Page 1

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution
User Guide
Version 2.0
August 2010
Page 2
Revision History
Version and Date Description of Changes
Version 2.0, August 2010 Added new models of supported controllers.
Version 1.1, August 2009 Applied extensive general editing improvements.
Version 1.0, July 2009 Initial release of this document.
LSI, the LSI logo, Fusion-MPT are trademarks or registered trademarks of LSI Corporation or its subsidiaries. All other brand and product names may be trademarks of their respective companies.
LSI Corporation reserves the right to make changes to the product(s) or information disclosed herein at any time without notice. LSI Corporation does not assume any responsibility or liability arising
out of the application or use of any product or service described herein, except as expressly agreed to in writing by LSI Corporation; nor does the purchase, lease, or use of a product or service from
LSI Corporation convey a license under any patent rights, copyrights, trademark rights, or any other of the intellectual property rights of LSI Corporation or of third parties.
This document contains proprietary information of LSI Corporation. The information contained herein is not to be used by or disclosed to third parties without the express written permission of
LSI Corporation.
Corporate Headquarters Email Website
Milpitas, CA globalsupport@lsi.com www.lsi.com
800-372-2447
Document Number: DB15-000543-02
Copyright © 2010 LSI Corporation
All Rights Reserved
Page 3

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Integrated RAID Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
1.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
1.2 Benefits and Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
1.2.1 Host Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
1.2.2 Metadata Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
1.2.3 SMART Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
1.2.4 Fusion-MPT Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Chapter 2: Overview of Integrated RAID Mirrored Volumes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
2.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
2.2 Integrated Mirroring and Integrated Mirroring Enhanced Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
2.3 Operation of Mirrored Volumes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
2.4 Mirrored Volume Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.4.1 Resynchronization with Concurrent Host I/O Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.4.2 Hot Swapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.4.3 Hot Spare Disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.4.4 Online Capacity Expansion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.4.5 Media Verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.4.6 Disk Write Caching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
2.4.7 NVSRAM Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
2.4.8 Background Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
2.4.9 Consistency Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
2.4.10 Make Data Consistent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
3.1 Mirrored Volume Configuration Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
3.2 Creating Mirrored Volumes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
3.2.1 Creating an Integrated Mirroring Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
3.2.2 Creating an Integrated Mirroring Enhanced or Integrated Mirroring + Striping Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
3.2.3 Expanding an Integrated Mirroring Volume with OCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
3.3 Managing Hot Spare Disks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
3.3.1 Creating Hot Spare Disks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
3.3.2 Deleting Hot Spare Disks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
3.4 Other Configuration Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
3.4.1 Viewing Volume Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
3.4.2 Running a Consistency Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
3.4.3 Activating an Array . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
3.4.4 Deleting an Array . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
3.4.5 Locating Disk Drives in a Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
3.4.6 Selecting a Boot Disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Chapter 4: Overview of Integrated Striping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
4.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
4.2 Integrated Striping Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
4.3 Integrated Striping Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 3
Page 4

Table of Contents SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
Chapter 5: Creating Integrated Striping Volumes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
5.1 Integrated Striping Configuration Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
5.2 Creating Integrated Striping Volumes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
5.3 Other Configuration Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
5.3.1 Viewing Volume Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
5.3.2 Activating an Array . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
5.3.3 Deleting an Array . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
5.3.4 Locating Disk Drives in a Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
5.3.5 Selecting a Boot Disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Appendix A: Using the SAS2 Integrated RAID Configuration Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
A.1 Hardware and Software Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
A.1.1 Controller Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
A.1.2 Operating System and Software Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
A.2 Interface Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
A.3 Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
A.3.1 Common Command-Line Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
A.3.2 CREATE Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
A.3.3 DELETE Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
A.3.4 DISPLAY Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
A.3.5 HOTSPARE Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
A.3.6 STATUS Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
A.3.7 LIST Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
A.3.8 MFGPAGE Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
A.3.9 CONSTCHK Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
A.3.10 ACTIVATE Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
A.3.11 LOCATE Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
A.3.12 LOGIR Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Page 4 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 5

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 1: Introduction to the Integrated RAID Solution | Overview
Chapter 1
Introduction to the Integrated RAID Solution
This chapter provides an introduction to the features and benefits of the LSI Integrated
RAID solution for LSI SAS2 controllers.
1.1 Overview The LSI Integrated RAID solution provides cost benefits for the server or workstation
market that requires the extra performance, storage capacity, and/or redundancy of a
RAID configuration. The LSI Integrated RAID solution includes the following RAID
features:
The Integrated Mirroring solution, which provides features of RAID 1
The Integrated Mirroring + Striping solution, which provides features of RAID 10
The Integrated Mirroring Enhanced solution, which provides features of RAID 1
Enhanced (RAID 1E)
The Integrated Striping solution, which provides features of RAID 0
By simplifying the configuration options and by providing firmware support in its SAS2
host adapters, LSI can offer the Integrated RAID solution at a lower cost than a
hardware RAID implementation.
LSI Fusion-MPT™ firmware supports I ntegrated Mirroring volumes, Integrated Mir roring
+ Striping volumes, Integrated Mirroring Enhanced volumes, and Integrated Striping
volumes. You can create up to two Integrated RAID volumes on each LSI SAS2
controller.
The LSI Integrated RAID solution supports the following LSI SAS2 controllers and the
host bus adapters based on these controllers:
LSISAS2004
LSISAS2008
LSISAS2108
LSISAS2208
LSISAS2304
LSISAS2308
LSI Integrated RAID firmware uses the same device drivers as the standard LSI
Fusion-MPT-based controllers. This eliminates the need for complex backup software or
expensive RAID hardware. To conserve system resources, the Integrated RAID firmware
operates independently from the operating system. The BIOS-based configuration
utility, documented in Chapter 3 and Chapter 5, makes it easy to configure mirrored
and striped volumes. The Integrated RAID solution is currently available as an optional
component of the Fusion-MPT architecture on LSI SAS2 controllers.
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 5
Page 6

Chapter 1: Introduction to the Integrated RAID Solution | Benefits and Features SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
1.2 Benefits and Features The LSI Integrated RAID solution has the following benefits and features:
Support for up to 10 disks per Integrated RAID volume, with one or two volumes on
each SAS2 controller. Each controller can support can support 14 volume drives,
including one or two hot spare disks.
Support for two-disk Integrated Mirroring volumes (RAID 1)
Support for online capacity expansion (OCE) for RAID 1 volumes. OCE allows you to
increase the size of a RAID 1 volume by replacing the disk drives with
higher-capacity drives.
Low-cost RAID volume creation, which meets the needs of most internal RAID
installations
Easy installation and configuration
Support for booting from any kind of Integrated RAID volume
Ability to operate without special operating system-specific software
High reliability and data integrity
— Nonvolatile write journaling
— Physical disks in a volume are not visible to the operating system (OS) or to
application software
Low host CPU and PCI bus utilization
Processing power provided by Fusion-MPT architecture
— Shared-memory architecture minimizes external memory requests
— Device hardware and firmware contain the functionality
1.2.1 Host Interface The Integrated RAID host interface uses the message-passing interface, as described in
the Fusion-MPT Message Passing Interface Specification. The Fusion-MPT interface gives
the host OS access to the RAID volumes as well as to additional non-RAID physical disks.
1.2.2 Metadata Support The Integrated RAID firmware supports metadata, which describes the logical drive
configuration stored on each member disk of a volume. After initialization, the
firmware queries each member disk to read the metadata and verify the configuration.
The firmware reduces the usable disk space for each member disk when it creates the
the volume, which makes room for the metadata.
1.2.3 SMART Support The Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (SMART) monitors disk drives
for signs of future disk failure and generates an alert if it detects such signs. The
Integrated RAID firmware polls each physical disk in the volume at regular intervals. If
the firmware detects a SMART ASC/ASCQ code on a physical disk in the volume, it
processes the SMART data and stores it in a log. The volume does not support SMART
directly because it is only a logical representation of the physical disks in the volume.
1.2.4 Fusion-MPT Support The Integrated RAID BIOS uses the LSI Fusion-MPT interface to communicate to the
SAS2 controller and firmware. This process includes reading the Fusion-MPT
configuration to access the parameters that define behavior between the SAS2
controller and the devices that connect to it. The Fusion-MPT drivers for all supported
operating systems implement the Fusion-MPT interface to communicate with the
controller and firmware.
Page 6 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 7

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 2: Overview of Integrated RAID Mirrored Volumes | Introduction
Chapter 2
Overview of Integrated RAID Mirrored Volumes
This chapter provides an overview of the LSI Integrated RAID features that support the
creation of mirrored arrays.
2.1 Introduction As a result of the shift towards network-attached storage (NAS), Internet service
providers need a cost-effective, fault-tolerant solution to protect the operating systems
on small form-factor, high-density, rack-mountable servers. The mirroring features of
the LSI Integrated RAID solution provide data protection for the system boot volume,
which safeguards the operating system and other critical information on servers and
high-performance workstations. The Integrated RAID solution supports the following
types of mirrored arrays:
2.2 Integrated Mirroring and Integrated Mirroring Enhanced Features
The Integrated Mirroring solution, which provides features of RAID 1
The Integrated Mirroring + Striping solution, which provides features of RAID 10
The Integrated Mirroring Enhanced solution, which provides features of RAID 1
Enhanced (RAID 1E)
These three mirroring solutions provide a robust, high-performance, fault-tolerant
solution to data storage needs at a lower cost than a dedicated RAID controller.
Mirrored volumes may have from two-to-ten disks to provide fault-tolerant protection
for critical data. Mirrored volumes also support one or two global hot spare drives, with
a maximum of 14 drives on each LSI SAS2 controller.
NOTE: Fourteen drives is the theoretical upper limit for a single LSI SAS2 controller,
although the controller itself may support fewer than 14 drives. You can also configure
one mirrored volume and one Integrated Striping volume on the same LSI SAS
controller.
Each SAS2 controller can have two global hot spare disks available to automatically
replace a failed disk in the one or two mirrored volumes configured on the controller.
The hot spares make the mirrored volumes even more fault-tolerant.
Integrated Mirroring, Integrated Mirroring + Striping, and Integrated Mirroring
Enhanced volumes support the following features:
Configurations of one or two mirrored volumes on each LSI SAS2 controller. Each
volume can consist of two mirrored disks for an Integrated Mirroring volume;
three-to-ten mirrored disks for an Integrated Mirroring Enhanced volume; or four,
six, eight, or ten mirrored disks for an Integrated Mirroring + Striping volume.
(Optional) Two global hot spare disks per LSI SAS2 controller to automatically
replace failed disks in mirrored volumes.
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 7
Page 8

Chapter 2: Overview of Integrated RAID Mirrored Volumes | Operation of Mirrored Volumes SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
Ability of mirrored volumes to run in optimal mode or in degraded mode if one
mirrored disk in an Integrated Mirroring volume fails or if one or more mirrored
disks fail in an Integrated Mirroring + Striping volume or Integrated Mirroring
Enhanced volume.
Support for hot swapping.
Support for online capacity expansion (OCE) for RAID 1 volumes. OCE allows you to
increase the size of a RAID 1 volume by replacing the existing disk drives with
higher-capacity disk drives. Data is protected during the expansion process, and the
RAID 1 volume remains online.
Presentation of a single, virtual drive to the operating system for each
mirrored volume.
Support for both SAS and SATA disks, although you cannot combine the two types
of disks in the same volume. However, an LSI SAS2 controller can support one
volume with SATA disks and a second volume with SAS disks.
Automatic background initialization after volume creation.
Consistency checking.
Fusion-MPT architecture.
Menu-driven, BIOS-based configuration utility.
Error notification, in which the drivers update an OS-specific event log.
Support for SCSI Enclosure Services (SES) status LED.
Write journaling, which allows automatic synchronization of potentially
inconsistent data after unexpected powerdown situations.
Use of metadata to store volume configuration on disks in a mirrored volume.
Automatic background resynchronization while host I/Os continue.
Background media verification, which ensures that data on mirrored volumes is
always accessible.
2.3 Operation of Mirrored Volumes
The LSI Integrated RAID solution supports one or two mirrored volumes on each LSI
SAS2 controller (or one mirrored volume and one Integrated Striping volume).
Typically, one of these volumes is the boot volume. Boot support is available through
the firmware of the LSI SAS2 controller that supports the standard Fusion-MPT
interface. The runtime mirroring of the boot disk is transparent to the BIOS, the drivers,
and the operating system. Host-based status software monitors the state of the
mirrored disks and reports any error conditions. The following figure shows an
Integrated Mirroring volume in which the second disk is a mirrored copy of the data on
the first (primary) disk.
Page 8 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 9
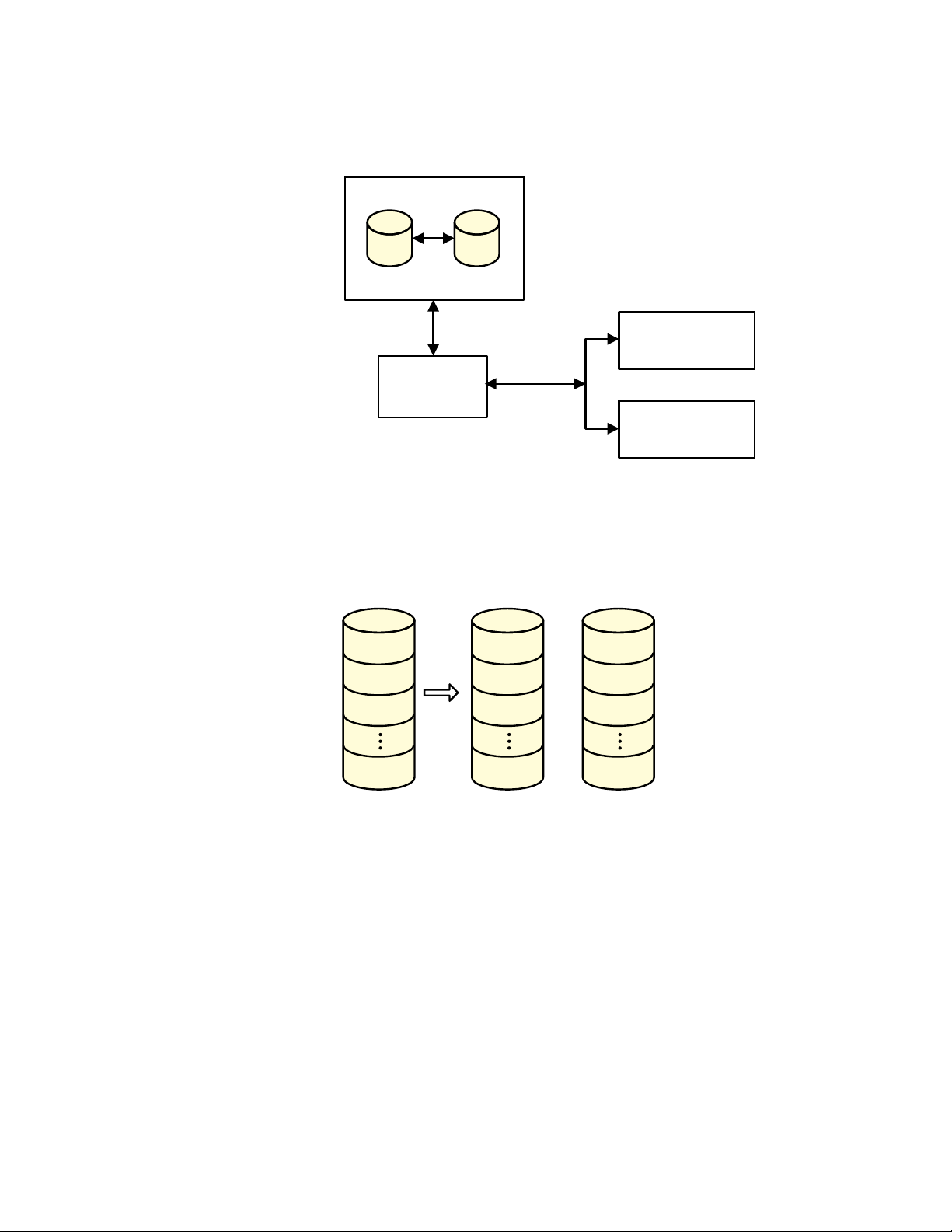
SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 2: Overview of Integrated RAID Mirrored Vol umes | Operation of Mirrored Volumes
Primary Mirror
Integrated Mirroring Volume
SAS
LSI
Fusion-MPT
SAS2 Controller
Memory Bus
NVSRAM
(For Write Journaling)
FLASH
(For Configuration)
3_00006-00
3_00007-00
LBA 1
LBA 2
LBA 3
LBA N
LBA 1
LBA 2
LBA 3
LBA N
LBA 1'
LBA 2'
LBA 3'
LBA N’
+
Physical ViewLogical View
Figure 1: Typical Integrated Mirroring Implementation
The following figure shows the logical view and physical view of an Integrated
Mirroring volume. Each logical block address (LBA) is mirrored on the second disk.
LSI Corporation Confidential
Figure 2: Integrated Mirroring Volume
You can configure an Integrated Mirroring Enhanced volume with up to 10 mirrored
disks. The following figure shows the logical view and physical view of an Integrated
Mirroring Enhanced volume with three mirrored disks. The firmware writes each
mirrored stripe to a disk and mirrors it to an adjacent disk. RAID 1E is another term for
this type of mirrored configuration.
| August 2010 Page 9
Page 10
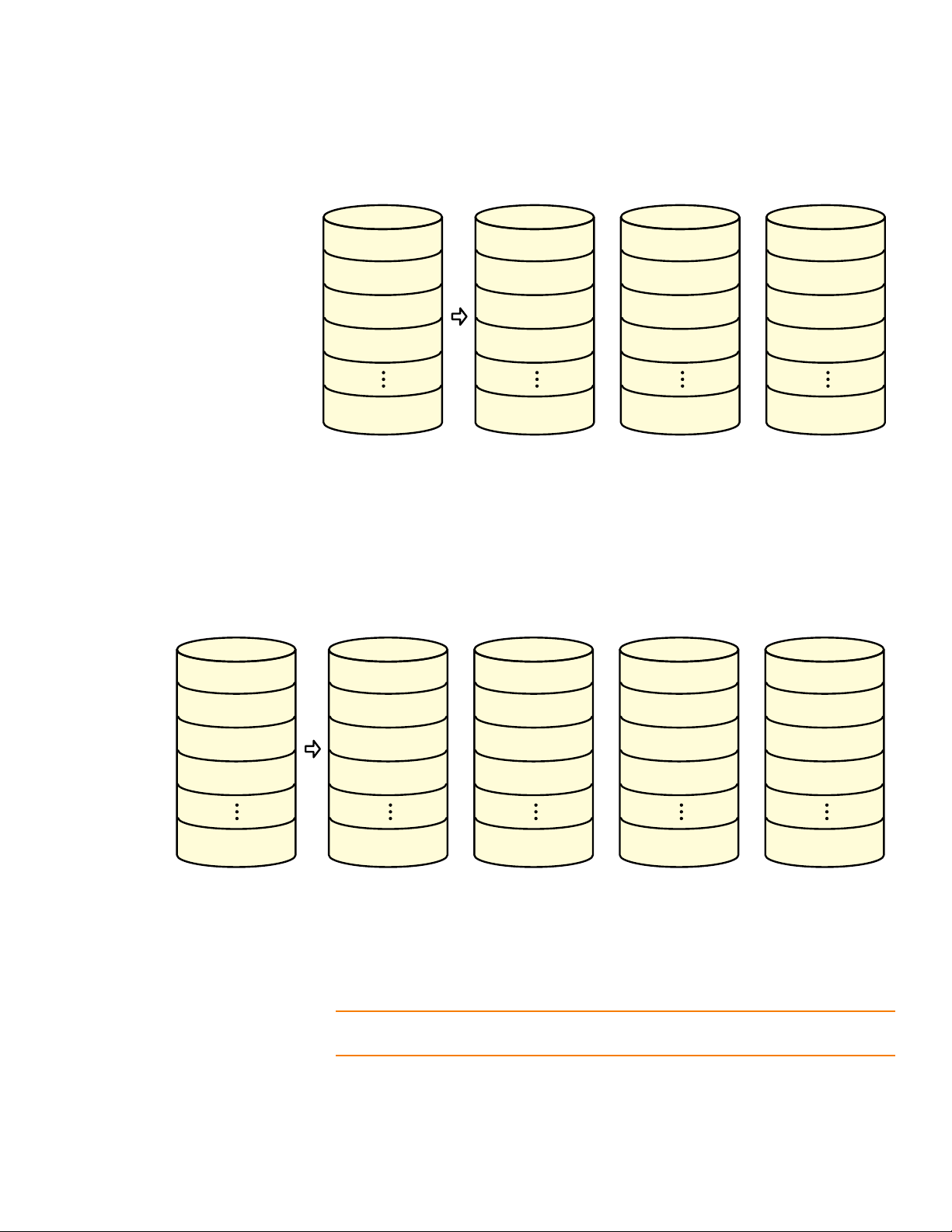
Chapter 2: Overview of Integrated RAID Mirrored Volumes | Operation of Mirrored Volumes SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
3_00008-00
Physical ViewLogical View
Mirrored Stripe 1
Mirrored Stripe 2
Mirrored Stripe 3
Mirrored Stripe 4
Mirrored Stripe N
Mirrored Stripe 1
Mirrored Stripe 2'
Mirrored Stripe 4
Mirrored Stripe 5'
Mirrored Stripe N-1'
+
Mirrored Stripe 1'
Mirrored Stripe 3
Mirrored Stripe 4'
Mirrored Stripe 6
Mirrored Stripe N
+
Mirrored Stripe 2
Mirrored Stripe 3'
Mirrored Stripe 5
Mirrored Stripe 6'
Mirrored Stripe N’
Physical ViewLogical View
Mirrored Stripe 1
Mirrored Stripe 2
Mirrored Stripe 3
Mirrored Stripe 4
Mirrored Stripe N
Mirrored Stripe 1
Mirrored Stripe 3
Mirrored Stripe 5
Mirrored Stripe 7
Mirrored Stripe N-1
+
Mirrored Stripe 1'
Mirrored Stripe 3'
Mirrored Stripe 5'
Mirrored Stripe 7'
Mirrored Stripe N-1'
+
Mirrored Stripe 2
Mirrored Stripe 4
Mirrored Stripe 6
Mirrored Stripe 8
Mirrored Stripe N
3_00009-00
+
Mirrored Stripe 2'
Mirrored Stripe 4'
Mirrored Stripe 6'
Mirrored Stripe 8'
Mirrored Stripe N’
Figure 3: Integrated Mirroring Enhanced with Three Disks
You can configure an Integrated Mirroring + Striping volume with an even number of
disks, ranging from four minimum to ten maximum. The following figure shows the
logical view and physical view of an Integrated Mirroring + Striping volume with four
mirrored disks. The firmware writes each mirrored stripe to a disk and mirrors it to an
adjacent disk. RAID 10 is another term for this type of mirrored/striped configuration.
Figure 4: Integrated Mirroring + Striping with Four Disks
The LSI SAS2 BIOS configuration utility enables you to create mirrored volumes during
initial setup and to reconfigure them in response to hardware failures or changes in
the environment.
CAUTION: The SAS2 BIOS CU deletes all existing data from the disks drives when you
select them to use for a mirrored volume.
Page 10 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 11

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 2: Overview of Integrated RAID Mirrored Volumes | Mirrored Volume Features
2.4 Mirrored Volume Features This section describes features of Integrated Mirroring, Integrated Mirroring + Striping,
and Integrated Mirroring Enhanced volumes. You can configure one or two mirrored
volumes on each LSI SAS2 controller.
2.4.1 Resynchronization with Concurrent Host I/O Operation
The Integrated RAID firmware allows host I/O transactions to continue on a mirrored
volume while it resynchronizes the volume in the background. The firmware
automatically starts resynchronizing data after a disk failure activates a hot spare, or
after a disk in a mirrored volume has been hot swapped.
2.4.2 Hot Swapping The Integrated RAID firmware supports hot swapping, and it automatically
resynchronizes the hot-swapped disk in the background without any host or user
intervention. The firmware detects hot-swap removal and disk insertion.
Following a hot-swap event, the firmware verifies that the new physical disk has
enough capacity for the mirrored volume. The firmware resynchronizes all replaced
hot-swapped disks, even if the same disk is re-inserted. In a mirrored volume with an
even number of disks, the firmware marks the hot-swapped disk as a secondary disk
and the other disk with data as the primary disk. The firmware resynchronizes all data
from the primary disk onto the new secondary disk. In a mirrored volume with an odd
number of disks, primary and secondary sets include three disks instead of two.
2.4.3 Hot Spare Disk You can configure two disks as global hot spare disks to protect data on the mirrored
volumes configured on the SAS2 controller. If the Integrated RAID firmware fails one of
the mirrored disks, it automatically replaces the failed disk with a hot spare disk and
then resynchronizes the mirrored data. The firmware automatically receives a
notification when a hot spare replaces the failed disk, and it then designates that disk
as the new hot spare.
2.4.4 Online Capacity Expansion The OCE feature enables you to expand the capacity of an existing two-disk Integrated
Mirroring (RAID 1) volume by replacing the original disk drives with higher-capacity
drives that have the same protocol (SAS or SATA).
NOTE: The new drives must have at least 50 GB more capacity than the original drives
of the volume.
After you replace the disk drives and run the OCE command, you must use a
commercial tool specific to the operating system to move or increase the size of the
partition on the volume.
2.4.5 Media Verification The Integrated RAID firmware supports a background media verification feature that
runs at regular intervals when the mirrored volume is in the Optimal state. If the
verification command fails for any reason, the firmware reads the other disk’s data for
this segment and writes it to the failing disk in an attempt to refresh the data. The
firmware periodically writes the current media verification logical block address to
nonvolatile memory so that the media verification can continue from where it stopped
prior to a power cycle.
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 11
Page 12

Chapter 2: Overview of Integrated RAID Mirrored Volumes | Mirrored Volume Features SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
2.4.6 Disk Write Caching By default, the Integrated RAID firmware disables disk write caching for mirrored
volumes. It does this to ensure that the write journal entry stored in nonvolatile static
RAM (NVSRAM) is always valid. If you enable disk write caching (not recommended),
you may cause the disk write log to be invalid.
2.4.7 NVSRAM Usage The Integrated RAID firmware requires at least a 32-KB NVSRAM to perform write
journaling for mirrored volumes on LSI SAS2 controllers. The NVSRAM also preserves
configuration information across reboots. The firmware uses write journaling to verify
that the disks in the mirrored volume are synchronized with each other.
2.4.8 Background Initialization Background initialization (BGI) is the process of copying data from primary to
secondary disks in a mirrored volume. The Integrated RAID firmware starts BGI
automatically as a background task when it creates a volume. The volume remains in
the Optimal state while BGI is in progress.
2.4.9 Consistency Check A consistency check is a background process that reads data from primary and
secondary disks in a mirrored volume and compares it to make sure the data is identical
on both disks. You can use the LSI SAS2 BIOS Configuration Utility to run a consistency
check on a mirrored volume.
2.4.10 Make Data Consistent If it is enabled in the Integrated RAID firmware, the make data consistent (MDC) process
starts automatically and runs in the background when you move a redundant volume
from one SAS controller to another SAS controller. MDC compares the data on the
primary and secondary disks. If MDC finds inconsistencies, it copies data from the
primary disk to the secondary disk.
Page 12 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 13

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes | Mirrored Volume Configuration Overview
Chapter 3
Creating Mirrored Volumes
This chapter explains how to create Integrated Mirroring, Integrated Mirroring +
Striping, and Integrated Mirroring Enhanced volumes with the LSI SAS2 BIOS
Configuration Utility (SAS2 BIOS CU).
3.1 Mirrored Volume Configuration Overview
The LSI SAS2 BIOS CU is a menu-driven utility program that enables you to easily
configure and manage Integrated RAID volumes. You can use the SAS2 BIOS CU to
create one or two mirrored volumes on each LSI SAS2 controller, with up to two
optional global hot spare disks. You must connect all disks in a mirrored volume to the
same LSI SAS2 controller.
Although you can use disks of different size in mirrored volumes, the smallest disk in
the volume determines the logical size of all disks in the volume. In other words, the
volume does not use the excess space of the higher-capacity member disk(s). For
example, if you create an Integrated Mirroring Enhanced volume with two 100-GB disks
and two 120-GB disks, the volume uses only 100 GB on each of the 120-GB disks.
Refer to Chapter 2, Overview of Integrated RAID Mirrored Volumes, for more information
about the features of Integrated Mirroring, Integrated Mirroring + Striping, and
Integrated Mirroring Enhanced volumes.
3.2 Creating Mirrored Volumes The SAS2 BIOS CU is part of the Fusion-MPT BIOS. When the BIOS loads during the
startup sequence and you see the message about the LSI Configuration Utility, press
Ctrl-C to start the SAS2 BIOS CU. After you do this, the message changes to:
Please wait, invoking SAS Configuration Utility...
After a brief pause, the main menu (Adapter List window) of the SAS2 BIOS CU appears.
On some systems, however, the following message appears next:
LSI Corp Configuration Utility will load following
initialization!
LSI Corporation Confidential
In this case, the SAS2 BIOS CU loads after the system completes its power-on self-test.
You can configure one or two Integrated Mirroring, Integrated Mirroring + Striping, and
Integrated Mirroring Enhanced volumes on each LSI SAS2 controller. You can also
configure one mirrored volume and one Integrated Striping volume on the same
controller, up to a maximum of 14 disk drives for the two volumes. This includes one or
two optional hot spare disks for the mirrored volume(s).
All physical disks in a volume must be either SATA (with extended command set
support) or SAS (with SMART support). You cannot combine SAS and SATA disks in
the same volume. However, you can create one volume with SAS disks and a second
volume with SATA disks on the same controller.
| August 2010 Page 13
Page 14

Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes | Creating Mirrored Volumes SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
Disks must have 512-byte blocks and must not have removable media.
Integrated mirroring volumes must have two disks, Integrated Mirroring Enhanced
volumes can have three-to-ten disks, and Integrated Mirroring + Striping volumes
can have an even number of disks ranging from four-to-ten disks.
NOTE: LSI strongly recommends that you create global hot spare disks for all mirrored
volumes to increase the level of data protection. If a disk in a mirrored volume fails, the
Integrated RAID firmware rebuilds it using one of the global hot spares, and the data is
safe. If you create two mirrored volumes on an LSI SAS 2 controller, either of the two
mirrored volumes can use the global hot spares if a disk fails.
3.2.1 Creating an Integrated Mirroring Volume
Follow these steps to create a two-disk Integrated Mirroring (RAID 1) volume with the
SAS2 BIOS CU. The steps begin with the Adapter List window that appears when the
SAS2 BIOS CU starts:
1. On the Adapter List window, use the arrow keys to select an LSI SAS adapter, and
then press Enter.
The Adapter Properties window appears, as the following figure shows.
Figure 5: Adapter Properties Window
2. Use the arrow keys to select RAID Properties, and then press Enter.
The Create Array window appears.
3. Select Create RAID 1 Volume.
The Create New Array window appears.
Page 14 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 15

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes | Creating Mirrored Volumes
4. Move the cursor to the RAID Disk column and select a line that has a No entry in this
column, indicating that the disk is not already part of the volume you are creating.
To add the disk to the new array, change the No to Ye s by pressing the space bar.
This is the Primary disk in the array.
CAUTION: The SAS2 BIOS CU deletes all existing data from the disks drives when you
select them to use in a mirrored volume.
5. Move the cursor to another line and press the space bar to add the second disk to
the array.
This is the Secondary disk in the array.
6. Press C to create the array.
A menu window appears.
7. From the menu options, select Save changes then exit this menu.
A processing message appears briefly, and then the SAS2 BIOS CU returns to
the Adapter Properties window. Initialization of the new array continues in
the background.
3.2.2 Creating an Integrated Mirroring Enhanced or Integrated Mirroring + Striping Volume
NOTE: To create a second Integrated Mirroring volume, repeat these instructions
starting with step 2. Alternatively, follow the instructions in the following section to
create an Integrated Mirroring Enhanced or Integrated Mirroring + Striping volume.
NOTE: See the instructions in Section 3.3, Managing Hot Spare Disks, if you want to
create one or two global hot spares.
Integrated Mirroring Enhanced volumes can have from three-to-ten physical disks.
Data is written to a disk and mirrored on an adjacent disk. Integrated Mirroring +
Striping volumes can have a minimum of four and a maximum of 10 physical disks, in
even numbers. In an Integrated Mirroring Enhanced or Integrated Mirroring + Striping
volume, the data is both mirrored and striped.
Follow these steps to create an Integrated Mirroring Enhanced (RAID 1E) or Integrated
Mirroring + Striping (RAID 10) volume with the SAS2 BIOS CU. The steps begin with the
Adapter List window that appears when the configuration utility starts:
1. On the Adapter List window, use the arrow keys to select an LSI SAS adapter, and
then press Enter.
The Adapter Properties window appears, as shown in Figure 5.
2. Use the arrow keys to select RAID Properties, and then press Enter.
The Create Array window appears.
LSI Corporation Confidential
3. Select Create RAID 1E Volume.
The Create New Array window appears.
| August 2010 Page 15
Page 16

Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes | Creating Mirrored Volumes SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
4. Move the cursor to the RAID Disk column and select a line that has a No entry in this
column, which indicates that the disk is not already part of the volume you are
creating. To add the disk to the new array, change the No to Yes by pressing the
space bar.
CAUTION: The SAS2 BIOS CU deletes all existing data from the disks drives when you
select them to use for a mirrored volume.
5. Move the cursor to another line and press the space bar to add another disk to
the array.
If you select an odd number of disks, the SAS2 BIOS CU creates an Integrated
Mirroring Enhanced array. If you select an even number of disks, it creates an
Integrated Mirroring + Striping array. As you add disks, the Array Size field changes
to reflect the size of the new array.
6. Press C to create the array.
A menu window appears.
7. From the menu options, select Save changes then exit this menu.
3.2.3 Expanding an Integrated Mirroring Volume with OCE
A processing message appears briefly, and then the SAS2 BIOS CU returns to the
Adapter Properties window. Initialization of the new array continues in the
background.
NOTE: To create a second Integrated Mirroring Enhanced or Integrated Mirroring +
Striping volume, repeat the instructions above.
NOTE: See the instructions in Section 3.3, Managing Hot Spare Disks, if you want to
create one or two global hot spares.
You can use the online capacity expansion (OCE) feature to expand the capacity of a
two-disk Integrated Mirroring (RAID 1) volume by replacing the original disks with two
higher-capacity disk drives while the volume remains online. This process maintains
data integrity at all times, even if one of the disks fails during the replacement process.
The new disks must have at least 50 GB more capacity than the disks they are replacing,
and they must use the same protocol (SAS or SATA) as the disks they are replacing.
Follow these steps to expand an existing RAID1 volume with OCE:
1. Physically replace one of the two volume disk drives with a drive that has at least
50 GB more capacity.
If necessary, you can identify the disks in the volume by following the instructions in
Section 3.4.5, Locating Disk Drives in a Volume.
2. Wait until synchronization completes on the new disk and the volume returns to the
Optimal state, as indicated in the Adapter Properties window of the SAS2 BIOS CU.
3. Physically replace the other volume disk drive with a drive that has at least 50 GB
more capacity.
Page 16 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 17

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes | Managing Hot Spare Disks
4. Again, wait until synchronization completes on the new disk and the volume
returns to the Optimal state.
5. In the Adapter List window of the SAS2 BIOS CU, use the arrow keys to select the LSI
SAS adapter with the RAID 1 volume, and then press Enter.
The Adapter Properties window appears.
6. Use the arrow keys to select RAID Properties, and then press Enter.
The Select New Array Type window appears.
7. Select View Existing Array.
The View Array window appears. If necessary, press Alt + N to switch to the RAID 1
volume with the new, higher-capacity disk drives.
8. Select Manage Array.
The Manage Array window appears.
9. Select Online Capacity Expansion.
A menu window appears with a warning message and with options to start the
expansion process or quit.
10. Press Y to start the expansion.
The RAID Properties window appears when the expansion process completes.
11. Run a commercial tool specific to the operating system to move or increase the size
of the partition on the newly expanded RAID1 volume.
3.3 Managing Hot Spare Disks You can create one or two global hot spare disks to protect the data on mirrored
volumes on an LSI SAS2 controller. You can also delete hot spare disks.
3.3.1 Creating Hot Spare Disks Follow these steps to add global hot spare disks to an existing volume. The steps begin
with the Adapter List window that appears when the configuration utility starts:
1. In the Adapter List window, use the arrow keys to select the LSI SAS adapter on
which you want to create hot spare disks, and then press Enter.
The Adapter Properties window appears, as shown in Figure 5.
2. Use the arrow keys to select RAID Properties, and then press Enter.
The Select New Array Type window appears.
3. Select View Existing Array.
The View Array window appears. If necessary, press Alt + N to switch to another
array on this adapter.
4. Select Manage Array.
LSI Corporation Confidential
The Manage Array window appears.
5. Select Manage Hot Spares, which is the first option, as shown in the
following figure.
| August 2010 Page 17
Page 18

Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes | Managing Hot Spare Disks SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
Figure 6: Manage Array Window
The Manage Hot Spares window appears.
6. Identify a disk that is not part of a RAID volume (i.e., the value in the Drive Status
column is not RAID) and that is not already identified as a hot spare disk.
A global hot spare disk must have 512-byte blocks and nonremovable media. The
disk type must be either SATA with extended command set support or SAS with
SMART support.
7. Select the Hot Spr (Hot Spare) field for this disk, and press the space bar.
The Hot Spare status changes to Ye s .
8. (Optional) Repeat the preceding step to select a second global hot spare disk
9. Press C to create the hot spare disk.
A menu window appears. An error message appears if the selected disk is not at
least as large as the smallest disk used in the existing volume(s). An error message
also appears if you try to add a SATA disk as a hot spare for volumes that use SAS
disks, or vice versa.
10. Select Save changes then exit this menu to create the hot spare disk(s).
The SAS2 BIOS CU pauses while it configures the global hot spares.
3.3.2 Deleting Hot Spare Disks Follow these steps to delete a global hot spare disk:
1. Access the Manage Hot Spares window by following steps 1 through 5 of the
previous section.
2. Select a hot spare disk for deletion, and press C.
3. Select Save changes then exit this menu to commit the changes.
The configuration utility pauses while it removes the global hot spare.
Page 18 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 19

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes | Other Configuration Tasks
3.4 Other Configuration Tasks This section explains how to perform other configuration and maintenance tasks for
mirrored volumes.
3.4.1 Viewing Volume Properties Follow these steps to view the RAID properties of the mirrored volume(s):
1. In the SAS2 BIOS CU, select an LSI SAS2 adapter from the Adapter List.
The Adapter Properties window appears.
2. Select RAID Properties.
The Select New Array Type window appears.
3. Select View Existing Array.
The View Array window appears, showing information about the array and each
disk in it. The window includes global hot spare information, if any exists.
NOTE: If you create one volume using SAS disks, another volume using SATA disks, and
one or two global hot spare disks, the hot spare disks only appear when you view the
mirrored volume that uses the same type of disks as the hot spare disks.
4. If the currently displayed array is not the one you want, press Alt + N to view
another array on the adapter.
3.4.2 Running a Consistency Check Use the Consistency Check command to verify that the data is synchronized on the
mirrored disks in the volume.
Follow these steps to run a consistency check on a selected mirrored volume:
1. In the Adapter List window, use the arrow keys to select an LSI SAS adapter.
The Adapter Properties window appears.
2. Use the arrow keys to select RAID Properties, and then press Enter.
The Select New Array Type window appears.
3. Select View Existing Array.
The View Array window appears. If necessary, press Alt + N to switch to another
array on this adapter.
4. Select Manage Array.
The Manage Array window appears.
5. Select Consistency Check on the Manage Array window.
A menu window appears.
6. Press Y to start the consistency check.
LSI Corporation Confidential
The consistency check runs a read-read-compare algorithm in the background. If it
encounters any data miscompares, it stores the information in a bad block table.
| August 2010 Page 19
Page 20

Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes | Other Configuration Tasks SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
3.4.3 Activating an Array A volume (array) can become inactive if, for example, you remove it from one controller
or computer and install it on a different one. The Activate Array option allows you to
reactivate an inactive volume. This option is available only when the selected volume is
currently inactive.
Follow these steps to activate a selected volume:
1. In the Adapter List window, use the arrow keys to select an LSI SAS adapter and
press Enter.
The Adapter Properties window appears.
2. Select RAID Properties, and then press Enter.
The Select New Array Type window appears.
3. Select View Existing Array.
The View Array window appears. If necessary, press Alt + N to switch to another
array on this adapter.
4. Select Manage Array.
The Manage Array window appears.
5. Select Activate Array on the Manage Array window.
A menu window appears.
6. Press Y to activate the array.
The array becomes active after a pause.
3.4.4 Deleting an Array CAUTION: Before you delete an array, be sure to back up all data on the array that you
want to keep.
Follow these steps to delete a selected volume (array):
1. In the Adapter List window, use the arrow keys to select an LSI SAS adapter.
The Adapter Properties window appears.
2. Use the arrow keys to select RAID Properties, and then press Enter.
The Select New Array Type window appears.
3. Select View Existing Array.
The View Array window appears. If necessary, press Alt + N to switch to another
array on this adapter.
4. Select Manage Array.
The Manage Array window appears.
5. Select Delete Array.
A menu window appears.
6. Either press Y to delete the array, or press N to cancel the deletion process.
Page 20 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 21

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes | Other Configuration Tasks
After a pause, the utility deletes the array. If there is another remaining array and
one or two hot spare disks, the BIOS checks the hot spare disks to determine if they
are compatible with the remaining volume. If they are not compatible (too small or
wrong disk type), the BIOS deletes them also.
3.4.5 Locating Disk Drives in a Volume You can use the SAS2 BIOS CU to locate and identify a specific physical disk drive in a
disk enclosure by flashing the drive’s LED. You can also flash the LEDs of all the disk
drives in a RAID volume, if they are in a disk enclosure.
When you add a disk drive to a new mirrored volume, the LED on the disk drive starts
flashing. The LED stops flashing when you finish creating the volume.
You can locate individual disk drives from the SAS Topology window by flashing their
LEDs. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Select the desired SAS2 controller on the Adapter List window, and press Enter.
The Adapter Properties window appears.
2. Highlight SAS Topology, and press Enter.
The SAS Topology window appears.
3. Select the disk in the Device Identifier column, and press Enter.
The LED on the disk flashes until you press a key to stop it.
4. To identify all the disk drives in a volume, select the volume in the left column of the
SAS Topology window, and press Enter.
The LEDs flash on all disk drives in the volume until you press a key to stop them.
NOTE: The LEDs on the disk drives flash as previously described if the firmware
configuration is correct and the drives are in a disk enclosure.
3.4.6 Selecting a Boot Disk You can select a boot disk in the SAS Topology window. The next time you boot the
computer, the firmware moves this disk to scan ID 0, making it the new boot disk. This
makes it easier to set BIOS boot device options and to keep the boot device constant
during device additions and removals. You can also select an alternative boot device. If
the BIOS cannot find the preferred boot device when it loads, it will attempt to boot
from the alternate device.
Follow these steps to select a boot disk:
1. In the SAS2 BIOS CU, select an adapter from the Adapter List.
2. Select the SAS Topology option. If a device is currently designated as the boot
device, the Device Info column on the SAS Topology window lists the word Boot, as
shown in the following figure.
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 21
Page 22

Chapter 3: Creating Mirrored Volumes | Other Configuration Tasks SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
Figure 7: Boot Device on SAS Topology Window
If a device is currently designated as the alternate boot device, the Device Info
column shows the word Alt.
3. To select the preferred boot disk, move the cursor to the disk, and press Alt + B.
4. To remove the boot designator, move the cursor to the current boot disk, and press
Alt + B.
This controller no longer has a disk designated as boot.
5. To change the boot disk, move the cursor to the new boot disk, and press Alt + B.
The Boot designator moves to this disk.
6. To select an alternate boot disk, move the cursor to the disk, and press Alt + A.
NOTE: To change the alternate boot device from one disk to another, follow steps 4
and 5, but use Alt + A instead of Alt + B.
Page 22 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 23

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 4: Overview of Integrated Striping | Introduction
Chapter 4
Overview of Integrated Striping
This chapter provides an overview of the LSI Integrated RAID features that support the
creation of striped arrays.
4.1 Introduction The LSI Integrated RAID solution enables you to create Integrated Striping volumes for
applications that require the faster performance and increased storage capacity of
striping. The low-cost Integrated Striping feature has many of the advantages of a more
expensive RAID striping solution. You can configure an Integrated Striping volume as
the boot disk or as a data disk.
The Integrated Striping solution provides better performance and more capacity than
individual disks, without burdening the host CPU. The firmware distributes host I/O
transactions over multiple disks and presents the disks as a single, logical drive. In
general, striping is transparent to the BIOS, the drivers, and the operating system.
You can use the LSI SAS2 BIOS CU to configure Integrated Striping volumes. These
volumes can consist of two-to-ten disks.
4.2 Integrated Striping Features Integrated Striping supports the following features:
Support for volumes with two-to-ten disks
Support for two Integrated Striping volumes with up to 14 drives total on a
SAS2 controller.
Support for combining one Integrated Striping volume and one Integrated
Mirroring, Integrated Mirroring + Striping, or Integrated Mirroring Enhanced
volume on a single controller.
Support for both SAS and SATA drives, although you cannot combine the two types
of drives in one volume
Fusion-MPT architecture
Easy-to-use SAS BIOS configuration utility
Error notification
Disk write caching, which is enabled by default on all Integrated Striping volumes
Use of metadata to store volume configurations on disks
OS-specific event log
Error display inside the Fusion-MPT BIOS
SCSI Enclosure Services (SES) status LED support for drives used in Integrated
Striping volumes
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 23
Page 24

Chapter 4: Overview of Integrated Striping | Integrated Striping Description SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
Disk 2
Segment 2
Segment 6
Segment 10
Disk 3 Disk 4
Segment 4
Segment 8
Segment 12
Disk 1
Segment 1
Segment 5
Segment 9
3_00010-00
LSI SAS2
Controller
Segment 3
Segment 7
Segment 11
SAS
Physical ViewLogical View
+
3_00011-00
Stripe 1
Stripe 2
Stripe 3
Stripe N
Stripe 1
Stripe 4
Stripe 7
Stripe N-2
Stripe 2
Stripe 5
Stripe 8
Stripe N-1
+
Stripe 3
Stripe 6
Stripe 9
Stripe N
4.3 Integrated Striping Description
On Integrated Striping volumes, the firmware writes data across multiple disks instead
of onto one disk. It does this by partitioning each disk’s storage space into 64-KB
stripes. The firmware interleaves the stripes round-robin so that the combined storage
space consists alternately of stripes from each disk.
The following figure shows an example of integrated striping: the firmware writes
segment 1 to disk 1, segment 2 to disk 2, segment 3 to disk 3, and so on. When the
firmware reaches the end of the disk list, it continues writing data at the next available
segment of disk 1.
Figure 8: Integrated Striping Example
The following figure shows a logical view and a physical view of an Integrated Striping
volume with three disks.
Figure 9: Integrated Striping – Logical and Physical Views
Speed is the primary advantage of the Integrated Striping solution because it transfers
data to or from multiple disks simultaneously. However, there is no data redundancy.
Back the data up on other media to avoid losing unsaved data if one disk fails.
Page 24 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 25

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 5: Creating Integrated Striping Volumes | Integrated Striping Configuration Over-
Chapter 5
Creating Integrated Striping Volumes
This chapter explains how to create Integrated Striping volumes using the LSI SAS2
BIOS Configuration Utility (SAS2 BIOS CU).
5.1 Integrated Striping Configuration Overview
5.2 Creating Integrated Striping Volumes
The LSI SAS2 BIOS CU is a menu-driven utility program that enables you to easily
configure and manage Integrated RAID volumes. You can use the SAS2 BIOS CU to
create one or two Integrated Striping volumes on each LSI SAS2 controller. Each
volume can have from two-to-ten drives. All disks in an Integrated Striping volume
must be connected to the same LSI SAS2 controller.
Although you can use disks of different size in Integrated Striping volumes, the smallest
disk in the volume determines the logical size of all disks in the volume. In other words,
the firmware does not use the excess space of the higher-capacity member disk(s). For
example, if you create an Integrated Striping volume with two 100-GB disks and two
120-GB disks, the firmware uses only 100 GB on each of the 120-MB disks for the
volume. The supported stripe size is 64 kilobytes.
Refer to Chapter 4 for more information about Integrated Striping volumes.
The SAS2 BIOS CU is part of the Fusion-MPT BIOS. When the BIOS loads during boot and
you see the message about the LSI Configuration Utility, press Ctrl-C to start the CU.
After you do this, the message changes to:
Please wait, invoking SAS Configuration Utility...
After a brief pause, the main menu of the SAS2 BIOS CU appears. On some systems,
however, the following message appears next:
LSI Corp Configuration Utility will load following
initialization!
LSI Corporation Confidential
In this case, the SAS2 BIOS CU loads after the system completes its power-on self-test.
You can configure one or two Integrated RAID volumes on each LSI SAS2 controller.
For a two-volume configuration, you can have two Integrated Striping (RAID 0)
volumes, two mirrored volumes, or one volume of each type. The two volumes can
have a maximum of 14 disk drives. (This configuration includes one or two hot spare
disks for mirrored volumes.)
The following guidelines apply when creating an Integrated Striping volume:
All physical disks in an Integrated Striping volume must be either SATA (with
extended command set support) or SAS (with SMART support). You cannot
combine SAS and SATA disks in the same volume. However, you can create one
volume with SAS disks and a second volume with SATA disks on the same controller.
| August 2010 Page 25
Page 26

Chapter 5: Creating Integrated Striping Volumes | Creating Integrated Striping Volumes SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
Disks must have 512-byte blocks and must not have removable media.
Integrated Striping volumes must have at least two disks and no more than 10 disks.
Integrated Striping volumes do not support hot spare disks.
Follow these steps to configure an Integrated Striping volume with the SAS2 BIOS CU,
after. The steps begin with the Adapter List window that appears when the SAS2 BIOS
CU starts.
1. On the Adapter List window, select an LSI SAS adapter, and press Enter.
The Adapter Properties window appears, as the following figure shows.
Figure 10: Adapter Properties Window
2. Select RAID Properties, and press Enter.
The Create Array window appears.
3. Select Create RAID 0 Volume.
The Create New Array window appears.
4. Move the cursor to the RAID Disk column, and select a line that has a No entry in this
column, which indicates that the disk is not already part of the volume you are
creating. To add the disk to the new array, change the No to Yes by pressing the
space bar.
5. Move the cursor to another line and press the space bar to add another disk to
the array.
6. Continue adding disks in this way until you have added the desired number of disks.
7. Press C to create the array.
A menu appears.
Page 26 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 27

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 5: Creating Integrated Striping Volumes | Other Configuration Tasks
8. From the menu options, select Save changes then exit this menu.
A Processing message appears briefly, and then the SAS2 BIOS CU returns to
the Adapter Properties window. Initialization of the new array continues in
the background.
NOTE: Repeat the previous instructions to create a second Integrated Striping volume,
if desired, and if enough additional disks are available.
5.3 Other Configuration Tasks This section explains how to perform other configuration and maintenance tasks for
Integrated Striping volumes.
5.3.1 Viewing Volume Properties Follow these steps to view the RAID properties of a volume:
1. In the SAS2 BIOS CU, select an LSI SAS2 adapter from the Adapter List.
The Adapter Properties window appears.
2. Select RAID Properties.
The Select New Array Type window appears.
3. Select View Existing Array.
The View Array window appears, showing information about the array and each
disk in it.
4. If the currently displayed array is not the one you want, press Alt + N to view
another array on the adapter.
5.3.2 Activating an Array A volume (array) can become inactive if, for example, you remove it from one controller
or computer and install it on a different one. The Activate Array option allows you to
reactivate an inactive volume. This option is available only when the selected volume is
currently inactive.
Follow these steps to activate a selected volume:
1. In the Adapter List window, use the arrow keys to select an LSI SAS adapter and
press Enter.
The Adapter Properties window appears.
2. Select RAID Properties, and then press Enter.
The Select New Array Type window appears.
3. Select View Existing Array.
The View Array window appears. If necessary, press Alt + N to switch to another
array on this adapter.
4. Select Manage Array.
LSI Corporation Confidential
The Manage Array window appears.
5. Select Activate Array on the Manage Array window.
A menu window appears.
| August 2010 Page 27
Page 28

Chapter 5: Creating Integrated Striping Volumes | Other Configuration Tasks SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
6. Press Y to activate the array.
The array becomes active after a pause.
5.3.3 Deleting an Array CAUTION: Before you delete an array, be sure to back up the data.
Follow these steps to delete a selected volume (array):
1. In the Adapter List window, use the arrow keys to select an LSI SAS adapter.
The Adapter Properties window appears.
2. Use the arrow keys to select RAID Properties, and then press Enter.
The Select New Array Type window appears.
3. Select View Existing Array.
The View Array window appears. If necessary, press Alt + N to switch to another
array on this adapter.
4. Select Manage Array.
The Manage Array window appears.
5. Select Delete Array.
A menu window appears.
6. Either press Y to delete the array, or press N to cancel the deletion process.
After a pause, the utility deletes the array.
5.3.4 Locating Disk Drives in a Volume You can use the SAS2 BIOS CU to locate and identify a specific physical disk drive in a
disk enclosure by flashing the drive’s LED. You can also flash the LEDs of all the disk
drives in a RAID volume, if they are in a disk enclosure.
When you add a disk drive to a new mirrored volume, the LED on the disk drive starts
flashing. The LED stops flashing when you finish creating the volume.
You can locate individual disk drives from the SAS Topology window by flashing their
LEDs. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Select the desired SAS2 controller on the Adapter List window and press Enter.
The Adapter Properties window appears.
2. Highlight SAS Topology, and press Enter.
The SAS Topology window appears.
3. Select the disk in the Device Identifier column, and press Enter.
The LED on the disk flashes until you press a key to stop it.
4. To identify all the disk drives in a volume, select the volume in the left column of the
SAS Topology window, and press Enter.
The LEDs flash on all disk drives in the volume until you press a key to stop them.
Page 28 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 29

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Chapter 5: Creating Integrated Striping Volumes | Other Configuration Tasks
NOTE: The LEDs on the disk drives flash, as previously described, if the firmware
configuration is correct and the drives are in a disk enclosure.
5.3.5 Selecting a Boot Disk You can select a boot disk in the SAS Topology window. The next time you boot the
computer, the firmware moves this disk to scan ID 0, making it the new boot disk. This
makes it easier to set BIOS boot device options and to keep the boot device constant
during device additions and removals. You can also select an alternative boot device. If
the BIOS cannot find the preferred boot device when it loads, it attempts to boot from
the alternate device.
Follow these steps to select a boot disk:
1. In the SAS2 BIOS CU, select an adapter from the Adapter List.
2. Select the SAS Topology option. If a device is currently designated as the boot
device, the Device Info column on the SAS Topology window lists the word Boot, as
the following figure shows.
LSI Corporation Confidential
Figure 11: Boot Device on SAS Topology Window
If a device is currently designated as the alternate boot device, the Device Info
column shows the word Alt.
3. To select the preferred boot disk, move the cursor to the disk, and press Alt + B.
4. To remove the boot designator, move the cursor to the current boot disk, and
press Alt + B.
This controller no longer has a disk designated as boot.
5. To change the boot disk, move the cursor to the new boot disk, and press Alt + B.
The Boot designator moves to this disk.
| August 2010 Page 29
Page 30

Chapter 5: Creating Integrated Striping Volumes | Other Configuration Tasks SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
6. To select an alternate boot disk, move the cursor to the disk and press Alt + A.
NOTE: To change the alternate boot device from one disk to another, follow steps 4 and
5 in this procedure, but use Alt + A instead of Alt + B.
Page 30 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 31

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Appendix A: | Hardware and Software Requirements
Appendix A
Using the SAS2 Integrated RAID Configuration Utility
This appendix explains how to use the command-line-driven SAS2 Integrated RAID
configuration utility (SAS2IRCU) to create Integrated RAID volumes on LSI SAS2
controllers in the manufacturing environment.
SAS2IRCU is a command-line utility that you can use to configure the Integrated RAID
functions of LSI SAS2 controllers. SAS2IRCU is a minimally interactive program that you
can execute from a command-line prompt or a shell script. When you use a SAS2IRCU
command, the program returns a status value to the operating system when it exits.
OEMs can use SAS2IRCU to configure Integrated RAID devices on the LSI family of
MPT2.0-based SAS2 controllers. You typically use this utility for system configuration
on the manufacturing floor.
NOTE: End users should not use the SAS2IRCU utility. Instead, they should use the LSI
SAS2 BIOS Configuration Utility (SAS2 BIOS CU) to create and manage Integrated RAID
volumes. For more information, see Chapter 3 and Chapter 5.
A.1 Hardware and Software Requirements
A.1.1 Controller Support SAS2IRCU supports the following LSI SAS2 controllers and the host bus adapters based
SAS2IRCU runs on the following platforms.
X86 or X64-compatible
United Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) 2
EM64T/AMD64
Sun SPARC® (v9)
SAS2IRCU works with storage devices that are compliant with existing SCSI standards.
on these controllers:
LSISAS2004
LSISAS2008
LSISAS2108
LSISAS2208
LSISAS2304
LSISAS2308
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 31
Page 32

Appendix A: | Interface Description SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
A.1.2 Operating System and Software Support
SAS2IRCU requires PCI™ 2.x or PCI 3.0 firmware and MPI v2.0. SAS2IRCU supports the
following operating systems:
WinPE 1.x (Server 2003/XP), WinPE 2.0 (Vista), WinPE 2.1 (Server 2008)
Requires Windows® driver v2.00.00.17 or greater.
UEFI 2.1
Linux® 2.6 Kernel - Red Hat® Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 5, SUSE® Linux Enterprise Server
(SLES) 10
Requires Linux driver v00.255.04.00 or greater.
MS-DOS® 6.22 and FreeDOS 1.0
SAS2IRCU runs on DOS only if the system BIOS supports 32-bit BIOS services,
including the PCI BIOS services. SAS2IRCU uses these services to locate the
controller and its interface registers because it must directly access the controller
chip’s interface registers.
A.2 Interface Description Format commands as follows for the SAS2IRCU command-line interface:
sas2ircu <controller_#> <command> <parameters>
Use a space to separate the program name, the controller number, the command, and
the parameters fields. The format of <parameters> is command specific.
Information passes between the user environment and the SAS2IRCU through the
command line, the standard output and standard error interfaces, and the program
return value. You can redirect the output streams as permitted by the operating
system. When the program exits, it returns a value of 0 if the command is successful.
Otherwise, it returns a value of 1.
If a RAID command fails, the SAS2IRCU prints the IOCStatus and IOCLogInfo on the
console. You can use this information to analyze the cause of the failure.
A.3 Commands The following table shows which commands the SAS2IRCU supports on each
operating system.
Table 1: SASIRCU Commands
SAS2IRCU
Command
CREATE X X X X
DELETE X X X X
DISPLAY X X X X
HOTSPARE X X X X
LIST X X X X
STATUS X X X X
MFGPAGE X — — —
Page 32 LSI Corporation Confidential
DOS Linux EFI WinPE
Operating System
| August 2010
Page 33

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Appendix A: | Commands
Table 1: SASIRCU Commands (Continued)
A.3.1 Common Command-Line Parameters
SAS2IRCU
Command
CONSTCHK X X X X
ACTIVATE X X X X
LOCATE X X X X
LOGIR X X X X
DOS Linux EFI WinPE
Operating System
The commands are not case sensitive. The command descriptions use the
following conventions:
Enter the text in italic exactly as shown on the command line.
Replace text enclosed in < > with a required parameter.
Replace text enclosed in [ ] with an optional parameter.
Enter parameters enclosed in { } one or more times, as required for the command
being executed.
Do not enter the command-line definition characters < >, [ ], and { } on the
command line.
This section describes command-line parameters that are common to more than one
command.
<controller_#>
The unique controller number that the program assigns to each PCI function found
on supported controller chips in the system, starting with controller # 0. For
example, in a system containing two LSISAS2008 controllers, controller # 0
references the first controller and controller # 1 references the other controller.
Valid controller number values are 0 to 255 (decimal).
<Enclosure:Bay>
The enclosure and bay/slot of a peripheral device attached to the bus. The
argument must use a colon (:) as a separator and must follow the enclosure:bay
format. Enclosure is a 16-bit EnclosureHandle value set by the I/O controller (IOC). A
value of 0 is invalid. Bay/Slot is a 16-bit slot value set by the IOC. Use the DISPLAY
command to get the enclosure and slot numbers of a drive.
A.3.2 CREATE Command The CREATE command creates Integrated RAID volumes on LSI SAS2 controllers.
When you add a disk to an Integrated RAID volume, the volume might not use all of the
disk’s storage capacity. For example, if you add a 300-GB disk drive to a volume that
only uses 200 GB of capacity on each disk drive, the volume does not use the remaining
100 GB of capacity on the disk drive.
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 33
Page 34

Appendix A: | Commands SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
The disk identified by the first Enclosure:Bay on the command line becomes the primary
disk drive when you create an Integrated Mirroring (RAID 1) volume. If the controller
resynchronizes the disk drives, the data on the primary disk drive becomes available
when you access the newly created volume.
When the IR firmware creates a RAID 1 volume, it starts a background initialization
of the volume. You can use the STATUS command to monitor the status of
the initialization.
Observe the following rules when creating Integrated RAID volumes and hot
spare disks:
All disks that are part of a volume, including hot spares for that volume, must be on
the same SAS2 controller.
You can create RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 1E, and RAID 10 Integrated RAID volumes.
You can create a maximum of two Integrated RAID volumes per controller.
The configuration of the Integrated RAID firmware determines the maximum and
minimum number of drives that you can use in Integrated RAID volumes. The
following fields of IOC Page 6 specify the configuration:
MaxDrivesRAID0, MaxDrivesRAID1, MaxDrivesRAID10, MaxDrivesRAID1E
MinDrivesRAID0, MinDrivesRAID1, MinDrivesRAID10, MinDrivesRAID1E,
MaxVolumes, MaxPhysDisks, MaxGlobalHotSpares, MaxPhysDisks (maximum
number of physical drives combined in all volumes on the controller)
For more information, refer to the description of the IOC configuration pages in the
Fusion MPT 2.0 MPI Specification Guide.
SAS2IRCU does not allow you to create an Integrated RAID volume that combines
SAS and SATA hard disk drives.
SAS2IRCU does not allow you to create an Integrated RAID volume that combines
SSDs (solid-state drives) and hard disk drives.
SAS2IRCU does allow you to use both SATA and SAS solid-state drives in a single
Integrated RAID volume, if the Integrated RAID firmware supports it. Support for
such a mixing is specified by values in static fields in Manufacturing Page 4 in the
MPI2 specification and is specific for SSD drives only.
Command Line sas2ircu <controller_#> create <volume_type> <size>
{<Enclosure:Bay>} [VolumeName] [noprompt]
Parameters <controller_#> – The index of the controller for the newly created volume.
<volume_type> – Volume type for the new volume. Valid values are RAID0,
RAID1, RAID10, or RAID1E.
<size> – Size of the RAID volume in Mbytes, or MAX for the maximum size
available.
<Enclosure:Bay> – The Enclosure:Bay value of the disk drive for the new RAID
volume. You can get these values from the output of the DISPLAY command. DOS
does not support addressing by Enclosure:Bay.
VolumeName – A user-specified string to identify the volume.
noprompt – This optional parameter prevents warnings and prompts from
appearing while the command is running.
Page 34 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 35

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Appendix A: | Commands
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Bad command-line arguments or operational failure.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
A.3.3 DELETE Command The DELETE command deletes all of the Integrated RAID volumes and hot spare drives
from the specified LSI SAS2 controller. The command does not change any other
controller configuration parameters.
Command Line sas2ircu <controller_#> delete [noprompt]
Parameters <controller_#> – The index of the controller with the volume(s) that you want
to delete.
noprompt – This optional parameter prevents warnings and prompts from
appearing while the command is running.
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Bad command-line arguments or operational failure.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
A.3.4 DISPLAY Command The DISPLAY command displays information about LSI SAS2 controller configurations,
including controller type, firmware version, BIOS version, volume information, physical
drive information, and enclosure. See the following Sample Output example.
The physical device information section displays the duplicate device of a dual-port
SAS drive.
Command Line sas2ircu <controller_#> display [filename]
Parameters <controller_#> – The index of the controller for which you want to
display information.
[filename] – An optional valid filename to store the command output to a file.
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Bad command-line arguments or operational failure.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 35
Page 36

Appendix A: | Commands SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
Sample Output Following is a sample of the information that the DISPLAY command returns.
Read configuration has been initiated for controller 0
-----------------------------------------------------------Controller information
-----------------------------------------------------------Controller type : SAS2008
BIOS version : 7.00.02.00
Firmware version : 00.250.19.0
Channel description : 1 Serial Attached
SCSI
Initiator ID : 112
Maximum physical devices : 62
Concurrent commands supported : 266
Slot : 3
Segment : 0
Bus : 64
Device : 1
Function : 0
RAID Support : Yes
------------------------------------------------------------
IR Volume information
------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------
Physical device information
------------------------------------------------------------
Initiator at ID #112
Device at ID #335524
Device is a Hard disk
Enclosure # : 2
Slot # : 2
Connector ID : 4
State : Ready (RDY)
Size (in MB)/(in sectors) : 70007/143374738
Manufacturer : HP
Model Number : DG072A9BB7
Firmware Revision : HPD0
Serial No : B365P720H7330709
Protocol : SAS
Drive Type : SAS
------------------------------------------------------------
Enclosure information
------------------------------------------------------------
Enclosure# : 1
Logical ID : 51234567:89012345
Numslots : 8
StartSlot : 0
Page 36 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 37

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Appendix A: | Commands
Logical drive status values are as follows:
Okay (OKY) – The volume is active and drives are functioning properly. User data
is protected if the current RAID level provides data protection.
Degraded (DGD) – The volume is active. User data is not fully protected because
the configuration has changed or a drive has failed.
Failed (FLD) – The volume has failed.
Missing (MIS) – The volume is missing.
Initializing (INIT) – The volume is initializing.
Online (ONL) – The volume is online.
Physical device status values are as follows:
Online (ONL) – The drive is operational and is part of a logical drive.
Hot Spare (HSP) – The drive is a hot spare that is available to replace a failed
drive in an array.
Ready (RDY) – The drive is ready for use as a normal disk drive, or it is ready to be
assigned to a disk array or a hot spare pool.
Available (AVL) – The drive may or may not be ready, and it is not suitable for
use in an array or a hot spare pool.
Failed (FLD) – The drive failed and is now offline.
Missing (MIS) – The drive has been removed or is not responding.
Standby (SBY) – The device is not a hard-disk device.
Out of Sync (OSY) – The drive, which is part of a logical drive, is not in sync
with other drives that are part of the logical drive.
Degraded (DGD) – The drive is part of a logical drive and is in degraded state.
Rebuilding (RBLD) – The drive is part of a logical drive and is
currently rebuilding.
Optimal (OPT) – The drive is optimal and is part of a logical drive.
Physical device Drive Type values are as follows:
SAS_HDD – The drive is a SAS HDD.
SATA_HDD – The drive is a SATA HDD.
SAS_SSD – The drive is a SAS SSD.
SATA_SSD – The drive is a SATA SSD.
Physical device Protocol values are as follows:
SAS – The drive supports SAS protocol.
SATA – The drive supports SATA protocol.
A.3.5 HOTSPARE Command The HOTSPARE command adds a hot spare drive to spare pool 0 or deletes a hot spare
drive. The capacity of the hot spare drive must be greater than or equal to the capacity
of the smallest drive in the RAID volume. You can verify this by using the DISPLAY
command on the drive.
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 37
Page 38

Appendix A: | Commands SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
Observe the following rules when creating hot spare disks:
You cannot create a hot spare disk unless at least one RAID1, RAID10, or RAID1E
volume already exists.
You cannot create a hot spare and add it to an inactive Integrated RAID volume.
For hard-disk drives, you cannot add a SAS hot spare disk if the existing volumes on
the controller use SATA disks. You cannot add a SATA hot spare disk if the existing
volumes on the controller use SAS disks.
For solid-state drives, you can add a SAS hot spare SSD to a volume with SATA SSDs
and you can add a SATA hot spare SSD to a volume with SAS SSDs, if the Integrated
RAID firmware allows it. This depends on the values in the static fields in
Manufacturing Page 4. For more information, see the Fusion-MPT 2.0 MPI
Specification Guide.
The maximum allowable number of hot spare drives depends on the value of the
MaxGlobalHotSpares field in IOC Page 6. (Normally, the maximum is two global hot
spares per controller.)
You cannot add an SSD hot spare to a volume that has HDDs, or vice versa.
Command Line sas2ircu <controller_#> hotspare [delete] <Enclosure:Bay>
Parameters <controller_#> – The index of the controller on which you want to create the
hot spare disk.
<Enclosure:Bay> – The Enclosure:Bay value for the hot spare disk drive. You can
get these values from the output of the DISPLAY command. DOS does not support
addressing by Enclosure:Bay.
delete – This optional command deletes the hot spare disk at enclosure:bay.
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Bad command-line arguments or operational failure.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
A.3.6 STATUS Command The STATUS command displays the current status of any existing Integrated RAID
volumes and the status of any operation that is currently in progress on the selected
controller. If an operation is not in progress, the SAS2IRCU prints a message indicating
this condition before it exits.
Command Line sas2ircu <controller_#> status
Parameters <controller_#> – The index of the controller with the volumes whose status
you want to display.
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Bad command-line arguments or operational failure.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
Page 38 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 39

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Appendix A: | Commands
Sample Output Following is an example of the information that the STATUS command returns when a
volume resynchronization is in progress:
Background command progress status for controller 0...
IR Volume 1
Volume ID : 6
Current operation : Synchronize
Volume status : Enabled
Volume state : Degraded
Physical disk I/Os : Not quiesced
Volume size (in sectors) : 70311936
Number of remaining sectors : 68250624
Percentage complete : 2.93%
Following is an example of the status information that the STATUS command returns if
a background volume operation is not in progress:
Background command progress status for controller 0...
IR Volume 1
Current operation : None
Volume ID : 6
Volume status : Enabled
Volume state : Optimal
Physical disk I/Os : Not quiesced
The possible values for the fields in the status data are as follows:
Current operation: Synchronize, Consistency Check, OCE, Background Init, or None
Volume status: Enabled or Disabled
Volume state: [Inactive] Optimal, Degraded, Missing, or Failed
Physical disk I/Os: Quiesced or Not quiesced
A.3.7 LIST Command The LIST command displays a listing of all controllers present in system, along with
each corresponding controller index. You use the controller index as an input
parameter for other SAS2IRCU commands.
Command Line sas2ircu list
Parameters None
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Command failed.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
Sample Output Following is an example of the output of the LIST command. The format and fields in
the output may vary depending on the types of installed controllers.
Adapter Vendor Device SubSys SubSys
Index Type ID ID Pci Address Ven ID Dev ID
----- --------- ------ ------ ---------------- ------- ----- 0 SAS2008 1000h 72h 00h:01h:00h:00h 1000h 00dah
1 SAS2008 1000h 72h 00h:05h:00h:00h 1000h 00dah
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 39
Page 40

Appendix A: | Commands SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide
A.3.8 MFGPAGE Command The MFGPAGE command updates information on manufacturing pages. Only DOS and
EFI support this command.
Command Line sas2ircu <controller_#> mfgpage <passcode> <mfgpage_#>
<offset> <value>
Parameters <controller_#> – The index of the controller with the manufacturing pages
you want to update.
<passcode> – The passcode required for DOS access.
<mfgpage_#> – The manufacturing page (4 or 10) that requires an update.
<offset> – The DWord offset of the specified manufacturing page that requires
an update, in hexadecimal format.
<value> – The value for the offset to be modified, in hexadecimal format.
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Bad command-line arguments or operational failure.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
A.3.9 CONSTCHK Command The CONSTCHK command sends requests to the Integrated RAID firmware to start a
consistency check operation on the specified volume.
Command Line sas2ircu <controller_#> constchk <volumeId> [noprompt]
Parameters <controller_#> – The index of the controller on which the consistency check
operation will run.
<volumeId> – The volume ID of an Integrated RAID volume, as listed in the
DISPLAY command, on which the consistency check operation will run.
noprompt – This optional parameter prevents warnings and prompts from
appearing while the command is running.
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Bad command-line arguments or operational failure.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
A.3.10 ACTIVATE Command The ACTIVATE command activates an inactive Integrated RAID volume.
Command Line sas2ircu <controller_#> activate <volumeId>
Parameters <controller_#> – The index of the controller with the volume that requires
activation.
<volumeId> – The volume ID of an Integrated RAID volume currently in the
Inactive state.
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Bad command-line arguments or operational failure.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
Page 40 LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010
Page 41

SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide Appendix A: | Commands
A.3.11 LOCATE Command The LOCATE command locates a specific drive in a volume by turning on its location
indicator and flashing its LED.
Command Line sas2ircu <controller_#> locate <Enclosure:Bay> <action>
Parameters <controller_#> – The index of the controller with the drives that you need
to locate.
<Enclosure:Bay> – The enclosure and bay number of the drive.
<action> – The possible actions are as follows:
— ON – Turn on the location indicator of the drive.
— OFF – Turn off the location indicator of the drive.
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Bad command-line arguments or operational failure.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
A.3.12 LOGIR Command The LOGIR command uploads or clears the Integrated RAID log information.
Command Line sas2ircu <controller_#> logir <action> [filename] [noprompt]
Parameters <controller_#> – The index of the controller with the logs that you need to
upload or clear.
<action> – The possible actions are as follows:
— UPLOAD – Upload the controller logs to a file.
— CLEAR – Clear the controller logs.
filename – This optional parameter specifies the filename where the logs must
be uploaded. The default filename is LOGIR.LOG.
noprompt – This optional parameter prevents warnings and prompts from
appearing while the command is running.
Program Return Value 0x00 SUCCESS: Command completed successfully.
0x01 FAILURE: Bad command-line arguments or operational failure.
0x02 ADAPTER_NOT_FOUND: Cannot find specified adapter.
LSI Corporation Confidential
| August 2010 Page 41
Page 42

 Loading...
Loading...