Page 1

APX 8000™/MAX® TNT/DSLMAX™
Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Part Number 7820-0802-003
For software version 8.0
May 2000
Page 2

Copyright© 2000 Lucent Technologies. All rights reserved.
This material is protected by the copyright laws of the United States and other countries. It may not be reproduced, distributed, or altered in any fashion by any
entity (either internal or external to Lucent Technologies), except in accordance with applicable agreements, contracts, or licensing, without the express
written consent of Lucent Technologies. For permis sion to reproduce or distribute, please em ai l your request to
Notice
techpubs@ascend.com.
Every effort was mad e to en sur e that the information in this document was complete and ac cu ra te at the time of printing, bu t inf ormation is subject to change.
Safety, Compliance, and Warranty Information
Before handling any Luc ent A ccess N etwor ks hard ware prod uct, rea d the Access Networks Safety and Compliance Guide included in your product package.
See that guide also to determine how products comply with the electromagnetic interference (EMI) and network compatibility requirements of your country.
See the warranty card include d in your product package for the limit ed warranty that Lucent Technologies provides for its products.
Security Statement
In rare instances, unauthoriz ed individuals make connecti ons t o the te lecommunications network through the use of access features.
Trademarks
4ESS, 5ESS, A Network of Expertise, AnyMedia, AqueView, AUDIX, B-STDX 8000, B-STDX 9000, ...Beyond Compare, CaseView, Cajun, CajunDocs,
CAJUNVIEW, Callmaster, CallVisor, CBX500, CellPipe, ChoiceNet, ClearReach, ComOS, cvMAX, DACScan, Dacsmate, Datakit, DEFINITY,
Definity One, DSLMAX, DSLTerminator, DSLPipe, DSLTNT, Elemedia, Elemedia Enhanced, EMMI, End to End Solutions, EPAC, ESS, EVEREST,
Gigabit-scaled campus netwo r king, Globalv iew, GRF, GX250, GX 550, HyperPATH, Inferno, InfernoSpaces, Intr agy, I ntragyAccess, IntragyCentral, Intu ity,
IP Navigator, IPWorX, LineReach, LinkReach, MAX, MAXENT, MAX TNT, Multiband, Multiband PLUS, MultibandRPM, MultiDSL, MultiVoice,
MultiVPN, Navis, NavisAccess, NavisConnect, NavisCore, NavisRadius, NavisXtend, NetCare, NetLight, NetPartner, OneVision,
Open Systems Innovations, OpenTrunk, P550, PacketStar, PathStar, Pinnacle, Pipeline, PMVision, PortMaster, SecureConnect, Selectools, Series56,
SmoothConnect, Stinger, SYSTIMAX, True Access, WaveLAN, WaveMANAGER, WaveMODEM, WebXtend, and Where Network Solutions Never End
are trademarks of Lucent Technologies. Advantage Pak, Advantage Services, AnyMedia, ...Beyond Compare, End to End Solutions, Inter.NetWorking,
MAXENT, and NetWork Knowledge Sol utions are service marks of Lucent Technologies. Other trademarks, service marks, and tra de names mentioned in
this publication belong to th ei r respective owners.
Copyrights for Third-Party Software Included in Lucent Access Networks Software Products
C++ Standard Template Library software cop yright© 1994 Hewlett-Packard Co mpany and copyright© 1997 Silic on Graphics. Permission to use, c opy,
modify, distribute, and sell this software and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee, provided that the above copyright no tice appear
in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear in supporting documentation. Neither Hewlett-Packard nor Silicon Graphics
makes any representations about the suitability of this software for any pu rpose. It is provided “as is” without expre ss or im pl ied wa rranty.
Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD ) UNIX software copyright© 1982, 1986, 1988, 1993 The Regents of Ca lifornia. All rights reserved. Redistribut ion and
use in source and binary forms, with or wit hout m odifi cation , are permitt ed prov ided th at the fol low ing co ndition s are met: 1. R edistribution s of source code
must retain the above co pyright notice, this list of condi t ion s, a nd the following disclaimer. 2. Redistributio ns in binary form must reproduce the a bove copyright notice, this list of conditions, and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/ or other materials provide d with the distribution. 3. A l l advertising
materials mentioning f ea tu res or use of this software must display the following acknowledgement: This product includes soft w a r e developed by the University of California, Berk eley, and its contributo rs. 4. Neit her the name of the Univ ersity no r the name s of its cont ributors m ay be us ed to en dorse or pro mote
products derived from this softw are w ithout specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE REGENTS AND CONTRIBUTORS “AS IS” AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE REGENTS OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS
OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY
OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
Ordering Information
You can order the most up-to-dat e product information and compu te r-based t r ai ni ng online at http://www.lucent.com/ins/bookstore.
Feedback
Lucent Technologies appreciates your co mm e nts, either positive or negative , abou t th is manual. Please send them to techpubs@ascend.com.
Lucent Technologies
Page 3

Customer Service
Customer Service provides a variety of options for obtaining information about Lucent
products and services, software upgrades, and technical assistance.
Finding information and software on the Internet
Visit the Web site at http://www.lucent.com/ins for technical information, product
information, and descriptions of available services.
Visit the FTP site at ftp://ftp.ascend.com for software upgrades, release notes, and
addenda.
Obtaining technical assistance
You can obtain technical assistance by telephone, email, fax, modem, or regular mail, as well
as over the Internet.
Gathering information you will need
If you need to contact Lucent for help with a problem, make sure that you have the following
information when you call or that you include it in your correspondence:
• Product name and model
• Software and hardware options
• Software version
• If supplied by your carrier, Service Profile Identifiers (SPIDs) associated with your line
• Your local telephone company’s switch type and operating mode, such as AT&T 5ESS
Custom or Northern Telecom National ISDN-1
• Whether you are routing or bridging with your Lucent product
• Type of computer you are using
• Description of the problem
Calling Lucent from within the United States
In the U.S., you can take advantage of Priority Technical Assistance or an Advantage service
contract, or you can call to request assistance.
Priority Technical Assistance
If you need to talk to an engineer right away, call (900) 555-2763 to reach the Priority Call
queue. The charge of $2.95 per minute does not begin to accrue until you are connected to an
engineer. Average wait times are less than 3 minutes.
Advantage Services
Advantage Services is a comprehensive selection of services. Installation services help get
your Lucent Wide Area Network (WAN) off to the right start. Ongoing maintenance and
85x11 Book Template (Preliminary) iii
Page 4

support services provide hardware and software solutions to keep your network operating at
peak performance. For more information, call (800) 272-3634.
Other telephone numbers
For a menu of Lucent’s services, call (800) 272-3634. Or call (510) 769-6001 for an operator.
Calling Lucent from outside the United States
You can contact Lucent by telephone from outside the United States at one of the following
numbers:
Telephone outside the United States (510) 769-8027
Austria/Germany/Switzerland
Benelux
France
Italy
Japan
Middle East/Africa
Scandinavia
Spain/Portugal
UK
For the Asia-Pacific region, you can find additional support resources at
http://www.lucent.com/ins/international/apac/.
Obtaining assistance through correspondence
Send your technical support questions to one of the following email addresses, or correspond
by fax, BBS, or regular mail with Customer Service in Lucent’s U.S. offices in Alameda, CA:
• Email from within the U.S.—support@ascend.com
• Email from Europe, the Middle East, or Africa—EMEAsupport@ascend.com
• Email from the Asia-Pacific region—apac.support@ascend.com
• Fax—(510) 814-2312
• Customer Support BBS (by mo dem)—(510) 814-2302
• Write to Lucent at the following address:
(+33) 492 96 5672
(+33) 492 96 5674
(+33) 492 96 5673
(+33) 492 96 5676
(+81) 3 5325 7397
(+33) 492 96 5679
(+33) 492 96 5677
(+33) 492 96 5675
(+33) 492 96 5671
Attn: Customer Service
Lucent Technologies
1701 Harbor Bay Parkway
Alameda, CA 94502-3002
USA
iv 85x11 Book Template (Preliminary)
Page 5

Contents
Customer Service..................................................................................................................... iii
About This Guide............................................................................ xvii
What is in this guide.............................................................................................................. xvii
What you should know ......................................................................................................... xvii
Documentation conventions................................................................................................. xviii
Documentation set................................................................................................................... xix
Chapter 1 Performing Basic Configuration.................................................... 1-1
Introduction to basic configuration........................................................................................ 1-1
Connecting to a new unit ....................................................................................................... 1-3
New APX 8000 unit........................................................................................................ 1-3
New MAX TNT or DSLTNT unit.................................................................................. 1-3
Configuring the shelf-controller IP address on a nonredundant unit..................................... 1-4
Setting the system date........................................................................................................... 1-5
Setting the system name.........................................................................................................1-5
Setting the log level................................................................................................................ 1-5
Configuring a default gateway............................................................................................... 1-6
Configuring basic DNS information...................................................................................... 1-6
Pinging the TAOS unit from a local host............................................................................... 1-7
Recommended basic security measures................................................................................. 1-7
Changing the Admin password....................................................................................... 1-8
Securing the serial port................................................................................................... 1-8
Assigning a Telnet password.......................................................................................... 1-8
Requiring acceptance of the pool address....................................................................... 1-9
Ignoring ICMP redirects........................................................... ...... ..... ........................... 1-9
Disabling directed broadcasts......................................................................................... 1-9
Configuring SNMP access to the unit........................................................................... 1-10
Overview of SNMP security.................................................................................. 1-10
Enabling SNMP in the TAOS unit........................................................................ 1-11
Setting community strings..................................................................................... 1-11
Setting up address security.................................................................................... 1-11
Where to go next.................................................................................................................. 1-12
Chapter 2 Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy
(APX 8000)....................................................................................... 2-1
Overview of redundancy operations...................................................................................... 2-1
Shelf-controller startup and primary election................................................................. 2-1
Normal operation............................................................................................................ 2-2
Controller switchover ..................................................................................................... 2-3
Log messages.................................................................................................................. 2-3
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide v
Page 6

Contents
Configuring the APX 8000 for shelf-controller redundancy................................................. 2-3
Assigning the system IP address..................................................................................... 2-4
Assigning an Ethernet IP address................................................................................... 2-4
Examples of setting shelf-controller Ethernet IP address........................................ 2-4
Defining the soft IP interface for fault tolerance............................................................ 2-5
Example of setting the soft IP address..................................................................... 2-5
Configuring shelf-controller redundancy........................................................................ 2-6
Physical interface profiles ....................................................................................... 2-6
Redundancy profile.................................................................................................. 2-6
Switching the primary controller at the command-line interface ................................... 2-8
Resetting shelf controllers and clearing controller NVRAM......................................... 2-8
Resetting the controllers.......................................................................................... 2-8
Clearing NVRAM............................................................................... ...... ............... 2-9
Obtaining status information about redundant shelf controllers............................................ 2-9
Viewing controller up time............................................................................................. 2-9
Viewing controller status............................................................................................ .. 2-10
Setting up a trap to monitor the secondary controller................................................... 2-11
Clearing the fatal-error history log ............................................................................. .. 2-11
Chapter 3 Configuring the Thermal Profile for Fan
Tray Operations (APX 8000) ........................................................... 3-1
Overview of the Thermal profile for fan tray operations....................................................... 3-1
Example of configuring thermal controls....................................................................... 3-2
Related log messages...................................................................................................... 3-3
Thermal alarms............................................................................................................... 3-3
Thermal status reporting........................................................................................................3-4
Fanstatus command......................................................................................................... 3-4
Thermalstatus command................................................................................................. 3-5
Chapter 4 Configuring Ethernet Cards........................................................... 4-1
Introduction to Ethernet slot cards......................................................................................... 4-1
Full-duplex 10/100Mbps Ethernet-2 slot card................................................................ 4-1
Full-duplex 10/100Mbps Ethernet-3 slot card................................................................ 4-1
Upgrading to the Ethernet-2 and Ethernet-3 slot cards................................................... 4-2
Overview of Ethernet configuration ...................................................................................... 4-2
Understanding the Ethernet-related profiles.......................................................................... 4-2
Ethernet profile............................................................................................................... 4-2
IP-Interface profile........................................................................................... ............... 4-3
Configuring duplex mode on the 100Mbps Ethernet port..................................................... 4-3
Chapter 5 Configuring Series56 II and
III Modem and Hybrid Access Cards
.......................................................................................................... 5-1
Overview of configuring modem cards................................................................................. 5-1
Specifying modem negotiation settings................................................................................. 5-2
Specifying modem modulation for Series56 II and III modem cards.................................... 5-3
Configuring an additional AT answer string for modem calls............................................... 5-3
Series56 II and III Call-Route profiles................................................................................... 5-4
Preventing Series56 II and III cards from delaying Frame Relay connections ..................... 5-5
Hybrid Access card implementation...................................................................................... 5-5
vi APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 7

Chapter 6 Configuring MultiDSP Cards
(MAX TNT, APX 8000)...................................................................... 6-1
Introduction to MultiDSP....................................................................... ..... ........................... 6-1
48-port MultiDSP card.................................................................................................... 6-2
96-port MultiDSP card.................................................................................................... 6-2
Card configuration constraints........................................................................................ 6-3
Using 48-port and 96-port MultiDSP cards............................................................. 6-3
Using Series56 cards with MultiDSP cards............................................................. 6-3
Supported MultiDSP services................................................................................................ 6-3
Data................................................................................................................................. 6-3
V.110............................................................................................................................... 6-3
PHS................................................................................................................................. 6-4
Voice over IP (VoIP)...................................................................................................... 6-4
Obtaining status information about a MultiDSP card.................................................. ...... .... 6-5
Displaying information about all installed cards............................................................ 6-5
Displaying information about an installed MultiDSP card............................................. 6-5
Verifying that installed software and software versions are correct............................... 6-6
Configuring a MultiDSP card................................................................................................ 6-6
Verifying that MultiDSP services are enabled ............................................................... 6-7
Verifying call routes for MultiDSP services................................................................... 6-8
Viewing the Call-Route profile and its Call-Route-Type parameter....................... 6-8
Viewing call-routing database entries ................................................................... 6-10
Verifying that configurations are correct for related services ...................................... 6-10
Adding an additional MultiDSP service....................................................................... 6-10
Contents
Chapter 7 Configuring T1 Cards..................................................................... 7-1
Introduction to T1 ..................................... ....................................... ...................................... 7-2
ISDN PRI........................................................................................................................7-2
Nailed or unchannelized T1............................................................................................ 7-2
Channelized line-side vs. trunk-side T1 ......................................................................... 7-2
Overview of T1 configuration................................................................................................ 7-3
Making a profile the working profile..................................................................................... 7-6
Assigning names to T1 line profiles ...................................................................................... 7-7
Enabling a line ..................................................... ...... ..... ........................................ ............... 7-8
Specifying the framing and encoding.................................................................................... 7-8
Configuring ISDN PRI signaling........................................................................................... 7-8
Configuring ISDN network-side emulation........................................................................... 7-9
Configuring overlap receiving on PRI lines .......................................................................... 7-9
Configuring inband robbed-bit signaling............................................................................. 7-11
Configuring NFAS .............................................................................................................. 7-13
Configuring a single NFAS group ................................................................................ 7-13
Configuring multiple NFAS groups ............................................................................. 7-13
Configuring ISDN NFAS for Japanese switch types.................................................... 7-15
Configuring T1 R1 and R1-Modified (Taiwan) with ANI and called-number processing . 7-15
Configuring clocking........................................................................................................... 7-17
Configuring the front-end transceiver.................................................................................. 7-17
Configuring channel usage................................................................................................... 7-18
Assigning telephone numbers to switched channels.................................................... ...... .. 7-19
Configuring trunk groups..................................................................................................... 7-20
Configuring nailed channels................................................................................................ 7-21
Configuring a back-to-back T1 connection ......................................................................... 7-21
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide vii
Page 8

Contents
Specifying analog encoding for TAOS unit codecs............................................................. 7-22
Configuring specialized options........................................................................................... 7-22
Sample T1 configuration...................................................................................................... 7-23
Default Call-Route profiles........................................ ..... ...... ....................................... ........ 7-24
Chapter 8 Configuring T1 FrameLine Cards
(MAX TNT, DSLTNT)........................................................................ 8-1
Introduction to T1 FrameLine.......................................................... ...................................... 8-1
Overview of supported features............................................................................................. 8-1
PPP.................................................................................................................................. 8-1
Frame Relay............................................ ........................................ ..... ........................... 8-2
Routing protocols............................................................................................................ 8-2
RADIUS..........................................................................................................................8-2
SNMP.............................................................................................................................. 8-2
Overview of T1 FrameLine configuration............................................................................. 8-2
Configuring the clock source................................................................................................. 8-3
Chapter 9 Configuring E1 Cards..................................................................... 9-1
Introduction to E1 ..................................... ....................................... ...................................... 9-2
ISDN Primary Rate Interface (PRI)................................................................................ 9-2
Nailed or unchannelized E1............................................................................................ 9-2
Overview of E1 configuration................................................................................................ 9-2
Understanding configuration requirements............................................................................ 9-4
Making a profile the working profile..................................................................................... 9-5
Assigning names to E1 line profiles ...................................................................................... 9-6
Enabling a line ..................................................... ...... ..... ........................................ ............... 9-7
Configuring a back-to-back connection................................................................................. 9-7
Specifying the framing........................................................................................................... 9-7
Specifying E1 signaling.........................................................................................................9-8
Configuring ISDN PRI signaling........................................................................................... 9-8
Configuring ISDN network-side emulation........................................................................... 9-9
Configuring E1 R1 signaling............................................................................................... 9-10
Configuring E1 R2 signaling............................................................................................... 9-10
Configuring DPNSS signaling............................................................................................. 9-12
Configuring overlap receiving on PRI lines........................................................................ 9-13
Configuring clocking........................................................................................................... 9-13
Configuring the front-end E1 transceiver ............................................................................ 9-13
Configuring channel usage................................................................................................... 9-14
Assigning telephone numbers to switched channels.................................................... ...... .. 9-14
Configuring trunk groups..................................................................................................... 9-14
Configuring nailed channels................................................................................................ 9-15
Specifying analog encoding for TAOS unit codecs............................................................. 9-16
Default Call-Route profiles........................................ ..... ...... ....................................... ........ 9-16
Chapter 10 Configuring E1 FrameLine Cards
(MAX TNT, DSLTNT)...................................................................... 10-1
Introduction to E1 FrameLine.......................................................... .................................... 10-1
Overview of supported features........................................................................................... 10-1
PPP................................................................................................................................ 10-2
Frame Relay............................................ ........................................ .............................. 10-2
viii APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 9

Contents
Routing protocols.......................................................................................................... 10-2
RADIUS........................................................................................................................ 10-2
SNMP............................................................................................................................ 10-2
Overview of E1 FrameLine configuration........................................................................... 10-2
Example E1 FrameLine configuration.......................................................................... 10-3
Administrative profiles for E1 FrameLine........................................................................... 10-4
Admin-State profile ............................................................................. ......................... 10-5
Device-State profile...................................................................................................... 10-5
Administrative commands and status information............................................................... 10-5
Configuring the clock source............................................................................................... 10-6
Chapter 11 Configuring T3 Cards.................................................................... 11-1
Introduction to T3 ..................................... ....................................... .................................... 11-1
Overview of T3 configuration.............................................................................................. 11-1
Understanding T3 configuration requirements.................................................................... 11-2
Understanding T3 slot card profiles..................................................................................... 11-3
T3 profile ...................................................................................................................... 11-3
Call-Route profile......................................................................................................... 11-3
T1 profiles..................................................................................................................... 11-4
Assigning a name to a T3 profile......................................................................................... 11-4
Enabling a line ..................................................... ...... ..... ........................................ ............. 11-5
Configuring the T3 physical link......................................................................................... 11-5
Configuring clocking........................................................................................................... 11-5
Chapter 12 Configuring Serial WAN (SWAN) Cards
(MAX TNT, DSLTNT)...................................................................... 12-1
Introduction to SWAN.................................................... ........................................ ............. 12-1
Overview of SWAN configuration...................................................................................... 12-1
Understanding SWAN card configuration requirements..................................................... 12-2
Making a profile the working profile................................................................................... 12-3
Assigning a name to a SWAN profile.................................................................................. 12-4
Enabling a line ..................................................... ...... ..... ........................................ ............. 12-4
Specifying a nailed group .................................................................................................... 12-4
Specifying the SWAN internal clock speed......................................................................... 12-5
Frame Relay configuration................................... ....................................... ......................... 12-6
Chapter 13 Configuring Unchannelized DS3 Cards
(MAX TNT, DSLTNT)...................................................................... 13-1
Introduction to unchannelized DS3...................................................................................... 13-1
Supported features................................................................................................................ 13-1
Overview of unchannelized DS3 configuration................................................................... 13-2
Using the UDS3 profile........................................................................................................ 13-2
Configuring the UDS3 physical link................................................ .................................... 13-2
Chapter 14 Configuring DS3-ATM Cards........................................................ 14-1
Introduction DS3-ATM.................................. ........................................ .............................. 14-1
Overview of DS3-ATM settings.......................................................................................... 14-1
Examples of DS3-ATM configurations............................................................................... 14-3
Configuring redundant cards ........................................................................................ 14-3
Looping back the line ................................................................................................... 14-4
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide ix
Page 10

Contents
Chapter 15 Configuring OC3-ATM Cards
(MAX TNT/DSLTNT)....................................................................... 15-1
Introduction to OC3-ATM.............................................. ...... ....................................... ........ 15-1
Overview of OC3-ATM settings.......................................................................................... 15-1
Using OC3-ATM ports as a clock source............................................................................ 15-3
Example of an OC3-ATM configuration............................................................................. 15-4
Chapter 16 Configuring STM-0 Cards............................................................. 16-1
Introduction to STM-0........................ ........................................ ..... .................................... 16-1
Using STM and T1 profiles ................................................................................................. 16-2
Sample STM-0 configurations............................................................................................. 16-2
Example of configuring an STM profile....................................................................... 16-2
Example of configuring a T1 data trunk....................................................................... 16-3
Chapter 17 Configuring DSL Connections
(DSLTNT)........................................................................................ 17-1
Introduction to DSL technologies........................................................................................ 17-1
IDSL overview.............................................................................................................. 17-1
ADSL overview............................................................................................................ 17-2
SDSL overview............................................................................................................. 17-3
DSL configuration................................................................................................................ 17-4
Configuring switched connections....................................................................................... 17-4
Configuring nailed connections........................................................................................... 17-5
Configuring data transfer rates............................................................................................. 17-6
Configuring data transfer rates for ADSL lines............................................................ 17-6
Configuring data transfer rates for SDSL lines ............................................................ 17-7
Configuring per-session data transfer rates .................................................................. 17-8
Configuring per-session data rates using modem rate control .............................. 17-9
Configuring per-session data rate limits.............................................................. 17-10
Sample log session showing rate control negotiation.......................................... 17-10
Configuring DSLPipe Plug and Play................................................................................. 17-12
How Plug and Play works........................................................................................... 17-12
DHCP server requirements......................................................................................... 17-13
TFTP server requirements .......................................................................................... 17-14
DSLPipe default configuration................................................................................... 17-14
Configuring the DSLTNT........................................................................................... 17-15
Configuring BOOTP Relay................................................................................. 17-15
Configuring the SDSL profile............................................................................. 17-15
Configuring a Frame Relay profile...................................................................... 17-16
Configuring a Connection profile........................................................................ 17-17
Configuring IDSL voice connections ................................................................................ 17-17
Incoming calls............................................................................................................. 17-18
Outgoing calls............................................................................................................. 17-18
Configuring the DSLTNT........................................................................................... 17-18
Configuring the IDSL profile........................... ........................................ ........... 17-18
Configuring a Connection profile for the remote device..................................... 17-19
Configuring trunk groups.................................................................................... 17-20
Configuring the Pipeline............................................................................................. 17-21
Configuring the Configure profile....................................................................... 17-21
Sample DSL configurations............................................................................................... 17-22
x APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 11

Contents
Sample Frame Relay IDSL configuration .................................................................. 17-22
Configuring the DSLTNT ................................................................................... 17-23
Configuring the Pipeline...................................................................................... 17-25
Sample ADSL nailed PPP connection........................................................................ 17-26
Configuring the ADSL profile............................................................................. 17-27
Configuring the Connection profile......................................... ..... ...... ................. 17-27
Configuring the DSLPipe.................................................................................... 17-28
Sample SDSL Frame Relay configuration using numbered interfaces ...................... 17-29
Configuring the Connection profile......................................... ............................ 17-30
Configuring the IP-Route profile......................................................................... 17-31
Configuring the SDSL profile............................................................................. 17-32
Configuring the Frame-Relay profile.................................................................. 17-32
Configuring the DSLPipe-S................................................................................. 17-33
Sample SDSL Frame Relay configuration using system-based routing..................... 17-34
Configuring the Connection profile......................................... ............................ 17-34
Configuring the SDSL profile............................................................................. 17-36
Configuring the Frame-Relay profile.................................................................. 17-36
Configuring the DSLPipe-S................................................................................. 17-36
Chapter 18 Signaling System 7 (SS7)............................................................. 18-1
Introduction to SS7......................................................... ........................................ ..... ...... .. 18-1
System requirements for SS7 operations............................................................................. 18-2
TAOS unit as terminator of data calls in an SS7 network............................................ 18-2
TAOS unit as terminator of voice and data calls in an SS7 network............................ 18-3
Interface between a signaling gateway and TAOS unit................................................ 18-4
Incoming calls............................................................................................................... 18-4
Continuity tests............................................................................................................. 18-4
Configuring an SS7 signaling gateway................................................................................ 18-4
Specifying the SS7 control protocol............................................................................. 18-6
Configuring transport-layer options.............................................................................. 18-6
System IP address considerations................................................................................. 18-7
Example of a basic configuration................................................................................. 18-8
T1 lines as SS7 data trunks........................................................................................... 18-8
Example of configuring a T3 card for SS7 data.................................................... 18-9
Example of configuring a T1 data trunk................................................................ 18-9
E1 lines as SS7 data trunks......................................................................................... 18-10
V.110 bearer capability for SS7 calls using IPDC...................................................... 18-11
SS7 link establishment timer ...................................................................................... 18-11
Two-wire continuity check on T1 and E1 lines.......................................................... 18-11
Outgoing continuity tests on T1 and T3..................................................................... 18-13
Digital milliwatt tone support on T1 and T3 .............................................................. 18-13
Analog milliwatt tone and variable tone support........................................................ 18-13
Reporting VoIP call statistics ..................................................................................... 18-14
When the unit reports VoIP statistics.................................................................. 18-14
ss7nmi debug-level command............................................................................. 18-15
Statistics and error reporting on SS7 connections ...................................................... 18-15
Command output when no errors are detected.................................................... 18-15
Command output showing errors ........................................................................ 18-18
Cause codes for SS7 ASGCP calls to the TAOS unit........................................................ 18-19
SS7 IPDC support for call ID and disconnect cause codes ........................................ 18-20
IPDC generation of a globally unique call ID..................................................... 18-20
Global-Call-ID parameter.................................................................................... 18-20
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide xi
Page 12

Contents
Start and Stop records.......................................................................................... 18-21
Disconnect cause codes ................................................................ ....................... 18-21
SNMP support for SS7....................................................................................................... 18-23
Chapter 19 Configuring Call Routing ............................................................. 19-1
Network, host, and dual-purpose devices ............................. ...... ....................................... .. 19-1
Understanding the call-routing database.............................................................................. 19-2
How call routes affect device usage ............................................................................. 19-3
Modem usage and database sort order.......................................................................... 19-3
HDLC channel usage and database sort order.............................................................. 19-4
Trunk line usage and sort order .................................................................................... 19-5
Working with Call-Route profiles........................................................................................ 19-5
Call-Route profile settings............................................................................................ 19-5
Outbound call routing by trunk group .......................................................................... 19-6
Multilink Frame Relay requirements with Hybrid Access........................................... 19-7
Example with two E1 lines in an MFR bundle...................................................... 19-7
Example with six E1 lines in an MFR bundle....................................................... 19-8
Concentrating multilink calls on one Hybrid Access card ........................................... 19-8
Dedicating Series56 cards to modem processing ......................................................... 19-9
Enabling Series56 cards to handle HDLC processing.................................................. 19-9
Another way to route incoming calls (deprecated).............................................................. 19-9
Call routing algorithms ........................................ ...... ....................................... ...... ........... 19-10
Localization of call routes within a quadrant.............................................................. 19-10
How the system finds a route...................................................................................... 19-11
Details of how a route is chosen................................................................................. 19-12
First pass: trunk group number.......................................... .................................. 19-12
Second pass: ISDN subaddresses........................................................................ 19-12
Third pass: telephone numbers............................................................................ 19-12
Fourth pass: destination device addresses........................................................... 19-13
Fifth pass: source device addresses..................................................................... 19-13
Last pass: comparison routing type..................................................................... 19-13
Appendix A Provisioning the Switch................................................................. A-1
Provisioning the switch for T1 access................................................................................... A-1
What you need from your T1 service provider..................................................................... A-2
What you need from your E1 service provider..................................................................... A-2
Index.......................................................................................... Index-1
xii APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 13

Figures
Figure 13-1 Example of unchannelized DS3 slot card application..................................... 13-1
Figure 14-1 DS3-ATM interface to ATM network............................................................. 14-1
Figure 15-1 OC3-ATM interface to ATM network............................................................. 15-1
Figure 16-1 Example STM-0 configuration........................................................................ 16-1
Figure 17-1 DSLPipe unit obtaining its configuration (Plug and Play)............................ 17-13
Figure 17-2 Incoming and outgoing voice calls................................................................ 17-18
Figure 17-3 IDSL connection with a Pipeline................................................................... 17-22
Figure 17-4 Sample ADSL PPP connection...................................................................... 17-26
Figure 17-5 Example SDSL setup with interface-based routing....................................... 17-30
Figure 17-6 Example SDSL setup with system-based routing.......................................... 17-34
Figure 18-1 TAOS terminating data calls in an SS7 network............................................. 18-2
Figure 18-2 TAOS unit terminating voice and data calls in an SS7 network...................... 18-3
Figure 19-1 Trunk group 8 connecting to a TAOS unit ...................................................... 19-6
Figure 19-2 Matching call information to a database entry............................................... 19-11
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide xiii
Page 14

Page 15

Tables
Table 1-1 Basic TAOS unit configuration tasks ................................................................ 1-2
Table 5-1 Modem configuration tasks ............................................................................... 5-2
Table 7-1 T1 line configuration tasks ................................................................................ 7-3
Table 9-1 E1 line configuration tasks ................................................................................ 9-2
Table 11-1 T3 line configuration tasks .............................................................................. 11-2
Table 11-2 Differences between T3 card configuration and T1 card configuration.......... 11-2
Table 12-1 SWAN-card configuration tasks...................................................................... 12-2
Table 12-2 SWAN card configuration............................................................................... 12-2
Table 13-1 Unchannelized DS3 line configuration tasks................................................... 13-2
Table 17-1 DSL data rate configuration parameters.......................................................... 17-6
Table 18-1 Signaling gateway platforms and protocol support ........................................ 18-1
Table 19-1 Fields in a call-routing database entry............................................................ 19-2
Table A-1 T1 access provisioning information.................................................................. A-1
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide xv
Page 16

Page 17

About This Guide
What is in this guide
This guide provides the following instructions for an APX 8000™, MAX TNT®, or
DSLTNT™
• Basic confi guration of your unit
• Configuring shelf controller redundancy (APX 8000 only)
• Configuring Ethernet and modem cards
• Configuring T1, E1, DS3, and other network slot cards
• Configuring the unit in a Signaling System 7 (SS7) network
• Configuring call routing
• Provisioning the switch
Note: This manual describes the f ull set of f eatures fo r APX 8000, MAX TNT, and DSLTNT
!
units running True Access™ Operating System (TAOS) software version 8.0.2 or later. Some
features might not be available with earlier versions or specialty loads of the software.
This manual hereafter refers to your product as a TAO S unit except when referring to features
specific to a particular unit.
multiservice access concentrator:
!
Warning: Before installing your TAOS u nit, be sure to read the safety instructions in the
Access Networks Safety and Compliance Guide. For information specific to your unit, see the
“Safety-Related Electrical, Physical, and Environmental Information” appendix in your unit’s
hardware installation guide.
What you should know
This guide is for the person who installs, configures, and maintains a TAOS unit. T o co nfigure
a unit, you need to understand the following:
• Wide Area Network (WAN) concepts
• Local Area Network (LAN) concepts
• Dial-in LAN connections such as Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and Multilink PPP (MP)
• Connection cost management and accounting
• Modems
• Frame Relay
• Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
• IP routing
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide xvii
Page 18

Documentation conventions
• Network security
Documentation conventions
Following are all the special characters and typographical conventions used in this manual:
Convention Meaning
Monospace text Represents text that appears on your computer’s screen, or that could
appear on your computer’s screen.
Boldface monospace text
Italics Represent variable information. Do not enter the words themselves in
[ ] Square brackets indicate an optional argument you might add to a
| Separates command choices that are mutually exclusive.
> Points to the next level in the path to a parameter or menu item. The
Key1-Key2 Represents a combination keystroke. To enter a combination key-
Press Enter Means press the Enter, or Return, key or its equivalent on your com-
Note:
Represents characters that you enter exactly as shown (unless the characters are also in italics—see Italics, below). If you could enter
the characters but are not specifically instructed to, they do not appear
in boldface.
the command. Enter the information they represent. In ordinary text,
italics are used for titles of publications, for some terms that would
otherwise be in quotation marks, and to show emphasis.
command. To include such an argument, type only the information
inside the brackets. Do not type the brackets unless they appear in bold
type.
item that follows the angle bracket is one of the options that appears
when you select the item that precedes the angle bracket.
stroke, press the first key and hold it down while you press one or
more other keys. Release all the keys at the same time. (For example,
Ctrl-H means hold down the Control key and press the H key.)
puter.
Introduces important additional information.
!
Caution:
!
Warning:
Warning:
xviii APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
W arns that a failure to follow the recom mended procedur e could result
in loss of data or damage to equipment.
Warns that a failure to take appropriate safety precautions could resu lt
in physical injury.
Warns of danger of electric shock.
Page 19

Documentation set
The APX 8000/MAX TNT/D SLTNT documentation set consists of the following manuals.
• Read me first:
– Access Networks Safety and Compliance Guide
Contains important safety instructions and country-specific compliance information
that you must read before installing a TAOS unit.
– TAOS Command-Line Interface Guide
Introduces the TAOS command-line environment and shows how to use the
command-line interface effectively. This manual describes keyboard shortcuts and
introduces commands, security levels, profile structure, and parameter types.
• Installation and basic configuration:
– APX 8000 Hardware Inst allation Gui de
Shows how to install APX 8000 hardware and includes APX 8000 technical
specifications.
– MAX TNT/DSLTNT Hardware Installation Guide
Shows how to install MAX TNT and DSLTNT hardware and includes technical
specifications for these units.
Documentation set
– APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide (this guide)
Shows how to configure the cards installed in a TAOS unit and their line attributes for
such functions as framing, signaling, and channel usage. It also describes how calls
are routed through the system and includes information about configuring the unit in a
Signaling System 7 (SS7) environment. This guide explains shelf controller
redundancy for an APX 8000 unit.
• Configuration:
– APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT ATM Configuration Guide
Describes how to configure Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) operations on a
T AOS unit. This guide explains how to configure physical layer attributes and how to
create permanent virtual circuit (PVC) and switched virtual circuit (SVC) ATM
interfaces. It includes information about ATM direct and ATM-Frame Relay circuits.
– APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Frame Relay Configuration Guide
Describes how to configure Frame Relay operations on a TAOS unit. This guide
explains physical layer configuration and restrictions and how to create permanent
virtual circuit (PVC) and switched virtual circuit (SVC) interfaces. It includes
information about Multilink Frame Relay (MFR) and link management, as well as
Frame Relay and Frame Relay direct circuits.
– APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT WAN, Routing, and Tunneling Configuration Guide
Shows how to configure LAN and WAN routing for analog and digital dial-in
connections on a TAOS unit. This guide includes information about IP routing, Open
Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing, Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
routing, multiprotocol routers, Virtual Routers (VRouters), and tunneling protocols.
– MultiVo ice™ for MAX TNT Configuration Guide
Shows how to configure the MultiVoice applicatio n to run on a MAX TNT unit in
both Signaling System 7 (SS7) and H.323 Voice over IP (VoIP) configurations.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide xix
Page 20

Documentation set
• RADIUS: TAOS RADIUS Guide and Reference
Describes how to set up a TAOS unit to use the Remote Authentication Dial-In User
Service (RADIUS) server and contains a complete reference to RADIUS attributes.
• Administration and troubleshooting: APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Administration
Guide
Describes how to administer a TAOS unit, including how to monitor the system and cards,
troubleshoot the unit, and configure the unit to use the Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP).
• Reference:
– APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Reference
An alphabetic reference to all commands, profiles, and parameters supported on
TAOS units.
– T AOS Glossary
Defines terms used in documentation for TAOS units.
xx APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 21

Performing Basic Configuration
Introduction to basic configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Connecting to a new unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Configuring the shelf-controller IP address on a nonredundant unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Setting the system date. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Setting the system name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Setting the log level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Configuring a default gateway. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Configuring basic DNS information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Pinging the TAOS unit from a local host. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Recommended basic security measures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Where to go next . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-12
1
Introduction to basic configuration
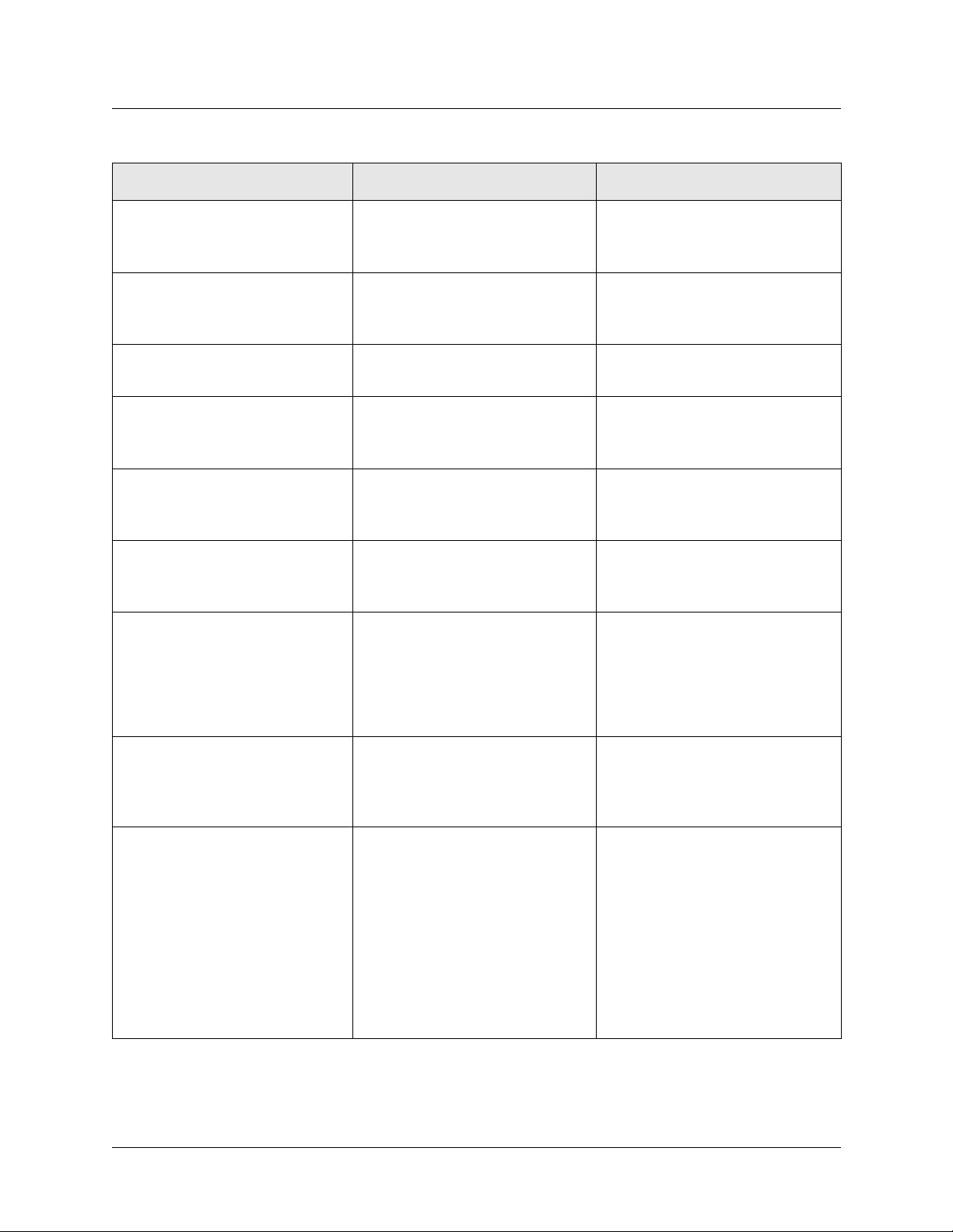
Table 1-1 lists the sections describing the tasks you must perform for the TAOS unit basic
configuration. The table includes a brief description of each task and lists the commands and
parameters you will use.
For information about more advanced configuration of your TAOS unit, see the following
configuration guide:
• APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT ATM Configuration Guide
• APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Frame Relay Configuration Guide
• APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT WAN, Routing, and Tunneling Configuration Guide
For information about commands, profiles, and parameters, see the
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Reference manual.
.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 1-1
Page 22
Performing Basic Configuration
Introduction to basic configuration
Table 1-1. Basic TAOS unit configuration tasks
Section Description of task Related commands or parameters
“Connecting to a new unit” on
page 1-3
“Configuring the shelf-cont roller IP
address on a nonredundant unit” on
page 1-4
“Setting the system date” on
page 1-5
“Setting the system name” on
page 1-5
“Setting the log level” on page 1-5 Specify the level of event
“Configuring a default gateway” on
page 1-6
“Configuring basic DNS
information” on page 1-6
Connect the TAOS unit to a
terminal or workstation and an
Ethernet network.
Specify the date and time for the
TAOS unit system clock.
Set the correct date and time with
the Date command.
Specify the name of the TAOS unit.
This name is used for
authentication.
information that the TAOS unit
displays at the console.
Designate a default gateway so that
the T AOS unit can forward packets
for which it has no route.
Specify a Domain Name System
(DNS) server so that you can use
names instead of IP addresses to
reach IP hosts.
admin> set ip-address
admin> date ymmddhhmm
System profile > Name
Log profile > Save-level
IP-Route > gateway-address
IP-global profile > Domain-name
IP-global profile >
DNS-primary-server
IP-global profile >
DNS-secondary-server
“Pinging the TAOS unit from a
local host” on page 1-7
“Recommended basic security
measures” on page 1-7
1-2 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
After configuring the TAOS unit
with its basic settings, you can use
Ping to verify that it is
communicating on the network.
Before making the TAOS unit
accessible to users, Lucent
recommends that you configure
some basic security on the unit.
Ping
User > Password
Serial > A uto-Logout
Serial > User
IP-global profile >
Must-Accept-Address-Assign
IP-global profile>
Ignore-ICMP-Redirects
SNMP profile
Page 23

Connecting to a new unit
To communicate with a new TAOS unit, you must assign an IP address to the shelf controller.
Once this is done, you can perform further configuration over a LAN using Telnet.
Use the following procedures to connect a new TAOS unit, if you have not already done so,
and assign an Ethernet IP address.
New APX 8000 unit
Use the following procedure to initially set up an APX 8000 unit:
1 Connect a PC terminal or workstation to the serial port on the shelf controller (s ee the APX
8000 Hardware Installation Guide). If the APX 8000 is equipped with redundant shelf
controllers, connect to the serial port on the primary controller.
2 Connect an Ethernet cable between the network and the Ethernet port on the shelf
controller (see the APX 8000 Hardware Installation Guide). If the APX 8000 is equipped
with redundant shelf controllers, connect to the Ethernet port on the primary controller.
3 Configure an IP address and network mask in the ip-interface profile.
Performing Basic Configuration
Connecting to a new unit
– For an APX 8000 unit with one shelf controller, see “Configuring the shelf-controller
IP address on a nonredundant unit” on page 1-4.
– For an APX 8000 unit with redundant shelf controllers, see “Assigning an Et hernet IP
address” on page 2-4.
4 Verify that the connection and IP address are correct by pinging any device on the
network.
5 If redundant controllers are used, set the secondary and soft IP addresses (see “Assigning
an Ethernet IP address” on page 2-4 and “Defining the soft IP interface for fault toler ance”
on page 2-5 for details).
6 Exit the terminal or workstation.
7 T e lnet fro m a workstat ion on t he LAN. The syst em will pro mpt you for the usernam e and
password.
User: admin
Password: Ascend
8 Complete the configuration.
New MAX TNT or DSLT NT unit
Use the following procedure to initially set up a MAX TNT or DSLTNT unit:
1 Connect a PC terminal or workstation to the serial port on the shelf controller (see the
MAX TNT/DSLTNT Hardware Installation Guide). Ensure that the speed is set to
9600 bps.
2 Connect an Ethernet cable to the network and to the Ethernet port on the shelf controller
(see the MAX TNT/DSLTNT Hardware Installation Guide).
3 Configure an IP address and network mask in the ip-interface profile (see
“Configuring the shelf-controller IP address on a nonredundant unit” on page 1-4).
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 1-3
Page 24

Performing Basic Configuration
Configuring the shelf-controller IP address on a nonredundant unit
4 Verify that the connection and the IP address are correct by pinging any device on the
network.
admin> ping 10.10.10.1
64 bytes from 10.10.10.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=0 ms
5 Exit the terminal or workstation.
6 Telnet to the MAX TNT or DSLTNT using a workstation on the LAN. The system will
prompt you for a username and passwor d.
User: admin
Password: Ascend
7 Complete the configuration.
Configuring the shelf-controller IP address on a
nonredundant unit
See “Assigning an Ethernet IP address” on page 2-4 for details about IP address configuration
for an APX 8000 unit with redundant shelf controllers.
All TAOS units have an Ethernet port on the shelf cont roller. This Ethernet port is designed for
out-of-band management and light traffic loads. It is not intended to be the primary Ethernet
interface for the system. If your unit will be routing heavy Ethernet traffic, use an Ethernet
card.
T o assign an IP address to the Ethernet interface of the shelf controller on a nonr edundant APX
8000 or a MAX TNT or DSLTNT, use the R ead and Li st commands to display the control ler’s
IP-Interface profile, then set the IP-Address parameter. For example:
admin> read ip-interface {{1 controller 1 } 0 }
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 controller 1 } 0 } read
admin> list
interface-address* = { { shelf-1 controller 1 } 0 }
ip-address = 0.0.0.0/0
2nd-ip-address = 0.0.0.0/0
rip-mode = routing-off
..
..
admin> set ip-address = 10.2.3.4/24
admin> write
After you assign the unit’s hostname and IP address, you might need to modify the host
information on your local Domain Name System (DNS) server to include the TAOS unit.
1-4 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 25

Setting the system date
If the system date displayed on your screen is incorrect, set the correct date and time with the
Date command. For example, to set the date and time to October 22, 2000, 8:50 in the
morning:
admin> date 0010220850
The format for setting the date and time is ymmddhhmm. Enter the hour in military (24-hour)
time.
Setting the system name
You can assign the TAOS unit a system name of up to 24 characters. Because the system name
is used for authenticating connections, keep it relatively simple and use only standard
characters.
Here is an example of how to set the TAOS unit system name:
Performing Basic Configuration
Setting the system date
admin> read system
SYSTEM read
admin> list
name = ""
system-rmt-mgmt = no
use-trunk-groups = no
idle-logout = 0
parallel-dialing = 5
single-file-incoming = yes
admin> set name = apx01
admin> write
Setting the log level
While you are configuring the TAOS unit, you might want to increase the log level to display
messages that can help you debug configuration settings. First display the current settings, then
enter a new log level.
To display the system-wide event-logging parameters, use the Read and List commands:
admin> read log
LOG read
admin> list
save-level = info
save-number = 100
syslog-enabled = no
host = 0.0.0.0
facility = local0
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 1-5
Page 26

Performing Basic Configuration
Configuring a default gateway
To change the log level, specify an option for the Save-Level parameter:
admin> set save-level = [none|emergency|alert|critical|error|warning|notice|info|debug]
admin> write
If your local network supports a Syslog server, you can configure the server’s IP address and
the Syslog facility number by setting the Host and Facility parameters in this profile.
Configuring a default gateway
If the TAOS unit does not have a route for the destination address of a packet, it forwards the
packet to the default router. Most sites use the default router (such as a GRF® router or a
UNIX host running the route daemon ) to dist ri b ute routi n g tas ks among devices. If you do not
configure a default route, the TAOS unit drops packets for which it has no route.
You configure the default route in the IP-Route profile. The name of the default IP-Route
profile is always Default, and its destination is always 0.0.0.0.
To configure the default route, first use the Read and List commands to display the default
IP-Route profile, and then set the Gateway-Address parameter. For example:
admin> read ip-route default
IP-ROUTE/default read
admin> list
name* = default
dest-address = 0.0.0.0/0
gateway-address = 0.0.0.0
metric =1
cost =1
preference = 100
third-party = no
ase-type = type-1
ase-tag = c0:00:00:00
private-route = no
active-route = no
admin> set gateway-address = 10.2.3.17
admin> set active-route=yes
admin> write
IP-ROUTE/default written
Configuring basic DNS information
The example in this section uses the domain name abc.com and sets the IP address of the
primary Domain Name System (DNS) server on the local network. Setting this basic
information enables you to access IP hosts by name instead of by IP address.
Here is an example that shows how to configure the DNS information:
admin> read ip-global
IP-GLOBAL read
admin> list
1-6 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 27

Performing Basic Configuration
Pinging the TAOS unit from a local host
domain-name = ""
dns-primary-server = 0.0.0.0
dns-secondary-server = 0.0.0.0
netbios-primary-ns = 0.0.0.0
netbios-secondary-ns = 0.0.0.0
must-accept-address-assign = no
pool-base-address = [ 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ]
..
..
admin> set domain-name = abc.com
admin> set dns-primary-server = 10.1.2.3
admin> set dns-secondary-server = 10.24.112.57
admin> write -f
Pinging the TAOS unit from a local host
After you configure the T AOS unit for IP network access, go to an IP host on the local network
and use the Ping command to verify that the unit can communicate on the network. For
example:
host-1% ping 10.2.3.4
In addition, you can verify that the TAOS unit is integrated into your DNS system. For
example:
host-1% ping apx01
Recommended basic security measures
The TAOS unit is shipped from the factory with all its security features set to defaults that
enable you to configure and set up the unit without any restrictions. Before you make the
TAOS unit generally accessible, you must change the default security settings to protect the
configured unit from unauthorized access.
Before bringing the TAOS unit online, Lucent recommends performing the following
important security measures:
•“Changing the Admin password” on page 1-8
•“Securing the serial port” on page 1-8
•“Assigning a Telnet password” on page 1-8
•“Requiring acceptance of the pool address” on page 1-9
•“Ignoring ICMP redirects” on page 1-9
•“Disabling directed broadcasts” on page 1-9
•“Configuring SNMP access to the unit” on page 1-10
For additional security measures, see the APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT WAN, Routing and
Tunneling Configuration Guide.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 1-7
Page 28

Performing Basic Configuration
Recommended basic security measures
Changing the Admin password
A user who knows the password to the Admin level can perform any operation on the
TAOS unit, including changing the configuration. The Admin password is set to Ascend by
default. Lucent recommends that you assign a secret password immediately to prevent
unauthorized users from gaining access to the unit by means of the default password.
Following is an example of changing the Admin password:
default> auth admin
Password: Ascend
admin> read user admin
USER/admin read
admin> set password = secret
admin>
USER/admin written
Note that the Allow-Password permission is set to No in the Admin login. Although this
setting protects the unit’s passwords, it also prevents the Save command from storing
passwords in a configuration file. To save passwords in a configuration file, you can set
Allow-Password to Yes in the Admin profile, or you can create another User profile for the
purpose of backing up the unit and set Allow-Password to Yes in that profile.
write
Securing the serial port
By default, when users connect to the serial po rt on the shelf cont roller, they are logged in with
the Admin User profile. To secure the serial port with a username and password, proceed as
follows:
1 Read the Serial profile:
admin> read serial { 1 17 2}
2 Set the User profile to null:
admin> set user =
3 Set Auto-Logout to Yes:
admin> set auto-logout = yes
This setting automatically logs out the current User profile if the Data Terminal Ready
signal (DTR) is lost on the serial port.
4 Write the profile:
admin> write
Now users connecting to the serial port must supply a valid us ername an d p assword for access
to the TAOS unit through the serial port.
Assigning a Telnet password
Lucent recommends that you assign a Telnet password, which can be up to 21 characters in
length, to prevent unauthorized Telnet sessions. A user who opens a Telnet session to the
TAOS unit is prompted to supply this password.
1-8 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 29

Following is an example of assigning a Telnet password:
admin> read ip-global
IP-GLOBAL read
admin> set telnet-password = SDwiw87
admin> write
IP-GLOBAL written
All users attempting to access the TAOS unit unit via Telnet are prompted for the Telnet
password. They are allowed three tries, each with a 60-second time limit, to enter the correct
password. If all three tries fail, the connection attempt times out.
Requiring acceptance of the pool address
During PPP negotiation, a caller can reject the IP address of fered by the TAOS unit and present
its own IP address for consideration. For security reasons, you might want to set the
Must-Accept-Address-Assign parameter to Yes to ensure that the TAOS unit terminates such a
call:
admin> read ip-global
IP-GLOBAL read
admin>
admin> write
IP-GLOBAL written
set must-accept-address-assign = yes
Performing Basic Configuration
Recommended basic security measures
If you enforce acceptance of the assigned address, the Answer-Defaults profile must enable
dynamic assignment, the caller’s configured profile must specify dy namic assignment, and the
caller’s PPP dial-in software must be configured to acquire its IP address dynamically. For
more details, see the APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT WAN, Routing and Tunneling
Configuration Guide.
Ignoring ICMP redirects
The Internet Message Control Protocol (ICMP) was d esigned to find the most ef ficient IP route
to a destination. ICMP redirect packets are one of the oldest route-discovery methods on the
Internet. They are also one of the least secure, because ICMP redirects can be counterfeited to
change the way a device routes packets. The following commands configure the TAOS unit to
ignore ICMP redirect packets:
admin> read ip-global
IP-GLOBAL read
admin>
admin> write
IP-GLOBAL written
set ignore-icmp-redirects = yes
Disabling directed broadcasts
Denial-of-service attacks known as “smurf” attacks typically use ICMP Echo Request packets
with a spoofed source address to direct packets to IP broadcast addresses. These attacks are
intended to degrade network performance, possibly to the point that the network becomes
unusable.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 1-9
Page 30

Performing Basic Configuration
Recommended basic security measures
To prevent the TAOS unit router from being used as an intermediary in this type of
denial-of-service attack laun ched from another network, you must dis able the TAOS unit from
forwarding the directed broadcasts it receives from another network. The following example
shows how to disable directed broadcasts that are not generated locally on all IP interfaces of a
TAOS unit with a four-port Ethernet card in shelf 1, slot 12:
admin> read ip-int {{1 c 1} 0}
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 controller 1 } 0 } read
admin> set directed-broadcast-allowed = no
admin> write
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 controller 1 } 0 } written
admin> read ip-int {{1 12 1} 0}
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 slot-12 1 } 0 } read
admin> set directed-broadcast-allowed = no
admin> write
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 slot-12 1 } 0 } written
admin> read ip-int {{1 12 2} 0}
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 slot-12 2 } 0 } read
admin> set directed-broadcast-allowed = no
admin> write
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 slot-12 2 } 0 } written
admin> read ip-int {{1 12 3} 0}
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 slot-12 3 } 0 } read
admin> set directed-broadcast-allowed = no
admin> write
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 slot-12 3 } 0 } written
admin> read ip-int {{1 12 4} 0}
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 slot-12 4 } 0 } read
admin> set directed-broadcast-allowed = no
admin> write
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 slot-12 4 } 0 } written
Configuring SNMP access to the unit
For Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) access, an SNMP manager must be
running on a host on the local IP network, and the TAOS unit must be able to find that host by
means of either a static route or RIP . In addition to these restrictions, the TAOS unit has its own
SNMP password security (community strings), which you must set up to protect the TAOS unit
from being reconfigured from an unauthorized SNMP station.
Overview of SNMP security
The SNMP profile contains SNMP-readable information about the un it and its SNMP security.
There are two levels of security:
• Community strings limit access to the TAOS unit to the community of SNMP managers
who know the strings.
• Address security excludes SNMP access unless it is initiated from a specified IP address.
1-10 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 31

Following are the parameters related to SNMP security:
SNMP
enabled = no
read-community = public
read-write-community = write
enforce-address-security = no
read-access-hosts = [ 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ]
write-access-hosts = [ 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ]
contact = ""
location = ""
queue-depth = 0
Enabling SNMP in the TAOS unit
If you leave the Enabled parameter in the SNMP profile set to No (the default), SNMP utilities
cannot access the TAOS unit. The following commands enable SNMP on a unit:
admin> read SNMP
SNMP read
admin>
admin> write
SNMP written
set enabled = yes
Performing Basic Configuration
Recommended basic security measures
Setting community strings
You can specify up to 32 characters as the Read-Write-Community string. The following
example changes the default community strings:
admin> read snmp
SNMP read
admin>
enabled = yes
read-community = ******
read-write-community = *****
enforce-address-security = no
read-access-hosts = [ 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ]
write-access-hosts = [ 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ]
contact = ""
location = here
queue-depth = 0
admin>
admin> set read-write-community = secret
admin> write
SNMP written
Setting up address securi ty
list
set read-community = private
If the Enforce-Address-Security parameter is set to No (its default value), any SNMP manager
that presents the correct community name is allowed access. If the parameter is set to Yes, the
T AOS unit checks th e sour ce IP address of the SNMP manager and allows access only to th ose
IP addresses listed in the Read-Access-Host and Write-Access-Host arrays. Each array can
include up to five host addresses.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 1-11
Page 32

Performing Basic Configuration
Where to go next
In the following example, commands enforce address security and specify a trus ted address for
read and write access:
admin> read snmp
SNMP read
admin> list
enabled = no
read-community = public
read-write-community = write
enforce-address-security = no
read-access-hosts = [ 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ]
write-access-hosts = [ 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ]
contact = ""
location = ""
admin>
admin> set read-access 1 = 10.2.3.4
admin> set write-access 2 = 10.2.56.123
admin> write
SNMP written
set enforce-address-security = yes
Where to go next
For APX 8000 units with two shelf controllers, proceed to Chapter 2 to configure
shelf-controller redundancy. Then proceed to the appropriate chapters to configure slot cards
for your unit.
For APX 8000 units with a single shelf controller and for MAX TNT and DSLTNT units,
proceed to the appropriate chapters to configure slot cards for your unit.
1-12 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 33

Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy
(APX 8000)
Overview of redundancy operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Configuring the APX 8000 for shelf-controller redundancy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Obtaining status information about redundant shelf controllers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
Overview of redundancy operations
The APX 8000 can operate with a single shelf controller or with two redundant shelf
controllers. When the APX 8000 runs with two shelf controllers, one controller takes on the
active role of primary controller while the other performs as the passive, secondary controller
that automatically takes over control of the system if the primary controller fails. In an APX
8000 with a single shelf controller, no controller redundancy exists.
In an APX 8000 with two shel f con t roll ers , the p ri mary s helf co nt roll er p erfo rms al l cont r ol ler
operations for the APX 8000:
• Managing the slot cards
2
• Maintaining a central repository of the unit’s configurations (including the current
NVRAM configuration)
• Performing call control and processing operations
• Managing all centralized functions, such as SNMP access and communication with a
RADIUS server.
In addition, all profiles are modified on the primary controller. When a conf iguration ch ange is
made on the primary controller, the entire configuration is copied to the secondary controller.
The secondary controller must be loaded with the same boot and operational code as the
primary controller.
Shelf-controller startup and primary election
When an APX 8000 with redundant controllers boots up, each shelf controller passes the
power-on self tests (POST) during the boot code loading process. The controllers establish
communication with each other over the packet bus, and exchange context information
(Redundancy profile and Redundancy-Stats profile information) through the heartbeat
protocol. Each controller has its own context (known as Context[1] or Context[2]), which is
associated with the controller’s serial number. The controllers use the context information to
track each other’s status.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 2-1
Page 34

Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy (APX 8000)
Overview of redundancy operations
The controllers next elect the controller that will be primary. The election process is based on a
hierarchical list of complex criteria. The first criterion in the list is evaluated and if the
criterion is found to be true, one of the controllers is made primary. If the criterion is found to
be false, the next criterion in the list is evaluated.
Following is an example of the initial criteria that might be used to designate the primary
controller:
1 If one controller is missing, the existing (current) controller is made primary.
2 If one controller is not communicating, the current controller is made primary.
3 If both controllers are communicating, the controllers use the Redundancy profile’s
Primary-Preference setting to determine which controller is primary.
4 If Primary-Preference is set to No-Preference, the controller that last acted as the
primary controller is made primary .
If a primary controller is still not determined, additional criterion are evaluated. If all election
criteria fail to designate a primary controller, the controller with more resources (for example,
more RAM) is made primary.
If the criteria cannot determine which controller is primary, the system selects the right
controller (slot 42) to be primary and the left controller (slot 41) becomes the secondary
controller.
Once a controller is elected as primary, the primary controller proceeds to load operational
code. When the primary is finished loading its code, the secondary controller loads its
operational image and gets a copy of the profiles.
Note: Both controllers must load the same boot and operational code version.
Normal operation
During normal operation, the two shelf controllers communicate with each other over the
packet bus in a back-and-forth heartbeat, exchanging context information . The statu s lights on
each controller indicate the following activities:
• The heartbeat (HRT) status light on each controller visually indicates that the heartbeat
• The primary (PRI) status light on each controlle r is lit if the controller is the pr imary and is
• The operational (OPR) status light is lit when the operational code is successfully loaded
The secondary controller does not perform controller operations unless the primary controller
resets or fails, or if you change the functionality of the shelf controllers. The secondary
controller’s main role is to monitor the primary and be ready to take over primary controller
functions. The secondary controller maintains the current configuration and the fatal-error
history log.
protocol is active by blinking on and off every 4 seconds in a regula r pattern that alternates
between the two controllers. In a TAOS unit that has only one shelf controller, the HRT
status light flashes on for 40 milliseconds every 4 seconds.
off if the controller is secondary.
onto the controller.
2-2 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 35

Controller switchover
If the primary controller fatals, the secondary controller automatically takes over as primary
controller. The new primary (old secondary) downs all slot cards and then brings the system
back up. All connections are dropped. After the primary shelf controller comes up, the slot
cards are reset. The system is now ready to take new calls. Each time a controller is selected as
the primary controller, an entry is made in the fatal-error history log.
A switchover, when control passes from the primary controller to the secondary, is initiated by
one of the following occurrences:
• The primary controller has a hardware or software problem that causes the module to
reset. The secondary is assigned to act as the primary.
• You enter the switchover command, Redundant-Controller-Switch at the
command line interface, which switches control from the primary to the secondary
controller.
APX 8000 slot cards communicate with the primary controller through the packet bus. The
primary controller is assigned virtual slot number 43, through which communication with the
slot cards occurs. If a switchover occurs, the new primary controller inherits virtual slot
number 43.
Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy (APX 8000)
Configuring the APX 8000 for shelf-controller redundancy
Log messages
Log messages are issued to notify you of significant events related to shelf cont roller
redundancy. For example, the following cases result in a log message:
• A shelf controller becomes primary.
• A fatal log entry is generated when a shelf controller has a software crash.
• A controller becomes primary when no secondary controller is present.
• The primary controller loses heartbeat communication with the secondary controller.
• The primary controller establishes heartbeat communication with the second ary controller.
Configuring the APX 8000 for shelf-controller
redundancy
Setting up the APX 8000 for shelf-controller redundancy includes the following tasks:
• Assigning the system IP address
• Assigning the shelf-controller Ethernet IP address
• Assigning the soft IP address
• Configuring shelf-controller redundancy
You can use the redundant-controller-switch command-line interface comman d to
switch primary controller functionality from one controller to the other. See “Switching the
primary controller at the command-line interface” on page 2-8 for instructions.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 2-3
Page 36

Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy (APX 8000)
Configuring the APX 8000 for shelf-controller redundancy
Assigning the system IP address
To configure an APX 8000 that has redundant shelf controllers, you must map system IP
settings to the unit’s soft IP interface. The soft IP interface is associated with the shelf
controller that is currently primary.
Set the IP-Global profile’s System-IP-Addr parameter to the address of the soft IP interface.
System-IP-Addr must not be set to a particular physical interface, such as the address of a shelf
controllers. In a redundant shelf-controller system, the physical address of the primary
controller changes according to which controller is currently primary, and the system IP
address must be a single, unchanging address that always maps to the current primary
controller.
Configuration of the soft IP interface address is described in the section “Defining the soft IP
interface for fault tolerance” on page 2-5.
Assigning an Ethernet IP address
An APX 8000 creates an IP interface for the Ethernet port of each shelf controller. The
IP-Interface profile index is based on each controller’s slot number. The left controller slot on
the TAOS unit is number 41, and the right controller slot is 42.
To list the IP interfaces, use the Dir command, as follows:
admin> dir ip-interface
6 06/17/1999 03:06:00 { { any-shelf any-slot 0 } 0 }
19 06/21/1999 23:54:02 { { shelf-1 left-controller 1}0}
19 06/25/1999 17:45:30 { { shelf-1 right-controller1}0}
The IP interface profile indicated by {{ she lf-1 left-controller 1 } 0} is for the
shelf controller in the first controller slot. The IP profile indicated by {{ shelf-1
right-controller 1 } 0} is for the shelf controller in the second controller slot. The
IP-Interface profile with the zero index {{ any-shelf any-slot 0 } 0} is reserved
for the soft IP interface.
Examples of setting shelf-cont rol ler Ethe rn et IP add re ss
Each shelf controller needs to be assigned an IP address. Following are examples that show
how to configure the Ethernet IP addresses.
In the following example, the shelf controller in the left controller slot position (slot 41) is the
primary controller. The primary controller is assigned the address 192.168.100.1/24:
admin> read ip-interface { { 1 41 1 } 0 }
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 left-controller 1 } 0 } read
admin> set ip-address = 192.168.100.1/24
admin> write
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 left-controller 1 } 0 } written
The following commands assign the address 192.168.100.2/24 to the secondary (right) shelf
controller. The commands must be performed on the primary (left) controller.
admin> read ip-interface { { 1 42 1 } 0 }
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 right-controller 1 } 0 } read
2-4 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 37

Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy (APX 8000)
Configuring the APX 8000 for shelf-controller redundancy
admin> set ip-address = 192.168.100.2/24
admin> write
IP-INTERFACE/{ { shelf-1 right-controller 1 } 0 } written
After you assign IP addresses to the controllers, you can verify that the TAOS unit is a valid IP
host on its configured networks by pinging other hosts on those networks, as shown in the
following example:
admin> ping 192.168.100.56
PING 192.168.100.56: 56 Data bytes
64 bytes from 192.168.100.56: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=0 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.100.56: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=0 ms
--- 192.168.100.56: Ping statistics --2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/0 ms
Defining the soft IP interface for fault tolerance
The APX 8000 supports an internal soft IP interface that is always available. It is associated
only with the primary controller and is hidden from the secondary controller.
The APX 8000 sets up the soft IP interface after you power on the unit and a controller
becomes primary. If a switchover occurs and the secondary controller becomes primary, the
soft IP interface is initialized and associated with the new primary controller. The soft IP
interface address is reachable as long as one IP interface on the APX 8000 (on an Ethernet
card, for example) is operational.
The IP-Interface profile with the zero index is reserved for the soft IP interface. For example,
the first line of the fo ll owing dir command output shows the zero index:
admin> dir ip-interface
6 06/17/1999 03:06:00 { { any-shelf any-slot 0 } 0 }
19 06/21/1999 23:54:02 { { shelf-1 left-controller 1}0}
19 06/25/1999 17:45:30 { { shelf-1 right-controller1}0}
If RIP is enabled, the APX 8000 advertises the soft IP interface address as a host route (with a
prefix length of /32) using the loopback interface. If RIP is not enabled, routers one hop away
from the APX 8000 must have a static route to the soft interface address.
Example of setting the soft IP address
You activate the soft IP interface by entering an IP address for {{ any-shelf any-slot
0} 0}. The following example shows how to set the soft IP address to 192.168.100.128/24:
admin> read ip-interface { 0 0 0 }
IP-INTERFACE/{ { any-shelf any-slot 0 } 0 } read
admin> set ip-addr = 192.168.100.128/24
admin> write
IP-INTERFACE/{ { any-shelf any-slot 0 } 0 } written
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 2-5
Page 38

Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy (APX 8000)
Configuring the APX 8000 for shelf-controller redundancy
Configuring shelf-controller redundancy
When setting up shelf-controller redundancy, you might need to configure the following
profiles:
• Physical interface profiles (such as IP-Interface, Serial, Ethernet, Ether-Info)
• Redundancy profile
Note: Lucent recommends that you modify profiles on the primary controller only. Modified
profiles are sent to the secondary controller.
During profile configuration, the write and delete command-line interface commands
check for permission before allowing you to write or delete any profile. Profile writes or
deletes are not allowed on the secondary controller, but you can force implementation of the
commands if you use the -f command option. Whe n you use -f, a warning message alerts
you that a profile written on the secondary might be overwritten by a transfer from the primary
controller.
Physical interface profiles
The profiles of the physical interfaces, such as IP-Interface, Serial, Ethernet, and Ether-Info,
are indexed by each controller’s slot number. The left shelf-controller slot is 41, and the right
shelf-controller slot is 42.
For example, to read the IP Interface profile for the shelf controller in the left controller slot,
enter the following command:
admin> read ip-interface { { 1 41 1 } 0 }
The APX 8000 has only one shelf, which is identified as shelf-1.
Redundancy pr ofile
The Redundancy profile maintains each controller’s configuration information (context). The
shelf controllers exchange context information during heartbeat communications and use it to
track each other’s status. The context information for each controller is stored as an array and
is identified as Context[1] or Context[2].
Configuration of the Redundancy profile primarily involves the following subprofiles and
parameters:
• Primary-Preference is a parameter that allows the user to indicate a p reference f or electing
• Context is a subprofile that contains context subprofiles for both controllers, Context[1]
• Context [N] is a subprofile that contains the context information for an individual
Note: Configuration of the Redundancy prof ile parameters must be done on ly on the primary
controller. Profiles written on the secondary controller can be overwritten.
a controller as primary.
and Context[2].
controller (Context[1] or Context[2]).
Use the read and write command-line interface commands to make Redundancy the
working profile and list the Redundancy profile contents.
2-6 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 39

Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy (APX 8000)
Configuring the APX 8000 for shelf-controller redundancy
admin> read redundancy
REDUNDANCY read
admin> list
[in REDUNDANCY]
context = [ { } { } ]
primary-preference = no-preference
The following example shows how you can configure the Primary-Preference parameter to
indicate a preference for the controller in the right shelf-controller slot to be elected primary:
admin> read redundancy
REDUNDANCY read
admin> set primary-preference = right-controller-preferred
admin> write
REDUNDANCY written
Note: Primary-Preference settings remain in effect after a reboot. For example, if the left
controller is configured with a particular setting, after a reboot the left controller still retains
that setting.
The Redundancy-Stats profile contains system-maintained statistical information about each
controller. The statistical information for each controller is located in Context-Stats[1] or
Context-Stats[2].
The following example shows how you can view the contents o f the Redun dan cy-Stats p rof ile:
admin> read redundancy-stats
REDUNDANCY-STATS read
admin> list
[in REDUNDANCY-STATS]
context-stats = [ { monitoring secondary defer-to-running-primary
no-function+
admin> list context 1
[in REDUNDANCY-STATS:context-stats[1]]
state = monitoring
function = secondary
select-reason = defer-to-running-primary
prior-function = no-function
last-reboot = crash
fan = { 317834728 }
admin> list context 2
[in REDUNDANCY-STATS:context-stats[2]]
state = monitoring
function = primary
select-reason = communication-loss
prior-function = no-function
last-reboot = crash
fan = { 317838764 }
The Redundancy and Redundancy-Stats profiles are visible through SNMP.
Refer to the APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Reference for additional information about the
Redundancy and Redundancy-Stats profiles.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 2-7
Page 40

Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy (APX 8000)
Configuring the APX 8000 for shelf-controller redundancy
Switching the primary controller at the command-li ne interface
You can man uall y switch primary shelf-controller functionality to the secondary controller by
entering the command redundant-controller-switch at the com mand-line interface.
This command causes the primary controller to give up bus (slot card) ownership and allow the
other controller to become primary. The switchover to the secondary controller occur only if
the secondary controller is present. After the bus is released, the old primary shelf controller
reboots and assumes the role of secondary controller.
Switchover takes place only if the following conditions are met:
• The secondary controller is present.
• The primary controller currently controls the bus.
• The secondary controller requests control of the bus, which is the normal operating state
of the secondary controller. The secondary controller is ready to automatically gain bus
ownership whenever the primary releases its ownership.
After you use the redundant-controller-switch command, a prompt appears that
asks for confirmation of your request. To switch primary controller functionality to the
secondary controller without being prompted for confirm ation, use the -f command option, as
follows:
admin> redundant-controller-switch -f
When the command is entered on the primary controller, controller functionality is switched to
the secondary controller. When the switchover command is entered on the secondary
controller, no switchover occurs.
If the switchover command is entered on the primary when the secondary is not requesting
control of the bus, no switchover occurs:
admin> redundant-controller-switch
The remote controller is not requesting the bus,
it cannot become PRIMARY!
If the switchover command is entered on the primary controller when only one controller is
present, a notice is displayed:
admin> redundant-controller-switch
There is no remote controller!
Resetting shelf controllers and clearing controller NVRAM
The shelf controllers can be reset from the command line with the reset command. The
controller’s NVRAM can be cleared from the command line with the nvram command. The
use of these commands is described in this section.
Refer to the APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSL TNT Refer en ce for additional information on the reset
and nvram command-line interface commands and command options.
Resetting the controllers
The reset command resets one or both APX 8000 redundant shelf controllers. When you
reset the unit, it restarts, and all active connections are terminated. All users are logged out, and
2-8 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 41

Clearing NVRAM
Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy (APX 8000)
Obtaining status information about redundant shelf controllers
the default security level is reactivated. In addition, a system reset can cause a WAN line to
temporarily be shut down due to momentary loss of signaling or framing information. Af ter a
reset, the unit runs power-on self-tests (POST).
The reset -r command resets the s econdary controller or both con trollers. The reset -f
command resets the controller where the command is invoked. When the primary controller is
reset, the secondary controller automatically takes over control and becomes primary.
Following is an example of what you enter to reset both controllers:
admin> reset -r b
The nvram command clears NVRAM and resets one or both APX 8000 redundant shelf
controllers.
The nvram -r command clears NVRAM and resets the secondary controller or both
controllers. The -f, -t, -u, and -c command options apply to the controller where the
command is invoked. When the nvram command is performed on the primary controller and
NVRAM is cleared and the controller reset, the secondary controller automatically takes over
control and becomes primary.
Enter the following command to clear NVRAM and reset the secondary shelf controller:
admin> nvram-r s
Enter the following command to clear NVRAM and reboot both shelf controllers:
admin> nvram-r b
Obtaining status information about redundant shelf
controllers
You can use the following methods to obtain information about the redundant shelf controllers:
• The command-line interface uptime command indicates the length of time the
controllers have been operational.
• The command-line interface show command provides status information about the
redundant shelf controllers.
• The Trap profile parameter Secondary-Controller-State-Change-Enabled allows a trap to
be sent to the NavisAccess™ manager whenever the secondary controller goes in or out of
service.
Following are descriptions of these methods.
Viewing controller up time
The uptime command reports the length of time th e primary con troller has been oper ational.
It also indicates the time elapsed since the secondary controller started communications with
the primary. If a controller reboots or if communication between the two controllers is
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 2-9
Page 42

Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy (APX 8000)
Obtaining status information about redundant shelf controllers
disrupted and then reestablished, the uptime command reports the time elapsed since the
secondary controller reestablished communications with the primary.
The uptime command do es not report the version number of code used by the controllers, but
instead reports the primary or secondary status of each co ntroller. The code version is obtained
with the version command.
The following example shows the uptime command entered on the primary controller. The
-a option displays the up time for all slot cards.
admin> uptime -a
06:28:41
{ shelf-1 slot-3 } 8t1-card 0 days 00:08:53 8.0
{ shelf-1 slot-12 } hdlc2-card 0 days 00:08:53 8.0
{ shelf-1 slot-16 } csmx-card 0 days 00:08:53 8.0
{ shelf-1 slot-19 } hdlc2-card 0 days 00:08:53 8.0
{ shelf-1 slot-23 } csmx-card 0 days 00:08:53 8.0
{ shelf-1 slot-32 } hdlc2-card 0 days 00:08:53 8.0
{ shelf-1 slot-34 } 4ether2-card 0 days 00:08:53 8.0
{ shelf-1 left-controller } [...] 0 days 00:40:37 ( SECONDARY )
{ shelf-1 right-controller } [...] 0 days 00:41:21 ( PRIMARY )
The following example shows the uptime command entered on the secondary controller:
admin> uptime -a
06:28:26
{ shelf-1 left-controller } [...] 0 days 00:40:37 ( SECONDARY )
{ shelf-1 right-controller } [...] 0 days 00:41:21 ( PRIMARY )
Viewing controller status
The show command reports the communications status of the primary and secondary
controllers and indicates which controller (left or right) is the primary and secondary shelf
controller.
When the show command is entered on either the primary or secon dary shelf co ntroller, UP is
reported for the other controller’s status if the current controller is able to communicate with
the other controller. DOWN is displayed if the other controller is present but not communicating
with the current controller. If the other controller is not present, the status of that controller is
reported as ABSENT with the show -a command.
The following example displays the show command entered on the primary controller, when
the right controller is primary:
admin> show
Controller { right-controller } ( PRIMARY ):
{ left-controller ) UP ( SECONDARY )
{ shelf-1 slot-1 0 } DOWN ether3-card
{ shelf-1 slot-3 0 } UP 8t1-card
{ shelf-1 slot-12 0 } UP hdlc2-card
{ shelf-1 slot-16 0 } UP csmx-card
{ shelf-1 slot-19 0 } UP hdlc2-card
{ shelf-1 slot-23 0 } UP csmx-card
{ shelf-1 slot-32 0 } UP hdlc2-card
{ shelf-1 slot-34 0 } UP 4ether2-card
2-10 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 43

Configuring Shelf-Controller Redundancy (APX 8000)
Obtaining status information about redundant shelf controllers
The following example displays the show comman d entered on the s econdary con troller when
the right controller is primary:
admin> show
Controller { left-controller } ( SECONDARY ):
{ right-controller ) UP ( PRIMARY )
Setting up a trap to monitor the secondary controller
In the Trap profile, you can configure the Secondary-Controller-State-Change-Enabled
parameter to send a trap to the NavisAccess manager whenever the secondary controller goes
in or out of service. When the parameter is set to yes, a trap is sent when the secondary
controller goes in or out of service. When the parameter is set to no, no trap is sent.
Use the read and list commands to make Trap the working profile and list its contents. Use
the set command to modify the settings in the profile.
The following example shows how to set the parameter to not send a trap to the NavisAccess
manager:
admin> set secondary-controller-state-change-enabled=no
Clearing the fatal-error history log
The clr-history command clears the fatal-error history log. In systems with redundant
shelf controllers, the clr-history command-line interface command is intended only for
use on the primary controller . The fatal-er ror log cannot be cleared on the s econdary controller ,
unless you force implementation of the command by using the -f command option.
When clr-history -f is used on the secondary controller, a warning message appears to
alert you that the cleared log can still be overwritten during transfer of information from the
primary controller during heartbeat communications.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 2-11
Page 44

Page 45

Configuring the Thermal Profile for Fan
3
Tray Operations (APX 8000)
Overview of the Thermal profile for fan tray operations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Thermal status reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Overview of the Thermal profile for fan tray operations
On the APX 8000, an on-board digital temperature chip on the shelf controller and a
temperature device at the intake end of the fan controller are used to measure incoming
ambient air temperature. The APX 8000 fan tray is capable of running at different speeds, and
of adjusting as needed to dissipate system heat or reduce unnecessary fan noise.
You control fan tray operations by configuring the Thermal profile. Fol lowi ng are the rel evant
settings, shown with default values:
[in THERMAL]
fantray-lownoise-rpm = 2500
operation-mode = full-speed-only
low-temperature-trigger = 34
high-temperature-trigger = 40
alarm-temperature-trigger = 55
Parameter Specifies
Fantray-Lownoise-RPM Number of revolutions pe r minute (RPM) of the fan tray when
the low noise speed has been selected. Valid values range from
2000 to 3000, with a default of 2500.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 3-1
Page 46

Configuring the Thermal Profile for Fan Tray Operations (APX 8000)
Overview of the Thermal profile for fan tray operations
Parameter Specifies
Operation-Mode Mode of operation in which the fan tray runs. When the
parameter is set to full-speed-only, the fans in the fan
tray operate at full speed at all times. (This is the default mode.)
When set to lownoise-speed-only, the fans operate at the
low noise speed (as specified in the Fantray-Lownoise-RPM
setting) at all times. When the parameter is set to
auto-regulation mode, the fan speeds are controlled
dynamically on the basis of temperature. In
auto-regulation mode, the fans run at low noise speed
when the system starts up. The system monitors the unit
temperature, and when it reaches a high-temperature threshold
(as specified in the High-Temperature-Trigger setting), it
switches the fans to full speed and logs a message. When the
unit temperature falls below the low-temperature threshold (as
specified in the Low-Temperature-Trigger setting), the system
switches the fans back to low noise speed.
Low-Temperature-Trigger Low-temperature threshold setting, from 0 to 60 degrees
Celsius (32 to 140 degrees Fahrenheit). If the fan tray is in
auto-regulation mode and this threshold is crossed, the system
switches the fans to low noise speed and logs a messag e. If you
specify a higher value than the High-Temperature-Trigger
setting, the system displays an error message when you attempt
to write the profile.
High-Temperature-Trigger High-temperature threshold setting, from 0 to 60 degrees
Celsius (32 to 140 degrees Fahrenheit). If the fan tray is in
auto-regulation mode and this threshold is crossed, the system
switches the fans to full speed and logs a message. If you
specify a lower value than the Low-Temperature-Trigger
setting, the system displays an error message when you attempt
to write the profile.
Alarm-Temperature-T rigger Temperature threshold setting, from 0 to 60 degrees Celsius (32
to 140 degrees Fahrenheit). If this threshold is crossed, the
system generates an Alarm event, the Alarm Relay on the shelf
controller is turned on, and the Alarm status light on the front
panel of the fan tray illuminates.
Example of configuring thermal controls
The commands in the following example show how to configure the fan tray to run the fans at
2500 RPM until the unit reaches a temperature of 37 degrees Celsius (98.6 degrees
Fahrenheit), at which time the system switches the fans to full speed and maintains that setting
until the unit temperature drops below 30 degrees Celsius (86 degrees Fahrenheit). If the
system ever reaches a temperature of 50 degrees Celsius (122 degrees Fahrenheit), the system
triggers alarms.
admin> read thermal
THERMAL read
admin> set operation-mode = auto-regulation
3-2 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 47

admin> write
THERMAL written
admin> list
[in THERMAL]
fantray-lownoise-rpm = 2500
operation-mode = auto-regulation
low-temperature-trigger = 30
high-temperature-trigger = 37
alarm-temperature-trigger = 50
Related log messages
When the fan tray is in auto-regulation mode, the system can generate the following Info log
messages to indicate that the system has switched the fans from low noise to full speed, or vice
versa:
LOG info, Shelf 1, Slot 42, Time: 10:31:39-Fantray now running in lownoise-mode (30 C)
LOG info, Shelf 1, Slot 42, Time: 10:34:40-Fantray now running at full speed (37 C)
Configuring the Thermal Profile for Fan Tray Operations (APX 8000)
Overview of the Thermal profile for fan tray operations
If you modify the fan operation mode setting in the Thermal profile, the system generates an
Info log message such as the following:
LOG info, Shelf 1, Slot 42, Time: 11:06:44-Fantray set to run in Auto-regulation mode
Thermal alarms
When the temperature of the system reaches the Alarm-temperature-trigg er threshold specified
in the Thermal profile, the s ystem is in an alarm s tate. When th is happens , the f ollowing events
occur:
• The system generates an Error log message such as the following:
• The Alarm relay on the shelf controller is enabled. This turns on whatever signal is
• The Alarm status light in the fan tray front panel turns ON.
When the temperature falls back 2 degrees Celsius below the Alarm temperature trigger
threshold, the alarm state is cleared and the following events occur:
• The system generates a Warning log message such as the following:
LOG error, Shelf 1, Slot 42, Time: 11:10:23-Temperature Alarm triggered (50 C)
connected to the Alarm relay on the shelf controller.
LOG warning, Shelf 1, Slot 42, Time: 11:11:33-Temperature Alarm cleared (48 C)
• The Alarm relay on the shelf controller is disabled.
• The Alarm status light in the fan tray front panel turns OFF.
The 2-degree temperature cushion retards system response slightly so that the Alarm state is
not triggered repeatedly around a threshold.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 3-3
Page 48

Configuring the Thermal Profile for Fan Tray Operations (APX 8000)
Thermal status reporting
Thermal status reporting
A power-on self test (POST) is run on the fan tray of the APX 8000 during the BOOT loader
and during the operational load. If the fan tray POST fails, the POST failure status light
(amber) flashes 10 times and the following log message is generated:
LOG emergency, Shelf 1, Slot 42, Time: 15:23:57-post failed, type (10)
In addition, two new commands are supported for displaying information about the fan tray
and the unit’s thermal status. Both commands, along with the automatic fan tray speed
regulation, are available on both shelf controllers in a redundant system.
Fanstatus command
The fanstatus command displays fan tray status information such as the fan revolutions
per minute (R PM), status (OK or BAD), and the unit’s ambient temperature. Note that the
current fan mode can be displayed as either full speed or low noise. For example, the following
output shows the fan mode set to full spe ed with an ambient temperat ure of 33 degrees Cels ius
(91.4 degrees Fahrenhe it):
admin> fanstatus
APX8000 Fantray status
Fantray ambient temperature: 33 C
Current fan mode: Full-speed
Fan # RPM Status
============================================
1 3367 GOOD
2 3214 GOOD
3 3075 GOOD
4 3075 GOOD
5 3214 GOOD
6 3289 GOOD
The following command output shows the fan mode set to low noise with an ambient
temperature of 27 degrees Celsius (80.6 degrees Fahrenheit):
admin> fanstatus
APX8000 Fantray status
Fantray ambient temperature: 27 C
Current fan mode: Low-noise
Fan # RPM Status
============================================
1 1992 GOOD
2 2050 GOOD
3 1992 GOOD
4 2020 GOOD
5 2050 GOOD
6 2020 GOOD
3-4 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 49

Configuring the Thermal Profile for Fan Tray Operations (APX 8000)
Thermalstatus command
The thermalstatus command displays a number of temperature-related values to show
the overall thermal status of the unit. For example, it displays:
• Ambient temperature at fan tray intake.
• Shelf controller temperature.
• High, Low, and Alarm temperature thresholds.
• Slot card temperature for slot cards that support temperature reporting. Currently, no slot
cards support thermal information repo rt ing.
• Power supply thermal status, and whether the power supplies are in an overheated state.
• Fan tray status, including the fan tr ay operati onal mode, n umber of revolut ions per m inute
at low-noise speed, and current revolutions per minute of each fan.
For example:
admin> thermalstatus
System Thermal status
Ambient temperature at intake : 27 C (80 F)
Shelf controller temperature : 35 C (95 F)
High temperature threshold : 36 C (96 F)
Low temperature threshold : 32 C (89 F)
Alarm temperature threshold : 38 C (100 F)
Slot cards:
(no slot cards contain thermal information)
Thermal status reporting
Power supply thermal status
Power Supply # Temp
=================================
A OK
B OK
C n/a
D OK
Fantray status
Fan operational mode: auto-regulation
Low-noise RPM: 2000
Current fan mode: Full-speed
Fan # RPM Status
============================================
1 3289 GOOD
2 3214 GOOD
3 3075 GOOD
4 3143 GOOD
5 3214 GOOD
6 3289 GOOD
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 3-5
Page 50

Page 51

Configuring Ethe rnet Cards
Introduction to Ethernet slot cards. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Overview of Ethernet configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Understanding the Ethernet-related profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Configuring duplex mode on the 100Mbps Ethernet port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Introduction to Ethernet slot cards
This chapter explains how to install and configure the Ethernet slot cards. For information
about configuring IP routing, see the APX 8000/MAX TNT DSLTNT WAN, Routing and
Tunneling Configuration Guide.
The following Ethernet slot cards are available for the platforms indicated:
• 10/100Mbps Ethernet-2 card with three 10Mbps ports and one 100Mbps
port—APX 8000, MAX TNT and DSLTNT units
• 10/100Mbps Ethernet-3 card with a single 100Mbps port—APX 8000 and MAX TNT
units
4
Full-duplex 10/100Mbps Ethernet-2 slot card
The Ethernet-2 card has three 10BaseT ports and one full-duplex 100BaseT port. If you are
replacing an older Ethernet card with the new Ethernet-2 card, you must create new Ethernet
profiles for the Ethernet-2 card. For details, see “Upgrading to the Ethernet-2 and Ethernet-3
slot cards” on page 4-2.
Full-duplex 10/100Mbps Ethernet-3 slot card
The Ethernet-3 slot card has one full-duplex 10/100Mbps port that is designed to have a high
packet-per-second throug hput to suppo rt Voice over IP (VoIP). The Ethernet-3 card autosenses
10Mbps or 100Mbps but do es not supp ort autoneg otiatio n, in which Ether net devices n egotiat e
a common speed and duplex mode.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 4-1
Page 52

Configuring Ethernet Cards
Overview of Ethernet configurati on
Upgrading to the Ethernet-2 and Ethernet-3 slot cards
To upgrade from an existing 10Mbps or 10/100Mbps Ethernet card to an Ethernet-2 or
Ethernet-3 slot card, proceed as in the following example:
1 Remove the existing Ethernet slot card.
2 Enter the Slot command with the -r option to remove the existing Ethernet profiles. For
example, if the Ethernet card was in slot 1:
admin> slot -r 1
slot 1 removed
3 Install the Ethernet-2 or Ethernet-3 slot card.
4 Configure Ethernet profiles for the new card as explained in the following sections of this
chapter.
Overview of Ethernet configuration
The Ethernet slot cards provide multiport Ethernet routing capabilities. The configuration of
each port on an Ethernet slot card is identical to the configuration of the Ethernet port on the
shelf controller. (For complete information about configuring the Ethernet ports for routing,
see the APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT WAN, Routing, and Tunneling Configuration Guide.)
All TAOS units have an Ethernet port on the shelf cont roller. This Ethernet port is designed for
out-of-band management and light traffic loads. It is not intended to be the primary Ethernet
interface for the system. If your TAOS unit will be routing heavy Ethernet traffic, use an
Ethernet card.
Understanding the Ethernet-related profiles
The APX 8000 creates the following profiles when it detects an Ethernet port:
• Ethernet profile
• IP-Interface profile
• SNMP profiles (Admin-State and a Device-State profile)
For an explanation of SNMP profiles, see the APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Administration
Guide.
Ethernet profile
TAOS creates a default Ethernet profile for each Ethernet port it detects, including the shelf
controller. The Ethernet profile specifies the link-layer configuration for the port.
For example, if an Ethernet-2 card installed in slot 4, you might see a screen similar to the
following:
admin> dir ethernet
5 08/06/1998 17:03:48 { shelf-1 controller 1 }
5 08/06/1998 17:11:46 { shelf-2 slot-4 1 }
5 08/06/1998 17:11:46 { shelf-2 slot-4 2 }
4-2 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 53

Configuring Ethernet Cards
Configuring duplex mode on the 100Mbps Ethernet port
5 08/06/1998 17:11:46 { shelf-2 slot-4 3 }
5 08/06/1998 17:11:46 { shelf-2 slot-4 4 }
If the 10/100 Mbps Ethernet-2 card is installed, the 100Mbps Ethernet port is displayed as
port 4.
IP-Interface profile
T AOS creates a default IP-Interface profile for each Ethernet port it detects, including the shelf
controller. You can create multiple IP interfaces for each physical Ethernet port, but the default
IP-Interface profile must have an IP address, or the other IP-In terface profiles for th e same port
will not function. For information about configuring IP-Interface profiles , see the
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT WAN, Routing, and Tunneling Configuration Guide.
Configuring duplex mode on the 100Mbps Ethernet
port
The Duplex-Mode parameter in the Ethernet profile allows you to set the physical Ethernet
interface of the 100BaseT port on the Ethernet-2 or Ethernet-3 card to full-duplex or
half-duplex mode. Full-duplex mode (the default) provides increased throughput, but
half-duplex mode enables the unit to operate with older equipment that does not support fu ll
duplex.
The following example sets the port to half-duplex mode:
admin> read ethernet { 1 7 4 }
ETHERNET/{ shelf-1 slot-7 4 } read
admin> list
[in ETHERNET/{ shelf-1 slot-7 4 }]
interface-address* = { shelf-1 slot-7 4 }
link-state-enabled = no
enabled = yes
ether-if-type = utp
bridging-enabled = no
filter-name = ""
duplex-mode = full-duplex
admin> set duplex-mode = half
admin> write
ETHERNET/{ shelf-1 slot-7 4 } written
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 4-3
Page 54

Page 55

Configuring Series56 II and
III Modem and Hybrid Access Cards
Overview of configuring modem cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Specifying modem negotiation settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Specifying modem modulation for Series56 II and III modem cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Configuring an additional AT answer string for modem calls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Series56 II and III Call-Route profiles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Preventing Series56 II and III cards from delaying Frame Relay connections . . . . . . . 5-5
Hybrid Access card implementation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
T yp ically, Series56 II™ and Seri es56 III Digital Modem slot cards do not requ ire any
configuration. Dependin g on your net work, si tuation s might requ ire you to change the w ay the
modems operate. This chapter describes how to modifiy modem configuration to
accommodate your networking environment. The chapter also provides some guidelines for
use of Hybrid Access (HDLC) cards.
5
Note: Modem cards are not supported on DSLTNT units, but DSLTNT units support Hybrid
Access cards.
Overview of configuring modem cards
When you make a change to the modem configuration, the change applies to all the modems in
the APX 8000 or MAX TNT unit. You configure modems in the Terminal-Server profile.
Table 5-1 lists common tasks you might have to perform to customize modem config urations,
the sections describing those tasks, and the associated parameters.
For complete information about the associated parameters, see the
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Reference.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 5-1
Page 56

Configuring Series56 II and III Modem and Hybrid Access Cards
Specifying modem negotiation settings
Table 5-1. Modem configuration tasks
Descript ion of task Section Associated parameters
Some analog modem calls might require
changes to the digital modem’s default
behavior to successfully complete
negotiation.
You might need to change the modulation
of Series56 II and III modems from the
default of V.90. For example, in some cases,
V.32 and V.34 modems do not successfully
complete modem training after reception of
the V.8bis tone from the APX 8000 and
MAX TNT unit Series56 II and III modems.
Configuring V.34 modulation can help this
problem.
You might need to modify the AT answer
strings that the APX 8000 and MAX TNT
unit sends to its modems . You can do this by
specifying an extra answer string in the
command line interfaces.
“Specifying modem negotiation
settings” on page 5-2
“Specifying modem modulation
for Series 56 II and III modem
cards” on page 5-3
“Configuring an additional AT
answer string for modem calls” on
page 5-3
V42/MNP
Max-Baud-Rate
Modem-Transmit-Level
Cell-Mode-First
Cell-Level
7-Even
Modem-Mod
AT-Answer-String
Because the Series56 II and III slot cards
can terminate both modem and HDLC calls,
the APX 8000 and MAX TNT unit creates
two call route profiles for each channel on
the card: one for a digital call and one for a
modem call.
“Series56 II and III Call-Route
profiles” on page 5-4
Specifying modem negotiation settings
Calls from analog modems are d irected f i rst to th e dig ital mod ems, where the connection must
be negotiated before being directed to by the terminal-server software. Options in the
Terminal-Server > Modem-Configuration subprofile allow you to m odify the way the digital
modems negotiate a connection.
To specify changes in how the negotiation occurs:
1 Read the Terminal-Server profile into the editing buffer:
admin> read terminal-server
TERMINAL-SERVER read
N/A
5-2 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 57

Configuring Series56 II and III Modem and Hybrid Access Cards
Specifying modem modulation for Series56 II and III modem cards
2 List the parameters in the Modem-Configuration subprofile. For example:
admin> list modem-configuration
v42/mnp = will-v42
max-baud-rate = 33600-max-baud
modem-transmit-level = -13-db-mdm-trn-level
cell-mode-first = no
cell-level = -18-db-cell-level
7-even = no
3 Modify the parameters as required.
For information about the parameters, see the APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Reference.
Specifying modem modulation for Series56 II and III
modem cards
The Modem-Mod parameter in the Terminal-Server profile allows you to specify the modem
modulation that Series56 II and III modems use. The possible settings are K56-Modulation,
V34-Modulation, and V90-Modulati on (the default).
To support the ITU-T standard V.8bis (Voice Call Ready), a 56Kbps modem in the APX 8000
and MAX TNT unit normally sends a tone at the beginning of modem training. This is
commonly referred to as CRe and is a dual tone (13 75Hz + 2 002 Hz) followed by a s ing le tone
at 400Hz with a combined duration of approximately 500ms. Although V.8bis is designed not
to interfere with V.32bis modem negotiation, some V.32 and V.34 modems do not successfully
complete modem training after reception of the V.8bis tone.
Note: If you configure the Series56 II and III modems to use V.34 modulation, they never
exceed the speeds used by V.34 modems (33.6Kbps), and they do not send the V.8bis tone.
To configure modem modulation for calls coming in to Series56 II and III modem cards,
proceed as in the following example:
admin> read terminal-server
TERMINAL-SERVER read
admin> set modem-configuration modem-mod = v34-modulation
admin> write
TERMINAL-SERVER write
Configuring an additi onal AT answ er st ring for m odem
calls
The AT-Answer-String parameter in the Terminal-Server profile enables you to specify extra
AT commands in the answer string of the system’s modem configuration.
The answer string is the last of four strings that the APX 8000 or MAX TNT sends to the
modem upon answering a call. Commands entered in this string might overwrite settings
specified elsewhere. For example, if the Max-Baud-Rate parameter sets the maximum baud
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 5-3
Page 58

Configuring Series56 II and III Modem and Hybrid Access Cards
Series56 II and III Call-Route profiles
rate and the AT-Answer-String parameter specifies a different baud rate, the answer string
overwrites the configured maximum baud rate.
Following is the relevant parameter, which is shown with its default setting:
[in TERMINAL-SERVER:modem-configuration]
AT-answer-string = ""
The value of this parameter must be valid AT commands, up to 36 characters. Do not begin the
string with AT. An AT is appended to the beginning of this string automatically before it is sent
to the modem. Also, do not include an A (answer) or a D (dial) command anywhere in the
string. An A command is app ended automatical ly to the end of this stri ng, and a D command in
the answer string causes the call to fail.
Note: Be very careful when entering AT commands in this parameter. The system does not
prevent you from entering incorrect strings.
The following example sets the AT-Answer-String parameter to S37=11, which causes the
following string to be sent to the modem:
ATS37=11A
When the modem receives this string, it forces a V.32bis 14400 connection.
admin> read terminal-server
TERMINAL-SERVER read
admin> set modem AT-answer-string = S37=11
admin> write
TERMINAL-SERVER written
Series56 II and III Call-Route pr ofil es
When you install a Series56 II or Series56 III slot card, the TAOS unit creates two call route
profiles for each channel on the card. One for a digital data call and one for a modem voice
call. For example:
admin >callroute -d
device # source type tg sa phone
1:14:01/0 0 0:00:00/0 voice-call-type 0 0
1:14:01/0 1 0:00:00/0 digital-call-type 0 0
1:14:02/0 0 0:00:00/0 voice-call-type 0 0
1:14:02/0 1 0:00:00/0 digital-call-type 0 0
1:14:03/0 0 0:00:00/0 voice-call-type 0 0
1:14:03/0 1 0:00:00/0 digital-call-type 0 0
1:14:04/0 0 0:00:00/0 voice-call-type 0 0
1:14:04/0 1 0:00:00/0 digital-call-type 0 0
1:14:05/0 0 0:00:00/0 voice-call-type 0 0
1:14:05/0 1 0:00:00/0 digital-call-type 0 0
Note that in Call-Route profiles, voice-call-type refers only to a modem call.
5-4 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 59

Configuring Series56 II and III Modem and Hybrid Access Cards
Preventing Series56 II and III cards from delaying Frame Relay connections
Preventing Series56 II and III cards from delaying
Frame Relay connections
If the APX 8000 or MAX TNT has a Frame Relay datalink that uses a single nailed channel,
you must install Series56 II or Series56 III slot cards in lower-numbered slots than the Hybrid
Access (HDLC) slot cards, or dedicate the Series56 cards to modem p rocessing by d eleting the
Digital Call-Type profiles. Otherwise, you are likely to experience delays in establishing
Frame Relay connections. See Chapter 19, “Configuring Call Routing” for more information.
Hybrid Access card implementation
Each ISDN call, and each channel of a nailed session, requires an HDLC channel to process
the HDLC-encapsulated data received from or destined to a WAN interface. Because the
following cards require HDLC channels, you might need to install a Hybrid Access card in
your unit:
• Eight-port E1 card
• Eight-port T1 card
• T3 card
The Hybrid Acces card is supported on the DSLTNT. On an APX 8000 or MAX TNT unit,
Series56 II and III cards also provide up to 48 HDLC channels per card.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 5-5
Page 60

Page 61

Configuring MultiDSP Cards
(MAX TNT, APX 8000)
Introduction to MultiDSP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Supported MultiDSP services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 -3
Obtaining status information about a MultiDSP card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
Configuring a MultiDSP card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
Introduction to MultiDSP
The MultiDSP card is a highly versatile, digital signal processor (DSP) slot card for
MAX TNT and APX 8 000 units.
The following services are supported by the MultiDSP card:
• Data (digital, analog)
• V.110 rate adaption standard for ISDN
6
• Personal Handyphone System (PHS), supporting PHS Internet Access Forum Standards
(PIAFS) 1.0, 2.0, 2.1
• Voice over IP (VoIP), including real-time fax functionality (MAX TNT only)
The MultiDSP support provided by a particular MultiDSP card or MAX TNT and APX 8000
unit depends on the following factors:
• The type of MultiDSP card(s) installed in the unit
• Software licenses (hash codes) currently downloaded on the unit shelf controller
• MultiDSP card use constraints (See “Card configuration constraints” on page 6-3 for
details.)
Analog modem service is, by default, always enabled. Each additional MultiDSP service has a
software license (hash code) that must be downloaded to the unit shelf controller for the
particular service to be enabled on a MAX TNT or APX 8000 unit. The hash codes enable
different types of calls to be serviced by the same DSP port on the card.
The MultiDSP services currently enabled (licensed) on MAX TNT and APX 8000 units can be
viewed in the Base profile. For details, see the“Configuring a MultiDSP card” on page 6-6.
MAX TNT and APX 8000 units support two types of MultiDSP cards—a 48-port card and a
96-port card. Each MultiDSP card type supports slightly different services. Following are
descriptions of each card.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 6-1
Page 62

Configuring MultiDSP Cards (MAX TNT, APX 8000)
Introduction to MultiDSP
48-port MultiDSP card
The 48-port MultiDSP card supports up to 48 ports of service.
Note: In MAX TNT and APX 8000 profiles and parameters, the 48-port MultiDSP card is
identified as madd or madd-card.
For a MAX TNT or APX 8000 unit with a 48-port MultiDSP card, Lucent recommends that
you limit the number of enabled MultiDSP services to two. Voice over IP (VoIP) is currently
supported on the MAX TNT only.
When two services are supported by the card, one service must be data and the other can be
V.110 PHS or VoIP. The following possible configurations are supported by the 48-port card:
• Data (analog and/or digital) service only
• V.110 service only
• PHS service only
• VoIP service only (MAX TNT only)
• Data and V.110 services
• Data and PHS services
• Data and VoIP services (MAX TNT only)
Downloaded software licenses (hash codes) determine which MultiDSP services are supported
by a particular unit and 48-port MultiDSP card. For example, if a unit is licensed to run both
data and VoIP, the ports on each installed 48-port MultiDSP card can handle data and/or VoIP
calls.
96-port MultiDSP card
The 96-port MultiDSP card supports up to 96 ports of service.
Note: In MAX TNT and APX 8000 profiles and parameters, the 96-port MultiDSP card is
identified as madd2-card.
A MAX TNT or APX 8000 unit with a 96-port MultiDSP card installed can have software
licenses for up to two of the following MultiDSP services: data and V.110. The following
possible configurations are supported by the 96-port card:
• Data (analog and/or digital) service only
• V.110 service only
• Data and V.110 services
Downloaded software licenses (hash codes) determine which MultiDSP services are supported
by a particular unit and 96-port MultiDSP card. For example, if a unit is licensed to run both
data and V.110, the ports on each installed 96-port MultiDSP card can handle data and/or V.110
calls.
6-2 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 63

Configuring MultiDSP Cards (MAX TNT, APX 8000)
Card configuration constraints
The following constraints affect the mixing of slot cards in MAX TNT and APX 8000 units.
Using 48-port and 96-port MultiDSP cards
You cannot mix 48-port and 96-port MultiDSP cards in the same MAX TNT or APX 8000
unit. However, you can use multiple 48-port or multiple 96-port MultiDSP in the same unit.
Using Series56 cards with MultiDSP cards
The single-slot Series56 II card and the single-slot Series56 III card can be used with a
MultiDSP card in the same MAX TNT or APX 8000 unit. The dual-slot Series56 modem card
cannot be used in a MAX TNT unit that has a MultiDSP card installed.
Supported MultiDSP services
The following sections describe the services (applications) supported by the MultiDSP card.
See “Configuring a MultiDSP card” on page 6-6 for information on configuring these services
in a unit.
Supported MultiDSP services
Data
V.110
The MultiDSP card supports calls made through analog modems that comply with standards
such as V.90, and digital calls made through the High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC)
protocol. Digital calls can come from an ISDN Primary Rate Interface (PRI) line, a Signaling
System 7 (SS7) network, or an E1 line with R2 signaling.
Although analog modem service is enabled by default, additional software licenses might be
required to support digital calls that use particular signaling schemes or protocols. For
example, a software license is required to support the R2 call setup signaling protocol. Also,
software licenses are required to support the Ascend SS7 Gateway Control Protocol (ASGCP)
and the IP Device Control (IPDC) protocol, which are the call s etup intermachin e trun k (I MT)
protocols for SS7.
For information about configuring a unit for specific types of digital calls, refer to s ubsequent
chapters in this guide and to the configuration guides listed under “Documentation set” on
page xxi.
V.110 is a rate adaption standard that allows telephones using the digital cellular Global
System for Mobile Communication (GSM) to connect to an ISDN network.
The V.110 service is supported by both the 48-port and 96-port MultiDSP card and requires a
V.110 software license. V.110 support also r equires a software license fo r the associated digital
signaling scheme, which can be PRI, R2, ASGCP IMT/SS7, or IPDC IMT/SS7.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 6-3
Page 64

Configuring MultiDSP Cards (MAX TNT, APX 8000)
Supported MultiDSP services
V.110 features supported by the MultiDSP card include the following:
• Asynchronous, answer-mode only (answer, but no call out), with 1 start bit, 8 data bits,
and 1 stop bit.
• Rate-adaptive mode. Supported rates are 2400bps, 4800bps, 9600bps (default), 19200bps
and 38400bps.
PHS
The Personal Handyphone System (PHS) provides mobile teleph one access to u sers located in
Japan and other Asian countries. PHS provides data communication services at bandwidths up
to 64Kbps and offers voice communication services.
The MultiDSP card supports the following data PIAFS standa rds:
• PIAFS 1.0: Fixed data rate of 32Kbps.
• PIAFS 2.0: Fixed data rate of either 32Kbps or 64Kbps for the duration of a call.
• PIAFS 2.1: Data rate that can dynamically switch between 32Kbps and 64Kbps during a
call, depending on the available wireless bandwidth.
A PHS software license is required to support PIAFS 1.0 and 2.0 functionalities. The license
supports fixed data rates of 32Kbps or 64Kbps. The data rate used by the unit is determined by
the rate from the PRI line.
To support PIAFS 2.1 functionality, two software licenses are required—the initial PHS
software license for PIAFS 1.0 and PI AFS 2.0, and a separate PHS PIAFS 2.1 softwar e
license. The two licenses are also available bundled into one license package.
Voice over IP (VoIP)
VoIP is a service that offers voice telephony across IP network infrastructures. The MultiDSP
VoIP implementation relies on the MultiVoice Gateway to connect calls to public and private
packet networks. The MulitDSP card’s VoIP implementation supports the In ternational
Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) standard for
H.323 signaling and messaging.
VoIP features supported by the MultiDSP card include the following:
• ITU-T H.323 signaling and messaging.
• Voice compression and packetization.
• Connection of each port to a single DS0 (voice calls).
• Cut-through of progress tone signals from the distant Public Switched Telephone Network
(PSTN).
PHS service is currently available only with Japan PRI signaling.
• Encoding schemes G.71 1 A-law, G.711
(coder/decoder) developed by Lucent).
• Silence suppression and detection for G.729, configured through a MAX TNT unit’s VoIP
profile. Silence suppression is automatically enabled for G.723.1.
• Real-time fax (T.38 fax).
6-4 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
µ-law, G.7 23.1, G.728, G.729, and RT-24 (a cod ec
Page 65

Configuring MultiDSP Cards (MAX TNT, APX 8000)
Obtaining status information about a MultiDSP card
A VoIP software license is required for MultiDSP suppo r t of the VoIP service. An additional
software license is required for support of real-time fax functionality.
VoIP functionalities, including real-time fax, are configured thr oug h the MAX TNT VoIP
profile.
For details about VoIP and MultiVoice configuration, refer to the MultiVoice for MAX TNT
Configuration Guide. In addition, see “Configuring a MultiDSP card” on page 6-6.
Obtaining status information about a MultiDSP card
Information can be displayed about all installed cards or only an installed MultiDSP card.
Displaying information about all installed cards
The show command displays the following information about currently installed slot cards,
including the MultiDSP card:
• Location of all installed cards by shelf number, slot number, and item or port number,
including the MultiDSP card
• Status of each card (for example, if the card is Up or Down)
• Type of cards currently installed
Note: The 48-port MultiDSP card is displayed with the name madd or madd-card. The
96-port MultiDSP card is displayed with the name madd2-card.
Use the show command to confirm that the MultiDSP card is listed as one of the installed
cards and is shown installed in the correct slot. For examp le, in a MAX TNT unit the command
displays the following information if the unit has only one shelf (s helf 1) and a 96-port
MultiDSP card is installed in slot 3:
admin> show
Shelf 1 ( standalone ):
{ shelf-1 slot-3 0 } UP madd2-card
Displaying information about an installed MultiDSP card
Use the show command with the MultiDSP card shelf number and slot number to display the
following information about a particular installed MultiDSP card:
• The card’s ports by shelf number, slot number, and port number
• Status of each port (for example, whether the port is Up or Down)
• The port service type (for example, modem)
Enter the show command, along with the shelf number and port number, to confirm that all
MultiDSP card ports are shown in the listing.
Note: For the 96-port MultiDSP card, the show shelf slot command displays
96 modems (ports). For the 48-port card, only the odd-numbered modems (1, 3, ..., 95) are
active. The modem -a command verifies that only 48 modems are available on the 48-port
card.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 6-5
Page 66

Configuring MultiDSP Cards (MAX TNT, APX 8000)
Configuring a MultiDSP card
For example, enter the following command to display information about a 96-port MultiDSP
card (identified as madd2-card) installed in shelf 1, slot 10 of a MAX TNT unit:
admin> show 1 10
{ shelf-1 slot-10 0 } UP madd2-card:
{ shelf-1 slot-10 1 } UP madd-modem-1
{ shelf-1 slot-10 2 } UP madd-modem-2
{ shelf-1 slot-10 3 } UP madd-modem-3
...
{ shelf-1 slot-10 96 } UP madd-modem-96
Verifying that installed software and software versions are correct
The dircode command displays descriptions and vers ion numb e rs of all softwar e current ly
installed on the unit’s flash memory card.
Use the dircode command to verify that the software version numbers for the system (shelf
controller) and MultiDSP card (shown as madd-card) are correct.
The following example shows the installed software versions for a MAX TNT system (shelf
controller) and 48-port MultiDSP card:
admin> dircode
Flash card code directory:
Card 1, directory size 16
shelf-controller 1838073 Thu Jan 6 19:15:52 2000 Version 8.0.0
madd-card 1336282 Thu Jan 6 19:16:00 2000 Version 8.0.0
Configuring a MultiDSP card
When a unit detects the presence of a card in one of its slots, the unit creates default profiles
appropriate for that type of card. Some default profiles might need to be reconfigured when a
new card is installed in a slot.
Minimal configuration is required to set up MultiDSP services on a unit. Licensed Multi DSP
services are automatically enabled. Depending on the type of MultiDSP card installed, 48 or 96
default call routes are created for each enabled service when the card is installed.
Configuration might be required for implementing VoIP MultiVoice functionalit y. VoIP
MultiVoice configuration is described in the MultiVoice for MAX TNT Co nfiguration Guide.
MultiDSP configuration includes the following tasks:
• Verifying that the correct software licenses are loaded on the MAX TNT or APX 8000
unit and that the desired MultiDSP services are enabled. The Base profile provides this
information.
• Confirming that the call routes are correct for the desired MultiDSP services. The
Call-Route profile controls call routing in the unit. The unit automatically generates call
routes for modem calls and licensed services when a MultiDSP card is installed or when
the slot -r and slot -u commands are issued.
6-6 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 67

Configuring MultiDSP Cards (MAX TNT, APX 8000)
• Verifying that all other configurations associated with the MultiDSP services have been
performed. For example, for VoIP MultiDSP support, all required configurations for VoIP ,
real-time fax (optional), and other desired MultiVoice features must also be performed .
• Adding support for an additional MultiDSP service, if necessary.
Verifying that MultiDSP services are enabled
The Base profile is a read-only, system-wide profile that displays enabled features, network
interfaces, and system information. Included in the Base profile are the MultiDSP services.
The Base profile indicates which MultiDSP services are currently enabled (licensed). Because
the MultiDSP modem function does not require a software license, no modem-related
parameter appears in the Base profile.
Display the Base Profile to verify that desired services are licensed on the unit. Use the get
base command to view the profile.
The following Base profile parameters relevant to the MultiDSP card. Verify that the
appropriate services are supported for your MultiDSP applications.
Base profile parameter Value if supported
Configuring a MultiDSP card
Data-Call-Enabled Yes if the unit supports data calls over ISDN (digital) lines.
The parameter is also used by Series56 and Hybrid Access
(HDLC) card s.
R2-Signaling-Enabled Yes for R2 signaling support.
SS7-ASG Yes for ASGCP SS7 IMT signaling support.
XCOM-SS7 Yes for IPDC SS7 IMT signaling support.
V110-Enabled Enabled if V.110 software is licensed on the unit.
PHS-Support Yes if Personal Handyphone System PIAFS 1.0, PIAFS 2.0
support is licensed on the unit. For PIAFS 2.1 support, the
PHS-2-1-Support parameter must also be enabled by a
software license.
PHS-2-1-Support Yes if PIAFS 2.1 support is licensed on the unit. The
PHS-Support parameter must also be enabled by a software
license. (The two PHS licenses are also available bundled
into one package.)
VoIP-Enabled Yes if VoIP is enabled by a software license.
RTFax-Enabled Yes if real-time fax (T.38) is licensed. For real-time fax
support, the VoIP-Enabled parameter must also be enabled
by a separate software license.
The following example shows relevant Base profile parameters and values for a unit installed
with a 48-port MultiDSP card that supports modem calls, digital HDLC calls, and PHS PIAFS
1.0 and PIAFS 2.0 calls (but not PIAFS 2.1 calls):
admin> get base
...
data-call-enabled = yes
...
phs-2-1-support = no
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 6-7
Page 68

Configuring MultiDSP Cards (MAX TNT, APX 8000)
Configuring a MultiDSP card
...
phs-support = yes
...
voip-enabled = no
...
v110-enabled = disabled
...
rtfax-enabled = no
...
Verifying call routes for MultiDSP service s
You can verify call routes for enabled MultiDSP services by viewing the Call-Route profiles
and the call route entries. Procedures for viewing the Call-Route profiles and entries are
described in this section.
Viewing the Call-Route profile and its Call-Route-Type parameter
When a 48-port or 96-port MultiDSP card is initially detected by the unit, the unit creates
Call-Route profiles for each MultiDSP service—modem, digital, PHS, VoIP or V.110.
Use the dir call-r command to display the Call Route profiles. The following example
displays Call Route profiles for a 48-port card (indicated by madd) installed in slot 5 of a
MAX TNT unit:
admin> show
Shelf 1 ( standalone ):
{ shelf-1 slot-5 0 } UP madd-card
admin> dir call-r
30 12/07/1999 10:22:12 {{{shelf-1 any-slot 0} 0} 0}
33 12/10/1999 18:25:32 {{{shelf-1 slot-5 0} 0} 0}
33 12/10/1999 18:25:32 {{{shelf-1 slot-5 0} 0} 1}
33 12/10/1999 18:25:32 {{{shelf-1 slot-5 0} 0} 2}
33 12/10/1999 18:25:32 {{{shelf-1 slot-5 0} 0} 3}
33 12/10/1999 18:25:32 {{{shelf-1 slot-5 0} 0} 4}
The first entry is the system default. The other profiles are for each of the MultiDSP services.
You can edit the pro fil e list to in clude only curre nt ly enabl ed MultiDSP services.
Each profile contains an index that uses the following format:
{{{shelf slot port} logical-item} entry}
The system index is the following:
{{{shelf-1 any-slot 0} 0} 0}
.
Each MultiDSP service has a unique entry field number. The following table displays the
entry number associated with each MultiDSP service type:
Call-Route profile
Associated MultiDSP service type
entry field number
0 Analog modem
6-8 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 69

Configuring MultiDSP Cards (MAX TNT, APX 8000)
Configuring a MultiDSP card
Call-Route profile
Associated MultiDSP service type
entry field number
1Digital
2PHS
3VoIP
4V.110
The following example shows a Call-Route profile for the VoIP service (entry is 3) on a
48-port MultiDSP card installed in slot 5:
33 12/10/1999 18:25:32 {{{shelf-1 slot-5 0} 0} 3}
About the Call-Route- Type parameter
Each Call-Route profile contains the Call-Route-Type parameters specific to that profile. The
Call-Route parameters might require configuration.
One Call-Route parameter, Call-Route-Type, specifies the type of call that the MAX TNT can
route to a host device. The following Call-Route-Type values apply to MultiDSP services.
Call-Route-Type values for
MultiDSP services
Description
Voice-Call-Type Call type for analog mode calls. The unit can route voice
bearer calls, excluding 3.1KHz audio calls, to a host
device.
Digital-Call-Type Call type for digital calls. The unit can route digital calls,
including 3.1KHz audio bearer channels, to a host device.
PHS-Call-Type Call type for PHS calls.
VOIP-Call-Type Call type for VoIP calls. VoIP calls can be routed to a host
device that accepts VoIP calls.
V110-Call-Type Call type for V.110 calls. Digital calls recognized as
containing V.110 rate-adapted bearer channels can be
routed to a host device.
Use the read call-route and list commands to view a specific profile’s parameters.
To identify the specific profile, you must include the profile’s index. The following example
shows Call Route parameters for the profile that covers the V.110 service (entry field is 4),
for a unit with a MultiDSP card in slot 5:
admin> read call-route { { { shelf-1 slot-50}0}4}
CALL-ROUTE/{ { { shelf-1 slot-50}0}4}
admin> list
[in CALL-ROUTE/{{{shelf-1 slot-5 } 0 4 }]
index* ={{{shelf-1 slot-5 0}0}4}
trunk-group = 0
phone-number = ““
preferred-source={{any-shelf any-slot0}0}
call-route-type = v110-call-type
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 6-9
Page 70

Configuring MultiDSP Cards (MAX TNT, APX 8000)
Configuring a MultiDSP card
Viewing call-routing d atabase entries
Unlike the Call Route profiles, entries in a call-routing database are created for the analog
modem service, digital service, and for each licensed MultiDSP service.
When a card comes up, the MAX TNT or APX 8000 unit creates a call-routing database. The
number of database entries created per service depend on the following:
• Type (48-port or 96-port) of MultiDSP card being used.
• Enabled MultiDSP services. (Analog modem service is always enabled.)
A call route entry is created for each available port and each enabled service. To view the
entries in the call-routing database, use the callroute -a command.
Note: For the 48-port MultiDSP card, only the 48 odd-numbered ports are available (port 1,
3, 5, ..., 95).
For example, if a 48-port MultiDSP card is installed in slot 5 of the MAX TNT and the
supported MultiDSP services are data (analog modem and digital) and PHS, 48 call route
entries are created for analog modem service, 48 call route entries are created for digital
service, and 48 call route entries are created for PHS service:
admin> callroute -a
1:05:01/0 0 0:00:00/0 voice-call-type 0 0
1:05:03/0 0 0:00:00/0 voice-call-type 0 0
...
1:05:95/0 0 0:00:00/0 voice-call-type 0 0
1:05:01/0 1 0:00:00/0 digital-call-type 0 0
1:05:03/0 1 0:00:00/0 digital-call-type 0 0
...
1:05:95/0 1 0:00:00/0 digital-call-type 0 0
1:05:01/0 2 0:00:00/0 phs-call-type 0 0
1:05:03/0 2 0:00:00/0 phs-call-type 0 0
...
1:05:95/0 2 0:00:00/0 phs-call-type 0 0
Verifying that configurations are correct for related services
Each MultiDSP service might require additional configuration for setting up that service on the
unit. For additional information and procedures, see the configuration guides listed und er
“Documentation set” on page xxi and the latest release note.
Adding an additional MultiDSP service
To enable an additional MultiDSP service, you must perform the following steps:
1 The unit must have the proper software license for the desired service. For further
information about adding MultiDSP software licenses, contact your Lucent Sales
Representative.
2 Once the unit is licensed for the new service, delete the existing profiles for MultiDSP
cards installed in the unit, and bring up the current profiles (that now include the new
license).
For example, if you want to delete the profiles and then bring up the current profiles for a
card installed in slot 5, enter the following commands:
6-10 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 71

Configuring MultiDSP Cards (MAX TNT, APX 8000)
Configuring a MultiDSP card
admin> slot -r 1 5
admin> slot -u
When the MultiDSP cards are brought up, the unit creates new profiles and call route entries
for each service, including the new service.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 6-11
Page 72

Page 73

Configuring T1 Cards
Introduction to T1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
Overview of T1 configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
Making a profile the working profile. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
Assigning names to T1 line profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
Enabling a line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
Specifying the framing and encoding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
Configuring ISDN PRI signaling. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
Configuring ISDN network-side emulation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
Configuring overlap receiving on PRI lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
Configuring inband robbed-bit signaling. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
Configuring NFAS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-13
Configuring T1 R1 and R1-Modified (Taiwan) with ANI and called-number processing7-15
7
Configuring clocking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-17
Configuring the front-end transceiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-17
Configuring channel usage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-18
Assigning telephone numbers to switched channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-19
Configuring trunk groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-20
Configuring nailed channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-21
Configuring a back-to-back T1 connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-21
Specifying analog encoding for TAOS unit codecs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-22
Configuring specialized options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-22
Sample T1 configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-23
Default Call-Route profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-24
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-1
Page 74

Configuring T1 Cards
Introduction to T1
Introduction to T1
A T1 line consists of 24 channels. Each channel can transmit and receive data or digitized
voice. The line uses framing and signaling to achieve synchronous and reliable transmission.
The most common configurations for T1 lines are ISDN Primary Rate Interface (PRI) and
nailed (leased) or unchannelized T1, including fractional T1. (For information about
provisioning your T1 line for use with the TAOS unit, see Appendix A, “Provisioning the
Switch.”)
ISDN PRI
In North America and Japan, a T1/PRI line typically supports 23 B channels and one
D chann e l. But if non-facility ass ociated sig naling (NFAS) is in use, more than one ISDN PRI
line on a single T1 card can share a single D channel. PRI configurations are used to receive
multiple, simultaneous ISDN calls from analog-modem and digital-services dial-in traffic.
Another common use of T1/PRI is to connect a Private Branch Exchange (PBX) to a central
office switch.
Nailed or unchannelized T1
Unchannelized T1 lines can be used for nailed connections such as to a Frame Relay network.
In such cases the configuration is static, and the TAOS unit treats the T1 line as if it were a
single connection at a fixed speed, without individual channels.
Typically, when you pay your telephone company for a leased (nailed) line, you pay more for
higher bandwidth. Anything in the range of 0bps to 1.544Mbps can be delivered on a T1 line,
and provisioned at some 64Kbps fraction of the full T1 bandwidth.
Channelized line-side vs. trunk-side T1
Calls entering the telephone network from the TAOS unit must enter the central office (CO)
through an ISDN PRI line. However, calls coming in on a channelized T1 line can enter either
on the line side or trunk side. For best results, ensure that the channelized T1 calls enter the
switch on the trunk side.
T1 lines that terminate on the line side of the switch undergo an additional analog-to-digital
conversion that reduces the data transfer rate. Some service providers and carriers have
agreements to ensure that a T1 always enters the trunk side of the CO switch, but in most
cases, no such agreement exists. The only way to guarantee a digital connection is to make sure
that calls from the TAOS unit enter the CO on the trunk side of the switch over an ISDN PRI or
a trunk-side T1 line.
7-2 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 75

Configuring T1 Cards
Overview of T1 configuration
Overview of T1 configuration
T a b le 7-1 lists the section s des cri bi ng com mon t asks you might have to perform to configure a
T1 line. The table includes a brief description of each task and lists the parameters you will
use.
For information about administering the T1 card, including such tasks as specifying a facilities
data link (FDL) and displaying the st atus of the line s, see the APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT
Administration Guide.
For complete information about the associated parameters, see the APX 8000/MAX
TNT/DSLTNT Reference.
Table 7-1. T1 line configuration tasks
Section Description of task Associated parameters
“Making a profile the working
profile” on page 7-6
“Assigning names to T1 line
profiles” on page 7-7
“Enabling a line” on page 7-8 Make a line available for use. Enabled
“Specifying the framing and
encoding” on page 7-8
“Configuring ISDN PRI
signaling” on page 7-8
“Configuring ISDN
network-side emulation” on
page 7-9
“Configuring overlap receiving
on PRI lines” on page 7-9
Before you can edit a profile, you must
make it the working profile.
Assign a name to the T1 profile. Name
Each T1 line requires framing and
encoding. Framing specifies the format
for the sequence of bits sent on the line.
Encoding affects the way data is
represented by the digital signals on the
line.
You must specify the type of network
switch providing ISDN service on a T1
PRI line.
ISDN emulation enables you to build,
send, receive, and process ISDN data.
T1 or E1 PRI lines with overlap
receiving enable the T AOS unit to gather
the complete called number from the
network switch via a series of
Information messages, enabling the use
of features such as called-number
authentication.
N/A
Frame-Type
Encoding
Switch-Type
ISDN-Emulation-Side
Signaling-Mode
Overlap-Receiving
PRI-Prefix-Number
Trailing-Digits
T302-Timer
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-3
Page 76

Configuring T1 Cards
Overview of T1 configuration
Table 7-1. T1 line configuration tasks (continued)
Section Description of task Associated parameters
“Configuring inband robbed-bit
signaling” on page 7-11
“Configuring NFAS” on
page 7-13
“Configuring T1 R1 and
R1-Modified (Taiwan) with ANI
and called-number processing”
on page 7-15
“Configuring clocking” on
page 7-17
If the lines use inband signaling, change
the signaling mode to robbed bit and
specify the type of robbed bit signaling
to use. You can also specify that the
TAOS unit process the numbers dialed
for use with Dialed Number
Identification Service (DNIS) and
Calling Number Identification (CLID)
authentication.
Specify non-facility associated signaling
(NFAS) if you want two or more PR I
lines to share a D channel.
R1 is a multifrequency inband signaling
system that uses a set of register signals
known as MFR1 tones as addressing
signals. R1 signaling can optionally be
used with Automatic Number
Identification (ANI), which is similar to
Caller ID (CLID).
Set Clock-Source to specify whether t he
T1 line can be used as the master clock
source for synchronous connections.
Signaling-Mode
Robbed-Bit-Mode
Collect-Incoming-Digits
DSP-DTMF-Input-Sample-Count
Switch-Type
NFAS-ID
NFAS-Group-ID
Signaling-Mode
R1-Use-ANIR
R1-First-Digit-Timer
R1-ANIR-Delay
R1-ANIR-Timer
R1-Modified
Clock-Source
Clock-Priority
Also specify the priority of the T1 lines
to be used for clocking.
“Configuring the front-end
transceiver” on page 7-17
“Configuring channel usage” on
page 7-18
“Assigning telephone numbers
to switched channels” on
page 7-19
“Configuring trunk groups” on
page 7-20
7-4 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Set the front-end type of the T1
transceiver to CSU (channel service
unit) or DSX (digital signal cross
connect), depending on the type of
device the TAOS unit connects to.
Specify how each of the 24 channels of a
T1 line is to be used.
Typically, you specify only the
rightmost digits necessary to distinguish
one number from another. These are
called add-on numbers.
A trunk group is a group of channels that
has been assigned a number.
Front-End-Type
DSX-Line-Length
CSU-Build-Out
Channel-Usage
Phone-Number
Trunk-Group
Page 77

Configuring T1 Cards
Overview of T1 configuration
Table 7-1. T1 line configuration tasks (continued)
Section Description of task Associated parameters
“Configuring nailed channels”
on page 7-21
“Configuring a back-to-back T1
connection” on page 7-21
“Specifying analog encoding for
TAOS unit codecs” on page 7-22
“Configuring specialized
options” on page 7-22
You must assign a nailed channel to a
group to make it available for use. The
group number can be referred to in a
Connection or Frame-Relay profile to
specify a permanent leased connection
using that group of nailed channels.
For diagnostic purposes you might
sometimes want to configure a
back- to-back connectionT1 connection
between ports on two TAOS unit units.
Codecs connected to T1 use a different
encoding standard for digitized analog
data than do codecs connected to E1.
The default for T1 is U-Law, the default
for E1 is A-Law.
Typically, the D channel of a PRI line
uses normal data. However, for some
connections, you might need to invert
the data to avoid transmitting a pattern
that the connection cannot handle
Nailed-Group
Signaling-Mode set to Inband (the
default)
Robbed-Bit-Mode set to
Wink-Start (the default)
Clock-Source set to Eligible (the
default)
Analog-Encoding
Data-Sense
Idle-Mode
Most installations use the default for the
Idle-Mode setting, which determines
what pattern the D channel looks for to
specify the idle indicator.
Chapter 19, “Configuring Call
Routing”
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-5
The TAOS unit uses call routing to
determine where to route incoming and
outgoing calls. The preferred way to set
up call-routing is to put all call-routing
information in one place: a Call-Route
profile.
If you do not use Call-Route profiles,
specify the physical address of a device
to which calls received on this channel
are routed.
Default-Call-Type
Call-by-Call-Service
Shelf
Slot
Item
Page 78

Configuring T1 Cards
Making a profile the working profile
Making a profile the working profile
When the T AOS u nit detects th at a T1 card has been installed, it creates a default T1 profile for
each of the eight lines on the card.
In the following display example, the Dir command shows eig ht default T1 pr ofiles created for
a card installed in slot 2:
admin> dir t1
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 2 }
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 4 }
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 5 }
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 6 }
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 7 }
305 12/11/1996 15:58:20 { shelf-1 slot-2 8 }
320 12/20/1996 20:55:31 { shelf-1 slot-2 3 }
317 01/08/1997 09:58:55 { shelf-1 slot-2 1 }
By default, the line is not enabled, which means that it is not available for use. Its default
signaling method is inband, typically used for channelized connections.
T o configure a T1 profile, first make it the working profile by reading it into the edit buffer. For
example:
admin> read t1 {1 2 1}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } read
Once you have read in a profile, it remains the working profile until you read in another
profile. You can use the Set command to change one or more of the profile’s parameters.
To save your configuration changes, use the Write command. For example:
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1} written
To list the parameters in a T1 profile, use the List command, as in the following example:
admin> list
[in T1/{ shelf-1 slot-6 4 }]
name = ""
physical-address* = { shelf-1 slot-6 4 }
line-interface = { no d4 ami eligible low-priority inband +
The following example shows the parameters in a T1 profile:
[in T1/{ shelf-1 slot-6 4 }:line-interface]
enabled = no
frame-type = d4
encoding = ami
clock-source = eligible
clock-priority = low-priority
signaling-mode = inband
robbed-bit-mode = wink-start
default-call-type = digital
switch-type = att-pri
7-6 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 79

Configuring T1 Cards
Assigning names to T1 line profiles
nfas-group-id = 0
nfas-id = 0
incoming-call-handling = internal-processing
call-by-call = 0
data-sense = normal
idle-mode = flag-idle
FDL = none
front-end-type = dsx
DSX-line-length = 1-133
CSU-build-out = 0-db
overlap-receiving = no
pri-prefix-number = ""
trailing-digits = 2
t302-timer = 10000
channel-config = [ { unused-channel 9 "" { any-shelf
any-slot +
maintenance-state = no
input-sample-count = one-sample
sendDisc-val = 0
hunt-grp-phone-number-1 = ""
hunt-grp-phone-number-2 = ""
hunt-grp-phone-number-3 = ""
collect-incoming-digits = no
r1-use-anir = no
r1-first-digit-timer = 340
r1-anir-delay = 350
r1-anir-timer = 200
r1-modified = no
Assigning names to T1 line profiles
In a T1 profile, the Name parameter enables you to assign the profile a name. The name can
include up to 16 characters. It is displayed after the line’s physical address in the Dir command
output. For example:
admin> read t1 {1 12 0}
admin> set name = T1 Trunk
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-12 0 } written
admin> dir T1
17 04/17/1997 19:00:02 { shelf-1 slot-12 0 } "T1 Trunk"
For T1 lines, the Line Status window displays the first eight characters of the name if one has
been assigned. For example:
T1 Trunk 1/12/0 LA la la la la la la la
If the name is longer than eight characters, the last character displayed is a plus sign (+).
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-7
Page 80

Configuring T1 Cards
Enabling a line
Enabling a line
By default each T1 line is disabled. To enable the T1 line, read its profile to make it the
working profile, then set the Line Interface subprofile’s Enabled paramete r to Yes, as in the
following example:
admin> read t1 {1 2 1}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } read
admin> set line enabled = yes
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } written
Specifying the framing and encoding
You must specify the framing and the encoding for each T1 line. If you are using ISDN, you
must specify the extended superframe (ESF) format, which consists of 24 consecutive frames,
separated by framing bits. If the line is not configured for ISDN signaling, use D4 framing
(also known as the superframe format), which is the default.
The T1 Encoding value sets the layer -1 line encoding used f or the physical links, which af fects
the way in which data is represented by the digital signals on the line. The default, alternate
mark inversion (AMI) encoding, is often used, although bipolar with 8-zero substitution
(B8ZS) encoding might be req uired if the line is configured for IS DN si gnaling . If set to Non e,
encoding is similar to AMI, but without density enforcement.
Your T1 service provider must provide the correct framing and encodin g valu es f or you r lines .
To specify the framing and encoding, set the Frame-Type and Encoding parameters:
admin> read t1 {1 2 1}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } read
admin> set line frame-type = [esf|d4]
admin> set encoding = [ami|b8zs|none]
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1} written
Configuring ISDN PRI signaling
When you set the signaling mode to ISDN, you must set channel 24 as the D channel. Note that
ISDN signaling often requires ESF framing and B8Z S encoding.
For ISDN signaling you must also specify the type of switch providing T1/ PRI s e rvice t o you r
TAOS unit. Obtain the information from your ISDN carrier. (For example, if your carrier is
AT&T, the switch type is ATT-PRI.)
Configure ISDN PRI service as follows:
admin> read t1 {1 2 1}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } read
admin> set line frame-type = esf
admin> set line encoding = b8zs
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn
7-8 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 81

Configuring ISDN network-side emulation
admin> set line switch-type = switchtype
admin> set line channel 24 channel-usage=d-channel
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1} written
To see a complete list of switch types supported on the TAOS unit, refer to the TAOS unit
online help or the APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Reference.
Configuring ISDN ne twork-side emulation
You can configure PRI lines to use either network-side or user-side ISDN emulation.
Previously, PRI lines on the TAOS unit supported only user-side emulation. Following is the
relevant parameter, shown with its default setting:
[in T1/{ any-shelf any-slot0 }:line-interface]
isdn-emulation-side = te
ISDN is a nonsymmetrical protocol used by telephone carriers to provide digital services to
end users. There are no ISDN links between telephone carrier Central Offices (COs). ISDN
links exist only between the CO and the customer. Therefore, an ISDN link can be viewed as
having two sides— the network side, or network terminating (NT) equipment, and the user
side, or terminal equipment (TE). The user side can connect only to t he netw or k s ide, and vi ce
versa. Both the network side and the user side perform the same functions, but the format of
the messages is different. For example, the network s ide must always s et a bit and the user si de
must always clear it. These differences allow either side to determine whether the other end is
the right one.
Configuring T1 Cards
ISDN emulation enables you to build, send , receive, and proces s ISDN data. ISDN moni toring,
on the other hand, allows you only to decode the ISDN data.
Configuring overlap receiving on PRI lines
Overlap receiving affects the procedure of establishing an incoming call received on a T1 or
E1 PRI line in the TAOS unit. With overlap receiving, the TAOS unit can gather the complete
called number from the network switch via a series of Information messages, enabling the use
of features such as called-number authentication.
The Q.931 specification states that either en-bloc receiving or overlap receiving can be used to
handle an incoming call. With en-bloc receiving, the Setup message received from the network
switch must contain all information required to process the call. With overlap receiving, the
Setup message can contain incomplete called number information, with the remainder of the
call information (if any) sent in one or more additional Information messages after the network
switch receives a Setup Acknowledge message from the called unit.
Following are the relevant parameters, which are shown with sample settings for T1 and E1
lines:
[in T1/{ shelf-1 slot-5 1 }:line-interface]
signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
overlap-receiving = yes
pri-prefix-number = 3069
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-9
Page 82

Configuring T1 Cards
Configuring overlap receiving on PRI lines
trailing-digits = 2
t302-timer = 10000
[in E1/{ shelf-1 slot-12 1 }:line-interface]
signaling-mode = isdn
overlap-receiving = yes
pri-prefix-number = 3069
trailing-digits = 2
t302-timer = 10000
To configure overlap receiving, you need to set some or all of the following parameters:
Parameter Specifies
Signaling-Mode Type of signaling on the T1 or E1 line. It must specify ISDN (or
Overlap-Receiving Enables/disables overlap receiving for incoming calls on the PRI line.
PRI-Prefix-Number Portion of the line’s telephone number to be used when matching the
Trailing-Digits
ISDN-NFAS, for T1) to use overlap receiving. If it is set to any other
value, Overlap-Receiving does not apply .
If set to No (the default), the PRI-Prefix-Number, Trailing-Digits, and
T302-Time parameters do not apply for overlap receiving.
called-party number in the Setup message from the network switch.
The reason for specifying this number is to enable the TAOS unit to
quickly determine when the called-party number is complete when
overlap receiving is in use. The unit uses this number and the specified
number of trailing digits to recognize that the called-party number is
complete, even if the caller did not include a Sending Complete code
(for example, by dialing the pound sign).
Typically, the PRI prefix is an ISDN-subscriber number, that might
include an area code or an area and country code combination (which
must be separated from the ISDN-subscriber number by a hyphen).
With this additional information, the TAOS unit looks for just the first
match of PRI-Prefix-Number against the called-party number in the
Setup message (first with area code, and if that fails, then without area
code).
The default null value disables the T302-Timer optimization.
Number of digits required to follow the prefix number for the
TAOS unit to consider the called number complete. Callers can
indicate Sending Complete by a method such as dialing the pound sign
(#). If a caller does not indicate Sending Complete and the TAOS unit
cannot determine whether the called number is complete, the
TAOS unit waits until the T302 timer expires even if the caller has
dialed all the required digits.
The Trailing-Digits setting enables the TAOS unit to reset the timer
when the specified number of digits has been received. Trailing-Digits
can specify a value from 1 to 6. The default value is 2.
7-10 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 83

Configuring T1 Cards
Configuring inband robbed-bit signaling
Parameter Specifies
T302-Timer Number of milliseconds that the system waits for additional called
number information for an incoming call. The val id rang e is from 100
to 30000 (.10 second and 30 seconds).
The default is 10000 (0.10 seconds).
The T AOS unit begins collecting the trailing digit information, and for
each call Setup message from the switch that does not include
“Sending Complete Information Element,” it starts the T302 timer (the
Setup Ack timer).
The TAOS unit stops the timer when it receives a message that
includes “Sending Complete Information Element.” The TAOS unit
assumes there are no more trailing digit digits to collect when the
T302 timer st ops or expires.
The following example enables overlap receiving on an E1 PRI line:
admin> read e1 {1 16 7}
E1/{ shelf-1 slot-16 7 } read
admin> set signaling-mode = isdn
admin> set overlap-receiving = yes
admin> set pri-prefix-number = 049-228-555
admin> set trailing-digits = 4
admin> set t302-timer = 5000
With this configuration, if a caller dials 049-228-555-1212, the TAOS unit matches the prefix,
finds four trailing digits, and immediately begins processing the call. It might use
called-number authentication (if applicable) before establishing a session. Similarly, if a local
caller dials 555-1212, the TAOS unit fails the first match, tries without the country code and
fails again, tries without the area code, and succeeds. It then finds four trailing digits and
begins processing the call.
Configuring inband robbed-bit signaling
When the line is configured for inband signaling, the TAOS unit does not receive
bearer-capability information from the carrier. Therefore, it cannot determine when a call is
voice-service or digital-service. For call-routing purposes, all calls in inband lines are treated
as digital calls. You can change this default by setting the Default-Call-Type parameter.
Trunk-side T1 lines must use wink-start call control, which is the default. It enables the switch
to seize the trunk by going off hook after receiving a 200ms wink.
Line-side T1 lines must use loop-start call control. Regardless of the type of call control
mechanism you choose, the switch must not forward dialed digits to the TAOS unit. Doing so
disrupts the handshaking process during multichannel calls. Lucent recomm e nds that
channelized T1 lines be trunk side rather than line side.
On lines configured for inband signaling, you must specify that the TAOS unit process the
calling and called dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) digits if you want to use Dialed Number
Identification Service (DNIS) and Calling Number Identification (CLID) authentication or
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-11
Page 84

Configuring T1 Cards
Configuring inband robbed-bit signaling
accounting. (On lines configured for PRI signaling, this information is presented as part of the
call setup message and does not require special configuration on the TAOS unit.)
To configure the TAOS unit to process the DTMF digits in a call, use the
Collect-Incoming-Digits and DSP-DTMF-Input-Sample-Count parameters in a T1 profile.
The Collect-Incoming-Digits parameter enables the TAOS unit to process the DTMF digits in
a call. The DSP-DTMF-Input-Sample-Count parameter specifies the number (one or two) of
Goertzel input samples that the TAOS unit computes to decode a DTMF digit. A setting of
Two-Samples creates a more accurate result.
To configure a T1 line for inband (robbed-bit) signaling, proceed as in the following example:
1 Read in the T1 profile:
admin> read t1 {1 2 1}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } read
2 List the Line-Interface subprofile:
admin> list line
enabled=no
frame-type=d4
encoding=ami
clock-source=eligible
clock-priority=middle-priority
signaling-mode=inband
robbed-bit-mode=wink-start
default-call-type = digital
collect-incoming-digits = no
dsp-dtmf=input-sample-count=one-sample
..
..
3 Enable the line:
admin> set enabled = yes
4 Specify inband signaling:
admin> set signaling-mode = inband
5 Specify the Robbed-Bit-Mode:
admin> set robbed-bit-mode = wink-start
6 Specify call type:
admin> set default call type = voice
7 If you are using DNIS or CLID authentication, set the TAOS unit to process the DTMF
digits and specify the sample size used to decode the digits:
admin> set collect-incoming-digits = yes
admin> set dsp-dtmf-input-sample-count = one-sample
8 Write the profile to save the changes:
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } written
7-12 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 85

Configuring NFAS
A group of T1 lines configured fo r NFAS signaling shares a D channel. One line in the group is
configured with a primary D channel, and another line is configured with a secondary
D channel. The secondary D channel is used only if the primary line fails or receives a signal
commanding a change to the other D channel. All lines within an NFAS group must reside on
the same slot card. Your service provider must supply you with the NFAS ID numbers for your
line.
The TAOS unit supports multiple NFAS groups on a single card. An NFAS group contains a
minimum of two PRIs. A T1 card supports up to four NFAS groups, and a T3 card supports up
to 14 NF A S group s. To configure an NF AS grou p, you must set the NFAS-group-ID parameter.
Lines with the same NFAS-group-ID value are in the same NFAS group.
Configuring a single NFAS group
To configure two T1 lines for NFAS, proceed as in the following example, in which the
administrator configures ports 3 and 4 of the card in slot 2 of shelf 1:
admin> read t1 {1 2 3}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 3 } read
Configuring T1 Cards
Configuring NFAS
admin> set line enabled = yes
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id = 0
admin> set channel 24 channel = nfas-primary
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 3 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 4}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 4 } read
admin> set line enabled = yes
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id = 1
admin> set line channel 24 channel = nfas-secondary-d
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 4 } written
Configuring multiple NFAS groups
T o configure multiple NFAS groups, you must first obtain an NFAS ID for each DS1 from
your service provider and an NFAS group ID for each group of PRI lines that shares a
D channel. Within an NFAS group, all PRIs share the same NFAS-group-ID value and have
unique NFAS-ID values.
T elcos ofte n use NFAS-ID=0 for the PRI with the primary D-Ch annel, and N FAS-ID=1 for the
PRI with the secondary D channel. You must set both the NFAS-group-ID parameter and the
NFAS-ID parameter for each DS1.
In the following example, an administrator configures two NFAS groups on a T1 card. Each
group contains four DS1s. The example uses the NFAS group IDs 1 and 2, but the actual
values you use depend on how your lines are provisioned.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-13
Page 86

Configuring T1 Cards
Configuring NFAS
admin> read t1 {1 2 1}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } read
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id = 0
admin> set line nfas-group-id = 1
admin> set channel 24 channel = nfas-primary
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 1 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 2}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 2 } read
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id = 1
admin> set line nfas-group-id = 1
admin> set line channel 24 channel = nfas-secondary
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 2 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 3}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 3 } read
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id = 2
admin> set line nfas-group-id = 1
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 3 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 4}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 4 } read
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id = 3
admin> set line nfas-group-id = 1
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 4 } written
The following commands configure NFAS group 2, which contains lines 5 through 8:
admin> read t1 {1 2 5}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 5 } read
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id = 0
admin> set line nfas-group-id = 2
admin> set channel 24 channel = nfas-primary
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 5 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 6}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 6 } read
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id = 1
admin> set line nfas-group-id = 2
admin> set line channel 24 channel = nfas-secondary
7-14 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 87

Configuring T1 R1 and R1-Modified (Taiwan) with ANI and called-number processing
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 6 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 7}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 7 } read
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id = 2
admin> set line nfas-group-id = 2
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 7 } written
admin> read t1 {1 2 8}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 8 } read
admin> set line signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line nfas-id = 3
admin> set line nfas-group-id = 2
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 8 } written
Configuring ISDN NFAS for Japanese switch types
Configuring T1 Cards
To introduce non-facility associated signaling (NFAS) support for Japanese switches, TAOS
unit supports implicit identification of the primary D-channel interface and explicit
identification of all other interfaces, as required by Japanese switches.
Following is an example of PRI/T1 line configuration for NFAS with a Japanese switch:
admin> read t1 { 1 1 1}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-1 1} read
admin> set line-interface signaling-mode = isdn-nfas
admin> set line-interface switch-type = japan-pri
admin> set line-interface nfas-group-id = 0
admin> set line-interface nfas-id = 0
admin> set line-interface channel 24 channel =
nfas-primary-d-channel
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-1 1} written
Configuring T1 R1 and R1-Modified (Taiwan) with ANI
and called-number processing
R1 is a multifrequency inband signaling system that uses a set of register signals known as
MFR1 tones as addressing signals. Each address (telepho ne number) is preceded by a KP pulse
and followed by an ST pulse denoting the end of addressing.
R1 signaling can optionally be used with Automatic Number Identification (ANI), which is
similar to Caller ID (CLID). When it is in use, you can specify whether to send an Automatic
Number ID Request (ANIR) to the switch. If you specify that the unit must send an ANIR to
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-15
Page 88

Configuring T1 Cards
Configuring T1 R1 and R1-Modified (Taiwan) with ANI and called-number processing
the switch, you can also specify how long it waits before sendin g the request, and how long the
ANIR signal lasts.
The following parameters enable R1 signaling on T1 lines and specify the timing of certain
signals from the switch. These parameters are shown with their default settings:
[in T1/{ any-shelf any-slot 0 }:line-interface]
signaling-mode = inband
r1-use-anir = no
r1-first-digit-timer = 240
r1-anir-delay = 350
r1-anir-timer = 200
r1-modified = no
Parameter Specifies
Signaling-Mode For T1 R1 signaling, you must set Signaling-Mode to R1-Inband.
R1-Use-ANIR Enab les/disables ANI processing (CLID). It is set to No by
default. If se t to Yes, the system performs ANI processing on
incoming calls.
R1-First-Digit-Timer Time in milliseconds to wait for the first digit from the switch after
sending the KP pulse. The default setting is 340 ms. The valid
range is from 0 to 1000.
R1-ANIR-Delay Time in milliseconds to wait before sending the ANIR signal after
receipt of the ST pulse from the switch. The default setting is
350 ms. The valid range is from 300 to 2000.
R1-ANIR-Timer Du ration in milliseconds of the ANIR signal. The default setting is
200 ms. The valid range is from 180 to 400.
R1-Modified Enables/disables a modified version R1 signaling that is required
in Taiwan. It is set to No by default, which indicates regular R1
signaling (described in the ITU recommendation Q.310- 332).
TAOS units located in Taiwan must set this parameter to Yes.
Following is an example that shows how to configure R1-Modified signaling (Taiwan) with
ANIR in a T1 profile:
admin> read t1 { 1 5 1}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-5 1 } read
admin> set line signal = r1-inband
admin> set line r1-use-anir = yes
admin> set line r1-first-digit-timer = 360
admin> set line r1-anir-delay = 360
admin> set line r1-anir-timer = 220
admin> set line r1-modified = yes
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-5 1 } written
7-16 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 89

Configuring clocking
You can configure the TAOS unit to use any of the T1 lines as a master phase-locked loop
(PLL) clock source for synchronous connections for an entire system. In synchronous
transmission, both the sending device and the receiving device must maintain synchronization
to determine where one block of data ends and the next begins.
From the T1 lines configured as eligible clock sources, the TAOS unit chooses a clock source
on the basis of priority. If multiple T1 lines are configured as eligible clock sources and have
an equal clock priority, the TAOS unit chooses one of them at random. Once chosen as the
clock source, the line used until it becomes unavailable or a higher-priority source becomes
available.
If no eligible external sources are available, the system uses an internal clock generated from
the primary shelf controller. Using the internal clock is generally not recommended.
The Clock-Source diagnostic command displays the current master clock source and any
available clock source. Sources from layer 2 up, which are preferred, are marked with an
asterisk.
Configuring T1 Cards
Configuring clocking
To specify a clock source and set a priority, proceed as follows after reading in the line’s T1
profile:
admin> set clock-source = eligible
admin> set clock-priority = high-priority
admin> write
Configuring the front-end transceiver
The front-end type of the T1 transceiver can be CSU or DSX.
If you are connecting the TAOS unit to a DSX, set the Front-End-Type to DSX. Wi th this
setting you must also specify the length of the physical T1 line in feet. The value must reflect
the longest line length you expect to encounter in your installation, up to a maximum of
655 feet (200m).
If you are not connecting the TAOS unit to a DSX, set Front-End-Type to CSU. Y ou migh t also
have to set a line buildout value to specify the amount of attenuation, in decibels, that the
TAOS unit must apply to the line. If the TAOS unit is too close to a repeater, you need to add
some attenuation to reduce the strength of the signal. Ask your service provider whether you
need attenuation and, if so, how much.
To specify DSX settings, proceed as in the following example after reading in the line’s T1
profile:
admin> set front-end-type = dsx
admin> set dsx-line-length = 1-133
admin> write
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-17
Page 90

Configuring T1 Cards
Configuring channel usage
To specify CSU settings, proceed as in the following example after reading in the line’s T1
profile:
admin> set front-end-type = csu
admin> set csu-build-out = 7.5-db
admin> write
Configuring channel usage
You must specify how each of the 24 channels of a T1 line is to be used. By default, T1
channels are configured as switched. (If you are going to set up the lines for NFAS, see
“Configuring NFAS” on page 7-13 for additional channel-configuration information.)
You can configure each of the 24 channels of a T1 line for one of the following uses:
• unused-channel—Channel is unused. Send the single idle code defined for this
channel.
• switched-channel—A switched channel, which will be robbed-bit or D channel,
depending on how the line is configured at a higher level.
• nailed-64-channel—Clear-channel 64Kbps circuit. Does not requi re any setup
information.
• d-channel—Channel is used for ISDN D channel signaling directed at the appropriate
controller for the physical interface.
• nfas-primary-d-channel—The primary D channel for a group of T1 lines with the
same NFAS ID. All other channels on the NFAS line must be set to
switched-channel, nailed-64-channel, or unused-channel. Within an
NFAS group, only one line should be configured to provide the primary ISDN D channel .
• nfas-secondary-d-channel—The secondary D channel for a group of T1 lines
with the same NFAS ID. All other channels on the NFAS line must be set to
switched-channel, nailed-64-channel, or unused-channel. Within an
NFAS group, you configure only one line to provide the secondary (backup) D channel.
To specify the channel usage:
1 List the Line-Interface parameters:
admin> list line-interface
2 Set the Channel-Usage parameter for the first channel:
admin> set channel 1 channel-usage=[unused-channel |
switched-channel |nailed-64-channel| d-channel| nfas-primary-d-channel| nfas-secondary-d-channel]
admin> write
7-18 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 91

Configuring T1 Cards
Assigning telephone numbers to switched channels
Assigning telephone numbers to switched channels
Channel assignments typically specify add-on numbers, not full telephone numbers. Add-on
numbers include only the rightmost digits needed to distinguis h on e nu mber f rom anoth er. For
example, if a line is assigned 23 numbers, all of which begin with 212-555-, the add-on
number is the unique set of digits to the right of these common digits.
The most common reason multichannel calls fail to add channels properly is that the calling
unit cannot use the add-on numbers it receives. To avoid this problem, make sure that the
add-on numbers you assign all have the same number of digits.
When a caller initiates a multichannel call, it first dials the base channel and then requests
additional numbers for dialing the additional channels. When it receives add-on numbers, the
caller integrates them with the number it dialed for the base channel as follows:
• If the add-on number has fewer digits than the dialed number, the caller pads the add-on
number with the leftmost digits that are included in the dialed number but not in the
add-on number. For example, if the add-on number is 6532 and the dialed-number is
9-212-555-1212, the caller uses 9-212-555-6532 to dial the next channel.
• If the add-on number has more digits than the dialed number, the caller discards extra
digits in the add-on numbers, starting with the leftmost digit.
• If the add-on number has the same number of digits as the dialed number, the entire
add-on number is used. For example, if 6532 is the add-on number and 6588 is the dialed
number, the caller uses 6532 to dial the next channel.
To assign add-on numbers to the channels of a T1 line, proceed as in the following example:
admin> list line channel
channel-config[1]={switched-channel 9 "" {any-shelf any-slot 0} 0 }
channel-config[2]={switched-channel 9 "" {any-shelf any-slot 0} 0 }
channel-config[3]={switched-channel 9 "" {any-shelf any-slot 0} 0 }
...
channel-config[24]={switched-channel 9 "" {any-shelf any-slot 0} 0}
admin>
admin> set 2 phone = 61
admin> set 3 phone = 62
admin> set 4 phone = 63
admin> set 5 phone = 64
set 1 phone = 60
In a hunt group, a group of channels is assigned the same telephone number. When a call
comes in on that number, the T AOS unit uses the first available channel to which the number is
assigned. Because channels in a hunt group share a common telephone number, the add-on
numbers in the profile are all the same.
The following example shows how to configure two groups o f fou r chan nel s wit h h unt gr oup s:
admin> set 6 phone = 70
admin> set 7 phone = 70
admin> set 8 phone = 70
admin> set 9 phone = 70
admin> set 10 phone = 72
admin> set 11 phone = 72
admin> set 12 phone = 72
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-19
Page 92

Configuring T1 Cards
Configuring trunk groups
admin> set 13 phone = 72
admin> write
Configuring trunk groups
Like nailed channels that have been assigned a group number, switched channels in a trunk
group can be referred to from a Connection profile and Call-Route profile to direct outbound
calls to use that specific bandwidth. Trunk groups also serve a variety of other purposes, such
as separating lines supplied by different carriers so those lines can be used as backup for each
other if one switch becomes unavailable. The decision to use trunk groups is a global one.
Once you have enabled the use of trunk groups, every switched channel must be assigned a
trunk group number or it will not be available for outbound calls.
Trunk groups limit the number of channels available to multichannel calls, because only
channels within the same trunk group can be aggregated.
To enable trunk groups, open the System profile and set Use-Trunk-Groups to Yes, as in the
following example:
admin> read system
SYSTEM read
admin> list
name = ""
system-rmt-mgmt = yes
use-trunk-groups = no
idle-logout = 0
parallel-dialing = 2
single-file-incoming = yes
analog-encoding = a-law
sessionid-base = 0
admin> set use-trunk-groups = yes
admin> write
Then assign the channels of each T1 line to a trunk group, as
in the following example:
admin> list line channel 1
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
admin> set trunk-group = 4
admin> list .. 2
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
admin> set trunk-group = 4
admin> list .. 3
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
7-20 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 93

phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
admin> set trunk-group = 4
admin> write
Note: Command history is very useful for repeating commands. Press the Up-Arrow to
redisplay the command, and then press Enter. (For more information, see the TAOS
Command-Line Interface Guide.)
Configuring nailed channels
The number of nailed (leased) channels must be the same at both ends of the connection. For
example, if there are five nailed channels at the local end, there must be five nailed channels at
the remote end. However, channel assignments do not have to match. For example Channel 1
might be switched at the local end and nailed at the remote end.
Note that channels in a nailed group must be contiguous on the T1 line.
Configuring T1 Cards
Configuring nailed channels
When you configure Connection profiles to use the leased connection, you must specify the
Nailed-Group number in the Telco-Options subprofile.
To configure a nailed channel, proceed as in the following example:
admin> list line channel 1
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
admin>
admin> set nailed = 3
admin> list .. 2
channel-usage = switched-channel
trunk-group = 9
phone-number = ""
call-route-info = { any-shelf any-slot 0 }
nailed-group = 0
admin>
admin> set nailed = 3
admin> write
set channel = nailed
set channel = nailed
Configuring a back-to-back T1 connection
For diagnostic purposes, you might sometimes want to configure a back-to-back T1
connection between ports on two TAOS units. In the T1 profile for one end of the line you
want to connect with a back-to-back connection, specify the following values:
• Signaling-Mode set to Inband (the default)
• Robbed-Bit-Mode set to Wink-Start (the default)
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-21
Page 94

Configuring T1 Cards
Specifying analog encoding for TAOS unit codecs
• Clock-Source set to Eligible (the default)
In T1 profile for the other end of the line, specify the following values:
• Signaling-Mode set to Inband (the default)
• Robbed-Bit-Mode set to Inc-W-200 or Inc-W-400
• Clock-Source set to Eligible (the default)
Connect the two ports with a T1-crossover cable. You can now configure Connection profiles
between the units and dial over the connection as you would over the WAN. (For information
about configuring Connection profiles, see the APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT WAN, Routing
and Tunneling Configuration Guide.)
Specifying analog encoding for TAOS unit codecs
Codecs connected to T1 use a different encoding standard for digitized analog data than do
codecs connected to E1. The default for T1 is U-Law, the default for E1 is A-Law.
To specify the analog encoding, proceed as in the following example:
1 Open the System profile:
admin> read system
2 Specify the analog encoding for all the codecs in the TAOS unit:
admin> set analog-encoding = u-law
3 Write the System profile to save the changes:
admin> write
SYSTEM written
Configuring specialized options
The settings describ ed in this section are not normally used. Depen di ng on your configuration,
however, you might need to change the default values.
Typically, the D channel of a PRI line uses normal data. However, for some connections you
might need to invert the data to avoid transmitting a pattern that the connection cannot handle.
Inversion changes 1s to 0s and 0s to 1s. Both sides of the connection must agree to use inverted
data.
Idle mode determines whether the D channel looks for a flag pattern (01111110) or a mark
pattern (11111111) as the idle indicator. The default setting, Flag-Idle, is usually correct.
To set these options, use the Data-Sense and Idle-Mode parameters:
admin> set data-sense = [normal|inv]
admin> set idle-mode = [mark-idle|flag-idle]
admin> write
7-22 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 95

Sample T1 configuration
This section provides an example of how to configure a T1 slot card. The example uses the
following setup:
• The card is in shelf 1, slot 2.
• All lines use PRI signaling.
• Switch type is NTI-PRI.
• The line is connected to a DSX and is less than 100 feet (30.5m ) long. It therefo re uses the
default settings for Front-End-Type and DSX-Line-Length.
• All the channels are switched (the default), with the exception of channel 24, which is set
for D channel signaling.
• All the channels are assigned to trunk group 9 (the default).
• The Default-Call-Type is digital (the default), so all calls received on this card are routed
to the Hybrid Access (HDLC) card.
• The rest of the line parameters are left at their default values.
To configure the T1 card as in this example:
1 Create a new T1 profile:
Configuring T1 Cards
Sample T1 configuration
admin> new t1
T1/{ any-shelf any-slot 0 } read
2 Set the physical address for the first T1 line:
admin> set physical-address ={ 1 2 1}
This applies the changes to the T1 line in the specified
slot.
3 List the contents of the line profile:
admin> list line-interface
enabled = no
frame-type = d4
encoding = ami
clock-source = eligible
clock-priority = middle-priority
signaling-mode = inband
robbed-bit-mode = wink-start
default-call-type = digital
switch-type = att-pri
nfas-id = 0
call-by-call = 0
data-sense = normal
idle-mode = flag-idle
FDL = none
front-end-type = dsx
DSX-line-length = 1-133
CSU-build-out = 0-db
channel-config = [ { switched-channel 9 "" { any-shelf
any-slot 0 } 0 } { switc+
maintenance-state = no
sendDisc-val = 0
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 7-23
Page 96

Configuring T1 Cards
Default Call-Route profiles
4 Enable the line:
admin> set enabled = yes
5 Set the frame type:
admin> set frame-type = est
6 Set the line encoding:
admin> set encoding = b8zs
7 Set the signaling mode:
admin> set signaling-mode = isdn
8 Set the switch type:
admin> set switch-type = nti-pri
9 Next, assign all the channels to trunk group 7:
admin> set channel 1 truck-group = 7
10 Press the Up-Arrow key or Ctrl-P to redisplay the Set command you just entered.
11 Use the Left Arrow key or Control-B to change the channel number and trunk group for
all the channels.
12 Change the channel usage of channel 24 to D Channel, because this channel carries the
signaling for the PRI line.
admin> set channel 24 channel-usage = d -channel
13 Write the profile to commit your changes:
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-2 2 } written
14 Because the T1 lines are all configured similarly, you can write the changes to the rest of
the lines by setting the physical address and then writing the same profile for each of the
lines:
admin> set physical-address = { 2 1 2}
admin> write
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-1 2 written
admin> set physical-address = { 2 1 3}
T1/{ shelf-1 slot-1 3} written
Continue until you have configured all the lines.
Default Call-Route profi les
When the TAOS unit detects that a T1 card has been installed, it creates on default Call-Route
profile associated with the card. For example
admin> dir call-r
9 12/11/1996 15:58:08 { { { any-shelf any-slot 0 } 0 } 0 }
13 01/06/1997 17:17:10 { { { shelf-1 slot-2 0 } 0 }
This default Call-Route profile routes outbound trunk calls to any line on the card. To handle
inbound modem and LAN-session traffic, you must configure specific call routes. For details,
see Chapter 19, “Configuring Call Routing.”
7-24 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 97

Configuring T1 FrameLine Cards
(MAX TNT, DSLTNT)
Introduction to T1 FrameLine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
Overview of supported features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
Overview of T1 FrameLine configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
Configuring the clock source. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
Introduction to T1 FrameLine
The T1 FrameLine slot card provides 10 unchannelized T1 lines, each of which can be used for
one nailed connection. Associated with each T1 line is a Serial Communications Adapter
(SCA), which is responsible for receiving and transmitting HDLC frames. Because there is
only one SCA per line, only one PPP or Frame Relay link (possibly with multiple DLCIs) can
be active per line.
Unlike other slot cards, such as the Series56 II and Series56 III Digital Modems cards or
Hybrid Access (HDLC) cards, call routing profiles are not used for the FrameLine card and are
ignored if they exist. The data pathway is directed to an on-board SCA device and cannot be
routed to another host card. All packetization of data occurs locally.
8
Overview of supported features
This section describes the T1 FrameLine slot card’s support for the following protocols:
• PPP
• Frame Relay
• Routing protocols
• SNMP
PPP
The T1 FrameLine slot card supports PPP as follows:
• Only one PPP session per line.
• Bandwidth per session is 1-24 DS0 channels.
• Channels need not be contiguous.
APX 8000 Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 8-1
Page 98

Configuring T1 FrameLine Cards (MAX TNT, DSLTNT)
Overview of T1 FrameLine configur ation
• Multilink Protocol (MP) and Multilink Protocol Plus (MP+) are not suppo rt ed. The
connection profile must specify only PPP.
• Users are authenticated by the local profile or RADIUS.
• Stac compression is not supported.
Frame Relay
The T1 FrameLine slot card supports Frame Relay as follows:
• Only one Frame Relay link, possibly containing multiple data-link connectio n ident if iers
(DLCIs), can be active per line.
• Bandwidth per link is 1-24 DS0 channels.
• Channels need not be contiguous.
• Up to 240 permanent virtual circuits (PVCs) are supported per card.
Routing protocols
The T1 FrameLine slot card supports only IP routing.
RADIUS
The T1 FrameLine slot card supports the same RADIUS accounting and authentication as the
digital modem cards.
SNMP
The T1 FrameLine slot card supports SNMP as follows:
• DS1 status and management are the same as for the eight-port T1 card.
• The T1 FrameLine slot card supports the accounting Management Information Base
(MIB) for session inform ation .
Overview of T1 FrameLine configuration
Configuring the T1 FrameLine slot card is similar to T1 s lot card configuration except that the
T1 FrameLine slot card has the following configuration restrictions:
• Signaling-Mode must be set to inband.
• The T1 FrameLine card can be used only for nailed Frame Relay or PPP links.
• You must set Channel-Usage to either Unused-Channel or Nailed-64-Channel.
• If Channel-Usage is Nailed-64-Channel and you are using nailed channels, the
Nailed-Group setting must be unique to the line. Two different T1 lines cannot share a
nailed group.
• Unlike the T1 card, channels in the same nailed group do not have to be contiguous. For
example, DS0 channels 1 and 3 can be in the same nailed group, with channel 2 unused.
• The following T1 profile parameters are not applicable for the FrameLine card:
8-2 Preliminary May 9, 2000 APX 8000 Physical Interface Configuration Guide
Page 99

Configuring T1 FrameLine Cards (MAX TNT, DSLTNT)
– Call-by-Call
– Channel-Usage
– Default-Call-Type
– Data Sense
– FDL
– Idle-Mode
– Maintenance-State
– NFAS-ID
– Robbed-Bit-Mode
– SendDisc-Val
– Switch-Type
For information about configuring T1 profiles, see Chapter 7, “Configuring T1 Cards.”
Configuring the clock source
Configuring the clock source
The T1 FrameLine slot card uses the same system-wide PLL synchronous clock source for
DS1 transmission as do the eight-port T1 and E1 cards. Any of the lines can serve as the clock
source for the unit. To configure the T1 FrameLine card’s clock source, use the same
parameters (Clock-Source and Clock-Priority) that you use for other cards.
All 10 lines must use the same clock sour ce. Clock ing on a per -li ne basi s is not su pported. The
clock source can be one of the 10 lines, or a line on another slot card, or it can be internally
generated from the primary shelf controller. Using the internal clock is not recommended. For
more information about configuring the clock source, see “Configuring clocking” on
page 7-17.
In addition, if the system clock source is from one of the 10 lines, it affects the timing on the
Time-division multiplexing (TDM) backplane, because TDM timing is based on the clock
source. This relationship exists even though the T1 FrameLine card does not use the TDM
backplane.
APX 8000/MAX TNT/DSLTNT Physical Interface Configuration Guide Preliminary May 9, 2000 8-3
Page 100

 Loading...
Loading...