Page 1

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
Configuration Manual
for v2 Routers
09-05-16
Page 2

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
USED SYMBOLS
Used symbols
Danger – Information regarding user safety or potential damage to the router.
Attention – Problems that can arise in specific situations.
Information, notice – Useful tips or information of special interest.
Firmware version
Current version of firmware is 5.3.4 (March 10, 2016).
GPL licence
Source codes under GPL licence are available free of charge by sending an email to:
info@conel.cz.
Conel s.r.o., Sokolska 71, 562 04 Usti nad Orlici, Czech Republic
Manual Rev. 1 released in CZ, March 11, 2016
i
09-05-16
Page 3

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
CONTENTS
Contents
1 Access to the Web Conf. 2
1.1 Secured access to web configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 Status 4
2.1 General Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.1.1 Mobile Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.1.2 Primary LAN, Secondary LAN, WiFi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.1.3 Peripheral Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.1.4 System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.2 Mobile WAN Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.3 WiFi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.4 WiFi Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.5 Network Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.6 DHCP Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.7 IPsec Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.8 DynDNS Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.9 System Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3 Configuration 18
3.1 LAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.2 VRRP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.3 Mobile WAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3.3.1 Connection to Mobile Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3.3.2 DNS Address Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.3.3 Check Connection to Mobile Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.3.4 Data Limit Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
3.3.5 Switch between SIM Cards Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
3.3.6 Dial-In access configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
3.3.7 PPPoE Bridge Mode Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
3.4 PPPoE Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
3.5 WiFi Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
3.6 WLAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
3.7 Backup Routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3.8 Firewall Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
3.9 NAT Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3.10 OpenVPN Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3.11 IPsec Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
3.12 GRE Tunnels Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
3.13 L2TP Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
ii
Page 4

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
CONTENTS
3.14 PPTP Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3.15 DynDNS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
3.16 NTP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
3.17 SNMP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
3.18 SMTP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
3.19 SMS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
3.19.1 Sending SMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
3.20 Expansion Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
3.21 USB Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
3.22 Startup Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
3.23 U p/Down script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
3.24 Automatic Update Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
4 Customization 104
4.1 User Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
5 Administration 106
5.1 Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
5.2 Change Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
5.3 Change Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
5.4 Set Real Time Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
5.5 Set SMS Service Center Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
5.6 Unlock SIM Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
5.7 Send SMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
5.8 Backup Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
5.9 Restore Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
5.10 U pdate Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
5.11 Reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
6 Configuration over Telnet 113
7 Glossary and Acronyms 115
8 Index 120
9 Recommended Literature 122
iii
Page 5

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
LIST OF FIGURES
List of Figures
1 Example of the Web Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2 Mobile WAN status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 WiFi Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4 WiFi Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
5 Network Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6 DHCP Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
7 IPsec Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
8 DynDNS Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
9 System Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
10 Example program syslogd start with the parameter -R . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
11 Example 1 – Network Topology for Dynamic DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
12 Example 1 – LAN Configuration Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
13 Example 2 – Network Topology with both Static and Dynamic DHCP Servers . 22
14 Example 2 – LAN Configuration Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
15 Example 3 – Network Topology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
16 Example 3 – LAN Configuration Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
17 Topology of VRRP configuration example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
18 Example of VRRP configuration – main router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
19 Example of VRRP configuration – backup router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
20 Mobile WAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
21 Example 1 – Mobile WAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
22 Example 2 – Mobile WAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
23 Example 3 – Mobile WAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
24 PPPoE configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
25 WiFi Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
26 WLAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
27 Backup Routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
28 Firewall Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
29 Topology for the Firewall Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
30 Firewall Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
31 Example 1 – Topology of NAT Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
32 Example 1 – NAT Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
33 Example 2 – Topology of NAT Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
34 Example 2 – NAT Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
35 OpenVPN Tunnels List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
36 OpenVPN tunnel configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
37 Topology of OpenVPN Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
38 IPsec Tunnels List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
39 IPsec Tunnels Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
40 Topology of IPsec Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
iv
Page 6

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
LIST OF FIGURES
41 GRE Tunnels List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
42 GRE Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
43 Topology of GRE Tunnel Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
44 L2TP Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
45 Topology of L2TP Tunnel Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
46 PPTP Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
47 Topology of PPTP Tunnel Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
48 DynDNS Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
49 Example of NTP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
50 OID Basic Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
51 SNMP Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
52 MIB Browser Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
53 SMTP Client Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
54 Example 1 – SMS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
55 Example 2 – SMS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
56 Example 3 – SMS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
57 Example 4 – SMS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
58 Expansion Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
59 Example of Ethernet to serial communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
60 Example of serial port extension . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
61 USB configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
62 Example 1 – USB port configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
63 Example 2 – USB port configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
64 Startup script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
65 Example of a Startup script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
66 Up/Down script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
67 Example of Up/Down script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
68 Example of Automatic Update 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
69 Example of Automatic Update 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
70 User modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
71 Added user module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
72 Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
73 Change Profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
74 Change Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
75 Set Real Time Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
76 Set SMS Service Center Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
77 Unlock SIM Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
78 Send SMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
79 Restore Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
80 Update Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
81 Reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
v
Page 7

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
LIST OF TABLES
List of Tables
1 Mobile Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2 Peripheral Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
3 System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
4 Mobile Network Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
5 Description of Periods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
6 Mobile Network Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
7 Traffic Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
8 Access Point State Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
9 State Information about Connected Clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
10 Information about Neighbouring WiFi Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
11 Description of Interfaces in Network Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
12 Description of Information in Network Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
13 DHCP Status Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
14 Configuration of the Network Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
15 Configuration of Dynamic DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
16 Configuration of Static DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
17 VRRP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
18 Check connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
19 Mobile WAN Connection Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
20 Check Connection to Mobile Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
21 Data Limit Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
22 Default and Backup SIM Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
23 Switch between SIM Card Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
24 Timeout Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
25 Dial-In access configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
26 PPPoE configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
27 WiFi Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
28 WLAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
29 Configuration of DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
30 Backup Routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
31 Filtering of Incoming Packets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
32 Forwarding filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
33 NAT Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
34 Configuration of send all incoming packets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
35 Remote Access Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
36 OpenVPN Tunnels Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
37 OpenVPN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
38 OpenVPN Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
39 IPsec Tunnels Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
40 IPsec Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
vi
Page 8

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
LIST OF TABLES
41 Example IPsec configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
42 GRE Tunnels Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
43 GRE Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
44 GRE Tunnel Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
45 L2TP Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
46 L2TP Tunnel Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
47 PPTP Tunnel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
48 PPTP Tunnel Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
49 DynDNS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
50 NTP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
51 SNMP Agent Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
52 SNMPv3 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
53 SNMP configuration – MBUS extension . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
54 SNMP Configuration – R-SeeNet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
55 Object identifier for binary input and output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
56 Object identifier for CNT port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
57 Object identifier for M-BUS port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
58 SMTP client configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
59 SMS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
60 Control via SMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
61 Control SMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
62 Send SMS on the serial Port 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
63 Send SMS on the serial Port 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
64 Send SMS on ethernet PORT1 configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
65 List of AT Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
66 Expansion Port Configuration 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
67 Expansion Port Configuration 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
68 CD Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
69 DTR Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
70 USB Port Configuration 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
71 USB Port Configuration 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
72 CD Signal description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
73 DTR Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
74 Automatic Update Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
75 User modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
76 Users Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
77 Add User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
78 Telnet commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
1
Page 9

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
1. ACCESS TO THE WEB CONF.
1. Access to the Web Configuration
Attention! The cellular router will not operate unless the cellular carrier has been cor-
rectly configured and the account activated and provisioned for data communications.
For UMTS and LTE carriers, a SIM card must be inserted into the router. Do not insert
the SIM card when the router is powered up.
You can monitor the status, configuration and administration of the router via the Web
interface. To access the router over the web interface, enter http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx into the
URL for the browser where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the router IP address. The router’s default IP
address is 192.168.1.1. The default username is root and the default password is root.
When you successfully enter login information on the login page, web interface will be
displayed. The left side of the web interface displays the menu. You will find links for the
Status, Configuration, Customization and Administration of the router.
Name and Location displays the router’s name, location and SNMP configuration (see
3.17). These fields are user-defined for each router.
Figure 1: Example of the Web Configuration
2
09-05-16
Page 10

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
1. ACCESS TO THE WEB CONF.
For enhanced security, you should change the default password. If the router’s default
password is set, the menu item Change password is highlighted in red.
If the green LED is blinking, you may restore the router to its factory default settings by
pressing RST on front panel. The configuration will be restored to the factory defaults and the
router will reboot. (The green LED will be on during the reboot.)
1.1 Secured access to web configur ation
The Web interface can be accessed through a standard web browser via a secure HTTPS
connection.
Access the web interface by entering https://192.168.1.1 in the web browser. You may
receive a message that there is a problem with the website’s security certificate. If you do,
click on Continue to this website. If you want to prevent this message, you can follow the
procedure described below.
There is the self-signed HTTPS certificate in the router. If you want to use your own
certificate (e.g. in combination with the dynamic DNS service), you need to replace the
/etc/certs/https_cert and /etc/certs/https_key files in the router.
If you decide to use the self-signed certificate in the router to prevent the security message
(domain disagreement) from pop up every time you log into the router, you can take the following steps. Note: You will have to use the domain name based on the MAC address of the
router and it is not guaranteed to work with every combination of an operating system and a
browser.
• Add the DNS record to your DNS system: Edit /etc/hosts (Linux/Unix OS) or
C:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc\hosts (Windows OS) or configure your own DNS
server. Add a new record with the IP address of your router and the domain name
based of the MAC address of the router (MAC address of the first network interface seen
in Network Status in the Web interface of the router.) Use dash separators instead of
colons. Example: A router with the MAC address 00:11:22:33:44:55 will have a domain
name 00-11-22-33-44-55.
• Access the router via the new domain name address (E.g. https://00-11-22-33-44-55).
If you see the security message, add an exception so the next time the message will
not pop up (E.g. in Firefox Web browser). If there is no possibility to add an exception,
export the certificate to the file and import it to your browser or operating system.
3
Page 11

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
2. STATUS
2. Status
2.1 General Status
You can access a summary of basic router information and its activities by opening the
General page. This page is the default dialog displayed when you login to the device. Information is divided into several sections, based upon the type of router activity or the properties
area: Mobile Connection, Primary LAN, Peripherals Ports and System Information. If your
router is equipped with WIFI expansion port, there is also WIFI section.
2.1.1 Mobile Connection
Item Description
SIM Card Identification of the SIM card (Primary or Secondary)
Interface Defines the interface
Flags Displays network interface flags
IP Address IP address of the interface
MTU Maximum packet size that the equipment is able to transmit
Rx Data Total number of received bytes
Rx Packets Received packets
Rx Errors Erroneous received packets
Rx Dropped Dropped received packets
Rx Overruns Lost received packets because of overload
Tx Data Total number of sent bytes
Tx Packets Sent packets
Tx Errors Erroneous sent packets
Tx Dropped Dropped sent packets
Tx Overruns Lost sent packets because of overload
Uptime Indicates how long the connection to the cellular network has
been established
Table 1: Mobile Connection
4
Page 12

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
2. STATUS
2.1.2 Primary LAN, Secondary LAN, WiFi
Items displayed in this part have the same meaning as items in the previous part. Moreover, the MAC Address item shows the MAC address of the corresponding router’s interface
(Primary LAN – eth0, Secondary LAN – eth1, WiFi – wlan0). Visible information depends on
configuration (see 3.1 or 3.5).
2.1.3 Peripheral Ports
Item Description
Expansion Port 1 Expansion port fitted to the position 1 (None indicates that this
position is equipped with no port)
Expansion Port 2 Expansion port fitted to the position 2 (None indicates that this
position is equipped with no port)
Binary Input State of binary input
Binary Output State of binary output
Table 2: Peripheral Ports
2.1.4 System Information
Item Description
Firmware Version Information about the firmware version
Serial Number Serial number of the router (in case of N/A is not available)
Profile Current profile – standard or alternative profiles (profiles are used
for example to switch between different modes of operation)
Supply Voltage Supply voltage of the router
Temperature Temperature in the router
Time Current date and time
Uptime Indicates how long the router is used
Table 3: System Information
5
Page 13

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
2. STATUS
2.2 Mobile WAN Status
The XR5i v2 routers do not display the Mobile WAN status option.
The Mobile WAN menu item contains current information about connections to the mobile
network. The first part of this page (Mobile Network Information) displays basic information
about mobile network the router operates in. There is also information about the module,
which is mounted in the router.
Item Description
Registration State of the network registration
Operator Specifies the operator’s network the router operates in
Technology Transmission technology
PLMN Code of operator
Cell Cell the router is connected to
LAC Location Area Code – unique number assigned to each location area
Channel Channel the router communicates on
Signal Strength Signal strength of the selected cell
Signal Quality Signal quality of the selected cell:
• EC/IO for UMTS and CDMA (it’s the ratio of the signal received
from the pilot channel – EC – to the overall level of the spectral
density, ie the sum of the signals of other cells – IO)
• RSRQ for LTE technology (Defined as the ratio
• The value is not available for the EDGE technology
CSQ Cell Signal Quality, relative value is given by RSSI (dBm). 2–9 range
means Marginal, 10–14 range means OK, 15–16 range means Good,
20–30 range means excellent.
Neighbours Signal strength of neighboring hearing cells
Manufacturer Module manufacturer
Model Type of module
Revision Revision of module
IMEI IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) number of module
ESN ESN (Electronic Serial Number) number of module (for CDMA routers)
MEID MEID number of module
ICCID Integrated Circuit Card Identifier is international and unique serial
number of the SIM card.
Table 4: Mobile Network Information
6
N ×RSRP
RSS I
)
Page 14

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
2. STATUS
If a neighboring cell is highlighted in red, there is a risk that the router may repeatedly
switch between the neighboring cell and the primary cell. This can affect the performance of
the router. To prevent this, re-orient the antenna or use a directional antenna.
The next section of this window displays historical information about the quality of the cellular WAN connection during each logging period. The router has standard intervals, such as
the previous 24 hours and last week, and also includes information one user-defined interval.
Period Description
Today Today from 0:00 to 23:59
Yesterday Yesterday from 0:00 to 23:59
This week This week from Monday 0:00 to Sunday 23:59
Last week Last week from Monday 0:00 to Sunday 23:59
This period This accounting period
Last period Last accounting period
Table 5: Description of Periods
Item Description
Signal Min Minimal signal strength
Signal Avg Average signal strength
Signal Max Maximal signal strength
Cells Number of switch between cells
Availability Availability of the router via the mobile network (expressed as a percent-
age)
Table 6: Mobile Network Statistics
Tips for Mobile Network Statistics table:
• Availability is expressed as a percentage. It is the ratio of time connection to the mobile
network has been established to the time that router has been is turned on.
• Placing your cursor over the maximum or minimum signal strength will display the last
time the router reached that signal strength.
7
Page 15

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
2. STATUS
The middle part of this page displays information about transferred data and the number
of connections for both SIM cards (for each period).
Item Description
RX data Total volume of received data
TX data Total volume of sent data
Connections Number of connection to mobile network establishment
Table 7: Traffic Statistics
The last part (Mobile Network Connection Log) displays information about the mobile net-
work connections and any problems that occurred while establishing them.
Figure 2: Mobile WAN status
8
09-05-16
Page 16

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
2. STATUS
2.3 WiFi
This item is available only if the router is equipped with a WiFi module.
Selecting the WiFi item in the main menu of the web interface will display information about
the WiFi access point (AP) and associated stations.
Item Description
hostapd state dump Time the statistical data relates to
num_sta Number of connected stations
num_sta_non_erp Number of connected stations using 802.11b in 802.11g
BSS connection
num_sta_no_short_slot_time Number of stations not supporting the Short Slot Time
num_sta_no_short_preamble Number of stations not supporting the Short Preamble
Table 8: Access Point State Information
Detailed information is displayed for each connected client. Most of them have an internal
character. Here are two examples:
Item Description
STA MAC address of connected device (station)
AID Identifier of connected device (1 – 2007). If 0 is displayed, the station is
not currently connected.
Table 9: State Information about Connected Clients
Figure 3: WiFi Status
9
Page 17

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
2. STATUS
2.4 WiFi Scan
This item is available only if the router is equipped with a WiFi module.
Selecting the WiFi Scan item scans for neighboring WiFi networks and displays the re-
sults. Scanning can only be performed if the access point (WiFi AP) is off.
Item Description
BSS MAC address of access point (AP)
TSF A Timing Synchronization Function (TSF) keeps the timers for
all stations in the same Basic Service Set (BSS) synchronized.
All stations shall maintain a local TSF timer.
freq Frequency band of WiFi network [kHz]
beacon interval Period of time synchronization
capability List of access point (AP) properties
signal Signal level of access point (AP)
last seen Last response time of access point (AP)
SSID Identifier of access point (AP)
Supported rates Supported rates of access point (AP)
DS Parameter set The channel on which access point (AP) broadcasts
ERP Extended Rate PHY – information element providing backward
compatibility
Extended supported
rates
RSN Robust Secure Network – The protocol for establishing a se-
Table 10: Information about Neighbouring WiFi Networks
Supported rates of access point (AP) that are beyond the scope
of eight rates mentioned in Supported rates item
cure communication through wireless network 802.11
10
Page 18

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
2. STATUS
Figure 4: WiFi Scan
11
09-05-16
Page 19

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
2. STATUS
2.5 Network Status
To view information about the interfaces and the routing table, open the Network item in
the Status menu. The upper part of the window displays detailed information about the active
interfaces only:
Interface Description
eth0, eth1 Network interfaces (Ethernet connection)
ppp0 Active PPP connection to the mobile network – wireless module is con-
nected via USB interface
wlan0 WiFi interface
tun0 OpenVPN tunnel interface
ipsec0 IPSec tunnel interface
gre1 GRE tunnel interface
usb0 USB interface
Table 11: Description of Interfaces in Network Status
Each of the interfaces displays the following information:
Item Description
HWaddr Hardware (unique) address of networks interface
inet IP address of interface
P-t-P IP address second ends connection
Bcast Broadcast address
Mask Mask of network
MTU Maximum packet size that the equipment is able to transmit
Metric Number of routers, over which packet must go trought
RX
• packets – received packets
• errors – number of errors
• dropped – dropped packets
• overruns – incoming packets lost because of overload
• frame – wrong incoming packets because of incorrect packet size
Continued on next page
12
Page 20

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
2. STATUS
Continued from previous page
Item Description
TX
collisions Number of collisions on physical layer
txqueuelen Length of front network device
RX bytes Total number of received bytes
TX bytes Total number of transmitted bytes
You may view the status of the mobile network connection on the network status screen.
If the connection to the mobile network is active, it will appear in the system information as an
usb0 interface. The Route Table is displayed at the bottom.
For the XR5i v2 routers, interface ppp0 indicates the PPPoE connection.
• packets – transmit packets
• errors – number of errors
• dropped – dropped packets
• overruns – outgoing packets lost because of overload
• carrier – wrong outgoing packets with errors resulting from the
physical layer
Table 12: Description of Information in Network Status
Figure 5: Network Status
13
Page 21

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
2. STATUS
2.6 DHCP Status
Information about the DHCP server activity is accessible via DHCP item. The DHCP server
provides automatic configuration of the client devices connected to the router. The DHCP
server assigns each device an IP address, subnet mask, default gateway (IP address of router)
and DNS server (IP address of router).
For each client in the list, the DHCP status window displays the following information.
Item Description
lease Assigned IP address
starts Time that the IP address was assigned
ends Time that the IP address lease expires
hardware ethernet Unique hardware MAC address
uid Unique ID
client-hostname Host computer name
Table 13: DHCP Status Description
The DHCP status may occasionally display two records for one IP address. This may be
caused by resetting the client network interface.
Figure 6: DHCP Status
Note: Records in the DHCP Status window are divided into two separate parts – Active DHCP
Leases (Primary LAN) and Active DHCP Leases (WLAN).
14
09-05-16
Page 22

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
2. STATUS
2.7 IPsec Status
Selecting the IPsec option in the status menu of the web page will bring up the information
for any IPsec Tunnels that have been established. If the tunnel has been built correctly, the
screen will display IPsec SA established (highlighted in red in the figure below.)
Figure 7: IPsec Status
2.8 DynDNS Status
The router supports DynamicDNS using a DNS server on www.dyndns.org. If Dynamic
DNS is configured, the status can be displayed by selecting menu option DynDNS. Refer to
www.dyndns.org for more information on how to configure a Dynamic DNS client.
You can use the following servers for the Dynamic DNS service:
• www.dyndns.org
• www.spdns.de
• www.dnsdynamic.org
• www.noip.com
Figure 8: DynDNS Status
15
Page 23

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
2. STATUS
When the router detects a DynDNS record update, the dialog displays one or more of the
following messages:
• DynDNS client is disabled.
• Invalid username or password.
• Specified hostname doesn’t exist.
• Invalid hostname format.
• Hostname exists, but not under specified username.
• No update performed yet.
• DynDNS record is already up to date.
• DynDNS record successfully update.
• DNS error encountered.
• DynDNS server failure.
The router’s SIM card must have public IP address assigned or DynDNS will not function
correctly.
2.9 System Log
If there are any connection problems you may view the system log by selecting the System
Log menu item. Detailed repor ts from individual applications running in the router will be dis-
played. Use the Save Log button to save the system log to a connected computer. (It will be
saved as a text file with the .log extension.) The Save Report button is used for creating detailed reports. (It will be saved as a text file with the .txt extension. The file will include statistical
data, routing and process tables, system log, and configuration.)
The default length of the system log is 1000 lines. After reaching 1000 lines a new file is
created for storing the system log. After completion of 1000 lines in the second file, the first
file is overwritten with a new file.
The Syslogd program will output the system log. It can be started with two options to modify
its behavior. Option "-S" followed by decimal number sets the maximal number of lines in one
log file. Option "-R" followed by hostname or IP address enables logging to a remote syslog
daemon. (If the remote syslog deamon is Linux OS, there has to be remote logging enabled
(typically running "syslogd -R"). If it’s the Windows OS, there has to be syslog server installed,
e.g. Syslog Watcher). To start syslogd with these options, the "/etc/init.d/syslog" script can
be modified via SSH or lines can be added into Startup Script (accessible in Configuration
section) according to figure 10.
16
Page 24

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
2. STATUS
Figure 9: System Log
The following example (figure) shows how to send syslog information to a remote server at
192.168.2.115 on startup.
Figure 10: Example program syslogd start with the parameter -R
17
09-05-16
Page 25

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3. Configuration
3.1 LAN Configuration
To enter the Local Area Network configuration, select the LAN menu item in the Configuration section. The Primary LAN subitem is for the router’s main Ethernet interface (ETH). If
the router has additional Ethernet ports (PORT1 or PORT2), they are configured using the
Secondary LAN subitem. For routers with two additional Ethernet ports, PORT1 and PORT2
are automatically bridged together.
Item Description
DHCP Client Enables/disables the DHCP client function.
• disabled – The router does not allow automatic allocation IP ad-
dress from a DHCP server in LAN network.
• enabled – The router allows automatic allocation IP address from
a DHCP server in LAN network.
IP address Specifies a fixed set of IP addresses for the network interfaces ETH.
Subnet Mask Specifies a Subnet Mask for the IP address.
Bridged Activates/deactivates the bridging function on the router.
• no – The bridging function is inactive (default).
• yes – The bridging function is active.
Media type Specifies the type of duplex and speed used in the network.
• Auto-negation – The router automatically sets the best speed
and duplex mode of communication according to the network’s
possibilities.
• 100 Mbps Full Duplex – The router communicates at 100Mbps,
in the full duplex mode.
• 100 Mbps Half Duplex – The router communicates at 100Mbps,
in the half duplex mode.
• 10 Mbps Full Duplex – The router communicates at 10Mbps, in
the full duplex mode.
• 10 Mbps Half Duplex – The router communicates at 10Mbps, in
the half duplex mode.
Continued on next page
18
Page 26

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
Default Gateway Specifies the IP address of default gateway. When entering the IP
address of default gateway, every packet for which the destination IP
address was not found in the routing table, is sent to this IP address.
DNS server Specifies the IP address of the DNS server. When the IP address is not
found the Routing Table, the router forwards an IP address requests to
the DNS server.
Table 14: Configuration of the Network Interface
The router considers the last address in the network range to be broadcast address,
regardless of the address is set as a broadcast or not. Connection (ping) to the broadcast
address does not work.
The Default Gateway and DNS Server items are only used if the DHCP Client item is set
to disabled and if the Primary or Secondary LAN is selected by the Backup Routes system
as the default route. (The selection algorithm is described in section 3.7). Since FW 5.3.0,
Default Gateway and DNS Server are also supported on bridged interfaces (e.g. eth0 + eth1).
Only one bridge can be active on the router. The Only DHCP Client, IP Address and Subnet
Mask parameters are used to configure the bridge. Primary LAN has higher priority when both
interfaces (eth0, eth1) are added to the bridge. Other interfaces (wlan0 – wifi) can be added to
or deleted from an existing bridge at any time. The bridge can be created on demand for such
interfaces, but not if it is configured by their respective parameters.
The DHCP server assigns the IP address, gateway IP address (IP address of the router)
and IP address of the DNS server (IP address of the router) to the connected clients. If these
values are filled in by the user in the configuration form, they will be preferred.
The DHCP server supports static and dynamic assignment of IP addresses. Dynamic
DHCP assigns clients IP addresses from a defined address space. Static DHCP assigns IP
addresses that correspond to the MAC addresses of connected clients.
Item Description
Enable dynamic
DHCP leases
IP Pool Start Starting IP addresses allocated to the DHCP clients.
IP Pool End End of IP addresses allocated to the DHCP clients.
Lease time Time in seconds that the IP address is reserved before it can be re-
Select this option to enable a dynamic DHCP server.
used.
Table 15: Configuration of Dynamic DHCP Server
19
Page 27

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Item Description
Enable static
DHCP leases
MAC Address MAC address of a DHCP client.
IP Address Assigned IP address.
Do not to overlap ranges of static allocated IP addresses with addresses allocated by the
dynamic DHCP server. IP address conflicts and incorrect network function can occur if
you overlap the ranges.
Example 1: Configure the network interface to connect to a dynamic DHCP server:
• The range of dynamic allocated addresses is from 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.4.
• The address is allocated 600 second (10 minutes).
Figure 11: Example 1 – Network Topology for Dynamic DHCP Server
Select this option to enable a static DHCP server.
Table 16: Configuration of Static DHCP Server
20
Page 28

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Figure 12: Example 1 – LAN Configuration Page
21
09-05-16
Page 29

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Example 2: Configure the network interface to connect to a dynamic and static DHCP server:
• The range of allocated addresses is from 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.4.
• The address is allocated for 600 seconds (10 minutes).
• The client with the MAC address 01:23:45:67:89:ab has the IP address 192.168.1.10.
• The client with the MAC address 01:54:68:18:ba:7e has the IP address 192.168.1.11.
Figure 13: Example 2 – Network Topology with both Static and Dynamic DHCP Servers
Figure 14: Example 2 – LAN Configuration Page
22
09-05-16
Page 30
LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
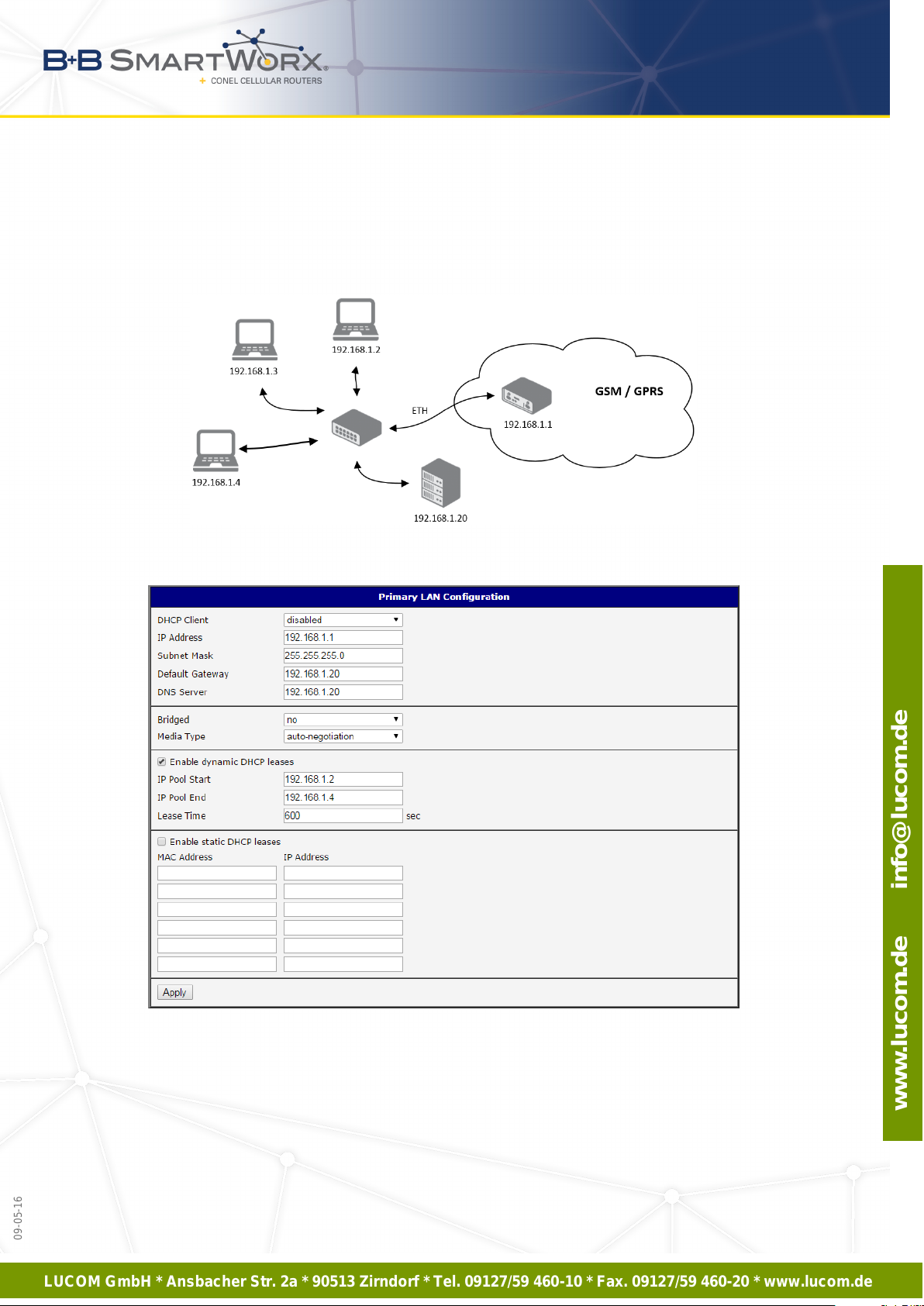
Example 3: Configure the network interface to connect to a default gateway and DNS server:
• Default gateway IP address is 192.168.1.20
• DNS server IP address is 192.168.1.20
Figure 15: Example 3 – Network Topology
Figure 16: Example 3 – LAN Configuration Page
23
09-05-16
Page 31

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.2 VRRP Configuration
Select the VRRP menu item to enter the VRRP configuration. VRRP protocol (Virtual
Router Redundancy Protocol) allows you to transfer packet routing from the main router to
a backup router in case the main router fails. (This can be used to provide a wireless cellular
backup to a primary wired router in critical applications.) If the Enable VRRP is checked, you
may set the following parameters.
Item Description
Virtual Server IP Address This parameter sets the virtual server IP address. This ad-
dress must be the same for both the primary and backup
routers. Devices on the LAN will use this address as their
default gateway IP address.
Virtual Server ID This parameter distinguishes one virtual router on the net-
work from another. The main and backup routers must use
the same value for this parameter.
Host Priority The active router with highest priority set by the parameter
Host Pr iority, is the main router. According to RFC 2338, the
main router should have the highest possible priority – 255.
The backup router(s) have a priority in the range 1 – 254
(default value is 100). A priority value of 0 is not allowed.
Table 17: VRRP configuration
You may set the Check connection flag in the second part of the window to enable automatic test messages for the cellular network. In some cases, the mobile WAN connection
could still be active but the router will not be able to send data over the cellular network. This
feature is used to verify that data can be sent over the PPP connection and supplements
the normal VRRP message handling. The currently active router (main/backup) will send test
messages to the defined Ping IP Address at periodic time intervals (Ping Interval) and wait for
a reply (Ping Timeout). If the router does not receive a response to the Ping command, it will
retry up to the number of times specified by the Ping Probes parameter. After that time, it will
switch itself to a backup router until the PPP connection is restored.
Item Description
Ping IP Address Destinations IP address for the Ping commands. IP Address can
not be specified as a domain name.
Ping Interval Interval in seconds between the outgoing Pings.
Ping Timeout Time in seconds to wait for a response to the Ping.
Ping Probes Maximum number of failed ping requests.
Table 18: Check connection
You may use the DNS server of the mobile carrier as the destination IP address for the test
messages (Pings).
24
Page 32

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
The Enable traffic monitoring option can be used to reduce the number of messages that
are sent to test the PPP connection. When this parameter is set, the router will monitor the
interface for any packets different from a ping. If a response to the packet is received within the
timeout specified by the Ping Timeout parameter, then the router knows that the connection is
still active. If the router does not receive a response within the timeout period, it will attempt to
test the mobile WAN connection using standard Ping commands.
Example of the VRRP protocol:
Figure 17: Topology of VRRP configuration example
Figure 18: Example of VRRP configuration – main router
25
09-05-16
Page 33

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Figure 19: Example of VRRP configuration – backup router
26
09-05-16
Page 34

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.3 Mobile WAN Configuration
The XR5i v2 routers do not display the Mobile WAN configuration option.
Select the Mobile WAN item in the Configuration menu section to enter the cellular network
configuration page.
3.3.1 Connection to Mobile Network
If you mark the Create connection to mobile network checkbox, then the router automatically attempts to establish a connection after booting up. You can specify the following parameters for each SIM card separately, or to toggle between the SIM cards, specify two different
APNs.
Item Description
APN Network identifier (Access Point Name)
Username User name for logging into the GSM network
Password Password for logging into the GSM network
Authentication Authentication protocol in the GSM network:
• PAP or CHAP – The router selects the authentication method.
• PAP – The router uses the PAP authentication method.
• C HAP – The router uses the CHAP authentication method.
IP Address Specifies the IP address of SIM card. You manually enter the IP ad-
dress, only when mobile network car rier assigned the IP address.
Phone Number Specifies the telephone number the router dials for a GPRS or CSD
connection. The router uses a default telephone number *99***1 #.
Operator Specifies the carrier code. You can specify the parameter as the PLNM
preferred carrier code.
Network type Specifies the type of protocol used in the mobile network.
• Automatic selection – The router automatically selects the trans-
mission method according to the availability of transmission technology.
• Furthermore, according to the type of router – It’s also possible to
select a specific method of data transmission (GPRS, UMTS, . . . )
PIN Specifies the PIN used to unlock the SIM card. Use a PIN parameter
only if the network requires a SIM card router. The SIM card is blocked
after several failed attempts to enter the PIN.
Continued on next page
27
Page 35

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
MRU Specifies the Maximum Receive Unit which is the maximum size of a
packet that the router can receive in a given environment. The default
value is 1500 B. Other settings can cause the router to incorrectly transmit data.
MTU Specifies the Maximum Transmission Unit which is the maximum size
of a packet that the router can transmit in a given environment. The default value is 1500 B. Other settings can cause the router to incorrectly
transmit data.
Table 19: Mobile WAN Connection Configuration
The following list contains tips for working with the Mobile WAN configuration form:
• If the MTU size is set incorrectly, then the router does not exceed the data transfer. When
you set the MTU value low, more frequent fragmentation of data occurs. More frequent
fragmentation means a higher overhead and also the possibility of packet damage during
defragmentation. On the contrary, a higher MTU value can cause the network to drop
the packet.
• If the IP address field is left blank, when the router establishes a connection, then the
mobile network carrier automatically assigns an IP address. If you assign an IP address,
then the router accesses the network quicker.
• If the APN field is left blank, then the router automatically selects the APN using the IMSI
code of the SIM card. If the PLMN (operator number format) is not in the APN list, then
the router uses the default APN "internet". The mobile network carrier defines the APN.
• If you enter the word blank in the APN field, then the router interprets the APN as blank.
ATTENTION:
• If only one SIM card is installed in the router (or the router has one only one
SIM card slot), the router switches between the APN options. A router with
two SIM cards switches between SIM cards.
• The correct PIN must be filled in. SIM cards with two APNs will use the same
PIN for both APNs. An incorrect PIN can block the SIM card.
Parameters identified with an asterisk require you to enter the appropriate information only
if this information is required by the mobile network carrier.
28
Page 36

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
When the router is unsuccessful in establishing a connection to mobile network, verify
accuracy of the entered data. Alternatively, you can try a different authentication method or
network type.
3.3.2 DNS Address Configuration
The DNS Settings parameter is designed for easier configuration on the client side. When
you set the value to get from opertor the router attempts to automatically obtain an IP address
from the primary and secondary DNS server of the mobile network carrier. To specify the IP
addresses of the Primary DNS servers manually, from the DNS Server pull down list, select
the value set manually.
3.3.3 Check Connection to Mobile Network Configuration
If the Check Connection item is set to enabled or enabled + bind, it activates checking
the connection to the mobile network. The router will automatically send ping requests to the
specified domain or IP address (Ping IP Address item) at regular time intervals (Ping Interval).
In case of unsuccessful ping, a new one will be sent after ten seconds. If it fails to ping the IP
address three times in a row, the router terminates the current connection and tries to establish
new ones. Checking can be set separately for two SIM cards or two APNs. Send an IMCP to
an IP address that you know is still functional. (The operator’s DNS server, for example.)
If the Check Connection item is set to the enabled option, ping requests are sent on the
basis of routing table. Thus, the requests may be sent through any available interface. If you
require each ping request to be sent through the network interface, which was created when
establishing a connection to the mobile operator, it is necessary to set the Check Connection
item to enabled + bind. The disabled option deactivates checking the connection to the mobile
network.
Item Description
Ping IP Address Specifies the destination IP address or domain name for ping
queries.
Ping Interval Specifies the time intervals between the outgoing pings.
Table 20: Check Connection to Mobile Network Configuration
If you mark the Enable Traffic Monitoring checkbox, then the router stops sending ping
request to the Ping IP Address and it monitors the data stream on the connection to mobile
network. If this connection is without data longer than the Ping Interval, then the router sends
a ping request to the Ping IP Address.
Enabling the Check Connection function for mobile networks is necessary for uninterrupted and lasting operation of the router.
29
Page 37

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
3.3.4 Dat a Limit Configuration
Item Description
Data limit Specifies the maximum expected amount of data transmitted (sent
and received) over GPRS in one billing period (month).
Warning Threshold Specifies the percentage of the "Data Limit" in the range of 50 % to
99 %. If the data limit is exceeded, the router sends an SMS in the
following form Router has exceeded (value of Warning Threshold)
of data limit.
Accounting Start Specifies the day of the month in which the billing cycle starts for
the SIM card used. When the service provider that issued the SIM
card specifies the start billing period, the router begins to count
the amount of transferred data starting on this day.
Table 21: Data Limit Configuration
If the parameters Switch to backup SIM card when data limit is exceeded and switch to default
SIM card when data limit isn’t exceeded (see next subsection) or Send SMS when data limit
is exceeded (see SMS configuration) are not selected, the data limit will be ignored.
3.3.5 Switch between SIM Cards Configuration
At the bottom of this configuration form you can specify the rules for toggling between the
two APNs, a single SIM card, or between the two SIM cards if you have inserted two SIM
cards. The router can automatically toggle between the network setups in the following cases:
• the active connection to mobile network is lost,
• the data limit is exceeded,
• the binary input on the front panel is activated.
Item Description
Default SIM card Specifies the default APN or SIM card. The router attempts to es-
tablish a connection to mobile network using the default. If you
specify this parameter as none, then the router boots up in the
off line mode and it is necessary to establish a connection to the
mobile network using an SMS message.
Backup SIM card Specifies the backup APN or SIM card.
Table 22: Default and Backup SIM Configuration
30
09-05-16
Page 38

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
If you select none from the Backup SIM card drop down list, then the following parameters
cause the router to go into the of f line mode:
• Switch to other SIM card when connection fails,
• Switch to backup SIM card when roaming is detected and switch to default SIM card
when home network is detected,
• Switch to backup SIM card when data limit is exceeded and switch to default SIM card
when data limit isn’t exceeded.
Item Description
Switch to other SIM card when
connection fails
Switch to backup SIM card when
roaming is detected and switch
to default SIM card when home
network is detected
Switch to backup SIM card when
data limit is exceeded and switch
to default SIM card when data
limit isn’t exceeded
Switch to backup SIM card when
binary input is active switch to
default SIM card when binary input isn’t active
Switch to default SIM card after
timeout
Table 23: Switch between SIM Card Configurations
If the connection to mobile network fails, the router will
switch to the secondary SIM card or secondary APN
of the SIM card. The router will switch to the backup
SIM card if the router is unable to establish a connection to mobile network after 3 attempts or the Check
the connection to mobile network option is selected
and the router detects that the connection to mobile
network has failed.
If roaming is detected, this option forces the router to
switch to the secondary SIM card or secondary APN
of the SIM card. If the home network is detected, this
option enables switching back to the default SIM card.
For proper operation, it is necessary to enable
roaming on your SIM card!
This option enables the router to switch to the secondary SIM card or secondary APN of the SIM card
when the data limit of default APN is exceeded. This
option also enables switching back to default SIM
card, when data limit is not exceeded.
This parameter forces the router to switch to the secondary SIM card or secondary APN of the SIM card
when binary input ’bin0’ is active. If the binary input
isn’t active, this option enables switching back to the
default SIM card.
This parameter defines the method the router will use
to try to switch back to the default SIM card or default APN. This parameter defines the method, how
the router will try to switch back to default SIM card or
default APN.
31
Page 39

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
The following parameters specifies the length of time that the router waits before attempting
to change back to the default SIM card or APN.
Item Description
Initial timeout Specifies the length of time that the router waits before the first
attempt to change back to the primary SIM card or APN, the range
of this parameter is from 1 to 10000 minutes.
Subsequent Timeout Specifies the length of time that the router waits after an unsuc-
cessful attempt to change to the default SIM card, the range is
from 1 to 10000 min.
Additive constants Specifies the length of time that the router waits for any further
attempts to change back to the primary SIM card or APN. The
length time is the sum of the time specified in the "Subsequent
Timeout" parameter and the time specified in this parameter, the
range is from 1 to 10000 minutes.
Table 24: Timeout Configuration
Example:
If you mark the Switch to default SIM card after timeout check box, and you enter the following
values:
• Initial Timeout – 60 min,
• Subsequent Timeout – 30 min,
• Additional Timeout – 20 min.
The first attempt to change to the primary SIM card or APN is carried out after 60 minutes.
When the first attempt fails, a second attempt is made after 30 minutes. A third attempt is
made after 50 minutes (30+20). A fourth attempt is made after 70 minutes (30+20+20).
32
Page 40

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.3.6 Dial-In access configuration
Dial-In access configuration is supported for these routers only: ER75i, UR5, ER75i v2
and UR5 v2.
You may define access over CSD connection by selecting the Enable Dial-In Access function. Access can be secured by using the Username and Password. If the router does not have
a connection to a mobile network, you may use this function to gain access to the router via
dial-up connections. The router waits two minutes to accept connections. If no one logs on
during this time the router will make another attempt to establish a GPRS connection.
Item Description
Username User name for secured Dial-In access.
Password Password for secured Dial-In access.
Table 25: Dial-In access configuration
3.3.7 PPPoE Bridge Mode Configuration
If you mark the Enable PPPoE bridge mode check box, the router activates the PPPoE
bridge protocol. PPPoE (point-to-point over ethernet) is a network protocol for encapsulating
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) frames inside Ethernet frames. The bridge mode allows you to
create a PPPoE connection from a device behind the router. For example, a PC connected to
the ETH port of the router. You assign the IP address of the SIM card to the PC.
The changes in settings will apply after clicking the Apply button.
33
Page 41

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Figure 20: Mobile WAN Configuration
34
09-05-16
Page 42

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Example 1: The figure below displays the following scenario: the connection to the mobile
network is controlled on the address 8.8.8.8 with the time interval of 60 seconds for the primary SIM card and on the address www.google.com with the time interval 80 seconds for the
secondary SIM card. In the case of data stream on the router, the control pings are not sent,
but the data stream is monitored.
Figure 21: Example 1 – Mobile WAN Configuration
Example 2: The following configuration illustrates a scenario in which the router changes to
a backup SIM card after exceeding the data limits of 800MB. The router sends a warning SMS
upon reaching 400MB. The accounting period starts on the 18th day of the month.
Figure 22: Example 2 – Mobile WAN Configuration
Example 3: The Primary SIM card changes to the off line mode after the router detects
roaming. The first attempt to change back to the default SIM card is executed after 60 minutes,
the second attempt is executed after 40 minutes, the third attempt is executed after 50 minutes
(40+10).
Figure 23: Example 3 – Mobile WAN Configuration
35
09-05-16
Page 43

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.4 PPPoE Configuration
PPPoE (Point-to-Point over Ethernet) is a network protocol which encapsulates PPPoE
frames into Ethernet frames. The router uses the PPPoE client to connect to devices supporting a PPPoE bridge or server. The bridge or ser ver is typically an ADSL router.
To open the PPPoE Configuration page, select the PPPoE menu item. If you mark the
Create PPPoE connection check box, then the router attempts to establish a PPPoE connection after boot up. After connecting, the router obtains the IP address of the device to which
it is connected. The communications from a device behind the PPPoE server is forwarded to
the router.
Item Description
Username Username for secure access to PPPoE
Password Password for secure access to PPPoE
Authentication Authentication protocol in GSM network
• PAP or CHAP – The router selects the authentication method.
• PAP – The router uses the PAP authentication method.
• C HAP – The router uses the CHAP authentication method.
MRU Specifies the Maximum Receiving Unit. The MRU identifies the max-
imum packet size, that the router can receive in a given environment. The default value is 1492 bytes. Other settings can cause incorrect data transmission.
MTU Specifies the Maximum Transmission Unit. The MTU identifies the
maximum packet size, that the router can transfer in a given environment. The default value is 1492 bytes. Other settings can cause
incorrect data transmission.
Table 26: PPPoE configuration
Figure 24: PPPoE configuration
Setting a bad packet size value (MRU, MTU) can cause unsuccessful transmission.
36
Page 44

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.5 WiFi Configuration
This item is available only if the router is equipped with a WiFi module.
Configure the WiFi network by selecting the WiFi item in the main menu of the router web
interface. Activate WiFi by selecting Enable WiFi at the top of the form. You may also set the
following properties:
Item Description
Operating mode WiFi operating mode:
• access point (AP) – The router becomes an access point to
which other devices in station (STA) mode can connect.
• st ation (STA) – The router becomes a client station. It receives
data packets from the available access point (AP) and sends
data from cable connection via the WiFi network.
SSID Unique identifier of WiFi network.
Broadcast SSID Method of broadcasting the unique identifier of SSID network in bea-
con frame and type of response to a request for sending the beacon
frame.
• Enabled – SSID is broadcasted in beacon frame
• Zero length – Beacon frame does not include SSID. Requests
for sending beacon frame are ignored.
• Clear – All SSID characters in beacon frames are replaced by
0. Original length is kept. Requests for sending beacon frames
are ignored.
Probe Hidden
SSID
Country Code Code of the country where the router is installed. This code must be
Probes hidden SSID (only for station (STA) mode)
entered in ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 format. If a country code isn’t specified
and the router has not implemented a system to determine this code,
it will use "US" as the default country code.
If no country code is specified or if the wrong country code is entered,
then the router violate country-specific regulations for the use of the
WiFi frequency bands.
Continued on next page
37
Page 45

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
HW Mode HW mode of WiFi standard that will be supported by WiFi access
point.
• IEE 802.11b
• IEE 802.11b+g
• IEE 802.11b+g+n
• IEE 802.11a
• IEE 802.11a+n
Channel The channel, where the WiFi AP is transmitting.
BW 40 MHz The option for HW mode 802.11n which allows transmission on two
standard 20 MHz channels simultaneously. The option is also available in the STA mode and it has to be enabled in both the AP and the
STA mode if using the high throughput mode.
WMM Basic QoS for WiFi networks is enabled by checking this item. This
version doesn’t guarantee network throughput. It is suitable for simple applications that require QoS.
Authentication Access control and authorization of users in the WiFi network.
• Open – Authentication is not required (free access point).
• Shar ed – Base authentication using WEP key.
• WPA-PSK – Authentication using better authentication meth-
ods PSK-PSK.
• WPA2-PSK – WPA -PSK using new encryption AES.
Encryption Type of data encryption in the WiFi network:
• None – No data encryption.
• WEP – Encryption using static WEP keys. This encryption can
be used for Shared authentication.
• TKIP – Dynamic encryption key management that can be used
for WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK authentication.
• AES – Improved encryption used for WPA2-PSK authentica-
tion.
Continued on next page
38
Page 46

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
WEP Key Type Type of WEP key for WEP encryption:
• ASCII – WEP key in ASCII format.
• HEX – WEP key in hexadecimal format.
WEP Default Key This item specifies the default WEP key.
WEP Key 1-4 Items for different four WEP keys:
• WEP key in ASCII format must be entered in quotes. This key
can be specified in the following lengths.
– 5 ASCII characters (40b WEP key)
– 13 ASCII characters (104b WEP key)
– 16 ASCII characters (128b WEP key)
• WEP key must be entered in hexadecimal digits. This key can
be specified in the following lengths.
– 10 hexadecimal digits (40b WEP key)
– 26 hexadecimal digits (104b WEP key)
– 32 hexadecimal digits (128b WEP key)
WPA PSK Type Type of key for WPA-PSK authentication.
• 256-bit secret
• ASCII passphrase
• PSK File
WPA PSK Key for WPA-PSK authentication. This key must be entered accord-
ing to the selected WPA PSK type as follows.
• 256-bit secr et – 64 hexadecimal digits
• ASCII passphrase – 8 to 63 characters
• PSK File – absolute path to the file containing the list of pairs
(PSK key, MAC address)
Continued on next page
39
Page 47

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
Access List Mode of Access/Deny list.
• Disabled – Access/Deny list is not used.
• Accept – Clients in Accept/Deny list can access the network.
• Deny – Clients in Access/Deny list cannot access the network.
Accept/Deny List Accept or Denny list of client MAC addresses that set network ac-
cess. Each MAC address is separated by new line.
Syslog Level Logging level, when system writes to the system log.
• Verbose debugging – The highest level of logging.
• Debugging
• Informational – Default level of logging.
• Notification
• Warning – The lowest level of communicativeness.
Extra options Allows the user to define additional parameters.
Table 27: WiFi Configuration
40
09-05-16
Page 48

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Figure 25: WiFi Configuration
41
09-05-16
Page 49

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.6 WLAN Configuration
This item is available only if the router is equipped with a WiFi module.
The WiFi LAN and DHCP server page is displayed by selecting WLAN in the configuration
section. You will then be able to set the following properties (see table below). Use the Enable
WLAN interface check box at the top of this form to enable WiFi LAN interface.
Item Description
Operating Mode WiFi operating mode:
• access point (AP) – The router becomes an access point
to which other devices in station (STA) mode can be con-
nected.
• st ation (STA) – Router becomes a client station. It will re-
ceive data packets from the available access point (AP) and
send data from cable connection via the WiFi network.
DHCP Client Activates/deactivates DHCP client.
IP Address Fixed set IP address of WiFi network interface.
Subnet Mask Subnet mask of WiFi network interface.
Bridged Activates bridge mode:
• no – Bridged mode is not allowed (default value). WLAN
network is not connected with LAN network of the router.
• yes – Bridged mode is allowed. WLAN network is connected
with one or more LAN networks of the router. In this case,
the setting of most items in this table are ignored. Instead,
the router uses the settings of the selected network interface
(LAN).
Default Gateway IP address of the default gateway. When entering the IP address
of the default gateway, all packets for which the record was not
found in the routing table will be sent to this address.
DNS Server Address to which all DNS queries are forwarded.
Table 28: WLAN Configuration
42
Page 50

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Use Enable dynamic DHCP leases item at the bottom of this form to enable dynamic
allocation of IP addresses using the DHCP server. You may also specify these values:
Item Description
IP Pool Start Beginning of the range of IP addresses which will be assigned to DHCP
clients.
IP Pool End End of the range of IP addresses which will be assigned to DHCP
clients.
Lease Time Time in seconds for which the client may use the IP address.
Table 29: Configuration of DHCP Server
All changes in settings will apply after pressing the Apply button.
Figure 26: WLAN Configuration
43
09-05-16
Page 51

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
3.7 Backup Routes
By using the configuration form on the Backup Routes page, you can back up the primary connection with alternative connections to the Internet/mobile network. Each backup
connection can be assigned a priority. Switching between connections is done based upon
set priorities and the state of the connections (for Primar y LAN and Secondary LAN).
If the Enable backup routes switching option is checked, the default route is selected according to the settings in the chart below. (Options include Enable backup routes switching for
Mobile WAN, Enable backup routes switching for PPPoE, Enable backup routes switching for
WiFi STA, Enable backup routes switching for Primary LAN or Enable backup routes switching
for Secondary LAN.)
Network interfaces belonging to individual backup routes should display a flag that says
they are RUNNING. This check fixes, for example, the disconnection of an Ethernet cable.
Attention! If you want to use a mobile WAN connection as a backup route, then mark
the Check Connection check box, and on the Mobile WAN page, select the enable + bind
option, see chapter 3.3.1.
Figure 27: Backup Routes
44
09-05-16
Page 52

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
If you unmark the Enable backup routes switching check box, the backup routes system
operates in the backward compatibility mode. The router selects the default route based on
implicit priorities of the enabled settings for each of the network interfaces, as the case may
be enabling services that set these network interfaces. The following list contains the names
of backup routes and corresponding network interfaces in order of implicit priorities:
• Mobile WAN (pppX, usbX)
• PPPoE (ppp0)
• WiFi STA (wlan0)
• Secondary LAN (eth1)
• Primary LAN (eth0)
Example: The router selects the Secondary LAN as the default route only if you unmark the
Create connection to mobile network check box on the Mobile WAN page. Alternatively, if you
unmark the Create PPPoE connection check box on the PPPoE page. To select the Primary
LAN, delete the IP address for the Secondary LAN and disabled the DHCP Client for the
Secondary LAN.
Item Description
Priority Prior ity for the type of connection.
Ping IP Address Destination IP address of ping queries to check the connection.
(The address can not be specified as a domain name.)
Ping Interval The time intervals between consecutive ping queries.
Table 30: Backup Routes
All changes in settings will be applied after pressing the Apply button.
45
Page 53

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.8 Firewall Configuration
The first security element which incoming packets pass is a check of the enabled source
IP addresses and destination ports. You can specify the IP addresses as an IP address from
which you can remotely access the router and the internal network connected behind a router.
To enable this function, marking the Enable filtering of incoming packets check box located
at the top of the Firewall Configuration page. Accessibility is checked against the IP address
table. This means that access is permitted only to addresses specified in the table. It is possible to specify up to eight remote IP addresses for access. You can specify the following
parameters:
Item Description
Source IP address from which access to the router is allowed.
Protocol Specifies the protocol used for remote access:
• all – Access for all protocols is active.
• TCP – Access for the TCP protocol is active.
• UDP – Access for the UDP protocol is active.
• ICMP – Access for the ICMP protocol is active.
Target Port The port number on which access to the router is allowed.
Action Specifies the type of action the router performs:
• allow – The router allows the packets to enter the network.
• deny – The router denies the packets from entering the network
Table 31: Filtering of Incoming Packets
The next section of the configuration form specifies the forwarding policy. If you unmark
the Enabled filtering of forwarded packets check box, then packets are automatically accepted.
If you activate this function, and a packet is addressed to another network interface, then the
router sends the packet to the FORWARD chain. When the FORWARD chain accepts the
packet and there is a rule for forwarding it, the router sends the packet. If a forwarding rule is
unavailable, then the router drops the packet.
This configuration form also contains a table for specifying the filter rules. It is possible
to create a rule to allow data with the selected protocol by specifying only the protocol, or to
create stricter rules by specifying values for source IP addresses, destination IP addresses,
and ports.
46
Page 54

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Item Description
Source IP address from which access to the router is allowed.
Destination IP address of destination device.
Protocol Specifies the protocol used for remote access:
• all – Access for all protocols is active.
• TCP – Access for the TCP protocol is active.
• UDP – Access for the UDP protocol is active.
• ICMP – Access for the ICMP protocol is active.
Target Port Specifies the port number on which access to the router is allowed.
Action Specifies the type of action the router performs:
• allow – The router allows the packets to enter the network.
• deny – The router denies the packets from entering the net-
work.
Table 32: Forwarding filtering
When you enable the Enable filtering of locally destined packets function, the router drops
receives packets requesting an unsupported service. The packet is dropped automatically
without any information.
As a protection against DoS attacks, the Enable protection against DoS attacks limits the
number of allowed connections per second to five. The DoS attac k floods the target system
with meaningless requirements.
47
Page 55

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Figure 28: Firewall Configuration
Example of the firewall configuration:
The router allows the following access:
• from IP address 171.92.5.45 using any protocol
• from IP address 10.0.2.123 using the TCP protocol on port 1000
• from IP address 142.2.26.54 using the ICMP protocol
48
09-05-16
Page 56

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Figure 29: Topology for the Firewall Configuration Example
Figure 30: Firewall Configuration Example
49
09-05-16
Page 57

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.9 NAT Configuration
To configure the address translation function, open the NAT Configuration page, click on
NAT in the Configuration section of the main menu. The router actually uses Port Address
Translation (PAT), which is a method of mapping a TCP/UDP port to another TCP/UDP port.
The router modifies the information in the packet header as the packets traverse a router. This
configuration form allows you to specify up to 16 PAT rules.
Item Description
Public Port Public port
Private Port Private port
Type Protocol type
Server IP address IP address where the router forwards incoming data.
Table 33: NAT Configuration
If you require more than sixteen NAT rules, then insert the remaining rules into the start
up script. The Startup Script dialog is located in the Configuration section of the main menu.
When creating your rules in the start up script, use the following format:
iptables -t nat -A napt -p tcp --dport [PORT\_PUBLIC] -j DNAT --to-destination
[IPADDR]:[PORT1\_PRIVATE]
Enter the IP address [IPADDR], the public ports numbers [PORT_PUBLIC], and private
[PORT_PRIVATE] in square bracket.
You use the following parameters to set the routing of incoming data from the PPP to a
connected computer.
Item Description
Send all remaining incoming
packets to default server
Default Server IP Address Specified the IP address for the default server.
Table 34: Configuration of send all incoming packets
Activates/deactivates forwarding unmatched incoming
packets to the default server. The prerequisite for the
function is that you specify a default server in the Default
Server IP Address field. The router can forward incoming data from a GPRS to a computer with the assigned
IP address.
50
Page 58

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
If you enable the following options and enter the port number, the router allows you to
remotely access to the router from a PPP interface.
Item Description
Enable remote HTTP access on port If field and port number are filled in, configura-
tion of the router over web interface is allowed
(disabled in default configuration).
Enable remote HTTPS access on port If field and port number are filled in, configura-
tion of the router over web interface is allowed
(disabled in default configuration).
Enable remote FTP access on port Select this option to allow the router using FTP.
Enable remote SSH access on port Select this option to allow access to the router
using SSH (disabled in default configuration).
Enable remote Telnet access on port Select this option to allow the router using Telnet.
Enable remote SNMP access on port Select this option to allow access to the router
using SNMP (disabled in default configuration).
Masquerade outgoing packets Activates/deactivates the network address trans-
lation function.
Table 35: Remote Access Configuration
Example 1: NAT configuration with one connection to the router:
Figure 31: Example 1 – Topology of NAT Configuration
51
09-05-16
Page 59

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Figure 32: Example 1 – NAT Configuration
It is important to mark the Send all remaining incoming packets to default server check box
for this configuration. The IP address in this example is the address of the device behind the
router. The default gateway of the devices in the subnetwork connected to router is the same
IP address as displayed in the Default Server IP Address field. The connected device replies
if a PING is sent to the IP address of the SIM card.
52
Page 60

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Example 2: Configuration with more equipment connected.
Figure 33: Example 2 – Topology of NAT Configuration
Figure 34: Example 2 – NAT Configuration
53
09-05-16
Page 61

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
In this example there is additional equipment connected behind the router, using a Switch.
Every device connected behind the router has its own IP address. This is the address to enter
in the Server IP Address field in the NAT configuration. All of these devices will be communicating on port 80, but you can configure the Port Forwarding in the NAT configuration Public
Port and Private Port fields. It is now configured to access 192.168.1.2:80 socket behind the
router when accessing 10.0.0.1:81 from the Internet, and so on. If you send the ping request to
the public IP address of the router (10.0.0.1), the router will respond as usual (not forwarding).
If you access the IP address 10.0.0.1 in the browser (it is port 80), nothing will happen – Port
80 in the Public Port list is not defined, and you have not checked the Enable remote HTTP
access on port 80. And since the Send all remaining incoming packets to default server is not
enabled, the attempt to connect will fail.
54
09-05-16
Page 62

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.10 OpenVPN Tunnel Configuration
Select the OpenVPN item to configure an OpenVPN tunnel. The OpenVPN tunnel function
allows you to create a secure connection between two separate LAN networks. The router
allows you to create up to four OpenVPN tunnels.
Item Description
Create Activates/deactivates the individual tunnel configurations.
Description Displays the name of the tunnel specified in the configuration form.
Edit Opens the OpenVPN tunnel configuration form.
Table 36: OpenVPN Tunnels Overview
Figure 35: OpenVPN Tunnels List
Item Description
Description Specifies the description or name of tunnel.
Protocol Specifies the communication protocol.
• UDP – The OpenVPN communicates using UDP.
• TCP server – The OpenVPN communicates using TCP in
server mode.
• TCP client – The OpenVPN communicates using TCP in
client mode.
UDP/TCP port Specifies the port of the relevant protocol (UDP or TCP).
Remote IP Address Specifies the IP address of opposite tunnel side. You can also
use the domain name.
Remote Subnet Specifies the IP address of a network behind opposite side of the
tunnel.
Remote Subnet Mask Specifies the subnet mask of a network behind opposite side of
the tunnel.
Continued on next page
55
Page 63

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
Redirect Gateway Activates/deactivates redirection of data on Layer 2.
Local Interface IP
Address
Remote Interface
IP Address
Ping Interval Specifies the time interval after which the router sends a mes-
Ping Timeout Specifies the time interval during which the router waits for a
Renegotiate Interval Specifies the renegotiate period (reauthorization) of the Open-
Max Fragment Size Maximum size of a sent packet.
Compression Compression of the data sent:
NAT Rules Activates/deactivates the NAT rules for the OpenVPN tunnel:
Specifies the IP address of a local interface.
Specifies the IP address of the interface of opposite side of the
tunnel.
sage to opposite side of tunnel to verify the existence of the tunnel.
message sent by the opposite side. For proper verification of the
OpenVPN tunnel, set the Ping Timeout to greater than the Ping
Interval.
VPN tunnel. You can only set this parameter when the Authen-
ticate Mode is set to username/password or X.509 certificate.
After this time period, the router changes the tunnel encryption
to help provide the continues safety of the tunnel.
• none – No compression is used.
• LZO – A lossless compression is used, use the same set-
ting on both sides of the tunnel.
• not applied – NAT rules are not applied to the OpenVPN
tunnel.
• applied – NAT rules are applied to the OpenVPN tunnel.
Continued on next page
56
Page 64

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
Authenticate Mode Specifies the authentication mode:
• none – No authentication is set.
• Pre-shared secret – Specifies the shared key function for
both sides of the tunnel.
• Username/password – Specifies authentication using a
CA Certificate, Username and Password.
• X.509 Certificate (multiclient) – Activates the X.509 au-
thentication in multi-client mode.
• X.509 Certificate (client) – Activates the X.509 authenti-
cation in client mode.
• X.509 Certificate (server) – Activates the X.509 authenti-
cation in server mode.
Pre-shared Secret Specifies the pre-shared secret which you can use for every au-
thentication mode.
CA Certificate Specifies the CA Certificate which you can use for the user-
name/password and X.509 Certificate authentication modes.
DH Parameters Specifies the protocol for the DH parameters key exchange which
you can use for X.509 Certificate authentication in the server
mode.
Local Certificate Specifies the certificate used in the local device. You can use this
authentication certificate for the X.509 Certificate authentication
mode.
Local Private Key Specifies the key used in the local device. You can use the key
for the X.509 Certificate authentication mode.
Username Specifies a login name which you can use for authentication in
the username/password mode.
Password Specifies a password which you can use for authentication in the
username/password mode.
Extra Options Specifies additional parameters for the OpenVPN tunnel, such as
DHCP options. The parameters are proceeded by two dashes.
For possible parameters see the help text in the router using SSH
– run the openvpnd --help command.
Table 37: OpenVPN Configuration
57
Page 65

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the Apply button.
Figure 36: OpenVPN tunnel configuration
58
09-05-16
Page 66

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Example of the OpenVPN tunnel configuration:
Figure 37: Topology of OpenVPN Configuration Example
OpenVPN tunnel configuration:
Configuration A B
Protocol UDP UDP
UDP Port 1194 1194
Remote IP Address 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
Remote Subnet 192.168.2.0 192.168.1.0
Remote Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Local Interface IP Address 19.16.1.0 19.16.2.0
Remote Interface IP Address 19.16.2.0 19.18.1.0
Compression LZO LZO
Authenticate mode none none
Table 38: OpenVPN Configuration Example
Examples of different options for configuration and authentication of OpenVPN tunnel can be
found in the application note OpenVPN Tunnel [5].
59
Page 67

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
3.11 IPsec Tunnel Configuration
To open the IPsec Tunnel Configuration page, click IPsec in the Configuration section of
the main menu. The IPsec tunnel function allows you to create a secured connection between
two separate LAN networks. The router allows you to create up to four IPsec tunnels.
To encrypt data between the local and remote subnets, specify the appropriate values in
the subnet fields on both routers. To encrypt the data stream between the routers only,
leave the local and remote subnets fields blank.
If you specify the protocol and port information in the Local Protocol/Port field, then the
router encapsulates only the packets matching the settings.
Item Description
Create Activates/deactivates the individual IPsec tunnels.
Description Displays the name of the tunnel specified in the configuration of
the tunnel.
Edit Opens the IPsec tunnel configuration form.
Table 39: IPsec Tunnels Overview
Figure 38: IPsec Tunnels List
Item Description
Description Name or description of the tunnel.
Remote IP Address IP address of remote side of the tunnel. It is also possible to enter
the domain name.
Remote ID Identifier (ID) of remote side of the tunnel. It consists of two parts:
a hostname and a domain-name.
Remote Subnet IP address of a network behind remote side of the tunnel.
Continued on next page
60
09-05-16
Page 68

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
Remote Subnet Mask Subnet mask of a network behind remote side of the tunnel.
Remote Protocol/Port Specifies Protocol/Port of remote side of the tunnel. The general
form is protocol/port, for example 17/1701 for UDP (protocol 17)
and port 1701. It is also possible to enter only the number of
protocol, however, the above mentioned format is preferred.
Local ID Identifier (ID) of local side of the tunnel. It consists of two parts:
a hostname and a domain-name.
Local Subnet IP address of a local network.
Local Subnet Mask Subnet mask of a local network.
Local Protocol/Port Specifies Protocol/Port of a local network. The general form is
protocol/port, for example 17/1701 for UDP (protocol 17) and
port 1701. It is also possible to enter only the number of protocol,
however, the above mentioned format is preferred.
Encapsulation Mode Specifies the IPsec mode, according to the method of encap-
sulation. You can select the tunnel mode in which the entire IP
datagram is encapsulated or the transport mode in which only IP
header is encapsulated.
NAT traversal Enable/disables NAT address translation on the tunnel. If you
use NAT between the end points of the tunnel, then enable this
parameter.
IKE Mode Specifies the mode for establishing a connection (main or ag-
gressive). If you select the aggressive mode, then the router establishes the IPsec tunnel faster, but the encryption is permanently set to 3DES-MD5. We recommend that you not use the
aggressive mode due to lower security!
IKE Algorithm Specifies the means by which the router selects the algorithm:
• auto – The encryption and hash algorithm are selected au-
tomatically.
• manual – The encryption and hash algorithm are defined
by the user.
IKE Encryption Encryption algorithm – 3DES, AES128, AES192, AES256.
IKE Hash Hash algorithm – MD5, SHA1, SHA256, SHA384 or SHA512.
Continued on next page
61
Page 69

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
IKE DH Group Specifies the Diffie-Hellman groups which determine the strength
of the key used in the key exchange process. Higher group numbers are more secure, but require additional time to compute the
key.
ESP Algorithm Specifies the means by which the router selects the algorithm:
• auto – The encryption and hash algorithm are selected au-
tomatically.
• manual – The encryption and hash algorithm are defined
by the user.
ESP Encryption Encryption algorithm – DES, 3DES, AES128, AES192, AES256.
ESP Hash Hash algorithm – MD5, SHA1, SHA256, SHA384 or SHA512.
PFS Enables/disables the Perfect Forward Secrecy function. The
function ensures that derived session keys are not compromised
if one of the private keys is compromised in the future.
PFS DH Group Specifies the Diffie-Hellman group number (see IKE DH Group).
Key Lifetime Lifetime key data part of tunnel. The minimum value of this pa-
rameter is 60 s. The maximum value is 86400 s.
IKE Lifetime Lifetime key service part of tunnel. The minimum value of this
parameter is 60 s. The maximum value is 86400 s.
Rekey Margin Specifies how long before a connection expires that the router
attempts to negotiate a replacement. Specify a maximum value
that is less than half of IKE and Key Lifetime parameters.
Rekey Fuzz Percentage of time for the Rekey Margin extension.
DPD Delay Time after which the IPsec tunnel functionality is tested.
DPD Timeout The period during which device waits for a response.
Authenticate Mode Specifies the means by which the router authenticates:
• Pre-shared key – Sets the shared key for both sides of the
tunnel.
• X.509 Certificate – Allows X.509 authentication in multi-
client mode.
Pre-shared Key Specifies the shared key for both sides of the tunnel. The prereq-
uisite for entering a key is that you select pre-shared key as the
authentication mode.
Continued on next page
62
Page 70

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
CA Certificate Certificate for X.509 authentication.
Remote Certificate Certificate for X.509 authentication.
Local Certificate Certificate for X.509 authentication.
Local Private Key Private key for X.509 authentication.
Local Passphrase Passphrase used during private key generation.
Extra Options Specifies the additional parameters of the IPsec tunnel for exam-
ple, secure parameters.
Table 40: IPsec Tunnel Configuration
The IPsec function supports the following types of identifiers (ID) for both sides of the
tunnel, Remote ID and Local ID parameters:
• IP address (for example, 192.168.1.1)
• DN (for example, C=CZ,O=Conel,OU=TP,CN=A)
• FQDN (for example, @director.conel.cz) – the @ symbol proceeds the FQDN.
• User FQDN (for example, director@conel.cz)
The certificates and private keys have to be in the PEM format. Use only certificates containing
start and stop tags.
The random time, after which the router re-exchanges new keys is defined as follows:
Lifetime - (Rekey margin + random value in range (from 0 to Rekey margin * Rekey Fuzz/100))
The default exchange of keys is in the following time range:
• Minimal time: 1h - (9m + 9m) = 42m
• Maximal time: 1h - (9m + 0m) = 51m
We recommend that you maintain the default settings. When you set key exchange times
higher, the tunnel produces lower operating costs, but the setting also provides less security.
Conversely, when you reducing the time, the tunnel produces higher operating costs, but
provides for higher security.
The changes in settings will apply after clicking the Apply button.
63
Page 71

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Figure 39: IPsec Tunnels Configuration
64
09-05-16
Page 72

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Example of the IPSec tunnel configuration:
Figure 40: Topology of IPsec Configuration Example
IPsec tunnel configuration:
Configuration A B
Remote IP Address 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
Remote Subnet 192.168.2.0 192.168.1.0
Remote Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Local Subnet 192.168.1.0 192.168.2.0
Local Subnet Mas: 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Authenticate mode pre-shared key pre-shared key
Pre-shared key test test
Table 41: Example IPsec configuration
Examples of different options for configuration and authentication of IPsec tunnel can be found
in the application note IPsec Tunnel [6].
65
Page 73

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.12 GRE Tunnels Configuration
GRE is an unencrypted protocol.
To open the GRE Tunnel Configuration page, click GRE in the Configuration section of
the main menu. The GRE tunnel function allows you to create an unencrypted connection
between two separate LAN networks. The router allows you to create four GRE tunnels.
Item Description
Create Activates/deactivates the individual GRE tunnels.
Description Displays the name of the tunnel specified in the configuration form.
Edit Opens the GRE tunnel configuration form.
Table 42: GRE Tunnels Overview
Figure 41: GRE Tunnels List
Item Description
Description Description of the GRE tunnel.
Remote IP Address IP address of the remote side of the tunnel.
Remote Subnet IP address of the network behind the remote side of the tunnel.
Remote Subnet Mask Specifies the mask of the network behind the remote side of the
tunnel.
Local Interface IP
Address
Remote Interface IP
Address
Multicasts Activates/deactivates sending multicast into the GRE tunnel:
IP address of the local side of the tunnel.
IP address of the remote side of the tunnel.
• disabled – Sending multicast into the tunnel is inactive.
• enabled – Sending multicast into the tunnel is active.
Continued on next page
66
Page 74

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
Pre-shared Key Specifies an optional value for the 32 bit shared key in numeric
format, with this key the router sends the filtered data through
the tunnel. Specify the same key on both routers, otherwise the
router drops received packets.
Table 43: GRE Tunnel Configuration
Attention, the GRE tunnel does not pass through NAT.
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the Apply button.
Figure 42: GRE Tunnel Configuration
67
09-05-16
Page 75

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Example of the GRE Tunnel configuration:
Figure 43: Topology of GRE Tunnel Configuration Example
GRE tunnel configuration:
Configuration A B
Remote IP Address 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
Remote Subnet 192.168.2.0 192.168.1.0
Remote Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Table 44: GRE Tunnel Configuration Example
Examples of different options for configuration of GRE tunnel can be found in the application
note GRE Tunnel [7].
68
Page 76

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.13 L2TP Tunnel Configuration
L2TP is an unencrypted protocol.
To open the L2TP Tunnel Configuration page, click L2TP in the Configuration section of the
main menu. The L2TP tunnel function allows you to create a password protected connection
between 2 LAN networks. The router activates the tunnels after you mark the Create L2TP
tunnel check box.
Item Description
Mode Specifies the L2TP tunnel mode on the router side:
• L2TP server – Specify an IP address range offered by
the server.
• L2TP client – Specify the IP address of the server.
Server IP Address IP address of the server.
Client Start IP Address IP address to start with in the address range. The range is
offered by the server to the clients.
Client End IP Address The last IP address in the address range. The range is offered
by the server to the clients.
Local IP Address IP address of the local side of the tunnel.
Remote IP Address IP address of the remote side of the tunnel.
Remote Subnet Address of the network behind the remote side of the tunnel.
Remote Subnet Mask The mask of the network behind the remote side of the tunnel.
Username Username for the L2TP tunnel login.
Password Password for the L2TP tunnel login.
Table 45: L2TP Tunnel Configuration
Figure 44: L2TP Tunnel Configuration
69
Page 77

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Example of the L2TP Tunnel configuration:
Figure 45: Topology of L2TP Tunnel Configuration Example
Configuration of the L2TP tunnel:
Configuration A B
Mode L2TP Server L2TP Client
Server IP Address — 10.0.0.1
Client Start IP Address 192.168.2.5 —
Client End IP Address 192.168.2.254 —
Local IP Address 192.168.1.1 —
Remote IP Address — —
Remote Subnet 192.168.2.0 192.168.1.0
Remote Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Username username username
Password password password
Table 46: L2TP Tunnel Configuration Example
70
Page 78

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
3.14 PPTP Tunnel Configuration
PPTP is an unencrypted protocol.
Select the PPTP item in the menu to configure a PPTP tunnel. PPTP tunnel allows password protected connections between two LANs. It is similar to L2TP. The tunnels are active
after selecting Create PPTP tunnel.
Item Description
Mode Specifies the L2TP tunnel mode on the router side:
• PPTP server – Specify an IP address range offered by
the server.
• PPTP client – Specify the IP address of the server.
Server IP Address IP address of the server.
Local IP Address IP address of the local side of the tunnel.
Remote IP Address IP address of the remote side of the tunnel.
Remote Subnet Address of the network behind the remote side of the tunnel.
Remote Subnet Mask The mask of the network behind the remote side of the tunnel
Username Username for the PPTP tunnel login.
Password Password for the PPTP tunnel login.
Table 47: PPTP Tunnel Configuration
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the Apply button.
Figure 46: PPTP Tunnel Configuration
The firmware also supports PPTP passthrough, which means that it is possible to create a
tunnel through the router.
71
09-05-16
Page 79

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Example of the PPTP tunnel configuration:
Figure 47: Topology of PPTP Tunnel Configuration Example
Configuration of the PPTP tunnel:
Configuration A B
Mode PPTP Server PPTP Client
Server IP Address — 10.0.0.1
Local IP Address 192.168.1.1 —
Remote IP Address 192.168.2.1 —
Remote Subnet 192.168.2.0 192.168.1.0
Remote Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Username username username
Password password password
Table 48: PPTP Tunnel Configuration Example
72
Page 80

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
3.15 DynDNS Configuration
The DynDNS function allows you to access the router remotely using an easy to remember custom hostname. This DynDNS client monitors the IP address of the router and updates the address whenever it changes. In order for DynDNS to function, you require a public IP address, either static or dynamic, and an active Remote Access service account at
www.dyndns.org. Register the custom domain (third-level) and account information specified
in the configuration form. You can use other services, too – see the table below, Server item.
To open the DynDNS Configuration page, click DynDNS in the main menu.
Item Description
Hostname The third order domain registered on the www.dyndns.org server.
Username Username for logging into the DynDNS server.
Password Password for logging into the DynDNS server.
Server Specifies a DynDNS service other than the www.dyndns.org. Possible
other services:
www.spdns.de
www.dnsdynamic.org
www.noip.com
Enter the update server service information in this field. If you leave this
field blank, the default server members.dyndns.org will be used.
Table 49: DynDNS Configuration
Example of the DynDNS client configuration with the domain conel.dyndns.org:
Figure 48: DynDNS Configuration Example
To access the router’s configuration remotely, you will need to have enabled this option in the
NAT configuration (bottom part of the form), see chapter 3.9.
73
09-05-16
Page 81

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.16 NTP Configuration
The NTP configuration form allows you to configure the NTP client. To open the NTP page,
click NTP in the Configuration section of the main menu. NTP (Network Time Protocol) allows
you to periodically set the internal clock of the router. The time is set from servers that provide
the exact time to network devices.
• If you mark the Enable local NTP service check box, then the router acts as a NTP server
for other devices in the local network (LAN).
• If you mark the Synchronize clock with NTP server check box, then the router acts as a
NTP client. This means that the router automatically adjusts the internal clock every 24
hours.
Item Description
Primary NTP Server
Address
Secondary NTP
Server Address
Timezone Specifies the time zone where you installed the router.
Daylight Saving Time Activates/deactivates the DST shift.
The figure below displays an example of a NTP configuration with the primary server set
to ntp.cesnet.cz and the secondary server set to tik.cesnet.cz and with the automatic change
for daylight saving time enabled.
IP or domain address of primary NTP server.
IP or domain address of secondary NTP server.
• No – The time shift is inactive.
• Yes – The time shift is active.
Table 50: NTP Configuration
Figure 49: Example of NTP Configuration
74
Page 82

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
3.17 SNMP Configuration
The SNMP page allows you to configure the SNMP v1/v2 or v3 agent which sends information about the router (and its expansion ports) to a management station. To open the
SNMP page, click SNMP in the Configuration section of the main menu. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) provides status information about the network elements such as
routers or endpoint computers. In the version v3, the communication is secured (encrypted).
To enable the SNMP service, mark the Enable the SNMP agent check box.
Item Description
Name Designation of the router.
Location Location of where you installed the router.
Contact Person who manages the router together with information how to contact
this person.
Table 51: SNMP Agent Configuration
To enable the SNMPv1/v2 function, mark the Enable SNMPv1/v2 access check box. It is
also necessary to specify a password for access to the Community SNMP agent. The default
setting is public.
You can define a different password for the Read community (read only) and the Write
community (read and write) for SNMPv1/v2. You can also define 2 SNMP users for SNMPv3.
You can define a user as read only (Read), and another as read and write (Write). The router
allows you to configure the parameters in the following table for every user separately. The
router uses the parameters for SNMP access only.
To enable the SNMPv3 function, mark the Enable SNMPv3 access chec k box, then specify
the following parameters:
Item Description
Username User name
Authentication Encryption algorithm on the Authentication Protocol that is
used to verify the identity of the users.
Authentication Password Password used to generate the key used for authentication.
Privacy Encryption algorithm on the Privacy Protocol that is used to
ensure confidentiality of data.
Privacy Password Password for encryption on the Privacy Protocol.
Table 52: SNMPv3 Configuration
75
09-05-16
Page 83

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
In addition, you can continue with this configuration:
• Activating the Enable I/O extension function allows you monitor the binary I/O inputs on
the router.
• Selecting the Enable XC-CNT extension lets you monitor the expansion port CNT inputs
and outputs status.
• Selecting Enable M-BUS extension and entering the Baudrate, Parity and Stop Bits lets
you monitor the meter status connected to the expansion port MBUS status.
Item Description
Baudrate Communication speed
Parity Control parity bit:
• none – Data will be sent without parity.
• even – Data will be sent with even parity.
• odd – Data will be sent with odd parity.
Stop Bits Number of stop bits.
Table 53: SNMP configuration – MBUS extension
Parameters Enable XC-CNT extension and Enable M-BUS extension cannot be checked
at the same time.
Selecting Enable reporting to supervisory system and entering the IP Address and Period
lets you send statistical information to the monitoring system, R-SeeNet.
Item Description
IP Address IP address
Period Period of sending statistical information (in minutes).
Table 54: SNMP Configuration – R-SeeNet
76
09-05-16
Page 84

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Each monitored value is uniquely identified using a numerical identifier OID – Object Iden-
tifier. This identifier consists of a progression of numbers separated by a point. The shape
of each OID is determined by the identifier value of the parent element and then this value is
complemented by a point and current number. So it is obvious that there is a tree structure.
The following figure displays the basic tree structure that is used for creating the OIDs.
Figure 50: OID Basic Structure
The SNMP values that are specific for Conel routers create the tree starting at OID =
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140. You interpret the OID in the following manner:
iso.org.dod.internet.private.enterprises.conel
This means that the router provides for example, information about the binary input and
output. The following table shows the range of used OID values:
OID Description
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.3.1.0 Binary input BIN0 (values 0,1)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.3.2.0 Binary output OUT0 (values 0,1)
Table 55: Object identifier for binary input and output
77
09-05-16
Page 85

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
For the expansion port CNT, the following range of OID is used:
OID Description
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.1.0 Analogy input AN1 (range 0-4095)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.2.0 Analogy input AN2 (range 0-4095)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.3.0 Counter input CNT1 (range 0-4294967295)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.4.0 Counter input CNT2 (range 0-4294967295)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.5.0 Binary input BIN1 (values 0,1)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.6.0 Binary input BIN2 (values 0,1)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.7.0 Binary input BIN3 (values 0,1)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.8.0 Binary input BIN4 (values 0,1)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.9.0 Binary output OUT1 (values 0,1)
Table 56: Object identifier for CNT port
For the expansion port M-BUS, the following range of OID is used:
OID Description
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.1.0 IdNumber – meter number
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.2.0 Manufacturer
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.3.0 Version – specified meter version
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.4.0 Medium – type of metered medium
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.5.0 Status – errors report
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.6.0 0. VIF – value information field
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.7.0 0. measured value
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.8.0 1. VIF – value information field
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.9.0 1. measured value
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.10.0 2. VIF – value information field
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.11.0 2. measured value
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.12.0 3. VIF – value information field
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.13.0 3. measured value
.
.
.
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.100.0 47. VIF – value information field
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.101.0 47. measured value
Table 57: Object identifier for M-BUS port
The meter address can be from range 0 – 254, where the number 254 is broadcast.
78
.
.
.
Page 86

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Starting with firmware version 3.0.4, all v2 routers with board RB-v2-6 and newer provide information About the internal temperature of the device (OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.3.3) and
power voltage (OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.3.4).
The list of available and supported OIDs and other details can be found in the application note
SNMP Object Identifier [8].
Figure 51: SNMP Configuration Example
79
09-05-16
Page 87

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Figure 52: MIB Browser Example
In order to access a particular device enter the IP address of the SNMP agent which is
the router, in the Remote SNMP agent field. The dialog displayed the internal variables in the
MIB tree after entering the IP address. Furthermore, you can find the status of the internal
variables by entering their OID.
The path to the objects is:
iso → org → dod → internet → private → enterprises → conel → protocols
The path to information about the router is:
iso → org → dod → internet → mgmt → mib-2 → system
80
Page 88

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
3.18 SMTP Configuration
You use the SMTP form to configure the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol client (SMTP) for
sending e-mails.
Item Description
SMTP Server Address IP or domain address of the mail server.
SMTP Port Port the SMTP server is listening on.
Secure Method none, SSL/TLS, or STARTTLS. Secure method has to be sup-
ported by the SMTP server.
Username Name for the e-mail account.
Password Password for the e-mail account. The password can contain the
following special characters * + , - . / : = ? ! # % [ ] _ { } ~
The following special characters are not allowed: “ $ & ’ ( ) ; < >
Own E-mail Address Address of the sender.
Table 58: SMTP client configuration
The mobile service provider can bloc k other SMTP servers, then you can only use the SMTP
server of the service provider.
Figure 53: SMTP Client Configuration Example
You send e-mails from the Startup script. The Startup Script dialog is located in the Con-
figuration section of the main menu. The router also allows you to send e-mails using an SSH
connection. Use the email command with the following parameters:
-t e-mail address of the receiver
-s subject, enter the subject in quotation marks
-m message, enter the subject in quotation marks
-a attachment file
-r number of attempts to send e-mail (default setting: 2)
81
09-05-16
Page 89

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Commands and parameters can be entered only in lowercase.
Example of sending an e-mail:
email –t name@domain.com –s "subject" –m "message" –a c:\directory\abc.doc –r 5
The command above sends an e-mail address to name@domain.com with the subject
"subject", body message "message" and attachment "abc.doc" directly from the directory
c:\directory\. The router attempts to send the message five times.
82
09-05-16
Page 90

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
3.19 SMS Configuration
The SMS Configuration page is not available for the XR5i v2 routers.
Open the SMS Configuration page, click SMS in the Configuration section of the main
menu. The router can automatically send SMS messages to a cell phone or SMS message
server when certain events occur. The form allows you to select which events generate an
SMS message.
Item Description
Send SMS on power up Activates/deactivates the sending of an SMS mes-
sage automatically on power up.
Send SMS on connect to mobile
network
Send SMS on disconnect to mobile network
Send SMS when datalimit
exceeded
Send SMS when binary input on
I/O port (BIN0) is active
Send SMS when binary input on
expansion port (BIN1 – BIN4) is
active
Add timestamp to SMS Activates/deactivates the adding a time stamp to the
Phone Number 1 Specifies the phone number to which the router sends
Phone Number 2 Specifies the phone number to which the router sends
Phone Number 3 Specifies the phone number to which the router sends
Unit ID The name of the router. The router sends the name
BIN0 – SMS SMS text messages when activate the first binary in-
Activates/deactivates the sending of an SMS message automatically when the router is connected to
a mobile network.
Activates/deactivates the sending of an SMS message automatically when the router is disconnection
from a mobile network.
Activates/deactivates the sending of an SMS message automatically when the data limit exceeded.
Send an SMS message when the binary input on the
I/O port (BIN0) goes active. The text of the message
is set using parameter BIN0.
Automatic sending SMS message after binary input
on expansion port (BIN1 – BIN4) is active. Text of
message is intended parameter BIN1 – BIN4.
SMS messages. This time stamp has a fixed format
YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.
the generated SMS.
the generated SMS.
the generated SMS.
in the SMS.
put on the router.
Continued on next page
83
Page 91

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
Item Description
BIN1 – SMS SMS text messages when activate the binary input on
the expansion port.
BIN2 – SMS SMS text messages when activate the binary input on
the router.
BIN3 – SMS SMS text messages when activate the binary input on
the router.
BIN4 – SMS SMS text messages when activate the binary input on
the router.
Table 59: SMS Configuration
After you enter a phone number in the Phone Number 1 field, the router allows you to
configure the control of the device using an SMS message. You can configure up to three
numbers for incoming SMS messages. To enable the function, mark the Enable remote control
via SMS check box. The default setting of the remote control function is active.
Item Description
Phone Number 1 Specifies the first phone number allowed to access the router us-
ing an SMS.
Phone Number 2 Specifies the second phone number allowed to access the router
using an SMS.
Phone Number 3 Specifies the third phone number allowed to access the router
using an SMS.
Table 60: Control via SMS
• If you leave the phone number field blank, then you can restart the router using an
SMS Reboot message from any phone number.
• If you enter one or more phone numbers, then you can control the router using SMS
messages sent only from the specified phone numbers.
• If you enter the wild card character ∗, then you can control the router using SMS
messages sent from any phone number.
84
Page 92

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Control SMS messages do not change the router configuration. For example, if the router is
changed to the off line mode using an SMS message, then the router remains in this mode.To
return the router to the on-line mode, reboot or power cycle the device. The behavior is the
same for every SMS control message.
To control the router using an SMS, send only message text containing the control command. You can send control SMS messages in the following form:
SMS Description
go online sim 1 The router changes to SIM1 (APN1)
go online sim 2 The router changes to SIM2 (APN2)
go online Changes the router to the online mode
go offline Changes the router to the off line mode
set out0=0 Sets the binary output to 0
set out0=1 Sets the binary output to 1
set out1=0 Sets the binary output of XC-CNT to 0
set out1=1 Sets the binary output of XC-CNT to 1
set profile std Sets the standard profile
set profile alt1 Sets the alternative profile 1
set profile alt2 Sets the alternative profile 2
set profile alt3 Sets the alternative profile 3
reboot The router reboots
get ip The router responds with the IP address of the SIM card
Table 61: Control SMS
Choosing Enable AT-SMS protocol on expansion port 1 and Baudrate makes it possible to
send/receive an SMS on the serial Port 1.
Item Description
Baudrate Communication speed on the expansion port 1
Table 62: Send SMS on the serial Port 1
Choosing Enable AT-SMS protocol on expansion port 2 and Baudrate makes it possible to
send/receive an SMS on the serial Port 2.
Item Description
Baudrate Communication speed on the expansion port 2
Table 63: Send SMS on the serial Port 2
85
Page 93

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Setting the parameters in the Enable AT-SMS protocol over TCP frame, you can enable
the router to send and receive SMS messages on a TCP port. This function requires you to
specify a TCP port number. The router sends SMS messages using a standard AT command.
Item Description
TCP Port TCP port on which will be allowed to send/receive SMS messages.
Table 64: Send SMS on ethernet PORT1 configuration
3.19.1 Sending SMS
If you establish a connection to the router using a serial interface or Ethernet, then you can
use AT commands to manage SMS messages. The following table lists only the commands
that the router supports. For other AT commands the router sends an OK response. The
router sends an ERROR response for complex AT commands.
AT Command Description
AT+CGMI Returns the specific identity of the manufacturer.
AT+CGMM Returns the specific model identity of the manufacturer.
AT+CGMR Returns the specific model revision identity of the manufacturer.
AT+CGPADDR Displays the IP address of the usb0 interface.
AT+CGSN Returns the product serial number.
AT+CIMI Returns the International Mobile Subscriber Identity number (IMSI).
AT+CMGD Deletes a message from the location.
AT+CMGF Sets the presentation format for short messages.
AT+CMGL Lists messages of a certain status from a message storage area.
AT+CMGR Reads a message from a message storage area.
AT+CMGS Sends a short message from the device to entered tel. number.
AT+CMGW Writes a short message to the SIM storage.
AT+CMSS Sends a shor t message from the SIM storage location.
AT+COPS? Identifies the mobile networks available
AT+CPIN Used to query and enter a PIN code.
AT+CPMS Selects the SMS memory storage types, to be used for short message
operations.
AT+CREG Displays network registration status.
AT+CSCA Sets the short message service center (SMSC) number
AT+CSCS Selects the character set.
Continued on next page
86
Page 94

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Continued from previous page
AT Command Description
AT+CSQ Returns the signal strength of the registered network.
AT+GMI Returns the specific identity of the manufacturer.
AT+GMM Returns the specific model identity of the manufacturer.
AT+GMR Returns the specific model revision identity of the manufacturer.
AT+GSN Returns the product serial number.
ATE Determines whether or not the device echoes characters.
ATI Transmits the manufacturer specific information about the device.
Table 65: List of AT Commands
A detailed description and examples of these AT commands can be found in the application
note AT commands [9].
87
09-05-16
Page 95

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
Example 1: SMS sending configuration.
After powering up the router, the phone with the number entered in the dialog receives an SMS
in the following form:
Router (Unit ID) has been powered up. Signal strength –xx dBm.
After connecting to mobile network, the phone with the number entered in the dialog receives
an SMS in the following form:
Router (Unit ID) has established connection to mobile network. IP address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
After disconnecting from the mobile network, the phone with the number entered in the dialog
receives an SMS in the following form:
Router (Unit ID) has lost connection to mobile network. IP address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Figure 54: Example 1 – SMS Configuration
88
09-05-16
Page 96

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Example 2: Configuration for sending SMS via serial interface on the Port 1.
Figure 55: Example 2 – SMS Configuration
89
Page 97

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Example 3: Control the router using an SMS from any phone number.
Figure 56: Example 3 – SMS Configuration
90
Page 98

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
Example 4: Control the router using an SMS from two phone numbers.
Figure 57: Example 4 – SMS Configuration
91
Page 99

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
3. CONFIGURATION
3.20 Expansion Port Configuration
Configuration of the expansion port can be done via Expansion Port 1 or Expansion Port 2
items in the menu.
In the upper part of the configuration window, the port can be enabled and the type of the
connected port is shown in the Port Type item. Other items are described in the table below:
Item Description
Baudrate Applied communication speed.
Data Bits Number of data bits.
Parity Control parity bit:
• none – data will be sent without parity.
• even – data will be sent with even parity.
• odd – data will be sent with odd parity.
Stop Bits Number of stop bits.
Split Timeout Time to rupture reports. If the gap between two characters exceeds
the parameter in milliseconds, any buffered characters will be sent
over the Ethernet port.
Protocol Protocol:
• TCP – communication using a linked protocol TCP.
• UDP – communication using a unlinked protocol UDP.
Mode Mode of connection:
• TCP server – The router will listen for incoming TCP connection
requests.
• TCP client – The router will connect to a TCP ser ver on the
specified IP address and TCP port.
Server Address When set to TCP client above, it is necessary to enter the Server ad-
dress and TCP port.
TCP Port TCP/UDP port used for communications. The router uses the value for
both the server and client modes.
Inactivity Timeout Time period after which the TCP/UDP connection is interrupted in case
of inactivity.
Table 66: Expansion Port Configuration 1
92
09-05-16
Page 100

LUCOM GmbH * Ansbacher Str. 2a * 90513 Zirndorf * Tel. 09127/59 460-10 * Fax. 09127/59 460-20 * www.lucom.de
www.lucom.de info@lucom.de
09-05-16
3. CONFIGURATION
If you mark the Reject new connections check box, then the router rejects any other con-
nection attempt. This means that the router no longer supports multiple connections.
If you mark the Check TCP connection check box, the router verifies the TCP connection.
Item Description
Keepalive Time Time after which the router verifies the connection.
Keepalive Interval Length of time that the router waits on an answer.
Keepalive Probes Number of tests that the router performs.
Table 67: Expansion Port Configuration 2
When you mark the Use CD as indicator of the TCP connection check box, the router uses
the carrier detection (CD) signal to verify the status of the TCP connection. The CD signal
verifies that another device is connected to the other side of the cable.
CD Description
Active TCP connection is enabled
Nonactive TCP connection is disabled
Table 68: CD Signal Description
When you mark the Use DTR as control of TCP connection check box, the router uses the
data terminal ready (DTR) single to control the TCP connection. The remote device sends a
DTR single to the router indicating that the remote device is ready for communications.
DTR Description server Description client
Active The router allows the establishment of
TCP connections.
Nonactive The router denies the establishment of
TCP connections.
Table 69: DTR Signal Description
Since firmware 3.0.9, all v2 routers provide a program called getty which allows user to connect
to the router via the serial line (router must be fitted with an expansion port RS232!). Getty
displays the prompt and after entering the username passes it on login program, which asks
for a password, verifies it and runs the shell. After logging in, it is possible to manage the
system as well as a user is connected via telnet.
93
The router initiates a TCP connection.
The router terminates the TCP connection.
 Loading...
Loading...