initiate the process at an adequate altitude. This leaves you eno ugh time to observe and
appropriately deal with wind direction and any other aircraft in your vicinity.
The Pasha 4 is easy to land. The final leg of the landing approach must be into the
wind. During this final glide the paraglider should be decelerated slowly and at
approximately one meter above the ground, according to conditions, the pilot should
flare the canopy. The glider may climb again, gaining h eight, if too much brake is used
too early. Strong wind landings require correspondingly less brake. Do not apply full
brake before the pilot is safely on the ground. The final glide during the landing
approach should be straight and not marked by steep or alternating turns as these can
result in a dangerous pendulum effect near the ground.
Attention! Do not allow the canopy to fall onto the leading edge with energ y. This can
destroy the material and affects the life of the ribs at the leading edge!
TOWING
The Pasha 4 is certified for towing. The Pasha 4 has no out of the ordinary towing
characteristics, although a relatively low angle of attack and thus lo w tow tensi on shoul d
be maintained during launch and the initial part of the tow. The Pasha 4 has no
tendencies towards deep stall/parachuting. Therefore we allow tow- launched flights
with a similar technique to that described above. There is sufficient margin to countersteer the glider in a normal towing situation. Make sure you use proper equipment,
experienced personnel and all relevant safety precautions for towing. We
recommending the use of a winching adapter: this should be mounted on the upper e nd
of the main karabiner.
WARNING!! Please always ensure that the brake lines are adjusted to the lengths
recommended here. Setting them shorter could lead to a tendenc y to stall during towed
flight. Apart from this, there are no special procedures.
16
MOTORISED FLIGHT
Note!! Although, motorized flight can be a great success due to the gliders very easy
take-off characteristics, stability and good handling, al ways use a certified combination
of engine - harness and glider. If in doubt check with your federation. Contact the
manufacturer or importer for the current legality of motorized flight.
WARNING!! The Pasha 4 is not suitable for jumps from aircraft.
WARNING!! The Pasha 4 is not designed to be used for aerobatics.
EXTREME FLYING MANOEUVRES
This section describes flying conditions whic h can be deliberatel y induced, or which can
develop unintentionally due to turbulence or pilot error. Any pilot who flies through
turbulence is sure to be faced with these special flight co nditions at some point. So take
a good look at these flight manoeuvres or prepare for them by SIV (safet y training over
water). Mastering these flying conditions sig nificantly improves your active flight safet y.
Sufficient height, as well as carrying a reserve parachute, is imperativ e.
WARNING!! All the critical flight conditions described here require a thorough
knowledge; otherwise carrying them out may be very dangerous. Sufficient height above
the ground is imperative. Bear in m ind that all deformations of the canop y can increase
the sink rate by 2 - 10 m/sec, depending on the degree of deformation. Carrying out
these manoeuvres wrongly may lead to a crash.
Remember this is a glider with unspectacular reactions to disturbances in the air.
Whenever in doubt, raise the brakes and l et the glider fly. The glider has a high i nternal
pressure, resistance to tucking and very high degree of passive safety. It is
recommended that at this stage you alrea dy practise an active flying style. The ke y to
active piloting is keeping the glider above your head at all times. We recommend in
principle that you hold the brak e handle in your hand whenev er possible, or fly with your
hands through the brake handles, to allow you to react immediately to any possible
disturbances.
WARNING!! If you fly with your ha nds through the brake handles, you may lose valuable
time in activating the rescue system.
Asymmetric collapse:
A negative angle of attack can cause all or par t of the leading-edge of the Pasha 4 to
collapse (e.g. in turbulent air). Basically the Pasha 4 will re-open spontaneously from
closures of up to 70% with a change of direction of up to 180°. The time this takes, and
the associated height loss, can however be noticeably re duced by appropr iate action by
the pilot. Apply opposite br ake on the inflat ed side, the outside of the curv e, to stop the
turning movement of the canopy. This should be accompanied by appropriate weightshift. If you react immediately, 30% brake on the open side should suffice to hold the
canopy on a straight course. In the event of a big collapse, this braking should be
applied very carefully to avoid stalling the remaini ng inflated wing. The pilot's correction
for direction can be aided by a pumpin g out the deflatio n; a slow, long pumping action of
the brake of the deflated side of the wing helps the

17
(&(
canopy to re-inflate. If the pilot does not correct, the Pasha 4 usually self-recovers.
However, if it does not self recover and the pilot does not correct the canopy can enter a
stable spiral dive.
“Cravat” / Line-over:
In the event of some lines becoming tangled during flight (whatever the cause), the
following action is recommended:
The pilot stabilizes the glider b y gently appl ying the brakes. Ple ase be a ware that in this
condition the brake pressure can be higher and the brake travel shorter.
Without pilot input a line-over will result in a stable spiral dive.
Here are the various options to untangle a line-over:
- pumping the collapsed side.
- pulling the stabilizer line or lines causing the problem.
- should both measures fail, it may be possible to unta ngle the line-over by inducing a
full stall. This manoeuvre, however, should only be carried out b y advanced pilots with
experience in extreme flight situations and with sufficient altitude available.
Attention! If these manoeuvres fail or if in any doubt, the pilot shoul d instantly use their
emergency parachute system!
Front Tuck:
A front tuck can be induced by strongly pulling the A-risers or by sudden, heavy
turbulence. The entire leading edge spontaneously collapses. Gentle braking on both
sides will reduce the lateral pendulum motions and simultaneously accelerate reinflation. The Pasha 4 generally self recovers from an initiated front tuck.
When having a very large front tuck, a frontal rosette can happen (the wingtips move
forwards: shaping a horseshoe). Gentle braking can avoid this deformation.
A quick recognition of the situation and a quick reaction by braking on both sides as
long as the collapsed wing is beh ind the pilot helps the recovery and limit s the altitude
loss.

18
(&(
Parachutal stall (deep stall):
In a parachutal stall the paraglider has no forward momentum combined with a high
descent rate. A parachutal stall can be caused by, among other reas ons, a too slow exit
from a B-line stall or severe turbulence. Porous can opies (UV influ ence) or canopies out
of trim (stretched or shrunken lines) are muc h mor e susc eptible to a parac hutal stall a nd
therefore should not be flown. These are some of the reasons regular checks should be
carried out on your glider.
A wet canopy or temperatures below zero centigrade (0°C) may also cause a stable
parachutal stall. The Pasha 4 will usually spontaneousl y recover from a parachutal stall
within 2-3 seconds. If the canopy remains in a parac hutal stall, it is sufficient to gently
push both A risers forward or to push the accelerator.
Attention! If brakes are applied while in a parachutal stall, the glider may sudd enly enter
a full stall!
If a parachutal stall occurs on landing approach, the pilot should prepare for a hard
landing and make a parachute roll land ing. In close proximity to the ground, due to the
forward surging pendulum effect, a recovery may be more dangerous than a hard
landing in parachutal stall.
Full-stall:
To induce a full stall, apply ful l brake on both sides. The glid er slows down steadil y until
it stalls completely. The canopy suddenly surges backwards a long way. In spite of this
uncomfortable reaction of the canopy, both brake lines must be consequently held do wn
with all your strength until the canopy is stabi lized ( directl y o verhe ad). T his usua lly takes
3-6 seconds. The Pasha 4 generally flies backwards during a full stall but doesn't
always form a front rosette. A frontal rosette can be formed by entering the full stall
slowly. When entering (braking) fast, the canop y will not always form the desired front
rosette. Attention! Always apply both brakes evenly!
To recover from a full stall, Smoothly release both brakes simultaneous ly until 90% of
leading edge reopens, then release brakes rapi dly. The glider ends the full stall on its
own without surging forward.
WARNING!! If the brakes are rele ased rapidly and asymme trically, the glider ma y surge
almost 90° and suffer an extensive asymmetric collapse.
The danger of overcorrecting and overreacting exists during all extreme flight
manoeuvres. Thus, any corrective action must be gentle and steady and done with feel!

19
(&(
Spin (or negative spin):
Pulling brake on one side too fast or too hard can result in a negative spin. During a spin
the canopy turns relatively fast around the centre section of the canopy while the inner
wing flies backwards (hence the term negative).
There are two usual reasons for an unintentional spin:
• One brake line is being pulled down too far and too fast (e.g. when inducing a spiral
dive)
• When flying at low speed one side is being braked too hard (e.g. when thermaling).
To recover from an unintentional spin, the pulle d down brake line should be immediately
released as soon as a spin is suspected. The canopy will accelerate and return to its
normal straight and stable flying position, without losing too much height. If the spin is
allowed to develop for some time, the glider surges a long way for ward on one side and
a dynamic asymmetric collapse or a line-over can occur. Gently apply the brakes to
avoid side or central collapse of the c anopy and the possibility of a cravat (one of the
tips becoming entangled in the lines).
WARNING!! If you are LOW and are in an unintentional spin, or if the canopy is c aught
in a cravat USE YOUR RESERVE.
Wingover:
To induce a wingover the pilot flies consecutive alternating turns to gradually steepen
the angle of bank. During wingovers with a high bank angle, the outsid e wing begins to
unload. Further increase of the angle of bank must be avoided, because any poss ible
resulting collapse may be quite dynamic!
WARNING! Full-stall, spin and wingover (over 90 degree angle of bank) are
prohibited aerobatic manoeuvres and may not be performed during normal flying.
Incorrect recovery procedures or overreacting of the pilot may have dangerous
consequences! Attention! The Pasha 4 is not designed to be used for aerobatics.
Alternative (emergency) steering:
If for some reason it becomes impossible to control t he Pasha 4 with the brake l ines the
D-risers may be used to steer and land the canopy. Attention! Of course the range is
much shorter (10-15 cm) then with the brakes. It is also possible to control the direction
of the flight by pulling on a stabilizer line or by weight-shifting.

20
RAPID DESCENTS
Spiral dive:
A spiral dive is the fastest way to lose altitude, however, the very hi gh G-forces make it
difficult to sustain a spiral dive for long and it can place high loads on the pilot and
glider. By tensing ones abdominal muscl es and a higher body tensio n you can to some
extent resist the high G-forces. Don't forget proper breathing! As soon as any, even
slight, light dizziness or impaired vision is noticed the spiral should be exited
immediately.
The Pasha 4 has a very effective spiral dive. This allows rapid descent without stalling.
To enter a spiral dive the pilot should weight-shift on one side while slo wly pulling the
brake gradually on the same side as weight-shifting. During a spiral dive the angle of
bank can be controlled by increasing or reducing the amount of inside brake. When
spiral diving the Pasha 4 it is recommended that the outside brake is lightly applied. This
helps stabilize the wing and enables an easier and safer exit from the spiral. To exit,
release the inside brake slowly. The Pasha 4 did not show a tendency to remain in a
stable spiral during testing. At high sink s peeds or if the pilot keeps his weight on the
inside, the wing can stay in a continued deep spir al and ha s to be activ ely exited. This is
done by weight shifting to the outside and gentler braking of the outside wing.
WARNING!! Nearly all gliders will have a tend ency to stay in the spiral if the sink-rate
exceeds around 15-m/s, depending on weight -shifting, wing loading and G-force. In fact
most gliders need a counter-input to end a turn.
Attention! Due to energy retention, the glider will climb a lot after a deep spiral-dive
release. If you apply inner brake and decelerate the glider for two or three turns, big
pendulum effects can be avoided.
WARNING!! Practise spiralling with caution and lower sink-rates to get a feel for the
gliders behaviour. A pilot who is dehydrated or not accustomed to spiralling can lose
consciousness in a steep spiral dive!
Big ears:
When in big-ears, the horizontal speed is higher than the sink rate, unlike a spiral dive
or a B-line stall. This rapid descent techni que is used to quickly and horizontally exit a
dangerous area in the desired direction. In order to collapse the outside wing, pull the
outside A-lines.
When the pilot holds the outside A1-risers on both sides and pulls them down, the
Pasha 4 easily tucks the outside wings and enters a stable descent mode. The pilot
keeps hold of the brake handles along with the outside A1-risers in his hands. By
braking on one side and weight-shifting, the canopy remain s steerable.
Big-ears substantially reduces the risk of canopy stability problems in turbu lent air. To
exit Big-ears release the A1-risers. The canopy does slowly self-recover. If not, or to
quicken the recovery, the pilot can gently apply brakes to the glider.
WARNING! Never do big-ears in spirals, as this may drastically reduce the number of
lines taking the already high loads, causing structural failure.

21
(&(
Attention! All rapid descent techniques should first be practised in calm air and with
sufficient height so the pilot can use them in emergency situations! By far the best
technique is to fly correctly and safely, so you never have to descend rapidly!
B-line stalls:
WARNING: Although it is possible to induce a B-sta ll with the Pasha 4, we recommen d
avoiding this manoeuvre, as very high loads occur on the ribs. Thus shortening the life
of the canopy!
To induce a B-line stall symmetrically pu ll down slo wly on both B-risers, u ntil the ca nopy
folds (parallel to its long axis). The airflo w over the top surface is almost fully detached
and the canopy enters a vertical descent flight mode without forward movement. Further
pulling of the B-risers reduces the surface area m ore and i ncreases the sink rate. (Up to
8 m/s) Be careful, pulling too far or too rapidly may cause a frontal horseshoe to form.
To exit from this flight mode release the B-risers at first rapidly but then gently (1 sec).
The canopy surges forward re-attaching the airflow over the top surface and resumes
normal flight. When the B-risers are released, the brakes shou ld not be activated. This
will give the canopy the chan ce to gain speed and res ume normal flight. On exit from a
B-line stall on no account just release the B-risers, as this can cause overloading. If
canopy does not recover apply both brakes gently to recover or pull the A-risers, until
the canopy regains forward speed.
Summary:
For all extreme manoeuvres and rapid descents please note:
• first practise manoeuvres with an instructor during safety training!
• before inducing any manoeuvre the pilot must check that there are no other
airspace users below him!
• during the manoeuvre the pilot must have the canopy within his view!
LOOKING AFTER YOUR PARAGLIDER
Looking after your canopy correctly will prolong the life of your paraglider.
Deterioration: a few tips!
• The canopy is mainly made of NYLON, cloth which, like any synthetic material,
deteriorates through excessive exposure to UV. Hence, it is recommended that you
reduce UV exposure to a minimum by keeping the paraglider packed away when
not in use. Even when packed in the bag do not leave it in the sun.
• Keep the canopy and lines clean as dirt may penetrate into the fibre and damage
the lines or the cloth.
• Ensure that the lines are not folded tightly. It's extremely important to avoid any
sharp bending of the lines, especially the main lines. Pay careful attention to the
lines to avoid damaging them. Any over stretching of lines apart from the strain
imposed during normal flight, should be av oided as over stretching is irreversible.

22
(&(
• Be careful, not to allow snow, sand or stones to enter inside the canopy's cells: the
weight can change the angle of attack, or even stall the glider; additionally the
sharp edges can destroy the cloth!
• Check line lengths after tree or water landings. They can stretch or shrink lines.
• Never drag the wing over rough ground! This will damage the cloth on the wear
points. When preparing the wing on a takeoff with rough gr ound, don't pull the wing
over it (i.e. by pulling the brakes). Please try to pack the wing on soft ground.
• Uncontrolled strong wind takeoffs or landing s can result in the leading edge of the
canopy hitting the ground at high speed which may cause rips in the profile and
damage the rib material.
• Clean the paraglider with fresh water after contact with salt water. Salt water crystal
can reduce line strength, even after rinsing in fresh water. Replace lines
immediately after contact with salt water. Also check canopy material after water
landings, as waves can place unev en forces and cause cloth to distort in specific
areas. Always remove gliders from the water by holding only the trailing edge.
• Prevent lines from catching on anything as they may be ove r stretched. Do not step
onto the lines. Although the lines were tested with a bending test they can be
damaged if stepped on whilst on a hard surf ace, or if they come into contact with
sharp objects.
• Do not always fold the canopy symmetrically to the centre cell as this can cause
constant stress on the centre cell (centre cell always to the outside).
• Clean the paraglider with water and a soft sponge. Do not use any chemicals or
spirits for cleaning, as these can permanently damage the cloth.
Storage:
• Store the paraglider in a dry space at ambient temperature away from chemicals
and UV light.
• Never pack or store the glider wet. This shortens the life of the cloth Always dry
glider thoroughly before any packing or storage.
• During transport it has to be considered, that some materials of the paraglider are
temperature sensitive. Avoid subjecting your wing to high temperatures (e.g. the
luggage space of a parked car in the sun)!
When sending your wing as a parcel, take extr a care with packing.
Repairs and checks:
• Tears in the canopy must be professionally sewn. Adhesive patches are only
adequate for very minor damage.
• Repairs should only be carried out by the manufacturer, distributor or authorized
workshops. Only original spare parts may be used!
• The lines m ust be checked after every 50 hours flying time and whenev er the flight
behaviour changes

23
(&(
• Any changes to the canopy lines or risers, except those approved by the
manufacturer, will void the certificate of airworthiness.
• The Pasha 4 must be checked as a minimum, after two years or after 100 flying
hours by the manufacturer or authorized workshops.
Disposal:
• The synthetic materials used in a paraglider need professional disposal. Please
send disused canopies back to us: we will dismantle and dispose of it.
In Conclusion:
The Pasha 4 is a modern paraglider. Yo u will enjoy many safe years of flying with your
Pasha 4 if you look after it correctly and a dopt a mature and responsible approach to
the demands and dangers flying can pose.
It must be clearly understood that all air spor ts are potentially dangerous and that your
safety is ultimately dependent upon you. We strongly urge you to fly safely. This
includes your choice of flying conditions as well as safety margins during flying
manoeuvres. We recommend once more that you only fly with a certified harness,
reserve parachute, and helmet. Also the certification placard must be present on the
glider. Every pilot should be suitably qualified, have a valid license and 3rd party
insurance.
The Pasha 4 is delivered with a stuff-sack, Velcro compression strap, MAC PARA
backpack, repair kit and user manual.

24
TREATING NATURE WITH RESPECT
Finally the call to practise our sport with respect for nature and wildlife! Don't walk
outside marked routes, don't leave any waste, don't make needless noise and respect
the sensitive biological balance in the mountain eco system: especially in the takeoff
area!
LINE PLANS
Line descriptions:
The following printed line plans show the line configurations and line lengths.

25
Line plan Pasha 4 -39

26
Line plan Pasha 4 - 42

27
FULL LINE LENGTHS
Full line lengths Pasha 4-42
All lengths are measured from the loop of the main line up to the attachment point
on the canopy. Brake lines are measured from the main brake line up to the
trailing edge.
Center A B C D
E Brakes
1 8708 8579 8661 8849 9029 9905
2 8621 8490 8572 8761 8925 9560
3 8626 8501 8583 8767 8919 9340
4 8614 8492 8572 8756 8905 9290
5 8494 8381 8456 8642 8775 9135
6 8462 8358 8432 8614 8729 8895
7 8510 8414 8484 8650 8746 8790
8 8488 8395 8447 8605 8711 8820
9 8345 8260 8306 8428 8528 8760
10 8248 8170 8208 8310 8675
11 8209 8133 8166 8243 8595
12 8185 8113 8138 8179 8430
13 8126 8051 8053 8067 8400
14 8101 8027 7993 8029 8375
15 7770 7670 8375
16 7557 7528 7537 7574 8325
8355
8390

28
MANUAL FOR PARAGLIDER CHECKS
Check-intervals
All paragliders used in flight must be checked at least every 24 months. For paragliders
used by paragliding schools the period is 12 months.
Personnel authorised to carry out checks
A valid flying license and training course by National association are the basis for
permission to carry out paraglider checks
Identification of glider
An identity sticker with details of certification and serial number is attached to the glider.
Components of the check
Porosity
The porosity should be checked with a porosity meter (JDC). Compare the resultant
data with the producer's manual.
Porosity measures should be taken on at least three point s of both the top and bottom
surface. The first point should be placed 20-30 cm from leading edge in the middle of
canopy. Second and third points are placed left and right from first measure point at
25% of the span. One additional measurement should be made on the top surface of
the wing tip.
The identified time should be higher than 30 second (JDC). In the event of the result
being less than 30 seconds, the result of the check is a fail.
Overall strength check
The check of canopy strength should be made with a Bettsometer (B.M.A.A approved
Patent No. GB 2270768 Clive Betts Sales). On the top and bottom surfaces make small
holes with a needle at the Aline attachment points. The exact verification should be
made in accordance with the Bettsometer user manual.
Line strength check
Line strengths should be as specified in accordance with the certification requirements.
One main line should be taken from each array and have its strength checked with a
tension-meter.
Required strengths should be higher than:
• A + B main lines x measur ed value > 8 x maximum take-off weight and higher
then 800 kg for the A + B arrays.
• C + D mean lines x measured value > 6 x maximum take-off weight and higher
then 600 kg for the A + B arrays.
Replacements for damaged lines must be with ne w original lines. Lin e lengt hs are taken
from the lines data page.

29
(&(
Line length measurement
Lines should be separated and each line measured under a tension of 5 kg.
Measurement is made from the line karabiner to the canopy accordin g to the method of
certification. Rib numbering begins in the middle of canopy and leads to the wing tip.
Measured full lengths should be documente d in the ins pection rec ord and are compared
with certified full line lengths protocol. Lengths sh ould not differ by more than 20 mm.
The opposite sides should be checked for symmetry.
Canopy line-attachment points check
Attachment points should be checked for damage and stretching. Defects, loops and
flares should be repaired.
Canopy fabric check
Ribs, diagonal ribs, top and bottom surface should be checked. Any damage to sewing
or tears to the fabric, which could influence flying characteristics must be repaired.
Lines
All lines should be checked for tears, breaks any damage to the sheath or signs of wear.
Special attention should be paid to the se wing of the li ne loops. Dama ged lines must be
replaced.
The results should be documented in the inspection record.
Connector check
All line carabineers, trimmers (if used), speed systems and pulleys shoul d be inspected
for visible damage. Open or improperly secured connectors should be secured in
accordance with the producers recommendations.
Risers
Both risers should be checked for tears, signs of wear or any damage and measured
with a pull of 5 daN strength. Measured dat a should be documented in the inspection
record. The difference must not be higher then 5 mm when compared to specified
lengths.
Final check
The glider sticker and check sticker must be inspected f or readability and correctness.
The check must be documented with date, signature and stamp on the canopy and in
the user manual.

30
CHECKS
Name Company Date Signature & Stamp

31
TEST FLIGHT CERTIFICATE
Paraglider type:
PASHA 4 – 42
Serial number: ________________________________
Test flown on: ________________________________
by
MAC PARA TECHNOLOGY
________________________________
Confirmation by dealer: ________________________________
Technical data
Biplace
Pasha 4 Pasha 4
Size 39 42
Zoom flat [%] 96 100
Area flat
[m
2
]
39,31 42,65
Area projected
[m
2
]
35,46 38,48
Span flat [m] 14,56 15,17
Span projected [m] 12,31 12,82
Aspect ratio flat - 5,4 5,4
Root cord [m] 3,35 3,49
Cells - 54 54
Weight [kg] 8,6 9,0
Weight range [kg] 125-190 145-220
Min.speed [km/h] 22-24 22-24
Speed Trimmers closed [km/h] 36-38 36-38
Speed Trimmers open [km/h] 42-45 42- 4 5
Top speed (accelerator) [km/h] - Glide ratio - 8,6 8,6
Min. Sink rate [m/s] 1,1 1,1
Cetification with trimmers - EN EN - B

32
 Loading...
Loading...