
LXLS11002
2-LAYER SWITCHER A ND SCALER
USER MANUAL
LXLS11002
V. 01 – 16/02/2016 2 ©Velleman nv
To all residents of the European Union
Important environmental information about this product
This symbol on the device or the package indicates that disposal of the device after its lifecycle could
harm the environment. Do not dispose of the unit (or batteries) as unsorted municipal waste; it
should be taken to a specialized company for recycling. This device should be returned to your
distributor or to a local recycling service. Respect the local environmental rules.
If in doubt, contact your local waste disposal authorities.
Thank you for choosing Luxibel®! Please read the manual thoroughly before bringing this device into service. If
the device was damaged in transit, don't install or use it and contact your dealer.
Use this device with original accessories only. Velleman nv cannot be held responsible in the event
of damage or injury resulting from (incorrect) use of this device. For more info concerning this
product and the latest version of this manual, please visit our website www.luxibel.com. The
information in this manual is subject to change without prior notice.
© COPYRIGHT NOTICE
The copyright to this manual is owned by Velleman nv. All worldwide rights reserved. No part of this
manual may be copied, reproduced, translated or reduced to any electronic medium or otherwise without the
prior written consent of the copyright holder.

Operators Safety
Summary
The general safety information in this summary is for operating personnel.
Do Not Remove Covers or Panels
There are no user-serviceable parts within the unit. Removal of the top cover will
expose dangerous voltages. To avoid personal injury, do not remove the top
cover. Do not operate the unit without the cover installed.
Power Source
This product is intended to operate from a power source that will not apply more
than 230 volts rms between the supply conductors or between both supply
conductor and ground. A protective ground connection by way of grounding
conductor in the power cord is essential for safe operation.
Grounding the Product
This product is grounded through the grounding conductor of the power cord. To
avoid electrical shock, plug the power cord into a properly wired receptacle before
connecting to the product input or output terminals. A protective-ground
connection by way of the grounding conductor in the power cord is essential for
safe operation.
Use the Proper Power Cord
Use only the power cord and connector specified for your product. Use only a
power cord that is in good condition. Refer cord and connector changes to
qualified service personnel.
Use the Proper Fuse
To avoid fire hazard, use only the fuse having identical type, voltage rating, and
current rating characteristics. Refer fuse replacement to qualified service
personnel.
Do Not Operate in Explosive Atmospheres
To avoid explosion, do not operate this product in an explosive atmosphere.
Terms in This Manual and Equipment
Marking
WARNING
Highlights an operating procedure, practice, condition, statement, etc,
which, if not strictly observed, could result in injury or death of
personnel.
Note
Highlights an essential operating procedure,
condition or statement.
CAUTION
The exclamation point within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert
the user to the presence of important operating and maintenance
(servicing) instructions in the literature accompanying the appliance.
Change History
The table below lists the changes to the Video Processor User Manual.
Format Time
ECO# Description
Principal
V1.0
2015-05-18
0000#
Release
Vira
V1.1
2015-08-06
0001#
1. Update the front and back
panel.
2. Update the menu tree.
3. Update the windows control
program.
4. Update the common questions
and solutions.
Vira

1. Introduction
This chapter is designed to introduce you to the VENUS X1 User Manual. Areas to
be covered are:
Chapter Structure
How to Use This Manual
Terms and Definitions
System Overview
Application Questions

1. Introduction
Chapter Structure
Chapter Structure
The following chapters provide instructions for all aspects of VENUS X1
operations.
Chapter 1 Introduction
Chapter 2 Hardware Orientation
Chapter 3 Hardware Installation
Chapter 4 Menu Orientation
Chapter 5 Communication Software Guideline
Chapter 6 System Setup and Operations
Chapter 7 Common Questions and Solutions
Appendix A Specification
Appendix B Contact Information
Appendix C Software Upgrade
Appendix D Optional Module Installation and Replacement
Instruction

1. Introduction
How to Use This Manual
How to Use This
Manual
Following are important tips for streamlining your use of this User Manual in
its electronic ―PDF‖ form.
Navigating
Use Acrobat Reader’s ―bookmarks‖ to navigate to the desired location.
All chapter files have the same bookmark structure for instant navigation
to any section. Please note:
Extensive hyperlinks are provided within the chapters.
Use Acrobat’s
―
Go to Previous
View‖ and ―Return to next View
‖
buttons to trace your complete navigational path.
Use the ―Previous
Page‖ and ―Next
Page‖ buttons to go to the previous
or next page within a file.
Use Acrobat’s extensive search capabilities, such as the ―Find‖ tool
and ―Search
Index‖ tool to perform comprehensive searches as required.
Table of Contents and Index
Use the Table of Contents bookmarks to navigate a desired topic.
Click any item to instantly jump to that section of the guide. You
can also use the Index to jump to specific topics within a chapter.
Each page number in the Index is a hyperlink.
General Operations
To ensure trouble-free operation, please follow all procedures as listed
below:
For detailed installation instructions, refer to chapter 3 ―Hardware
Installation‖ on page 39.
For communication software control guide, refer to Chapter 5,
―
Communication Software Control Guide‖ on page 64.
For system setup and operations, refer to Chapter 6, ―System Setup
and Operations‖ on page 92.
Should you have any questions regarding the installation or operation of
VENUS X1, please consult with the factory. Refer to Appendix B, ―Contact
information‖ on page 127.

1. Introduction
Terms and Definitions
Terms and Definitions
The following terms and definitions are used throughout this guide.
“ASCII”: American Standard for Information Interchange. The standard
code consisting of 7-bit coded characters (8 bits including parity check)
used to exchange information between data processing systems, data
communication systems, and associated equipment. The ASCII set
contains control characters and graphic characters.
“Aspect ratio”: The relationship of the horizontal dimension to the
vertical dimension of an image. In viewing screens, standard TV is 4:3,
or 1.33:1; HDTV is 16:9, or 1.78:1. Sometimes the ―:1‖ is implicit,
making TV = 1.33 and HDTV = 1.78.
“AV”: Audio visual, or audio video.
A “Background” is an unscaled source, typically originating from a
computer. A background source appears at the system’s lowest priority
— visually in back of all other sources.
“Baudrate”:Named of J.M.E. Baudot, the inventor of the Baudot
telegraph code. The number of the electrical oscillations per second,
called baud rate. Related to, but not the same as, transfer rate in bits
per second (bps).
“Blackburst”: The video waveform without the video elements. It
includes the vertical sync, horizontal sync, and the chroma burst
information. Blackburst is used to synchronize video equipment to
align the video output. One signal is normally used to set up an entire
video system or facility. Sometimes it is called House sync.
“BNC”: Bayonet Neill-Concelman. A cable connector used extensively
in television and named for its inventors. A cylindrical bayonet
connector that operates with a twist-locking motion. To make the
connection, align the tw o curved grooves in the collar of the male
connector with the two projections on the outside of the female collar,
push, and twist. This allows the connector to lock into place without
tools.
“Brightness”: Usually refers to the amount or intensity of video light
produced on a screen without regard to color. Sometimes called ―black
level.
―CAT
5‖:
Category 5. Describes the network cabling standard that
consists of four unshielded twisted pairs of copper wire terminated by
RJ-45 connectors. CAT 5 cabling supports data rates up to 100 Mbps.
CAT 5 is based on the EIA/TIA 568 Commercial Building
Telecommunications Wiring Standard.
“Color bars”: A standard test pattern of several basic colors (white,
yellow, cyan, green, magenta, red, blue, and black) as a reference for
system alignment and testing. In NTSC video, the most commonly

1. Introduction
Terms and Definitions
used color bars are the SMPTE standard color bars. In PAL video, the
most commonly used color bars are eight full field bars. In the
computer, the most commonly used color bars are two rows of
reversed color bars.
“Color burst”: In color TV systems, a burst of subcarrier frequency
located on the back porch of the composite video signal. This serves
as a color synchronizing signal to establish a frequency and phase
reference for the chroma signal. Color burst is 3.58 MHz for NTSC and
4.43 MHz for PAL.
“Color temperature”: The color quality, expressed in degrees
Kelvin(K), of a light source. The higher the color temperature, the bluer
the light. The lower the temperature, the redder the light. Benchmark
color temperature for the A/V industry include 5000°K, 6500°K, and
9000°K.
“Contrast ratio”: The radio of the high light output level divided by the
low light output level. In theory, the contrast radio of the television
system should be at least 100:1, if not 300:1. In reality, there are
several limitations. In the CRT, light from adjacent elements
contaminate the area of each element. Room ambient light will
contaminate the light emitted from the CRT. Well-controlled viewing
conditions should yield a practical contrast ratio of 30:1 to 50:1.
“DVI”: Digital Visual Interface. The digital video connectivity standard
that was developed by DDWG (Digital Display Work Group). This
connection standard offers two different connectors: one with 24 pins
that handles digital video signals only, and one with 29 pins that
handles both digital and analog video.
“EDID”: Extended Display Identification Data – EDID is a data structure
used to communicate video display information, including native
resolution and vertical interval refresh rate requirements, to a source
device. The source device will then output the optimal video format for
the display based on the provided EDID data, ensuring proper video
image quality. This communication takes place over the DDC – Display
Data Channel.
“Ethernet”: A Local Area Network (LAN) standard officially known as
IEEE 802.3. Ethernet and other LAN technologies are used for
interconnecting computers, printers, workstations, terminals, servers,
etc. within the same building or campus. Ethernet operates over
twisted pair and over coaxial cable at speeds starting at 10Mbps. For
LAN interconnectivity, Ethernet is physical link and data link protocol
reflecting the two lowest layers of the OSI Reference Model.
“Frame”: In interlaced video, a frame is one complete image. A video
frame is made up of two fields, or two sets of interlaced lines. In a film,
a frame is one still image of a series that makes up a motion image.

1. Introduction
Terms and Definitions
“Gamma”: The light output of a CRT is not linear with respect to the
voltage input. The difference between what you should have and what
is actually output is known as gamma.
“HDMI” - High – Definition Multimedia Interface: An interface used
primarily in consumer electronics for the transmission of
uncompressed high definition video, up to 8 channels of audio, and
control signals, over a single cable. HDMI is the de facto standard for
HDTV displays, Blu-ray Disc players, and other HDTV electronics.
Introduced in 2003, the HDMI specification has gone through several
revisions.
“HDSDI”: The high-definition version of SDI specified in SMPTE-292M.
This signal standard transmits audio and video with 10 bit depth and
4:2:2 color quantization over a single coaxial cable with a data rate of
1.485 Gbit/second. Multiple video resolutions exists including
progressive 1280x720 and interlaced 1920x1080 resolution. Up to 32
audio signals are carried in the ancillary data.
“JPEG” (Joint photographic Expects Group): Commonly used
method of lossy compression for photographic images using a discreet
cosine transfer function. The degree of compression can be adjusted,
allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality.
JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in
image quality. Produces blocking artifacts.
“MPEG”: Motion image Expect Group. A standard committee under the
auspices of the International Standards Organization working on
algorithm standards that allow digital compression, storage and
transmission of moving image information such as motion video,
CD-quality audio, and control data at CD-ROM bandwidth. The MPEG
algorithm provides inter-frame compression of video images and can
have an effective compression rate of 100:1 to 200:1.
“NTSC”: The color video standard used in North America and some
other parts of the world created by the National Television Standards
Committee in the 1950s. A color signal must be compatible with
black-and-white TV sets. NTSC utilizes an interlaced video signals,
525 lines of resolution with a refresh rate of 60 fields per second (60
Hz). Each frame is comprised of two fields of 262.5 lines each, running
at an effective rate of 30 frames per second.
“PAL”: Phase Alternate Line. A television standard in which the phase
of the color carrier is alternated from line to line. It takes four full
images (8 fields) for the color-to-horizontal phase relationship to return
to the reference point. This alternation helps cancel out phase errors.
For this reason, the hue control is not needed on a PAL TV set. PAL, in
many transmission forms, is widely used in Western Europe, Australia,
Africa, the Middle East, and Micronesia. PAL uses 625-line, 50-filed

1. Introduction
Terms and Definitions
(25 fps) composite color transmission system.
“Operator”: Refers to the person who uses the system.
“PIP”: image-in-image. A small image within a larger image created by
scaling down one of the images to make it smaller. Each image
requires a separate video source such as a camera, VCR, or computer.
Other forms of PIP displays include image-by-image (PBP) and
image-with-image (PWP), which are commonly used with 16:9 aspect
display devices. PBP and PWP image formats require a separate
scaler for each video window.
“Polarity”: The positive and negative orientation of a signal. Polarity
usually refers to the direction or a level with respect to a reference (e.g.
positive sync polarity means that sync occurs when the signal is going
in the positive direction).
“RJ-45”: Registered Jack-45. A connector similar to a telephone
connector that holds up to eight wires, used for conn ecting Ethernet
devices.
―RS-232”: An Electronic Industries Association (EIA) serial digital
interface standard specifying the characteristics of the communication
path between two devices using either DB-9 or DB-25 connectors.
This standard is used for relatively short-range communication and
does not specify balanced control lines. RS-232 is a serial control
standard with a set number of conductors, data rate, word length, and
type of connector to be used. The standard specifies component
connection standards with regard to the computer interface. It is also
called RS-232-C, which is the third version of the RS-232 standard,
and is functionally identical to the CCITT V.24 stand ard.
“Saturation”: Chroma, chroma gain. The intensity of the color, or the
extent to which a given color in any image is free from white. The less
white in a color, the truer the color or the greater its saturation. On a
display device, the color control adjusts the saturation. Not to be
confused with the brightness, saturation is the amount of pigment in a
color, and not the intensity. Low saturation is like adding white to the
color. For example, a low-saturated red looks pink.
“Scaling”: A conversion of a video or computer graphic signal from a
starting resolution to a new resolution. Scaling from one resolution to
another is typically done to optimize the signal for input to an image
processor, transmission path or to improve its quality when presented
on a particular display.
“SDI”: Serial Digital Interface. The standard based on a 270 Mbps
transfer rate. This is a 10-bit, scrambled, polarity independent interface
with common scrambling for both component ITU-R 601 and
composite digital video and four channels of (embedded) digital audio.
“Seamless Switching”: A feature found on many video switchers. This

1. Introduction
Terms and Definitions
feature causes the switcher to wait until the vertical interval to switch.
This avoid a glitch (temporary scrambling) which normally is seen
when switching between sources.
“SMPTE”: Society of Motion image and Television Engineers. A global
organization, based in the United States, that sets standards for
baseband visual communications. This includes film as well as video
and television standards.
“S-Video”: A composite video signal separated into the luma (―Y‖ is for
luma, or black and white information; brightness) and the chroma (―C
‖
is an abbreviation for chroma, or color information).
“Sync”: Synchronization. In video, sync is a means of controlling the
timing of an event with respect to other events. This is accomplished
with timing pulses to insure that each step in a process occurs at the
correct time. For example, horizontal sync determines exactly when to
begin each horizontal scan line. Vertical sync determines when the
image is to be refreshed to start a new field or frame. There are many
other types of sync in video system.(Also known as ―sync
signal‖
or
―
sync pulse.‖)
“TCP/IP”: Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. The
communication protocol of the Internet. Computers and devices with
direct access to the Internet are provided with a copy of the TCP/IP
program to allow them to send and receive information in an
understandable form.
“USB”: Universal Serial Bus. USB was developed by seven PC and
telecom industry leaders (Compaq, DEC, IBM, Intel, Microsoft, NEC,
and Northern Telecom). The goal was easy plug-and-play expansion
outside the box, requiring no additional circuit cards. Up to 127
external computer devices may be added through a USB hub, which
may be conveniently located in a keyboard or monitor. USB devices
can be attached or detached without removing computer power. The
number of devices being designed for USB continues to grow, from
keyboards, mice, and printers to scanners, digital cameras, and ZIP
drives.
“VESA”: Video Electronics Standards Association. A nonprofit number
organization dedicated to facilitating and promoting personal computer
graphics through improved standards for the benefit of the end-user.
www.vesa.org
“VGA”: Video Graphics Array. Introduced by IBM in 1987, VGA is an
analog signal with TTL level separate horizontal and vertical sync. The
video outputs to a 15-pin HD connector and has a horizontal scan
frequency of 31.5 kHz and vertical frequency of 70 Hz (Mode 1, 2) and
60 Hz (Mode 3). The signal is non-interlaced in modes 1, 2, and 3 and
interlaced when using the 8514/A card (35.5 kHz, 86 Hz) in mode 4. It

1. Introduction
Terms and Definitions
has a pixel by line resolution of
640×480
with a color palette of 16 bits
and 256,000 colors.
“YCrCb”: Used to describe the color space for interlaced component
video.
“YPbPr”: Used to describe the color space for progressive-scan
(non-interlaced) component video.

1. Introduction
System Overview
System Overview
VENUS X1 is a multiple outputs video processor that accepts a wide
variety of video signals, including DVI, VGA, HDMI. CVBS, SDI
(SD/HD/3G compatible) and USB. VENUS X1 combines truly seamless,
fade in fade out, glitch-free switching with advanced scaling technologies
to meet the requirements of high quality, high resolution video
presentations.
VENUS X1 also launches the latest, user defined image size and
coordinate, dual image processing, multiple cascade mapping, different
user configurations and controlling, key in and out and other advanced
functions for high-end show.
VENUS X1 supports EDID editing for VGA, DVI, HDMI input ports and
read EDID for output ports, support EDID modify by windows control
program. PC modified EDID, users can edit the EDID of input port
according to the resolution of outputs to achieve the optimal input
resolution.
VENUS X1 also supports local front panel operation, remote widows
based software control by RS232, USB, Ethernet, and WIFI control. In
addition, VENUS X1 is based on replaceable input optional modules
structure, with different modules, you can reach more possibility and
application range.

1. Introduction
Application Question
Application Questions
RGBlink offers solutions to demanding technical problems. Any application
questions, or required further information, please contact with our
Customer Support Engineers. Refer to Appendix B for contact details.

2. Hardware Orientation
In This Chapter
This chapter provides detailed information about the VENUS X1 hardware.
The following topics are discussed:
VENUS X1 Back Panel
VENUS X1 Front Panel
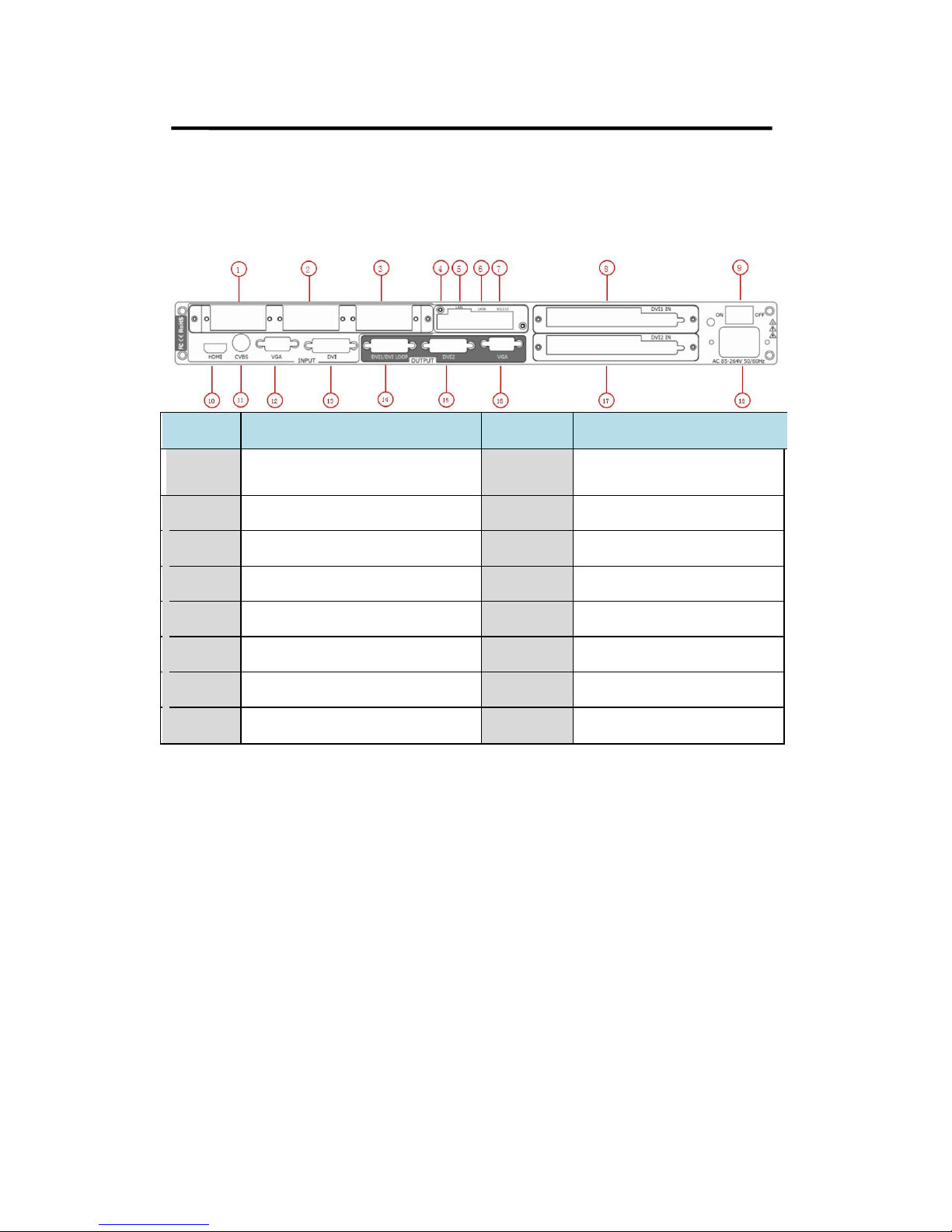
2. Hardware Orientation
Back Panel
Back
Panel
The figure below illustrates the professional interface and control signals of
VENUS X1 back panel.
NO INTERFACE
NO INTERFACE
1. 2. 3
S. V. D. C. U. H and Audio
Optional Module
11 CVBS Input BNC
4
Dial Switch
12 VGA Input DB15
5
10/100M Interface
13 DVI Input DVI-I
6
USB Interface
14 DVI/DVI LOOP Output DVI-I
7
RJ11 (RS232) Interface
15 DVI Output DVI-I
8. 17 Sending card interface
16 VGA Output DB15
9
Switch
18 Power IEC-3 port
10 HDMI Input HDMI-A
CONT Interface
4: Dial Switch
If the two dial switches are upwards, the device is in normal work, and if
they are downwards, the device is in upgrade state. OLED module light is
off when the device is in upgrade state. Some of the button lights turn on,
and the device will not work.
5: 10/100M UDP Interface
Used to connect the windows control program or device upgrade.
6: USB Interface
Used to connect the windows control program or device upgrade.

2. Hardware Orientation
Back Panel
7: RS232 Interface
Used to connect the windows control program or device upgrade.
INPUT Interface
It includes 1 HDMI input by HDMI-A interface, 1 CVBS inputs by BNC
interface, 1 VGA input by DB15 interface, and 1 DVI input by DVI-I
interface, which can be compatible with HDMI.
10: HDMI Input
HDMI input, input the image signal from computer.
11: CVBS Input
CVBS input, input standard video signal from players, cameras etc.,
supported resolution 480i and 576i via BNC. Supported standards include:
PAL, NTSC and SECAM.
12: VGA Input
VGA input, input the video signal from HD player and computer, etc.
Compatible with YPbPr via the DB15 interface.
13: DVI Input
DVI input, input the video signal from computer, DVI signal generator. If the
EDID is HDMI, the DVI can be compatible with HDMI 1.3.
(This connector can not support hot-plugging).
OUTPUT Interface
8.17: Sending Card Interface
Sending card module port. Compatible with Linsn, DBstar, Colorlight, Nova
sending card, etc. The power is supplied by video processor.
14: DVI/DVI LOOP Output

2. Hardware Orientation
Back Panel
DVI output, connect to the monitor or LED screen which has DVI interface
(This connector can not support hot-plugging).
DVI loop out, connect to the DVI input of the next VENUS X1 or the device
with DVI input.
15: DVI Output
DVI output, connect to the monitor or LED screen which has DVI interface
(This connector can not support hot-plugging).
16: VGA Output
VGA output, connect to monitor or projector which has VGA interface.
Optional Module
1. 2. 3: S. V. D. C. U. H and Audio Optional Module
Compatible with SDI, VGA, DVI, CVBS, USB, HDMI and audio optional
module. Module 1 and Module 2 support all these inputs, and Module 3
only supports digital input. SDI optional module includes 1 3G-SDI input
and 1 SDI loop out. VGA optional module includes 1 VGA input (DB15port).
DVI optional module includes 1 DVI-I (compatible with HDMI) input. HDMI
optional module includes 1 HDMI input and 1 HDMI loop out. CVBS
optional module includes 1 CVBS input and 1 CVBS backup input. USB
optional includes 1 USB input and 1 USB backup input. Each audio
optional module includes 5 3.5mm analog audios and 1 balanced analog
audio.
3G-SDI Input (S Optional Module): Input video signal from HD camera
and radio processing equipment, connect SDI interface via 75 ohms
impedance BNC port.
SDI Loop Out (S Optional Module): Connect to the SDI input of the next
VENUS X1 or the device with SDI input.

2. Hardware Orientation
Back Panel
VGA Input (V Optional Module): Input the video signal from HD player
and computer, etc. input signal via the DB15 interface.
DVI Input (D Optional Module): Input the video signal from computer, DVI
signal generator. Connect to the same DVI interface on VENUS X1.
(This connector does not support hot-plugging).
HDMI Input (H Optional Module): Input the image signal from computer.
HDMI Loop Out (H Optional Module): Connect to the HDMI input of the
next level VENUS X1 or the device with HDMI input.
CVBS Input (C Optional Module): Input standard video signal from
players, cameras etc.
USB Input (U Optional Module): Can access the USB device or mobile
hard disk with USB storage function. Support general image and video
formats.
Analog Audio Input (Audio Optional Module): Input the video signals
from the DVD player, hardware player and digital box.
Analog Audio Output (Audio Optional Module): Connect to the audio
devices such as speaker.
Switch and Power
9. 18: Power Interface and Switch
AC 85-264V 50/60Hz IEC-3 Power Interface.
For more details about the input/output numbers, supported resolutions,
signal level, format standard, etc, please refer to Specification part.

2. Hardware Orientation
Back Panel
Interface Protection Block
We equip the interface protection blocks on both sides of the back panel,
the purpose are as follows:
1. Protect the interfaces, it avoids the interface damage that may caused if
the back panel hits the ground.
2. Tie the input and output cables, to avoid the cables loose by the external
touch, which may cause signal interrupt. The tie method shown as
follows:
2. Hardware Orientation
Front Panel
Front Panel
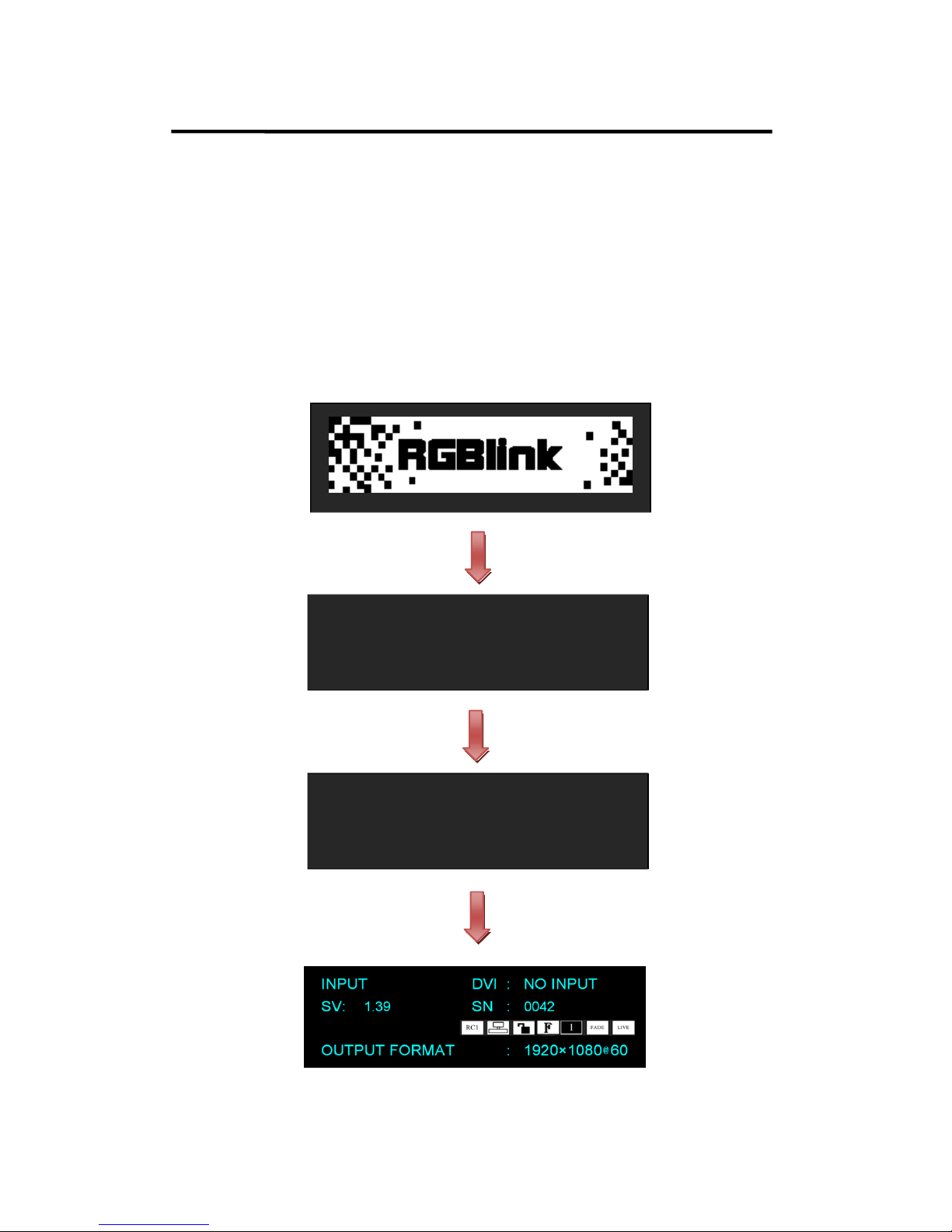
Plug in the power cord and push power to ON position. OLED module on
the front panel will show RGBlink and go into its self verification before it
load last setting config and send processed image to the target monitor.
System default DVI input. User can operate VENUS X1 through the menus
on OLED module.
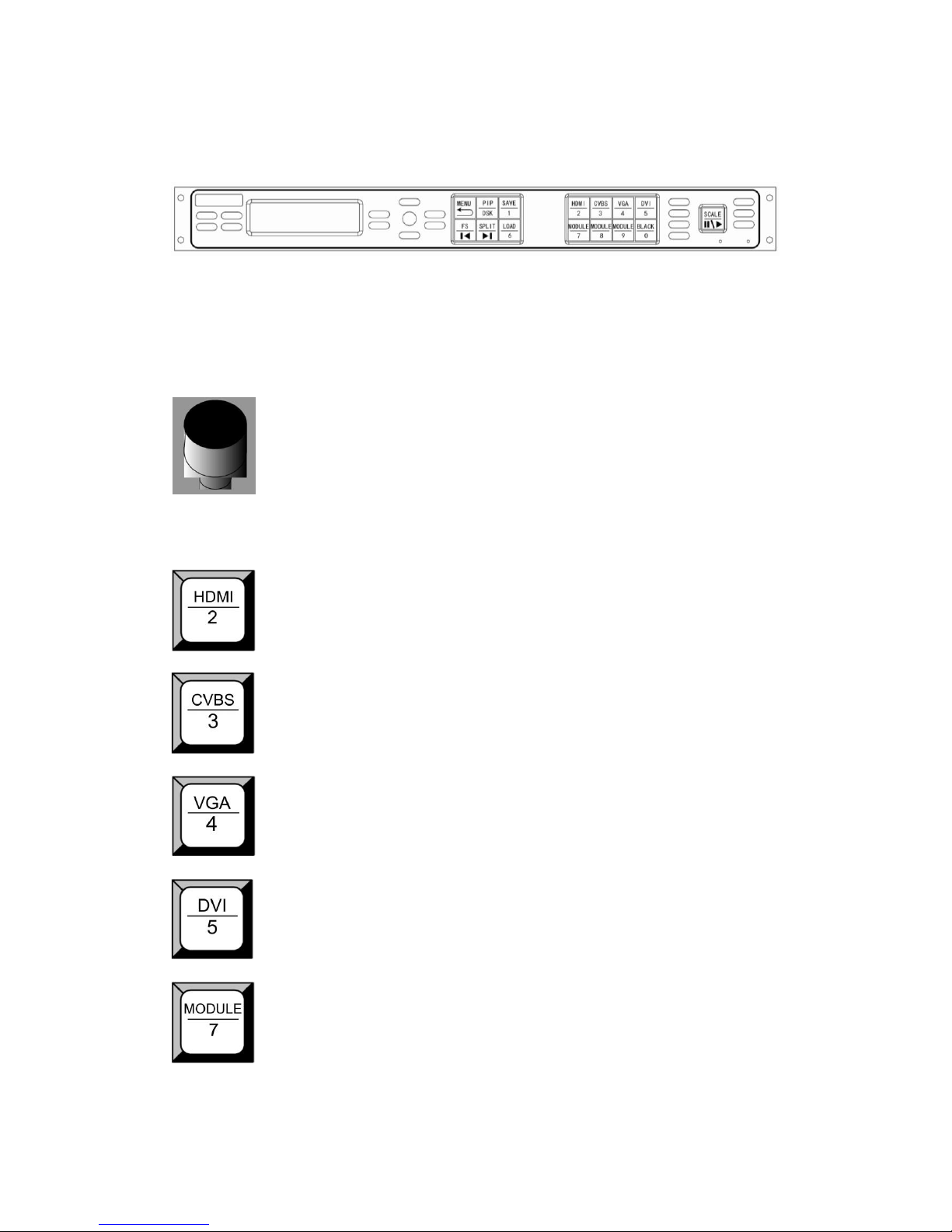
VENUS X1 front panel as shown in figure:
亮彩系列
AVDSP SERIES VENUS X1
INIT DEVICE [> ]

2. Hardware Orientation
Front Panel
Note:
INPUT DVI: NO INPUT--System default DVI signal, there is no input or the
DVI signal is invalid.
SV: 1.39--The software version is 1.39.
SN: 0042--The serial number is 0042.
: Recall Save 1.
: Single device.
: Unlock state.
: Full size display.
: Single image. :
Fade in fade out.
: Live video.
OUTPUT FORMAT: 1920×1080@60--The current output format is
1920×1080@60.
2. Hardware Orientation
Front Panel
VENUS X1 front panel as following:
OLED Panel
Used to show button men u and menus for interactive communication;
Menu Button
Used to adjust menu on OLED and for information interaction. Push the
rotary button to confirm current options.
Signal Buttons
HDMI input selection button, push the button, its LED light turns on, output
will be switched to this channel.
CVBS input selection button, push the button, its LED light turns on, output
will be switched to this channel.
VGA and YPbPr input selection button, push the button, its LED light turns
on, output will be switched to this channel.
DVI input selection button, push the button, its LED light turns on, output will
be switched to this channel.
Optional module input selection button 7, push the button, its LED light turns
on, output will be switched to this channel. Support signals include: SDI,
VGA, DVI, CVBS, USB and HDMI.

2. Hardware Orientation
Front Panel
Optional module input selection button 8, push the button, its LED light turns
on, output will be switched to this channel. Support signals include: SDI,
VGA, DVI, CVBS, USB and HDMI.
Optional module input selection button 9, push the button, its LED light turns
on, output will be switched to this channel. Support signals include: SDI, DVI,
HDMI and audio.
Black button, push the button, its LED light turns on, the output will be
switched to black, push the button again, its LED light is off, and output the
video image.
Besides BLACK, user can define this button as FREEZE, TEST PATTERN
and BRIGHT.
If define this button as FREEZE, push the button, its LED light turns on, and
freeze the image. Push the button again, its LED light is off, and output the
video image.
If define this button as TEST PATTERN, push the button, its LED light turns
on, the output will be switched to test pattern. Push the button again, its LED
light is off, and output the video image.
If define this button as BRIGHT, push the button, its LED light turns on, user
can adjust the brightness, contrast, saturation, sharpness, color red, color
green, color blue and gamma. If image quality distorts by improper operation,
it can be recover by reset.
For more details, please refer to: How to User Define the BLACK Key.
Function
PIP and DSK function reuse button: Push the button, its LED light turns on,
and PIP function is open. Push the button again, its LED light turns off, close
2. Hardware Orientation
Front Panel
the PIP function, and change to the single image. OLED shows as follows:
—>PIP ON
LAYOUT PIP L+T
SELECT IMAGE A
SWAP IMAGE OFF
—>ALPHA 0
For details, please refer to PIP function and How to Set up the PIP.
Note
VENUS X1 V1.1 can not support DSK function
button.
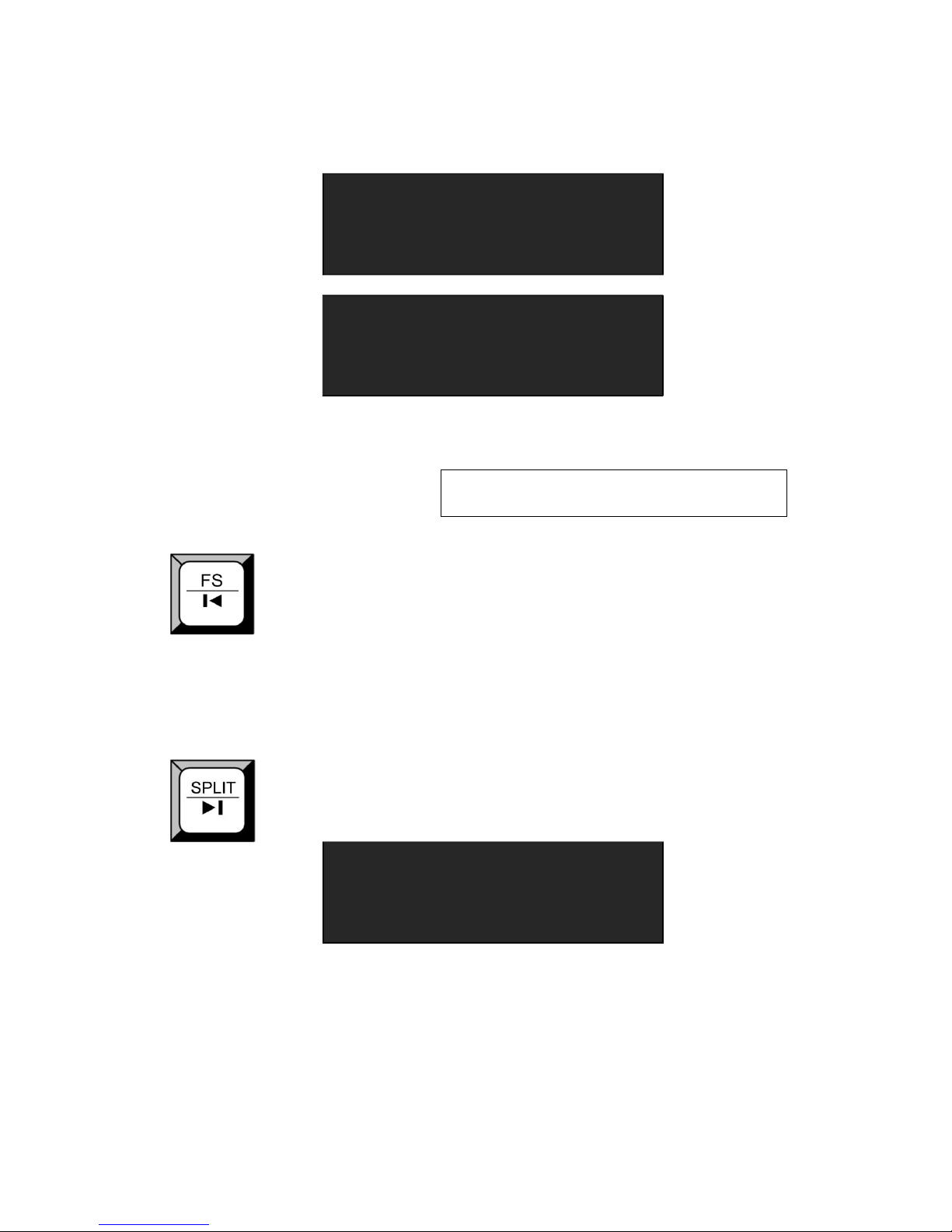
Full size and screen size reuse button. Push the button, its LED light turns
on, the image is screen size display, push the button again, the image will
full size display.
When connect USB signal, it reused the move previous button, push the
button to play the previous USB video file.
Split function button: push the button, its LED light turns on, OLED menu
shows as follows:
—>FIXED SPLIT >>
NORMAL SPLIT
>>
Turn the knob, and choose the split mode, for example, choose <NORAML
SPLIT>, push the knob to confirm. Turn the knob, and set the <SPLIT> as
―ON‖
, push the knob to confirm. The [SPLIT] button light turns on, and
enable the split function. OLED menu shows as follows:

2. Hardware Orientation
Front Panel
—>SPLIT ON
H TOTAL 1920
V TOTAL 1080
H POS 0
—>V POS 0
H SIZE 1920
V SIZE 1080
RESET
For details, please refer to SPLIT Function and How to Set up the SPLIT.
Note
The split function is only available for DVI port
and the HDMI LOOP port of EXT 9, it needs a
signal distributor if split with DVI port.
Note
SPLIT reuse function: PIP mode, SPLIT button is
select image A or image B.
When connect USB signal, it reused the move next button, push the button
to play the next USB video file.
Save button: Push the butt on to enter SAVE mode, turn the knob or push the
number button which light up to save.
VENUS X1 supports 36 saving modes, and the button 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0 means SAVE1~10.
The OLED menu will show finish after finish saving.
For details, please refer to SAVE Function and How to Save the Parameter.
LOAD button: Push it to enter LOAD mode, turn the knob or push the
number button which light up to load the saved parameters.
VENUS X1 supports 36 loading modes, and the button 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
0 means LOAD user mode 1~10.

2. Hardware Orientation
Front Panel
The OLED menu will show finish after finish loading.
For details, please refer to LOAD Function and How to Load the Saved
Parameter.
Advanced menu button: Push the button to enter the menu items. Turn the
knob to select the relevant submenu. For details, please refer to MENU in
menu orientation.
ESC reuse function button: Push the MENU to exit the menu.
Effect switch function: Push the MENU button two times to enter the effect
switch function menu.
For details please refer to: Special Effect Switching.
Push the MENU for 3 seconds will lock the panel, and push MENU for 5
seconds to unlock.
Push the MENU and SCALE button for 3 seconds can switch the language.
Scale function button: For image size adjustment, push the button to enter
the scale menu. Turn the knob to select the relevant submenus. For details,
please refer to SCALE FUNCTION in menu orientation and How to Set the
Size and Position of the Single Image.
When connect the USB signal, push the button, the video or image will stop
or play.
Besides SCALE, user can define this button as TAKE.
If define this button as TAKE, push the button, its LED light turns on, choose
the signal that will switch, and push the SCALE (TAKE) button, the signal
will be switched to the LED screen.
For more details, please refer to: How to User Define the SCALE Key.
VENUS X1
User Manual
39
3. Hardware Installation
In This Chapter
This chapter provides comprehensive installation instruction for VENUS X1
hardware:
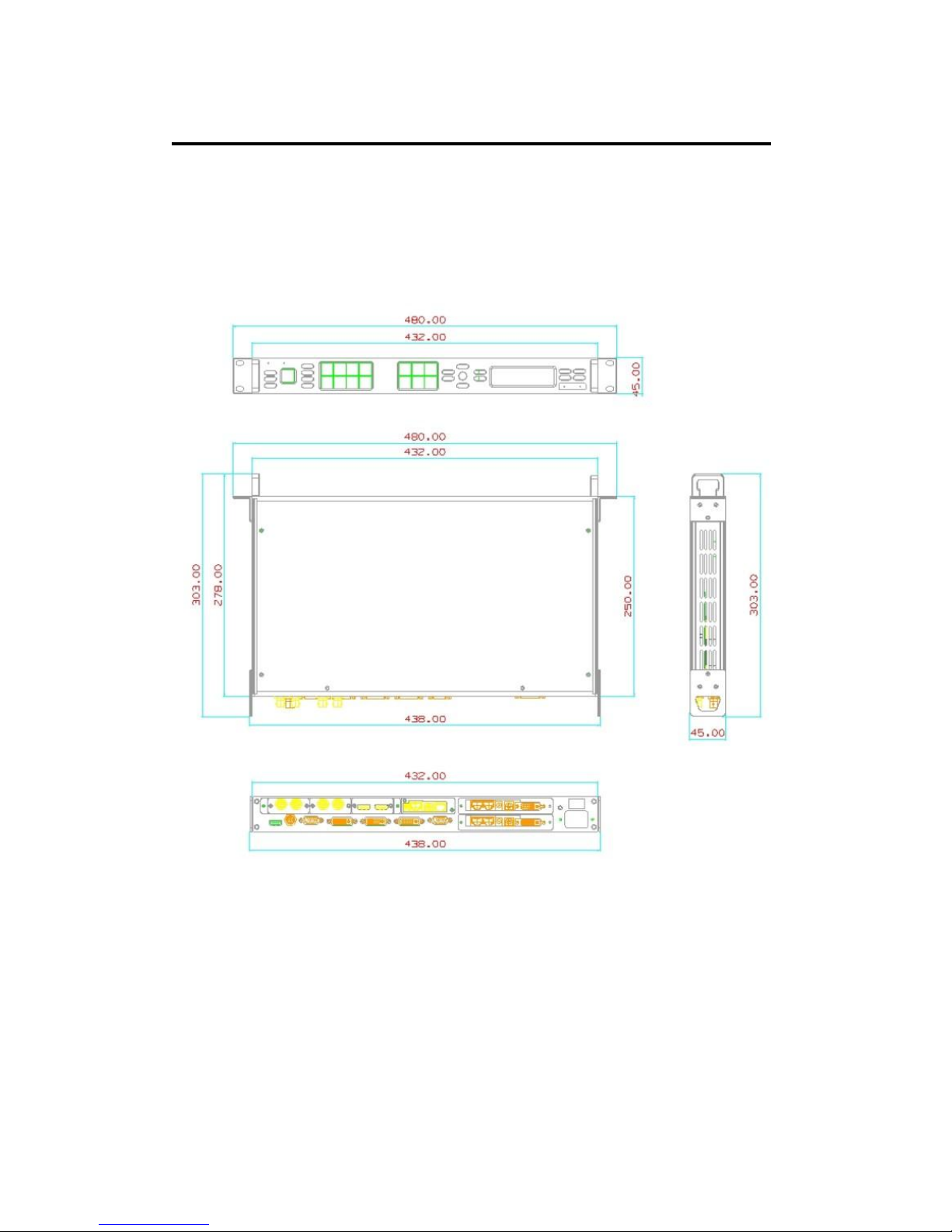
Following is the mechanic info of VENUS X1 for your reference.

Safety Precautions
For all VENUS X1 processor installation procedures, please observe the
following important safety and handling rules to avoid damage to yourself
and the equipment.
To protect users from electric shock, ensure that the chassis connects
to earth via the ground wire provided in the AC power Cord.
The AC Socket-outlet should be installed near the equipment and be
easily accessible.
Unpacking and Inspection
Before opening VENUS X1 processor shipping box, inspect it for damage.
If you find any damage, notify the shipping carrier immediately for all claims
adjustments. As you open the box, compare its contents against the
packing slip. If you find any shortages, contact your sales representative.
Once you have removed all the components from their packaging and
checked that all the listed components are present, visually inspect the
system to ensure there was no damage during shipping. If there is damage,
notify the shipping carrier immediately for all claims adjustments.
Site Preparation
The environment in which you install your VENUS X1 should be clean,
properly lit, free from static, and have adequate power, ventilation, and
space for all components.

4. Menu Orientation
In This Chapter
This chapter describes all VENUS X1 processor menus, including how they
are accessed, the functions that are available, and descriptions of each
menu tree (in block diagram format).
The following topics are discussed:
• MENU
INPUT
OUTPUT
PICTURE
PIP
SPLIT
TRANSITION
SCALE
SAVE SETUP
SYSTEM
LANGUAGE
FACTORY RESET
• QUICK MENU
SPECIAL EFFECTS SWITCHING
SAVE FUNCTION
LOAD FUNCTION
PIP FUNCTION
SPLIT FUNCTION
SCALE FUNCTION

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
MENU
Push the MENU to menu items, menu as shown: Turn the knob to select
menu items. -> before the menu means it’s in selected state. Push the knob
to enter corresponding setting or view the menu.

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
INPUT
Push the [MENU] button, OLED display menu, push the knob to select
<INPUT>, show menus as follows:
INPUT DETAIL: Show the current input source and input format.
ZOOM: It can adjust the image zoom size and positions, settings including
as follows:

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
V UP--image to up zoom.
V DOWN--image to down zoom.
V UP/DOWN--image to up and down zoom.
H LEFT--image to left zoom.
H RIGHT--image to right zoom.
H LIFT/RIGHT--image to left and right zoom.
CENTER--image from center to the edges zoom.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
reset.
For details, please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Zoom the
Image.
VGA ADJUST: Adjust VGA input signal, sub menu as follows:
AUTO ADJUST: Auto adjust VGA input signal H POS, V POS, CLOCK,
PHASE, auto adjust to display in full screen image.
Note
Comments customers to use this operation in
adjusting the VGA input shiftment.
H POS: Image horizontal position.
V POS: Image vertical position.
CLOCK: Input signal clock.
PHASE: Input image phase.
Note
Only comments to professional operator.
ADC AUTO ADJUST: Mainly for brightness auto adjusting.
DVI/EXT ADJUST: When DVI or optional module input signal image shift,
please adjust image’s H POS and V POS to display in full screen image.
Sub menu as follows:
H POS: Image horizontal position.

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
V POS: Image vertical position.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
reset.
EDID MANAGE: Choose the detination port and source file, VENUS X1
supports the EDID manage ports and types are as follows:
Supported EDID
Manage Port
Supported EDID Manage Type
VGA
RGBVGA, OUT_VGA, FOLLOW, CUSTOM
DVI
RGBDVI, RGBHDMI, OUT_DVI1, OUT_DVI2,
FOLLOW, CUSTOM
EXT_HDMI
RGBDVI, RGBHDMI, OUT_DVI1, OUT_DVI2,
FOLLOW, CUSTOM
EXT_VGA
RGBVGA, OUT_VGA, FOLLOW, CUSTOM
EXT_DVI
RGBDVI, RGBHDMI, OUT_DVI1, OUT_DVI2,
FOLLOW, CUSTOM
VGA SIGNAL TYPE: Program VGA button is VGA signal or YPbPr signal.
USB CONTROL: Sub menu as follows:
USB PORT: Can choose PORT A or PORT B.
PLAY MODE: Can choose photo or movie.
PLAY FILE: Choose the file that will play.
PLAY ORDER: Can choose REPEAT ALL, SHUFFLE, ORDER, SINGLE
CYCLE, SINGLE TRACK, PLAY LIST.
PLAY STATE: Can choose PLAY or PAUSE. EXT
CVBS CONTROL: Sub menu as follows: CVBS
PORT: Can choose PORT A or PORT B. INPUT
FORMAT: Show the input format of CVBS.
OUTPUT
Push the [MENU] button to go into the menu items, and turn the knob to

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
select <OUTPUT>, show menus as follows:
STANDARD: Push the knob to select left or right menu item, turn the knob
to enter corresponding setting or view the menu. Users can choose
different output formats by turning the knob, this option includes 21
common standard output resolutions, shown as follows:
800×600@60, 1024×768@60, 1024×768@75, 1280×720@50,
1280×720@60, 1280×768@60, 1280×800@60, 1280×1024@60,
1360×768@60, 1366×768@60, 1400×1050@60, 1440×900@60,
1536×1536@60, 1600×1200@60, 1680×1050@60, 1920×1080@50,
1920×1080@60, 1920×1200@60, 2048×1152@60, 2560×812@60,
2560×816@60.
CUSTOMIZED: The special display project or LED screen application
would like to require special resolution settings to meet the requirement.
Details please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Choose and
Custom the Output Resolution.
SCREEN PARAMETERS: Sub menu as follows:
H SIZE: Width setting.
V SIZE: Height setting.
H POS: Horizontal phase setting.
V POS: Vertical phase setting.
MODE: Can choose SCREEN SIZE or FULL SIZE.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
factory reset.
For details, please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Realize
the Screen Size Switching.
OUTPUT ADJUST: Output adjust menus, sub menu as follows:
DVI1, setting as following:
DVI MODE: Can set the protocol as HDMI or DVI, default is DVI output,
HDMI signal output will enable when HDMI option checked.

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
BIT DEPTH: Can set the image bit depth. DVI default 8 bit, user don’t need
to set it. HDMI default 10 bit, and can choose 8 bit or 12 bit.
DATE RANGE: DVI1 output range, can set as RGB (graphic mode or
YCbCr (video mode), RGB output scale range from 0 to 255, YCbCr
range from 16 to 235.
DE ADJUST: DE adjust, sub menu as following:
DE ON/OFF: Can choose to open or close, when choose open, it can be
adjusted to DE, as follows:
H SIZE: Width setting.
V SIZE: Height setting.
H POS: Horizontal phase setting.
V POS: Vertical phase setting.
When the signal source of the screen appear black side, can use this
function to shift the black out of the screen.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
reset.
ASPECT RATIO: Aspect ratio setting, user can choose 4:3, 16:9 and
DEFAULT.
PICTURE
Push the [MENU] button to go into the menu items, turn the knob button to
select <PICTURE>, show menus as follows:
IMAGE QUALITY: Image quality setting, the sub-menu as following:
BRIGHTNESS: It can change the image brightness via BRIGHTNESS
setting.
CONTRAST: It can change the image contrast via CONTRAST setting.
SATURATION: It can change the image saturation via SATURATION
setting.

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
SHARPNESS: It can change the image sharpness via SHARPNESS
setting.
COLOR RED: It can change the image color red via this setting. COLOR
GREEN: It can change the image color green via this setting. COLOR
BLUE: It can change the image color blue via this setting. GAMMA:
Gamma setting, push it to adjust the image gamma value; Gamma
values include: -1.2, -1.4, -1.6, 1, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6, and sRGB.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
reset.
Note
Users can set according to their actual situation,
this function mainly suitable for these
professional operator who knows how to set the
image quality correctly. Others are not
comments to do these operations. If image
distorted by improper operation, it can be
initialized operated to recover by factory reset.
TEXT OVERLAY: Text overlay function, settings are as follows:
TEXT OVERLAY: Can select ―ON‖ or ―OFF‖, system default off.
PRESET: Can preset value of the following functions, and total 13 modes:
User: User mode.
WhOnBk1: White On Black 1.
WhOnBk2: White On Black 2.
BkOnWh1: Black On White 1.
BkOnWh2: Black On White 2.
GrnOnBk1: Green On Black 1.
GrnOnBk2: Green On Black 2.
GrnOnWh1: Green On White 1.
GrnOnWh2: Green On White 2.
RedOnBk1: Red On Black 1.

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
RedOnBk2: Red On Black 2.
RedOnWh1: Red On White 1.
RedOnWh2: Red On White 2.
BLEND MODE: Blend mode, with two modes, ―Mode
1‖
and
―
Mode 2‖.
Mode 1: Graphic content locate at the top and is non-transparent,
background transparency is controlled by double-image transparency;
Mode 2: Graphic content is controlled by double-image transparency, the
background is completely transparent.
BLEND LEVEL: Can set the image display transparency, the regulating
range is among 0 to 16.
ABOVE/BELOW:
ABOVE: In image 2, if the pixel value is higher than the setting value, then
the image is the graphic content pixel, otherwise, it is the graphic
background pixel. It should combined with "AND/OR" conditions when
judging.
BELOW: In image 2, if the pixel value is lower than the setting value, then
the image is the graphic content pixel, otherwise, it is the graphic
background pixel. It should combined with "AND/OR" conditions when
judging.
KEY IN/OUT:
KEY IN: Delete the background, and keep the text title.
KEY OUT: Delete the text title, and keep the background.
RED: Red limit, cut-off point condition of ABOVE and BELOW condition in
red channel, the range is 0 ~ 248.
GREEN: Green limit, cut-off point condition of ABOVE and BELOW
condition in green channel, the range is 0 ~ 248.
BLUE: Blue limit, cut-off point condition of ABOVE and BELOW condition in
blue channel, the range is 0 ~ 248.
For details, please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Realize

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
the Text Overlay Setting.
PIP
Push the [MENU] button to go into the menu items, turn the knob button to
select <PIP>, show menus as follows:
PIP: Choose ON to set PIP mode.
LAYOUT: There are 7 PIP layouts, can choose PIP layouts anyone, the
corresponding results are as follows.
PIP L+T PBP L+R PBP T+B
SELECT: Can choose to set the size or position of IMAGE A or IMAGE B
individually.
Note
User can also select image A or image B by
function reuse key [SPLIT/6]
SWAP IMAGE: It can set PIP to swap exchange, when choose ON, it can
switch IMAGE A and IMAGE B.
ALPHA: Use can set the image transparency, the regulating range is
among 0 to 16.
For details, please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Set up the
PIP.
Note
User can also push the [PIP/DSK] button to set
up the PIP.

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
SPLIT
Push the [MENU] button to go into the menu items, turn the knob button to
select <SPLIT>, the split modes include <FIXED SPLIT> and <NORMAL
SPLIT>.
FIXED SPLIT: Sub menus are as follows:
SPLIT: Split function, can choose ―ON‖ or ―OFF‖. System default ―OFF‖.
HORIZONTAL SPLIT: Horizontal fixed split, choose it and push the number
button to set the total horizontal screen number.
VERTICAL SPLIT: Vertical fixed split, choose it and push the number button
to set the total vertical screen number.
SPLIT INDEX: Use can choose the split index, and the LED display will
show the corresponding image.
NORMAL SPLIT: For normal split, user should enable the split function, that
is, turn the knob, and set the <SPLIT> as ―ON‖, push the knob to confirm.
System default ―OFF‖. User can set the normal split in the sub menus:
SPLIT: Split function, can choose ―ON‖ or ―OFF‖.
H TOTAL: The total width points of LED display that will split.
V TOTAL: The total height points of LED display that will split.
H POS: The horizontal position of the device when do split.
V POS: The vertical position of the device when do split.
H SIZE: The width of the device when do split.
V SIZE: The height of the device when do split.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
reset.
For details please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Set up the
SPLIT.
Note
User can also push the [SPLIT] button to set up
the SPLIT.

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
TRANSITION
Push the [MENU] button to go into the menu items, turn the knob button to
select <TRANSITION>, show menus as follows:
DEINTERLACE: Force Deinterlace function, can choose ―ON‖ or ―OFF‖.
ON: Force deinterlace.
OFF: No deinterlace.
IMAGE ENHANCE: Image enhancement function, used for image edge
sharpening, color reduction and image scaling.
MODE: Special effects switching mode.
DISSOLVE: Fade in fade out effects switching.
CUT: Fast switching.
WIPE SOUARE IN:
WIPE SOUARE OUT:
WIPE TOP LIEFT IN:
WIPE TOP LIEFT OUT:
WIPE TOP RIGHT IN:
WIPE TOP RIGHT OUT:
WIPE BOTTOM LEFT IN:
WIPE BOTTOM LEFT OUT:

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
WIPE BOTTOM RIGHT IN:
WIPE BOTTOM LEFT OUT:
WIPE LEFT IN:
WIPE LEFT OUT:
WIPE RIGHT IN: WIPE
RIGHT OUT:
WIPE TOP IN:
WIPE TOP OUT:
WIPE BOTTOM IN:
WIPE BOTTOM OUT:
Note: Means the image emerging.
Means the image disappearing.
Arrows represents the direction of the image move, that is, the image that
arrow point, is compressed or stretched to the direction that arrow indicates,
until disappear or full screen.
FADE TIME: Switch time setting. Rotate the knob to choose the time and
push the knob to confirm. The switching time ranges from 0 to 3S.
ALPHA: It can set the image transparency, the regulating range is among

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
0 to 16.
Note
User can also push the [MENU] button two times
to set up the TRANSITION.
SCALE
Push the [MENU] button to go into the menu items, turn the knob button to
select <SCALE>, show menus as follows:
H SIZE: Width setting.
V SIZE: Height setting.
H/V SIZE: Width and height equal proportion scale setting.
H POS: Horizontal phase setting.
V POS: Vertical phase setting.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
reset.
For details, please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Set up the
Size and Position of the Single Image.
Note
User can also push the [SCALE] button to set up
the size and position.
SAVE SETUP
Push the [MENU] button to go into the menu items, turn the knob button to
select <SAVE SETUP>, show menus as follows:
SAVE TO: VENUS X1 provides 36 save modes, users can save the current
operation to SAVE1 to SAVE36.
Note
User can also push the [SAVE/1] button to save
the parameters.
RECALL SAVE: It can recall the saved user modes via this function.

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
Note
User can also push the [LOAD/6] button to recall
the saved parameters.
DELAY CALL: Set delay the output time. When more than one equipment
power on, and the processor is the end equipment in order to improve
question that can’t identify the input signal and phenomenon that LED
screen appear messy code and flash screen, now need to delay the input
time.
REAL-TIME SAVE: User can enable or disable the real-time save function,
the device will automatically save the modified parameters if choose ―ON‖.
SYSTEM
Push the [MENU] button to go into the menu items, turn the knob button to
select <SYSTEM>, show menus as follows:
SN: Show the serial number of the device.
VERSION: Show the COM version, firmware version, mainboard version,
EXT mainboard version, EXT INPUT1 version and EXT INPUT2 version.
TECH SUPPORT: Show the sales, customer service, email, website and
telephone.
DATE&TIME: User can view and change the date and time, view the
current time, last time, total time and boot times.
ETHERNET: Network setting, include IP address, subnet mask and
gateway. System default IP address is 192.168.0.100, subnet mask is
255.255.255.000, gateway is 192.168.000.001.
LOCK FRONT PANEL: Through this setting can choose whether to lock
the keys, if the key is locked, the equipment will remind: "Buttons are
locked! Press MENU key and hold 5s to release!"
LICENSE SETUP: The device will not work if excess the prescribed time,

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
there are no signal output, it needs to input password and modify the using
time to continue to work.
HOT BACKUP: User can enable or disable the hot backup function.
Choose ―ON‖ to set the backup signal for BACKUP_1 to BACKUP_5. It will
switch to the backup signal if interrupt signal.
FAN CONTROL: User can enable or disable the auto speed function, set
the current speed and view the current temperature.
DEVICE STATUS: Show the video status, MB status and EXT status.
USER DEFINED BUTTON: User can define the BLACK and SCALE key.
BLACK KEY: System default black function. Push the button, its LED light
turns on, the output will be switched to black, push the button again, its
LED light is off, and output the video image.
Besides BLACK, user can define this button as FREEZE, TEST PATTERN
and BRIGHT.
If define this button as FREEZE, push the button, its LED light turns on, and
freeze the image. Push the button again, its LED light is off, and output the
video image.
If define this button as TEST PATTERN, push the button, its LED light turns
on, the output will be switched to test pattern. Push the button again, its
LED light is off, and output the video image.
If define this button as BRIGHT, push the button, its LED light turns on,
user can adjust the brightness, contrast, saturation, sharpness, color red,
color green, color blue and gamma. If image quality distorts by improper
operation, it can be recover by reset.
For more details, please refer to: How to User Define the BLACK Key.
SCALE KEY: System default scale function. Push the button to enter the
scale menus. Turn the knob to select the relevant submenus.
Besides SCALE, user can define this button as TAKE.
If define this button as TAKE, push the button, its LED light turns on,

4. Menu Orientation
MENU
choose the signal that will switch, and push the SCALE (TAKE) button, the
signal will be switched to the LED display.
For more details, please refer to: How to User Define the SCALE Key.
OLED LUMINANCE: Set the OLED luminance, the adjustment range is
1~15.
LANGUAGE
Through this option, user can choose Chinese or English according to their
needs to operate the interface more quickly.
FACTORY RESET
Enter FACTORY RESET to reset the IP, choose YES and push the knob to
confirm, then VENUS X1 is reset to its factory settings. After 5 seconds, it
completes factory settings and is ready for more operations.

4. Menu Orientation
QUICK MENU
QUICK MENU
Quick menu function are including: Special effects switching function, SAVE
function, LOAD function, PIP function, SPLIT function, SCALE function,
these functions are separate button defined, so not included in the MENU.
SPECIAL EFFECTS SWITCHING
Push the [MENU] button two times, and enter the effect switch function
menu, effect menu shown as follows:
DEINTERLACE: Force Deinterlace function, can choose ―ON‖ or ―OFF‖.
ON: Force deinterlace.
OFF: No deinterlace.
IMAGE ENHANCE: Image enhancement function, used for image edge
sharpening, color reduction and image scaling.
MODE: Special effects switching mode.
DISSOLVE: Fade in fade out effects switching.
CUT: Fast switching.

4. Menu Orientation
QUICK MENU
WIPE SOUARE IN:
WIPE SOUARE OUT:
WIPE TOP LIEFT IN:
WIPE TOP LIEFT OUT:
WIPE TOP RIGHT IN:
WIPE TOP RIGHT OUT:
WIPE BOTTOM LEFT IN:
WIPE BOTTOM LEFT OUT:
WIPE BOTTOM RIGHT IN:
WIPE BOTTOM LEFT OUT:
WIPE LEFT IN:
WIPE LEFT OUT:
WIPE RIGHT IN: WIPE
RIGHT OUT:

4. Menu Orientation
QUICK MENU
WIPE TOP IN:
WIPE TOP OUT:
WIPE BOTTOM IN:
WIPE BOTTOM OUT:
Note: Means the image emerging.
Means the image disappearing.
Arrows represents the direction of the image move, that is, the image that
arrow point, is compressed or stretched to the direction that arrow indicates,
until disappear or full screen.
FADE TIME: Switch time setting. Turn the knob to choose the time and
push the knob to confirm. The switching time ranges from 0 to3S.
ALPHA: It can set the image transparency, the regulating range is among
0 to 16.
SAVE FUNCTION
Push the [SAVE/1] button, the button led light turn on, and enter the save
function menu. OLED module show as follows:
SAVE TO
—>SAVE 1
Button is on can be saved
Button flashes will be overwrite
User can operate according to the OLED module information.
For details please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Save the
Parameter.

4. Menu Orientation
QUICK MENU
LOAD FUNCTION
Push the [LOAD/6] button, the button led light turn on, and enter the load
function menu. OLED module show as follows:
RECALL SAVE
—>SAVE 1
Button on is ready for recall
Button flashes means just recall
User can operate according to the OLED module information.
For details please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Load the
Saved Parameter.
PIP FUNCTION
Push the [PIP/DSK] button, the button led light turn on, and enter the PIP
function menu. OLED module show as follows:
PIP: Choose ON to set PIP mode.
LAYOUT: There are 7 PIP layouts, Can choose PIP layouts anyone, the
corresponding results are as follows.
PIP L+T PBP L+R PBP T+B
SELECT: Can choose to set the size or position of IMAGE A or IMAGE B
individually.

4. Menu Orientation
QUICK MENU
Note
Function reuse key [SPLIT], select image A or
image B.
SWAP IMAGE: It can set PIP to swap exchange, when choose ON, it can
switch IMAGE A and IMAGE B.
ALPHA: Use can set the image transparency, the regulating range is
among 0 to 16.
For details, please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Set up the
PIP.
SPLIT FUNCTION
Push the [SPLIT] button, the button led light turn on, and enter the SPLIT
function menus. The split modes include <FIXED SPLIT> and <NORMAL
SPLIT>.
FIXED SPLIT: Sub menus are as follows:
SPLIT: Split function, can choose ―ON‖ or ―OFF‖. System default ―OFF‖.
HORIZONTAL SPLIT: Horizontal fixed split, choose it and push the number
button to set the total horizontal screen number.
VERTICAL SPLIT: Vertical fixed split, choose it and push the number button
to set the total vertical screen number.
SPLIT INDEX: Use can choose the split index, and the LED display will
show the corresponding image.
NORMAL SPLIT: For normal split, user should enable the split function, that
is, turn the knob, and set the <SPLIT> as ―ON‖, push the knob to confirm.
System default ―OFF‖. User can set the normal split in the sub menus:
SPLIT: Split function, can choose ―ON‖ or ―OFF‖.
H TOTAL: The total width points of LED display that will split.
V TOTAL: The total height points of LED display that will split.

4. Menu Orientation
QUICK MENU
H POS: The horizontal position of the device when do split.
V POS: The vertical position of the device when do split.
H SIZE: The width of the device when do split.
V SIZE: The height of the device when do split.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
reset.
For details please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Set up the
SPLIT.
SCALE FUNCTION
Push the [SCALE] button, the button led light turns on, and enter the
SCALE function menus. User can adjust the following items by the knob or
umber buttons :
H SIZE: Width setting.
V SIZE: Height setting.
H/V SIZE: Width and height equal proportion scale setting.
H POS: Horizontal phase setting.
V POS: Vertical phase setting.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
reset.
For details, please refer to the instructions in the manual: How to Set up the
Size and Position of the Single Image.

5. Communication Software Guideline
In This Chapter
This chapter provides detailed information about the control
communication software. The following topics are discussed:
Software Installation
Software Operation
How to Connect Windows Control Program by RS232
Interface
How to Connect Windows Control Program by USB Interface
How to Connect Windows Control Program LAN Interface

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Installation
Software Installation
VENUS X1 video processor is configured with user friendly communication
software, support drag and drop operation for edit and display. Also it can
be customized with schedule function.
Double click to install, English version default
for use, click ―Next‖ to next dialog:
And in next dialog is the user agreement of the software, click Agree to go
on:

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Installation
User can select ―Chan
ge‖
to choose the VENUS X1 install software:

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Installation
Click ―Next‖ to go on:
Click ―Next‖ to go on:

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Installation
Click ―Next‖ to go on:
Click ―Finish‖ and ready to run VENUS X1 console.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Software Operation
Install communication which comes with the package of VENUS X1 device.
Double click icon from home screen to run the
software.
Double click icon to run the softw are.
VENUS X1 communication software interface as shown:
Connection
Besides the power cord, the product default equip with the RS-232 line,
DB9F line, and RJ11 (6 B4C) line to connect VENUS X1 to the windows
control program.
For more detailed information, please refer to: ―How to Connect Windows
Control Program by RS232 Interface‖. In addition, we also equipped with
USB line, you can also connect the computer and video processor with it to
control PC software. Please refer to ―How to Connect Windows Control
Program by USB Interface‖ for more detailed information.
Note
RS 232 serial cable and USB cable can do
100M program upgrade.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Ethernet, user can fill any number less than 1023 in local port, the remote
port must be 192.168.0.100 and the remote port must be 1000. After
setting above, click the icon to connect with the net work. If
successful connect, the icon becomes , status on the left button
showing .
Use
File Toolbar
: Open script. User can open saved script and alter its parameters.
: Save script. Save current user parameters as script to the
prescribed path.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Communication Toolbar
: Open COM
: Close COM
: Set COM.
Device Toolbar
: Synchronization.
: Save to flash.
: Load form flash.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
: Factory setup.
Schedule Toolbar
: Customize schedule.
: Execute schedule. Execute tasks according to schedule.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Output Resolution Toolbar
User can choose different output resolution by selecting from pull down list.
VENUS X1 has 21 output resolutions for users selection.
Note
Same as MENU OUTPUT STANDARD
Display Mode Toolbar
Choose to work in one window or two window.
Layout Toolbar
In single channel mode, the dialog is in grey and it is in limited use.
And in dual channel mode, user can set the device to work in PIP or PBP
mode directly with quick preset layout button as following.
Aspect Ratio Toolbar
Users can select 4:3, 16:9 or Normal in the pull-down options.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Note
Same as MENU OUTPUT ASPECT
RATIO.
Signal Input Toolbar
The white area displays the name of input signal when click the input
interface on the left. The red box means current selected interface.
When user select two window mode, click the input interface on the left to
choose the channel signal. The green box means current select channel 2.
Screen Parameter Toolbar
User can set size and position of the screen, mainly applies to LED screens
users. After setting screen parameter, in PIP or PBP mode, the image will
display on corresponding screen.
Note
Same as MENU OUTPUT SCREEN
PARAMETERS

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Image Toolbar
Scale, zoom or crop the image. Image 2 can’t choose in one window mode.
Same operation in tw o window mode.
Display Toolbar
Users can set the display mode and gamma. There are three modes, black,
live video and freeze frame. It outputs black signal when choose black, and
the video plays in live mode and stop playing in freeze mode.
Generally, it is not recommend to set the gamma, since LED screen itself
has Gamma function. For further information, users can contact with our
customer service.
Output Toolbar
User can customize the brightness and the contrast.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Note
Same as MENU PICTURE
IMAGE QUALTY
Images Display Toolbar
User can customize the image position and size by dragging the image in
this area. This process is sync to the parameters in image toolbars.
User Mode Toolbar
Users can recall the saved user mode1, mode2 or mode3.
Log Toolbar
User can save or delete the operate log file.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Information Toolbar
It is the VENUS X1 connect state, device name, software version and
serial number.
Control
Synchronizati on:
Read the current parameters of VENUS X1.
Device IP:
Users can set equipment IP, mask and gateway, usually used in one
computer control or remote control several computers. It takes effect
immediately after users change IP through serial port; and when users
change IP through network, it takes effect after reopen the software.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Output Adjust:
Choose the output port and set the output mode, data range, bit depth and
DE.
EDID Manage :
Choose the EDID date source and input port.
VENUS X1 supports the EDID manage ports and types are as follows:

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Supported EDID
Manage Port
Supported EDID Manage Type
VGA
RGBVGA, OUT_VGA, FOLLOW, CUSTOM
DVI
RGBDVI, RGBHDMI, OUT_DVI1, OUT_DVI2,
FOLLOW, CUSTOM
EXT_HDMI
RGBDVI, RGBHDMI, OUT_DVI1, OUT_DVI2,
FOLLOW, CUSTOM
EXT_VGA
RGBVGA, OUT_VGA, FOLLOW, CUSTOM
EXT_DVI
RGBDVI, RGBHDMI, OUT_DVI1, OUT_DVI2,
FOLLOW, CUSTOM
Audio:
User can enable or disable the audio function. If choose ―ON‖, user can set
the volume, mode, DVI and DP.
Graphic Overlay:
Choose the preset mode, blend mode, and set the alpha and color.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Split Joint:
User can enable or disable the split joint function. When choose ―ON‖,
choose the split mode, and set Equ Split or UnEqu Split according to actual
need.
Hot Backup:
User can enable or disable the hot backup function. Choose ―ON‖ to set the
backup signal for BACKUP_1 to BACKUP_5. It will switch to the backup
signal if interrupt signal.
Device Update:
Factory Setup:
Click ―Factory Setup‖, previously saved user mode will be cleared.

5. Communication Software Guideline
Software Operation
Language
This software supports both Chinese and English, user can switch the
language by ―Langu
age‖
option.
Admin
Advance Debug: User should input the password in the ―Admin
Password‖ dialog for advance debug:
Note
Advance is only done by engineer. If need,
please connect us for password.
Help
Version Explain: Show the content of software update history.
About: Show software version and company information.

5. Communication Software Guideline
How to Connect Windows Control Program by RS232 Interface
How to Connect Window Control Program
by RS232 Interface
Firstly, install the control software in your PC.
Take out the RS 232 cable as following(RS-232, with 9-pin on one end,
RJ 11 on the other side). Connect one side of the RJ11 download line to
the RS232 on the video processor VENUS X1, and the other side to be
connected to the serial port on the PC.
There is no any serial port on your PC, you will need another Serial to USB
adapter. Connect one end of the RJ11 download line to the RS232 on the
video processor. Connect the end of USB-side to the PC; Ensure the cable
connection is good. Turn on the Video Processor VENUS X1.
Right click the [My Computer] on the home screen of control PC. Enter
[Attribute], Find [Hardware] Option, as following.

5. Communication Software Guideline
How to Connect Windows Control Program by RS232 Interface
Click [Device Manager] ―+‖ on the left, check the COM number, as following,
COM1 is offered.
Remember the COM you are using and then run the control software, find
[Communication] option. In default, first time user have to click
button, as following:

5. Communication Software Guideline
How to Connect Windows Control Program by RS232 Interface
Check and tap [Serial], Serial Port , for example, is COM6 which is checked
from device manager. Set VENUS X1 Boud Rate to be :115200, Click
[Confirm] after setting.
Click [open serial], check if [COM] icon is on the bottom right
corner,when there is the prompt green showing on
the software, it means the communication is ok , and you can use the
software to control the device now.
Note
If power off during communication, should close
the port , by first, and plug in out of the USB
and do communication.

5. Communication Software Control Guide
How to Connect Window Control Program by USB Interface
How to Connect Windows Control
Program by USB Interface
Install the driver.
Connect the USB cable to the PC and the video processor. Turn on the
VENUS X1, for the first time to use USB, the PC will remind finding the new
hardware and ask to install the driver for this new driver:
Install from the list or specified location, press ―NEXT‖:
Press ―brows
er‖
to find the driver, and press ―NEXT‖:

5. Communication Software Control Guide
How to Connect Window Control Program by USB Interface
When the installation finish, can go to check the installed COM port inside
the device management, as following image shows:

5. Communication Software Control Guide
How to Connect Window Control Program by USB Interface
Install the console software, and run after install, shows the interface of the
console as following:
Select the COM as installed just now, and set the VENUS X1 Boud Rate to
be: 115200.

5. Communication Software Control Guide
How to Connect Window Control Program by USB Interface
Press to start communication, when there is green point in the right
down corner showing on the software, it means the communication is ok,
and you can use the software to control the device now, the software
operation is the same as VENUS X1.

5. Communication Software Control Guide
How to Connect Windows Control Program by LAN Interface
How to Connect Windows Control
Program by LAN Interface
First, install the windows control software to the control computer;
Connect VENUS X1 and computer with cable, the connection diagram is
as follow:
Power on VENUS X1 and start the network function, specific steps as
below:
The first step: push MENU button, login MENU—SY STEM—ETHERNET,
check the IP address of the equipment, the equipment factory default IP
address : 192.168.0.100.
The second step: check computer IP address:
Click start, then press button Run ,
Enter <cmd>,then click< ok> ,
Enter <ipconfig>

5. Communication Software Control Guide
How to Connect Windows Control Program by LAN Interface
Then press <Enter> button, the IP address (the red circle) will display on
the computer: 192.168.0.132 .
The third step: Equipment IP address :192.168.0.100.
Computer IP address :192.168.0.132.
The fourth step: the two IP address are in the same band, i.e.192.168.0.XXX, the
fourth section numbers (XXX) will not repeat previous.
If so, the communication connection can be built by line CAT5.
Note
If computer IP address and equipment IP
address are not in same band, For example, the
computer IP address is 218.032.010.201;We
need to revise the computer IP address to
192.168.0.xxx.
Open network connections, right click on
properties, Select Internet protocol

5. Communication Software Control Guide
How to Connect Windows Control Program by LAN Interface
(TCP/IP),then Click properties,
,
, , Now we can revise the
equipment IP address to the same band with
that of computer 192.168.0.XXX;
The fifth step: Open windows control software, click ico,
Interface display as below:
Select [Enternet]:
Input equipment IP address, click [OK].
Click to open the serial port, if the [Comm] button (in the lower-right
corner of the control software interface) is green, and log outputs
information smoothly, then you would control the device through PC
software.

6. System Setup and Operations
In This Chapter
This chapter provides comprehensive instructions for system setup and
operations. The following topics are discussed:
Interface and Input Signal Option
How to Realize Single Image Switching
How to Set up the PIP
How to Set up the SPLIT
How to Set the Size and Position of the Single Image
How to Choose and Custom Output Resolution
How to Realize the Screen Size Setting
How to Zoom the Image
How to Realize the Text Overlay Setting
How to User Define the BLACK Key
How to User Define the SCALE Key
How to Use Black Out
How to Realize LAN Remote Control Settings
How to Save the Parameter
How to Load the Saved Parameter

6. System Setup and Operations
Interface and Input Signal Option
Interface and Input Signal Option
VENUS X1 Back Panel:
NO INTERFACE
NO INTERFACE
1. 2. 3
S. V. D. C. U. H and Audio
Optional Module
11 CVBS Input BNC
4
Dial Switch
12 VGA Input DB15
5
10/100M Interface
13 DVI Input DVI-I
6
USB Interface
14 DVI/DVI LOOP Output DVI-I
7
RJ11 (RS232) Interface
15 DVI Output DVI-I
8. 17 Sending card interface
16 VGA Output DB15
9
Switch
18 Power IEC-3 port
10 HDMI Input HDMI-A
14. 15. DVI output, use for connecting the sending card of LED screen,
and support output formats as following:
800×600@60, 1024×768@60, 1024×768@75, 1280×720@50,
1280×720@60, 1280×768@60, 1280×800@60, 1280×1024@60,
1360×768@60, 1366×768@60, 1400×1050@60, 1440×900@60,
1536×1536@60, 1600×1200@60, 1680×1050@60, 1920×1080@50,
1920×1080@60, 1920×1200@60, 2048×1152@60, 2560×812@60,
2560×816@60.
16. VGA output, connect to monitor or projector which has VGA interface.
Interface, and support output formats as following:
800×600@60, 1024×768@60, 1024×768@75, 1280×720@50,
1280×720@60, 1280×768@60, 1280×800@60, 1280×1024@60,

6. System Setup and Operations
Interface and Input Signal Option
1360×768@60, 1366×768@60, 1400×1050@60, 1440×900@60,
1536×1536@60, 1600×1200@60, 1680×1050@60, 1920×1080@50,
1920×1080@60, 1920×1200@60, 2048×1152@60, 2560×812@60,
2560×816@60.
14. DVI Loop out, connect to the DVI input of the next VENUS X1 or the
device with DVI input.
10. HDMI Input(HDMI-A Port) Input the image signal from computer.
11. CVBS Input(BNC Port)Can receive standard video signal from
players, cameras etc. Input supported resolution 480i and 576i via BNC.
Supported standards include: PAL, NTSC and SECAM.
12. VGA Inpu(t DB15 Port)Can support HD player, computer, video signal.
Input signal through the DB15 interface.
13. DVI Input(DVI-I Port)Input the video signal from computer, DVI signal
generator. If the EDID is HDMI, the DVI can be compatible with HDMI 1.3.

6. System Setup and Operations
SOURCE SELECT:
>DVI
How to Realize Single Image Switching
How to Realize Single Image Switching
System default DVI to the current input source, if need seamless switching
other source such as VGA, push the VGA button, OLED module show as
follows:
SOURCE SELECT:
->VGA
DVI button light turns off after pushing VGA button. VGA button light will be
on if the VGA signal is effective and stable. And if the VGA signal is invalid
or no input, VGA button light will flash.
The same method can switch the signals among CVBS, HDMI and optional
input signal.

6. System Setup and Operation
How to Set up the PIP
How to Set up the PIP
Push the [PIP/DSK] button, button LED light turns on, and enter to the PIP
function menu. OLED module show as follows:
->PIP ON
LAYOUT PIP L+T
SELECT IMAGE A
SWAP WINDOW OFF
->ALPHA 0
LAYOUT: Can choose PIP layouts, the corresponding results are as
follows:
PIP L+T PBP L+R PBP T+B
SWAP WINDOW: It can set PIP to swap exchange, when choose ON, it
can exchange IMAGE A and IMAGE B.
ALPHA: Can set the image transparency, the regulating range is 0 to 16.
SELECT: Can choose to set the size or position of IMAGE A or IMAGE B
individually.
Note
User can also push [SPLIT] function reuse key to
select IMAGE A or IMAGE B.

6. System Setup and Operation
How to Set up the SPLIT
How to Set up the SPLIT
SPLIT is used when multiple VENUS X1 are used in cascade mode. When
do cascade, connect the signals to the signal distributor first, and then
connect from the outputs of the signal distributor to each input of VENUS X1.
The operations are as follows:
Push the [SPLIT] button, the button LE D light will turn on, and enter the split
function menus. Turn the knob to choose the split mode, there are two split
modes, fixed split and normal split, the OLED module show as follows:
—>FIXED SPLIT >>
NORMAL SPLIT >>
FIXED SPLIT: Menus are as follows:
->SPLIT OFF
HORIZONTAL SPLIT 1
VERTICAL SPLIT 1
SPLIT INDEX 1
SPLIT: Split function, can choose ―ON‖ or ―OFF‖. System default ―OFF‖.
HORIZONTAL SPLIT: Horizontal fixed split, choose it and push the number
button to set the total horizontal screen number.
VERTICAL SPLIT: Vertical fixed split, choose it and push the number button
to set the total vertical screen number.
SPLIT INDEX: Use can choose the split index, and the LED screen will show
the corresponding image.
NORMAL SPLIT: For normal split, user should enable the split function, that
is, turn the knob, and set the <SPLIT> as ―ON‖, push the knob to confirm.
System default ―OFF‖. User can set the normal split in the sub menus:

6. System Setup and Operation
How to Set up the SPLIT
—>SPLIT ON
H TOTAL 1920
H TOTAL 1080
H POS 0
—>V POS 0
H SIZE 1920
V SIZE 1080
RESET
SPLIT: Split function, can choose ―ON‖ or ―OFF‖.
H TOTAL: LED screen Horizontal total size.
V TOTAL: LED screen Vertical total size.
H POS: This device display image Horizontal size.
V POS: This device display image Vertical size.
H SIZE: This device display image Width setting.
V SIZE: This device display image Height setting.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
reset.
Save the parameters after setting.

6. System Setup and Operation
How to Set the Size and Position of the Single Image
How to Set the Size and Position of the
Single Image
Push the [SCALE] button, and enter the scale function menus, the OLED
module show as follows:
->H SIZE 1920
V SIZE 1080
H/V SIZE 0
H POS 0
->H POS 0
RESET
User can adjust the following items by the knob or number buttons.
H SIZE: Width setting.
V SIZE: Height setting.
H/V SIZE: Width and height equal proportion scale setting.
H POS: Horizontal phase setting.
V POS: Vertical phase setting.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover by
reset.

6. System Setup and Operation
How to Choose and Custom Output Resolution
How to Choose and Custom Output
Resolution
Choose standard resolution:
Push the [MENU] button to enter the menu items, turn the knob and choose
<OUTPUT>, push the knob to confirm, turn the knob to choose
<STANDARD>, push the knob to confirm, turn the knob again to choose
the output resolution according to actual need.
Customized resolution setting:
Push the [MENU] button to enter the menu items, turn the knob and choose
<OUTPUT>, push the knob to confirm, turn the knob to choose
<CUSTOMIZED>, push the knob to confirm.
CUSTOMIZED:
->1920×1080@60
Turn knob on each digital position, and change the value of the digital by
the digital buttons on the front panel. For example, input 1536 as following:
CUSTOMIZED:
*1536
×
After the digital, push Knob will add *, means before the * is the horizontal
size. Same operation for vertical size, for example input1536 as following:
CUSTOMIZED:
*1536×1536@
After the digital, push the knob will add @, means before the @ is the

6. System Setup and Operation
How to Choose and Custom Output Resolution
vertical size, and after the @ is the refresh rate. Only digital 50 or digital 60
supports for the refresh rate. Use the digital buttons to finish the settings,
For example, input refresh rate 60.
CUSTOMIZED:
*1536×1536@60
After input all the values, push knob to enable VENUS X1 to output this
resolution. VENUS X1 will take 5~10 seconds to enable this output
resolution.
Note
All the resolution inside the value 2048 x 1152 x
60 = 141557760 can support.
For example:
1) 1536x1536x60=141557760 is OK.
2) 2560x1536x60=235929600 is too big, can not
support.
3) 2560x1152x50 is OK.

6. System Setup and Operation
How to Realize the Screen Size Setting
How to Realize the Screen Size Setting
VENUS X1 supports the screen parameters to meet the requirement where
user want to switch between scale screen size and full display size (like
monitor). This is only enable for a single display window. Following is an
example of a screen size is1408 x 832.
Operator can defined the VENUS X1 output resolution from standard
output resolution list or customized the output resolution which is higher
than1408 x 832. For this application 1440x900 is an example:
Push the [MENU] button to go into the main menu, turn the knob and
choose <OUTPUT>, push the knob to confirm, turn the knob to choose
<SCREEN PARAMETERS>, push the knob and goes into the SCREEN
PARAMETERS menus as following:
H SIZE--Horizontal pixels, turn the knob or use the digital button to input
the value1408.
V SIZE--Vertical pixels, turn the knob or use the digital button to input the
value 832.
H POS--Horizontal position, default value is 0, set the value as the way of H
SIZE and V SIZE.
V POS--Vertical position, default value is 0, set the value as the way of H
SIZE and V SIZE.
MODE-- Mode option, choose SCREEN SIZE.
RESET: If image quality distorts by improper operation, it can be recover
by reset.

6. System Setup and Operation
How to Zoom the Image
How to Zoom the Image
The image can be zoom in horizontal or vertical separately, to meet the
special effects required.
Push the [MENU] button to go into the menu items, turn the knob and
choose <INPUT>, push the knob to confirm. Turn the knob, and choose
<ZOOM>, show the menus as following:
V UP--Zoom in vertical and the image will be zoom in to the top direction
from its bottom.
V DOWN--Zoom in vertical and the image will be zoom in to the down
direction from its top.
V UP/DOWN--Zoom in vertical but in both top and down direction from its
middle.
H LEFT--Zoom in horizontal and the image will be zoom in to the left
direction from its right.
H RIGHT--Zoom in horizontal and the image will be zoom in to the right
direction from its left.
H LIFT/RIGHT--Zoom in horizontal but in both left and right direction from
its middle.
CENTER--Zoom in 4 corner direction from center.

6. System Setup and Operation
How to Realize the Text Overlay Setting
How to Realize the Text Overlay Setting
Before setting the text overlay, please make sure the input channel of the
text. For example, set VGA input as the text channel. Then make sure the
channel that the text will overlay, for example, overlay the text on DVI
channel. The operations are as follows:
1. Push the VGA button to make sure there is VGA input.
2. Push the DVI button to make sure there is DVI input.
3. Push the [MENU] button, turn the knob, choose <PICTURE>, push the
knob to confirm, turn the knob, and choose <TEXT OVERLAY>, push
the knob to confirm.
IMAGE QUALITY >>
->TEXT OVERLAY >>
Then enter into TEXT OVERLAY menu items, turn the knob, and
choose <TEXT OVERLAY>, push the knob to confirm, turn the knob
again, and choose ―ON‖ to enable the text overlay function.
*TEXT OVERLAY ON
PRESET USER MODE
BLEND MODE MODE1
BLEND LEVEL 0
4. Make sure VGA input is IMAGE B, and DVI input is IMAGE A, if not,
choose <SWAP WINDOW> option by push [PIP/DSK] button, and
choose ―ON‖ for <SWAP WINDOW>.
PIP ON
LAYOUT PIP L+T
SELECT IMAGE A
->SWAP WINDOW ON
5. Choose the VGA image in ―IMAGE
B‖
in <SELECT> option by pushing

6. System Setup and Operation
How to Realize the Text Overlay Setting
<PIP/DSK> button, and push [SCALE] button to adjust the size and
position of VGA image, then set the VGA image to the required position.
->H SIZE 1920
V SIZE 1080
H/V SIZE 0
H POS 0
->V POS 0
RESET
The standard position and size is: ensure the VGA image overlay on the
DVI image, display normally and without black edges. If there are black
edges around VGA image, choose <ZOOM> option in <INPUT> to
adjust.
6. Set the text overlay mode: choose <PRESET> option in <TEXT
OVERLAY>, push the knob to enter into the <PRESET> menu items.
Turn the knob to choose the preset mode, for example, set the VGA text
as WhOnBk, choose WhOnBk1 or WhOnBk2 (Note: Text Overlay only
support monochrome subtitles), user can also adjust the <BLEND
MODE> or <BLEND LEVEL> to get a better effect.
TEXT OVERLAY ON
->PRESET WhOnBk2
BLEND MODE MODE1
BLEND LEVEL 0
7. Push the [SAVE/1] button to save the above parameters.

6. System Setup and Operation
How to User Define the BLACK Key
How to User Define the BLACK Key
System default the [BLACK] button as black function. Push the button, its
LED light turns on, the output will be switched to black, push the button
again, its LED light is off, and output the video image.
For more details, please refer to: How to Use Black Out.
Besides BLACK, user can define this button as FREEZE, TEST PATTERN
and BRIGHT, the operations are as follows:
1. Push the [MENU] button to enter to the menu items, turn the knob, and
choose <SYSTEM>:
->SYSTEM >>
LANGUAGE/语言 ENG
FACTORY RESET >>
2. Push the knob to confirm, turn the knob, and choose <USER DEFINED
BUTTON>:
FAN CONTROL >>
DEVICE STATUS
>>
->USER DEFINED BUTTON >>
OLED LUMINANCE 13
3. Push the knob to confirm, turn the knob, and choose <BLACK KEY>:
->BLACK KEY BLACK
SCALE KEY SCALE
4. Push the knob to confirm, turn the knob, and choose <FREEZE>, <TEST
PATTERN> or <BRIGHT>, push the knob to confirm.

6. System Setup and Operation
How to User Define the BLACK Key
->BLACK KEY FREEZE
SCALE KEY SCALE
(1) If choose <FREEZE>, push the button, its LED light turns on, and
freeze the image.
FREEZE IMAGE
Push the button again, its LED light is off, and output the video image.
VIDEO IMAGE
(2) If choose <TEST PATTERN>, push the button, its LED light turns
on, the output will be switched to test pattern.
->TEST PATTERN 35
AUTO SWITCH OFF
There are 66 kinds of test patterns. If choose <AUTO SWITCH>,
VENUS X1 will output all the test patterns one by one, and the interval
between is 1 to10S.
Push the button again, its LED light is off, and output the video image.
VIDEO IMAGE

6. System Setup and Operation
How to User Define the BLACK Key
(3) If choose <BRIGHT>, push the button, its LED light turns on,
user can adjust the brightness, contrast, saturation, sharpness, color
red, color green, color blue and gamma. If image quality distorts by
improper operation, it can be recover by reset.
->BRIGHTNESS 50
CONTRAST 50
SATURATION 50
SHARPNESS 50
->COLOR RED 50
COLOR GREEN 50
COLOR BLUE 50
GAMMA LINEAR
->RESET

6. System Setup and Operation
How to User Define the SCALE Key
How to User Define the SCALE Key
System default the [SCALE] button as scale function. push the button to
enter the scale menu. Turn the knob to select the relevant sub menus.
For more details, please refer to: How to Set the Size and Position of the
Single Image.
Besides SCALE, user can define this button as TAKE, the operations are
as follows:
1. Push the [MENU] button to enter to the menu items, turn the knob, and
choose <SYSTEM>:
->SYSTEM >>
LANGUAGE/语言 ENG
FACTORY RESET >>
2. Push the knob to confirm, turn the knob, and choose <USER DEFINED
BUTTON>:
FAN CONTROL >>
DEVICE STATUS
>>
->USER DEFINED BUTTON >>
OLED LUMINANCE 13
3. Push the knob to confirm, turn the knob, and choose <SCALE KEY>:
BLACK KEY BLACK
->SCALE KEY SCALE
4. Push the knob to confirm, turn the knob, and choose <TAKE>, push the
knob to confirm.
 Loading...
Loading...