Page 1

FTXL-I-O_100059358_2000005000_Rev U
Installation & Operation Manual
Models: 400, 500, 600, 725, & 850
WARNING
Save this manual for future reference.
is manual must only be used by a
quali ed heating installer / service
technician. Read all instructions,
including this manual and the FTXL
Service Manual, before installing.
Perform steps in the order given.
Failure to comply could result in
severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
Page 2

Contents
HAZARD DEFINITIONS .................................................... 2
PLEASE READ BEFORE PROCEEDING ........................ 3
THE FTXL -- HOW IT WORKS....................................... 4-5
RATINGS ........................................................................... 6
1. DETERMINE BOILER LOCATION
Provide Air Openings to Room .......................................... 9
Flooring and Foundation ................................................... 9
Residential Garage Installation .......................................... 9
Vent and Air Piping ............................................................ 9
Prevent Combustion Air Contamination ............................. 9
Corrosive Contaminants and Sources ............................. 10
Using an Existing Vent System to Install a New Boiler ... 10
Removing a Boiler from Existing Common Vent .............. 11
2. PREPARE BOILER
Remove Boiler from Wood Pallet ..................................... 14
Gas Conversions ......................................................... 14-15
Model 400 - 500 .......................................................... 14
Models 600 - 850 ........................................................ 15
3. GENERAL VENTING
Direct Venting Options ..................................................... 16
Install Vent and Combustion Air Piping ........................... 17
Requirements for Installation in Canada .......................... 18
Sizing ............................................................................... 18
Min./Max. Combustion Air & Vent Piping Lengths ............18
Materials ............................................................................18
Optional Room Air ............................................................ 19
PVC/CPVC .................................................................. 20-21
Polypropylene ................................................................... 22
Stainless Steel Vent ......................................................... 23
4. SIDEWALL DIRECT VENTING
Vent/Air Termination - Sidewall ................................... 24-27
Determine Location ................................................ 24-26
Prepare Wall Penetrations ..................................... 26-27
Multiple Vent/Air Terminations ......................................... 27
Sidewall Termination - Optional Concentric Vent ....... 28-30
5. VERTICAL DIRECT VENTING
Vent/Air Termination - Vertical .................................... 31-32
Determine Location ..................................................... 31
Prepare Roof Penetrations ......................................... 32
Multiple Vent/Air Terminations ......................................... 32
Vertical Termination - Optional Concentric Vent ......... 33-34
Alternate Vertical Concentric Venting ......................... 35-36
6. HYDRONIC PIPING
System Water Piping Methods ......................................... 37
Low Water Cutoff Device ................................................. 37
Chilled Water System ....................................................... 37
Freeze Protection ............................................................. 37
General Piping Information .............................................. 37
Relief Valve Installation ................................................... 38
Near Boiler Piping Components ....................................... 39
Circulator Sizing ............................................................... 39
Near Boiler Piping Connections ....................................... 40
Piping Diagrams .....................................................42-47
7. GAS CONNECTIONS
Connecting Gas Supply Piping ........................................ 48
Natural Gas ...................................................................... 49
Pipe Sizing for Natural Gas ........................................ 49
Natural Gas Supply Pressure Requirements ............. 49
Propane Gas .................................................................... 49
Pipe Sizing for Propane Gas ...................................... 49
Propane Supply Pressure Requirements ................... 49
Check Inlet Gas Supply ................................................... 50
Gas Pressure ................................................................... 51
Gas Valve Replacement .................................................. 51
8. FIELD WIRING
Line Voltage Connections ................................................ 52
Low Voltage Connections ................................................ 52
Wiring of the Cascade ...................................................... 54
9. CONDENSATE DISPOSAL
Condensate Drain ............................................................ 56
10. STARTUP ............................................................. 57-63
11. OPERATING INFORMATION
General ............................................................................. 64
Cascade ........................................................................... 68
Sequence of Operation ............................................... 69-70
FTXL Control Module ....................................................... 71
Status Display Screens ............................................... 72-74
12. MAINTENANCE
Maintenance and Annual Startup ................................ 75-79
13. DIAGRAMS
Wiring Diagram ........................................................... 80
Ladder Diagram ......................................................... 81
Revision Notes .................................................. Back Cover
Hazard defi nitions
e following de ned terms are used throughout this manual to bring attention to the presence of hazards of various risk levels
or to important information concerning the life of the product.
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
CAUTION
NOTICE
2
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious
injury.
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious
injury.
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate
injury.
CAUTION used without the safety alert symbol indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, may result in property damage.
NOTICE indicates special instructions on installation, operation, or maintenance that are important but not
related to personal injury or property damage.
Page 3

Please read before proceeding
WARNING
NOTICE
WARNING
WARNING
Installer – Read all instructions, including
this manual and the FTXL Service Manual,
before installing. Perform steps in the
order given.
User – is manual is for use only by
a qualified heating installer/service
technician. Refer to the User’s Information
Manual for your reference.
Have this boiler serviced/inspected by
a quali ed service technician, at least
annually.
Failure to comply with the above could
result in severe personal injury, death or
substantial property damage.
When calling or writing about the boiler
– Please have the boiler model and serial
number from the boiler rating plate.
Consider piping and installation when
determining boiler location.
Any claims for damage or shortage in
shipment must be led immediately
against the transportation company by the
consignee.
Factory warranty (shipped with unit) does
not apply to units improperly installed or
improperly operated.
Failure to adhere to the guidelines on this
page can result in severe personal injury,
death, or substantial property damage.
If the information in this manual is not
followed exactly, a re or explosion may
result causing property damage, personal
injury or loss of life.
is appliance MUST NOT be installed in
any location where gasoline or ammable
vapors are likely to be present.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
When servicing boiler –
Boiler operation –
Boiler water –
Freeze protection fl uids –
Installation & Operation Manual
WARNING
• To avoid electric shock, disconnect electrical supply
before performing maintenance.
• To avoid severe burns, allow boiler to cool before
performing maintenance.
• Do not block ow of combustion or ventilation air to
the boiler.
• Should overheating occur or gas supply fail to shut o ,
do not turn o or disconnect electrical supply to
circulator. Instead, shut o the gas supply at a location
external to the appliance.
• Do not use this boiler if any part has been under water.
e possible damage to a ooded appliance can be
extensive and present numerous safety hazards. Any
appliance that has been under water must be replaced.
• oroughly ush the system to remove debris. Use
an approved pre-commissioning cleaner (see Start-Up
Section), without the boiler connected, to clean the system
and remove sediment. e high-e ciency heat exchanger
can be damaged by build-up or corrosion due to sediment.
NOTE: Cleaners are designed for either new systems or
pre-existing systems. Choose accordingly.
• NEVER use automotive antifreeze. Use only inhibited
propylene glycol solutions, which are speci cally
formulated for hydronic systems. Ethylene glycol is
toxic and can attack gaskets and seals used in hydronic
systems.
DO NOT install units in rooms or
environments that contain corrosive
contaminants (see Table 1A on page 10).
Failure to comply could result in severe
personal injury, death, or substantial
property damage.
• Do not try to light any appliance.
• Do not touch any electric switch; do
not use any phone in your building.
• Immediately call your gas supplier
from a near by phone. Follow the
gas supplier’s instructions.
• If you cannot reach your gas supplier,
call the re department.
• Installation and service must be
performed by a quali ed installer,
service agency, or the gas supplier.
3
Page 4

The FTXL - How it works...
1. Stainless steel heat exchanger
Allows system water to ow around specially designed tubes for
maximum heat transfer, while providing protection against ue gas
corrosion.
2. Heat exchanger top plate
Removal of the top plate allows access to the combustion chamber
and tube sheet.
3. Blower
e blower pulls in air and gas through the venturi (item 5). Air
and gas mix inside the blower and are pushed into the burner, where
they burn inside the combustion chamber.
4. Gas valve
e gas valve senses the negative pressure created by the blower,
allowing gas to ow only if the gas valve is powered and combustion
air is owing.
5. Venturi
e venturi controls air and gas ow into the burner.
6. Flue gas sensor (limit rated)
is sensor monitors the ue gas exit temperature. e control
module will modulate and shut down the boiler if the ue gas
temperature gets too hot. is protects the ue pipe from
overheating.
7. Boiler outlet temperature sensor (limit rated)
is sensor monitors boiler outlet water temperature (system
supply). If selected as the controlling sensor, the control module
adjusts boiler ring rate so the outlet temperature is correct.
8. Boiler inlet temperature sensor
is sensor monitors return water temperature (system return). If
`selected as the controlling sensor, the control module adjusts the
boiler ring rate so the inlet temperature is correct.
9. Temperature and pressure gauge ( eld installed, not
shown)
Monitors the outlet temperature of the boiler as well as the
system water pressure.
10. Electronic LCD display
e display features a high resolution liquid crystal screen, four (4)
buttons, and a navigation dial. A serial and USB port support
additional communication with the control.
11. Flue pipe adapter
Allows for the connection of the PVC vent pipe system to the
boiler.
12. Burner (not shown)
Made with metal ber and stainless steel construction, the burner
uses pre-mixed air and gas and provides a wide range of ring rates.
13. Water outlet (system supply)
A 2" or 2-1/2" NPT (depending on the model) water connection that
supplies hot water to the system.
14. Water inlet (system return)
A 2" or 2-1/2" NPT (depending on the model) water connection that
returns water from the system to the heat exchanger.
15. Gas connection pipe
readed pipe connection of 1". is pipe should be connected to
the incoming gas supply for the purpose of delivering gas to the
boiler.
16. SMART SYSTEM Control Module
e SMART SYSTEM Control responds to internal and external
signals to regulate the blower, gas valve, and pump functions to meet
heating demand. An optional remote connectivity allows boiler
settings to be monitored and modi ed when connected to the
internet.
17. Manual air vent
A manual air vent is used to remove trapped air from the heat
exchanger shell.
18. Air intake adapter
Allows for the connection of the PVC air intake pipe to the boiler.
19. High voltage junction box
e junction box contains the connection points for the line voltage
power and all pumps.
20. Boiler drain connection
A 1" NPT drain connection is provided for easy access in the
event the boiler needs to be drained .
Installation & Operation Manual
21. Low voltage connection board
e connection board provides easy access for connecting
external low voltage devices.
22. Low voltage wiring connections (knockouts)
Conduit connection points for the low voltage connection
board.
23. Condensate trap
e condensate trap is sized for a 1/2" PVC outlet connection
pipe.
24. Bezel (hinged)
Provides access to the gas train, heat exchanger, and display.
25. Ignition electrode
Provides direct spark for igniting the burner.
26. Flame inspection window
e quartz glass window provides a view of the burner surface
and ame.
27. Gas shuto valve (Models 500 - 850 only)
A manual valve is provided to isolate the gas valve from the
boiler.
28. Relief valve ( eld installed, not shown)
Protects the heat exchanger from an over pressure condition.
e relief valve provided with the unit is set at 50 PSI.
29. Flame sensor
Used by the control module to detect the presence of burner
ame.
30. Line voltage wiring connections (knockouts)
Conduit connection points for the high voltage junction box.
31. Front panel
Removable panel to gain access to the internal components.
32. Power switch
Turns 120 VAC ON/OFF to the boiler.
33. Pump relay board
e pump relay board is used to connect the boiler, system and
DHW pumps.
34. Transformer
e transformer provides 24V power to the integrated control.
35. High limit sensor (housed with the outlet temperature
sensor)
Device that monitors the outlet water temperature. If the
temperature exceeds its setting, the integrated control will break
the control circuit, shutting the boiler down.
36. Low water cuto probe (LWCO)
Protects the heat exchanger from overheating, by ensuring
adequate water is supplied to the boiler. In the event of
inadequate water levels, the boiler will shut down.
37. Stainless steel ue collector
Flue gas and condensate enter the stainless steel ue collector
through the retubes. A 1" drain connection allows condensate
to ow through the collector into a condensate trap for
disposal.
38. Reset switch
Reset switch for the low water cuto . Hold the switch for 10
seconds to reset.
39. Test switch
e test switch permits manual triggering of the LWCO safety
circuit to test the contacts and evaluate the integrity of the
circuit. Hold the switch for 10 seconds to test.
40. Combustion measurement port
A port near the ue vent which provides access for a combustion
analyzer probe.
41. Burner plate (not shown)
e burner plate attaches the blower to the burner and the heat
exchanger. Removal allows easy access to the burner for
inspection or replacement.
4
Page 5
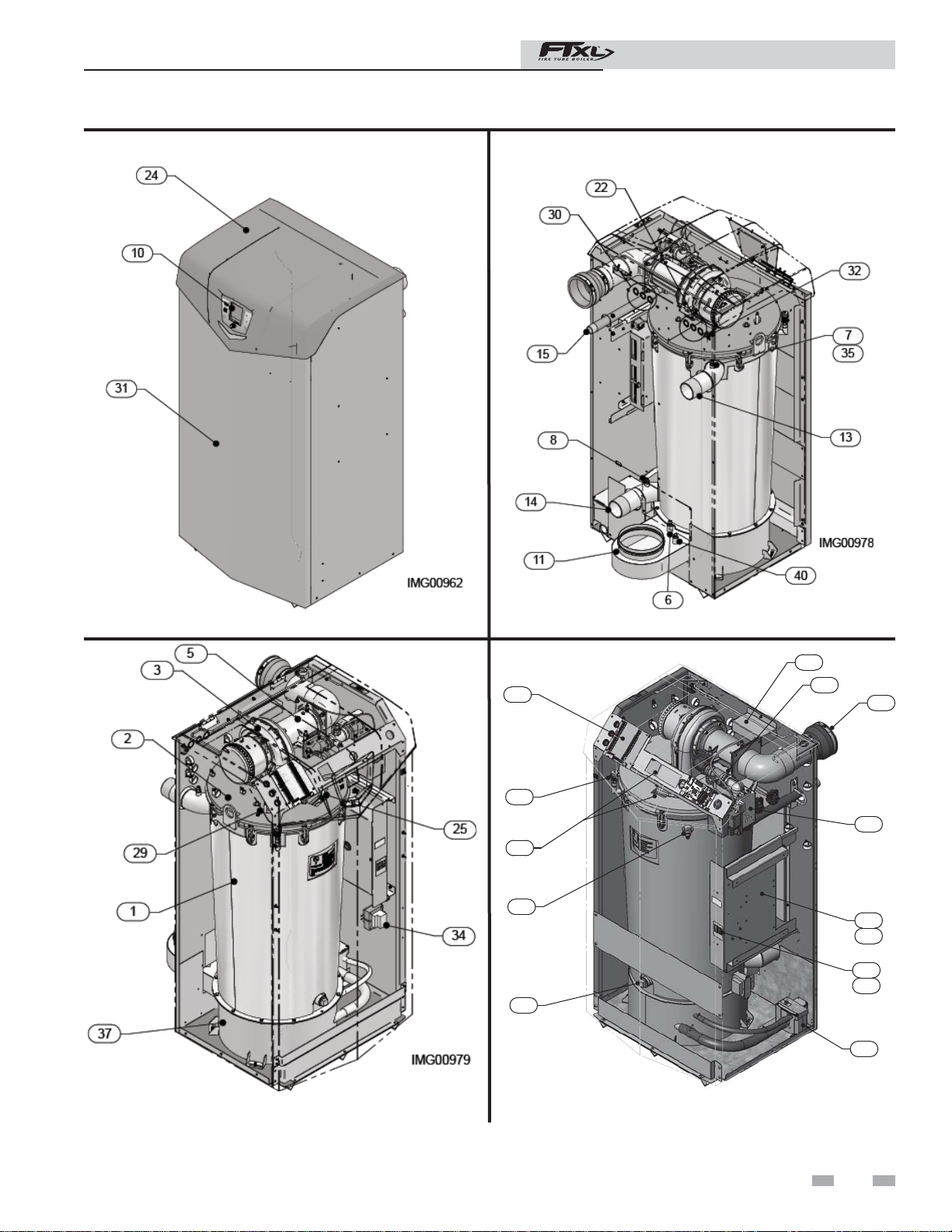
The FTXL - How it works... (continued)
Models 400 - 850
Installation & Operation Manual
Front View
Rear View
21
17
26
36
20
19
27
18
4
16
33
38
39
23
Left Side (inside unit)
DIR #2000544916 00
Right Side (inside unit)
5
Page 6
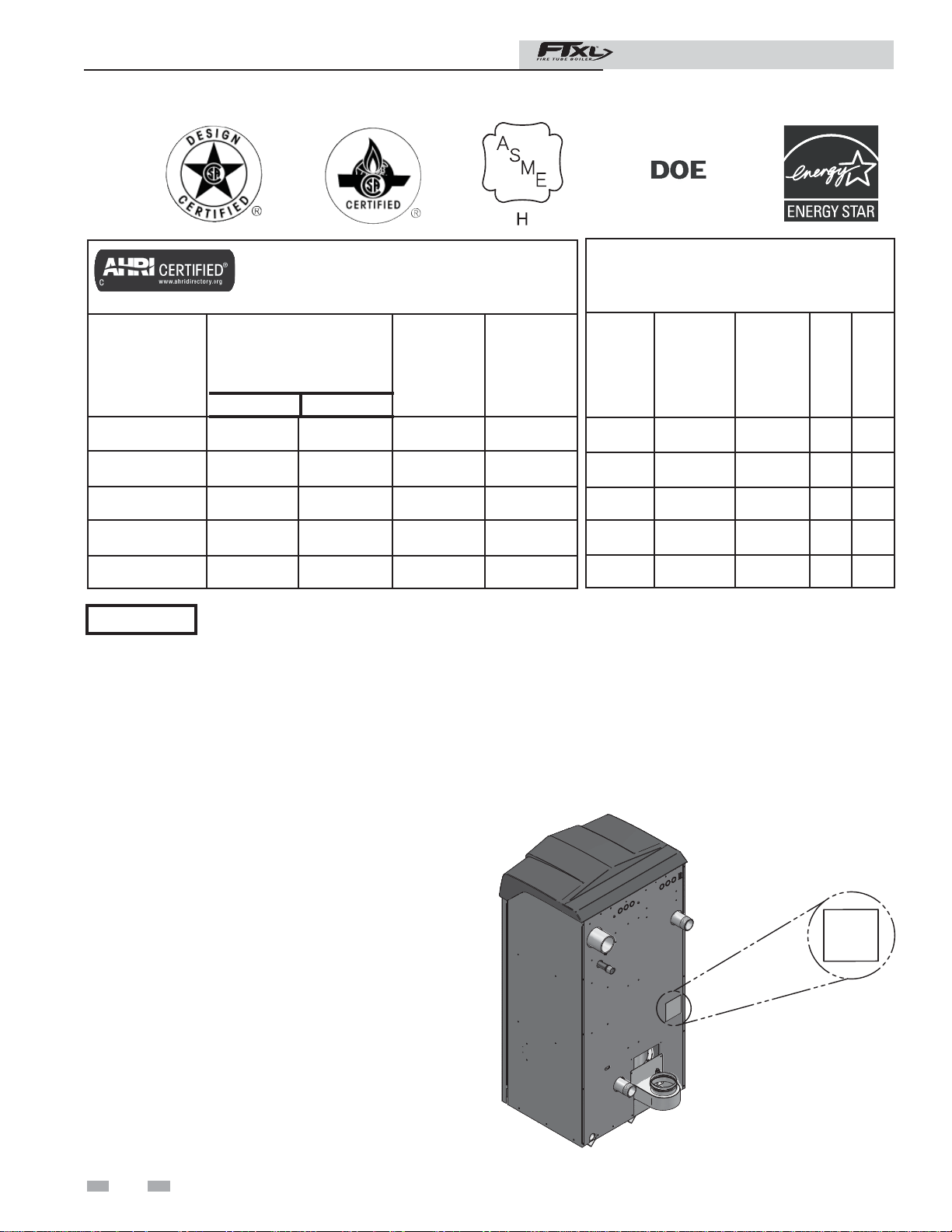
Ratings
Installation & Operation Manual
FTXL Boiler
AHRI Rating
Model Number
Note: Change “N” to
“L” for L.P. gas models.
FTX400N 40 399 392 341
FTX500N 50 500 489 425
FTX600N 85.7 600 585 509
FTX725N 103.5 725 705 613
FTX850N 121.5 850 825 717
NOTICE
Min Max
Maximum allowed working pressure is located on the rating plate.
Notes:
1. e ratings are based on standard test procedures
prescribed by the United States Department of Energy.
2. Net AHRI ratings are based on net installed radiation of
su cient quantity for the requirements of the building
and nothing need be added for normal piping and pickup.
Ratings are based on a piping and pickup allowance of 1.15.
Input
MBH
(Note 4)
Gross
Output
MBH
(Note 1)
Other Specifi cations
Net
AHRI
Ratings
Water,
MBH
(Note 2)
6. Ratings have been con rmed by the Hydronics Section of
AHRI.
7. FTXL boilers comply with the requirements of CSD-1
Section CW-400 requirements as a temperature operation
control. e manual reset high limit provided with the
FTXL is listed to UL353.
Boiler
Water
Content
Gallons
13.2 2" 1" 4" 4"
11.9 2" 1" 4" 4"
11.9 2" 1" 4" 4"
17.2 2 1/2" 1" 4" 6"
15.9 2 1/2” 1” 4” 6”
Water
Connections
Gas
Connections
Air
Size
Vent
Size
(Note 3)
3. FTXL boilers require special gas venting. Use only the vent
materials and methods speci ed in the FTXL Installation
and Operation Manual.
4. Standard FTXL boilers are equipped to operate from sea
level to 4,500 feet only with no adjustments. e boiler will
de-rate by 4% for each 1,000 feet above sea level up to 4,500
feet.
5. High altitude FTXL boilers are equipped to operate from
3,000 to 12,000 feet only. e boiler will not de-rate up
to 5,400 feet and will de-rate by 1.6% for each 1,000 feet
above 5,400 feet. High altitude models are manufactured
with a di erent control module for altitude operation, but
the operation given in this manual remains the same as the
standard boilers. A high altitude label (as shown in Fig. A)
is also a xed to the unit.
De-rate values are based on proper combustion calibration
and CO2’s adjusted to the recommended levels.
6
UNIT EQUIPPED FOR
HIGH ALTITUDE
3,000 FT. TO 12,000 FT.
IMG01068
Figure A High Altitude Label Location
Page 7

1 Determine boiler location
Installation & Operation Manual
Installation must comply with:
• Local, state, provincial, and national codes, laws,
regulations, and ordinances.
• National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 – latest edition.
• Standard for Controls and Safety Devices for Automatically
Fired Boilers, ANSI/ASME CSD-1, when required.
• National Electrical Code.
• For Canada only: B149.1 Installation Code, CSA C22.1
Canadian Electrical Code Part 1 and any local codes.
NOTICE
e FTXL gas manifold and controls
met safe lighting and other performance
criteria when the boiler underwent tests
speci ed in ANSI Z21.13 – latest edition.
Before locating the boiler, check:
1. Check for nearby connection to:
• System water piping
• Venting connections
• Gas supply piping
• Electrical power
2. Locate the appliance so that if water connections should
leak, water damage will not occur. When such locations
cannot be avoided, it is recommended that a suitable
drain pan, adequately drained, be installed under the
appliance. e pan must not restrict combustion air
ow. Under no circumstances is the manufacturer to be
held responsible for water damage in connection with
this appliance, or any of its components.
3. Check area around the boiler. Remove any combustible
materials, gasoline and other ammable liquids.
WARNING
4. e FTXL must be installed so that gas control system
components are protected from dripping or spraying
water or rain during operation or service.
5. If a new boiler will replace an existing boiler, check for
and correct system problems, such as:
• System leaks causing oxygen corrosion or heat
exchanger cracks from hard water deposits.
• Incorrectly-sized expansion tank.
• Lack of freeze protection in boiler water causing system
and boiler to freeze and leak.
• Debris le from existing piping, if not ushed and
cleaned with an appropriate cleaner.
6. Check around the boiler for any potential air contaminants
that could risk corrosion to the boiler or the boiler
combustion air supply (see Table 1A on page 10).
Prevent combustion air contamination. Remove any of
these contaminants from the boiler area.
WARNING
Failure to keep boiler area clear and free
of combustible materials, gasoline, and
other ammable liquids and vapors can
result in severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
DO NOT install units in rooms or
environments that contain corrosive
contaminants (see Table 1A on page 10).
Failure to comply could result in severe
personal injury, death, or substantial
property damage.
WARNING
WARNING
is appliance is certi ed as an indoor
appliance. Do not install the appliance
outdoors or locate where the appliance will
be exposed to freezing temperatures or to
temperatures that exceed 100°F.
Do not install the appliance where the
relative humidity may exceed 93%. Do not
install the appliance where condensation
may form on the inside or outside of the
appliance, or where condensation may fall
onto the appliance.
Failure to install the appliance indoors
could result in severe personal injury,
death, or substantial property damage.
is appliance requires a special venting
system. e vent connection to the appliance
must be made with the starter CPVC/
stainless steel pipe section provided with
the appliance. e eld provided PVC vent
ttings must be cemented to the CPVC pipe
section. Use only the vent materials, primer
and cement speci ed in this manual to make
the vent connections. Failure to follow this
warning could result in re, personal injury,
or death.
Closet and alcove installations
A closet is any room the boiler is installed in which is less than
171 cubic feet for FTX400 models, 193 cubic feet for FTX500
models, 223 cubic feet for FTX600 models, 247 cubic feet for
FTX725 models and 278 cubic feet for FTX850 models.
An alcove is any room which meets the criteria for a closet with
the exception that it does not have a door.
Example: Room dimensions = 5 feet long, 4 feet wide,
and 8 foot ceiling = 5 x 4 x 8 = 160 cubic feet. is would
be considered a closet for a FTXL Boiler.
WARNING
For closet and alcove installations as shown
in FIG.’s 1-1 and 1-2, CPVC or stainless
steel vent material must be used inside
the structure. e ventilating air openings
shown in FIG.’s 1-1 and 1-2 are required
for this arrangement. Failure to follow this
warning could result in re, personal injury,
or death.
Provide clearances:
Clearances from combustible materials
1. Hot water pipes—at least 1/4" (6 mm) from combustible
materials.
2. Vent pipe – at least 1" (25 mm) from combustible materials.
3. See FIG.’s 1-1 and 1-2 on page 8 for other clearance
minimums.
Clearances for service access
1. See FIG.’s 1-1 and 1-2 on page 8 for recommended
service clearances. If you do not provide the minimum
clearances shown, it may not be possible to service the
boiler without removing it from the space.
7
Page 8

A
A
Installation & Operation Manual
1 Determine boiler location (continued)
Figure 1-1 Closet Installation - Minimum Required Clearances
CLOSET INSTALLATION
1/4" (6 MM) MINIMUM CLEARANCE
AROUND HOT WATER PIPES
1" (25 MM) MINIMUM CLEARANCE
AROUND VENT PIPE
WARNING
18" (457 MM)
TOP
VENTILATING
AIR OPENING
CLOSED DOOR
For closet installations, CPVC,
polypropylene or stainless steel
vent material MUST BE used in
a closet structure due to elevated
temperatures. Failure to follow
this warning could result in re,
*
personal injury, or death.
0"
LEFT
14" (356 MM)
REAR
AREA OF EACH OPENING
*
1 SQ. INCH PER 1000 BTU PER HOUR INPUT
WITH A MINIMUM OF 100 SQ. INCHES.
:
6" (152 MM)
FRONT
6"
0"
RIGHT
VENTILATING
AIR OPENING
IMG00982
*
Figure 1-2 Alcove Installation - Minimum Required Clearances
ALCOVE INSTALLATION
1/4" (6 MM) MINIMUM CLEARANCE
ROUND HOT WATER PIPES
1" (25 MM) MINIMUM CLEARANCE
ROUND VENT PIPE
WARNING
18" (457 MM)
TOP
For alcove installations, CPVC,
polypropylene or stainless steel
vent material MUST BE used in
an alcove structure due to elevated
temperatures. Failure to follow
this warning could result in re,
personal injury, or death.
OPEN DOOR
0"
LEFT
14" (356 MM)
REAR
6" (152 MM)
FRONT
0"
RIGHT
IMG00983
8
Page 9

1 Determine boiler location
Installation & Operation Manual
Provide air openings to room:
FTXL alone in boiler room
1. No air ventilation openings into the boiler room are
needed when clearances around the FTXL are at least
equal to the SERVICE clearances shown in FIG.’s 1-1
and 1-2. For spaces that do NOT supply this clearance,
provide two openings as shown in FIG. 1-1. Each
opening must provide one square inch free area per
1,000 Btu/hr of boiler input.
Recommended service clearances
FRONT - 30" (762 mm)
TOP - 18" (610 mm)
REAR - 24" (610 mm)
FTXL in same space with other gas or oil-fi red
appliances
1. Follow the National Fuel Gas Code (U.S.) or CSA B149.1
(Canada) to size/verify size of the combustion/ventilation
air openings into the space.
WARNING
2. Size openings only on the basis of the other appliances in
the space. No additional air opening free area is needed
for the FTXL because it takes its combustion air from
outside (direct vent installation).
e space must be provided with
combustion/ventilation air openings
correctly sized for all other appliances
located in the same space as the FTXL.
Do not install the boiler in an attic.
Failure to comply with the above warnings
could result in severe personal injury,
death, or substantial property damage.
Flooring and foundation
Flooring
e FTXL is approved for installation on combustible
ooring, but must never be installed on carpeting.
WARNING
If ooding is possible, elevate the boiler su ciently to prevent
water from reaching the boiler.
Do not install the boiler on carpeting even
if foundation is used. Fire can result,
causing severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
Residential garage installation
Precautions
Take the following precautions when installing the appliance
in a residential garage. If the appliance is located in a
residential garage, it should be installed in compliance with
the latest edition of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1
and/or CAN/CGA-B149 Installation Code.
• Appliances located in residential garages and in
adjacent spaces that open to the garage and are not part
of the living space of a dwelling shall be installed so that
all burners and burner ignition devices are located not
less than 18 inches (46 cm) above the oor.
• e appliance shall be located or protected so that it is
not subject to physical damage by a moving vehicle.
Vent and air piping
e FTXL requires a special vent system, designed for
pressurized venting.
e boiler is to be used for either direct vent installation or
for installation using indoor combustion air. When room
air is considered, see the General Venting Section. Note
prevention of combustion air contamination below when
considering vent/air termination.
Vent and air must terminate near one another and may be
vented vertically through the roof or out a side wall, unless
otherwise speci ed. You may use any of the vent/air piping
methods covered in this manual. Do not attempt to install the
FTXL using any other means.
Be sure to locate the boiler such that the vent and air piping
can be routed through the building and properly terminated.
e vent/air piping lengths, routing and termination method
must all comply with the methods and limits given in this
manual.
Prevent combustion air contamination
Install air inlet piping for the FTXL as described in this
manual. Do not terminate vent/air in locations that can allow
contamination of combustion air. Refer to Table 1A, page
10 for products and areas which may cause contaminated
combustion air.
WARNING
You must pipe combustion air to the boiler
air intake. Ensure that the combustion air
will not contain any of the contaminants
in Table 1A, page 10. Contaminated
combustion air will damage the boiler,
resulting in possible severe personal
injury, death or substantial property
damage. Do not pipe combustion air
near a swimming pool, for example. Also,
avoid areas subject to exhaust fumes from
laundry facilities. ese areas will always
contain contaminants.
9
Page 10

Installation & Operation Manual
1 Determine boiler location (continued)
Table 1A Corrosive Contaminants and Sources
Products to avoid:
Spray cans containing chloro/ uorocarbons
Permanent wave solutions
Chlorinated waxes/cleaners
Chlorine-based swimming pool chemicals
Calcium chloride used for thawing
Sodium chloride used for water so ening
Refrigerant leaks
Paint or varnish removers
Hydrochloric acid/muriatic acid
Cements and glues
Antistatic fabric so eners used in clothes dryers
Chlorine-type bleaches, detergents, and cleaning solvents
found in household laundry rooms
Adhesives used to fasten building products and other
similar products
Areas likely to have contaminants
Dry cleaning/laundry areas and establishments
Swimming pools
Metal fabrication plants
Beauty shops
Refrigeration repair shops
Photo processing plants
Auto body shops
Plastic manufacturing plants
Furniture re nishing areas and establishments
New building construction
When using an existing vent system to
install a new boiler:
WARNING
Check the following venting components before installing:
• Material - For materials listed for use with this appliance,
see Section 3 - General Venting. For polypropylene or
stainless steel venting, an adapter of the same
manufacturer must be used at the ue collar connection.
• Size - To ensure proper pipe size is in place, see Table 3A.
Check to see that this size is used throughout the vent
system.
• Manufacturer - For a stainless steel or polypropylene
application, you must use only the listed manufacturers
and their type product listed in Tables 3E and 3G for CAT
IV positive pressure venting with ue producing
condensate.
• Supports - Non-combustible supports must be in place
allowing a minimum 1/4" rise per foot. e supports
should adequately prevent sagging and vertical slippage,
by distributing the vent system weight. For additional
information, consult the vent manufacturer’s
instructions for installation.
• Terminations - Carefully review Sections 3 through 5 to
ensure requirements for the location of the vent and air
terminations are met and orientation of these t the
appropriate image from the Sidewall or Vertical
options listed in the General Venting Section. For
stainless steel vent, only use terminations listed in Table
3H for the manufacturer of the installed vent.
• Seal - With prior requirements met, the system should be
tested to the procedure listed in parts (c) through (f) of
the Removal of an Existing Boiler Section on page 11.
Failure to follow all instructions can result
in ue gas spillage and carbon monoxide
emissions, causing severe personal injury
or death.
Remodeling areas
Garages with workshops
10
With polypropylene and stainless steel vent, seal and connect
all pipe and components as speci ed by the vent manufacturer
used; with PVC/CPVC vent, see the Installing Vent or Air
Piping Section on pages 20 and 21.
WARNING
If any of these conditions are not met,
the existing system must be updated
or replaced for that concern. Failure to
follow all instructions can result in ue gas
spillage and carbon monoxide emissions,
causing severe personal injury or death.
Page 11

Installation & Operation Manual
1 Determine boiler location (continued)
When removing a boiler from existing
common vent system:
DANGER
At the time of removal of an existing boiler, the following steps
shall be followed with each appliance remaining connected
to the common venting system placed in operation, while
the other appliances remaining connected to the common
venting system are not in operation.
a. Seal any unused openings in the common venting
system.
b. Visually inspect the venting system for proper size and
horizontal pitch and determine there is no blockage
or restriction, leakage, corrosion, or other de ciencies,
which could cause an unsafe condition.
c. Test vent system – Insofar as is practical, close all
building doors and windows and all doors between the
space in which the appliances remaining connected to
the common venting system are located and other spaces
of the building. Turn on clothes dryers and any appliance
not connected to the common venting system. Turn on
any exhaust fans, such as range hoods and bathroom
exhausts, so they will operate at maximum speed. Do not
operate a summer exhaust fan. Close replace dampers.
Do not install the FTXL into a common
vent with any other appliance. is
will cause ue gas spillage or appliance
malfunction, resulting in possible severe
personal injury, death, or substantial
property damage.
g. Any improper operation of the common venting
system should be corrected so the installation conforms
with the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1/
NFPA 54 and/or CAN/CSA B149.1, Natural Gas and
Propane Installation Code. When resizing any portion
of the common venting system, the common venting
system should be resized to approach the minimum
size as determined using the appropriate tables in Part
11 of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1/NFPA
and/or CAN/CSA B149.1, Natural Gas and Propane
Installation Code.
d. Place in operation the appliance being inspected. Follow
the lighting instructions. Adjust thermostat so appliance
will operate continuously.
e. Test for spillage at the dra hood relief opening a e r
5 minutes of main burner operation. Use the ame of a
match or candle, or smoke from another source.
f. A er it has been determined that each appliance
remaining connected to the common venting system
properly vents when tested as outlined herein, return
doors, windows, exhaust fans, replace dampers, and any
other gas-burning appliance to their previous conditions
of use.
11
Page 12

Installation & Operation Manual
1 Determine boiler location
Combustion and ventilation air
requirements for appliances drawing air
from the equipment room
Provisions for combustion and ventilation air must be in
accordance with Air for Combustion and Ventilation, of the
latest edition of the National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54 / ANSI
Z223.1, in Canada, the latest edition of CGA Standard B149
Installation Code for Gas Burning Appliances and Equipment,
or applicable provisions of the local building codes.
e equipment room MUST be provided with properly sized
openings and/or be of su cient volume to assure adequate
combustion air and proper ventilation for all gas red appliances
in the equipment room to assure adequate combustion air and
proper ventilation.
e requirements shown are for the appliance only; additional
gas red appliances in the equipment room will require an
increase in the net free area and/or volume to supply adequate
combustion air for all appliances.
Figure 1-4_Combustion Air Through Ducts
2. If combustion and ventilation air is taken from the
outdoors using a duct to deliver the air to the
equipment room, each of the two openings should be
sized based on a minimum free area of one square inch
per 2000 Btu/hr (11 cm2 per kW) of input (see FIG. 1-4).
IMG01075
No combustion air openings are needed when the appliance is
installed in a space with a volume NO LESS than 50 cubic feet
per 1,000 Btu/hr of all installed gas red appliances and the
building MUST NOT be of “Tight Construction”3.
A combination of indoor and outdoor combustion air may
be utilized by applying a ratio of available volume to required
volume times the required outdoor air opening(s) size(s). is
must be done in accordance with the National Fuel Gas Code,
NFPA 54 / ANSI Z223.1.
IMG01076
Figure 1-5_Combustion Air from Interior Space
3. If air is taken from another interior space combined with
the equipment room:
(a) Two spaces on same story: Each of the two openings
speci ed above should have a net free area of one square
inch for each 1000 Btu/hr (22 cm2 per kW) of input, but
not less than 100 square inches (645 cm2) (see FIG. 1-5).
(b) Two spaces on di erent stories: One or more openings
should have a net free area of two square inches per 1000
Btu/hr (44 cm2 per kW).
IMG01074
Figure 1-3_Combustion Air Direct from Outside
1. If air is taken directly from outside the building
with no duct, provide two permanent openings to
the equipment room each with a net free area of one square
inch per 4000 Btu/hr input (5.5 cm2 per kW) (see FIG. 1-3).
12
IMG01077
Figure 1-6_Combustion Air from Outside - Single Opening
Page 13

Installation & Operation Manual
1 Determine boiler location (continued)
4. If a single combustion air opening is provided to bring
combustion air in directly from the outdoors, the
opening must be sized based on a minimum free area
2
of one square inch per 3000 Btu/hr (7 cm
per kW). is
opening must be located within 12” (30 cm) of the top of
the enclosure (see FIG. 1-6).
Combustion air requirements are based on the latest edition
of the National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54 / ANSI Z223.1; in
Canada refer to the latest edition of CGA Standard CAN/CSA
B149.1. Check all local code requirements for combustion air.
All dimensions based on net free area in square inches. Metal
louvers or screens reduce the free area of a combustion air
opening a minimum of approximately 25%. Check with
louver manufacturers for exact net free area of louvers.
Where two openings are provided, one must be within 12"
(30 cm) of the ceiling and one must be within 12" (30 cm) of
the oor of the equipment room. Each opening must have a
net free area as speci ed in Table 1B. Single openings shall
commence within 12" (30 cm) of the ceiling. e minimum
dimension of air openings shall not be less than 3" (80 mm).
CAUTION
Under no circumstances should the
equipment room ever be under negative
pressure. Particular care should be taken
where exhaust fans, attic fans, clothes dryers,
compressors, air handling units, etc., may
take away air from the unit.
e combustion air supply must be completely free of any
ammable vapors that may ignite or chemical fumes which
may be corrosive to the appliance. Common corrosive chemical
fumes which must be avoided are uorocarbons and other
halogenated compounds, most commonly present as refrigerants
or solvents, such as Freon, trichlorethylene, perchlorethylene,
chlorine, etc. ese chemicals, when burned, form acids which
quickly attack the stainless steel heat exchanger, headers, ue
collectors, and the vent system.
e result is improper combustion and a non-warrantable,
premature appliance failure.
EXHAUST FANS: Any fan or equipment which exhausts air
from the equipment room may deplete the combustion air
supply and/or cause a downdra in the venting system. Spillage
of ue products from the venting system into an occupied
living space can cause a very hazardous condition that must be
corrected immediately.
TABLE - 1B
MINIMUM RECOMMENDED COMBUSTION
AIR SUPPLY TO EQUIPMENT ROOM
FIG. 1-3 FIG. 1-4 FIG. 1-5 FIG. 1-6
Inside Air from
2 Ducts Delivered from Interior
2
Space
Same Story
2
Top
Opening, in
(cm2)
400
(2,581)
500
(3,226)
600
(3,871)
725
(4,677)
850
(5,484)
2
Opening, in
Bottom
400
(2,581)
500
(3,226)
600
(3,871)
725
(4,677)
850
(5,484)
2
(cm2)
*Outside Air from
1 Opening Directly from
Outdoors, in
(cm2)
2
1
134
(865)
167
(1,078)
200
(1,291)
242
(1,561)
284
(1,832)
Model
Number
FTX400
FTX500
FTX600
FTX725
FTX850
*Outside Air from
2 Openings Directly from
2
1
Bottom
Opening, in
(cm2)
100
(646)
125
(807)
150
(968)
182
(1,174)
213
(1,374)
Outdoors
Top
Opening, in
(cm2)
100
(646)
125
(807)
150
(968)
182
(1,174)
213
(1,374)
*Outside Air from
2 Ducts Delivered from
Outdoors
2
Top
Opening, in
(cm2)
2
200
(1,291)
250
(1,613)
300
(1,936)
363
(2,342)
425
(2,742)
1
Bottom
Opening, in
(cm2)
200
(1,291)
250
(1,613)
300
(1,936)
363
(2,342)
425
(2,742)
e above requirements are for the appliance only; additional gas red appliances in the equipment room will require an increase
in the net free area and/or volume to supply adequate combustion air for all appliances.
No combustion air openings are needed when the appliance is installed in a space with a volume NO LESS than 50 cubic feet per
1,000 Btu/hr of all installed gas red appliances. Buildings MUST NOT be of *“Tight Construction”
1
Outside air openings shall directly communicate with the outdoors.
2
Combined interior space must be 50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btu/hr input. Buildings MUST NOT be of *“Tight Construction”.
3
”Tight Construction” is de ned as a building with less than 0.40 ACH (air changes per hour). For buildings of “Tight
3
.
Construction”, provide air openings into the building from outside.
13
Page 14

2 Prepare boiler
Remove boiler from wood pallet
1. A er removing the outer shipping carton from the boiler,
remove the parts box.
2. To remove the boiler from the pallet (a er removing the
front door):
a. Remove the three (3) lag bolts from inside the front
of the boiler (FIG. 2-1).
b. Remove the two (2) L-brackets and the two (2) lag
bolts inside the L-brackets on the rear of the boiler.
Once the lag bolts have been removed, re-install the
screws on the rear of the boiler.
c. Disconnect the ribbon cable and remove the bezel
(no tools required for removal) before removing the
boiler from the pallet or moving the boiler.
NOTICE
Figure 2-1 Boiler Mounted on Shipping Pallet
Do not drop the boiler or bump the jacket
on the oor or pallet. Damage to the boiler
can result.
FRONT
REAR
Installation & Operation Manual
Models 400 and 500 Only (Venturi w/LP
Orifi ces)
1. Remove the top bezel from the unit (no tools required for
removal).
2. Disconnect the air inlet piping from the venturi by loosening
the band clamp around the rubber boot coupling. Slide the
rubber boot o of the venturi.
3. Disconnect gas piping from the venturi by loosening the
threaded nut on the venturi (replace gasket if damaged).
4. Remove the bolts connecting the venturi to the fan and then
proceed to remove the Natural venturi from the unit (FIG.’s
2-2A and 2-2B).
5. Install the LP venturi onto the fan taking note of the
following:
a. e UP arrow on the plastic housing is indeed
pointing up.
b. e threaded connection for the gas piping is facing
towards the front of the unit. Reinstall the
bolts connecting the venturi to the fan.
6. Reassemble the gas pipe to the threaded connection on
the venturi. Install the new gasket provided in the kit and
ensure it is seated properly before tightening the nut.
REMOVE THE
LAG BOLTS (QTY. 3)
FROM INSIDE THE FRONT
OF THE BOILER
Gas conversions
WARNING
Table 2A LP Conversion Kit
For a boiler already installed, you must
turn o gas supply, turn o power and
allow boiler to cool before proceeding.
You must also completely test the boiler
a er conversion to verify performance
as described under Start-up, Section 10
of this manual. Failure to comply could
result in severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
For the 400 and 500 Models you must
install a propane venturi to operate the
FTXL on propane gas.
Models 600 - 850 do not require a venturi
change for propane operation, but they
will require a valve adjustment.
REMOVE THE
L-BRACKETS (QTY. 2)
AND LAG BOLTS (QTY. 2)
7. Reconnect the rubber boot on the air inlet to the venturi
inlet and tighten the band clamp at this connection.
8. A er installation is complete, attach the propane conversion
label (in the conversion kit bag) next to the boiler rating
plate. Attach the LP caution label (in the conversion kit bag)
to the rear of the boiler underneath the gas supply piping.
9. Replace the top bezel removed in Step 1 and resume
operation.
WARNING
A er converting to LP, check combustion
per the Start-up procedure in Section 10
of this manual. Failure to check and verify
combustion could result in severe personal
injury, death, or substantial property damage.
Models 400 and 500: Inspect the O-ring
DANGER
when the blower is disassembled. e O-ring
must be in good condition and must be
installed. Failure to comply will cause a gas
leak, resulting in severe personal injury or
death.
Model Description Kit Number
400 - 500
LP Kit 100189174
14
Page 15

2 Prepare boiler (continued)
A
Installation & Operation Manual
Figure 2-2A 400 Model_Venturi with LP Orifi ce
BLOWER
O-RING
VENTURI
SCREWS
QTY. 3
GAS VALVE
IMG01069
Figure 2-2B 500 Model_Venturi with LP Orifi ce
BLOWER
O-RING
Models 600 - 850
1. Li the top bezel (prop the bezel up for service).
2. Remove the cover on top of the gas valve (FIG. 2-3).
3. Use a combustion analyzer to verify CO2 is within the range
of 9.0 – 11.0%. If not, adjust the screw counterclockwise
incrementally to raise CO2 and clockwise to lower CO2
(FIG. 2-3).
4. A er adjustment is complete, attach the propane
conversion label (in the conversion kit bag) next to the
boiler rating plate. Attach the LP caution label (in the
conversion kit bag) to the rear of the boiler underneath
the gas supply piping.
5. Replace the gas valve cover and lower the bezel.
WARNING
Figure 2-3 Gas Valve Adjustment - Models 600 - 850
Failure to check and verify combustion
could result in severe personal injury,
death, or substantial property damage.
COVER
VENTURI
SCREWS
QTY. 5
GAS COCK
GAS VALVE
IMG01070
LLEN WRENCH
ADJUSTMENT SCREW
15
Page 16

3 General venting
Direct venting options - Sidewall Vent
Installation & Operation Manual
IMG01060
Two Pipe Sidewall
See page 24 for more details
Direct venting options - Vertical Vent
IMG01061
PVC/CPVC Concentric Sidewall
Models 400 - 600 Only
See page 28 for more details
IMG01062
Two Pipe Vertical
See page 31 for more details
16
IMG01063
PVC/CPVC
Concentric Vertical
Models 400 - 600 Only
See page 33 for more details
IMG01064
Vertical Vent, Sidewall Air
Page 17
3 General venting (continued)
Install vent and combustion air piping
DANGER
WARNING
WARNING
NOTICE
WARNING
e FTXL boiler must be vented and
supplied with combustion and ventilation
air as described in this section. Ensure the
vent and air piping and the combustion
air supply comply with these instructions
regarding vent system, air system, and
combustion air quality. See also Section 1
of this manual.
Inspect nished vent and air piping
thoroughly to ensure all are airtight and
comply with the instructions provided and
with all requirements of applicable codes.
Failure to provide a properly installed vent
and air system will cause severe personal
injury or death.
is appliance requires a special venting
system. Use only approved stainless steel,
PVC, CPVC or polypropylene pipe and
ttings listed in Tables 3E, 3F, and 3H for
vent pipe, and ttings. Failure to comply
could result in severe personal injury,
death, or substantial property damage.
DO NOT mix components from di erent
systems. e vent system could fail,
causing leakage of ue products into the
living space. Mixing of venting materials
will void the warranty and certi cation of
the appliance.
Installation must comply with local
requirements and with the National
Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 for U.S.
installations or CSA B149.1 for Canadian
installations.
For closet and alcove installations, CPVC,
polypropylene or stainless steel material
MUST BE used in a closet/alcove structure.
Failure to follow this warning could result
in re, personal injury, or death.
Installation & Operation Manual
e FTXL boiler vent and air piping can be installed through
the roof or through a sidewall. Follow the procedures in this
manual for the method chosen. Refer to the information in this
manual to determine acceptable vent and air piping length.
You may use any of the vent/air piping methods covered in this
manual. Do not attempt to install the FTXL boiler using any
other means.
You must also install air piping from outside to the boiler
air intake adapter unless following the Optional Room Air
instructions on page 19 of this manual. e resultant installation
is direct vent (sealed combustion).
e FTXL is certi ed as a Category II/IV boiler. All venting
systems used with this boiler must be suitable for Category IV
operation except for factory approved common vent systems
operating as allowed in the Common Venting Section on page
20.
Air intake/vent connections
1. Combustion Air Intake Connector (FIG. 3-1) - Used to
provide combustion air directly to the unit from outdoors. A
tting is provided on the unit for nal connection.
Combustion air piping must be supported per guidelines
listed in the National Mechanical Code, Section 305, Table
305.4 or as local codes dictate.
2. Vent Connector (FIG.'s 3-2 thru 3-7) - Used to provide a
passageway for conveying combustion gases to the
outside. A transition tting is provided on the unit for
nal connection. Vent piping must be supported per the
National Building Code, Section 305, Table 305.4 or as
local codes dictate.
Figure 3-1 Near Boiler Air Piping
AIR
CAUTION
NOTICE
WARNING
Improper installation of venting systems
may result in injury or death.
Follow the instructions in Section 1, page
11 of this manual when removing a boiler
from an existing vent system.
Do not connect any other appliance to
the vent pipe or multiple boilers to a
common vent pipe. Failure to comply
could result in severe personal injury,
death, or substantial property damage.
IMG00986
17
Page 18

3 General venting
Installation & Operation Manual
Requirements for installation in
Canada
1. Installations must be made with a vent pipe system
certi ed to ULC-S636.
2. e rst three (3) feet of plastic vent pipe from the
appliance ue outlet must be readily accessible for visual
inspection.
3. e components of the certi ed vent system must not be
interchanged with other vent systems or unlisted
pipe/ ttings. For concentric vent installations, the inner
vent tube must be replaced with eld supplied certi ed vent
material to comply with this requirement.
4. e 4" Concentric Vent Kit available from Lochinvar (see
Section 4 – Sidewall Termination – Optional Concentric
Vent) and the 4" Concentric Vent Kit available from IPEX
are both approved for use on the FTXL (400 - 600
models only) boiler. Both kits are listed to the ULC-S636
standard for use in Canada.
Sizing
e FTXL uses model speci c combustion air intake and vent
piping sizes as detailed in Table 3A below.
Table 3A Air Intake/Vent Piping Sizes
Model
400 4" (102 mm) 4" (102 mm) 0.00% 0.00%
500 4" (102 mm) 4" (102 mm) 0.40% 0.40%
600 4" (102 mm) 4" (102 mm) 1.20% 1.20%
725 4" (102 mm) 6" (152 mm) 1.20% 1.20%
850 4" (102 mm) 6" (152 mm) 1.40% 1.40%
NOTICE
Minimum / Maximum allowable
combustion air and vent piping lengths
are as follows:
Combustion Air = 12 equivalent feet (3.7 m) minimum / 100
equivalent feet (30.5 m) maximum
Vent = 12 equivalent feet (3.7 m) minimum / 100 equivalent
feet (30.5 m) maximum
When determining equivalent combustion air and vent
length, add 5 feet (1.5m) for each 90° elbow and 3 feet (.9 m)
for each 45° elbow.
EXAMPLE: 20 feet (6 m) of PVC pipe + (3) 90° elbows +
(3) 45° elbows + (1) concentric vent kit (100140484) = 49
equivalent feet (15 m) of piping.
NOTICE
18
Pipe Diameter De-rate per 25 feet of Vent
Air Intake Vent Direct Vent Room Air
Increasing or decreasing combustion air
or vent piping sizes is not authorized.
e appliance output rating will reduce
by up to 1.5% for each 25 feet of vent
length.
Table 3B Concentric Vent Kit Equivalent Vent Lengths
Model Kit Number
400 100140484 5' (1.5 m)
500 - 600 100140484 30' (9 m)
Equivalent
Vent Length
Air inlet pipe materials:
e air inlet pipe(s) must be sealed. Choose acceptable
combustion air inlet pipe materials from the following list:
PVC, CPVC, Polypropylene or ABS
Dryer Vent or Sealed Flexible Duct (not recommended for
roo op air inlet)
Galvanized steel vent pipe with joints and seams sealed as
speci ed in this section.
Type “B” double-wall vent with joints and seams sealed as
speci ed in this section.
AL29-4C, stainless steel material to be sealed to
speci cation of its manufacturer.
*Plastic pipe may require an adapter (not provided)
to transition between the air inlet connection on the
appliance and the plastic air inlet pipe.
WARNING
NOTICE
Sealing of Type “B” double-wall vent material or
galvanized vent pipe material used for air inlet piping
on a sidewall or vertical roo op Combustion Air Supply
System:
a. Seal all joints and seams of the air inlet pipe using
either Aluminum Foil Duct Tape meeting UL
Standard 723 or 181A-P or a high quality UL Listed
silicone sealant such as those manufactured by Dow
Corning or General Electric.
b. Do not install seams of vent pipe on the bottom of
horizontal runs.
c. Secure all joints with a minimum of three (3) sheet
metal screws or pop rivets. Apply Aluminum Foil
Duct Tape or silicone sealant to all screws or rivets
installed in the vent pipe.
d. Ensure that the air inlet pipes are properly supported.
Using air intake materials other than
those speci ed can result in personal
injury, death or property damage.
e use of double-wall vent or insulated
material for the combustion air inlet
pipe is recommended in cold climates
to prevent the condensation of airborne
moisture in the incoming combustion
air.
Page 19

3 General venting (continued)
Installation & Operation Manual
e PVC, CPVC, or ABS air inlet pipe should be cleaned and
sealed with the pipe manufacturer’s recommended solvents
and standard commercial pipe cement for the material used.
e PVC, CPVC, ABS, Dryer Vent or Flex Duct air inlet pipe
should use a silicone sealant to ensure a proper seal at the
appliance connection and the air inlet cap connection. Dryer
vent or ex duct should use a screw type clamp to seal the vent
to the appliance air inlet and the air inlet cap. Proper sealing
of the air inlet pipe ensures that combustion air will be free of
contaminants and supplied in proper volume.
Follow the polypropylene manufacturer’s instructions when
using polypropylene material as an inlet pipe.
When a sidewall or vertical roo op combustion air supply
system is disconnected for any reason, the air inlet pipe
must be resealed to ensure that combustion air will be free of
contaminants and supplied in proper volume.
DANGER
Failure to properly seal all joints and seams
as required in the air inlet piping may
result in ue gas recirculation, spillage
of ue products and carbon monoxide
emissions causing severe personal injury
or death.
Optional room air
NOTICE
Commercial applications utilizing the FTXL boiler may be
installed with a single pipe carrying the ue products to the
outside while using combustion air from the equipment
room. In order to use the room air venting option the
following conditions and considerations must be followed.
• e unit MUST be installed with the appropriate
bird screen (Table 3C).
• e equipment room MUST be provided with
properly sized openings to assure adequate
combustion air. Please refer to instructions provided
with the room air kit.
• Using the room air kit makes the unit vulnerable to
combustion air contamination from within the
building. Please review Section 1, Prevent
Combustion Air Contamination, to ensure proper
installation.
• Vent system and terminations must comply with the
standard venting instructions set forth in this
manual.
NOTICE
Optional room air is intended for
commercial applications. Combustion
air piping to the outside is recommended
for residential applications.
ere will be a noticeable increase in the
noise level during normal operation from
the inlet air opening.
WARNING
Table 3C Optional Room Air Kit
Model Description Kit Number
400 - 850
Air contamination
Pool and laundry products and common household and hobby
products o en contain uorine or chlorine compounds. When
these chemicals pass through the boiler, they can form strong
acids. e acid can eat through the boiler wall, causing serious
damage and presenting a possible threat of ue gas spillage or
boiler water leakage into the building.
Please read the information given in Table 1A, page 10,
listing contaminants and areas likely to contain them. If
contaminating chemicals will be present near the location of the
boiler combustion air inlet, have your installer pipe the boiler
combustion air and vent to another location, per this manual.
WARNING
WARNING
When utilizing the single pipe method,
provisions for combustion and ventilation
air must be in accordance with Air for
Combustion and Ventilation, of the latest
edition of the National Fuel Gas Code,
ANSI Z223.1, in Canada, the latest edition
of CGA Standard B149 Installation
Code for Gas Burning Appliances and
Equipment, or applicable provisions of
the local building codes.
Room Air Kit 100157616
If the boiler combustion air inlet is located in
a laundry room or pool facility, for example,
these areas will always contain hazardous
contaminants.
To prevent the potential of severe personal
injury or death, check for areas and products
listed in Table 1A, page 10 before installing
the boiler or air inlet piping.
If contaminants are found, you MUST:
• Remove contaminants permanently.
—OR—
• Relocate air inlet and vent terminations
to other areas.
19
Page 20

3 General venting
Common venting
FTXL boilers may be common vented; however, the following
criteria MUST BE followed:
1. Only FTXL boilers may be connected to the common
vent. DO NOT mix other manufacturer’s appliances or
other Lochinvar models.
Installation & Operation Manual
Table 3D Flue Damper Kits
Flue Damper Kits
Model Damper Size Kit Number
2. FTXL boilers connected to the common vent must all be
of the same size.
3. Each FTXL boiler must have a Lochinvar supplied ue
damper installed (see Table 3D).
4. A condensate drain must be installed above the ue
damper.
5. Only vertical direct vent, positive pressure, Category
IV or vertical/chimney vent, negative pressure, Category
II may be used when common venting FTXL boilers.
Sidewall common venting is not allowed.
6. FTXL boilers in a common vent must be connected and
controlled with the integral FTXL SMART SYSTEM
Cascade.
a. e Leader may be controlled through the FTXL
SMART SYSTEM control through BMS (external
0 - 10V signal), ModBus, BACnet, or its own internally
calculated set point.
b. e Cascade (Members) must be controlled by the
FTXL Leader boiler using the Lead/Lag Cascade
option.
For approved common vent sizing, contact the factory.
WARNING
NOTICE
NOTICE
When FTXL boilers are common vented,
the criteria above MUST BE followed.
Failure to follow all these requirements
will result in severe personal injury, death,
or substantial property damage.
When FTXL boilers are common vented,
hot water generators must be piped
to the primary heating loop and tank
thermostats must not be connected to the
FTXL.
A field supplied inline condensate
collection section MUST BE installed
directly above the back ow preventer.
400 4" 100056141
500 4” 100056141
600 4” 100056141
725 6” 100056142
850 6” 100056142
PVC/CPVC
is product has been approved for use with the PVC/CPVC
vent materials listed in Table 3E on page 21.
Installing vent and air piping
WARNING
NOTICE
NOTICE
WARNING
e vent connection to the appliance
must be made with the starter CPVC pipe
section provided with the appliance if
PVC/CPVC vent is to be used. e eld
provided vent ttings must be cemented
to the CPVC pipe section using an “All
Purpose Cement” suitable for PVC and
CPVC pipe. Use only the vent materials,
primer, and cement speci ed in Table 3E
to make the vent connections. Failure to
follow this warning could result in re,
personal injury, or death.
Use only cleaners, primers, and solvents
that are approved for the materials which
are joined together.
All PVC vent pipes must be glued, properly
supported, and the exhaust must be
pitched a minimum of a 1/4 inch per foot
back to the boiler (to allow drainage of
condensate).
Insulation should not be used on PVC
or CPVC venting materials. e use of
insulation will cause increased vent wall
temperatures, which could result in vent
pipe failure.
20
Page 21

3 General venting (continued)
Installation & Operation Manual
Table 3E PVC/CPVC Vent Pipe and Fittings
Approved PVC/CPVC Vent Pipe and Fittings
Item Material Standard
PVC Schedule 40, 80 ANSI/ASTM D1785
Vent pipe
Vent fi ttings
Pipe Cement /
Primer
NOTICE: DO NOT USE CELLULAR (FOAM) CORE PIPE
NOTE: In Canada, CPVC and PVC vent pipe, ttings and cement/
primer must be ULC-S636 certi ed.
1. Work from the boiler to vent or air termination. Do not
exceed the lengths given in this manual for the air or vent
piping.
2. Cut pipe to the required lengths and deburr the inside
and outside of the pipe ends.
3. Chamfer outside of each pipe end to ensure even
cement distribution when joining.
4. Clean all pipe ends and ttings using a clean dry rag.
(Moisture will retard curing and dirt or grease will prevent
adhesion.)
Figure 3-2 Near Boiler PVC/CPVC Venting - Models 400 - 600
PVC - DWV ANSI/ASTM D2665
CPVC Schedule 40, 80 ANSI/ASTM F441
PVC Schedule 40 ANSI/ASTM D2466
PVC Schedule 80 ANSI/ASTM D2467
CPVC Schedule 80 ANSI/ASTM F439
PVC - DWV ANSI/ASTM D2665
PVC ANSI/ASTM D2564
CPVC ANSI/ASTM F493
Figure 3-3 Near Boiler PVC/CPVC Venting - Models
725 - 850
VENT
5. Dry t vent or air piping to ensure proper t up
before assembling any joint. e pipe should go
a third to two-thirds into the tting to ensure
proper sealing a er cement is applied.
6. Priming and Cementing:
a. Handle ttings and pipes carefully to prevent
contamination of surfaces.
b. Apply a liberal even coat of primer to the tting
socket and to the pipe end to approximately 1/2"
beyond the socket depth.
c. Apply a second primer coat to the tting
socket.
d. While primer is still wet, apply an even coat of
approved cement to the pipe equal to the depth of
the tting socket along with an even coat of
approved cement to the tting socket.
e. Apply a second coat of cement to the pipe.
f. While the cement is still wet, insert the pipe into
the tting, if possible twist the pipe a 1/4 turn as
you insert it. NOTE: If voids are present,
su cient cement was not applied and joint could
be defective.
g. Wipe excess cement from the joint removing
ring or beads as it will needlessly so en the
pipe.
VENT
4" COUPLING
( FIELD SUPPLIED )
4" CPVC
STARTER PIECE
( FACTORY SUPPLIED )
4" CPVC PIPE SUPPLIED WITH
BOILER MUST BE USED FOR VENT CONNECTION
NOTE: CPVC VENT OR STAINLESS STEEL PIPE AND
VENT FITTINGS MUST BE USED IN CLOSET AND
ALCOVE INSTALLATIONS.
IMG00987
6" COUPLING
( FIELD SUPPLIED )
6" CPVC
STARTER PIECE
( FACTORY SUPPLIED )
6" CPVC PIPE SUPPLIED WITH
BOILER MUST BE USED FOR VENT CONNECTION
NOTE: CPVC VENT OR STAINLESS STEEL PIPE AND
VENT FITTINGS MUST BE USED IN CLOSET AND
ALCOVE INSTALLATIONS
IMG00988
21
Page 22

D
3”
D
4”
Installation & Operation Manual
3 General venting
Polypropylene
is product has been approved for use with polypropylene
vent with the manufacturers listed in Table 3F.
All terminations must comply with listed options in this
manual and be a single-wall vent o ering.
For support and special connections required, see the
manufacturer's instructions. All vent is to conform to standard
diameter and equivalent length requirements established.
When determining equivalent combustion air and vent length
for polypropylene single-wall piping:
• 1 foot of Duravent 4 inch single-wall pipe is equivalent
to 1.6 feet of piping
Flexible polypropylene
For use of ex pipe, it is recommended to have the vent material
in 32°F or higher ambient space before bending at installation.
No bends should be made to greater than 45° and ONLY
installed in vertical or near vertical installations (FIG. 3-4).
Figure 3-4 Near Boiler Flexible Polypropylene Venting
uravent
“A” DIM
3” FLEX
3” RIGID
10 FT
20 FT
30 FT
40 FT
50 FT
60 FT
70 FT
80 FT
90 FT
Centrotherm 3”
“A” DIM
3” FLEX
3” RIGID
10 FT
20 FT
30 FT
40 FT
50 FT
60 FT
70 FT
80 FT
90 FT
60 FT
53 FT
47 FT
40 FT
33 FT
27 FT
20 FT
13 FT
7 FT
45 FT
40 FT
35 FT
30 FT
25 FT
20 FT
15 FT
10 FT
5 FT
“B” DIM
4” FLEX
“B” DIM
4” FLEX
90 FT
80 FT
70 FT
60 FT
50 FT
40 FT
30 FT
20 FT
10 FT
90 FT
80 FT
70 FT
60 FT
50 FT
40 FT
30 FT
20 FT
10 FT
CHIMNEY
CAP
B
A
*NOTES: 1) FLEX PIPE MAY ONLY BE RUN IN A VERTICAL ORIENTATION
2) ALL VENT LENGTHS REPRESENTED IN ABOVE CHARTS ARE
EQUIVALENT LENGTHS.
3) SECTION A IS EQUIVALENT FEET OF RIGID PIPE, WHICH MAY
INCLUDE 45 AND 90° ELBOWS. PLEASE SEE SIZING SECTION
FOR DETERMINING EQUIVALENT FEET.
Table 3F Polypropylene Vent Pipe and Fittings
uravent
“A” DIM
4” RIGID
10 FT
20 FT
30 FT
40 FT
50 FT
60 FT
70 FT
80 FT
90 FT
Centrotherm 4”
“A” DIM
4” RIGID
10 FT
20 FT
30 FT
40 FT
50 FT
60 FT
70 FT
80 FT
90 FT
“B” DIM
4” FLEX
30 FT
27 FT
23 FT
20 FT
17 FT
13 FT
10 FT
7 FT
3 FT
“B” DIM
4” FLEX
33 FT
29 FT
26 FT
22 FT
18 FT
15 FT
11 FT
7 FT
4 FT
5” FLEX
90 FT
80 FT
70 FT
60 FT
50 FT
40 FT
30 FT
20 FT
10 FT
IMG00840
NOTICE
e installer must use a speci c vent starter
adapter at the ue collar connection. e
adapter is supplied by the vent manufacturer
to adapt to its vent system. See Table 3F
for approved vent adapters. Discard CPVC
starter piece.
NOTICE
All vent connections MUST be secured by
the vent manufacturer's joint connector
(FIG. 3-5).
WARNING
Insulation should not be used on
polypropylene venting materials. e use
of insulation will cause increased vent wall
temperatures, which could result in vent pipe
failure.
WARNING
Use only the adapters and vent system listed
in Tables 3F and 3G. DO NOT mix vent
systems of di erent types or manufacturers.
Failure to comply could result in severe
personal injury, death, or substantial property
damage.
NOTICE
Installations must comply with applicable
national, state, and local codes. For Canadian
installation, polypropylene vent must be listed
as a ULC-S636 approved system.
NOTICE
Installation of a polypropylene vent system
should adhere to the vent manufacturer’s
installation instructions supplied with the
vent system.
Figure 3-5 Near Boiler Polypropylene Venting
4” POLYPROPYLENE ADAPTER
4” POLYPROPYLENE JOINT
CONNECTOR REQUIRED
AT ALL THE COMPONENTS
OF THE VENT SYSTEM
4” POLYPROPYLENE ADAPTER
MODELS 400 - 600
IMG00990
Approved Polypropylene Vent Manufacturers
Make Model
Centrotherm Eco Systems InnoFlue SW/Flex
Duravent (M & G Group) PolyPro Single-Wall / PolyPro Flex
6” POLYPROPYLENE PIPE
6” POLYPROPYLENE ADAPTER
Table 3G Approved Polypropylene Terminations
Model Manufacturer Vent Model Vent Type Adapter Number Joint Connector Sidewall Kit*
Single-Wall
Flex
Single-Wall
Flex
Single-Wall
Flex
Single-Wall
Flex
ISAAL0404 IANS04 --
4PPS-AD 4PPS-LB 4PPS-HLK --
ISAAL0606 -- --
6PPS-06PVCM-
6PPF
-- 6PPS-HLK --
400-600
725-850
Centrotherm
Eco Systems
DuraVent
(M & G)
Centrotherm
Eco Systems
DuraVent
(M & G)
Innofl ue
PolyPro
Innofl ue
PolyPro
* ese parts are only needed if the sidewall termination assembly is used (see FIG. 4-5B on page 27).
22
MODELS 725 - 850
Retaining Bracket /
ISTAGL0404
IATP0606 /
ISTAGL0606
IMG00989
Adapter*
IATP0404/
Page 23

3 General venting (continued)
Stainless steel vent
is product has been approved for use with stainless steel
using the manufacturers listed in Table 3H.
WARNING
NOTICE
NOTICE
NOTICE
Table 3H Stainless Steel Vent Pipe and Fittings
Approved Stainless Steel Vent Manufacturers
Manufacturer Model
Dura Vent (M & G) FasNSeal Vent / FasNSeal Flex*
Z-Flex Z-Vent
Heat Fab Saf-T Vent
Metal Fab Corr/Guard
Security Chimney Secure Seal
ICC VIC
Jeremias --
*Use of FasNSeal Flex smooth inner wall vent is to be used
in vertical or near vertical sections only, taking precaution
to ensure no sagging occurs of the vent system. Connect to
the FasNSeal rigid vent using specially designed adapters and
sealing method, see manufacturer’s instructions.
Use only the materials, vent systems, and
terminations listed in Tables 3G and 3I.
DO NOT mix vent systems of di erent
types or manufacturers. Failure to comply
could result in severe personal injury,
death, or substantial property damage.
e installer must use a speci c vent starter
adapter at the ue collar connection,
supplied by the vent manufacturer to
adapt to its vent system. See Table 3I for
approved vent adapters. Discard CPVC
starter piece.
Installations must comply with applicable
national, state, and local codes. Stainless
steel vent systems must be listed as a
UL-1738 approved system for the United
States and a ULC-S636 approved system
for Canada.
Installation of a stainless steel vent system
should adhere to the stainless steel vent
manufacturer’s installation instructions
supplied with the vent system.
Installation & Operation Manual
Figure 3-6 Near Boiler Stainless Steel Venting Models
400 - 600
4" STAINLESS
STEEL PIPE
4" STAINLESS
STEEL ADAPTER
IMG00991
Figure 3-7 Near Boiler Stainless Steel Venting Models
725 - 850
STAINLESS
STEEL PIPE
STAINLESS
STEEL ADAPTER
IMG00992
Table 3I Approved Stainless Steel Adapters and Terminations
Model Manufacturer
DuraVent (M & G)
(Fas-N-Seal)
Heat Fab (Saf-T-Vent) 9401PVC 9401PVC
Z-Flex (Z-Vent) 2SVSLA04 2SVSLA04
Flue Intake Flue Intake
FSA-4PVCM-4FNSF F303759
Adapter Termination
400-600
Metal Fab (Corr/Guard) 4CGPVCA 4CGPVCA
725-850
Security Chimney
(Secure Seal)
Jeremias SWKL4-PVC SWKL4-PVC SWKL4-WRC SWKL4-90ET
DuraVent (M & G)
(Fas-N-Seal)
Heat Fab (Saf-T-Vent) 9601PVC 9601PVC 9601PVC 9601PVC
Metal Fab (Corr/Guard) 6FCGPVCA 6FCGPVCA
Security Chimney
(Secure Seal)
ICC HE-6DSA-F --
Jeremias SWKL6-PVC SWKL4-PVC SWKL6-WRC SWKL4-90ET
SS4PVCU SS4PVCU
FSA-6PVCM-6FNSF
300538
SS6PVCU SS6PVCU
FSBS4
FSRC4 (R.C.)
0492
5400CI
2SVSTP04
2SVSRCX04
4CGSWHT
4CGSWC
SS4STU
SS4RCBU
F303759 FSBS6
6FCGSWMC
6FCGSWC
SS6STU
SS6RCBU
HE-6MC-F
HE-6RC-F
FSAIH04
303888
9414TERM
2SVSTEX0490
4CGSW90LT
SS4ST90AU
FSAIH04
303888
6CGSW90L
SS6ST90AU
--
23
Page 24

Installation & Operation Manual
4 Sidewall direct venting
Vent/air termination – sidewall
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
CAUTION
NOTICE
Determine location
Locate the vent/air terminations using the following
guidelines:
1. e total length of piping for vent or air must not exceed
the limits given in the General Venting Section on page
18 of this manual.
2. You must consider the surroundings when terminating
the vent and air:
a. Position the vent termination where vapors will
not damage nearby shrubs, plants or air
conditioning equipment or be objectionable.
b. e ue products will form a noticeable plume as
they condense in cold air. Avoid areas where the
plume could obstruct window views.
c. Prevailing winds could cause freezing of
condensate and water/ice buildup where ue
products impinge on building surfaces or plants.
d. Avoid possibility of accidental contact of ue
products with people or pets.
e. Do not locate the terminations where wind eddies
could a ect performance or cause recirculation,
such as inside building corners, near adjacent
buildings or surfaces, window wells, stairwells,
alcoves, courtyards, or other recessed areas.
WARNING
24
Follow instructions below when
determining vent location to avoid
possibility of severe personal injury, death,
or substantial property damage.
A gas vent extending through an exterior
wall shall not terminate adjacent to a
wall or below building extensions such
as eaves, parapets, balconies, or decks.
Failure to comply could result in severe
personal injury, death, or substantial
property damage.
Do not connect any other appliance to the
vent pipe or multiple boilers to a common
vent pipe except as noted in Section 3
on page 20. Failure to comply could
result in severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
Sidewall venting commercial products will
result in large exhaust plumes in cold
climates. Consideration should be taken
when locating in proximity to windows,
doors, walkways, etc.
Installation must comply with local
requirements and with the National
Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54 / ANSI Z223.1
for U.S. installations or CSA B149.1 for
Canadian installations.
Sidewall vent and air inlet terminations
must terminate in the same pressure
zone.
f. Do not terminate above any door or window.
Condensate can freeze, causing ice formations.
g. Locate or guard vent to prevent condensate damage
to exterior nishes.
Figure 4-1A PVC/CPVC/ Polypropylene Sidewall
Termination of Air and Vent w/Field Supplied Fittings
3. e air piping must terminate in a down-turned elbow
as shown in FIG. 4-1A. is arrangement avoids
recirculation of ue products into the combustion air
stream.
4. e vent piping must terminate in an elbow pointed
outward or away from the air inlet, as shown in FIG. 4-1A.
WARNING
Do not exceed the maximum lengths of the
outside vent piping shown in FIG. 4-1B.
Excessive length exposed to the outside could
cause freezing of condensate in the vent pipe,
resulting in potential boiler shutdown.
Figure 4-1B PVC/CPVC/Polypropylene Sidewall
Termination of Air and Vent
FROM BOILER
VENT PIPE
CONNECTION
POSSIBLE ORIENTATIONS
TO BOILER
INTAKE AIR
CONNECTION
VENT / AIR
TERMINATION
GRADE OR
SNOW LINE
12"
MIN
TO
OVERHANG
12"
MIN
Table 4A Sidewall Vent Kits
4"
6"
Centerline
Width
5 5/8"
(143 mm)
7 3/4"
(197 mm)
Model Kit Number Air Vent
400 - 600 100157611
725 - 850 100157613
4"
(102 mm)
4"
(102 mm)
(102 mm)
(152 mm)
Page 25

Installation & Operation Manual
4 Sidewall direct venting (continued)
Vent/air termination – sidewall
Figure 4-2A PVC/CPVC/ Polypropylene Sidewall
Termination Models 400 - 850 w/Field Supplied Fittings
TO BOILER
INTAKE AIR
CONNECTION
FROM BOILER
VENT PIPE
CONNECTION
12" (305 MM) MIN
GRADE OR
SNOW LINE
Figure 4-2B Stainless Steel Sidewall Termination Models
725 - 850 w/Field Supplied Fittings
BIRD SCREEN
12" (305 MM) MIN
15" (381 MM) MAX
BIRD SCREEN
c. Do not terminate closer than 4 feet (1.2 m)
horizontally from any electric meter, gas meter,
regulator, relief valve, or other equipment. Never
terminate above or below any of these within 4 feet
(1.2 m) horizontally.
6. Locate terminations so they are not likely to be damaged by
foreign objects, such as stones or balls, or subject to buildup
of leaves or sediment.
Figure 4-3A Clearance to Gravity Air Inlets w/Field
Supplied Fittings
12” (305 MM)
MIN
BIRD
SCREEN
(TYPICAL)
TO BOILER INTAKE
NOTICE
AIR CONNECTION
FROM BOILER VENT
PIPE CONNECTION
GRADE OR
SNOW LINE
PVC/CPVC or ABS is acceptable air inlet pipe material.
12" (305 MM) MIN
15" (381 MM) MAX
12" (305 MM) MIN
5. Maintain clearances as shown in FIG.’s 4-1A thru 4-4B,
pages 24 thru 26. Also maintain the following:
a. Vent must terminate:
• At least 6 feet (1.8 m) from adjacent walls.
• No closer than 12 inches (305 mm) below roof
overhang.
• At least 7 feet (2.1 m) above any public walkway.
• At least 3 feet (.9 m) above any forced air intake
within 10 feet (3 m).
• No closer than 12 inches (305 mm) below or
horizontally from any door or window or any other
gravity air inlet.
b. Air inlet must terminate at least 12 inches (305 mm)
above grade or snow line; at least 12 inches (305 mm)
below the vent termination (FIG. 4-1B); and the vent
pipe must not extend more than 24 inches (610 mm)
vertically outside the building.
12” (305 MM)
MIN
12” (305 MM)
MIN
Figure 4-3B Clearance to Gravity Air Inlets
12"
MIN.
VENT / AIR
TERMINATION
12"
MIN.
12"
MIN.
25
Page 26
4 Sidewall direct venting
Vent/air termination – sidewall
Figure 4-4A Clearance to Forced Air Inlets w/Field
Supplied Fittings
IF LESS
THAN 10’ (3 M)
Installation & Operation Manual
3. Use a sidewall termination plate as a template for correct
location of hole centers.
4. Follow all local codes for isolation of vent pipe when passing
through oors or walls.
5. Seal exterior openings thoroughly with exterior caulk.
36” (914 MM)
MIN
FORCED AIR
INLET
BIRD
SCREEN
(TYPICAL)
7’ (2.1 M) MIN ABOVE ANY
PUBLIC WALKWAY
Figure 4-4B Clearance to Forced Air Inlets
IF LESS
THAN 10’
VENT / AIR
TERMINATION
7' MIN. ABOVE ANY
PUBLIC WALKWAY
36"
MIN.
FORCED AIR
INLET
Prepare wall penetrations
1. Air pipe penetration:
a. Cut a hole for the air pipe. Size the air pipe hole as
close as desired to the air pipe outside diameter.
2. Vent pipe penetration:
a. Cut a hole for the vent pipe. For either combustible
or noncombustible construction, size the vent pipe
hole with at least a 1/2 inch clearance around the vent
pipe outer diameter:
• 5½ inch hole (140 mm) hole for 4 inch (102 mm)
vent pipe
• 7½ inch hole (191 mm) hole for 6 inch (152 mm)
vent pipe
b. Insert a galvanized metal thimble in the vent pipe
hole as shown in FIG. 4-5A.
Figure 4-5A A Typical Sidewall Termination Assembly - Models
400 - 850 PVC/CPVC/ Polypropylene or Stainless Steel
SIDEWALL
TERMINATION PLATE
VENT
PIPING
BIRD SCREEN
ELBOW
BIRD SCREEN
GALVANIZED
THIMBLE
(WHEN REQUIRED BY LOCAL CODES)
ELBOW
AIR PIPING
Prepare wall penetrations (Factory
Supplied Option)
1. Use the factory supplied wall plate as a template to locate
the vent and air intake holes and mounting holes.
Air pipe penetration:
a. Cut a hole for the air pipe. Size the air pipe hole as
close as desired to the air pipe outside
diameter.
Vent pipe penetration:
a. Cut a hole for the vent pipe. For either combustible or
noncombustible construction, size the vent pipe hole
with at least a 1/2 inch clearance around the vent pipe
outer diameter:
• 5½ inch hole (140 mm) hole for 4 inch (102 mm)
vent pipe
• 7½ inch hole (191 mm) hole for 6 inch (152 mm)
vent pipe
Drill 3/16" diameter holes for inserting the plastic anchors
into the wall.
2. For Polypropylene Only: Install the vent and air intake
sidewall adapters from Table 3G on page 22 into the vent
plate. Slide the sidewall retaining bracket down the
sidewall adapters ush to the vent plate (FIG. 4-4A).
3. For PVC/CPVC Only: Install the vent and air intake
piping through the wall into the vent plate openings.
Use RTV silicone sealant to seal the air pipe. Use the
cement/primer listed in Table 3E on page 21 to seal the
vent pipe.
26
Page 27

A
Installation & Operation Manual
4 Sidewall direct venting (continued)
4. Mount and secure the vent plate to the wall using stainless
steel screws.
5. Seal all gaps between the pipes and wall. Seal around the
plate to the wall assuring no air gaps.
6. Assemble the vent cap to the vent plate (see FIG.’s 4-5B
and 4-5C). Insert the stainless steel screws into the vent
cap screw hole openings and securely attach the vent cap
to the vent plate.
7. Seal all wall cavities.
8. PVC/CPVC terminations are designed to accommodate any
wall thickness of standard constructions per the directions
found in this manual.
9. Stainless steel terminations are designed to penetrate walls
with a thickness up to 9.25 inches of standard construction.
Figure 4-5B PVC/CPVC Sidewall Termination Assembly
VENT
AIR
AIR PIPING
CENTERLINE WIDTH
Multiple vent/air terminations
1. When terminating multiple FTXL’s terminate
each vent/air connection as described in this manual
(FIG. 4-6A).
WARNING
2. Place wall penetrations to obtain minimum clearance of
12 inches (305 mm) between vent pipe and adjacent air
inlet elbow, as shown in FIG. 4-6B for U.S. installations.
For Canadian installations, provide clearances required
by CSA B149.1 Installation Code.
3. e air inlet of a FTXL is part of a direct vent connection.
It is not classi ed as a forced air intake with regard to
spacing from adjacent boiler vents.
Figure 4-6A Multiple Vent Terminations w/
Field Supplied Fittings (must also comply with
Figure 4-1A)
All vent pipes and air inlets must terminate
at the same height to avoid possibility of
severe personal injury, death, or substantial
property damage.
VENT
VENT PIPING
WALL PLATE
GALVANIZED
THIMBLE
VENT PLATE
VENT CAP
Table 4B Sidewall Vent Centerline Dimensions
AIR
12” (305 MM) MIN
15” (381 MM) MAX
12” (305 MM) MIN. BETWEEN EDGE
OF AIR PIPE AND ADJACENT VENT
PIPE
Model Air Vent Centerline Width
400 - 600 4" (102 mm) 4"(102 mm) 5 5/8" (143 mm)
725 - 850 4" (102 mm) 6" (152 mm) 7 3/4" (197 mm)
Figure 4-5C Polypropylene Sidewall Termination Assembly
SIDEWALL
ADAPTER
(AIR)
WALL
PLATE
SIDEWALL
DAPTER
(VENT)
GALVANIZED
THIMBLE
IMG00085
SIDEWALL
RETAINING
PLATE
VENT
PLATE
VENT
CAP
Figure 4-6B Multiple Vent Terminations (must also
comply with Figure 4-1B)
12" MIN. BETWEEN EDGE OF AIR
INLET AND ADJACENT VENT OUTLET
VENT
AIR
VENT / AIR
TERMINATION
27
Page 28

Installation & Operation Manual
4 Sidewall direct venting
Sidewall termination – optional concentric vent: Models 400 - 600 Only
Description and usage
Lochinvar o ers an optional concentric combustion air
and vent pipe termination kit (#100140484 for 4" (102 mm)
diameter - Models 400 - 600). Both combustion air and vent
pipes must attach to the termination kit. e termination kit
must terminate outside the structure and must be installed as
shown below in FIG. 4-7.
e required combustion vent pipe materials are listed in
Table 3E, on page 21 of this manual.
Figure 4-7 Concentric Sidewall Termination - Models
400 - 600
OVERHANG
OR ROOF
3. Cut one (1) hole (7 inch (178 mm) diameter for #100140484
installations into the structure to install the termination kit.
4. Partially assemble the concentric vent termination kit.
Clean and cement using the procedures found in these
instructions.
a. Cement the Y concentric tting to the larger kit pipe
(FIG. 4-8).
b. Cement the rain cap to the smaller diameter kit pipe
(FIG. 4-8).
Figure 4-8 Kit Contents_100140484 - Models 400 - 600
RAIN CAP
12" (305 MM)
MIN
12" (305 MM)
MIN
GRADE / SNOW LINE
Sidewall termination installation
1. Determine the best location for the termination kit
(see FIG. 4-7).
2. Reference the Determine Location Section on page 24 of
this manual for general termination considerations.
6" (152 MM) TO 4" (102 MM) REDUCER
6" (152 MM) DIA.
"Y" CONCENTRIC
FITTING
6" (152 MM) DIA.
"FLEXIBLE" PIPE
COUPLING
6" (152 MM) DIA.
4" (102 MM) DIA.
28
Page 29

Installation & Operation Manual
4 Sidewall direct venting (continued)
Sidewall termination – optional concentric vent: Models 400 - 600 Only
Figure 4-9 Concentric Vent Dimensional Drawing - Models 400 - 600
"A"
"C" DIA.
"B" DIA.
(152 MM)
"G"
(537 MM)
NOTICE
"B" DIA. PVC
VENT / EXHAUST
ABC DEF GH
60" 4" 6" 21 1/8" 10" 7 5/8" 3" 6 5/8"
(1524 MM)
(102 MM)
Instead of cementing the smaller pipe
to the rain cap, a eld-supplied stainless
steel screw may be used to secure the
two (2) components together when eld
disassembly is desired for cleaning (see FIG.
4-10).
WARNING
When using the alternate screw assembly
method, drill a clearance hole in the rain
cap and a pilot hole in the vent pipe for
the screw size being used. Failure to drill
adequate holes may cause cracking of PVC
components, allowing combustion products
to be recirculated. Failure to follow this
warning could result in personal injury or
death.
WARNING
Do not operate the appliance with the rain
cap removed or recirculation of combustion
products may occur. Water may also collect
inside the larger combustion air pipe and
ow to the burner enclosure. Failure to
follow this warning could result in product
damage or improper operation, personal
injury, or death.
Figure 4-10 Rain Cap to Vent Pipe Alternate Assembly
"H" DIA.
"D"
(76 MM)
"E"
"F"
(168 MM)
3"
(76 MM)
(254 MM) (194 MM)
5. Install the Y concentric tting and pipe assembly through
the structure’s hole from an inside wall.
NOTICE
Do not allow insulation or other materials
to accumulate inside the pipe assembly
when installing through the hole.
6. Install the rain cap and small diameter pipe assembly
into the Y concentric tting and large pipe assembly
from an outside wall. Ensure small diameter pipe is
fastened tightly into the rubber adapter for #100140484
installations.
7. Secure the assembly to the structure as shown in
FIG. 4-11 using eld-supplied metal strapping or
equivalent support material.
NOTICE
NOTICE
Ensure termination location clearance
dimensions are as shown in FIG. 4-7.
If assembly needs to be extended to
allow sidewall thickness requirement, the
two (2) pipes supplied in the kit may
be replaced by using the same diameter,
eld-supplied standard schedule 40 PVC
for #100140484. Do not extend dimension
D* more than 60 inches (1524 mm) (see
FIG. 4-9).
STAINLESS STEEL SCREW
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
DRILL CLEARANCE HOLE IN
RAIN CAP & PILOT HOLE
IN VENT PIPE
NOTICE
If assembly depth needs to be reduced,
dimension D can be as short as possible.
29
Page 30

Installation & Operation Manual
4 Sidewall direct venting
Sidewall termination – optional concentric vent: Models 400 - 600 Only
Figure 4-11 Concentric Vent Sidewall Attachment
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
ELBOW
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
COMBUSTION AIR
VENT
STRAP
COMBUSTION AIR
VENT
CAUTION
DO NOT use eld-supplied couplings
to extend pipes. Air ow restriction
will occur and may cause intermittent
operation.
8. Cement appliance combustion air and vent pipes to the
concentric vent termination assembly. See FIG. 4-11
for proper pipe attachment.
9. Operate the appliance one (1) heat cycle to ensure
combustion air and vent pipes are properly connected
to the concentric vent termination connections.
Multiventing sidewall terminations
When two (2) or more direct vent appliances are vented
near each other, each appliance must be individually vented
(see FIG. 4-12). When two (2) or more direct vent appliances
are vented near each other, two (2) vent terminations may
be installed as shown in FIG. 4-12. It is important that vent
terminations be made as shown to avoid recirculation of ue
gases.
VENT
COMBUSTION
AIR
Figure 4-12 Concentric Vent and Combustion Air Termination
30
12"
MINIMUM
Page 31

5 Vertical direct venting
Vent/air termination – vertical
Installation & Operation Manual
WARNING
Follow instructions below when
determining vent location to avoid
possibility of severe personal injury, death
or substantial property damage.
Determine location
Locate the vent/air terminations using the following
guidelines:
1. e total length of piping for vent or air must not exceed
the limits given in the General Venting Section on page
18 of this manual.
2. Prepare the vent termination and the air termination
elbow (FIG. 5-1A) by inserting bird screens. Bird screens
should be obtained locally.
3. e vent must terminate at least 3 feet above the highest
place in which the vent penetrates the roof and at least
2 feet above any part of a building within 10 horizontal
feet.
4. e air piping must terminate in a down-turned 180°
return pipe no further than 2 feet (.6 m) from the center
of the vent pipe. is placement avoids recirculation of
ue products into the combustion air stream.
5. e vent piping must terminate in an up-turned coupling
as shown in FIG. 5-1A. e top of the coupling must
be at least 1 foot above the air intake. When the vent
termination uses a rain cap as illustrated in FIG. 5-1B
maintain at least 36" (914 mm) above the air inlet. e
air inlet pipe and vent pipe can be located in any desired
position on the roof, but must always be no further than
2 feet (.6 m) apart and with the vent termination at least
1 foot above the air intake.
6. Maintain the required dimensions of the nished
termination piping as shown in FIG. 5-1A.
Figure 5-1A PVC/CPVC/Polypropylene Vertical
Termination of Air and Vent
ALTERNATE INTAKE LOCATIONS:
INTAKE PIPES MAY BE LOCATED
ANYWHERE WITHIN 24" (610 MM)
OF VENT PIPE
BIRD SCREEN
(TYPICAL)
COUPLING
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
VENT OUTLET
12" MINIMUM
ABOVE AIR INLET
VENT
6" (152 MM) MINIMUM
ABOVE ROOF /
SNOW LINE
COMBUSTION
AIR
Figure 5-1B Stainless Steel Vertical Termination of Air
and Vent
ALTERNATE INTAKE LOCATIONS:
INTAKE PIPES MAY BE LOCATED
ANYWHERE WITHIN 24” (610 MM)
OF VENT PIPE
BIRD SCREEN
(TYPICAL)
6" (152 MM) MINIMUM
ABOVE ROOF /
SNOW LINE
VENT OUTLET
36” (914 MM) MINIMUM
ABOVE AIR INLET
VENT
COM,BUSTION
AIR
8. Locate terminations so they are not likely to be damaged by
foreign objects, such as stones or balls, or subject to buildup
of leaves or sediment.
7. Do not extend exposed vent pipe outside of building
more than shown in this document. Condensate could
freeze and block vent pipe.
WARNING
Roo op vent and air inlet terminations
must terminate in the same pressure
zone, unless vertical vent sidewall air is
set up as shown in the General Venting Vertical Vent, Sidewall Air Section.
31
Page 32

5 Vertical direct venting
R
Vent/air termination – vertical
Prepare roof penetrations
1. Air pipe penetration:
a. Cut a hole for the air pipe. Size the air pipe hole as
close as desired to the air pipe outside diameter.
Installation & Operation Manual
Figure 5-2 Vertical Terminations with Multiple Boilers
2. Vent pipe penetration:
a. Cut a hole for the vent pipe. For either combustible
or noncombustible construction, size the vent pipe
hole with at least a 1/2 inch clearance around the
vent pipe outer diameter:
• 5½ inch hole (140 mm) hole? for 4 inch (102 mm)
vent pipe
• 7½ inch hole (191 mm) hole? for 6 inch (152 mm)
vent pipe
b. Insert a galvanized metal thimble in the vent pipe
hole (when required by local codes).
3. Space the air and vent holes to provide the minimum
spacing shown in FIG.’s 5-1A and 5-1B, page 31.
4. Follow all local codes for isolation of vent pipe when
passing through oors, ceilings, and roofs.
5. Provide ashing and sealing boots sized for the vent pipe
and air pipe.
Multiple vent/air terminations
1. When terminating multiple FTXL boilers, terminate each
vent/air connection as described in this manual (FIG.
5-2).
WARNING
Terminate all vent pipes at the same
height and all air pipes at the same height
to avoid recirculation of ue products and
the possibility of severe personal injury,
death, or substantial property damage.
12" (305 MM) MINIMUM
VERTICALLY FROM VENT
VENT
AIR
VENT
AIR
OUTLET TO ANY AIR INLET
12" (305 MM) MINIMUM FROM EDGE
OF AIR INTAKE PIPE TO ADJACENT
VENT PIPE FROM ANOTHER BOILE
Figure 5-3 Alternate Vertical Terminations with Multiple
Boilers
VENT
VENT
12" (305 MM) MINIMUM
VERTICALLY FROM VENT
OUTLET TO ANY AIR INLET
AIR
AIR
2. Place roof penetrations to obtain minimum clearance
of 12 inches (305 mm) between edge of air intake
elbow and adjacent vent pipe of another boiler for U.S.
installations (see FIG. 5-2). For Canadian installations,
provide clearances required by CSA B149.1 Installation
Code.
3. e air inlet of a FTXL boiler is part of a direct vent
connection. It is not classi ed as a forced air intake with
regard to spacing from adjacent boiler vents.
32
Page 33

A
Installation & Operation Manual
5 Vertical direct venting (continued)
Vertical termination – optional concentric vent: Models 400 - 600 Only
Description and usage
Lochinvar o ers an optional concentric combustion air and
vent pipe termination kit. Both combustion air and vent
pipes must attach to the termination kit. e termination kit
must terminate outside the structure and must be installed as
shown in FIG. 5-4.
Field supplied pipe and ttings are required to complete the
installation.
e required combustion vent pipe ttings are listed in
Table 3E, on page 21 of this manual.
Vertical termination installation
1. See Section 5, Vertical Direct Venting - Determine
Location (where applicable).
Figure 5-4 Concentric Vertical Termination
VENT
COMBUSTION
AIR
12" (305 MM) (18" (457 MM)
FOR CANADA) MINIMUM
CLEARANCE ABOVE HIGHEST
NTICIPATED SNOW
LEVEL. MAXIMUM OF
24" (610 MM) ABOVE ROOF.
2. Cut one (1) hole (7 inch (178 mm) diameter for #100140484
installations) into the structure to install the termination
kit.
3. Partially assemble the concentric vent termination kit.
Clean and cement following the cleaning procedures in
these instructions.
a. Cement the Y concentric tting to the larger
diameter kit pipe (see FIG. 4-8, page 28).
b. Cement rain cap to the smaller diameter kit pipe (see
FIG. 4-8, page 28).
NOTICE
Instead of cementing the smaller pipe
to the rain cap, a eld supplied stainless
steel screw may be used to secure the
two (2) components together when eld
disassembly is desired for cleaning (see
FIG. 4-10, page 29).
WARNING
When using the alternate screw assembly
method, drill a clearance hole in the rain
cap and a pilot hole in the vent pipe for
the screw size being used. Failure to drill
adequate holes may cause cracking of PVC
components, allowing combustion products
to be recirculated. Failure to follow this
warning could result in personal injury or
death.
Figure 5-5 Do Not Install U-Bend to Rain Cap
33
Page 34

Installation & Operation Manual
5 Vertical direct venting
Vertical termination – optional concentric vent: Models 400 - 600 Only
WARNING
Do not operate the appliance with
the rain cap removed or recirculation
of combustion products may occur.
Water may also collect inside the larger
combustion air pipe and ow to the
burner enclosure. Failure to follow this
warning could result in product damage
or improper operation, personal injury,
or death.
4. Install the Y concentric tting pipe assembly up through
the structure’s hole and eld supplied roof boot/ ashing.
NOTICE
Do not allow insulation or other materials
to accumulate inside the pipe assembly
when installing through the hole.
5. Secure the assembly to the roof structure as shown
below in FIG. 5-6 using eld supplied metal strapping or
equivalent support material.
Figure 5-6 Concentric Vent Roof Installation
COMBUSTION
AIR
ROOF BOOT /
FLASHING
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
VENT
12" (305 MM) (18" (457 MM) FOR CANADA)
MINIMUM CLEARANCE ABOVE HIGHEST
ANTICIPATED SNOW LEVEL. MAXIMUM OF
24” (610 MM) ABOVE ROOF.
CAUTION
DO NOT use eld-supplied couplings
to extend pipes. Air ow restriction will
occur.
6. Install the rain cap and the small diameter pipe assembly
into the roof penetration assembly. Ensure the small
diameter pipe is fastened tightly into the rubber adapter
for #100140484 installations.
7. Cement the appliance combustion air and vent pipes to
the concentric vent termination assembly. See FIG. 5-6
for proper pipe attachment.
8. Operate the appliance through one (1) heat cycle to ensure
combustion air and vent pipes are properly connected to
the concentric vent termination connections.
Multiventing vertical terminations
When two (2) or more direct vent appliances are vented
near each other, each appliance must be individually vented
(see FIG. 5-7). When two (2) or more direct vent appliances
are vented near each other, two (2) vent terminations may
be installed as shown in FIG. 5-7. It is important that vent
terminations be made as shown to avoid recirculation of ue
gases.
NOTICE
NOTICE
SUPPORT
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
ELBOW
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
VENT
COMBUSTION
AIR
Ensure termination height is above the
roof surface or anticipated snow level
(12 inches (305 mm) in U.S.A. or 18
inches (457 mm) in Canada) as shown in
FIG. 5-4, page 33.
If assembly is too short to meet height
requirement, the two (2) pipes supplied
in the kit may be replaced by using the
same diameter, eld supplied standard
schedule 40 PVC for 100140484. Do
not extend dimension D* more than 60
inches (1524 mm) (see FIG. 4-9, page 29).
Figure 5-7 Concentric Vent and Combustion Air Vertical
Termination
12”
MINIMUM
COMBUSTION
AIR (TYPICAL)
12” (18” FOR CANADA)
MINIMUM CLEARANCE
ABOVE HIGHEST
ANTICIPATED SNOW
LEVEL. MAXIMUM OF
24” ABOVE ROOF.
34
Page 35

Installation & Operation Manual
5 Vertical direct venting (continued)
Alternate vertical concentric venting
is appliance may be installed with a concentric vent
arrangement where the vent pipe is routed through an
existing unused venting system; or by using the existing
unused venting system as a chase for vent and combustion
air routing.
Concentric Venting Arrangement
e venting is to be vertical through the roof. e annular
space between the O.D. of the vent pipe and the I.D. of the
existing unused venting system is utilized for the combustion
air source.
e minimum size of the existing vent system required to
achieve enough annular space for combustion air can be
found in Table 5A.
e upper and lower termination as well as any other unsealed
joints in the existing vent system must be sealed to ensure that
all combustion air is drawn from under the vent cap as shown
in FIG.’s 5-8 and 5-9.
Approved venting materials must be used as speci ed in
Table 3E on page 21.
Follow all vent / air termination and clearance requirements
per this section to the appropriate example. Installation must
comply with local requirements and with the National Fuel
Gas Code.
e maximum allowable equivalent vent and air intake
lengths for this venting arrangement are to be determined
from the General Venting Section.
If an existing unused venting system is converted for use
with this method of concentric venting, the installer must
ensure that the existing venting system is clean and free from
particulate contamination that will harm this appliance and
cause increased nuisance calls or maintenance. See Table 1A
on page 10 for a list of corrosive contaminants and sources.
Figure 5-8 Concentric Vent Example 1
FLUE EXHAUST
SEAL
COMBUSTION AIR
EXISTING
SEALED
CAP
12"
MIN.
SEAL
FLUE
OUTLET
*For concept illustration only. Individual installations
may vary due to job site specifi c equipment.
AIR INLET
W/ SCREEN
IMG01065
Figure 5-9 Concentric Vent Example 2
FLUE EXHAUST
COMBUSTION
AIR INLET
W/ SCREEN
SEAL
EXISTING
SEALED
CAP
SEAL
SEAL
Two example scenarios of a concentric venting arrangement
are shown for illustrative purposes in FIG.’s 5-8 and 5-9.
Table 5A Alternate Vertical Concentric Vent / Chase Sizes
Model
Vent / Air
Inlet Size
Minimum Existing
Vent / Chase Size
400 - 600 4" 7"
725 - 850 6" 10"
FLUE OUTLET
IMG01066
*For concept illustration only. Individual installations
may vary due to job site specifi c equipment.
35
Page 36

5 Vertical direct venting
Existing vent as a chase
Follow all existing termination and clearance requirements and
allowable pipe lengths. Use only approved venting materials
listed in the General Venting Section of this manual.
Figure 5-10 Existing Vent as a Chase
Installation & Operation Manual
FLUE EXHAUST
SEAL
EXISTING
SEAL
*For concept illustration only. Individual installations
may vary due to job site specifi c equipment.
AIR INLET
CAP
FLUE OUTLET
IMG01067
36
Page 37

6 Hydronic piping
System water piping methods
e FTXL is designed to function in a closed loop system
pressurized to not less than 12 psi (83 kPa) (Non-metallic
system piping must have an oxygen barrier to be considered
a closed loop). A temperature and pressure gauge is included
to monitor system pressure and outlet temperature and
should be located on the boiler outlet.
It is important to note that the boiler has a minimal amount
of pressure drop which must be accounted for when sizing
the circulators. Each boiler installation must have an air
elimination device, which will remove air from the system.
Install the boiler so the gas ignition system components
are protected from water (dripping, spraying, etc.) during
appliance operation or basic service of circulator replacement,
valves, and others.
Observe a minimum of 1/4 inch (6 mm) clearance around all
un-insulated hot water pipes when openings around the pipes
are not protected by non-combustible materials.
Low water cutoff device
is boiler comes equipped with a low water cuto device.
On a boiler installed above radiation level, some states and
local codes require a low water cuto device at the time of
installation.
Installation & Operation Manual
General piping information
IMPORTANT
Basic steps are listed below along with illustrations on the
following pages (FIG.’s 6-5 through 6-10), which will guide you
through the installation of the FTXL (reference FIG.’s 6-3A and
6-3B).
1. Connect the system return marked “Inlet”.
2. Connect the system supply marked “Outlet”.
3. Install purge and balance valve or shuto valve and drain
on system return to purge air out of each zone.
4. Install a back ow preventer on the cold feed make-up
water line.
5. Install a pressure reducing valve on the cold feed make-up
water line, (15 psi (103 kPa) nominal). Check temperature
and pressure gauge (shipped separately), which should read
a minimum pressure of 12 psi (83 kPa).
6. Install a circulator as shown on the piping diagrams in this
section. Make sure the circulator is properly sized for the
system and friction loss.
7. Install an expansion tank on the system supply. Consult the
tank manufacturer’s instruction for speci c information
relating to tank installation. Size the expansion tank for the
required system volume and capacity.
8. Install an air elimination device on the system supply.
All boiler piping must contain an oxygen
barrier. is will help prevent any excess
oxygen from entering the system.
Chilled water system
If the boiler supplies hot water to heating coils in air handler
units, ow control valves or other devices must be installed to
prevent gravity circulation of heater water in the coils during
the cooling cycle. A chilled water medium must be piped in
parallel with the heater.
Freeze protection
Freeze protection for new or existing systems must use
glycol that is specially formulated for this purpose. is
includes inhibitors, which prevent the glycol from attacking
the metallic system components. Make certain to check that
the system uid is correct for the glycol concentration and
inhibitor level. e system should be tested at least once
a year and as recommended by the producer of the glycol
solution. Allowance should be made for the expansion of the
glycol solution in the system piping.
WARNING
Use only inhibited propylene glycol
solutions, which are speci cally formulated
for hydronic systems. Ethylene glycol is
toxic and can attack gaskets and seals used
in hydronic systems.
9. Install a drain valve at the lowest point of the system.
Note: e boiler cannot be drained completely of water
without purging the unit with an air pressure of 15 psi
(103 kPa).
10. is appliance is supplied with a relief valve sized in
accordance with ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code,
Section IV (“Heating Boilers”). Pipe the discharge of the
safety relief valve to prevent injury in the event of pressure
relief. Pipe the discharge to a drain. Provide piping that is
the same size as the safety relief valve outlet. Never block
the outlet of the safety relief valve.
NOTICE
11. Install a eld supplied strainer to prevent damage to the
heat exchanger caused by debris entering from the system
piping. When installing in a pre-existing system, a strainer/
lter capable of removing debris le in the system is
recommended.
See the piping illustrations included in this section, FIG.’s 6-5
and 6-10 for suggested guidelines in piping the FTXL.
NOTICE
e relief valve, tee and any other necessary
ttings are shipped in the install kit with the
boiler and are to be eld installed (FIG.’s 6-1
and 6-2).
Please note that these illustrations are
meant to show system piping concept only,
the installer is responsible for all equipment
and detailing required by local codes.
37
Page 38

6 Hydronic piping
Installation & Operation Manual
Relief valve and temperature and
pressure gauge installation
Basic steps are listed below to guide you through the
installation of the relief valve, and temperature and pressure
gauge provided with the unit.
1. Install the tee directly to the outlet connection of the
heat exchanger with the 3/4 inch tting positioned
vertically and on the top (see FIG. 6-2).
2. For Models 725 - 850 install the 3/4 inch close nipple
in the tee. Install the relief valve on the 3/4 inch close
nipple (FIG. 6-2). For Models 400 - 600 install the
relief valve directly into the 3/4 inch tting on the tee
(FIG. 6-1).
3. Install the close nipple on the downstream side of
the relief valve tee (FIG. 6-1).
4. Install the tee with the 1 inch tting positioned
vertically and on the top (FIG. 6-1).
5. Install a eld provided close nipple on the downstream
side of the ow switch (if used), see FIG.’s 6-1 and 6-2.
6. Install a eld provided tee with the gauge tting
positioned vertically and on the top (FIG.’s 6-1 and
6-2)
7. Install the temperature and pressure gauge provided
with the unit into the top tting of the tee (a bushing
may be necessary) installed in Step 6 (FIG.’s 6-1 and
6-2).
Figure 6-1 Flow Switch, Relief Valve and Temperature and
Pressure Gauge Installation_Models 400 - 600
FLOW SWITCH
(OPTIONAL)
PADDLE
(OPTIONAL)
TEMPERATURE AND
PRESSURE GAUGE
TEE WITH FITTING
ON TOP
(FIELD PROVIDED)
CLOSED NIPPLE
(FIELD PROVIDED)
TEE WITH 1" FITTING
ON TOP
(FIELD PROVIDED)
RELIEF VALVE
TEE WITH 3/4"
FITTING ON TOP
CLOSE NIPPLE
(FIELD PROVIDED)
IMG00993
Figure 6-2 Flow Switch, Relief Valve and Temperature and
Pressure Gauge Installation_Models 725 - 850
NOTICE
If using a ow switch, be sure to install
the ow switch so that the arrow on the
ow switch is pointing in the direction
of the ow.
FLOW SWITCH
(OPTIONAL)
PADDLE
(OPTIONAL)
TEMPERATURE AND
PRESSURE GAUGE
TEE WITH FITTING
ON TOP
(FIELD PROVIDED)
CLOSED NIPPLE
(FIELD PROVIDED)
TEE WITH 1" FITTING
ON TOP (FIELD PROVIDED)
RELIEF VALVE
TEE WITH 3/4"
FITTING ON TOP
CLOSE NIPPLE
(FIELD PROVIDED)
IMG00994
38
Page 39

6 Hydronic piping (continued)
Installation & Operation Manual
Near boiler piping components
1. Boiler system piping:
Boiler system piping MUST be sized per the pipe
requirements listed in Table 6B. Reducing the pipe size
can restrict the ow rate through the boiler, causing
inadvertent high limit shutdowns and poor system
performance. Flow rates are based on a full ow
application.
2. Boiler system circulating pump:
Field supplied. e boiler circulating pump should be
based on system requirements.
3. Domestic hot water circulating pump:
Field supplied. e pump MUST be sized to meet
the speci ed minimum ow requirements listed in
FIG. 6-4. Consult the indirect water heater operating
guide to determine ow characteristics for the selected
product used.
4. Variable speed boiler circulator:
FTXL boilers are capable of controlling a variable speed
boiler circulator. Variable speed circulators MUST
be sized to meet the speci ed minimum ow requirements
listed in FIG. 6-4 on page 41 at full speed. To be used
in primary/secondary systems only.
5. Boiler isolation valves:
Field supplied. Full port ball valves are required. Failure
to use full port ball valves could result in a restricted ow
rate through the boiler.
6. Check valves:
Field supplied. Check valves are recommended for
installation as shown in FIG.’s 6-5 through 6-10. Failure
to install check valves could result in a reverse ow
condition during pump(s) o cycle.
7. Domestic indirect hot water isolation valves:
Field supplied. Full port ball valves are required. Failure
to use full port ball valves could result in a restricted ow
rate through the boiler.
8. Anti-scald mixing valve:
Field supplied. An anti-scald mixing valve is
recommended when storing domestic hot water above
115°F (46°C).
9. Unions:
Field supplied. Recommended for unit serviceability.
10. Temperature and pressure gauge:
Factory supplied. e temperature and pressure gauge is
shipped loose. It is the responsibility of the contractor to
install the temperature and pressure gauge on the boiler
water outlet.
11. Pressure relief valve:
Factory supplied. e pressure relief valve is sized to
ASME speci cations.
12. Boiler purge valve:
Field supplied. e boiler purge valve is used to
remove entrapped air from the heat exchanger during
start-up.
13. System temperature sensor:
Lochinvar supplies a system temperature sensor. e
sensor is to be installed in the heating loop downstream
from the boiler hot water piping and heating loop
junction. e sensor should be located far enough
downstream to sense system diluted water temperature.
14. Water Meter:
Field supplied. A water meter to monitor makeup water is
recommended. Makeup water volume should not exceed
5% of total system per year.
15. Y-Strainer:
Field supplied. Install a Y-strainer or equivalent multi purpose strainer just before the boiler pump at the inlet
of the heat exchanger. is item is used to remove system
debris from older hydronic systems and to protect newer
systems.
16. Motorized isolation valve (optional):
Field supplied. A motorized isolation valve can be used
to isolate the boiler from the system piping.
Circulator sizing
e FTXL heat exchanger does have a pressure drop, which
must be considered in your system design. Refer to the
graphs in FIG. 6-4 for pressure drop through the FTXL heat
exchanger.
39
Page 40

Installation & Operation Manual
R
6 Hydronic piping
Near boiler piping connections
Figure 6-3A Near Boiler Piping w/Y-Strainer
SYSTEM PUMP
SYSTEM SUPPLY SENSOR
DIRT SEPARATOR
FROM
SYSTEM
Y-STR AINER
BOILER PUMP
DIR #2000546697 00
Figure 6-3B Near Boiler Piping w/Low Loss Header
T
O
S
Y
S
T
E
M
F
R
O
S
M
Y
S
T
E
M
WATER
METER
EXPANSION TANK
BOILER PUMP
40
SYSTEM PUMP
SYSTEM SENSOR
Y-STRA INER
DIR #2000546698 00
Variable speed pump option
Variable speed pump setup
Before operation, ensure the following:
- Pump is set for an input signal of 0 - 10VDC
by the dip switches on the pump control
- Pump is set for external signal control
(if applicable)
- Pump is set for linear output (if applicable)
- If pump does not come equipped with a
0 - 10 VDC input option, an optional module
TO
SYSTEM
WATE
METER
Table 6A1 Minimum Flow Rate with the Boiler at Full Fire
Table 6A2 Absolute Minimum Flow Rate @ Low Fire
will be required from the vendor
SMART SYSTEM / Multi-temperature
loop control option
e FTXL boiler is capable of producing up to three
(3) set point temperatures to meet di erent space
heating demands. When using more than one
temperature demand it is necessary to protect the
lower temperature loop(s) from overheating. To help
aid with this protection, Lochinvar o ers the MultiTemperature Loop Control Board Kit (100167843).
CAUTION
NOTICE
TEMPERATURE RISE APPLICATIONS
MODEL FLOW RATE (GPM)
FTX(N,L)400 10
FTX(N,L)500 12
FTX(N,L)600 15
FTX(N,L)725 18
FTX(N,L)850 21
ABSOLUTE MINIMUM FLOW RATE
MODEL FLOW RATE (GPM)
FTX(N,L)400 4
FTX(N,L)500 4
FTX(N,L)600 4
FTX(N,L)725 4
FTX(N,L)850 4
e maximum allowable water ow rate
through a single FTXL boiler is 105 GPM
(Models 400 - 600) and 150 GPM (Models
725 - 850). Exceeding this ow rate will
result in damage to the heat exchanger and/
or piping.
Reference Table 6A1 for the minimum
recommended ow rate through a single
FTXL boiler at full re to maintain a 80°F
temperature rise. Reference Table 6A2 for
the absolute minimum ow rate through a
single FTXL boiler.
[Based on 80°F Temperature Rise]
Page 41

6 Hydronic piping (continued)
Figure 6-4 Pressure Drop vs. Flow
HEX Pressure Drop
(Full Flow Application)
FTX725-850 FTX400-600
Installation & Operation Manual
15 ft
14 ft
13 ft
12 ft
11 ft
10 ft
9 ft
(Feet of Head)
8 ft
7 ft
6 ft
5 ft
4 ft
3 ft
Pressure Drop
2 ft
1 ft
0 ft
FTX400-600
FTX725-850
Flow Rate
Table 6B Sizing Information for Temperature Rise Applications_20°F, 30°F, 40°F, 60°F and 80°F
TEMPERATURE RISE APPLICATIONS
20°F 30°F 40°F 60°F
GPM FT/HD GPM FT/HD GPM FT/HD GPM FT/HD GPM FT/HD
Model
MINIMUM
PIPE
SIZE
15 ft
14 ft
13 ft
12 ft
11 ft
10 ft
9 ft
8 ft
7 ft
6 ft
5 ft
4 ft
3 ft
2 ft
1 ft
0 ft
80°F
400 2" 39 3.5 26 2.8 20 2.5 13 2.4 10 2.3
500 2" 49 4.8 33 3.4 24 2.9 16 2.5 12 2.4
600 2" 59 4.4 39 3.2 29 2.8 20 2.5 15 2.3
725 2 1/2" 71 4.9 47 3.5 35 3.0 24 2.7 18 2.6
850 2 1/2" 83 5.7 55 3.9 41 3.3 28 2.8 21 2.6
41
Page 42

Installation & Operation Manual
6 Hydronic piping
Figure 6-5 Multiple Boilers - Alternate - Fixed or Variable Flow Primary System Piping
Number of Units
2 3 4 5678
Manifold Pipe Sizes in Inches (mm)
3 1/2 (89) 4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 6 (152) 8 (203) 10 (254)
3 1/2 (89) 4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 6 (152) 8 (203) 10 (254)
3 1/2 (89) 4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 6 (152) 8 (203) 10 (254)
4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 8 (203) 8 (203) 8 (203) 10 (254)
4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 8 (203) 8 (203) 8 (203) 10 (254)
DRAIN
(TYPICAL)
2-WAY MOTORIZED
VALVE (OPTIONAL)
Model
400
500
600
725
850
RELIEF
VALVE
(TYPICAL)
ISOLATION
VALVE
FROM SYSTEM
BALL VALVE
(TYPICAL)
DIFFERENTIAL
PRESSURE
BYPASS
BYPASS
EXPANSION
TANK
PRESSURE
GAUGE
Y-STRAINER
(TYPICAL)
AIR SEPARATOR
DRAIN PORT
(TYPICAL)
PRESSURE
REDUCING VALVE
SYSTEM SUPPLY
SENSOR
SYSTEM
CIRCULATOR
TO SYSTEM
BACK FLOW
PREVENTER
WATER
METER
MAKE UP
WATER
DIR #2000546062 00
CAUTION
NOTICE
42
Mixing valves are required for the protection of low temperature loops.
Please note that these illustrations are meant to show system piping concept only, the installer is responsible
for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
Page 43

6 Hydronic piping (continued)
Figure 6-6 Single Boiler - Multiple Temperatures
Installation & Operation Manual
WATER
METER
LOOP SENSOR (3X)
CHECK VALVE
PRESSURE
REDUCING
VALVE
TEMPERATURE
LOOP 1
MAKE UP WATER
SYSTEM SUPPLY
BACK FLOW
PREVENTER
PRESSURE
GAUGE
EXPANSION
TANK
DRAIN POINT
(TYPICAL)
INDIRECT DHW
TANK
HOT WATER OUT
ANTI-SCALD
MIXING VALVE
COLD WATER IN
TEMPERATURE
LOOP 2
SENSOR
AIR SEPARATOR
DOMESTIC
HOT WATER
CIRCULATOR
TEMPERATURE
LOOP 3
PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
UNION
(TYPICAL)
TEMPERATURE / PRESSURE
BALL VALVE
(TYPICAL)
DRAIN
(TYPICAL)
GAUGE
WIRES TO
LOOP SENSORS
120VAC TO
PUMPS
TO
SYSTEM
FROM
SYSTEM
Y-STRAINER
BOILER CIRCULATOR
FLOW CHECK
VALVE (TYPICAL)
MULTI-TEMP
LOOP CONTROL
(OPTIONAL)
24VAC SIGNAL
TO MIXING VALVES
SHIELDED
CABLE TO
BOILER
CONTROL
DIR #2000546092 00
BOILER
CAUTION
NOTICE
Mixing valves are required for the protection of low temperature loops.
Please note that these illustrations are meant to show system piping concept only, the installer is responsible
for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
43
Page 44

6 Hydronic piping
Figure 6-7 Single Boiler - Primary/Secondary Piping
MAY SUBSTITUTE
LOW LOSS HEADER
AIR SEPARATOR
DRAIN POINT
(TYPICAL)
SYSTEM SUPPLY SENSOR
SYSTEM
CIRCULATOR
Installation & Operation Manual
M
E
T
S
Y
S
M
O
R
F
NOT TO EXCEED 4 PIPE DIA OR MAX. OF 12" APART
BALL VALVE
(TYPICAL)
Y
S
O
T
MAKE UP W ATER
WATER METER
BACK FLOW
PREVENTER
PRESSURE REDUCING
VALVE
M
E
T
S
PRESSURE
GAUGE
ANTI-SCALD
MIXING VALVE
INDIRECT DHW
TANK
HOT WATER OUT
COLD WATER IN
FLOW CHECK
VALVE (TYPICAL)
EXPANSION TANK
UNION
(TYPICAL)
DOMESTIC
HOT WATER
CIRCULATOR
Y-STRAINER
BOILER CIRCULATOR
CHECK VALVE
TEMPERATURE-PRESSURE
GAUGE
PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
DIR #2000559501_000
BOILER
CAUTION
NOTICE
NOTICE
44
Indirect water heaters are capable of transferring a limited number of Btu’s into the water. Ensure boiler
output does not exceed indirect water heater transfer capabilities.
Please note that these illustrations are meant to show system piping concept only, the installer is responsible
for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
System ow should always remain higher than the required ow for the boiler(s) when the boiler(s) is in
operation to prevent short cycling and high limit issues.
Page 45

6 Hydronic piping (continued)
Figure 6-8 Multiple Boilers - Multiple Temperatures
Model
400
500
600
725
850
TEMPERATURE
LOOP 3
TEMPERATURE
LOOP 2
TEMPERATURE
LOOP 1
LOOP SENSOR (3X)
SYSTEM SUPPLY
SENSOR
AIR SEPARATOR
MAKE UP WATER
WATER METER
Installation & Operation Manual
Number of Units
2 3 4 5678
Manifold Pipe Sizes in Inches (mm)
3 1/2 (89) 4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 6 (152) 8 (203) 10 (254)
3 1/2 (89) 4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 6 (152) 8 (203) 10 (254)
3 1/2 (89) 4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 6 (152) 8 (203) 10 (254)
4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 8 (203) 8 (203) 8 (203) 10 (254)
4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 8 (203) 8 (203) 8 (203) 10 (254)
WIRES TO
LOOP SENSORS
120VAC
TO PUMPS
MULTI-TEMP
LOOP CONTROL
(OPTIONAL)
24V SIGNAL TO
MIXING VALVES
SHIELDED CABLE
TO BOILER CONTROL
Y-STRAINER
BOILER CIRCULATOR
BACK FLOW
PREVENTER
PRESSURE
GAUGE
PRESSURE
REDUCING
VALVE
DRAIN POINT
(TYPICAL)
ANTI-SCALD
MIXING VALVE
CAUTION
CAUTION
BALL VALVE
(TYPICAL)
TEMPERATURE/
PRESSURE
GAUGE
EXPANSION
INDIRECT DHW
TANK
TANK
COLD WATER IN
DOMESTIC
HOT WATER
CIRCULATOR
PRESSURE
RELIEF
VALVE
BOILER 1
FLOW
CHECK
VALVE
(TYPICAL)
BOILER 2
DIR #2000546165 00
Indirect water heaters are capable of transferring a limited number of Btu’s into the water. Ensure boiler
output does not exceed indirect water heater transfer capabilities.
Mixing valves are required for the protection of low temperature loops.
NOTICE
Please note that these illustrations are meant to show system piping concept only, the installer is responsible
for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
45
Page 46

6 Hydronic piping
Figure 6-9 Multiple Boilers - Primary/Secondary Piping
Model
3 1/2 (89) 4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 6 (152) 8 (203) 10 (254)
3 1/2 (89) 4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 6 (152) 8 (203) 10 (254)
3 1/2 (89) 4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 6 (152) 8 (203) 10 (254)
4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 8 (203) 8 (203) 8 (203) 10 (254)
4 (102) 5 (127) 6 (152) 8 (203) 8 (203) 8 (203) 10 (254)
AIR SEPARATOR
DRAIN POINT
(TYPICAL)
SYSTEM SUPPLY SENSOR
MAY SUBSTITUTE
LOW LOSS HEADER
400
500
600
725
850
Installation & Operation Manual
Number of Units
2 3 4 5678
Manifold Pipe Sizes in Inches (mm)
M
E
T
S
Y
S
BALL VALVE
(TYPICAL)
C
X
E
O
T
T
O
N
M
O
FR
F
O
.
X
A
M
R
O
A
I
D
E
P
I
P
4
D
E
E
T
R
A
P
A
"
2
1
SYSTEM CIRCULATOR
E
T
S
Y
S
TO
MAKE UP WATER
WATER METER
BACK FLOW
PREVENTER
PRESSURE REDUCING
VALVE
PRESSURE GAUGE
INDIRECT DHW
TANK
ANTI-SCALD
MIXING VALVE
HOT WATER OUT
COLD WATER IN
DOMESTIC
HOT WATER
CIRCULATOR
VALVE (TYPICAL)
M
FLOW CHECK
EXPANSION
TANK
BOILER
CIRCULATOR
(TYPICAL)
TEMPERATURE /
PRESSURE GAUGE
BOILER 1
(LEADER)
BOILER 2
(MEMBER 1)
Y-STRAINER
(TYPICAL)
PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
BOILER 3
(MEMBER 2)
DIR #2000559502_000
BOILER 4
(MEMBER 3)
CAUTION
NOTICE
NOTICE
46
Indirect water heaters are capable of transferring a limited number of Btu’s into the water. Ensure boiler
output does not exceed indirect water heater transfer capabilities.
Please note that these illustrations are meant to show system piping concept only, the installer is responsible
for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
System ow should always remain higher than the required ow for the boiler(s) when the boiler(s) is in
operation to prevent short cycling and high limit issues.
Page 47

Installation & Operation Manual
6 Hydronic piping (continued)
Figure 6-10 Single Boiler - Multiple Temperatures with DHW Piped as a Zone
TEMPERATURE
LOOP 3
TO
SYSTEM
MAKE UP WATER
WATER
METER
BACK FLOW
PREVENTER
PRESSURE
GAUGE
TEMPERATURE
LOOP 2
TEMPERATURE
LOOP 1
LOOP SENSOR (3X)
BALL VALVE
(TYPICAL)
AIR SEPARATOR
SYSTEM
SUPPLY SENSOR
WIRES TO
LOOP SENSORS
120VAC TO
PUMPS
FROM
SYSTEM
Y-STRAINER
BOILER CIRCULATOR
MULTI-TEMP
LOOP CONTROL
(OPTIONAL)
24VAC SIGNAL
TO MIXING VALVES
EXPANSION
TANK
CAUTION
PRESSURE
REDUCING
VALVE
DRAIN POINT
INDIRECT DHW
TANK
HOT WATER OUT
ANTI-SCALD
MIXING VALVE
COLD WATER IN
(TYPICAL)
DOMESTIC
HOT WATER
CIRCULATOR
PRESSURE RELIEF
UNION
(TYPICAL)
DRAIN
VALVE
TEMPERATURE /
PRESSURE GAUGE
FLOW CHECK
VALVE (TYPICAL)
SHIELDED
CABLE TO
BOILER
BOILER
DIR #2000546252 00
Indirect water heaters are capable of transferring a limited number of Btu’s into the water. Ensure boiler
output does not exceed indirect water heater transfer capabilities.
CAUTION
NOTICE
NOTICE
Mixing valves are required for the protection of low temperature loops.
Please note that these illustrations are meant to show system piping concept only, the installer is responsible
for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
Please note that the installer is responsible for ensuring DHW prioritization when piped as a zone.
47
Page 48

7 Gas connections
Connecting gas supply piping
Installation & Operation Manual
1. Remove the top access panel and refer to FIG.’s 7-1 and
7-2 to pipe gas to the boiler.
a. Install ground joint union for servicing, when
required.
b. Install a manual shuto valve in the gas supply
piping outside boiler jacket when required by local
codes or utility requirements.
c. In Canada – When using manual main shuto
valves, it must be identi ed by the installer.
2. Install sediment trap / drip leg.
Figure 7-1 Gas Supply Piping - Model 400 - 600
MANUAL
SHUTOFF VALVE
(FACTORY SUPPLIED)
GAS SUPPLY
SEDIMENT TRAP/
DRIP LEG
UNION
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
IMG01004
Figure 7-2 Gas Supply Piping - Models 725 - 850
MANUAL
SHUTOFF VALVE
(FACTORY SUPPLIED)
3. Support piping with hangers, not by the boiler or its
accessories.
WARNING
e gas valve and blower will not support
the weight of the piping. Do not attempt
to support the weight of the piping with
the boiler or its accessories. Failure to
comply could result in severe personal
injury, death, or substantial property
damage.
4. Purge all air from the gas supply piping.
5. Before placing the boiler in operation, check the boiler
and its gas connection for leaks.
a. e appliance must be disconnected from the gas
supply piping system during any pressure testing of
that system at a test pressure in excess of 1/2 PSIG
(3.5 kPa).
b. e appliance must be isolated from the gas supply
piping system by closing a manual shuto valve
during any pressure testing of the gas supply piping
system at test pressures equal to or less than 1/2 PSIG
(3.5 kPa).
c. e appliance and its gas connection must be leak
tested before placing it in operation.
WARNING
Do not check for gas leaks with an open
ame – use the bubble test. Failure to use
the bubble test or check for gas leaks can
cause severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
6. Use pipe sealing compound compatible with propane
gases. Apply sparingly only to male threads of the pipe
joints so that pipe dope does not block gas ow.
GAS SUPPLY
SEDIMENT TRAP/
DRIP LEG
UNION
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
48
IMG01002
Page 49

7 Gas connections (continued)
Installation & Operation Manual
WARNING
WARNING
Figure 7-3 Inlet Pipe with Backup Wrench
Failure to apply pipe sealing compound
as detailed in this manual can result
in severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
Use two wrenches when tightening gas
piping at boiler (FIG. 7-3), using one
wrench to prevent the boiler gas line
connection from turning. Failure to
support the boiler gas connection pipe
to prevent it from turning could damage
gas line components.
USE BACKUP WRENCH TO
PREVENT PIPE FROM ROTATING
Natural gas supply pressure requirements
1. Pressure required at the gas valve inlet pressure port:
• Maximum 14 inches w.c. (3.5 kPa) with no ow
(lockup) or with boiler on.
• Models 400 & 600 - 850: Minimum 4 inches w.c. (.99
kPa) with gas owing (verify during boiler startup).
Model 500 Only: Minimum 5 inches w.c. (1.25 kPa) with
gas owing (verify during boiler startup).
2. Install 100% lockup gas pressure regulator in supply line
if inlet pressure can exceed 14 inches w.c. (3.5 kPa) at any
time. Adjust lockup regulator for 14 inches w.c. (3.5 kPa)
maximum.
Propane Gas:
WARNING
Pipe sizing for propane gas
1. Contact gas supplier to size pipes, tanks, and 100% lockup
gas pressure regulator.
FTXL boilers are typically shipped ready to
re on natural gas. Check boiler rating plate
to determine which fuel the boiler is set for.
If set to natural gas, it may be converted to
LP by installing a LP venturi or by making
a gas valve adjustment (see pages 14 and 15).
In order to operate on LP gas, a LP venturi
MUST BE installed or a gas valve adjustment
MUST BE made. Failure to comply could
result in severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
NOTICE
Maximum inlet gas pressure must not
exceed the value speci ed. Minimum
value listed is for the purposes of input
adjustment.
Natural gas:
Pipe sizing for natural gas
1. Refer to Table 7A for pipe length and diameter. Based on
rated boiler input (divide by 1,000 to obtain cubic feet per
hour).
a. Table 7A is only for natural gas with speci c gravity
0.60 inches, with a pressure drop through the gas
piping of 0.3 inches w.c.
b. For additional gas pipe sizing information, refer to
ANSI Z223.1 (or B149.1 for Canadian installations).
Propane Supply Pressure Requirements
1. Adjust propane supply regulator provided by the gas
supplier for 14 inches w.c. (3.2 kPa) maximum pressure.
2. Pressure required at gas valve inlet pressure port:
• Maximum 14 inches w.c. (3.2 kPa) with no ow (lockup)
or with boiler on.
• Minimum 8 inches w.c. (1.9 kPa) with gas owing (verify
during boiler startup).
WARNING
Ensure that the high gas pressure regulator
is at least 10 feet (3 m) upstream of the
appliance.
49
Page 50

7 Gas connections
Table 7A Natural Gas Pipe Size Chart
Capacity of Schedule 40 Metallic Pipe in Cubic Feet of Natural Gas Per Hour
(based on .60 speci c gravity, 0.30" w.c. pressure drop)
Installation & Operation Manual
Pipe
Size
(Inches)
1/2 131 90 72 62 55 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
3/4 273 188 151 129 114 104 95 89 83 79 70 63 58 N/A
1 514 353 284 243 215 195 179 167 157 148 131 119 109 102
1 1/4 1,060 726 583 499 442 400 368 343 322 304 269 244 224 209
1 1/2 1,580 1,090 873 747 662 600 552 514 482 455 403 366 336 313
2 3,050 2,090 1,680 1,440 1,280 1,160 1,060 989 928 877 777 704 648 602
2 1/2 4,860 3,340 2,680 2,290 2,030 1,840 1,690 1,580 1,480 1,400 1,240 1,120 1,030 960
3 8,580 5,900 4,740 4,050 3,590 3,260 3,000 2,790 2,610 2,470 2,190 1,980 1,820 1,700
4 17,500 12,000 9,660 8,270 7,330 6,640 6,110 5,680 5,330 5,040 4,460 4,050 3,720 3,460
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 125 150 175 200
Length of Pipe in Straight Feet
Check inlet gas supply
NOTICE
WARNING
e gas piping must be sized for the proper ow and length of
pipe, to avoid excessive pressure drop. Both the gas meter and
the gas regulator must be properly sized for the total gas load.
If you experience a pressure drop greater than 1 inch w.c.
(249 Pa), the meter, regulator, or gas line is undersized or in
need of service. Perform the steps below when checking inlet
gas supply:
1. Turn the main power switch to the “OFF” position.
2. Shut o gas supply at the manual gas valve in the gas
piping to the appliance.
3. On Models 400 - 500 loosen the set screw one (1) full turn
from inside the pressure tap on top of the gas valve. On
Models 600 - 850 remove the 1/8" (3 mm) pipe plug on the
inlet ange to the valve and install a suitable 1/8" (3 mm)
tting ( eld supplied) for the manometer tubing. Place
the tubing of the manometer over the tap once the set
screw is loosened or the 1/8" (3 mm) tting is installed
(depending on model) as shown in FIG.’s 7-5 and 7-6 on
page 51.
CSA or UL listed exible gas connections
are acceptable, but you must exercise
caution to ensure that the line has adequate
capacity to allow your boiler to re at full
rate. Consult with local codes for proper
installation or service procedures.
DO NOT adjust gas valve outlet pressure.
Attempting to alter the gas valve outlet
pressure could result in damage to the valve,
causing potential severe personal injury,
death, or substantial property damage.
4. Slowly turn on the gas supply at the eld installed
manual gas valve.
5. Turn the power switch to the “ON” position.
6. Adjust the temperature set point on the control panel of
the SMART SYSTEM control module to call for heat.
7. Observe the gas supply pressure as the burner res at
100% of rated input. Percent of burner input will be
displayed on the control panel.
8. Ensure inlet pressure is within speci ed range.
Minimum and maximum gas supply pressures are
speci ed in this section of the manual.
9. If gas supply pressure is within normal range and no
adjustments are needed, proceed on to Step 11.
10. If the gas pressure is out of range, contact the gas utility,
gas supplier, quali ed installer or service agency to
determine the necessary steps to provide proper gas
pressure to the control.
11. Turn the power switch to the “OFF” position.
12. Shut o the gas supply at the manual gas valve in the gas
piping to the appliance.
13. Remove the manometer from the pressure tap on top of
the gas valve. On Models 400 - 500 re-tighten the set
screw inside the pressure tap. On Models 600 - 850
remove the 1/8" (3 mm) eld supplied tting and
reinstall the pipe plug removed in Step 3.
50
Page 51

7 Gas connections (continued)
Installation & Operation Manual
WARNING
When re-tightening the set screw, be sure
to tighten securely to prevent gas leaks.
Do not check for gas leaks with an open
ame -- use the bubble test. Failure to use
the bubble test or check for gas leaks can
cause severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
14. Turn on the gas supply at the manual gas valve.
15. Turn the power switch to the “ON” position.
16. Adjust the temperature set point on the control panel of
the SMART SYSTEM control module to the desired
water temperature so the appliance will call for heat.
17. Check burner performance by cycling the system while
you observe burner response. e burner should ignite
promptly. Flame pattern should be stable. Turn system
o and allow burner to cool, then cycle burner again to
ensure proper ignition and ame characteristics.
Figure 7-5 Inlet Gas Supply Check - Model 400 - 500
LOOSEN THE SET SCREW ONE (1) FULL TURN
AND PLACE THE MANOMETER TUBING OVER
THE PRESSURE TAP
Gas pressure
e gas pressure must remain between 4 inches w.c.
(.99 kPa) on Model 400 and Models 600 - 850 or minimum
5 inches w.c. (1.25 kPa) on Model 500, and maximum 14
inches w.c. (3.5 kPa) for Natural gas and between 8 inches
w.c. (1.9 kPa) minimum and 14 inches w.c. (3.2 kPa)
maximum for LP gas during standby (static) mode and while
in operating (dynamic) mode. If an in-line regulator is used,
it must be a minimum of 10 feet (3 m) from the FTXL boiler.
It is very important that the gas line is properly purged by the
gas supplier or utility company. Failure to properly purge the
lines or improper line sizing, will result in ignition failure.
e problem is especially noticeable in NEW LP installations
and also in empty tank situations. is can also occur when
a utility company shuts o service to an area to provide
maintenance to their lines.
Gas valve replacement
e gas valve MUST NOT be replaced with a conventional
gas valve under any circumstances. As an additional safety
feature, this gas valve has a anged connection to the venturi
and blower.
WARNING
Failure to follow all precautions could
result in re, explosion, or death!
DETAIL
IMG01005
Figure 7-6 Inlet Gas Supply Check - Models 600 - 850
REMOVE THE 1/8" (3 MM) PIPE PLUG ON
THE INLET FLANGE TO THE VALVE AND
INSTALL A SUITABLE 1/8" (3 MM) FITTING
(FIELD SUPPLIED) FOR THE MANOMETER
TUBING.
DETAIL
IMG01006
WARNING
DO NOT adjust gas valve outlet pressure.
Attempting to alter the gas valve outlet
pressure could result in damage to the
valve, causing potential severe personal
injury, death, or substantial property
damage.
51
Page 52

8 Field wiring
Installation & Operation Manual
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD – For
your safety, turn o electrical power
supply before making any electrical
connections to avoid possible electric
shock hazard. Failure to do so can cause
severe personal injury or death.
NOTICE
Wiring must be N.E.C. Class 1.
If original wiring as supplied with boiler
must be replaced, use only type 105°C
wire or equivalent.
Boiler must be electrically grounded as
required by National Electrical Code
ANSI/NFPA 70 – latest edition.
CAUTION
Label all wires prior to disconnection
when servicing controls. Wiring errors
can cause improper and dangerous
operation.
Figure 8-1 Line Voltage Field Wiring Connections
120V SUPPLY
NEUTRAL
GROUND
SERVICE
SWITCH
LINE
W
G
BK
Line voltage connections
1. Connect 120 VAC power wiring to the line voltage terminal
strip in the junction box, as shown in FIG. 8-1.
2. Provide and install a fused disconnect or service switch
(15 amp recommended) as required by the code (see
FIG. 8-1).
3. When connecting a domestic hot water (DHW) pump,
connect the wiring to the line voltage terminal strip as
shown in FIG. 8-1.
4. To activate a system pump, wire as shown in FIG. 8-1. Dry
contacts are sized for 1.5 hp/120V, 3 hp/240V or 30 amps.
Low voltage connections
1. Route all low voltage wires through the knockouts in the
rear of the boiler, as shown in FIG. 8-2.
2. Continue to route the wires through the plastic bushings to
the le of the low voltage connection board.
3. Connect low voltage wiring to the low voltage connection
board as shown in FIG. 8-3 on page 55 of this manual and
the boiler wiring diagram. Make certain the wires will stay
well away from the top of the heat exchanger.
Figure 8-2 Routing Field Wiring
LOW VOLTAGE
CONNECTION
BOARD
SYSTEM
PUMP
BOILER
PUMP
DOMESTIC
HOT WATER
PUMP
BK
G
W
BK
G
W
BK
G
W
L2/N
L1
G
Installation must comply with:
1. National Electrical Code and any other national, state,
provincial, or local codes, or regulations.
2. In Canada, CSA C22.1 Canadian Electrical Code Part 1,
and any local codes.
52
LOW VOLTAGE
WIRING KNOCKOUT S
LINE VOLTAGE
WIRING KNOCKOUTS
LINE VOLTAGE
JUNCTION BOX
IMG01008
Thermostat
1. Connect the room thermostats or end switches (isolated
contact only) to heat/loop demand 1, 2, or 3, as shown in
FIG. 8-3.
2. Install the thermostat on the inside wall away from
in uences of dra s, hot or cold water pipes, lighting
xtures, television, sunlight, or replaces.
3. ermostat anticipator (if applicable):
a. If connected directly to boiler, set for 0.1 amps.
b. If connected to relays or other devices, set to match
total electrical power requirements of connected
devices. See device manufacturers’ speci cations
and thermostat instructions for details.
Page 53

8 Field wiring (continued)
Installation & Operation Manual
Outdoor temperature sensor
1. Mount the sensor on an exterior wall, shielded from
direct sunlight or ow of heat or cooling from other
sources.
2. Route sensor wires through a knockout at the rear of the
boiler (see FIG. 8-2).
3. Connect the outdoor temperature sensor (FIG. 8-3) to
the outdoor sensor terminals on the connection board
to enable outdoor reset operation of the FTXL. If xed
temperature operation is required, do not install outdoor
sensor.
DHW (Domestic Hot Water)
thermostat
Connect storage indirect water heater (DHW) thermostat
(FIG. 8-3) to the DHW thermostat terminals on the
connection board. If a tank sensor is connected (see DHW
Tank Sensor below) the tank thermostat is ignored.
DHW tank sensor
By installing a tank sensor, the SMART SYSTEM control can
perform the tank thermostat function. e SMART SYSTEM
control automatically detects the presence of this sensor, and
generates a DHW call for heat when the tank temperature
drops 6°F (3°C) below the tank set point, and nishes the call
for heat when the tank temperature reaches the tank set point.
e tank sensor included with the Lochinvar Squire® indirect
DHW tanks (100170544) is the only sensor suitable for use
with the SMART SYSTEM control. Connect the sensor leads
to the Tank Sensor terminals on the low voltage connection
board (FIG. 8-3).
WARNING
If 100170544 is not compatible with the indirect tank, a
tank thermostat can be used to control the boiler. e
tank thermostat should be installed per the manufacturer’s
instructions and wired to the DHW ermostat terminals on
the low voltage connection board (FIG. 8-3).
Failure to use the correct sensor may
result in the tank temperature being either
above or below the set point.
Low gas pressure switch
1. If a switch is provided to detect low gas pressure, remove
the jumper wire from the terminals on the connection
board and connect them to its normally open contacts
(FIG. 8-3).
2. If both a high and low gas pressure switch is used, connect
their respective contacts in series, and connect them to the
terminals on the connection board (FIG. 8-3).
Variable speed system pump
If a variable speed pump is used in the primary loop, and
a 0-10V signal is available from the pump speed control,
this signal can be used by the SMART SYSTEM control to
anticipate changes in the building heat load. By connecting
this 0 - 10V signal to the 0 - 10V SYS PUMP IN terminals, the
boiler (or cascade) can modulate up and down as the primary
ow increases and decreases.
Boiler pump speed output
is 0 - 10V output is available to control the speed of a variable
speed boiler pump. e SMART SYSTEM control will vary the
speed of this pump in order to maintain a minimum T across
the heat exchanger, as well as prevent high limit lockouts when
the ow in the primary loop is extremely low. NOTE: is
feature is to be used with Primary / Secondary piping systems
only. A system supply sensor MUST be installed. Connect this
output to the 0 - 10V input on the boiler pump speed control.
Rate output
is output provides a 0 - 10V signal that is proportional to the
ring rate of the boiler. is may be used by a BMS system to
monitor the actual rate of the boiler.
ModBus/BACnet
When an optional ModBus or BACnet interface module is
installed, the RS-485 cable is connected to these terminals. Use
shielded, 2-wire twisted pair cable. If desired, the shield can
be connected to ground by installing a jumper wire between
terminals 1 and 3 on connector X5 on the optional ModBus or
BACnet interface module.
Louver proving switch
1. When the operation of the louvers needs to be veri ed
before the boiler res, remove the jumper wire from
these terminals and connect them to the normally open
contacts on its proving switch (FIG. 8-3).
High gas pressure switch
1. If a switch is provided to detect excessive gas pressure,
remove the jumper wire from the terminals on the
connection board, and then connect them to its normally
closed contacts (FIG. 8-3).
Flow switch
1. A ow switch is used to guarantee ow through the boiler
before allowing it to re. e ow switch must be installed
at the boiler outlet.
2. Remove the jumper wire from the terminals on the
connection board and connect these terminals to the
normally open contacts on the ow switch (FIG. 8-3).
System supply sensor
1. By installing the system supply sensor into the supply of
the primary loop, the temperature of the system supply can
be controlled. e SMART SYSTEM control automatically
detects the presence of this sensor, and controls the boiler
ring rate to maintain the system supply temperature to
the set point (if outlet sensor control is currently selected).
53
Page 54

8 Field wiring
See the FTXL Service Manual for instructions on how to
use the inlet sensor as the controlling sensor. When the
inlet sensor is programmed as the controlling sensor, it is
vital that the SYSTEM SUPPLY sensor be installed. DO
NOT INSTALL THE SYSTEM SUPPLY SENSOR INTO
THE SYSTEM RETURN.
2. e 100170581 sensor provided with the boiler must be
used for the system sensor.
3. Connect these terminals to the system supply sensor
(FIG. 8-3).
Boiler management system
1. An external control may be connected to control either
the ring rate or the set point of the boiler. If the
external control uses a set of contacts to enable the boiler,
connect the contacts to the heat/loop demand 1 terminals.
Otherwise, the SMART SYSTEM control will be enabled by
the 0-10V signal.
2. Make sure the (-) terminal is connected to the (-) or
common output terminal of the external control, and the
(+) terminal is connected to the 0 - 10 VDC or (+) terminal
of the external control. Make sure that the (-) voltage is not
below ground.
Runtime contacts
e SMART SYSTEM control closes a set of dry contacts
whenever the burner is running. is is typically used by
Building Management Systems to verify that the boiler is
responding to a call for heat.
Alarm contacts
e SMART SYSTEM control closes another set of contacts
whenever the boiler is locked out or the power is turned o .
is can be used to turn on an alarm, or signal a Building
Management System that the boiler is down.
DHW recirculation sensor
e FTXL is able to control a DHW recirculation pump. To
operate this feature, a 100170581 temperature sensor must be
installed in the circulation loop return. Connect this sensor to
the DHW recirculation sensor terminals on the Low Voltage
Connection Board.
DHW recirculation pump
When the DHW recirculation sensor (as described above) is
connected, the FTXL SMART SYSTEM control will output
24VAC to control a DHW recirculation pump relay ( eld
supplied). Connect the coil of the DHW recirculation pump
relay to the 24VAC recirculation pump relay coil terminals on
the Low Voltage Connection Board.
Wiring of the cascade
When wiring the boilers for Cascade operation, select one boiler
as the Leader boiler. e remaining boilers will be designated as
Members. See page 63 “Con guration of the Cascade” for a
detailed explanation of this procedure.
54
Installation & Operation Manual
Connect the system supply sensor and outdoor air sensor (if
used) to the Leader boiler. For the Cascade system to work
properly the system supply sensor must be installed. e
location of the system supply sensor should be downstream
of the boiler connections in the main system loop (FIG.’s 6-5
through 6-10). e system supply sensor should be wired to
the Low Voltage Connection Board at the terminals marked
for the system sensor (see FIG. 8-3). e Leader control will
use the water temperature at the system supply sensor to
control the operation of the Cascade.
If outdoor air reset is desired, the outdoor air sensor should be
wired to the Low Voltage Connection Board at the terminals
marked for the outdoor air sensor (FIG. 8-3). If the outdoor
air sensor is connected, the Leader control will calculate the
water temperature set point based on the programmed reset
curve parameters. If the outdoor air sensor is not connected,
the Leader control will maintain the xed water temperature
set point that is programmed into the control.
If a ermostat or Zone Control enable output is available,
it should be wired to the Low Voltage Connection Board
on the Leader boiler at the terminals marked for one of the
heat/loop demands 1-3 (FIG. 8-3). If the boilers are to run
continuously, connect a jumper wire between the R and W
terminals for the heat/loop demand input. is will initiate a
call for heat on the Cascade.
Communication between the Leader boiler and the Member
boilers is accomplished by using shielded, 2-wire twisted
pair communication cable. Connect one of the twisted pair
wires to Cascade terminal A on each of the Low Voltage
Connection boards, and the other wire of the twisted pair to
Cascade terminal B on each of the Low Voltage Connection
Boards. Connect the shield wires to one of the shield
terminals on the Low Voltage Connection Boards (FIG. 8-3).
If more than two boilers are on the Cascade, daisy chain the
wiring from the Cascade terminals on the second boiler to the
Cascade terminals on the third boiler, then from the third to
the forth, and so on. e connections between boilers can be
made in any order, regardless of the addresses of the boilers.
Try to keep each cable as short as possible.
When the Member 1 boiler is programmed as an alternate
leader this allows the Member 1 boiler to automatically
assume control of the Cascade should it lose communication
with the Leader boiler. When programmed to YES, it is
recommended that the Member 1 boiler have its own set of
external sensors installed (such as the system supply sensor),
to maintain the same level of temperature control as with the
Leader boiler. Voltage signals (such as 0 - 10V system pump
speed input) can be connected to both boilers.
WARNING
When communication is re-established with the Leader boiler,
Member 1 will automatically relinquish control of the Cascade
to the Leader boiler.
Do not connect the sensors connected to
the Leader boiler to the Member 1 boiler.
e actual water temperatures will be
higher than expected, which could lead
to property damage, personal injury, or
death.
Page 55

8 Field wiring (continued)
Figure 8-3 Low Voltage Field Wiring Connections
SYSTEM SUPPLY SENSOR
OUTDOOR SENSOR
DHW RECICULATION S ENSOR
TANK SENSOR
TO
NEXT
BOILER
A
B
SHIELD
Installation & Operation Manual
IMG01073
NOTE:
CONNECTION BOARD SPLIT FOR
ILLUSTRATION PURPOSES
AB
SYSTEM
BUILDING
MANAGEMENT
SPEED
CONTROL
SYSTEM PUMP
PUMP
BOILER
NEEDED
WIRE AS
A
B
FROM
PREVIOUS
BOILER
SHIELD
COM
NO
RELAY
RECIRCULATION PUMP
LOUVER
LOUVER RELAY
PROVING SWITCH
FLOW SWITCH
TANK THERMOSTAT
ROOM THERMOSTAT 3
ROOM THERMOSTAT 2
ROOM THERMOSTAT 1
55
Page 56

9 Condensate disposal
Installation & Operation Manual
Condensate drain
1. e FTXL is a high e ciency appliance that produces
condensate.
2. e condensate trap is sized for a 1/2" PVC outlet
connection pipe.
3. Plug the wiring connection from the condensate trap into
the connector located on the back of the unit.
4. Slope condensate tubing down and away from the boiler
into a drain or condensate neutralizing lter. Condensate
from the FTXL will be slightly acidic (typically with a pH
from 3 to 5). Install a neutralizing lter if required by
local codes.
A Neutralizer Kit (FIG. 9-1) is available from the factory.
e neutralizer kit must be placed on a surface that is
a minimum of 3 inches lower than the condensate trap
with eld supplied piping (vacuum break) installed
between the condensate trap and the neutralizer kit.
5. Do not expose condensate line to freezing temperatures.
NOTICE
Use materials approved by the authority
having jurisdiction. In the absence of other
authority, PVC and CPVC pipe must comply
with ASTM D1785 or D2845. Cement and
primer must comply with ASME D2564 or
F493. For Canada use CSA or ULC certi ed
PVC or CPVC pipe, ttings, and cement. Do
not use copper or black iron pipe, or ttings.
NOTICE
To allow for proper drainage on large
horizontal runs, a second line vent may
be required and tubing size may need to
increase to 1 inch (25 mm).
The condensate line must remain
unobstructed, allowing free flow of
condensate. If condensate is allowed to freeze
in the line or if the line is obstructed in any
other manner, condensate can exit from
the boiler tee, resulting in potential water
damage to property.
6. A condensate removal pump is required if the boiler is
below the drain. When installing a condensate pump, select
one approved for use with condensing boilers and furnaces.
e pump should have an over ow switch to prevent
property damage from condensate spillage. e switch
should be wired in series with the blocked drain switch
inside the boiler (see FIG. 10-1 on page 59).
Figure 9-1 Condensate Disposal
56
NEUTRALIZER KIT
(OPTIONAL)
3" MINIMUM BEL OW
CONDENSATE TRAP
VACUUM
BREAK
FLOOR DRAIN
OR DRAIN PAN
IMG01009
NOTE: Neutralizer shown
for illustrative purposes only.
Actual neutralizer may vary.
Page 57

10 Start-up
Pre-Commissioning Cleaning
1. Prior to ll and start-up, ush the entire heating system.
2. Clean the entire heating system with an approved precommissioning cleaner (comparable to Sentinel X300
and Fernox F3) in accordance with the manufacturer’s
recommendation to remove debris and prolong the life of
the heat exchanger.
3. Clean all water ltering devices in the system.
4. Flush the cleaning solution out of the entire system and
re ll.
Fill water
Check/control fi ll water chemistry
IMPORTANT
e manufacturer recommends the following for properly
lling your boiler with the appropriate water chemistry for
closed loop boilers. Good ll water quality will help extend
the life of the appliance by reducing the e ects of lime scale
buildup and corrosion in closed loop systems.
Hardness between 5 and 12 grains per gallon
1. Consult local water treatment companies for hard water
areas (above 12 grains per gallon hardness).
2. Hardness levels that are above 12 grains/gallon can lead
to lime scale buildup throughout the boiler system. If the
ll water is below 5 grains/gallons, usually due to use of a
water so ener, it is recommended to mix in some potable
water at the inlet to increase the hardness of the water to
above 5 grains/gallons.
pH between 6.5 and 8.5
1. pH levels below 6.5 can cause an increase in the rate of
corrosion. pH of 8.5 or higher can potentially cause lime
scale buildup.
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) less than 350 ppm
1. Total dissolved solids are all minerals, salts, metals, and
charged particles that are dissolved in water.
2. e greater the amounts of TDS present, the higher the
corrosion potential due to increased conductivity in the
water.
Chloride concentration less than 150 ppm
1. Do not ll boiler or operate with water containing
chlorine in excess of 150 ppm.
2. Filling with fresh drinking water should be acceptable.
3. Do not use the boiler to directly heat swimming pool or
spa water.
Conduct water quality testing prior to
installing the appliance. Various solutions
are available to adjust water quality.
Installation & Operation Manual
Boiler water
CAUTION
CAUTION
Table 10A Boiler Water Chemistry
Speci cation Range
Dissolved Solids < 2000 ppm
• Monitoring pH, chlorides, TDS, and hardness
levels can prolong the life of the appliance by reducing
lime scale buildup, corrosion, and erosion. Check for
leaks to ensure that fresh water is not entering the
system.
• Continual fresh makeup water will reduce boiler life.
• Mineral buildup in the heat exchanger reduces heat
transfer, overheats the stainless steel heat exchanger,
and causes failure.
• e addition of oxygen carried in by makeup water
can cause internal corrosion in system components.
• Leaks in the boiler or piping must be repaired at
once to prevent excessive makeup water. For this
purpose, it is recommended to install a water meter
to easily check the amount of makeup water entering
the system. Makeup water volume should not exceed
5% of the total system volume per year. NOTE: When
makeup water is added, make sure the chemical
additives are added to maintain the correct level.
• An approved multi-metal corrosion inhibitor
(comparable to Sentinel X100 or Fernox F1) is
recommended at the correct concentration and in the
manner recommended by the manufacturer.
Do not use petroleum based cleaning or
sealing compounds in the boiler system.
Gaskets and seals in the system may be
damaged. is can result in substantial
property damage.
DO NOT use "homemade cures" or "boiler
patent medicines". Serious damage to
boiler, personnel, and/or property may
result.
BOILER WATER CHEMISTRY
pH Level 6.5 to 9.5
Chloride < 150 ppm
Freeze protection
WARNING
1. Use glycol only if needed for freeze protection.
2. Propylene glycol is the recommended freeze protection.
3. Make sure to ush the boiler system before adding glycol.
4. Determine the freeze protection uid quantity using
system water content, following the uid manufacturer's
instructions. Boiler water content is listed on page 6.
Remember to include expansion tank water content.
Ethylene glycol is toxic, DO NOT use as
your freeze protection. Ethylene glycol has a
sweet aroma which children and pets could
mistake as food and ingest; leading to death.
57
Page 58

10 Start-up
Installation & Operation Manual
5. Local codes may require a back ow preventer or actual
disconnect from city water supply.
6. When using freeze protection uid with automatic ll,
it is suggested to install a water meter to monitor water
makeup. Freeze protection uid may leak before the
water begins to leak, causing the concentration to drop,
which reduces the freeze protection level.
7. e freeze protection set points may be lowered when
freeze protection uid is used (see the FTXL Service
Manual).
8. Consult the glycol manufacturer for details on the
suggested mix of glycol and water for the desired freeze
protection level and the de-rate e ect it will have on the
boiler output.
Test / replace freeze protection fl uid
1. For systems using freeze protection uids, follow the
uid manufacturer's instructions.
2. Freeze protection uid must be replaced periodically
due to degradation of inhibitors over time.
3. It is recommended to test the glycol concentration
annually and adjust within the desired set points.
Oxygen prevention
CAUTION
Dissolved oxygen can have a negative e ect on the boiler
system. Oxygen can cause iron oxide to generate iron
deposits. Oxygen may also increase the rate of corrosion
on non-stainless steel parts of the system. A low pH level
combined with oxygen further enhances its corrosive e ects.
A er boiler installation, check for air leaks in the following
areas:
• Suction gasket
• Pump
• Air valve
• O-ring gaskets
Precautions include installing a water meter to evaluate the
fresh water volume entering the system (should be no more
than 5% system volume). Additional volumes of fresh water
could indicate that a leak is present.
Eliminate all system leaks. Continual
fresh makeup water will reduce boiler
life. Minerals can build up in the
heat exchanger, reducing heat transfer,
overheating the heat exchanger, and
causing heat exchanger failure.
Fill and test water system
1. Fill system only a er ensuring the water meets the
requirements of this manual.
2. Close automatic and manual air vents and boiler drain
valve.
3. Fill to correct system pressure. Correct pressure will vary
with each application.
a. e minimum cold water ll pressure for a system is
12 psi.
b. Pressure will rise when the boiler is turned ON and
system water temperature increases.
4. At initial ll and during boiler startup and testing, check
the system thoroughly for any leaks. Repair all leaks before
proceeding further.
Purge air from water system
1. Purge air from system:
a. Connect a hose to the purge valve (see purge/drain
valve in the piping diagrams on pages 42 through 47).
Route the hose to an area where water can drain and be
seen.
b. Close the boiler or system isolation valve between the
purge valve and ll connection to the system.
c. Close zone isolation valves.
d. Open the quick- ll valve on the cold water makeup
line.
e. Open purge valve.
f. Open the isolation valves one zone at a time. Allow
water to run through the zone, pushing out the air.
Run until no noticeable air ow is present. Close
the zone isolation valves and proceed with the next
zone. Follow this procedure until all zones are purged.
g. Close the quick- ll water valve and purge valve and
remove the hose. Open all isolation valves. Watch that
system pressure rises to correct cold- ll pressure.
h. A er the system has operated for a while, eliminate
any residual air by using the manual air vents located
throughout the system.
i. If purge valves are not installed in the system, open the
manual air vents in the system one at a time, beginning
with the lowest oor. Close the vent when water
squirts out. Repeat with remaining vents.
2. Open the automatic air vent (diaphragm-type or bladder
type expansion tank systems only) one turn.
3. Open other vents:
a. Starting on the lowest oor, open air vents one at a
time until water squirts out.
b. Repeat with remaining vents.
4. Re ll to correct pressure.
58
Page 59

10 Start-up (continued)
Installation & Operation Manual
Check for gas leaks
WARNING
WARNING
Figure 10-1 Condensate Trap
Before starting the boiler, and during
initial operation, smell near the oor and
around the boiler for gas odorant or any
unusual odor. Remove the top access
panel and smell the interior of the boiler
enclosure. Do not proceed with startup
if there is any indication of a gas leak.
Use an approved leak detection solution.
Repair any leaks at once.
DO NOT adjust gas valve outlet pressure.
e gas valve is factory set for the correct
outlet pressure. is setting is suitable
for natural gas and propane, requiring
no eld adjustment. Attempting to
alter the gas valve outlet pressure could
result in damage to the valve, causing
potential severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
WARNING
Propane boilers only – Your propane
supplier mixes an odorant with the propane
to make its presence detectable. In some
instances, the odorant can fade, and the
gas may no longer have an odor. Before
startup (and periodically therea er), have
the propane supplier verify the correct
odorant level in the gas.
Check thermostat circuit(s)
1. Disconnect the two external wires connected to each
of the heat/loop demand terminals on the connection
board.
2. Connect a voltmeter across these two incoming wires.
Close each thermostat, zone valve, and relay in the
external circuit one at a time and check the voltmeter
reading across the incoming wires.
3. ere should NEVER be a voltage reading.
4. If a voltage does appear under any condition, check and
correct the external wiring. ( is is a common problem
when using 3-wire zone valves.)
FRONT VIEW
TO FLOOR DRAIN
OR NEUTRALIZER KIT
1/2” PVC / CPVC CONNECTION
REAR VIEW
FROM CONDENSATE
VENT ON BOILER
FROM CONDENSATE
DRAIN ON BOILER
DIR #2000507911 00
5. Once the external thermostat circuit wiring is checked
and corrected if necessary, reconnect the external
thermostat circuit wires to the connection board. Allow
the boiler to cycle.
Inspect condensate system
Inspect/check condensate lines and fi ttings
1. Inspect the condensate drain line, condensate PVC
ttings and condensate trap.
59
Page 60

10 Start-up
Final checks before starting the boiler
Installation & Operation Manual
Check vent piping and air piping
Read the FTXL Service Manual to familiarize yourself with
SMART SYSTEM control module operation. Read this
manual, page 61 for proper steps to start boiler.
Verify the boiler and system are full of water and all system
components are correctly set for operation.
Verify the preparation procedures of Section 10, pages 57
through 59 have been completed.
Verify electrical connections are correct and securely
attached.
Inspect vent piping and air piping for signs of deterioration
from corrosion, physical damage or sagging. Verify air
piping and vent piping are intact and correctly installed
per this manual.
Start the boiler
1. Read and follow the Operating instructions in FIG. 10-2,
page 61.
If boiler does not start correctly
1. Check for loose connections, blown fuse or service switch
o ?
2. Is boiler water temperature above 200°F (93°C)?
3. Is thermostat set below room temperature?
4. Is gas turned on at meter or boiler?
1. Check for gastight seal at every connection, seam of air
piping, and vent piping.
WARNING
Check gas piping
1. Check around the boiler for gas odor following the
procedure on page 48 of this manual (connecting gas
supply piping).
WARNING
Propane boilers – verify conversion
1. Verify propane conversion has been completed per the
Propane Conversion instructions.
WARNING
Venting system must be sealed gastight
to prevent ue gas spillage and carbon
monoxide emissions, which will result in
severe personal injury or death.
If you discover evidence of any gas leak,
shut down the boiler at once. Find the
leak source with a bubble test and repair
immediately. Do not start the boiler again
until corrected. Failure to comply could
result in severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
DO NOT adjust gas valve outlet pressure.
e gas valve is factory-set for the correct
outlet pressure. is setting is suitable
for natural gas and propane, requiring
no eld adjustment. Attempting to
alter the gas valve outlet pressure could
result in damage to the valve, causing
potential severe personal injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
5. Is incoming gas pressure less than 4 inches w.c. (.99 kPa)?
If none of the above corrects the problem, refer to the
Troubleshooting Section of the FTXL Service Manual.
Check system and boiler
Check water piping
1. Check system piping for leaks. If found, shut down the
boiler and repair immediately. (See WARNINGS on pages
57 - 59 (startup) regarding failure to repair leaks.)
2. Vent any remaining air from the system using manual
vents. Air in the system will interfere with circulation and
cause heat distribution problems and noise.
60
WARNING
FTXL boilers are typically shipped ready
to re on natural gas. Check boiler rating
plate to determine which fuel the boiler
is set for. If set to natural gas, it may be
converted to LP by installing a LP venturi
or by making a gas valve adjustment (see
pages 14 and 15). In order to operate on
LP gas, a LP venturi MUST BE installed
or a gas valve adjustment MUST BE made.
Failure to comply could result in severe
personal injury, death, or substantial
property damage.
Check fl ame and combustion
1. Turn the main power o to the boiler by placing the
“On/O ” switch in the OFF position.
2. Remove the brass plug from the combustion
measurement port inside the ue collector. NOTE:
Combustion measurements will be made at this point.
3. Turn the main power on to the boiler by placing the
“On/O ” switch in the ON position.
Page 61

C
10 Start-up (continued)
Figure 10-2 Operating Instructions
FOR YOUR SAFETY READ BEFORE OPERATING
WARNING: If you do not follow these instructions exactly, a fire or explosion
may result causing property damage, personal injury, or loss of life.
Installation & Operation Manual
A. This appliance does not have a pilot. It is
equipped with an ignition device which
automatically lights the burner. Do not
to light the burner by hand.
B. BEFORE OPERATING smell all around
the a pp lia nce area fo r gas. Be s ure to
smell next to the floor because some gas
is heavier than air and will settle on the
floor.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
•
D o not tr y to light an y ap p liance.
•
Do not touch any electric switch; do
not use any phone in your building.
try
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
1. STOP!
above on this label.
2. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
3. Turn off all electric power to the
appliance.
4. This appliance is equipped with an
ignition device which automatically lights
the burner. Do not try to light the burner
by hand.
5. R emove top cover.
6. Turn gas shutoff valve counterclockwise
to “OFF”. Handle will be perpendicular to
pipe. Do not force.
7. Wait five (5) minutes to clear out any gas.
If you then smell gas, ST OP! Follo w “B”
in the safety information above this label.
If you don’t smell gas, go to next step.
Read the safety information
Immediately call your gas supplier from a
•
neighbor’s phone. Follow the gas supplier’s
instructions.
If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call
•
the fire department.
C. Use only your hand to turn the gas control knob.
Never use tools. If the handle will not turn by
hand, don’t try to r epai r it, call a qualified service
technician. Fo rce or att empted repa ir may
resul t in a f ire or explosi on .
D. Do not use this appliance if any part has been
under water. Immediately call a qualified
service technician to inspect the appliance and
to replace any part of the control s ystem and
any gas control which has been under water.
8. Turn gas shutoff valve clockwise to “ON”.
Handle w ill be parallel to pipe.
9. Install top cover.
10. Turn on a ll electric power to appl ian ce .
11. Set thermostat to desired setting.
12. If th e appliance will not operate, follow the
instructions “To T urn Off Gas To Appliance” and
call your service technician or gas supplier.
TO TURN OFF GAS TO APPLIANCE
1. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
2. Turn off all electric power to the appliance
if service is to be performed.
3. R emove top cover.
4. Turn gas shut off valve counterclockwise to
“OFF” . Handle will be per pendicular to pipe.
Do not force
5. Install top cover.
LBL 2284 REV
61
Page 62

10 Start-up
Installation & Operation Manual
Check fl ame and combustion (continued)
4. Place the boiler into the active position by pressing the
RIGHT SELECT [ON] key (FIG. 11-1, page 71).
5. Locate the pinhole button above the RESET button on
the display board (FIG. 11-1). Insert a thin wire (such as
a paper clip) into the hole and press the button once and
hold for 5 seconds to place the boiler into Service Mode.
In Service Mode the boiler will re at ignition speed and
will then modulate up to full re.
6. Insert the probe from a combustion analyzer into the
combustion measurement port (see FIG. 10-3). ere
is a stop underneath the combustion measurement port
to prevent the probe from collecting condensate at the
bottom of the ue collector.
7. Once the boiler has modulated up to full re, measure
the combustion. e values should be in the range listed
in Table 10A below. e CO levels should be less than
150 ppm for a properly installed unit.
If the combustion is not within the speci ed range,
reference the Troubleshooting Section of the FTXL
Service Manual for possible causes and corrective actions.
Figure 10-3 Combustion Measurement Port
Set space heating operation
Determine controlling sensor
For space heating systems, the temperature control can be
based on one of three sensors; the inlet, outlet, or system
supply sensor. e SMART SYSTEM control is programmed
at the factory to control the temperature of the outlet
sensor. e control will automatically switch to the system
supply sensor once it is connected. If it is desired to base
the temperature control on the inlet sensor, the appropriate
parameter must be changed in the control. See the FTXL
Service Manual for a detailed explanation of this procedure.
Verify space heat circulator mode
e Space Heating Mode controls both the system pump
(if connected), and the boiler pump. When the SMART
SYSTEM control receives a space heating call for heat, it
turns on the system pump. If the set point is not met, or
the system sensor is not connected, it also turns on the
boiler pump. A er the space heating call for heat ends, the
system pump continues to run for a short period of time.
e system pump can be programmed to run continuously,
except during outdoor shutdown. Other settings may a ect
the operation of the boiler and system pumps, as explained
on the following pages. If the boiler pump was running, it
continues to run for a short period of time as well. ese
pump delays are factory set to 30 seconds. If di erent delays
are desired, the appropriate parameters in the control must
be changed. See the FTXL Service Manual for a detailed
explanation of this procedure.
IMG00978
COMBUSTION MEASUREMENT
PORT
Table 10A Flue Products Chart
Natural Gas Propane
CO
2
8.0% - 10% 3.0% - 6.5% 9.0% - 11% 4.1% - 6.9%
O
2
CO
2
O
2
8. Once the combustion analysis is complete, test the
safety shuto device by turning the manual shuto
valve to the OFF position and ensuring that the boiler
shuts down and registers an alarm. Turn the manual
shuto switch to the ON position and reset the control.
9. Turn the main power o to the boiler and replace the
plug in the ue sample port.
10. Place the boiler back into normal operation.
WARNING
You must replace the plug in the ue
sample port to prevent ue gas spillage
into the room. Failure to comply could
62
result in severe personal injury, death,
or substantial property damage.
Adjust set point temperature(s)
NOTICE
Please note that the brackets ([]) denote
screen status.
e NAVIGATION dial may be used during normal
operation to adjust the space heating and tank set point
temperatures.
1. From the Status Screen press the NAVIGATION dial.
2. Turn the NAVIGATION dial counterclockwise to select
the appropriate set point.
3. Press the NAVIGATION dial to adjust the temperature.
Rotate the NAVIGATION dial to change the setting.
4. Once the desired temperature is displayed, press the
RIGHT SELECT [SAVE] key.
5. If necessary repeat Steps 3 and 4 to make adjustments to
additional set points.
6. Press the RIGHT SELECT [HOME[ key to upload the
changes.
7. If the RIGHT SELECT [SAVE] key is not pressed, the
new settings will be discarded.
Page 63

10 Start-up (continued)
Set domestic hot water (DHW) operation
Verify DHW mode
Installation & Operation Manual
ere are two (2) modes of operation for DHW. In Normal
Mode, when a DHW demand begins, the control will start
the DHW pump, turn o the boiler pump (if running), and
modulate to bring the outlet temperature to the DHW boiler
set point. e maximum ring rate may be limited in this
mode if desired.
In Zone Mode it is assumed that the indirect DHW tank is
piped as a zone on the primary loop. When a DHW demand
begins, the control will turn on the DHW pump output, and
raise the system temperature set point to the DHW boiler set
point (if higher). e boiler pump will be turned on. e
system pump may be forced on, forced o , or not changed,
depending on the System Pump Mode selected (reference
the FTXL Service Manual for details). In this mode, any
low temperature zones (such as radiant heating) may need
additional controls to limit the water temperature sent to
those zones.
Set DHW boiler target temperature
When in the DHW Mode, the control will modulate to
maintain the boiler outlet temperature or system supply
temperature to a set point. is set point is set at the factory
to 180°F. If a di erent set point is desired, the appropriate
parameter in the control must be changed. See the FTXL
Service Manual for a detailed explanation of this procedure.
Set maximum DHW fan speed
If the rated input of the indirect tank is less than the maximum
output of the boiler, change the maximum DHW fan speed
setting to limit the boiler output accordingly. See the FTXL
Service Manual for a detailed explanation of this procedure.
Set clock
NOTICE
e SMART SYSTEM control has a built-in clock that it
uses for its night setback feature and for logging events. is
clock must be set when the boiler is installed, and anytime the
boiler has been powered o for more than 4 hours. Use the
following procedure to set the clock:
1. Press and hold the LEFT SELECT [MENU] key for at
least 5 seconds.
2. The display changes to read [PASSWORD],
with four (4) zeros below it.
3. Press the RIGHT SELECT [SAVE] key.
4. e display will then show a menu with the time and
date and temperature unit.
5. Press the NAVIGATION dial twice.
6. Turn the NAVIGATION dial to adjust the hours. Press
the NAVIGATION dial.
Please note that the brackets ([]) denote
screen status.
7. Turn the NAVIGATION dial to adjust the minutes. Press
the NAVIGATION dial.
8. Turn the NAVIGATION dial to adjust the month. Press
the NAVIGATION dial.
9. Turn the NAVIGATION dial to adjust the date. Press the
NAVIGATION dial.
10. Turn the NAVIGATION dial to adjust the year. Press the
RIGHT SELECT [SAVE] key.
11. Press the RIGHT SELECT [HOME] key.
NOTICE
e clock is automatically updated whenever a PC is connected
and the Win_Pro-Installer program is started.
Confi guration of the cascade
NOTICE
When installed in a Cascade system, the individual controls must
be programmed for cascade operation. is is accomplished by
accessing the control parameters.
Press the [MENU] key for at least ve (5) seconds. Input
the Installer code as described in the FTXL Service Manual.
Once the control parameters have been accessed, use the
NAVIGATION DIAL to select the Control Mode parameters.
Press the NAVIGATION DIAL to access these parameters.
Rotate the NAVIGATION dial to select the parameter
“Cascade Address”. Press the NAVIGATION dial to access
this parameter. Each appliance in the Cascade system must be
programmed with its own address. e boiler designated as the
Leader will have an address of 0. e remaining boilers in the
Cascade will be Members and have addresses from 1 - 7. Rotate
the NAVIGATION dial to select the appropriate address. Press
the RIGHT SELECT SAVE key.
Press the RIGHT SELECT HOME key to upload the address
into the control. Repeat this procedure for all boilers in the
Cascade, designating the Leader control and the Member
controls.
e internal clock does not adjust for
Daylight Savings Time and therefore, will
require a manual adjustment.
Please note that the brackets ([]) denote
screen status.
63
Page 64

11 Operating information
General
How the boiler operates
e FTXL uses an advanced stainless steel heat exchanger
and electronic control module that allows fully condensing
operation. e blower pulls in air and pushes ue products
out of the boiler through the heat exchanger and ue piping.
e control module regulates blower speed to control the
boiler ring rate. e gas valve senses the amount of air
owing into the boiler and allows only the right amount of
gas to ow.
Installation & Operation Manual
SMART SYSTEM Multi-temp loop control
e FTXL boiler is capable of producing up to three (3) set
point temperatures to meet di erent space heating demands.
is device controls the temperatures of up to three (3) separate
loops, based on the settings for the three (3) heat/loop demands
(reference Lochinvar kit 100167843).
How the control module operates
e SMART SYSTEM control module receives inputs from
boiler sensors and external devices. e control module
activates and controls the blower and gas valves to regulate
heat input and switches the boiler, Domestic Hot Water
(DHW), DHW recirculation, and system pumps on and o
as needed. e user programs the module to meet system
needs by adjusting control parameters. ese parameters set
operating temperatures and boiler operating modes. Boiler
operation can be based on boiler outlet water temperature,
boiler inlet water temperature, system temperature, a 0 - 10V
signal, Modbus, or BACnet, depending on the parameter
settings.
Control inputs and outputs
Room thermostat
ere are three (3) heat/loop demand connections available
on this control. ese inputs tell the boiler to provide water
for space heating. Each demand connection has its own set
point and outdoor air reset curve. When multiple demands
have a call for heat the control will give priority to the
demand with the highest set point.
Example: Assume that both heat/loop demand 1 and heat/
loop demand 2 have a call for heat. Demand 1 has a set point
of 110°F. Demand 2 has a set point of 140°F. e boiler will
regulate the system temperature to 140°F until Demand 2 has
been satis ed. Once Demand 2 has been satis ed the boiler
will provide 110°F water to the system.
CAUTION
When multiple temperature loops are
used, mixing valves are required for the
protection of any low temperature loops.
0 - 10V input (set point or power)
e FTXL can be controlled by a Building Management System
(BMS) using a 0 - 10 VDC signal. e control can be con gured
by the installer to use this signal to either control set point or
ring rate.
e FTXL can also be programmed to accept a call for heat
from a 0 - 10V signal, reference the FTXL Service Manual for a
detailed explanation of this procedure.
DHW priority
e SMART SYSTEM control allows the connection of a DHW
thermostat or tank sensor to the low voltage connection board.
When a tank sensor is connected, the DHW thermostat input
is ignored. When a boiler is programmed for DHW Normal
Mode, the maximum ring rate can be limited to match the
input rating of the indirect tank coil.
DHW / space heating (SH) cycling
If a DHW call for heat is received while a space heating call is
in progress, and the DHW is in Normal Mode, the control will
start the DHW pump and shut the boiler pump o . e system
pump will remain on. For stand-alone boilers, if the space
heating call is still active while the DHW call is in operation,
the control will wait for 30 minutes (time adjustable by installer)
then it will switch back to the space heating demand. ere is
a timer to switch from space heating to DHW and a timer to
switch from DHW to space heating. e control will switch
back and forth until one of the heat demands end. is function
does not apply to cascade systems.
64
Page 65

Installation & Operation Manual
11 Operating information (continued)
Programmable controlling sensor
e control module is programmed to use the outlet
sensor as the control sensor by default. If a system supply
sensor is connected, the control automatically uses it as
the control sensor. For stand-alone boilers, the control
sensor can be changed by the installer to the inlet sensor.
If the inlet sensor is chosen as the controlling sensor, it is
recommended that the system supply sensor be installed in
the system supply in order to provide the best control of
the inlet temperature.
Anti-cycling
A er the burner turns o , the control will delay the next
burner cycle for a set time period (time is adjustable by the
installer). e time delay will be bypassed if the inlet water
temperature drops too far during the delay.
Boiler and system pump control
e boiler pump will run whenever the burner is ring,
unless the DHW is programmed for Normal Mode and the
boiler is heating the DHW tank. e boiler pump will run
during Freeze Protection Mode as well. It will continue to
run for a short time a er the burner turns o or the Freeze
Protection Mode ends.
e system pump will run whenever there is a space
heating call for heat, or the boiler goes into Freeze
Protection Mode. It may be programmed to run during
a DHW call for heat when the DHW is programmed for
Zone Mode. It will continue to run for a short time a er
the end of the heat demand or the Freeze Protection Mode.
e system pump can be programmed to run continuously
if desired, except during outdoor shutdown and/or a
DHW call for heat.
DHW recirculation pump control
When a DHW recirculation loop is used, the FTXL boiler
can control the recirculation pump. To activate this
function, simply install the DHW recirculation sensor into
the return water from the DHW circulation loop. e
control will turn on the DHW recirculation pump when
the return water drops 10°F (5.5°C) below the DHW tank
set point, and will turn back o when the return water
rises to within 5°F (2.5°C) of the DHW tank set point.
e control will turn the DHW recirculation pump o
whenever DHW night setback is active.
Temperature control
Modulation
e FTXL is capable of modulating its ring rate from a
minimum of 10% to a maximum of 100%. e ring rate is
dictated by the call for heat (i.e., space heating or domestic hot
water), the heating load, ramp delay (if enabled), and various
other temperature limitations.
Ramp delay
For systems with lower ow, the SMART SYSTEM can limit
the ring rate (when enabled) when a space heating call for heat
starts, when the set point is controlled by the BMS, or when
switching from a DHW call for heat to a space heating call for
heat. ere are six (6) limits that can be programmed, as well
as six (6) time intervals corresponding to each limit. e sixth
limit will also limit the ring rate for the rest of the call for heat.
Gradient limiting
If during operation of the boiler the outlet water temperature
is rising too quickly, the control will reduce the ring rate to its
lowest setting.
Outdoor air reset
If an outdoor air sensor is connected, the control module will
calculate the set points of the three (3) space heating demands
based on the programmed reset curves. e installer can change
the slope of the reset curves by several adjustable parameters.
e user can limit the maximum set points for each demand
using the space heating set points.
Boost function
If outdoor air reset is active, and any space heating demand
has been active continuously for a set period of time (time
adjustable by installer) and there has been no DHW demands,
the control can increase the set point of that demand by a
xed number of degrees (adjustable by installer). is process
will continue until the space heating demand ends, the set
point reaches the programmed set point or a maximum of
20 increases has occurred. Once the system heat demand is
satis ed, the set point will revert to the value determined by the
reset curve.
65
Page 66

11 Operating information
Installation & Operation Manual
Night setback
e controller may be programmed to reduce the space heating
and DHW set points during certain times each week. Seven
di erent start and stop times may be programmed for the space
heating setback and seven start and stop times for the DHW
setback.
Vacation mode
Vacation Mode is used to lower the Space Heat (SH) and/or
DHW set points much like night setback. e set points will
remain lowered until Vacation Mode is disabled. Night setback
will not function when Vacation Mode is enabled.
Flame current support
To prevent nuisance shutdowns when the boiler is ring at
minimum rates, the control will increase the ring rate when
the ame signal drops too low.
Freeze protection
DO NOT install the boiler in a room likely to freeze.
e following integral feature of the SMART SYSTEM control
module provides some protection for the boiler only -- not for
the system.
• e SMART SYSTEM control module provides
freeze-up protection as follows when the boiler
water temperature drops below 45°F (7°C):
• Below 45°F (7°C), the boiler and system pumps
operate constantly.
• Below 37°F (3°C), the boiler turns on.
• Boiler and pumps turn off if boiler water
temperature rises above 45°F (7°C).
• Lower temperatures may be programmed for systems
with anti-freeze solutions.
NOTICE
When system return temperatures
are maintained below the dew point,
condensation will form on the inside of the
boiler jacket causing some internal sheet
metal components to rust.
Protection features
Outlet temperature, fl ue temperature, and temperature
rise limiting
e outlet temperature is monitored by the boiler outlet
temperature sensor. When the outlet temperature exceeds
185°F, the unit will reduce the fan speed. If the outlet water
temperature exceeds 195°F (90°C) the control will shut the unit
down until it cools o .
e control module monitors the ue temperature by a sensor
located in the ue exhaust. If the ue temperature exceeds
215°F (102°C) the control will reduce the maximum fan speed.
If the ue temperature exceeds 225°F (107°C) the control will
shut the unit down. e unit will restart automatically once the
ue temperature drops 10°F (6°C) and the minimum o time
has expired.
e control monitors the temperature di erence between
the inlet and the outlet sensor. If this di erence exceeds 70°F
(39°C) the control will reduce the maximum fan speed. If the
temperature di erence exceeds 80°F (44°C) the control will
shut the unit down. e unit will restart automatically once the
temperature di erence has dropped below 70°F (39°C) and the
minimum o time has expired.
CAUTION
Low voltage blocking
e blower and gas valve require a minimum amount of
voltage in order to operate properly. If an ignition attempt is
made when the line voltage is temporarily low (such as during
a brownout), the control could enter a manual reset lockout.
To prevent this, the control monitors the voltage and blocks
any heat demands until the voltage returns to an acceptable
level.
is feature of the SMART SYSTEM
control module does not eliminate the
possibility of freezing. e installation must
still use recognized design, installation and
maintenance practice to prevent freeze
potential for the boiler and system.
66
Page 67

Installation & Operation Manual
11 Operating information (continued)
Monitor external limits
Connections are provided on the connection board for
a ow switch and a louver proving switch. e SMART
SYSTEM will shut o the burner and inhibit relighting
whenever either of these external limits open.
Run-time and alarm outputs
e boiler provides dry contacts for indicating when the
boiler is running, and when it is unable to operate.
Run-time and cycle counting
e control uses two timers to monitor the total hours of
burner operation. One timer monitors the time the boiler
is in the Space Heating Mode. e other timer monitors the
time the boiler is ring in the DHW Mode.
e control uses two (2) ignition counters to monitor
the amount of boiler cycles. e rst counter counts all
ignitions of the control. e second counter counts only
ignition attempts that have failed.
Service reminder
e control can be programmed for service reminder
noti cation. is noti cation will become active when
either a set time frame has expired, or a set amount of
running hours or cycles has expired (all adjustable by the
installer). e display will show a Maintenance Required
screen. e installer’s name and phone number can be
programmed into the control. is information will appear
on the Maintenance Required screen. e service reminder
noti cation can be reset or disabled by the installer.
Error logging
e control will hold in memory the last 10 lockouts. e
date and time of the occurrence will be recorded as well.
Only the 10 most current occurrences will be held in
memory.
Boiler temperature regulation
Operating temperature (target)
e SMART SYSTEM control module senses water
temperature and regulates boiler ring and ring rate to
achieve a target temperature. e target temperature can
be set between 32°F (0°C) and 190°F (88°C).
• Target temperature is xed when the outdoor
sensor is not installed.
• Target temperature is calculated as described
on this page under “Outdoor Reset Operation”
and “Target Temperature Boost” when the
outdoor sensor is connected.
High limit operations
e FTXL is equipped with adjustable automatic reset and
manual reset high limits. e automatic reset high limit has a
maximum set point of 200°F and the manual reset high limit
has a maximum set point of 210°F.
When the outlet temperature exceeds 200°F, the automatic
high limit action occurs. e boiler shuts down until the outlet
water temperature cools below 190°F, and a 60 second timer
has expired. If the outlet temperature continues to increase, the
manual reset high limit action will occur at 210°F.
High limit test procedure
NOTICE
1. Turn ON the main power to the boiler by placing the
ON/OFF switch in the ON position.
2. From the Status Screen, press the NAVIGATION dial to
access the Set Points Screen.
3. Press the LEFT SELECT (LIMITS) key.
4. Select the manual reset high limit (MRHL) by rotating
the NAVIGATION dial counterclockwise, then press
the NAVIGATION dial.
5. Decrease the set point of the MRHL to below the current
outlet temperature (or to its minimum setting, whichever
is higher) by turning the NAVIGATION dial
counterclockwise.
6. Press the RIGHT SELECT [SAVE] key.
7. Press the RIGHT SELECT [HOME] key. e new
parameter will upload to the control.
8. If the current outlet temperature is above the new MRHL
set point, the MRHL will function causing boiler lockout.
If this occurs, skip to Step 11.
9. If the current outlet temperature is below the new MRHL
set point, locate the pinhole (SERVICE button) below the
RESET button on the display board. Insert a thin probe
(such as a paper clip) into the hole and press the button
continuously for ve (5) seconds to place the boiler into
Service Mode. In Service Mode, the boiler will re at
ignition speed and will then modulate up to full re.
10. Once the outlet temperature rises up to the MRHL set
point, the MRHL will function, causing the boiler to shut
down and lock out.
11. Repeat Steps 2 through 7 to adjust the MRHL to its normal
setting.
Please note that the brackets ([]) denote
screen status.
67
Page 68

11 Operating information
Installation & Operation Manual
Low water cutoff protection
1. e SMART SYSTEM control module uses temperature
sensing of both supply and return areas of the heat
exchanger. If the ow rate is too low or the outlet
temperature too high, the control module modulates and
shuts the boiler down. is ensures boiler shutdown in
the event of low water or low ow conditions.
2. In addition, an electronic low water cuto control is
provided.
Outdoor reset operation, if used
Target temperature with outdoor reset
is feature improves the system’s e ciency as the outdoor
temperature warms up.
See the FTXL Service Manual to change the settings.
Reset curve
e reset curves look at outdoor air temperature and adjust
the set points.
Cascade
When multiple boilers are installed, they can be wired
together in a cascade sequence. A maximum of eight boilers
can be controlled from a single control. In this application
one boiler would be designated as the Leader control and all
others would be designated as Member controls. Member
1 can be con gured to take over control of the Cascade
should the Leader stop communicating with the Members.
e Leader control can be programmed to use Lead/Lag or
E ciency Optimization control methods.
Sequence of the cascade
To equalize the run time of all boilers on the Cascade, the ring
sequence will automatically be changed at set intervals.
For the rst 24 hours, the sequence will be changed once every
hour. e switching on/o sequence will be as follows:
TIME SWITCHING ON SEQUENCE
Start L-M1-M2-M3-M4-M5-M6-M7
1 hour M1-M2-M3-M4-M5-M6-M7-L
2 hours M2-M3-M4-M5-M6-M7-L-M1
A er the rst 24 hours, the sequence will change every night
at 2:00 a.m. If a boiler locks out or is used to heat an indirect
DHW tank, it will automatically be given the lowest priority
until 2:00 a.m.
DHW, Night Setback, and Ramp Delay operation with
cascade
For normal mode DHW operation any boiler(s) in the Cascade
can be selected to provide heat for a DHW call. Select a boiler
to be designated as the DHW boiler. Connect the DHW
thermostat or sensor to the terminals on the Low Voltage
Connection Board marked for the corresponding device. When
the boiler receives a DHW call, the Leader control will take that
boiler out of the Cascade sequence. If another boiler is available,
the Leader will start it up to take its place.
e DHW boiler will adjust its set point to the programmed
DHW boiler set point and will adjust its ring rate to maintain
this. Once the DHW call has been satis ed, the Leader control
will place that boiler back into the Cascade sequence.
Once the Leader boiler receives a call for heat from a room
thermostat, BMS, Modbus, or BACnet the control will
determine what the set point will be. If outdoor air reset is
desired, connect the outdoor air sensor to the terminals on
the Low Voltage Connection Board on the Leader boiler. e
set point will be calculated based on the programmed reset
curve parameters. See the FTXL Service Manual to program
the reset curve. If outdoor air reset is not desired, do not
connect the outdoor air sensor. A xed temperature set point
can be programmed into the control. See page 62 of this
manual to program the set point.
If the water temperature at the system supply sensor is less
than the set point + the turn-o o set - the o -on di erential,
then the control will initiate a call for heat on the Cascade
(see the FTXL Service Manual for an explanation of the o set
and di erential). e Leader will energize the lead boiler on
the Cascade. For a new startup this will be the Leader boiler.
68
Switching of the boiler between DHW operation and SH
operation when there is a call for both does not occur in Cascade
Mode.
When DHW is programmed for Zone Mode, connect the DHW
thermostat or tank sensor to the Leader boiler. When a DHW
call is received, the Leader will modulate the entire Cascade to
bring the system supply temperature up to the DHW boiler set
point (if higher).
Night Setback operation of the boilers within the Cascade is
available. Programming of the Night Setback will be done
through the Leader boiler. Refer to the FTXL Service manual for
information regarding Night Setback.
Ramp Delay operation of the boilers as described in the FTXL
Service Manual is available when the boilers are part of a
Cascade system.
Page 69

Installation & Operation Manual
11 Operating information (continued)
Sequence of operation
OPERATION DISPLAY
1. Upon a call for heat, the gas pressure switch(es) must be closed.
2. Once the gas pressure switch(es) are closed, the control turns
on the appropriate pumps (system and boiler pumps for space
heating, DHW pump for DHW). The fl ow switch and/or LWCO
must close.
3. The control turns on power to the louver relay. The louver
proving switch, and blocked drain switch must close.
4. The control starts the prepurge cycle by initiating the blower.
5. The control starts the trial for ignition by fi ring the spark
electrode and opening the gas valve.
6. If fl ame is not detected after the sparking ends, the control will
perform a postpurge, then start another prepurge cycle and try
to light the burner again. On the 500 and larger models, the control
will lock out if this second attempt also fails. On the 400 model,
the control will perform a total of 4 attempts before locking out.
69
Page 70

11 Operating information
Sequence of operation
OPERATION DISPLAY
7. If fl ame is detected, it holds the fi ring rate steady for a few
seconds to let the fl ame stabilize, then it begins to modulate the
fi ring rate based on a set point or some other command (such as
a 0-10V BMS signal).
8. If the space heating call for heat is active, and the tank thermostat
or sensor starts a DHW call for heat, the boiler will switch to the
DHW mode. If programmed for normal DHW operation (not as a
zone), the DHW pump will turn on fi rst, then the boiler pump will
turn off (boiler and DHW pump operation briefl y overlap to ensure
fl ow is maintained through the unit). This will divert the boiler’s
outlet water from the heating system and send it to the tank coil
instead. The control will then modulate to maintain the outlet
temperature to the DHW boiler set point.
Installation & Operation Manual
9. If the boiler is not part of a Cascade, and both the space heating
and DHW calls for heat remain active long enough, the boiler will
switch back and forth between the two heating modes until one of
them is satisfi ed.
10. Once both calls for heat are satisfi ed, the control will turn off
the burner. The blower will continue to run during the postpurge
period.
11. Any pumps that are running will continue to run for their respective
pump delay times before turning off, unless programmed to
remain on continuously. A 60 second anti-cycle period will start,
which will delay any new call for heat until it times out.
12. In Standby, ready to start a new cycle.
70
Page 71

Installation & Operation Manual
Y
11 Operating information (continued)
FTXL control module
Use the control panel (FIG. 11-1) to set temperatures, operating conditions, and monitor boiler operation.
Figure 11-1 Control Panel
USB
DRIVE
PC
CONNECTION
LEFT
SELECT KEY
NAVIGATION
DIAL
IMG01093
RESET
SWITCH
RIGHT
SELECT KE
e information on the bottom of the display shows the functions of the two SELECT keys (on either corner), and the
NAVIGATION dial (in the center):
MENU = Le SELECT Key
SETPOINTS = NAVIGATION Dial - Pressing Down
SHDN = Right SELECT Key
Access modes
User
e user can adjust space heating and tank target temperatures by
pressing the NAVIGATION dial when “SETPOINTS” is ashing at
the bottom of the display. e date and time, and the temperature units
can also be changed (see page 63).
To save parameters and exit programming:
Press the RIGHT SELECT [SAVE] key and then
press the RIGHT SELECT [HOME] key.
To enter a parameter and continue programming:
Press the RIGHT SELECT [SAVE] key 1 time to
return to the parameter listings; press again to
Installer
Most parameters are available only to the installer, accessible by
entering the installer password, see the FTXL Service Manual.
return to the menu listings. Remember to press
the RIGHT SELECT [HOME] key when nished
programming in order to save the changes made.
Saving parameters (reference the Parameter Table in the
FTXL Service Manual)
NOTICE
Please note that the brackets ([]) denote screen
status.
See the FTXL Service Manual for a detailed
description of parameters and access modes.
71
Page 72

11 Operating information
Figure 11-2 Status Display Screen
Installation & Operation Manual
A
(BOILER
STATUS)
B
(CALL FOR
HEAT)
C
(OPERATIONAL
INFORMATION)
D
(LEFT SELECT
KEY)
(RIGHT SELECT KEY)
E
(NAVIGATION DIAL)
Status Display Screens
NOTE: All screens show burner status, heat demands, lockout/blocking, pump status, and so keys.
Section Display Description
STANDBY
START e unit has begun a burn cycle and is checking all safety circuits.
e unit has not received a call for heat from a remote thermostat nor
has it received a call for heat from a DHW thermostat.
F
A
(Boiler Status
Bar)
B
(Call for Heat
Indicators)
PREPURGE e unit has initiated a prepurge period on a call for heat.
IGNITION e unit has begun a spark period to ignite the main burner.
e unit has red and is running at the displayed percentage.
%
e call for heat has been satis ed and the unit runs the fan for an
POSTPURGE
SHUTDOWN e unit has been placed in the OFF position.
SETPOINT MET e controlled temperature has exceeded its set point and its o set.
BLOCKED
additional postpurge period to clear the combustion chamber and
vent system of residual ue products.
e unit has detected a condition that has temporarily interrupted
the current call for heat.
Room ermostat 1 has a call for heat.
Room ermostat 2 has a call for heat.
Room ermostat 3 has a call for heat.
e tank thermostat or sensor has a call for heat.
Indicates which room thermostat demand has priority.
e unit is being controlled by a 0 - 10V BMS signal.
e member unit is supplying heat while in Cascade Mode.
72
Page 73

Installation & Operation Manual
11 Operating information (continued)
Status Display Screens (cont’d)
NOTE: All screens show burner status, heat demands, lockout/blocking, pump status, and so keys.
Section Display Description
a. SYSTEM TEMP
b. TANK TEMP
c. OUTDOOR TEMP
DETAILS SCREEN 1
DETAILS SCREEN 2
d. INLET TEMP
e. OUTLET TEMP
f. DHW RECIRC TEMP - e temperature read by the DHW
recirculation sensor (if connected).
a. DELTA T
b. FLUE TEMP
c. FLAME CURRENT
d. FAN SPEED
e. LOOP 1 TEMP - e temperature of Loop 1 reported by the
MTLC control.
f. LOOP 2 TEMP - e temperature of Loop 2 reported by the
MTLC control.
g. LOOP 3 TEMP - e temperature of Loop 3 reported by the
MTLC control.
C
(Operational
Information)
I/O SCREEN
BMS SCREEN
HISTORY SCREEN
LAST 10 FAULTS
a. GAS PRESS SW - e state of the gas pressure switch.
b. FLOW SW - e state of the ow switch.
c. LOUVER RELAY - e state of the louver relay output.
d. LOUVER SW - e state of the louver proving switch.
e. BLOCKED DRAIN - e state of the blocked drain switch.
f. GAS VALVE - e state of the gas valve output.
a. 0 - 10V BMS IN
b. 0 - 10V RATE OUT
c. BMS ADDRESS
d. BMS CONTROL?
e. SYS PUMP SPEED
f. BLR PUMP OUT
a. SH RUN TIME - Total time running for Space Heat (SH).
b. SH CYCLES - Total Space Heat (SH) demand cycles.
c. DHW RUN TIME - Total time running for DHW.
d. DHW CYCLES - Total DHW demand cycles.
e. POWER TIME - Total time powered ON.
f. IGNITIONS - Total number of successful ignitions.
g. IGN ATTEMPTS - Total number of ignition attempts.
a. FAULT NO.
b. FAULT
c. DATE
d. TIME
73
Page 74

11 Operating information
Status Display Screens (cont’d)
NOTE: All screens show burner status, heat demands, lockout/blocking, pump status, and so keys.
Section Display Description
Installation & Operation Manual
C
(Operational
Information
cont.)
D
(LEFT SELECT
key function)
E
(NAVIGATION
dial function)
F
(RIGHT SELECT
key function)
a. CASCADE STATUS
CASCADE STATUS
NIGHT SETBACK
USB Press the LEFT SELECT key to access the USB and Installer menu.
MODIFY
SHDN Press the RIGHT SELECT key to turn the boiler OFF.
ON Press the RIGHT SELECT key to turn the boiler ON.
NO Press the RIGHT SELECT key to cancel the shutdown operation.
SAVE Press the RIGHT SELECT key to save the current change.
b. CASCADE POWER
c. PRESENT
a. TRIGGER 1 - Next Space Heat (SH) night setback trigger.
b. TRIGGER 2 - Next DHW night setback trigger.
Pressing the NAVIGATION dial will allow the installer to change
the text.
74
HOME
Press the RIGHT SELECT key to return to the Status Screen and
upload parameter changes.
Page 75

Installation & Operation Manual
12 Maintenance
Maintenance and annual startup
Table 12A Service and Maintenance Schedules
Service technician
(see the following pages for instructions)
General:
• Address reported problems
• Inspect interior; clean and vacuum if
necessary;
• Clean condensate trap and fi ll with fresh
water
• Check for leaks (water, gas, fl ue,
condensate)
• Verify fl ue and air lines in good condition
and sealed tight
• Check system water pressure/system
piping/expansion tank
• Check fi ll water meter
• Test boiler water. When test indicates,
clean system water with approved
system restorer following manufacturer’s
information.
• Check control settings
ANNUAL START-UP
• Check ignition and fl ame sense
electrodes (sand off any deposits; clean
and reposition)
• Check wiring and connections
• Perform start-up checkout and
performance verifi cation per Section 10.
• Flame inspection (stable, uniform)
• Flame signal (at least 10 microamps at
high fi re)
• Clean the heat exchanger if fl ue
temperature is more than 54°F (30°C)
above return water temperature.
Owner maintenance
(see the FTXL User’s Information Manual for
instructions)
• Check boiler area
Daily
• Check pressure/temperature
gauge
• Check vent piping
• Check air piping
Monthly
Periodically
Every
6 months
• Check air and vent termination
screens
• Check relief valve
• Check condensate drain system
• Check air vents
• Test low water cutoff
• Reset button (low water cutoff)
• Check boiler piping (gas and
water) for leaks
• Operate relief valve
If combustion or performance
indicate need:
• Clean heat exchanger
• Remove and clean burner using
compressed air only
• Clean the blower wheel
End
of season
months
• Shut boiler down (unless boiler
used for domestic hot water)
75
Page 76

12 Maintenance
Installation & Operation Manual
WARNING
Follow the Service and maintenance procedures given throughout this manual and in component literature
shipped with the boiler. Failure to perform the service and maintenance could result in damage to the boiler
or system. Failure to follow the directions in this manual and component literature could result in severe
personal injury, death, or substantial property damage.
WARNING
e boiler should be inspected annually only by a quali ed service technician. In addition, the maintenance
and care of the boiler designated in Table 12A and explained on the following pages must be performed to
assure maximum boiler e ciency and reliability. Failure to service and maintain the boiler and system could
result in equipment failure.
WARNING
Electrical shock hazard – Turn o power to the boiler before any service operation on the boiler except as
noted otherwise in this instruction manual. Failure to turn o electrical power could result in electrical shock,
causing severe personal injury or death.
Address reported problems
1. Inspect any problems reported by the owner and correct
before proceeding.
Inspect boiler area
1. Verify that boiler area is free of any combustible materials,
gasoline and other ammable vapors and liquids.
2. Verify that air intake area is free of any of the contaminants
listed in Section 1 of this manual. If any of these are
present in the boiler intake air vicinity, they must be
removed. If they cannot be removed, reinstall the air and
vent lines per this manual and the FTXL Service Manual.
Inspect boiler interior
1. Li the top bezel (prop the bezel up for service) and
inspect the interior of the boiler.
2. Vacuum any sediment from inside the boiler and
components. Remove any obstructions.
Clean condensate trap
1. Inspect the condensate drain line, vent line, condensate
PVC ttings, and condensate trap.
Flush condensate trap with water
1. Remove the four (4) screws securing the top cover to the
condensate trap and remove the cover (FIG. 12-1).
2. Locate the plastic ball inside the oat tube. Verify there
is nothing under the ball causing it to not seat properly.
3. Fill with fresh water until the water begins to pour out of
the drain.
4. Replace the top cover and the screws removed in Step 1.
Figure 12-1 Condensate Trap
FROM CONDENSATE
VENT ON BOILER
FROM CONDENSATE
FRONT VIEW
TO FLOOR DRAIN
OR NEUTRALIZER KIT
1/2” PVC / CPVC CONNECTION
REAR VIEW
DRAIN ON BOILER
DIR #2000507911 00
Check all piping for leaks
WARNING
1. Inspect all water and gas piping and verify to be leak free.
2. Look for signs of leaking lines and correct any problems
found.
3. Check gas line using the procedure found in Section 7 -
Gas Connections.
Eliminate all system or boiler leaks.
Continual fresh makeup water will reduce
boiler life. Minerals can build up in sections,
reducing heat transfer, overheating heat
exchanger, and causing heat exchanger
failure. Leaking water may also cause severe
property damage.
76
Page 77

12 Maintenance (continued)
Installation & Operation Manual
Flue vent system and air piping
1. Visually inspect the entire ue gas venting system and air
piping for blockage, deterioration or leakage. Repair any
joints that show signs of leakage. Verify that air inlet pipe
is connected and properly sealed.
2. Verify that boiler vent discharge and air intake are clean
and free of obstructions.
WARNING
Failure to inspect for the above conditions
and have them repaired can result in
severe personal injury or death.
Check water system
1. Verify all system components are correctly installed and
operational.
2. Check the cold ll pressure for the system. Verify it is
correct (must be a minimum of 12 psi (82.7 kPa)).
3. Watch the system pressure as the boiler heats up (during
testing) to ensure pressure does not rise too high.
Excessive pressure rise indicates expansion tank sizing or
performance problem.
4. Inspect automatic air vents and air separators. Remove
air vent caps and brie y press push valve to ush vent.
Replace caps. Make sure vents do not leak. Replace any
leaking vents.
Check expansion tank
1. Expansion tanks provide space for water to move in
and out as the heating system water expands due to
temperature increase or contracts as the water cools.
Tanks may be open, closed or diaphragm or bladder
type. See Section 6 - Hydronic Piping for suggested best
location of expansion tanks and air eliminators.
Check fi ll water meter
1. Check ll water meter for water usage. If the amount
exceeds 5% of your system volume, you could have a
leak. Have the system checked for leaks and xed by a
quali ed service technician.
Test boiler water
1. Test boiler water. Reference the Crest Installation and
Operation Manual for guidelines. When test indicates,
clean system water with approved system restorer
following the manufacturer’s information.
Check boiler relief valve
1. Inspect the relief valve and li the lever to verify ow.
Before operating any relief valve, ensure that it is piped with
its discharge in a safe area to avoid severe scald potential.
Read Section 6 - Hydronic Piping before proceeding
further.
WARNING
WARNING
2. A er following the above warning directions, if the relief
valve weeps or will not seat properly, replace the relief
valve. Ensure that the reason for relief valve weeping is
the valve and not over-pressurization of the system due to
expansion tank waterlogging or undersizing.
Safety relief valves should be re-inspected
AT LEAST ONCE EVERY THREE YEARS,
by a licensed plumbing contractor or
authorized inspection agency, to ensure
that the product has not been a ected by
corrosive water conditions and to ensure
that the valve and discharge line have not
been altered or tampered with illegally.
Certain naturally occurring conditions may
corrode the valve or its components over
time, rendering the valve inoperative. Such
conditions are not detectable unless the
valve and its components are physically
removed and inspected. is inspection
must only be conducted by a plumbing
contractor or authorized inspection agency
– not by the owner. Failure to re-inspect the
boiler relief valve as directed could result in
unsafe pressure buildup, which can result in
severe personal injury, death, or substantial
property damage.
Following installation, the valve lever must
be operated AT LEAST ONCE A YEAR to
ensure that waterways are clear. Certain
naturally occurring mineral deposits may
adhere to the valve, rendering it inoperative.
When manually operating the lever, water
will discharge and precautions must be
taken to avoid contact with hot water and
to avoid water damage. Before operating
lever, check to see that a discharge line is
connected to this valve directing the ow of
hot water from the valve to a proper place
of disposal. Otherwise severe personal
injury may result. If no water ows, valve
is inoperative. Shut down the boiler until a
new relief valve has been installed.
77
Page 78

12 Maintenance
Installation & Operation Manual
Inspect ignition and fl ame sense
electrodes
1. Remove the ignition and ame sense electrodes from the
boiler heat exchanger access cover.
2. Remove any deposits accumulated on the ignition/ ame
sense electrode using sandpaper. If the electrodes cannot
be cleaned satisfactorily, replace with new ones.
3. Replace ignition/ ame sense electrode, making sure
gasket is in good condition and correctly positioned.
Check ignition ground wiring
1. Inspect boiler ground wire from the heat exchanger
access cover to ground terminal strip.
2. Verify all wiring is in good condition and securely
attached.
3. Check ground continuity of wiring using continuity
meter.
4. Replace ground wires if ground continuity is not
satisfactory.
Check all boiler wiring
Figure 12-2 Burner Assembly - Model 400 - 850
FAN TOP PLATE
GASKET
BURNER
GASKET
HEX TOP PLATE
FIBER BOARD
HEAT EXCHANGER
1. Inspect all boiler wiring, making sure wires are in good
condition and securely attached.
Check control settings
1. Set the SMART SYSTEM control module display to
Parameter Mode and check all settings. See Section 1 of
the FTXL Service Manual. Adjust settings if necessary.
See Section 1 of the FTXL Service Manual for adjustment
procedures.
2. Check settings of external limit controls (if any) and
adjust if necessary.
Perform start-up and checks
1. Start boiler and perform checks and tests speci ed in
Section 10 - Start-up.
2. Verify cold ll pressure is correct and that operating
pressure does not go too high.
Check burner fl ame
1. Inspect ame through observation window.
2. If the ame is unsatisfactory at either high re or low re,
turn o boiler and allow boiler to cool down. Remove the
burner and clean it thoroughly using a vacuum cleaner
or compressed air. Do not use compressed air to clean
burner if performed inside a building.
3. Remove the burner, reference FIG. 12-2.
4. When replacing the burner, ensure gasket is in good
condition and positioned correctly (FIG. 12-2).
IMG01072
78
Page 79

12 Maintenance (continued)
Installation & Operation Manual
Check fl ame signal
1. At high re the ame signal shown on the display should
be at least 10 microamps.
2. A lower ame signal may indicate a fouled or damaged
ame sense electrode. If cleaning the ame sense electrode
does not improve, ground wiring is in good condition,
and ground continuity is satisfactory, replace the ame
sense electrode.
3. See Section 3 - Troubleshooting in the FTXL Service
Manual for other procedures to deal with low ame
signal.
Review with owner
1. Review the FTXL User’s Information Manual with the
owner.
2. Emphasize the need to perform the maintenance schedule
speci ed in the FTXL User’s Information Manual (and in
this manual as well).
3. Remind the owner of the need to call a licensed contractor
should the boiler or system exhibit any unusual behavior.
4. Remind the owner to follow the proper shutdown
procedure and to schedule an annual start-up at the
beginning of the next heating season.
7. Disconnect the condensate hose from the condensate trap
and route to drain.
8. Use a vacuum cleaner to remove any accumulation on the
boiler heating surfaces. Do not use any solvent.
9. Using a clean cloth dampened with warm water, wipe out
the combustion chamber. Rinse out debris with a low
pressure water supply.
10. Allow the heat exchanger to thoroughly dry.
11. Reinstall the condensate hose, heat exchanger top plate,
burner, fan plate, fan, venturi, and bezel (FIG. 12-2).
12. Perform a combustion analysis by following the instructions
in Section 10 - Start-up - Check Flame and Combustion, on
pages 59 and 61 of this manual.
13. Resume operation.
Cleaning boiler heat exchanger
1. Shut down boiler:
• Follow the “To Turn O Gas to Appliance” instructions
for the boiler in Section 10 - Startup.
• Do not drain the boiler unless it will be exposed to
freezing temperatures. If using freeze prevention uid
in system, do not drain.
2. Allow time for the boiler to cool to room temperature if it
has been ring.
3. Remove the bezel from the unit.
4. Remove the screw securing the fan and venturi from the
fan plate and set aside.
5. Remove the nuts securing the fan plate and burner from
the heat exchanger plate and set aside (FIG. 12-2).
6. Loosen the heat exchanger bolts to remove the heat
exchanger top plate (FIG. 12-2).
WARNING
e boiler contains ceramic ber materials.
Use care when handling these materials per
instructions in the FTXL Service Manual.
Failure to comply could result in severe
personal injury.
79
Page 80

13 Diagrams
Figure 13-1 Wiring Diagram
CONNECTION BOARD
BELL JUMPER
ALARM BELL
SILENCING SWITCH
ALARM
CONTACTS
RUN-TIME
CONTACTS
24 VAC RECIRC
PUMP RELAY COIL
24 VAC LOUVER
RELAY COIL
LOUVER
PROVING SWITCH
GAS PRESSURE
SWITCH
SWITCH
THERMOSTAT
HEAT/LOOP
DEMAND
HEAT/LOOP
DEMAND
HEAT/LOOP
DEMAND
SYSTEM
SENSOR
OUTDOOR
SENSOR
DHW RECIRC
SENSOR
TANK
SENSOR
SHIELD
A
CASCADE
B
SHIELD
BMS
IN
SYS PUMP
IN
BLR PUMP
OUT
RATE
OUT
SHIELD
MODBUS
OPTION
SHIELD
SHIELD
GROUNDING
JUMPER
FLOW
TANK
+
+
+
+
-
A
B
3
2
1
0-10V
0-10V
0-10V
0-10V
X5-1
X5-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
CN2
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
CN1
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
CN4
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
CN3
RIBBON CABLE
MODBUS BOARD
MTR-01
LOW VOLTAGE
120 VAC
HIGH VOLTAGE
DAMPER
R/BL
CN5-12
BR/W
CN5-1
P/BL
CN5-9
R/W
CN5-2
GY/BL
CN5-10
BL/BK
CN5-16
Y
CN5-11
BL/W
CN5-3
PR/BK
CN5-8
PR/W
CN5-4
O/BK
CN5-15
BK
CN5-13
BK/W
CN5-6
GY/W
CN5-14
P/W
CN5-7
O/BL
CN5-5
LWCO
PROBE
T
LWCO RESET
CN6
CN8-3
CN8-1
CN8-2
BL
BL
R
G
G
R
X6-2
X6-4
X6-1
X6-3
O
X4-1
GY
X4-2
X4-3
G
X4-4
BK
X1-1
W
X1-2
G
X1-3
RELAY
TEST
SWITCH
Installation & Operation Manual
BOX DEPICTS
OPTIONAL ITEMS
PR
PR
O/BK
CONXUS
BL
T
DU
FLUE DAMPER
M
2
3
LWCO
BOARD
J3-6
J3-5
J3-4
J3-3
J3-2
J2-1
J2-2
Y
INTEGRATED
BIC
CONTROL
X-7
1
X4-11
X4-07
X4-14
X4-06
X4-13
X4-12
X4-5
X4-4
X4-8
X4-10
X4-9
X4-2
X4-1
x4-3
X5-3
O
Y
X6
X9-1
X9-2
X9-3
X9-4
BOX DEPICTS
DUAL SENSOR
SINGLE HOUSING
OR
X1-3
BR
X1-4
X1-2
PR
X1-6
X1-5
X1-8
X1-1
X5-7
X5-16
X5-8
X5-15
X5-9
X5-1
X5-2
X5-10
X5-11
X5-4
X5-12
X5-6
X5-5
X5-13
X5-14
X2-2
X2-1
X1-7
TR2
CN2-4
CN2-2
CN2-3
CN2-1
ON/OFF
SWITCH
BK
W
G
R
FAN
RELAY
1 2 3 4 5
R
T
W
BK
Y/BK
BL
O
BLOCKED DRAIN SWITCH
P
O/BK
R/BK
GY
P/BK
W/BK
PR
Y
BK
Y
W/R
RELAY
BOARD
CN1-5
K1
CN1-6
CN1-3
K2
CN1-4
CN1-1
K3
CN1-2
W
BK
1 2G3
BLOWER
-T
OPERATING SENSOR S1a
-T
HIGH LIMIT SENSOR S1b
-T
INLET SENSOR S2
-T
FLUE SENSOR S3a
-T
FLUE SENSOR S3b
GAS VALVE
@24VAC
FLAME SENSOR
SPARK
ROD
HIGH VOLTAGE SPARK LEADCAUTION
JUNCTION
BOX
OR
OR
BR
BR
PR
PR
TRANSFORMER
3.5A
G
L
L
GND
N
DHW
PUMP
BOILER
PUMP
SYSTEM
PUMP
120V
SUPPLY
N
Notes:
1. All wiring must be installed in accordance with: local, state, provincial and national code requirem ents per either N.E.C. in USA or C.S.A. in Canada.
2. If any original equipment wire as supplie d with the appliance must be replaced, it must be replaced with wire having same wire gauge (AWG) and
rated for a minimum of 105°C. Exceptions: Rep lacement high voltage spark lead and ribbon cables must be purchased from the factory. Use of a
non-approved spark lead or ribbon cables can lead to operational problems which could result in non-repairable damage to the integrated controller or
other components.
3. Actual connector block locations may vary from those shown on diagrams. Refer to actual components for proper connector block locations when
using diagrams to troubleshoot unit.
80
WIRING DIAGRAM
LBL20426 REV C
Page 81

13 Diagrams (continued)
Figure 13-2 Ladder Diagram
120VAC
TERMINAL STRIP
120V SUPPLY "L"
ON / OFF
SWITCH
BELL
ALARM
SWITCH
SILENCING
SENSOR
OUTDOOR
SENSOR
DHW RECTRC
SENSOR
SENSOR
CASCADE
SYS PUMP
BLR PUMP
MODBUS
SYSTEM
TANK
SHIELD
SHIELD
BMS
OUT
RATE
OUT
SHIELD
SHIELD
CONTACTS
RUN-TIME
CONTACTS
+
IN
+
IN
+
+
1
2
6
13
ALARM
A
B
-
-
-
-
A
B
X4-3
CN5-5
0-10V
0-10V
0-10V
0-10V
X1-6
X5-9
S6
S5
S7
S4
INTEGRATED CONTROL
3.15A
120 VAC
3.5A
SENSOR
OPERATING
SENSOR
HIGH LIMIT
SENSOR
SENSOR
SENSOR
CONNECTION
BOARD
1
2
3
4
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
F2
F1
5A
F3
.8A
24 VAC
13
13
19
21
17
19
15
17
13
15
15
12
10
CONXUS
DU
RIBBON CABLE
INLET
FLUE
FLUE
JUNCTION BOX
SYSTEM PUMP
RELAY
DHW PUMP
RELAY
BOILER PUMP
RELAY
24V DC
SUPPLY
CONNECTION BOARD
HEAT/LOOP
HEAT/LOOP
HEAT/LOOP
THERMOSTAT
LOW GAS
PRESSURE
SWITCH
BIC
S2
S1a
S1b
S3a
S3b
CN5-1
CN5-9
CN5-2
CN5-9
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6 X6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN6
CN8-1
X6-1
X6-2
CN8-2
CN8-3 X6-3
BLOWER
RELAY
FLOW
SWITCH
DEMAND
DEMAND
DEMAND
TANK
M
O
D
B
U
S
X1-1
X1-2
X1-3
X1-4
X5-1
HIGH GAS
PRESSURE
SWITCH
X6
X4-1
X4-2
X4-3
TERMINAL STRIP
120V SUPPLY "N"
BLOWER
12
3
BLOWER
RELAY
SYSTEM PUMP
RELAY
DHW PUMP
RELAY
BOILER PUMP
RELAY
14
1
22
2
20
3
18
18
16
11
11
9
INTEGRATED
CONTROL
X7
X7
X5-6
X5-4
X5-12
X5-5
X5-13
X5-14
X4-7
X4-14
X4-6
X4-13
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X6
X9-2
X9-1
X9-3
Installation & Operation Manual
NEUTRAL
L
GROUND
IN
SYSTEM
PUMP
CONTACTS
BOILER
PUMP
CONTACTS
DHW
PUMP
CONTACTS
RELAY BOARD
J3-6
LWCO
LWCO
CN5-15
LWCO
PROBE
LWCO RESET
RECIRC PUMP
RELAY COIL
RELAY COIL
PROVING SWITCH
24VAC
LOUVER
24VAC
LOUVER
TEST
SWITCH
GAS VALVE
BLOWER
SPARK
ROD
J3-5
J3-3
J2-1
J2-2
5
6
10
BOARD
BOARD
6
7
8
9
BLOCKED
DRAIN SWITCH
J3-4
X4-8
J3-2
X4-12
CN5-7 X4-1
CN5-6 X4-9
CN5-14
X4-2
CN5-13
X4-10
CN5-16
X5-3
CN5-11
X4-11
CN5-3
X4-5
DAMPER RELAY
FLUE DAMPER
M
3
X4-4
CN5-4
X5-2
X5-10
X5-11
X2-2
X2-1
1
X5-16
2
4
X5-15
5
TR2
X1-7
FLAME ROD
X5-7
X5-8
CAUTION HIGH VOLTAGE SPARK LEAD
NOTES:
1. Where possible, switches are shown without utilities (gas, water or
electricity) connected to the unit. As such, actual switch states may
vary from those shown on diagrams depending upon whether utilities
are connected or a fault condition is present.
2. See wiring diagram for additional notes.
L
OUT
SYSTEM
PUMP
BOILER
PUMP
DHW
PUMP
INTEGRATED
CONTROL
12
GAS VALVE
RELAY
BOX DEPICTS
OPTIONAL ITEMS
LOW VOLTAGE
120 VAC
HIGH VOLTAGE
LADDER DIAGRAM
LBL20427 REV C
81
Page 82

Notes
Installation & Operation Manual
82
Page 83

Notes
Installation & Operation Manual
83
Page 84

Revision Notes: Revision A (ECO #C15743) initial release.
Revision B (ECO #C16066) refl ects updates made to the room air kit on
page 19 along with updates made to the wiring and ladder diagrams.
Revision C (ECO C17014) refl ects the standardization of pressure drop
information on pages 49 and 50 as well as the the addition of the system
supply sensor note on page 53.
Revision D (Process #3000001405_Change #500002005) refl ects the
addition of the ICC and Jeremias information along with updated SAP
numbers.
Revision E (PCP# 3000001143 / CN# 500002167) refl ects the addition
of edits made to Boiler Water on page 3, along with the addition of the
Important and Notice items under General Piping Information on page
37, as well as edits to section 10 (Start-up) on pages 57 and 58. SAP
part numbers have been updated.
Revision F (PCP# 3000002702 / CN# 500003259) refl ects an update to
the wiring diagram on page 80.
Revision G (PCP# 3000001665 / CN# 500001821) refl ects the addition
of Step 4 under the Common Venting section on page 20 as well as
edits made to the Multiventing Vertical Terminations section on page 34.
Revision H (PCP# 3000003998 / CN# 500004062) refl ects a change to
the Duravent Polypro Adapter number in Table 3G on page 22.
Revision J (PCP# 3000004157 / CN# 500004298) refl ects an update
to the minimum gas supply pressure to 5" for the FTX500 models on
pages 49 and 51.
Revision K (PCP# 3000004438 / CN# 500005574) refl ects an update to
the fl ue temperatures on page 66 along with the addition of the Energy
Star logo.
Revision L (PCP# 3000006133 / CN# 500007549) refl ects the addition
of a PVC-DWV vent fi tting in Table 3E on page 27 and a size change in
the tee fi ttings on Figures 6-1 and 6-2 on page 38.
Revision M (PCP# 3000008948 / CN# 500008926) refl ects the addition
of the condensate collection notice on page 20.
Revision N (PCP# 3000009267 / CN# 500009031) refl ects changes
made to water chemistry information on pages 3, 7, 37-47, 57-58, and
75.
Revision P (PCP# 3000008755 / CN# 500008634) refl ects changes to
condensate trap information on pages 4, 5, 56, 59, and 76.
Revision R (PCP #3000010423 / CN #500010150) refl ects an update to
the neutralizer information on page 56.
Revision T (PCP #3000022019 / CN #500012007) refl ects edits made
to Table 3I on page 23.
Revision U (PCP #3000025312 / CN #500015340) refl ects an update to
the piping diagrams on pages 44 and 46.
FTXL-I-O_MM #100059358_DIR #2000005000_Rev U
06/18
 Loading...
Loading...