Page 1

P4SAD
(SiS 645 Chipset, S-478)
With DDR 266/ 333 Memory
For Pentium® 4 400MHz FSB PC System
Main Board
User’s Manual
(Ver.:1.0)
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright©2001 by this company. No part of this document may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrievable system,
or translated into any natural or computer language, in any form or
by any means without prior written permission. This manual and the
information contained here are protected by copyright. All rights
reserved.
Copyright 2001. All Rights Reserved.
Revision History
Revision Date Release Notes
1.0 Dec.-2001 First Official Release
Page 3

Warning and disclaimer
This manual is designed to provide information about the Pentium®4
main-board. Effort have been made to make this manual as accurate
as possible, but no warranty or fitness is implied. All the information
is provided on an 'as is' basis. The author and his corresponding
publishing company shall have neither liability nor responsibility to
any person or entity with respect to any loss or damages arising
from the information contained in this manual or from the use of the
system board that accompanies it.
Information contained in this manual is subject to change without
notice. The manufacturer of the system board will not be held
responsible for technical or editorial omissions made herein, nor for
the incidental or consequential damages resulting from its
furnishing, performance, functionality or use. Subsequent changes to
this manual will be incorporated into the next edition. We welcome
any suggestion regarding this manual or our computer products.
Trademarks
● Intel® and Pentium® are registered trademarks of Intel® Corporation.
● IBM
®
is a registered trademark of International Business Machines
Corporation.
● Microsoft
®
is a registered trademark of Microsoft® Corporation.
● PCI
®
is a registered trademark of PCI® Special Interest Groups.
● AWARD
®
is a registered trademark of Award Software Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Page 4
1
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction…………………………………………1
1-1 Main Specifications……………………………………………………2
1-2 System Configuration……………………………………………..……4
1-3 Notice of Hardware Installation………….……………………....……5
Chapter 2 Installation……………….……………………….…6
2-1 Component Locations …………………..…………………………..…6
2-2 Layout Reference……………………………………………..………..7
2-3 CPU Installation………………. ……………………………………8
2-3-1 S1: CPU Frequency Selector…………………………………………11
2-3-2 CPU and System Cooling………………………….…………………12
2-4 Connectors………..……………………………………………………13
2-4-1 Front Panel…………………………………………………….………13
2-4-2 Back Panel Connectors………………………………………………15
2-4-3 Power Supply Connector……………………………………………17
2-4-4 Floppy Disk Connector………………………………………………18
2-4-5 IDE1 and IDE2………………………………………………………19
2-4-6 Internal Audio Connecotrs……………………………………………20
2-4-7 IR1: IrDA Connector…………………………………………………21
2-4-8 WOL1:WakeUp On LAN (Optional)………………………………22
2-5 Memory…………………………………………………………………2
3
2-5-1 Memory Installation…………………………………………………24
Chapter 3 Software Installation………………………………25
3-1 Notice of Driver Installation…………………………………………25
3-2 How to Install Software Drivers…………………………………….26
Page 5
2
Chapter 4 The BIOS…..………………………………………28
4-1 Updating the BIOS……………………………………………………29
4-2 The CMOS Memory…………………………………………………30
4-3 The BIOS Setup Pages………………………………………………32
4-3-1 Standard CMOS Setup………………………………………………35
4-3-2 BIOS Features Setup…………………………………………………39
4-3-3 Chipset Features Setup………………………………………..……43
4-3-4 Integrated Peripherals………………………………………..……...46
4-3-5 Power Management Setup………………………………………….51
4-3-6 PNP/PCI Configuration Setup……………………………………….54
4-3-7 PC Health Status……………………………………………………56
4-3-8 Frequency/Voltage Control.…………………………………………57
4-3-9 Passwords Setting……………………………………………………..59
Chapter 5 Appendix………………………………….………61
5-1 Memory Map………………………………………………….………61
5-2 I/O Map………………………………...….………………………….62
5-3 Time & DMA Channels Map…………………………………………63
5-4 Interrupt Map………………………………………….……………...64
5-5 RTC & CMOS RAM Map………………………………………….65
5-6 ISA I/O Address Map……………………………………………..66
Chapter 6 Q & A…………………………………………………………………68
Important Warnings:
STOP
WARNING: NEVER run the processor without the heatsink properly and firmly
attached. This will damage the processor within SECONDS. Also do NOT try to use
Pentium Heatsinks, these will NOT fit and do NOT provide adequate cooling.
STOP
WARNING: Make sure your power supply can deliver the power your system needs.
We recommend AT LEAST a 250W power supply. Even better, get a 300W power
supply, especially when using many peripherals.
Page 6
1
Chapter 1 Introduction
Thank you for purchasing this high quality motherboard, we are confident that you will be
able to use this motherboard to your full satisfaction. This manual is divided into 6 main
sections, as described below:
.
Introduction
The introduction contains information on the main specifications for this motherboard, the
package contents and cautionary notes.
Hardware Installation
The Hardware Installation section is the most important in the manual. It describes in detail
how to set the motherboard up for operation. Read all information and follow all steps,
especially if you are a new user.
Software Installation
The software section describes the drivers that need be installed to make your OS operates
properly. The drivers are provided on the driver CD.
BIOS Setup
Information on how to enter the BIOS setup and change settings is given here. In addition
all individual BIOS items are described. Although some BIOS setting information is given
in the hardware installation section where appropriate, refer to the BIOS Setup Section for
details.
Appendix
Provides useful information
Q & A
Page 7
2
1-1 Main Specifications
PCB board size and form factor: 24.5cm x 30.5cm, ATX type.
PCB layer: 4 layers
Supported CPUs
Can support the latest 400MHz system bus Socket-478 Intel P4 CPUs up to 2.2GHz or
higher speed.
Chipset Northbridge
The SiS
®
645 Host & Memory & AGP controller integrates a high performance host
interface for Intel Pentium 4 processor, a high performance memory controller, an AGP
interface, and SiS MuTIOL Technology connecting with SiS 961 MuTIOL Media IO. It
dispatches transactions to Memory, I/O interface and AGP bus.
Chipset Southbridge
The SiS 961 supports PCI Rev2.2 specification at 33MHz. The integrated IDE controllers
feature Dual Independent IDE channels supporting PIO mode 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and Ultra DMA
33/ 66/ 100MHz; AC97 audio codec (using the on-board ALC201A audio codec); USB
controller with root hub and four function ports.
Memory
This motherboard comes equipped with three Double Data Rate (DDR) Memory Module
sockets to support DDR 200MHz/ 266MHz/ 333MHz-compliant (128, 256MB, or 512MB)
DDR Modules up to 3GB.
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
This motherboard comes with an AGP slot with support for AGP cards for high
performance. The AGP 66MHz 4X mode is supported as well, further increasing system
performance.
PCI Expansion Slots
With six 32-bit PCI (Rev. 2.2) expansion slots, which can support Bus Master PCI cards,
such as LAN or Video-grabber cards (PCI supports up to 133MB/s maximum throughput),
this motherboard is ready for the most demanding applications.
Page 8

3
CNR Slot
A Communication Networking Riser (C.N.R.) slot can be fitted with CNR MODEM, or
MODEM/ LAN 10/100M card.
USB interface
With support for up to 4 USB ver 1.1 ports, two on-board, this motherboard provides ample
USB expansion room.
IDE interface
This motherboard comes with an onboard PCI Bus Master IDE controller with two
connectors that support four ATA66/ 33 devices on two channels. Supports UDMA/66,
UDMA/33, PIO Modes 3 & 4 and Bus Master IDE DMA Mode 2, and Enhanced IDE
devices, such as CD-R/ RW, DVD-ROM, CD-ROM, Tape Backup and LS-120 drives. An
IDE-3/4 RAID function is optional.
Super Multi-I/O
This functionality is integrated into the southbridge of the chipset. It provides two highspeed UART compatible serial ports and one parallel port with EPP and ECP capabilities.
Infrared (IrDA) Connector
This functionality is also integrated into the southbridge of the chipset. The IrDA connector
supports an optional IR remote control device for wireless interfacing with external
peripherals, personal gadgets, or an optional remote controller.
System BIOS
This motherboard comes with a 2MB BIOS that provides CPU/ SDRAM frequency, boot
block write protection, and HD/ SCSI/ CD/ Floppy boot selection. DMI is also supported
through BIOS, which allows hardware to communicate within a standard protocol creating
a higher level of compatibility.
Special Function
A. Over 300W P4 type power supply is needed, meanwhile over 250W PIII type
power supply is acceptable but not guaranteed for proper function.
B. AC-97 Sound Codec chip provides “ amplifier“ function.
Page 9
4
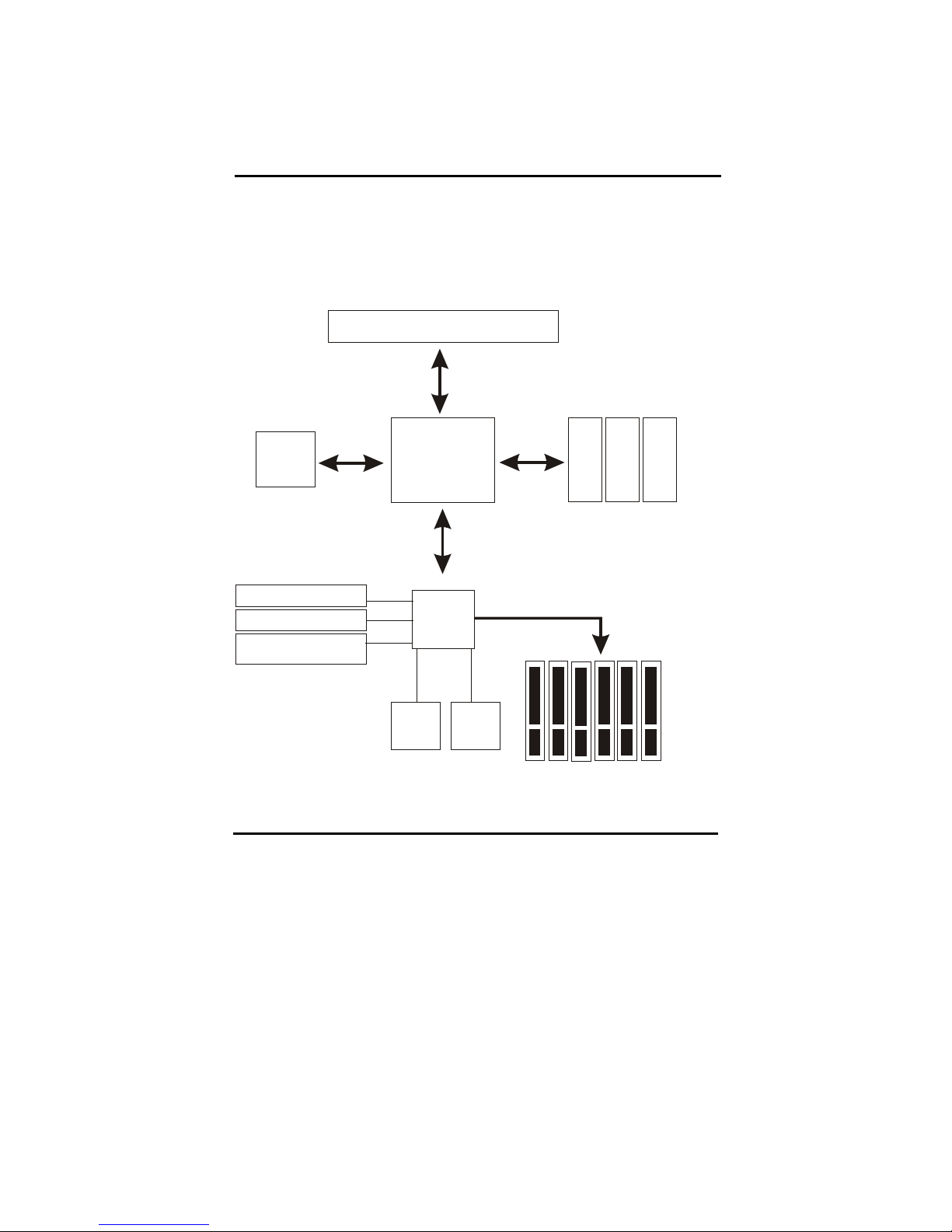
1-2 System Configurations
Below is the SiS 645 chipset based system configuration:
SiS
645
Intel Pentium 4 processor
System Bus
3. 2G B/ s
2.1GB/sec or
2.7GB/sec
8-Bit Hub
Inter face
26MB/s
AGP4X (1.5V)
1.06GB/s
D
D
R
2
6
6
/
3
3
3
SiS
961
A GP
Graphics
AC-97 Modem CODEC
(o ption al)
2 ATA100 IDE Channels
4 USB 1.1 P orts
PCI Bus
SIO
Flash
BIOS
D
D
R
2
6
6
/
3
3
3
D
D
R
2
6
6
/
3
3
3
Page 10

5
1-3 Notice of Hardware Installation
Before hardware installation, make sure you have checked the following things.
A. Check the package
If any of these items is missing or damaged, contact the dealer from whom you purchase.
Leave this main board in its original package until you are ready to install it. In the
package, there are:
➨
This motherboard
➨
1 Manual
➨
1 Driver Installation CD-ROM
➨
1 IDE ATA 66/100 Flat-Cable
➨
1 Floppy Disk Drive Flat-Cable
B. Make sure power is off.
During hardware installation, be sure that there is no power connected during this period.
C. Avoid ESD (Electrical Static Discharge.)
While installing the main board, wear a grounded wristband or ankle strap to avoid ESD
(Electrical Static Discharge).
Page 11

6
Chapter 2 Installation
This mainboard is very user-friendly during installation. The CPU speed is
auto-detection, the default DDR memory speed is DDR-266 set on S1. User just
needs to check memory speed & set S1 to complete installation. Over-clocking &
Over-Voltage are not suggestted by vendor.
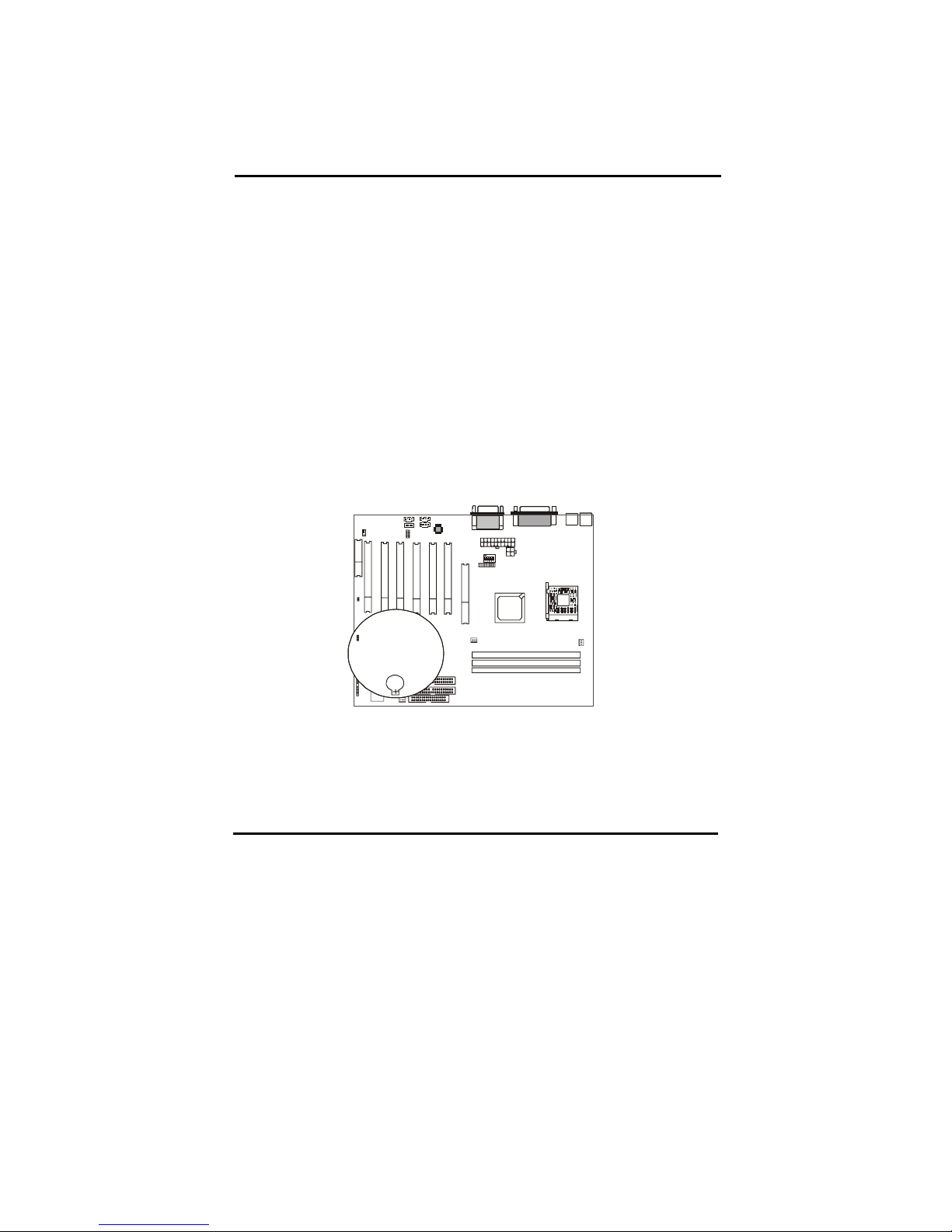
2-1 Component Locations
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 ATX Power Supply
2 AUX _1 Power S upply
3 SiS 645 Chipset
4 CPU S ocket- 478
5 FAN1
6 DIMM
7 FAN2
8 IDE & F DD
9 SiS 961
10 FAN3
11 Bat tery
12 BIOS
13 CNR Slot
14 WOL1
15 PCI slot
16 CD_IN
17 VIDEO_IN
18 Sound Codec
19 AGP slot
20 GAME PORT
LI NE-IN
LINE -OUT
MI C-IN
21 LPT, COM
22 USB
23 PS/2 Mouse
& K/ B
Page 12

7
2-2 Layout Reference
FAN 3
FAN 2
FAN 1
PS/2 Mouse
& K/B
USB
Socket-478
COM1
COM2
LINE-OUT
LINE-IN
MIC-IN
Sound Codec
CNR1
USB2
WOL1
F
D
C
1
I
D
E
1
I
D
E
2
JP 4
JP 1
PW_BN
PW_LED
EXTSMI
HD_LED
RESET
SPEAKER
AUX_1
BIOS
IR 1
S1
AUX_IN
VIDEO IN
CD_IN
J4
Page 13

8
2-3 CPU Installation
The first step in the installation of your CPU is the insertion of the CPU into the 478 pins
CPU socket. Please follow the steps as outlined below carefully to avoid damage to the
CPU.
Avoid Static Electricity
The Intel P4 processors and your motherboard contain sensitive electronic components that
can be easily damaged by static electricity. We recommend that you leave the processor in
its original packaging until you are ready to install it. You should only touch the edges of
the processor, NEVER touch the processor pins to avoid static discharge.
First take a moment to inspect your CPU for obvious damage due to shipping or handling.
Be sure that no noticeable damage exists before proceeding. You should have the following
items:
1 Intel P4 processor.
1 good heatsink and fan assembly.
Step 1
The following figure shows the processor socket. Note that the release lever on the right
side of the socket is down and latched. This position is used to lock the processor in place.
The lever must be raised to install the processor. To do this, first push the lever sideways to
unlatch it, then raise it all the way up (approximately 90 degrees).
Step 2
The processor pin array at the top two corners is angled and has no pins in the corners.
Notice that at the top of the socket on the motherboard (near where it says "Socket 478")
the corners also do not have positions for pins. The processor must be positioned so the
pins match up properly. When you do that, the corner of processor that is cut off will be
positioned next to the release pivot.
It should take no force to install the processor, this is a zero insertion force (ZIF) socket. If
it takes any force you are doing something wrong. Check the pin alignment and also make
sure the release lever is raised up completely.
Page 14

9
After placing the CPU lower the release lever to lock the processor in place.
Now with the processor properly installed, you can proceed to install the heatsink. It is
important to note that If you have never installed a heatsink on an Intel PIII or Celeron
processor before it may be difficult. We recommend you do a dry run a few times before
doing the final installation. To allow you to do this read the following instructions. Do not
remove the film on the thermally conductive compound until you are ready to do the final
installation.
STOP
WARNING: Never run the processor without the heatsink properly
and firmly attached.
Step3
The picture below shows the bottom of the heatsink. Notice the step in the heatsink surface,
this portion fits over the top of the socket, where the legend "Socket 478" is molded into
the plastic. The heatsink must be mounted with this step above the top of the socket or the
heatsink will not be touching the processor properly.
The next picture shows the removal of the plastic film from the thermally conductive
compound. The thermal compound is a thin layer of material that increases the efficiency
of the heatsink by filling microscopic surface voids in the processor or heatsink surface
with a thermally conductive material. Please do not remove the plastic film until you have
practiced installing the heatsink and mounting the clips on the socket. It can take a few tries
to get used to doing this.
Page 15

10
The following picture shows a side view of the heatsink with the retaining clip at the
bottom of the heatsink. Make sure this retaining clip is at the bottom of the heatsink before
trying to install it.
The following picture shows the non-moveable end of the heatsink retaining clip installed
on the lug at the bottom of the processor socket. This end of the clip simply slides over the
lug when you tilt the heatsink / fan assembly towards the lug.
Now lock the locking clip for the retaining strap over the lug at the other (pivot end) of the
processor socket. This is an easy procedure after you do it a few times, but initially it will
require you to use a finger on one hand to push the latch down and use your other hand to
push the latch in. This is the part you need to practice to install the clip properly. When you
are holding the heatsink, make sure you do apply pressure to the fan. You could damage it
and cause thermal failure of the processor.
STOP
WARNING: Be careful not to scrape the motherboard during the mounting
of the fan or else damage may occur to the motherboard.
Now connect the wire from the heatsink fan to the FAN1 connector on the motherboard.
This connector is keyed and can only be installed one way. If you use a heatsink assembly
that has three cooling fans, connect one to FAN1 and the other FAN2. For more
information on the FAN connectors, refer to the FAN connector section later in this
section.
Page 16
11
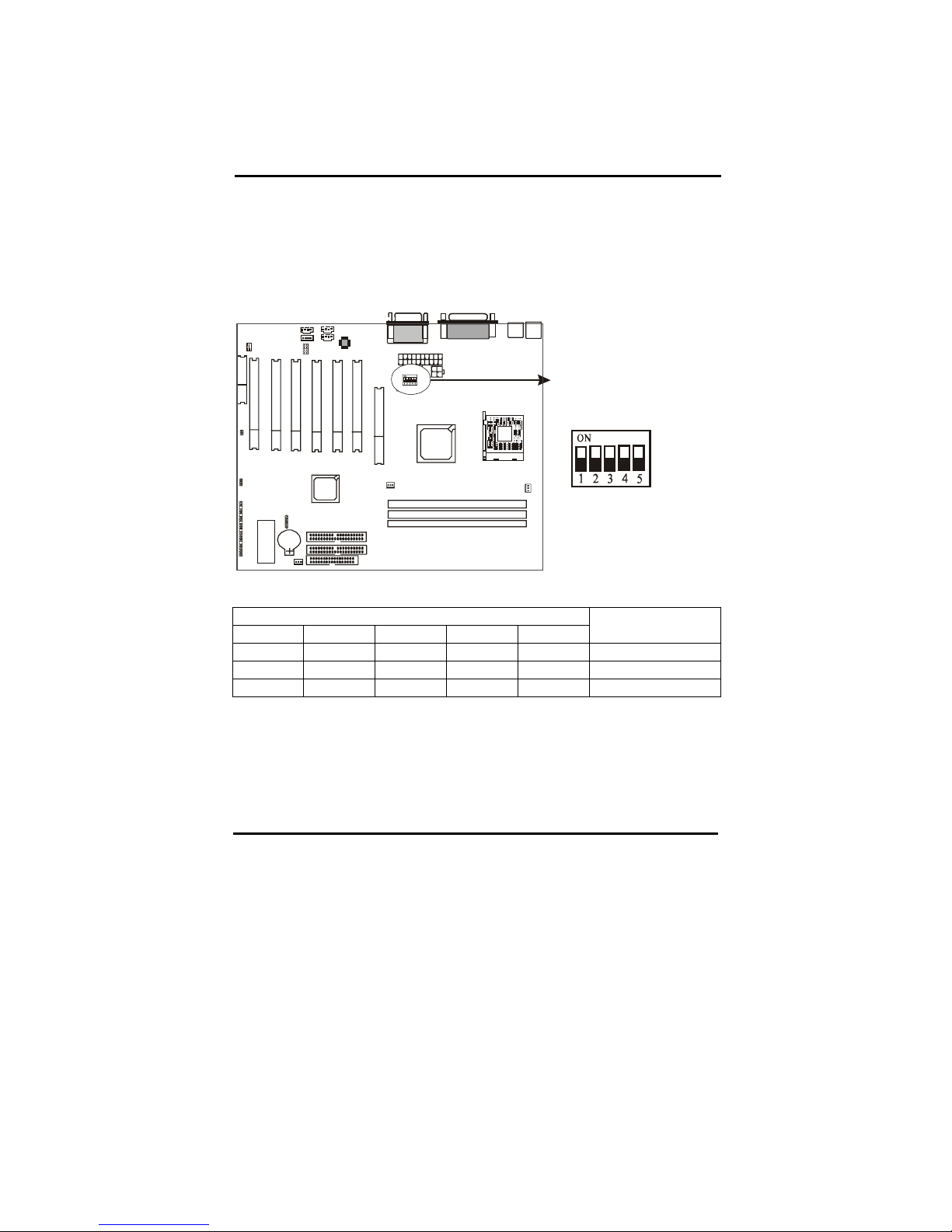
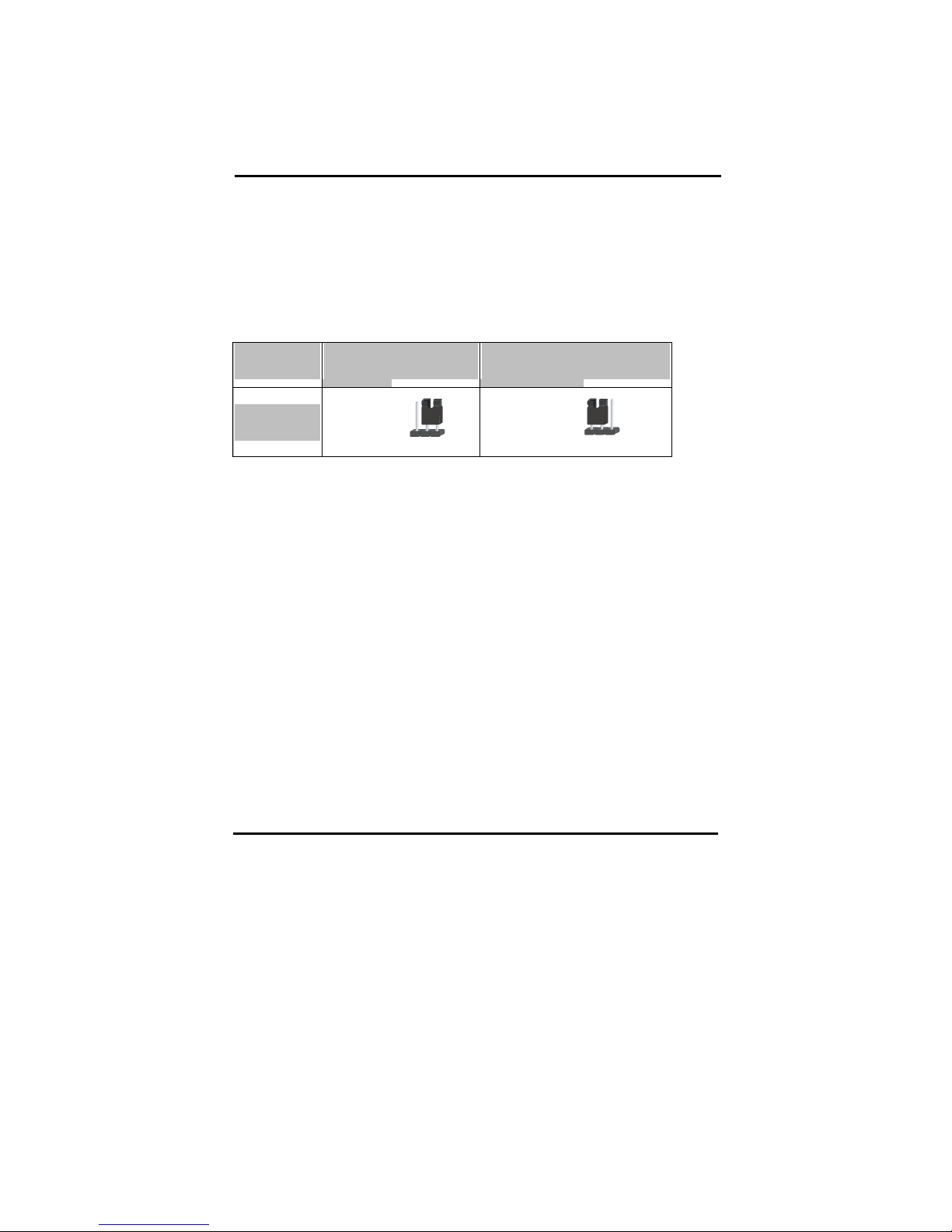
2-3-1 S1: Memory Type Selector
S1 is a 5-pin DIP switch which provides DDR type selection, Please select correct
DIP switch according to your memory type.
Memory Type Selector
S1
1 2 3 4 5
DDR CLK
OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF DDR200
OFF ON OFF OFF OFF DDR266(default)
OFF OFF ON OFF OFF DDR333
Page 17
12
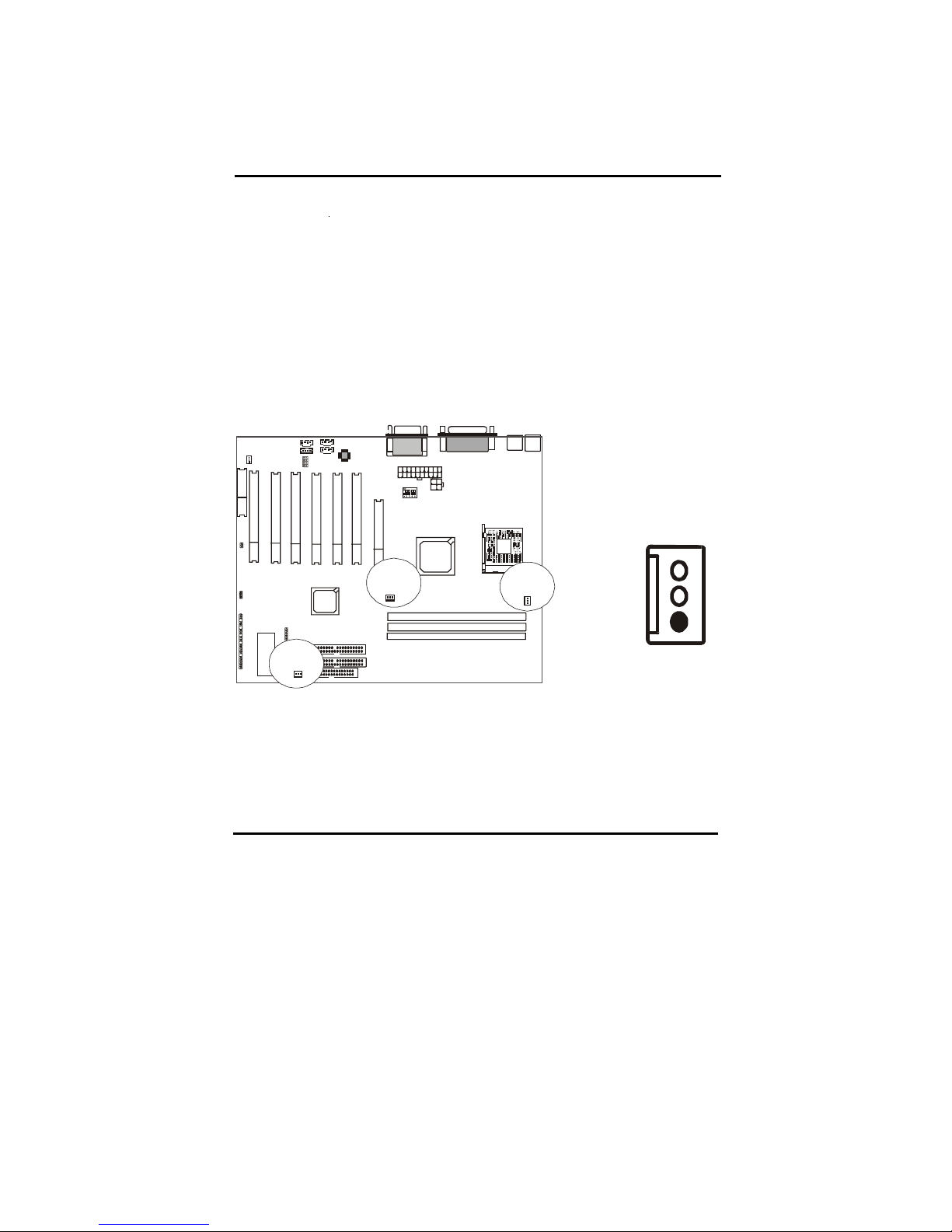
2-3-2 CPU and System Cooling
Any attempt to operate the Intel P4 Processor without a suitable cooling
solution will result in permanent damage to the processor and potentially other
components within the system.
FAN Headers
Your motherboard allows the use of in all 3 FANs. Of these 3 FANs, 1 can be
used by the CPU Heatsink assembly. The other 2 FAN Headers allow
connection of a Chassis Fan and a Power Supply FAN respectively. For a the
location of the FAN connectors, refer to the following picture:
Battery
Fan Signal
GND
+12V
SENSE
FAN 3
FAN 2
FAN 1
Page 18
13
2-4 Connectors
There are many connectors on this main board. Refer to the following pages for
details.
2-4-1 Front Panel
Front panel has connectors as “SPEAKER,” “RESET,” “HDD_LED,”
“SUSLED,” “PWR_LED,” “SOFT-PWR.” Please refer the details as below.
PW_LED
SPEAKER
RESET
HD_LED
PW_BN
EXTSMI
Page 19

14
SPEAKER is a 4-pin keyed Berg strip. This speaker connector is for the internal
case speaker. This speaker will enable the BIOS to give spoken messages in case
of boot up trouble. The BIOS been codes also use this speaker. For Games and
Music this speaker will not be used, but rather the back panel line-out connector.
RESET connector is a 2 -pin keyed Berg strip, connected to the push button reset
switch on the case front panel. Shorting both pin 1 & pin 2 can reset the system,
which is similar to the power off and then on again.
HDD-LED (Hard Disk activity LED connector) is a 2-pin keyed Berg strip. It is
used to connect to front panel Hard Disk LED. This LED will light up whenever
one of your IDE devices is being accessed.
PWR-LED is a 3-pin connector. It is used to connect to the LED on the case front
panel. The LED shows the status of the power.
SOFT_PWR with a 2-pin Berg strip on case front panel indicates the current
power status of system. It is used to connect to the Power Button on the front
panel of the case (if there is).
Page 20

15
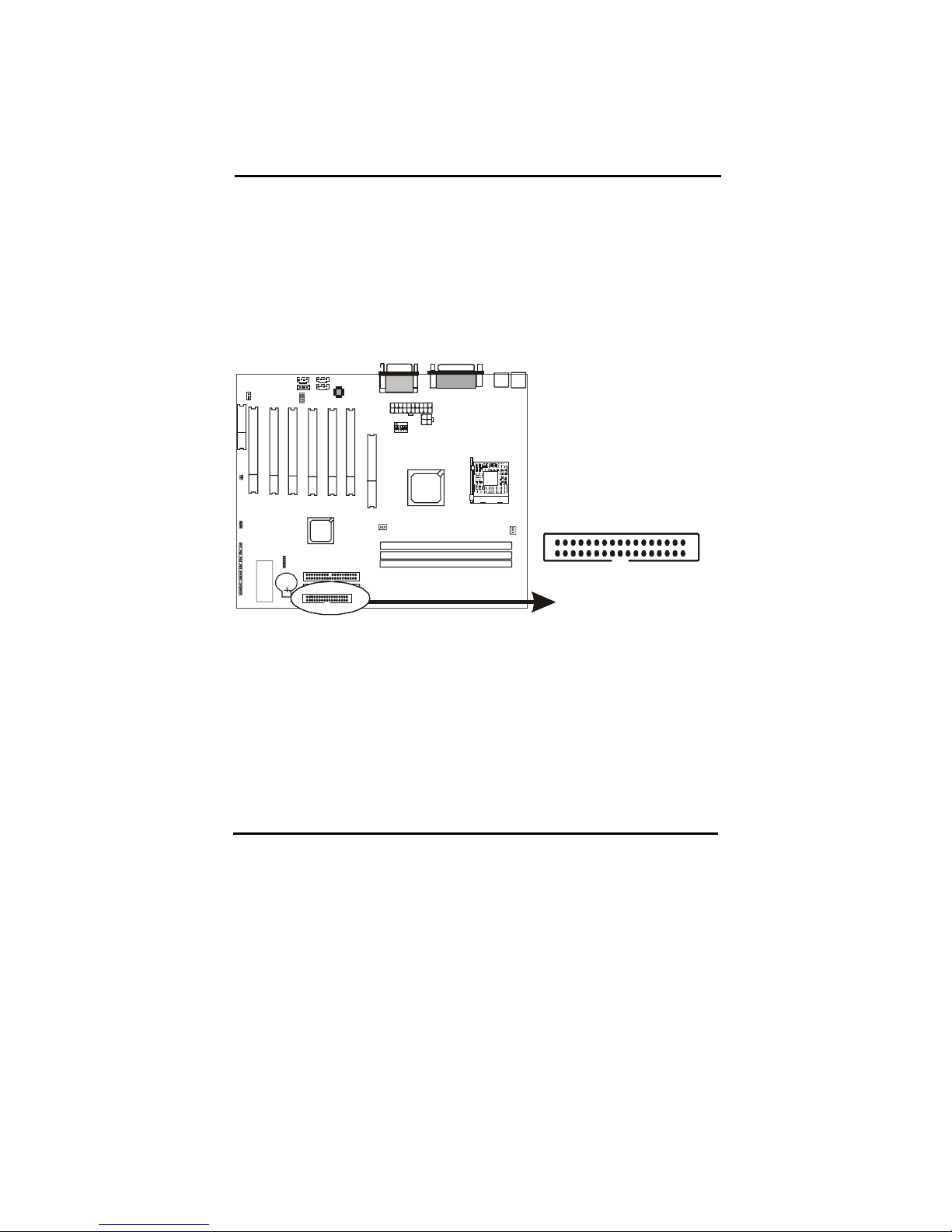
2-4-2 Back Panel Connectors
There are PS/2 keyboard/ mouse, USB, COM1/2, LPT1, MIC, LINE-IN,
LINE-OUT and GAME Ports on case back panel. Please refer to more details
as below.
Page 21
16
COM1/COM2
The onboard serial port 1 and port 2 are the 9-pin D-subminiature male
connector COM1 and COM2. COM1 and COM2 can be disabled in BIOS
setup. Please refer to Chapter 3 “Integrated Peripherals” for more information.
PS2 Keyboard/ Mouse
The Keyboard can be plugged in in only one way. Please do nor force the
connector in, it may get damaged by use of excessive force. It is easy to make
the mistake of reversing the PS/2 keyboard and mouse connectors. If your
keyboard does not work, check this first. The keyboard must be inserted into
the lower connector.
The Mouse can be plugged in in only one way, too. Please do not force the
connector in, it may get damaged by use of excessive force.
LPT
The onboard parallel port is a 25-pin female connector. It supports standard
printer port, Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP), Extended Capabilities Port (ECP),
Standard Parallel Port (SPP).
USB:USB (Universal Serial Bus) Connector
Universal Serial Bus connector, marked as “USB,”is used to connect USB
devices. There are 2 USB connectors on this main board.
Midi/Game Port & External Audio Connectors
Midi/Game port has 15 pins connecting to the game joystick. External Audio
connectors are ”LINE-OUT,LINE-IN, MIC-IN ” for audio functions.
Page 22

17
2-4-3 Power Supply Connector
This main board needs P4 power supply which contains ATX, AUX_1 power
connectors, ATX power supply connector has 20 pins, which is especially
designed for ATX case. AUX_1 power supply connector has 4 pins. The
ATX power supply supports the function of the “Soft Power On Momentary
switch” which connects the front panel switch to the 2-pin SOFT-PWR on the
system board. While the power switch on the back of ATX power is turned on,
the full power will not go into the system board until the front panel switch is
momentarily pressed. Push the switch again to turn off the power to the system
board.
Power Supply
AT X P OW ER
AUX_1
Page 23
18
2-4-4 Floppy Disk Connector
Floppy Disk Connector has 34 pins and allows connection of a floppy drive.
In all two floppy drives can be connected to the mother board, known as
floppy A and B. The BIOS allows you to disable the floppy controller if you
do not use any floppy driver, that will free an Interrupt. The BIOS also allows
swapping of floppy A and B although this will not be useful to most users.
FLOPPY DISK
FDD
Page 24

19
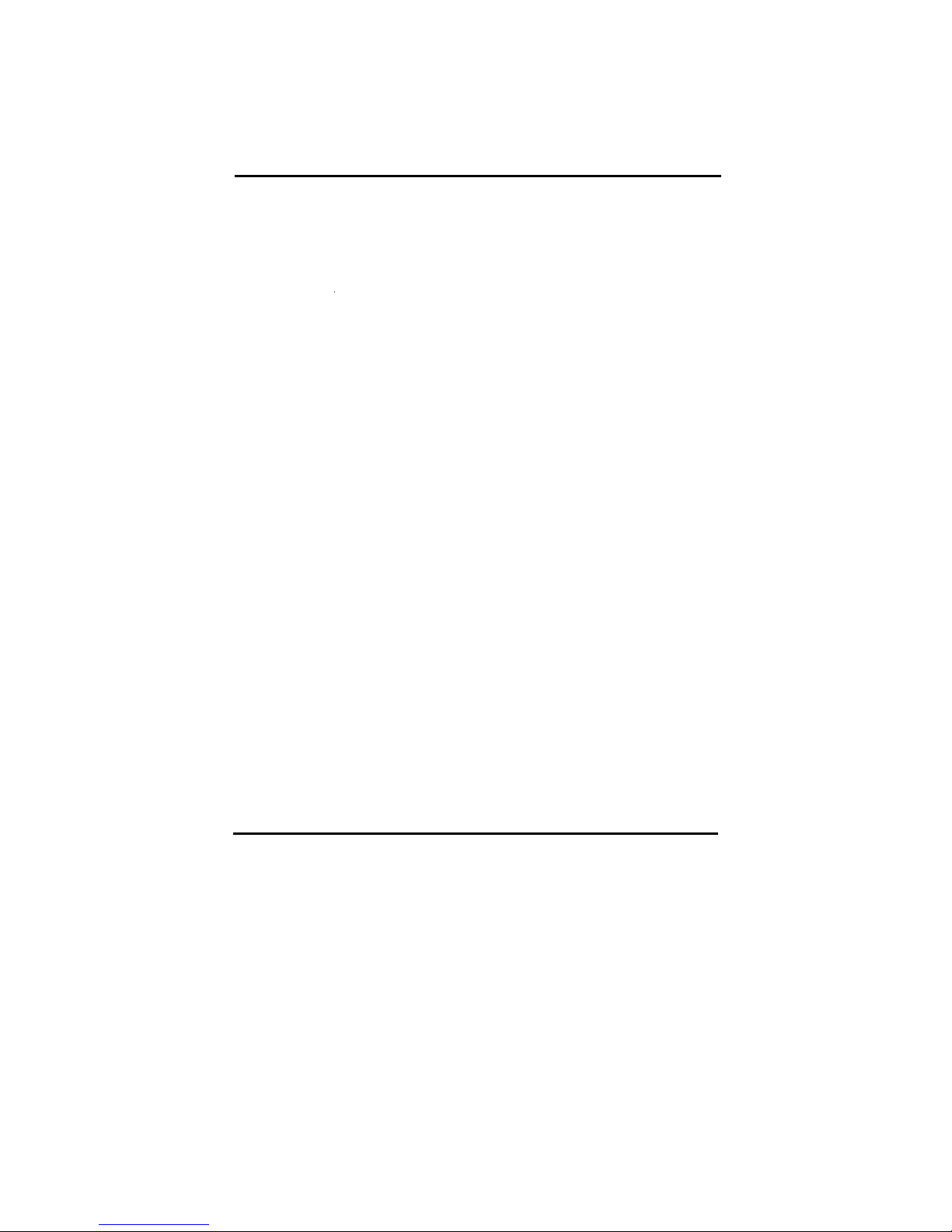
2-4-5 IDE1 and IDE2
The IDE connectors are used to connect IDE devices such as Harddisks and CDROM drives to the motherboard. Each connector constitutes an IDE channel, each
channel accepts 2 IDE devices, one Master and one Slave. The IDE 1 connector is
also known as the primary channel, IDE 2 is the secondary channel. Therefore the
primary Master is the IDE device connected to IDE1 as Master, the primary Slave
is the IDE device conneced to IDE 1 as Slave. Jumpers on the IDE device
determine Master and Slave settings. Your harddisk or CD-ROM should have a
sticker with jumper settings. Make sure that you set these jumpers correct. Please
use the following advice as reference:
If you have only device connected to an IDE connector, always set it as
Master.
If you have one HDD and CD-ROM in your system, then connect the HDD
to IDE1 as Master, and the CD-ROM to IDE 2 as Master
If you have one Harddisk and one CD-ROM connected to the same IDE
connector set the HDD to Master and the CD-RAM to Slave.
IDE2
IDE1
Page 25
20
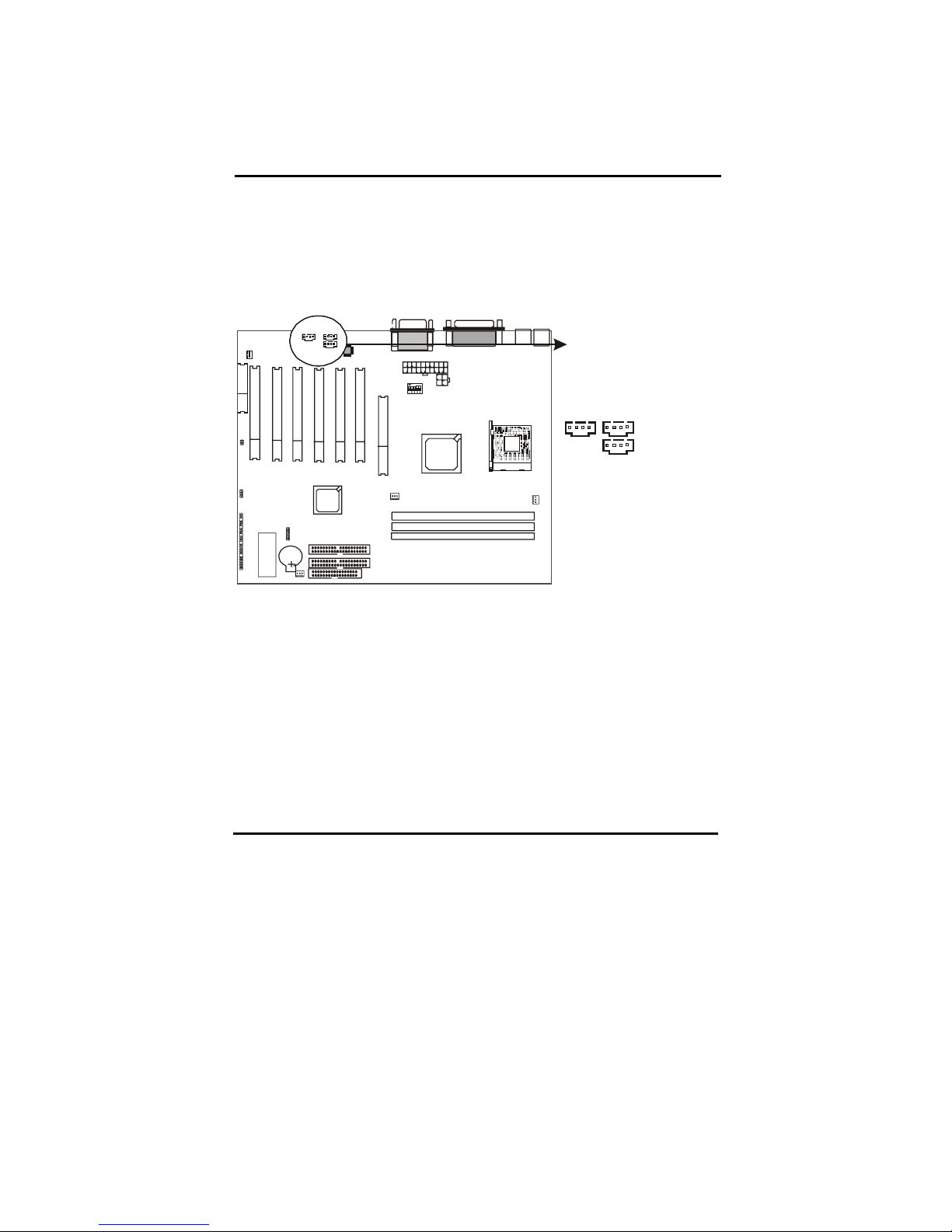
2-4-6 Internal Audio Connectors
Internal Audio Connectors are “CD_IN”,”AUX_IN”, “VIDEO_IN connectors”. It is a
CD ROM external audio input signal to line-out (speaker) of the main board.
CD_IN VIDEO_IN
AUX_IN
Page 26

21
2-4-7 IR1: IrDA Connector
IR connector supports wireless infrared module. With this module and application
software like Laplink, or Win95 Direct Cable Connection, user can transfer data to
or from laptops, notebooks, PDA and printers. This connector supports HPSIR,
ASKIR, and Fsat IR.
Attach Infrared module to IR connector. Be sure to put in the right direction
during installation.
Battery
Pin1
IR 1: IrDA
Connector
IR1
1 VCC
2 NONE
3 IRRX
4 GND
5 IRTX
Page 27

22
2-4-8 WOL1: Wake up on LAN (Optional)
Wake up on LAN marked as “WOL1,” is a 3-pin connector. To support this
feature, a network card is required for the system and network management
software must be installed, too.
WOL1 (Wake up on LAN) function requirement:
Power supply should be able to offer at least 1A current driving
ability to the signal “5V trickle voltage.”
Page 28

23
2-5 Memory
This motherboard supports only Dual Inline Memory Modules (DIMMs). Three
sockets are available for 2.5 Volt unbuttered DDR (Double Data Rate). The sizes
that are supported are: 128, 256, or 512MB memory sizes between 128MB to
512MB can be formed this way. Refer to the picture below for the position of the
DIMM slots:
DDR1
DDR2
DDR3
Page 29

24
2-6-1 Memory Installation
The DIMM modules can be inserted in DIMM slots 1 to 3. Because of the three
notches in the DIMM module it can be inserted in only one way. Please refer to
the picture below for information on how to insert the DIMM modules.
DDR
STOP
WARNING:
Make sure that you unplug your power supply when adding or removing
memory modules or other system components. Failure to do so may cause
severe damage to both your motherboard and expansion cards
Page 30

25
Chapter3 Software Install
3-1 Notice of CD Driver Installation
This CD contains below drivers. The user must read “Index” before installing
required drivers. Index offers all the information on all the drivers.
CD driver is always updated with the latest version, so the actual CD
content may be somewhat different from the above picture.
1. Main boards: 6va693a, 6va693am, 6va694, 6vapm, 6vmple1_2, 6vple1,
I810, I815e, I845, Intv, K7mkle, K7vat, Ktapro, Kx133, Net2100, P4sad,
P4smd, P4vas, Tv2100, Vap266a (please select P4SAD directory for this
main board)
2. DX8: Windows DirectX8 driver.
3. Flashrom: BIOS flash upgrade utility .
Page 31

26
3-2 How to Install Software Driver
User needs to complete above 3 Drivers below to complete installation. Read
drivers from your CD-ROM Driver firstly, and find P4SAD directory which tells
you the roots of Drivers.
Installation Procedure:
1. Setup 1: Install SiS AGP driver
(Path root:\ SISdrive\ agp, then select your OS and press setup.exe)
2. Setup2: Install VGA Driver
(Path root:\ SISdrive\ vga, then select your OS and press setup.exe)
Page 32

27
3. Setup3: Install Sound Driver
(Path root:\ SISdrive\ audio\ Setup.exe)
Page 33
28
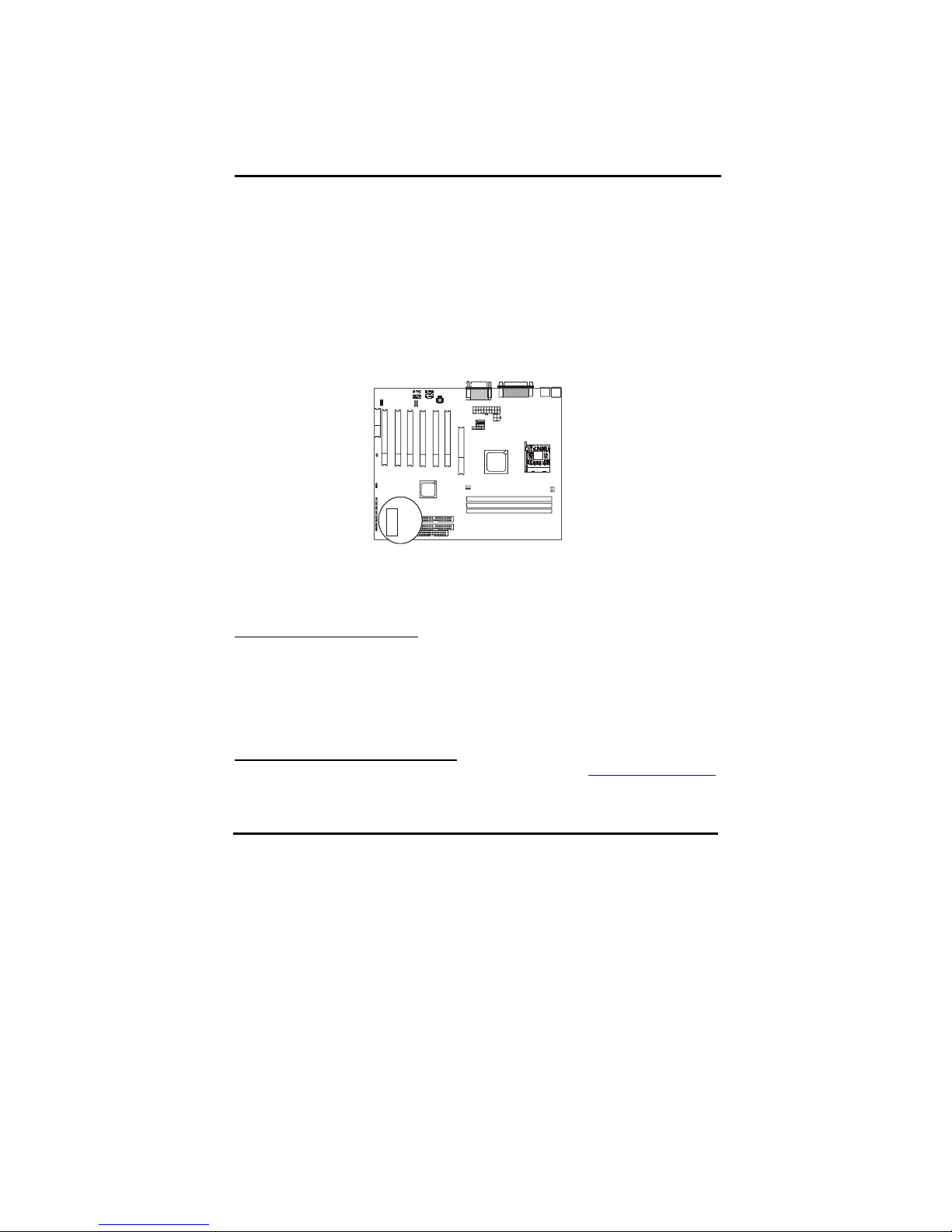
Chapter4 The BIOS
The BIOS is a piece of software (Basic Input Output System) that performs most low level
tasks. When you start up your system, the BIOS is the first code that gets to run. The BIOS
resides in a FLASH ROM, and the code in the FLASH ROM can be updated through a
special utility called AWDFLASH. (Award Flash). This is generally not necessary, but in
some cases updating the BIOS is necessary to support new devices that were not on the
market at the time the motherboard was released. For the physical location of the BIOS
FLASH ROM IC on your motherboard, refer to the picture below:
BIOS
The BIOS IC is inserted in an IC socket, which means that it can be removed and
exchanged for another IC if necessary.
Is updating my BIOS necessary?
As a general rule if your system is functioning properly and you are not an experienced
user, do not try to update the BIOS. Only if you have specific problems that a BIOS update
may solve may it be advisable to update the BIOS.
The update process is pretty complex, and you should bear in mind that if updating the
BIOS goes wrong you may render your system unbootable. Therefore, do not update unless
you know what you are doing.
Finding the latest official BIOS revision
For the latest official BIOS revision, please go to our website at www.lucky-star.com.tw
.
On the support page you can find the latest BIOS files for our motherboards.
Page 34
29
4-1 Updating the BIOS
As said, this procedure is complicated, only update your BIOS when you experience
problems with your system. Because each BIOS release completely overwrites the previous
version and there is no need to update to intermediate BIOS releases when updating the
BIOS. Therefore always use the latest BIOS revision when doing a BIOS update. The
BIOS update procedure is as follows:
In order to flash update the BIOS, you will need 2 files:
The BIOS binary file (.bin file from the website)
AWDFLASH.EXE utility file. (This utility can be downloaded from our website)
Create a directory on your C harddisk drive: and name it FLASH
Put the BIOS .bin file and the AWDFLASH utility in the FLASH directory.
You may want to jot the BIOS .bin file name down on a piece of paper.
Restart the computer, press DEL to go into the BIOS, then please disable the
following:
System BIOS Cacheable (in Advanced Chipset Features)
Video BIOS Shadow (in Advanced BIOS Features)
Save the changes by selecting ‘save and exit’, and restart the computer.
Press Ctrl + F5 just before Windows is starting up (right after the second BIOS
screen) for a DOS boot, you will see the message "Windows is bypassing all your
startup files". You end up at a DOS prompt.
Now type cd FLASH to change to the newly created directory.
Here type AWDFLASH mybios.bin /py /cc /sn /cd, where mybios.bin is the file name
for the BIOS binary file you want your BIOS to upgrade to. Now the upgrading will
begin.
STOP
WARNING:
Do NOT in any way disturb the system during upgrading. If for any reason
the system is stalled your system may not be able to boot again.
After the upgrading has ended press F1 to reset, press DEL to go into BIOS and make
the following changes:
Load Setup Defaults.
Go into the Frequency/Voltage Control page to adjust your CPU speed and voltage
(please make sure the CPU voltage matches your CPU specs, in case of doubts leave it
to ‘default’).
Save your settings and you are done.
Page 35
30
4-2 The CMOS memory
The BIOS uses the CMOS memory to store all the settings that have been made through the
BIOS Setup pages.
Battery
The CMOS memory remembers all settings, even when the system is switched off, by use
of a 3V Lithium battery. If this battery runs low CMOS is unable to keep its settings and
you will need to replace the battery. The BIOS will give you an error message when it
detects a low battery voltage. The error message ‘CMOS checksum error’ may also point to
a low battery problem.
Restoring default settings
You can load default values into the CMOS memory by selecting ‘Load Optimized
Defaults’ in the BIOS Setup. If you need to force the CMOS settings to default without
entering the BIOS Setup page you can use the JP6 jumper. For the location of the jumper
and the battery, refer to the following picture:
Battery
JP 4
Normally JP4 will be in the 2-3 position, this will connect the battery to the southbridge of
the chipset which contains the CMOS memory. If JP4 is temporarily set to 1-2 this will
interrupt the battery electricity flow, and the CMOS memory will be erased, this will
however only work if the power supply is not switched on. Now at the next reboot the
BIOS will automatically load the CMOS default values.
Page 36
31
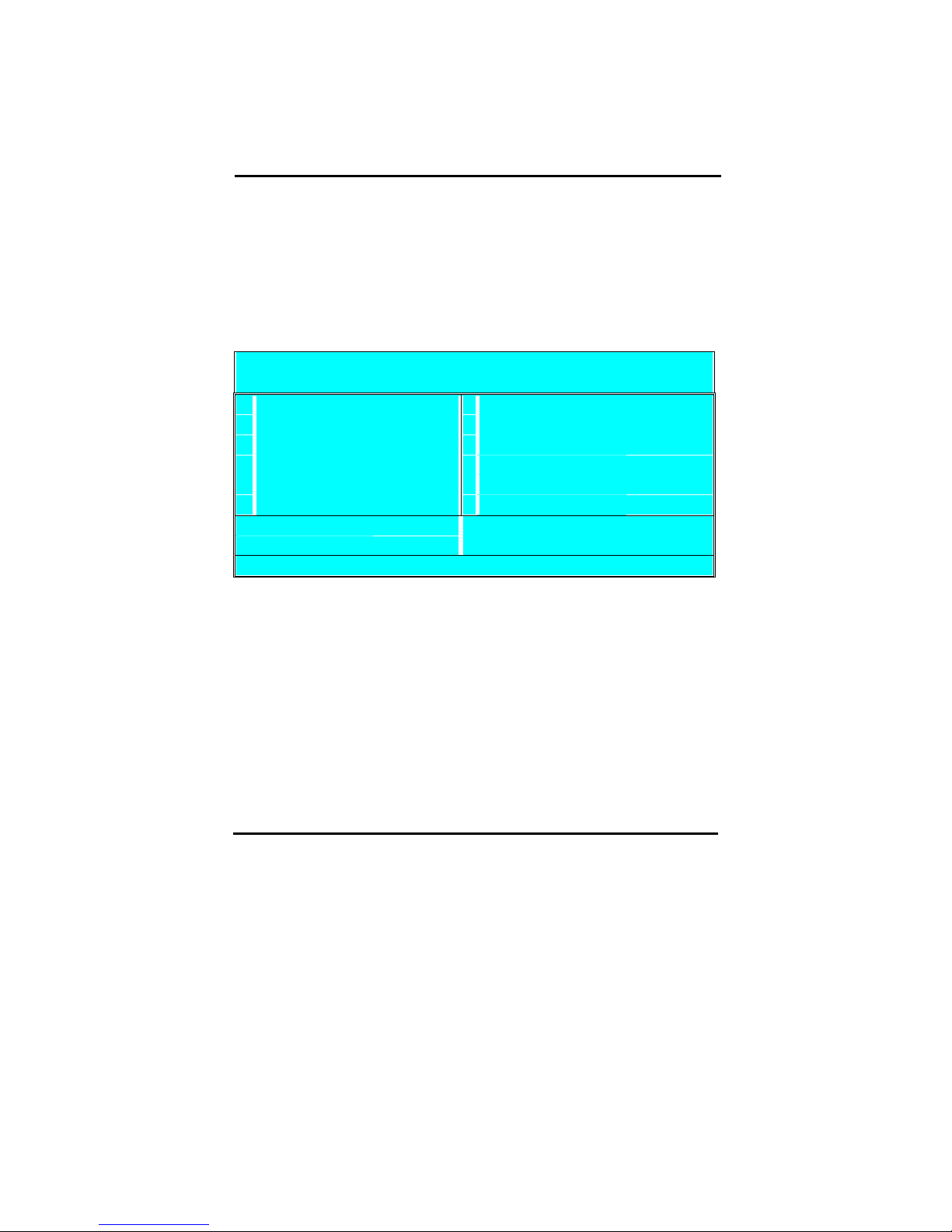
Take the following steps to clear CMOS memory:
Take the power cord from the power supply.
Temporarily set JP4 to 1–2, and set it back to 2-3.
Put the power cord back and restart the system, the default values will
be loaded.
CMOS Status
JP4 Retain CMOS settings Clear CMOS Settings
CMOS
12 3
12 3
The following part of this chapter will describe the individual BIOS Setup pages and all the
items that can be adjusted to fine tune your system.
Page 37
32
4-3 The BIOS Setup Pages
To enter the BIOS Setup pages, thke the following steps:
Start up the system.
After memory counting has finished, press [DEL] to enter the BIOS Setup
pages.
Now the following menu will appear:
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
"
Standard CMOS Features
"
PC Health Status
"
Advanced BIOS Features
"
Frequency/Voltage Control
"
Advanced Chipset Features
Load Optimized Defaults
"
Integrated Peripherals
Set Password
"
Power Management Setup
Save & Exit Setup
"
PnP/PCI Configurations
Exit Without Saving
Esc : Quit F9: Menu in BIOS
↑ ↓ → ← : Select Item
F10 : Save & Exit Setup
Time, Date, Hard Disk Type . . .
Selecting items
To Select items, use the following method:
Use the arrow keys to move between items and select fields.
Press [enter] to enter the selected submenu.
Submenus
All items that start with a " are submenus. Pressing [enter] when a submenu is
selected will enter that submenu.
Modifying selected items
The [Up]/[Down] keys can be used to modify values within the selected fields.
Note that some fields also let you enter values directly.
Page 38
33
Hot Keys
Throughout the BIOS Setup Pages the hot keys will give you access to a group of
commands. Refer to the following table for the hot keys and their function:
Key Command Description
F10
Save & Exit Setup Saves the changes made and reboots the system.
[Esc]
Quit Returns to the previous menu
F1
Help General Help
F2
Help Help for specific item
F5
Previous values Restores the previous values. These are the values that the
user started the current session with.
F7
Optimized Defaults Loads all options with the Optimized Default values.
Save & Exit Setup
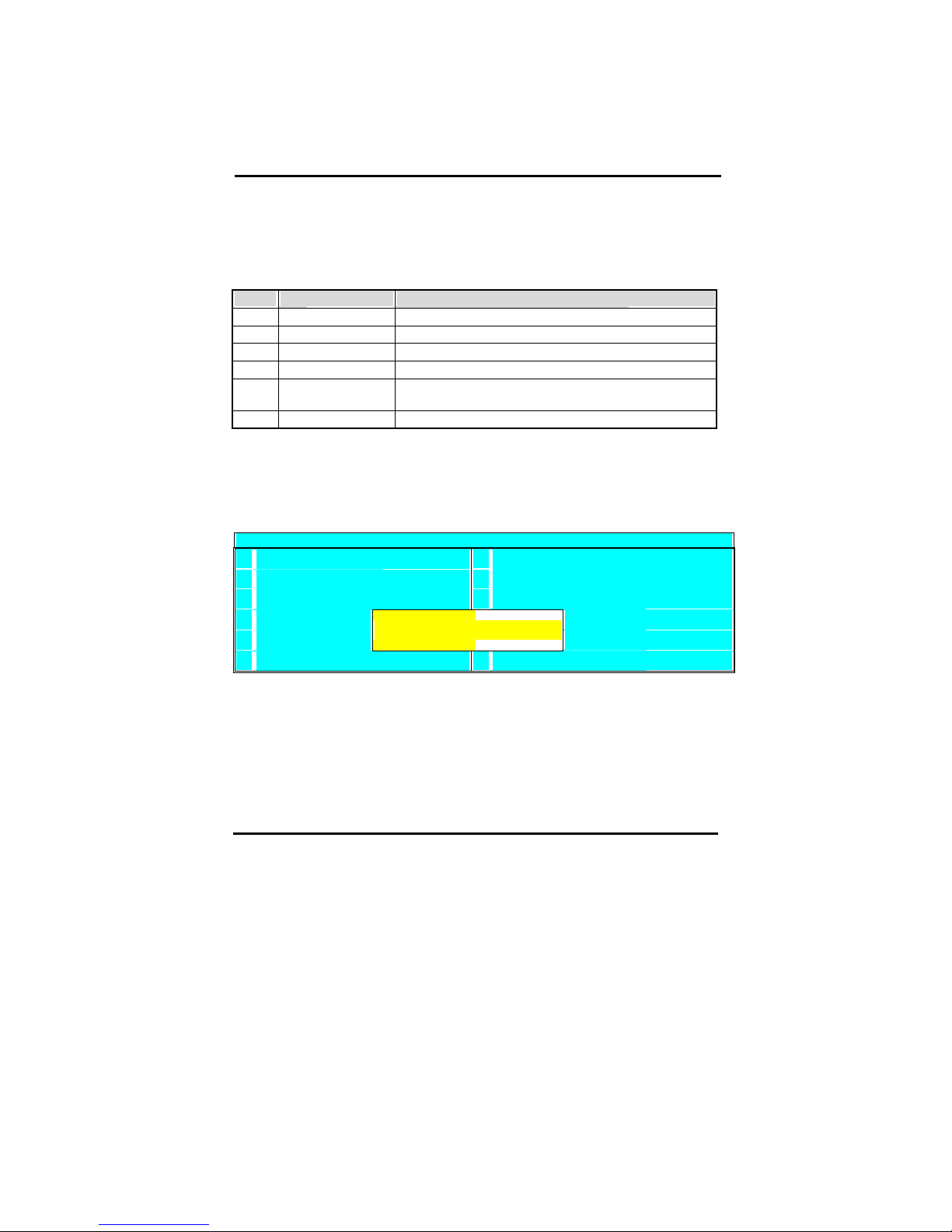
When you select the [SAVE & EXIT SETUP] option from the Main Menu, all
changes that you made will be saved to the CMOS memory and the setup utility
will exit, rebooting your system.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
"
Standard CMOS Features
"
PC Health Status
"
Advanced BIOS Features
"
Frequency/Voltage Control
"
Advanced Chipset Features
Load Optimized Defaults
"
Integrated Periph
"
Power Manag
Save to CMOS and Exit (Y/N)?
etup
"
PnP/PCI Conf
Exit: Without Saving
Pressing [Y] and [enter] will save the changes, pressing [N] and [enter] will keep
the old settings.
Page 39
34
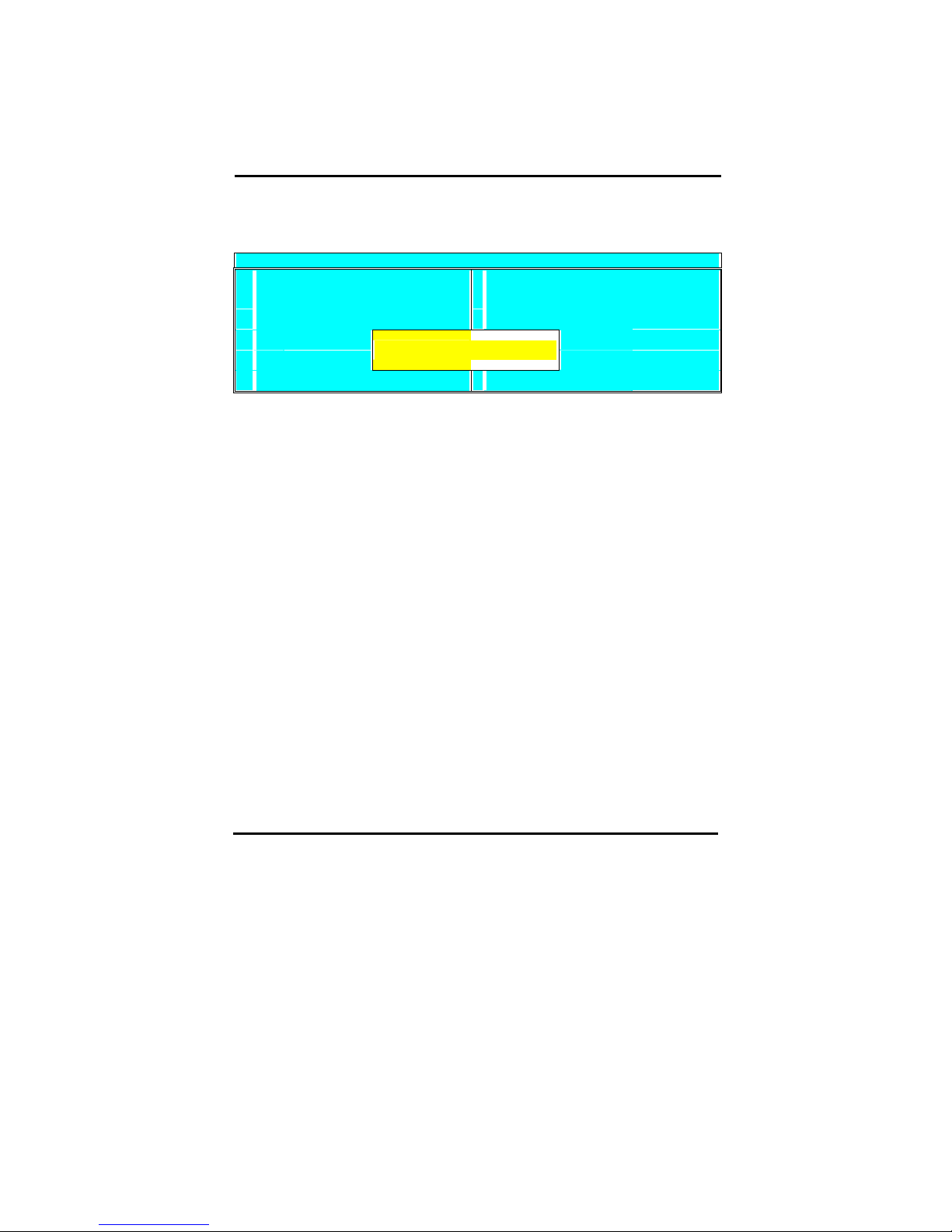
Exit Without Saving
Selecting ‘Exit Without Saving’ will exit Setup without saving changes to CMOS.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
"
Standard CMOS Features
"
PC Health Status
"
Advanced BIOS Features
"
Frequency/Voltage Control
"
Advanced Chipset Features
Load Optimized Defaults
"
Integrated Periphral
"
Power Manag
Quit without Saving (Y/N)?
tup
"
PnP/PCI Conf
Exit: Without Saving
Pressing [Y] and [enter] will Exit without saving, pressing [N] and [enter] will not Exit.
Page 40
35
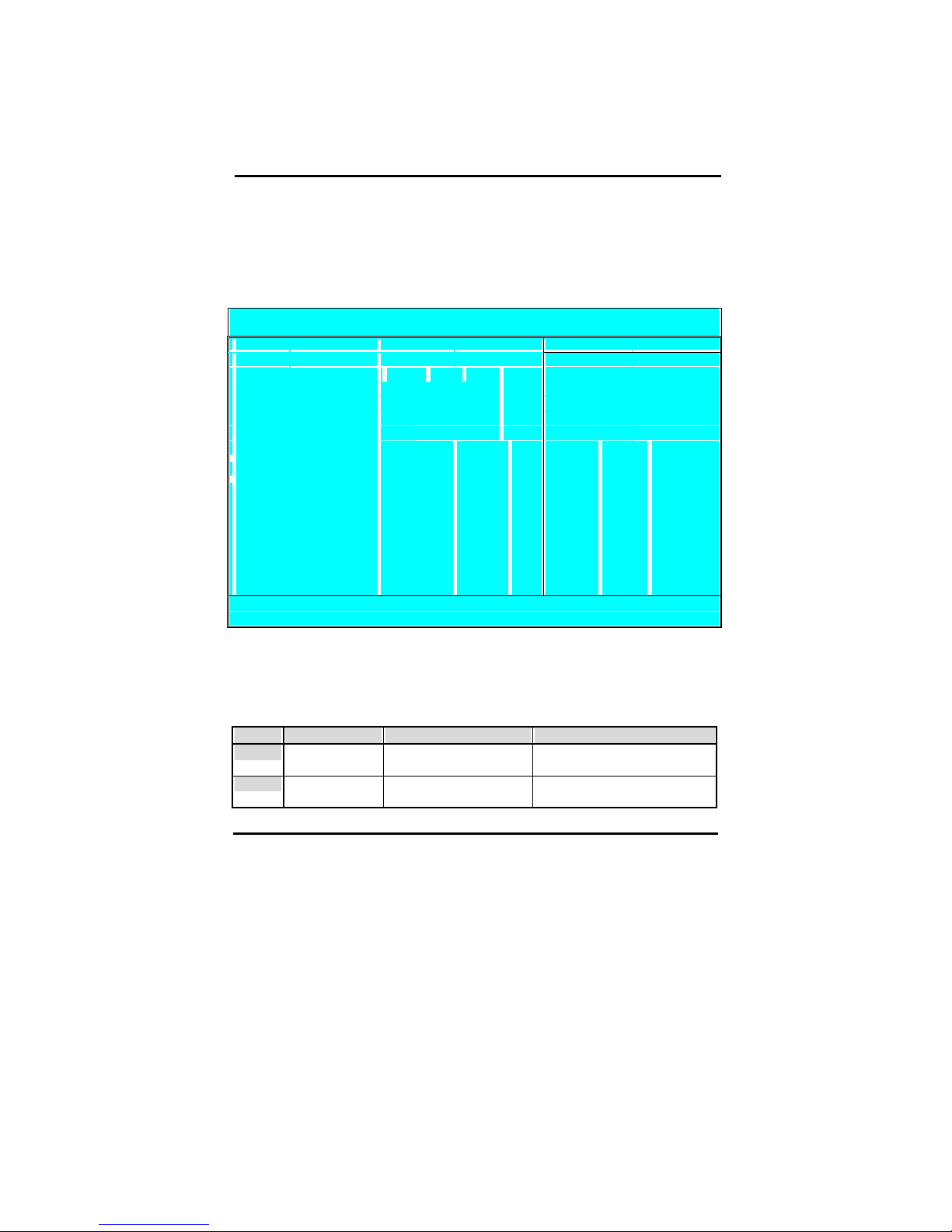
4-3-1 Standard CMOS Setup
Select the [STANDARD CMOS SETUP] option from the Main Menu and press [Enter]
key.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features
Date (mm:dd:
yy)
M
on, Aug 18, 2001
I
tem Hel
p
Time (hh:mm:ss) 11 : 51 : 58
Menu Level "
"
IDE Primary Master
Press Enter None
"
IDE Primary Slave
Press Enter None Change the day, month, year and Century
"
IDE Secondary Master
Press Enter None
"
IDE Secondary Slave
Press Enter None
Drive A 1.44M, 3.5 in.
Drive B None
Floppy 3 Mode Support Disabled
Video EGA / VGA
Halt On All, But Keyboard
Base Memory: 640K
Extended Memory: 31744K
Total Memory: 32768K
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / - / PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
This screen allows you to change the basic CMOS Settings such as date and time,
harddisk type etc. After you have made the changes you need to make press
[ESC] to return to the main menu.
Date and Time
Default Possible Settings Notes
Date
Weekday, month,
day ,year
Type the current date.
(weekday auto changes)
Using the P-Up / P-Dn keys to
toggle is possible
Time
hh:mm:ss Type the current time 24-hour clock format. (15:15:00
= 3:15:00)
Page 41
36
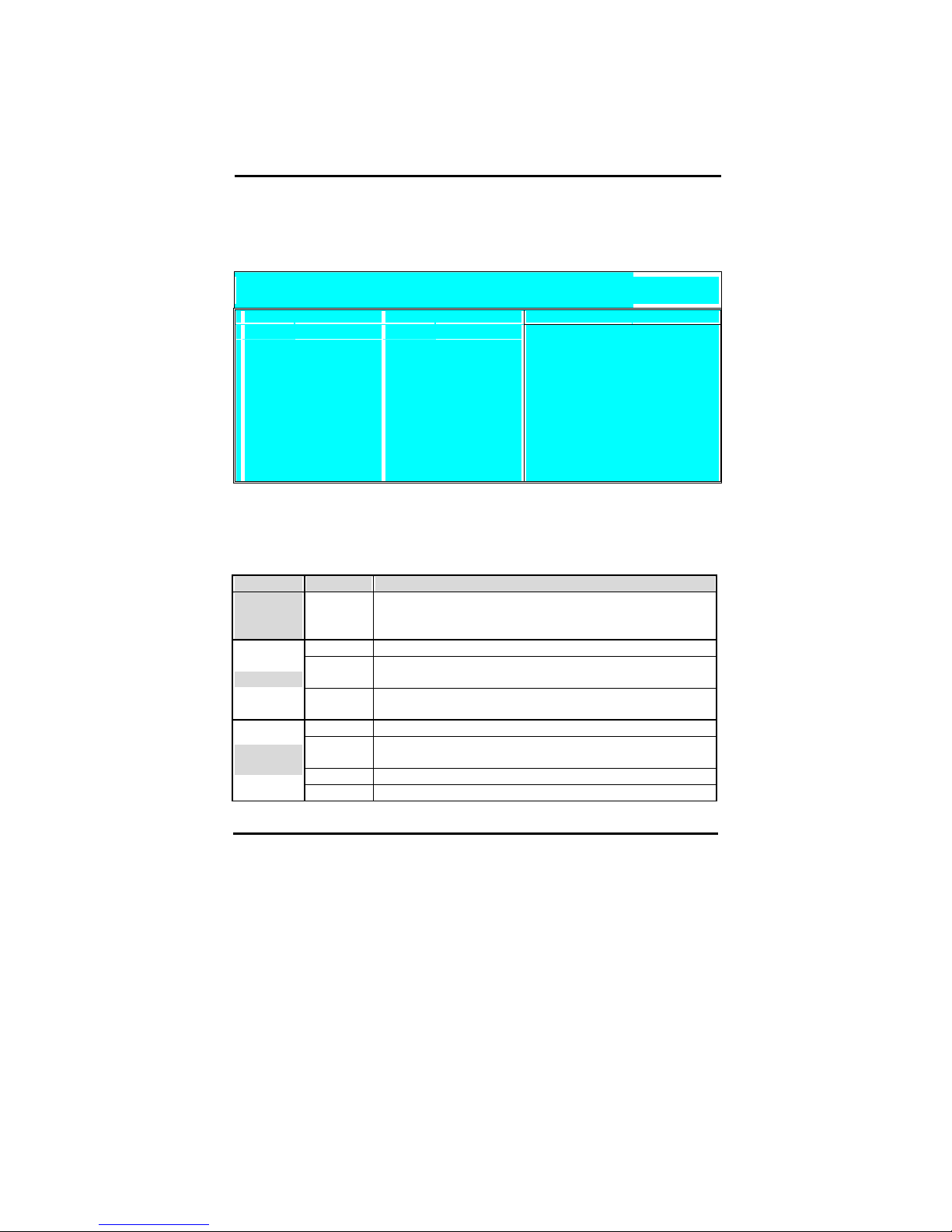
IDE Devices
When you select one of the IDE devices, a submenu will pop up. Refer to the
picture below.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
IDE xxxx
IDE HDD Auto Detection Press Ente
r
I
tem Hel
p
IDE Primary Master Auto
Menu Level " "
Access Mode Auto
To auto-detect the HDD’s size, head… on this
Capacity 0 MB channel
Cylinder 0
Head 0
Precomp 0
Landing Zone 0
Sector 0
This Menu is the same for all 4 IDE devices:
Primary Master IDE 1 first device
Primary Slave IDE 1 second device
Secondary Master IDE 2 first device
Secondary Slave IDE 2 second device
Values Meaning
IDE HDD
Auto
Detection
Press Enter
Pressing Enter will make the BIOS auto detect the IDE device
on this channel. The result will be displayed below, starting
with the ‘capacity’ item. (These items are read only)
Auto This will auto detect the device at each boot up.
Manual
This will use the setting set by the user. No auto detection at
start up will take place.
IDE xxx
None
This setting means no device is present. This will prevent the
BIOS from looking for a device and speed up booting.
CHS Selects the CHS access mode.
LBA
Logical Block Addressing, for HDD drives larger than 504MB
(All modern HDDs)
Large For very large HDDs.
Access
Mode
Auto The BIOS will automatically detect the best access mode.
Page 42

37
Drive A and Drive B
The Drive A / B items allow you select the type of device that you have attached
to the Floppy (FDD1) connector on the motherboard. You can select between
different floppy disk drive types by using the Page-Up and Page-Down keys. If
you press [enter] while Drive A or B is selected the following menu will pop up
that will allow to choose a device as well:
Drive X
None … [ ]
360K, 5.25 in. ... [ ]
1.2M, 5.25 in. … [ ]
720K, 3.5 in. … [ ]
1.44M, 3.5 in. …
[ ]
2.88M, 3.5 in. … [ ]
↑ ↓
: Move Enter:Accept ESC: Abort
Video
The Video item allows you to select a video mode. Since most modes are outdated
we advise you to always select EGA/VGA. You can select between different
video modes by using the Page-Up and Page-Down keys. If you press [enter] a
menu pops up.
(Mono is for a monochrome screen that can only display one color)
Video
EGA/VGA …
[ ]
CGA 40 ... [ ]
CGA 80 … [ ]
MONO … [ ]
↑ ↓
: Move Enter:Accept ESC: Abort
Page 43

38
Halt On
The BIOS will stop booting when an error is detected. You can set through this
item what errors will stop the system booting. You can select between different
error modes by using the Page-Up and Page-Down keys.
Values Meaning
All Errors Stop booting on all errors.
No Errors Always Boot, no matter what error is detected.
ALL, BUT
KEYBOARD
Stop booting on all errors, but not on a keyboard error.
All, but
diskette
Stop booting on all errors, but a diskette error.
Halt On
All, but
disk/key
Stop booting on all errors, but keyboard and diskette errors.
Page 44

39
4-3-2 BIOS Features Setup
Select the [Advanced BIOS Features] option from the Main Menu and press [Enter] key.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
Advanced BIOS Features
Virus Warnin
g
Disabled
I
tem Hel
p
CPU L1 & L2 Cache Enabled
CPU L2 Cache ECC Checking Enabled
Menu Level "
Quick Power On Self Test Enabled Allows you to choose the VIRUS warning
First Boot Device Floppy feature for IDE Hard Disk boot sector
Second Boot Device HDD 0 protection. If this function is enabled and
Third Boot Device LS 120 someone attempt to write data into this area,
Boot Other Device Enabled BIOS will show a warning message on
Swap Floppy Drive Disabled screen and clarm beep.
Boot Up Floppy Seek Disabled
Boot Up NumLock Status On
Gate A20 Option Fast
Typematic Rate Setting Disabled
X Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) 6
X Typematic Delay (Msec) 250
Security Option Setup
OS Select For DRAM > 64 MB Non-OS2
HDD S.M.A.R.T. Capability Disabled
Report No FDD For WIN 95 No
Video BIOS Shadow Enabled
Small Logo (EPA) Show Enabled
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / - /PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
The screen is not as long on your monitor. You can use the arrow keys to scroll down and
up the page. The following explains all individual items and their meaning.
Page 45

40
Virus protection
Values Meaning
Enabled
The BIOS will give a beep and a warning whenever an attempt
is made to write to the boot sector of the HDD.
Virus
Warning
Disabled The BIOS will allow write attempts to the boot sector
CPU Cache settings
Values Meaning
Disabled
CPU L1 &
L2 Cache
Enabled
Enabled This will enable CPU Internal L2 cache of your CPU.
CPU L2
Cache ECC
Checking
Disabled (Not recommended)
Quick Power On Self Test
Values Meaning
Enabled
The BIOS will execute test routines that test most parts of the
motherboard during boot up.
Quick
Power On
Self Test
Disabled
The BIOS will skip the tests, speeding up the boot process.
Errors will on the other hand not be detected.
Floppy Drive Settings
Values Meaning
Enabled
This will swap floppy A and B. Most systems not even have 2
floppy drives, so this item is irrelevant .
Swap Floppy
Drive
Disabled Floppy A and B are not swapped
Enabled
The BIOS will test whether the floppy has 40 or 80 tracks
during boot up. All new floppy drives are 80 tracks.
Boot-up
Floppy Seek
Disabled The BIOS will not test the amount of tracks.
Boot Devices
The first to third boot device items allow you to select what device the system should boot
from. If the BIOS fails to boot from the first boot device, it will attempt to boot from the
second boot device, if that fails too, the third boot device is tried. If you set the boot other
device item to enabled, the BIOS will try to boot from other devices if the first to third
choices all fail. If you set this item to disabled, the BIOS will not boot if the first to third
devices all fail to boot.
Page 46

41
Values Meaning
Floppy
The system attempt to boot from diskette.
(first boot device default)
LS 120
The system will attempt to boot from an attached LS 120 drive.
(Third boot device default)
HDD 0
The system will attempt to boot from the first HDD.
(Second boot device default)
SCSI
The system will attempt to boot from the first device attached to
the first SCSI interface.
CD-ROM The system will attempt to boot from the first CD-ROM found.
HDD1 The system will attempt to boot from the second HDD.
HDD2 The system will attempt to boot from the third HDD.
HDD3 The system will attempt to boot from the fourth HDD.
ZIP100 The system will attempt to boot from an attached ZIP 100 drive
LAN
The system will attempt to boot over the network. You will
require a LAN card with boot BIOS for this option to function.
First ~ Third
boot device
Disabled This disables booting from this device.
Keyboard Typematic Rate and Delay Settings
If you set the typematic rate setting item to disabled, the system will use the defaults of 6
and 250 for the rate and delay items. If you set it to enabled you can select the values
yourself. Refer to the table below:
Values Meaning
Typematic
Rate
6 ~ 30
This value sets the amount of time a character is repeated per
second if it is kept down on the keyboard. Choose from the
following values: 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 24, 30.
Typematic
Delay
250 ~ 1000
This value sets the amount of time in ms before a character
starts repeating after it was pressed on the keyboard. Choose
from 250, 500, 750 and 1000 ms.
Page 47

42
Security Option
The security option item allows you to select when the password needs to be entered. Refer
to the table below:
Values Meaning
Setup
Password must be entered only when the user wants to enter the
BIOS setup.
Security
Option
System The password must always be entered at boot.
OS Select for DRAM > 64MB
Values Meaning
Non-OS2 If your OS is not OS2, always select this setting.
OS select for
DRAM >
64MB
OS2 Select this setting only if your OS is OS2
HDD S.M.A.R.T. Capability
Values Meaning
Disabled Default setting.
HDD
S.M.A.R.T.
Capability
Enabled
Some Harddisks support SMART, a diagnostic standard that
allows the HDD to tell the system about problems. Enable this
item only if your HDD support SMART.
Report No FDD For WIN 95
Values Meaning
Yes
Report No
FDD For
WIN 95
No
Shadow Option
This shadow options allow the BIOS to shodow (write to RAM) certain parts of the BIOS
code. This will speed up running the code, since running from RAM is much faster than
running from FLASH ROM.
Values Meaning
Enabled
This will allow the BIOS to write the video BIOS to RAM. This
will speed up execution and is the default setting.
Video BIOS
Shadow
Disabled No shadowing is allowed.
Page 48
43
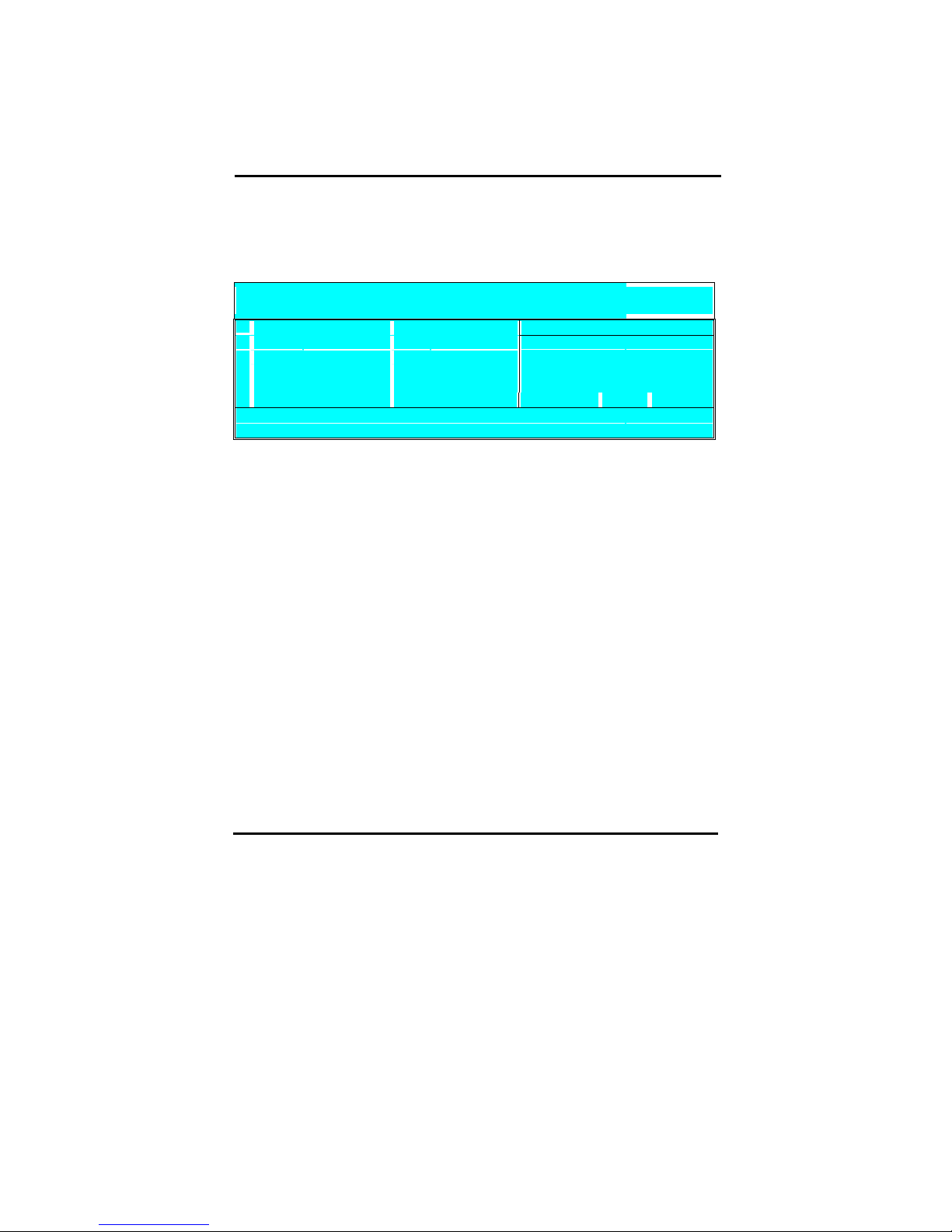
4-3-3 Chipset Features Setup
Select the [Advanced BIOS Features] option from the Main Menu and press [Enter] key.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
Advanced BIOS Features
Advanced DRAM Control 1 Press Enter Item Help
Prefetch Caching Disabled
Memory Hole at 15-16M Disabled
Menu Level "
AGP Aperture Size 64MB
Graphic Window WR Combin Enabled
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / - /PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Page 49
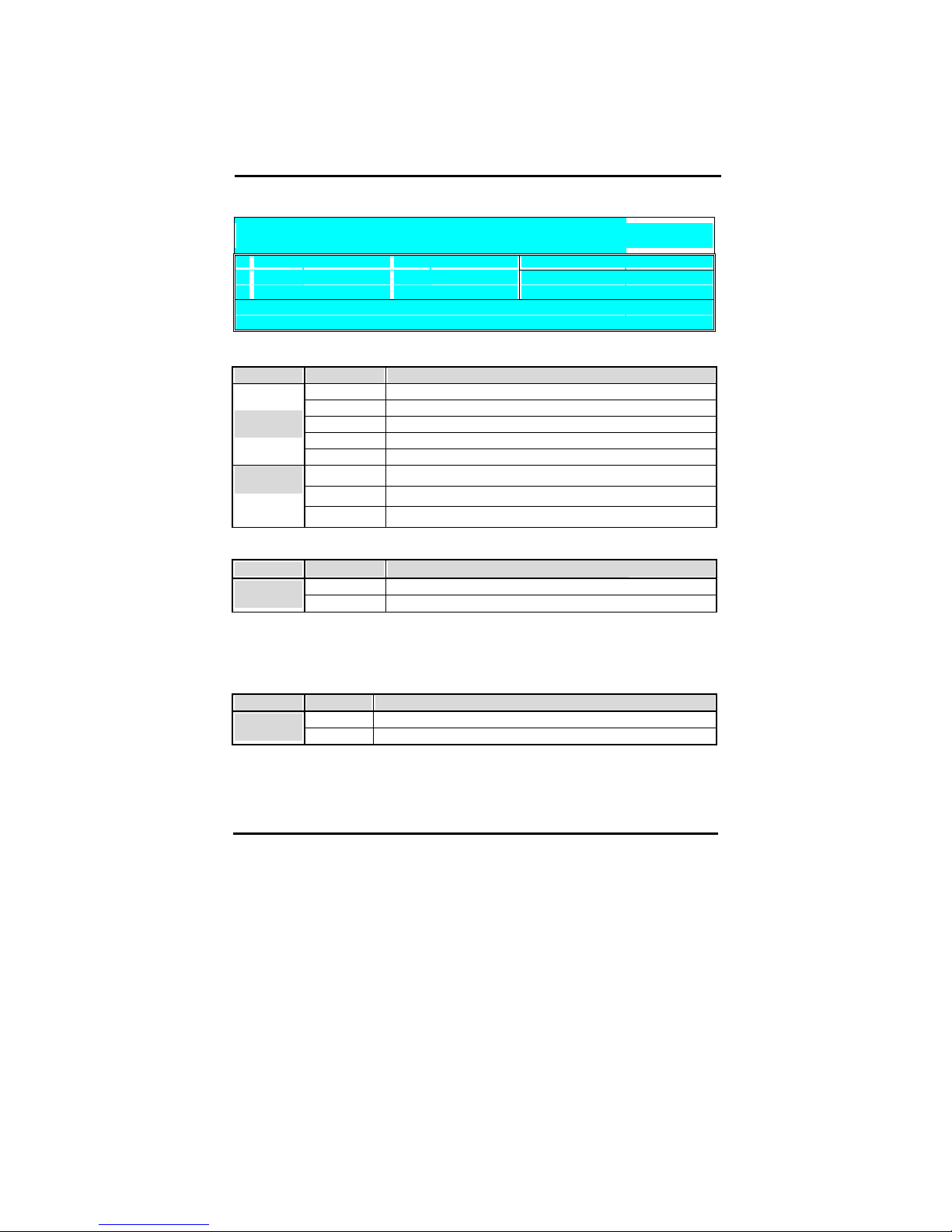
44
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
Advanced DRAM Control 1
System Performance
N
ormal Mode
I
tem Hel
p
CAS Latency Setting 2.5T
Menu Level "
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / - /PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
DRAM Control
Values Meaning
Safe Mode
Normal Mode
Fast Mode
Turbo Mode
System
Performance
Ultra Mode
2
2.5
CAS Latency
Time
3
Perfetch Caching
Values Meaning
Disabled
Perfetch
Caching
Enabled
Memory Hole
Some old devices need a memory hole to be present between 15M and 16M. CPU Cycles
matching the hole will be passed on to the PCI bus instead of accessing the memory.
Normally you can disable this setting, but if one of your devices needs it set it to enabled.
Values Meaning
Disabled There is no memory hole.
Memory Hole
at 15M-16M
Enabled A memory hole exists between 15 and 16MB.
Page 50
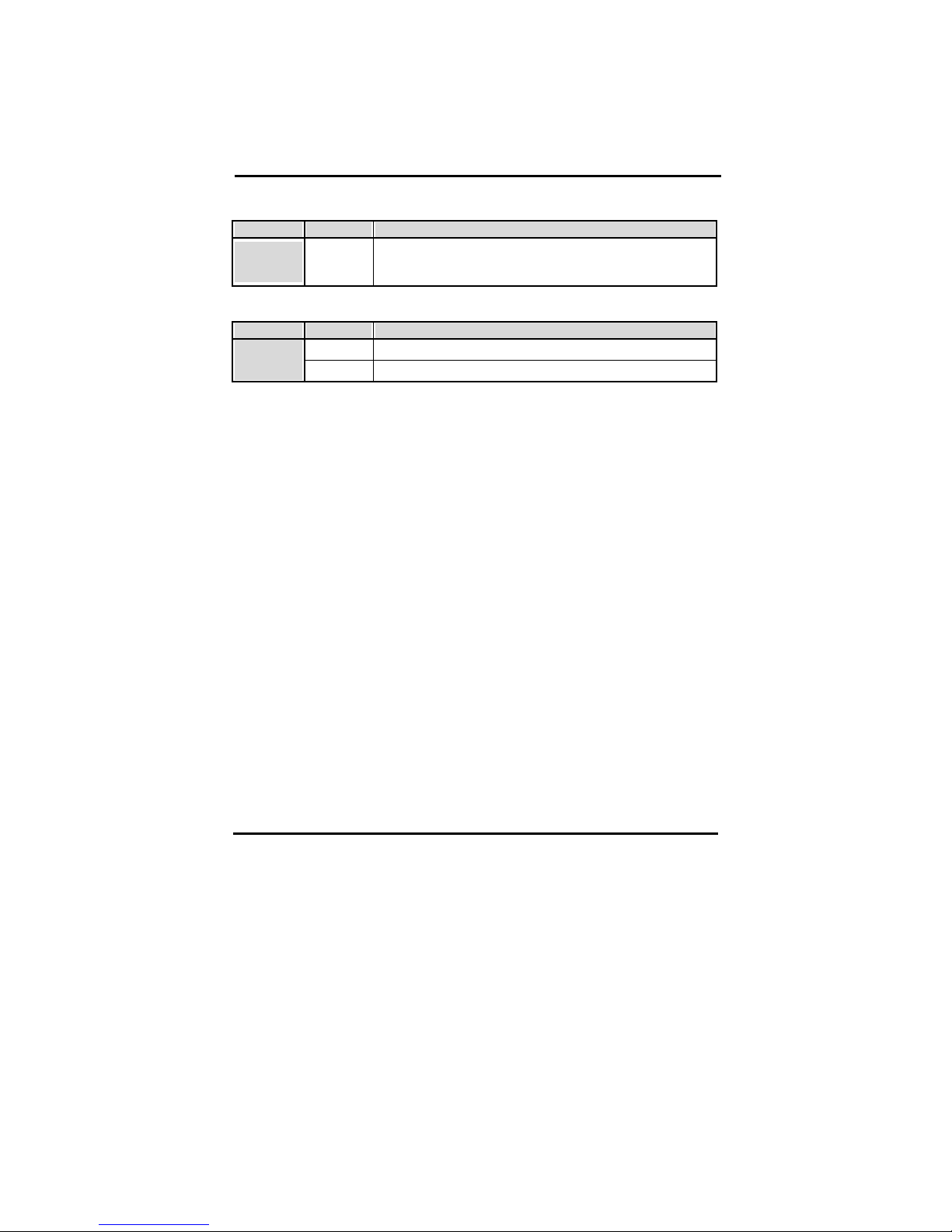
45
AGP Aperture Size (MB)
Values Meaning
On-Chip
Video
Window Size
4, 8, 16, 32,
64, 128,
256MB
Graphic Window WR Combin
Values Meaning
Enabled
Graphic
Window WR
Combin
Disabled
Page 51
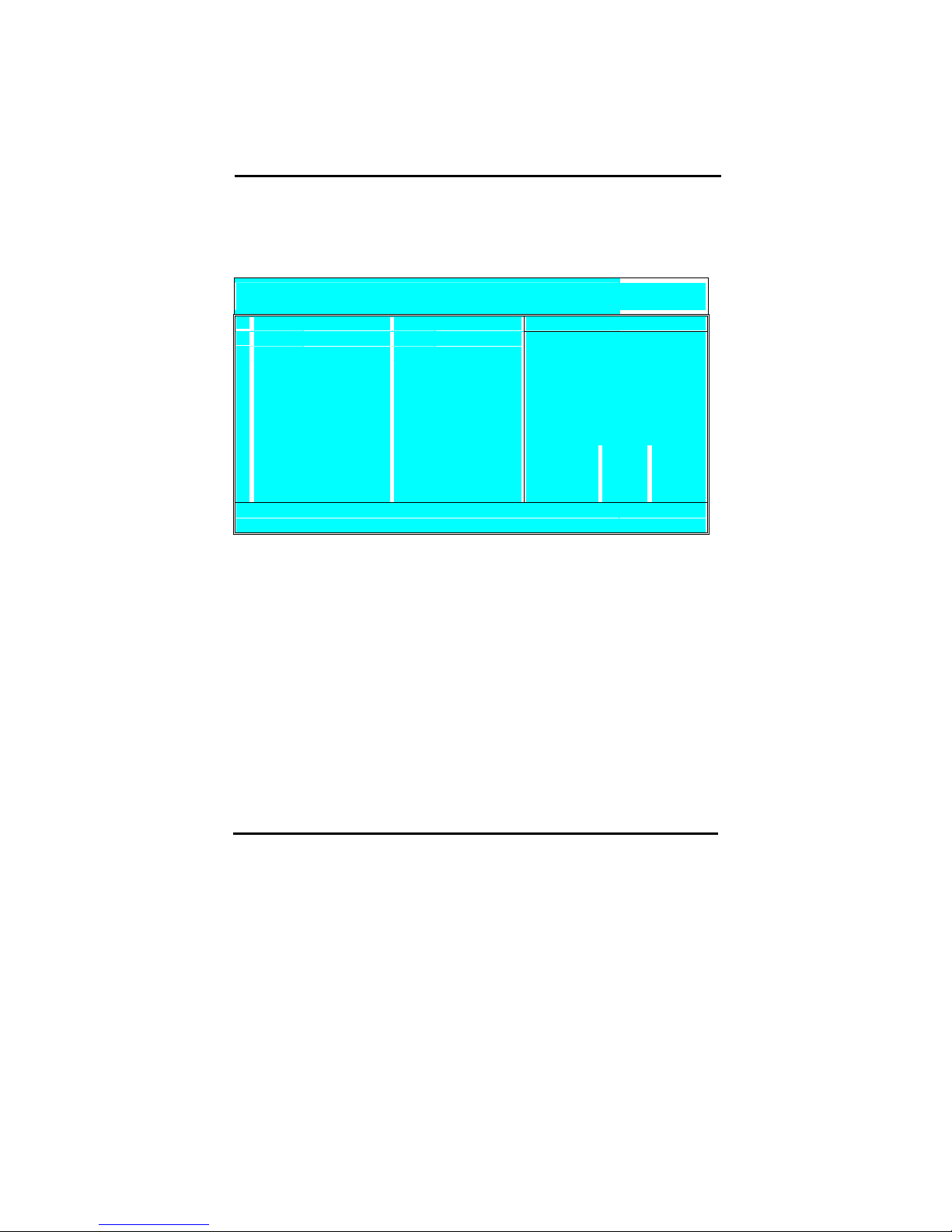
46
4-3-4 Integrated Peripherals
Select the [Integrated Peripherals] option from the Main Menu and press [Enter] key.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
Integrated Peripherals
SIS OnChip IDE Device Press Enter Item Help
"
SIS OnChip PCI Device Press Enter
"
Onboard Super IO Device Press Enter
Menu Level "
USB Control Enabled
USB Keyboard Support Disabled
IDE HDD Block Mode Enabled
Init Display First PCI Slot
AGP Auto Calibration Enabled
IDE Access Interface Auto
USB1 Access Interface Embedded Bus
USB0 Access Interface Embedded Bus
Audio Access Interface Embedded Bus
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / -/ PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Page 52

47
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
SIS OnChip IDE Device
Internal PCI/ IDE
B
oth
I
tem Hel
p
IDE Primary Master PIO Auto
IDE Primary Slave PIO Auto
Menu Level "
IDE Secondary Master PIO Auto
IDE Secondary Slave PIO Auto
Primary Master UltraDMA Auto
Primary Slave UltraDMA Auto
Secondary Master UltraDMA Auto
Secondary Slave UltraDMA Auto
IDE Burst Mode Enabled
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / -/ PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
IDE Channel Settings
The following table explains IDE channel settings and what they mean:
Values Meaning
Disabled
Primary
Secondary
Internal PCI/
IDE
Both
Auto
The BIOS will assign a PIO mode to this device automatically
when appropriate
Mode 0
Mode 1
Mode 2
Mode 3
xxx PIO
Mode 4
Select a PIO Mode here. PIO mode 0 is slowest, PIO mode 4 is
fastest, check your HDD to see what PIO mode it supports.If
your IDE device supports UDMA mode, then it best to enable
that mode since it is considerably faster than PIO mode. (Set to
auto for auto-detection)
Auto
The BIOS will automatically use Ultra DMA Mode if the IDE
device supports it.
xxx - UDMA
Disabled This will disable the use of Ultra DMA for this device.
Enabled
Block mode allows faster transfer of data between the system
and the HDD. Most modern HDDs support it.
IDE HDD
Block Mode
Disabled Block Mode is not used.
Page 53

48
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
SIS OnChip PCI Device
SIS-7012 AC97 Audio
E
nabled
I
tem Hel
p
SIS-7013 S/W Modem Disabled
System Share Memory Size 32 MB
Menu Level "
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / -/ PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
AC97 Setting
Values Meaning
Enabled This will allow use of a onboard AC97 sound codec.
SIS-7012
AC97 Audio
Disabled
If you do not need a onboard AC97 sound codec, set this item
to disabled.
Enabled
SIS-7013 S/W
Modem
Disabled
System Share Memory Size
Values Meaning
System Share
Memory Size
4, 8, 16, 32,
64MB
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
OnChip Super IO Device
Onboard FDC Controller
E
nabled
I
tem Hel
p
Onboard Serial Port 1 3F8/IRQ4
Onboard Serial Port 2 2F8/IRQ3
Menu Level "
UART Mode Select Normal
UR2 Duplex Mode Half
Onboard Parallel Port 378/IRQ7
Parallel Port Mode SPP
ECP Mode Use DMA 3
Game Port Address 201
Midi Port Address 330
Midi Port IRQ 10
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / -/ PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Page 54
49
Page 55
50
Floppy Drive
Values Meaning
Enabled This will allow use of a floppy drive.
Onboard
FDD
Controller
Disabled If you do not need a floppy drive, set this item to disabled.
COM ports (Serial Ports)
Values Meaning
Auto The bios will automatically use serial ports.
Disabled
If you do not need the serial port in question, set this item to
disabled.
3F8/IRQ4
2F8/IRQ3
3E8/IRQ4
Onboard
serial port 1 /
2
2E8/IRQ3
Set an IO address and an IRQ to be used by serial ports.
IR Control
Values Meaning
Normal
IrDA Allows use of the IR port in IrDA mode.
ASKIR Allows use of the IR port in ASKIR mode.
UART Mode
Select
SCR Allows use of the IR port in SCR mode.
Half Select if your IR device supports Half duplex only.
UR2 Duplex
Mode
Full For IR devices that support full duplex.
Paraller Port (Printer Port)
Values Meaning
Disabled Disables use of the parallel port.
3BC/ IRQ7
378/ IRQ7
Onboard
Parallel Port
278/ IRQ5
Select and IO Address and an IRQ to be used by the parallel
port.
SPP Enableds use of SPP devices.
EPP Enables use of EPP devices.
ECP Enables use of EPP devices.
Parallel Port
Mode
ECP Enables use of ECP + EPP devices.
ECP mode
use DMA
1 or 3
Select either DMA channel 1 or 3 (This is only relevant if ECP
was selected above). Default is channel 3.
Page 56
51
Game Port
Values Meaning
201 Setting game port address at 201
209 Setting game port address at 209.
Game Port
Disabled Disabled game port.
MIDI
Values Meaning
300 Set mpu401 port address at 300.
330 Set mpu401 port address at 330.
Midi Port
Address
Disabled Without midi port or none AC97 m/b
5 Set mpu-40 port IRQ address at 5.
Midi Port
IRQ
10 Set mpu-40 port IRQ address at 5.
USB Setting
Values Meaning
Enabled This will allow use of a USB drive.
USB
Controller
Disabled If you do not need a USB drive, set this item to disabled.
Enabled This will allow use of a USB keybaord.
USB
Keyboard
Support
Disabled If you do not need a USB keyboard, set this item to disabled.
Display Initialization
Values Meaning
PCI Slot
The BIOS will first search for a VGA adapter on the PCI bus, if
one is found it will be used as primary display.
Inie Display
First
Onboard The onboard AGP is first scanned.
Page 57

52
4-3-5 Power Management Setup
Select the [Power Management Setup] option from the Main Menu and press [Enter] key.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
Power Management Setup
ACPI Function
E
nabled
I
tem Hel
p
ACPI Suspend Type S1 (POS)
Menu Level "
Video Off Method DPMS
Video Off In Suspend DPMS Supported
Switch Function Break/ Wake
Modem Use IRQ 3
Hot Key Function As Power Off
HDD off After Disabled
Power Button Override Instant-Off
"
PM Wake Up Events Press Enter
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select PU / PD / + / - : value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
ACPI Function
For a detailed description of ACPI and what it does, refer to the FAQ chapter, ACPI
section. ACPI can be either enabled or disabled on this BIOS Setup page. For the ACPI
Suspend type there are two options:
S1 (POS)
S3 (STR)
STR is the so called Suspend to RAM suspend type. This will save the sytem context all to
RAM and it will shut down the system. The standby voltage of the power supply backs up
the RAM contents. (Therefore we recommend to use a power supply that can support a
current of 1A at the standby line). When the user want the system to wake up again, the
sytem is powered up, the BIOS detects a STR and the system restores itself to where it left
off. Start up time is much faster than a normal boot would take.
Power Management
Pressing [enter] when the power management item is selected will have the following sub
menu appear:
Page 58

53
Values Meaning
Enabled
ACPI
Function
Disabled
1 – 15 Min
Will power down the HDD if it is idle for the amount of
minutes selected here.
HDD off
After
Disabled Will not power down the HDD.
Video Options
Values Meaning
Blank
Screen
The screen will be blank (black) only.
V/H sync +
blank
The vertical and horizontal sync pulses will be stopped, and the
screen will be blank.
Video Off
Method
DPMS
support
If your monitor supports DPMS, it can be switched off through
that.
Modem IRQ
Values Meaning
NA This disables the modem IRQ
Modem Use
IRQ
3 - 11
Select an IRQ line that will be assigned to your modem here.
Choose from: 3 (default), 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11.
Power Button
Values Meaning
Instant-off
Switches the system off immediately when pressing the power
button.
power button
Overeide
Delay 4 Sec
This requires you to press the power button for at least 4
seconds before the system switches off.
Page 59
54
Wake Events
When the system as entered dose or suspend mode, it can wake up through a wake event.,
These wake up events are triggered by interrupts that are monitored by the BIOS. If you
press [Enter] when the Wake Up Event item is selected you will see the following sub
menu appear:
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
PM Wake Up Event
IRQ [3-7, 9-15], NMI
E
nabled
I
tem Hel
p
IRQ 8 Break Suspend Disabled
Menu Level "
RING Power Up Control Enabled
PCIPME Power Up Control Enabled
USB Port Wake Up Control Enabled
Hot Key Power Up Control Enabled
PS2 Mouse Power Up Control Enabled
KB Power ON Password Enter
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select PU / PD / + / - : value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Page 60

55
4-3-6 PnP / PCI Configurations
Select the [PnP / PCI Configurations] option from the Main Menu and press [Enter] key.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
PnP / PCI Configurations
Reset Configuration Data Disabled
I
tem Hel
p
Resources Controlled by Auto (ESCD)
Menu Level "
X IRQ Resources Press Enter
Default is Disabled. Select Enabled to reset
PCI/VGA Palette snoop Disabled Extended System Configuration Data ESCD>
When you exit Setup if you have installed a
new add-on and the system reconfiguration
has Cause such a serious conflict that the OS
cannot boot
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / - /PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Reset Configuration Data
Values Meaning
Disabled
This will not reset the system configuration data (IRQs, DMAs)
on reboot.
Reset
Configuratio
n Data
Enabled
This will reset the configuration data. Remember to enable this
item every time you make a change to your system (such as
switching PCI cards etc).
Resources Controlled by
Values Meaning
Manual
The table will show the below items: “Reset Configuration
Data, IRQ-3 assigned to, DMA-0 assigned to.” The user can
adjust the shown items as required.
Resources
Controlled
By
Auto
The table will not show the above items, and the system will
automatically assign the above setup.
Page 61

56
Resources
If you set the Resources Controlled by item to Auto (ESCD), the BIOS will manage all
resources for you. If you set it to manual to two items below will allow you to assign the
resources manually.
Values Meaning
PCI/ISA
PnP
This setting means the BIOS will assign the interrupt as needed.
This means that it is not fixed to a device
IRQ-x
assigned to
(x = 3 to 15)
Legacy ISA
If you need to make sure that a certain interrupt is assigned to
an ISA device, set that interrupt to legacy ISA.
PCI/ISA
PnP
This setting means the BIOS will assign the DMA Channel as
needed, it is not fixed to a device
DMA-x
assigned to
(x = 0, 1, 3,
5, 6, 7)
Legacy ISA
If you need to make sure that a certain DMA channel is
assigned to an ISA device, set that channel to legacy ISA.
PCI / VGA Palette Snoop
Values Meaning
Disabled Default setting.
PCI / VGA
Palette
Snoop
Enabled
This will allow the system to look at the palette the VGA uses
to display. Some applications speed up with this setting but it is
mostly obsolete.
Page 62

57
4-3-7 PC Health Status
Select the [PC Health Status] option from the Main Menu and press [Enter] key.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
PC Health Status
Shutdown Temperature Disabled
I
tem Hel
p
Voltage 0
Voltage 1
Menu Level "
Voltage 2
Voltage 3
Voltage 4
Voltage 5
Voltage 6
Voltage 7
Voltage Battery
Temperature 1
Temperature 2
Temperature 3
Fan 1 Speed
Fan 2 Speed
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / - / PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Shutdown Temperature
Values Meaning
Disabled
60℃/ 140℉, 65℃/ 149℉, 70℃/ 158℉,
Shutdown
Temperature
60℃/ 140℉, 65℃/ 149℉, 70℃/ 158℉, 75℃/ 167℉,
Page 63

58
4-3-8 Frequency/ Voltage Control
Select the [Frequency / Voltage Control] option from the Main Menu and press [Enter]
key.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
Frequency / Voltage Control
CPU Clock Radio 0X
I
tem Hel
p
Auto Detect PCI Clk Enabled
Spread Specrurm Disabled
Menu Level "
CPU Host/SDRAM/PCI Clock k Default
↑ ↓ → ←
: Move Enter: Select + / - / PU / PD: value F10: save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
F5 : Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Page 64
59
CPU Clock Ratio
Values Meaning
CPU Clock
Ratio
X8 ~ X50
Auto Detect PCI Clk
Values Meaning
Enabled
If set to enabled the BIOS will detect the values for the PCI
clock.
Auto Detec
DIMM/ PCI
Clk
Disabled
If disabled, the BIOS will use the values set on this page and on
the Advanced Chipset Features page.
Spread Spectrum
Values Meaning
Disabled
+/-0.25%
+/-0.37%
+/-0.50%
Spread
Spectrum
+/-0.75%
CPU Clock
Values Meaning
CPU Clock
Min = 100
Max = 132
Page 65

60
4-3-9 Passwords
The BIOS Setup program allows you to specify passwords in the Main menu. The
passwords control access to the BIOS during system startup. The passwords are not case
sensitive. In other words, it makes no difference whether you enter a password using upper
or lowercase letters. The BIOS Setup program allows you to specify two separate
passwords:
Supervisor password
User password.
The function of the supervisor password depends on the setting for the Security Option
item on the Advanced BIOS Features page. If set to System, the supervisor password must
be given every time the system boots, if set to setup, the password must be given only
when you want to enter the BIOS Setup.
The user password has the same functionality, with the only difference that anybody
logging in with the user password may only change the user password when entering the
BIOS Setup page. All other items in the BIOS Setup will be disabled (unchangeable).
When both passwords are disabled, anyone may access all BIOS Setup program functions.
Setting the password
To set the Supervisor password, select the Set Supervisor Password item in the main BIOS
Setup Menu. Now a dialog will pop up asking you to enter a password.
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
"
Standard CMOS Features
"
Frequency/Voltage Control
"
Advanced BIOS Features
Load Optimized Defaults
"
Advanced Chipset Features
Set Supervisor Password
"
Integrated Peripherals
Set User Password
"
Power Manag
xit Setup
"
PnP/PCI Conf
Enter Password:
ithout Saving
Now you can enter your password, after entering the password the menu will pop up again
and will ask you to reconfirm the password. After entering and pressing [enter] the
password will be stored to CMOS RAM and the password will be enabled.
Page 66
61
Disabling the password
To disable the password, simply press [enter] without entering any other letters or numbers. This will
disable the password, the BIOS will tell you by displaying the following dialog:
CMOS SETUP UTILITY Copyright © 1984 – 2001 Award Software
"
Standard CMOS Features
"
Frequency/Voltage Control
"
Advanced BIOS Features
Load Optimized Defaults
"
Advanced Chipset Features
Set Supervisor Password
"
Integrated Peripherals
Set User Password
"
Power Manag
xit Setup
"
PnP/PCI Conf
Password Disabled!!!
Press any key to continue
ithout Saving
Password Unknown
If you forgot the password, you can clear the password by erasing the CMOS RAM. The
RAM data containing the password information is powered by the onboard button cell
battery. Please refer to the CMOS RAM section earlier in this chapter. After clearing the
CMOS memory, hold down <Delete> during bootup and enter BIOS setup to re-enter user
preferences.
Page 67
62
Chapter 5 Appendix
5-1 Memory Map
Address range Size Description
00000-7FFFF 512K Conventional memory
80000-9FBFF 127K Extended conventional memory
9FC00-9FFFF 1K Extended BIOS data area if PS/2 mouse is
installed
A0000-C7FFF 160K Available for hi DOS memory
C8000-DFFFF 96K Available for hi DOS memory and adapter
ROMs
E0000-EEFFF 60K Available for UMB
EF000-EFFFF 4K Video service routine for monochrome &
CGA adapter
F0000-F7FFF 32K BIOS CMOS setup utility
F8000-FCFFF 20K BIOS runtime service routine (2)
FD000-FDFFF 4K Plug and play ESCD data area
FE000-FFFFF 8K BIOS runtime service routine (1)
Page 68

63
5-2 I/O Map
000-01F DMA controller (master)
020-021 Interrupt controller (master)
022-023 Chipset control registers. I/O ports
040-05F Timer control registers
060-06F Keyboard interface controller (8042)
070-07F RTC ports & CMOS I/O ports
080-09F DMA register
0A0-0BF Interrupt controller (slave)
0C0-0DF DMA controller (slave)
0F0-0FF Math coprocessor
1F0-1FB Hard disk controller
278-27F Parallel port 2
2B0-2DF Graphics adapter controller
2F8-2FF Serial port 2
360-36F Network ports
378-37F Parallel port 1
3B0-3BF Monochrome & parallel port adapter
3C0-3CF EGA adapter
3D0-CDF CGA adapter
3F0-3F7 Floppy disk controller
3F8-3FF Serial port-1
Page 69
64
5-3 Time & DMA Channels Map
Time map:
Timer channel 0 system timer interrupt
Timer channel 1 DRAM refresh request
Timer channel 2 speaker tone generator
DMA channels:
DMA channel 0 available
DMA channel 1 onboard ECP (option)
DMA channel 2 floppy disk (SMC chip)
DMA channel 3 onboard ECP (default)
DMA channel 4 cascade for DMA controller 1
DMA channel 5 available
DMA channel 6 available
DMA channel 7 available
Page 70
65
5-4 Interrupt Map
NMI: non-maskable interrupt
IRQ(H/W):
0 system timer interrupt from timer 0
1 keyboard output buffer full
2 cascade for IRQ 8-15
3 serial port2
4 serial port1
5 parallel port 2
6 floppy disk (SMC chip)
7 parallel port 1
8 RTC clock
9 available
10 available
11 available
12 PS/2 mouse
13 math coprocessor
14 onboard hard disk (IDE1) channel
15 onboard hard disk (IDE2) channel
Page 71
66
5-5 RTC & CMOS RAM Map
RTC & CMOS :
00 seconds
01 seconds alarm
02 minutes
03 minutes alarm
04 hours
05 hours alarm
06 day of week
07 day of month
08 month
09 year
0a status register a
0b status register b
0c status register c
0d status register d
0e diagnostic status byte
0f shutdown byte
10 floppy disk drive type byte
12 hard disk type byte
13 reserve
14 equipment type
15 base memory low byte
16 base memory high byte
17 extension memory low byte
18 extension memory high byte
19-2d
2e-2f
30 Reserved for extension memory low byte
31 reserved for extension memory high byte
32 date century byte
33 information flag
34-3f reserve
40-7f reserved for chipset setting data
Page 72
67
5-6 ISA I/O Address Map
I/O Address (HEX) I/O device
000 - 01F DMA Controller 1, 8237A-5
020 - 03F Interrupt Controller 1, 8259A
040 - 05F System Timer, 8254-2
060 - 06F 8042 Keyboard Controller
070 - 07F real-time Clock/CMOS and NMI Mask
080 - 09F DMA Page Register, 74LS612
0A0 - 0BF Interrupt Controller 2, 8259A
0C0 - 0DF DMA Controller 2, 8237A-5
0F0 - 0FF i486 Math Coprocessor
1F0 - 1F8 Fixed Disk Drive Adapter
200 - 207 Game I/O
20C - 20D Reserved
21F Reserved
278 - 27F Parallel Printer Port 2
2B0 - 2DF Alternate Enhanced Graphic Adapter
2E1 GPIB Adapter 0
2E2 - 2E3 Data Acquisition Adapter 0
2F8 - 2FF Serial Port 2 (RS-232-C)
300 - 31F Prototype Card
360 - 363 PC Network (Low Address)
364 - 367 Reserved
368 - 36B PC Network (High Address)
36C - 36F Reserved
378 - 37F Parallel Printer Port 1
380 - 38F SDLC, Bisynchronous 2
3B0 - 3BF Monochrome Display and Printer Adapter
Page 73

68
I/O Address (HEX) I/O device
390 - 393 Cluster
3A0 - 3AF Bisynchronous 1
3C0 - 3CF Enhanced Graphics Adapter
3D0 - 3DF Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter
3F0 - 3F7 Diskette Drive Controller
3F8 - 3FF Serial Port 1 (RS-232-C)
6E2 - 6E3 Data Acquisition Adapter 1
790 - 793 Cluster Adapter 1
AE2 - AE3 Data Acquisition Adapter 2
B90 - B93 Cluster Adapter 2
EE2 - EE3 Data Acquisition Adapter 3
1390 - 1393 Cluster Adapter 3
22E1 GPIB Adapter 1
2390 - 2393 Cluster Adapter 4
42E1 GPIB Adapter 2
62E1 GPIB Adapter 3
82E1 GPIB Adapter 4
A2E1 GPIB Adapter 5
C2E1 GPIB Adapter 6
E2E1 GPIB Adapter 7
Page 74

69
Chapter 6 Q & A
6-1 Errors Messages During Power On Self Test
During power on self test (post), BIOS will automatically detect the system
devices. Below is the question that users most often meet. The user may press
“Esc” key to skip the full memory test.
1. Beep sound
On power on, the system make beep sound to offer different messages. If the
system is configured correctly, it prompts a short beep to show device
configuration is done correctly. When VGA card and DIMM modules are not
plugged well, the system makes longer and constant beep sounds.
2. BIOS ROM checksum error
It indicates the checksum of the BIOS code is not right and system will always
halt on power on screen. Contact the dealer to exchange a new BIOS.
3. CMOS battery fails
It indicates the CMOS battery does not work. Contact the dealer to exchange a
new battery.
4. CMOS checksum error
It indicates the CMOS checksum is incorrect. Load the default values in BIOS to
solve this problem. This error may result from a weak BIOS, so exchange a new
BIOS if necessary.
5. Hard disk initialize
Please wait a moment…
Some hard drives require more time to initialize.
Page 75
70
6. Hard disk install failure
The system can not find or initialize the hard drive controller or the drive. Check
if the controller is set correctly. If no hard disk is installed, “Hard drive
selection” must be set to “none.”
7. Keyboard error or no keyboard present
This means the system can not initialize the keyboard. Check if the keyboard is
plugged well and be sure no keys are pressed during power on self test.
8. Memory test fails
There will be more information to specify the type and location of the memory
error.
9. Primary master hard disk fail
The BIOS find an error in the primary master hard disk drive.
10. Primary slave hard disk fail
The BIOS finds an error in the primary slave hard disk drive.
11. Secondary master hard disk fail
The BIOS finds an error in the secondary slave master hard disk drive.
12. Secondary slave hard disk fail
The BIOS finds an error in the secondary slave IDE hard disk drive.
 Loading...
Loading...