Page 1

1
SEMI AUTOMATIC UPPER ARM
Blood Pressure Monitor
Model 1100
Features:
• Semi-Automatic
• Easy-to-read Display
• 60 Automatic Memories
• Beeping Reminder
Table of Contents:
Introduction....................................... 2
Name/Function of Each Part............... 2
Preliminary Remarks ...........................3
About Blood Pressure..........................3
Blood Pressure Standard.....................3
Blood Pressure Fluctuation..................4
Display Explanations ...........................4
Installing Batteries..............................4
Applying the Cuff.................................5
Taking a Measurement ........................6
Recalling Memory................................7
Helpful Tips.........................................7
Troubleshooting...................................7
Cautionary Notes.................................8
Specifications .....................................8
y
Page 2
INDEX
y
2
Introduction
Blood pressure measurements determined with your Lumiscope Blood Pressure Monitor are
equivalent to those obtained by a trained observer using cuff/stethoscope auscultation method,
within the limits prescribed by the American National Standard, Electronic or Automated
Sphygmomanometers. This monitor is to be used by adult consumers in a home environment.
• Please read this manual carefully before use, for specific information on your own blood
pressure, contact your physician. Please be sure to keep this manual.
Attention: Consult the accompanying
documents.
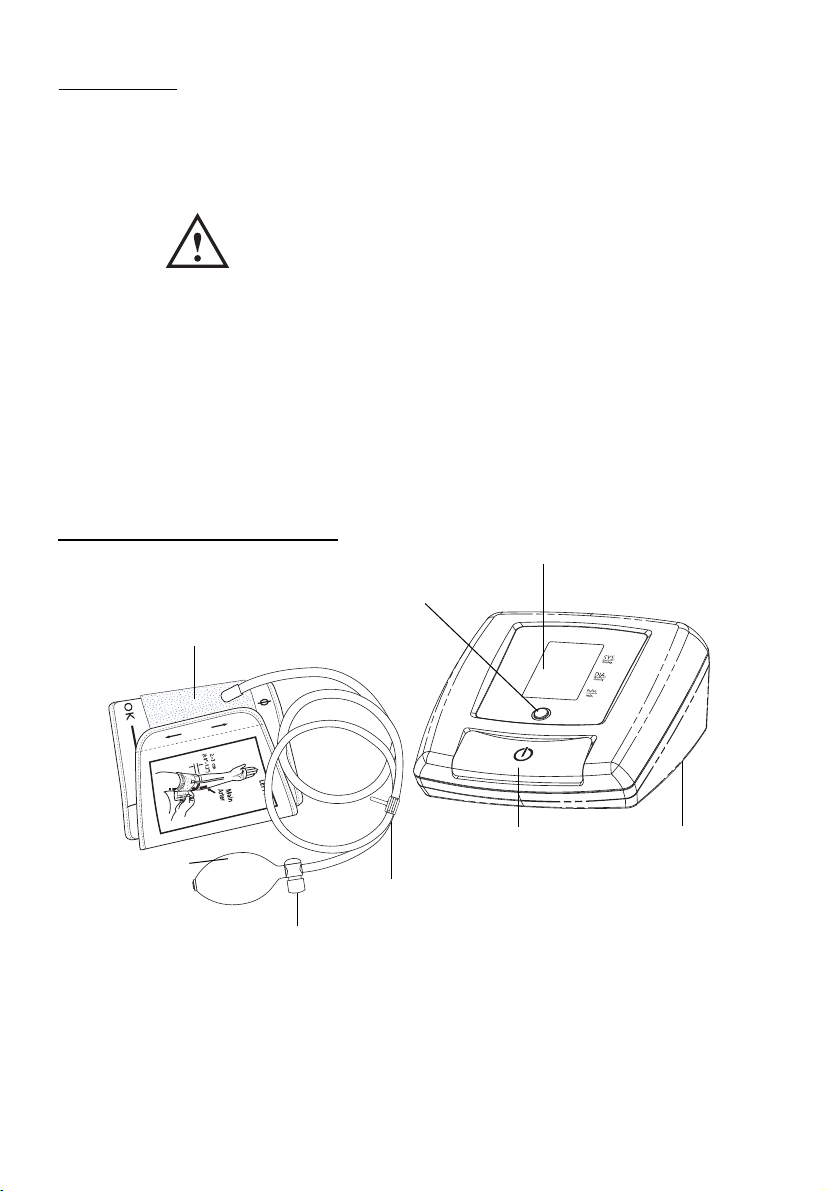
Name/Function of Each Part:
Battery
Compartment
LCD Display
Power Button
Arm Cuff
Inflating Bulb
Air Release Valve
Air Tube and Connector
Memory Recall Button
Page 3

3
About Blood Pressure
What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted on the artery tube while blood flows through the arteries.
The pressure measured when the heart contracts and sends blood out of the heart is systolic
(highest). The pressure measured when the heart dilates with blood flowing back into the heart
is called diastolic (lowest) blood pressure.
Why Measure Your Blood Pressure?
Among the various health problems afflicting modern people, problems associated with high
blood pressure are by far the most common. High blood pressure’s dangerously strong
correlation with cardiovascular disease has made measuring blood pressure a necessity for
identifying those at risk.
Blood Pressure Standard
The World Health Organization (WHO) and National High Blood Pressure Education Program
Coordinating Committee have developed a blood pressure standard, according to which areas of
low- and high-risk blood pressure are identified. This standard, however, is a general guideline
and blood pressures vary between different people, age groups, etc.
It is important that you consult with your physician regularly. Your physician will tell you your
normal blood pressure range as well as the point at which you will be considered at risk.
Page 4

4
Blood Pressure Fluctuation
Blood pressure fluctuates all the time! You
should not be overly worried if you encounter
two or three measurements at high levels. Blood
pressure changes over the month and even
throughout the day. It is also influenced by
season and temperature.
Display Explanation
Display: Icons:
Systolic Pressure
Diastolic Pressure
Pulse Rate
Appears when manual cuff inflation is
needed
Appears when manual cuff deflation is
needed
Appears when batteries should be
replaced
Shows the pulse rate per minute
Occurs when a mistake was made during
measurement
Installing Battery
1. Press down and lift the battery cover in the direction of the
arrow to open the battery compartment.
2. Install or replace 2 “AA” sized batteries in the battery
compartment according to the indications inside the
compartment.
3. Replace the battery cover by clicking in the bottom
hooks first, then push in the top end of the battery
door.
You need to replace the batteries when:
1. The low battery icon appears on display.
2. The POWER button is pushed and nothing
appears on display.
No. of Memory
Sequence
Page 5

5
Applying the arm cuff
1. Plug in the cuff, connecting tube to the unit.
2. Unwrap the arm cuff, leaving the “Index” end of the cuff through the D-ring of the cuff.
3. Put your left arm through the cuff loop. The "OK" range indication
should be positioned closer to yourself with the rubber tube pointing in
the direction of your arm. Position the artery mark ( ) over the main
artery (on the inside of your arm) in the upper arm.
y
y
y
y
y
4. Turn your left palm upward and place the edge
of the arm cuff at approximately 2 to 3 cm
above the inner side of the elbow joint. Tighten
the cuff by pulling the "Index" end of the cuff.
5. If the Index line falls within the OK range,
indicated at the edge of the cuff, this cuff is
suitable for your use. If the Index line falls out of
the OK range, you may need a special cuff for
measurement. Please visit www.lumiscope.net
or contact our service department at
1-800-672-8293 for more information regarding
additional cuffs.
Page 6

Taking a Measurement
1. Press the POWER button. All displays will appear for approximately one second
before returning to “0”. If the downward arrow “ “ flashes, there is air
remaining in the cuff. Release it by pressing the “Air Release Valve” until “0”
appears on display.
The unit is ready for measurement at this point.
2. Pump the bulb to increase pressure in the arm cuff. The display will
show the pressure reading within the cuff. Continue pumping until
the pressure reaches approximately 50~60 mmHg above your
normal systolic pressure. Three short beeps will be heard if you
pump the pressure to 170 mmHg, to remind you to stop.
If the cuff pressure is not enough, an upward arrow
( ) will display and two short beeps will be heard
to remind you that you should continue pumping.
3. Sit still and wait for the monitor to deflate and
measure your blood pressure. It is important to
remain still and quiet during measurement. Any
significant movement may affect measurement results.
4. Upon completion of the measurement cycle, the monitor will
display systolic, diastolic, and pulse readings and the unit will
make a long beep. Measurement is now complete, and the
reading is automatically stored in the monitor. The display will
indicate a downward arrow ( ). Keep pressing the air release
valve above the bulb until all pressure in cuff is released.
5. Press the POWER button to turn off the power. If no button is
pressed, the unit will shut off automatically in
approximately one minute.
6
Page 7

Recalling Memory
1. To recall stored blood pressure readings from memory,
simply press the Memory button. The last set of
memorized readings will be displayed.
2. Another press of the Memory button will recall the
previous set of readings.
3. All readings stored in memory will be displayed with its
sequence number.
7
Helpful T
ips
Here are a few helpful tips to help you obtain more accurate readings:
• Do not measure your blood pressure immediately after consuming a large meal. To obtain
more accurate readings, please wait one hour before measuring.
• Do not smoke or drink alcohol before measuring your blood pressure.
• You should not be physically tired or exhausted while taking a measurement.
• It is important that you relax during measurement. Take a 15-minute rest before a reading.
• Do not take measurements if you are under stress or under tension.
• Take your blood pressure at normal body temperature. If you are feeling cold or hot, wait a
while before taking a measurement.
• If the monitor is stored at very low temperature (near freezing), have it placed at a warm
location for at least one hour before using it.
• Wait about 5 minutes before taking the next pressure measurement.
If any abnormality should arise during use, please check the following points:
Troubleshooting
Symptom
No display when the
POWER button is pressed
EE mark shown on display
or the blood pressure value
is displayed excessively
low (high)
Check Point
Have the batteries run down?
Have the batteries’ polarities been
positioned incorrectly?
Is the cuff placed correctly?
Is the cuff pressure pumped enough?
(50~60 mmHg above normal systolic
value?)
Did you talk or move during
measurement?
Did you shake the arm with the cuff on?
Correction
Replace with two new batteries
Re-insert the batteries in the correct
positions.
Wrap the cuff properly so that it is
positioned correctly.
Measure it again and pump up 50~60
mmHg more than normal systolic
value.
Measure it again quietly.
Page 8

8
Specifications:
Measurement Method : Oscillometric
Measurement Range : Pressure: 20~280mmHg; Pulse: 40~180 beats/min
Pressure Sensor : Semi conductor
Accuracy : Pressure: ± 3mmHg; Pulse: ± 5% of reading
Inflation : Manual Inflation
Deflation : Automatic Pressure Release Valve
Memory capacity : 60 memories
Auto-shut-off : 1 minute after last button operation
Operating Environment : Temperature: 5 °C ~ 45 °C (41 °F~113 °F); Humidity: 40 ~ 85%
Storage Environment : Temperature: -10 °C ~ 60 °C (14 °F~140 °F );
Humidity: 10 ~ 95%
Power Source : 3V DC, two ‘AA’ Batteries
Dimensions : 115 (L) X 94.5 (W) X 60.5 (H) mm
Weight : 320 g (G.W.) (No Batteries)
Arm circumference : Adult: 24 ~36 cm (9.4”~14.2”) (standard)
*Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Cautionary Notes:
1. The unit contains high-precision assemblies. Therefore, avoid extreme temperatures,
humidity, and direct sunlight. Avoid dropping or strongly shocking the main unit, and protect it
from dust.
2. Clean the blood pressure monitor body and the cuff carefully with a slightly damp, soft cloth.
Do not iron, wash or use chemical cleaner on the cuff. Never use thinner, alcohol or petrol
(gasoline) as cleaner.
3. Leaky batteries can damage the unit. Remove the batteries when the unit will not used for a
long period of time.
4. The unit should not be operated by children.
5. If the unit is stored near freezing, allow it to acclimate at room temperature before use.
6. Your Lumiscope Blood Pressure Monitor is not field serviceable. You should not use any tool
to open the device nor should you attempt to adjust anything inside the device. If you have
any problems, please contact the store or the doctor from whom you purchased your
Lumiscope Blood Pressure Monitor.
7. For users diagnosed with common arrhythmia (atrial or ventricular premature beats or atrial
fibrillation), diabetes, poor circulation of blood, kidney problems, or for users who have
suffered a stroke, the device might not be suitable for use.
8. Do not use on unconcious patients.
Page 9

9
Two-Year Limited Warranty:
Lumiscope guarantees this product free from defects in material and workmanship for a period
of two years from the date of purchase, except as noted below:
This Lumiscope product warranty does not cover damage caused by misuse or abuse, the
attachment of any unauthorized accessory, alteration to the product, or any other conditions
whatsoever that are beyond the control of Lumiscope. Lumiscope shall not be responsible for
any type of incidental, consequential, or special damage. All implied warranties, including, but
not limited to those implied warranties of fitness and merchantability, are limited to the total
duration of two years from the original date of purchase.
To obtain warranty service on your Lumiscope Blood Pressure Monitor, please contact the
Lumiscope Repair Department at 1-800-672-8293 or visit www.lumiscope.net. There is a $15
fee for return shipping and handling. Please make checks payable to The Lumiscope Co., Inc.
Upon receipt, Lumiscope will repair or replace, as appropriate, this blood pressure monitor and
return it to you. Warranty is solely through the Lumiscope Repair Department. Service of this
product by anyone other than the Lumiscope Repair Department voids warranty.
In the event that Lumiscope does not abide by the terms of this warranty, the consumer may
seek breach of contract remedies in the New York State Federal courts of law. This warranty
gives you specific legal rights and you may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so
the above limitation may not apply to you.
Distributed By
The Lumiscope Co., Inc.
www.lumiscope.net
Repair Department: 1-800-672-8293
Made and Printed in China
 Loading...
Loading...