Page 1

XLReportGen
User Manual
Version 3.8
2009-05
Copyright© 2003-2009 LJZsoft Corporation
All rights reserved
Page 2

Contents
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION...........................................................................................................1
1.1 OVERVIEW......................................................................................................................................1
1.2 FEATURES.......................................................................................................................................1
CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION AND STARTUP...............................................................................5
2.1 SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS............................................................................................................5
2.2 INSTALLING XLREPORTGEN ..........................................................................................................5
2.3 UNINSTALLING XLREPORTGEN .....................................................................................................5
2.4 COMMAND LINE .............................................................................................................................6
CHAPTER 3 QUICK START...............................................................................................................8
3.1 LEARNING HOW TO USE XLREPORTGEN.........................................................................................8
3.2 SAMPLE DATABASE ........................................................................................................................8
3.3 STEPS OF REPORTING......................................................................................................................9
3.4 MY FIRST REPORT ........................................................................................................................10
3.4.1 Creating a report template...................................................................................................10
3.4.2 Creating an XRF file............................................................................................................11
3.4.3 Configuring the report.........................................................................................................11
3.4.4 Inputting a function..............................................................................................................11
3.4.5 Understanding the function..................................................................................................12
3.4.6 Running an XRF file.............................................................................................................12
3.4.7 Opening a report..................................................................................................................13
3.4.8 Modifying the report template..............................................................................................13
3.4.9 Modifying the function.........................................................................................................13
3.4.10 Generating the report again...............................................................................................14
3.5 SAMPLES.......................................................................................................................................15
CHAPTER 4 REPORT TEMPLATES ..............................................................................................17
- I -
Page 3

4.1 ABOUT REPORTS ..........................................................................................................................17
4.2 ABOUT REPORT TEMPLATES.........................................................................................................17
4.3 EXCEL BASIC CONCEPTS ..............................................................................................................17
4.3.1 Workbooks and Worksheets.................................................................................................17
4.3.2 Formulas..............................................................................................................................18
4.3.3 Names...................................................................................................................................18
4.3.4 Headers and Footers............................................................................................................18
4.3.5 Page Breaks.........................................................................................................................19
4.3.6 Drawings, Pictures and Diagrams.......................................................................................19
4.3.7 Charts...................................................................................................................................19
4.3.8 Formatting...........................................................................................................................19
4.4 TABLE REPORTS ...........................................................................................................................20
4.4.1 About Table Reports.............................................................................................................20
4.4.2 Creating a Worksheet for a Fixed Table Report..................................................................21
4.4.3 Creating a Worksheet for a Variable Table Report.............................................................21
4.4.4 Formatting Cells for Pictures..............................................................................................22
4.5 CHARTS ........................................................................................................................................24
4.5.1 About Charts........................................................................................................................24
4.5.2 Creating a Blank Chart........................................................................................................24
CHAPTER 5 REPORTING WITH XLREPORTGEN.....................................................................25
5.1 CREATING AND OPENING XRF FILES ...........................................................................................25
5.1.1 About XRF files....................................................................................................................25
5.1.2 Create a new XRF file..........................................................................................................25
5.1.3 Open an XRF file..................................................................................................................25
5.1.4 Save an XRF file...................................................................................................................25
5.2 CONFIGURING FILES.....................................................................................................................26
5.2.1 About files.............................................................................................................. ..............26
5.2.2 Configuring file information................................................................................................26
- II -
Page 4

5.2.3 Converting files....................................................................................................................27
5.3 CONFIGURING DATA SOURCES.....................................................................................................30
5.3.1 About data source................................................................................................................30
5.3.2 Adding, modifying and deleting a data source.....................................................................30
5.4 CONFIGURING PARAMETERS.........................................................................................................31
5.4.1 About parameters.................................................................................................................31
5.4.2 Adding, modifying and deleting a parameter.......................................................................32
5.5 INPUTTING FUNCTIONS.................................................................................................................33
5.6 RUNNING XRF FILES....................................................................................................................33
5.6.1 Windows mode.....................................................................................................................34
5.6.2 Command line mode.............................................................................................................34
5.7 USING EXCEL FORMULAS.............................................................................................................34
5.8 SORTING, GROUPING AND TOTALING...........................................................................................37
5.8.1 Sorting data..........................................................................................................................37
5.8.2 Totaling................................................................................................................................38
5.8.3 Grouping data and subreports.............................................................................................39
5.8.4 Subtotaling...........................................................................................................................39
5.9 CHARTING ....................................................................................................................................41
5.10 PICTURES....................................................................................................................................43
5.10.1 Inserting pictures into a report template............................................................................43
5.10.2 Inserting pictures into a report..........................................................................................43
5.11 USING PARAMETERS...................................................................................................................44
5.12 PROGRAMMING...........................................................................................................................47
5.12.1 Using add-ins, macros.......................................................................................................47
5.12.2 Making XRF files programmatically..................................................................................48
CHAPTER 6 FUNCTION REFERENCE..........................................................................................49
6.1 REPORT FUNCTION.......................................................................................................................49
6.1.1 Report Function...................................................................................................................49
- III -
Page 5

6.1.2 Fixed Table Report Function...............................................................................................49
6.1.3 Non-group Variable Table Report Function........................................................................53
6.1.4 Group Variable Table Report Function...............................................................................57
6.2 NAME FUNCTION..........................................................................................................................62
6.3 EXECSQL FUNCTION ...................................................................................................................64
CHAPTER 7 MENUS, TOOLBAR AND SHORTCUT KEYS........................................................66
7.1 FILE MENU ...................................................................................................................................66
7.2 EDIT MENU...................................................................................................................................66
7.3 REPORT MENU..............................................................................................................................66
7.4 TOOLS MENU................................................................................................................................67
7.5 HELP MENU..................................................................................................................................67
7.6 TOOLBAR......................................................................................................................................67
7.7 SHORTCUT KEYS ..........................................................................................................................68
CHAPTER 8 HINTS AND TIPS.........................................................................................................70
CHAPTER 9 XRF FILE REFERENCE.............................................................................................74
9.1 XRF FILE FORMAT.......................................................................................................................74
9.2 [DATA SOURCE] SECTION.............................................................................................................75
9.3 [FILE] SECTION ...........................................................................................................................77
9.4 [PARAMETER] SECTION............................................................................................................79
CHAPTER 10 LICENSE AND SUPPORT........................................................................................80
10.1 LICENSE......................................................................................................................................80
10.2 TECHNICAL SUPPORT..................................................................................................................81
- IV -
Page 6
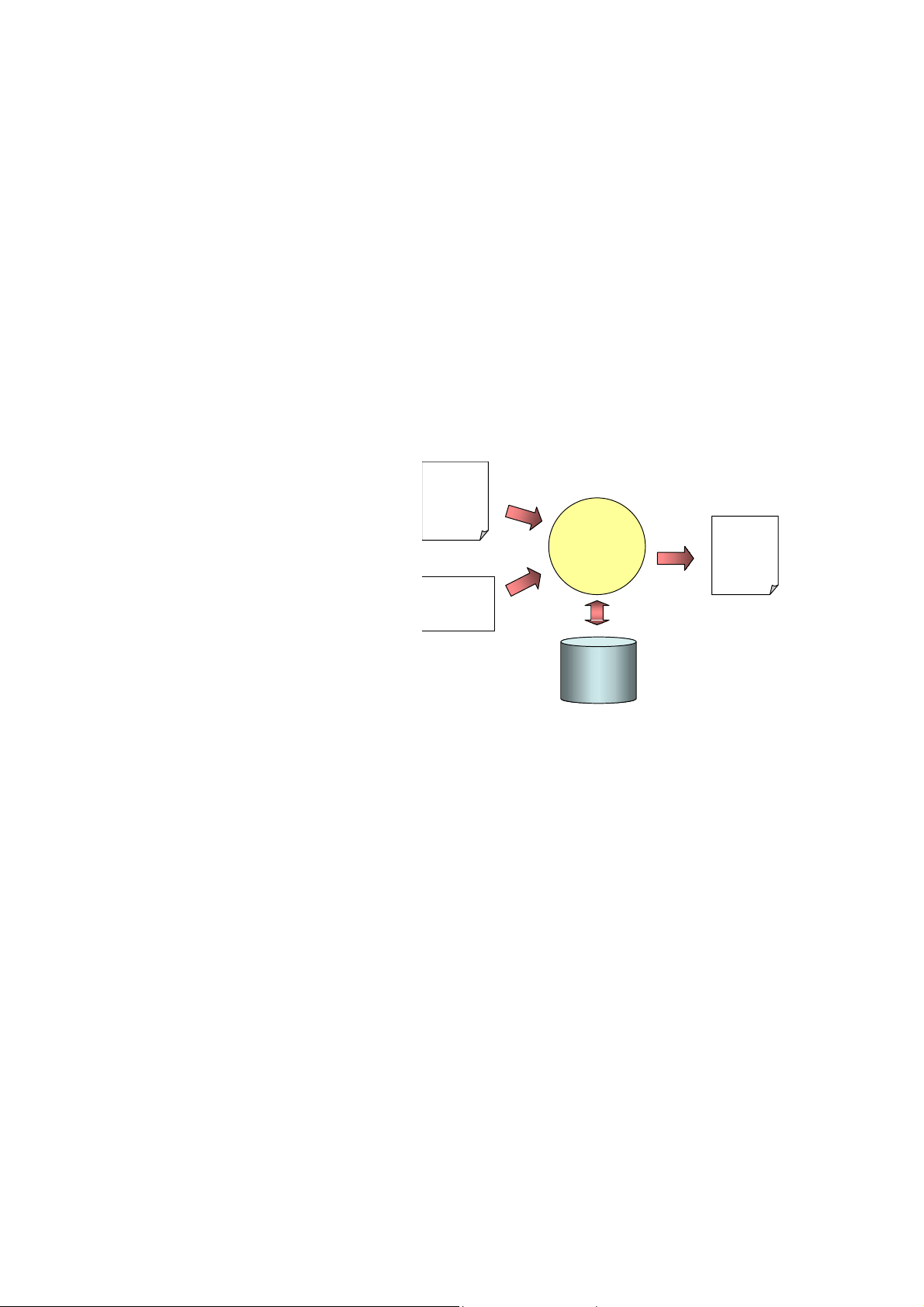
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
XLReportGen is a report generator for Microsoft Excel that outputs reports in
Microsoft Excel spreadsheet format. If you know how to use Microsoft Excel
and write SQL statements, you can use XLReportGen to create all kinds of
reports as you need.
To create a report,
XLReportGen need to read a
report template file and an XRF
Report
Template
XLReportGen
Report
file. The report template file is a
SQL
Microsoft Excel workbook that
defines the layouts and formats
Database
of a report. The XRF file
contains SQL statements and some information, and tells XLReportGen how
to get data from database and how to put data into a report. First XLReportGen
creates a blank report using the report template file, and then executes SQL
statements in the XRF file to get data from database, and fills data into the
report to generate the desired report in Microsoft Excel spreadsheet format.
1.2 Features
XLReportGen includes the following features:
Using Microsoft Excel as your reporting tool
Just use Microsoft Excel as your reporting tool. You design reports like layouts,
formats and styles directly using Microsoft Excel. And you will get reports in
Microsoft Excel spreadsheet format as a result. Microsoft Excel is powerful,
- 1 -
Page 7

flexible and familiar. You do not need to buy and learn extra reporting tools.
Making report template directly using Microsoft Excel
The main advantage of using XLReportGen is based on the fact that all
formatting is done directly in Microsoft Excel. You can take full advantage of
Microsoft Excel including cell formatting, formulas, filtering and sorting,
drawing and pictures, charts, multiple sheets, page setup, headers and footers,
preview and printing, VBA, macros, and more.
Accessing to databases using SQL
XLReportGen executes SQL statements to extract data from database.
Supports all type SQL: DML, DDL and DCL. Multiple SQL statements can be
executed in one report building process. You can perform queries on
databases, insert data into databases, and create database objects like tables.
The power of SQL can be harnessed for maximum efficiency in reporting.
Creating reports without programming experience
You know how to use Microsoft Excel and how to write SQL, it is enough. It
does not require programming to create reports.
Connection to all databases using ODBC
XLReportGen connects to databases using ODBC. Access to all databases
which support ODBC such as Oracle, DB2, Sybase, Informix, Microsoft SQL
Server, Teradata, MySQL, Microsoft Access, dBase.
Supporting multi-databases in one report
XLReportGen supports multi-databases in one report. You can get data from
some different databases such as Oracle, DB2 and Microsoft SQL Server, and
put these data into one report.
Generating reports with parameters
XLReportGen gives you an opportunity to create reports with parameters. You
may use parameters in SQL statements. You will be asked to input the values
of parameters while creating reports.
- 2 -
Page 8

Supporting Windows mode and command line mode
XLReportGen supports command line mode. So it is possible to call
XLReportGen from other program. For developers, you can integrate
XLReportGen into your application.
Creating complex reports
You can create complex reports. The complexity might come from report
formatting as well as report content.
Creating reports with charts
XLReportGen enables you to include sophisticated, colorful charts in your
reports. You can use charts any time you want to improve the usefulness of a
report.
Creating reports with pictures
XLReportGen can insert pictures from the graphics files, position and size the
pictures according to your instruction.
Many reports in one Microsoft Excel workbook
One Microsoft Excel workbook may contain many reports. You can generate a
book of reports in one generating process.
Conversion of file formats
XLReportGen is a converter too. You can convert Microsoft Excel workbook to
and from other formats, such as HTML, XML, CSV, text, DBF, DIF, and Lotus
1-2-3. You also can convert data from database to other file format.
Generating reports automatically
The process of report generation can be fully automated, periodically or on
events. XLReportGen can be scheduled with Windows Scheduled Tasks or
other tools.
One time configuration
With on time configuration, you can repeatedly generate reports especially
periodic reports such as daily, weekly, monthly and annual reports.
- 3 -
Page 9

Flexible deployment
XLReportGen can be run on your desktop or server.
- 4 -
Page 10

Chapter 2 Installation and Startup
2.1 Software Requirements
Microsoft Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows
XP, Windows 2003, Windows Vista or later.
Microsoft Office 97/98, Office 2000, Office XP, Office 2003 or later.
2.2 Installing XLReportGen
Run the installation program, and follow the instructions to complete
XLReportGen installation.
If you don’t have Microsoft Office installed, please install it first.
If your environment is Windows 95/98 and Office 97, and you don’t have VB6.0
run-time files installed, please install it. For Windows 2000, Windows XP,
Windows 2003 and Office 2000 or later, you do not need to install VB6.0
run-time files because they are included in OS and Office. To install VB6.0
run-time files, just run vbrun60sp5.exe, and follow the instructions.
If you don’t have ODBC Driver installed for the database you want to access,
please install it.
If your OS is Windows 95/98 and you don’t have Microsoft Data Access
Components 2.0 (MDAC_TYP) or later installed, please install it. For Windows
2000, Windows XP and Windows 2003, you do not need to install MDAC_TYP
because it is preinstalled in OS. To install MDAC_TYP, just run mdac_typ.exe,
and follow the instructions.
2.3 Uninstalling XLReportGen
1. Quit XLReportGen.
- 5 -
Page 11

2. Double-click the Add/Remove Programs icon in the Windows Control
Panel.
3. Do one of the following:
For Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows 2003 Edition:
Click XLReportGen in the Currently installed programs box, and then click the
Change/Remove button.
For Windows 98 and Windows NT 4.0:
Click XLReportGen on the Install/Uninstall tab, and then click the
Add/Remove button.
4. Follow the instructions on the screen to complete uninstalling the program.
2.4 Command Line
XLReportGen can be run in Windows mode or command line mode. The
syntax of command is:
excelreport <xrf file name> [-C] [-D] [-I interval] [-U1 user1] [-P1 pwd1] …
[-U10 user10] [-P10 pwd10] [pa1 pa2 … pa10]
xrf file name Specifying an XRF (.xrf) file that tells XLReportGen how to get
data from data sources and how to put data into a report.
-C Run XLReportGen in command line mode.
-D Display the generated report with Microsoft Excel.
-I interval Log the processing records message. If interval is greater than
1, it is the interval of records. If interval is less than 1, it is the
percent of interval.
-U1 user1 …
Specify the user names. user1 is the user name of the first
-U10 user10
-P1 pwd1 ... Specify the passwords. pwd1 is the password of the first data
data source. user2 is the user name of the second data
source……
- 6 -
Page 12

-P10 pwd10 source. Pwd2 is the password of the second data source……
pa1 … pa10 The values of the parameters defined in the XRF file. You can
use parameters in SQL statements. XLReportGen will replace
the names of the parameters in a SQL statement with the
actual values before it executes the SQL statement. You can
use no more than 10 parameters in one report.
For example, you have defined two parameters in your XRF file. The first
parameter is the sales date, and the second is the category of the product. You
can run XLReportGen in command line mode as follows:
excelreport c:\excelreport\myreport.xrf -c 1996-05-01 “Dairy Products”
- 7 -
Page 13

Chapter 3 Quick Start
3.1 Learning how to use XLReportGen
You can teach yourself how to use XLReportGen by choosing from the
methods available in this section:
You can study the sample reports and sample database included with
XLReportGen.
You can use the detailed descriptions and instructions in the “My First
Report”.
3.2 Sample Database
XLReportGen comes with Sample.mdb, a sample database you can use when
learning the program. Sample.mdb is a Microsoft Access database. Virtually all
of the examples in this manual are based on Sample.mdb data.
The sample reports access the sample database through the ODBC data
source name “Report Sample”. When you install XLReportGen, you can
choose to add the ODBC data source name. And you also can add the ODBC
data source name manually.
To create the System DSN “Report Sample”, do as follows:
1. Click the Windows Start button, choose Settings, and then click Control
Panel.
2. On computers running Microsoft Windows 2000 or later, double-click
Administrative Tools, and then double-click Data Sources (ODBC). The
ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog box appears. On computers
running previous versions of Microsoft Windows, double-click 32-bit ODBC or
ODBC.
3. Select the System DSN tab, and then press Add button.
- 8 -
Page 14

4. Choose Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb), then press Finish button.
5. In the ODBC Microsoft Access Setup dialog box, type Report Sample in
the Data Source Name box.
6. Press the Select button, and browse to select Sample.mdb.
7. Press OK button to close the ODBC Microsoft Access Setup dialog box.
8. Press OK button to close the ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog
box.
3.3 Steps of Reporting
To create a report with XLReportGen, you should do as follows:
1. Prepare works
Before you create a report, you should determine the layout of the report, and
know where and how to get the data.
You must know how to access the databases you are reporting from. So you
need the data source name, user name and password. If you don’t have data
sources added, please add data sources first. Run ODBC Administrator, you
can add a new data source. For detailed information about configuring ODBC,
refer to ODBC Administrator Help.
2. Make a report template file
Create a report template file using Microsoft Excel. For detailed information
about report template, refer to “Report Templates” in this document.
3. Create an XRF file
Create an XRF file with an .xrf extension using XLReportGen. There are tow
steps to create an XRF file.
(1) Configure the report
Define the names of data sources, the name of the report template file, the
name of the report file and the name of the log file. If you want to use
parameters in SQL statements, define these parameters.
- 9 -
Page 15

(2) Write functions
Write functions and SQL statements that specify how to get data from data
sources and how to put data into the report.
For detailed information, refer to “Reporting with XLReportGen” in this
document.
4. Run the XRF file
Run the XRF file to generate a report file. For detailed information about
running report, refer to “Running an XRF File” in this document.
3.4 My First Report
The following tutorial has been designed to guide you to create your first report.
In this tutorial, you will get an introduction to the program as you create a
Customer List report. The Customer List is one of the most basic business
reports and typically has information such as Customer Name, City, Country,
and Contact Name.
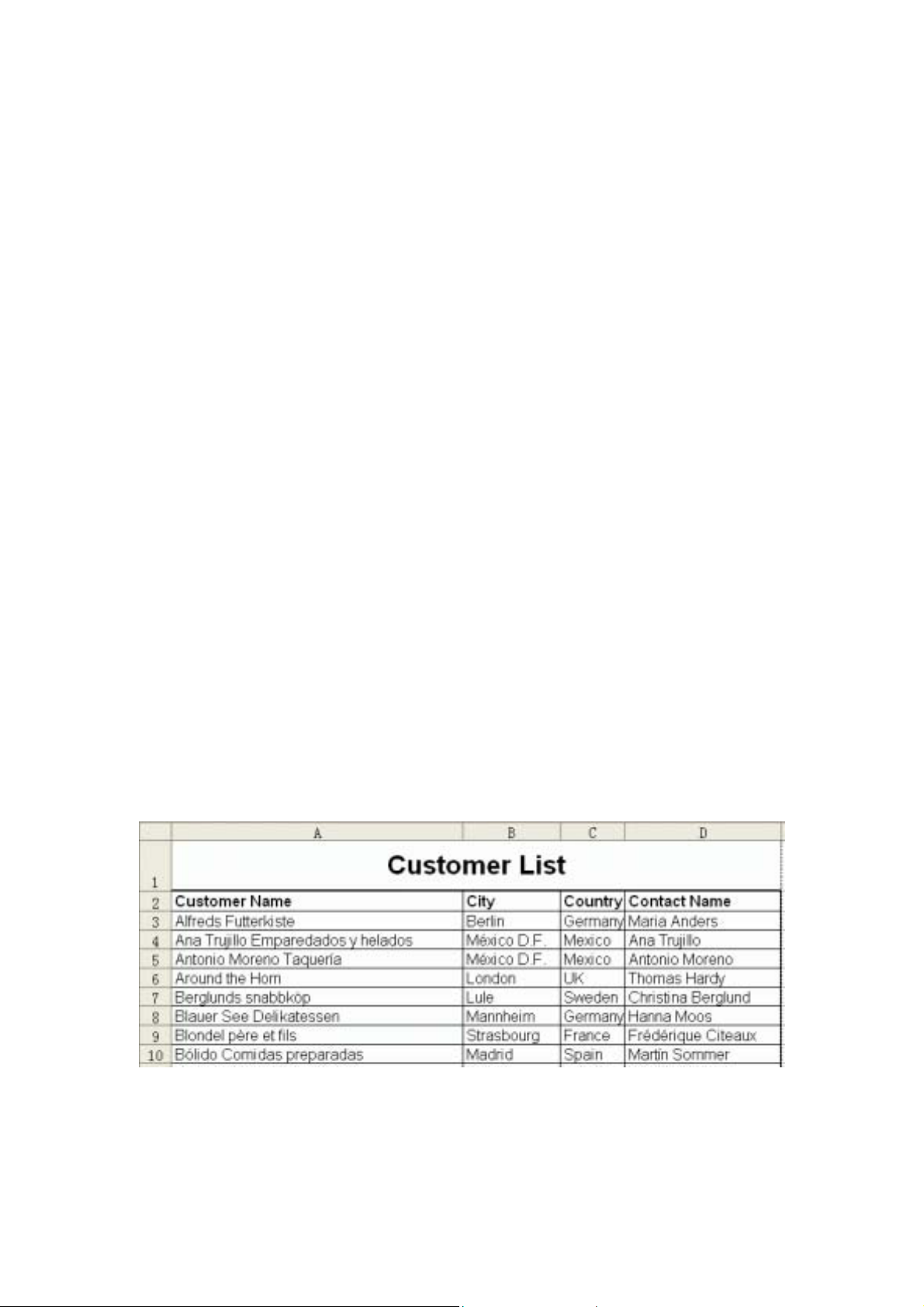
3.4.1 Creating a report template
1. Run Microsoft Excel, a new workbook will open.
2. Select the cell A1, type “Customer Name”. In the same way, you input “City”,
“Country” and “Contact Name” into the cells B1, C1 and D1.
3. Format the text of A1, B1, C1 and D1 as you like, including font, font size,
font colour, bold, background, alignment and border.
4. You can change the width of these columns. The report template you have
made is as follows:
5. Click Save on the File menu, chose a directory such as “C:\Report”, type
- 10 -
Page 16

custlist.xls in the File name box and press Save button.
6. Click Close on the File menu.
3.4.2 Creating an XRF file
1. Run XLReportGen.
2. Click New on the File menu.
3. Click Save on the File menu, chose the directory to which you have saved
the report template, type custlist.xrf in the File name box and press Save
button.
3.4.3 Configuring the report
1. On the Report menu, click Configuration. The Configuration dialog box
appears.
2. Click the File tab.
In the Template File box, type custlist.xls; In the Report File box, type
Report\custlist.xls; In the Log File box, type Log\custlist.log.
3. Click the Data Source tab.
Press New button, the New Data Source dialog box appears. In the Name
box, type Report Sample, press OK button.
4. On the Configuration dialog box, press OK button.
3.4.4 Inputting a function
In the editor windows, input a function as follows:
@F1=Report(sheet=1 cell=A2)
SELECT CompanyName
,CityName
,CountryName
,ContactName
- 11 -
Page 17

FROM Customers, Cities, Countries
WHERE Customers.CityCode = Cities.CityCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Cities.CountryCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Countries.CountryCode
ORDER BY CompanyName,CityName,CountryName
;
You can test the SQL statement in a query tool such as Microsoft Access or
Microsoft Query.
3.4.5 Understanding the function
Before going any further, let us understand this function.
1. The Report function will execute the SQL statement, get data from data
source, and put data into the report.
2. The sheet argument identifies a worksheet, and the value 1 is the index
number of the worksheet. So it is the first worksheet.
3. The cell argument specifies the cells that the first record will be filled into.
The value is A2. So XLReportGen will fetch the first record, put the value of
CompanyName field into A2, the value of CityName field into B2, the value of
CountryName field into C2, and the value of ContactName field into D2. An
then it fetch the next record, put them into A3,B3,C3 and D3……
3.4.6 Running an XRF file
1. On the Report menu, click Run, the Run Report dialog box appears.
2. Press Start button to run the XRF file.
3. XLReportGen will generate a report.
4. After the status is Done, click Close button.
- 12 -
Page 18

3.4.7 Opening a report
1. On the File menu, click Open Report File to open the report you have
generated.
You can view and check the report.
2. On the File menu, click Open Log File to open the log file that recorded the
log information in the report generating..
You can check the log.
3. Close the report file and the log file.
3.4.8 Modifying the report template
1. On the File menu, click Open Template File to open the report template.
2. Change the width of columns. It is very useful to copy some sample data
from the report file into the report template for formatting.
3. Insert a new row on the top, type Customer List as the report title.
4. Add borders for the range “A2:D4”. The external border can be different from
the internal border. The report template you have made is as follows:
4. Save and close the template file.
3.4.9 Modifying the function
In the editor windows, modify the function as follows:
@F1=Report(sheet=1 cell=A3 reserve=2)
SELECT CompanyName
,CityName
- 13 -
Page 19
,CountryName
,ContactName
FROM Customers, Cities, Countries
WHERE Customers.CityCode = Cities.CityCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Cities.CountryCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Countries.CountryCode
ORDER BY CompanyName,CityName,CountryName
;
1. Change the value of cell argument because you insert a row.
2. The reserve argument specifies the number of records for that you reserve
some rows. You have reserve two blank rows in the report template so that the
format of the last row/column border may be different from the others.
3.4.10 Generating the report again
1. Save the XRF file.
2. Run the XRF file to generate the report.
3. Open the report, view and check the report.
The report should now look similar to the following:
Now you have created a report.
- 14 -
Page 20
3.5 Samples
After XLReportGen is installed, some sample reports are installed too. Use
these reports to learn XLReportGen. The sample reports can be changed to
adapt to your own needs.
The sample reports include a sample database, some report template files
(.xls) and XRF files (.xrf). They are located in the Application Data\LJZsoft
under All Users or your profile folder. XLReportGen was tested with Microsoft
Office 2007. Please download the sample reports for Microsoft Office 2007
from our website.
Directory Description
{commonappdata}\LJZsoft\Common\Sa
mpleDatabase
{commonappdata}\LJZsoft\XLReportGe
n\Samples
{commonappdata}\LJZsoft\XLReportGe
n\Samples\Report
{commonappdata}\LJZsoft\XLReportGe
n\Samples\Log
{commonappdata} is the path to the Application Data folder under All Users. If
you install XLReportGen without administrative privileges, {commonappdata}
is the path to the Application Data folder under the current user. The
Contains the sample database
“Sample.mdb”.
Contains the report template
files (.xls) and the XRF files
(.xrf).
Contains the report files (.xls)
generated by XLReportGen.
Contains the log files created by
XLReportGen during generating
report files.
Application Data folder is usually at:
Windows 95/98: C:\windows\All Users\Application Data\
Windows NT: C:\WinNT\Profiles\All Users\Application Data\
Windows 2000/XP: C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\
- 15 -
Page 21

Windows Vista: C:\ProgramData\
- 16 -
Page 22

Chapter 4 Report Templates
4.1 About Reports
The report generated by XLReportGen is a Microsoft Excel workbook that
contains one or more worksheets. The layouts, formats and styles of the report
are defined by a report template, and the data of the report are got from
databases such as Oracle, DB2.
4.2 About Report Templates
To make a report using XLReportGen, you should create a report template first.
This report template is a Microsoft Excel workbook that defines the layouts,
formats and styles of the report. In the Microsoft Excel report template, you can
input static contents such as titles, descriptions, comments, a cover, a
company logo, format the static content, and define the format of the cells you
will fill data.
XLReportGen will generate the report based on the report template file. All
static contents and the layouts, formats and styles defined in the report
template file will be brought to the final report file.
4.3 Excel Basic Concepts
If you have known these concepts of Microsoft Excel, please skip this section.
For more detail information about Microsoft Excel, refer to Microsoft Excel
Help.
4.3.1 Workbooks and Worksheets
A Microsoft Excel workbook is a file that contains one or more worksheets,
- 17 -
Page 23

which you can use to organize various kinds of related information. You can
enter and edit data on several worksheets simultaneously and perform
calculations based on data from more than one worksheet. When you create a
chart, you can place the chart on the same worksheet as its related data or on
a separate chart sheet.
Worksheet is the primary document that you use in Microsoft Excel to store
and work with data. It also called a spreadsheet. A worksheet consists of cells
that are organized into columns and rows; a worksheet is always stored in a
workbook.
4.3.2 Formulas
Formulas are equations that perform calculations on values in your worksheet.
A formula starts with an equal sign (=). A formula can contain any or all of the
following: functions, references, operators, and constants. You can perform
calculations using formulas.
4.3.3 Names
A name is a word or string of characters that represents a cell, range of cells,
formula, or constant value. Use easy to understand names, such as Products
to refer to hard to understand ranges, such as Sales!C20:C30.
4.3.4 Headers and Footers
Headers and footers are areas in the top and bottom margins of a worksheet.
You can add a header and footer on each worksheet. You can insert a page
number, date and time, graphic, file name in a header and footer, and change
the font in header and footer text. You can have only one custom header and
one custom footer on each worksheet. If you create a new custom header or
footer, it replaces any other custom header or footer on the worksheet.
- 18 -
Page 24

4.3.5 Page Breaks
Microsoft Excel will break pages automatically. You can manually insert
horizontal or vertical page breaks.
4.3.6 Drawings, Pictures and Diagrams
You can add graphics to your worksheets and charts to make them more
visually appealing, to create eye-catching reports, or to add emphasis. For
example, you can display a logo on your worksheet, create a flowchart, and
use graphics in chart data markers. You can make your worksheet interactive
by using graphic objects as hyperlinks or by assigning buttons to macros.
4.3.7 Charts
Charts are visually appealing and make it easy for users to see comparisons,
patterns, and trends in data. To create a chart, you must first enter the data for
the chart on the worksheet. Then select that data and create a chart. A chart is
linked to the worksheet data it's created from and is updated automatically
when you change the worksheet data.
4.3.8 Formatting
You can use these formatting features of Microsoft Excel to effectively display
your data.
Format text and individual characters
To make text stand out, you can format all of the text in a cell or selected
characters. You can set font, color, alignment of the text.
Rotate text and borders
The data in a column is often very narrow while the label for the column is
much wider. Instead of creating unnecessarily wide columns or abbreviated
- 19 -
Page 25

labels, you can rotate text and apply borders that are rotated to the same
degree as the text.
Add borders, colors, and patterns
To distinguish between different types of information in a worksheet, you can
apply borders to cells, shade cells with a background color, or shade cells with
a color pattern.
Number formats
You can use number formats to change the appearance of numbers, including
dates and times, without changing the number behind the appearance. The
number format does not affect the actual cell value that Microsoft Excel uses to
perform calculations.
Conditional formatting
The conditional format is a format, such as cell shading or font color, that Excel
automatically applies to cells if a specified condition is true.
Style
The style is a combination of formatting characteristics, such as font, font size,
and indentation, that you name and store as a set. When you apply a style, all
of the formatting instructions in that style are applied at one time.
4.4 Table Reports
4.4.1 About Table Reports
A table is made up of rows and columns of cells that you can fill with text and
graphics. Tables are often used to make reports, and organize and present
information.
XLReportGen supports two types of table reports: fixed table report, variable
table report.
Fixed table report: The number of rows and columns in the table is fixed. When
- 20 -
Page 26
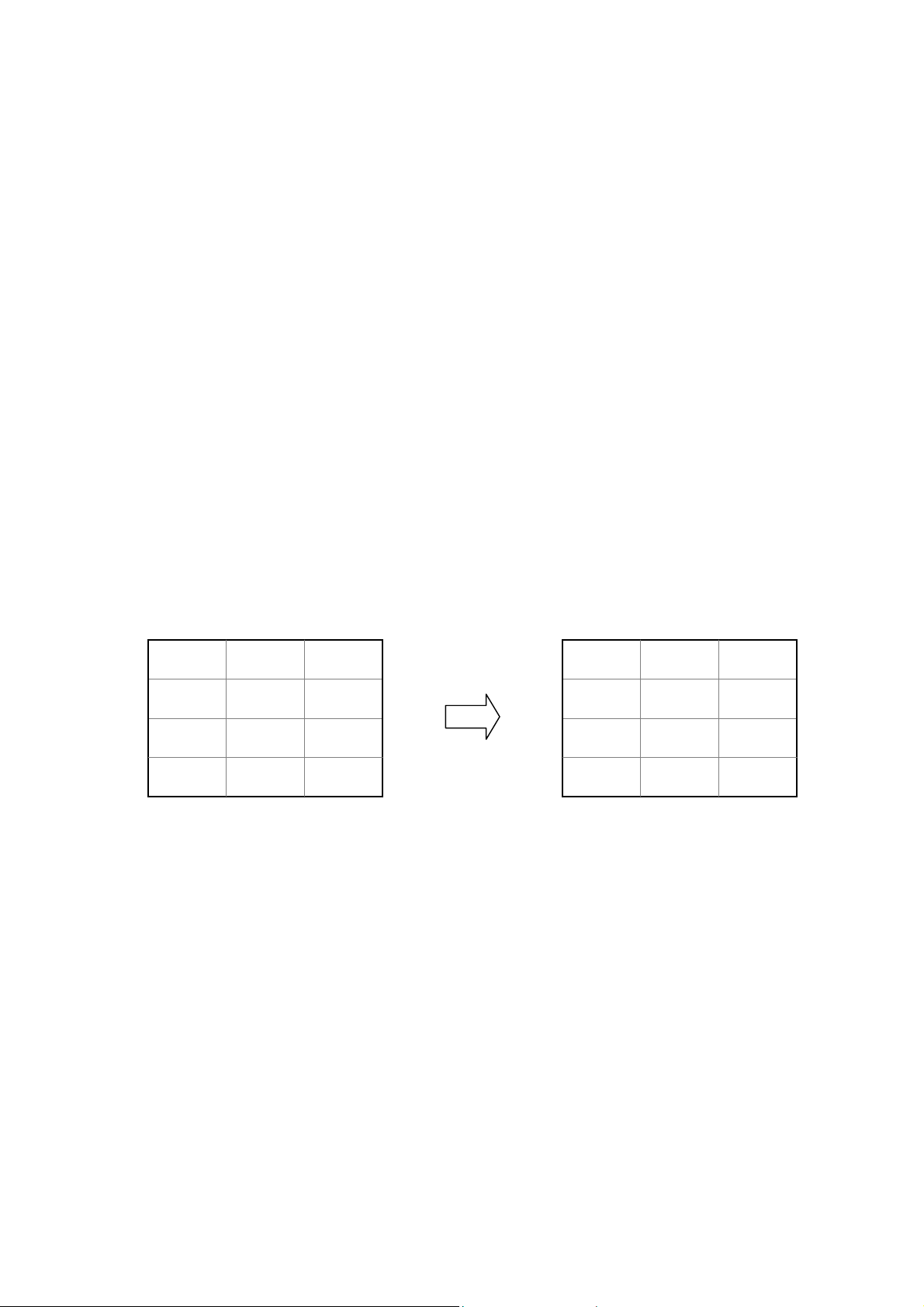
XLReportGen executes a SQL statement, directly puts the result data into cells
in the table.
Variable table report: The number of rows or columns in the table is unfixed,
and it is variable as the number of result records. When XLReportGen
executes a SQL statement, it repeats the table rows or columns for each
record or group, and then puts data into cells of the table.
4.4.2 Creating a Worksheet for a Fixed Table Report
For a fixed table report, you need to create a worksheet in the report template
file according to the report. The format of the worksheet is the same as the
format in the report, but cells that should be filled data into are blank. When
XLReportGen executes a SQL statement, the data values from data source
will be filled into these cells.
BA
BA
1
1
2
2
3
3
The fixed table defined
in the report template file
The fixed table filled data
by rows in the re port file
BA
BA
3.4141
3.4141
5.2202
5.2202
2.783
2.783
4.4.3 Creating a Worksheet for a Variable Table Report
For a variable table report, you also need to create a worksheet in the report
template file according to the report. But you just need to reserve some
rows/columns in the worksheet for one or two records. XLReportGen will add
some rows/columns according to the number of the records returned from data
source.
- 21 -
Page 27

SalesItem IdDate
SalesItem IdDate SalesItem IdDate
SalesItem IdDate
1503 1998-01-01
1503 1998-01-01
2003 1998-01-02
2003 1998-01-02
2503 1998-01-03
2503 1998-01-03
3503 1998-01-05
3503 1998-01-05
5503 1998-01-10
5503 1998-01-10
1503 1998-01-21
1503 1998-01-21
2003 1998-01-25
2003 1998-01-25
1003 1998-01-31
1003 1998-01-31
The variable-rows tab le defined
in the report template file
One record from data source can be put into two or more rows/columns. To do
this, you need to create a repeat range that includes two or more
rows/columns.
The format of the last row/column border can be different from the others. For
example, the outside borders used double lines, and the inside borders used
single lines. To do this, you should reserve the blank rows/columns for 2
records. When XLReportGen inserts some blank rows/columns, the new
rows/columns will inherit the format of the first row/column in the reserved
rows/columns.
XLReportGen will repeat the range for each record. Ranges can be nested.
The inside range is the detail range for detail record, and the external range is
The variable-rows table filled data
by rows in the report file
the group range for group. XLReportGen will repeat the inside range for each
record, and repeat the group range for each group.
4.4.4 Formatting Cells for Pictures
To enhance the visual impact of your report, you can insert pictures into your
report. XLReportGen supports many popular graphics file formats: bitmap,
JPG, GIF, PNG, TIFF and so on. For the graphics file formats XLReportGen
- 22 -
Page 28

supports, refer to Microsoft Excel Help.
You should store the path and name of the graphics files in the database, and
identify the image fields in the report function. XLReportGen will read the
graphics files, and insert them into the cells in the report file.
To specify the positioning option and size, you should write a formatting
expression into the cell in the report template file. XLReportGen will get the
text of the cell, and insert a picture into the cell according to the instruction in
the format expression. The format expression for pictures as follows:
[placement] [size]
The placement specifies the positioning option, and can be one of the
following values. The default value is MNS.
Values Description
MAS Move and size with cells.
MNS Move but don't size with cells.
NMS Don't move or size with cells.
The size specifies the size of a picture. Possible values are STRETCH, Wnnn
or / and Hnnn. "STRETCH" means that the picture is resized to fit within the
cell. “W100” means that the width of the picture is set to 100 points. “H50”
means that the height of the picture is set to 50 points. The default means the
original size. If you just specify the width or height of the picture, not both,
XLReportGen will retain the original proportions of the picture when
XLReportGen resize it.
Example
w84
Remarks
On the supposition that the original picture is size 144 x 168 points.
XLReportGen will insert a picture, set the positioning option to Move but don't
size with cells, set the height of the picture to 72 points, and the width to 84
points.
- 23 -
Page 29

4.5 Charts
4.5.1 About Charts
Charts are visually appealing and make it easy for users to see comparisons,
patterns, and trends in data. You can use Microsoft Excel to add sophisticated,
colorful charts in your reports. For example, you can see at a glance whether
sales are falling or rising over quarterly periods, or how the actual sales
compare to the projected sales. You can create a chart on its own sheet or as
an embedded object on a worksheet.
4.5.2 Creating a Blank Chart
To create a chart in the report using XLReportGen, you need to add a chart in
the report template file. The chart will be brought into the report file with the
same chart type, display option, number format, titles, data labels and legends.
To add a chart in the template file:
1. Open the report template file using Microsoft Excel.
2. Enter the sample data for the chart on the worksheet.
3. Select that data and use the Chart Wizard to step through the process of
choosing the chart type and the various chart options, or use the Chart toolbar
to create a basic chart that you can format later.
4. Customize the chart. For example, change the chart type, colors, lines, fills,
number formats, titles, data labels and legends in charts.
5. After you have finished the customization, delete data from the chart. You
should keep a blank chart in the report template file. You can put data using
Report function in XLReportGen.
For more detail information, refer to Microsoft Excel Help.
- 24 -
Page 30

Chapter 5 Reporting with XLReportGen
5.1 Creating and Opening XRF Files
5.1.1 About XRF files
To generate a report with XLReportGen, you must create an XRF file with
an .xrf extension. The XRF file contains information such as the name of the
report template file, the name of the report file, log file name, data sources,
parameters and functions. The XRF file tells XLReportGen how to get data
from data sources and how to put data into a report.
5.1.2 Create a new XRF file
On the File menu, click New.
5.1.3 Open an XRF file
1. On the File menu, click Open.
2. In the Look in list, click the drive, folder, or Internet location that contains
the file you want to open.
3. In the folder list, locate and open the folder that contains the file.
4. Click the file, and then press Open button.
5.1.4 Save an XRF file
On the File menu, click Save. If you're saving the file for the first time, you'll be
asked to give it a name.
If you want save a file to another name, do as follows:
1. On the File menu, click Save As.
2. In the File name box, enter a new name for the file.
- 25 -
Page 31

3. Press Save button.
5.2 Configuring Files
5.2.1 About files
You should specify the report template file, report file, report file type and log
file. The report template file defines layouts, formats and styles of the report.
The report file is the report you want to generate. The type of the report file can
be different from the template file. The log file records the log information in the
report generating.
The file path can be a relative path or an absolute path. If it is a relative path,
the base path is the path of the XRF file. In the paths and names of the report
file, template file and log file, you can use parameters. For detailed information
about parameters, refer to “Configuring Parameters” in this document.
5.2.2 Configuring file information
1. On the Report menu, click Configuration. The Configuration dialog box
appears.
2. Click the File tab.
3. Input the path and name of the template file, the report file and the log file
into their text box.
4. In the File Type box, click the file type you want. If the file type of the report
is same as the template file, click the (Default) in the File Type box.
5. If you want to protect the report, select the Protect Report check box. If the
check box is selected, the Excel report generated is protected, and can not be
modified. If you select Random Password option button, a random password
will be created to protect the report. If you select Input Password option
button, you can input a password to protect the report.
- 26 -
Page 32

6. Press OK button to confirm the changes, press Cancel button to discard the
changes.
5.2.3 Converting files
You can convert a file from Microsoft Excel to and from another file format. For
example, the template file is a Lotus 1-2-3 file with a .wk3 extension, and the
report file is a HTML file with a .htm extension. For most file formats, Microsoft
Excel converts only the active sheet. To convert the other sheets, open the
template file, switch to the sheet you want to save, and save it.
The file formats XLReportGen supports can be one of these. What file format
XLReportGen supports is dependent on your Microsoft Excel. For example,
Microsoft Excel 2003 supports XML, but Microsoft Excel 97/2000 does not
support it. For more information about converting files, please refer to
Microsoft Excel Help. The file “xconv.cfg” located in the XLReportGen directory
contains the information of file formats. You can expand it if your Microsoft
Excel supports more file formats.
File Format Name Value Description Extension Converter
xlWorkbookNormal -4143 Microsoft Excel Workbook Xls Office97
xlTemplate 17 Template Xlt Office97
xlAddIn 18 Microsoft Excel Add-In xla Office97
xlHtml 44 Web Page htm html Office2000
xlWebArchive 45 Single File Web Page mht mhtml Office2003
xlXMLSpreadsheet 46 XML Spreadsheet xml Office2003
XlCSV 6 CSV (comma delimited) csv Office97
xlCSVMac 22 CSV (comma delimited)
(Macintosh)
xlCSVMSDOS 24 CSV (comma delimited)
(MS-DOS)
xlCSVWindows 23 CSV (comma delimited)
(Windows)
xlCurrentPlatformText -4158 Text (Tab-delimited) txt Office97
xlTextMac 19 Text (Tab-delimited)
(Macintosh)
csv Office97
csv Office97
csv Office97
txt Office97
- 27 -
Page 33

xlTextMSDOS 21 Text (Tab-delimited)
(MS-DOS)
xlTextWindows 20 Text (Tab-delimited)
(Windows)
xlTextPrinter 36 Formatted Text
(Space-delimited)
xlUnicodeText 42 Unicode Text txt Office2000
xlExcel2 16 Microsoft Excel 2.0
Worksheet
xlExcel2FarEast 27 Microsoft Excel 2.0
Worksheet Far East
xlExcel3 29 Microsoft Excel 3.0
Worksheet
xlExcel4 33 Microsoft Excel 4.0
Worksheet
xlExcel4Workbook 35 Microsoft Excel 4.0
Workbook
xlExcel5 39 Microsoft Excel 5.0/95
Workbook
xlExcel9795 43 Microsoft Excel 97-2003 &
5.0/95 Workbook
XlDBF2 7 DBF 2 (dBASE II) dbf Office97
XlDBF3 8 DBF 3 (dBASE III) dbf Office97
XlDBF4 11 DBF 4 (dBASE IV) dbf Office97
XlDIF 9 DIF (data interchange
format)
xlSYLK 2 SYLK (symbolic link format) slk Office97
xlWJ2WD1 14 WD1 (1-2-3) wd1 Office97
xlWK1 5 WK1 (1-2-3) wk1 Office97
xlWK1ALL 31 WK1, ALL (1-2-3) wk1 Office97
xlWK1FMT 30 WK1, FMT (1-2-3) wk1 Office97
xlWK3 15 WK3 (1-2-3) wk3 Office97
xlWK3FM3 32 WK3, FM3 (1-2-3) wk3 Office97
xlWK4 38 WK4 (1-2-3) wk4 Office97
xlWKS 4 WKS (Works) wks Office97
xlWorks2FarEast 28 Works Far East wks Office97
xlWQ1 34 WQ1 (Quattro Pro/DOS) wq1 Office97
txt Office97
txt Office97
prn Office97
xls Office97
xls Office97
xls Office97
xls Office97
xlw Office97
xlw Office97
xls Office2000
dif Office97
For Microsoft Excel 2007, please copy “xconv2007.cfg” to “xconv.cfg”. This file
contains the information of file formats for Microsoft Excel 2007.
File Format Name Value Description Extension
- 28 -
Page 34

xlOpenXMLWorkbook 51 Excel Workbook xlsx
xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled 52 Excel Macro-enabled
Workbook
xlExcel12 50 Excel Binary Workbook xlsb
xlExcel8 56 Excel 97-2003 Workbook xls
xlWorkbookNormal -4143 Excel 97-2003
WorkbookNormal
xlOpenXMLTemplateMacroEnabled 53 Excel Macro-enabled
Workbook Template
xlOpenXMLTemplate 54 Excel Template xltx
xlTemplate 17 Excel 97-2003 Template xlt
xlOpenXMLAddIn 55 Excel Add-in xlam
xlAddIn 18 Excel 97-2003 Add-In xla
xlHtml 44 Web Page htm html
xlWebArchive 45 Single File Web Page mht mhtml
xlXMLSpreadsheet 46 XML Spreadsheet xml
xlCSV 6 CSV (comma delimited) csv
xlCSVMac 22 CSV (comma delimited)
(Macintosh)
xlCSVMSDOS 24 CSV (comma delimited)
(MS-DOS)
xlCSVWindows 23 CSV (comma delimited)
(Windows)
xlCurrentPlatformText -4158 Text (Tab-delimited) txt
xlTextMac 19 Text (Tab-delimited)
(Macintosh)
xlTextMSDOS 21 Text (Tab-delimited)
(MS-DOS)
xlTextWindows 20 Text (Tab-delimited)
(Windows)
xlTextPrinter 36 Formatted Text
(Space-delimited)
xlUnicodeText 42 Unicode Text txt
xlExcel5 39 Microsoft Excel 5.0/95
Workbook
XlDIF 9 DIF (data interchange
format)
xlSYLK 2 SYLK (symbolic link
format)
xlsm
xls
xltm
csv
csv
csv
txt
txt
txt
prn
xlw
dif
slk
Note: Some of these file formats may not be available to you, depending on the
- 29 -
Page 35

language support (U.S. English, for example) that you’ve selected or installed.
5.3 Configuring Data Sources
5.3.1 About data source
A data source identifies a database computer you want to access. Because of
accessing data through ODBC, XLReportGen can access a wide range of data
sources, such as Oracle, DB2, Sybase, Informix, Microsoft SQL Server,
Teradata, MySQL, Microsoft Access, dBase. XLReportGen supports more
than one data sources in one report. You can get data from some different
databases such as Oracle, DB2 and Microsoft SQL Server, and put them into
one report.
You can define a connection to a data source using an ODBC data source
name or a connection string. If you use an ODBC data source name to make a
connection, you should specify a user name and a password. If you use a
connection string to make a connection, you also should specify a data source
name that you can reference in functions.
5.3.2 Adding, modifying and deleting a data source
1. On the Report menu, click Configuration. The Configuration dialog box
appears.
2. Click the Data Source tab.
3. If you want to add a data source, press New button, the New Data Source
dialog box appears.
To define a connection using an ODBC data source name, click Using
ODBC data source name option, input data source name, user name and
password, press OK button.
To define a connection using a connection string, click Using connection
- 30 -
Page 36

string option, input data source name, and connection string, press OK
button.
4. If you want to modify a data source, click the data source name in the Data
Source list box, and press Edit button, the Edit Data Source dialog box
appears.
To define a connection using an ODBC data source name, click Using
ODBC data source name option, change data source name, user name
and password, press OK button.
To define a connection using a connection string, click Using connection
string option, change data source name, and connection string, press OK
button.
5. If you want to delete a data source, click the data source name in the Data
Source list box, and press Delete button, the confirmation dialog box appears.
Press Yes button to delete the data source.
6. You can test a data source. Click the data source name in the Data Source
list box, and Press Test button to display the information of connection to the
data source.
7. Select or clear the Encrypt Password check box. If the check box is
selected, passwords will be saved in an encrypted format. Or passwords will
be saved in plain text.
8. Press OK button to confirm the changes, press Cancel button to discard the
changes.
5.4 Configuring Parameters
5.4.1 About parameters
You can use parameters in SQL statements. These values need to be
provided to XLReportGen before it executes these SQL statements. To use a
- 31 -
Page 37

parameter, you must declare it first. When XLReportGen generate a report, it
will prompt you to input the value of the parameter. XLReportGen will replace
the parameter name in the SQL statements with the actual value before it
submits the SQL statements to data sources.
A parameter has a name, a title and a default value. The name of a parameter
identifies the parameter. You can use the names in SQL statements. The titles
will be displayed in the prompt dialog box when XLReportGen is run.
Note: XLReportGen will replace all strings that are the same as the names of
the parameters. You should be careful to define a unique name for each
parameter. It is a good choice a name begins with the “$” character. For
example, you give the name “$ReportDate” for a parameter. Parameters are
case-sensitive.
5.4.2 Adding, modifying and deleting a parameter
1. On the Report menu, click Configuration. The Configuration dialog box
appears.
2. Click the Parameter tab.
3. If you want to add a parameter, press New button, the New Parameter
dialog box appears. Input parameter name, parameter title and default value,
press OK button.
4. If you want to modify a parameter, click the parameter name in the
Parameter list box, and press Edit button, the Edit Parameter dialog box
appears. Change the name, title and default value of the parameter, press OK
button.
5. If you want to delete a parameter, click the parameter name in the
Parameter list box, and press Delete button, the confirmation dialog box
appears. Press Yes button to delete the parameter.
6. Press OK button to confirm the changes, press Cancel button to discard the
- 32 -
Page 38

changes.
5.5 Inputting Functions
You should input functions in the editor window. A function includes a SQL
statement and some arguments. XLReportGen executes the SQL statement,
and determines whether or how to add data into the report. XLReportGen
sequentially executes functions.
Each function is begin with the “@” character. Syntax:
@functionno=functionname(arguments)
sqlstatement
The functionno is a label of the report function.
The functionname represents a report function.
The arguments for a function define various properties for the function. For
example, the “sheet” argument identifies a worksheet in the Excel workbook.
An argument takes the form Name="Value". The argument value can be
delimited by single or double quotes.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement.
For more detailed information about functions, see “Function Reference” in this
document.
You can use comments in text. A comment is the “/*” characters, followed by
any sequence of characters (including new lines), followed by the “*/”
characters. You cannot nest comments.
5.6 Running XRF Files
You can run an XRF file to generate a report in Microsoft Excel spreadsheet
format. XLReportGen supports Windows mode and command line mode.
- 33 -
Page 39

5.6.1 Windows mode
1. On the Report menu, click Run, the Run Report dialog box appears.
2. If you want to display the generated report, select the Display Report with
Microsoft Excel check box.
3. Press Start button to run the XRF file.
4. If parameters are defined in the XRF file, XLReportGen will pop up a prompt
dialog box. Input the values of the parameters, and press OK button.
5. While XLReportGen is being run, it will display some information such as
status, SQL count, error count, function No., records count and log information.
6. You can interrupt the running. Click End button to interrupt it. XLReportGen
will immediately save and close the report.
7. Click Close button after completion.
8. If you want to open the report, click Open Report File on the File menu.
9. If you want to check the log, click Open Log File on the File menu.
5.6.2 Command line mode
You can run an XRF file in command line. You have defined two parameters in
the XRF file “myreport.xrf”. The first parameter is sales date “$SalesDate”, and
the second is the category of the products “$Category”. You can run
XLReportGen in command line mode as follows:
excelreport c:\excelreport\myreport.xrf -c 1996-05-01 “Dairy Products”
XLReportGen will replace “$SalesDate” in SQL statements with “1996-05-01”,
replace “$Category” with “Dairy Products”, and then submit SQL statements to
data sources.
5.7 Using Excel Formulas
Formulas are equations that perform calculations on values in your worksheet.
- 34 -
Page 40

A formula starts with an equal sign (=). For example, the following formula
multiplies 2 by 3 and then adds 5 to the result.
=5+2*3
A formula can also contain any or all of the following: functions, references,
operators, and constants. For more detail information about formulas,
functions and references, refer to Microsoft Excel Help.
In a report template file, you can use all kind of Microsoft Excel formulas. And
then all formulas in the report template file will be brought to the final report file.
Example
Show Unit Price, Quantity, Discount and Amount. The Amount will be changed
if an end user changes Unit Price, Quantity or Discount.
You can use a formula to show Amount.
1. Create a template file as follows, and define the formula "=C2*D2*(1-E2)" in
cell F2. You must use the relative reference.
2. Write the report function as follow, and use COPYRANGE to copy the
formula to all following cells for each record. For the first record, XLReportGen
will directly put data into row 2. For the other records, it will copy row 2 to the
current row, and then put data into the current row. So the formula in cell F2
will copy to cell F3, F4… and Microsoft Excel will automatically change the
formula to "=C3*D3*(1-E3)" …
@F1=Report(sheet="Sheet1" cell=A2 copyrange=2:2)
SELECT c.CompanyName AS Customer
,p.ProductName
,d.Quantity
,d.UnitPrice
- 35 -
Page 41

,d.Discount
FROM Orders o
, Customers c
, OrderDetails d
, Products p
WHERE o.CustomerID = c.CustomerID
AND o.OrderID = d.OrderID
AND d.ProductID = p.ProductID
AND YEAR(o.OrderDate) = YEAR('1996-04-01')
AND MONTH(o.OrderDate) = MONTH('1996-04-01')
ORDER BY 1, 2
3. Generate the report.
Example
Add totals such as Total Quantity, Total Amount.
You can use the math functions of Microsoft Excel, such as SUM.
1. Create a report template file as follows, define the formula of total quantity
as "=SUM(C7:C8)" in cell C9, and the formula of total amount as
"=SUM(D7:D8)" in cell D9. You must use the relative reference.
2. Write the report function as follow. When XLReportGen insert some rows
according to the records, Microsoft Excel will automatically change the
formulas.
- 36 -
Page 42

@F2=REPORT(sheet="Report2" type=var cell=B7 reserve=2)
SELECT c.CategoryName, SUM(d.Quantity), Sum(d.UnitPrice * d.Quantity *
(1-d.Discount))
FROM Orders o
,OrderDetails d
,Products p
,Categories c
WHERE o.OrderID = d.OrderID
AND d.ProductID = p.ProductID
AND p.CategoryID = c.CategoryID
AND YEAR(o.OrderDate) = YEAR('1996-04-01')
AND MONTH(o.OrderDate) = MONTH('1996-04-01')
GROUP BY c.CategoryName
ORDER BY c.CategoryName
;
3. The following is the generated report. The formula of total quantity is
changed to “=SUM(C7:C14)”, and the formula of total amount is changed to
“=SUM(D7:D14)”.
5.8 Sorting, Grouping and Totaling
5.8.1 Sorting data
Sorting means placing data in some kind of order to help you find and evaluate
- 37 -
Page 43

it. For example, you may want to have a customer list sorted alphabetically by
name or by country.
To sort your data, you can use SQL. Use the ORDER BY clause to have your
results displayed in a sorted order.
SELECT EmployeeID
,LastName
,FirstName
,HireDate
FROM Employees
ORDER BY HireDate; /* ascending sort */
In the example above, results will come back in ascending order by hire date.
To explicitly specify ascending or descending order, add ASC or DESC, to the
end of your ORDER BY clause. The following is an example of a descending
order sort.
ORDER BY HireDate DESC; /* descending sort */
5.8.2 Totaling
You can sum the values, count all the values or only those values that are
distinct from one another, and determine the maximum, minimum, average. To
add totals, there are two ways.
1. You can add the totals using the math functions of Microsoft Excel, such as
SUM. For more detail information, refer to “Using Excel Formulas” in this
document.
2. You can use the aggregate functions in SQL statement, such as COUNT,
SUM, AVG, MAX, MIN.
(1) In the fixed table report, you can add a total directly using a separate SQL.
(2) In the variable table report, you must add the total first using a Fixed Table
report function before you use the Variable Table report function. Because the
- 38 -
Page 44

cell address of the total field will change after you use Variable Table report
function.
5.8.3 Grouping data and subreports
Grouped data is data that is sorted and broken up into meaningful groups. In a
customer list, for example, a group might consist of all those customers living
in the same Region.
To group data in a report, you should use GROUP VARIABLE TABLE
REPORT function. For more detail information, refer to “Group Variable Table
Report” in this document.
Using the feature of grouping data, you can make subreports within a report. A
subreport would typically be used to perform one-to-many lookups such as
Customer / Order / OrderDetails.
To make sub reports within the main report,
1. Write a JOIN SQL statement to access data from two or more tables. For
example, you can join Customers, Orders and OrderDetails tables.
2. Use GROUP VARIABLE TABLE REPORT function.
For more detail information, refer to the samples invoice.xrf,
product_catalog.xrf and sales_detail.xrf within XLReportGen.
5.8.4 Subtotaling
A subtotal is a summary that totals or sums numeric values in a group. You
can sum the values in each group, count all the values in each group, and
determine the maximum, minimum, average in each group. For example,
determine the total sales per sales representative in a sales report.
To add subtotals, you can use the functions of Microsoft Excel or aggregate
functions in SQL statement.
1. You can add sub-totals using math functions of Microsoft Excel, such as
- 39 -
Page 45

SUM.
(1) The range of SUM function should contain cells for detail records in the
report template file.
(2) The range of SUM function must contain at least one row/column that is not
included in the range for the details. For example, the row 13 is for the details,
you should add blank row 14, and write the function as SUM(H13:H14). If you
do not want to show the blank row in the report, you may hide the row.
(3) You should use the relative references. For example, SUM(H13:H14).
Microsoft Excel will change the function automatically when XLReportGen
adds some rows in the report.
2. If you want to have a total and sub-totals,
(1) You can add the total using SUMIF function. The range of SUMIF function
must contain one row/column that is not included in the range of the group. For
example, the range of the group is rows 1:15, you should add blank row 16,
and write the function as SUMIF(G:G,"Subtotal:",H1:H16). You may hide the
blank row.
(2) You can add the total using the aggregate function in SQL statement. You
must add the total first using a Fixed Table report function before you use the
Variable Table report function. Because the cell address of the total field will
change after you use Variable Table report function.
3. You can add sub-totals using the aggregate function in SQL statement too.
(1) Use aggregate function and GROUP BY clause, get summary data for each
group, and insert results into a temporary table.
(2) If you have the different kinds of summaries, repeat the step 1, and insert
results into another temporary table.
(3) Use group table report function, and join the detail data and the summary
data using JOIN. The summary fields must be included in the group list.
For more detail information, please refer to the samples invoice.xrf and
- 40 -
Page 46

sales_detail.xrf within XLReportGen.
5.9 Charting
Charts are visually appealing and make it easy for users to see comparisons,
patterns, and trends in data. You can use Microsoft Excel to add sophisticated,
colorful charts in your reports. For example, you can see at a glance whether
sales are falling or rising over quarterly periods, or how the actual sales
compare to the projected sales.
To create a chart in a report, you should create the chart in the template file.
You can create a chart on its own sheet or as an embedded object on a
worksheet. For more detail information how to create chart, refer to Microsoft
Excel Help.
To create a chart in the report template file, you can use some sample data.
Using sample data, you can set the various chart options. After you have made
the report template, you delete the sample data. When you generate the report,
XLReportGen will put data into the report, and you get the chart. For more
detail information about charting, refer to the sample monthly_sales.xrf within
XLReportGen.
Example
The following function provides data for the chart: Sales by Categories.
@F2=REPORT(sheet="Report2" type=var cell=B7 reserve=2)
SELECT c.CategoryName
, SUM(d.Quantity)
, Sum(d.UnitPrice * d.Quantity * (1-d.Discount))
FROM Orders o
,OrderDetails d
,Products p
,Categories c
- 41 -
Page 47

WHERE o.OrderID = d.OrderID
AND d.ProductID = p.ProductID
AND p.CategoryID = c.CategoryID
AND YEAR(o.OrderDate) = YEAR('$ReportMonth-01')
AND MONTH(o.OrderDate) = MONTH('$ReportMonth-01')
GROUP BY c.CategoryName
ORDER BY c.CategoryName
Result
The worksheet of the chart defined in the report template:
The chart defined in the report template is a blank chart.
The worksheet of the chart generated in the report:
The chart generated in the report:
- 42 -
Page 48

5.10 Pictures
5.10.1 Inserting pictures into a report template
To make eye-catching reports, you can add pictures to your reports. You can
insert pictures into the report template directly in Microsoft Excel. For example,
you want to display a logo in your report. You can insert the logo graphics file
into the report template. For more information about adding pictures to
worksheets, refer to Microsoft Excel Help.
5.10.2 Inserting pictures into a report
Except for inserting the static pictures during report design, you want to insert
pictures during report buliding process. You hope a reporting tool to pull
pictures from database into Excel report. XLReportGen can insert pictures
from the graphics files, and support all graphics file format that Microsoft Excel
support.
To insert pictures into a report using XLReportGen, you should do as follows:
1. Store the path and name of the graphics files in the database
You stored the path and file name of the pictures in database, did not store the
pictures. The file path can be a relative path, an absolute path or a URL. For
example, you store "images\emp1.jpg" in Photo field.
2. Identify the image fields in the report function
Write a report function in the XRF file, and identify the image fields using
IMAGE argument. For example,
@F1=Report(sheet="Employee Profile" ... image=photo)
3. Specify the positioning option and size in the report template
To specify the positioning option and size, you should write a formatting
expression into the cell in the report template file. XLReportGen will get the
- 43 -
Page 49

text of the cell, and insert a picture into the cell according to the instruction in
the format expression.
4. Run XLReportGen to generate report with pictures
During report generating process, XLReportGen will read the graphics files,
and insert them into the report according to your instruction. If the path and file
name of the picture is “”, XLReportGen will return “”. XLReportGen will return
“#Error” if it does not find the file of the picture.
For more detail information about pictures, refer to the samples
employee_profile.xrf, product_catalog.xrf within XLReportGen.
5.11 Using Parameters
To use a parameter, you must define it first. If you have defined a parameter
name, you can use it in SQL statements. When XLReportGen is run, it will
replace the parameter name in the SQL statements with the actual value
before it submits the SQL statements to data sources. Besides in SQL
statements, you can use parameters in the paths and names of report file and
log file.
In fact, XLReportGen will replace all strings that are the same as the names of
the parameters. You should be careful to define a unique name for each
parameter. It is a good choice a name begins with the “$” character.
Example
Input an order id to get the order information. The field OrderID is numeric
type.
1. Defining a parameter
Define a parameter as follows:
Name: $OrderID
Title: Order ID (>=10248)
- 44 -
Page 50

Default: 10360
2. Using a parameter
You can use the parameter “$OrderID” in SQL statements. For example:
SELECT o.OrderID
,o.OrderDate
,SUM(d.UnitPrice * d.Quantity * (1-d.Discount)) AS Amount
FROM Orders o, OrderDetails d
WHERE o.OrderID = d.OrderID
AND o.OrderID = $OrderID
GROUP BY o.OrderID, o.OrderDate
;
Example
Define two parameters. The first parameter is sales date, and the second is the
category of the products. The field OrderDate is date type, and CategoryName
is char type.
1. Defining parameters
Define parameters as follows:
Name1: $SalesDate
Title1: Sales Date
Default1: 1996-05-01
Name2: $Category
Title2: Category of Products
Default2:
2. Using parameters
You can use the parameters “$SalesDate”, “$Category” in SQL statements.
For example:
SELECT ……
FROM Orders, OrderDetails, Products, Categories
- 45 -
Page 51

WHERE ……
AND OrderDate = ‘$SalesDate’
AND CategoryName LIKE '$Category%'
;
/* For Microsoft Jet SQL, LIKE '$Category*' */
Example
Get the information from the database, table and column that you identify when
the report is generated.
1. Defining parameters
Define parameters as follows:
Name1: $Database
Title1: Database Name
Default1:
Name2: $Table
Title2: Table Name
Default2:
Name3: $Column
Title3: Column Name
Default3:
2. Using parameters
You can use the parameters “$Database”, “$Table” and “$Column” in SQL
statements. For example:
USE $Database;
or
DATABASE $Database;
SELECT $Column
FROM $Table
;
- 46 -
Page 52

Example
Use parameters in the path and name of the report file and log file.
1. Defining a parameter
Define a parameter as follows:
Name: $CustomerID
Title: Customer ID
Default: C000001
2. Using a parameter
ReportFileName=report\report_$CustomerID.xls
LogFileName=log\report_$CustomerID.log
or
ReportFileName=report\$CustomerID\report.xls
LogFileName=log\$CustomerID\report.log
5.12 Programming
5.12.1 Using add-ins, macros
In Microsoft Excel, you can automate a task with a macro. A macro is a series
of commands and functions that are stored in a Microsoft Visual Basic module
and can be run whenever you need to perform the task.
You can write macros in the report template file, and can use automatic
macros, such as Auto_Open, Auto_Close to automate a task. For examples,
you can use Auto_Open macro to make the template, or use Auto_Close to
change the report after XLReportGen puts data into the report.
Add-ins, files in the XLStart directory are not loaded when Microsoft Excel is
called by a program, and Auto_Open macros won’t be run when you open the
file from a program. XLReportGen has an option to process it.
To use the option:
- 47 -
Page 53

1. On the Tools menu, click Option. The Options dialog box appears.
2. Click Excel tab, select Enable addins when Excel starts up or Enable
Auto_Open macro.
3. Press OK button.
5.12.2 Making XRF files programmatically
Sometimes you want to make an XRF file programmatically. You can do this
because the XRF file is a text file. You can write a program to make an XRF file
using C, perl or DOS shell, and then run XLReportGen to generate report. The
two steps can be written into a batch file.
1. Write a program to make the XRF file as you need.
2. Write a batch file to call the program and XLReportGen in command line
mode.
For example, you write a batch file runrpt.bat as follows. changexrf is an
executable file that reads template.txt and output template.xrf. First runrpt.bat
call changexrf to make the XRF file, and then call XLReportGen to generate
the report.
@echo off
if "%1"=="" goto usage
goto process
:usage
echo Usage: runrpt ReportDate
echo ReportDate Date format 'YYYY-MM-DD'
goto :EOF
:process
changexrf %1 <"template.txt" >"template.xrf"
ExcelReport "template.xrf" –C %1
- 48 -
Page 54

Chapter 6 Function Reference
6.1 Report Function
6.1.1 Report Function
The REPORT function executes a SQL statement to get data from data source,
and put data into a worksheet in the report file. The REPORT function can
make three types of reports:
Fixed table report
Non-group variable table report
Group variable table report
6.1.2 Fixed Table Report Function
In a fixed table report, the number of rows and columns is fixed. XLReportGen
executes a SQL statement to get data from data source, and directly fills data
vales into the cells of a worksheet in the report file.
Syntax
Report(…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
TYPE = “fix”
SHEET = sheet
FILLORDER = fillorder
CELL= celllist
RANGE = range
IMAGE = fieldlist
PAGEBREAK = pagelength
- 49 -
Page 55

CONNECT = datasource
The TYPE argument specifies the report type. "fix" means a fixed table report.
The SHEET argument identifies a worksheet in the report template. The sheet
is the name or index number of the worksheet. The index number starts at 1.
The FILLORDER argument specifies the order in which XLReportGen fills data.
Possible values are row or col. "row" means to fill data by rows, and "col"
means to fill data by columns. Default is row.
The CELL argument specifies the positions where data values will be inserted.
The celllist is the list of cells or fields separated by the “,” character. For a table
report, the celllist identifies the cells in a worksheet. For example,
“A2,B2,B3,D2,D3”. The cells in the celllist should correspond to the data
source fields in the SQL statement. The value of the first field is put into the
first cell, and the value of the second field is put into the second cell ……
XLReportGen will use the next cell if you omit a cell except the first cell. If
FILLORDER=“row”, the next cell is the right cell. If FILLORDER=“col”, the next
cell is the below cell.
The RANGE or COPYRANGE argument specifies the range in the worksheet
to be used for the records. XLReportGen will skip or repeat the range for each
record. You can reference a range of cells like “2:4” or “B2:D5”. The default
range is the area that includes all cells for the records. For RANGE argument,
XLReportGen will skip the rows/columns of the range for each record. For
COPYRANGE argument, it will copy the original range to the range where data
will be filled for each record.
The IMAGE argument specifies the fields are picture files. The fieldlist is the
list of data source fields separated by the “,” character. You can identify a field
using the name of field or the index number of field, but not simultaneously. In
data source, you stored the path and file name of the picture, not the picture.
The file path can be a relative path, an absolute path or a URL. If it is a relative
- 50 -
Page 56

path, the base path is the path of the report template file.
The PAGEBREAK argument specifies the page breaks. The unit of page
length is r that means record. For example, “6r” or “6” means that
XLReportGen will insert a page break per 6 records. Default is no page break.
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the XRF file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement such as a SELECT statement.
Example
The following function makes the report: Top 5 Employees for Sales.
@F1=REPORT(sheet="Report6" type=fix cell=B7)
SELECT TOP 5 e.FirstName + ' ' + e.LastName
, SUM(d.Quantity)
, Sum(d.UnitPrice * d.Quantity * (1-d.Discount)) AS SalesAmount
FROM Orders o
,OrderDetails d
,Products p
,Employees e
WHERE o.OrderID = d.OrderID
AND d.ProductID = p.ProductID
AND o.EmployeeID = e.EmployeeID
AND YEAR(o.OrderDate) = 1996
AND MONTH(o.OrderDate) = 04
GROUP BY e.FirstName, e.LastName
ORDER BY 3 DESC
- 51 -
Page 57

;
Result
The fixed table report defined in the report template:
The fixed table report generated in the report:
Remarks
1. The SQL statement will get the information of top 5 employees for sales,
including employee name, quantity of products, and sales amount.
2. type=“fix”. It is a fixed table report.
3. sheet = “Report6”. XLReportGen will put data into the worksheet “Report6”
in the report file.
4. cell=B7. The cells corresponding to the first record are “B7,C7,D7”.
5. The default range is “B7:D7”.
6. XLReportGen executes the SQL statement, and gets data from data source.
First, it fetches the first record, puts the value of the first field into cell B7, the
value of the second field into cell C7, and the value of the third field into D7.
And then it fetches the next record, skips one row, and puts data into cells B8,
C8, and D8……
- 52 -
Page 58

6.1.3 Non-group Variable Table Report Function
In a variable table report, the number of rows or columns in the table is unfixed,
and it is variable as the number of the result records. XLReportGen executes a
SQL statement to get data from data source, inserts some blank rows/columns
or copy a range for each record, then fills data values into the cells of a
worksheet in the report file.
Syntax
Report(…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
TYPE = “var”
SHEET = sheet
FILLORDER = fillorder
CELL= celllist
RANGE = range
IMAGE = fieldlist
RESERVE = reserverecords
PAGEBREAK = pagelength
NODATA = nodataoption
CONNECT = datasource
The TYPE argument specifies the report type. "var" means a variable table
report. Default is var.
The SHEET argument identifies a worksheet in the report template. The sheet
is the name or index number of the worksheet. The index number starts at 1.
The FILLORDER argument specifies the order in which XLReportGen fills data.
Possible values are row, col, rowrange or colrange. "row" means to insert
entire rows and fill data by rows. "col" means to insert entire columns and fill
- 53 -
Page 59

data by columns. "rowrange" means to insert range and fill data by rows.
"colrange" means to insert range and fill data by columns. Default is row.
The CELL argument specifies the positions where data values will be inserted.
The celllist is the list of cells or fields separated by the “,” character. For a table
report, the celllist identifies the cells in a worksheet. For example,
“A2,B2,B3,D2,D3”. The cells in the celllist should correspond to the data
source fields in the SQL statement. The value of the first field is put into the
first cell, and the value of the second field is put into the second cell ……
XLReportGen will use the next cell if you omit a cell except the first cell. If
FILLORDER=“row”, the next cell is the right cell. If FILLORDER=“col”, the next
cell is the below cell.
The RANGE or COPYRANGE argument specifies the range in the worksheet
to be used for the records. XLReportGen will skip or repeat the range for each
record. You can reference a range of cells like “2:4” or “B2:D5”. The default
range is the area that includes all cells for the records. For RANGE argument,
XLReportGen will insert the blank rows/columns of the range for each record.
For COPYRANGE argument, it will copy the original range and insert the
copied range for each record.
The IMAGE argument specifies the fields are picture files. The fieldlist is the
list of data source fields separated by the “,” character. You can identify a field
using the name of field or the index number of field, but not simultaneously. In
data source, you stored the path and file name of the picture, not the picture.
The file path can be a relative path, an absolute path or a URL. If it is a relative
path, the base path is the path of the report template file.
The RESERVE argument specifies the number of the records for which you
reserved some rows/columns in the report template for the report. The
reserverecords represents the number of the records you reserved in the
report template. Possible values are 1 or 2. One means you reserved some
- 54 -
Page 60

rows/columns for one record, and two means some rows/columns for two
records. Default is 1.
The PAGEBREAK argument specifies the page breaks. The unit of page
length is r that means record. For example, “6r” or “6” means that
XLReportGen will insert a page break per 6 records. Default is no page break.
The NODATA argument specifies an option when no data are returned from
data source. If the value is "delrange", XLReportGen will delete the range
when no data are returned. If the value is "delsheet", XLReportGen will delete
the sheet when no data are returned. Default is to do nothing.
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the XRF file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement such as a SELECT statement.
Example
The following function will makes the report: Mail Label.
@F1=Report(sheet="Mail Label" type=var cell=B7,B8,B9,B10 copyrange=1:11
pagebreak = 4r)
SELECT CompanyName
,Address
,CityName & ', ' & CountryName
,PostalCode
FROM Customers, Cities, Countries
WHERE Customers.CityCode = Cities.CityCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Cities.CountryCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Countries.CountryCode
- 55 -
Page 61

ORDER BY CompanyName
;
Result
The non-group variable table report defined in the report template:
The non-group variable table report generated in the Excel report:
Remarks
1. The SQL statement will get the information of customers including company
name, address, city name, country name, and postal code.
2. type=“var”. It is a variable table report. And there is no GROUP argument,
- 56 -
Page 62

so it is a non-group variable table report.
3. sheet="Mail Label". XLReportGen will put data into the worksheet “Mail
Label” in the Excel report file.
4. cell=B7,B8,B9,B10. These cells correspond to the first record.
5. copyrange=1:11. Because the default range is “B7:B9”, you must specify a
range explicitly. XLReportGen will copy the range for each record.
6. pagebreak = 4r. XLReportGen will add a page break per 4 records.
7. XLReportGen executes the SQL statement, and gets data from data source.
First, it fetches the first record, copy the range, and fill data. And then it fetches
the next record…… One page contains 4 mail labels.
6.1.4 Group Variable Table Report Function
The Group Variable Table Report function generates a variable table report
and group data. In a variable table report, the number of rows or columns in
the table is unfixed, and it is variable as the number of the result records.
XLReportGen executes a SQL statement to get data from data source, copy
the group range for each group, copy the detail range for each record, then fills
data into the worksheet.
Syntax
Report(…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
TYPE = “var”
SHEET = sheet
FILLORDER = fillorder
CELL= celllist
RANGE = range
GROUP= grouplist
- 57 -
Page 63

GROUPRANGE = grouprange
IMAGE = fieldlist
PAGEBREAK = pagelength
NODATA = nodataoption
CONNECT = datasource
The TYPE argument specifies the report type. "var" means a variable table
report. Default is var.
The SHEET argument identifies a worksheet in the report template. The sheet
is the name or index number of the worksheet. The index number starts at 1.
The FILLORDER argument specifies the order in which XLReportGen fills data.
Possible values are row, col, rowrange or colrange. "row" means to insert
entire rows and fill data by rows. "col" means to insert entire columns and fill
data by columns. "rowrange" means to insert range and fill data by rows.
"colrange" means to insert range and fill data by columns. Default is row.
The CELL argument specifies the positions where data values will be inserted.
The celllist is the list of cells or fields separated by the “,” character. For a table
report, the celllist identifies the cells in a worksheet. For example,
“A2,B2,B3,D2,D3”. The cells in the celllist should correspond to the data
source fields in the SQL statement. The value of the first field is put into the
first cell, and the value of the second field is put into the second cell ……
XLReportGen will use the next cell if you omit a cell except the first cell. If
FILLORDER=“row”, the next cell is the right cell. If FILLORDER=“col”, the next
cell is the below cell.
The RANGE or COPYRANGE argument specifies the range in the worksheet
to be used for the details. XLReportGen will skip or repeat the range for each
record. You can reference a range of cells like “2:4” or “B2:D5”. The default
range is the area that includes all cells for the details. For RANGE argument,
XLReportGen will insert the blank rows/columns of the range for each record.
- 58 -
Page 64

For COPYRANGE argument, it will copy the original range and insert the
copied range for each record. But if the range of any group is not same as the
range of the details, RANGE is same as COPYRANGE.
The GROUP argument specifies the group of the report. The grouplist is the
list of data source fields separated by the “,” character. You can identify a field
using the name or index number of the field, but not simultaneously. In one
report, there may be up to 10 groups. The first GROUP is group one, the
second is group two...... Notes: the order of the groups should be in
accordance with the order of the ORDER BY clause in the SQL statement.
The GROUPRANGE argument follows the GROUP argument, and specifies
the range of the group in the worksheet. For example, the grouprange of level
1 must follow the group of level 1, and the grouprange of level 2 must follow
the group of level 2. XLReportGen will repeat the group range for each group.
The range of the group should contain the range of the details and the area
that includes all cells for this group. You reference a group range like “2:4” or
“B2:D5”. For example, there are two groups, the range of the group one
contains all cells for the group one and the range of the group two, and the
range of the group two contains all cells for the group two and the range of the
details. The default range is the area that includes all cells for this group and
the range or group range for the lower level group.
The IMAGE argument specifies the fields are picture files. The fieldlist is the
list of data source fields separated by the “,” character. You can identify a field
using the name of field or the index number of field, but not simultaneously. In
data source, you stored the path and file name of the picture, not the picture.
The file path can be a relative path, an absolute path or a URL. If it is a relative
path, the base path is the path of the report template file.
The PAGEBREAK argument specifies the page breaks. The unit of page
length is r or g. "r" means record, "g1" means group one, "g2" means group
- 59 -
Page 65

two...... For example, “6r” or “6” means that XLReportGen will insert a page
break per 6 records, “1g1” or “1g” means a page break per group one, and
“1g1,6r” means a page break per group one or 6 records. Default is “” that
means no page break.
The NODATA argument specifies an option when no data are returned from
data source. If the value is "delrange", XLReportGen will delete the range
when no data are returned. If the value is "delsheet", XLReportGen will delete
the sheet when no data are returned. Default is to do nothing.
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the XRF file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement such as a SELECT statement.
Example
The following function will makes the report: Customer Profile.
@F1=Report(sheet="Customer Profile" cell=A6,B7,C7,D7,D8,E7,E8,E9
range=6:9 group=1 pagebreak = 6r)
SELECT LEFT(CompanyName,1)
,CompanyName
,ContactName
,'Phone: ' & Phone
,'Fax: ' & Fax
,Address
,CityName & ', ' & CountryName
,PostalCode
FROM Customers, Cities, Countries
- 60 -
Page 66

WHERE Customers.CityCode = Cities.CityCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Cities.CountryCode
AND Customers.CountryCode = Countries.CountryCode
ORDER BY CompanyName
;
Result
The group varibale table report defined in the report template:
The group varibale table report generated in the report:
Remarks
1. The SQL statement will get the information of customers including company
name, contact name, phone, fax, address, city name, country name, and
postal code.
2. There are GROUP argument, so it is a group variable table report.
3. sheet=" Customer Profile". XLReportGen will put data into the worksheet
“Customer Profile” in the report file.
4. group=1. XLReportGen will group data by the first letter of the company
name.
- 61 -
Page 67

5. cell= A6,B7,C7,D7,D8,E7,E8,E9. These cells correspond to the first record.
6. range=6:9. Because the default range is “B7:E9”, you must specify a range
explicitly. XLReportGen will copy the range for each record.
7. There is no grouprange. XLReportGen will give a default. The default
grouprange is “6:9”.
8. pagebreak = 6r. XLReportGen will add a page break per 6 records.
9. XLReportGen executes the SQL statement, gets data from data source, and
puts data into the worksheet “Customer Profile” in the report file. Because the
range is same as the group range, XLReportGen will copy the range for each
record, fill the value of the first field per group, and fill the values of other fields
per record. One page contains the information of 6 records.
6.2 Name Function
The Name function executes a SQL statement, and assigns the values to the
names defined in the Excel workbook. XLReportGen will just fetch the first
record, no matter how many records are returned from data source.
Syntax
Name(…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
NAME= namelist
CONNECT= datasource
The NAME argument specifies the names you want assign values to. The
namelist is the list of names separated by the “,” character. For example,
“BeginDate, EndDate” means two names: BeginDate and EndDate that should
be defined in the report template. The names in the namelist should
correspond to the fields in the SQL statement. The value of the first field is put
into the first name, and the value of the second field is put into the second
- 62 -
Page 68

name …
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the XRF file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement such as a SELECT statement.
Example
The following function executes a SQL statement, assigns the values of fields
to names.
@F1=NAME(NAME=BeginDate,EndDate)
SELECT min_date, max_date
FROM tmp0
;
Remarks
XLReportGen executes the SQL statement, get data from data source. It
assigns the value of field “min_date” to the name “BeginDate” and the value of
field “max_date” to the name “EndDate”.
You should define the names in the report template first. To define and use a
name, do as follows:
1. Run Microsoft Excel program, and open the report template file.
2. On the Insert menu, click Name, and click Define.
3. In the Name box, enter a name such as BeginDate. In the Reference box,
enter “=1”.
4. In a cell such as C4, enter “=BeginDate”.
5. On the Format menu, click Cells, and then click the Number tab. Click Date
type, and select format you want to use.
- 63 -
Page 69

6.3 ExecSQL Function
The EXECSQL function executes a SQL statement, but does not return result
to report.
Syntax
ExecSQL(…)
sqlstatement
Arguments
CONNECT= datasource
The CONNECT argument specifies the connection to a data source. The
CONNECT can takes a string that expresses a data source name or a number
that expresses a data source index. The index number of data source is the
sequential number defined in the XRF file, and starts at 1. The default implies
the first data source.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement that can be DDL (Data Definition
Language), DML (Data Manipulation Language) and even DCL (Data Control
Language).
Using EXECSQL function, you can open a database, create a temporary table,
insert data into a temporary table, update data, execute a stored procedure,
and drop a table. It is very useful to create a temporary table, and prepare data
for REPORT function.
Example
The following functions will create a table tmp0, and add some records into
table. No result is returned to the report file.
@F1=EXECSQL()
CREATE TABLE tmp0 (
min_date DATE,
max_date DATE)
- 64 -
Page 70

;
@F2=EXECSQL()
INSERT INTO tmp0
SELECT …
;
- 65 -
Page 71

Chapter 7 Menus, Toolbar and Shortcut Keys
7.1 File Menu
The File menu offers the following commands:
New Creates a new XRF file.
Open Opens an existing XRF file.
Close Closes an opened XRF file.
Save Saves an opened XRF file using the same filename.
Save As Saves an opened XRF file to a specified file name.
Open Report
Template
Open Report File Opens an existing report file.
Open Log File Opens an existing log file.
Recent Files Opens last XRF files you closed.
Exit Exits XLReportGen.
Opens an existing report template file.
7.2 Edit Menu
The Edit menu offers the following commands:
Undo Reverse previous editing operation.
Cut
Copy Copies text from the document to the clipboard.
Paste Pastes text from the clipboard into the document.
Delete Deletes the selection.
Select All Selects the entire text.
Find Finds the specified text.
Find Next Finds the next matching text.
Replace Replaces specific text with different text.
Go to Goes to specified line or function in the document.
Deletes text from the document and moves it to the
clipboard.
7.3 Report Menu
The Report menu offers the following commands:
Configuration
Configures the file names, data sources and
parameters.
- 66 -
Page 72

Run Runs the XRF file to generate a report.
7.4 Tools Menu
The Tools menu offers the following commands:
Option Sets options.
7.5 Help Menu
The Help menu offers the following commands:
Help Context Starts the online help system.
Tutorial Starts a brief step-by-step tutorial.
Tip of the Day
Hints and Tips
Shortcut Keys Shows the keyboard map.
Home Page
Support
Buy Now Buy XLReportGen immediately.
About Displays the version number of XLReportGen.
Displays a dialog containing a useful tip about
XLReportGen.
Displays miscellaneous hints and tips on how to use
XLReportGen productively.
Takes you to the home page of XLReportGen web
site.
Takes you to the support page of XLReportGen web
site.
7.6 Toolbar
The toolbar provides quick access to many features. The buttons on the
toolbar perform the following commands:
Buttons Commands
Creates a new XRF file.
Opens an existing XRF file.
Saves an opened XRF file using the same filename.
Open the report template file.
- 67 -
Page 73

Open the report file.
Deletes text from the document and moves it to the
clipboard.
Copies text from the document to the clipboard.
Pastes text from the clipboard into the document.
Reverse previous editing operation.
Finds the specified text.
Goes to specified line or function in the document.
Runs the XRF file to generate a report.
Starts the online help system.
Buy XLReportGen immediately.
7.7 Shortcut Keys
Shortcut Keys Commands
Ctrl+N Creates a new XRF file.
Ctrl+O Opens an existing XRF file.
Ctrl+S Saves an opened XRF file using the same filename.
Ctrl+U Reverse previous editing operation.
Ctrl+X
Ctrl+C Copies text from the document to the clipboard.
Deletes text from the document and moves it to the
clipboard.
Ctrl+V Pastes text from the clipboard into the document.
Delete Deletes the selection.
Ctrl+A Selects the entire text.
Ctrl+F Finds the specified text.
- 68 -
Page 74

F3 Finds the next matching text.
Ctrl+H Replaces specific text with different text.
Ctrl+G Goes to specified line or function in the document.
F2 Configures the file names, data sources and parameters.
F5 Runs the XRF file to generate a report.
F1 Starts the online help system.
- 69 -
Page 75

Chapter 8 Hints and Tips
You can run XLReportGen from the command line. The format is:
excelreport <xrf file name> [-c] [-d] [-u1 user1] [-p1 pwd1] … [pa1 pa2 …]
For example:
excelreport c:\excelreport\monthlysales.xrf -c 199605
XLReportGen can be scheduled with Windows Scheduled Tasks or other tools.
The process of generating reports can be fully automated, periodically or on
events.
XLReportGen comes with a sample database Sample.mdb and some sample
reports. You can use them when learning the program. To use the sample
reports, you must add a data source named “Report Sample” to specify the
sample database.
To make a report template, you can use some sample data. It is very useful
especially for formatting. After you have made the report template, you delete
the sample data.
To create a chart in the report template file, you can use some sample data.
Using sample data, you can set the various chart options. After you have made
the report template, you delete the sample data.
You can use formulas to perform calculations in a report template file.
XLReportGen is a converter too. Besides Microsoft Excel workbook, you can
generate a report in other file format such as HTML, XML, Lotus 1-2-3, CSV,
- 70 -
Page 76

text. You also can convert data from database to other file format.
You can protect the generated report so that it can not be modified. To protect
the report, select the Protect Report check box in the Configuration dialog
box.
You can edit an XRF file (.xrf) with a text editor such as Notepad.
If you associate XLReportGen with the file extension “.xrf”, an XRF file with the
extension “.xrf” will open in XLReportGen when you double-click the file. The
information:
File Extension: .xrf
Action: open
Application: "C:\Program Files\LJZsoft\ExcelReport.exe" “%1”
For the report template file, report file and log file, it is possible to give a
relative path. If it is a relative path, the base path is the path of the XRF file.
In the SQL statements, you can use parameters. To use parameters, you must
define them first.
In the paths and names of the report file, template file and log file, you can use
parameters. To use parameters, you must define them first.
The default log file is ExcelReport.log under the XLReportGen program
directory. If you do not define the log file name, or can not create the log file
defined, you can find log information in the ExcelReport.log under the
XLReportGen program directory.
- 71 -
Page 77

You should be careful to define a unique name for each parameter, because
XLReportGen will replace all strings that are the same as the names of the
parameters. It is a good choice a name begins with the “$” character such as
“$ReportDate”.
In the text editor window, you can use comments. A comment is the “/*”
characters, followed by any sequence of characters (including new lines),
followed by the “*/” characters. You cannot nest comments.
To add totals or subtotals, you can use the functions of Microsoft Excel or
aggregate functions in SQL statement.
To group data in a report, you should use GROUP VARIABLE TABLE
REPORT function.
In REPORT function, the order of groups should be in accordance with the
order of ORDER BY clause in the SQL statement.
You can create reports with pictures unsing XLReportGen. You should store
the path and name of the graphics file in the database, identify the image fields
in the report function, and specify the positioning option and size in the report
template file.
To convert from pixels to points, it is depend on the screen resolution (DPI). If
you have a 96 dpi screen (Windows PC), 4 pixels are equal to 3 points.
It is very useful to create a temporary table. You can prepare data using
- 72 -
Page 78

INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE/INSERT SELECT, and then make a report using
REPORT function.
To use add-ins or Auto_Open macros, you should set “Enable addins when
Excel starts up” or “Enable Auto_Open macro”.
You can write a program to make an XRF file using C, perl or DOS shell, and
then run XLReportGen to generate report. The two steps can be written into a
batch file.
If you do not save a password in the XRF file, a login dialog box will appear
when you run the XRF file in XLReportGen. You can input password
interactively to log on to the data source.
In general, group variable table report is slower than non-group variable table
report. But if the ranges of all groups are same as the range of details, it is
faster.
It may take a lot of time to add pagebreaks. If you change the default printer or
delete all printers on your computer, it will probably impact the performance.
XLReportGen supports Microsoft Excel 2007. You can use xlsx file as report
file and template file. Please copy “xconv2007.cfg” to “xconv.cfg”.
- 73 -
Page 79

Chapter 9 XRF File Reference
9.1 XRF File Format
The layout of an XRF file is as the following:
ExcelReport Version 2.0
[Data Source]
……
[File]
……
[Parameter]
……
[SQL]
……
“ExcelReport” is the flag of the XRF file. “Version 2.0” is the version of the XRF
file.
An XRF file contains several sections. The sections of [Data Source], [File],
and [Parameter] consist of a group of related settings. The sections and
settings are listed in the XRF file in the following format:
[section name]
keyname=value
In this example, [section name] is the name of a section. The enclosing
brackets ([]) are required, and the left bracket must be in the leftmost column
on the screen.
The keyname=value statement defines the value of each setting. A keyname is
the name of a setting. It can consist of any combination of letters and digits,
and must be followed immediately by an equal sign (=). The value can be an
integer, a string, or a quoted string, depending on the setting.
- 74 -
Page 80

You can include comments in these sections. You must begin each line of a
comment with a semicolon (;).
The [SQL] section consists of functions. Each function is begin with the “@”
character. Syntax:
@functionno=functionname(arguments)
sqlstatement
The functionno is the label of the function.
The functionname represents a function.
The arguments define various properties for the function. An argument takes
the form Name="Value". The argument value can be delimited by single or
double quotes.
The sqlstatement is a SQL statement.
You can use comments in [SQL] section. A comment is the “/*” characters,
followed by any sequence of characters (including new lines), followed by the
“*/” characters. You cannot nest comments.
9.2 [Data Source] Section
The [Data Source] section contains information how to connect to data
sources.
Name1=<name1>
Name2=<name2>
……
Name10=<name10>
These settings specify the names of data sources you want to connect to.
Name1 specifies the name of the first data source. Name2 specifies the name
of the second data source…… You can define up to 10 data sources in one
XRF file. You can make a connection to a data source using an ODBC data
- 75 -
Page 81

source name or a connection string. Even if you use a connection string to
make a connection, you should define a name that you can reference in
functions.
User1=<username1>
User2=<username2>
……
User10=<username10>
These settings specify the user names. If you use an ODBC data source name
to make a connection, you should define user name and password. If you use
a connection string to make a connection, XLReportGen will ignore the setting.
User1 specifies the user name of the first data source. User2 specifies the user
name of the second data source…… They are optional settings. If defined
default user and password in ODBC data source, you may not define them.
Password1=<password1>
Password2=<password2>
……
Password10=<password10>
These settings specify the user passwords. If you use an ODBC data source
name to make a connection, you should define user name and password. If
you use a connection string to make a connection, XLReportGen will ignore
the setting. Password1 specifies the password of the first data source.
Password2 specifies the password of the second data source…… They are
optional settings. If defined default user and password in ODBC data source,
you may not define them.
ConnectionString1=<connectionstring1>
- 76 -
Page 82

ConnectionString2=<connectionstring2>
……
ConnectionString10=<connectionstring10>
These settings specify the connection strings. If you defined a connection
string, XLReportGen will make a connection to the data source using the
connection string, and ignore the settings of the name, user and password. But
you must define a name that you can reference in functions.
ConnectionString1 specifies the connection string of the first data source.
ConnectionString2 specifies the connection string of the second data
source…… They are optional settings. If no connection string, XLReportGen
will make a connection to data source using the ODBC data source name.
EncryptPassword =Y/N
This setting specifies how to save the passwords of the data sources. If the
value is Y, the passwords will be saved in an encrypted format. If the value is N,
the passwords will be saved in plain text.
9.3 [FILE] Section
[FILE] section contains information about files.
ReportTemplateFileName=<templatefilename>
This setting specifies the name of the report template file. <templatefilename>
value is the name and path of the report template file. The file path can be a
relative path or an absolute path. If it is a relative path, the base path is the
path of the XRF file.
ReportFileName=<reportfilename>
This setting specifies the name of the report file. <reportfilename> value is the
- 77 -
Page 83

name and path of the report file. The file path can be a relative path or an
absolute path. If it is a relative path, the base path is the path of the XRF file. In
<reportfilename>, you can use parameters.
ReportFileType=<reportfiletype>
This setting specifies the type of the report file. <reportfiletype> value is the
name or value of the file format. For example, xlCSV or 6. What file format
XLReportGen supports is dependent on your Microsoft Excel.
ProtectReport=Y/N
This setting specifies whether the report generated is protected. If the value is
Y, the report is protected, and can not be modified. If the value is N, the report
is not protected. Default is N.
ProtectionPassword=<protectionpassword>
This setting specifies the password that is used to protect the report.
<protectionpassword> value is the password. This setting is valid when
ProtectReport is Y. If there is not this setting and ProtectReport is Y, a random
password will be created.
LogFileName=<logfilename>
This setting specifies the name of the log file. <logfilename> value is the name
and path of the log file. The file path can be a relative path or an absolute path.
If it is a relative path, the base path is the path of the XRF file. In <logfilename>,
you can use parameters.
- 78 -
Page 84

9.4 [PARAMETER] Section
[PARAMETER] section contains information about parameters.
Name1=<name1>
Name2=<name2>
……
Name10=<name10>
These settings specify the names of the parameters. Name1 specify the name
of the first parameter, Name2 specifies the name of the second parameter.…..
You can define up to 10 parameters in one XRF file.
Title1=<title1>
Title2=<title2>
……
Title10=<title10>
These settings specify the titles of the parameters. Title1 specifies the title of
the first parameter. Title2 specifies the title of the second parameter……
Default1=<default1>
Default2=<default2>
……
Default10=<default10>
These settings specify the default values of the parameters. Default1 specifies
the default value of the first parameter. Default2 specifies the default value of
the second parameter.…..
- 79 -
Page 85

Chapter 10 License and Support
10.1 License
Your Agreement to This License
You should carefully read the following terms and conditions before using,
installing, copying, or distributing this software. Your use, installation, copying,
or distribution of XLReportGen indicates your acceptance of this agreement
("License").
NO WARRANTY
XLREPORTGEN IS DISTRIBUTED "AS IS". NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND
IS EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED. THE AUTHOR WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR
DATA LOSS, DAMAGES, LOSS OF PROFITS OR ANY OTHER KIND OF
LOSS WHILE USING OR MISUSING THIS SOFTWARE.
Evaluation
XLReportGen is not free software. You may use this software for evaluation
purposes without charge for a period of 30 days. If you use this software after
the 30 day evaluation period, you must purchase it.
Use
Each Licensed Copy of this Software may either be used by a user who uses
the software personally on one or more computers, or installed on a single
computer used nonsimultaneously by multiple people, but not both. This is not
a concurrent use license. If you install the Software onto a multi-user platform,
server or network, each and every individual user of the Software must be
licensed separately.
- 80 -
Page 86

Distribution
You may copy the evaluation version of this software and documentation as
you wish, and give exact copies of the original evaluation version to anyone,
and distribute the evaluation version of the software and documentation in its
unmodified form via electronic means. You are specifically prohibited from
charging, or requesting donations without permission from the author.
You may not modify, copy, share, distribute, re-sell, transfer or sub-license the
full version of this software except that you may make copies for archive
purposes only. Any such unauthorized use shall result in immediate and
automatic termination of this license.
Edition
There are 2 types of editions issued for XLReportGen.
1) XLReportGen Standard Edition
User can execute no more than 50 SQL statements in one report processing.
2) XLReportGen Professional Edition
User can execute SQL statements unlimitedly in one report processing.
10.2 Technical Support
If you encounter any problems in usage of XLReportGen, and need the
technical support:
Go to our support web site at:
http://www.ljzsoft.com/support.htm
Send email to support@ljzsoft.com
- 81 -
 Loading...
Loading...