LOGIC LF3304QC10, LF3304QC15, LF3304QC12 Datasheet
DEVICES INCORPORATED
LF3304
Dual Line Buffer/FIFO
LF3304
DEVICES INCORPORATED
FEATURES DESCRIPTION
❑❑
❑ 100 MHz Data Rate for Video and
❑❑
other High-Speed Applications
❑❑
❑ One 24-bit, Two 12-bit, Three
❑❑
8-bit Data Paths, or One Double
Depth 12-bit
❑❑
❑ Dual Modes: Line Buffer or FIFO
❑❑
❑❑
❑ User-Programmable FIFO Flags
❑❑
❑❑
❑ User-Resettable Read and Write
❑❑
Pointers
❑❑
❑ Single 3.3 V Power Supply,
❑❑
5 V Tolerant I/O
❑❑
❑ 100-lead PQFP
❑❑
The LF3304 is a dual line buffer/
FIFO, designed to operate at HDTV
rates. The LF3304 will operate in
two distinct modes: Line Buffer and
FIFO. In these modes the two memories can operate independently or
with common control.
The LF3304 comprises two 12-bit 4K
memories configurable in a variety of
ways including: Two 12-bit 4K deep
line buffers (independent lengths),
Three 8-bit 4K deep line buffers
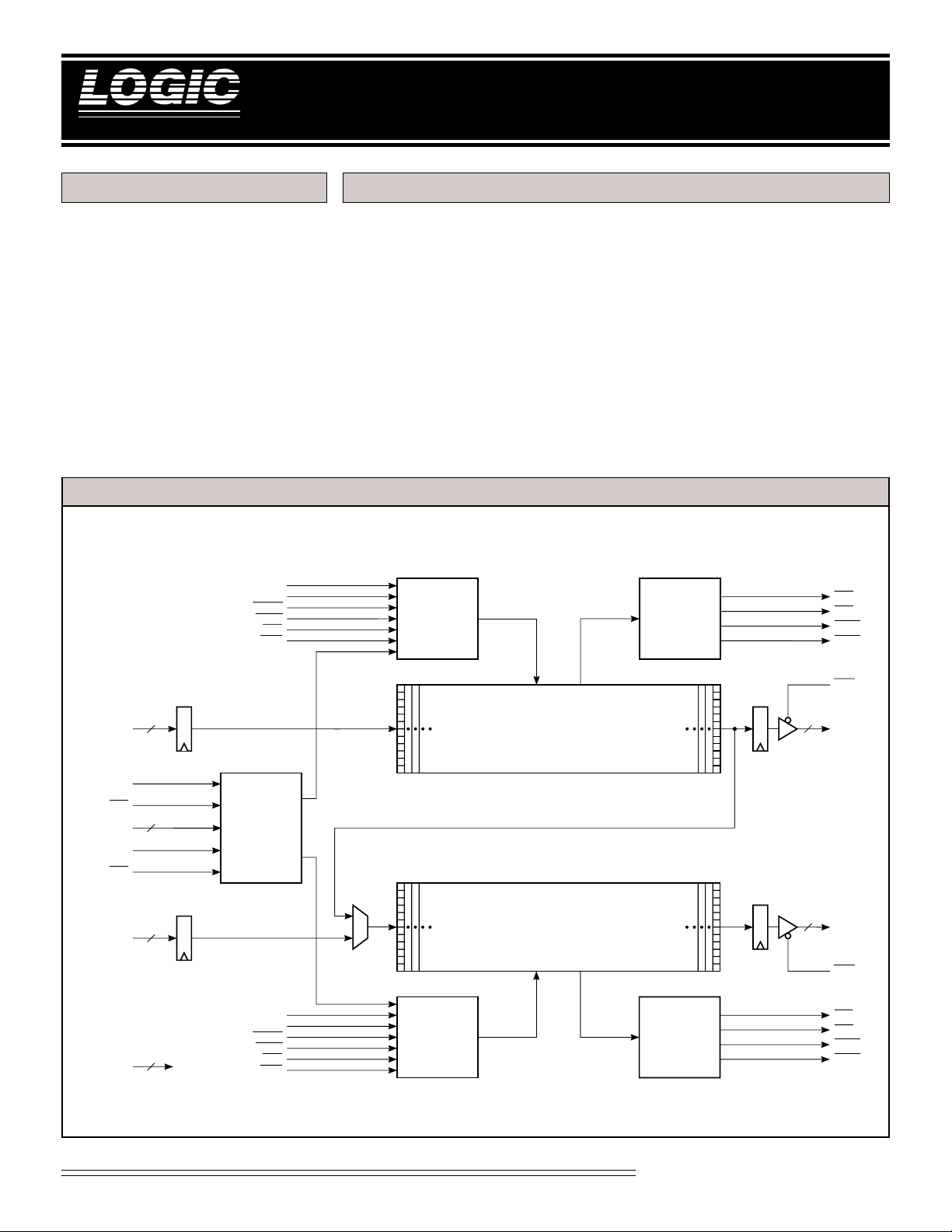
LF3304 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Dual Line Buffer/FIFO
(common lengths), One 12-bit 8K
deep line buffer, or Two 12-bit 4K
FIFOs (independent operation).
In FIFO mode, independent Read
and Write Resets give the designer
control over the internal pointers
providing flexibility not commonly
found in ordinary FIFOs.
The LF3304 operatates at a maximum
data rate of 100 MHz and is available
in a 100-lead PQFP package.
AIN11-0
ADDRA
LENGTH
ADDRB
BIN11-0
MODE1-0
LDA
11-0
LDB
WCLKA
RCLKA
WENA
RENA
RRA
RWA
12
12
12
2
MASTER
CONTROL
WCLKB
RCLKB
WENB
RENB
RRB
RWB
RAM ARRAY 1
CONTROL
VARIABLE LENGTH RAM ARRAY A
4K x 12-bit
VARIABLE LENGTH RAM ARRAY B
4K x 12-bit
RAM ARRAY 2
CONTROL
FLAG
GENERATOR
FLAG
GENERATOR
12
12
FFA
EFA
PAFA
PAEA
OEA
AOUT11-0
BOUT11-0
OEB
FFB
EFB
PAFB
PAEB
Video Imaging Products
1
08/16/2000–LDS.3304-F
DEVICES INCORPORATED
LF3304
Dual Line Buffer/FIFO
LINE BUFFER MODE
SIGNAL DEFINITIONS
Power
VCC and GND
+3.3 V power supply. All pins must
be connected.
Clocks
WCLKA — Write Clock A
WCLKA and RCLKA must be tied
together for RAM Array A to properly
operate as a Line Buffer. The rising edge
of xCLKA strobes all appropriate
enabled registers.
RCLKA — Read Clock A
See WCLKA description.
WCLKB — Write Clock B
WCLKB and RCLKB must be tied
together for RAM Array B to properly
operate as a Line Buffer. The rising
edge of xCLKB strobes all appropriate
enabled registers.
RCLKB — Read Clock B
See WCLKB description.
Inputs
AIN11-0 — Data Input A
AIN11-0 is the 12-bit registered data
input port.
BIN11-0 — Data Input B
BIN11-0 is the 12-bit registered data
input port.
LENGTH11-0 — Line Buffer Length
The 12-bit value is used to specify the
length of each of the RAM Arrays. An
integer value ranging from 0 to 4095 is
used to select a delay ranging from 2 to
4097 clock cycles. The value placed on
LENGTH11-0 is equal to the desired delay
minus 8. To set the length of RAM Array A
the data presented on LENGTH11-0 is
loaded into the device on the active edge of
WCLKA in conjunction with LDA being
driven LOW. To set the length of RAM
Array B the data presented on
LENGTH11-0 is loaded into the device
on the active edge of WCLKB in
conjunction with LDB being driven
LOW. If an equal length is desired for
both RAM Arrays, the data presented
on LENGTH11-0 is loaded into the
device on the active edge of WCLK
(WCLKA and WCLKB tied together) in
conjuction with LDx (LDA and LDB
tied together) being driven LOW.
MODE1-0 — Mode Select
The mode select inputs determine the
operating mode of the LF3304 (Table 1) for
data being input on the next clock cycle.
When switching between modes, the
internal pipeline latencies of the device
must be observed. After switching
operating modes, either the user must
allow enough clock clycles to pass to flush
the internal RAM Array or RWx and RRx
must be driven LOW together before valid
data will appear on the outputs.
Controls
LDA — RAM Array A Load
When LDA is LOW, data on
LENGTH11-0 is latched in the length
register on the rising edge of xCLKA.
LDB — RAM Array B Load
When LDB is LOW, data on
LENGTH11-0 is latched in the length
register on the rising edge of xCLKB.
WENA — Write Enable A
Driving WENA LOW places the device in
programmable delay mode and driving
WENA HIGH places RAM Array A in
recirculate mode (programmable circular
buffer). When in recirculate mode, the
write pointer position remains fixed while
data on AIN11-0 is ignored. When
switching back from recirculate mode to
TABLE 1. DEVICE CONFIGURATION
MODE1-0 Mode Select
0 0 Dual Line Buffer
0 1 Cascaded Line Buffer
1 0 Dual FIFO
1 1 Reserved
delay mode, RWA and RRA should be
brought LOW to properly reset the Write
and Read pointers.
RENA — Read Enable B
In Line Buffer mode, RENA must be
kept LOW.
WENB — Write Enable B
Driving WENB LOW places the device in
programmable delay mode and driving
WENB HIGH places RAM Array B in
recirculate mode (programmable circular
buffer). When in recirculate mode, the
write pointer position remains fixed
while data on BIN11-0 is ignored. When
switching back from recirculate mode to
delay mode, RWB and RRB should be
brought LOW to properly reset the Write
and Read pointers.
RENB — Read Enable B
In Line Buffer mode, RENB must be
kept LOW.
RWA — Reset Write A
The write address pointer is reset to the
first physical location when RWA is set
LOW. After power up, the LF3304
requires a Reset Write for initialization
because the write address pointer is not
defined at that time.
RRA — Reset Read A
The read address pointer is reset to the
first physical location when RRA is set
LOW. After power up, the LF3304
requires a Reset Read for initialization
because the read address pointer is not
defined at that time.
Video Imaging Products
8
2
08/16/2000–LDS.3304-F
DEVICES INCORPORATED
LF3304
Dual Line Buffer/FIFO
RWB — Reset Write B
See RWA Description.
RRB — Reset Read B
See RRA description.
OEA — Output Enable A
When OEA is LOW, AOUT11-0 is
enabled for output. When OEA is
HIGH, AOUT11-0 is placed in a highimpedence state.
OEB — Output Enable B
When OEB is LOW, BOUT11-0 is
enabled for output. When OEB is
HIGH, BOUT11-0 is placed in a highimpedence state.
Outputs
AOUT11-0 — Data Output A
AOUT11-0 is the 12-bit registered
data output port.
BOUT11-0 — Data Output B
BOUT11-0 is the 12-bit registered
data output port.
FIFO MODE
SIGNAL DEFINITIONS
Power
VCC and GND
+3.3 V power supply. All pins must be
connected.
Clocks
WCLKA — Write Clock A
Data present on AIN11-0 is written
into the LF3304 on the rising edge of
WCLKA when the device is configured
for writing.
RCLKA — Read Clock A
Data is read from the LF3304 and
presented on the output port (AOUT11-0)
after tD has elapsed from the rising
edge of RCLKA when the device is
configured for reading and the output
port is enabled. WCLKA and RCLKA
can be tied together and driven by the
same external clock or they may be
controlled by separate external clocks.
WCLKB — Write Clock B
Data present on BIN11-0 is written into
the LF3304 on the rising edge of
WCLKB when the device is configured
for writing.
RCLKB — Read Clock B
Data is read from the LF3304 and
presented on the output port (BOUT11-0)
after tD has elapsed from the rising
edge of RCLKB when the device is
configured for reading and the output
port is enabled. WCLKB and RCLKB
can be tied together and driven by the
same external clock or they may be
controlled by separate external clocks.
Inputs
AIN11-0 — Data Input A
AIN11-0 is the 12-bit registered data
input port.
BIN11-0 — Data Input B
BIN11-0 is the 12-bit registered data
input port.
ADDRA — Address A
If LDA is LOW, on the rising edge of
WCLKA data present on AIN11-0 is
written into the PAFA or PAEA register
depending on ADDRA (see Table 2).
The LSB, AIN0, corresponds to the LSB
of PAFA and PAEA registers. The MSB,
AIN11, corresponds to the MSB of PAFA
and PAEA registers.
ADDRB — Address B
If LDB is LOW, on the rising edge of
WCLKB data present on BIN11-0 is
written into the PAFB or PAEB register
depending on ADDRB (see Table 2).
The LSB, BIN0, corresponds to the LSB
of PAFB and PAEB registers. The MSB,
BIN11, corresponds to the MSB of PAFB
and PAEB registers.
MODE1-0 — Mode Select
The mode select inputs determine the
operating mode of the LF3304 (Table 1) for
data being input on the next clock cycle.
When switching between modes, the
internal pipeline latencies of the device
must be observed. After switching
operating modes, either the user must
allow enough clock clycles to pass to flush
the internal RAM Array or RWx and RRx
must be driven LOW together before valid
data will appear on the outputs.
LENGTH — Non-Flag Pins
In FIFO Mode, the unused LENGTH pins
(LENGTH11, LENGTH10, LENGTH5,
LENGTH4) must be tied LOW.
TABLE 2. LOADING PROGRAMMABLE FLAG REGISTERS
ADDRA ADDRB LDA LDB WCLKA WCLKB Operation
0 x 0 x x PAEA Register
1 x 0 x x PAFA Register
x 0 x 0 x PAEB Register
x 1 x 0 x PAFB Register
3
Controls
LDA — RAM Array A Load
When LDA is LOW, data on AIN11-0 is
latched in the LF3304 on the rising edge
of WCLKA.
Video Imaging Products
08/16/2000–LDS.3304-F
DEVICES INCORPORATED
LF3304
Dual Line Buffer/FIFO
LDB — RAM Array B Load
When LDB is LOW, data on BIN11-0 is
latched in the LF3304 on the rising
edge of WCLKB.
WENA — Write Enable A
If WENA is LOW, data on AIN11-0 is
written to the device on the rising edge
of WCLKA. When RAM Array A is
full, WENA is ignored.
RENA — Read Enable A
If RENA is LOW, data from RAM Array
A is read and presented on AOUT11-0
after tD has elapsed from the rising
edge of RCLKA if the output port is
enabled. If RENA goes HIGH, the last
value loaded in the RAM Array A
output register will remain unchanged.
When RAM Array A is empty, RENA is
ignored.
WENB — Write Enable B
If WENB is LOW, data on BIN11-0 is
written to the device on the rising edgle
of WCLKB. When RAM Array B is full,
WENB is ignored.
RENB — Read Enable B
If RENB is LOW, data from RAM Array
B is read and presented on BOUT11-0
after tD has elapsed from the rising
edge of RCLKB if the output port is
enabled. If RENB goes HIGH, the last
value loaded in the RAM Array B
output register will remain unchanged.
When RAM Array B is empty, RENB is
ignored.
RWA — Reset Write A
The write address pointer is reset to the
first physical location when RWA is set
LOW. After power up, the LF3304
requires a Reset Write for initialization
because the write address pointer is not
defined at that time.
RRA — Reset Read A
The read address pointer is reset to the first
physical location when RRA is set LOW.
After power up, the LF3304 requires a Reset
Read for initialization because the read
address pointer is not defined at that time.
RWB — Reset Write B
See RWA Description.
RRB — Reset Read B
See RRA description.
OEA — Output Enable A
When OEA is LOW, AOUT11-0 is
enabled for output. When OEA is
HIGH, AOUT11-0 is placed in a highimpedence state. The flag outputs are
not affected by OEA.
OEB — Output Enable B
When OEB is LOW, BOUT11-0 is
enabled for output. When OEB is
HIGH, BOUT11-0 is placed in a highimpedence state. The flag outputs are
not affected by OEB.
Outputs
AOUT11-0 — Data Output A
AOUT11-0 is the 12-bit registered data
output port.
BOUT11-0 — Data Output B
BOUT11-0 is the 12-bit registered data
output port.
FFA — Full Flag A
FFA goes LOW when RAM Array A is
full of data. When FFA is LOW, RAM
Array A can not be written to. The Full
Flag is synchronized to the rising edge
of WCLKA.
EFA — Empty Flag A
EFA goes LOW when the read pointer is
equal to the write pointer, indicating that
RAM Array A is empty. When EFA is
LOW, read operations can not be
performed. The Empty Flag is synchronized to the rising edge of RCLKA.
FFB — Full Flag B
FFB goes LOW when RAM Array B is full
of data. When FFB is LOW, RAM Array B
can not be written to. The Full Flag is
synchronized to the rising edge of WCLKB.
EFB — Empty Flag B
EFB goes LOW when the read pointer
is equal to the write pointer, indicating
that RAM Array B is empty. When EFB
is LOW, read operations can not be
performed. The Empty Flag is synchronized to the rising edge of RCLKB.
PAFA — Programmable Almost-Full Flag A
PAFA goes LOW when the write
pointer is (Full – N) locations ahead of
the read pointer. N is the value stored
in the PAFA register and has no default
value. PAFA is synchronized to the
rising edge of WCLKA.
PAEA — Programmable Almost-Empty Flag A
PAEA goes HIGH when the write
pointer is (N + 1) location ahead of the
read pointer. N is the value stored in
the PAEA register and has no default
value. PAEA is synchronized to the
rising edge of RCLKA.
PAFB — Programmable Almost-Full Flag B
PAFB goes LOW when the write pointer
is (Full – N) locations ahead of the read
pointer. N is the value stored in the
PAFB register and has no default value.
PAFB is synchronized to the rising
edge of WCLKB.
PAEB — Programmable Almost-Empty Flag B
PAEB goes HIGH when the write
pointer is (N + 1) location ahead of the
read pointer. N is the value stored in
the PAEB register and has no default
value. PAEB is synchronized to the
rising edge of RCLKB.
Video Imaging Products
4
08/16/2000–LDS.3304-F
 Loading...
Loading...