Page 1

Talking Wrist Style
Blood Pressure Monitor
Model 1145
Page 2

1 2
Introduction
Thank you for selecting the Lumiscope Model 1145
Talking Wrist Type Blood Pressure Monitor. The 1145
features voice announcement and playback of blood
pressure measurements for added convenience and has
been designed to provide you with many years of reliable
service. The unit can help you measure and track the
following values:
• Systolic pressure
• Diastolic pressure
• Mean arterial pressure
• Pulse rate
• Historic record of up to 60 measurements per user
(maximum 2 users)
Readings taken by the 1145 are equivalent to
those obtained by a trained observer using the
cuff and stethoscope auscultation method, within
the limits prescribed by “EN1060-3 Non-invasive
Sphygmomanometers-Part 3: Supplementary
requirements for electro-mechanical blood pressure
measuring systems.” The monitor’s accuracy in
measuring diastolic pressure was tested using the fifth
Korotkoff sound method.
Please read this manual thoroughly before using the
product.
Key Features
1. TALK / VOLUME button
2. LCD
3.
ON / OFF button
4. Speaker
5. USER 1 / UP ARROW
button
6. USER 2 / DOWN ARROW
button
7.
SET button
Contents
Introduction .............................................................2
Key Features ............................................................
2
Front View ..........................................................2
Rear View ..........................................................3
LCD Symbols .....................................................3
Safety and Care Instructions ....................................4
Safety Precautions ............................................. 4
Caring for Your Blood Pressure Monitor .............. 5
About Blood Pressure ...............................................5
How the Blood Pressure Monitor Works ....................7
Getting Started ........................................................ 7
Installing and Replacing the Batteries ................ 7
Setting Date, Time and Measurement Units ........8
Positioning the Wrist Cuff ................................... 8
Voice Playback of Blood Pressure Measurements .....
9
Volume Control ..................................................9
Taking a Blood Pressure Measurement .................... 9
Recalling Measurements Stored in Memory ...........11
Deleting a Measurement Record from Memory ......12
Deleting the Latest Record ............................... 12
Deleting All Records ......................................... 13
Troubleshooting ..................................................... 13
Technical Specifications .........................................15
Warranty ................................................................ 16
Blood Pressure Log Book ....................................... 17
1
2
3
5
4
6
7
Page 3
PRECAUTIONS
Please observe the following safety precautions when
setting up and using your blood pressure monitor.
• This device is intended for adult use only.
• This device is intended for non-invasive measuring
and monitoring of arterial blood pressure. It is not
intended for use on extremities other than the wrist
or for functions other than obtaining a blood pressure
measurement.
• Do not confuse self-monitoring with self-diagnosis.
This unit allows you to monitor your blood pressure.
Do not begin or end medical treatment based solely
on the measurements of this device. Consult a
physician for treatment advice.
• If you are taking medication, consult your physician
to determine the most appropriate time to measure
your blood pressure. Never change a prescribed
medication without consulting your physician.
• This unit is not suitable for continuous monitoring
during medical emergencies or operations.
• If the cuff pressure exceeds 40 kPa (300 mmHg), the
unit will automatically deflate. Should the cuff not
deflate when pressures exceeds 40 kPa (300mmHg),
detach the cuff from the wrist and press the
button to stop inflation.
• To avoid measurement errors, carefully read this
manual before using the product.
User Shows which user
profile (1 or 2 is
being displayed)
Memory
If “MEM” shows,
the displayed
measurement value is
from the memory and
not necessarily from
the last reading
Weak battery
Batteries are low
and need to be
replaced
Inflating
Unit is inflating
with air to obtain
the needed level of
pressure
Deflating
Wrist cuff air is
exhausting or
deflating
Millimeter(s) of
mercury
Measurement unit
for blood pressure
Kilopascal
Measurement unit
for blood pressure
Voice activation
Voice announcing
your blood
pressure measured
kPa
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION EXPLANATION
Systolic pressure
The highest blood
pressure measured
Diastolic pressure
The lowest blood
pressure measured
Time (hour: minutes)
Current time
Mean arterial
pressure
Average blood
pressure measured
(see “What is Mean
Arterial Pressure
(MAP)?” for more
information)
Pulse Pulse rate per
minute
Display Explanation
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION EXPLANATION
3 4
2
1
1. Wrist cuff
2. Battery compartment
Page 4
6
on the arterial wall when there is no distension outward
or inward. MAP is an excellent way to evaluate the
stress on the walls of your blood vessels, and can be
used to evaluate excessive load on the cardiovascular
system. Show your MAP history to your doctor to
provide additional information that may help him or her
understand your situation.
Why measure your blood pressure?
Blood pressure measurement can highly reflect one’s
health condition. High blood pressure is potentially linked
to serious illnesses such as stroke, heart disease and
kidney failure.
Since there is no symptom most of the time, many
hypertensive people do not realize they are at risk until
their health is seriously threatened.
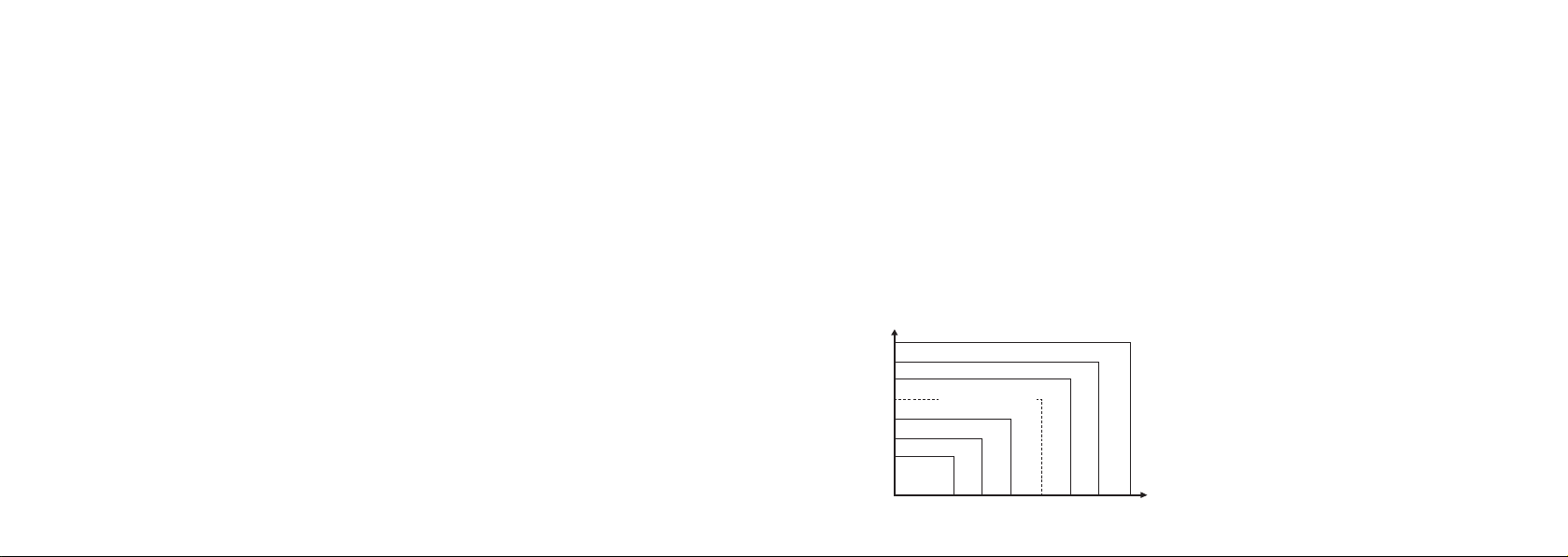
What is the standard blood pressure classification?
Figure 3 illustrates the blood pressure classifications
by World Health Organization (WHO) and International
Society of Hypertension (ISH) in 1999.
Reference material: 1999 World Health Organization
International Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the
management of hypertension, Journal of Hypertension,
1999, 17(2): 151-183.
NOTE:
• Blood pressure is considered high when either the
diastolic or systolic blood pressure value exceeds the
normal range. When a patient’s systolic and diastolic
blood pressures fall into different categories, the
higher category should apply.
• Only a physician can tell you your normal blood
pressure range and the point at which you are at risk.
Consult your physician to obtain these values. If the
measurements taken with these products fall outside
the range, consult your physician.
Why does my blood pressure fluctuate
throughout the day?
Individual blood pressure varies greatly both on a daily
and a seasonal or temperature basis. These variations
may be more pronounced in hypertensive patients.
Normally the blood pressure rises while at work and is at
its lowest during sleep.
5
Caring for your Blood pressure monitor
To ensure you receive the maximum benefit from
using this product, please observe the following care
guidelines.
• When not in use, store the unit in a dry place away
from direct sunlight.
• Do not immerse the unit in water. If it comes in
contact with water, dry it immediately with a soft lintfree cloth.
• Use a soft, slightly moistened cloth to wipe off the unit
and cuff. Do not use abrasive or corrosive cleaning
agents, as these may cause damage.
• Remove the batteries whenever you are planning to
store the unit for a long period of time.
• When replacing batteries, use new batteries as
specified in this user manual. Do not mix new and old
batteries.
• Do not place objects such as stickers on the wrist cuff
or unit, as these may impair the measurement.
• Do not subject the unit to excessive force, shock,
dust, temperature changes, or humidity. Such
treatment may result in malfunction, a shorter
electronic life span, damaged batteries, or distorted
parts.
• Do not tamper with the internal components. Doing
so will terminate the product warranty and may cause
damage.
• The unit contains no user- serviceable parts.
• If you no longer need to use this product, protect
the environment by bringing it to your dealer or
designated collection point for proper disposal.
About Blood Pressure
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the force generated by the blood
against the walls of arteries during cardiac contraction
and relaxation (e.g., the pumping action of the heart).
What are systolic pressure and diastolic pressure?
When ventricles contract and pump blood out of the
heart, blood pressure reaches its maximum value.
This highest pressure in the cycle is known as systolic
pressure. When the heart relaxes between heartbeats,
the lowest blood pressure is diastolic pressure.
What is mean arterial pressure (MAP)?
The mean arterial pressure (MAP) is the average
pressure that forces blood through the arteries. It is
not the average of the systolic and diastolic blood
pressure; rather, MAP corresponds to a state of balance
between the compressive and expansive forces acting
120 130 140 150 160 170 180
110
100
95
90
85
80
Grade 3 hypertension (severe)
Grade 2 hypertension (moderate)
Grade 1 hypertension (mild)
Subgroup borderline
High-normal Blood Pressure
Normal Blood Pressure
Optimal Blood
Pressure
Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg)
Systolic blood pressure (mmHg)
Page 5
8
all the batteries at the same time - it is dangerous to
mix old and new batteries.
Contact your local waste
disposal authority for instructions on how to dispose
of used batteries. Used batteries can be harmful to
the environment, and should not be thrown out with
household trash.
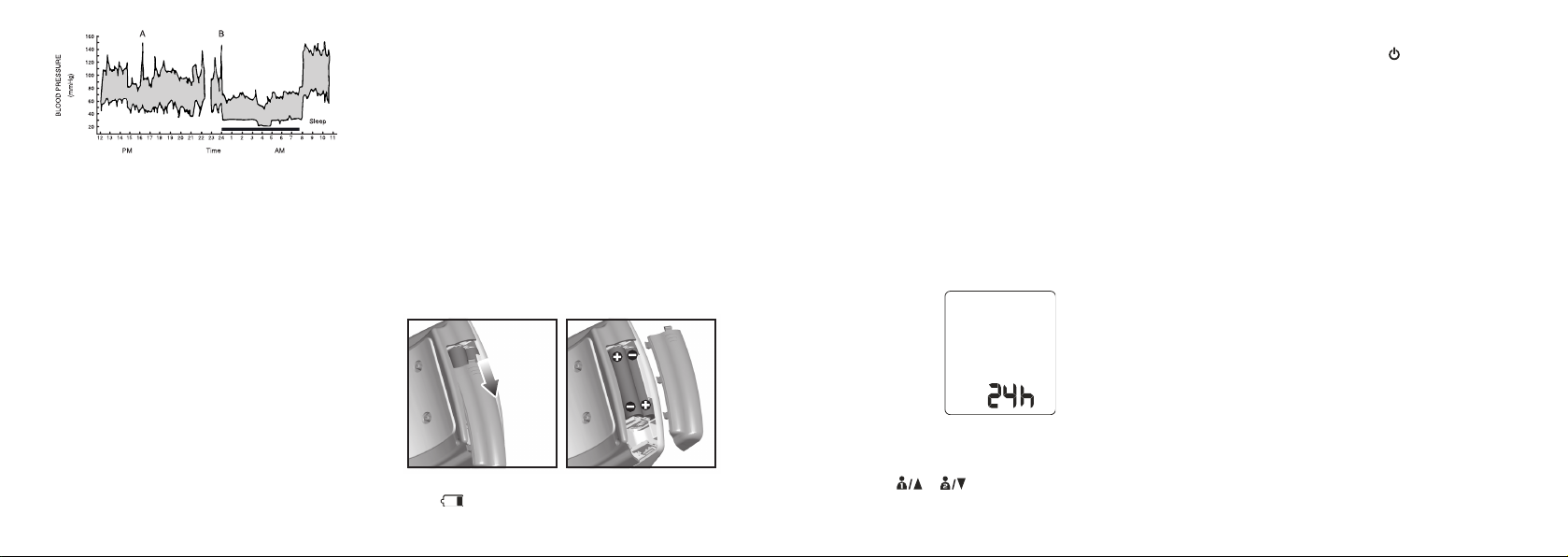
Setting Date, Time And Measurement Units
It is important to set the clock before using your blood
pressure monitor, so that a time stamp can be assigned
to each record that is stored in the memory.
1. When the unit is off, press and hold SET for 2 seconds
to enter the setting mode.
2. The setting order is as follows: 12/24 hour format,
hour, minute, year, month/day or day / month format,
month, date, and measurement unit (kPa or mmHg).
3. Press
or to increase / decrease a value or
change the setting.
4. Press
SET to accept the change and switch to the
next setting.
5. When you are finished, press
to exit the setup
menu.
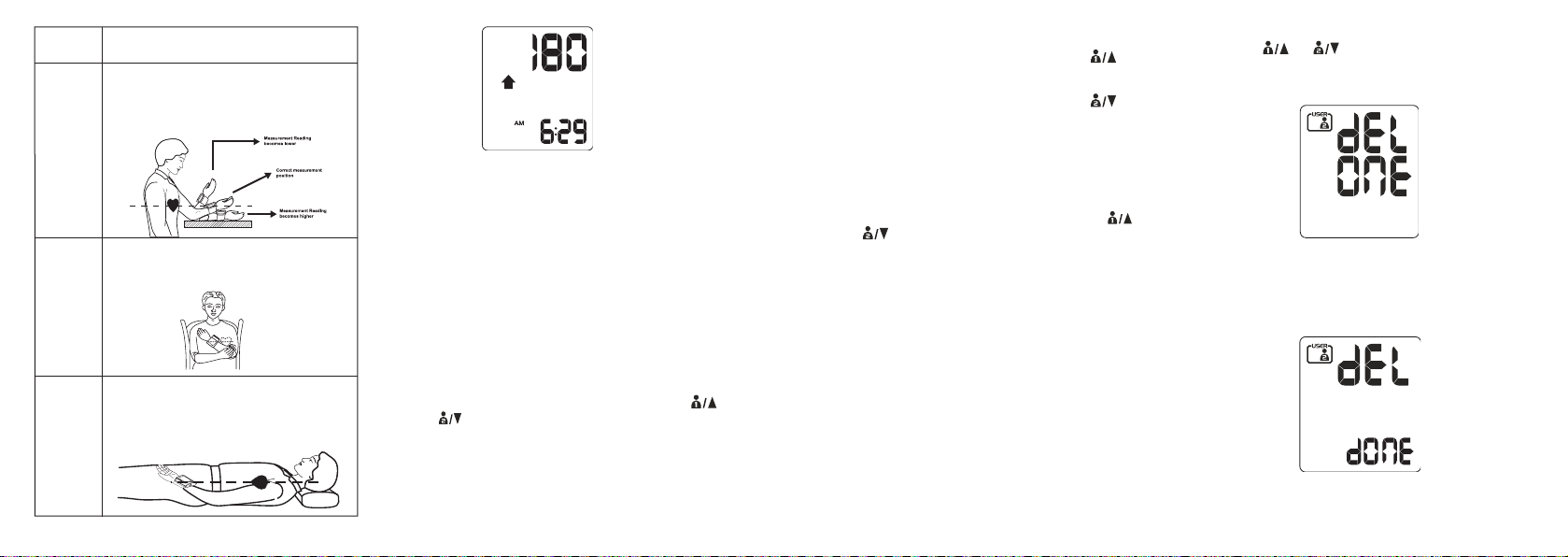
Positioning The Wrist Cuff
It is important to properly position the wrist cuff to
ensure that you receive an accurate reading.
1. Remove all accessories (watch, bracelet, etc.) from
your left wrist. If your physician has diagnosed you
with poor circulation in your left arm, use your right
wrist.
2. Roll or push up your sleeve to expose the skin.
3. Apply the cuff to your left wrist with your palm facing
up.
4. Position the edge of the cuff about 0.4 inches (1cm)
from the bottom of your palm.
5. Fasten the wrist cuff around your wrist, leaving no
extra room between the cuff and your skin. If the cuff
is too loose, the measurement will not be accurate.
7
The graph above illustrates the variations over a single
day with measurement taken every 5 minutes. The thick
line represents sleep time. The rises in blood pressure
at 4PM (A in the graph) and 12AM (B in the graph)
correspond to an attack of pain and sexual intercourse
(Beven, Honour & Stott, Clin. Sci. 36:329, 1969).
How The Blood Pressure Monitor Works
This product uses the Oscillometric Measuring method to
detect your blood pressure. Before every measurement,
the unit establishes a “zero pressure” equivalent to the
air pressure.
Then it starts inflating the wrist cuff to 180mmHg or
higher until it senses that it has blocked your blood
in the artery. After that, the deflation process starts,
during which time the unit detects pressure oscillations
generated by beat-to-beat pulsatile, which is used to
determine the systolic, mean and diastolic pressure, and
also your pulse rate. Any motion during this period will
result in an incorrect measurement. After all readings are
determined and displayed on the LCD, the measurement
is finished and the wrist cuff automatically deflates.
Getting Started
Installing And Replacing The Batteries
1. Slide off the battery cover.
2. Install the batteries by matching the correct polarity,
as shown below. Always use the correct battery type
(2 alkaline LR03 AAA-size).
3. Replace the cover.
NOTE: Replace the batteries whenever the weak battery
mark shows, the display is dim, or the display
does not illuminate when the power is on. Replace
Page 6
10
NOTE: When volume level 0 is selected, the unit is
on mute and you will not hear any voice messages
announced.
Taking A Blood Pressure Measurement
You can choose to take your blood pressure while sitting
or lying down. Below are some helpful tips for taking a
measurement:
• Be sure to set the clock before taking your first
measurement, or whenever you replace the batteries,
so that the date and time are stored in the memory
with your history. For instructions, refer to p. 8.
• It is important to relax when taking your blood
pressure. Try to take a 15-minute rest before you
begin.
• Do not lean backward or bend your wrist inward while
taking a measurement.
• Avoid talking or moving your fingers and hand while
taking a measurement. Rapid movements or other
activities may alter your reading.
• Wait at least an hour before taking your blood
pressure if you have just eaten a large meal.
• Do not smoke or drink alcohol before taking your
blood pressure.
• Do not measure your blood pressure if you are under
stress.
• Wait at least 3 minutes between measurements. This
allows your blood circulation to recover.
• For a meaningful comparison, try to measure
under similar conditions. For example, take daily
measurements at approximately the same time, on
the same wrist, or as directed by a physician.
• To stop the measurement process at any time, press
• The unit automatically switches off 1 minute after
taking a measurement. To save the battery life, press
as soon as you are finished to turn off the unit.
To take a measurement:
1. Choose the position you from which you wish to
measure - sitting or lying down.
2. Position your body so that your wrist is parallel with
your heart, using the chart and illustrations below as
a guide.
3. Relax your hand and press
to turn on the unit.
A voice message will remind you to relax and remain
still. It then begins inflating the wrist cuff. Once the
pressure reaches 180 mmHg, it will slowly deflate
until the measurement results show on the LCD.
9
Voice Playback Of Blood Pressure
Measurements
The 1145 features voice playback during and after
blood pressure measurement results, as well as
general instructions to help you prepare for taking
measurements. When the unit has finished taking your
measurement, your blood pressure readings, pulse and
blood pressure classification are announced.
If you want to repeat the announcement, simply press
TALK / VOLUME
.
Anytime you recall a measurement record from memory,
it will also be announced. Press TALK / VOLUME
if you
need to repeat the playback of any record.
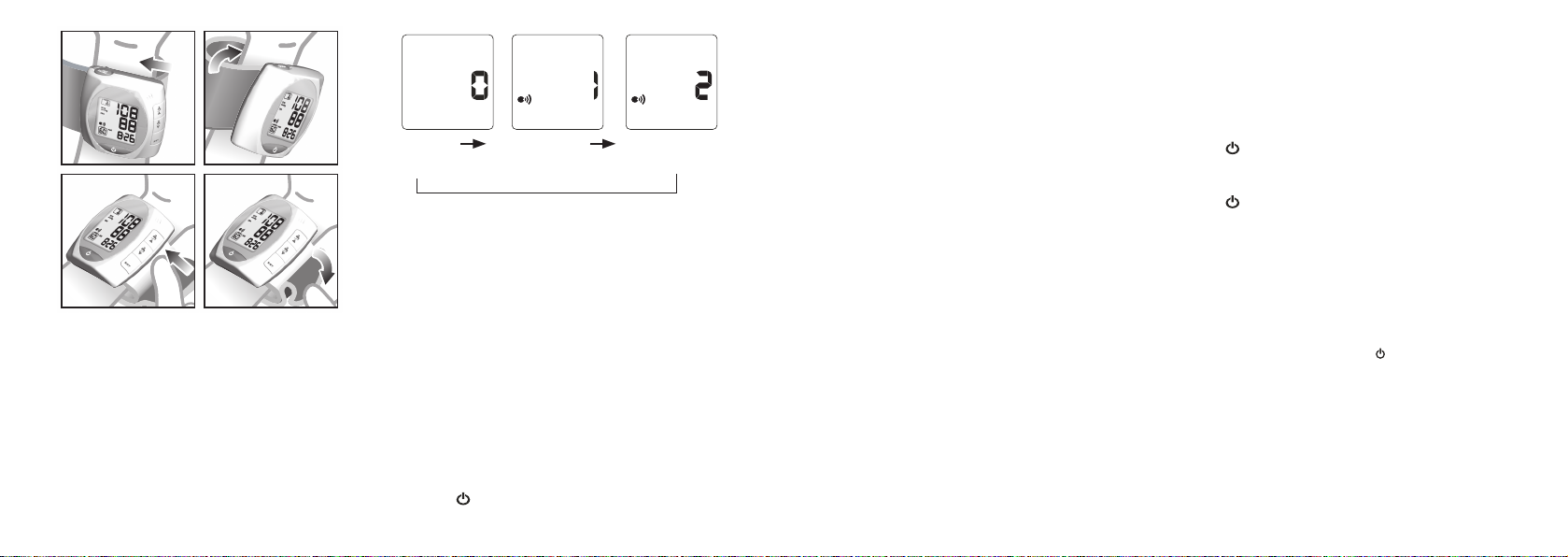
Volume Control
To adjust the volume level:
1. Press and hold TALK / VOLUME until volume level
flashes on the LCD.
2. Press TALK / VOLUME to adjust volume level.
3. Press
when you have finished adjusting the
volume.
0 1 2
(MUTE) (Volume is LOW) (Volume is HIGH)
Page 7
12
Recalling Measurements Stored In Memory
To view a history of User 1’s records, press
.
To view a history of User 2’s records, press .
NOTE:
• The most recent record (1) is shown first. Each new
measurement is assigned to the first (1) record.
All other records are pushed back one digit (e.g., 2
becomes 3, and so on), and the last record (60) is
dropped from the list.
• Press the corresponding user button again (
or
) to see additional records.
• Press and hold the corresponding user button to autoadvance to additional records.
• The date and time of measurement are shown with
each record.
• Memory records will be kept even when the batteries
become exhausted and are replaced.
Deleting A Measurement Record From Memory
You have the option of deleting your latest measurement
record or entire measurement history. This is useful if
measurements have not been accurately recorded and
need to be recorded again.
Deleting The Latest Record
1. Press or to recall the latest measurement
record for User 1 or User 2.
2. Press and hold
SET until the LCD shows “dEL ONE”.
3. Press
SET to delete the latest recorded measurement
for User 1 or User 2. After you have confirmed
deleting the latest record, the screen shows dEL
dONE.
11
NOTE: This unit can intelligently adjust the cuff pressure
and inflate to a higher-pressure level (>180 mmHg)
when needed.
Your systolic and diastolic pressure readings flash on the
LCD, followed by MAP and pulse per minute readings
every 2 seconds. At the same time, your measurement
results and the blood pressure classification will also be
announced.
4. To repeat the announcement, simply press TALK /
VOLUME.
5. If you want to save the record to memory, press
or and the results will be saved to User 1’s or
User 2’s memory accordingly.
The measurement is stored as the first (MEM 1) entry in
the user record you selected; the last entry (MEM 60) is
dropped, and all the entries in between move up 1 digit
(e.g. 58 becomes 59, and so on).
Lying
down
Position your wrist on a support, cushion, or
your thigh so that it is parallel with your heart
with the palm facing up.
IF YOU
ARE...
Sitting
down
with an
armrest
Sitting
down
with no
armrest
Place your elbow on a table, using an object
as a support under your forearm. Your wrist
should be parallel with your heart with the
palm facing up.
Place your arm across your chest with the
wrist parallel to your heart. Hold your elbow
with the other hand.
THEN...
Page 8

14
Problem Symptom Check This Remedy
Error
message
Err shows
on the
display.
A measurement error
occurred
Relax for a
moment and then
measure again
Err 1, 2, or
3 shows
on the
display
The wrist cuff
is not secure
Refasten the cuff
and then measure
again
Err 4
shows on
the display
The monitor
detected
motion while
measuring
Movement
can affect the
measurement.
Relax for a
moment and then
measure again
Err 5
shows on
the display
Pressure is
over 37.3 kPa
(280 mmHg)
Relax for a
moment and then
measure again
Err 6
shows on
the display
Deflation
period was too
long
Movement
can affect the
measurement.
Relax for a
moment and then
measure again
Problem Symptom Check This Remedy
Error
message
Err 7 or 8
shows on
the display
A calibration
error occurred
Retake the
measurement. If the
problem persists,
contact the retailer
or our customer
service department
for further
assistance. Refer
to the warranty for
contact information
and return
instructions
Settings
are wrong
Date and
time are
incorrect
The clock was
not set or reset
after installing
new batteries
Reset the clock
Measurement unit
(kPa or
mmHg) are
incorrect
The
measurement
unit was not set
or reset after
installing new
batteries
Reset the
measurement unit
13
4. If you decide to abort the delete action instead, press
to go back to the main screen.
Deleting All Records
1. Press
or to recall the latest measurement
record for User 1 or User 2.
2. Press and hold
SET until the LCD shows “dEL ONE”.
3. Press
to show the option of deleting your entire
measurement history; the LCD displays “DEL ALL”.
4. Press
SET to delete all measurement records. After
you have confirmed deleting all records, the screen
shows dEL dONe.
5. If you decide to abort the delete action instead, press
once OR press twice to go back to the
main screen.
Troubleshooting
This section includes a list of error messages and
frequently asked questions for problems you may
encounter with your blood pressure monitor. If the
product is not operating as you think it should, check
here before arranging for servicing.
Problem Symptom Check This Remedy
No
power
Display is
dim or will
not light up
Batteries are
exhausted
Replace with new
batteries
Batteries
are inserted
incorrectly
Insert the
batteries correctly
Low
batteries
shows
on the
display
Batteries
are low
Replace
with new
batteries
Page 9

16
Accuracy:
Pressure …………………… +/- 3 mmHg
(+/- 0.4 kPa)
Pulse ……………………… +/- 5%
Power supply ……………… 3V DC, 2 LR03 / AAA /
UM4-size 1.5V batteries
Power save ………………… Auto power off after 1
minute of non-activity
Operating environment:
Operation ………………… 50°F to 104°F
(10°C to 40°C)
Storage / Transport ………… -4°F to 140°F
(-20°C to 60°C)
Humidity range …………… 10% to 83% relative
humidity
Limited Two-Year Warranty
Lumiscope guarantees this product free from defects in material and
workmanship for a period of two years from the date of purchase,
except as noted below:
This Lumiscope product warranty does not cover damage caused
by misuse or abuse, the attachment of any unauthorized accessory,
alteration to the product, or any other conditions whatsoever that
are beyond the control of Lumiscope. Lumiscope shall not be
responsible for any type of incidental, consequential, or special
damage. All implied warranties, including, but not limited to those
implied warranties of fitness and merchantability, are limited to the
total duration of two years from the original date of purchase.
To obtain warranty service on your Lumiscope Blood
Pressure Monitor, please contact the Lumiscope Repair Department
at 1-800-672-8293 or visit www.lumiscope.net. There is a $15 fee
for return shipping and handling. Please make checks payable to
The Lumiscope Co., Inc.
Upon receipt, Lumiscope will repair or replace, as appropriate, this
blood pressure monitor and return it to you. Warranty is solely
through the Lumiscope Repair Department. Service of this product
by anyone other
than the Lumiscope Repair Department voids
warranty.
In the event that Lumiscope does not abide by the terms of this
warranty, the consumer may seek breach of contract remedies in
the New York State Federal courts
of law. This warranty gives you
specific legal rights and you may also have other rights which vary
from state to state.
Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental
or consequential damages, so the above limitation may not apply
to you.
15
Problem Symptom Check This Remedy
No user
memory
Cannot find
a record
The memory
was not saved
after taking a
measurement
Retake the
measurement.
Press or
to save
the corresponding
user’s memory
The record was
stored to the
wrong user
memory
Press to
view User 1’s
record. Press
to view
User 2’s record
Technical Specifications
Measuring method ………… Oscillometric
Measurement location .….….Wrist
Memory …………………… 60 records per user
Maximum number of users … 2
Dimensions ……………… 3.5 x 3.4 x 1.2 inches
(90 x 86 x 30.8 mm)
Weight …………………… 6.3 oz (180g) without
batteries
Cuff circumference ………… 5.3 to 7.7 inches (13.5 to
19.5 cm)
Measuring range:
Pressure ………………… 30 to 280 mmHg (4.0 to
37.3 kPa)
Pulse ……………………… 40 to 200 pulse/min
Page 10

10
17
Name: Age: Weight: (kg/lbs)
Date
Time
SYS
DIS
MAP
158
90
110
155
95
112
S
S
M
M
O
O
OCT OCT
10PM 10PM
8.0
10.7
13.3
16.0
18.7
21.3
24.0
26.7
29.3
85
90
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
200
220
kPa mmHg
17
Distributed By
The Lumiscope Co., Inc.
www.lumiscope.net
Repair Department: 1-800-672-8293
Made and Printed in China
Blood Pressure Log Book
To create a log of your blood pressure history, complete
the personal information section at the top, then enter
the details (date, time, and measurements) for each
reading you take.
To plot your history, use an S (systolic), D (diastolic) and
M (mean arterial pressure) to mark the points where
each measurement falls on the chart, then connect the
points to view your history over time.
Page 11

 Loading...
Loading...