Page 1

USER’S
GUIDE
2 Gbit/s Fibre Channel
Host Adapters
LSI7102XP-LC, LSI7102LXP-LC
LSI7202XP-LC, LSI7202LXP-LC
LSI7402XP-LC
LSI7202EP-LC, LSI7202EP
LSI7402EP-LC, LSI7402EP
August 2005
Version 2.1
®
DB15-000264-02
Page 2

This document contains proprietary information of LSI Logic Corporation. The
information contained herein is not to be used by or disclosed to third parties
without the express written permission of an officer of LSI Logic Corporation.
LSI Logic products are not intended for use in life-support appliances, devices,
or systems. Use of any LSI Logic product in such applications without written
consent of the appropriate LSI Logic officer is prohibited.
Document DB15-000264-02, August 2005
This document describes Version 2.1 of the LSI Logic family of 2 Gbit/s
Fibre Channel host adapters and will remain the official reference source for all
revisions/releases of this product until rescinded by an update.
LSI Logic Corporation reserves the right to make changes to any products herein
at any time without notice. LSI Logic does not assume any responsibility or
liability arising out of the application or use of any product described herein,
except as expressly agreed to in writing by LSI Logic; nor does the purchase or
use of a product from LSI Logic convey a license under any patent rights,
copyrights, trademark rights, or any other of the intellectual property rights of
LSI Logic or third parties.
Copyright © 2002, 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
TRADEMARK ACKNOWLEDGMENT
LSI Logic, the LSI Logic logo design, Fusion-MPT, IntraServer, and MyStorage
are trademarks or registered trademarks of LSI Logic Corporation. Sun, Sun
Microsystems, and Solaris are trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun
Microsystems, Inc. SPARCis a registered trademark of SPARC International, Inc.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group. All other brand and product
names may be trademarks of their respective companies.
DB
To receive product literature, visit us at http://www.lsilogic.com.
For a current list of our distributors, sales offices, and design resource
centers, view our web page located at
http://www.lsilogic.com/contacts/index.html
ii
Copyright © 2002, 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Audience
Organization
Preface
This book is the primary reference and user’s guide for the LSI Logic
family of 2 Gbit/s Fibre Channel host adapter boards. It contains a
complete functional description of these boards as well as complete
physical and electrical specifications. LSI Logic uses Class 1 transceivers
on the host adapter boards contained in this user’s guide.
This document assumes that you have some familiarity with
Fibre Channel protocol and related support devices and will benefit
persons installing and using these boards.
This document has the following chapters:
• Chapter 1, Installation Procedures, provides both quick and detailed
installation instructions.
• Chapter 2, 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics, describes the
physical and operational environments of the host adapters.
• Chapter 3, Firmware Installation Procedure, describes the
installation and configuration procedures for the Fusion-MPT™ and
Fibre Channel drivers.
• Chapter 4, BIOS Features, describes the installation procedures for
the Fibre Channel BIOS and Configuration Utility.
2 Gbit/s Fibre Channel Host Adapters User’s Guide iii
Copyright © 2002, 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Related Publications
LSIFC929X Dual Channel Fibre Channel I/O Processor Technical
Manual, Document No. DB14-000202-01
LSIFC919X Single Channel Fibre Channel I/O Processor Technical
Manual, Document No. DB15-000225-01
Fusion-MPT™ Device Management User’s Guide, Volume 1.2,
Document No. DB15-000186-01
PCI Local Bus Specification, Rev. 2.2
PCI-X/133 Local Bus Specification, Rev. 1.0a
PCI Express Base Specification, Rev. 1.0a
Revision Record
Revision Date Remarks
1.0 10/02 Preliminary release
2.0 04/03 Final release
2.1 08/05 Updated to add the LSI7102LXP-LC, LSI7202LXP-LC, LSI7202EP,
LSI7202EP-LC, LSI7402EP, and LSI7402EP-LC.
iv Preface
Copyright © 2002, 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 5

Contents
Chapter 1
Installation Procedures
1.1 General Description 1-1
1.2 Quick Installation Procedure 1-2
1.3 Detailed Installation Procedure 1-3
1.3.1 Before You Start 1-3
1.3.2 Installing the Host Adapter 1-3
Chapter 2
2 Gbit/s FC
Host Adapter Characteristics
2.1 General Description 2-1
2.2 Features 2-3
2.2.1 PCI-X Interface 2-3
2.2.2 PCI Express Interface 2-4
2.2.3 FC Interface 2-4
2.3 Physical Environment 2-4
2.3.1 Electrical Characteristics 2-5
2.3.2 Thermal, Atmospheric Characteristics 2-5
2.3.3 Electromagnetic Compliance 2-6
2.3.4 Safety Characteristics 2-6
2.4 Operational Environment 2-6
2.4.1 PCI-X Interface 2-6
2.4.2 PCI Express Interface 2-6
2.4.3 FC Interface 2-7
2.4.4 FC Link Activity/Link Fault LED 2-7
2.5 PCI System ID Values 2-7
2.6 PCI Subsystem ID Values 2-8
2.7 Unique World Wide Name 2-9
2 Gbit/s Fibre Channel Host Adapters User’s Guide v
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 6

2.8 Physical Characteristics 2-9
2.8.1 LSI7102XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-9
2.8.2 LSI7102XP-LC Connector and Indicator LED 2-10
2.8.3 LSI7102LXP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-12
2.8.4 LSI7102LXP-LC Connector and Indicator LED 2-13
2.8.5 LSI7202XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-14
2.8.6 LSI7202XP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-15
2.8.7 LSI7202LXP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-16
2.8.8 LSI7202LXP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-17
2.8.9 LSI7202EP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-18
2.8.10 LSI7202EP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-19
2.8.11 LSI7202EP Host Adapter Configuration 2-20
2.8.12 LSI7202EP Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-21
2.8.13 LSI7402XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-22
2.8.14 LSI7402XP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-23
2.8.15 LSI7402EP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-24
2.8.16 LSI7402EP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-25
2.8.17 LSI7402EP Host Adapter Configuration 2-26
2.8.18 LSI7402EP Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-27
Chapter 3
Firmware Installation Procedure
3.1 FC Firmware 3-2
3.1.1 Features 3-2
3.1.2 Description 3-2
3.2 Download New FC Firmware 3-3
3.3 Update the FC Firmware 3-4
3.3.1 GUI Update Tool for Windows and Linux Platforms 3-4
3.3.2 Command Line Update Tool for Solaris, Linux, and
3.3.3 Command Line Update Tool for DOS 3-7
3.4 Advanced User: Adjusting Default Firmware Settings 3-8
3.4.1 Adjusting Link Speed 3-9
3.4.2 Adjusting Interrupt Coalescing 3-10
3.5 Troubleshooting 3-12
Windows 3-4
vi Contents
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 7

Chapter 4
BIOS Features
4.1 LSI Logic Boot BIOS 4-2
4.1.1 LSI Logic Boot BIOS Features 4-2
4.1.2 BIOS Overview 4-2
4.1.3 LSI Logic BIOS Boot Specification (BBS) 4-2
4.2 Starting the LSI Logic Boot BIOS Configuration Utility 4-3
4.3 Using the LSI Logic Boot BIOS CU 4-3
4.4 Main Menu 4-3
4.4.1 Adapter Properties Menu 4-4
4.4.2 Persistent ID Menu 4-4
4.4.3 Device Properties Menu 4-5
4.4.4 Boot Adapter List Menu 4-5
4.4.5 Global Properties Menu 4-6
4.5 Exiting the LSI Logic Boot BIOS Configuration Utility 4-6
4.6 Troubleshooting 4-6
4.7 OpenBoot BIOS 4-7
4.7.1 OpenBoot BIOS Features 4-7
4.7.2 Identifying the FC Devices 4-8
4.7.3 Verifying Installation 4-9
4.7.4 Adapter-Specific Settings 4-10
4.7.5 Interrupt Coalescing 4-13
4.7.6 Set FC Link Speed 4-14
4.7.7 Persistent Device Naming 4-15
4.7.8 Manual Selection of FC Topology 4-17
Customer Feedback
Contents vii
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 8

viii Contents
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 9

Figures
1.1 Hardware Connections for the LSI Logic Host Adapter 1-4
1.2 Inserting the LSI Logic Host Adapter 1-5
2.1 LSI7102XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-10
2.2 LSI7102XP-LC Connector and Indicator LED 2-11
2.3 LSI7102LXP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-12
2.4 LSI7102LXP-LC Connector and Indicator LED 2-13
2.5 LSI7202XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-14
2.6 LSI7202XP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-15
2.7 LSI7202LXP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-16
2.8 LSI7202LXP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-17
2.9 LSI7202EP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-18
2.10 LSI7202EP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-19
2.11 LSI7202EP Host Adapter Configuration 2-20
2.12 LSI7202EP Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-21
2.13 LSI7402XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-22
2.14 LSI7402XP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-23
2.15 LSI7402EP-LC Host Adapter Configuration 2-24
2.16 LSI7402EP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-25
2.17 LSI7402EP Host Adapter Configuration 2-26
2.18 LSI7402EP Connectors and Indicator LEDs 2-27
3.1 LSIUtil Device Selection 3-5
3.2 LSIUtil Download Options 3-6
3.3 LSIUtil File Download 3-6
3.4 MPTUtil Device Selection 3-7
3.5 MPTUtil Options 3-8
3.6 Interrupt Coalescing Values 3-11
4.1 Select Controller 4-15
4.2 Select Device 4-16
4.3 Inserting Disk Name in Command Line 4-16
4.4 Setting Device 0 as Persistent 4-16
4.5 Clearing Persistent Device Map 4-16
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
ix
Page 10

x
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 11

Tables
2.1 LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Descriptions 2-2
2.2 Hardware and Software Requirements 2-3
2.3 Maximum Power Requirements 2-5
2.4 LED Appearance to Represent Link Status 2-7
2.5 PCI System ID Values 2-8
2.6 PCI Subsystem ID Values 2-8
2.7 LSI7102XP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs 2-11
2.8 LSI7102LXP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs 2-13
2.9 LSI7202XP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs 2-15
2.10 LSI7202LXP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs 2-17
2.11 LSI7202EP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs 2-19
2.12 LSI7202EP Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs 2-21
2.13 LSI7402XP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs 2-23
2.14 LSI7402EP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs 2-25
2.15 LSI7402EP Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs 2-27
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
xi
Page 12

xii
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 13
Chapter 1
Installation Procedures
This chapter contains general information about the LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s
family of Fibre Channel (FC) host adapters. It also provides host adapter
installation instructions. This chapter describes these topics in the
following sections:
• Section 1.1, “General Description”
• Section 1.2, “Quick Installation Procedure”
• Section 1.3, “Detailed Installation Procedure”
1.1 General Description
LSI Logic provides high-performance, cost-effective 2 Gbit/s FC
controllers and host adapters. The LSI Logic controllers and their
associated host adapters that support 2 Gbit/s FC contained in this
User’s Guide are as follows:
Controller Host Adapter
LSIFC919X LSI7102XP-LC, LSI7102LXP-LC
LSIFC929X LSI7202XP-LC, LSI7202LXP-LC, LSI7202EP-LC, LSI7202EP,
Installing these host adapters into your PCI-X system allows you to
connect FC devices. You can use these FC boards in computer systems
with a standard bracket type or with a low profile bracket
(LSI7102LXP-LC or LSI7202LXP-LC).
For specific information about the FC controllers, refer to LSIFC929X Dual
Channel Fibre Channel I/O Processor Technical Manual and LSIFC919X
Single Channel Fibre Channel I/O Processor Technical Manual.
2 Gbit/s Fibre Channel Host Adapters User’s Guide 1-1
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
LSI7402XP-LC, LSI7402EP-LC, LSI7402EP
Page 14

1.2 Quick Installation Procedure
This section provides an overview of the installation procedure. If you are
an experienced computer user with prior host adapter installation and FC
setup experience, this section may describe the procedure sufficiently. If
you prefer more detailed guidance for installing the host adapter, proceed
to Section 1.3, “Detailed Installation Procedure.”
For safe and proper installation, refer to the user’s manual supplied with
your computer and perform the following steps:
Step 1. Ground yourself before removing this host adapter board.
Step 2. Remove the host adapter from the packaging and check that it
is not damaged.
Figure 1.1 on page 1-4 illustrates an example of this host
adapter board. Also refer to Chapter 2, “2 Gbit/s FC Host
Adapter Characteristics,” to see more detailed drawings of the
2 Gbit/s host adapter boards.
Step 3. Open your PC cabinet and select an appropriate open PCI slot.
Step 4. Insert the host adapter board.
Step 5. Make any configuration changes.
Step 6. Close your PC cabinet cover.
Step 7. Connect the FC cable to the host adapter.
1-2 Installation Procedures
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 15

1.3 Detailed Installation Procedure
This section provides step-by-step instructions for installing the host
adapter. If you are experienced in these tasks, you may prefer to use
Section 1.2, “Quick Installation Procedure.”
1.3.1 Before You Start
Before starting, look through the following task list to get an over all idea of
the steps you will perform. If you are not confident you can perform the
tasks as described here, LSI Logic recommends getting assistance.
Each FC host adapter channel that you install can act as a host for up
to 126 Arbitrated Loop FC devices, not including the adapter itself. Follow
the detailed instructions in Section 1.3.2, “Installing the Host Adapter,”
to install your host adapter board successfully.
1.3.2 Installing the Host Adapter
For safe and proper installation, refer to the user’s manual supplied with
your computer and perform the following steps to install the host adapter.
Step 1. Ground yourself before removing this host adapter board.
Step 2. Remove the host adapter from the packaging and check that it
is not damaged.
Figure 1.1 illustrates an example of this host adapter board.
Also refer to Chapter 2, “2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter
Characteristics,” to see more detailed drawings of the 2 Gbit/s
host adapter boards.
Step 3. Switch off the computer and unplug the power cords for all
components in your system.
Step 4. Remove the cover from your computer according to the
instructions in the user’s manual for your system, to access the
PCI slots.
Caution: Ground yourself by touching a metal surface before
removing the cabinet top. Static charges on your body can
damage electronic components. Handle plug-in boards by
the edge; do not touch board components or gold
Detailed Installation Procedure 1-3
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 16
connector contacts. LSI Logic recommends using a static
ground strap.
Step 5. Locate the slots for PCI plug-in board installation.
Refer to the user’s manual supplied with your computer to
confirm the location of the PCI slots.
This host adapter requires a 32-bit or 64-bit PCI slot that allows
bus master operation. If a 32-bit PCI slot is used, the portion of
the J1 connector opposite the bracket remains uninserted.
Refer to Table 1.2 for details.
Note: For this host adapter to function as a 64-bit device, it must
be inserted into a 64-bit PCI slot. If the host adapter is
inserted into a 32-bit PCI slot, it functions as a 32-bit
device.
Step 6. On the back of the computer, remove the blank bracket panel
that is aligned with the PCI slot you intend to use. Save the
bracket screw.
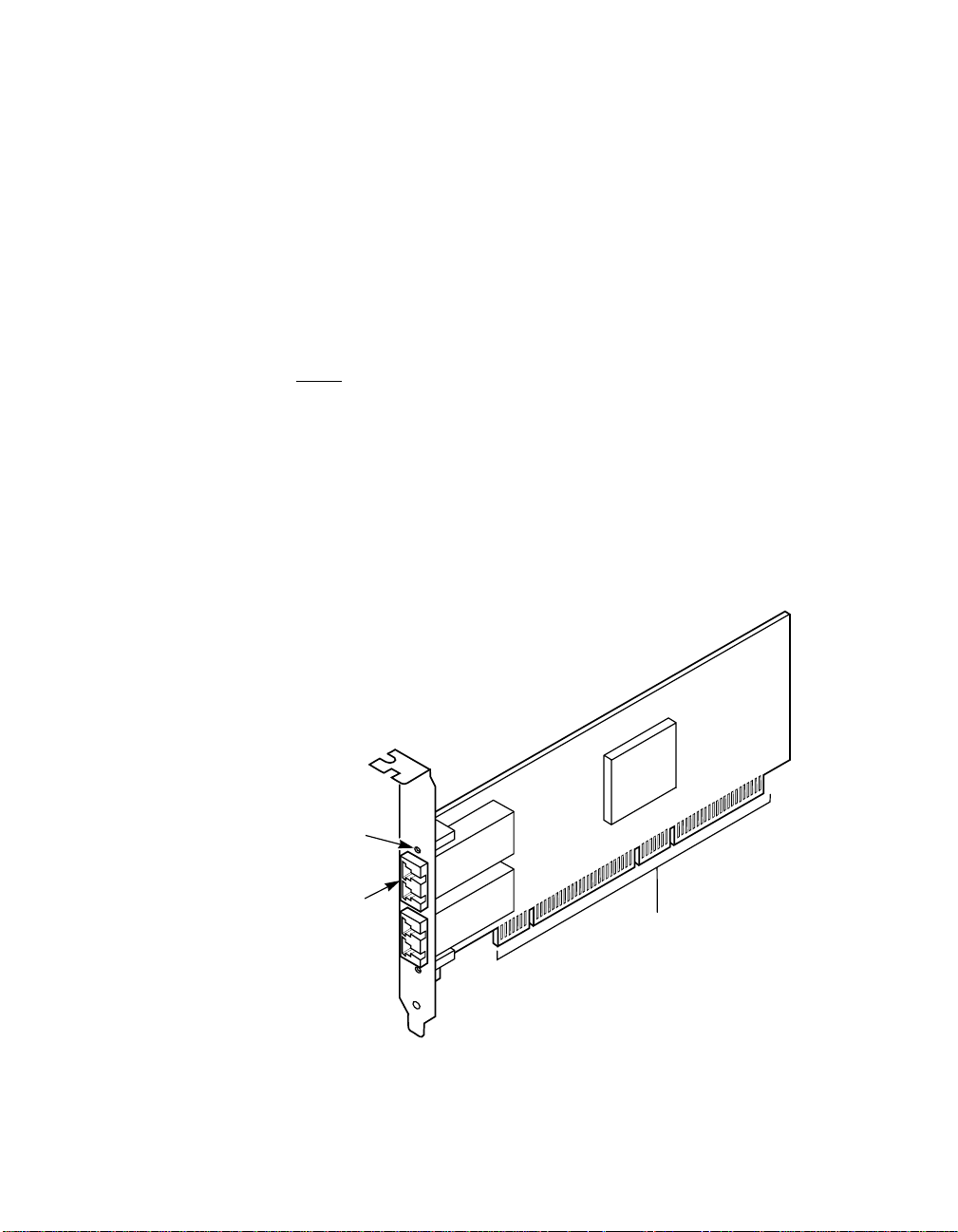
Figure 1.1 Hardware Connections for the LSI Logic Host Adapter
Fibre Channel
Link Activity/
Link Fault LED
SFP
Transceiver
1-4 Installation Procedures
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
LSI Logic Host Adapter
PCI Bus Edge Connector J1
Page 17

Step 7. Carefully insert PCI Bus edge connector J1 (see Figure 1.1)of
the host adapter into the PCI slot.
Make sure the edge connector is properly aligned before
pressing the board into place, as shown in Figure 1.2. The
bracket around the Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP)
transceiver cages should fit where you removed the blank panel.
Figure 1.2 Inserting the LSI Logic Host Adapter
Bracket Screw
32-Bit PCI Slots
64-Bit PCI Slots
Step 8. Secure the board with the bracket screw (see Figure 1.2), then
make the external FC link connection.
Detailed Installation Procedure 1-5
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 18

1-6 Installation Procedures
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 19

Chapter 2
2 Gbit/s FC
Host Adapter
Characteristics
This chapter provides specific details about the physical environment
associated with the 2 Gbit/s family of FC host adapters. This chapter
includes the following sections:
• Section 2.1, “General Description”
• Section 2.2, “Features”
• Section 2.3, “Physical Environment”
• Section 2.4, “Operational Environment”
• Section 2.5, “PCI System ID Values”
• Section 2.6, “PCI Subsystem ID Values”
• Section 2.7, “Unique World Wide Name”
• Section 2.8, “Physical Characteristics”
2.1 General Description
The LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s family of FC host adapters makes use of state-ofthe-art, 2 Gbit/s FC technology to provide the highest possible
performance and most flexible storage configuration available. These
LSI Logic host adapters support 1 Gbit/s or 2 Gbit/s FC speeds, and
detect and correctly set the speed of operation automatically. LSI Logic
host adapters are available with LC optical interfaces using optical
SFP transceivers.
These LSI Logic FC host adapters offer the highest degree of integration
available for your PCI-X or PCI Express based computer system,
allowing for maximum performance, optimized use of system resources,
and true Plug and Play installation.
2 Gbit/s Fibre Channel Host Adapters User’s Guide 2-1
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 20

This manual serves as a step-by-step guide during the installation of your
LSI Logic host adapter.
Table 2.1 lists the 2 Gbit/s FC host adapters discussed in this User’s
Guide.
Table 2.1 LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Descriptions
Adapter Description
LSI7102XP-LC 2 Gbit/s, PCI-X, single-port, standard height bracket, optical
LSI7102LXP-LC 2 Gbit/s, PCI-X, single-port, low-profile bracket, optical
LSI7202XP-LC 2 Gbit/s, PCI-X, dual-port, standard height bracket, optical
LSI7202LXP-LC 2 Gbit/s, PCI-X, dual-port, low-profile bracket, optical
LSI7202EP-LC
LSI7202EP
LSI7402XP-LC 2 Gbit/s, PCI-X, quad-port, standard height bracket, optical
LSI7402EP-LC
LSI7402EP
2 Gbit/s, PCI Express, dual-port, standard height bracket,
optical
2 Gbit/s, PCI Express, dual-port, standard height bracket, no
optics
2 Gbit/s, PCI Express, quad-port, standard height bracket,
optical
2 Gbit/s, PCI Express, quad-port, standard height bracket, no
optics
Hardware and Software Support – The LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s family of FC
host adapter supports most major software operating systems, such as
Sun Solaris (2.6 and greater), Windows Server (NT 4.0, 2000, XP, 2003),
Linux (RedHat, Suse, Caldera, Turbo), NetWare, and UnixWare. These
host adapters use the Fusion-MPT architecture for all major operating
systems. Fusion-MPT architecture offers the unique feature of having a
single binary operating system driver that supports FC devices and other
bus architectures. Refer to the Fusion-MPT Device Management User’s
Guide for details regarding software support for this family of host
adapters.
Before you use any of this family of host adapters, make sure your system
meets the specific hardware and software requirements shown in T able 2.2.
2-2 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 21
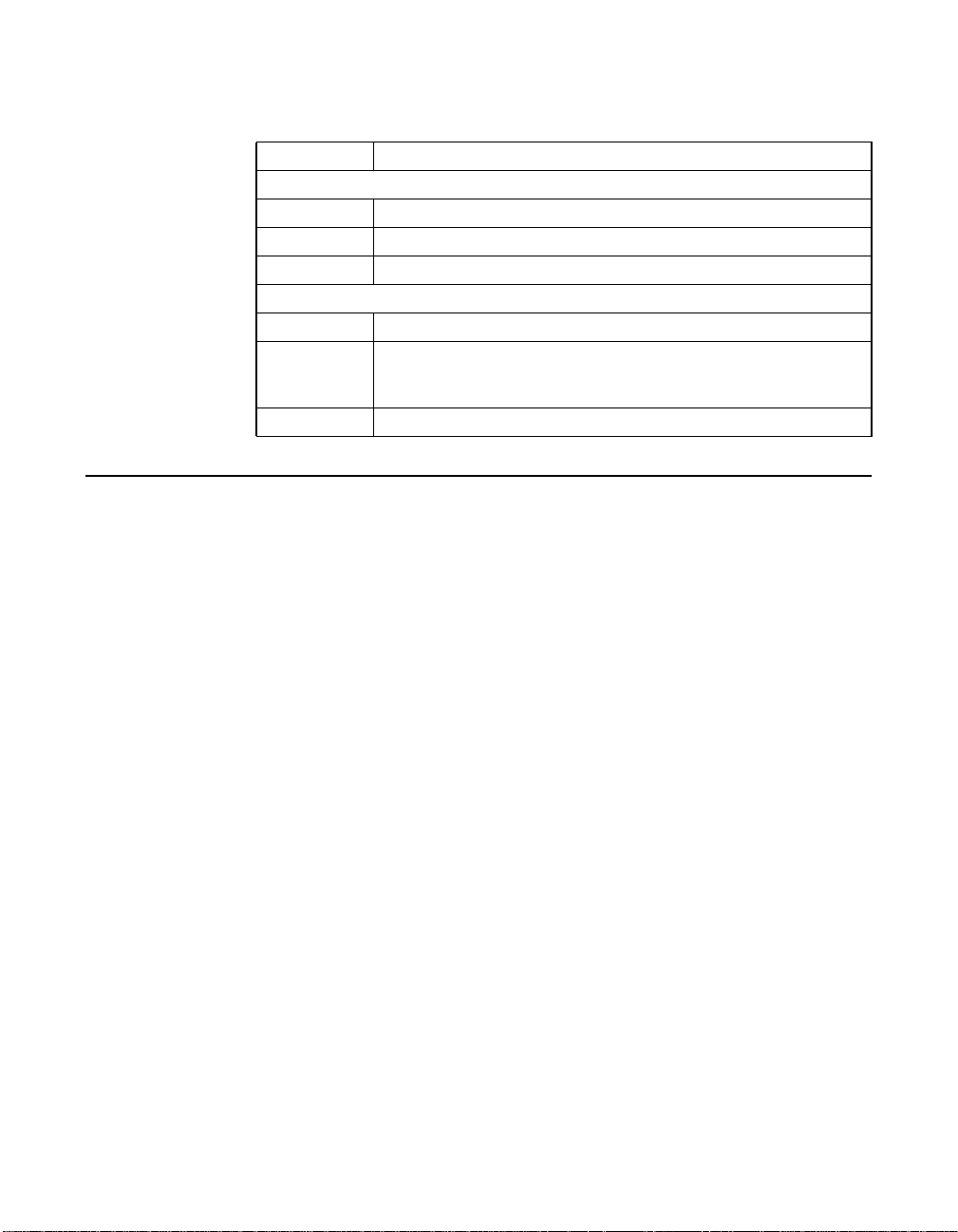
Table 2.2 Hardware and Software Requirements
Component Requirements
For Solaris SPARC hardware environments
Hardware Any Sun Microsystems computer with a 3.3 V PCI slot
Software Solaris 8 operating environment
Firmware OpenBoot PROM, version 2.1 or greater
For Intel IA-32 or IA-64 hardware environments
Hardware Any Intel-compatible system with 3.3 V PCI slots
Software
Firmware Any Intel-compatible BIOS system
2.2 Features
This section provides an overview of the PCI-X Interface, the PCI
Express Interface, and the FC Interface for the 2 Gbit/s family of host
adapters.
2.2.1 PCI-X Interface
Windows Server (NT 4.0, 2000, XP, 2003)
Linux (Red Hat, Suse, Caldera, Turbo),
NetWare, and UnixWare.
PCI-X interfaces I/O components to the processor and memory
subsystems in equipment ranging from PCs to servers. The PCI-X interface
operates as a 64-bit DMA bus master capable of 64-bit addressing.
The PCI-X interface includes the following features:
• Full 64-bit DMA bus master
• LSIFC929X/LSIFC919X functionality:
– Zero wait-state bus master data bursts up to 1 Kbyte
– Host adapters comply with PCI Local Bus Specification, Rev. 2.2
– 3.3 V interface
• Serial EEPROM configuration storage
• Host adapters comply with PCI-X/133 Local Bus Specification,
Rev. 1.0a
Features 2-3
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 22

2.2.2 PCI Express Interface
The PCI Express (launched in 2002) interface is a new serial I/O
interface standard being used in next generation computer, storage and
communications platforms. This scalable interface allows vendors to
choose the number of 2.5 Gbit serial lanes (two to 16) most suitable to
their product design and application need.
The PCI Express interface featured on the LSI Logic Fibre to PCI
Express boards includes:
• 8 serial I/O lanes, 2.5 GHz, full duplex
• Fully PCI-compatible software model
• Serial EEPROM configuration storage
2.2.3 FC Interface
The LSIFC929X and LSIFC919X processors contain the FC functionality
for all the LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s FC host adapters. The LSIFC929X and
LSIFC919X processors generate signal timing and link protocol in
compliance with FC standards.
The FC interface includes these features:
• 2 Gbit/s serial link
• LSIFC929X and LSIFC919X processor functionality:
– Class 3, Arbitrated Loop (AL), Fabric, Point-to-Point
– 2 Kbyte frame payloads
– Multiframe buffering
• Link activity/link fault LED
2.3 Physical Environment
This section provides information about the physical, electrical, thermal,
and safety characteristics of the LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s family of FC host
adapters. Additionally, these boards are compliant with FCC
electromagnetic standards.
2-4 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 23

2.3.1 Electrical Characteristics
Table 2.3 lists the maximum power requirements and includes all of the
LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s FC host adapter boards under normal operation.
Table 2.3 Maximum Power Requirements
Host Adapter PCI +3.3 V Over the Operating Range
LSI7102XP-LC 4.7 W @ 3.6 V 0 ˚C to 55 ˚C
LSI7102LXP-LC 4.7 W @ 3.6 V 0 ˚C to 55 ˚C
LSI7202XP-LC 6.5 W @ 3.6 V 0 ˚C to 55 ˚C
LSI7202LXP-LC 6.5 W @ 3.6 V 0 ˚C to 55 ˚C
LSI7202EP-LC 11.5 W @ 12.6 V 0 ˚C to 55 ˚C
LSI7202EP
LSI7402XP-LC
LSI7402EP-LC 16.0 W @ 12.6 V 0 ˚C to 55 ˚C
LSI7402EP
10.7 W @ 12.6 V
plus SFP power, if any
14.7 W @ 3.6 V
plus 4.2 W @ 5.25 V
14.4 W @ 12.6 V
plus SFP power, if any
2.3.2 Thermal, Atmospheric Characteristics
0˚Cto55˚C
0˚Cto55˚C
0˚Cto55˚C
The thermal, atmospheric characteristics of the LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s family
of FC host adapters are:
• Temperature range: 0 °Cto55°C (dry bulb), 100 linear feet per
minute (LFPM) airflow minimum
• Relative humidity range: 5% to 90% noncondensing
• Maximum dew point temperature: 32 °C
The following parameters define the storage and transit environment for
the LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s family of FC host adapters:
• Storage Temperature: −45 °C to +85 °C (dry bulb)
• Relative Humidity Range: 0% to 95%, noncondensing
Physical Environment 2-5
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 24

2.3.3 Electromagnetic Compliance
These boards are designed and implemented to minimize susceptibility
to electromagnetic emissions, and the effects of electromagnetic
discharge. The boards are tested to comply with Class B and carry
markings for CE, VCCI, Canada, C-Tick, and the FCC.
2.3.4 Safety Characteristics
The bare boards meet the requirements of flammability rating UL 94 V-0.
The bare boards are also marked with the supplier name or trademark,
type, and UL flammability rating. Because these boards are installed in
a PCI bus slot, all voltages are below the SELV 42.4 V limit.
2.4 Operational Environment
Use the LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s family of FC host adapters in PCI-X or PCI
Express computer systems with an Industry Standard
Architecture/Extended Industry Standard Architecture (ISA/EISA) bracket
type. The LSI Logic-supplied FC BIOS and firmware operate the host
adapters. An on-board flash memory device and a serial EEPROM are
provided to allow BIOS code and OpenBoot code support over the PCI
bus.
2.4.1 PCI-X Interface
The PCI-X interface operates as a 64-bit DMA bus master. The edge
connector makes the PCI-X connection, which provides connections on
both the front and back of the board. The signal definitions and pin
numbers conform to the PCI-X/133 Specification, Revision 1.0a. Refer to
that specification for details regarding the signal assignments.
2.4.2 PCI Express Interface
The LSI Logic PCI Express interface operates as a x8 lane DMA bus
master. The narrow edge connector makes the PCI Express connection,
which provides connections on both the front and back of the board. The
signal definitions and pin numbers conform to the PCI Express base
Specification, Revision 1.0a. Refer to that specification for details
regarding the signal assignments.
2-6 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 25

2.4.3 FC Interface
The FC interface varies, depending on which LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s host
adapter you have selected. Refer to Section 2.8, “Physical
Characteristics,” page 2-9 for details.
2.4.4 FC Link Activity/Link Fault LED
The LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s host adapters provide dual-purpose LEDs that
indicate activity on the FC link. These LEDs (one per port) are visible
near the ports on the bracket. Figure 2.4 shows the appearance of the
Link Activity/Link Fault LED that represents the given link status for each
of the LSI Logic host adapters.
Table 2.4 LED Appearance to Represent Link Status
Adapter Link Activity Fault
LSI7102XP-LC Off Green Blinking Yellow
LSI7102LXP-LC Off Green Blinking Yellow
LSI7202XP-LC Off Green Blinking Yellow
LSI7202LXP-LC Off Green Blinking Yellow
LSI7202EP-LC Off Green Blinking Yellow
LSI7202EP Off Green Blinking Yellow
LSI7402XP-LC Off Green Blinking Yellow
LSI7402EP-LC Off Green Blinking Yellow
LSI7402EP Off Green Blinking Yellow
2.5 PCI System ID Values
All LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s host adapters share common PCI Vendor ID (VID)
values and are assigned device ID (DID) values to allow drivers and
BIOS to recognize them as 2 Gbit/s capable FC products. Table 2.1
provides the VID and DID for all LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s FC host adapters.
PCI System ID Values 2-7
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 26

Table 2.5 PCI System ID Values
Host Adapter VID Number DID Number
LSI7102XP-LC 0x1000 0x0628
LSI7102LXP-LC 0x1000 0x0628
LSI7202XP-LC 0x1000 0x0626
LSI7202LXP-LC 0x1000 0x0626
LSI7402XP-LC 0x1000 0x0626
LSI7202EP-LC 0x1000 0x0626
LSI7202EP 0x1000 0x0626
LSI7402EP-LC 0x1000 0x0626
LSI7402EP 0x1000 0x0626
2.6 PCI Subsystem ID Values
All LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s host adapters are assigned PCI Subsystem Vendor
IDs (SVIDs) and Subsystem IDs (SSIDs) to allow drivers and BIOS to
differentiate the individual host adapter variants. The SVID and SSID are
listed below. Table 2.6 provides the SVID and SSID for all the LSI Logic
2 Gbit/s FC host adapters discussed in this user’s guide.
Table 2.6 PCI Subsystem ID Values
Host Adapter SVID Number SSID Number
LSI7102XP-LC 0x1000 0x0530
LSI7102LXP-LC 0x1000 0x0530
LSI7202XP-LC 0x1000 0x1010
LSI7202LXP-LC 0x1000 0x1010
LSI7402XP-LC 0x1000 0x1020
LSI7202EP-LC 0x1000 0x1180
LSI7202EP 0x1000 0x1170
LSI7402EP-LC 0x1000 0x1090
LSI7402EP 0x1000 0x1190
2-8 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 27

2.7 Unique World Wide Name
Each LSI Logic FC host adapter is provided with a unique World Wide
Name, specified by IEEE. The last 12 hexadecimal characters of this
address appear on a host adapter label. This address is stored in the
host adapter serial EEPROM.
2.8 Physical Characteristics
The LSI Logic 2 Gbit/s family of FC host adapters includes one to four
external FC connectors, depending on the host adapter you have
chosen. The host adapters are all available with optical or copper
interconnects. No host adapter configuration is necessary.
2.8.1 LSI7102XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
The LSI Logic LSI7102XP-LC is a single channel 2 Gbit/s FC adapter.
One LC optical connector is used for I/O, which is accessible through the
module bracket. The LSI7102XP-LC host adapter uses the LSIFC919X
processor, providing one Fusion-MPT channel.
The LSI7102XP-LC is a PCI short card; the dimensions are
6.625 inches x 2.53 inches. The external FC connections are made
through a 2 Gbit/s SFP optical module.
The component height on the top and bottom of the board conforms to
the PCI-X/133 Specification, Revision 1.0a. Figure 2.1 illustrates the
major components on the LSI7102XP-LC.
Unique World Wide Name 2-9
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 28

Figure 2.1 LSI7102XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
LSI7102XP-LC
LSIFC919X
Osc.
Port 0, SFP
J1_T
2.8.2 LSI7102XP-LC Connector and Indicator LED
The LSI7102XP-LC I/O bracket is configured as shown in Figure 2.2. The
LC connector provides the connection from the adapter channel to the
FC subsystem. The indicator LED indicates link status, activity, and link
fault.
Voltage
Regulator
Flash
(Back)
SRAM (X2)
2-10 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 29

Figure 2.2 LSI7102XP-LC Connector and Indicator LED
Port 0
Port 0 LED
Table 2.7 describes the LSI7102XP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LED
appearance that indicates a valid link, presence of link activity, or a fault
on the link.
Table 2.7 LSI7102XP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs
Link Activity Fault
LED Appearance Off Green Blinking Yellow
Physical Characteristics 2-11
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 30

2.8.3 LSI7102LXP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
The LSI Logic LSI7102LXP-LC is a single channel 2 Gbit/s FC adapter.
One LC optical connector is used for I/O, which is accessible through the
module bracket. The LSI7102LXP-LC host adapter uses the LSIFC919X
processor, providing one Fusion-MPT channel.
The LSI7102LXP-LC is a PCI short card; the dimensions are
6.625 inches x 2.53 inches. The external FC connections are made
through a 2 Gbit/s SFP optical module.
The component height on the top and bottom of the board conforms to
the PCI-X/133 Specification, Revision 1.0a. Figure 2.3 illustrates the
major components on the LSI7102LXP-LC.
Figure 2.3 LSI7102LXP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
LSI7102XP-LC
LSIFC919X
Osc.
Port 0, SFP
Voltage
Regulator
Flash
(Back)
SRAM (X2)
2-12 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
J1_T
Page 31

2.8.4 LSI7102LXP-LC Connector and Indicator LED
The LSI7102LXP-LC I/O bracket is configured as shown in Figure 2.4.
The LC connector provides the connection from the adapter channel to
the FC subsystem. The indicator LED indicates link status, activity, and
link fault.
Figure 2.4 LSI7102LXP-LC Connector and Indicator LED
Port 0
Port 0 LED
Table 2.8 describes the LSI7102LXP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LED
appearance that indicates a valid link, presence of link activity, or a fault
on the link.
Table 2.8 LSI7102LXP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs
Link Activity Fault
LED Appearance Off Green Blinking Yellow
Physical Characteristics 2-13
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 32

2.8.5 LSI7202XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
The LSI Logic LSI7202XP-LC is a dual-channel, 2 Gbit/s FC adapter.
Two LC optical connectors, used for I/O, are accessible through the
module bracket. The LSI7202XP-LC uses the LSIFC929X, providing two
Fusion-MPT channels.
The LSI7202XP-LC is a PCI short card; the dimensions are 6.625 inches
x 2.53 inches. The external FC connections are made through the
2 Gbit/s SFP optical modules.
The component height on the top and bottom of the board conforms to
the PCI-X/133 Specification, Revision 1.0a. Figure 2.5 illustrates the
major components on the LSI7202XP-LC.
Figure 2.5 LSI7202XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
LSI7202XP-LC
Port 1, SFP
LSIFC929X
Osc.
Port 0, SFP
2-14 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
J1_T
Voltage
Regulator
Flash
(Back)
SRAM (X2)
Page 33

2.8.6 LSI7202XP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs
The LSI7202XP-LC I/O bracket is configured as shown in Figure 2.6. The
LC connectors provide the connections from the adapter channels to the
FC subsystem. The indicator LEDs indicate link status, activity, and link
fault.
Figure 2.6 LSI7202XP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs
Port 1 LED
Port 1
Port 0
Port 0 LED
Table 2.9 describes the LSI7202XP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LED
appearance that indicates a valid link, presence of link activity, or a fault
on the link.
Table 2.9 LSI7202XP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs
Link Activity Fault
LED Appearance Off Green Blinking Yellow
Physical Characteristics 2-15
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 34

2.8.7 LSI7202LXP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
The LSI Logic LSI7202LXP-LC is a dual-channel, 2 Gbit/s FC adapter.
Two LC optical connectors, used for I/O, are accessible through the
module bracket. The LSI7202LXP-LC uses the LSIFC929X, providing
two Fusion-MPT channels.
The LSI7202LXP-LC is a PCI short card; the dimensions are
6.625 inches x 2.53 inches. The external FC connections are made
through the 2 Gbit/s SFP optical modules.
The component height on the top and bottom of the board conforms to
the PCI-X/133 Specification, Revision 1.0a. Figure 2.7 illustrates the
major components on the LSI7202LXP-LC.
Figure 2.7 LSI7202LXP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
LSI7202XP-LC
Port 1, SFP
LSIFC929X
Osc.
Port 0, SFP
Voltage
Regulator
Flash
(Back)
SRAM (X2)
2-16 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
J1_T
Page 35

2.8.8 LSI7202LXP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs
The LSI7202LXP-LC I/O bracket is configured as shown in Figure 2.8.
The LC connectors provide the connections from the adapter channels to
the FC subsystem. The indicator LEDs indicate link status, activity, and
link fault.
Figure 2.8 LSI7202LXP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs
Port 1 LED
Port 1
Port 0
Port 0 LED
Table 2.10 describes the LSI7202LXP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LED
appearance that indicates a valid link, presence of link activity, or a fault
on the link.
Table 2.10 LSI7202LXP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs
Link Activity Fault
LED Appearance Off Green Blinking Yellow
Physical Characteristics 2-17
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 36

2.8.9 LSI7202EP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
The LSI Logic LSI7202EP-LC is a dual-channel, 2 Gbit/s FC adapter.
Two LC optical connectors, used for I/O, are accessible through the
module bracket. The LSI7202EP-LC uses the LSIFC929X, providing two
Fusion-MPT channels.
The LSI7202EP-LC is a PCI short card; the dimensions are 6.875 inches
x 4.2 inches. The external FC connections are made through the 2 Gbit/s
SFP optical modules.
The component height on the top and bottom of the board conforms to
the PCI Express Specification, Revision 1.0a. Figure 2.9 illustrates the
major components on the LSI7202EP-LC.
Figure 2.9 LSI7202EP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
LSI7202EP-LC
Port 1, SFP
Port 0, SFP
Osc.
LSIFC929X
PCI Express
Bridge
Flash
(Back)
Voltage
Regulator
SRAM
Flash
(Back)
SRAM (X2)
(X2)
2-18 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 37

2.8.10 LSI7202EP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs
The LSI7202EP-LC I/O bracket is configured as shown in Figure 2.10.
The Port 0 and Port 1 connectors provide the connections from the
adapter channels to the FC subsystem. The indicator LEDs indicate link
status, activity, and link fault.
Figure 2.10 LSI7202EP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs
Port 1 LED
Port 1
Port 0
Port 0 LED
Table 2.11 describes the LSI7202EP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LED
appearance that indicates a valid link, presence of link activity, or a fault
on the link.
Table 2.11 LSI7202EP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs
Link Activity Fault
LED Appearance Off Green Blinking Yellow
Physical Characteristics 2-19
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 38

2.8.11 LSI7202EP Host Adapter Configuration
The LSI Logic LSI7202EP is a dual-channel, 2 Gbit/s FC adapter. Two
connectors, used for I/O, are accessible through the module bracket. The
LSI7202EP uses the LSIFC929X, providing two Fusion-MPT channels.
The LSI7202EP is a PCI short card; the dimensions are 6.875 inches
x 4.2 inches. The external FC connections are made through the 2 Gbit/s
SFP optical modules.
The component height on the top and bottom of the board conforms to
the PCI Express Specification, Revision 1.0a. Figure 2.11 illustrates the
major components on the LSI7202EP.
Figure 2.11 LSI7202EP Host Adapter Configuration
LSI7202EP
Port 1, SFP
Port 0, SFP
Osc.
LSIFC929X
PCI Express
Bridge
Flash
(Back)
Voltage
Regulator
SRAM
Flash
(Back)
SRAM (X2)
(X2)
2-20 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 39

2.8.12 LSI7202EP Connectors and Indicator LEDs
The LSI7202EP I/O bracket is configured as shown in Figure 2.12. The
Port 0 and Port 1 connectors provide the connections from the adapter
channels to the FC subsystem. The indicator LEDs indicate link status,
activity, and link fault.
Figure 2.12 LSI7202EP Connectors and Indicator LEDs
Port 1 LED
Port 1
Port 0
Port 0 LED
Table 2.12 describes the LSI7202EP Link Activity/Link Fault LED
appearance that indicates a valid link, presence of link activity, or a fault
on the link.
Table 2.12 LSI7202EP Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs
Link Activity Fault
LED Appearance Off Green Blinking Yellow
Physical Characteristics 2-21
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 40

2.8.13 LSI7402XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
The LSI Logic LSI7402XP-LC is a quad-channel, 2 Gbit/s FC adapter.
Four LC optical connectors, used for I/O, are accessible through the
module bracket. The LSI7402XP-LC uses two LSIFC929X devices,
providing four Fusion-MPT channels.
The LSI7402XP-LC is a PCI short card; the dimensions are
6.875 inches x 4.2 inches. The external FC connections are made
through the 2 Gbit/s SFP optical modules.
The component height on the top and bottom of the board conforms to
the PCI-X/133 Specification, Revision 1.0a. Figure 2.13 illustrates the
major components on the LSI7402XP-LC.
Figure 2.13 LSI7402XP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
LSI7402XP-LC
Port 3, SFP
Port 2, SFP
Port 1, SFP
Port 0, SFP
Osc.
LSIFC929X
PCI-X Bridge
J1_T
Flash
(Back)
LSIFC929X
Voltage
Regulator
SRAM
Flash
(Back)
SRAM (X2)
(X2)
2-22 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 41

2.8.14 LSI7402XP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs
The LSI7402XP-LC I/O bracket is configured as shown in Figure 2.14.
The LC connector provides the connection from the adapter channel to
the FC subsystem. The indicator LEDs indicate link status, activity, and
link fault.
Figure 2.14 LSI7402XP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs
Port 3
Port 2
Port 1
Port 0
Port 3 LED
Port 1 LED
Port 2 LED
Port 0 LED
Table 2.13 describes the LSI7402XP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LED
appearance that indicates a valid link, presence of link activity, or a fault
on the link.
Table 2.13 LSI7402XP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs
Link Activity Fault
LED Appearance Off Green Blinking Yellow
Physical Characteristics 2-23
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 42

2.8.15 LSI7402EP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
The LSI Logic LSI7402EP-LC is a quad-channel, 2 Gbit/s FC adapter.
Four LC optical connectors, used for I/O, are accessible through the
module bracket. The LSI7402EP-LC uses two LSIFC929X devices,
providing four Fusion-MPT channels.
The LSI7402EP-LC is a PCI short card; the dimensions are
6.875 inches x 4.2 inches. The external FC connections are made
through the 2 Gbit/s SFP optical modules.
The component height on the top and bottom of the board conforms to
the PCI Express Specification, Revision 1.0a. Figure 2.15 illustrates the
major components on the LSI7402EP-LC.
Figure 2.15 LSI7402EP-LC Host Adapter Configuration
LSI7402EP
Port 3, SFP
Port 2, SFP
Port 1, SFP
Port 0, SFP
Osc.
LSIFC929X
PCI Express
Bridge
Flash
(Back)
LSIFC929X
Voltage
Regulator
SRAM
Flash
(Back)
SRAM (X2)
(X2)
2-24 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 43

2.8.16 LSI7402EP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs
The LSI7402EP-LC I/O bracket is configured as shown in Figure 2.16.
The LC connectors provide the connections from the adapter channels to
the FC subsystem. The indicator LEDs indicate link status, activity, and
link fault.
Figure 2.16 LSI7402EP-LC Connectors and Indicator LEDs
Port 3
Port 2
Port 1
Port 0
Port 3 LED
Port 1 LED
Port 2 LED
Port 0 LED
Table 2.14 describes the LSI7402EP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LED
appearance that indicates a valid link, presence of link activity, or a fault
on the link.
Table 2.14 LSI7402EP-LC Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs
Link Activity Fault
LED Appearance Off Green Blinking Yellow
Physical Characteristics 2-25
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 44

2.8.17 LSI7402EP Host Adapter Configuration
The LSI Logic LSI7402EP is a quad-channel, 2 Gbit/s FC adapter. Four
connectors, used for I/O, are accessible through the module bracket. The
LSI7402EP uses two LSIFC929X devices, providing four Fusion-MPT
channels.
The LSI7402EP is a PCI short card; the dimensions are
6.875 inches x 4.2 inches. The external FC connections are made
through the 2 Gbit/s SFP optical modules.
The component height on the top and bottom of the board conforms to
the PCI Express Specification, Revision 1.0a. Figure 2.17 illustrates the
major components on the LSI7402EP.
Figure 2.17 LSI7402EP Host Adapter Configuration
LSI7402EP
Port 3, SFP
Port 2, SFP
Port 1, SFP
Port 0, SFP
Osc.
LSIFC929X
PCI Express
Bridge
Flash
(Back)
LSIFC929X
Voltage
Regulator
SRAM
Flash
(Back)
SRAM (X2)
(X2)
2-26 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 45

2.8.18 LSI7402EP Connectors and Indicator LEDs
The LSI7402EP I/O bracket is configured as shown in Figure 2.18. The
Port 0, Port 1, Port 2, and Port 3 connectors provide the connections from
the adapter channels to the FC subsystem. The indicator LEDs indicate
link status, activity, and link fault.
Figure 2.18 LSI7402EP Connectors and Indicator LEDs
Port 3
Port 2
Port 1
Port 0
Port 3 LED
Port 1 LED
Port 2 LED
Port 0 LED
Table 2.15 describes the LSI7402EP Link Activity/Link Fault LED
appearance that indicates a valid link, presence of link activity, or a fault
on the link.
Table 2.15 LSI7402EP Link Activity/Link Fault LEDs
Link Activity Fault
LED Appearance Off Green Blinking Yellow
Physical Characteristics 2-27
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 46

2-28 2 Gbit/s FC Host Adapter Characteristics
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 47

Chapter 3
Firmware Installation
Procedure
This chapter provides information about installing and configuring FC
firmware and includes the following sections:
• Section 3.1, “FC Firmware”
• Section 3.2, “Download New FC Firmware”
• Section 3.3, “Update the FC Firmware”
• Section 3.4, “Advanced User: Adjusting Default Firmware Settings”
• Section 3.5, “Troubleshooting”
The LSI Logic FC chips and host adapters contain firmware that presents
a multiprotocol service layer based on the Fusion-MPT architecture. The
FC firmware provides FCP (SCSI-3 over FC) Initiator, FCP Target, and
LAN interface services to the host system.
The FC929X.ROM file contains the firmware to operate the LSIFC929X or
LSIFC919X controllers used on the associated 2 Gbit/s LSI Logic host
adapters. When updates are necessary,LSI Logic releases new firmware
to improve the functionality or performance of these host adapters. You
may download the latest firmware from the LSI Logic web site at:
http://drivers.lsilogic.com.
2 Gbit/s Fibre Channel Host Adapters User’s Guide 3-1
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 48

3.1 FC Firmware
This section includes the features, description, installation, and
configuration of the FC firmware. The installation method varies
depending on the operating system. LSI Logic provides firmware
installation tools for the Windows, Linux, and Solaris operating systems.
3.1.1 Features
The FC firmware for the LSI Logic FC chips supports the
following features:
• 1 Gbit/s and 2 Gbit/s FC transfers, with AutoNegotiation
(select 1 Gbit/s, 2 Gbit/s, or Auto)
• 64-bit/66 MHz host PCI bus and 133 MHz PCI-X bus
(backward-compatible with 32-bit/33 MHz)
• Transaction performance capability of > 70,000 I/Os per second
(both channels)
• Throughput capability of ~400 Mbytes/s, across 64-bit/66 MHz PCI
(both channels)
• Low host CPU utilization
• Interrupt coalescing, tunable to system requirements
• Auto Topology Detection for Arbitrated Loop, Fabric Loop, or
Direct Fabric attachment (user selects N_Port, NL_Port, or Auto)
• FC Class 3 support
• FC-Tape/FC-AL2 Class 3 confirmed delivery support
• Fusion-MPT common software interface
• Initiator, Target, and FC LAN capability
3.1.2 Description
The LSIFC929X and LSIFC919X controllers operate in an environment
where one or more host drivers serve as the interface layer between the
operating system and the Fusion-MPT services provided by the
LSI Logic FC firmware. The host driver is responsible for initializing the
controller, building request message frames, issuing request message
3-2 Firmware Installation Procedure
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 49

frames to the controller, and processing reply message frames received
from the controller.
The LSI Logic firmware translates Fusion-MPT message frames into
FC-specific sequences, frames, and primitives that are delivered to the
FC transmit and receive physical interfaces. The firmware-based
Link Services library transparently provides all link service support that the
host uses for all FC topologies. The firmware also manages all link
exceptions,which isolates the host driver from FC-unique exceptions.With
the Fusion-MPT architecture, parallel SCSI host drivers can be used with
the LSI Logic FC controllers with little or no additional functionality for FC.
3.2 Download New FC Firmware
To begin, you must first download new host adapter firmware
component(s) from the LSI Logic web site (www.lsilogic.com). Type the
following address into your preferred browser:
http://drivers.lsilogic.com
The web page presents three drop-down menus under Find Specific
Products. Make the following selections:
Step 1. Select Storage Adapters.
Step 2. Select Fibre Channel HBAs.
Step 3. Select LSI7202XP-LC (or other 2 Gbit/s LSI Logic host
adapter).
Step 4. Check the box next to BIOS/Firmware. Then click the Go
button.
This search locates the latest BIOS/Firmware available for your host
adapter. Save the file to your hard drive. You may have to unzip this file.
Typically, the download will contain three separate files:
FC929X.ROM —LSI Logic Firmware update
MPTBIOS.ROM —LSI Logic Boot BIOS update
LSI9x9f.ROM —LSI Logic Fcode update
Download New FC Firmware 3-3
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 50

These files represent updated code that you may store on your LSI Logic
host adapter using one of the methods described in the next sections.
3.3 Update the FC Firmware
The process of updating the FC firmware varies slightly, depending on
the operating system.
3.3.1 GUI Update Tool for Windows and Linux Platforms
With the MyStorage™ management software installed on either Windows
or Linux operating systems, you can use the MyStorage software to
update LSI Logic host adapters with new firmware (Section 3.2,
“Download New FC Firmware”). The CD-ROM media distributed with
many LSI Logic host adapter kits contains the MyStorage software;
alternatively, users can download the MyStorage software from the
LSI Logic web site (www.lsilogic.com).
Refer to LSI Logic MyStorage Management Software User’s Guide for
detailed usage instructions.
3.3.2 Command Line Update Tool for Solaris, Linux, and Windows
LSI Logic provides a FC Flash command line utility called LSIUtil to
update LSI Logic host adapters with new firmware (Section 3.2). The
software is available for the Windows, Linux, and Solaris operating
systems. This section provides the procedure for operating this program.
Note: The LSIUtil program will not operate properly unless an
LSI Logic OS driver is also installed.
Running the LSIUtil Program – The LSIUtil program may be used to
update the LSI Logic FC firmware of any 2 Gbit/s host adapter. Locate
and copy the LSIUtil.exe program and the FC929X.ROM code files
to a directory on your hard drive. To update the firmware, complete the
following steps:
Step 1. Ensure that the host adapter is properly installed in the system
PCI/PCI-X or PCI Express slot.
3-4 Firmware Installation Procedure
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 51

Step 2. Open a terminal window, and open the directory containing the
LSIUtil program.
Step 3. Execute the LSIUtil program.
Step 4. Select a device to update (Figure 3.1).
Figure 3.1 LSIUtil Device Selection
[root]# lsiutil
LSI Logic MPT Configuration Utility, Version 1.28, November 12,
2004
2 MPT Ports found
Port Name Chip Vendor/Type MPT Rev Firmware Rev
1. /proc/mpt/ioc0 LSI Logic FC929X 103 01021200
2. /proc/mpt/ioc1 LSI Logic FC929X 103 01021200
Select a device: [1-2 or 0 to quit]
Step 5. From the subsequent displayed list, select option menu 2 or 4
as shown (Figure 3.2).
Update the FC Firmware 3-5
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 52

Figure 3.2 LSIUtil Download Options
Step 6. When prompted, type the firmware file name.
Step 7. Type Yes, when asked to continue (Figure 3.3).
Figure 3.3 LSIUtil File Download
Enter firmware name: FC929X.ROM
Do you want to continue? [Yes or No, default is No] Y
Downloading image...
Download succeeded
The update process requires about 20–30 seconds. Upon completion,
the system should display this message: “download succeeded”.
Step 8. Reset the adapter using option 99, or reboot to begin running
the new firmware.
Step 9. Enter 0 to quit the program.
3-6 Firmware Installation Procedure
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 53

3.3.3 Command Line Update Tool for DOS
Using a DOS bootable floppy, users can use a FC Flash Utility called
MPTUtil to update LSI Logic adapters with new firmware (Section 3.2,
“Download New FC Firmware,” page 3-3). This section provides the
procedure for operating this program.
Note: The MPTUtil program will not operate properly from a
windows command window. It must be run from a DOS
floppy.
Running the MPTUtil Program – Use the MPTUtil program to
update the LSI Logic FC firmware on any 4 Gbit/s host adapter. Locate
the MPTUtil.exe program and FC929X.ROM code on your
distribution media, as well as the DOS4GW.exe file. Copy these files to
a blank, formatted diskette. Label it “FC Firmware diskette.”
To update the firmware, complete the following steps:
Step 1. Ensure that the host adapter is properly installed in the system
PCI slot.
Step 2. Insert the LSI Logic FC firmware diskette into drive A.
Step 3. Boot the system to the DOS prompt A:\>.
Step 4. Execute the MPTUtil program directly from the DOS command
line by typing at the prompt:
A:\ MPTutil
The MPTUtil program identifies all LSI Logic host adapters in the system,
and it allows you to select which adapter to update (Figure 3.4).
Figure 3.4 MPTUtil Device Selection
LSIMPTUTIL 1.00.00
Vendor Device
Choice ID ID Bus Device
------ ------ ------ --- --------- 1 1000h 0626h 0h 28h LSI 929X Fibre Channel Host
Adapter
2 Refresh
Which chip (0 to quit)? __
Update the FC Firmware 3-7
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 54

Step 5. The MPTUtil program displays a menu of options (Figure 3.5).
To update the firmware, select option a - Update Firmware.
Figure 3.5 MPTUtil Options
LSI Logic Corp. FC/SAS Serial EEPROM / FLASH Utility.
LSIMPTUTIL 1.00.00
Copyright (c) 2005 LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
*******************************************************************
Currents Port 0 Port 1
World Wide P/N... 0x100000062B092448 0x100000062B092449
World Wide P/N... 0x200000062B092448 0x200000062B092449
Topology......... Auto
Speed............ Auto
Device Pathing... All Paths to a device
Protocol Support. INIT TARG LAN
Firmware: LSIFC929X 1.02.12 (2005.06.15)
********************************************************************
a - Update Firmware
b - Update BIOS & Firmware
c - Upload current firmware to a file
d - Upload current BIOS to a file
f - Toggle Board Speed on Function 0
g - Toggle Board Speed on Finction 1
f - Toggle Topologies on Function 0
g - Toggle Topologies on Finction 1
l - Change Interrupt Coalescing Values on Port 0
m - Change Interrupt Coalescing Values on Port 1
x - Erase BIOS
y - Change Protocol Support
z - Change Adapters
q - Quit
Selection:
Step 6. When prompted, type the filename of the BIOS/Fcode update.
The update process commences and completes in about 20–
30 seconds.
Step 7. Exit the MPTUtil utility using the menu option q - Quit.
3.4 Advanced User: Adjusting Default Firmware Settings
Occasionally, a user may find it necessary to adjust default firmware
parameters set by LSI Logic during the original manufacturing process.
Adjustments to these parameters will affect future behavior of the
3-8 Firmware Installation Procedure
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 55

LSI Logic Adapter, and should be reserved for advanced users who fully
understand the implications of such changes.
The LSI Logic firmware supports several configuration options, defined
individually in Section 3.4.1, “Adjusting Link Speed,” and Section 3.4.2,
“Adjusting Interrupt Coalescing.” These options may be configured using
the MPTUtil utility menu, as described in the subsection entitled
“Running the MPTUtil Program”.
3.4.1 Adjusting Link Speed
The link speed of the LSI Logic host adapters is configurable. By default,
the link speed is set to Auto. This means the host adapter automatically
detects the link speed of all other nodes on the link and automatically
adjusts itself to work with those nodes. If this automatic operation fails
(for example, other nodes on a loop do not support AutoNegotiation), the
LSI Logic host adapters may be configured specifically to either the 2
Gbit/s or 1 Gbit/s speed.
Note: The LSI7202XP-LC, LSI7202EP-LC, and LSI7202EP each
have two FC ports and the LSI7402XP-LC, LSI7402XP-LC,
and LSI7402XP-LC each have four FC ports, so the link
speed must be configured for each port. The
LSI7102XP-LC has only one port.
Configure the link speed of the host adapter by following these steps:
Step 1. Toset the link speed of the host adapter, execute this command
from the DOS command line:
A:\ MPTutil
The MPTUtil program identifies all LSI Logic host adapters in
the system, and allows you to select which adapter to update
(Figure 3.4).
Step 2. The MPTUtil program displays a menu of options. (Figure 3.5).
To change the link speed on the LSI7202XP-LC Port 0 (lower
port, near the PCI connector), select the following menu option:
f-Toggle Board Speed on Function 0
To change the link speed on the LSI7202XP-LC Port 1 (upper
port from the PCI connector), select the following menu option:
Advanced User: Adjusting Default Firmware Settings 3-9
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 56

g - Toggle Board Speed on Function 1
Successively pressing the F key (for Function 0) or the G key
(for Function 1) toggles the PORT speed setting between these
three modes:
• AUTO
• 1 Gbit/s
• 2 Gbit/s
Step 3. Exit the FCUtil utility using the menu option q - Quit.
3.4.2 Adjusting Interrupt Coalescing
The LSI Logic host adapters can complete multiple I/O requests per host
interrupt. Interrupt coalescing is used to reduce CPU interrupts by
pooling multiple disk command completions (I/O) into one interrupt. This
feature may be enabled or disabled.
Important: LSI Logic has performed significant testing under multiple
I/O conditions and has determined that interrupt coalescing
can be very valuable for small transfer lengths or random,
transaction-oriented I/O workloads. For this type of
workload, LSI Logic recommends that the Interrupt
Coalescing values be set to a queue depth of 9, with a
timeout of 1280 (0x500) µs. This means that the host is
interrupted only once for 9 I/Os processed by the chip,
unless 1280 µs have passed since the host was last
interrupted. If the workload is of a large transfer length and
sequential, LSI Logic recommends that interrupt coalescing
be disabled to prevent performance degradation.
Note: The LSI7202XP-LC, LSI7202EP-LC, and LSI7202EP each
have two FC ports and the LSI7402XP-LC, LSI7402XP-LC,
and LSI7402XP-LC each have four FC ports, so Interrupt
Coalescing must be configured for each port. The
LSI7102XP-LC has only one port.
Use the following procedure to adjust Interrupt Coalescing depth and
timeout values:
Step 1. Toset the link speed of the host adapter, execute this command
from the DOS command line:
3-10 Firmware Installation Procedure
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 57

A:\ Mptutil
The MPTUtil program identifies all LSI Logic host adapters in
the system, and allows you to select which adapter to update.
(See Figure 3.4.)
Step 2. The MPTUtil program displays a menu of options. (See
Figure 3.5.)
To change Interrupt Coalescing on the LSI7202XP-LC Port 0,
select the following menu option:
1- Change Interrupt Coalescing Values on Port 0
The current values are displayed within a submenu that allows the values
to be changed (Figure 3.6).
Figure 3.6 Interrupt Coalescing Values
Flags – By default, the host adapter has Interrupt Coalescing enabled,
as indicated by the Flags value of 0x0001. If you want to disable Interrupt
Coalescing, enter a value of 0x0000 for Flags. Interrupt Coalescing
should only be disabled to resolve issues in unique system
configurations. Consult LSI Logic Host Adapter Support to verify the
need to disable Interrupt Coalescing for specific system configurations.
When enabled, two parameters are relevant for interrupt coalescing:
Coalescing Depth – Specifies the number of I/Os that must complete
before a host interrupt is generated. For example, if set to 4, then the
adapter waits until four I/Os complete before notifying the host CPU via
the interrupt mechanism. You can decrease this value to improve system
performance if the system contains lower performance servers and/or
peripherals.
Coalescing Timeout – This is failsafe time period that specifies the
maximum amount of time (in milliseconds) to interrupt regardless of
Coalescing depth.
Advanced User: Adjusting Default Firmware Settings 3-11
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 58

3.5 Troubleshooting
Some potential problems and their suggested solutions are as follows:
The firmware and BIOS revisions typically must be in sync for
proper operation.
Check with LSI Logic Technical Support to make sure that the Firmware
is the correct version to use with your BIOS. If the firmware revision is
not in sync with the BIOS revision, system failures may occur.
How do you identify the version number of the firmware?
The UNIX-compatible WHAT.EXE program for DOS included on your
distribution media can identify the ROM files on the diskette(s).
Examples:
what *.*
what *.* nt/*.*
Many types of errors are reported through the LED on the LSI Logic
Host Adapter boards.
When these errors occur, the LED flashes a four-digit sequence, which
is the error code. These types of errors should be reported to LSI Logic
Technical Support. The technical support representative will ask for
additional system configuration information, including the type of system
used, the FC configuration and type of peripherals (including version
numbers), and the sequence of events when the error occurred.
3-12 Firmware Installation Procedure
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 59

Chapter 4
BIOS Features
This chapter describes the Fibre Channel (FC) BIOS and
Configuration Utility and includes the following sections:
• Section 4.1, “LSI Logic Boot BIOS”
• Section 4.2, “Starting the LSI Logic Boot BIOS Configuration Utility”
• Section 4.3, “Using the LSI Logic Boot BIOS CU”
• Section 4.4, “Main Menu”
• Section 4.5, “Exiting the LSI Logic Boot BIOS Configuration Utility”
• Section 4.6, “Troubleshooting”
• Section 4.7, “OpenBoot BIOS”
A BIOS is the ROM code that the system loads to facilitate booting from
FC drives. The BIOS also contains an embedded configuration manager,
with which you configure options provided by the firmware. The LSI Logic
BIOS integrates with a standard system BIOS, extending the standard
disk service routine provided through INT13h.
Two types of BIOS are available for the LSI Logic host adapters:
• LSI Logic FC boot BIOS for Intel/AMD-based platforms, and
• LSI Logic FC OpenBoot BIOS for Solaris SPARC platforms.
Both the LSI Logic boot BIOS and OpenBoot BIOS are stored on the FC
host adapter boards.
2 Gbit/s Fibre Channel Host Adapters User’s Guide 4-1
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 60

4.1 LSI Logic Boot BIOS
This section provides the features, description, and installation of the
LSI Logic FC boot BIOS.
4.1.1 LSI Logic Boot BIOS Features
The LSI Logic FC boot BIOS supports:
• Selection and configuration for up to 256 adapters
• Boot device selection from any four host adapters
• Automatic INT13 drive mapping for FC drives
4.1.2 BIOS Overview
If Boot is enabled, the boot BIOS scans for FC Hard disks connected to
the FC host adapter. All discovered disks are enumerated with drive
letters and appended to a master list of disks discovered on the host.
Upon scan completion, the host serially inspects the master list of disks
beginning with drive letter A and attempts to boot from the first device it
finds with a boot record. If boot from FC is desired, you may elect to
remove or disable IDE drives, as these tend to get lower drive letter
assignments than FC devices.
Note: The Boot feature is disabled by default on all host adapters
shipped from LSI Logic.
4.1.3 LSI Logic BIOS Boot Specification (BBS)
The LSI Logic BIOS provides support for the BIOS Boot Specification
(BBS), which allows you to choose which device to boot from by
selecting the priority.
To use this feature, the system BIOS must be compatible with the BBS.
If your system supports the BBS, use the system BIOS setup menu to
select the boot and drive order. In the system BIOS setup, the Boot
Connection Devices menu appears with a list of available boot options.
Use that menu to select the device and rearrange the order. Then exit to
continue the boot process.
4-2 BIOS Features
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 61

4.2 Starting the LSI Logic Boot BIOS Configuration Utility
The LSI Logic boot BIOS allows you to change the default configuration
of your host adapters, using the embedded BIOS Configuration Utility
(CU).
When the BIOS loads, the following message appears on your monitor:
Press Ctrl-C to start LSI Logic Configuration Utility...
This message remains on your screen for about five seconds, giving you
time to start the utility. After you press CTRL+C, the message changes
to:
Please wait, invoking LSI Logic Configuration Utility...
After a brief pause, your computer monitor displays the Main menu of the
BIOS CU.
Note: Not all devices detected by the CU can be controlled by the
BIOS. Devices such as tape drives and scanners require
loading a device driver specific to that peripheral. The BIOS
CU allows parameters to be modified for these devices.
4.3 Using the LSI Logic Boot BIOS CU
This section provides the menu formats and user inputs availableto inform
users about the boot BIOS CU prior to running it. All BIOS CU screens
that display various menus are partitioned into fixed areas. This area
provides static general help text information.
4.4 Main Menu
When you invoke the LSI Logic boot BIOS CU, the Main menu appears.
This screen displays a scrolling list of up to 256 host adapters in the
system and information about each of them.
Use the arrow keys to highlight a host adapter. Then press ENTER to
view and modify the selected host adapter properties (and to gain access
to the attached devices). After selecting an adapter and pressing
Starting the LSI Logic Boot BIOS Configuration Utility 4-3
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 62

ENTER, the FC Link bus is scanned and the Adapter Properties screen
appears.
On the Main menu, two selections are the Boot Adapter List and
Global Properties menus.
Boot Adapter List allows selection and ordering of boot adapters. Refer
to Section 4.4.4, “Boot Adapter List Menu,” for details.
Global Properties allows changes to global scope settings. Refer to
Section 4.4.5, “Global Properties Menu,” for details.
Only host adapters with LSI Logic Control enabled can be accessed.
4.4.1 Adapter Properties Menu
The Adapter Properties menu allows you to view and modify adapter
settings. It also provides access to the device settings of a host adapter.
To display this menu, select a device under the Adapter field on the
Main menu and press ENTER.
4.4.2 Persistent ID Menu
You can use the Persistent ID menu simply to review the automatic
mapping between a drive World Wide Name (WWN) and its assigned
logical SCSI bus and Target ID. The screen also can force a drive to a
specific logical Target ID.
Selecting Add WWN at an unused location clears out the associated
WWN/DID field and allows you to enter the first 16 characters of the
WWN. Pressing ENTER afterwards allows the last 16 characters to be
entered. The Configuration Utility automatically adds any leading zeros,
if necessary. If an entry was put in by mistake, selecting Erase on the
appropriate line removes the entry.
Logical ID selection defaults to be the lowest ID available. This can be
changed by using the PLUS or MINUS keys to cycle the numbers. The
Bus field always defaults to 0 and cannot be changed. It is displayed
whenever an outside utility has reserved a different number.
The Next Page and Previous Page options are provided on the persistent
ID screens through the F2 key, which moves the screen forward or back
by 16 entries. However, the CU requires storing any modifications to the
4-4 BIOS Features
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 63

current page before new entries may be viewed or modified. A pop-up
confirmation window asks to store or discard changes, if needed.
4.4.3 Device Properties Menu
The Device Properties menu allows you to view and update individual
device settings for an adapter.
Note: The number of fields on the menu requires that you scroll
left/right to view all the information. When accessing this
menu, use the HOME and END keys to scroll to columns
currently not displayed. The scroll indicator on the bottom
of the menu shows the position of the cursor relative to the
first and last columns.
4.4.4 Boot Adapter List Menu
The Boot Adapter List menu specifies the order in which adapters boot
when more than one LSI Logic host adapter is in a system. Up to four
adapters in a system can be selected as bootable. Only one of the four
bootable adapters can control a boot volume.
To select this menu:
1. Press F2 while on the Main menu to move the cursor to the menu
area.
2. Move the cursor to Boot Adapter List with the arrow keys.
3. Press ENTER.
Adapters can be added or deleted using this menu. To add an adapter
to the boot list, press the INSERT key while on the Boot Adapter List.
Use the arrow keys to select the desired adapter, and press ENTER to
add it to the end of the Boot Adapter List.
To remove an adapter from the boot list, press the DELETE key while
the desired adapter is selected in the Boot Adapter List. You can also
change the boot order by using the PLUS or MINUS keys. For example,
place the cursor on the adapter that you want to change, and use the
PLUS or MINUS key to raise or lower the boot order, respectively.
Main Menu 4-5
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 64

4.4.5 Global Properties Menu
The Global Properties menu allows you to pause if an alert message has
been displayed, to view display boot information, and to set display and
video modes.
4.5 Exiting the LSI Logic Boot BIOS Configuration Utility
The Exit menu for the LSI Logic boot BIOS configuration utility is used
for all six of the menus listed in Section 4.4, “Main Menu,” page 4-3.
However, the available functionality is different for the Main menu and the
five subordinate menus.
To exit from the Adapter Properties, Persistent ID, Device Properties,
Boot Adapter List, or Global Properties menus, use the following
exit options:
Cancel exit Returns you to the previous menu.
Save changes then
exit this menu
Discard changes
then exit this menu
To exit from the Main menu, use the following exit options:
Cancel exit Returns you to the Main menu.
Exit the Configuration
Utility
Important: If you reboot the system without properly exiting from this
4.6 Troubleshooting
The LSI Logic boot BIOS Configuration Utility is a powerful tool. If you
disable all of your controllers while using it, pressing CTRL+A or
Implements any changes you made on the previous
menu and returns you to the Main menu.
Restores the default settings and returns you to the
Main menu.
Exits the configuration and automatically reboots your
system.
utility, some changes may not take effect.
4-6 BIOS Features
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 65

CTRL+E after memory initialization during reboot. This allows you to reenable and reconfigure.
The following messages may appear during the boot process:
• Adapter removed from boot order, parameters will be
updated accordingly! appears when an adapter is removed from
the system or is relocated behind a PCI bridge. This message is for
information only, and no further user action is required.
• Configuration data invalid, saving default configuration!
appears if none of the information in nonvolatile random access
memory (NVRAM) is valid. This message is for information only and
can occur when the BIOS is upgraded or when some external event
has rendered the NVRAM temporarily unreadable.
• Found FC Controller not in following Boot Order List, to
Add: Press Ctrl-C to start LSI Logic Configuration
Utility... appears when fewer than four adapters are in the boot
order and adapters exist in the system that are not in the boot order.
This message is for information only and indicates that more than
four adapters exist in the system. The additional adapters are not
managed by the CU.
4.7 OpenBoot BIOS
LSI Logic Solaris-capable, Fusion-MPT host adapters have Fcode
resident on board, allowing operation under the Sun Microsystems
OpenBoot console. All basic functionality is available in an OpenBoot
environment, including the ability to display devices connected to the
adapter and to boot devices on the adapter.
4.7.1 OpenBoot BIOS Features
The LSI Logic FC OpenBoot BIOS supports the following:
• Solaris SPARC2.6, Solaris SPARC 2.7, and Solaris 8 Open Firmware
environments
• Root Boot device selection from any target device
• Standard command line interface, with help query
• Configuration options and selection capability for each host adapter
OpenBoot BIOS 4-7
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 66

4.7.2 Identifying the FC Devices
The probe-scsi-all command identifies the FC devices on your FusionMPT adapter.
To show all disks available from the OpenBoot prompt, use the
probe-scsi-all command. Note that this command is used regardless of
whether the disks are FC or SCSI. All disks available on all Fusion-MPT
devices are displayed.
The following example shows the kind of information that is displayed
when you enter this command.
ok probe-scsi-all
/pci@8,600000/SUNW,qlc@4
LiD HA LUN ---Port WWN--- ----Disk description----
1 1 0 2100002037e4d65b SEAGATE ST318304FSUN18G 0726
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer-Ultra160,scsi@3,1
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer-Ultra160,scsi@3
Target 0
Unit 0 Disk IBM DDRS-34560D DC1B
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@2
MPT Version 1.00, Firmware Version 1.02.00
Target 0
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6615
WWN 2100002037109d76 Port ID d9
Target 1
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6258
WWN 210000203710565a Port ID 17
Target 2
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6258
WWN 2100002037105212 Port ID 1
Target 3
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6258
WWN 2100002037103da8 Port ID 26
4-8 BIOS Features
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 67

Target 4
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6258
WWN 210000203710324a Port ID 73
/pci@8,700000/scsi@6
Target 6
Unit 0 Removable Read Only device PLEXTOR CD-ROM PX-20TS
If the FC devices on your IntraServer™ adapter are not identified by your
system, check the following:
• Is the FC enclosure powered on?
• Does the LED on the adapter indicate Link? (Note that Link is valid
only after the device is probed.)
• Does the LED on the switch or remote enclosure indicate Link?
• Does the Link-SPEED parameter selected by the adapter match that
of the bus (1G, 2G, or Auto)?
If you do not see disks, the following additional debug information may
help to identify the problem.
4.7.3 Verifying Installation
Use the following procedure to verify installation of your Fusion-MPT
adapter in the system:
Step 1. Power-up the system.
Step 2. When the banner is displayed, press the STOP+A keys to
interrupt the boot process and stop at the ok prompt.
Step 3. Use the show-devs command to list the system devices. You
should see an output similar to the following:
ok show-devs
/SUNW,UltraSPARC-III@0,0
/virtual-memory
/memory@m0,0
/aliases
/options
/openprom
/chosen
/packages
OpenBoot BIOS 4-9
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 68

/upa@8,480000/SUNW,ffb@0,0
...
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@2
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1,1
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1
...
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@2/disk
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@2/tape
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1,1/disk
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1,1/tape
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1/disk
/pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1/tape
/pci@8,700000/scsi@6,1/tape
/pci@8,700000/scsi@6,1/disk
ok
• /pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1
identifies the first FC interface on an LSIFC929X-based adapter.
• /pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1,1
identifies the second FC interface on an LSIFC929X-based adapter.
• An LSIFC919X-based adapter shows only one such FC device.
Note: The above listing is an example. The show-devs output
may vary depending on your system and configuration. Use
the corresponding entries on your system, not the ones
given here.
If these devices are not listed, check to assure that the adapter is
correctly installed and reseat the adapter in the PCI slot if necessary.
4.7.4 Adapter-Specific Settings
In certain circumstances, advanced users may want to change settings
for an individual adapter or port, without affecting the other adapters in
the system. Specific examples of such settings are FC bus speed, host
adapter ID (SCSI only: not applicable to FC), and Interrupt Coalescing.
To select a specific Fusion-MPT adapter as the current adapter, use the
select command. Selecting a port or adapter brings the port online and
allows you to show or set certain adapter specific parameters.
4-10 BIOS Features
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 69

You should use caution while issuing the following commands because
some commands (such as forcing 1 Gbit/s operation on a 2 Gbit/s FC loop)
could render the bus unusable.
4.7.4.1 select Command
Use the select OpenBoot command to choose the adapter entry. This
opens the port to bring the port online.
ok select /pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1
4.7.4.2 .properties Command
Use the .properties command to show the adapter properties.
ok .properties
firmware-version 1.02.00
mpt-version 1.00
scsi-initiator-id 00 00 00 0f
assigned-addresses 81001010 00000000 00000700 00000000 00000100
compatible 70 63 69 31 33 65 39 2c 36 32 31 00 70 63 69 31
model LSI,929
reg 00001000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
version 1.00.16
device_type scsi-2
name IntraServer,fc
fcode-rom-offset 00000000
66mhz-capable
devsel-speed 00000001
class-code 00010000
interrupts 00000001
latency-timer 00000040
cache-line-size 00000010
max-latency 00000008
min-grant 0000001e
subsystem-id 00000621
subsystem-vendor-id 000013e9
revision-id 00000001
device-id 00000621
vendor-id 00001000
83001014 00000000 001a0000 00000000 00020000
8300101c 00000000 00190000 00000000 00010000
82001030 00000000 02000000 00000000 00100000
01001010 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000100
03001014 00000000 00000000 00000000 00020000
0300101c 00000000 00000000 00000000 00010000
02001030 00000000 00000000 00000000 00100000
OpenBoot BIOS 4-11
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 70

4.7.4.3 show-children Command
While you have the host adapter or port selected, use the show-children
command to display the devices currently connected to this adapter.
First, select the port or adapter shown (use the port name your
system assigns):
ok select /pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1
ok show-children
MPT Version 1.00, Firmware Version 1.02.00
Link is ready, port is online
WWN 100000a0b8040353 Port ID ef
Target 0
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6615
WWN 2100002037109d76 Port ID d9
Target 1
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6258
WWN 210000203710565a Port ID 17
Target 2
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6258
WWN 2100002037105212 Port ID 1
Target 3
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6258
WWN 2100002037103da8 Port ID 26
Target 4
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6258
WWN 210000203710324a Port ID 73
4-12 BIOS Features
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 71

4.7.5 Interrupt Coalescing
The LSI Logic host adapters can complete multiple I/O requests per host
interrupt. Interrupt coalescing is used to reduce CPU interrupts by
pooling multiple disk command completions (I/O) into one interrupt. This
feature may be enabled or disabled.
LSI Logic has performed significant testing under multiple I/O conditions
and has determined that interrupt coalescing can be very valuable for
small transfer lengths or random, transaction-oriented I/O workloads. For
this type of workload, LSI Logic recommends that the Interrupt
Coalescing values be set to a queue depth of 9, with a timeout of 1280
(0x500) µs. This means that the host is interrupted only once for 9 I/Os
processed by the chip, unless 1280 µs have passed since the host was
last interrupted. If the workload is of a large transfer length and
sequential, LSI Logic recommends that interrupt coalescing be disabled
to prevent performance degradation.
Although LSI Logic has determined that these settings are optimal for a
wide variety of situations, your own I/O load may benefit from a deeper
queue or a longer timeout. LSI Logic provides a mechanism to modify
these values and write them to the nonvolatile EEPROM on the adapter.
Select the port or adapter shown (use the port name your system assigns):
ok select /pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1
Then enter commands as shown in the following example:
ok show-interrupt-coalescing
Interrupt coalescing timeout is 500 (1280 decimal)
microseconds
Interrupt coalescing depth is 9 (9 decimal)
ok set-interrupt-coalescing
Note: The OpenBoot BIOS provides help when you enter a
command that does contain the proper arguments. In this
case, OpenBoot responds with:
usage is <timeout><depth> set-interrupt-coalescing
ok 100 8 set-interrupt-coalescing
OpenBoot BIOS 4-13
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 72

Interrupt coalescing timeout selected is 100 (256 decimal)
microseconds
Interrupt coalescing depth selected is 8 (8 decimal)
Interrupt coalescing has been set
Change will take effect after system reset
Note: The system must be power cycled before the changes take
4.7.6 Set FC Link Speed
There are two modes of operation for FC: 1 Gbit/s and 2 Gbit/s. It is
important to match the speed of the port with the speed of the loop or
fabric to which the port is attached.
LSI Logic has implemented autonegotiation on the 2 Gbit/s-capable,
Fusion-MPT devices. If you are experiencing difficulty with the
AutoNegotiate algorithm on your fabric or loop, or if you wish to set or
show the link speed for the adapter manually, use the following
procedure:
Select the port or adapter shown (use the port name your system assigns):
ok select /pci@8,700000/IntraServer,fc@1
effect. It is not sufficient to execute the reset-all command.
Then enter commands as shown in the following example:
ok show-link-speed
Link speed selected is 1 Gbaud
Current link speed is 1 Gbaud
ok set-link-speed
Note: The OpenBoot BIOS provides help when you enter a
usage is <link-speed> set-link-speed
ok a set-link-speed
Link speed selected is autobaud
Link speed has been set
Change will take effect after system power cycle
4-14 BIOS Features
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
command that does contain the proper arguments. In this
case, OpenBoot responds with:
Page 73

ok show-link-speed
Link speed selected is autobaud
Current link speed is 1 Gbaud
Note: The system must be power-cycled before the changes take
effect. It is not sufficient to execute the reset-all command.
4.7.7 Persistent Device Naming
One of the most powerful benefits of storage area networks (SANs) is
scalability; the freedom to quickly add or delete storage components. To
facilitate trouble-free SAN reconfigurations, you can save a list of devices
currently connected to the host adapter. Later, if certain devices are
powered off, the adapter ensures that the remaining devices appear at
the same mount point. Technically, the LSI Logic host adapter “locks” the
association of an FC target with an alias name reference. The LSI Logic
host adapter manages the details. When you mark a device persistent,
mapping information is saved on the LSI Logic host adapter in a
nonvolatile memory device.
The following is an example of how to save devices in the persistent
device table using LSI Logic Fcode:
Step 1. Select the controller you want to modify, making a selection
from the list as shown in Figure 4.1.
Figure 4.1 Select Controller
OpenBoot BIOS 4-15
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 74

Step 2. From the displayed list, select a device to mark persistent as
shown in Figure 4.2.
Figure 4.2 Select Device
/pci@1f,0/pci@1/IntraServer,fc@2/disk has been selected.
ok select /pci@1f,0/pci@1/IntraServer,fc@2
ok show-children
MPT Firmware Version 1.02.12
Target 0
Unit 0 Disk SEAGATE ST39173FC 6615
WWN 200000203710c4e8 PortID a3
Step 3. Type ^Y (Ctrl-Y) to insert disk name in the command line as
shown in Figure 4.3.
Figure 4.3 Inserting Disk Name in Command Line
Note: The OpenBoot BIOS (Fcode) provides help when you enter
a command that does contain the proper arguments. In this
case, OpenBoot responds with usage syntax.
Figure 4.4 Setting Device 0 as Persistent
Note: The command sequence in Figure 4.4 records an entry for
Figure 4.5 Clearing Persistent Device Map
Note: The command sequence in Figure 4.5 may be used to clear
Entry 1 has been deleted from the table, and the table is now empty.
4-16 BIOS Features
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
device 0, as item 0 in the persistent device list.
an entry in the persistent device map.
Page 75

4.7.8 Manual Selection of FC Topology
Under certain configurations, you may want to force the selection of FC
topology and disable the auto detect mechanism in the FC adapter. This
can be done on a port-by-port basis by using the following procedure.
Note: It should not be necessary to change from automatic
detection of topology. Also, firmware version 1.00.03 is the
earliest version to support this functionality.
The following is an example of how to select a manual topology N_Port
or NL_Port on a selected FC port.
Select the controller you want to modify, as follows:
ok show-disks
a) /pci@1f,0/pci@1/IntraServer,fc@2/disk
b) /pci@1f,0/pci@1/IntraServer,Ultra2-scsi@1/disk
c) /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/cdrom
d) /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk
e) /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/fdthree@14,3203f0
q) NO SELECTION
Enter Selection, q to quit: a
/pci@1f,0/pci@1/IntraServer,fc@2/disk has been selected.
Type ^Y ( Control-Y ) to insert it in the command line.
e.g. ok nvalias mydev ^Y for creating devalias mydev for
/pci@1f,0/pci@1/IntraServer,fc@2/disk
ok select /pci@1f,0/pci@1/IntraServer,fc@2
Then enter commands as shown in the following example:
ok show-topology
Topology selected is auto
Current topology is unknown (no link)
ok set-topology <-Command with no options provides help
usage is <topology> set-topology
topology = 1 NL_Port
topology = 2 N_Port
topology = a auto
OpenBoot BIOS 4-17
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 76

ok 1 set-topology
Topology selected is NL_Port
Topology has been set
Change will take effect after system power cycle
ok 2 set-topology
Topology selected is N_Port
Topology has been set
Change will take effect after system power cycle
ok a set-topology
Topology selected is auto
Topology has been set
Change will take effect after system power cycle
Note: The system must be power-cycled before the changes take
effect. It is not sufficient to execute the reset-all command.
4-18 BIOS Features
Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 77

Customer Feedback
We would appreciate your feedback on this document. Please copy the
following page, add your comments, and fax it to us at the number
shown.
If appropriate, please also fax copies of any marked-up pages from this
document.
Important: Please include your name, phone number, fax number, and
company address so that we may contact you directly for
clarification or additional information.
Thank you for your help in improving the quality of our documents.
2 Gbit/s Fibre Channel Host Adapters User’s Guide
Ver. 2.1 Copyright © 2002 - 2005 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 78

Reader’s Comments
Fax your comments to: LSI Logic Corporation
Technical Publications
M/S E-198
Fax: 408.433.4333
Please tell us how you rate this document: 2 Gbit/s Fibre Channel Host
Adapters User’s Guide. Place a check mark in the appropriate blank for
each category.
Excellent Good Average Fair Poor
Completeness of information ____ ____ ____ ____ ____
Clarity of information ____ ____ ____ ____ ____
Ease of finding information ____ ____ ____ ____ ____
Technical content ____ ____ ____ ____ ____
Usefulness of examples and
illustrations
Overall manual ____ ____ ____ ____ ____
____ ____ ____ ____ ____
What could we do to improve this document?
If you found errors in this document, please specify the error and page
number. If appropriate, please fax a marked-up copy of the page(s).
Please complete the information below so that we may contact you
directly for clarification or additional information.
Name
Telephone
Fax
Date
Title
Department Mail Stop
Company Name
Street
City, State, Zip
 Loading...
Loading...